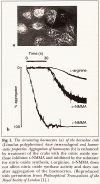
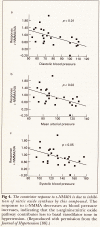
Abstract
Nitric oxide is involved in a wide range of physiological processes in humans and in animals. It controls vascular tone, acts as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in the central and peripheral nervous systems and influences the activity of the immune system. Substances that selectively enhance or inhibit its synthesis or removal and modify its effects, are likely to yield interesting therapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF









Contributor Information
Patrick Vallance, Senior Lecturer in Clinical Pharmacology, St George's Hospital Medical School, London.
Salvador Moncada, Research Director, Wellcome Research Laboratories, Beckenham.