Abstract
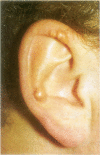
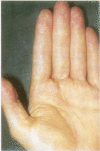
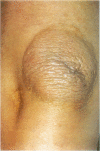
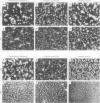
AIM: To present the clinical, dermatological, and histological features of a patient with generalised xanthomatosis, familial apolipoprotein (apo) E deficiency, and unusual type III hyperlipoproteinaemia (HLP). METHODS: The underlying molecular defect was disclosed using molecular biological techniques. The unusual xanthomas were histologically analysed and the morphology of the abnormal lipoprotein particles examined using electron microscopy. RESULTS: A 10 base pair deletion in exon 4 of the proband's apo epsilon gene (base pairs 4037-4046 coding for amino acids 209-212 of the mature protein) was identified. This is predictive for a reading frameshift encoding a premature stop (TGA) in codon 229. The mutation is responsible for delayed catabolism of atherogenic lipoprotein remnants, lipid storage in monocyte/macrophages, and phenotypic expression of xanthomatosis early in life. CONCLUSIONS: Familial apo E deficiency is a rare genetic disease which offers the unique opportunity to study the impact of apo E on lipoprotein metabolism and development of atherosclerosis in humans.
Full text
PDF
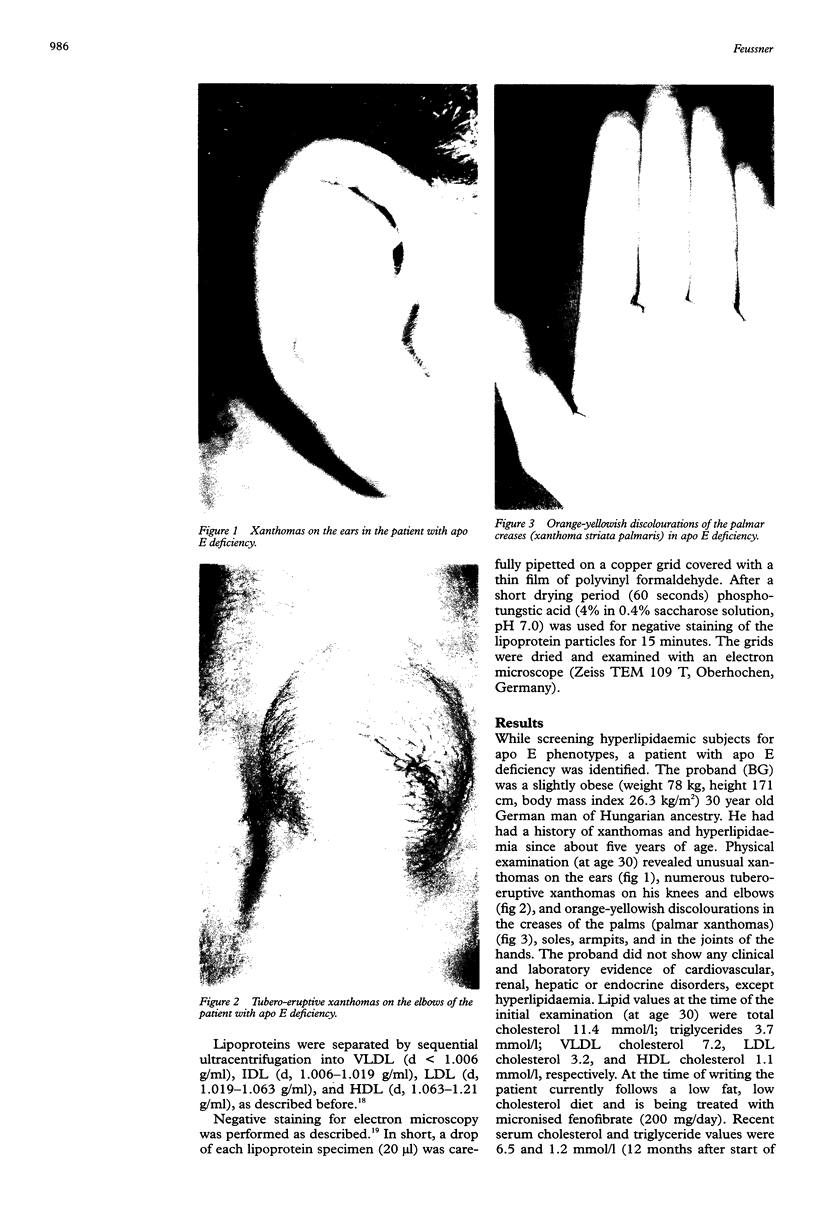
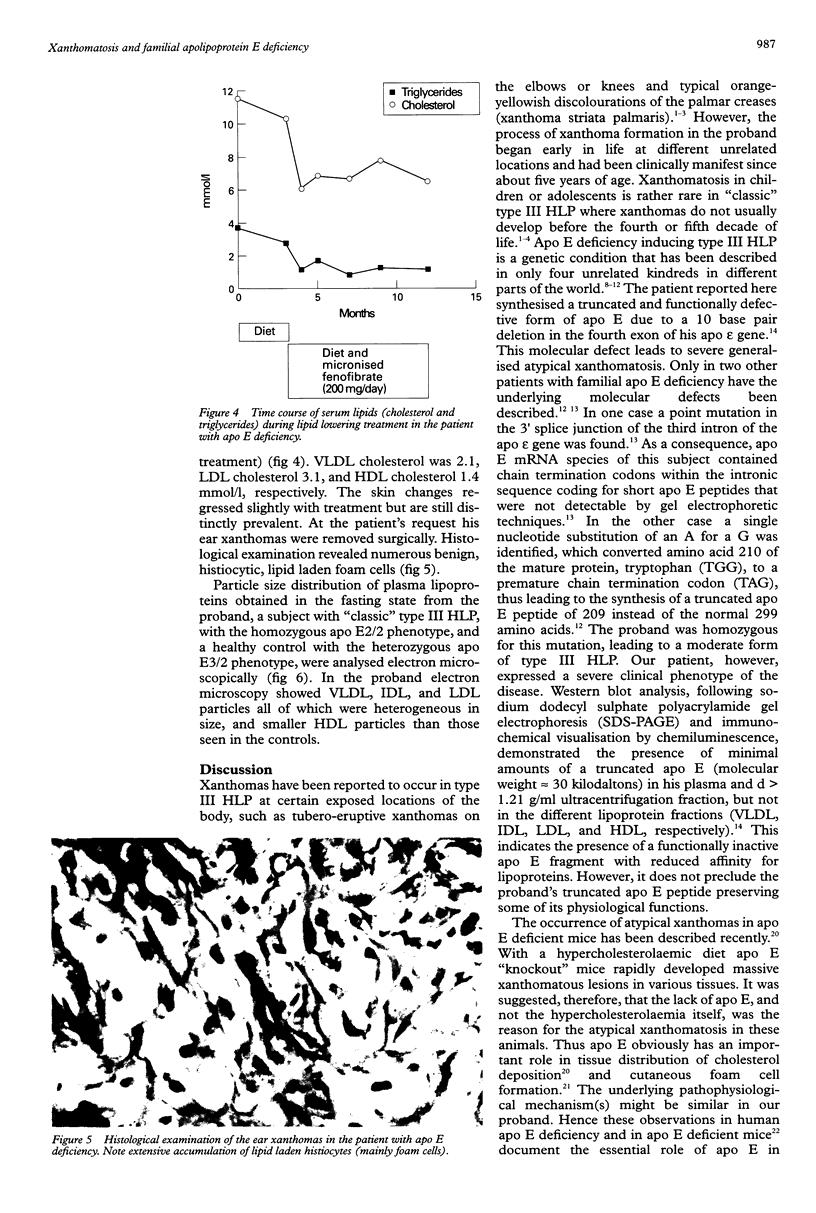
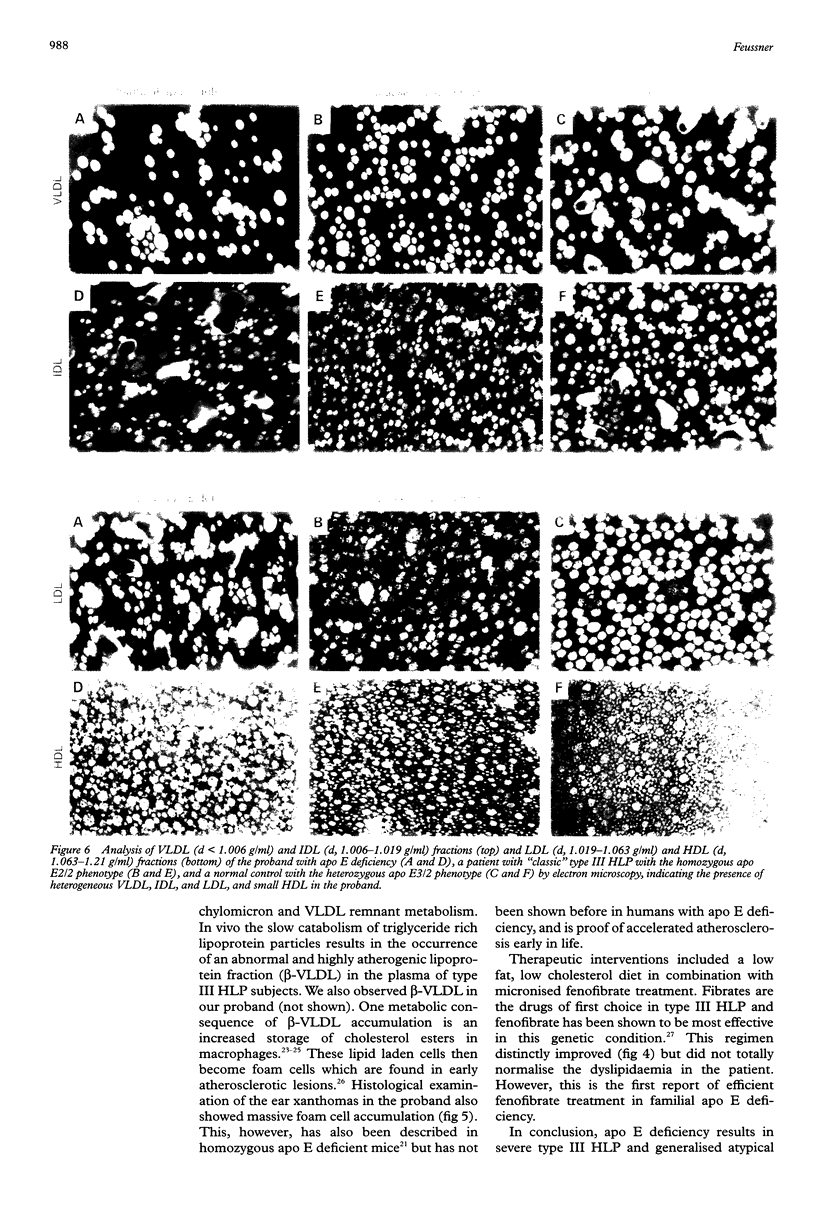

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Zech L. A., Gregg R. E., Schwartz D., Schaefer E. J. NIH conference. Type III hyperlipoproteinemia: diagnosis, molecular defects, pathology, and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1983 May;98(5 Pt 1):623–640. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-5-623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Lipoprotein metabolism in the macrophage: implications for cholesterol deposition in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:223–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G., Zannis V. I. The molecular basis of a familial apoE deficiency. An acceptor splice site mutation in the third intron of the deficient apoE gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2310–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J., Gregg R. E., Sing C. F. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Innerarity T. L. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed dogs and from humans with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):702–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Elias P. M., Mao-Qiang M., Fartasch M., Zhang S. H., Maeda N. Apolipoprotein E deficiency leads to cutaneous foam cell formation in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Feb;104(2):246–250. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12612790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feussner G., Dobmeyer J., Gröne H. J., Lohmer S., Wohlfeil S. A 10-bp deletion in the apolipoprotein epsilon gene causing apolipoprotein E deficiency and severe type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Feb;58(2):281–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feussner G., Wagner A., Kohl B., Ziegler R. Clinical features of type III hyperlipoproteinemia: analysis of 64 patients. Clin Investig. 1993 May;71(5):362–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00186624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feussner G., Wagner A., Ziegler R. Relation of cardiovascular risk factors to atherosclerosis in type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;92(2):122–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00219678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchart J. C., Davignon J., Bard J. M., Grothe A. M., Richard A., Fievet C. Effect of fenofibrate treatment on type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Am J Med. 1987 Nov 27;83(5B):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90874-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Schaefer E. J., Gascon P., Breser H. B., Jr Type III hyperlipoproteinemia associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Science. 1981 Dec 11;214(4526):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6795720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Herz J., Maeda N., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The two-receptor model of lipoprotein clearance: tests of the hypothesis in "knockout" mice lacking the low density lipoprotein receptor, apolipoprotein E, or both proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4431–4435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaka D., Teramoto T., Matsushima T., Yokoyama T., Yamada A., Aikawa T., Miyamoto Y., Kurokawa K. Apolipoprotein E deficiency with a depressed mRNA of normal size. Atherosclerosis. 