Abstract
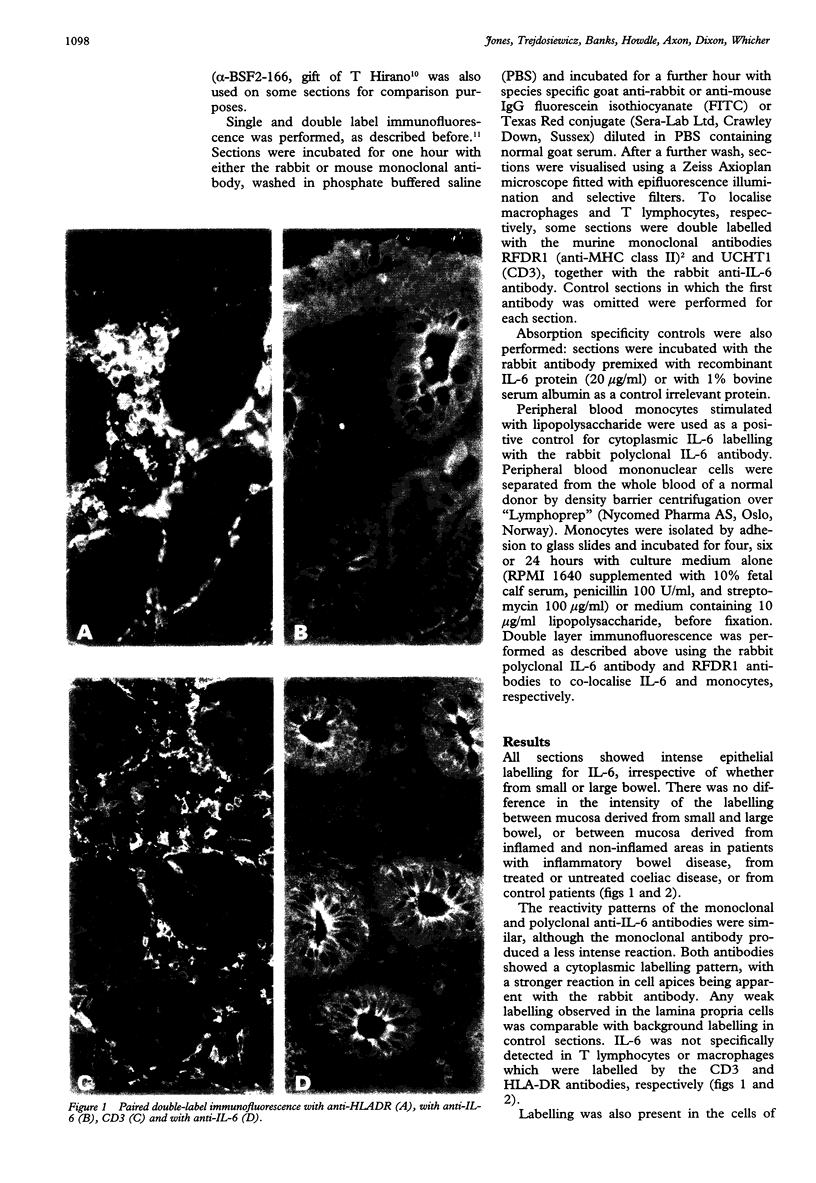
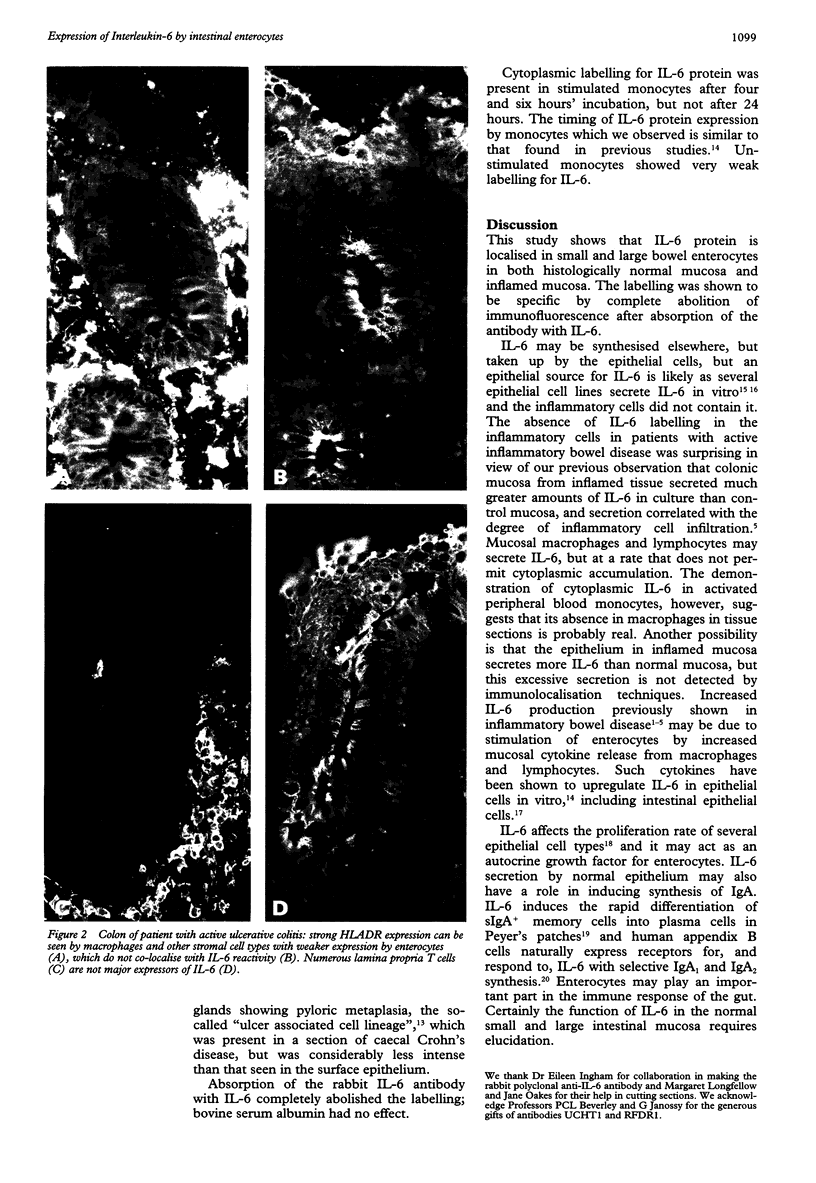
AIMS--To investigate the cellular source of the cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the small and large intestines of patients with inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, and in controls. METHODS--IL-6 was detected in frozen sections of bowel by single and double label indirect immunofluorescence using rabbit polyclonal and murine monoclonal anti-IL-6 antibodies. The murine monoclonal antibodies RFDR1 (anti-MHC class II) and UCHT1 (anti-CD3) were used to localise macrophages and T lymphocytes, respectively. Lipopolysaccharide stimulated peripheral blood monocytes were used as positive control cells for IL-6 protein. RESULTS--IL-6 was demonstrated in the small and large intestine of patients with inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, and in controls. The protein was present predominantly in enterocytes and colocytes in normal and inflamed mucosa, but not in the infiltrating inflammatory cells of the lamina propria. There were no discernable differences between patients with inflammatory bowel disease or coeliac disease and controls, nor between small and large bowel mucosa. Incubation of antibody with recombinant human IL-6 protein abolished the labelling. IL-6 protein was also present in lipopolysaccharide stimulated peripheral blood monocytes. CONCLUSIONS--The data suggest that enterocytes and colocytes may play an active part in the immune response of the gut. The presence of IL-6 in both inflamed and non-inflamed small and large intestine requires further investigation into the function of this cytokine in the gut.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer J., Ganter U., Geiger T., Jacobshagen U., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Kishimoto T., Andus T., Acs G., Gerok W. Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in cultured human blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1134–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beagley K. W., Eldridge J. H., Aicher W. K., Mestecky J., Di Fabio S., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R. Peyer's patch B cells with memory cell characteristics undergo terminal differentiation within 24 hours in response to interleukin-6. Cytokine. 1991 Mar;3(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90030-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromwell O., Hamid Q., Corrigan C. J., Barkans J., Meng Q., Collins P. D., Kay A. B. Expression and generation of interleukin-8, IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by bronchial epithelial cells and enhancement by IL-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1992 Nov;77(3):330–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihashi K., McGhee J. R., Lue C., Beagley K. W., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Mestecky J., Kiyono H. Human appendix B cells naturally express receptors for and respond to interleukin 6 with selective IgA1 and IgA2 synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):248–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI115284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross V., Andus T., Caesar I., Roth M., Schölmerich J. Evidence for continuous stimulation of interleukin-6 production in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):514–519. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges S., Svensson M., Svanborg C. Interleukin-6 response of epithelial cell lines to bacterial stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1295–1301. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1295-1301.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L. A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1535–1540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Sartor R. B., Haskill S. Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Gastroenterology. 1992 Nov;103(5):1587–1595. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Rawlings E., Burford G. D., Navarrete C., Ziegler A., Kelemen E. Separate ontogeny of two macrophage-like accessory cell populations in the human fetus. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4354–4361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J., Ray A., Tamm I., Sehgal P. B. Expression and function of interleukin-6 in epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Apr;45(4):327–334. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240450404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahida Y. R., Kurlac L., Gallagher A., Hawkey C. J. High circulating concentrations of interleukin-6 in active Crohn's disease but not ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1531–1534. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Establishment of an interleukin 6 (IL 6)/B cell stimulatory factor 2-dependent cell line and preparation of anti-IL 6 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):951–956. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee D. W., Aicher W. K., Eldridge J. H., Peppard J. V., Mestecky J., McGhee J. R. Transforming growth factor-beta enhances secretory component and major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression on rat IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cells. Cytokine. 1991 Nov;3(6):543–550. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90480-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama K., Sata M., Tanikawa K. Significance of interleukin-6 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991 Feb;26(1):20–28. doi: 10.1007/BF02779504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirota K., LeDuy L., Yuan S. Y., Jothy S. Interleukin-6 and its receptor are expressed in human intestinal epithelial cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58(4):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02890085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C., Walz G., Singaram C., Lipman M. L., Zanker B., Muggia A., Antonioli D., Peppercorn M. A., Strom T. B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-6 expression in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Jun;37(6):818–826. doi: 10.1007/BF01300378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejdosiewicz L. K., Smart C. J., Oakes D. J., Howdle P. D., Malizia G., Campana D., Boylston A. W. Expression of T-cell receptors TcR1 (gamma/delta) and TcR2 (alpha/beta) in the human intestinal mucosa. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):7–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. A., Pike C., Elia G. Induction of a novel epidermal growth factor-secreting cell lineage by mucosal ulceration in human gastrointestinal stem cells. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):82–85. doi: 10.1038/343082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]