A large number of structural determinations of compounds containing 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid and its various deprotonated forms, 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate or 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate, are biased. The reason for the bias follows from incorrectly applied constraints or restraints on the bridging hydrogen, which is involved in the intramolecular hydrogen bond between the neighbouring carboxylic/carboxylate and oxo/hydroxy groups. The present article examines the problem of the location and refinement of such a bridging hydrogen in a number of reported compounds. The analysis of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding is also discussed.
Keywords: crystal structure; resonance-assisted hydrogen bonds; refinement constraints; 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid; 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate
Abstract
A large number of structural determinations of compounds containing 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) and its various deprotonated forms, 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II) or 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III), are biased. The reason for the bias follows from incorrectly applied constraints or restraints on the bridging hydrogen, which is involved in the intramolecular hydrogen bond between the neighbouring carboxylic/carboxylate and oxo/hydroxy groups. This hydrogen bond belongs to the category of resonance-assisted hydrogen bonds. The present article suggests corrections for the following structure determinations that have been published in Acta Crystallographica: DUJZAK, JEVNAA, LUDFUL, NUQVEB, QIQJAD, SAFGUD, SEDKET, TIYZIM, TUJPEV, VABZIJ, WADXOR, YAXPOE [refcodes are taken from the Cambridge Structural Database [CSD; Groom et al. (2016 ▸). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179]. The structural features of the title molecules in all the retrieved structures, together with structures that contain 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV), are discussed. Attention is paid to the localization of the above-mentioned bridging hydrogen, which can be situated closer to the O atom of the carboxylate/carboxylic group or that of the hydroxy/oxo group. In some cases, it is disordered between the two O atoms. The position of the bridging hydrogen seems to be dependent on the pK a(base) although with exceptions. A stronger basicity enhances the probability of the presence of a phenolate (III). The present article examines the problem of the refinement of such a bridging hydrogen as well as that of the hydrogen atoms involved in the hydroxy and primary and secondary amine groups. It appears that the best model, in many cases, is obtained by fixing the hydrogen-atom position found in the difference electron-density map while refining its isotropic displacement parameter.
Chemical context
2-Hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I; alternatively 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid, DNSA), 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II; alternatively 3,5-dinitrosalicylate), 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III) and 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV), are molecules that have interesting structural and chemical features. Such molecules have been studied because of the proton transfer from the carboxylic group, which is dependent on its environment (e.g. Smith et al., 2007 ▸). Thus, three deprotonated forms of molecule I have been observed. The last one, IV, is deprived of all of the hydrogen atoms while the others differ in the localization of the hydrogen atom involved in the intramolecular hydrogen bond between the O atoms of the carboxylate/carboxylic and the hydroxy/oxo groups. In the different structures, this hydrogen atom may be closer to either oxygen atom, depending on the properties of each particular structure. In some cases, this hydrogen atom may even be disordered. In the following, it will be referred to as a bridging hydrogen.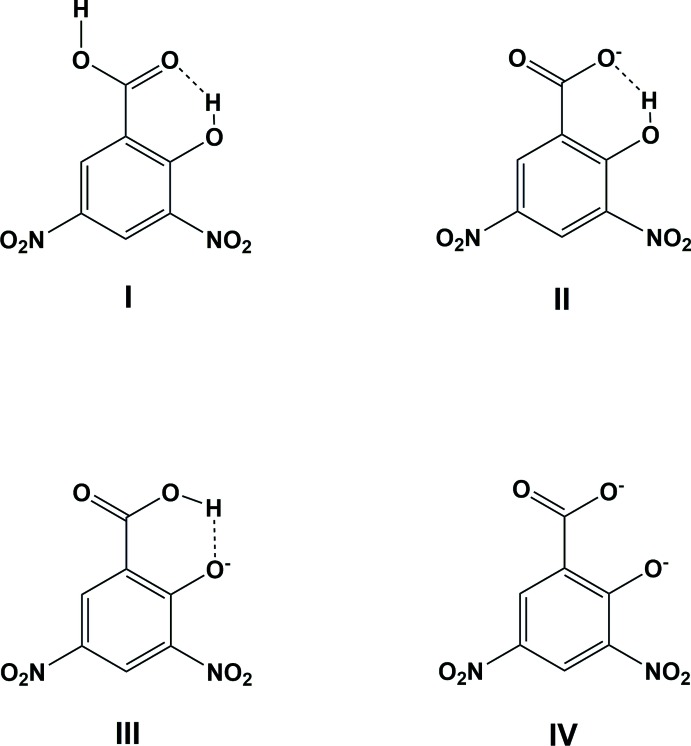
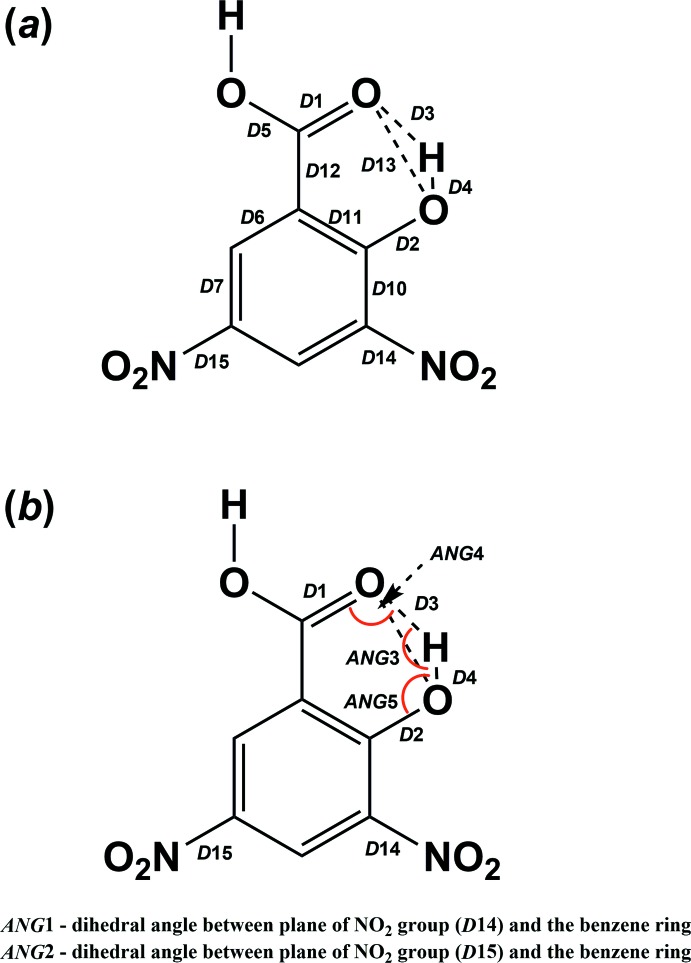
Such a bridging hydrogen is a part of a resonance-assisted moiety (Gilli & Gilli, 2009 ▸) composed of six atoms with the pertinent bonds being D1, D2, D3, D4, D11 and D12, as shown in Fig. 1 ▸ a. However, the delocalized bonds can be further extended within the molecule, especially to the C=O/C—OH bond (D1/D5 in Fig. 1 ▸ a). Resonance-assisted hydrogen bonds tend to be stronger and therefore the bridging hydrogen should be displaced towards the hydrogen-bond centre. On the other hand, O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bonds with a bridging hydrogen that is situated about its centre are usually observed for strong intramolecular hydrogen bonds with the O⋯O distances being shorter than 2.5 Å (Gilli & Gilli, 2009 ▸), while the O⋯H⋯O angles tend to be close to 180° (Jeffrey, 1995 ▸). The Ocarboxylate/carboxylicgroup⋯Ohydroxy/oxo group distance can be as short as 2.41 Å in some 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) or 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III); however, the O⋯H⋯O angle, which is ca 160°, situates it in a category of its own.
Figure 1.
Definition of bonds and various angles in I–IV.
The above-mentioned features of the intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond in the molecules considered herein have been ignored on many occasions by incorrectly applied constraints or severe restraints on the O—H distances, 0.82 or 0.84 Å, together with angle constraints/restraints equal to 109° as proposed by SHELXL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸, 2015 ▸).
A robust indication whether the bridging hydrogen has been positioned correctly follows from the bond distances C=O/C—O of the involved carboxylate/carboxylic and hydroxyl/oxo groups, although there are a few exceptions in which the bridging hydrogen is attached to the oxygen forming a slightly shorter C—O distance. These exceptions will be mentioned briefly below. Thus, it seems that a considerable number of the structures containing the molecules I–IV could have been determined more correctly with a more realistic description of the pertinent hydrogen bond in these molecular fragments.
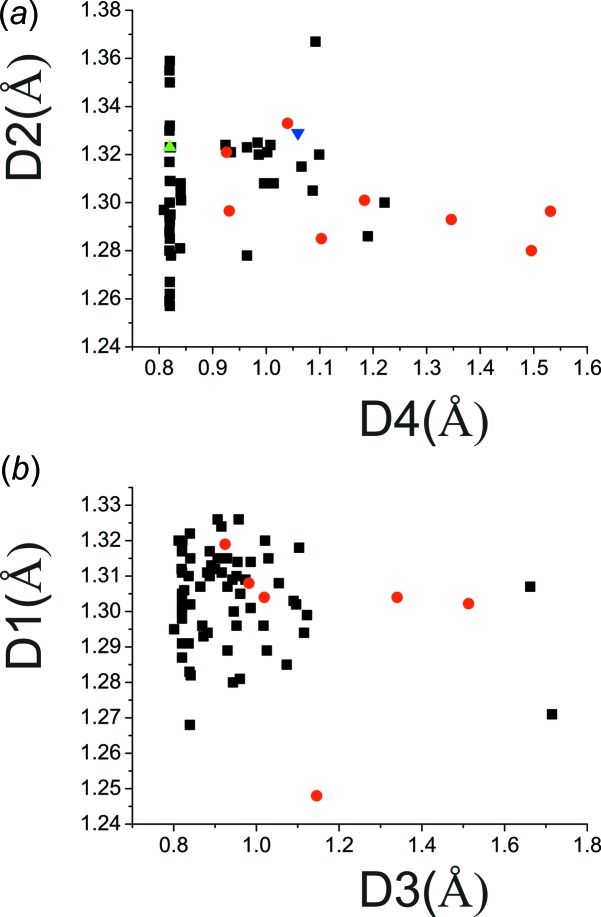
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 3.58, last update May 2017; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) indicated that 27 structures out of 53 reported as 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) seem to be suspect; 21 structures out of 70 reported as 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III) seem to be suspect, and nine structures out of 15 that contain a molecule of 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) also appear to be suspect. Figs. 2 ▸ a and 2 ▸ b illustrate this situation for 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) and 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III), respectively.
Figure 2.
The dependence of bond distances: (a) D2 on D4 for structures that were originally determined as 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II), or as containing 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I); (b) D1 on D3 for the structures that were determined as 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III). Colour code for symbols: black squares are the data retrieved from the CSD; red circles are the corrected title structures; green and blue triangles are the original and the corrected structure of LUDFUL, which contains a molecule of 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I).
It is plausible to expect that the environment affects the position of the bridging hydrogen. Therefore, it can be assumed that the proton transfer stemming from the carboxyl group will affect its position.
The data for the suspect structures published in Acta Crystallographica were retrieved from the journal’s web page and recalculated. Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸ contain an overview of those structures, which were successfully redetermined. In the following, these structures are referred to by their CSD refcodes; for the pertinent chemical names, see Table 2 ▸.
Table 1. Experimental details.
| DUJZAK | JEVNAA | LUDFUL | NUQVEB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | [Ag(C9H7NO)2](C7H3N2O7) | [Zn(C3H4N2)4](C7H3N2O7)2 | C7H4N2O7·C12H8N2 | C6H9N2 +·C7H3N2O7 − |
| M r | 625.30 | 791.93 | 408.33 | 336.27 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 | Monoclinic, C2/c | Monoclinic, P21/a | Triclinic, P
|
| Temperature (K) | 293 | 293 | 293 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.0154 (18), 7.6122 (15), 17.138 (3) | 25.0809 (15), 6.7251 (4), 18.9145 (10) | 14.8002 (15), 7.4029 (16), 16.0091 (16) | 5.8673 (7), 8.0991 (9), 15.2437 (17) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 104.38 (3), 90 | 90, 97.658 (6), 90 | 90, 96.395 (8), 90 | 86.844 (3), 84.252 (3), 81.209 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1139.3 (4) | 3161.9 (3) | 1743.1 (5) | 711.69 (14) |
| Z | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.11 | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.10 | 0.36 × 0.34 × 0.26 | 0.29 × 0.14 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART CCD area-detector | Bruker APEXII area-detector | Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 | Bruker APEX DUO CCD area-detector |
| Absorption correction | – | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1999) | – | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) |
| T min, T max | – | 0.846, 0.918 | – | 0.963, 0.990 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 3σ(I)] reflections | 10841, 4602, 4225 | 20634, 3635, 2152 | 8396, 4202, 1587 | 12709, 4943, 3677 |
| R int | 0.022 | 0.058 | 0.056 | 0.023 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.651 | 0.651 | 0.661 | 0.756 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R factors and goodness of fit | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.023, wR(F) = 0.053, S = 1.34 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.036, wR(F) = 0.075, S = 1.23 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.044, wR(F) = 0.083, S = 1.08 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.042, wR(F) = 0.109, S = 2.06 |
| No. of reflections | 4602 | 3635 | 4202 | 4943 |
| No. of parameters | 356 | 244 | 274 | 222 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.44, −0.30 | 0.23, −0.23 | 0.29, −0.31 | 0.40, −0.32 |
| Absolute structure | 1800 of Friedel pairs used in the refinement | – | – | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.004 (17) | – | – | – |
| QIQJAD | SAFGUD | SEDKET | TIYZIM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C9H8Cl2N5 +·C7H3N2O7 −·C3H7NO | [Ag(C12H6N2O2)](C7H3N2O7) | C5H9N2 +·C7H3N2O7 − | C6H12N3 +·C7H3N2O7 − |
| M r | 557.31 | 755.36 | 324.26 | 353.30 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
|
Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21 | Triclinic, P
|
| Temperature (K) | 294 | 174 | 293 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.0227 (5), 10.5507 (5), 12.5359 (6) | 11.757 (2), 18.297 (4), 13.223 (3) | 8.1183 (7), 6.0636 (5), 14.1453 (11) | 7.0109 (4), 10.6617 (8), 10.7454 (7) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 81.858 (1), 71.888 (1), 70.009 (1) | 90, 103.91 (3), 90 | 90, 91.904 (1), 90 | 93.075 (6), 95.863 (5), 104.944 (6) |
| V (Å3) | 1183.1 (1) | 2761.1 (11) | 695.93 (10) | 769.30 (9) |
| Z | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.34 | 0.81 | 0.13 | 1.09 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.16 × 0.14 × 0.08 | 0.3 × 0.24 × 0.2 | 0.40 × 0.27 × 0.11 | 0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector | Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra | Bruker SMART CCD | Agilent Xcalibur (Eos, Gemini) |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) |
| T min, T max | 0.93, 0.97 | 0.780, 0.910 | 0.959, 0.986 | 0.925, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 3σ(I)] reflections | 13936, 5507, 4441 | 12726, 5013, 3100 | 3523, 2301, 1444 | 4664, 2953, 2426 |
| R int | 0.019 | 0.052 | 0.040 | 0.026 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.661 | 0.603 | 0.595 | 0.618 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R factors and goodness of fit | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.056, wR(F) = 0.147, S = 3.41 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.062, wR(F) = 0.118, S = 1.64 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.041, wR(F) = 0.088, S = 1.16 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.041, wR(F) = 0.100, S = 1.64 |
| No. of reflections | 5507 | 5013 | 2301 | 2953 |
| No. of parameters | 340 | 444 | 212 | 229 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H-atom parameters constrained | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.80, −0.36 | 0.76, −0.63 | 0.11, −0.10 | 0.21, −0.18 |
| Absolute structure | – | – | 955 Friedel pairs used in the refinement | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | – | – | 0.5 | – |
| TUJPEV | (VABZIJ) | WADXOR | YAXPOE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||||
| Chemical formula | C10H12N3O3S+·C7H3N2O7 − | C8H13N2O+·C7H3N2O7 −·H2O | C9H17N2 +·C7H3N2O7 − | C26H29N2 +·C7H3N2O7 − |
| M r | 481.41 | 398.33 | 380.35 | 596.63 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
|
Triclinic, P
|
Monoclinic, P21/n | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 100 | 200 | 200 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.5551 (1), 10.5000 (2), 12.7576 (3) | 6.6691 (3), 11.3831 (4), 12.2900 (5) | 6.1537 (3), 19.1541 (14), 14.5527 (11) | 14.5648 (3), 12.9374 (3), 16.1619 (3) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 106.463 (1), 100.913 (1), 108.272 (1) | 89.727 (2), 76.771 (2), 76.930 (2) | 90, 98.343 (6), 90 | 90, 103.900 (1), 90 |
| V (Å3) | 993.72 (3) | 883.62 (6) | 1697.2 (2) | 2956.22 (11) |
| Z | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.16 | 0.52 × 0.13 × 0.10 | 0.30 × 0.13 × 0.10 | 0.51 × 0.26 × 0.17 |
| Data collection | ||||
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD | Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector | Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) |
| T min, T max | 0.955, 0.964 | 0.937, 0.987 | 0.920, 0.990 | 0.932, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 3σ(I)] reflections | 24261, 6717, 4398 | 17014, 4061, 3042 | 7800, 3339, 1976 | 29552, 7344, 5724 |
| R int | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.034 | 0.015 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.758 | 0.650 | 0.617 | 0.667 |
| Refinement | ||||
| R factors and goodness of fit | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.044, wR(F) = 0.104, S = 1.95 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.038, wR(F) = 0.086, S = 1.77 | R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046, wR(F 2) = 0.095, S = 1.33 | R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.054, wR(F) = 0.190, S = 1.80 |
| No. of reflections | 6717 | 4061 | 3339 | 7344 |
| No. of parameters | 301 | 258 | 268 | 399 |
| No. of restraints | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.31, −0.35 | 0.46, −0.23 | 0.36, −0.24 | 0.63, −0.28 |
| Absolute structure | – | – | – | – |
| Absolute structure parameter | – | – | – | – |
Table 2. Overview of the redetermined structures.
| REFCODE | Chemical name original/corrected if necessary |
|---|---|
| DUJZAKa | Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate |
| JEVNAAb | Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-N 3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate / tetrakis(1H-imidazole-N 3)zinc(II) bis(2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate) |
| LUDFULc | 1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate / phenazine 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid |
| NUQVEBd | 2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) / 2-amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (0.38) / 2-amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (0.62) |
| QIQJADe | 3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide solvate / 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate (0.55) 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (0.45) N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate / 3,5-diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate |
| SAFGUDf | Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-2N,N′)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate / bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-2N,N′)silver(I) 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate |
| SEDKETg | 3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate / 3,5-dimethylpyrazolium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate |
| TIYZIM h | 3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate |
| TUJPEVi | 4-[(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl]anilinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate |
| VABZIJj | 2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolatemonohydrate |
| WADXOR k | 1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate / 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-octahydropyrimido[1,2-a]azepin-1-ium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (0.73) / 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-octahydropyrimido[1,2-a]azepin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6–2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (0.37) |
| YAXPOEl | 4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate |
Notes: (a) Zhang & Jian (2009 ▸); (b) Huang et al. (2007 ▸); (c) Senthil Kumar et al. (2002 ▸); (d) Hemamalini & Fun (2010a ▸); (e) Sridhar et al. (2013 ▸); (f) Wang et al. (2012 ▸); (g) Wei et al. (2012 ▸); (h) Yamuna et al. (2014 ▸); (i) Malathy et al. (2015 ▸); (j) Hemamalini & Fun (2010b ▸); (k) Smith & Lynch (2016 ▸); (l) Dayananda et al. (2012 ▸).
Notably, JEVNAA turns out not to be a substituted benzoate but a phenolate. NUQVEB though reported as a substituted benzoate turns out to be present in a disordered benzoate and a phenolate form. QIQJAD though reported as a disordered benzoate and a phenolate turns out to be a substituted benzoate. SAFGUD was reported as a substituted benzoate but turns out to be a phenolate. WADXOR was reported as a substituted benzoate that is disordered over two positions but it turns out to be present both in a dominant benzoate as well as in a minor phenolate form. Finally, SEDKET was originally determined as a substituted phenolate but it turns out to be a benzoate.
Some of the retrieved structures were difficult or impossible to recalculate with sufficient accuracy: HILPOI (trimethoprimium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; Subashini et al., 2007 ▸) because of an abnormally low proportion of observed reflections (moreover the bridging hydrogen H6a is situated out of the plane between the carboxylate and hydroxy oxygen atoms, which seems to indicate an error) and VUZNEK (3,4-diaminopyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; Hemamalini & Fun, 2010b ▸) because of the disorder present in the structure.
Refinement of the title structures
For each structure, two methods have been applied for the refinement of the hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding. In Method 1, the positions of the bridging hydrogens as well as those of the hydroxy, primary and secondary amine and ammonium hydrogen atoms were fixed after their localization in the difference electron-density maps while their displacement parameters were refined. In Method 2, the positional parameters of the latter hydrogen atoms were refined while their displacement parameters were constrained in the usual manner: U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(Namine) or U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(Ohydroxy) or U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(Nammonium).
The appropriate sections of the difference electron-density maps of the title structures (see supplementary Fig. S1) show regions with the hydroxy, amine and ammonium hydrogen atoms. These sections comprise the maps that were obtained after the refinement of the models without the pertinent hydrogen atoms as well as the maps that were calculated by either refinement method. It can be seen from the supplementary Fig. S1 that one of the reasons that hinders the correct localization of the hydrogen atoms involved in the hydrogen bonds is an apparent non-spherical electron density of the donor and acceptor atoms. Thus, hydrogen-atom localization by X-ray diffraction is hindered not only by its weak scattering power, but also by the polarization of its electron density resulting from the proximity of the acceptor and by the asphericity of the electron density of the donor and acceptor atoms. Therefore, refinement Method 1 was given preference. The hydrogen bonds in the title structures are listed in Table 3 ▸, which shows that there might be quite a large difference between the results with the fixed and the refined positional parameters of such hydrogen atoms. In the following, a detailed description of the refinement of the recalculated structures is given:
Table 3. Hydrogen bonds (Å, °) in the redetermined structures.
