Abstract
Introduction
The Elongator complex, comprising six subunits (Elp1p-Elp6p), is required for formation of 5-carbamoylmethyl (ncm5) and 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl (mcm5) side chains on wobble uridines in 11 out of 42 tRNA species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Loss of these side chains reduces the efficiency of tRNA decoding during translation, resulting in pleiotropic phenotypes. Overexpression of hypomodified , which in wild-type strains are modified with mcm5s2U, partially suppress phenotypes of an elp3Δ strain.
Objectives
To identify metabolic alterations in an elp3Δ strain and elucidate whether these metabolic alterations are suppressed by overexpression of hypomodified .
Method
Metabolic profiles were obtained using untargeted GC-TOF-MS of a temperature-sensitive elp3Δ strain carrying either an empty low-copy vector, an empty high-copy vector, a low-copy vector harboring the wild-type ELP3 gene, or a high-copy vector overexpressing . The temperature sensitive elp3Δ strain derivatives were cultivated at permissive (30 °C) or semi-permissive (34 °C) growth conditions.
Results
Culturing an elp3Δ strain at 30 or 34 °C resulted in altered metabolism of 36 and 46 %, respectively, of all metabolites detected when compared to an elp3Δ strain carrying the wild-type ELP3 gene. Overexpression of hypomodified suppressed a subset of the metabolic alterations observed in the elp3Δ strain.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that the presence of ncm5- and mcm5-side chains on wobble uridines in tRNA are important for metabolic homeostasis.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s11306-016-1120-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Elongator complex, tRNA wobble uridine modifications, Translation, ELP3, Metabolomics, Metabolic profiling
Introduction
In eukaryotes, the Elongator complex is highly-conserved and comprises six subunits (Elp1p–Elp6p) (Otero et al. 1999; Y. Li et al. 2001; Krogan and Greenblatt 2001; Winkler et al. 2001; Hawkes et al. 2002; Nelissen et al. 2005). The complex is required for formation of 5-carbamoylmethyluridine (ncm5U), 5-methoxycarbonylmethyluridine (mcm5U) and 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine (mcm5s2U) modifications at wobble positions in tRNAs (Huang et al. 2005; Esberg et al. 2006; Chen et al. 2009; Lin et al. 2013; Mehlgarten et al. 2010; Karlsborn et al. 2014a). In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, loss-of-function mutations in any gene encoding an Elongator complex subunit gives rise to a multitude of phenotypes linked to several different cellular processes (Otero et al. 1999; Wittschieben et al. 1999; Winkler et al. 2002; Rahl et al. 2005; Tigano et al. 2015; Nedialkova and Leidel 2015; Frohloff et al. 2001; Chen et al. 2011; Q. Li et al. 2009). Phenotypes observed in yeast Elongator mutants, except the tRNA modification defect, are suppressed by overexpression of , which have the mcm5s2U modification in wild-type yeast. This discovery highlighted the importance of Elongator-complex-dependent tRNA modifications in translation (Esberg et al. 2006).
In an elp3Δ mutant enrichment of lysine-AAA codons in mRNAs decoded by having the Elongator complex dependent wobble uridine modification mcm5s2U result in reduced protein expression (Bauer et al. 2012). Replacing these lysine-AAA codons with the near-cognate G-ending AAG codon, decoded by a tRNA isoacceptor not requiring the Elongator complex dependent wobble uridine modification improved protein expression from the codon altered gene (Fernandez-Vazquez et al. 2013; Bauer et al. 2012). Moreover, ribosomal profiling studies performed with Elongator mutants revealed ribosomal pausing at the lysine-AAA and glutamine-CAA codons (Nedialkova and Leidel 2015; Zinshteyn and Gilbert 2013) and possibly the glutamic acid-GAA codons (Zinshteyn and Gilbert 2013). These results support the previous suggestion that the presence of the mcm5s2U modification in enhance translational efficiency (Esberg et al. 2006), probably because of improved codon-anticodon interactions (Johansson et al. 2008; Durant et al. 2005; Bauer et al. 2012; Vendeix et al. 2012; Rezgui et al. 2013; Tükenmez et al. 2015). However, whether the phenotypes are caused by global reduction of protein expression or altered protein expression from specific mRNAs, leading to downstream effects, is unknown. Moreover, whether the loss of modified wobble uridines causes metabolic alterations is yet to be determined.
Our study demonstrates that a large number of metabolites within an elp3Δ strain undergoes perturbed metabolism. Furthermore, the range of metabolites with altered levels expanded with growth of the elp3Δ strain at 34 °C; this is probably an effect of the temperature sensitivity phenotype of the elp3Δ mutant. Our study also shows that elevated levels of in the elp3Δ strain suppress some, but not all metabolic alterations.
Methods
Yeast strains, media, and genetic procedures
Yeast strains and plasmids used in this study are found in Online Resource 1 (Christianson et al. 1992; Lu et al. 2005; Sikorski and Hieter 1989). Genetic procedures, media, and yeast transformation have been described previously (Burke et al. 2000; Gietz and Schiestl 2007). An elp3 null mutant was generated by linear transformation of the diploid strain UMY2016/UMY2026 with an elp3::kanMX4 fragment (fragment amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)) generated from the elp3Δ strain in the yeast deletion collection (Open Biosystems). Transformants were selected on YEPD plates containing 200 µg/ml of G418. The heterozygous diploid generated was sporulated and tetrad dissection generated haploids UMY4238 and UMY4239. Insertion of the elp3::KanMX4 cassette in UMY4239 was verified by PCR and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis was used to determine the status of the wobble uridine nucleosides: ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U in yeast tRNA (Huang et al. 2005).
