Abstract
Dark septate endophytes (DSE) are a form-group of root endophytic fungi with elusive functions. Here, the genomes of two common DSE of semiarid areas, Cadophora sp. and Periconia macrospinosa were sequenced and analyzed with another 32 ascomycetes of different lifestyles. Cadophora sp. (Helotiales) and P. macrospinosa (Pleosporales) have genomes of 70.46 Mb and 54.99 Mb with 22,766 and 18,750 gene models, respectively. The majority of DSE-specific protein clusters lack functional annotation with no similarity to characterized proteins, implying that they have evolved unique genetic innovations. Both DSE possess an expanded number of carbohydrate active enzymes (CAZymes), including plant cell wall degrading enzymes (PCWDEs). Those were similar in three other DSE, and contributed a signal for the separation of root endophytes in principal component analyses of CAZymes, indicating shared genomic traits of DSE fungi. Number of secreted proteases and lipases, aquaporins, and genes linked to melanin synthesis were also relatively high in our fungi. In spite of certain similarities between our two DSE, we observed low levels of convergence in their gene family evolution. This suggests that, despite originating from the same habitat, these two fungi evolved along different evolutionary trajectories and display considerable functional differences within the endophytic lifestyle.
Introduction
The vast majority of land plants are known to form symbioses with diverse fungal endophytes. These are fungi that, during some point of their life cycle, colonize plant tissues without causing symptoms of tissue damage1–4. Apart from behaving as commensalistic symbionts, fungal endophytes can also act as latent pathogens, latent saprotrophs, and mutualistic symbionts2,5. Although colonization by these fungi can be restricted to aboveground tissues, as in the case of clavicipitaceous endophytes6, roots can also be colonized by a broad spectrum of fungal endophytes with potentially diverse functions7–10.
The presence of root endophytes with melanized and septated intraradical hyphae has been known for over a century11. Despite these fungal endophytes dominating several biomes and climatic regions, their functions in relation to plants and the greater ecosystem are still elusive12. Even though this form-group is known as dark septate endophytes (DSE)11,13, varying degrees of melanization can be found in some of these fungi and some can actually form hyaline structures either14. DSEs, the ‘Class 4 endophytes’ sensu Rodriguez et al.10, are mostly asexual filamentous ascomycetes belonging to diverse lineages of numerous orders, including Helotiales, Xylariales and Pleosporales8,11,15–18. Although DSEs can be found worldwide, they are more frequent in harsh, nutrient-limited environments such as arid and semiarid areas12,18,19. Their prevalence suggests that their importance in these ecosystems might be crucial. Several aspects of the lifestyle, ecology, and evolution of DSEs, and their mode of interaction with plants is not well understood8. Studies in experimental systems have suggested that fungal root endophytes could be latent pathogens10,20. The effects of root-colonizing endophytes on their hosts depends on the ontogenetic, physiologic and genotypic status of the host, as well as on the availability of organic/inorganic nutrients and environmental/experimental conditions2,10,17,21. Various degradative enzyme activities have been detected in DSEs22,23, which could indicate that they have a rich plant cell wall degrading enzyme (PCWDE) repertoire. Thus, DSEs could be important as (latent) saprobes, and also play a role in host nutrition through complex substrate degradation. DSEs might help to degrade organic matter in nutrient-poor soils in a similar way as ericoid mycorrhizal fungi – mutualistic symbionts that benefit the host plant by mobilizing complex substrates in nutrient poor environments24.
Root-associated fungi and DSE communities of (semi−) arid environments and grasslands have been studied in detail and the results suggest that there are core members of those communities common to disparate regions16,25–27. Our knowledge of the biology and functions of DSEs in those environments is limited compared to those of other DSEs such as the helotialean root endophytes of woody plants (especially conifers) like the Phialocephala fortinii s.l. – Acephala applanata species complex (PAC)28, and the genome of one member of this complex was sequenced recently29. Although the biogeographic distribution of DSEs is not properly understood, it seems that the DSE communities of forest ecosystems remarkably differ from those of grasslands, e.g., we are not aware of any PAC fungi colonizing plants in grassland ecosystems.
Although comparative genomics could provide insights into fundamental biological and evolutional questions, to date, only few genomes of taxonomically distinct endophytic fungi became available. These include the genomes of clavicipitaceous shoot/systemic endophytes6,30, other non-root colonizing fungi like Xylona heveae31, Pestalotiopsis fici32 and Phialocephala scopiformis33, and root endophytes including Serendipita indica34 (formerly Piriformospora indica, Sebacinales, Basidiomycotina), Colletotrichum trifolium35 and the DSE fungi Harpophora oryzae36, Phialocephala subalpina29 and Microdochium bolleyi37. These endophytic fungi have highly distinct genomic toolboxes, diverse ancestral lifestyles and different habitats. Therefore, based on currently available genomic information, it is almost impossible to construct an overall view of fungal endophytic lifestyle. Further data is needed to uncover common genomic features, like in the case of the ectomycorrhizal (EcM) lifestyle that independently arose multiple times during evolution from saprotrophic ancestors38. The EcM lifestyle is associated with the loss of PCWDE-encoding genes and with the diversification of lineage-specific symbiosis-related genes38–41. In contrast to ectomycorrhizal fungi, the endophytic lifestyle of ascomyceteous root colonizers such as C. tofieldiae, H. oryzae and P. subalpina, is not accompanied by a reduction in the PCWDE repertoire5,29,35,36.
Here, we perform in-depth analyses of the genomes of two dominant DSEs that originate from semiarid grasslands. These fungi – Cadophora sp. and Periconia macrospinosa – albeit from the same environment, represent taxonomically distant species with different host preferences16,18. As these species are common and widespread members of DSE communities of semiarid sandy grasslands16,19,42, they likely play key roles in the functioning of such ecosystems. We analyze their repertoires of CAZymes, PCWDEs and other relevant gene families and compare these to that of other ascomycetes to understand whether independently evolved DSE lineages possess common genomic signatures and to gain insights into their lifestyle. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comparative genome analysis of two different fungal root endophytes that belong to the same habitat.
Materials and Methods
Fungal strains used for genome sequencing
We analyzed two DSEs: Cadophora sp. (strain DSE1049) and P. macropsinosa (strain DSE2036). Cadophora sp. DSE1049 represents a helotialean root endophyte that mainly colonizes non-gramineous plants16,43. It has been detected all over Europe43 and in other diverse geographic regions including Antarctica44,45 and Argentina46. Cadophora sp. DSE1049 is not conspecific with any described species of the Cadophora genus which comprises several root endophytes including C. finlandica and C. orchidicola18. The strain DSE1049 was isolated from healthy roots of Salix rosmarinifolia from grasslands near Fülöpháza, Hungary16. P. macrospinosa, on the other hand, is a well-known pleosporalean root colonizer belonging to Periconiaceae, Pleosporales47. This taxa is one of the most dominant and widespread DSEs in grassland ecosystems worldwide, and is associated with gramineous plants12,16,48. The strain DSE2036 was isolated from healthy roots of Festuca vaginata from the same site as mentioned above16,42.
Both species has melanized hyphae in culture and brownish isolates. Both species colonized leek and maize roots in in vitro experiments, formed intraradical structures (e.g. like microsclerotia (Fig. 1a)) characteristic of DSEs16. Intraradical hyphae of Cadophora sp. DSE1049 are typically dark, and can easily be stained by common fungal blue dyes (Fig. 1a). In contrast, P. macrospinosa usually have hyaline intraradical hyphae that cannot be visualized by typical fungi stains, and within the roots, only certain structures (e.g. microsclerotia, chlamydospores and conidiophores) are melanized (Fig. 1b)16,49,50.
Figure 1.