The upper entries for each hydrogen bond refer to refinement Method 1: fixed hydrogen-atom positions, which were obtained from the difference electron-density maps, and refined displacement parameters. The lower entries refer to refinement Method 2: refined hydrogen-atom positions and constrained displacement parameters.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUJZAK | ||||
| O1—H1aa⋯O8 | 0.759 (2) | 1.859 (2) | 2.606 (3) | 167.96 (14) |
| 0.97 (4) | 1.64 (4) | 2.603 (3) | 175 (3) | |
| O2—H2aa⋯O9 | 0.922 (2) | 1.727 (2) | 2.631 (3) | 166.48 (15) |
| 0.75 (4) | 1.90 (4) | 2.636 (3) | 165 (4) | |
| O3—H3b⋯O9 | 1.040 (2) | 1.495 (2) | 2.481 (3) | 155.88 (12) |
| 1.11 (4) | 1.41 (4) | 2.480 (3) | 160 (3) | |
| JEVNAA | ||||
| O2—H1a⋯O1 | 1.039 (2) | 1.496 (2) | 2.498 (2) | 160.4 (1) |
| 0.89 (2) | 1.65 (3) | 2.503 (2) | 160 (2) | |
| N2—H2a⋯O3 | 0.967 (2) | 1.890 (2) | 2.838 (3) | 165.9 (1) |
| 0.84 (2) | 2.02 (2) | 2.845 (3) | 169 (2) | |
| N4—H4a⋯O1i | 0.943 (2) | 1.924 (1) | 2.784 (2) | 150.6 (1) |
| 0.86 (2) | 1.95 (2) | 2.792 (2) | 165 (2) | |
| LUDFUL | ||||
| O3—H3a⋯O2 | 1.059 (1) | 1.530 (1) | 2.513 (2) | 151.7 (1) |
| 1.06 (2) | 1.51 (2) | 2.516 (2) | 156 (2) | |
| O1—H1a⋯N3 | 1.163 (1) | 1.416 (1) | 2.552 (2) | 163.2 (1) |
| 1.14 (2) | 1.44 (2) | 2.552 (2) | 166 (2) | |
| NUQVEB | ||||
| O7—H1o7⋯O1 | 0.919 (1) | 1.531 (1) | 2.4202 (12) | 161.55 (6) |
| 1.14 (2) | 1.31 (2) | 2.4178 (12) | 163 (2) | |
| O1—H1o1⋯O7 | 0.931 (1) | 1.513 (1) | 2.4202 (12) | 163.52 (6) |
| 1.31 (2) | 1.14 (2) | 2.4178 (12) | 163 (2) | |
| N2—H2a⋯O7ii | 0.892 (1) | 2.079 (1) | 2.9655 (14) | 172.84 (6) |
| 0.87 (1) | 2.095 (14) | 2.9674 (14) | 176.5 (12) | |
| N2—H2b⋯O1iii | 0.846 (1) | 2.165 (1) | 2.8526 (14) | 138.40 (6) |
| 0.88 (2) | 2.146 (14) | 2.852 (1) | 137.3 (11) | |
| N2—H2b⋯O2iii | 0.846 (1) | 2.413 (1) | 3.1741 (14) | 150.02 (6) |
| 0.88 (2) | 2.384 (14) | 3.1736 (15) | 150.3 (11) | |
| N1—H1⋯O6ii | 0.898 (1) | 1.783 (1) | 2.6781 (13) | 174.83 (6) |
| 0.90 (1) | 1.784 (14) | 2.6773 (14) | 173.3 (13) | |
| QIQJAD | ||||
| N3—H3n⋯O2 | 0.862 (2) | 1.994 (2) | 2.854 (2) | 174.8 (1) |
| 0.81 (3) | 2.05 (3) | 2.854 (3) | 175 (3) | |
| N3—H4n⋯O8iv | 0.863 (2) | 2.059 (1) | 2.921 (2) | 176.9 (1) |
| 0.85 (2) | 2.07 (2) | 2.920 (2) | 173 (3) | |
| N2—H2n⋯O1 | 0.897 (2) | 1.831 (2) | 2.728 (2) | 177.5 (1) |
| 0.81 (3) | 1.93 (3) | 2.731 (2) | 171 (2) | |
| N5—H5n⋯N4v | 0.866 (1) | 2.141 (1) | 2.9992 (19) | 171.1 (1) |
| 0.84 (2) | 2.17 (2) | 2.999 (2) | 171 (2) | |
| N5—H6n⋯O8vi | 0.863 (2) | 2.041 (2) | 2.760 (2) | 140.2 (1) |
| 0.78 (2) | 2.12 (3) | 2.764 (2) | 141 (2) | |
| O3—H3o⋯O1 | 0.926 (1) | 1.562 (1) | 2.4572 (18) | 161.3 (1) |
| 0.99 (3) | 1.49 (3) | 2.4569 (19) | 164 (3) | |
| SAFGUD | ||||
| O8—H7⋯O7 | 1.155 (4) | 1.346 (4) | 2.462 (6) | 159.6 (3) |
| 1.05 (7) | 1.57 (7) | 2.452 (7) | 138 (6) | |
| SEDKET | ||||
| O1—H2a⋯O2 | 1.22 (5) | 1.34 (5) | 2.476 (3) | 149 (5) |
| 1.27 (3) | 1.29 (3) | 2.477 (3) | 151 (3) | |
| O2—H2a⋯O1 | 1.34 (5) | 1.22 (5) | 2.476 (3) | 149 (5) |
| 1.29 (3) | 1.27 (3) | 2.477 (3) | 151 (3) | |
| N1—H1⋯O1vii | 1.11 (5) | 1.92 (5) | 2.799 (4) | 133 (3) |
| 0.99 (4) | 2.00 (3) | 2.804 (4) | 137 (3) | |
| N1—H1⋯O7vii | 1.11 (5) | 1.94 (5) | 2.850 (4) | 137 (3) |
| 0.99 (4) | 2.03 (3) | 2.855 (4) | 140 (3) | |
| N2—H2⋯O3 | 0.96 (3) | 1.77 (3) | 2.685 (4) | 158 (3) |
| 0.99 (3) | 1.75 (3) | 2.684 (4) | 157 (3) | |
| TIYZIM | ||||
| O2b—H2b⋯O1b | 0.982 (1) | 1.516 (1) | 2.4473 (16) | 156.3 (1) |
| 1.02 (2) | 1.48 (2) | 2.4476 (16) | 156 (2) | |
| N3a—H3aa⋯N1aa viii | 0.904 (1) | 1.932 (1) | 2.797 (2) | 159.6 (1) |
| 0.91 | 1.92 | 2.797 (2) | 162 | |
| N3a—H3ab⋯O2b ix | 0.901 (1) | 2.565 (1) | 3.1297 (17) | 121.4 (1) |
| 0.91 | 2.58 | 3.1298 (17) | 120 | |
| N3a—H3ab⋯O2b ix | 0.901 (1) | 2.565 (1) | 3.1297 (17) | 121.4 (1) |
| 0.91 | 2.58 | 3.1297 (18) | 120 | |
| N3a—H3ab⋯O3b ix | 0.901 (1) | 2.072 (1) | 2.9537 (17) | 165.8 (1) |
| 0.91 | 2.06 | 2.9542 (17) | 165 | |
| N3a—H3ac⋯O1b x | 0.893 (1) | 2.061 (1) | 2.815 (2) | 141.5 (1) |
| 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.815 (2) | 144 | |
| N3a—H3ac⋯O7b x | 0.893 (1) | 2.484 (1) | 2.9712 (19) | 114.7 (1) |
| 0.91 | 2.46 | 2.9706 (19) | 116 | |
| TUJPEV | ||||
| O6—H6a⋯O5 | 1.184 (1) | 1.295 (1) | 2.4268 (16) | 156.58 (6) |
| 1.24 (2) | 1.21 (2) | 2.4280 (17) | 165.3 (14) | |
| N1—H1a⋯O6xi | 1.002 (1) | 2.068 (1) | 3.0655 (17) | 173.55 (7) |
| 0.89 | 2.24 | 3.0694 (17) | 155 | |
| N1—H1b⋯N3v | 0.793 (1) | 2.292 (1) | 3.0393 (15) | 157.3 (1) |
| 0.89 | 2.20 | 3.0382 (15) | 157 | |
| N1—H1c⋯O4v | 0.832 (2) | 1.831 (1) | 2.663 (2) | 177.1 (1) |
| 0.89 | 1.77 | 2.660 (2) | 175 | |
| N2—H2a⋯O5 | 0.970 (1) | 1.844 (1) | 2.7852 (15) | 162.64 (9) |
| 0.827 (17) | 1.986 (16) | 2.7900 (16) | 164.0 (18) | |
| VABZIJ | ||||
| N3—H1n3⋯O6x | 0.973 (1) | 1.754 (1) | 2.7182 (14) | 170.48 (8) |
| 0.91 (1) | 1.823 (14) | 2.7214 (14) | 170.8 (15) | |
| N4—H1n4⋯O1w | 0.909 (1) | 1.840 (1) | 2.7348 (15) | 167.76 (8) |
| 0.91 (2) | 1.833 (15) | 2.7323 (16) | 172.0 (15) | |
| O1w—H2w1⋯O1xii | 0.917 (1) | 1.890 (1) | 2.7886 (14) | 166.21 (6) |
| 0.82 (2) | 1.995 (19) | 2.7906 (15) | 162.7 (16) | |
| O1w—H1w1—O3iii | 0.915 (1) | 2.040 (1) | 2.9352 (14) | 165.84 (7) |
| 0.89 (2) | 2.064 (18) | 2.9357 (15) | 168.0 (17) | |
| O7—H7⋯O1 | 1.019 (1) | 1.433 (1) | 2.4340 (13) | 165.94 (7) |
| 0.96 (2) | 1.505 (16) | 2.4358 (13) | 162.0 (16) | |
| WADXOR | ||||
| N8a—H8a⋯O11b | 0.960 (2) | 1.933 (2) | 2.864 (2) | 162.83 (11) |
| 0.91 (2) | 1.96 (2) | 2.869 (2) | 174.1 (17) | |
| O11b—H21b⋯O21b | 1.145 (2) | 1.303 (6) | 2.433 (6) | 167.3 (3) |
| 1.07 (9) | 1.48 (9) | 2.430 (6) | 145 (7) | |
| O2b—H2b⋯O12b | 1.103 (2) | 1.385 (2) | 2.471 (2) | 166.81 (13) |
| 0.91 (3) | 1.61 (3) | 2.475 (3) | 159 (3) | |
| YAXPOE | ||||
| N1—H71⋯O1iv | 0.945 (1) | 1.954 (1) | 2.813 (2) | 150.01 (8) |
| 0.90 (2) | 1.98 (2) | 2.812 (2) | 154.0 (19) | |
| N1—H71⋯O2iv | 0.945 (1) | 2.302 (2) | 3.032 (2) | 133.62 (8) |
| 0.90 (2) | 2.36 (2) | 3.034 (2) | 131.8 (17) | |
| O7—H7⋯O1 | 0.924 (2) | 1.668 (1) | 2.505 (2) | 148.96 (9) |
| 0.92 (3) | 1.71 (3) | 2.504 (2) | 142 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x +  , −y +
, −y +  , −z + 1; (ii) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z; (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z; (iv) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (v) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1; (vi) x − 1, y + 1, z; (vii) −x + 1, y +
, −z + 1; (ii) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z; (iii) −x + 1, −y, −z; (iv) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1; (v) −x + 1, −y + 2, −z + 1; (vi) x − 1, y + 1, z; (vii) −x + 1, y +  , −z + 1; (viii) −x, −y, −z; (ix) x + 1, y, z; (x) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (xi) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1; (xii) x, y + 1, z.
, −z + 1; (viii) −x, −y, −z; (ix) x + 1, y, z; (x) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (xi) −x, −y + 2, −z + 1; (xii) x, y + 1, z.
DUJZAK (Zhang & Jian, 2009 ▸): C—Haryl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 Å while U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H3b as well as those of the hydroxy hydrogen atoms H1aa and H2aa were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined.
JEVNAA (Huang et al., 2007 ▸): C—Haryl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 Å while U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H1a as well as those of the secondary amine hydrogen atoms H2a and H4a were located in the difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined.
LUDFUL (Senthil Kumar et al., 2002 ▸): C—Haryl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 Å while U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H3a as well as that of the hydroxy hydrogen atom H1a were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined.
NUQVEB (Hemamalini & Fun, 2010a ▸): The subroutine TwinRotMax of PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸) indicated non-merohedral twinning: h2 = −h1; k2 = −k1; l2 = −0.488 h1 − 0.153k1 + l1. The refinement was carried out on the non-overlapped reflections only. The refined value of the second domain fraction converged to the value −0.0006 (4). Therefore the value of the second domain fraction was set to 0 and was not refined further. C—Haryl and C—Hmethyl were constrained to be equal to 0.95 and 0.98 Å, respectively. U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl) and U iso(Hmethyl) = 1.5U eq(Cmethyl). The positions of the disordered bridging hydrogens H1o1 and H1o7 as well as those of the primary (H2a, H2b) and the secondary amine hydrogen atoms (H1a) were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined; in the case of the bridging hydrogens H1o1 and H1o7, their isotropic displacement parameters were refined to be equal while their occupational parameters were refined under the condition that their sum was equal to 1.
QIQJAD (Sridhar et al., 2013 ▸): The subroutine TwinRotMax of PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸) indicated non-merohedral twinning: h2 = −1.018h1 + 0.054k1; k2 = −0.673h1 + 1.018k1; l2 = −0.039h1 + 0.116k1 − l1. The refined value of the second domain fraction converged to the value 0.028 (13). Therefore the value of the second domain fraction was set to 0 and was not refined further. C—Hsp 2 and C—Hmethyl were constrained to equal to 0.93 and 0.96 Å, respectively. U iso(Hsp 2) = 1.2U eq(Csp 2) and U iso(Hmethyl) = 1.5U eq(Cmethyl). The positions of the bridging hydrogen H3o and those of the primary (H3n, H4n, H5n, H6n) as well as of the secondary (H2n) amine hydrogen atoms were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined.
SAFGUD (Wang et al., 2012 ▸): C—Haryl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 Å while U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl). The bridging hydrogen H7 was located in a difference electron-density map and its position was fixed while its isotropic displacement parameter U iso(H7) was refined.
SEDKET (Wei et al., 2012 ▸): The non-centrosymmetric structure is composed of the light atoms only (the heaviest atom is O) and the data collection was carried out with Mo Kα radiation. The article by Wei et al. (2012 ▸) does not indicate whether the Friedel pairs were merged and nor does it contain the value of the Flack parameter. The Flack parameter was set to 0.5 without being refined in the present model. C—Haryl and C—Hmethyl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 and 0.96 Å, respectively. U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl) and U iso(Hmethyl) = 1.5U eq(Cmethyl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H2a as well as those of the secondary amine hydrogen atoms H1 and H2 were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined.
TIYZIM (Yamuna et al. (2014 ▸): C—Haryl and C—Hmethylene were constrained to be equal to 0.95 and 0.99 Å, respectively. U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl) and U iso(Hmethylene) = 1.5U eq(Cmethylene). The position of the bridging hydrogen H2b as well as those of the ammonium hydrogen atoms (H3aa, H3ab, H3ac) were found in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined; in the case of the ammonium hydrogen atoms (H3ab, H3ac,), their displacement parameters were constrained to be equal to that of H3aa.
TUJPEV (Malathy et al., 2015 ▸): C—Haryl were constrained to be equal to 0.93 Å while U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl). C—Hmethyl were constrained to be equal to 0.96 Å while U iso(Hmethyl) = 1.5U eq(Cmethyl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H6a as well as those of the secondary amine group H2a and of the ammonium hydrogen atoms H1a, H1b and H1c were found in a difference-electron map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined; in the case of the ammonium hydrogen atoms (H1b, H1c), their displacement parameters were constrained to be equal to that of H1a.
VABZIJ (Hemamalini & Fun, 2010c ▸): C—Haryl, C—Hmethyl, C—Hmethine were constrained to be equal to 0.93, 0.96 and 0.98 Å, respectively. U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl), U iso(Hmethine) = 1.2U eq(Cmethine), U iso(Hmethyl) = 1.5U eq(Cmethyl). The position of the bridging hydrogen H7 as well as those of the secondary amine hydrogen atom H1n4 and of the water hydrogen atoms H1w1 and H1w2 were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their displacement parameters were refined.
WADXOR (Smith & Lynch, 2016 ▸): The non-centrosymmetric structure is composed of light atoms only (the heaviest atoms present in the structure are oxygens) and the data collection was carried out with Mo Kα radiation. The original article reported the refined Flack parameter to be equal to −0.1 (13); however, the refinement using JANA2006 (Petříček et al., 2014 ▸) did not converge and therefore the Flack parameter was set to 0.5 without being refined. C—Haryl and C—Hmethylene were constrained to be equal to 0.95 and 0.99 Å, respectively, except for the distances between the methylene atom C11 and the attached hydrogen atoms H12a and H13a, which were restrained to 0.99 (1) Å (Müller, 2009 ▸). [The reason for the different treatment of the latter methylene group was its vicinity to the disordered methylene groups centered on C10 and C12a.] U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl) and U iso(Hmethylene) = 1.2U eq(Cmethylene). There were two types of occupational disorder present in the structure. The first one was related to the fragments with the methylene carbon atoms C9a, C10a and the attached respective pairs of hydrogen atoms H91a, H92a and H10a, H11a, as well as to C13a and C12a with the attached respective pairs of hydrogen atoms H16a, H17a and H14a, H15a. The occupation parameter of C13 was refined while those of the related atoms were either set equal to that of C13 (i.e. C12a and attached hydrogen atoms) or its complement to 1 (C9a and C10a and attached hydrogen atoms). The displacement parameters of the disordered pairs of atoms C9a and C13a as well as C10a and C12a were set to be equal, i.e. that of C13a equalled that of C9a while that of C10a equalled that of C12a. The second type of occupational disorder referred to the fragments C2b—H61b, C2b–O2b—H2b and C6b—H6b, C6b—O21b—H21b. This means that the occupation parameters of H61b, H21b were set equal to the refined occupational parameter of O21b while being complements to 1 for H6b, O2b, H2b. The positions of the bridging hydrogens H2b and H21b as well as that of the primary amine hydrogen atom H8a were located in a difference electron-density map. Their positional parameters were fixed during the refinement while their isotropic displacement parameters were refined; in the case of bridging hydrogens H2b and H21b, their isotropic displacement parameters were constrained to be equal.
YAXPOE (Dayananda et al., 2012 ▸): C—Haryl and C—Hmethylene were constrained to equal to 0.95 and 0.99 Å, respectively. U iso(Haryl) = 1.2U eq(Caryl) and U iso(Hmethylene) = 1.5U eq(Cmethylene). The bridging hydrogen H7 was located in a difference electron-density map. Its positional parameters were fixed while U iso(H7a) was refined. A high instability factor Δ in the weighting scheme (0.0064) was applied in order to avoid a large number of reflections with (I obs − I calc)/σ(w) > 10 where σ(w) = [σ2(I) + ΔI 2]−1/2. [This condition generates A alerts for Δ = 0.0004, which has been used in other refinements of the title structure, when running checkCIF (Spek, 2009 ▸).] The residual electron-density map contains peaks which are difficult to interpret (see supplementary Fig. S1).
Discussion of the interdependence of bond lengths and angles
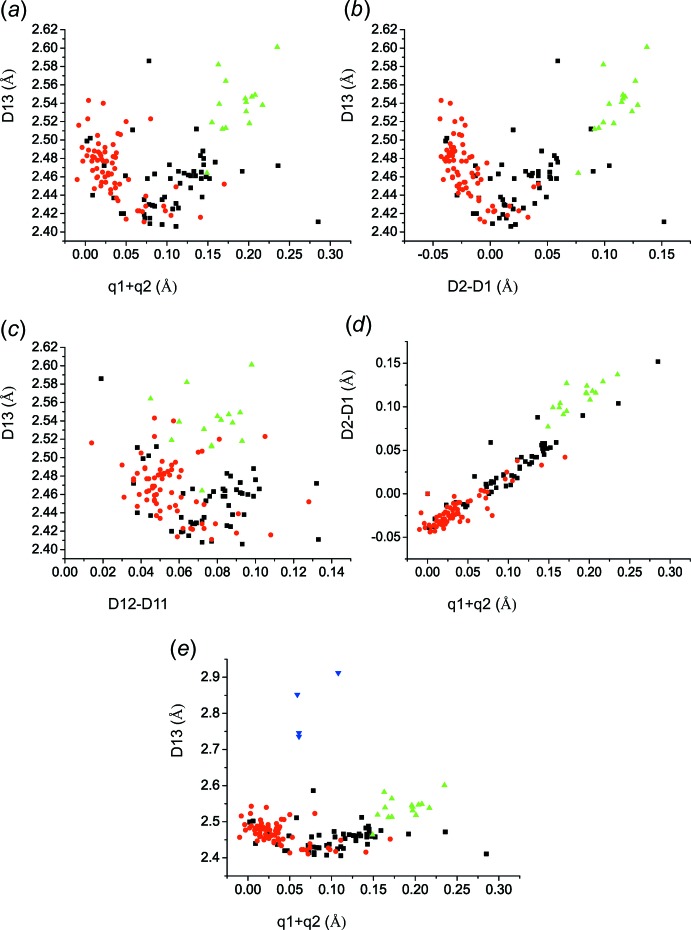
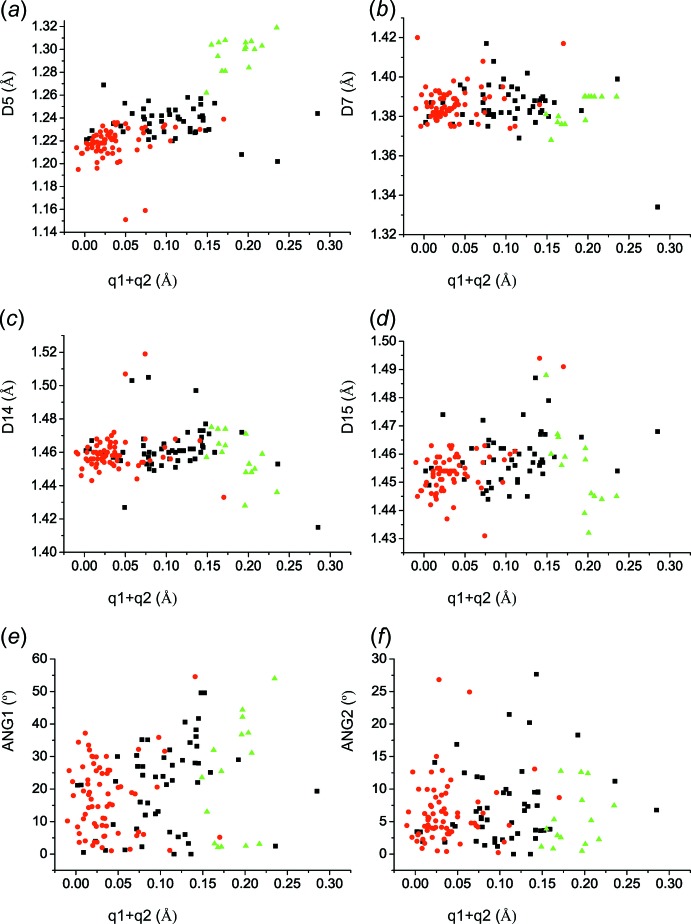
For this discussion, the definition of the various bonds and angles in the moieties of I–IV (shown in the scheme), are illustrated in Figs. 1 ▸ a and 1b, respectively. As already pointed out, the dependence D2 on D4 and D1 on D3 (Fig. 2 ▸) has shown that a large number of structures are biased by incorrectly applied constraints or restraints on the bridging hydrogen. However, a dubious or incorrect localization of the bridging hydrogen or the acid hydrogen is believed to affect the positions of the non-hydrogen atoms only minutely, and therefore even the biased structures can be considered further. The parameters q1 = D2 − D1 and q2 = D12 − D11 express the electron delocalization within the fragment D1–D12–D11–D2. The introduction of the parameters q1 and q2 follows an analogous discussion of resonance-assisted hydrogen bonds in the enol forms of β-diketone fragments (Gilli et al., 1989 ▸, 2009 ▸). Fig. 3 ▸ a shows that the distance where the structures with 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III; red circles) transform into 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II; black squares) corresponds to the shortest distance D13min ≃ 2.41 Å, which in turn corresponds to (q1 + q2) ≃ 0.08 Å. This implies that this is the region where the bridging hydrogen has the greatest tendency to be situated about the centre of the O⋯O intramolecular hydrogen bond or disordered about it. A very similar dependence is shown in Fig. 3 ▸ b, where only distances D1 and D3 are compared. The observed dependence means that the elongation of one C—O bond takes place mostly at the cost of the shortening of the neighbouring C=O bond; in other words, the distance between these two O atoms, D13 ≃ [(D13min)2 + (D2 − D1)2]1/2 (Fig. 1) ▸. Table 4 ▸ lists the structures in which the title molecules are present in different forms. In the recalculated structure of SEDKET (Table 2 ▸) and e.g. the reported structures of KEZJIJ (Song et al., 2007 ▸) and KEZJIJ01 (Smith et al., 2007 ▸) that refer to the structure determination of 2-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate, the bridging hydrogen is attached to the O atom having the shorter C—O bond distance.
Figure 3.
The dependence of distances: (a) D13 on (q1 + q2); (b) D13 on D2 − D1; (c) D13 on D12—D11; (d) D2 − D1 on (q1 + q2); (e) D13 on (q1 + q2), also for the structures with 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV), which are shown as blue triangles. Colour code for symbols: green triangles refer to the structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I), black squares are the structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II), and red circles are the structures with 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III).
Table 4. Overview of selected structures with different forms of the molecules: 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I); 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II); 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III); 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV).