Cell sampling and metabolite extraction using untargeted GC-TOF-MS metabolomics
Strains UMY4239 (elp3::KanMX4) and UMY4238 were transformed with one of the following plasmids: empty pRS315, pRS315 containing the wild-type ELP3 gene, pRS425 or pRS425 containing the tRNA genes tK(UUU), tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC). Three replicates of each strain derivative were cultivated in synthetic defined media at either 30 or 34 °C until cell density was ~0.5 OD600 units. At ~0.5 OD600 units, cells amounting to 1 OD unit were harvested in triplicate from each biological replicate by centrifugation at 0 °C. The supernatant was discarded and the cells were washed with 2 ml of ice-cold phosphate buffered saline (PBS) then centrifuged again at 0 °C. The supernatant was discarded and pellets were suspended in a 90:10 mixture of Methanol and MilliQ (MQ) water which was pre-chilled on dry ice. Suspended pellets were stored at −80 °C until metabolite extraction.
Metabolites were extracted by grinding the pellets with glass beads for 3 min at 30 Hz followed by centrifugation at 14,000 RPM for 10 min. A 200 µL aliquot of the supernatant was transferred to a GC-vial and evaporated using a SpeedVac. Derivatization of the metabolic extract was performed using 30 µL of methoxyamine (16 h at room temperature). The extract was then trimethylsilylated by adding 30 µL of N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide (MSTFA) to the vial and incubating for 1 h at 25 °C. Subsequently, 30 µL of heptane containing 15 ng/µL methyl stearate was added to the vial.
Samples were analysed using combined gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC/TOFMS). For retention indices, an n-alkane series (C8–C40) was included in the analysis (Schauer et al. 2005). A 1 μL volume of derivatized sample was injected into a split/splitless injector, in splitless mode, on an Agilent CTC PAL Systems Autosampler with a 10 μL syringe (Agilent Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA). The autosampler injected samples into an Agilent Technologies 7890A GC System (Agilent Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA). The Agilent Technologies 7890A GC System was equipped with a 30 m × 0.250 mm-diameter fused, silica capillary column with a bonded 0.25 μm Durabond DB-5MSUI stationary phase (part no: 122-5222UI, Agilent J&W GC columns). The injector temperature was set to 260 °C, front inlet septum purge flow set to 3 mL min−1, and gas flow rate through the column set to 1 mL min−1. Column temperature was held at 70 °C for 2 min, then increased by 20 °C min−1 to 320 °C, and held for 8 min. The column effluent was led into the ion source of a Pegasus HT GC-TOF-MS (LECO Corp., St Joseph, MI, USA). The transfer line and ion source temperatures were 270 and 200 °C, respectively. Detector voltage was set to 1650 V. Ions were generated by a −70 V electron beam at an ionization current of 2.0 mA, and 20 spectra s−1 were recorded in the mass range 50–800 m/z. The acceleration voltage was turned on after a solvent delay of 270 s.
Data processing of samples subjected to GC-TOF-MS
Unprocessed MS files from GC/TOF–MS analysis were exported in NetCDF format to MATLAB software R2013a (Mathworks, Natick, MA). All data pretreatment procedures, including baseline correction, chromatogram alignment, time-window setting and multivariate curve resolution (MCR) (Jonsson et al. 2005) were performed in MATLAB using custom scripts. Peak detection against mass spectra libraries (targeted data processing) was performed with an in-house script. Metabolites were identified by using NIST MS Search 2.0 software to compare the mass spectra of all detected compounds with spectra in: the NIST library 2.0, the in-house mass spectra library established by Swedish Metabolomics Centre, and the mass spectra library maintained by the Max Planck Institute in Golm (http://csbdb.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/csbdb/gmd/gmd.html).
A retention index comparison was performed, with a retention index deviation < ± 10 (in addition to a high spectral match) resulting in a positive ID. Generated peaks were analysed in tandem using the spectral database found at www.massbank.jp. The data was normalized using all 11 internal standards (eluting over the whole chromatographic time range). A principal component analysis (PCA), using peak areas for the internal standards, was conducted and the T-score value for each sample was used to normalize the resolved data by dividing the peak areas of each sample with its corresponding score value. Multivariate analysis was performed with SIMCA-P + 13 software (Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden). Data from the analysis and peak-spectra is available as (Online Resource 12–13).
Data analysis
Data was preprocessed for an integrity check and transformed into the binary logarithm [base of 2; log(2)] for downstream analysis (Stacklies et al. 2007). Extreme outliers were replaced by the median of the data within biological replicates, and data was subjected to pareto scaling (Dieterle et al. 2006). Heatmaps were generated using the heatmap.2 function in the gplots package in R software with data transformed into the common logarithm [base of 10; log(10)] using averages of metabolite levels.
PCA is an unsupervised method for finding the directions that best explain the variance in a data set (X) without referring to classification labels (Y). PCA was performed using the prcomp syntax in R (William N. Venables 2002) or SIMCA, version 14.0.0.1359 (Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden).
Partial least-squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) is a supervised method that uses multivariate regression techniques to extract information that can predict classification (Y) via linear combination of original variables (X). PLS-DAs were performed on log(2)-transformed metabolite concentrations that had been centered according to the means using SIMCA, version 14.0.0.1359 (Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden); unit-variance scaling was applied as previously described (Slupsky et al. 2007).
A permutation test was performed (20 permutations) to assess the significance of classification, and prediction accuracy was determined (Max Kuhn. Contributions from Jed Wing and Steve Weston and Andre Williams. caret: Classification And REgression Training, 2008, R package version 3.45) (Bijlsma et al. 2006). Variable Importance in Projection (VIP) in PLS-DA is a weighted sum of the squares of the PLS loadings that accounts for the amount of explained Y-variation in each dimension for each component (Max Kuhn. Contributions from Jed Wing and Steve Weston and Andre Williams. caret: Classification And Regression Training, 2008).
Results
Loss of ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides in tRNA result in an altered metabolic profile
We subjected an elp3Δ strain carrying either an empty low copy LEU2 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-empty) or the same vector containing the wild-type ELP3 gene (elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3) to metabolic profiling using non-targeted GC-TOF-MS (Fig. 1). This metabolic profiling was conducted to investigate whether loss of the ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides in yeast tRNA causes metabolic alterations. We also included samples of the wild-type strain carrying an empty high-copy LEU2 vector (WT-h.c.-empty) to investigate whether metabolism of the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain represents that of the wild-type strain.