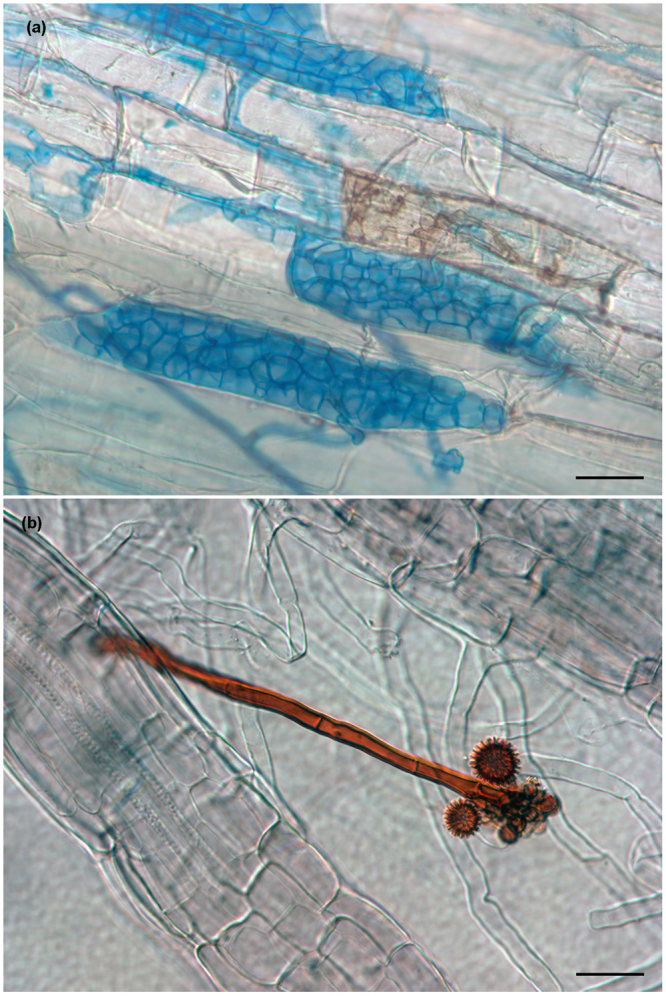
Characteristic structures of Cadophora sp. and Periconia macrospinosa in an artificial inoculation system with Zea mays. (a) Intra- and intercellular septate hyphae and microsclerotia of Cadophora sp. are visualized after staining with aniline blue. Intracellular pigmented hyphal structures in the root can also be seen. (b) P. macrospinosa colonization of roots with barely stainable hyphae. Its pigmented conidiophore can be seen with characteristic spiny conidia. Scale bars 30 µm.
Nucleic acid extraction
Cadophora sp. DSE1049 and P. macrospinosa DSE2036 were maintained in modified Melin-Norkrans (MMN) liquid medium51 containing 3 g/L glucose and were grown as a free-living vegetative mycelium for two weeks at room temperature in the dark. For harvesting, the mycelium was dried on filter paper, flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and ground into a powder. DNA was extracted from 2.5 g mycelium using the DNeasy Plant Maxi kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (doing on-column RNase treatment). In addition, total RNA was isolated from 0.5 g mycelium using the RNeasy Plant Midi Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, including DNase treatment.
Genome sequencing and annotation
Genomes and transcriptomes of both P. macrospinosa DSE2036 and Cadophora sp. DSE1049 were sequenced using the Illumina platform. For genomic sequencing, 500 ng of DNA was sheared to 270 bp using the covaris E210 (Covaris) and size selected using SPRI beads (Beckman Coulter). The fragments were treated with end-repair, A-tailing, and ligation of Illumina adapters using the TruSeq Sample Prep Kit (Illumina). For transcriptomics, stranded cDNA libraries were generated using the Illumina TruSeq Stranded RNA LT kit. mRNA was purified from 1 µg of total RNA using magnetic beads containing poly-T oligos, fragmented, and reversed transcribed using random hexamers and SSII (Invitrogen), followed by second strand synthesis. The fragmented cDNA was treated with end-pair, A-tailing, adapter ligation, and eight cycles of PCR.
All libraries were quantified using KAPA Biosystem’s next-generation sequencing library qPCR kit, run on a Roche LightCycler 480 real-time PCR instrument, and multiplexed into pools of two libraries. Samples were prepared for sequencing on the Illumina HiSeq sequencing platform using the TruSeq paired-end cluster kit v3, and Illumina’s cBot instrument to generate clustered flowcells. Sequencing of the flowcells was performed on the Illumina HiSeq. 2000 sequencer using a TruSeq SBS sequencing kit 200 cycles, v3, following a 2 × 150 indexed run recipe.
Genomic reads were initially assembled with two sets of assembly parameters using Velvet52. Simulated 2-kbp and 3-kbp-long mate-pair libraries were derived from these initial Velvet assemblies and combined with the original set of reads using AllPathsLG release version R4771053. Mitochondria were separately assembled with Velvet and then AllPathsLG to produce single mitochondrial contigs for each genome. Illumina reads of stranded RNA-seq data were used as the input for de novo assembly of RNA contigs. Reads were assembled into consensus sequences using Rnnotator (v. 3.3.2)54.
Both genomes were annotated using the JGI Annotation Pipeline55 and made available via the JGI fungal portal MycoCosm55. The genomes of Cadophora sp. and P. macropsinosa can be accessed at http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Cadsp1 and http://genome.jgi.doe.gov/Perma1 respectively, and these Whole Genome Shotgun projects have been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession Cadophora sp., PCYN00000000 and Periconia macrospinosa, PCYO00000000.
Clustering/phylogenomic analyses
For comparison of our two DSEs to other fungi, available genomes of 32 ascomycetes with different lifestyles including saprotrophic, mutualistic or pathogenic species were selected (Supplementary Table S1). Non-redundant predicted protein sequences from the genomes of 34 fungi species were clustered based on similarity using Mcl 14-13756 based on a similarity metric derived from blast score and alignment coverage as described in Ohm et al.30. An inflation parameter of 2.0 was used for clustering. To obtain sequence similarity measures, we use all-vs-all blastp as implemented in mpiBLAST 1.6.0, using an E-value cut-off of 10 (the default value).
To infer an organismal phylogeny, we identified single copy clusters that contained a single protein per species and included representatives of at least 25 species. Multiple alignments for these clusters were obtained using PRANK v.14060357. Ambiguously aligned regions of the alignments were removed with GBlocks 0.91b58 using the default, stringent settings. Next, we concatenated protein family alignments into a supermatrix, excluding any alignment having less than 50 amino acid residues. This resulted in a supermatrix of 929 protein families and 169,432 amino acid sites. Maximum Likelihood trees were inferred from this alignment using the WAG model of sequence evolution with gamma-distributed rate heterogeneity in RAxML 8.1.359. and bootstrap support estimated in 100 replicates (Supplementary Fig. S1).
COMPARE-analysis
We analyzed the genome evolution of DSEs and related ascomycetes by reconstructing gene duplication and loss histories across all recognized gene families in the 34 species listed in Supplementary Table S1. To this end, we aligned each protein cluster as above, and inferred ML gene trees in RAxML 8.1.3 under the WAG model with gamma-distributed rate heterogeneity. Gene trees were then reconciled with the species tree by TreeFix v1.1.1060 using 100 iterations and RAxML as the tree inference algorithm and the default duplication/loss cost model. We then identified protein orthogroups within reconciled gene trees using the ortholog coding algorithm61 and mapped the origins and losses of the resulting orthogroups on the organismal phylogeny using Dollo parsimony. For functional characterization of the duplication and loss events, we used Pfam domains and gene ontology terms. Pfam domains were scanned using PfamScan.pl, which utilized Hmmer version 3.1b1. We detected at least one known Pfam domain in 263,141 proteins (64.2%). For enrichment analyses, we used the hypergeometric test with Bonferroni correction for multiple hypothesis testing.
CAZymes
We screened for carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) within the 34 genomes used in this study and also the three further genomes of DSE fungi, Harpophora oryzae36, Phialocephala subalpina29 and Microdochium bolleyi37 published recently. The detection, and family assignment of all CAZymes were performed as previously described62–64. BLAST and Hmmer searches were conducted against sequence libraries and Hmm profiles in the CAZy database (http://www.cazy.org). All positive hits were manually examined for final validation. We took into account all CAZyme classes, including Glycoside Hydrolases (GH), Carbohydrate Esterases (CE), Glycoside Transferases (GT), Polysaccharide Lyases (PL), Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBM) and Auxiliary redox enzymes (AA), both of which are thought to break down cell wall components, including lignin62. CAZymes selection for PCWDE were carried out using the CAZy database pipeline62. The copy numbers of each subfamilies of CAZyme families and PCWDEs were used as dataset for principal component analyses (PCA).
