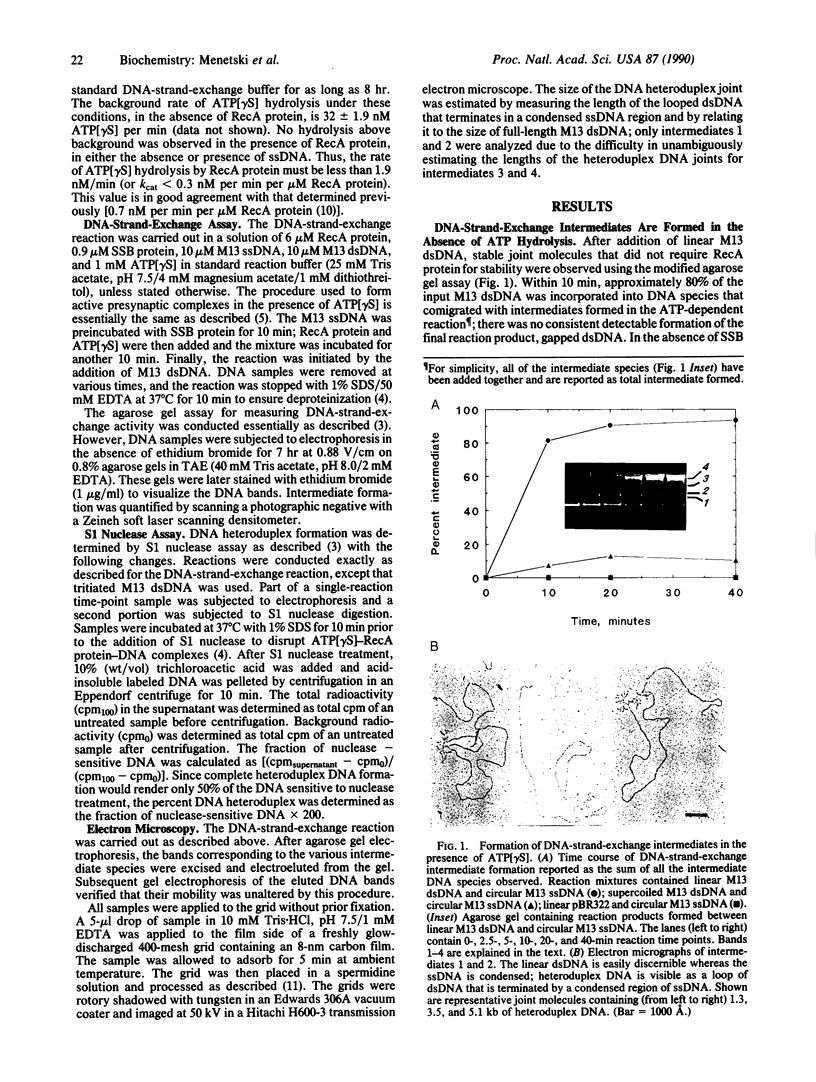
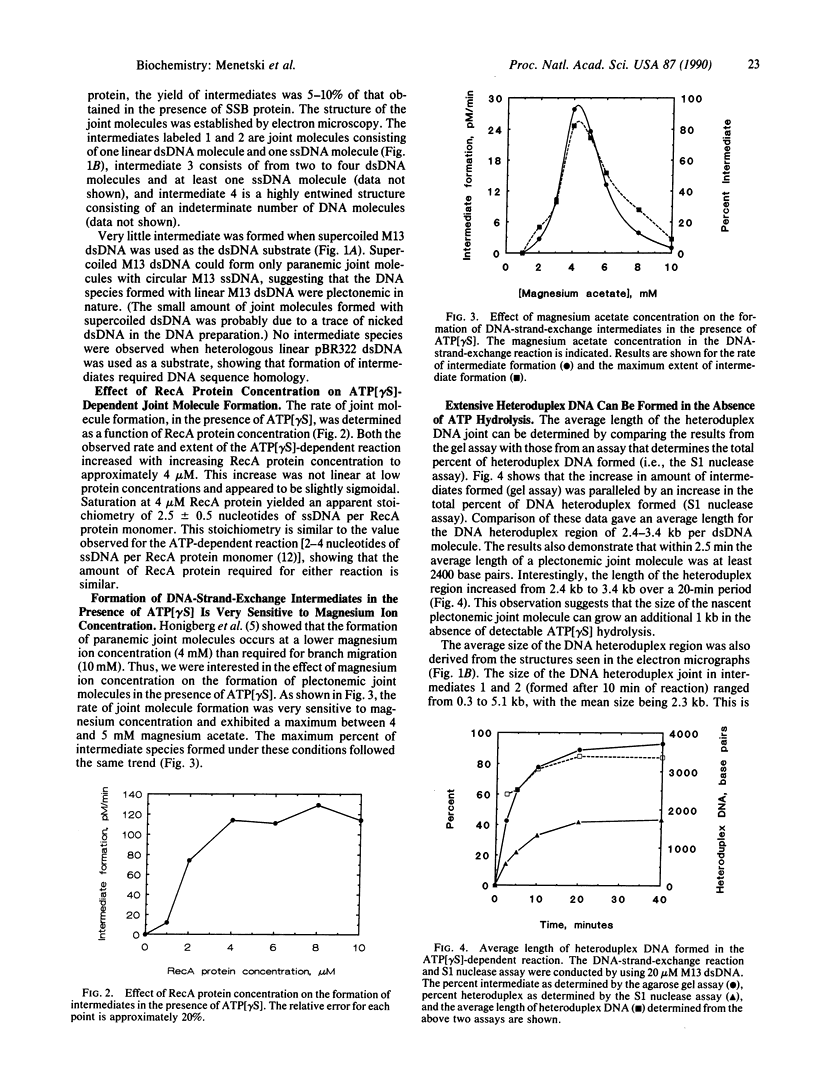
Abstract
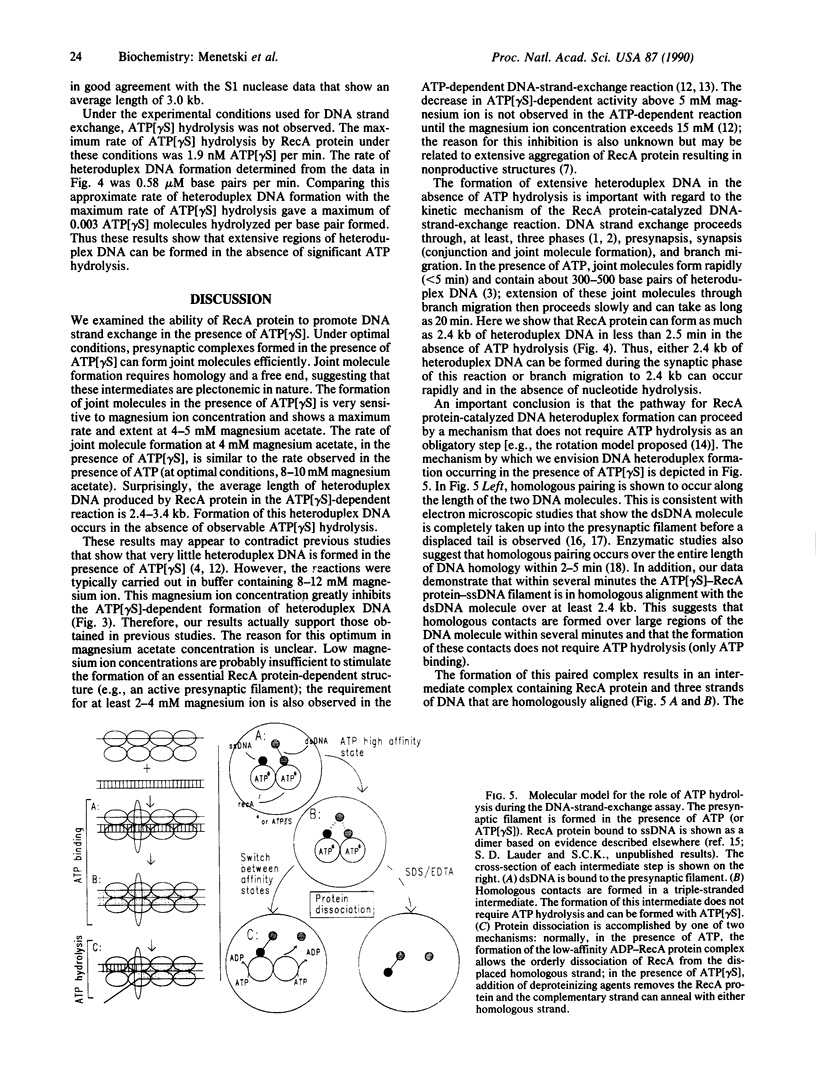
A question remaining to be answered about RecA protein function concerns the role of ATP hydrolysis during the DNA-strand-exchange reaction. In this paper we describe the formation of joint molecules in the absence of ATP hydrolysis, using adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (ATP[gamma S]) as nucleotide cofactor. Upon the addition of double-stranded DNA, the ATP[gamma S]-RecA protein-single-stranded DNA presynaptic complexes can form homologously paired molecules that are stable after deproteinization. Formation of these joint molecules requires both homology and a free homologous end, suggesting that they are plectonemic in nature. This reaction is very sensitive to magnesium ion concentration, with a maximum rate and extent observed at 4-5 mM magnesium acetate. Under these conditions, the average length of heteroduplex DNA within the joint molecules is 2.4-3.4 kilobase pairs. Thus, RecA protein can form extensive regions of heteroduplex DNA in the presence of ATP[gamma S], suggesting that homologous pairing and the exchange of the DNA molecules can occur without ATP hydrolysis. A model for the RecA protein-catalyzed DNA-strand-exchange reaction that incorporates these results and its relevance to the mechanisms of eukaryotic recombinases are presented.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. recA protein of Escherichia coli promotes branch migration, a kinetically distinct phase of DNA strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3433–3437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. recA protein-promoted DNA strand exchange. Stable complexes of recA protein and single-stranded DNA formed in the presence of ATP and single-stranded DNA binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8523–8532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Stasiak A. Structure of helical RecA-DNA complexes. Complexes formed in the presence of ATP-gamma-S or ATP. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):677–697. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Radding C. M. By searching processively RecA protein pairs DNA molecules that share a limited stretch of homology. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90397-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Formosa T. The uvsX protein of bacteriophage T4 arranges single-stranded and double-stranded DNA into similar helical nucleoprotein filaments. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4484–4491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Shores C. G. RecA protein rapidly crystallizes in the presence of spermidine: a valuable step in its purification and physical characterization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):158–162. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg S. M., Gonda D. K., Flory J., Radding C. M. The pairing activity of stable nucleoprotein filaments made from recA protein, single-stranded DNA, and adenosine 5'-(gamma-thio)triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11845–11851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Meyn M. S., Camerini-Otero R. D. Partial purification and characterization of a recombinase from human cells. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Evans D. H., Morrison P. T. Purification and characterization of an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that catalyzes homologous pairing and strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Enhancement of Escherichia coli RecA protein enzymatic function by dATP. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5871–5881. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Interaction of recA protein with single-stranded DNA. Quantitative aspects of binding affinity modulation by nucleotide cofactors. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):281–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Transfer of recA protein from one polynucleotide to another. Kinetic evidence for a ternary intermediate during the transfer reaction. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Varghese A., Kowalczykowski S. C. Properties of the high-affinity single-stranded DNA binding state of the Escherichia coli recA protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1205–1212. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Register J. C., 3rd, Christiansen G., Griffith J. Electron microscopic visualization of the RecA protein-mediated pairing and branch migration phases of DNA strand exchange. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12812–12820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Lehman I. R. The formation of plectonemic joints by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Requirement for ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):170–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman L. J., Kowalczykowski S. C. Relationship of the physical and enzymatic properties of Escherichia coli recA protein to its strand exchange activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7375–7385. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutte B. C., Cox M. M. Homology-dependent changes in adenosine 5'-triphosphate hydrolysis during recA protein promoted DNA strand exchange: evidence for long paranemic complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5616–5625. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Stasiak A. Z., Koller T. Visualization of RecA-DNA complexes involved in consecutive stages of an in vitro strand exchange reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:561–570. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Nitiss J., Resnick M. A. ATP-independent DNA strand transfer catalyzed by protein(s) from meiotic cells of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlin B. E., Clark A. J. Overproduction of the Escherichia coli recA protein without stimulation of its proteolytic activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):386–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.386-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Interaction of the recA protein of Escherichia coli with adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8850–8855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]