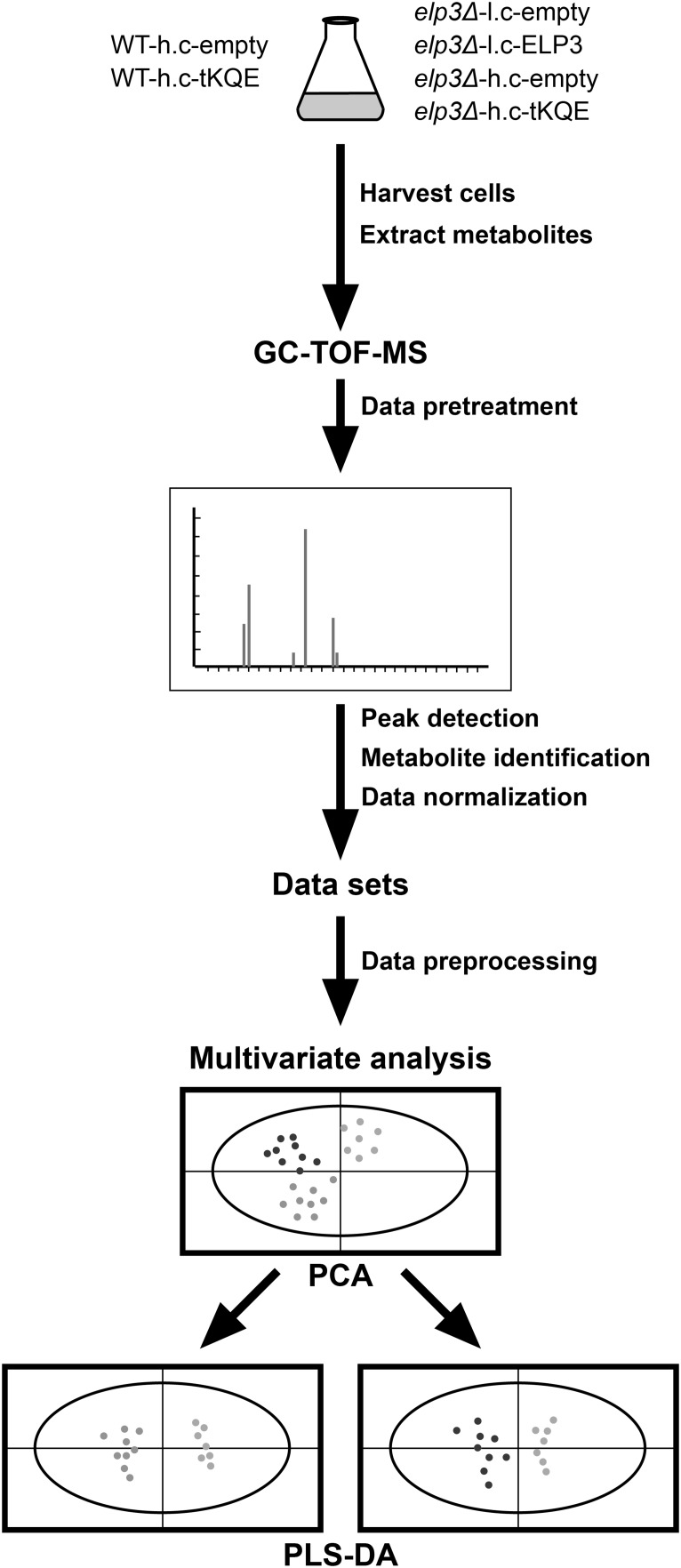
Fig. 1.
Overview of the pipeline for metabolic profiling of wild-type and elp3Δ strains carrying indicated plasmids. The UMY4238 and UMY4239 yeast strains contained either: an empty low-copy pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-empty); a pRS315 vector containing the wild-type ELP3 gene (elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3); an empty high copy pRS425 vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty, WT-h.c.-empty); or a high copy pRS425 vector carrying the tRNA genes tK(UUU), tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC) (elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE, WT-h.c.-tKQE). Yeast strains were cultivated logarithmically to an OD600 value of ~0.5 at 30 or 34 °C and harvested. Metabolites were extracted and then quantified using GC-TOF-MS. Metabolite data was analyzed using multivariate analysis (PCA, PLS-DA) which separated the metabolites according to different classes representing the elp3Δ strains containing various plasmid constructs
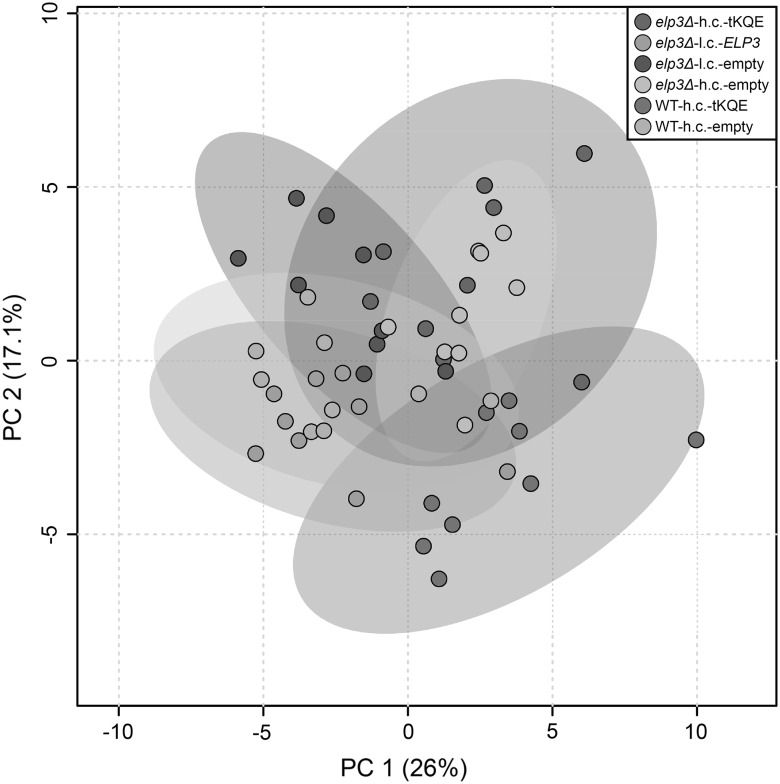
Since elp3Δ strains are temperature sensitive (Ts), we cultured strains to ~0.5 OD600 units under permissive (30 °C) and semi-permissive (34 °C) growth conditions, as metabolic changes may be more pronounced at elevated temperatures. From our metabolite extracts, 111 metabolites could be measured using GC-TOF-MS, 41 of which could be identified while the remaining were unidentified. We performed a PCA of all the strains used and all 111 metabolites detected in this study to get an overview of metabolism in the strains. The PCA results showed that the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain clusters with the WT-h.c.