The structures are ordered by ascending pK a value of the base. The corresponding values of (q1 + q2), D13, D1, D2 and D5 (cf. Fig. 1 ▸) are also given.
| Refcode | Base and its form present in the structure | pK a | ΔpK a | Type | (q1 + q2) (Å) | D13 (Å) | D1 (Å) | D2 (Å) | D5 (Å) | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GORXAM a | 1,4-dioxane | −3.9 | −6.08 | I | 0.204 0.196 | 2.547 2.545 | 1.219 1.220 | 1.337 1.336 | 1.307 1.300 | Two independent molecules |
| 2 | GORXEQa | 1,4-dioxane | −3.9 | −6.08 | I | 0.235 | 2.601 | 1.206 | 1.343 | 1.319 | |
| 3 | GORXEQ01a | 1,4-dioxane | −3.9 | −6.08 | I | 0.197 | 2.531 | 1.222 | 1.346 | 1.302 | |
| 4 | AJEBOGb | 4-cyanopyridinium | 1.92 | −0.26 | III | 0.003 | 2.523 | 1.324 | 1.28 | 1.213 | |
| 5 | ABULAM c | 2-aminoanilinium | <2 | <-0.18 | III | 0.011 | 2.447 | 1.309 | 1.282 | 1.219 | |
| 6 | PIDCAIc | 2-aminoanilinium | <2 | <-0.18 | III | 0.009 | 2.44 | 1.314 | 1.285 | 1.229 | Wrongly attached hydrogen due to C=O distances. Originally determined as type II but it should be III. |
| 7 | PERBAR d | 3-carbamoylpyridinium | 3.35 | 1.2 | II | 0.17 | 2.452 | 1.287 | 1.329 | 1.239 | Wrongly attached hydrogen due to C=O distances. Originally determined as type II but it is probably III. Disorder present in the structure. |
| 8 | GIFMUEe | 1-naphthylammonium | 3.92 | 1.74 | III | 0.011 | 2.488 | 1.31 | 1.279 | 1.224 | |
| 9 | MIPROSf | 8-aminoquinolinium | 3.95 | 1.77 | II | 0.072 | 2.408 | 1.278 | 1.300 | 1.237 | The bridging hydrogen is situated about the centre. |
| 10 | ABUKUFg | 4-chloroanilinium | 3.98 | 1.80 | II | 0.094 | 2.435 | 1.276 | 1.297 | 1.242 | |
| 11 | YIVHIWh | 4-iodoanilinium | 4.18 | 1.63 | II | 0.129 | 2.461 | 1.285 | 1.321 | 1.228 | |
| 12 | GIFNUFi | 1,10-phenanthrolinium | 4.27 | 2.09 | II | 0.096 | 2.428 | 1.280 | 1.297 | 1.232 | Determined as the type III but it is probably II (Fig. 1 ▸). The chemical name was correct. |
| 13 | FOXHADj | 2-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridinium | 4.33 | 2.15 | II | 0.047 | 2.42 | 1.307 | 1.292 | 1.228 | 100 K; the reported hydrogen H3 is situated out of the plane formed by C⋯O bonds and is superficial. |
| 14 | KEZJIJj | 2-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridinium | 4.33 | 2.15 | III | 0.07 | 2.422 | 1.293 | 1.296 | 1.231 | C=O distances are about equal. The recalculation has shown that the bridging hydrogen is about the centre of the hydrogen bond, slightly closer to atom O2, which forms a shorter C=O bond. |
| 15 | KEZJIJ01j | 2-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridinium | 4.33 | 2.15 | III | 0.066 | 2.423 | 1.295 | 1.299 | 1.221 | C=O distances are about equal, the hydrogen is attached to the O atom forming a shorter C=O bond. |
| 16 | FICXIZk | cytosinium | 4.60 | 2.42 | II | 0.098 | 2.423 | 1.285 | 1.310 | 1.234 | The type according to the C=O distances should be II; the bridging hydrogen was wrongly attached. |
| 17 | ABUJUEl | anilinium | 4.60 | 2.42 | II | 0.129 | 2.448 | 1.280 | 1.323 | 1.231 | |
| 18 | ABUKOZ m | 4-fluoroanilinium | 4.65 | 2.47 | II | 0.142 | 2.465 | 1.273 | 1.325 | 1.252 | |
| 19 | GIFMOYn | quinolinium | 4.85 | 2.67 | III | 0.05 | 2.414 | 1.294 | 1.285 | 1.235 | The title molecule has similarly long C=O distances. |
| 20 | ZAJHATo | 2-amminobenzoic acid | 4.96 | 2.78 | II | 0.135 | 2.461 | 1.282 | 1.324 | 1.227 | |
| 21 | AJEBIAp | pyridinium | 5.23 | 3.05 | I and II | 0.142 0.163 | 2.458 2.582 | 1.250 | 1.308 | 1.257 | Two independent molecules |
| 22 | EGABOFq | 2-methylquinolinium | 5.71 | 3.53 | II | 0.285 | 2.411 | 1.207 | 1.359 | 1.244 | Outlier |
| 23 | AJECEX01r | 2,6-diaminopyridin-1-ium | 6.13 | 3.95 | II | 0.072 0.121 | 2.435 2.464 | 1.298 1.295 | 1.309 1.332 | 1.241 1.237 | One of the title molecules has similarly long C=O distances. |
| 24 | AJECIBs | 2-aminopyrimidinium | 6.82 | 4.64 | II | 0.114 0.145 | 2.466 2.473 | 1.277 1.270 | 1.308 1.323 | 1.241 1.238 | |
| 25 | TUMWABt | 1H-imidazol-3-ium | 6.95 | 4.77 | III | −0.01 | 2.457 | 1.320 | 1.279 | 1.214 | |
| 26 | LUMJOUu | hydrazinium | 8.12 | 5.94 | III | 0.014 | 2.459 | 1.318 | 1.275 | 1.211 | |
| 27 | SEDKETv | 3,5-dimethylpyrazolium | 9 | 6.82 | III | 0.037 | 2.481 | 1.300 | 1.282 | 1.224 | |
| 28 | SEDKETv (corrected) | 3,5-dimethylpyrazolium | 9 | 6.82 | II | 0.027 | 2.476 | 1.305 | 1.277 | 1.229 | The bridging hydrogen after recalculation is closer to oxygen O1, which forms the shorter C=O bond (C12—O1). |
| 29 | LUDDETw | benzylammonium | 9.33 | 7.15 | III | 0.002 | 2.483 | 1.305 | 1.269 | 1.218 | |
| 30 | LUDDET01w | benzylammonium | 9.33 | 7.15 | III | 1.311 1.311 | 1.275 1.279 | 1.217 1.219 | |||
| 31 | INELUIx | 1-phenylethylammonium | 9.79 | 7.61 | III | 0.009 0.009 | 2.467 2.482 | 1.309 1.320 | 1.272 1.277 | 1.221 1.214 | |
| 32 | MILLOIy | dicyclohexylammonium | 10.4 | 8.22 | III | 0.028 | 2.464 | 1.289 | 1.273 | 1.225 | The C=O distances of the title molecule are similar. |
| 33 | ACIFATz | 4-sulfamoylanilinium | 10.6 | 8.42 | III | 0.028 | 2.462 | 1.315 | 1.287 | 1.209 | |
| 34 | EGUTIJaa | methylammonium | 10.6 | 8.42 | III | 0.011 | 2.481 | 1.314 | 1.276 | 1.218 | |
| 35 | EGUTOPbb | triethylammonium | 10.78 | 8.6 | II | 0.082 | 2.429 | 1.275 | 1.286 | 1.248 | |
| 36 | EGUTOP01bb | triethylammonium | 10.78 | 8.6 | II | 0.072 | 2.419 | 1.275 | 1.288 | 1.242 | |
| 37 | FOGZILcc | diethylammonium | 11.09 | 8.91 | III | 0.004 | 2.489 | 1.308 | 1.270 | 1.217 | |
| 38 | XEBFAM dd | piperidinium C5H11N | 11.28 | 9.1 | II and IV | 0.078 0.061 | 2.586 2.736 | 1.219 1.234 | 1.278 1.253 | 1.255 1.271 | One molecule of DNSA (I) is fully ionized, the other is in form II. |
| 39 | YEJZAOee | guanidinium | 12.5 | 10.32 | II | 0.079 | 2.415 | 1.291 | 1.305 | 1.235 | |
| 40 | YEJZAO01ee | guanidinium | 12.5 | 10.32 | II | 0.073 | 2.415 | 1.292 | 1.300 | 1.239 |
References for the pK a values: (a) https://chemaxon.com/products/calculators-and-predictors#pka; (b) https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB0688145_EN.htm; (c) Dean (1987 ▸); (d) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/nicotinamide#section=pK a; (e) https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zhang/liming/pdf/pKas_of_Organic_Acids_and_Bases.pdf; (f) http://binarystore.wiley.com/store/10.1002/jcc.23068/asset/supinfo/JCC_23068_sm_SuppInfo.pdf?v=1&s=e864a51d58b4cdc175f6b69c92ceddb546201e3b; (g) http://sites.chem.colostate.edu/diverdi/all_courses/CRC%20reference%20data/dissociation%20constants%20of%20organic%20acids%20and%20bases.pdf; (h) http://sites.chem.colostate.edu/diverdi/all_courses/CRC%20reference%20data/dissociation%20constants%20of%20organic%20acids%20and%20bases.pdf; (i) http://chemicalland21.com/specialtychem/finechem/1,10-PHENANTHROLINE.htm; (j) https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB5195697_EN.htm; (k) http://www.drugfuture.com/chemdata/cytosine.html; (l) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/aniline#section=pKa; (m) http://sites.chem.colostate.edu/diverdi/all_courses/CRC%20reference%20data/dissociation%20constants%20of%20organic%20acids%20and%20bases.pdf; (n) Hosmane & Liebman (2009 ▸); (o) http://www.csun.edu/\~hcchm003/321/Ka.pdf; (p) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/pyridine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (q) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jcc.23068; (r) https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB0236195_EN.htm; (s) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2-aminopyridine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (t) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/imidazole#section=pKa; (u) http://evans.rc.fas.harvard.edu/pdf/evans_pKa_table.pdf; (v) https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB2707394_EN.htm; (w) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/benzylamine#section=pK a; (x) https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB04325; (z) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/dicyclohexylamine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (z) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/sulfanilamide#section=Dissociation-Constants; (aa) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/methylamine#section=pK a; (ab) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/triethylamine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (ac) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/diethylamine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (ad) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/piperidine#section=Dissociation-Constants; (ae) https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/guanidine#section=pK a.
References to publications with the chemical names of the determined compounds (original and corrected ones if necessary): (1) Senthil Kumar et al. (1999 ▸): 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane solvate, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane (1:1)]; (2) Senthil Kumar et al. (1999 ▸): 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane solvate, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane (2:1); (3) Senthil Kumar et al. (1999 ▸): 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane solvate, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 1,4-dioxane (2:1); (4) Smith et al. (2003a ▸): 4-cyanopyridinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, 4-cyanopyridinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (5) Smith et al. (2011 ▸): 2-aminoanilinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (6) Khan et al. (2013 ▸): 2-aminoanilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate, 2-aminoanilinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (7) Jin et al. (2013 ▸): 3-carbamoylpyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate, 3-carbamoylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (8) Smith et al. (2007 ▸): 1-naphthylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, 1-naphthylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (9) Smith et al. (2001b ▸): 8-aminoquinolinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; (10) Smith et al. (2011 ▸): 4-chloroanilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (11) Jones et al. (2014 ▸): (4-iodoanilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (12) Smith et al. (2007 ▸): 1,10-Phenanthrolinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; (13) Singh et al. (2014 ▸): 2-(pyridin-2-yl)pyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (14) Song et al. (2007 ▸): 2,2′-bipyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (15) Smith et al. (2007 ▸): 2,2′-bipyridinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (16) Smith et al. (2005a ▸): cytosinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, cytosinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (17) Smith et al. (2011 ▸): anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (18) Smith et al. (2011 ▸): 4-fluoroanilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (19) Smith et al. (2007 ▸): quinolinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, quinolinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (20) Smith et al. (1995 ▸): 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid 2-aminobenzoic acid, 2-ammoniumbenzoic acid 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (21) Smith et al. (2003a ▸): pyridinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid; (22) Zhang et al. (2014 ▸): 2-methylquinolinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (23) Gao et al. (2015 ▸): 2,6-diaminopyridin-1-ium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (24) Smith et al. (2003a ▸): 2-aminopyrimidinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate ethanol solvate, 2-aminopyrimidinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate ethanol (2:2:1); (25) Jin et al. (2015b ▸): 1H-imidazol-3-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (26) Fu et al. (2015 ▸): hydrazinium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (27) Wei et al. (2012 ▸): (3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate); (28) this work: (3,5-dimethylpyrazolium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (29) Smith et al. (2002b ▸): benzylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, benzylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (30) Jin et al. (2015a ▸): benzylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (31) Smith et al. (2003b ▸): (S)-(−)-1-phenylethylaminium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, (S)-(−)-1-phenylethylaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (32) Ng et al. (2001 ▸): dicyclohexylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (33) Smith et al. (2001c ▸): 4-ammoniobenzenesulfonamide 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, 4-ammoniobenzenesulfonamide 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (34) Smith et al. (2002a ▸): methylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, methylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (35) Smith et al. (2002a ▸): triethylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; (36) Rajkumar & Chandramohan (2017 ▸): triethylammonium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate; (37) Smith et al. (2005b ▸): diethylammonium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate, diethylammonium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate; (38) Smith et al. (2006 ▸): tris(piperidinium) bis(3,5-dinitrosalicylate) monohydrate, tris(piperidinium) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate 2-olate-3,5-dinitrobenzoate monohydrate; (39) Smith et al. (2001a ▸): guanidinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; (40) Fu et al. (2015 ▸): guanidinium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate.
Fig. 3 ▸ a and 3b also show that the bridging hydrogen cannot be situated near the centre of the intramolecular O⋯O hydrogen bond in structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I). Fig. 3 ▸ c shows a similar dependence of D13 on (D12 − D11). It can be seen that the adjacent C—C conjugated bonds are less, but still sensitive to the bonding of the hydroxy hydrogen atom to one of the neighbouring C—O groups. These properties indicate that the O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bonding with the pertinent O⋯O distance D13 belongs to the category of resonance-assisted hydrogen bonds (Gilli et al., 1989 ▸, 2009 ▸; Sobczyk et al., 2005 ▸).
Fig. 3 ▸ d compares both dependences shown in Figs. 3 ▸ a and 3b. It can be seen that the dependence of (D2 − D1) on (q1 + q2) is fairly linear. The dependence seems to show the narrowest spread for the 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II), which are represented by the black squares. Importantly, the line for each class of molecules intercepts the D2 − D1 axis at different values. The structures that contain 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) molecules (green triangles) are clearly separated from the rest of the structures although they show a similar trend. Figs. 3 ▸ a–3d also show outliers that do not fit the overall trends and which are most probably the structures determined as 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) instead of 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III) and vice versa. Fig. 3 ▸ e shows the same as Fig. 3 ▸ a except for the addition of a few known structures that contain a 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV), which are indicated by blue triangles. Their positions can be explained by the fact that the carboxylate groups are substantially inclined to the benzene ring in such compounds, which causes elongation of the distance between the carboxylate and oxo group, and these molecules will not be considered further.
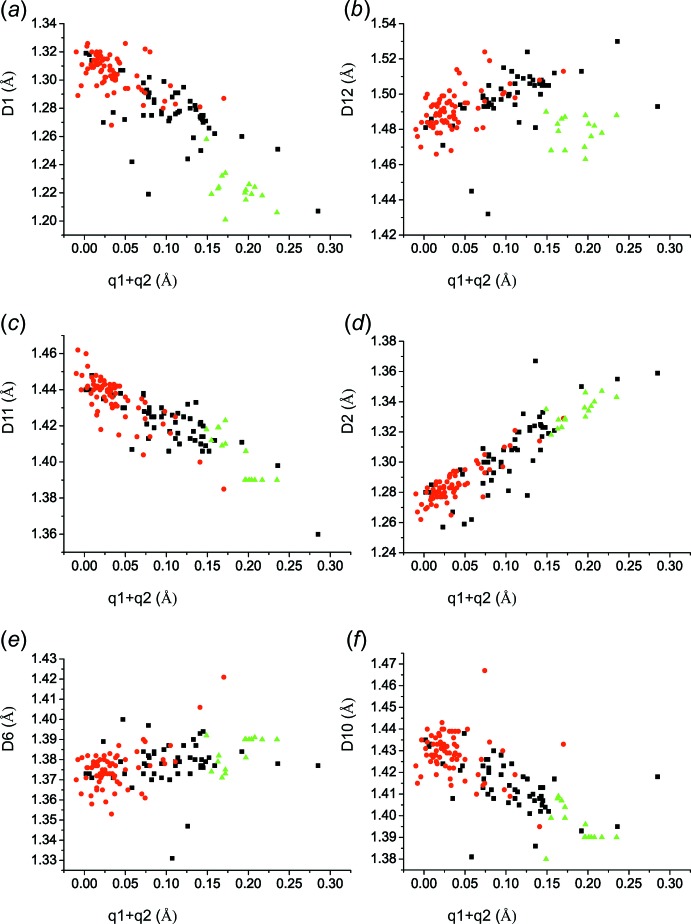
The alternation of the inclinations (Fig. 4 ▸ a–4d) of the dependences of D1, D12, D11, and D2 on (q1 + q2) are in agreement with the delocalization of the electron density in these bonds. The 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) molecules (green triangles) and the 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II; black squares) are situated apart from the 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III; red circles) in the given figures. The fact that D1 tends to be shortest in 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) molecules (Fig. 4 ▸ a) can be explained by the elongation of bond D5 in the latter molecules because of the attachment of the hydrogen atom and the concomitant shortening of D1. The bond lengths D1 (Fig. 4 ▸ a) are equal to 1.28–1.30 Å at (q1 + q2) ≃ 0.08 where the highest probability for the occurrence of a symmetric intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond takes place. The corresponding values of D12, D11, D2, D6 and D10 are 1.49 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ b), 1.43 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ c), 1.30 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ d), 1.37–1.39 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ e) and 1.41–1.43 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ f).
Figure 4.
The dependence of bond distances: (a) D1 on (q1 + q2); (b) D12 on (q1 + q2); (c) D11 on (q1 + q2); (d) D2 on (q1 + q2); (e) D6 on (q1 + q2); (f) D10 on (q1 + q2). The colour code for the symbols is the same as in Fig. 3 ▸.
Fig. 5 ▸ a shows the dependence of D5 on (q1 + q2). Comparing Fig. 5 ▸ a to Fig. 4 ▸ a, which shows the dependence of D1 on (q1 + q2), an indirect proportionality of both dependences can be observed. The bond length D5 is equal to 1.22–1.24 Å for (q1 + q2) ≃ 0.08 Å. The dependence of D5 on (q1 + q2) (Fig. 5 ▸ a) is similar to that of bond D12 (Fig. 4 ▸ b) in 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) and 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III), but not in molecules of 2-hydroxo-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I). It is interesting that 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I) molecules are in line with other forms of the title molecules for the dependences in Fig. 5 ▸ c and Fig. 4 ▸ d. Bond D7 is rather distant from the carboxylic group (Fig. 5 ▸ b) and the delocalization within the pyridine ring is no longer clear. The same holds for bonds D14 and D15 (Figs. 5 ▸ c and 5d). Figs. 5 ▸ e and 5f show the inclinations, ANG1 and ANG2, of the nitro groups involving bonds D14 and D15, respectively, toward the ring plane.
Figure 5.
The dependence of bond distances: (a) D5 on (q1 + q2); (b) D7 on (q1 + q2); (c) D14 on (q1 + q2). The dependence of dihedral angles: (e) ANG1 on (q1 + q2); (f) ANG2 on (q1 + q2). [ANG1 and ANG2 are the dihedral angles of the nitro groups involving bonds D14 and D15, respectively, toward the ring plane.] The colour code of the symbols is the same as in Fig. 3 ▸.
Fig. 6 ▸ a–6c show dependences in which the localization of the bridging hydrogen takes place. It seems that the most obtuse angles of O⋯H⋯O (ANG3) occur for (q1 + q2) in the range <0.06–0.10> Å, i.e. for the shortest distances of D13 (2.41 Å). It is questionable whether the position of a bridging hydrogen in the transition zone between 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) and 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III) facilitates its positional disorder, which occurs e.g. in NUQVEB, because of the impossibility of angle ANG3 approaching 180°. The dependence of the angles ANG4 and ANG5 (Fig. 1 ▸ b) shows once more the effect of incorrectly applied constraints, which are manifested by values close to 109.54° (cf. Figs. 2 ▸ a and 2b).
Figure 6.
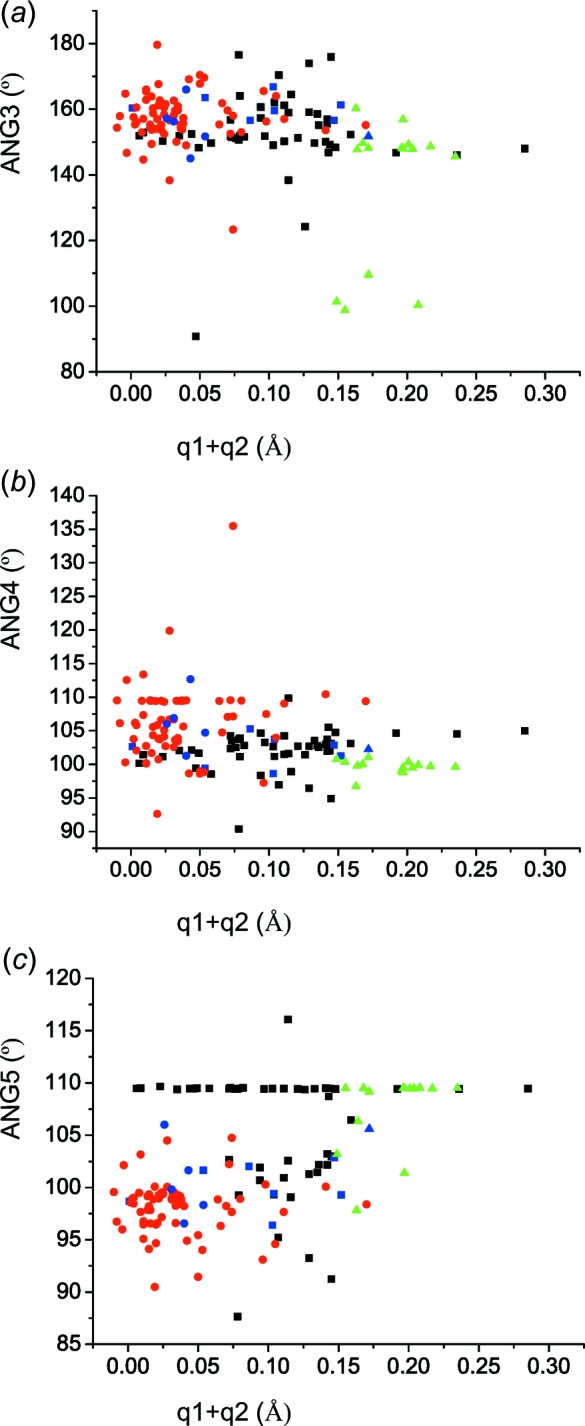
(a) Dependence of the O⋯H⋯O angle ANG3 on (q1 + q2); (b) dependence of ANG4 on (q1 + q2); (c) dependence of ANG5 on (q1 + q2). Colour code for symbols: green triangles refer to the structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I), black squares are the structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II), and red circles are the structures with 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III); blue triangles, squares and circles are the recalculated structures with 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I), 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II) and 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III), respectively.
The previous discussion has shown the correlations of D1 and D5 on (q1 + q2) (Figs. 4 ▸ a and 5a, respectively), and the indirect dependence of D1 on D5. Therefore, the position of the bridging hydrogen is expected to be related to the environment of the molecules, i.e. to be dependent on ΔpK a = pK a(base) − pK a(acid). The value of ΔpK a is correlated with the occurrence of a structure where the base and the acid components are not ionized, thus forming a co-crystal (Δ < 0), or ionized forming a salt (ΔpK a > 3) (Childs et al., 2007 ▸). It is difficult to predict the form in which the acid and the base are present for 0 < ΔpK a < 3 (Childs et al., 2007 ▸).
In Table 4 ▸, the structures are ordered according to ascending values of the pK a values of the bases, i.e. according to increasing basicity. The corresponding values of ΔpK a are compared with (q1 + q2) and D13. The pK a of 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I; 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid) is reported as 2.18 (Smith & Wermuth, 2014 ▸; Hemamalini & Fun, 2010a ▸), although a value of 1.53 has been reported in the literature (https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB9172047_EN.htm). The weakest bases given at the top of Table 4 ▸ are not able to deprotonate the title molecule, which remains in the form of 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I). On the other hand, the bases with the largest values of pK a (see the bottom of Table 3 ▸) are able to deprive the title molecule of the hydroxy and acid hydrogen atoms, so in such cases the resulting molecule would be in the form of 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoate (IV). The compounds with moderate basicities are able to deprotonate the acid hydrogen atom but not the bridging hydrogen; hence, the resulting forms are 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (II) or 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III). These structures appear in the intermediate region of Table 4 ▸. A more radical transfer of the acid hydrogen atom should cause a more significant shortening of bond D5, which should be concomitant with the elongation of bond D1. Such an elongation of bond D1 (cf. Fig. 1 ▸ a) should support the formation of a 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (III).
Summary
(1) The bridging hydrogen in the molecules discussed (I–III) is involved in a resonance-assisted hydrogen bond, which is part of a hexagonal 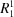 (6) ring. The system of conjugated bonds in the title molecules, however, comprises more atoms than the ring in which the bridging hydrogen is involved. In particular, the whole carboxylate/carboxylic group affects the discussed intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond.