Meiosis-related genes
Since teleomorphs and sexual state have never been observed in P. macrospinosa and Cadophora sp., we examined their genomes for meiosis-related genes. Protein sequences for the genes involved in meiosis were checked as described in Toome et al.65. Protein sequences were obtained from the Saccharomyces Genome Database66, and subjected to BLAST searches using the Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa genomes from MycoCosm55 as a reference. We searched for the presence of the core meiotic genes according to Halary et al.67 in all of the 34 genomes analyzed.
Small secreted proteins
We screened for secreted proteins in Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa using the SignalP 4.1 server68 with default settings for eukaryotic organisms. Putative small secreted proteins (SSP) were predicted considering peptides both with and without trans-membrane segments. Signal peptides between 80–300 amino acids were considered as SSPs.
Genes encoding melanin synthesis pathway proteins
Based on literature data69,70, we searched for proteins involved in melanin biosynthesis using BLAST. We focused on DHN-melanin synthesis – the main form of melanin produced by ascomycetes – and categorized protein sequences according to Tsai et al.:69 Alb1 – polyketide synthase AAC39471.1; Arp1 – scytalone dehydratase (PF02982) AAC49843.1; Arp2 – 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN) reductase AAF03314.1; Abr1 – brown 1 AAF03353.1; Ayg1 – yellowish-green 1 AAF03354.1; Abr2 – brown 2 AAF03349.1. Abr1 and Abr2 were not separated, but discussed together as Abr1–2 due to highly overlapping results.
Aquaporins
We searched for annotations of aquaporins in the MycoCosm resource to collect the sequences of major intrinsic proteins (MIP) – both aquaporin and aquaporin-like genes. Non-MIPs (Cadsp_426096) and proteins without Pfam domains (Perma_660761 and Perma_725695) were excluded from further analyses. For phylogenetic analysis of aquaporins, we merged the collected protein sequences with the fungal aquaporin dataset of Xu et al.71. Following the classification of Verma et al.72, we categorized the proteins into main groups of aquaporins: AQP, AQGP and its subgroup XIP. Maximum Likelihood analysis of aquaporins was carried out with raxmlGUI v. 1.373 running RAxML 8.1.359 and ML bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates. The phylogenetic tree was visualized and edited using MEGA674.
Secreted peptidases and lipases
To assess the diversity of secreted peptidases and lipases, we collected genes using the search terms “protease or peptidase” and “lipase” in MycoCosm. Prediction of secretion signals was conducted using SignalP75 and analyzed on the SignalP 4.1 server using the default settings for eukaryotic organisms. Secreted protease sequences were used in BLASTp searches (e-value cut-off = 1e-04) against the MEROPS database76 (http://merops.sanger.ac.uk/): aspartic (A), cysteine (C), serine (S), metallo (M) and threonine (T) peptidases, class with unknown activities (U) and peptidase inhibitors (I) were separated. Putative secreted lipases of the 34 fungi were classified according to their best hits in a BLASTp (e-value cut-off = 1e-04) search against the Lipase Engineering Database (http://www.led.uni-stuttgart.de/). Secreted lipase protein sequences were grouped into the main classes and their superfamilies. Protein sequences of both types of enzyme were cross checked with a BLAST search (e-value cut-off = 1e-04) against the NCBI NR protein database.
Results and Discussion
Genomes
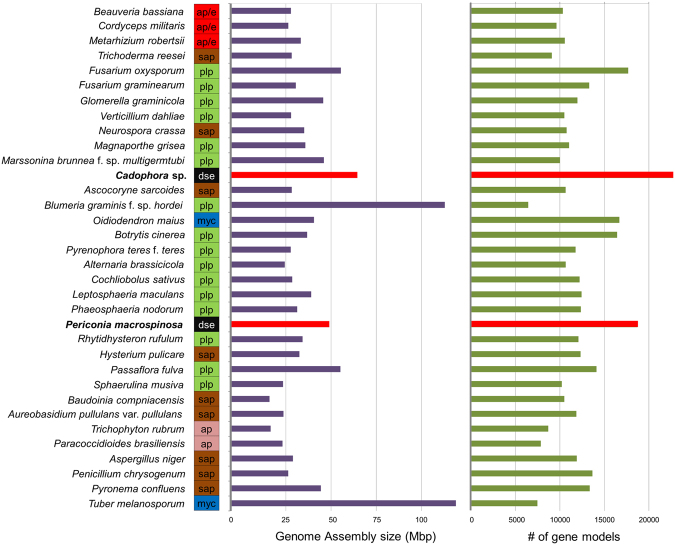
In the present study, we sequenced the genomes of two common DSEs, Cadophora sp. and Periconia macrospinosa, originating from the same semiarid grassland habitat (Table 1). Cadophora sp. has relatively big genome size of 70.46 Mb (GC content: 45.82%) including 22,766 gene models, and P. macrospinosa has still large, 54.99 Mb genome (GC content: 47.24%) with 18,750 models (Fig. 2; Table 1). In comparison with other ascomycetes included in this study, the two DSEs, especially Cadophora sp., have larger genome sizes and higher numbers of predicted proteins (Fig. 2; Supplementary Table S1). The number of gene models of functionally classified proteins (KOG) is similar between the Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa genomes (Supplementary Fig. S2). The genomes of both DSEs are also larger than the average genome size of previously sequenced ascomycetous species77, and Cadophora sp. is similar in size to Phialocephala subalpina (79.7 Mb), a common DSE in forest ecosystems29. The larger genome size of Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa is caused by expansion of the protein coding gene inventory, and not by transposable element (TE) proliferation, as seen in several fungi78,79, causing genome size expansion in several fungi and oomycetes such as the pathogens Phytophthora infestans80, Blumeria graminis f.sp. hordei81 and Leptosphaeria species82, and the ectomycorrhizal ascomycete Cenococcum geophilum83.
Table 1.
Genome statistics of Cadophora sp. DSE1049 and Periconia macrospinosa DSE2036.
| Genome Assembly | Cadophora sp. | Periconia macrospinosa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome Assembly size (Mbp) | 70,46 | 54,99 | |
| Sequencing read coverage depth | 79,2x | 139,4x | |
| # of contigs | 1294 | 2470 | |
| # of scaffolds | 1193 | 1566 | |
| # of scaffolds > = 2Kbp | 1092 | 1217 | |
| Scaffold N50 | 71 | 101 | |
| Scaffold L50 (Mbp) | 0,24 | 0,14 | |
| # of gaps | 101 | 904 | |
| % of scaffold length in gaps | 0,001 | 0,018 | |
| Three largest Scaffolds (Mbp) | 1,38; 1,24; 1,23 | 1.32, 0.77, 0.70 | |
| External gene models/length (bp) | |||
| Average | gene | 1583 | 1564 |
| transcript | 1401 | 1418 | |
| exon | 460 | 537 | |
| intron | 91 | 91 | |
| Median | gene | 1358 | 1340 |
| transcript | 1200 | 1202 | |
| exon | 292 | 338 | |
| intron | 58 | 61 | |
| Description | |||
| Average | protein length (aa) | 409 | 411 |
| exons per gene | 3,04 | 2,64 | |
| # of gene models | 22766 | 18750 | |
| Median | protein length (aa) | 338 | 337 |
| exons per gene | 3 | 2 | |
| CEGMA | % | 100 | 100 |
| ESTs | |||
| # sequences total | 39120 | 40915 | |
| # mapped to genome | 38428 | 38019 | |
| % mapped to genome | 0,982 | 0,929 | |
Figure 2.
Genome size and number of predicted genes of Cadophora sp. and Periconia macrospinosa as compared with other ascomycetes. DSEs are labeled with bold names and red bars. After each species name, its type of lifestyle is indicated as follows: red (ap/e; animal pathogens/endophytes?), brown (sap; saprotrophs), green (plp; plant pathogens), black (dse, dark septate endophytes), blue (myc; mycorrhizal fungi), or pink (ap; animal pathogen). For complete species names and further information see Supplementary Table S1.