-empty strain, indicating that metabolism in these strains is similar (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Metabolic variation of the wild-type and elp3Δ strain containing indicated plasmids. The UMY4238 and UMY4239 yeast strains containing either: an empty low-copy pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-empty); a pRS315 vector containing the wild-type ELP3 gene (elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3); an empty high copy pRS425 vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty, WT-h.c.-empty); or a high copy pRS425 vector carrying the tRNA genes tK(UUU), tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC) (elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE, WT-h.c.-tKQE) were grown logarithmically to an OD600 of ~0.5 at 30 °C and harvested. Metabolites were extracted and then quantified using GC-TOF-MS. Each dot in the PCA analysis represents a technical replicate from three different biological replicates
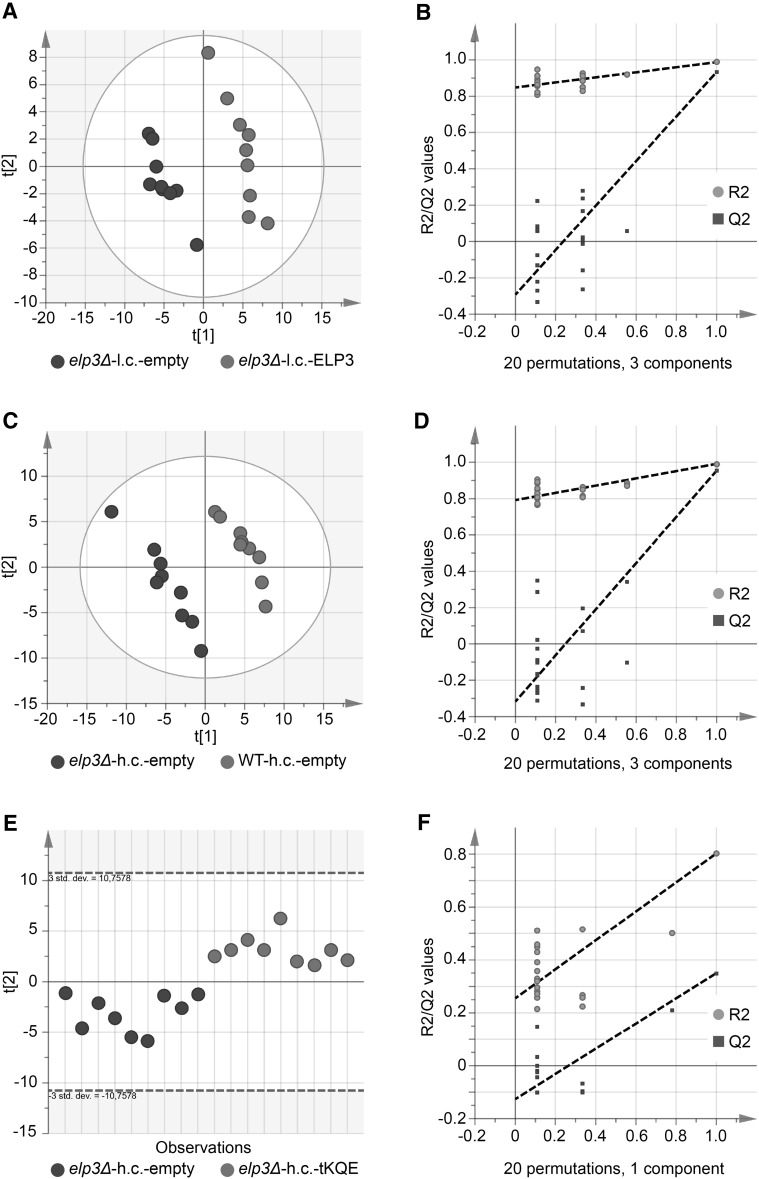
We looked for alterations in levels of specific metabolites in the elp3Δ strain using partial least squares regression discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) (Figs. 3a–f, 4a–d). Metabolites with a variable importance for the projection (VIP) below one were excluded (Chong and Jun 2005). Briefly, PLS-DA allows analysis of large sample sets structured in the form of classes. The classes are separated according to a comparison between all variables within one class and all variables within another class, and subsequent prediction of the variables that account for the class separation. Variables that are good predictors for separating one class from another have a high VIP score, while variables with a low VIP score do not contribute to class separation.
Fig. 3.
