Abstract
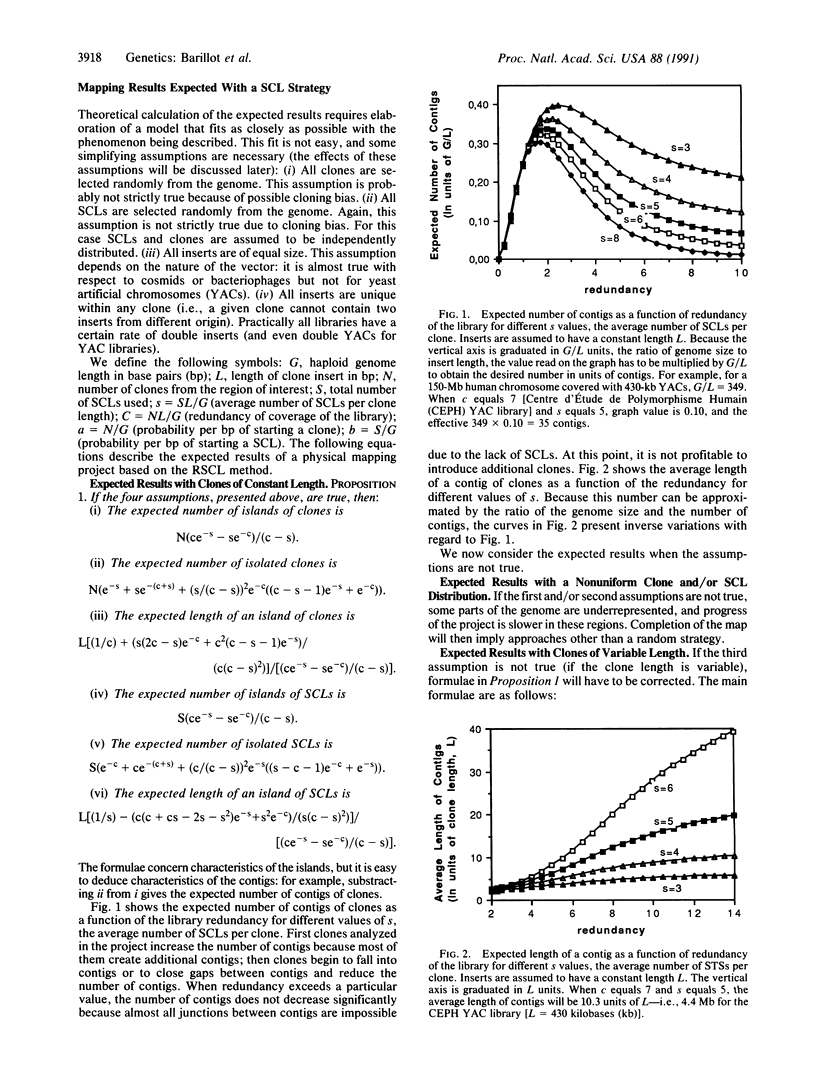
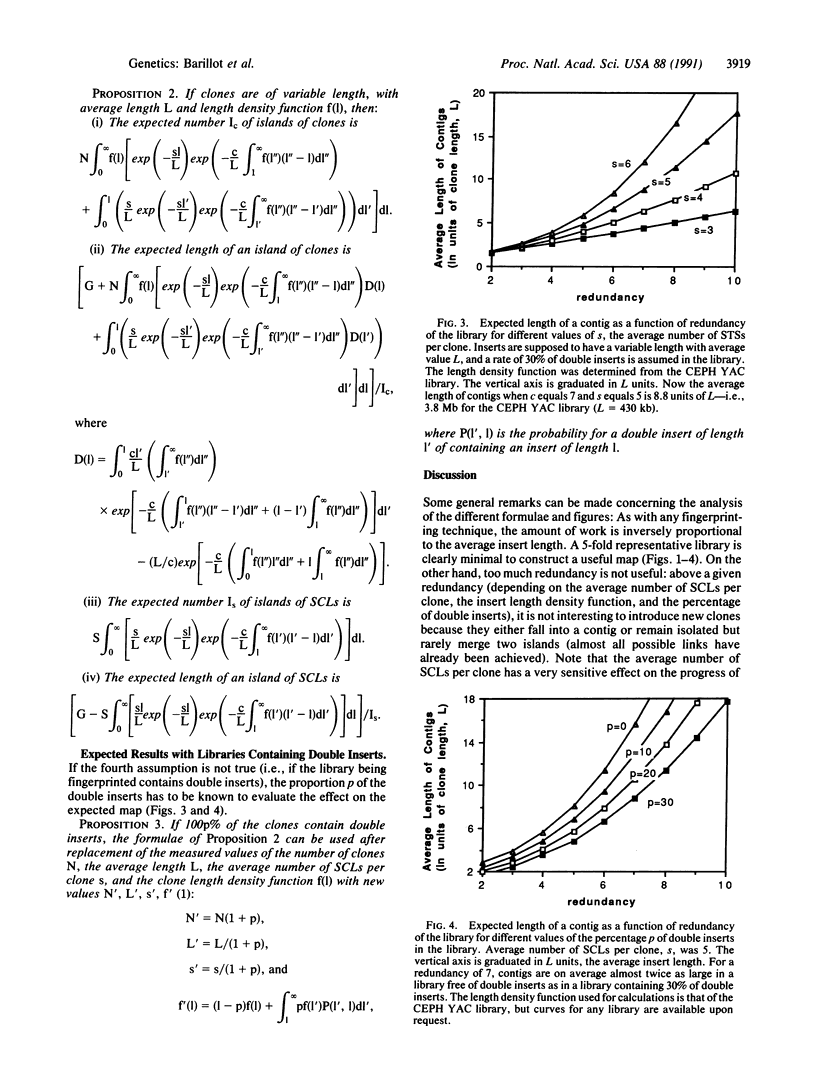
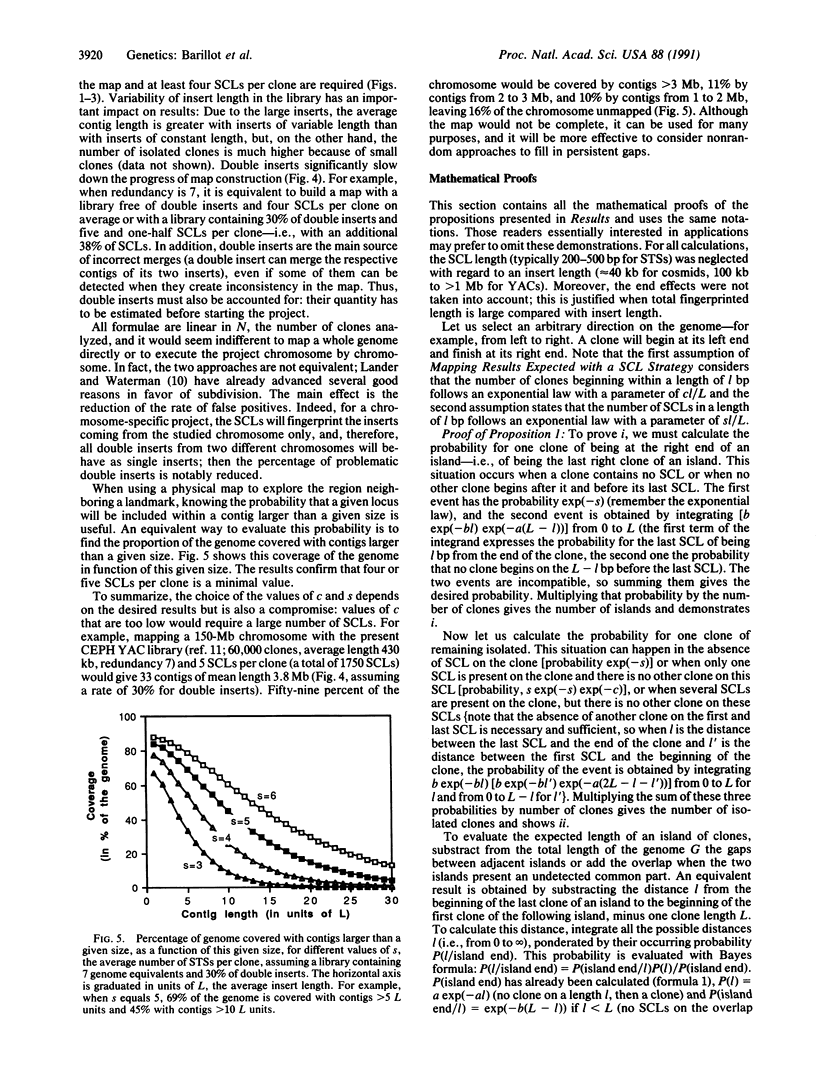
An approach to physical mapping is analyzed here. This procedure consists of fingerprinting random clones with single-copy landmarks extracted randomly from a region of interest. Results are presented in terms of number of contigs (sets of overlapping clones), number of isolated clones, average length of a contig, and coverage of the genome by contigs larger than a given size. (i) The expected results of an ideal project are presented. (ii) Certain problems that could influence progress of the map (variability in clone insert length, double inserts, etc.) are considered. (iii) An optimal project, which consists of a 7-fold representative library fingerprinted with an average of five sequence-tagged sites per clone, is analyzed. (iv) We present strategical considerations for the proposed approach, and a strategy that minimizes the number of laboratory tests without significant information loss is proposed: clones are arranged on a matrix and pooled according to rows and columns. A fingerprint is determined for each pool, and analysis allows retrieval of the positive clones. This method reduces the number of laboratory tests done by a factor of 160.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen H. M., Abderrahim H., Cann H. M., Dausset J., Le Paslier D., Cohen D. Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library containing seven haploid human genome equivalents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4256–4260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig A. G., Nizetic D., Hoheisel J. D., Zehetner G., Lehrach H. Ordering of cosmid clones covering the herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-I) genome: a test case for fingerprinting by hybridisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Lewis K. A. Physical mapping of complex genomes by cosmid multiplex analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5030–5034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuspa A., Vollrath D., Cheng Y., Kaiser D. Physical mapping of the Myxococcus xanthus genome by random cloning in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Waterman M. S. Genomic mapping by fingerprinting random clones: a mathematical analysis. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels F., Craig A. G., Zehetner G., Smith G. P., Lehrach H. Molecular approaches to genome analysis: a strategy for the construction of ordered overlapping clone libraries. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Sep;3(3):203–210. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallings R. L., Torney D. C., Hildebrand C. E., Longmire J. L., Deaven L. L., Jett J. H., Doggett N. A., Moyzis R. K. Physical mapping of human chromosomes by repetitive sequence fingerprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6218–6222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



