Abstract
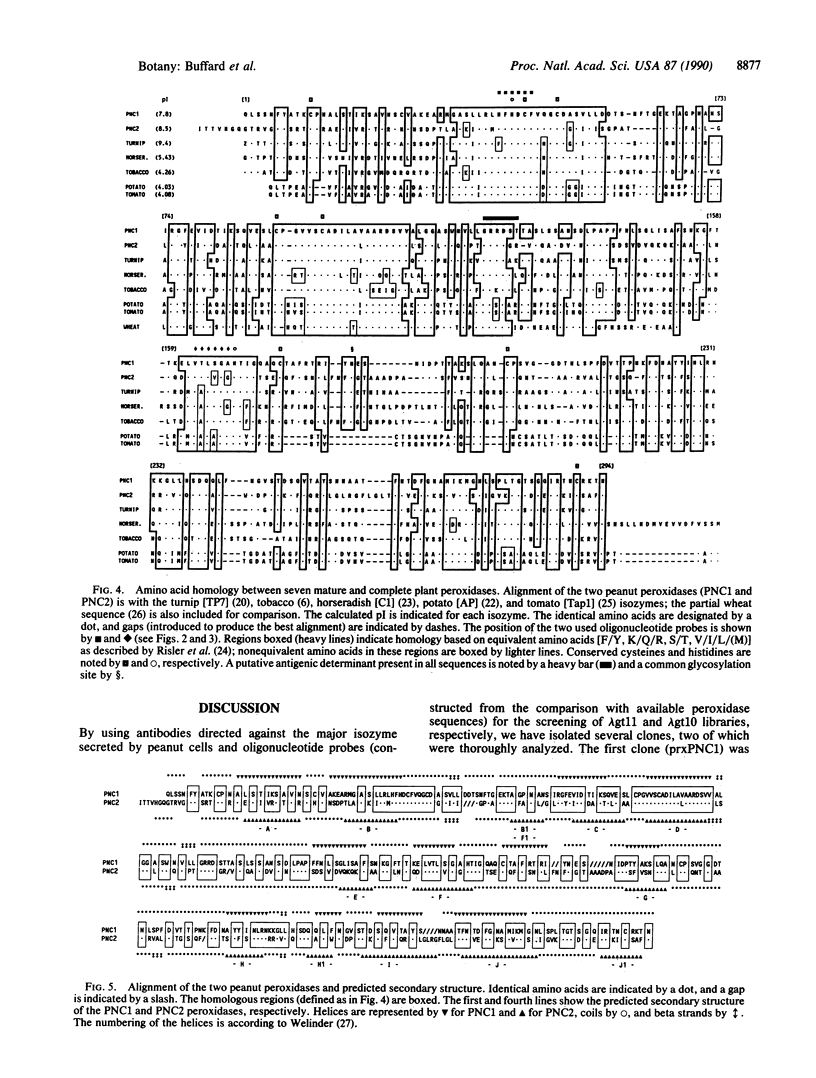
We have isolated, cloned, and characterized two cDNAs corresponding to the mRNAs for cationic peroxidases synthesized by cultured peanut cells. The first clone was obtained from a phage lambda gt11 library screened with antibodies directed against the major secreted isozyme. Its predicted amino acid sequence, deduced from the 1228-base-pair (bp) cDNA, revealed a 22-amino acid signal peptide and a 294-amino acid mature protein (Mr, 31,228). The second clone was isolated from a lambda gt10 library screened with oligonucleotides corresponding to the regions for acid/base catalysis and the fifth ligand of heme. This cDNA (1344 bp) encodes a protein (330 amino acids) with a mature peptide of 307 residues (Mr, 32,954). The two peanut peroxidases are 46% homologous. The estimated gene copy numbers of these peroxidases might be close to 1 or 2 per haploid genome. A comparison of the amino acid sequence of these peanut peroxidases with other known isozymes shows two already known regions of homology (the region for acid/base catalysis and the fifth ligand of heme). Moreover, some new characteristics appeared such as a glycosylation site identical in five of the seven isozymes, a putative antigenic determinant common to all the isozymes, and a region of the highest homology. A secondary structure prediction showed that it corresponds to a 16-amino acid helix linked to the next one by a long stretch of beta strands and coils and might represent a critical structural element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles F. B., Dunn L. J., Morgens P., Callahan A., Dinterman R. E., Schmidt J. Induction of 33-kD and 60-kD Peroxidases during Ethylene-Induced Senescence of Cucumber Cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jul;87(3):609–615. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.3.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biou V., Gibrat J. F., Levin J. M., Robson B., Garnier J. Secondary structure prediction: combination of three different methods. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):185–191. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama K., Takemura H., Shibayama S., Kobayashi K., Choi J. K., Shinmyo A., Takano M., Yamada Y., Okada H. Structure of the horseradish peroxidase isozyme C genes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 May 2;173(3):681–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrimini L. M., Bradford S., Rothstein S. Peroxidase-Induced Wilting in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):7–18. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrimini L. M., Burkhart W., Moyer M., Rothstein S. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the lignin-forming peroxidase from tobacco: Molecular analysis and tissue-specific expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrimini L. M., Rothstein S. Tissue specificity of tobacco peroxidase isozymes and their induction by wounding and tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):438–442. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazza G., Welinder K. G. Covalent structure of turnip peroxidase 7. Cyanogen bromide fragments, complete structure and comparison to horseradish peroxidase C. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risler J. L., Delorme M. O., Delacroix H., Henaut A. Amino acid substitutions in structurally related proteins. A pattern recognition approach. Determination of a new and efficient scoring matrix. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E., Kolattukudy P. E. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and abscisic acid induction of a suberization-associated highly anionic peroxidase. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):223–232. doi: 10.1007/BF02464885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welinder K. G. Covalent structure of the glycoprotein horseradish peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.7). FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80804-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welinder K. G. Plant peroxidases. Their primary, secondary and tertiary structures, and relation to cytochrome c peroxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):497–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]