Reconstructing genome evolution in DSEs
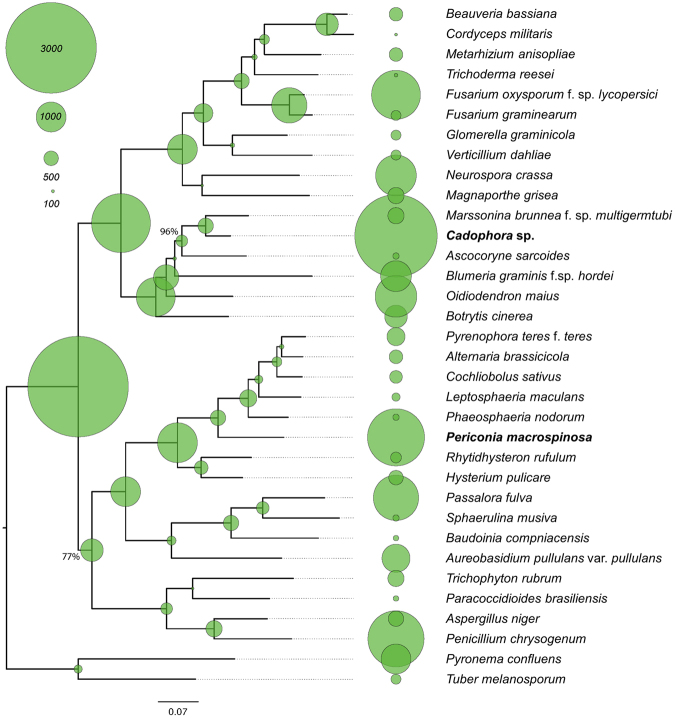
Markov clustering resulted in 21,768 clusters (at I = 2.0), from which patterns of genome evolution were inferred (Fig. 3). We found 9,478 clusters that did not contain any DSE fungi. These included large clusters of permeases, transferases and other enzymes related to common cellular processes of plant associated fungi (Supplementary Table S2). A total of 272 and 211 clusters were specific for Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa, respectively, while only 26 clusters contained proteins of the two DSEs only. Interestingly, for both species there is a high number of protein clusters that do not contain any known Pfam domains (>55%). The lack of functional annotation for the majority of DSE-specific clusters shows that many of the proteins of these fungi have no similarity to the characterized fraction of the protein space. This could imply DSE fungi have evolved unique genetic innovations.
Figure 3.
Genome-wide reconstruction of gene duplication histories of Cadophora sp., Periconia macrospinosa and another 32 ascomycetes. Green circles indicate observed (on terminal branches) and reconstructed (on internal nodes) copy numbers. The two DSEs are marked in bold.
Only twelve of the 26 clusters shared by both DSEs contained known Pfams (Supplementary Table S2). The largest DSE-specific clusters contained genes of heterokaryon incompatibility (HET), toxicity, transferase and kinase activities and unknown function (Supplementary Table S3). Surprisingly, HET genes were highly expanded in the DSE genomes, especially in Cadophora. We detected significantly more HET genes (using the search term PF06985) in Cadophora sp. (470) and P. macrospinosa (177) than in other Ascomycota (57 genes on average, Supplementary Table S3). Genes containing the functionally uncharacterized domain PF12013 are also expanded in the DSE genomes. This domain, which is also found in other ascomycetes and eukaryotes, contains two segments that are likely to be C2H2 zinc-binding domains. Furthermore, the NACHT domain (PF05729), which is linked to HET proteins and is likely responsible for vegetative incompatibility, is also overrepresented in DSE genomes (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3). Although our knowledge of the HET genes and their biological significance in filamentous fungi is still limited84, their role in (non-)self-recognition and hyphal fusion could imply that DSEs need particularly sophisticated mechanisms for managing intra- or interspecies hyphal encounters85.
Of the species-specific clusters of Cadophora sp. (272) and P. macrospinosa (211) 35 and 26 contained known Pfam domains, respectively (Supplementary Table S2). These protein clusters exhibit different functions, including transferase and kinase activities. While the largest cluster specific to Cadophora sp. with a Pfam comprised 46 endonucleases of the DDE superfamily (PF13358), the largest cluster specific to P. macrospinosa with a Pfam comprised HET domain-containing proteins (Supplementary Table S2).
We analyzed gene duplication/loss events in two DSEs and 32 other ascomycetes with diverse lifestyles. Altogether, 13,966 reconciled gene trees, supplemented with 6,991 clusters that contained less than four proteins were used for mapping gene duplications and losses. We found that 65,443 gene duplications and 194,331 gene losses were required to explain genome evolution in the examined species under Dollo parsimony. The inferred numbers of duplications and losses, as well as the reconstructed ancestral genome sizes, are shown in Fig. 3. Both DSEs showed high numbers of species-specific gene duplications: 2,757 and 1,931 in Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa, respectively (Fig. 3). Enrichment analyses on the gene families that showed duplications in Cadophora sp., in P. macrospinosa, or both species revealed that several terms related to oxidation-reduction processes, peptidase and kinase activities, and transmembrane transport were enriched (Supplementary Table S3). On the Cadophora sp. branch, we inferred a total of 2,757 gene duplications in 1,329 clusters. Of these, 221 clusters were species-specific, but only 14 of them contained Pfams, which had six GO terms overrepresented. In P. macrospinosa, we inferred 1,931 duplications in 940 clusters. P. macrospinosa had 155 species-specific clusters, of which 14 also had Pfams. We found 131 clusters showing duplications in both species, of which 84 had Pfams (Supplementary Table S2). Enrichment analysis also revealed clusters in which Cadophora sp., P. macrospinosa, or both fungi lost genes. While Cadophora sp. lost gene clusters that comprised a total of ten GO terms, P. macrospinosa lost even more clusters that added up to 63 GO terms. The two DSEs lost nine shared gene clusters (Supplementary Table S2).
Taken together, analyses of the DSE genomes show significant expansions of certain gene families, including a high number of species-specific gene duplications in both Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa. This, together with low levels of convergence in gene family evolution, suggests that, despite originating from the same habitat, these two DSEs evolved along different evolutionary trajectories and display considerable functional differences.
CAZymes
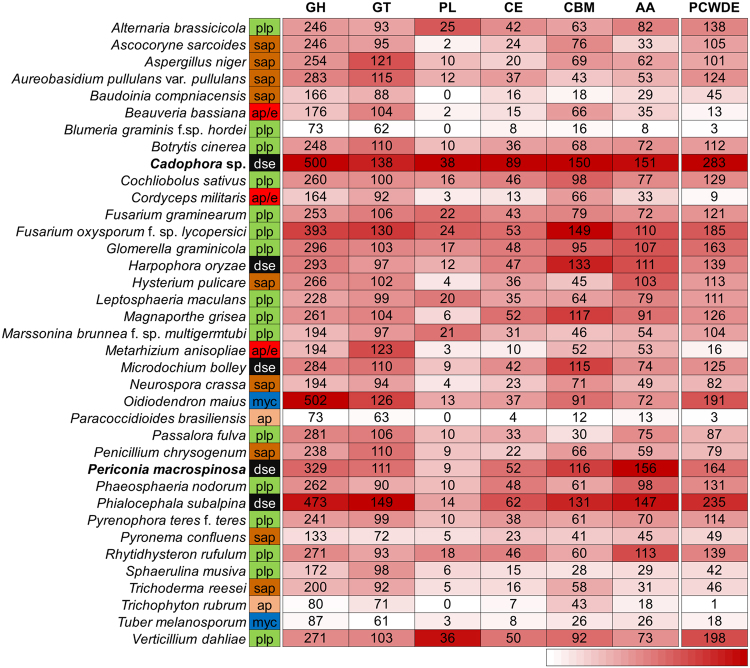
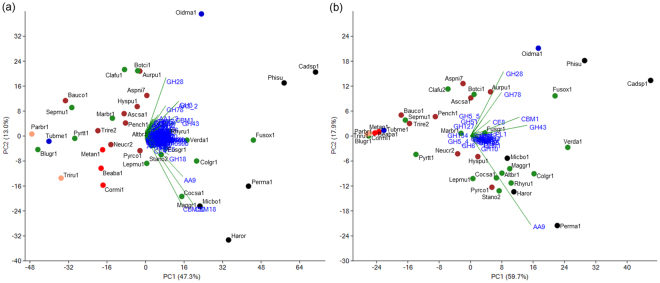
The genomes of Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa contained 1,066 and 773 genes encoding putative CAZymes, respectively (Fig. 4; Supplementary Table S4). These numbers are significantly higher than the average for the other 32 species in our analysis, even when the effect of genome-size differences is taken into account (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3). We found Cadophora sp. to have the highest number of CAZymes, followed by Phialocephala subalpina (976), Fusarium oxysporum (859), Oidiodendron maius (841), P. macrospinosa, Harpophora oryzae (693), Glomerella graminicola (666) and Microdochium bolleyi (634) (Fig. 4; Supplementary Table S4). All five DSE fungi analyzed were among the first eight taxa with highest number of CAZymes (Fig. 4; Supplementary Table S4) Principal component analysis (PCA) based on CAZymes separated the five DSEs and the root colonizing F. oxysporum, which also has endophytic stage in its life cycle from all the other taxa (Fig. 5a). The GH superfamily is the most represented class of CAZymes found within our two DSE genomes, with the enlarged families being GH3 (b-glucosidase/b-xylosidase), GH16 (b-galactosidase/b-glucanase), GH18 (chitinases) and GH43 (a-arabinofuranosidase/b-xylosidase). We also found high gene numbers of GH78 (a-rhamnosidase) family, but only in Cadophora sp. In general, the DSEs possessed relatively high number of genes in the CAZyme superfamilies and families/subfamilies across the Ascomycota taxa examined. This was the case, for example, for CBM1, CBM18 and CBM50 among the CBMs, and AA3_2 and AA9 among the AAs (Supplementary Table S4).