(6) ring. The system of conjugated bonds in the title molecules, however, comprises more atoms than the ring in which the bridging hydrogen is involved. In particular, the whole carboxylate/carboxylic group affects the discussed intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond.
(2) The transition region between the forms of 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoates (II) and 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III) takes place for C—O (D1) ≃ 1.28–1.30 Å, C—O (D2) ≃ 1.30 Å, O⋯O distance D13 ≃ 2.41 Å and (q1 + q2) ≃ 0.08 Å. Simultaneously, the highest probability for the presence of the bridging hydrogen to be in the centre of the hydrogen bond is expected in this transition region. However, the hydrogen atom can also be disordered over two positions as occurs in NUQVEB.
(3) The bridging hydrogen in the discussed intramolecular hydrogen bond can be situated at the centre between both oxygen atoms with approximately equal C—O bond distances. Therefore, the bridging hydrogen can not be situated at the centre of the intramolecular O⋯H⋯O hydrogen bond in compounds containing 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid (I).
(4) In some rare cases (e.g. recalculated SEDKET, KEZJIJ and KEZJIJ01), the bridging hydrogen is bonded to the oxygen atom that forms the shorter C—O bond distance (Table 3 ▸). It would be of interest to see how the localization of the bridging hydrogen develops with changing temperature in such cases.
(5) Table 4 ▸ shows the occurrence of the different forms of the molecules (see scheme) and the dependence on basicity. Alhough it would be expected that the increasing basicity should support the occurrence of 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolates (III) and, of course, for very strong bases, 3,5-dinitro-2-oxidobenzoates (IV), there are many exceptions to this rule.
(6) The positioning of the hydrogen atoms can be affected by the asphericity of the electron density of the donor and acceptor atoms.
(7) It is essential to calculate difference electron-density maps in order to locate correctly the bridging hydrogen atom, and any other hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding.
(8) The present overview has shown that the application of constraints and restraints is frequently incorrect.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, DUJZAK, JEVNAA, NUQVEB, QIQJAD, SEDKET, VABZIJ, WADXOR, YAXPOE, LUDFUL, SAFGUD, TIYZIM, TUJPEV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IVsup5.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) V. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Vsup6.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIsup7.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VII. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIIsup8.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VIII. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIIIsup9.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IX. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IXsup10.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) X. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Xsup11.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) XI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452XIsup12.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452NUQVEBsup13.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452QIQJADsup14.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452SEDKETsup15.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452TIYZIMsup16.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452TUJPEVsup17.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VABZIJsup18.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452WADXORsup19.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452YAXPOEsup20.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452sup21.pdf
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Crystal data
| [Ag(C9H7NO)2](C7H3N2O7) | F(000) = 628 |
| Mr = 625.30 | Dx = 1.823 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 4356 reflections |
| a = 9.0154 (18) Å | θ = 3.6–27.6° |
| b = 7.6122 (15) Å | µ = 0.95 mm−1 |
| c = 17.138 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 104.38 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1139.3 (4) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4225 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.022 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 3.6° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| 10841 measured reflections | k = −9→8 |
| 4602 independent reflections | l = −22→22 |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.023 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.053 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.34 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| 4602 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.025 |
| 356 parameters | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
| 48 constraints | Absolute structure: 1800 of Friedel pairs used in the refinement |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.004 (17) |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.Number of fixed parameters 9. |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ag1 | 0.062197 (18) | 0.74282 (3) | 0.668863 (11) | 0.01868 (5) | |
| O1 | −0.0993 (2) | 0.4630 (2) | 0.64021 (12) | 0.0202 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.1741 (2) | 0.5061 (2) | 0.77196 (12) | 0.0214 (6) | |
| N1 | −0.1154 (2) | 0.7667 (3) | 0.55616 (13) | 0.0177 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.2685 (2) | 0.8371 (3) | 0.75427 (14) | 0.0163 (7) | |
| C1 | −0.1280 (3) | 0.9181 (4) | 0.51463 (18) | 0.0222 (9) | |
| H1a | −0.061241 | 1.009276 | 0.535386 | 0.0267* | |
| C2 | −0.2362 (3) | 0.9448 (4) | 0.44205 (18) | 0.0243 (9) | |
| H2a | −0.240923 | 1.051917 | 0.415439 | 0.0291* | |
| C3 | −0.3354 (3) | 0.8130 (4) | 0.41016 (19) | 0.0209 (9) | |
| H3a | −0.407848 | 0.829471 | 0.361612 | 0.0251* | |
| C4 | −0.3270 (3) | 0.6506 (4) | 0.45167 (18) | 0.0169 (8) | |
| C5 | −0.4264 (3) | 0.5079 (4) | 0.42259 (17) | 0.0209 (9) | |
| H5a | −0.500744 | 0.518344 | 0.37429 | 0.0251* | |
| C6 | −0.4131 (3) | 0.3554 (4) | 0.46539 (17) | 0.0217 (9) | |
| H6a | −0.477402 | 0.261662 | 0.445311 | 0.026* | |
| C7 | −0.3036 (3) | 0.3371 (3) | 0.53948 (17) | 0.0184 (8) | |
| H7a | −0.297965 | 0.232672 | 0.568204 | 0.0221* | |
| C8 | −0.2057 (3) | 0.4717 (3) | 0.56954 (16) | 0.0148 (8) | |
| C9 | −0.2139 (3) | 0.6331 (3) | 0.52566 (16) | 0.0141 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.3159 (3) | 0.9993 (4) | 0.74633 (17) | 0.0188 (9) | |
| H10a | 0.256892 | 1.069872 | 0.706108 | 0.0225* | |
| C11 | 0.4512 (3) | 1.0703 (4) | 0.79567 (18) | 0.0220 (9) | |
| H11a | 0.480885 | 1.184529 | 0.787703 | 0.0264* | |
| C12 | 0.5373 (3) | 0.9693 (4) | 0.85495 (18) | 0.0210 (9) | |
| H12a | 0.627346 | 1.01397 | 0.887796 | 0.0252* | |
| C13 | 0.4907 (3) | 0.7960 (3) | 0.86712 (16) | 0.0171 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.5743 (3) | 0.6845 (4) | 0.92853 (17) | 0.0200 (8) | |
| H14a | 0.665083 | 0.723938 | 0.962749 | 0.024* | |
| C15 | 0.5225 (3) | 0.5197 (4) | 0.93771 (17) | 0.0206 (8) | |
| H15a | 0.577789 | 0.447807 | 0.978539 | 0.0247* | |
| C16 | 0.3863 (3) | 0.4570 (3) | 0.88620 (16) | 0.0173 (8) | |
| H16a | 0.35178 | 0.344669 | 0.8937 | 0.0208* | |
| C17 | 0.3043 (3) | 0.5596 (3) | 0.82528 (16) | 0.0142 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.3541 (2) | 0.7340 (5) | 0.81443 (13) | 0.0140 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.1402 (2) | −0.0134 (3) | 0.92525 (13) | 0.0259 (7) | |
| O4 | −0.4152 (2) | −0.3755 (3) | 0.69139 (13) | 0.0284 (7) | |
| O5 | −0.3271 (2) | −0.5961 (3) | 0.76858 (13) | 0.0271 (7) | |
| O6 | 0.1238 (2) | −0.5247 (2) | 0.98352 (12) | 0.0211 (6) | |
| O7 | 0.1679 (2) | −0.2659 (4) | 1.03546 (11) | 0.0286 (6) | |
| O8 | −0.0981 (2) | 0.1498 (2) | 0.70180 (12) | 0.0237 (7) | |
| O9 | 0.06657 (19) | 0.2138 (2) | 0.81885 (11) | 0.0196 (6) | |
| N3 | −0.3217 (2) | −0.4436 (3) | 0.74764 (14) | 0.0173 (7) | |
| N4 | 0.1088 (2) | −0.3645 (3) | 0.98085 (13) | 0.0152 (7) | |
| C19 | −0.1970 (3) | −0.3339 (4) | 0.79254 (18) | 0.0130 (8) | |
| C20 | −0.1027 (3) | −0.3992 (3) | 0.86303 (15) | 0.0126 (7) | |
| H20a | −0.114934 | −0.512855 | 0.880295 | 0.0151* | |
| C21 | 0.0095 (2) | −0.2908 (3) | 0.90660 (15) | 0.0114 (8) | |
| C22 | 0.0326 (3) | −0.1188 (3) | 0.88194 (16) | 0.0130 (8) | |
| C23 | −0.0605 (3) | −0.0603 (3) | 0.80708 (16) | 0.0129 (7) | |
| C24 | −0.1770 (3) | −0.1678 (3) | 0.76332 (17) | 0.0132 (8) | |
| H24a | −0.240539 | −0.128661 | 0.715089 | 0.0159* | |
| C25 | −0.0307 (3) | 0.1145 (3) | 0.77245 (16) | 0.0148 (8) | |
| H1aa | −0.091407 | 0.377732 | 0.663815 | 0.047 (14)* | |
| H2aa | 0.145536 | 0.395004 | 0.783901 | 0.043 (11)* | |
| H3b | 0.135279 | 0.095353 | 0.887993 | 0.17 (3)* |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ag1 | 0.01622 (8) | 0.01722 (9) | 0.01945 (10) | −0.00339 (11) | −0.00154 (6) | 0.00024 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0199 (10) | −0.0063 (8) | −0.0065 (8) | 0.0058 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0185 (9) | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0231 (11) | −0.0065 (8) | −0.0049 (8) | 0.0030 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0190 (9) | 0.0152 (14) | 0.0181 (11) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0008 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0145 (10) | 0.0161 (11) | 0.0187 (12) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0049 (9) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0254 (14) | 0.0145 (12) | 0.0263 (16) | −0.0042 (12) | 0.0056 (12) | 0.0044 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0325 (15) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0239 (16) | 0.0069 (13) | 0.0093 (12) | 0.0104 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0214 (13) | 0.0247 (13) | 0.0154 (15) | 0.0059 (12) | 0.0021 (12) | 0.0023 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0136 (12) | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0150 (15) | 0.0026 (11) | 0.0031 (10) | 0.0005 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0160 (12) | 0.0289 (15) | 0.0156 (14) | 0.0005 (12) | −0.0002 (10) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0156 (12) | 0.0247 (14) | 0.0217 (16) | −0.0092 (12) | −0.0009 (11) | −0.0062 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0179 (12) | 0.0175 (14) | 0.0187 (14) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0018 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0139 (12) | 0.0146 (12) | 0.0140 (13) | 0.0001 (11) | 0.0000 (9) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0147 (12) | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0132 (13) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0032 (9) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0208 (13) | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0198 (15) | −0.0021 (12) | 0.0084 (11) | 0.0021 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0259 (14) | 0.0166 (13) | 0.0254 (16) | −0.0085 (12) | 0.0099 (12) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0180 (12) | 0.0226 (14) | 0.0235 (15) | −0.0108 (12) | 0.0074 (11) | −0.0101 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0138 (11) | 0.0232 (14) | 0.0156 (14) | −0.0032 (10) | 0.0064 (10) | −0.0059 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0118 (11) | 0.0285 (14) | 0.0182 (15) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0010 (10) | −0.0071 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0143 (12) | 0.0281 (15) | 0.0175 (15) | 0.0038 (12) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0160 (12) | 0.0146 (12) | 0.0208 (15) | −0.0018 (11) | 0.0035 (10) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0107 (11) | 0.0149 (12) | 0.0165 (14) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0025 (9) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0115 (9) | 0.0160 (11) | 0.0156 (11) | 0.0014 (17) | 0.0052 (8) | 0.0001 (15) |
| O3 | 0.0215 (10) | 0.0236 (11) | 0.0279 (12) | −0.0066 (9) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0016 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0212 (10) | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0267 (12) | −0.0044 (9) | −0.0110 (8) | −0.0010 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0295 (10) | 0.0195 (10) | 0.0288 (12) | −0.0130 (9) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0016 (9) |
| O6 | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0236 (11) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0059 (8) |
| O7 | 0.0340 (9) | 0.0225 (9) | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0057 (15) | −0.0121 (7) | −0.0015 (13) |
| O8 | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0156 (10) | 0.0204 (11) | −0.0061 (9) | −0.0028 (8) | 0.0051 (8) |
| O9 | 0.0209 (8) | 0.0129 (12) | 0.0223 (10) | −0.0061 (8) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0009 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0141 (10) | 0.0190 (11) | 0.0169 (12) | −0.0064 (10) | 0.0001 (9) | −0.0044 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0115 (10) | 0.0169 (11) | 0.0154 (12) | 0.0012 (9) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0025 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0080 (11) | 0.0164 (12) | 0.0135 (15) | −0.0043 (10) | 0.0009 (10) | −0.0044 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0158 (12) | 0.0082 (11) | 0.0137 (13) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0098 (9) | 0.0122 (17) | 0.0103 (11) | 0.0048 (10) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0086 (11) | 0.0150 (13) | 0.0147 (14) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0033 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0133 (11) | 0.0110 (12) | 0.0134 (13) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0015 (9) | −0.0007 (9) |
| C24 | 0.0120 (12) | 0.0135 (13) | 0.0142 (15) | 0.0018 (11) | 0.0033 (10) | 0.0004 (11) |
| C25 | 0.0153 (12) | 0.0109 (11) | 0.0177 (14) | 0.0006 (10) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0010 (10) |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C8 | 1.347 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.415 (4) |
| O1—H1aa | 0.7585 (19) | C13—C18 | 1.415 (3) |
| O2—C17 | 1.359 (3) | C14—H14a | 0.93 |
| O2—H2aa | 0.922 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.361 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.344 (4) | C15—H15a | 0.93 |
| N1—C9 | 1.365 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.406 (3) |
| N2—C10 | 1.325 (4) | C16—H16a | 0.93 |
| N2—C18 | 1.371 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.365 (4) |
| C1—H1a | 0.93 | C17—C18 | 1.429 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.392 (4) | O3—C22 | 1.333 (3) |
| C2—H2a | 0.93 | O3—H3b | 1.040 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.364 (4) | O4—N3 | 1.227 (3) |
| C3—H3a | 0.93 | O5—N3 | 1.219 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.419 (4) | O6—N4 | 1.226 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.418 (4) | O7—N4 | 1.215 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.423 (4) | O8—C25 | 1.242 (3) |
| C5—H5a | 0.93 | O9—C25 | 1.275 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.362 (4) | O9—H3b | 1.4952 (19) |
| C6—H6a | 0.93 | N3—C19 | 1.458 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.408 (4) | N4—C21 | 1.473 (3) |
| C7—H7a | 0.93 | C19—C20 | 1.385 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.367 (4) | C19—C24 | 1.388 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.433 (4) | C20—H20a | 0.93 |
| C10—H10a | 0.93 | C20—C21 | 1.373 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.408 (4) | C21—C22 | 1.408 (4) |
| C11—H11a | 0.93 | C22—C23 | 1.419 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.354 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.394 (3) |
| C12—H12a | 0.93 | C23—C25 | 1.508 (4) |
| C12—C13 | 1.416 (4) | C24—H24a | 0.93 |
| C8—O1—H1aa | 118.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.2 (2) |
| C17—O2—H2aa | 111.60 (19) | H14a—C14—C15 | 119.88 |
| C1—N1—C9 | 118.3 (2) | C14—C15—H15a | 119.61 |
| C10—N2—C18 | 118.4 (2) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1a | 118.43 | H15a—C15—C16 | 119.61 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.1 (2) | C15—C16—H16a | 119.71 |
| H1a—C1—C2 | 118.43 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2a | 120.19 | H16a—C16—C17 | 119.71 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.6 (3) | O2—C17—C16 | 123.8 (2) |
| H2a—C2—C3 | 120.19 | O2—C17—C18 | 116.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3a | 120.26 | C16—C17—C18 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.5 (2) | N2—C18—C13 | 121.8 (3) |
| H3a—C3—C4 | 120.27 | N2—C18—C17 | 119.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.8 (2) | C13—C18—C17 | 118.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C9 | 117.8 (2) | C22—O3—H3b | 102.89 (19) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 119.5 (2) | C25—O9—H3b | 102.84 (17) |
| C4—C5—H5a | 120 | O4—N3—O5 | 124.3 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.0 (2) | O4—N3—C19 | 117.5 (2) |
| H5a—C5—C6 | 120 | O5—N3—C19 | 118.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6a | 119.4 | O6—N4—O7 | 124.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.2 (2) | O6—N4—C21 | 116.66 (19) |
| H6a—C6—C7 | 119.4 | O7—N4—C21 | 119.1 (2) |
| C6—C7—H7a | 119.72 | N3—C19—C20 | 118.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 120.6 (2) | N3—C19—C24 | 118.9 (2) |
| H7a—C7—C8 | 119.72 | C20—C19—C24 | 122.3 (2) |
| O1—C8—C7 | 123.5 (2) | C19—C20—H20a | 121.04 |
| O1—C8—C9 | 116.5 (2) | C19—C20—C21 | 117.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.0 (2) | H20a—C20—C21 | 121.04 |
| N1—C9—C4 | 121.7 (2) | N4—C21—C20 | 116.7 (2) |
| N1—C9—C8 | 119.6 (2) | N4—C21—C22 | 120.67 (19) |
| C4—C9—C8 | 118.7 (2) | C20—C21—C22 | 122.7 (2) |
| N2—C10—H10a | 118.33 | O3—C22—C21 | 122.3 (2) |
| N2—C10—C11 | 123.3 (2) | O3—C22—C23 | 120.0 (2) |
| H10a—C10—C11 | 118.33 | C21—C22—C23 | 117.7 (2) |
| C10—C11—H11a | 120.58 | C22—C23—C24 | 120.0 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 118.8 (3) | C22—C23—C25 | 120.6 (2) |
| H11a—C11—C12 | 120.58 | C24—C23—C25 | 119.4 (2) |
| C11—C12—H12a | 119.87 | C19—C24—C23 | 119.2 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.3 (2) | C19—C24—H24a | 120.38 |
| H12a—C12—C13 | 119.87 | C23—C24—H24a | 120.38 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 123.1 (2) | O8—C25—O9 | 125.0 (2) |
| C12—C13—C18 | 117.4 (2) | O8—C25—C23 | 118.9 (2) |
| C14—C13—C18 | 119.6 (3) | O9—C25—C23 | 116.1 (2) |
| C13—C14—H14a | 119.88 | O3—H3b—O9 | 155.88 (12) |
Bis(quinolin-8-ol)silver(I) 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (DUJZAK). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C11—H11a···O5i | 0.93 | 2.48 | 3.335 (4) | 152 |
| O1—H1aa···O8 | 0.7585 (19) | 1.859 (2) | 2.606 (3) | 167.96 (14) |
| O2—H2aa···O9 | 0.922 (2) | 1.727 (2) | 2.631 (3) | 166.48 (15) |
| O3—H3b···O9 | 1.040 (2) | 1.4952 (19) | 2.481 (3) | 155.88 (12) |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y+2, z.
