Abstract
Potassium is accumulated in plant vacuoles against an inside-positive membrane potential. The mechanism facilitating energized K+ transport has remained obscure. However, electrogenic activity of the inorganic pyrophosphatase (H(+)-PPase) at the vacuolar membrane is dependent on cytoplasmic K+, raising the possibility that the enzyme translocates K+ into the vacuole. Membrane currents generated by the H(+)-PPase were measured (using a patch clamp technique) in intact vacuoles isolated from Beta vulgaris storage tissue. A significant orthophosphate-dependent outward current mediated by the enzyme in reverse mode is evoked only when potassium is present at the vacuolar face of the tonoplast, suggesting that potassium is a translocated ion. Furthermore, current-voltage analysis of the effects of extravacuolar potassium and pH on the reversal potential of the H(+)-PPase-generated current points to direct translocation of K+ and H+ by the enzyme. Thus the H(+)-PPase represents a distinct class of eukaryote translocase and could facilitate vacuolar K+ accumulation in vivo.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry P. H., Lynch J. W. Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch-clamp analysis. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(2):101–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01870526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackford S., Rea P. A., Sanders D. Voltage sensitivity of H+/Ca2+ antiport in higher plant tonoplast suggests a role in vacuolar calcium accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9617–9620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Lerner H. R., Reinhold L. Evidence for a highly specific k/h antiporter in membrane vesicles from oil-seed rape hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1991 Nov;97(3):1212–1220. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.3.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
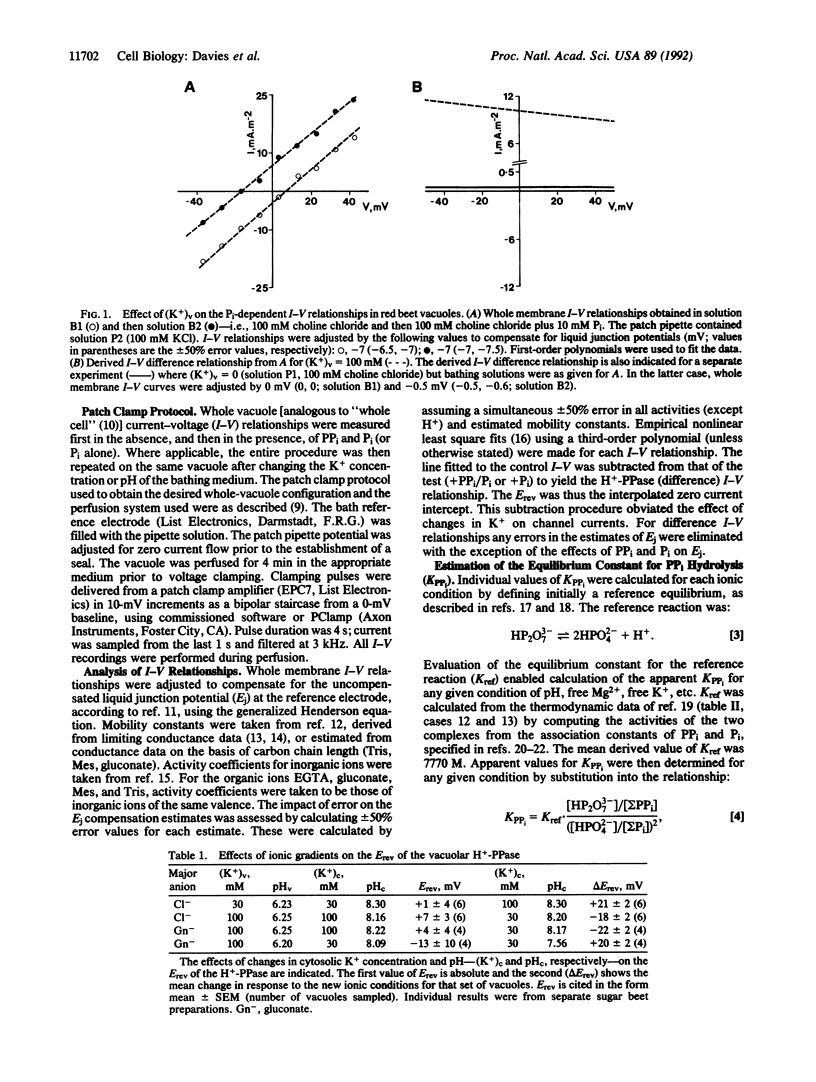
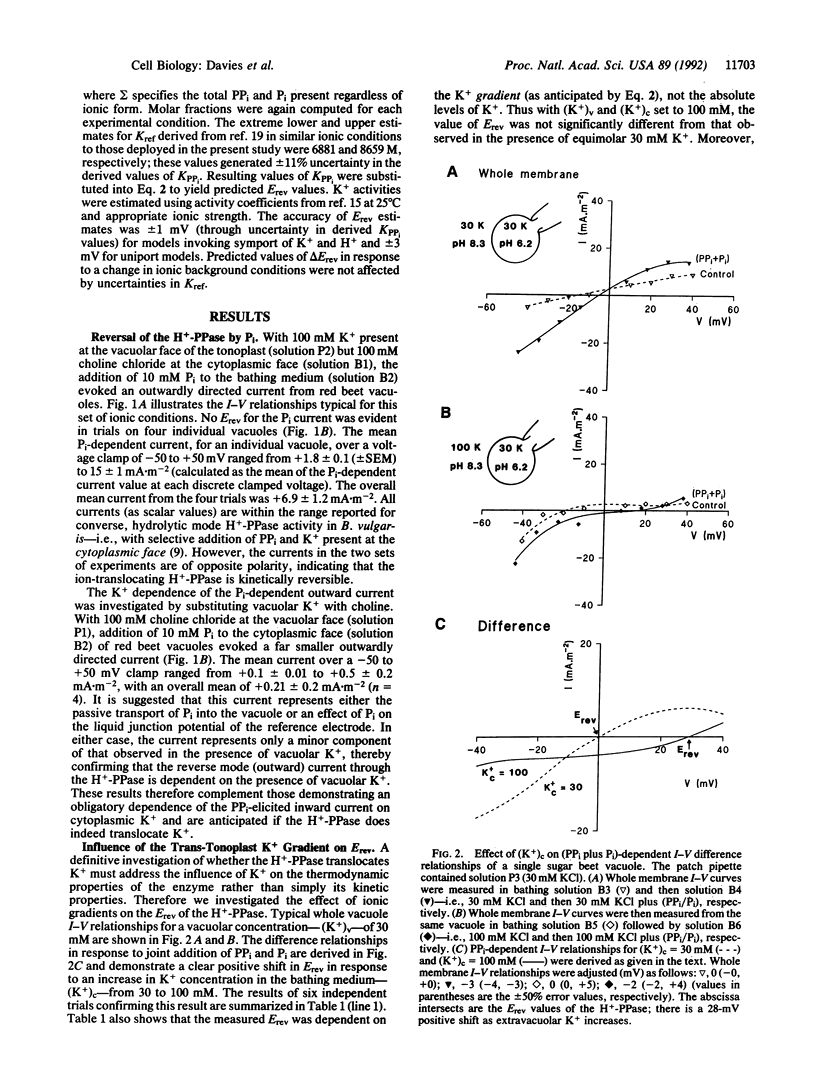
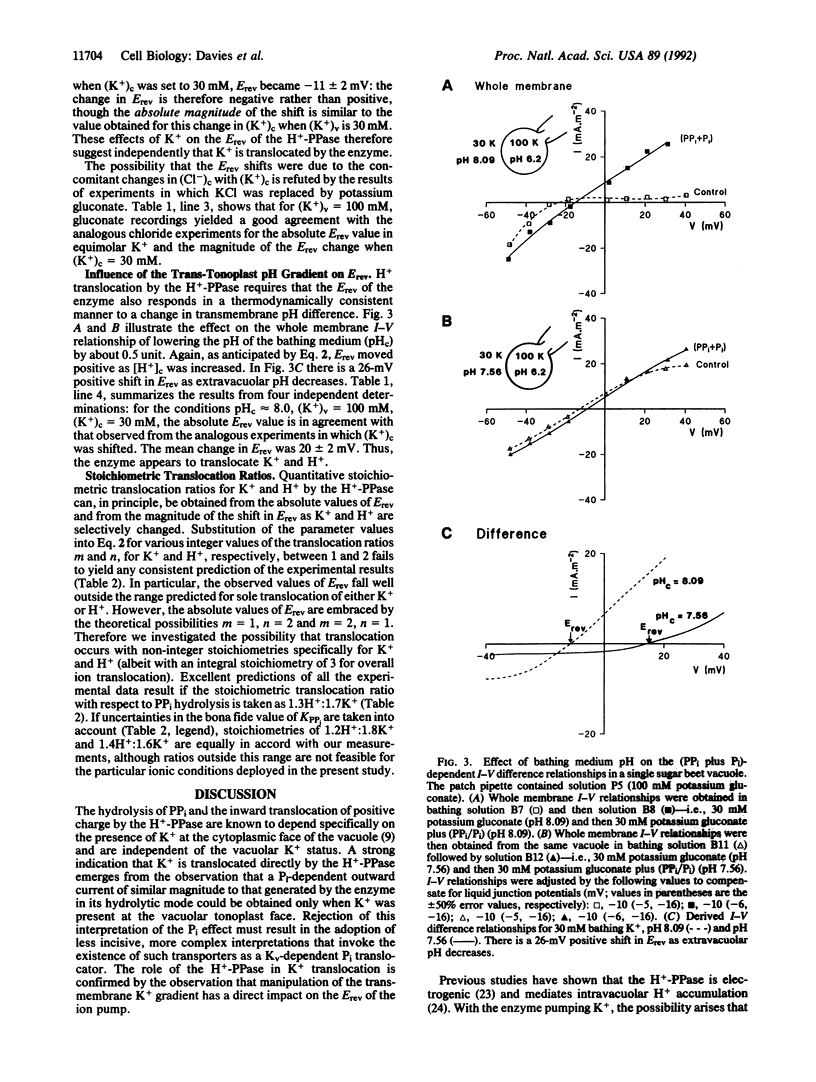
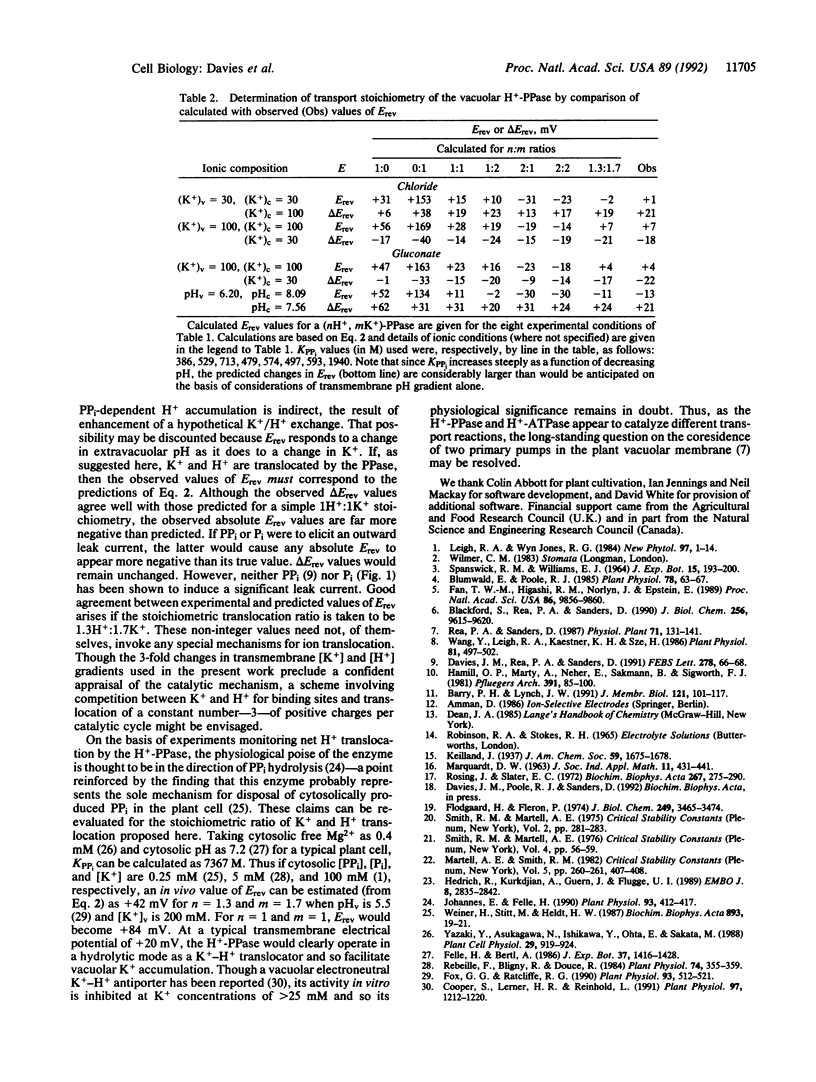
- Davies J. M., Rea P. A., Sanders D. Vacuolar proton-pumping pyrophosphatase in Beta vulgaris shows vectorial activation by potassium. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):66–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80085-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan T. W., Higashi R. M., Norlyn J., Epstein E. In vivo 23Na and 31P NMR measurement of a tonoplast Na+/H+ exchange process and its characteristics in two barley cultivars. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9856–9860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Fleron P. Thermodynamic parameters for the hydrolysis of inorganic pyrophosphate at pH 7.4 as a function of (Mg2+), (K+), and ionic strength determined from equilibrium studies of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3465–3474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. G., Ratcliffe G. P NMR Observations on the Effect of the External pH on the Intracellular pH Values in Plant Cell Suspension Cultures. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):512–521. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Kurkdjian A., Guern J., Flügge U. I. Comparative studies on the electrical properties of the H+ translocating ATPase and pyrophosphatase of the vacuolar-lysosomal compartment. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2835–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannes E., Felle H. Proton Gradient Across the Tonoplast of Riccia fluitans as a Result of the Joint Action of Two Electroenzymes. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):412–417. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeille F., Bligny R., Douce R. Is the cytosolic pi concentration a limiting factor for plant cell respiration? Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):355–359. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Slater E. C. The value of G degrees for the hydrolysis of ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 25;267(2):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Leigh R. A., Kaestner K. H., Sze H. Electrogenic h-pumping pyrophosphatase in tonoplast vesicles of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):497–502. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