Figure 4.
Number of genes encoding carbohydrate active enzymes (CAZymes) and plant cell wall degrading enzymes (PCWDE) in Cadophora sp., Periconia macrospinosa and other 35 fungi including three further DSE species. Major CAZyme classes are shown separately, including Glycoside Hydrolases (GH), Glycoside Transferases (GT), Polysaccharide Lyases (PL), Carbohydrate Esterases (CE), Carbohydrate-Binding Modules (CBM), and Auxiliary redox enzymes (AA). After each species name, its type of lifestyle is indicated as follows: red (ap/e; animal pathogens/endophytes), brown (sap; saprotrophs), green (plp; plant pathogens), black (dse, dark septate endophytes), blue (myc; mycorrhizal fungi), or pink (ap; animal pathogen). For each class of enzyme, white-to-red shading corresponds to lower to higher copy numbers. For detailed information on CAZymes copy numbers see Supplementary Table S4.
Figure 5.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of carbohydrate active enzymes (CAZymes) and plant cell wall degrading enzymes (PCWDEs) of Cadophora sp., Periconia macrospinosa, and 35 other ascomycetes including three further DSE species. (a) PCA based on CAZyme copynumbers. PC1 accounts for 47.3% of the variation and PC2 for 13%. (b) PCA based on gene copy numbers of plant cell wall degrading families. PC1 accounts for 59.7% of the variation and PC2 for 17.9%. The different fungal lifestyles are labelled in red (ap/e; animal pathogens/endophytes?), brown (sap; saprotrophs), green (plp; plant pathogens), black (dse, dark septate endophytes), blue (myc; mycorrhizal fungi), or pink (ap; animal pathogen). For complete species names and further information see Supplementary Table S5.
We also found Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa to be enriched (p value < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3) in proteins with PCWDE domains (283 and 164, respectively), and a PCA based on PCWDEs separated our DSEs from other species (Fig. 5b). Cadophora sp. has the highest number of PCWDE genes out of all ascomycetes analyzed in this study (Supplementary Table S5). This species has even more PCWDEs than the pathogenic Colletotrichum species (>240)83,86,87, and the other helotialean DSE, P. subalpina (235) (Supplementary Table S5). Even though the most abundant PCWDE domains were the same (GH43, CBM1, and AA9) for both DSEs, the two species were separated from each other in the PCA (Fig. 5b). In this analysis the five DSE did not form a separate group as when the whole CAZomes were analyzed.
The fact that these DSEs possess a high number of CAZymes and PCWDE domains suggests that they have a particular and broad spectrum of degrading enzymes and possible plant cell wall degrading capacity. Several genomic studies showed that an expanded CAZyme and PCWDE repertoire was linked with saprobic and/or plant pathogenic abilities of fungi30,38,88–90. This is consistent with the fact that those fungi are able to break down complex plant polysaccharides - a feature that is important for establishing infection and accessing nutrients during necrotrophic and saprotrophic growth. The PCA of PCWDEs revealed a loose association between DSE fungi, root colonizing plant pathogens (Fusarium oxysporum and Verticillium dahliae) and the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus, O. maius, along the first axis (Fig. 5b). However, these species dispersed along the second axis, indicating that they have substantial differences with respect to PCWDE domains. Schlegel et al.29 found a similar expansion of CAZyme and PCWDE genes in the genome of P. subalpina. The copy numbers of PCWDEs in this fungus are quite similar to those in Cadophora sp. and the PCA also showed their similarity in PCWDEs, which might be consistent with their close phylogenetic relationship (Helotiales) and similar lifestyle (DSE). In our study and in the study of Schlegel et al.29, ectomycorrhizal species, which are generally characterized by a reduced CAZyme repertoire (especially of PCWDEs)38, showed fundamental differences from root endophytes in terms of these genes. The ectomycorrhizal lifestyle, which has arisen from saprobic ancestors multiple times, is linked to convergent loss of genes encoding PCWDEs38. Similarly, the non-root colonizing endophyte X. heveae was also found to have reduced spectra of these enzyme families31.
The number of CAZymes in the helotialean DSE is even higher than that in ericoid mycorrhizal species where saprobic capacities of the fungal partner has great importance91. The observation that all sequenced DSE fungi show signs of CAZyme family expansion suggests that PCW degradation may be one of the most important attributes of DSE fungi. These enzymes are undoubtedly involved in saprotrophic activity, and might be prerequisite for root colonization and interaction with the host plant.
Meiosis-related genes
DSEs are generally considered as asexual fungi, and up until now, the in vitro induction of the sexual form (ascomata) has only ever been reported once for one genus42. Numerous homologs of meiosis-related genes could be identified in both the Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa genome: 93 and 89 of the 127 meiosis-related genes searched were found, respectively (Supplementary Table S6). However, out of the two genes (ndt80 and ime1) considered to play a vital role in meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae92, one or both were absent in Cadophora sp., and P. macrospinosa, respectively. Other genes considered as essential for meiosis in S. cerevisiae and other eukaryotes (e.g., sum1 and xrs2) were also missing from the genomes of the two DSEs. Out of 31 meiosis genes which were previously determined as core genes67, 28 and 26 orthologues were found in Cadophora sp. (lacks dmc1, hop1, and rad51) and P. macrospinosa (lacks dmc1, hop1, rad51, mus81 and rec8) genomes, respectively (Supplementary Table S6). Compared to the other 32 genomes representing both sexual and asexual ascomycetes, the lack of three and five core genes in DSE genomes is not exceptional even in fungi capable for sexual reproduction (Supplementary Table S6). So, the 73% and 70% of all meiosis-related genes (90% and 84% of all core meiosis genes sensu Halary et al.67) found in the Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa genomes are not unambiguous indicators of the the absence of potential meiotic processes. This might indicate previous existence of sexual reproduction in these DSEs and we cannot rule out the existence of cryptic sexual reproduction either. Probably, the expansion of the HET genes in these species is associated with the low selective pressure at the MAT locus, and just as proposed in case of black yeasts93, a parasexual cycle may play an important role in generating diversity.
SSPs
Small secreted proteins are important players in fungal-plant interactions41,78,94. We predicted a total of 1,912 and 1,543 SSP genes in Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa, respectively, which represent significant percentages (8.4% and 8.2%) of the proteomes. Large number of the SSPs with no homology with previously identified SSPs is not surprising considering that the majority of known SSPs are taxon specific38–41,83. Multiple SSPs play a role in the symbiotic interactions of mycorrhizae38,41 and the root endophyte Piriformospora indica34, so we may assume that some of the predicted SSPs of the DSEs are symbiosis-related. Although the precise mechanisms by which Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa suppress plant defense are unknown, the SSPs predicted from their genomes could be candidate effectors95.