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Crystal data
| [Zn(C3H4N2)4](C7H3N2O7)2 | F(000) = 1616 |
| Mr = 791.93 | Dx = 1.664 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 3242 reflections |
| a = 25.0809 (15) Å | θ = 2.1–26.9° |
| b = 6.7251 (4) Å | µ = 0.87 mm−1 |
| c = 18.9145 (10) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 97.658 (6)° | Platelet, yellow |
| V = 3161.9 (3) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Data collection
| Bruker APEX-II area-detector diffractometer | 3635 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2152 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.058 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 1.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1999) | h = −32→31 |
| Tmin = 0.846, Tmax = 0.918 | k = −8→8 |
| 20634 measured reflections | l = −24→24 |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.036 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F) = 0.075 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| S = 1.23 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.007 |
| 3635 reflections | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 244 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 32 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 1400 (500) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Number of fixed parameters: 9 |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.47960 (10) | 0.4200 (3) | 0.62639 (13) | 0.0460 (10) | |
| H1 | 0.444004 | 0.398202 | 0.633096 | 0.0552* | |
| C2 | 0.50386 (10) | 0.3369 (4) | 0.57533 (13) | 0.0484 (10) | |
| H2 | 0.488745 | 0.248295 | 0.540565 | 0.0581* | |
| C3 | 0.56018 (9) | 0.5299 (3) | 0.63970 (12) | 0.0401 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.591591 | 0.597819 | 0.656666 | 0.0481* | |
| C4 | 0.59325 (9) | 0.9065 (4) | 0.83991 (12) | 0.0404 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.591722 | 0.823229 | 0.87885 | 0.0485* | |
| N4 | 0.62879 (7) | 1.0508 (3) | 0.83789 (11) | 0.0471 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.57665 (9) | 1.0451 (4) | 0.73735 (13) | 0.0444 (9) | |
| H6 | 0.560952 | 1.074705 | 0.691199 | 0.0533* | |
| C7 | 0.73999 (9) | 0.4553 (3) | 0.34225 (11) | 0.0329 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.79245 (9) | 0.5059 (3) | 0.36676 (12) | 0.0342 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.817639 | 0.51762 | 0.335092 | 0.0411* | |
| C9 | 0.80717 (8) | 0.5388 (3) | 0.43803 (12) | 0.0311 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.77048 (8) | 0.5210 (3) | 0.48978 (12) | 0.0302 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.71702 (8) | 0.4593 (3) | 0.46099 (11) | 0.0282 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.70286 (9) | 0.4300 (3) | 0.38898 (12) | 0.0323 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.667845 | 0.392676 | 0.371656 | 0.0388* | |
| C13 | 0.67545 (9) | 0.4249 (3) | 0.50834 (12) | 0.0333 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.51487 (7) | 0.5429 (3) | 0.66784 (9) | 0.0373 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.55523 (8) | 0.4075 (3) | 0.58408 (10) | 0.0438 (8) | |
| N3 | 0.56024 (7) | 0.8957 (3) | 0.77961 (9) | 0.0354 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.61854 (9) | 1.1406 (4) | 0.77303 (14) | 0.0479 (10) | |
| H5 | 0.637064 | 1.247402 | 0.75675 | 0.0575* | |
| N5 | 0.72386 (8) | 0.4225 (3) | 0.26644 (10) | 0.0427 (8) | |
| N6 | 0.86351 (7) | 0.5897 (3) | 0.46068 (11) | 0.0403 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.78238 (6) | 0.5518 (2) | 0.55681 (8) | 0.0378 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.68832 (6) | 0.4695 (2) | 0.57640 (8) | 0.0420 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.63104 (6) | 0.3579 (2) | 0.48669 (8) | 0.0426 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.67630 (7) | 0.3835 (3) | 0.24643 (8) | 0.0575 (7) | |
| O5 | 0.75772 (7) | 0.4340 (3) | 0.22570 (9) | 0.0662 (8) | |
| O6 | 0.89634 (7) | 0.5475 (3) | 0.42013 (9) | 0.0658 (8) | |
| O7 | 0.87622 (6) | 0.6730 (3) | 0.51757 (9) | 0.0568 (7) | |
| Zn1 | 0.5 | 0.70908 (6) | 0.75 | 0.03866 (15) | |
| H1a | 0.728641 | 0.508268 | 0.579335 | 0.108 (11)* | |
| H2a | 0.580668 | 0.367714 | 0.552562 | 0.088 (9)* | |
| H4a | 0.657593 | 1.098579 | 0.870594 | 0.106 (11)* |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0323 (14) | 0.0558 (17) | 0.0507 (17) | −0.0069 (12) | 0.0086 (12) | −0.0071 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0460 (16) | 0.0536 (18) | 0.0448 (17) | −0.0064 (13) | 0.0033 (12) | −0.0116 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0327 (13) | 0.0485 (16) | 0.0396 (16) | −0.0053 (11) | 0.0071 (11) | 0.0037 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0366 (14) | 0.0491 (16) | 0.0343 (15) | 0.0066 (12) | 0.0004 (11) | 0.0062 (12) |
| N4 | 0.0332 (12) | 0.0568 (15) | 0.0484 (15) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0048 (10) | −0.0044 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0416 (15) | 0.0568 (17) | 0.0336 (15) | −0.0015 (12) | 0.0004 (12) | 0.0077 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0344 (13) | 0.0369 (14) | 0.0264 (14) | 0.0024 (10) | 0.0002 (10) | −0.0008 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0332 (13) | 0.0366 (14) | 0.0337 (15) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0030 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0254 (12) | 0.0287 (13) | 0.0382 (15) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0003 (10) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0342 (14) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0013 (10) | 0.0006 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0288 (12) | 0.0245 (12) | 0.0310 (14) | 0.0011 (9) | 0.0030 (10) | −0.0013 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0281 (12) | 0.0306 (14) | 0.0370 (15) | 0.0009 (9) | −0.0002 (10) | 0.0004 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0312 (14) | 0.0356 (15) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0067 (11) | −0.0026 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0341 (11) | 0.0433 (13) | 0.0357 (12) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0086 (9) | −0.0001 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0437 (12) | 0.0526 (14) | 0.0371 (13) | 0.0034 (10) | 0.0126 (10) | −0.0035 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0321 (10) | 0.0442 (12) | 0.0288 (11) | 0.0016 (9) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0042 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0393 (15) | 0.0540 (18) | 0.0499 (18) | −0.0090 (12) | 0.0040 (12) | 0.0069 (14) |
| N5 | 0.0414 (13) | 0.0517 (14) | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0032 (10) | 0.0004 (10) | −0.0005 (10) |
| N6 | 0.0327 (11) | 0.0435 (13) | 0.0438 (14) | −0.0038 (9) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0059 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0445 (10) | 0.0308 (10) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0026 (7) | −0.0054 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0399 (10) | 0.0552 (11) | 0.0313 (10) | −0.0055 (8) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0066 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0561 (11) | 0.0400 (10) | −0.0091 (8) | 0.0079 (7) | −0.0084 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0395 (10) | 0.0890 (14) | 0.0408 (11) | −0.0047 (9) | −0.0063 (8) | −0.0048 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0499 (11) | 0.1146 (17) | 0.0361 (11) | −0.0057 (10) | 0.0133 (9) | −0.0036 (10) |
| O6 | 0.0351 (10) | 0.1012 (16) | 0.0635 (13) | −0.0075 (10) | 0.0156 (9) | −0.0121 (11) |
| O7 | 0.0430 (10) | 0.0799 (14) | 0.0453 (11) | −0.0182 (9) | −0.0029 (8) | −0.0108 (10) |
| Zn1 | 0.0355 (2) | 0.0455 (3) | 0.0352 (3) | 0 | 0.00566 (17) | 0 |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—H1 | 0.93 | C8—H8 | 0.93 |
| C1—C2 | 1.331 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.367 (3) |
| C1—N1 | 1.377 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.435 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.93 | C9—N6 | 1.462 (3) |
| C2—N2 | 1.362 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.440 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C10—O1 | 1.280 (3) |
| C3—N1 | 1.320 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.375 (3) |
| C3—N2 | 1.328 (3) | C11—C13 | 1.480 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.93 | C12—H12 | 0.93 |
| C4—N4 | 1.322 (3) | C13—O2 | 1.319 (3) |
| C4—N3 | 1.319 (3) | C13—O3 | 1.220 (3) |
| N4—C5 | 1.361 (3) | N2—H2a | 0.967 (2) |
| N4—H4a | 0.9427 (18) | C5—H5 | 0.93 |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | N5—O4 | 1.231 (3) |
| C6—N3 | 1.381 (3) | N5—O5 | 1.223 (3) |
| C6—C5 | 1.335 (3) | N6—O6 | 1.231 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.378 (3) | N6—O7 | 1.217 (3) |
| C7—C12 | 1.377 (3) | O1—H1a | 1.4955 (15) |
| C7—N5 | 1.454 (3) | O2—H1a | 1.0386 (15) |
| H1—C1—C2 | 124.94 | C9—C10—O1 | 125.18 (18) |
| H1—C1—N1 | 124.94 | C11—C10—O1 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 110.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.4 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 126.81 | C10—C11—C13 | 120.78 (19) |
| C1—C2—N2 | 106.4 (2) | C12—C11—C13 | 117.85 (18) |
| H2—C2—N2 | 126.81 | C7—C12—C11 | 120.69 (19) |
| H3—C3—N1 | 124.28 | C7—C12—H12 | 119.65 |
| H3—C3—N2 | 124.28 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.66 |
| N1—C3—N2 | 111.44 (19) | C11—C13—O2 | 117.03 (18) |
| H4—C4—N4 | 124.35 | C11—C13—O3 | 122.6 (2) |
| H4—C4—N3 | 124.35 | O2—C13—O3 | 120.3 (2) |
| N4—C4—N3 | 111.3 (2) | C1—N1—C3 | 104.66 (19) |
| C4—N4—C5 | 107.74 (19) | C2—N2—C3 | 107.4 (2) |
| C4—N4—H4a | 133.8 (2) | C2—N2—H2a | 121.3 (2) |
| C5—N4—H4a | 118.5 (2) | C3—N2—H2a | 131.3 (2) |
| H6—C6—N3 | 125.29 | C4—N3—C6 | 105.04 (18) |
| H6—C6—C5 | 125.29 | N4—C5—C6 | 106.5 (2) |
| N3—C6—C5 | 109.4 (2) | N4—C5—H5 | 126.75 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 120.8 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 126.75 |
| C8—C7—N5 | 119.8 (2) | C7—N5—O4 | 117.82 (19) |
| C12—C7—N5 | 119.40 (19) | C7—N5—O5 | 119.10 (18) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.27 | O4—N5—O5 | 123.08 (19) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.5 (2) | C9—N6—O6 | 117.66 (19) |
| H8—C8—C9 | 120.27 | C9—N6—O7 | 119.73 (19) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 123.06 (18) | O6—N6—O7 | 122.61 (18) |
| C8—C9—N6 | 116.8 (2) | C10—O1—H1a | 98.67 (13) |
| C10—C9—N6 | 120.16 (19) | C13—O2—H1a | 102.66 (16) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 114.56 (19) | O1—H1a—O2 | 160.37 (10) |
Tetrakis(1H-imidazole-κN3)zinc(II) bis(2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate) (JEVNAA) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O3i | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.327 (3) | 154 |
| O2—H1a···C10 | 1.0386 (15) | 2.110 (2) | 2.820 (3) | 123.5 (1) |
| O2—H1a···O1 | 1.0386 (15) | 1.4955 (15) | 2.498 (2) | 160.4 (1) |
| N2—H2a···O3 | 0.967 (2) | 1.8902 (16) | 2.838 (3) | 165.87 (12) |
| N4—H4a···O1ii | 0.9427 (18) | 1.9236 (14) | 2.784 (2) | 150.60 (13) |
| N4—H4a···O7ii | 0.9427 (18) | 2.4336 (18) | 2.873 (3) | 108.36 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1, z+1/2; (ii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Crystal data
| C7H4N2O7·C12H8N2 | Dx = 1.556 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 408.33 | Melting point: 471 K |
| Monoclinic, P21/a | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 14.8002 (15) Å | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| b = 7.4029 (16) Å | θ = 5–12° |
| c = 16.0091 (16) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| β = 96.395 (8)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1743.1 (5) Å3 | Rhombic, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.36 × 0.34 × 0.26 mm |
| F(000) = 840 |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Data collection
| Enraf-Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.056 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Graphite monochromator | h = 0→19 |
| w scans | k = −9→9 |
| 8396 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
| 4202 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections every 150 reflections |
| 1587 reflections with I > 3σ(I) | intensity decay: 2% |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.044 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F) = 0.083 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.006 |
| 4202 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 274 parameters | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 40 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 5100 (500) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Number of fixed parameters: 6 |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O3 | 0.98761 (10) | 0.2874 (2) | 0.46747 (9) | 0.0599 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.85079 (8) | 0.4309 (2) | 0.24121 (9) | 0.0539 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.98636 (12) | 0.4161 (3) | 0.33159 (12) | 0.0373 (7) | |
| O7 | 1.12739 (10) | 0.6537 (3) | 0.15665 (10) | 0.0716 (7) | |
| C4 | 1.17200 (13) | 0.4785 (3) | 0.36328 (13) | 0.0421 (8) | |
| H4a | 1.234071 | 0.501018 | 0.373432 | 0.0506* | |
| C5 | 1.12429 (13) | 0.5256 (3) | 0.28746 (12) | 0.0378 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.84456 (9) | 0.3110 (2) | 0.36758 (9) | 0.0632 (7) | |
| C2 | 1.03254 (14) | 0.3661 (3) | 0.40995 (13) | 0.0430 (8) | |
| C3 | 1.12654 (13) | 0.3980 (3) | 0.42348 (12) | 0.0423 (8) | |
| N1 | 1.18089 (15) | 0.3455 (3) | 0.50174 (12) | 0.0665 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.88704 (14) | 0.3818 (3) | 0.31414 (14) | 0.0457 (9) | |
| C6 | 1.03232 (13) | 0.4947 (3) | 0.27113 (12) | 0.0386 (7) | |
| H6a | 1.001506 | 0.526882 | 0.219465 | 0.0463* | |
| O6 | 1.25212 (10) | 0.6448 (3) | 0.23814 (10) | 0.0804 (8) | |
| O4 | 1.14445 (14) | 0.2742 (3) | 0.55587 (13) | 0.1291 (12) | |
| N2 | 1.17129 (12) | 0.6128 (3) | 0.22290 (12) | 0.0504 (8) | |
| O5 | 1.26041 (12) | 0.3839 (3) | 0.51002 (10) | 0.0996 (10) | |
| N3 | 0.68389 (10) | 0.3729 (2) | 0.18982 (10) | 0.0388 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.50803 (11) | 0.3575 (3) | 0.10509 (11) | 0.0517 (7) | |
| C17 | 0.57960 (14) | 0.2988 (3) | 0.06927 (13) | 0.0505 (9) | |
| C19 | 0.61248 (13) | 0.4326 (3) | 0.22726 (12) | 0.0377 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.74378 (15) | 0.2489 (3) | 0.06912 (15) | 0.0552 (9) | |
| H8a | 0.802687 | 0.252957 | 0.096215 | 0.0663* | |
| C16 | 0.66987 (13) | 0.3064 (3) | 0.11118 (13) | 0.0405 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.52369 (13) | 0.4267 (3) | 0.18296 (13) | 0.0413 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.45074 (14) | 0.4976 (3) | 0.22251 (15) | 0.0533 (9) | |
| H12a | 0.392387 | 0.498106 | 0.194132 | 0.064* | |
| C14 | 0.55304 (15) | 0.5655 (3) | 0.34545 (14) | 0.0522 (9) | |
| H14a | 0.561295 | 0.610201 | 0.400052 | 0.0627* | |
| C13 | 0.46523 (15) | 0.5645 (3) | 0.30108 (15) | 0.0555 (10) | |
| H13a | 0.416606 | 0.610633 | 0.326453 | 0.0666* | |
| C15 | 0.62592 (14) | 0.5020 (3) | 0.30951 (13) | 0.0442 (8) | |
| H15a | 0.683759 | 0.504497 | 0.338918 | 0.053* | |
| C10 | 0.6400 (2) | 0.1763 (4) | −0.05197 (16) | 0.0789 (12) | |
| H10a | 0.631177 | 0.131533 | −0.10654 | 0.0946* | |
| C11 | 0.56781 (17) | 0.2291 (3) | −0.01395 (15) | 0.0689 (11) | |
| H11a | 0.509671 | 0.219906 | −0.042373 | 0.0827* | |
| C9 | 0.72833 (18) | 0.1879 (3) | −0.01060 (16) | 0.0685 (12) | |
| H9a | 0.777245 | 0.152877 | −0.038619 | 0.0822* | |
| H3a | 0.919191 | 0.279002 | 0.440153 | 0.138 (12)* | |
| H1a | 0.773139 | 0.402666 | 0.229166 | 0.105 (8)* |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O3 | 0.0634 (10) | 0.0734 (13) | 0.0442 (9) | −0.0001 (9) | 0.0122 (8) | 0.0094 (9) |
| O1 | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0749 (13) | 0.0545 (10) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0096 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0315 (11) | 0.0413 (14) | 0.0394 (12) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0046 (10) | −0.0033 (11) |
| O7 | 0.0556 (10) | 0.1066 (17) | 0.0520 (10) | −0.0111 (10) | 0.0040 (8) | 0.0199 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0326 (11) | 0.0468 (15) | 0.0457 (13) | 0.0043 (11) | −0.0016 (11) | −0.0111 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0414 (15) | 0.0398 (12) | 0.0028 (10) | 0.0059 (10) | −0.0035 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0445 (9) | 0.0836 (14) | 0.0637 (10) | −0.0069 (9) | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0161 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0493 (13) | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0377 (12) | 0.0029 (12) | 0.0073 (11) | −0.0033 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0449 (12) | 0.0468 (16) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0128 (11) | −0.0024 (10) | −0.0056 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0646 (15) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0420 (13) | 0.0141 (14) | −0.0078 (12) | −0.0014 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0413 (13) | 0.0461 (16) | 0.0509 (14) | −0.0004 (12) | 0.0098 (11) | −0.0019 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0334 (11) | 0.0433 (14) | 0.0381 (12) | 0.0051 (10) | −0.0003 (10) | −0.0035 (11) |
| O6 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.1225 (17) | 0.0871 (12) | −0.0130 (10) | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0119 (12) |
| O4 | 0.1041 (16) | 0.197 (3) | 0.0807 (15) | −0.0108 (16) | −0.0151 (13) | 0.0758 (17) |
| N2 | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0590 (15) | 0.0567 (13) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0116 (10) | −0.0046 (12) |
| O5 | 0.0575 (11) | 0.177 (2) | 0.0581 (11) | 0.0108 (14) | −0.0193 (9) | −0.0056 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0310 (9) | 0.0431 (12) | 0.0419 (10) | −0.0041 (9) | 0.0024 (8) | 0.0009 (10) |
| N4 | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0533 (14) | 0.0545 (12) | 0.0017 (10) | −0.0065 (9) | −0.0035 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0538 (14) | 0.0491 (17) | 0.0469 (14) | 0.0046 (13) | −0.0024 (12) | −0.0024 (13) |
| C19 | 0.0354 (12) | 0.0362 (14) | 0.0412 (13) | −0.0040 (11) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0023 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0564 (15) | 0.0521 (18) | 0.0588 (16) | 0.0030 (13) | 0.0136 (13) | −0.0013 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0459 (13) | 0.0339 (14) | 0.0419 (13) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0057 (11) | 0.0018 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0352 (11) | 0.0378 (15) | 0.0504 (13) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0032 (10) | −0.0008 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0355 (13) | 0.0510 (17) | 0.0730 (17) | 0.0020 (12) | 0.0041 (12) | −0.0052 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0630 (15) | 0.0471 (17) | 0.0484 (14) | −0.0037 (14) | 0.0143 (13) | −0.0049 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0512 (18) | 0.0728 (18) | 0.0032 (13) | 0.0208 (13) | −0.0040 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0481 (16) | 0.0418 (13) | −0.0029 (12) | 0.0012 (11) | 0.0047 (12) |
| C10 | 0.107 (2) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0504 (16) | 0.009 (2) | 0.0051 (17) | −0.0198 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0775 (19) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0533 (17) | 0.0057 (16) | −0.0147 (14) | −0.0148 (15) |
| C9 | 0.089 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0602 (18) | 0.0060 (17) | 0.0270 (15) | −0.0069 (16) |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O3—C2 | 1.329 (3) | N4—C17 | 1.332 (3) |
| O3—H3a | 1.0592 (14) | N4—C18 | 1.344 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.282 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.428 (3) |
| O1—H1a | 1.1628 (13) | C17—C11 | 1.421 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.410 (3) | C19—C18 | 1.423 (3) |
| C1—C7 | 1.487 (3) | C19—C15 | 1.407 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.373 (3) | C8—H8a | 0.93 |
| O7—N2 | 1.219 (2) | C8—C16 | 1.413 (3) |
| C4—H4a | 0.93 | C8—C9 | 1.349 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (3) | C18—C12 | 1.412 (3) |
| C4—C3 | 1.371 (3) | C12—H12a | 0.93 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.347 (3) |
| C5—N2 | 1.459 (3) | C14—H14a | 0.93 |
| O2—C7 | 1.234 (3) | C14—C13 | 1.410 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.404 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.361 (3) |
| C3—N1 | 1.464 (3) | C13—H13a | 0.93 |
| N1—O4 | 1.194 (3) | C15—H15a | 0.93 |
| N1—O5 | 1.204 (3) | C10—H10a | 0.93 |
| C6—H6a | 0.93 | C10—C11 | 1.346 (4) |
| O6—N2 | 1.217 (2) | C10—C9 | 1.400 (4) |
| N3—C19 | 1.346 (3) | C11—H11a | 0.93 |
| N3—C16 | 1.346 (3) | C9—H9a | 0.93 |
| C2—O3—H3a | 105.60 (13) | C16—C17—C11 | 117.8 (2) |
| C7—O1—H1a | 113.94 (15) | N3—C19—C18 | 119.68 (18) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 119.58 (18) | N3—C19—C15 | 120.03 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.63 (17) | C18—C19—C15 | 120.28 (19) |
| C7—C1—C6 | 119.79 (17) | H8a—C8—C16 | 120.23 |
| H4a—C4—C5 | 120.49 | H8a—C8—C9 | 120.23 |
| H4a—C4—C3 | 120.49 | C16—C8—C9 | 119.5 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.01 (18) | N3—C16—C17 | 119.52 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.58 (19) | N3—C16—C8 | 120.61 (17) |
| C4—C5—N2 | 119.83 (17) | C17—C16—C8 | 119.86 (19) |
| C6—C5—N2 | 118.58 (17) | N4—C18—C19 | 121.90 (19) |
| C7—O2—H3a | 102.24 (13) | N4—C18—C12 | 119.74 (18) |
| O3—C2—C1 | 120.09 (17) | C19—C18—C12 | 118.35 (19) |
| O3—C2—C3 | 122.05 (17) | C18—C12—H12a | 119.82 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 117.84 (19) | C18—C12—C13 | 120.35 (19) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.34 (18) | H12a—C12—C13 | 119.82 |
| C4—C3—N1 | 116.79 (18) | H14a—C14—C13 | 119.52 |
| C2—C3—N1 | 121.86 (19) | H14a—C14—C15 | 119.52 |
| C3—N1—O4 | 119.3 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 121.0 (2) |
| C3—N1—O5 | 118.0 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.0 (2) |
| O4—N1—O5 | 122.7 (2) | C12—C13—H13a | 119.52 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 115.30 (19) | C14—C13—H13a | 119.52 |
| O1—C7—O2 | 123.93 (18) | C19—C15—C14 | 119.05 (18) |
| C1—C7—O2 | 120.76 (18) | C19—C15—H15a | 120.48 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.59 (17) | C14—C15—H15a | 120.48 |
| C1—C6—H6a | 120.21 | H10a—C10—C11 | 119.51 |
| C5—C6—H6a | 120.2 | H10a—C10—C9 | 119.51 |
| O7—N2—C5 | 118.45 (16) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.0 (2) |
| O7—N2—O6 | 122.87 (19) | C17—C11—C10 | 120.6 (2) |
| C5—N2—O6 | 118.66 (17) | C17—C11—H11a | 119.71 |
| C19—N3—C16 | 119.31 (15) | C10—C11—H11a | 119.71 |
| C19—N3—H1a | 119.38 (14) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.3 (3) |
| C16—N3—H1a | 120.79 (14) | C8—C9—H9a | 119.37 |
| C17—N4—C18 | 117.41 (17) | C10—C9—H9a | 119.37 |
| N4—C17—C16 | 122.14 (19) | O3—H3a—O2 | 151.72 (10) |
| N4—C17—C11 | 120.09 (19) | O1—H1a—N3 | 163.24 (10) |
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid–phenazine (1/1) (LUDFUL). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C13—H13a···O4i | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.334 (3) | 151 |
| O3—H3a···O2 | 1.0592 (14) | 1.5297 (14) | 2.5132 (19) | 151.72 (10) |
| O1—H1a···N3 | 1.1628 (13) | 1.4160 (14) | 2.5515 (19) | 163.24 (10) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+1.
