Abstract
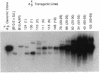
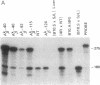
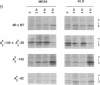
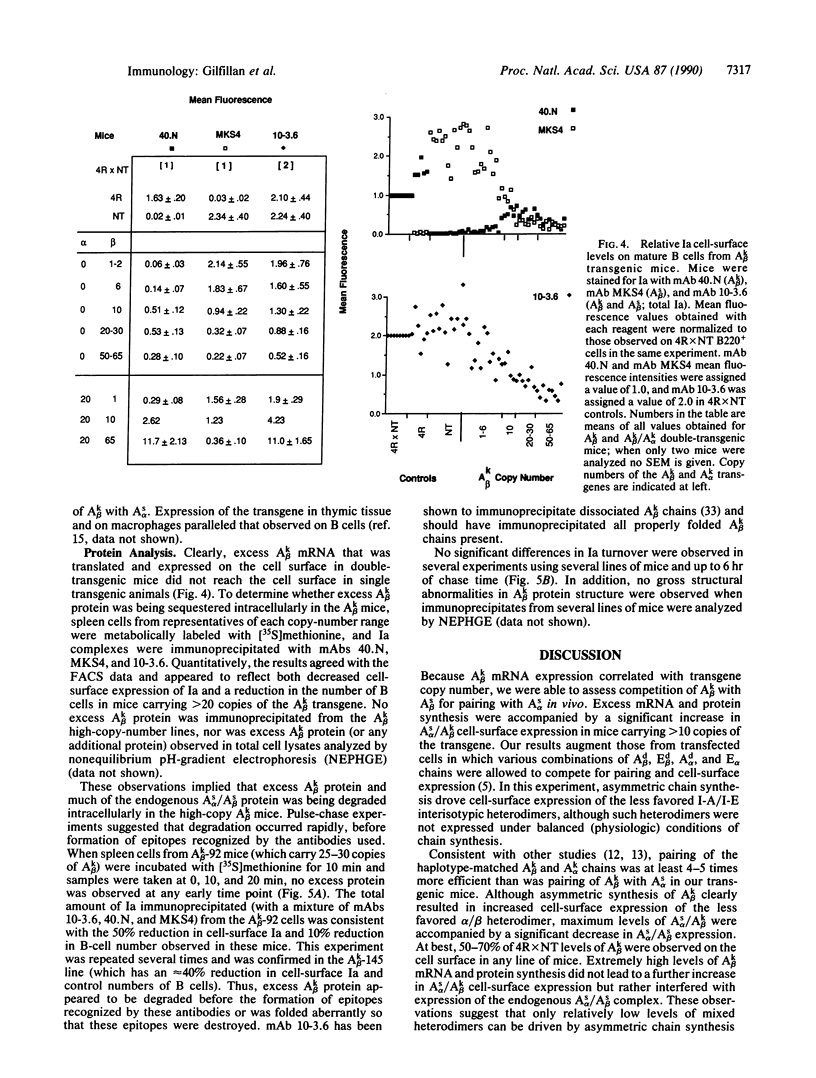
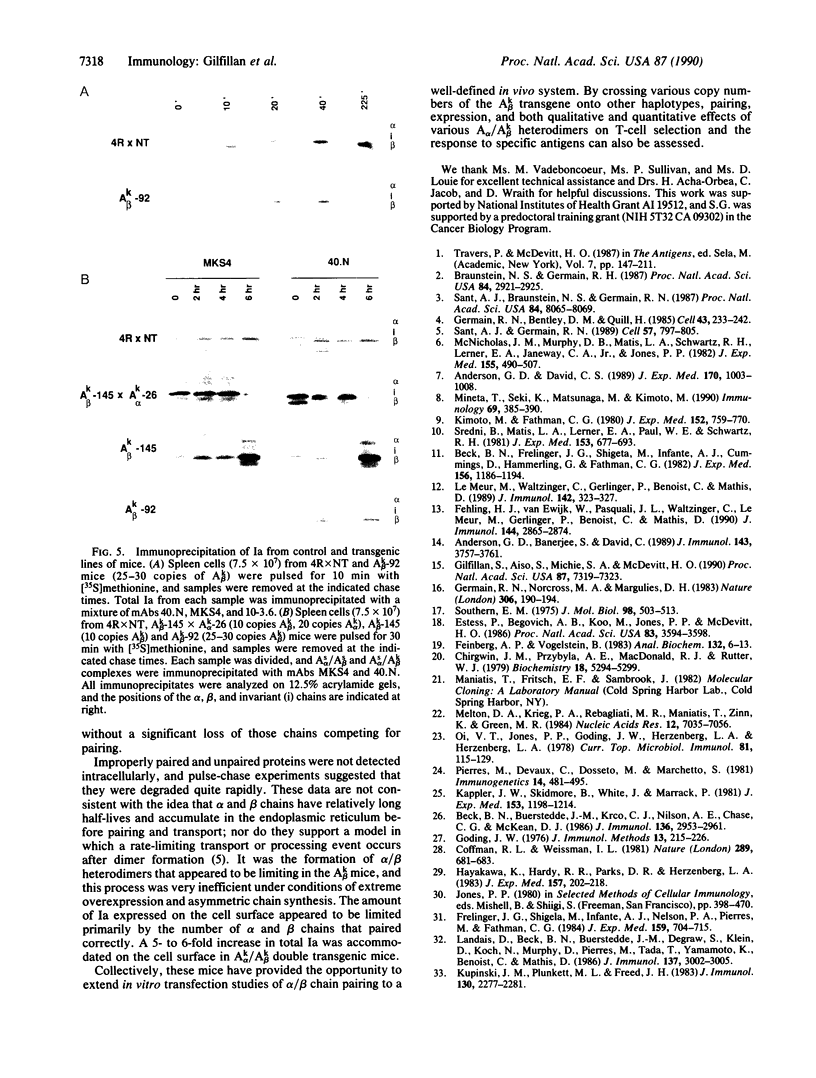
We have recently described 12 lines of H-2s/s mice carrying from 1 to 65 copies of an A beta k transgene. The transgene was coexpressed with the endogenous allele, and A beta K mRNA expression correlated well with transgene copy number. Overexpression of the transgene was associated with a variety of defects, including a significant reduction in I-A cell-surface expression. In this paper, we assess the effect of increased levels of A beta k mRNA synthesis on I-A cell-surface expression in these mice. Crossing representatives from several lines of A beta k mice to A alpha k transgenic mice demonstrated that the A beta k mRNA was translated and expressed at high levels on the cell surface in association with A alpha k. In H-2s/s (A alpha s /A beta s) mice carrying greater than 10 copies of the A beta k transgene, excess A beta k mRNA and protein synthesis did drive cell-surface expression of the less favored A alpha s/A beta k heterodimers. However, the highest levels of A beta k detected on the cell surface were only 50-70% of those observed in [B10.A(4R) x nontransgenic]F1 controls. Maximum levels of A alpha s/A beta k cell-surface expression were accompanied by a significant reduction in A alpha s/A beta s expression. Unpaired and improperly paired complexes were not detected intracellularly and appeared to be degraded quite rapidly. Thus, only a fraction of the chains competing for pairing reached the cell surface under conditions of asymmetric chain synthesis in these mice. This markedly reduced total Ia cell-surface levels in mice carrying greater than 10 copies of the A beta k transgene.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. D., Banerjee S., David C. S. MHC class II A alpha and E alpha molecules determine the clonal deletion of V beta 6+ T cells. Studies with recombinant and transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3757–3761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson G. D., David C. S. In vivo expression and function of hybrid Ia dimers (E alpha A beta) in recombinant and transgenic mice. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. N., Buerstedde J. M., Krco C. J., Nilson A. E., Chase C. G., McKean D. J. Characterization of cell lines expressing mutant I-Ab and I-Ak molecules allows the definition of distinct serologic epitopes on A alpha and A beta polypeptides. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2953–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck B. N., Frelinger J. G., Shigeta M., Infante A. J., Cummings D., Hämmerling G., Fathman C. G. T cell clones specific for hybrid I-A molecules. Discrimination with monoclonal anti-I-Ak antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1186–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein N. S., Germain R. N. Allele-specific control of Ia molecule surface expression and conformation: implications for a general model of Ia structure-function relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2921–2925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. B220: a B cell-specific member of th T200 glycoprotein family. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):681–683. doi: 10.1038/289681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Begovich A. B., Koo M., Jones P. P., McDevitt H. O. Sequence analysis and structure-function correlations of murine q, k, u, s, and f haplotype I-A beta cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehling H. J., van Ewijk W., Pasquali J. L., Waltzinger C., Le Meur M., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Functional consequences of overexpressed Ia antigens in AK alpha/AK beta transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2865–2874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelinger J. G., Shigeta M., Infante A. J., Nelson P. A., Pierres M., Fathman C. G. Multiple functional sites on a single Ia molecule defined using T cell clones and antibodies with chain-determined specificity. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):704–715. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Bentley D. M., Quill H. Influence of allelic polymorphism on the assembly and surface expression of class II MHC (Ia) molecules. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Norcross M. A., Margulies D. H. Functional expression of a transfected murine class II MHC gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):190–194. doi: 10.1038/306190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan S., Aiso S., Michie S. A., McDevitt H. O. Immune deficiency due to high copy numbers of an Ak beta transgene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7319–7323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. The "Ly-1 B" cell subpopulation in normal immunodefective, and autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):202–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Skidmore B., White J., Marrack P. Antigen-inducible, H-2-restricted, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridomas. Lack of independent antigen and H-2 recognition. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1198–1214. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto M., Fathman C. G. Antigen-reactive T cell clones. I. Transcomplementing hybrid I-A-region gene products function effectively in antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupinski J. M., Plunkett M. L., Freed J. H. Assignment of antigenic determinants to separated I-A kappa chains. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2277–2281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landias D., Beck B. N., Buerstedde J. M., Degraw S., Klein D., Koch N., Murphy D., Pierres M., Tada T., Yamamoto K. The assignment of chain specificities for anti-Ia monoclonal antibodies using L cell transfectants. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):3002–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Meur M., Waltzinger C., Gerlinger P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Restricted assembly of MHC class II molecules in transgenic mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):323–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicholas J. M., Murphy D. B., Matis L. A., Schwartz R. H., Lerner E. A., Janeway C. A., Jr, Jones P. P. Immune response gene function correlates with the expression of an Ia antigen. I. Preferential association of certain Ae and E alpha chains results in a quantitative deficiency in expression of an Ae:E alpha complex. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):490–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mineta T., Seki K., Matsunaga M., Kimoto M. Existence of mixed isotype A beta E alpha class II molecules in Ed alpha gene-introduced C57BL/6 transgenic mice. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):385–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Devaux C., Dosseto M., Marchetto S. Clonal analysis of B- and T-cell responses to Ia antigens. I. Topology of epitope regions on I-Ak and I-Ek molecules analyzed with 35 monoclonal alloantibodies. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):481–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00350120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Braunstein N. S., Germain R. N. Predominant role of amino-terminal sequences in dictating efficiency of class II major histocompatibility complex alpha beta dimer expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8065–8069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Germain R. N. Intracellular competition for component chains determines class II MHC cell surface phenotype. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):797–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredni B., Matis L. A., Lerner E. A., Paul W. E., Schwartz R. H. Antigen-specific T cell clones restricted to unique F1 major histocompatibility complex determinants. Inhibition of proliferation with monoclonal anti-Ia antibody. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):677–693. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]