Abstract
AIMS--To evaluate the role of hepatocyte expression of leucocyte adhesion molecules and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens in the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis. METHODS--The expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), lymphocyte function associated antigen 3 (LFA-3), and MHC class I and II antigens on hepatocyte membrane in relation to the histological and biochemical activities was studied in patients with chronic B hepatitis, chronic persistent hepatitis (CPH) n = 23; chronic active hepatitis (CAH) n = 20; chronic D hepatitis (CAH) n = 6; and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis (CPH n = 4, CAM n = 6). Six of the latter were hepatitis C virus antibody positive. RESULTS--In chronic B hepatitis ICAM-1 and MHC-I were expressed significantly more in patients with CAH than in those with CPH (p < 0.001), while the expression of LFA-3 and MHC-II showed no significant difference, irrespective of serum HBeAg or hepatitis B virus DNA. Similar findings were noted in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Regardless of the viral aetiology, patients with CAH had a significantly higher degree of ICAM-1 and MHC-I expression than LFA-3 (p < 0.001 v ICAM-1 and MHC-I, respectively) and MHC-II (p < 0.001 v ICAM-1 and MHC-I, respectively) expression. Those with CPH showed little or no difference in the expression of these four molecules. Furthermore, serum ALT values positively correlated with the hepatocyte expression of ICAM-1 (p < 0.001) and MHC-I (p < 0.001), but not LFA-3 (p > 0.05) and MHC-II (p > 0.05). CONCLUSIONS--In chronic viral hepatitis hepatocyte expression of ICAM-1 and MHC-I might be important for immunosurveillance against virally infected hepatocytes, while the expression of LFA-3 and MHC-II does not seem to have a role in the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis.
Full text
PDF
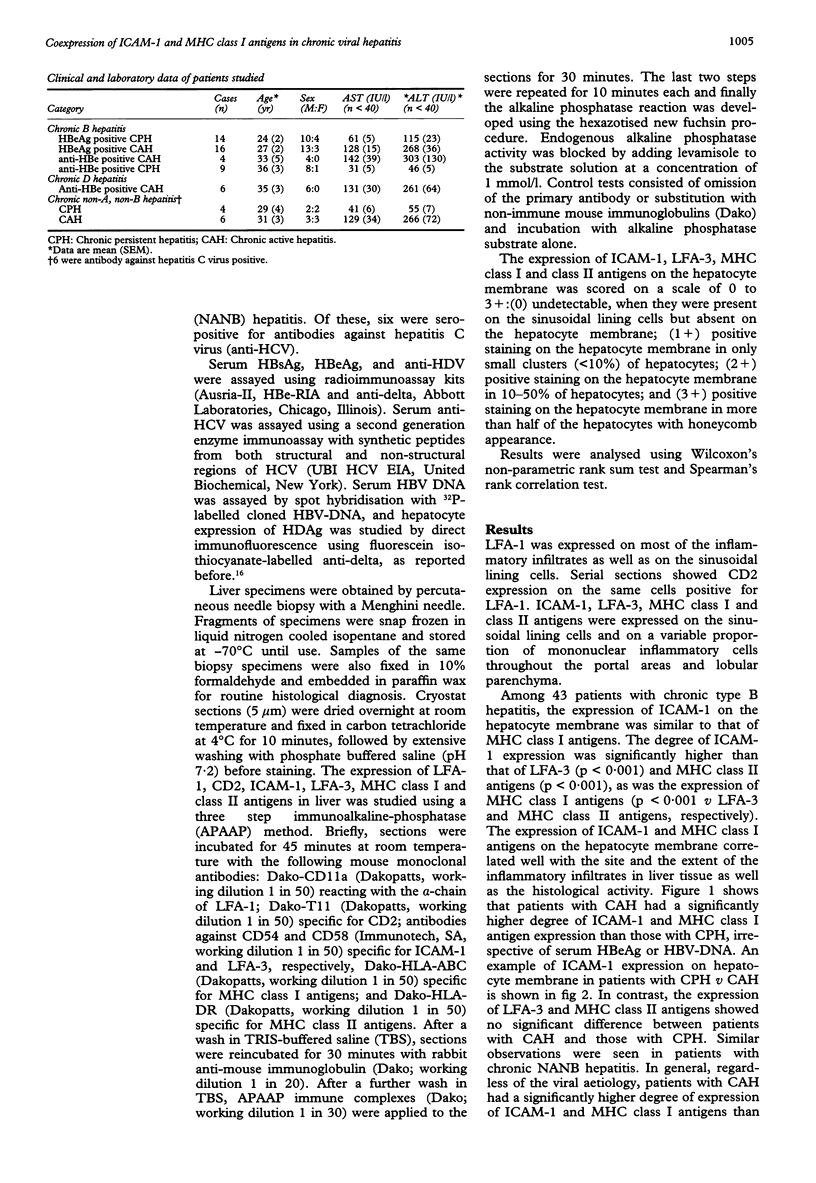
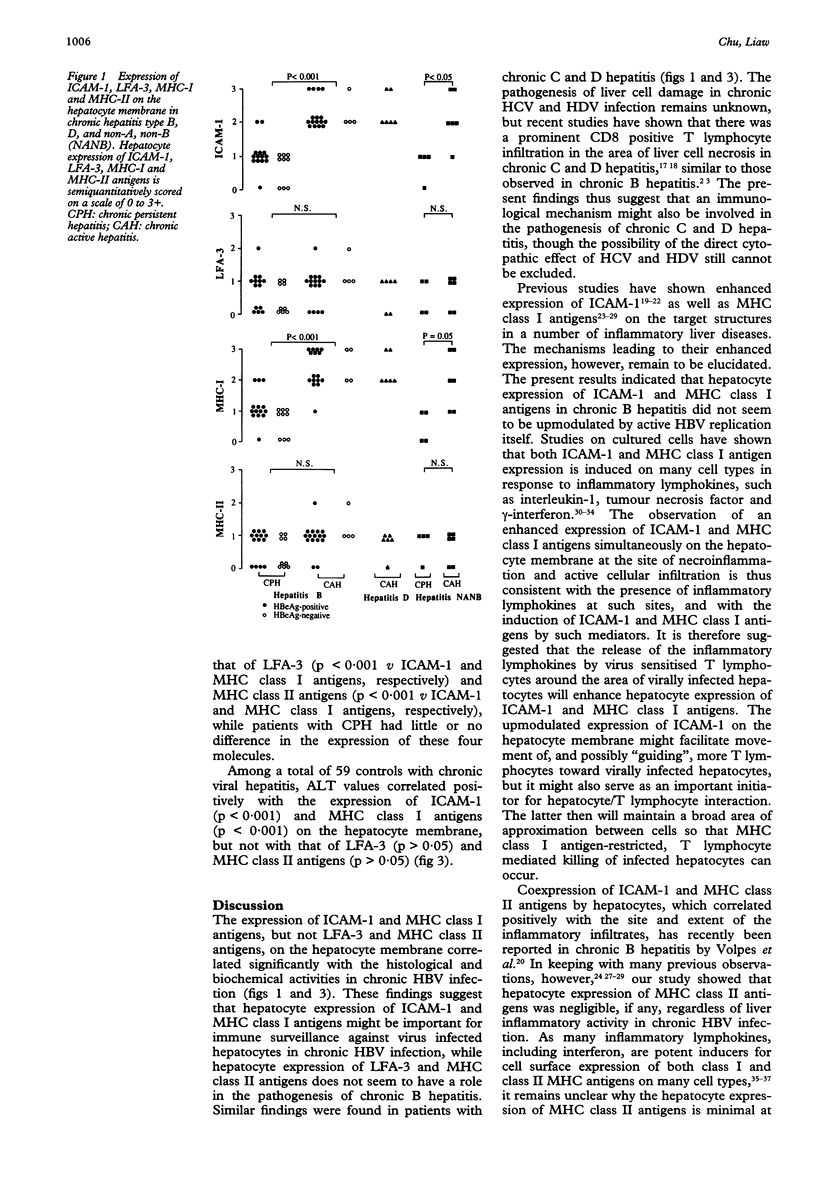
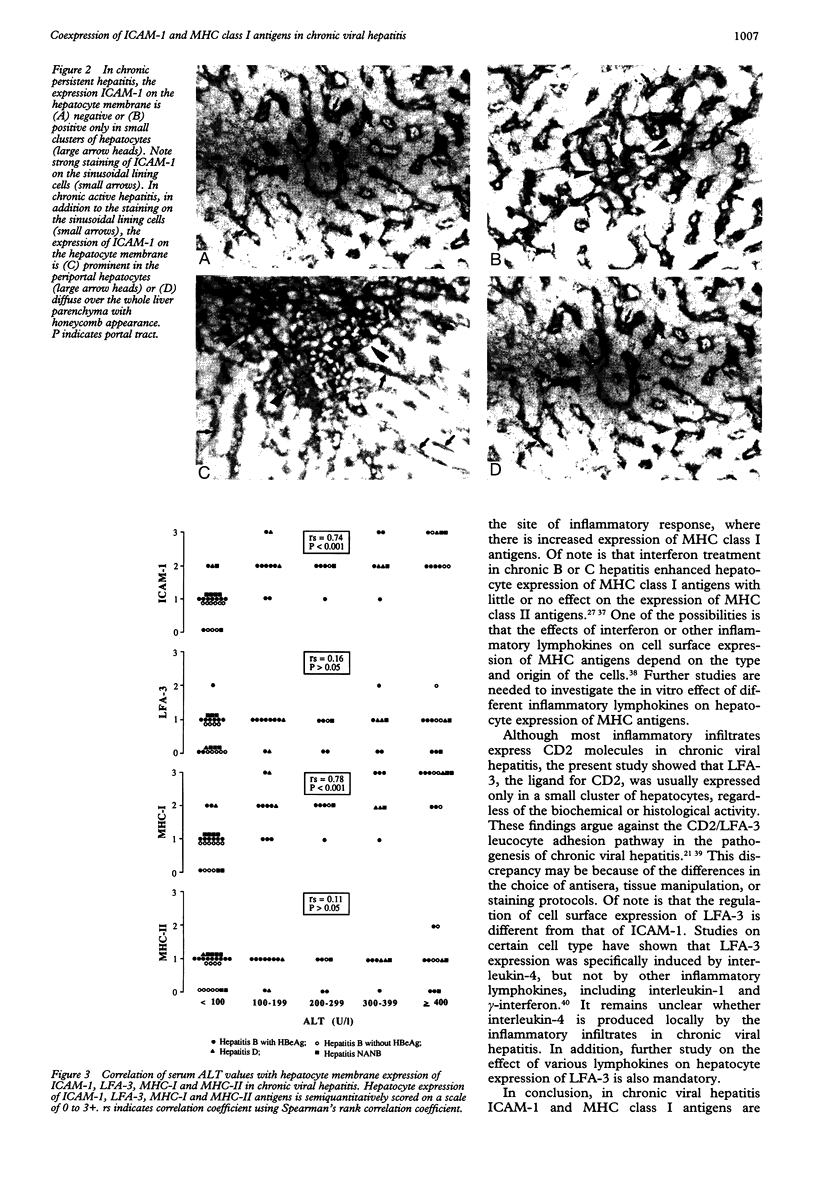

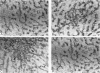
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H., Hubscher S. G., Shaw J., Rothlein R., Neuberger J. M. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on liver allografts during rejection. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1122–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Autschbach F., Meuer S. C., Moebius U., Manns M., Hess G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Thoenes W., Dienes H. P. Hepatocellular expression of lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 in chronic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballardini G., Bianchi F. B., Mirakian