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Crystal data
| C6H9N2+·C7H3N2O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 336.27 | F(000) = 348 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.569 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.8673 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 5139 reflections |
| b = 8.0991 (9) Å | θ = 2.7–32.4° |
| c = 15.2437 (17) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| α = 86.844 (3)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 84.252 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 81.209 (3)° | 0.29 × 0.14 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 711.69 (14) Å3 |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Data collection
| Bruker APEX DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4943 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3677 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.023 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 32.5°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.963, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −12→11 |
| 12709 measured reflections | l = −22→23 |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.109 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 2.06 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| 4943 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.009 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
| 34 constraints |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Number of fixed parameters: 15 |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| N1 | 0.50355 (15) | 0.28624 (11) | 0.24318 (6) | 0.0153 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.82331 (16) | 0.41649 (12) | 0.19964 (6) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.67739 (18) | 0.36376 (13) | 0.26429 (7) | 0.0152 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.35124 (18) | 0.22197 (14) | 0.30471 (7) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.233313 | 0.167725 | 0.285731 | 0.0198* | |
| C3 | 0.36539 (18) | 0.23424 (14) | 0.39257 (7) | 0.0180 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.54266 (19) | 0.31918 (15) | 0.41642 (7) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.556083 | 0.332079 | 0.477169 | 0.024* | |
| C5 | 0.69461 (19) | 0.38301 (14) | 0.35491 (7) | 0.0186 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.811136 | 0.439959 | 0.372833 | 0.0223* | |
| C6 | 0.2014 (2) | 0.16274 (17) | 0.46143 (8) | 0.0262 (4) | |
| H6a | 0.118019 | 0.252439 | 0.498084 | 0.0394* | |
| H6b | 0.090144 | 0.110743 | 0.432458 | 0.0394* | |
| H6c | 0.289083 | 0.078457 | 0.498608 | 0.0394* | |
| O1 | 0.17284 (13) | 0.61818 (10) | 0.14277 (5) | 0.0201 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.10549 (15) | 0.60964 (11) | 0.31689 (5) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.28472 (15) | 0.76461 (12) | 0.38855 (5) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.93312 (14) | 0.99538 (11) | 0.26216 (6) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.99966 (15) | 1.02486 (11) | 0.11988 (6) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.55543 (14) | 0.76370 (11) | −0.07523 (5) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| O7 | 0.26607 (14) | 0.63258 (10) | −0.01549 (5) | 0.0199 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.25052 (15) | 0.70323 (12) | 0.31961 (6) | 0.0172 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.89095 (16) | 0.97282 (12) | 0.18597 (6) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.33912 (17) | 0.70052 (13) | 0.15501 (7) | 0.0141 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.38900 (17) | 0.74506 (13) | 0.23906 (7) | 0.0144 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.56997 (17) | 0.83259 (13) | 0.24874 (7) | 0.0156 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.601439 | 0.859704 | 0.305724 | 0.0187* | |
| C10 | 0.70326 (17) | 0.87968 (13) | 0.17493 (7) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.66121 (18) | 0.84357 (13) | 0.09021 (7) | 0.0157 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.753695 | 0.879143 | 0.040052 | 0.0188* | |
| C12 | 0.48279 (17) | 0.75522 (13) | 0.08058 (7) | 0.0139 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.43623 (18) | 0.71649 (13) | −0.01006 (7) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| H1o7 | 0.20768 | 0.615457 | 0.041923 | 0.044 (6)* | 0.62 (3) |
| H1o1 | 0.186813 | 0.613081 | 0.081569 | 0.044 (6)* | 0.38 (3) |
| H2a | 0.809476 | 0.397973 | 0.143402 | 0.035 (4)* | |
| H2b | 0.928572 | 0.469891 | 0.211657 | 0.048 (5)* | |
| H1 | 0.481117 | 0.276133 | 0.186443 | 0.032 (4)* |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0168 (5) | 0.0130 (4) | −0.0032 (3) | −0.0023 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0147 (4) | −0.0085 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0166 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0152 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0022 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0142 (5) | 0.0162 (5) | 0.0192 (5) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0015 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0168 (5) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0239 (6) | 0.0127 (5) | −0.0043 (5) | −0.0035 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0201 (6) | 0.0169 (5) | −0.0054 (4) | −0.0041 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0219 (6) | −0.0077 (5) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0047 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0192 (4) | 0.0259 (4) | 0.0176 (4) | −0.0108 (3) | −0.0027 (3) | −0.0010 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0275 (4) | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0220 (4) | −0.0141 (4) | 0.0034 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0290 (5) | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0120 (4) | −0.0097 (4) | −0.0019 (3) | −0.0062 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0215 (4) | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0302 (5) | −0.0036 (3) | −0.0110 (3) | −0.0066 (4) |
| O5 | 0.0227 (4) | 0.0276 (5) | 0.0354 (5) | −0.0122 (4) | −0.0009 (3) | 0.0022 (4) |
| O6 | 0.0280 (4) | 0.0278 (5) | 0.0128 (4) | −0.0102 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | −0.0006 (3) |
| O7 | 0.0229 (4) | 0.0252 (4) | 0.0139 (4) | −0.0096 (3) | −0.0034 (3) | −0.0010 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0145 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0002 (4) |
| N4 | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0275 (5) | −0.0027 (4) | −0.0051 (4) | −0.0025 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0150 (5) | −0.0010 (4) | −0.0022 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0145 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0156 (5) | 0.0169 (5) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0038 (4) | −0.0031 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0210 (5) | −0.0030 (4) | −0.0035 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0148 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0179 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | −0.0007 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | −0.0020 (4) | −0.0018 (4) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | −0.0021 (4) | −0.0026 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—C1 | 1.3498 (15) | O1—H1o1 | 0.9310 (8) |
| N1—C2 | 1.3674 (14) | O2—N3 | 1.2280 (14) |
| N1—H1 | 0.8977 (9) | O3—N3 | 1.2338 (13) |
| N2—C1 | 1.3353 (14) | O4—N4 | 1.2402 (14) |
| N2—H2a | 0.8921 (9) | O5—N4 | 1.2273 (13) |
| N2—H2b | 0.8456 (10) | O6—C13 | 1.2340 (13) |
| C1—C5 | 1.4139 (15) | O7—C13 | 1.3022 (15) |
| C2—H2 | 0.95 | O7—H1o7 | 0.9185 (8) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3602 (16) | N3—C8 | 1.4564 (13) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4174 (17) | N4—C10 | 1.4544 (15) |
| C3—C6 | 1.5049 (16) | C7—C8 | 1.4197 (15) |
| C4—H4 | 0.95 | C7—C12 | 1.4357 (14) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3643 (16) | C8—C9 | 1.3874 (16) |
| C5—H5 | 0.95 | C9—H9 | 0.95 |
| C6—H6a | 0.98 | C9—C10 | 1.3750 (15) |
| C6—H6b | 0.98 | C10—C11 | 1.3934 (16) |
| C6—H6c | 0.98 | C11—H11 | 0.95 |
| H6a—H6b | 1.6003 | C11—C12 | 1.3787 (16) |
| H6a—H6c | 1.6003 | C12—C13 | 1.4939 (15) |
| H6b—H6c | 1.6003 | H2a—H2b | 1.4990 (2) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2964 (14) | ||
| C1—N1—C2 | 123.29 (9) | O2—N3—O3 | 122.52 (9) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 120.41 (9) | O2—N3—C8 | 119.61 (9) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 116.29 (10) | O3—N3—C8 | 117.87 (10) |
| C1—N2—H2a | 120.74 (11) | O4—N4—O5 | 123.30 (10) |
| C1—N2—H2b | 120.05 (10) | O4—N4—C10 | 118.02 (9) |
| H2a—N2—H2b | 119.20 (10) | O5—N4—C10 | 118.69 (10) |
| N1—C1—N2 | 118.98 (10) | O1—C7—C8 | 124.03 (9) |
| N1—C1—C5 | 117.27 (9) | O1—C7—C12 | 119.84 (10) |
| N2—C1—C5 | 123.75 (11) | C8—C7—C12 | 116.12 (10) |
| N1—C2—H2 | 119.38 | N3—C8—C7 | 121.67 (10) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.25 (11) | N3—C8—C9 | 116.48 (9) |
| H2—C2—C3 | 119.38 | C7—C8—C9 | 121.84 (9) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.54 (10) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.37 |
| C2—C3—C6 | 122.15 (11) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.26 (10) |
| C4—C3—C6 | 121.31 (10) | H9—C9—C10 | 120.37 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 118.95 | N4—C10—C9 | 118.68 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.10 (10) | N4—C10—C11 | 119.25 (9) |
| H4—C4—C5 | 118.95 | C9—C10—C11 | 122.05 (10) |
| C1—C5—C4 | 119.51 (11) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.64 |
| C1—C5—H5 | 120.24 | C10—C11—C12 | 118.72 (9) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.24 | H11—C11—C12 | 120.64 |
| C3—C6—H6a | 109.47 | C7—C12—C11 | 121.98 (10) |
| C3—C6—H6b | 109.47 | C7—C12—C13 | 119.00 (10) |
| C3—C6—H6c | 109.47 | C11—C12—C13 | 119.02 (9) |
| H6a—C6—H6b | 109.47 | O6—C13—O7 | 123.12 (10) |
| H6a—C6—H6c | 109.47 | O6—C13—C12 | 120.31 (10) |
| H6b—C6—H6c | 109.47 | O7—C13—C12 | 116.57 (9) |
| C7—O1—H1o7 | 98.33 (6) | O1—H1o7—O7 | 161.55 (6) |
| C7—O1—H1o1 | 101.65 (8) | O7—H1o7—H1o1 | 166.67 (6) |
| C13—O7—H1o7 | 104.71 (9) | O1—H1o1—O7 | 163.52 (6) |
| C13—O7—H1o1 | 99.43 (7) | O1—H1o1—H1o7 | 171.56 (5) |
2-Amino-5-methylpyridinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (NUQVEB). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O4i | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.4107 (16) | 169 |
| C4—H4···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.38 | 3.2397 (15) | 151 |
| C5—H5···O2iii | 0.95 | 2.43 | 3.2361 (16) | 143 |
| O7—H1o7···O1 | 0.9185 (8) | 1.5313 (8) | 2.4202 (12) | 161.55 (6) |
| O1—H1o1···O7 | 0.9310 (8) | 1.5130 (8) | 2.4202 (12) | 163.52 (6) |
| N2—H2a···O7iv | 0.8921 (9) | 2.0783 (9) | 2.9655 (14) | 172.84 (6) |
| N2—H2b···O1iii | 0.8456 (10) | 2.1644 (9) | 2.8526 (14) | 138.40 (6) |
| N2—H2b···O2iii | 0.8456 (10) | 2.4133 (10) | 3.1741 (14) | 150.02 (6) |
| N1—H1···O6iv | 0.8977 (9) | 1.7828 (9) | 2.6781 (13) | 174.83 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y−1, z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Crystal data
| C9H8Cl2N5+·C7H3N2O7−·C3H7NO | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 557.31 | F(000) = 572 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.564 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.0227 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 6413 reflections |
| b = 10.5507 (5) Å | θ = 2.3–28.2° |
| c = 12.5359 (6) Å | µ = 0.34 mm−1 |
| α = 81.858 (1)° | T = 294 K |
| β = 71.888 (1)° | Plate, colourless |
| γ = 70.009 (1)° | 0.16 × 0.14 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 1183.1 (1) Å3 |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 5507 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4441 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.019 |
| ω scans | θmax = 28.0°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | h = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.93, Tmax = 0.97 | k = −13→13 |
| 13936 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.056 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.147 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| S = 3.41 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| 5507 reflections | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| 340 parameters | (Δ/σ)max = 0.020 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmax = 0.80 e Å−3 |
| 48 constraints | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Number of fixed parameters: 18 |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.32107 (18) | 1.06764 (19) | 0.15844 (16) | 0.0464 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.2718 (2) | 1.0232 (2) | 0.08378 (15) | 0.0485 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.2713 (2) | 1.0903 (2) | −0.02046 (16) | 0.0529 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.3231 (2) | 1.2001 (2) | −0.04951 (19) | 0.0621 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.323127 | 1.245173 | −0.11886 | 0.0745* | |
| C5 | 0.3741 (2) | 1.2420 (2) | 0.02358 (19) | 0.0632 (10) | |
| H5 | 0.410127 | 1.314857 | 0.001937 | 0.0758* | |
| C6 | 0.3745 (2) | 1.1807 (2) | 0.12857 (17) | 0.0537 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.40816 | 1.211924 | 0.177727 | 0.0645* | |
| C7 | 0.32753 (18) | 0.99894 (19) | 0.26974 (15) | 0.0437 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.35068 (19) | 0.8912 (2) | 0.47363 (15) | 0.0449 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.19780 (18) | 0.99408 (18) | 0.36291 (15) | 0.0418 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.45735 (16) | 0.95248 (17) | 0.28531 (13) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.46755 (16) | 0.89842 (17) | 0.38722 (13) | 0.0484 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.37354 (18) | 0.8352 (2) | 0.56859 (14) | 0.0613 (8) | |
| N4 | 0.21299 (15) | 0.93978 (16) | 0.46191 (12) | 0.0454 (6) | |
| N5 | 0.06397 (16) | 1.04599 (17) | 0.35102 (13) | 0.0504 (7) | |
| Cl1 | 0.21444 (7) | 0.88366 (6) | 0.11855 (5) | 0.0685 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.20368 (7) | 1.04039 (8) | −0.11161 (5) | 0.0772 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.7671 (2) | 0.7509 (2) | 0.50260 (17) | 0.0495 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.92521 (19) | 0.68875 (18) | 0.50532 (16) | 0.0456 (8) | |
| C12 | 1.0399 (2) | 0.68056 (19) | 0.40501 (17) | 0.0482 (8) | |
| C13 | 1.1855 (2) | 0.6217 (2) | 0.4120 (2) | 0.0565 (9) | |
| C14 | 1.2169 (3) | 0.5728 (2) | 0.5120 (2) | 0.0650 (11) | |
| H14 | 1.31429 | 0.535992 | 0.515021 | 0.078* | |
| C15 | 1.1014 (3) | 0.5795 (2) | 0.6070 (2) | 0.0608 (10) | |
| C16 | 0.9560 (2) | 0.63637 (19) | 0.60559 (18) | 0.0537 (9) | |
| H16 | 0.879592 | 0.639442 | 0.671313 | 0.0645* | |
| N6 | 1.3082 (2) | 0.6096 (2) | 0.3083 (2) | 0.0763 (10) | |
| N7 | 1.1324 (3) | 0.5213 (2) | 0.7146 (3) | 0.0870 (14) | |
| O1 | 0.74835 (14) | 0.79734 (16) | 0.40757 (12) | 0.0638 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.66684 (16) | 0.75284 (17) | 0.58991 (13) | 0.0695 (7) | |
| O3 | 1.01381 (16) | 0.72881 (16) | 0.30779 (13) | 0.0651 (7) | |
| O4 | 1.3027 (2) | 0.5624 (2) | 0.22939 (18) | 0.0962 (10) | |
| O5 | 1.4096 (2) | 0.6460 (3) | 0.3106 (2) | 0.1311 (14) | |
| O6 | 1.2621 (3) | 0.4654 (3) | 0.7114 (2) | 0.1272 (14) | |
| O7 | 1.0297 (3) | 0.5356 (3) | 0.7980 (2) | 0.1153 (15) | |
| C17 | 0.8968 (2) | 0.2419 (2) | 0.13898 (19) | 0.0638 (10) | |
| H17 | 0.997049 | 0.225753 | 0.10284 | 0.0765* | |
| C18 | 0.6486 (3) | 0.3564 (4) | 0.1366 (3) | 0.1002 (16) | |
| H18a | 0.600566 | 0.362237 | 0.079827 | 0.1503* | |
| H18b | 0.612084 | 0.441665 | 0.171497 | 0.1503* | |
| H18c | 0.628154 | 0.287766 | 0.192178 | 0.1503* | |
| C19 | 0.8613 (4) | 0.3905 (3) | −0.0204 (2) | 0.0959 (16) | |
| H19a | 0.812684 | 0.38463 | −0.07367 | 0.1439* | |
| H19b | 0.842404 | 0.483699 | −0.008394 | 0.1439* | |
| H19c | 0.965894 | 0.347377 | −0.048929 | 0.1439* | |
| N8 | 0.8043 (2) | 0.32305 (17) | 0.08649 (14) | 0.0588 (8) | |
| O8 | 0.86513 (17) | 0.18476 (18) | 0.23111 (12) | 0.0693 (7) | |
| H3n | 0.459992 | 0.808642 | 0.579383 | 0.067 (7)* | |
| H4n | 0.300684 | 0.831649 | 0.62665 | 0.058 (6)* | |
| H2n | 0.560448 | 0.867423 | 0.392878 | 0.069 (7)* | |
| H5n | −0.01125 | 1.040769 | 0.406749 | 0.056 (6)* | |
| H6n | 0.043449 | 1.086703 | 0.2906 | 0.052 (6)* | |
| H3o | 0.911378 | 0.756483 | 0.330791 | 0.131 (12)* |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0541 (11) | 0.0483 (10) | −0.0081 (8) | −0.0060 (7) | −0.0055 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0578 (11) | 0.0464 (10) | −0.0118 (8) | −0.0044 (8) | −0.0068 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0364 (9) | 0.0682 (13) | 0.0443 (10) | −0.0090 (9) | −0.0049 (8) | −0.0047 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0457 (11) | 0.0737 (15) | 0.0546 (12) | −0.0053 (10) | −0.0119 (9) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0580 (13) | 0.0599 (13) | 0.0701 (14) | −0.0224 (11) | −0.0153 (11) | 0.0054 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0589 (12) | 0.0502 (11) | −0.0107 (9) | −0.0112 (9) | 0.0032 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0527 (11) | 0.0433 (10) | −0.0115 (8) | −0.0076 (7) | −0.0053 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0316 (8) | 0.0564 (11) | 0.0446 (10) | −0.0113 (8) | −0.0096 (7) | −0.0050 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0502 (10) | 0.0430 (9) | −0.0112 (7) | −0.0074 (7) | −0.0072 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0622 (10) | 0.0469 (9) | −0.0126 (7) | −0.0079 (6) | −0.0007 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0679 (10) | 0.0450 (9) | −0.0113 (7) | −0.0098 (6) | −0.0005 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0343 (8) | 0.0949 (14) | 0.0468 (9) | −0.0152 (9) | −0.0110 (7) | 0.0078 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0618 (10) | 0.0417 (8) | −0.0119 (7) | −0.0077 (6) | −0.0027 (7) |
| N5 | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0730 (11) | 0.0421 (9) | −0.0106 (7) | −0.0102 (7) | −0.0001 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.0784 (4) | 0.0786 (4) | 0.0600 (3) | −0.0419 (3) | −0.0150 (3) | −0.0059 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.0721 (4) | 0.1162 (5) | 0.0522 (3) | −0.0373 (4) | −0.0190 (3) | −0.0090 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0386 (10) | 0.0504 (11) | 0.0597 (12) | −0.0073 (8) | −0.0180 (9) | −0.0107 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0404 (10) | 0.0417 (10) | 0.0597 (12) | −0.0103 (8) | −0.0219 (9) | −0.0067 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0395 (10) | 0.0464 (10) | 0.0641 (12) | −0.0136 (8) | −0.0218 (9) | −0.0030 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0512 (11) | 0.0826 (15) | −0.0101 (8) | −0.0220 (10) | −0.0101 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0504 (12) | 0.0533 (12) | 0.1065 (19) | −0.0093 (10) | −0.0465 (13) | −0.0135 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0692 (15) | 0.0506 (12) | 0.0797 (15) | −0.0144 (10) | −0.0492 (13) | −0.0036 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0578 (12) | 0.0501 (11) | 0.0625 (13) | −0.0162 (9) | −0.0287 (10) | −0.0069 (9) |
| N6 | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0779 (14) | 0.1062 (18) | −0.0082 (9) | −0.0156 (10) | −0.0157 (12) |
| N7 | 0.113 (2) | 0.0759 (15) | 0.1066 (19) | −0.0325 (14) | −0.0800 (17) | 0.0073 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0374 (7) | 0.0841 (11) | 0.0645 (9) | −0.0093 (7) | −0.0222 (7) | 0.0067 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0428 (8) | 0.0946 (12) | 0.0601 (9) | −0.0074 (8) | −0.0121 (7) | −0.0108 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0427 (8) | 0.0802 (10) | 0.0653 (9) | −0.0151 (7) | −0.0148 (7) | 0.0074 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0575 (10) | 0.1277 (17) | 0.0882 (13) | −0.0110 (11) | −0.0135 (9) | −0.0195 (12) |
| O5 | 0.0520 (11) | 0.164 (2) | 0.181 (2) | −0.0480 (13) | 0.0026 (13) | −0.0623 (18) |
| O6 | 0.1283 (19) | 0.1273 (18) | 0.142 (2) | 0.0037 (15) | −0.1080 (17) | −0.0100 (15) |
| O7 | 0.142 (2) | 0.159 (2) | 0.0879 (15) | −0.0849 (19) | −0.0675 (16) | 0.0370 (15) |
| C17 | 0.0454 (11) | 0.0753 (15) | 0.0575 (13) | −0.0065 (10) | −0.0078 (10) | −0.0085 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0568 (15) | 0.129 (3) | 0.120 (2) | −0.0180 (16) | −0.0417 (16) | −0.009 (2) |
| C19 | 0.123 (3) | 0.0831 (19) | 0.0697 (17) | −0.0251 (18) | −0.0261 (16) | 0.0120 (14) |
| N8 | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0601 (11) | 0.0548 (10) | −0.0096 (9) | −0.0229 (9) | −0.0033 (8) |
| O8 | 0.0558 (9) | 0.0937 (12) | 0.0520 (9) | −0.0195 (8) | −0.0165 (7) | 0.0097 (8) |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.374 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.427 (3) | C13—N6 | 1.471 (3) |
| C1—C7 | 1.488 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.396 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.369 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.385 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.378 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.93 | C15—N7 | 1.479 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.362 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.93 |
| C5—H5 | 0.93 | N6—O4 | 1.192 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (3) | N6—O5 | 1.213 (4) |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | N7—O6 | 1.221 (4) |
| C7—C9 | 1.464 (2) | N7—O7 | 1.202 (4) |
| C7—N1 | 1.291 (2) | O3—H3o | 0.9258 (14) |
| C8—N2 | 1.342 (2) | C17—H17 | 0.93 |
| C8—N3 | 1.303 (3) | C17—N8 | 1.305 (3) |
| C8—N4 | 1.345 (2) | C17—O8 | 1.226 (3) |
| C9—N4 | 1.322 (2) | C18—H18a | 0.96 |
| C9—N5 | 1.312 (2) | C18—H18b | 0.96 |
| N1—N2 | 1.343 (2) | C18—H18c | 0.96 |
| N2—H2n | 0.8973 (16) | C18—N8 | 1.425 (3) |
| N3—H3n | 0.8624 (18) | H18a—H18b | 1.5677 |
| N3—H4n | 0.8630 (15) | H18a—H18c | 1.5677 |
| N5—H5n | 0.8658 (14) | H18b—H18c | 1.5677 |
| N5—H6n | 0.8630 (16) | C19—H19a | 0.96 |
| C10—C11 | 1.503 (3) | C19—H19b | 0.96 |
| C10—O1 | 1.267 (3) | C19—H19c | 0.96 |
| C10—O2 | 1.231 (2) | C19—N8 | 1.470 (3) |
| C11—C12 | 1.405 (2) | H19a—H19b | 1.5677 |
| C11—C16 | 1.382 (3) | H19a—H19c | 1.5677 |
| C12—C13 | 1.402 (3) | H19b—H19c | 1.5677 |
| C12—O3 | 1.321 (3) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.20 (18) | C11—C12—O3 | 122.09 (17) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.86 (19) | C13—C12—O3 | 120.57 (17) |
| C6—C1—C7 | 116.9 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 122.17 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.2 (2) | C12—C13—N6 | 118.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.6 (2) | C14—C13—N6 | 119.10 (19) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.02 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.79 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.0 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.4 (2) |
| H4—C4—C5 | 120.02 | H14—C14—C15 | 120.79 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.63 | C14—C15—C16 | 122.1 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.7 (2) | C14—C15—N7 | 119.4 (2) |
| H5—C5—C6 | 118.63 | C16—C15—N7 | 118.5 (2) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 117.3 (2) | C11—C16—C15 | 119.19 (18) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 121.37 | C11—C16—H16 | 120.41 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.36 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.41 |
| C1—C7—C9 | 124.50 (16) | C13—N6—O4 | 118.2 (2) |
| C1—C7—N1 | 115.60 (15) | C13—N6—O5 | 117.0 (3) |
| C9—C7—N1 | 119.58 (16) | O4—N6—O5 | 124.8 (2) |
| N2—C8—N3 | 118.61 (17) | C15—N7—O6 | 116.6 (2) |
| N2—C8—N4 | 120.57 (17) | C15—N7—O7 | 118.1 (3) |
| N3—C8—N4 | 120.81 (16) | O6—N7—O7 | 125.3 (3) |
| C7—C9—N4 | 120.53 (16) | C10—O1—H3o | 101.27 (12) |
| C7—C9—N5 | 120.93 (16) | C12—O3—H3o | 99.28 (14) |
| N4—C9—N5 | 118.52 (15) | H17—C17—N8 | 116.69 |
| C7—N1—N2 | 117.85 (14) | H17—C17—O8 | 116.69 |
| C8—N2—N1 | 123.77 (16) | N8—C17—O8 | 126.6 (2) |
| C8—N2—H2n | 122.42 (17) | H18a—C18—H18b | 109.47 |
| N1—N2—H2n | 113.82 (14) | H18a—C18—H18c | 109.47 |
| C8—N3—H3n | 122.28 (17) | H18a—C18—N8 | 109.47 |
| C8—N3—H4n | 121.07 (18) | H18b—C18—H18c | 109.47 |
| H3n—N3—H4n | 116.2 (2) | H18b—C18—N8 | 109.47 |
| C8—N4—C9 | 117.69 (14) | H18c—C18—N8 | 109.47 |
| C9—N5—H5n | 119.55 (17) | H19a—C19—H19b | 109.47 |
| C9—N5—H6n | 124.81 (16) | H19a—C19—H19c | 109.47 |
| H5n—N5—H6n | 115.64 (18) | H19a—C19—N8 | 109.47 |
| C11—C10—O1 | 115.76 (15) | H19b—C19—H19c | 109.47 |
| C11—C10—O2 | 119.27 (19) | H19b—C19—N8 | 109.47 |
| O1—C10—O2 | 124.96 (19) | H19c—C19—N8 | 109.47 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.51 (18) | C17—N8—C18 | 120.7 (2) |
| C10—C11—C16 | 119.71 (16) | C17—N8—C19 | 119.5 (2) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 120.74 (18) | C18—N8—C19 | 119.6 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 117.3 (2) | O1—H3o—O3 | 161.33 (12) |
3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazin-2-ium 3,5-dinitro-2-hydroxybenzoate N,N-dimethylformamide monosolvate (QIQJAD) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C19—H19a···O4i | 0.96 | 2.47 | 3.401 (4) | 163 |
| N3—H3n···O2 | 0.8624 (18) | 1.9939 (16) | 2.854 (2) | 174.78 (11) |
| N3—H4n···O8ii | 0.8630 (15) | 2.0586 (14) | 2.921 (2) | 176.91 (12) |
| N2—H2n···O1 | 0.8973 (16) | 1.8310 (15) | 2.728 (2) | 177.45 (12) |
| N5—H5n···N4iii | 0.8658 (14) | 2.1409 (13) | 2.9992 (19) | 171.06 (11) |
| N5—H6n···O8iv | 0.8630 (16) | 2.0412 (16) | 2.760 (2) | 140.22 (10) |
| O3—H3o···O1 | 0.9258 (14) | 1.5621 (12) | 2.4572 (18) | 161.33 (12) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (iv) x−1, y+1, z.
