Abstract
We have previously reported the cloning and structural analysis of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA copies from the human hepatoma cell line PLC/PRF/5. Here we show that the cloned DNA fragments of 10.7 kb and 10.5 kb contain intact coding sequences for HBsAg since Ltk- cells transfected with these DNAs secrete considerable amounts of HBsAg. We show for the 10.7-kb fragment that multiple readthrough messages composed of viral as well as cellular sequences are transcribed. These RNAs differ only in their 3' sequences. Furthermore, the 10.7-kb insert leads to a substantial increase in HBsAg produced compared with HBV DNA and with the 10.5-kb insert. We provide evidence that the different 3' sequences on the HBsAg transcripts account for the augmentation of expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J., Bey E. M., Geddes E. W., Lecatsas G. Establishment of a continuously growing cell line from primary carcinoma of the liver. S Afr Med J. 1976 Dec 18;50(54):2124–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbere-Garapin F., Chousterman S., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. Cloning of the active thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3755–3759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Gray P., Valenzuela P., Rall L. B., Rutter W. J. Integration of hepatitis B virus sequences and their expression in a human hepatoma cell. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):535–538. doi: 10.1038/286535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
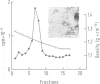
- Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Hoggan M. D., Holland P. V., Chanock R. M. Biophysical properties of Australia antigen. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.763-768.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Core and E antigen synthesis in rodent cells transformed with hepatitis B virus DNA is associated with greater than genome length viral messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):683–699. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
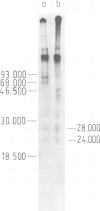
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S., Neel B. G., Astrin S. M. Activation of a cellular onc gene by promoter insertion in ALV-induced lymphoid leukosis. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):475–480. doi: 10.1038/290475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Esty A. C., Subramani S., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Elements in the long terminal repeat of murine retroviruses enhance stable transformation by thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1855–1872. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Construction of a modular dihydrofolate reductase cDNA gene: analysis of signals utilized for efficient expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1304–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch S., Freytag von Loringhoven A., Kahmann R., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. The genetic organization of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA in the human hepatoma cell line PLC/PRF/5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6871–6886. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch S., von Loringhoven A. F., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. Amplification and rearrangement in hepatoma cell DNA associated with integrated hepatitis B virus DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshy R., Koch S., von Loringhoven A. F., Kahmann R., Murray K., Hofschneider P. H. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA: evidence for integration in the single-stranded gap. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U. R., Fitch W. M. Evolutionary selection for perfect hairpin structures in viral DNAs. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):582–585. doi: 10.1038/298582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Wigler M., Axel R., Silverstein S. The transfer and stable integration of the HSV thymidine kinase gene into mouse cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90308-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel C., Louise A., Gervais M., Chenciner N., Dubois M. F., Tiollais P. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.100-105.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Standring D. N., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Transcription of hepatitis B virus by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1766–1773. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Greene R., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Hu S. L., Botchan M. Analysis of the sites of integration of viral DNA sequences in rat cells transformed by adenovirus 2 or SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):569–584. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rutter W. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in cultured murine cells initiates within the presurface region. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.563-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Variable protein composition of hepatitis B surface antigen from different donors. Virology. 1982 Dec;123(2):436–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratowa C., Doehmer J., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Recombinant retroviral DNA yielding high expression of hepatitis B surface antigen. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1573–1578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the hepatitis B virus: evidence for a causal association. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:40–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Darnell J. E. Presence of cell and virus specific sequences in the same molecules of nuclear RNA from virus transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 21;232(29):73–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio232073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Schäfer-Ridder M., Stratowa C., Wong T. K., Hofschneider P. H. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in unselected cell culture transfected with recircularized HBV DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1213–1216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]