Score plots summarizing the PLS-DA modelling of strains grown at 30 °C. a PLS-DA score plot when modelling the elp3Δ strain with an empty low copy pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-empty) against the elp3Δ strain containing the wild-type ELP3 gene on a pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3). b Random permutation (20 randomizations) test-validation plot of PLS-DA model in (a). c PLS-DA score plot when modelling the elp3Δ strain with an empty high copy pRS425 vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty) against the wild-type strain with an empty pRS425 vector (WT-h.c.-empty). d Random permutation (20 randomizations) test-validation plot of PLS-DA model in (c). e PLS-DA score plot when modelling the elp3Δ strain with an empty high copy pRS425 vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty) against the elp3Δ strain containing a pRS425 vector carrying the tRNA genes tK(UUU), tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC) (elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE). f Random permutation (20 randomizations) test-validation plot of PLS-DA model in (e). The PLS-DA model in e only has one valid component and is therefore portrayed by one vector. Each dot in a, c and e represents a technical replicate from three different biological replicates
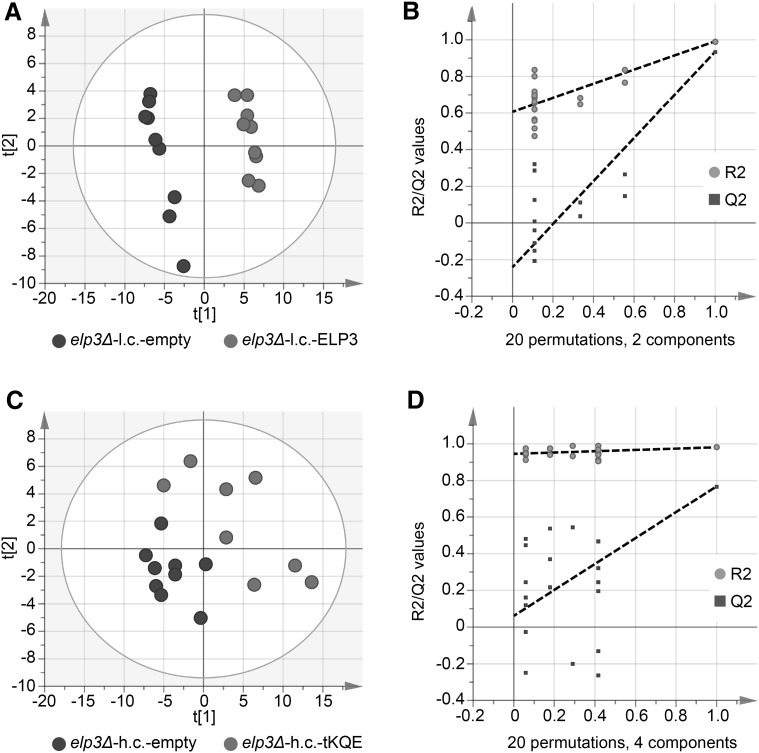
Fig. 4.
Score plots summarizing the PLS-DA modelling of strains grown at 34 °C. a PLS-DA score plot when modelling the elp3Δ strain with an empty low copy pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-empty) against the elp3Δ strain containing the wild-type ELP3 gene on a pRS315 vector (elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3). b Random permutation (20 randomizations) test-validation plot of PLS-DA model in a. c PLS-DA score plot when modelling the elp3Δ strain with an empty high copy pRS425 vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty) against the elp3Δ strain containing a pRS425 vector carrying the tRNA genes tK(UUU), tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC) (elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE). d Random permutation (20 randomizations) test-validation plot of PLS-DA model in (c). Each dot in a, c and e represents a technical replicate from three different biological replicates
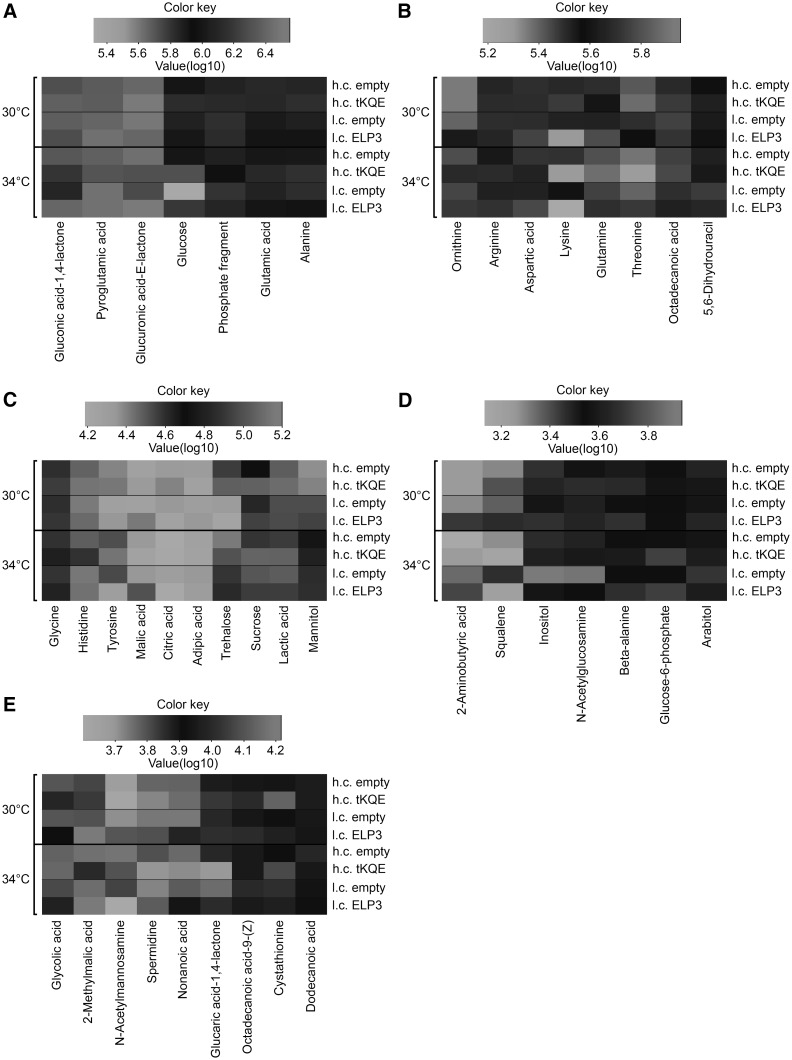
A comparison of the metabolic profiles of only identified metabolites showed that permissive growth (30 °C) of the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain resulted in elevated levels of primarily Ornithine, Lysine and N-Acetylglucosamine, and reduced levels of Glutamine, Beta-alanine, Malic acid, Aspartic acid, Pyroglutamic acid, Alanine, Threonine, 2-Aminobutyric acid, 5,6-Dihydrouracil and Tyrosine when compared to the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain (Fig. 5a–e, Online Resource 2–3). Semi-permissive growth (34 °C) of the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain also resulted in elevated levels of Ornithine, Lysine and N-Acetylglucosamine when compared to the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain (Fig. 5a–e, Online Resource 2–3). We also observed that the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain accumulated eight additional metabolites with known identity at 34 °C (Online Resource 4), indicating more pronounced metabolic changes with growth at elevated temperatures.