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Crystal data
| [Ag(C12H6N2O2)](C7H3N2O7) | F(000) = 1512 |
| Mr = 755.36 | Dx = 1.817 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 5197 reflections |
| a = 11.757 (2) Å | θ = 3.2–25.4° |
| b = 18.297 (4) Å | µ = 0.81 mm−1 |
| c = 13.223 (3) Å | T = 174 K |
| β = 103.91 (3)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 2761.1 (11) Å3 | 0.3 × 0.24 × 0.2 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra diffractometer | 5013 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3100 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.052 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −14→11 |
| Tmin = 0.780, Tmax = 0.910 | k = −17→22 |
| 12726 measured reflections | l = −15→13 |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.062 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F) = 0.118 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| S = 1.64 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.016 |
| 5013 reflections | Δρmax = 0.76 e Å−3 |
| 444 parameters | Δρmin = −0.63 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 56 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 2400 (800) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Number of fixed parameters 3 |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ag1 | 0.21070 (4) | 0.44031 (3) | 0.52479 (4) | 0.0538 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.4796 (5) | 0.5138 (3) | 0.6221 (4) | 0.043 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.440696 | 0.558209 | 0.60689 | 0.0511* | |
| C2 | 0.5975 (6) | 0.5153 (3) | 0.6692 (4) | 0.046 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.637009 | 0.559483 | 0.684873 | 0.0553* | |
| C3 | 0.6551 (5) | 0.4500 (3) | 0.6925 (4) | 0.046 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.734391 | 0.449118 | 0.725729 | 0.0547* | |
| C4 | 0.5946 (5) | 0.3859 (3) | 0.6661 (4) | 0.035 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.6523 (8) | 0.3141 (4) | 0.6884 (5) | 0.068 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.5912 (10) | 0.2510 (4) | 0.6718 (6) | 0.093 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.4628 (6) | 0.2534 (3) | 0.6228 (4) | 0.042 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.3994 (7) | 0.1881 (3) | 0.6033 (4) | 0.052 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.435089 | 0.143184 | 0.6224 | 0.0623* | |
| C9 | 0.2837 (7) | 0.1928 (4) | 0.5555 (5) | 0.063 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.238665 | 0.150616 | 0.540161 | 0.0756* | |
| C10 | 0.2345 (6) | 0.2592 (3) | 0.5304 (5) | 0.052 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.155582 | 0.26107 | 0.496188 | 0.0629* | |
| C11 | 0.4065 (5) | 0.3197 (3) | 0.5966 (4) | 0.032 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.4742 (5) | 0.3885 (3) | 0.6197 (4) | 0.033 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.0851 (5) | 0.4150 (3) | 0.2774 (5) | 0.054 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.109147 | 0.367048 | 0.293174 | 0.0649* | |
| C14 | 0.0376 (5) | 0.4324 (4) | 0.1743 (5) | 0.060 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.029151 | 0.397085 | 0.122358 | 0.0717* | |
| C15 | 0.0032 (5) | 0.5033 (3) | 0.1508 (5) | 0.051 (3) | |
| H15 | −0.030371 | 0.516779 | 0.082274 | 0.0617* | |
| C16 | 0.0190 (5) | 0.5550 (3) | 0.2306 (4) | 0.040 (2) | |
| C17 | −0.0145 (5) | 0.6317 (3) | 0.2063 (5) | 0.051 (3) | |
| C18 | −0.0094 (5) | 0.6826 (3) | 0.2940 (5) | 0.053 (3) | |
| C19 | 0.0474 (5) | 0.6578 (3) | 0.4023 (5) | 0.042 (2) | |
| C20 | 0.0689 (5) | 0.7058 (3) | 0.4858 (5) | 0.052 (3) | |
| H20 | 0.048099 | 0.754726 | 0.475014 | 0.063* | |
| C21 | 0.1204 (6) | 0.6817 (4) | 0.5833 (5) | 0.058 (3) | |
| H21 | 0.134626 | 0.713123 | 0.64029 | 0.0692* | |
| C22 | 0.1503 (5) | 0.6091 (4) | 0.5941 (5) | 0.054 (3) | |
| H22 | 0.186352 | 0.59254 | 0.660553 | 0.0653* | |
| C23 | 0.0818 (5) | 0.5847 (3) | 0.4195 (4) | 0.036 (2) | |
| C24 | 0.0637 (4) | 0.5318 (3) | 0.3326 (4) | 0.032 (2) | |
| C25 | 0.6150 (6) | 0.4142 (3) | 0.9276 (4) | 0.041 (2) | |
| C26 | 0.5079 (6) | 0.4527 (3) | 0.8869 (4) | 0.040 (2) | |
| C27 | 0.4074 (5) | 0.4101 (3) | 0.8426 (4) | 0.037 (2) | |
| C28 | 0.4091 (5) | 0.3351 (3) | 0.8456 (4) | 0.041 (2) | |
| H28 | 0.341998 | 0.308064 | 0.817616 | 0.0498* | |
| C29 | 0.5156 (6) | 0.3004 (3) | 0.8924 (4) | 0.041 (2) | |
| C30 | 0.6177 (5) | 0.3387 (3) | 0.9323 (4) | 0.043 (2) | |
| H30 | 0.687051 | 0.314123 | 0.961804 | 0.0515* | |
| C31 | 0.2956 (6) | 0.4467 (4) | 0.7881 (5) | 0.047 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.4179 (4) | 0.4525 (2) | 0.5968 (3) | 0.0338 (17) | |
| N2 | 0.2929 (4) | 0.3229 (2) | 0.5519 (3) | 0.0387 (18) | |
| N3 | 0.0989 (4) | 0.4627 (2) | 0.3563 (3) | 0.0413 (18) | |
| N4 | 0.1317 (4) | 0.5603 (2) | 0.5163 (3) | 0.0405 (18) | |
| N5 | 0.7267 (6) | 0.4510 (4) | 0.9628 (4) | 0.059 (3) | |
| N6 | 0.5168 (6) | 0.2209 (3) | 0.9002 (4) | 0.055 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.7646 (5) | 0.3117 (3) | 0.7273 (4) | 0.092 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.6406 (5) | 0.1892 (3) | 0.6987 (4) | 0.102 (3) | |
| O3 | −0.0421 (4) | 0.6544 (2) | 0.1169 (3) | 0.069 (2) | |
| O4 | −0.0501 (5) | 0.7444 (2) | 0.2776 (4) | 0.081 (2) | |
| O5 | 0.8168 (5) | 0.4145 (3) | 0.9750 (4) | 0.090 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.7298 (5) | 0.5169 (3) | 0.9762 (4) | 0.084 (2) | |
| O7 | 0.5025 (4) | 0.5233 (2) | 0.8850 (3) | 0.0617 (19) | |
| O8 | 0.2936 (4) | 0.5168 (3) | 0.7945 (3) | 0.066 (2) | |
| O9 | 0.2137 (4) | 0.4111 (3) | 0.7370 (3) | 0.064 (2) | |
| O10 | 0.4286 (5) | 0.1877 (2) | 0.8580 (4) | 0.070 (2) | |
| O11 | 0.6096 (5) | 0.1916 (2) | 0.9512 (4) | 0.068 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.388884 | 0.531747 | 0.83591 | 0.019 (12)* |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ag1 | 0.0474 (4) | 0.0492 (3) | 0.0603 (3) | 0.0150 (3) | 0.0038 (2) | 0.0149 (3) |
| C1 | 0.054 (5) | 0.035 (4) | 0.041 (3) | −0.006 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C2 | 0.052 (5) | 0.041 (4) | 0.048 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C3 | 0.031 (4) | 0.063 (4) | 0.043 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.008 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C4 | 0.036 (4) | 0.034 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| C5 | 0.085 (7) | 0.078 (6) | 0.048 (4) | 0.014 (5) | 0.031 (4) | 0.006 (4) |
| C6 | 0.201 (12) | 0.037 (5) | 0.065 (5) | 0.012 (6) | 0.081 (7) | 0.001 (4) |
| C7 | 0.033 (4) | 0.059 (5) | 0.035 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C8 | 0.088 (6) | 0.023 (3) | 0.051 (4) | 0.010 (4) | 0.029 (4) | 0.005 (3) |
| C9 | 0.074 (6) | 0.053 (5) | 0.067 (5) | −0.009 (4) | 0.025 (4) | −0.008 (4) |
| C10 | 0.039 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.064 (4) | −0.003 (4) | 0.012 (3) | −0.014 (4) |
| C11 | 0.043 (4) | 0.026 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.010 (3) | 0.002 (2) |
| C12 | 0.043 (4) | 0.031 (3) | 0.028 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.002 (2) |
| C13 | 0.052 (5) | 0.034 (4) | 0.071 (5) | −0.002 (3) | 0.005 (4) | −0.001 (3) |
| C14 | 0.055 (5) | 0.055 (5) | 0.064 (4) | 0.000 (4) | 0.003 (4) | −0.024 (4) |
| C15 | 0.046 (4) | 0.057 (4) | 0.045 (4) | −0.004 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C16 | 0.029 (3) | 0.038 (3) | 0.051 (4) | 0.000 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C17 | 0.039 (4) | 0.054 (4) | 0.055 (4) | 0.002 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.021 (4) |
| C18 | 0.036 (4) | 0.042 (4) | 0.077 (5) | −0.003 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.005 (4) |
| C19 | 0.035 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.057 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C20 | 0.046 (4) | 0.031 (3) | 0.079 (5) | 0.000 (3) | 0.012 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
| C21 | 0.049 (5) | 0.055 (5) | 0.067 (5) | 0.002 (4) | 0.010 (4) | −0.013 (4) |
| C22 | 0.046 (4) | 0.070 (5) | 0.042 (4) | −0.003 (4) | 0.001 (3) | −0.006 (4) |
| C23 | 0.027 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C24 | 0.019 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.046 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C25 | 0.058 (5) | 0.037 (4) | 0.028 (3) | −0.010 (3) | 0.010 (3) | −0.004 (3) |
| C26 | 0.062 (5) | 0.032 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C27 | 0.039 (4) | 0.038 (4) | 0.035 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C28 | 0.057 (5) | 0.041 (4) | 0.030 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C29 | 0.068 (5) | 0.029 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C30 | 0.047 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.036 (3) | 0.005 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C31 | 0.057 (5) | 0.041 (4) | 0.048 (4) | 0.011 (4) | 0.023 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| N1 | 0.036 (3) | 0.031 (3) | 0.033 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| N2 | 0.033 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.044 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| N3 | 0.040 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.003 (2) |
| N4 | 0.035 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| N5 | 0.057 (4) | 0.072 (5) | 0.044 (3) | −0.015 (4) | 0.003 (3) | −0.009 (3) |
| N6 | 0.090 (5) | 0.039 (4) | 0.044 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.004 (3) |
| O1 | 0.083 (4) | 0.104 (4) | 0.088 (4) | 0.034 (4) | 0.022 (3) | 0.021 (3) |
| O2 | 0.095 (5) | 0.085 (4) | 0.115 (5) | 0.014 (4) | 0.002 (4) | −0.007 (4) |
| O3 | 0.066 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.026 (3) |
| O4 | 0.101 (4) | 0.040 (3) | 0.095 (4) | 0.019 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| O5 | 0.052 (4) | 0.100 (4) | 0.111 (4) | −0.002 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.031 (3) |
| O6 | 0.091 (4) | 0.051 (3) | 0.090 (4) | −0.024 (3) | −0.015 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| O7 | 0.088 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.057 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.021 (3) | −0.002 (2) |
| O8 | 0.069 (4) | 0.060 (3) | 0.072 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.009 (2) |
| O9 | 0.042 (3) | 0.084 (4) | 0.066 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.012 (2) | −0.002 (3) |
| O10 | 0.107 (5) | 0.039 (3) | 0.067 (3) | −0.016 (3) | 0.025 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| O11 | 0.089 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.081 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.036 (3) | 0.022 (2) |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ag1—N1 | 2.404 (4) | C16—C24 | 1.392 (7) |
| Ag1—N2 | 2.348 (5) | C17—C18 | 1.476 (9) |
| Ag1—N3 | 2.335 (4) | C17—O3 | 1.220 (8) |
| Ag1—N4 | 2.376 (5) | C18—C19 | 1.498 (8) |
| C1—H1 | 0.93 | C18—O4 | 1.227 (8) |
| C1—C2 | 1.376 (8) | C19—C20 | 1.386 (8) |
| C1—N1 | 1.334 (7) | C19—C23 | 1.400 (8) |
| C2—H2 | 0.93 | C20—H20 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.373 (8) | C20—C21 | 1.359 (9) |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C21—H21 | 0.93 |
| C3—C4 | 1.372 (8) | C21—C22 | 1.373 (9) |
| C4—C5 | 1.475 (10) | C22—H22 | 0.93 |
| C4—C12 | 1.402 (8) | C22—N4 | 1.341 (8) |
| C5—C6 | 1.349 (12) | C23—C24 | 1.478 (7) |
| C5—O1 | 1.298 (10) | C23—N4 | 1.349 (7) |
| C6—C7 | 1.493 (13) | C24—N3 | 1.344 (7) |
| C6—O2 | 1.283 (10) | C25—C26 | 1.430 (9) |
| C7—C8 | 1.399 (9) | C25—C30 | 1.384 (8) |
| C7—C11 | 1.385 (8) | C25—N5 | 1.450 (9) |
| C8—H8 | 0.93 | C26—C27 | 1.418 (8) |
| C8—C9 | 1.357 (10) | C26—O7 | 1.293 (7) |
| C9—H9 | 0.93 | C27—C28 | 1.373 (8) |
| C9—C10 | 1.353 (9) | C27—C31 | 1.496 (8) |
| C10—H10 | 0.93 | C28—H28 | 0.93 |
| C10—N2 | 1.347 (8) | C28—C29 | 1.407 (8) |
| C11—C12 | 1.481 (7) | C29—C30 | 1.380 (8) |
| C11—N2 | 1.326 (7) | C29—N6 | 1.458 (8) |
| C12—N1 | 1.344 (7) | C30—H30 | 0.93 |
| C13—H13 | 0.93 | C31—O8 | 1.286 (8) |
| C13—C14 | 1.381 (9) | C31—O9 | 1.223 (8) |
| C13—N3 | 1.339 (8) | N5—O5 | 1.230 (9) |
| C14—H14 | 0.93 | N5—O6 | 1.218 (8) |
| C14—C15 | 1.373 (9) | N6—O10 | 1.216 (8) |
| C15—H15 | 0.93 | N6—O11 | 1.257 (8) |
| C15—C16 | 1.396 (8) | O7—H7 | 1.346 (4) |
| C16—C17 | 1.473 (8) | O8—H7 | 1.155 (4) |
| H1—C1—C2 | 118.04 | C19—C18—O4 | 120.9 (6) |
| H1—C1—N1 | 118.04 | C18—C19—C20 | 121.6 (5) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 123.9 (5) | C18—C19—C23 | 119.3 (5) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.88 | C20—C19—C23 | 119.1 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.2 (5) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.84 |
| H2—C2—C3 | 120.88 | C19—C20—C21 | 120.3 (6) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.34 | H20—C20—C21 | 119.84 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.3 (5) | C20—C21—H21 | 121.42 |
| H3—C3—C4 | 120.34 | C20—C21—C22 | 117.2 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.7 (6) | H21—C21—C22 | 121.42 |
| C3—C4—C12 | 119.3 (5) | C21—C22—H22 | 117.46 |
| C5—C4—C12 | 119.0 (5) | C21—C22—N4 | 125.1 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.9 (8) | H22—C22—N4 | 117.46 |
| C4—C5—O1 | 118.9 (7) | C19—C23—C24 | 121.2 (5) |
| C6—C5—O1 | 119.2 (8) | C19—C23—N4 | 120.8 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.3 (7) | C24—C23—N4 | 118.0 (5) |
| C5—C6—O2 | 121.4 (9) | C16—C24—C23 | 120.2 (5) |
| C7—C6—O2 | 119.3 (7) | C16—C24—N3 | 122.5 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.6 (6) | C23—C24—N3 | 117.2 (4) |
| C6—C7—C11 | 120.4 (6) | C26—C25—C30 | 121.2 (5) |
| C8—C7—C11 | 120.0 (6) | C26—C25—N5 | 122.7 (5) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 121.23 | C30—C25—N5 | 116.1 (6) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 117.5 (6) | C25—C26—C27 | 117.1 (5) |
| H8—C8—C9 | 121.23 | C25—C26—O7 | 122.2 (5) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.26 | C27—C26—O7 | 120.5 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 119.5 (6) | C26—C27—C28 | 122.1 (5) |
| H9—C9—C10 | 120.26 | C26—C27—C31 | 120.1 (5) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 118.01 | C28—C27—C31 | 117.8 (5) |
| C9—C10—N2 | 124.0 (6) | C27—C28—H28 | 121 |
| H10—C10—N2 | 118.01 | C27—C28—C29 | 118.0 (5) |
| C7—C11—C12 | 119.5 (5) | H28—C28—C29 | 121 |
| C7—C11—N2 | 121.3 (5) | C28—C29—C30 | 122.6 (5) |
| C12—C11—N2 | 119.2 (5) | C28—C29—N6 | 118.3 (5) |
| C4—C12—C11 | 119.8 (5) | C30—C29—N6 | 119.1 (5) |
| C4—C12—N1 | 121.2 (5) | C25—C30—C29 | 118.7 (5) |
| C11—C12—N1 | 118.9 (5) | C25—C30—H30 | 120.65 |
| H13—C13—C14 | 117.83 | C29—C30—H30 | 120.65 |
| H13—C13—N3 | 117.83 | C27—C31—O8 | 116.2 (5) |
| C14—C13—N3 | 124.3 (5) | C27—C31—O9 | 120.8 (6) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 121.04 | O8—C31—O9 | 122.9 (6) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 117.9 (6) | C1—N1—C12 | 117.9 (4) |
| H14—C14—C15 | 121.04 | C10—N2—C11 | 117.6 (5) |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.29 | C13—N3—C24 | 117.3 (5) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 119.4 (5) | C22—N4—C23 | 117.5 (5) |
| H15—C15—C16 | 120.29 | C25—N5—O5 | 118.4 (6) |
| C15—C16—C17 | 120.1 (5) | C25—N5—O6 | 120.0 (6) |
| C15—C16—C24 | 118.5 (5) | O5—N5—O6 | 121.6 (6) |
| C17—C16—C24 | 121.4 (5) | C29—N6—O10 | 118.3 (5) |
| C16—C17—C18 | 118.1 (5) | C29—N6—O11 | 117.2 (5) |
| C16—C17—O3 | 122.0 (6) | O10—N6—O11 | 124.5 (5) |
| C18—C17—O3 | 119.9 (6) | C26—O7—H7 | 99.4 (4) |
| C17—C18—C19 | 119.0 (5) | C31—O8—H7 | 103.7 (4) |
| C17—C18—O4 | 120.1 (6) | O7—H7—O8 | 159.6 (3) |
Bis(1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione-κ2N,N')silver(I) 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SAFGUD) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O10i | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.180 (7) | 131 |
| C8—H8···O7ii | 0.93 | 2.32 | 3.220 (7) | 162 |
| C9—H9···O6ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.243 (9) | 138 |
| C13—H13···O4iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.209 (7) | 137 |
| C22—H22···O8 | 0.93 | 2.36 | 3.251 (7) | 160 |
| O7—H7···C31 | 1.346 (4) | 1.922 (7) | 2.833 (8) | 119.1 (3) |
| O7—H7···O8 | 1.346 (4) | 1.155 (4) | 2.462 (6) | 159.6 (3) |
| O8—H7···C26 | 1.155 (4) | 2.013 (6) | 2.781 (7) | 120.3 (3) |
| O8—H7···O7 | 1.155 (4) | 1.346 (4) | 2.462 (6) | 159.6 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Crystal data
| C5H9N2+·C7H3N2O7− | F(000) = 336 |
| Mr = 324.26 | Dx = 1.547 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.1183 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 1025 reflections |
| b = 6.0636 (5) Å | θ = 2.5–22.6° |
| c = 14.1453 (11) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| β = 91.904 (1)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 695.93 (10) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.40 × 0.27 × 0.11 mm |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 2301 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1444 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.040 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.986 | k = −7→7 |
| 3523 measured reflections | l = −16→12 |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.041 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| wR(F) = 0.088 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.033 |
| S = 1.16 | Δρmax = 0.11 e Å−3 |
| 2301 reflections | Δρmin = −0.10 e Å−3 |
| 212 parameters | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 3100 (400) |
| 37 constraints | Absolute structure: 955 of Friedel pairs used in the refinement |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.5 |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.Number of fixed parameters 10. |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.2262 (4) | 0.7164 (5) | 0.2338 (2) | 0.0464 (11) | |
| N2 | 0.2203 (3) | 0.6196 (5) | 0.3198 (2) | 0.0478 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.3519 (4) | 0.7226 (6) | 0.5525 (2) | 0.0412 (12) | |
| N3 | 0.2179 (3) | 1.3158 (5) | 0.7705 (2) | 0.0509 (12) | |
| N4 | 0.5552 (4) | 0.7120 (5) | 0.8913 (2) | 0.0501 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.5417 (3) | 0.5285 (4) | 0.70239 (16) | 0.0462 (9) | |
| O2 | 0.4266 (3) | 0.5357 (4) | 0.53811 (15) | 0.0582 (10) | |
| O3 | 0.2657 (3) | 0.8100 (4) | 0.49006 (14) | 0.0507 (8) | |
| O4 | 0.1415 (3) | 1.4013 (4) | 0.70419 (18) | 0.0652 (10) | |
| O5 | 0.2270 (3) | 1.3968 (4) | 0.85025 (18) | 0.0709 (11) | |
| O6 | 0.5263 (4) | 0.7839 (5) | 0.96960 (17) | 0.0853 (12) | |
| O7 | 0.6549 (4) | 0.5664 (5) | 0.87980 (17) | 0.0719 (12) | |
| C1 | 0.1300 (5) | 0.6431 (8) | 0.0685 (2) | 0.0762 (19) | |
| H1a | 0.132119 | 0.800298 | 0.060733 | 0.1144* | |
| H1b | 0.027525 | 0.586015 | 0.043068 | 0.1144* | |
| H1c | 0.219699 | 0.578396 | 0.035744 | 0.1144* | |
| C2 | 0.1466 (4) | 0.5878 (6) | 0.1713 (2) | 0.0469 (13) | |
| C3 | 0.0892 (4) | 0.4058 (7) | 0.2187 (3) | 0.0553 (14) | |
| H3 | 0.029651 | 0.288588 | 0.192446 | 0.0663* | |
| C4 | 0.1373 (4) | 0.4313 (6) | 0.3133 (2) | 0.0481 (13) | |
| C5 | 0.1093 (5) | 0.2896 (7) | 0.3966 (3) | 0.0669 (16) | |
| H5a | 0.025142 | 0.183251 | 0.380914 | 0.1003* | |
| H5b | 0.20964 | 0.214551 | 0.414477 | 0.1003* | |
| H5c | 0.074882 | 0.379302 | 0.448238 | 0.1003* | |
| C12 | 0.4691 (4) | 0.7102 (6) | 0.7196 (2) | 0.0372 (12) | |
| C7 | 0.3736 (3) | 0.8233 (6) | 0.6477 (2) | 0.0348 (11) | |
| C8 | 0.2972 (4) | 1.0181 (6) | 0.6641 (2) | 0.0380 (12) | |
| H8 | 0.239805 | 1.089516 | 0.615013 | 0.0456* | |
| C9 | 0.3044 (4) | 1.1108 (6) | 0.7534 (2) | 0.0381 (11) | |
| C10 | 0.3902 (4) | 1.0091 (6) | 0.8274 (2) | 0.0403 (12) | |
| H10 | 0.393751 | 1.071121 | 0.887603 | 0.0483* | |
| C11 | 0.4704 (4) | 0.8133 (6) | 0.8100 (2) | 0.0380 (11) | |
| H2a | 0.507 (5) | 0.485 (9) | 0.620 (3) | 0.145 (19)* | |
| H1 | 0.289 (6) | 0.878 (9) | 0.225 (3) | 0.130 (19)* | |
| H2 | 0.258 (4) | 0.707 (6) | 0.373 (2) | 0.063 (12)* |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0502 (18) | 0.049 (2) | 0.0399 (18) | 0.0006 (15) | −0.0027 (14) | −0.0034 (15) |
| N2 | 0.0497 (19) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0422 (18) | −0.0046 (17) | −0.0047 (14) | −0.0066 (17) |
| C6 | 0.0393 (19) | 0.047 (2) | 0.037 (2) | −0.0016 (18) | 0.0053 (16) | −0.0027 (18) |
| N3 | 0.0500 (19) | 0.043 (2) | 0.060 (2) | −0.0003 (17) | 0.0048 (16) | −0.0031 (18) |
| N4 | 0.065 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0387 (19) | 0.0015 (17) | −0.0037 (16) | 0.0042 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0564 (15) | 0.0414 (15) | 0.0407 (14) | 0.0091 (13) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0072 (12) |
| O2 | 0.0704 (17) | 0.0626 (18) | 0.0414 (14) | 0.0205 (15) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0156 (14) |
| O3 | 0.0581 (14) | 0.0600 (17) | 0.0333 (13) | 0.0050 (14) | −0.0083 (11) | 0.0013 (12) |
| O4 | 0.0703 (17) | 0.0521 (17) | 0.0721 (18) | 0.0185 (15) | −0.0141 (14) | 0.0031 (15) |
| O5 | 0.092 (2) | 0.0593 (19) | 0.0617 (17) | 0.0072 (16) | 0.0048 (14) | −0.0187 (15) |
| O6 | 0.148 (3) | 0.075 (2) | 0.0326 (16) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0069 (15) | −0.0032 (15) |
| O7 | 0.092 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0510 (16) | 0.0308 (19) | −0.0083 (14) | 0.0090 (16) |
| C1 | 0.086 (3) | 0.096 (4) | 0.047 (2) | −0.014 (3) | −0.009 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C2 | 0.043 (2) | 0.054 (3) | 0.0434 (19) | 0.005 (2) | −0.0046 (17) | −0.009 (2) |
| C3 | 0.049 (2) | 0.057 (3) | 0.060 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.0075 (18) | −0.022 (2) |
| C4 | 0.039 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0027 (19) | 0.0037 (17) | −0.003 (2) |
| C5 | 0.066 (3) | 0.060 (3) | 0.074 (3) | 0.000 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.012 (2) |
| C12 | 0.0351 (19) | 0.041 (2) | 0.036 (2) | −0.0079 (18) | 0.0025 (15) | 0.0010 (17) |
| C7 | 0.0342 (17) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0316 (17) | −0.0052 (17) | 0.0004 (13) | 0.0031 (16) |
| C8 | 0.041 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0349 (19) | −0.0032 (18) | −0.0036 (15) | 0.0039 (17) |
| C9 | 0.041 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0416 (19) | −0.0045 (17) | 0.0020 (15) | −0.0015 (17) |
| C10 | 0.049 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0325 (19) | −0.0038 (18) | 0.0020 (16) | −0.0017 (17) |
| C11 | 0.0419 (19) | 0.041 (2) | 0.0312 (17) | −0.0038 (19) | −0.0025 (14) | 0.0049 (17) |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—N2 | 1.353 (4) | H1a—H1b | 1.5677 |
| N1—C2 | 1.330 (5) | H1a—H1c | 1.5677 |
| N1—H1 | 1.11 (5) | H1b—H1c | 1.5677 |
| N2—C4 | 1.327 (5) | C2—C3 | 1.380 (5) |
| N2—H2 | 0.96 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.93 |
| C6—O2 | 1.304 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.389 (5) |
| C6—O3 | 1.229 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.482 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.484 (4) | C5—H5a | 0.96 |
| N3—O4 | 1.223 (4) | C5—H5b | 0.96 |
| N3—O5 | 1.231 (4) | C5—H5c | 0.96 |
| N3—C9 | 1.452 (5) | H5a—H5b | 1.5677 |
| N4—O6 | 1.220 (4) | H5a—H5c | 1.5677 |
| N4—O7 | 1.213 (4) | H5b—H5c | 1.5677 |
| N4—C11 | 1.457 (4) | C12—C7 | 1.433 (4) |
| O1—C12 | 1.277 (4) | C12—C11 | 1.422 (4) |
| O1—H2a | 1.22 (5) | C7—C8 | 1.358 (5) |
| O2—H2a | 1.34 (5) | C8—H8 | 0.93 |
| C1—H1a | 0.96 | C8—C9 | 1.382 (4) |
| C1—H1b | 0.96 | C9—C10 | 1.384 (4) |
| C1—H1c | 0.96 | C10—H10 | 0.93 |
| C1—C2 | 1.494 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.380 (5) |
| N2—N1—C2 | 108.2 (3) | N2—C4—C3 | 106.8 (3) |
| N2—N1—H1 | 121 (2) | N2—C4—C5 | 122.3 (3) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 131 (2) | C3—C4—C5 | 130.9 (3) |
| N1—N2—C4 | 110.1 (3) | C4—C5—H5a | 109.47 |
| N1—N2—H2 | 117 (2) | C4—C5—H5b | 109.47 |
| C4—N2—H2 | 132 (2) | C4—C5—H5c | 109.47 |
| O2—C6—O3 | 121.3 (3) | H5a—C5—H5b | 109.47 |
| O2—C6—C7 | 117.2 (3) | H5a—C5—H5c | 109.47 |
| O3—C6—C7 | 121.5 (3) | H5b—C5—H5c | 109.47 |
| O4—N3—O5 | 123.2 (3) | O1—C12—C7 | 121.3 (3) |
| O4—N3—C9 | 118.1 (3) | O1—C12—C11 | 124.1 (3) |
| O5—N3—C9 | 118.7 (3) | C7—C12—C11 | 114.5 (3) |
| O6—N4—O7 | 122.1 (3) | C6—C7—C12 | 119.5 (3) |
| O6—N4—C11 | 117.8 (3) | C6—C7—C8 | 118.1 (3) |
| O7—N4—C11 | 120.1 (3) | C12—C7—C8 | 122.3 (3) |
| C12—O1—H2a | 106 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.87 |
| C6—O2—H2a | 106 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.3 (3) |
| H1a—C1—H1b | 109.47 | H8—C8—C9 | 119.87 |
| H1a—C1—H1c | 109.47 | N3—C9—C8 | 119.6 (3) |
| H1a—C1—C2 | 109.47 | N3—C9—C10 | 119.3 (3) |
| H1b—C1—H1c | 109.47 | C8—C9—C10 | 121.0 (3) |
| H1b—C1—C2 | 109.47 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.77 |
| H1c—C1—C2 | 109.47 | C9—C10—C11 | 118.5 (3) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 122.8 (3) | H10—C10—C11 | 120.77 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 108.1 (3) | N4—C11—C12 | 120.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 129.1 (3) | N4—C11—C10 | 115.7 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.58 | C12—C11—C10 | 123.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 106.8 (3) | O1—H2a—O2 | 149 (5) |
| H3—C3—C4 | 126.58 |
3,5-Dimethylpyrazolium 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (SEDKET). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1a···O7i | 0.96 | 2.49 | 3.176 (5) | 128 |
| C5—H5a···O4ii | 0.96 | 2.47 | 3.395 (5) | 162 |
| C10—H10···O6iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.369 (4) | 164 |
| O1—H2a···O2 | 1.22 (5) | 1.34 (5) | 2.476 (3) | 149 (5) |
| O2—H2a···O1 | 1.34 (5) | 1.22 (5) | 2.476 (3) | 149 (5) |
| N1—H1···O1i | 1.11 (5) | 1.92 (5) | 2.799 (4) | 133 (3) |
| N1—H1···O7i | 1.11 (5) | 1.94 (5) | 2.850 (4) | 137 (3) |
| N2—H2···O3 | 0.96 (3) | 1.77 (3) | 2.685 (4) | 158 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1; (ii) −x, y−3/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+2.
