Abstract
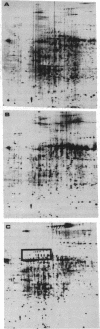
We describe a quantitative two-dimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of nuclear extract from 24-hr sea urchin embryos. The extract was fractionated by using a weak cation-exchange resin, and eight known DNA-binding proteins were shown to be entirely included in a salt eluate that releases proteins containing basic domains. This fraction and a lower-salt fraction containing the majority of the protein species were mapped two-dimensionally by using new algorithms that permit reproducible spot identification, storage of intensity and map-position data, and subtractive comparison of one pattern with respect to another. By reference to a previously characterized DNA-binding factor, spot intensity could be interpreted in terms of the number of molecules per embryo nucleus. A map was constructed displaying all nuclear proteins containing basic domains that are present within the concentration range per nucleus of a set of known DNA-binding factors of the sea urchin embryo. The map includes 265 spots that fulfill both of these criteria, probably representing about 100 different protein species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Hög C., Teplow D. B., Cutting A. E., Zeller R. W., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulatory factors of the sea urchin embryo. I. Purification by affinity chromatography and cloning of P3A2, a novel DNA-binding protein. Development. 1991 May;112(1):335–350. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Thézé N., Thiebaud P., Hill R. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental appearance of factors that bind specifically to cis-regulatory sequences of a gene expressed in the sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1074–1088. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron R. A., Davidson E. H. Cell type specification during sea urchin development. Trends Genet. 1991 Jul;7(7):212–218. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90367-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Leffers H., Rasmussen H. H., Madsen P., Honoré B., Gesser B., Dejgaard K., Olsen E., Ratz G. P., Lauridsen J. B. The master two-dimensional gel database of human AMA cell proteins: towards linking protein and genome sequence and mapping information (update 1991). Electrophoresis. 1991 Nov;12(11):765–801. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman J. A., Davidson E. H. Expression of spatially regulated genes in the sea urchin embryo. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):260–268. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman J. A., Moore J. G., Calzone F. J., Britten R. J., Hood L. E., Davidson E. H. Automated sequential affinity chromatography of sea urchin embryo DNA binding proteins. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1992 Apr;1(2):136–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting A. E., Hög C., Calzone F. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Rare maternal mRNAs code for regulatory proteins that control lineage-specific gene expression in the sea urchin embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7953–7957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H. Lineage-specific gene expression and the regulative capacities of the sea urchin embryo: a proposed mechanism. Development. 1989 Mar;105(3):421–445. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser D. F., Merril C. R. 'Catalysts' for polyacrylamide gel polymerization and detection of proteins by silver staining. Appl Theor Electrophor. 1988;1(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Calzone F. J., Cutting A. E., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulatory factors of the sea urchin embryo. II. Two dissimilar proteins, P3A1 and P3A2, bind to the same target sites that are required for early territorial gene expression. Development. 1991 May;112(1):351–364. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski M. T., Gan L., Venuti J. M., Sawadogo M., Klein W. H. Sea urchin USF: a helix-loop-helix protein active in embryonic ectoderm cells. Dev Biol. 1991 Dec;148(2):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90280-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaud P., Goodstein M., Calzone F. J., Thézé N., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Intersecting batteries of differentially expressed genes in the early sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1999–2010. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thézé N., Calzone F. J., Thiebaud P., Hill R. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Sequences of the CyIIIa actin gene regulatory domain bound specifically by sea urchin embryo nuclear proteins. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Feb;25(2):110–122. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080250203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson C. R., Kozlowski M. T., Klein W. H. Ectoderm nuclei from sea urchin embryos contain a Spec-DNA binding protein similar to the vertebrate transcription factor USF. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):259–272. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Dearolf C. R., Prakash K., Parker C. S. Synthetic oligonucleotides recreate Drosophila fushi tarazu zebra-stripe expression. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):855–867. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiang M., Lu S. Y., Musso M., Karsenty G., Klein W. H. A G-string positive cis-regulatory element in the LpS1 promoter binds two distinct nuclear factors distributed non-uniformly in Lytechinus pictus embryos. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1345–1355. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao A. Z., Vansant G., Bell J., Humphreys T., Maxson R. Activation of the L1 late H2B histone gene in blastula-stage sea urchin embryos by Antennapedia-class homeoprotein. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;34(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90088-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Berg O. G. Facilitated target location in biological systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):675–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]