Fig. 5.
Metabolic alterations upon loss of ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides in tRNA. The UMY4239 elp3Δ strains contained either: an empty pRS315 low copy vector (l.c. empty); a pRS315 vector carrying the wild-type ELP3 gene (l.c. ELP3); an empty pRS425 high copy vector (h.c. empty); or a pRS425 high copy vector carrying the tRNA genes tK(UUU); tQ(UUG) and tE(UUC) (h.c. tKQE). These yeast strains were grown logarithmically to ~0.5 OD600 at 30 or 34 °C and harvested. Metabolites were extracted and then quantified using GC-TOF-MS. Metabolites were hierarchically organized into five clusters as represented by a–e based on metabolite abundance (see Online Resource 2). Red signifies metabolite enrichment and green signifies metabolite reduction
Semi-permissive (34 °C) growth of the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain showed reduced levels of Beta-alanine and Glutamine, as observed at permissive growth (30 °C) (Fig. 5a–e, Online Resource 2–4). In addition, semi-permissive growth of the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain showed reduced levels of Malic acid, Aspartic acid and Threonine. Surprisingly, we did not observe significantly reduced levels of Pyroglutamic acid, Alanine, 2-Aminobutyric acid, 5,6-Dihydrouracil and Tyrosine after semi-permissive growth, as when the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain grew at 30 °C. Instead, semi-permissive growth of this strain resulted in reduced levels of Gluconic acid 1,4-lactone, Glucose, Trehalose, Octadecanoic acid and Glucuronic acid-E-lactone.
Moreover, we observed that several unidentified metabolites had a VIP score above one, indicating altered metabolism of these metabolites in the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain compared to the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain at both 30 and 34 °C (Online Resource 5–6). The amounts of identified and unidentified metabolites with altered levels in the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain and the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain were higher when these strains grew at 34 °C (Online Resource 5–6). Our results show that semi-permissive growth of the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain resulted in more metabolic alterations than permissive growth. More metabolites started to increase or decrease at 34 °C in the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain while levels of these metabolites were more or less constant at both 30 and 34 °C in the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain.
Elevated levels of hypomodified partially suppress certain metabolic alterations
All phenotypes tested in yeast Elongator mutants to date have been partially suppressed by elevated levels of various combinations of hypomodified (Esberg et al. 2006; Chen et al. 2011; Tigano et al. 2015; Fernandez-Vazquez et al. 2013; Bauer et al. 2012; Nedialkova and Leidel 2015). Thus, we were interested in investigating whether the metabolic alterations in elp3Δ cells are suppressed by elevated levels of . We compared the PLS-DA model of the elp3Δ strain that either contained an empty pRS425 high-copy vector (elp3Δ-h.c.-empty) or overexpressed (elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE) with the PLS-DA model that compared the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty strain with the elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strain.
PLS-DA modelling of the comparison between the elp3Δ-h.c.-empty strain and the elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE strain produced models with lower Q2-values than PLS-DA models of the comparison between the elp3Δ-l.c.-empty and elp3Δ-l.c.-ELP3 strains (Figs. 3a–f, 4a–d, Online Resource 7). This result indicates that very few metabolic alterations are suppressed by overexpression of in the elp3Δ strain. However, the growth defect of the elp3Δ strain at 34 °C was partially suppressed by overexpression of the aforementioned tRNAs (data not shown).
At permissive (30 °C) growth we observed suppression of alteration of beta-alanine metabolism, and weak suppression of alterations of Glutamine, Tyrosine, Ornithine and Lysine metabolism from a comparison between metabolic patterns of identified metabolites from the elp3Δ-h.c.-empty and elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE strains grown at 30 °C. We did not observe suppression of the altered metabolism of: Malic acid, Aspartic acid, Pyroglutamic acid, Alanine, Threonine, 2-Aminobutyric acid, 5,6-Dihydrouracil and N-Acetylglucosamine (Fig. 5a–e, Online Resource 2, 8).
Next, we investigated whether overexpression of in the elp3Δ strain led to a unique suppression pattern of metabolic alterations during growth at 34 °C. A comparison between the metabolite patterns of the elp3Δ-h.c.-empty and elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE strains grown at 34 °C revealed that elevated levels of suppressed alterations in Lysine and Ornithine metabolism. However, changes in Beta-alanine and Glutamine metabolism were not suppressed in elp3Δ-h.c.-tKQE strains grown at 34 °C. Elevated levels of partially suppressed alterations in Lactic acid, Tyrosine, Alanine and Glutamic acid metabolism at 34 °C. Moreover, an analytical trend indicated that alterations in several other metabolites may be weakly suppressed (Fig. 5a–e, Online Resource 2, 9).
Several unidentified metabolites were suppressed in the elp3Δ strains at both 30 and 34 °C (Online Resource 10–11). Overall, our results indicate that suppression of certain metabolic alterations varies with elevated levels of in the elp3Δ strain depending on the growth temperature. However, Ornithine and Lysine are exceptions in the elp3Δ strain as alterations of these metabolites are partially suppressed with elevated levels of the three tRNAs at both 30 and 34 °C.
Discussion
Mutations in genes encoding Elongator complex subunits have been linked to a multitude of phenotypes in S. cerevisiae (Otero et al. 1999; Wittschieben et al. 1999; Winkler et al. 2002; Rahl et al. 2005; Tigano et al. 2015; Nedialkova and Leidel 2015; Frohloff et al. 2001; Chen et al. 2011; Q. Li et al. 2009). Many investigations in Eukaryotes support a role for the complex in formation of the ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides in tRNA [Reviewed in (Karlsborn et al. 2014b)]. Furthermore, phenotypes observed in yeast Elongator mutants can be suppressed by overexpression of various combinations of (Esberg et al. 2006; Chen et al. 2011; Tigano et al. 2015; Fernandez-Vazquez et al. 2013; Bauer et al. 2012; Nedialkova and Leidel 2015). This suppression has been ascribed to restoring translational efficiency of codons normally read by by compensating the reduced codon-anticodon interaction of the hypomodified tRNAs with elevated levels of these three tRNA species (Esberg et al. 2006; Chen et al. 2011).