1991 May;88(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(91)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse P., Brewer H. B., 3rd, Meng M. S., Skarlatos S. I., LaRosa J. C., Brewer H. B., Jr Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency and type III hyperlipoproteinemia due to a premature stop codon in the apolipoprotein E gene. J Lipid Res. 1992 Nov;33(11):1583–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luley C., Baumstark M. W., Wieland H. Rapid apolipoprotein E phenotyping by immunofixation in agarose. J Lipid Res. 1991 May;32(5):880–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Itoh H., Takeda M., Kajinami K., Wakasugi T., Koizumi J., Takeda R., Asagami C. A young type III hyperlipoproteinemic patient associated with apolipoprotein E deficiency. Metabolism. 1989 Feb;38(2):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Development of accelerated atherosclerosis. Concepts derived from cell biology and animal model studies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983 Aug;107(8):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik Y. K., Chang D. J., Reardon C. A., Davies G. E., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the human apolipoprotein E gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Gregg R. E., Ghiselli G., Forte T. M., Ordovas J. M., Zech L. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Familial apolipoprotein E deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1206–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI112704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Utermann G., Weber W., Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Innerarity T. L. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in health and disease. Am Heart J. 1987 Feb;113(2 Pt 2):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ree J. H., Gijbels M. J., van den Broek W. J., Hofker M. H., Havekes L. M. Atypical xanthomatosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice after cholesterol feeding. Atherosclerosis. 1995 Jan 20;112(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)05419-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]