Abstract
The inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (InsP3) receptor consists of a homotetramer of highly conserved 313 kd subunits that contain multiple transmembrane regions in the C-terminal part of the protein. The receptor was expressed in COS cells and its domain structure was studied by mutagenesis. Deletion of the transmembrane regions from the receptor results in the synthesis of a soluble receptor protein that efficiently binds InsP3 but which instead of associating into homotetramers remains monomeric. This result suggests a role for the transmembrane regions in the association of the receptor subunits into tetramers but not in ligand binding. To localize the ligand binding site, further cDNAs encoding truncated receptor proteins were constructed. Assays of InsP3 binding to these truncated InsP3 receptors revealed that sequences in the N-terminal fourth of the InsP3 receptor are sufficient for ligand binding. Accordingly, each subunit of the InsP3 receptor homotetramer contains an independent ligand binding site that is located on the N-terminal ends of each subunit and is separated from the putative channel-forming transmembrane regions by greater than 1400 amino acids. Gel filtration experiments demonstrate a large conformational change of the receptor as a function of ligand binding, suggesting a mechanism by which ligand binding might cause channel opening.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick C. C., Saito A., Fleischer S. Isolation and characterization of the inositol trisphosphate receptor from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2132–2136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. Y., Kim H. K., Lee S. Y., Moon K. H., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Chung H. K., Rhee S. G. Molecular cloning and expression of a complementary DNA for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2157285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Snyder S. H. Calcium flux mediated by purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in reconstituted lipid vesicles is allosterically regulated by adenine nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi T., Yoshikawa S., Miyawaki A., Wada K., Maeda N., Mikoshiba K. Primary structure and functional expression of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding protein P400. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):32–38. doi: 10.1038/342032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Transmembrane topography and evolutionary conservation of synaptophysin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H. P., Rousseau E., Liu Q. Y., Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):315–319. doi: 10.1038/331315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Misra M., Xu L., Smith H. A., Meissner G. The ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel complex of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Evidence for a cooperatively coupled, negatively charged homotetramer. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16776–16785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Wensel T., Stryer L. Kinetics of calcium channel opening by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):32–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
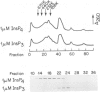
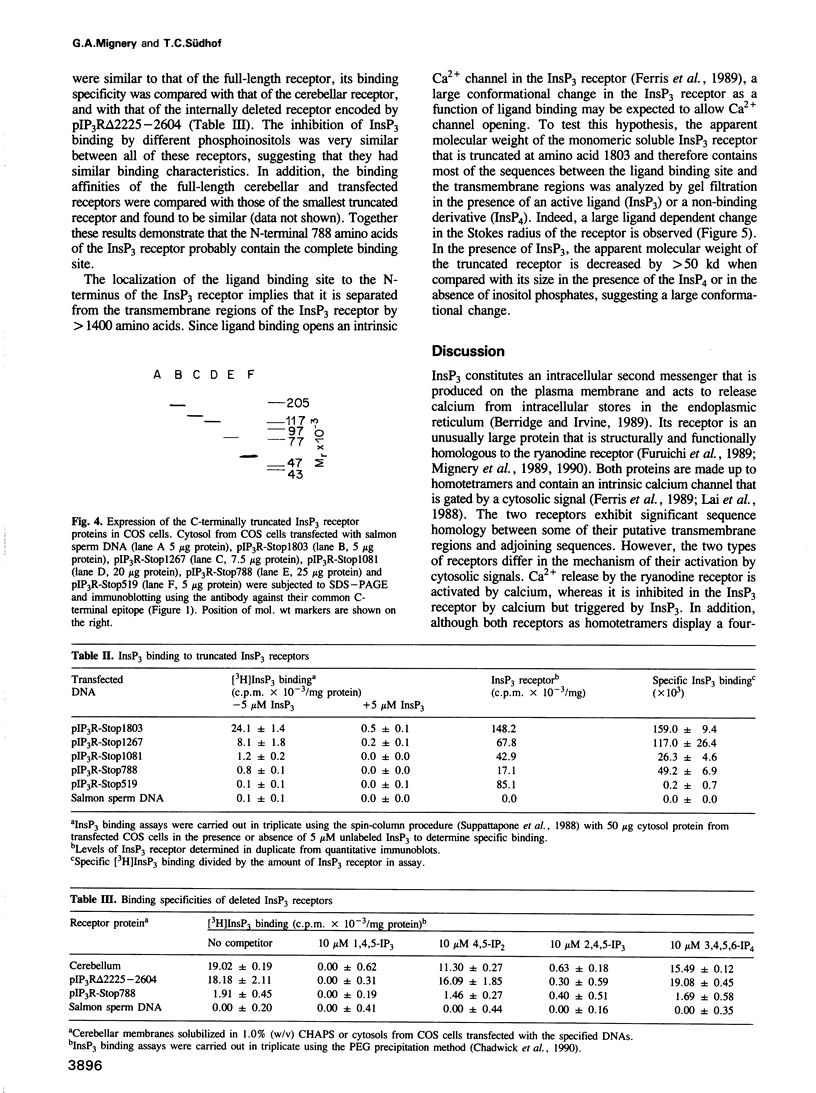
- Mignery G. A., Newton C. L., Archer B. T., 3rd, Südhof T. C. Structure and expression of the rat inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12679–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignery G. A., Südhof T. C., Takei K., De Camilli P. Putative receptor for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate similar to ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):192–195. doi: 10.1038/342192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Potter B. V., Taylor C. W. Molecular target sizes of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors in liver and cerebellum. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):393–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2650393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Matthews G., Neher E. Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):499–504. doi: 10.1038/334499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
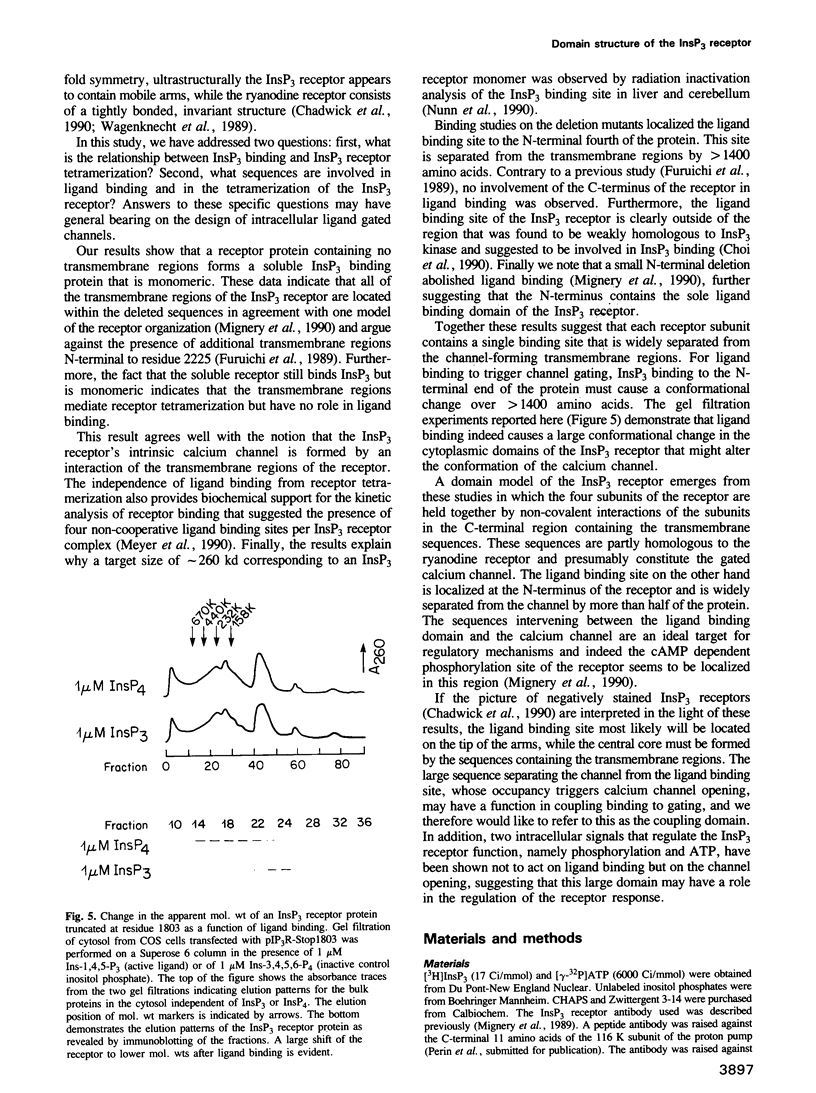
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Solubilization, purification, and characterization of an inositol trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1530–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Matsumoto T., Ishida H., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Ueda M., Hanaoka M., Hirose T. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):439–445. doi: 10.1038/339439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., Grassucci R., Frank J., Saito A., Inui M., Fleischer S. Three-dimensional architecture of the calcium channel/foot structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989 Mar 9;338(6211):167–170. doi: 10.1038/338167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzato F., Fujii J., Otsu K., Phillips M., Green N. M., Lai F. A., Meissner G., MacLennan D. H. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2244–2256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]