R., Fallani M., Pisi E., Bottazzo G. F. HLA-A,B,C, HLA-D/DR and HLA-D/DQ expression on unfixed liver biopsy sections from patients with chronic liver disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):35–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbatis C., Woods J., Morton J. A., Fleming K. A., McMichael A., McGee J. O. Immunohistochemical analysis of HLA (A, B, C) antigens in liver disease using a monoclonal antibody. Gut. 1981 Dec;22(12):985–991. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.12.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Bourgeade M. F., Creasey A. A., Merigan T. C. Interferon increases HLA synthesis in melanoma cells: interferon-resistant and -sensitive cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Peterson A., Gorga J. C., Herrmann S. H., Burakoff S. J. Synergistic T cell activation via the physiological ligands for CD2 and the T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1145–1156. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billard C., Ferbus D., Kolb J. P., Rosa F., Perrot J. Y., Merlin G., Janiaud P., Raynaud N., Thang M. N., Fellous M. Qualitative differences in effects of recombinant alpha-, beta- and gamma-interferons on human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1986 May-Jun;137C(3):259–272. doi: 10.1016/s0771-050x(86)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burra P., Hubscher S. G., Shaw J., Elias E., Adams D. H. Is the intercellular adhesion molecule-1/leukocyte function associated antigen 1 pathway of leukocyte adhesion involved in the tissue damage of alcoholic hepatitis? Gut. 1992 Feb;33(2):268–271. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Liaw Y. F. Intrahepatic expression of pre-S1 and pre-S2 antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection in relation to hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis delta virus superinfection. Gut. 1992 Nov;33(11):1544–1548. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.11.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Liaw Y. F. Studies on the composition of the mononuclear cell infiltrates in liver from patients with chronic active delta hepatitis. Hepatology. 1989 Dec;10(6):911–915. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Shyu W. C., Kuo R. W., Liaw Y. F. HLA class I antigen display on hepatocyte membrane in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: its role in the pathogenesis of chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):712–717. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durandy A., Virelizier J. L., Griscelli C. Enhancement by interferon of membrane HLA antigens in patients with combined immunodeficiency with defective HLA expression. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):173–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggink H. F., Houthoff H. J., Huitema S., Gips C. H., Poppema S. Cellular and humoral immune reactions in chronic active liver disease. I. Lymphocyte subsets in liver biopsies of patients with untreated idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis, chronic active hepatitis B and primary biliary cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):17–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A., Barnaba V., Natali P., Balsano C., Musca A., Balsano F. Expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on human hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):449–454. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukusato T., Gerber M. A., Thung S. N., Ferrone S., Schaffner F. Expression of HLA class I antigens on hepatocytes in liver disease. Am J Pathol. 1986 May;123(2):264–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P. F., Wadgymar A., Autenried P. The regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex products. Transplantation. 1986 Apr;41(4):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Robbins E., Nagy J. A., Springer T. A., Burakoff S. J. The functional significance, distribution, and structure of LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3: cell surface antigens associated with CTL-target interactions. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):611–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kürzinger K., Reynolds T., Germain R. N., Davignon D., Martz E., Springer T. A. A novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): cellular distribution, quantitative expression, and structure. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malizia G., Dino O., Pisa R., Caltagirone M., Giannuoli G., Di Marco V., Aragona E., Calabrese A., Raiata F., Craxi A. Expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1991 Mar;100(3):749–755. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)80021-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hercend T., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. The human T-cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:23–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moingeon P., Chang H. C., Wallner B. P., Stebbins C., Frey A. Z., Reinherz E. L. CD2-mediated adhesion facilitates T lymphocyte antigen recognition function. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):312–314. doi: 10.1038/339312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi Y., Hobbs K. E., Thomas H. C., Scheuer P. J. Expression of beta-2-microglobulin on hepatocytes after liver transplantation. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):551–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onji M., Kikuchi T., Kumon I., Masumoto T., Nadano S., Kajino K., Horiike N., Ohta Y. Intrahepatic lymphocyte subpopulations and HLA class I antigen expression by hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatogastroenterology. 1992 Aug;39(4):340–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Rieber E. P., Eisenburg J., Hoffmann R., Balch C. M., Paumgartner G., Riethmüller G. Involvement of the cytotoxic/suppressor T-cell subset in liver tissue injury of patients with acute and chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances HLA-A,B,C and HLA-DR gene expression in human tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):975–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Brown D., Lever A., Iwarson S., Schaff Z., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. HLA class I antigens on the hepatocyte membrane during recovery from acute hepatitis B virus infection and during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):349–353. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Lever A., Iwarson S., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. Cytotoxic T-cell responses to the nucleocapsid proteins of HBV in chronic hepatitis. Evidence that antibody modulation may cause protracted infection. J Hepatol. 1987 Feb;4(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Plunkett M. L., Dustin M., Sanders M. E., Shaw S., Springer T. A. The T lymphocyte glycoprotein CD2 binds the cell surface ligand LFA-3. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):400–403. doi: 10.1038/326400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E., Quinones R., Gress R. E., Springer T. A., Sanders M. E. Two antigen-independent adhesion pathways used by human cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):262–264. doi: 10.1038/323262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw S., Luce G. E. The lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1 and CD2/LFA-3 pathways of antigen-independent human T cell adhesion. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1037–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpes R., van den Oord J. J., Desmet V. J. Hepatic expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in viral hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):148–154. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacholtz M. C., Patel S. S., Lipsky P. E. Leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 is an activation molecule for human T cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):431–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]