Abstract
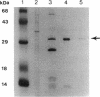
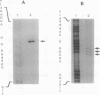
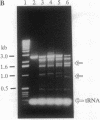
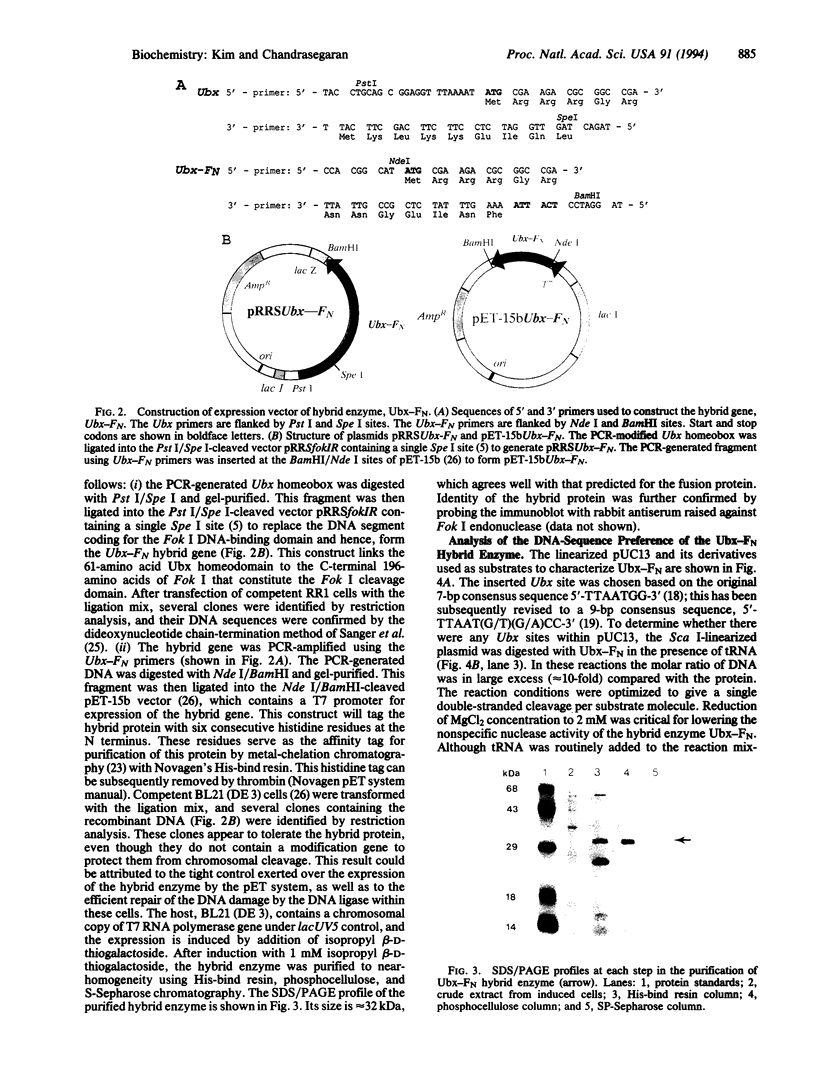
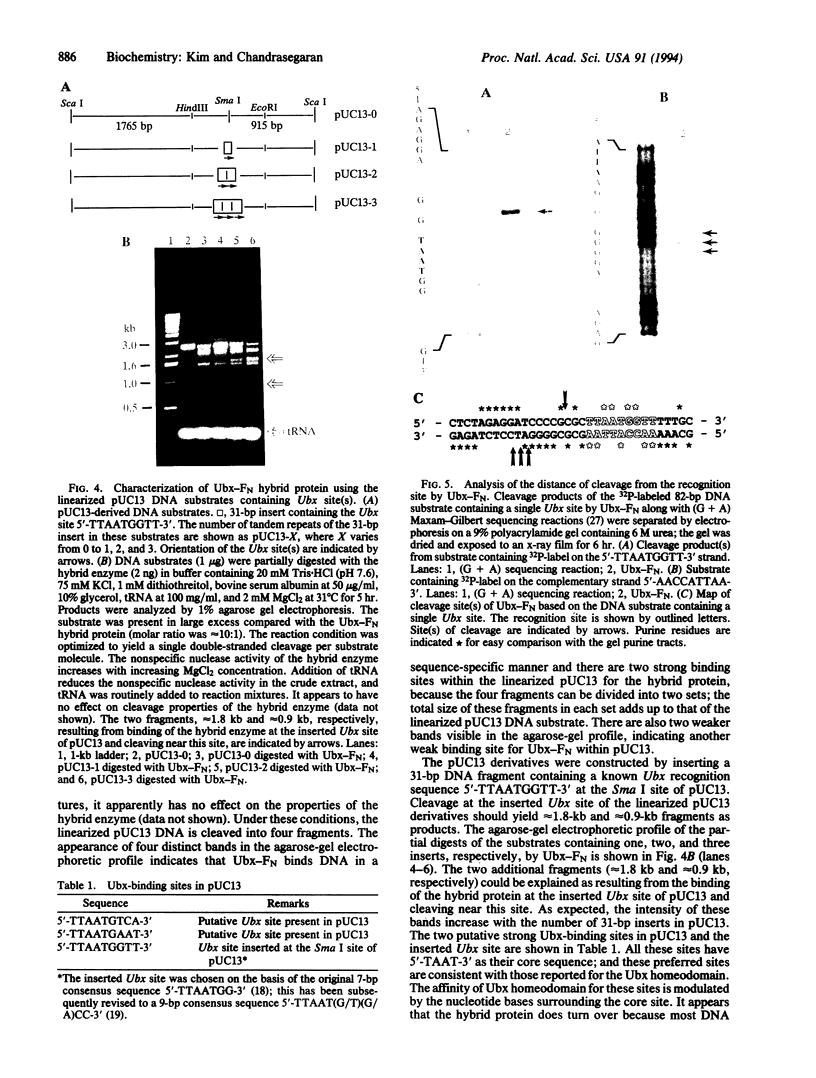
Fok I restriction endonuclease recognizes the nonpalindromic pentadeoxyribonucleotide 5'-GGATG-3'.5'-CATCC-3' in duplex DNA and cleaves 9 and 13 nt away from the recognition site. Recently, we reported the presence of two distinct and separable domains within this enzyme: one for the sequence-specific recognition of DNA (the DNA-binding domain) and the other for the endonuclease activity (the cleavage domain). Here, we report the construction of a chimeric restriction endonuclease by linking the Drosophila Ultrabithorax homeodomain to the cleavage domain (FN) of Fok I restriction endonuclease. The hybrid enzyme, Ubx-FN, was purified, and its cleavage properties were characterized. The hybrid enzyme shows the same DNA sequence-binding preference as that of Ubx; as expected, it cleaves the DNA away from the recognition site. On the 5'-TTAATGGTT-3' strand the hybrid enzyme cleaves 3 nt away from the recognition site, whereas it cuts the complementary 5'-AACCATTAA-3' strand 8, 9, or 10 nt away from the binding site. Similarly engineered hybrid enzymes could be valuable tools in physical mapping and sequencing of large eukaryotic genomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Pendergrast P. S., Gunasekera A. Conversion of a helix-turn-helix motif sequence-specific DNA binding protein into a site-specific DNA cleavage agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2882–2886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., Young K. E., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Optimal DNA sequence recognition by the Ultrabithorax homeodomain of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1179–1186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekker S. C., von Kessler D. P., Beachy P. A. Differential DNA sequence recognition is a determinant of specificity in homeotic gene action. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4059–4072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrin L. J., Camerini-Otero R. D. Selective cleavage of human DNA: RecA-assisted restriction endonuclease (RARE) cleavage. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1494–1497. doi: 10.1126/science.1962209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Scott M. P. What determines the specificity of action of Drosophila homeodomain proteins? Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):883–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90492-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissinger C. R., Liu B. S., Martin-Blanco E., Kornberg T. B., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90453-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita K., Kotani H., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. The fokI restriction-modification system. I. Organization and nucleotide sequences of the restriction and modification genes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5751–5756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob M. Conferring new cleavage specificities of restriction endonucleases. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:321–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16030-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koob M., Grimes E., Szybalski W. Conferring operator specificity on restriction endonucleases. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1084–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.2842862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kur J., Koob M., Burkiewicz A., Szybalski W. A novel method for converting common restriction enzymes into rare cutters: integration host factor-mediated Achilles' cleavage (IHF-AC). Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90437-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Chandrasegaran S. Alteration of the cleavage distance of Fok I restriction endonuclease by insertion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2764–2768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Wu L. P., Chandrasegaran S. Functional domains in Fok I restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Wu L. P., Clarke R., Chandrasegaran S. C-terminal deletion mutants of the FokI restriction endonuclease. Gene. 1993 Oct 29;133(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90227-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney M. C., Moran L. S., Jack W. E., Feehery G. R., Benner J. S., Slatko B. E., Wilson G. G. Nucleotide sequence of the FokI restriction-modification system: separate strand-specificity domains in the methyltransferase. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):193–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y. Q., Billeter M., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. The structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain determined by NMR spectroscopy in solution: comparison with prokaryotic repressors. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin J. A., Ebright R. H., Dervan P. B. Orientation of the Lac repressor DNA binding domain in complex with the left lac operator half site characterized by affinity cleaving. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5233–5236. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund C. M., Smith H. O., Chandrasegaran S. Construction of an efficient overproducer clone of HinfI restriction endonuclease using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90052-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Doucette-Stamm L. A., Riba L., Housman D. E., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of human chromosome 4 mediated by triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1639–1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1836279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Kanazawa S. New restriction endonucleases from Flavobacterium okeanokoites (FokI) and Micrococcus luteus (MluI). Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski W., Kim S. C., Hasan N., Podhajska A. J. Class-IIS restriction enzymes--a review. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:13–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90345-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Vershon A. K., Liu B., Johnson A. D., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]