Genes belonging to melanin synthesis pathways
Many fungal species produce pigments such as melanin, which is generally produced via the DHN-melanin synthesys pathway and plays crucial roles in an array of cellular processes, including defense or pathogenicity96. We searched for homologs of the genes of the DHN-melanin synthesis pathway, namely Alb1, Arp1, Arp2, Abr1–2 and Ayg1, in all 34 fungi. As expected, high numbers of melanin synthesis related genes were found in the pigmented ascomycetes, including the ericoid mycorrhizal O. maius, but also in the two DSEs (Supplementary Table S7). The total numbers of genes related to DHN-melanin synthesis were similar in all three of these species: 134 genes in Cadophora sp., 133 in P. macrospinosa, and 151 in O. maius. However, Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa differed with respect to the most dominant melanin synthesys-related genes. For example, although Alb1 homologues (PKSP) were overrepresented in both DSEs (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3), their number was higher in P. macrospinosa (67 genes). In contrast, Cadophora sp. possessed more Arp1 (scytalone dehydratase), Arp2 (THN reductase) and Abr1–2 homologues (3, 79 and 27, respectively) (Supplementary Table S7). It has been demonstrated that these pigments serve to protect fungal cells, especially from reactive oxygen species produced by host immune defenses97. Moreover, as pigments can be advantageous to plant-associated fungi in habitats with strong UV-radiation, which is consistent with the high numbers of homologues identified in grassland-inhabiting DSE fungi.
Aquaporins
We found 15 and 9 MIP genes in the Cadophora sp. and P. macrospinosa genomes, respectively. Out of all the genomes screened in this study, Cadophora sp. had the most MIP genes (Supplementary Table S8). Although the majority of the MIPs were aquaporins, aquaglyceroporins and X-intrinsic proteins were also present. The aquaporin gene tree shows that the majority of aquaporin genes found in the two DSEs belong to known groups of aquaporins. Nonetheless, two new lineages of aquaporins were identified from DSE genomes (Supplementary Fig. S3). The expansion of aquaporin genes, along with potentially novel clades in Cadophora sp., could suggest a major role for these proteins in DSE fungi. Whether these genes are upregulated during the symbiotic phase in DSE fungi, as reported in EcM fungi40,83, represents an interesting future research question. Gene numbers may indicate some similarities with ectomycorrhizal fungi in the aquaporin-related MIPs40.
Secreted peptidases and lipases
The total number of genes encoding secreted peptidases in Cadophora sp. was enlarged, however only the aspartic peptidase family were significantly higher than average (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3) when compared to other ascomycetes (Supplementary Table S9). In general, plant-associated fungi had more secreted peptidase genes than fungi with other lifestyle in our analysis. Accordingly, PCA grouped DSE fungi with other plant-associated species including O. maius, plant pathogens, and the three hypocrealean entomopathogen/endophyte species (Supplementary Fig. S4a). Cadophora sp. was enriched in secreted lipases (48) (p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test, Supplementary Table S3) compared to the 33 species analyzed in this study (Supplementary Fig. S4b; Supplementary Table S9), followed by O. maius (30) and P. macrospinosa (29). Separation of DSE fungi from the other species along the PC1 axis was correlated with abH03 superfamily copy numbers (Candida rugosa lipase like) (Supplementary Fig. S4b).
Since all the plant-associated fungi in this study, except T. melanosporum, had genomes enriched with secreted peptidases and lipases, these enzymes are likely to be important for plant colonization by DSEs. Compared to saprobes and human pathogens, peptidases are more abundant in these fungi mainly due to expansions in the serine protease and metalloprotease families. A similar trend has previously been observed in the plant pathogenic Colletotrichum spp86,98. The majority of secreted proteases in Cadophora sp. were subtilisins (S8A), a family of serine proteases associated with virulence, penetration and colonization of hosts99,100. On the other hand, the two DSE fungi exhibit different patterns of metallopeptidases copy numbers. For instance, while M43 proteases were the most abundant metallopeptidase family in Cadophora sp, they were completely absent in P. macrospinosa. These metallopeptidases are also expanded in Piriformospora indica, and their upregulation during colonization of dead roots34, which supports a role for proteases in degrading plant tissues.
Secreted lipases were overrepresented in the two DSEs, in other plant-associated fungi, and in entomopathogenic/endophytic species, compared to other Ascomycota (Supplementary Table S10). This is not surprising considering that several lipases are known to play important roles in plant pathogenicity. By catalyzing the hydrolysis of ester bonds of the fatty acid polymers in the plant cuticle, these lipases facilitate fungal penetration101. Secreted lipases are likely to serve as virulence factors in the colonization of arthropods102 and in fungal-plant interactions101. Moreover, lipases are highly expressed symbiosis-related factors involved in ectomycorrhizal symbiosis40. For example, the third most expressed gene in T. melanosporum during EcM symbiosis40 was a secreted lipase. Importantly, several homologs of this same lipase were in both DSEs, indicating its possible role in root colonization by endophytes.
Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed the genomes of two independently evolved DSE fungi, which originated from the same environment. In comparison to other ascomycetes, we found that the DSEs have an increased genome size, a larger gene repertoire, and an expanded number of CAZymes, including PCWDEs. Aside from these common fundamental features, we also found major differences between the two fungi. Based on gene copy numbers, Cadophora sp. has a larger toolbox for saprobic capacity. According to DSE-specific gene clusters – both shared and unique ones – endophytes have no common DSE-specific function, but rather diverse roles. We found that all sequenced DSE fungi show signs of CAZyme family expansion. The complex carbohydrate degrading capacity could be a key characteristic of the lifestyle of DSE fungi.
Genome-wide reconstruction of gene duplication and loss histories revealed high numbers of species-specific gene duplications in the two DSEs and low levels of convergence in gene family evolution. This too confirms the striking functional diversity among DSE fungi. The results of our comparative genomics analyses reinforce this apparent diversity, and imply that an endophytic lifestyle does not comprise a homogenous ecological guild. As previously hypothesized23, functional diversity could be the key aspect of DSE function, and this complementarity might play a role in completing the plant holobiont103 and ensuring survival in nutrient-limited environments.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (NKFIH/OTKA K109102). The work by the U.S. Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02- 05CH11231. L.G.N was supported by the ‘Momentum Program’ of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (Contract # LP-2014/12).
Author Contributions
G.M.K. and L.G.N. designed the research. D.G.K., J.B.N., L.T. and G.M.K. carried out experiments and DNA/RNA extractions. K.B., M.H., B.H., J.J., A.K., J.H.P.L., A.L., M.N., R.A.O., I.V.G., J.W.S. sequenced, assembled, annotated the genomes, and coordinated these works. G.M.K., L.G.N. and D.G.K. performed further analyses. D.G.K., G.M.K. and L.G.N. wrote the manuscript. All authors checked, discussed and commented the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-018-24686-4.
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Petrini, O. In Microbial Ecology of Leaves (eds Andrews, J. H. & Hirano, S. S.) 179–197, 10.1007/978-1-4612-3168-4_9 (Springer New York, 1991).
- 2.Porras-Alfaro A, Bayman P. Hidden Fungi, Emergent Properties: Endophytes and Microbiomes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011;49:291–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saikkonen K, Faeth SH, Helander M, Sullivan TJ. FUNGAL ENDOPHYTES: A Continuum of Interactions with Host Plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1998;29:319–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.319. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schulz B, Boyle C. The endophytic continuum. Mycol. Res. 2005;109:661–686. doi: 10.1017/S095375620500273X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fesel PH, Zuccaro A. Dissecting endophytic lifestyle along the parasitism/mutualism continuum in Arabidopsis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016;32:103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2016.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schardl CL, et al. Plant-Symbiotic Fungi as Chemical Engineers: Multi-Genome Analysis of the Clavicipitaceae Reveals Dynamics of Alkaloid Loci. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hardoim PR, et al. The Hidden World within Plants: Ecological and Evolutionary Considerations for Defining Functioning of Microbial Endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015;79:293–320. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00050-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Andrade-Linares, D. R. & Franken, P. In Symbiotic Endophytes, Soil Biology 37 (ed. Aroca, R.) 311–334, 10.1007/978-3-642-39317-4_16 (Springer-Verlag, 2013).