In this study, we used untargeted GC-TOF-MS based metabolomics to investigate the extent of metabolic alterations in an elp3Δ strain. We found that loss of the ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides in tRNA resulted in an altered metabolism, and that only a subset of these alterations were suppressed by overexpression of . This was surprising, as all phenotypes tested in yeast elp3Δ strains to date, except the tRNA modification defect, have been at least partially suppressed by elevated levels of various combinations of these three tRNAs (Esberg et al. 2006; Chen et al. 2011; Tigano et al. 2015; Fernandez-Vazquez et al. 2013; Bauer et al. 2012). Therefore, suppression of most of the metabolic alterations observed in an elp3Δ mutant may require elevated levels of additional tRNA species that normally have the ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U wobble uridine nucleosides.
It is possible that some metabolic alterations in the elp3Δ strain could be transient, or observed only when cells are exposed to certain stress conditions. Furthermore, metabolic alterations observed in the elp3Δ strain could, in part, be a global metabolic adaptation of the primary metabolic defects due to inefficient translation. If elp3Δ cells adapt to specific metabolic defects by reconfiguring global metabolism, the stress tolerance may be influenced, as the altered metabolism may cause the cell to be in an unfavourable state of metabolic homeostasis. Thus, overexpression of in the elp3Δ strain could suppress certain primary metabolic defects and alter the metabolic homeostasis into a more favourable state, resulting in a cellular metabolism better equipped to handle sudden changes in cell physiology due to stress exposure. To differentiate between primary and secondary metabolic defects in the elp3Δ strain, an instantaneous elimination of the ncm5U, mcm5U and mcm5s2U tRNA modifications is required. However, there are no known enzymes that specifically remove these modifications. Moreover, the long half-life of tRNAs means that a rapid depletion of Elongator would not generate an immediate loss of the modifications, but instead a gradual depletion of modified tRNA species during cellular growth.
Ribosomal profiling studies of Elongator mutants have shown increased ribosome pausing when lysine-AAA and glutamine-CAA codons are in the ribosomal A-site (Nedialkova and Leidel 2015). Increased ribosome pausing in an elp6Δ mutant can be alleviated by overexpression of which lack the mcm5- side chain (Nedialkova and Leidel 2015). These results indicate that global translation efficiency is affected by loss of these side chains in tRNA, and further, that defective translation due to increased ribosome pausing is suppressed by overexpression of the aforementioned tRNA species. Nonetheless, even if ribosomal pausing occurs on AAA and CAA codons, it is possible that only a few mRNAs have translation defects which result in altered protein expression and likely an altered metabolism.
Concluding remarks
Overall, our metabolic profiling data shows that elp3Δ strains have widespread metabolic alterations. These metabolic alterations can be restored by complementation of the elp3Δ strains with the wild type ELP3, whereas only a few metabolic alterations are suppressed by overexpression of . Our metabolic profiling also revealed unidentified metabolites which are altered in the elp3Δ strain. In the future, more comprehensive databases over yeast metabolites could allow identification of these metabolites, making it possible for our data set to be of valuable use in future studies of the Elongator complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Marcus Johansson, Hans Stenlund, Anders Nordström and Thomas Moritz for comments on the manuscript and the Swedish metabolomics center for help in analyzing metabolites by GC-TOF-MS.
Funding
Anders S. Byström is supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Foundation (13 0301), Swedish Research Council (621-2012-3576), Karin and Harald Silvanders Foundation and Insamlingsstiftelsen Umeå University.
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
Author Anders S. Byström declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Tony Karlsborn declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author A K M Firoj Mahmud declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Hasan Tükenmez declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Footnotes
A. K. M. Firoj Mahmud and Hasan Tükenmez has contributed equally to this work.
References
- Bauer F, Matsuyama A, Candiracci J, Dieu M, Scheliga J, Wolf DA, et al. Translational control of cell division by Elongator. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t] Cell Reports. 2012;1(5):424–433. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijlsma S, Bobeldijk I, Verheij ER, Ramaker R, Kochhar S, Macdonald IA, et al. Large-scale human metabolomics studies: a strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Analytical Chemistry. 2006;78(2):567–574. doi: 10.1021/ac051495j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D, Dawson D, Stearns T. Methods in Yeast Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Huang B, Eliasson M, Ryden P, Byström AS. Elongator complex influences telomeric gene silencing and DNA damage response by its role in wobble uridine tRNA modification. [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t] PLoS Genetics. 2011;7(9):e1002258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Tuck S, Byström AS. Defects in tRNA modification associated with neurological and developmental dysfunctions in Caenorhabditis elegans elongator mutants. PLoS Genetics. 2009;5(7):e1000561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong I-G, Jun C-H. Performance of some variable selection methods when multicollinearity is present. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems. 2005;78(1–2):103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2004.12.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson TW, Sikorski RS, Dante M, Shero JH, Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterle F, Ross A, Schlotterbeck G, Senn H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics. Analytical Chemistry. 2006;78(13):4281–4290. doi: 10.1021/ac051632c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durant PC, Bajji AC, Sundaram M, Kumar RK, Davis DR. Structural effects of hypermodified nucleosides in the Escherichia coli and human tRNA(Lys) anticodon loop: The effect of nucleosides s(2)U, mcm(5)U, mcm(5)s(2)U, mnm(5)s(2)U, t(6)A, and ms(2)t(6)A. Biochemistry. 2005;44(22):8078–8089. doi: 10.1021/bi050343f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esberg A, Huang B, Johansson MJ, Byström AS. Elevated levels of two tRNA species bypass the requirement for elongator complex in transcription and exocytosis. Molecular Cell. 2006;24(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Vazquez J, Vargas-Perez I, Sanso M, Buhne K, Carmona M, Paulo E, et al. Modification of tRNA(Lys) UUU by elongator is essential for efficient translation of stress mRNAs. PLoS Genetics. 2013;9(7):e1003647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohloff F, Fichtner L, Jablonowski D, Breunig KD, Schaffrath R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Elongator mutations confer resistance to the Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin. EMBO Journal. 2001;20(8):1993–2003. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.8.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz RD, Schiestl RH. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nature Protocols. 2007;2(1):31–34. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes NA, Otero G, Winkler GS, Marshall N, Dahmus ME, Krappmann D, et al. Purification and characterization of the human elongator complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277(4):3047–3052. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110445200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B, Johansson MJO, Byström AS. An early step in wobble uridine tRNA modification requires the Elongator complex. RNA. 2005;11(4):424–436. doi: 10.1261/rna.7247705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson MJO, Esberg A, Huang B, Björk GR, Byström AS. Eukaryotic wobble uridine modifications promote a functionally redundant decoding system. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2008;28(10):3301–3312. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01542-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson P, Johansson AI, Gullberg J, Trygg J, A J, Grung B, et al. High-throughput data analysis for detecting and identifying differences between samples in GC/MS-based metabolomic analyses. Analytical Chemistry. 2005;77(17):5635–5642. doi: 10.1021/ac050601e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsborn T, Tükenmez H, Chen C, Byström AS. Familial dysautonomia (FD) patients have reduced levels of the modified wobble nucleoside mcmsU in tRNA. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014;454(3):441–445. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsborn T, Tükenmez H, Mahmud AK, Xu F, Xu H, Byström AS. Elongator, a conserved complex required for wobble uridine modifications in eukaryotes. RNA Biology. 2014;11(12):1519–1528. doi: 10.4161/15476286.2014.992276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogan NJ, Greenblatt JF. Characterization of a six-subunit holo-elongator complex required for the regulated expression of a group of genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2001;21(23):8203–8212. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.23.8203-8212.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q, Fazly AM, Zhou H, Huang S, Zhang Z, Stillman B. The elongator complex interacts with PCNA and modulates transcriptional silencing and sensitivity to DNA damage agents. PLoS Genetics. 2009;5(10):e1000684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Takagi Y, Jiang Y, Tokunaga M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, et al. A multiprotein complex that interacts with RNA polymerase II elongator. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(32):29628–29631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100274200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin FJ, Shen L, Jang CW, Falnes PO, Zhang Y. Ikbkap/Elp1 deficiency causes male infertility by disrupting meiotic progression. PLoS Genetics. 2013;9(5):e1003516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J, Huang B, Esberg A, Johansson MJO, Byström AS. The Kluyveromyces lactis γ-toxin targets tRNA anticodons. RNA. 2005;11(11):1648–1654. doi: 10.1261/rna.2172105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlgarten C, Jablonowski D, Wrackmeyer U, Tschitschmann S, Sondermann D, Jäger G, et al. Elongator function in tRNA wobble uridine modification is conserved between yeast and plants. Molecular Microbiology. 2010 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedialkova DD, Leidel SA. Optimization of Codon Translation Rates via tRNA Modifications Maintains Proteome Integrity. Cell. 2015;161(7):1606–1618. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelissen H, Fleury D, Bruno L, Robles P, De Veylder L, Traas J, et al. The elongata mutants identify a functional Elongator complex in plants with a role in cell proliferation during organ growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005;102(21):7754–7759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502600102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero G, Fellows J, Li Y, de Bizemont T, Dirac AM, Gustafsson CM, et al. Elongator, a multisubunit component of a novel RNA polymerase II holoenzyme for transcriptional elongation. Molecular Cell. 1999;3(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahl PB, Chen CZ, Collins RN. Elp1p, the yeast homolog of the FD disease syndrome protein, negatively regulates exocytosis independently of transcriptional elongation. Molecular Cell. 2005;17(6):841–853. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rezgui VA, Tyagi K, Ranjan N, Konevega AL, Mittelstaet J, Rodnina MV, et al. tRNA tKUUU, tQUUG, and tEUUC wobble position modifications fine-tune protein translation by promoting ribosome A-site binding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2013;110(30):12289–12294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300781110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer N, Steinhauser D, Strelkov S, Schomburg D, Allison G, Moritz T, et al. GC-MS libraries for the rapid identification of metabolites in complex biological samples. FEBS Letters. 2005;579(6):1332–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski RS, Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slupsky CM, Rankin KN, Wagner J, Fu H, Chang D, Weljie AM, et al. Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Analytical Chemistry. 2007;79(18):6995–7004. doi: 10.1021/ac0708588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacklies W, Redestig H, Scholz M, Walther D, Selbig J. pcaMethods–a bioconductor package providing PCA methods for incomplete data. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(9):1164–1167. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tigano M, Ruotolo R, Dallabona C, Fontanesi F, Barrientos A, Donnini C, et al. Elongator-dependent modification of cytoplasmic tRNALysUUU is required for mitochondrial function under stress conditions. Nucleic Acids Research. 2015;43(17):8368–8380. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tükenmez H, Xu H, Esberg A, Byström AS. The role of wobble uridine modifications in +1 translational frameshifting in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Research. 2015;43(19):9489–9499. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables William N, Ripley BD. Modern applied statistics with S. New York: Springer; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vendeix FA, Murphy FVT, Cantara WA, Leszczynska G, Gustilo EM, Sproat B, et al. Human tRNA(Lys3)(UUU) is pre-structured by natural modifications for cognate and wobble codon binding through keto-enol tautomerism. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2012;416(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler GS, Kristjuhan A, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Svejstrup JQ. Elongator is a histone H3 and H4 acetyltransferase important for normal histone acetylation levels in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99(6):3517–3522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022042899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler GS, Petrakis TG, Ethelberg S, Tokunaga M, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, et al. RNA polymerase II elongator holoenzyme is composed of two discrete subcomplexes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(35):32743–32749. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105303200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittschieben BO, Otero G, de Bizemont T, Fellows J, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ohba R, et al. A novel histone acetyltransferase is an integral subunit of elongating RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Molecular Cell. 1999;4(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80194-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinshteyn B, Gilbert WV. Loss of a conserved tRNA anticodon modification perturbs cellular signaling. PLoS Genetics. 2013;9(8):e1003675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.