Abstract
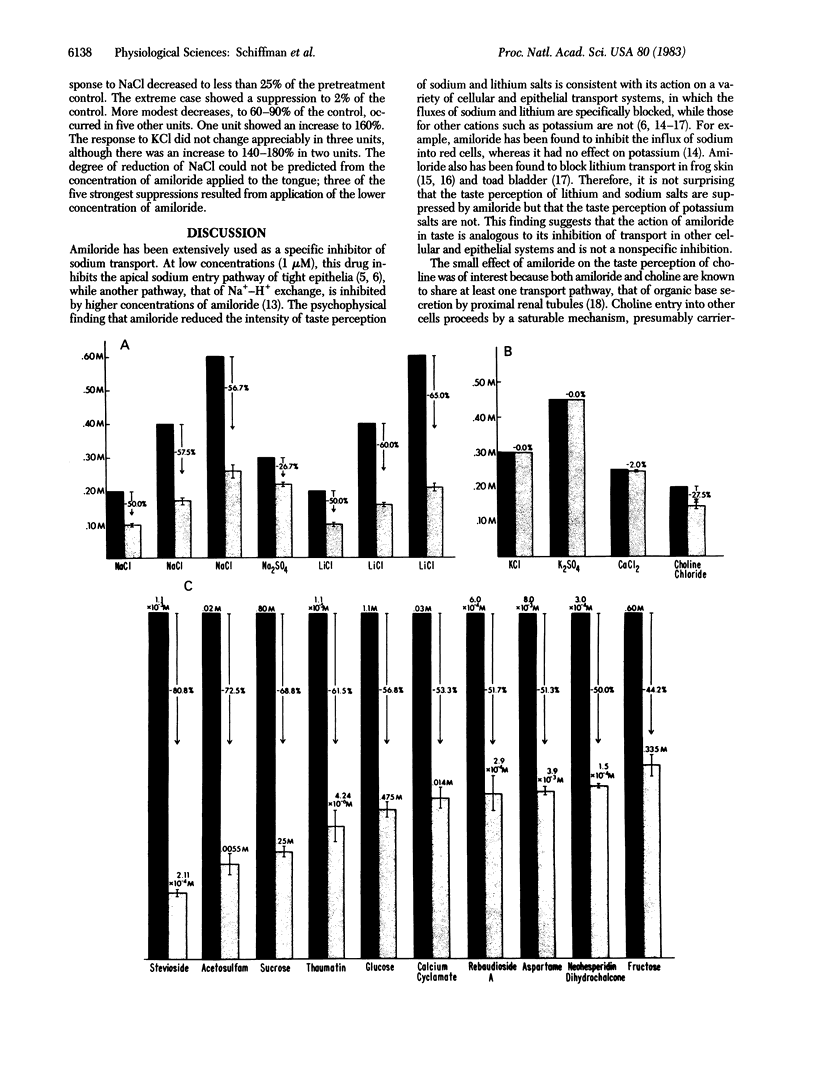
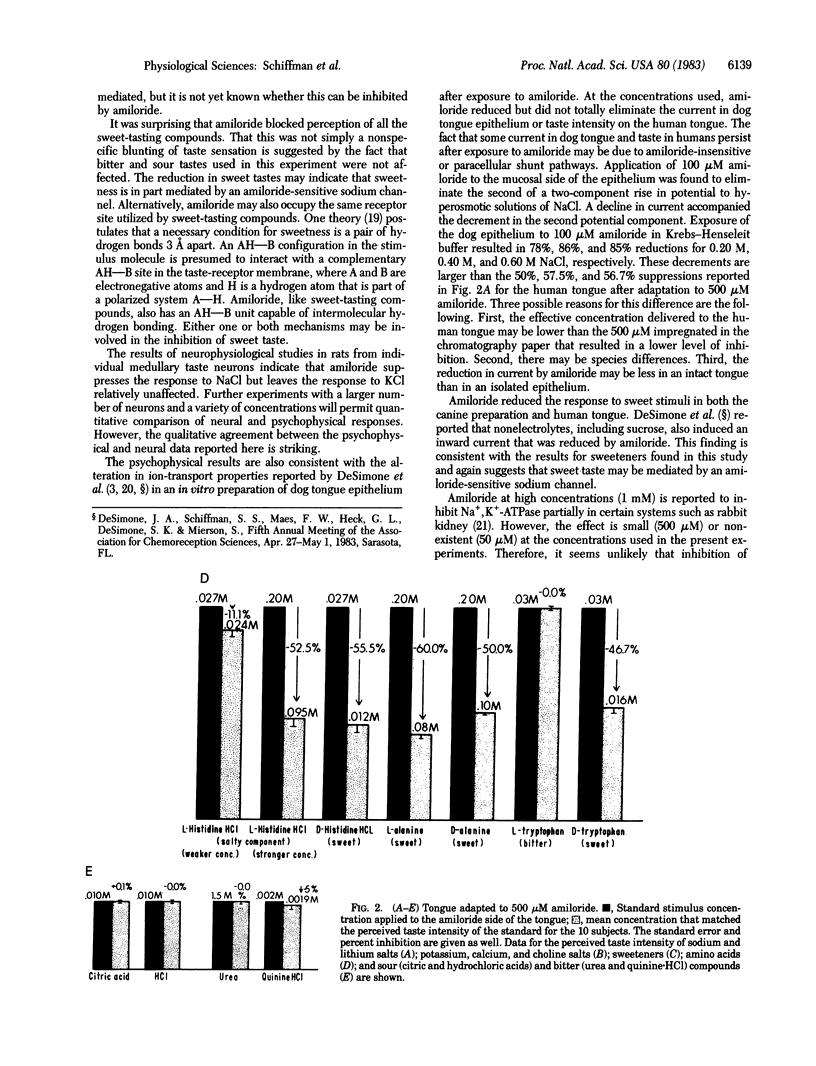
The diuretic amiloride, a potent inhibitor of sodium transport in a variety of epithelial systems, was applied to the human tongue. Application of amiloride reduced the taste intensity of sodium and lithium salts and of sweeteners ranging widely in chemical structure. The sweeteners included saccharides, glycosides, dipeptides, proteins, and amino acids. Amiloride did not affect perception of potassium or calcium salts, bitter and sour tastes, or amino acids without a sweet or salty component. These findings were supported by neurophysiological studies in rat, which showed that amiloride diminished the NaCl response relative to KCl. The results are consistent with the position that an amiloride-sensitive transport mechanism is involved in taste perception of sodium and lithium salts and of sweeteners.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves J., Cereijido M. The effect of amiloride on sodium and potassium fluxes in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):709–718. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEIDLER L. M. A theory of taste stimulation. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):133–139. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benos D. J. Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C131–C145. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candia O. A., Chiarandini D. J. Transport of lithium and rectification by frog skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 25;307(3):578–589. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90302-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J. A., Heck G. L., DeSimone S. K. Active ion transport in dog tongue: a possible role in taste. Science. 1981 Nov 27;214(4524):1039–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.7302576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallbäck D. A., Jodal M., Lundgren O. Vascular anatomy and tissue osmolality in the filiform and fungiform papillae of the cat's tongue. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Apr;105(4):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb00112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H. Rapid penetration of potassium and other salts into the frog tongue papilla. Jpn J Physiol. 1978;28(1):33–45. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.28.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera F. C. Inhibition of lithium transport across toad bladder by amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1972 Feb;222(2):499–502. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.2.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Amiloride inhibition of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F374–F379. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F., Leblanc G. Transient current changes and Na compartimentalization in frog skin epithelium. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jul 21;358(2):135–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00583924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennick B. R. Renal tubule transport of organic cations. Am J Physiol. 1981 Feb;240(2):F83–F89. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.2.F83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S. S., Erickson R. P. A psychophysical model for gustatory quality. Physiol Behav. 1971 Oct;7(4):617–633. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(71)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S. S., Lindley M. G., Clark T. B., Makino C. Molecular mechanism of sweet taste: relationship of hydrogen bonding to taste sensitivity for both young and elderly. Neurobiol Aging. 1981 Fall;2(3):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(81)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., Mandel L. J. Amiloride directly inhibits the Na,K-ATPase activity of rabbit kidney proximal tubules. Science. 1983 May 27;220(4600):957–958. doi: 10.1126/science.6302840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolston D. C., Erickson R. P. Concept of neuron types in gustation in the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1979 Sep;42(5):1390–1409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1979.42.5.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