- 9.Vandenkoornhuyse P. Extensive Fungal Diversity in Plant Roots. Science (80-.). 2002;295:2051–2051. doi: 10.1126/science.295.5562.2051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rodriguez RJ, White JF, Jr, Arnold AE, Redman RS. Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol. 2009;182:314–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jumpponen A, Trappe JM. Dark septate endophytes: a review of facultative biotrophic root-colonizing fungi. New Phytol. 1998;140:295–310. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1998.00265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mandyam K, Jumpponen A. Seeking the elusive function of the root-colonising dark septate endophytic fungi. Stud. Mycol. 2005;53:173–189. doi: 10.3114/sim.53.1.173. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Haselwandter K, Read DJ. Fungal associations of roots of dominant and sub-dominant plants in high-alpine vegetation systems with special reference to mycorrhiza. Oecologia. 1980;45:57–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00346707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Peterson RLL, Wagg C, Pautler M. Associations between microfungal endophytes and roots: do structural features indicate function? Botany. 2008;86:445–456. doi: 10.1139/B08-016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Addy HD, Piercey MM, Currah RS. Microfungal endophytes in roots. Can. J. Bot. 2005;83:1–13. doi: 10.1139/b04-171. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Knapp DG, Pintye A, Kovács GM. The Dark Side Is Not Fastidious – Dark Septate Endophytic Fungi of Native and Invasive Plants of Semiarid Sandy Areas. PLoS One. 2012;7:e32570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Newsham KK. A meta-analysis of plant responses to dark septate root endophytes. New Phytol. 2011;190:783–793. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sieber, T N.; Grünig, C. R. in Plant Roots: The hidden half (ed. Eshel, A., Beeckman, T.) 1–49 (CRC Press, 2013).
- 19.Kovács GM, Szigetvári C. Mycorrhizae and other root-associated fungal structures of the plants of a sandy grassland on the Great Hungarian Plain. Phyt. - Ann. Rei Bot. 2002;42:211–223. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hiruma K, et al. Root Endophyte Colletotrichum tofieldiae Confers Plant Fitness Benefits that Are Phosphate Status Dependent. Cell. 2016;165:464–474. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mayerhofer MS, Kernaghan G, Harper KA. The effects of fungal root endophytes on plant growth: a meta-analysis. Mycorrhiza. 2013;23:119–128. doi: 10.1007/s00572-012-0456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caldwell BA, Jumpponen A, Trappe JM. Utilization of Major Detrital Substrates by Dark-Septate, Root Endophytes. Mycologia. 2000;92:230. doi: 10.2307/3761555. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Knapp DG, Kovács GM. Interspecific metabolic diversity of root-colonizing endophytic fungi revealed by enzyme activity tests. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016;92:fiw190. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiw190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Smith, S. E. & Read, D. J. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. (Academic Press, 2008).
- 25.Porras-Alfaro A, et al. Novel Root Fungal Consortium Associated with a Dominant Desert Grass. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008;74:2805–2813. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02769-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Porras-Alfaro A, Herrera J, Natvig DO, Lipinski K, Sinsabaugh RL. Diversity and distribution of soil fungal communities in a semiarid grassland. Mycologia. 2011;103:10–21. doi: 10.3852/09-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Khidir HH, et al. A general suite of fungal endophytes dominate the roots of two dominant grasses in a semiarid grassland. J. Arid Environ. 2010;74:35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.07.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Grünig CR, Queloz V, Sieber TN, Holdenrieder O. Dark septate endophytes (DSE) of the Phialocephala fortinii s.l. – Acephala applanata species complex in tree roots: classification, population biology, and ecology. Botany. 2008;86:1355–1369. doi: 10.1139/B08-108. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schlegel M, et al. Globally distributed root endophyte Phialocephala subalpina links pathogenic and saprophytic lifestyles. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:1015. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3369-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ohm RA, et al. Diverse Lifestyles and Strategies of Plant Pathogenesis Encoded in the Genomes of Eighteen Dothideomycetes Fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1003037. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gazis R, et al. The genome of Xylona heveae provides a window into fungal endophytism. Fungal Biol. 2016;120:26–42. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2015.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang X, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis fici reveals its lifestyle and high potential for synthesis of natural products. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:28. doi: 10.1186/s12864-014-1190-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Walker AK, et al. Full Genome of Phialocephala scopiformis DAOMC 229536, a Fungal Endophyte of Spruce Producing the Potent Anti-Insectan Compound Rugulosin. Genome Announc. 2016;4:e01768–15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01768-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zuccaro A, et al. Endophytic Life Strategies Decoded by Genome and Transcriptome Analyses of the Mutualistic Root Symbiont Piriformospora indica. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002290. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hacquard S, et al. Survival trade-offs in plant roots during colonization by closely related beneficial and pathogenic fungi. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:11362. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Xu X-H, et al. The rice endophyte Harpophora oryzae genome reveals evolution from a pathogen to a mutualistic endophyte. Sci. Rep. 2015;4:5783. doi: 10.1038/srep05783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.David AS, et al. Draft Genome Sequence of Microdochium bolleyi, a Dark Septate Fungal Endophyte of Beach Grass. Genome Announc. 2016;4:e00270–16. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00270-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kohler A, et al. Convergent losses of decay mechanisms and rapid turnover of symbiosis genes in mycorrhizal mutualists. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:410–415. doi: 10.1038/ng.3223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Martin F, Kohler A, Murat C, Veneault-Fourrey C, Hibbett DS. Unearthing the roots of ectomycorrhizal symbioses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;14:760–773. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Martin F, et al. Périgord black truffle genome uncovers evolutionary origins and mechanisms of symbiosis. Nature. 2010;464:1033–1038. doi: 10.1038/nature08867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Martin F, et al. The genome of Laccaria bicolor provides insights into mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature. 2008;452:88–92. doi: 10.1038/nature06556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Knapp DG, Kovács GM, Zajta E, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW. Dark septate endophytic pleosporalean genera from semiarid areas. Persoonia - Mol. Phylogeny Evol. Fungi. 2015;35:87–100. doi: 10.3767/003158515X687669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Glynou K, et al. The local environment determines the assembly of root endophytic fungi at a continental scale. Environ. Microbiol. 2016;18:2418–2434. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Arenz BE, Held BW, Jurgens JA, Farrell RL, Blanchette RA. Fungal diversity in soils and historic wood from the Ross Sea Region of Antarctica. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006;38:3057–3064. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.01.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Blanchette RA, et al. An Antarctic Hot Spot for Fungi at Shackleton’s Historic Hut on Cape Royds. Microb. Ecol. 2010;60:29–38. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9664-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bruzone MC, Fontenla SB, Vohník M. Is the prominent ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Rhizoscyphus ericae absent in the Southern Hemisphere’s Ericaceae? A case study on the diversity of root mycobionts in Gaultheria spp. from northwest Patagonia, Argentina. Mycorrhiza. 2015;25:25–40. doi: 10.1007/s00572-014-0586-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tanaka K, et al. Revision of the Massarineae (Pleosporales, Dothideomycetes) Stud. Mycol. 2015;82:75–136. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2015.10.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mandyam K, Fox C, Jumpponen A. Septate endophyte colonization and host responses of grasses and forbs native to a tallgrass prairie. Mycorrhiza. 2012;22:109–119. doi: 10.1007/s00572-011-0386-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mandyam K, Jumpponen A. Seasonal and temporal dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal and dark septate endophytic fungi in a tallgrass prairie ecosystem are minimally affected by nitrogen enrichment. Mycorrhiza. 2008;18:145–155. doi: 10.1007/s00572-008-0165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Barrow JR. Atypical morphology of dark septate fungal root endophytes of Bouteloua in arid southwestern USA rangelands. Mycorrhiza. 2003;13:239–247. doi: 10.1007/s00572-003-0222-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Marx DH. The influence of ectotrophic mycorrhizal fungi on the resistance of pine roots to pathogenic infections. II. Production, identification, and biological activity of antibiotics produced by Leucopaxillus cerealis var. piceina. Phytopathology. 1969;59:411–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18:821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gnerre S, et al. High-quality draft assemblies of mammalian genomes from massively parallel sequence data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011;108:1513–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017351108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Martin J, et al. Rnnotator: an automated de novo transcriptome assembly pipeline from stranded RNA-Seq reads. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:663. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Grigoriev IV, et al. MycoCosm portal: gearing up for 1000 fungal genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D699–D704. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Enright AJ, Van Dongen S, Ouzounis CA. An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:1575–1584. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.7.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Loytynoja A, Goldman N. Phylogeny-Aware Gap Placement Prevents Errors in Sequence Alignment and Evolutionary Analysis. Science (80-.). 2008;320:1632–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.1158395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Talavera G, Castresana J, Kjer K, Page R, Sullivan J. Improvement of Phylogenies after Removing Divergent and Ambiguously Aligned Blocks from Protein Sequence Alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007;56:564–577. doi: 10.1080/10635150701472164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wu Y-C, Rasmussen MD, Bansal MS, Kellis M. TreeFix: Statistically Informed Gene Tree Error Correction Using Species Trees. Syst. Biol. 2013;62:110–120. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nagy, L. G. et al. Latent homology and convergent regulatory evolution underlies the repeated emergence of yeasts. Nat. Commun. 5, (2014). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 62.Levasseur A, Drula E, Lombard V, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. Expansion of the enzymatic repertoire of the CAZy database to integrate auxiliary redox enzymes. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2013;6:41. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-6-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lombard V, Golaconda Ramulu H, Drula E, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D490–D495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cantarel BL, et al. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:D233–D238. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Toome M, et al. Genome sequencing provides insight into the reproductive biology, nutritional mode and ploidy of the fern pathogen Mixia osmundae. New Phytol. 2014;202:554–564. doi: 10.1111/nph.12653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cherry JM, et al. Saccharomyces Genome Database: the genomics resource of budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:D700–D705. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Halary S, et al. Conserved Meiotic Machinery in Glomus spp., a Putatively Ancient Asexual Fungal Lineage. Genome Biol. Evol. 2011;3:950–958. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evr089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods. 2011;8:785–786. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tsai H, Wheeler MH, Chang YC, Chang YUNC. A Developmentally Regulated Gene Cluster Involved in Conidial Pigment Biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus A Developmentally Regulated Gene Cluster Involved in Conidial Pigment Biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Bacteriol. 1999;181:6469–6477. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.20.6469-6477.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Eisenman HC, Casadevall A. Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012;93:931–940. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3777-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Xu H, Cooke JEK, Zwiazek JJ. Phylogenetic analysis of fungal aquaporins provides insight into their possible role in water transport of mycorrhizal associations. Botany. 2013;91:495–504. doi: 10.1139/cjb-2013-0041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Verma RK, Prabh ND, Sankararamakrishnan R. New subfamilies of major intrinsic proteins in fungi suggest novel transport properties in fungal channels: implications for the host-fungal interactions. BMC Evol. Biol. 2014;14:173. doi: 10.1186/s12862-014-0173-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Silvestro D, Michalak I. raxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RAxML. Org. Divers. Evol. 2012;12:335–337. doi: 10.1007/s13127-011-0056-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013;30:2725–2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S, Heijne G. Von. A Neural Network Method for Identification of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Signal Peptides and Prediction of their Cleavage Sites. Int. J. Neural Syst. 1997;8:581–599. doi: 10.1142/S0129065797000537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ, Finn R. Twenty years of the MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D343–D350. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mohanta TK, Bae H. The diversity of fungal genome. Biol. Proced. Online. 2015;17:8. doi: 10.1186/s12575-015-0020-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Raffaele S, Kamoun S. Genome evolution in filamentous plant pathogens: why bigger can be better. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012;10:417. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Casacuberta E, González J. The impact of transposable elements in environmental adaptation. Mol. Ecol. 2013;22:1503–1517. doi: 10.1111/mec.12170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Haas BJ, et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature. 2009;461:393–398. doi: 10.1038/nature08358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Spanu PD, et al. Genome Expansion and Gene Loss in Powdery Mildew Fungi Reveal Tradeoffs in Extreme Parasitism. Science (80-.). 2010;330:1543–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.1194573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Grandaubert J, et al. Transposable element-assisted evolution and adaptation to host plant within the Leptosphaeria maculans-Leptosphaeria biglobosa species complex of fungal pathogens. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:891. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Peter M, et al. Ectomycorrhizal ecology is imprinted in the genome of the dominant symbiotic fungus Cenococcum geophilum. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:12662. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Fedorova N, Badger J, Robson G, Wortman J, Nierman W. No Title. BMC Genomics. 2005;6:177. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kubicek CP, et al. Comparative genome sequence analysis underscores mycoparasitism as the ancestral life style of Trichoderma. Genome Biol. 2011;12:R40. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-4-r40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Gan P, et al. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the hemibiotrophic stage shift of Colletotrichum fungi. New Phytol. 2013;197:1236–1249. doi: 10.1111/nph.12085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Baroncelli R, Sreenivasaprasad S, Sukno SA, Thon MR, Holub E. Draft Genome Sequence of Colletotrichum acutatum Sensu Lato (Colletotrichum fioriniae) Genome Announc. 2014;2:e00112-14–e00112-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00112-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Riley R, et al. Extensive sampling of basidiomycete genomes demonstrates inadequacy of the white-rot/brown-rot paradigm for wood decay fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014;111:9923–9928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400592111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Parrent J, James TY, Vasaitis R, Taylor AF. Friend or foe? Evolutionary history of glycoside hydrolase family 32 genes encoding for sucrolytic activity in fungi and its implications for plant-fungal symbioses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009;9:148. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Eastwood DC, et al. The Plant Cell Wall-Decomposing Machinery Underlies the Functional Diversity of Forest Fungi. Science (80-.). 2011;333:762–765. doi: 10.1126/science.1205411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Grelet, G., Martino, E., Dickie, I. A., Tajuddin, R. & Artz, R. in Molecular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis (ed. Martin, F. M.) 405–419 (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016), https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118951446.ch22.
- 92.Vershon AK, Pierce M. Transcriptional regulation of meiosis in yeast. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000;12:334–339. doi: 10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Teixeira MM, et al. Exploring the genomic diversity of black yeasts and relatives (Chaetothyriales, Ascomycota) Stud. Mycol. 2017;86:1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2017.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Plett JM, et al. A Secreted Effector Protein of Laccaria bicolor Is Required for Symbiosis Development. Curr. Biol. 2011;21:1197–1203. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.05.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Lo Presti L, et al. Fungal Effectors and Plant Susceptibility. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2015;66:513–545. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-043014-114623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Langfelder K, Streibel M, Jahn B, Haase G, Brakhage AA. Biosynthesis of fungal melanins and their importance for human pathogenic fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003;38:143–158. doi: 10.1016/S1087-1845(02)00526-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tsai HF, Chang YC, Washburn RG, Wheeler MH, Kwon-Chung KJ. The developmentally regulated alb1 gene of Aspergillus fumigatus: Its role in modulation of conidial morphology and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 1998;180:3031–3038. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.12.3031-3038.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.O’Connell RJ, et al. Lifestyle transitions in plant pathogenic Colletotrichum fungi deciphered by genome and transcriptome analyses. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:1060–1065. doi: 10.1038/ng.2372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Prusky D, McEvoy JL, Leverentz B, Conway WS. Local Modulation of Host pH by Colletotrichum Species as a Mechanism to IncreaseVirulence. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2001;14:1105–1113. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.9.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Olivieri F, Eugenia Zanetti M, Oliva CR, Covarrubias AA, Casalongué CA. No Title. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2002;108:63–72. doi: 10.1023/A:1013920929965. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Voigt CA, Schäfer W, Salomon S. A secreted lipase of Fusarium graminearum is a virulence factor required for infection of cereals. Plant J. 2005;42:364–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Beys da Silva WO, Santi L, Schrank A, Vainstein MH. Metarhizium anisopliae lipolytic activity plays a pivotal role in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infection. Fungal Biol. 2010;114:10–15. doi: 10.1016/j.mycres.2009.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Vandenkoornhuyse P, Quaiser A, Duhamel M, Le Van A, Dufresne A. The importance of the microbiome of the plant holobiont. New Phytol. 2015;206:1196–1206. doi: 10.1111/nph.13312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.