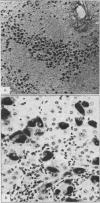
Abstract
Two hundred and fifty six consecutive liver biopsy specimens (without secondary malignancy) collected over five years were reviewed to characterise the pattern of liver diseases encountered in the Kuwait region. A relatively high proportion of chronic active hepatitis (19%) and cirrhosis (40%) was found. Localisation of HBsAg was carried out by the histochemical orcein method and the immunohistological peroxidase-antiperoxidase (PAP) procedure. The PAP technique was superior to orcein both in quality and quantity in addition to its specificity. Three immunohistological staining patterns were observed: diffuse pancytoplasmic , partial perinuclear, and peripheral cytoplasmic. The positivity rate of HBsAg in chronic hepatitis was 29% and 27%, in all cases of cirrhosis. The results of immunohistology and serology of HBsAg were compared in 52 patients in whom both tests were carried out; almost one third of chronic active liver diseases were positive by both methods. Our data clearly show the sensitivity of immunohistology and its value in detecting HBsAg, especially in retrospective studies where serology is not always available. Additionally, the data show that hepatitis B infection is often associated with the development of chronic liver disease in Kuwait.
Full text
PDF

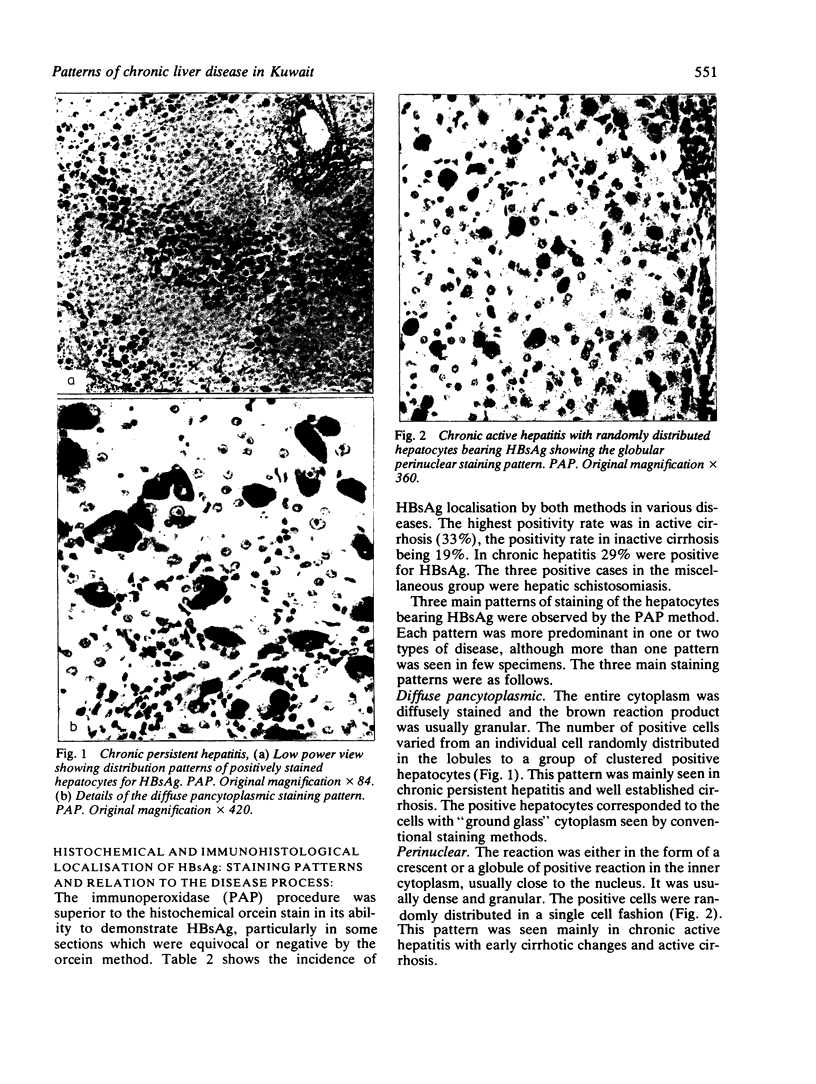
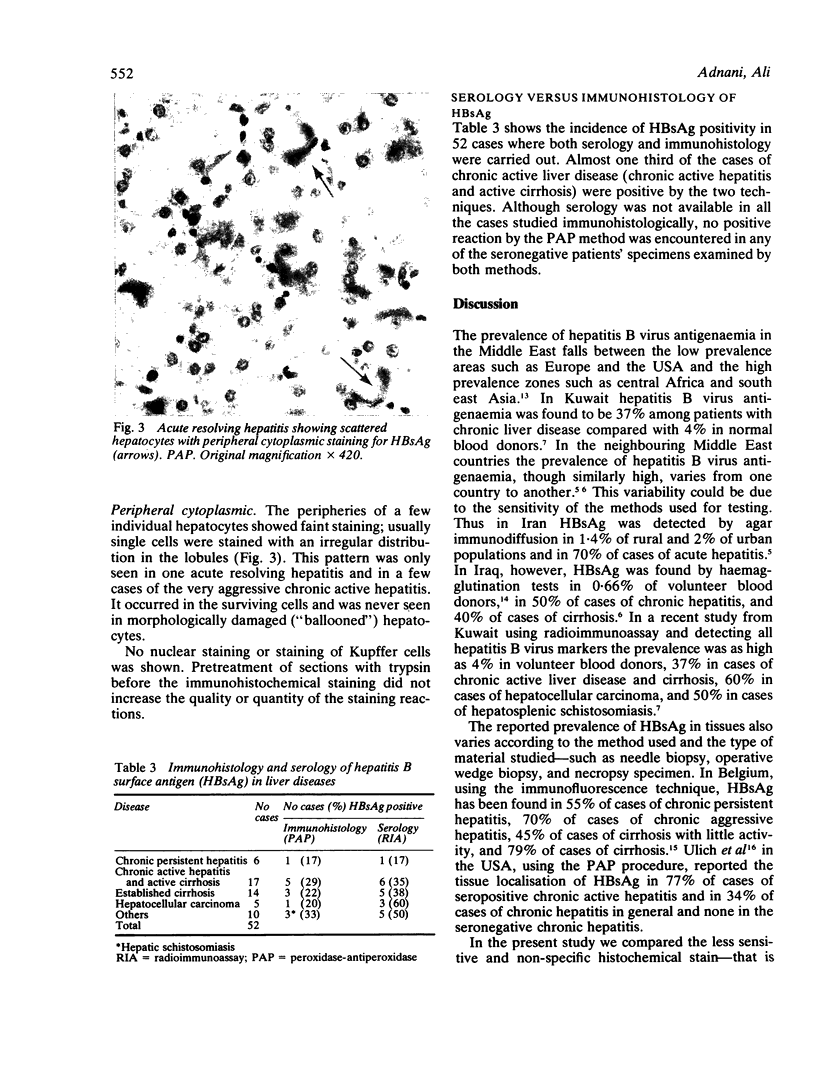


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al Adnani M. S., Al Kasab F. M., Al Alusi F. A. Hepatitis B surface antigenaemia in sickle cell disease. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1286–1286. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Balaghi S. M., Kassir Z., Thewaini A. J. Hepatitis B surface antigen in various liver diseases in Iraq. J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Dec;80(12):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nakib B., Al-Nakib W., Bayoumi A., Al-Liddawi H., Bashir A. A. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) markers among patients with chronic liver disease in Kuwait. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(3):348–350. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90187-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony P. P., Ishak K. G., Nayak N. C., Poulsen H. E., Scheuer P. J., Sobin L. H. The morphology of cirrhosis: definition, nomenclature, and classification. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(4):521–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassily S., Farid Z., Higashi G. I., Kamel I. A., El-Masry N. A., Watten R. H. Chronic hepatitis B antigenaemia in patients with hepatosplenic schistosomiasis. J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 Nov-Dec;82(11-12):248–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. Immunoperoxidase localisation of hepatitis B antigen (HB) in formalin-paraffin processed liver tissue. Histochemistry. 1975 Jul 30;44(2):133–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00494074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. C., Gregory J. The unmasking of antigens in paraffin sections of tissue by trypsin. Experientia. 1977 Oct 15;33(10):1400–1401. doi: 10.1007/BF01920206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deodhar K. P., Tapp E., Scheuer P. J. Orcein staining of hepatitis B antigen in paraffin sections of liver biopsies. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jan;28(1):66–70. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Giustino V., Sherlock S. Cell-mediated immunity in patients positive for hepatitis-associated antigen. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 30;4(5843):754–756. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5843.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. N., Neurath A. R. Immunohistologic demonstration of hepatitis B viral antigens in liver with reference to its significance in liver injury. Lab Invest. 1979 Jan;40(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowoslawski A., Krawczynski K., Nazarewicz T., Slusarczyk J. Immunopathological aspects of hepatitis type B. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;270(2):229–239. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadi S., Farrohi K., McCollum R. W., Le Bouvier G. L. Hepatitis-B antigen in Iran: frequency and subtype. Lancet. 1972 Dec 23;2(7791):1377–1378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92833-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Chronic hepatitis. Gut. 1974 Jul;15(7):581–597. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.7.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikata T., Uzawa T., Yoshiwara N., Akatsuka T., Yamazaki S. Staining methods of Australia antigen in paraffin section--detection of cytoplasmic inclusion bodies. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Feb;44(1):25–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulich T. R., Cheng L., Gitnick G. L., Thorne C. A., Lewin K. J. Chronic active hepatitis of hepatitis B and non-A, non-B etiology. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982 Jan;6(1):33–39. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198201000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]