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Crystal data
| C6H12N3+·C7H3N2O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 353.30 | F(000) = 368 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.525 Mg m−3 |
| a = 7.0109 (4) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| b = 10.6617 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 2218 reflections |
| c = 10.7454 (7) Å | θ = 4.2–72.3° |
| α = 93.075 (6)° | µ = 1.09 mm−1 |
| β = 95.863 (5)° | T = 173 K |
| γ = 104.944 (6)° | Irregular, yellow |
| V = 769.30 (9) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur (Eos, Gemini) diffractometer | 2953 independent reflections |
| Graphite monochromator | 2426 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.0416 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.026 |
| ω scans | θmax = 72.5°, θmin = 4.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO and CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) | h = −8→5 |
| Tmin = 0.925, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −12→13 |
| 4664 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.041 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F) = 0.100 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| S = 1.64 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.013 |
| 2953 reflections | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 229 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 46 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 740 (130) |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Number of fixed parameters: 12 |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1b | −0.19161 (17) | 0.67539 (12) | 0.52684 (11) | 0.0294 (4) | |
| O2b | −0.38292 (17) | 0.47166 (12) | 0.40838 (12) | 0.0313 (4) | |
| O3b | −0.25511 (17) | 0.37712 (12) | 0.26158 (12) | 0.0312 (4) | |
| O4b | 0.41258 (19) | 0.58639 (13) | 0.16853 (13) | 0.0365 (5) | |
| O5b | 0.59776 (18) | 0.75622 (13) | 0.28239 (14) | 0.0382 (5) | |
| O6b | 0.3446 (2) | 0.93719 (14) | 0.62658 (15) | 0.0474 (5) | |
| O7b | 0.02822 (19) | 0.91655 (13) | 0.61477 (13) | 0.0410 (5) | |
| N1b | 0.1720 (2) | 0.88469 (14) | 0.58118 (14) | 0.0301 (5) | |
| N2b | 0.4396 (2) | 0.67347 (14) | 0.25363 (14) | 0.0281 (5) | |
| C1b | −0.0455 (2) | 0.68023 (16) | 0.46268 (15) | 0.0225 (5) | |
| C2b | −0.0572 (2) | 0.57873 (15) | 0.36597 (15) | 0.0217 (5) | |
| C3b | 0.0987 (2) | 0.57933 (16) | 0.29810 (15) | 0.0228 (5) | |
| H3b | 0.086172 | 0.512562 | 0.233219 | 0.0273* | |
| C4b | 0.2738 (2) | 0.67709 (16) | 0.32422 (15) | 0.0238 (5) | |
| C5b | 0.2967 (2) | 0.77664 (16) | 0.41630 (15) | 0.0244 (5) | |
| H5b | 0.418494 | 0.842618 | 0.433677 | 0.0292* | |
| C6b | 0.1392 (2) | 0.77850 (16) | 0.48267 (15) | 0.0244 (5) | |
| C7b | −0.2405 (2) | 0.46767 (16) | 0.33986 (15) | 0.0245 (5) | |
| N1a | −0.2235 (2) | 0.05127 (14) | −0.17301 (14) | 0.0305 (5) | |
| N2a | −0.0146 (2) | 0.22579 (13) | −0.06967 (13) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| N3a | 0.3467 (2) | 0.20531 (13) | 0.28160 (13) | 0.0254 (4) | |
| C1a | −0.0395 (2) | 0.12591 (16) | −0.15749 (16) | 0.0272 (6) | |
| H1a | 0.06324 | 0.111094 | −0.202772 | 0.0327* | |
| C2a | −0.3211 (3) | 0.10665 (17) | −0.08987 (17) | 0.0314 (6) | |
| H2a | −0.457443 | 0.07432 | −0.079116 | 0.0377* | |
| C3a | −0.1954 (3) | 0.21356 (17) | −0.02572 (17) | 0.0294 (6) | |
| H3a | −0.225845 | 0.269084 | 0.03706 | 0.0353* | |
| C4a | 0.1719 (2) | 0.32466 (17) | −0.02832 (15) | 0.0268 (5) | |
| H4aa | 0.242014 | 0.351332 | −0.101965 | 0.0322* | |
| H4ab | 0.142708 | 0.403798 | 0.008481 | 0.0322* | |
| C5a | 0.3076 (2) | 0.27759 (16) | 0.06668 (16) | 0.0271 (5) | |
| H5aa | 0.324487 | 0.193134 | 0.033664 | 0.0326* | |
| H5ab | 0.440667 | 0.340434 | 0.079114 | 0.0326* | |
| C6a | 0.2253 (2) | 0.26206 (16) | 0.19085 (15) | 0.0279 (6) | |
| H6aa | 0.218227 | 0.347891 | 0.227027 | 0.0335* | |
| H6ab | 0.08712 | 0.206021 | 0.17726 | 0.0335* | |
| H2b | −0.339134 | 0.554144 | 0.46148 | 0.075 (9)* | |
| H3aa | 0.329781 | 0.119532 | 0.260701 | 0.045 (4)* | |
| H3ab | 0.475827 | 0.248704 | 0.284554 | 0.045 (4)* | |
| H3ac | 0.313145 | 0.21209 | 0.359189 | 0.045 (4)* |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1b | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0277 (6) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0098 (5) | −0.0050 (5) |
| O2b | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0327 (7) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0088 (5) | −0.0060 (5) |
| O3b | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0317 (7) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | −0.0082 (5) |
| O4b | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0413 (8) | 0.0085 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | −0.0042 (6) |
| O5b | 0.0231 (6) | 0.0380 (8) | 0.0506 (9) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0111 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| O6b | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0552 (10) | −0.0009 (6) | −0.0052 (7) | −0.0197 (7) |
| O7b | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0333 (7) | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0162 (6) | −0.0121 (6) |
| N1b | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0060 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| N2b | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0343 (8) | 0.0074 (6) | 0.0092 (6) | 0.0063 (6) |
| C1b | 0.0234 (8) | 0.0236 (8) | 0.0201 (8) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C2b | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0207 (8) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C3b | 0.0265 (8) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0208 (8) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0017 (6) |
| C4b | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0080 (7) | 0.0064 (7) | 0.0057 (7) |
| C5b | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0050 (7) |
| C6b | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0018 (7) | −0.0001 (6) |
| C7b | 0.0247 (8) | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0051 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| N1a | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0252 (8) | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0011 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| N2a | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0034 (5) | 0.0002 (6) |
| N3a | 0.0268 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0245 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C1a | 0.0286 (9) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0278 (9) | 0.0087 (7) | 0.0051 (7) | −0.0018 (7) |
| C2a | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0316 (10) | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0047 (7) | 0.0073 (7) | 0.0060 (8) |
| C3a | 0.0301 (9) | 0.0311 (9) | 0.0289 (9) | 0.0095 (7) | 0.0092 (7) | 0.0016 (7) |
| C4a | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0052 (7) | 0.0000 (7) |
| C5a | 0.0237 (8) | 0.0295 (9) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0055 (7) | −0.0021 (7) |
| C6a | 0.0301 (9) | 0.0306 (9) | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0125 (7) | 0.0053 (7) | 0.0016 (7) |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1b—C1b | 1.284 (2) | N1a—C2a | 1.376 (3) |
| O2b—C7b | 1.308 (2) | N2a—C1a | 1.348 (2) |
| O2b—H2b | 0.9820 (12) | N2a—C3a | 1.375 (2) |
| O3b—C7b | 1.222 (2) | N2a—C4a | 1.4622 (19) |
| O4b—N2b | 1.232 (2) | N3a—C6a | 1.483 (2) |
| O5b—N2b | 1.2248 (17) | N3a—H3aa | 0.9042 (14) |
| O6b—N1b | 1.2313 (18) | N3a—H3ab | 0.9009 (13) |
| O7b—N1b | 1.225 (2) | N3a—H3ac | 0.8932 (14) |
| N1b—C6b | 1.464 (2) | C1a—H1a | 0.95 |
| N2b—C4b | 1.458 (2) | C2a—H2a | 0.95 |
| C1b—C2b | 1.440 (2) | C2a—C3a | 1.351 (2) |
| C1b—C6b | 1.428 (2) | C3a—H3a | 0.95 |
| C2b—C3b | 1.373 (2) | C4a—H4aa | 0.99 |
| C2b—C7b | 1.496 (2) | C4a—H4ab | 0.99 |
| C3b—H3b | 0.95 | C4a—C5a | 1.517 (2) |
| C3b—C4b | 1.382 (2) | C5a—H5aa | 0.99 |
| C4b—C5b | 1.378 (2) | C5a—H5ab | 0.99 |
| C5b—H5b | 0.95 | C5a—C6a | 1.507 (2) |
| C5b—C6b | 1.378 (2) | C6a—H6aa | 0.99 |
| N1a—C1a | 1.318 (2) | C6a—H6ab | 0.99 |
| C1b—O1b—H2b | 99.82 (10) | C6a—N3a—H3ab | 109.46 (13) |
| C7b—O2b—H2b | 106.90 (11) | C6a—N3a—H3ac | 111.76 (15) |
| O6b—N1b—O7b | 123.30 (15) | H3aa—N3a—H3ab | 110.21 (16) |
| O6b—N1b—C6b | 117.72 (16) | H3aa—N3a—H3ac | 106.71 (14) |
| O7b—N1b—C6b | 118.97 (13) | H3ab—N3a—H3ac | 107.27 (13) |
| O4b—N2b—O5b | 123.59 (16) | N1a—C1a—N2a | 111.91 (16) |
| O4b—N2b—C4b | 117.89 (12) | N1a—C1a—H1a | 124.04 |
| O5b—N2b—C4b | 118.52 (14) | N2a—C1a—H1a | 124.04 |
| O1b—C1b—C2b | 120.19 (13) | N1a—C2a—H2a | 124.86 |
| O1b—C1b—C6b | 124.76 (15) | N1a—C2a—C3a | 110.28 (15) |
| C2b—C1b—C6b | 115.00 (15) | H2a—C2a—C3a | 124.86 |
| C1b—C2b—C3b | 121.54 (13) | N2a—C3a—C2a | 106.10 (16) |
| C1b—C2b—C7b | 119.88 (15) | N2a—C3a—H3a | 126.95 |
| C3b—C2b—C7b | 118.56 (14) | C2a—C3a—H3a | 126.95 |
| C2b—C3b—H3b | 120.01 | N2a—C4a—H4aa | 109.47 |
| C2b—C3b—C4b | 119.99 (15) | N2a—C4a—H4ab | 109.47 |
| H3b—C3b—C4b | 120.01 | N2a—C4a—C5a | 112.62 (14) |
| N2b—C4b—C3b | 119.03 (14) | H4aa—C4a—H4ab | 106.12 |
| N2b—C4b—C5b | 119.24 (13) | H4aa—C4a—C5a | 109.47 |
| C3b—C4b—C5b | 121.73 (16) | H4ab—C4a—C5a | 109.47 |
| C4b—C5b—H5b | 120.69 | C4a—C5a—H5aa | 109.47 |
| C4b—C5b—C6b | 118.62 (13) | C4a—C5a—H5ab | 109.47 |
| H5b—C5b—C6b | 120.69 | C4a—C5a—C6a | 111.50 (15) |
| N1b—C6b—C1b | 120.26 (15) | H5aa—C5a—H5ab | 107.36 |
| N1b—C6b—C5b | 116.59 (13) | H5aa—C5a—C6a | 109.47 |
| C1b—C6b—C5b | 123.09 (15) | H5ab—C5a—C6a | 109.47 |
| O2b—C7b—O3b | 121.86 (14) | N3a—C6a—C5a | 112.35 (15) |
| O2b—C7b—C2b | 115.78 (14) | N3a—C6a—H6aa | 109.47 |
| O3b—C7b—C2b | 122.33 (16) | N3a—C6a—H6ab | 109.47 |
| C1a—N1a—C2a | 105.01 (14) | C5a—C6a—H6aa | 109.47 |
| C1a—N2a—C3a | 106.69 (13) | C5a—C6a—H6ab | 109.47 |
| C1a—N2a—C4a | 125.73 (15) | H6aa—C6a—H6ab | 106.43 |
| C3a—N2a—C4a | 127.56 (14) | O1b—H2b—O2b | 156.29 (9) |
| C6a—N3a—H3aa | 111.33 (12) |
3-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)propanaminium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (TIYZIM) . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4a—H4aa···O4bi | 0.99 | 2.53 | 3.359 (2) | 141 |
| O2b—H2b···O1b | 0.9820 (12) | 1.5161 (11) | 2.4473 (16) | 156.29 (9) |
| O2b—H2b···C1b | 0.9820 (12) | 2.1471 (15) | 2.7833 (18) | 121.00 (8) |
| N3a—H3aa···N1aii | 0.9042 (14) | 1.9318 (14) | 2.797 (2) | 159.6 (1) |
| N3a—H3ab···O2biii | 0.9009 (13) | 2.5650 (12) | 3.1297 (17) | 121.35 (10) |
| N3a—H3ab···O3biii | 0.9009 (13) | 2.0721 (11) | 2.9537 (17) | 165.79 (10) |
| N3a—H3ac···O1biv | 0.8932 (14) | 2.0610 (13) | 2.815 (2) | 141.47 (11) |
| N3a—H3ac···O7biv | 0.8932 (14) | 2.4844 (13) | 2.9712 (19) | 114.74 (8) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x, −y, −z; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Crystal data
| C10H12N3O3S+·C7H3N2O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 481.41 | F(000) = 496 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.609 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.5551 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 6718 reflections |
| b = 10.5000 (2) Å | θ = 1.8–32.6° |
| c = 12.7576 (3) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| α = 106.463 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 100.913 (1)° | Prism, yellow |
| γ = 108.272 (1)° | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm |
| V = 993.72 (3) Å3 |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 6717 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4398 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.955, Tmax = 0.964 | k = −15→15 |
| 24261 measured reflections | l = −19→16 |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.104 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.95 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| 6717 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.013 |
| 301 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
| 48 constraints |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger.Number of fixed parameters: 9 |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | −0.02012 (4) | 0.65156 (4) | 0.38514 (3) | 0.03475 (15) | |
| O1 | −0.12136 (12) | 0.56298 (10) | 0.26952 (9) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| O2 | −0.09555 (13) | 0.65440 (11) | 0.47594 (9) | 0.0468 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.47434 (14) | 0.55510 (13) | 0.32058 (11) | 0.0626 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.29155 (15) | 1.24477 (12) | 0.38430 (11) | 0.0434 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.13845 (14) | 0.60248 (12) | 0.42019 (10) | 0.0376 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.39246 (16) | 0.57705 (15) | 0.40555 (12) | 0.0536 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.07464 (15) | 0.82919 (13) | 0.38935 (12) | 0.0322 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.21693 (19) | 0.93183 (16) | 0.47844 (13) | 0.0511 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.28732 (19) | 1.06857 (16) | 0.47796 (14) | 0.0514 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.21467 (16) | 1.10142 (13) | 0.38945 (12) | 0.0344 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.07052 (18) | 1.00124 (15) | 0.30229 (13) | 0.0444 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.00046 (17) | 0.86380 (15) | 0.30181 (13) | 0.0421 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.24788 (17) | 0.58299 (13) | 0.35471 (13) | 0.0355 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.2306 (2) | 0.56568 (16) | 0.23936 (14) | 0.0473 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.3761 (2) | 0.55015 (16) | 0.22381 (16) | 0.0511 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.4452 (3) | 0.5287 (2) | 0.12416 (18) | 0.0766 (11) | |
| O4 | 0.51685 (14) | 0.76882 (14) | 0.75724 (10) | 0.0657 (6) | |
| O5 | 0.25004 (13) | 0.72390 (11) | 0.65907 (9) | 0.0495 (5) | |
| O6 | 0.03442 (11) | 0.74382 (11) | 0.75483 (8) | 0.0431 (4) | |
| O7 | −0.13539 (17) | 0.8490 (2) | 0.89544 (14) | 0.0980 (10) | |
| O8 | −0.12065 (16) | 0.7660 (2) | 1.03000 (12) | 0.0975 (9) | |
| O9 | 0.46550 (16) | 0.90412 (15) | 1.25865 (10) | 0.0717 (7) | |
| O10 | 0.66293 (15) | 0.90569 (15) | 1.17611 (11) | 0.0749 (7) | |
| N4 | −0.06158 (16) | 0.80710 (17) | 0.96062 (13) | 0.0598 (7) | |
| N5 | 0.51466 (16) | 0.88865 (13) | 1.17407 (12) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.31789 (15) | 0.78551 (13) | 0.85956 (12) | 0.0326 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.14714 (16) | 0.77857 (13) | 0.85292 (12) | 0.0328 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.10840 (16) | 0.80786 (15) | 0.95755 (13) | 0.0389 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.22578 (17) | 0.84024 (15) | 1.06095 (13) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.38931 (16) | 0.84763 (14) | 1.06263 (12) | 0.0365 (6) | |
| C16 | 0.43735 (16) | 0.82163 (13) | 0.96389 (12) | 0.0356 (6) | |
| C17 | 0.36856 (18) | 0.75728 (15) | 0.75210 (13) | 0.0400 (6) | |
| H1a | 0.188848 | 1.256572 | 0.342213 | 0.088 (4)* | |
| H1b | 0.353568 | 1.297412 | 0.446823 | 0.088 (4)* | |
| H1c | 0.348288 | 1.238627 | 0.338232 | 0.088 (4)* | |
| H2 | 0.265121 | 0.908789 | 0.538567 | 0.0613* | |
| H2a | 0.186499 | 0.630039 | 0.50234 | 0.068 (5)* | |
| H3 | 0.383907 | 1.138439 | 0.537561 | 0.0617* | |
| H5 | 0.020222 | 1.025766 | 0.243815 | 0.0533* | |
| H6 | −0.096798 | 0.794538 | 0.242417 | 0.0506* | |
| H8 | 0.139615 | 0.565054 | 0.185878 | 0.0568* | |
| H10a | 0.551947 | 0.608597 | 0.142286 | 0.1149* | |
| H10b | 0.362955 | 0.522551 | 0.058321 | 0.1149* | |
| H10c | 0.46505 | 0.441064 | 0.1077 | 0.1149* | |
| H14 | 0.194965 | 0.856742 | 1.128171 | 0.0484* | |
| H16 | 0.549353 | 0.82833 | 0.967386 | 0.0428* | |
| H6a | 0.115577 | 0.727699 | 0.69023 | 0.132 (9)* |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.03683 (17) | 0.03321 (18) | 0.0360 (2) | 0.01370 (13) | 0.01260 (14) | 0.01423 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0462 (5) | 0.0373 (5) | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0089 (4) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0087 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0524 (6) | 0.0510 (6) | 0.0532 (7) | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0309 (5) | 0.0276 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0518 (6) | 0.0718 (8) | 0.0660 (9) | 0.0313 (6) | 0.0248 (6) | 0.0153 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0374 (6) | 0.0502 (9) | 0.0178 (5) | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0202 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0476 (6) | 0.0413 (6) | 0.0327 (7) | 0.0235 (5) | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0169 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0495 (7) | 0.0628 (9) | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0136 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0350 (6) | 0.0317 (7) | 0.0316 (8) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0112 (5) | 0.0120 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0588 (9) | 0.0433 (9) | 0.0382 (9) | 0.0107 (7) | −0.0053 (7) | 0.0197 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0380 (8) | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0029 (7) | −0.0033 (7) | 0.0129 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0400 (7) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0153 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0478 (8) | 0.0446 (8) | 0.0438 (10) | 0.0195 (7) | 0.0064 (7) | 0.0235 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0392 (7) | 0.0397 (8) | 0.0403 (9) | 0.0118 (6) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0159 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0374 (9) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0113 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0553 (9) | 0.0506 (9) | 0.0426 (10) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0194 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0605 (9) | 0.0379 (8) | 0.0574 (12) | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0141 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0921 (14) | 0.0731 (13) | 0.0819 (15) | 0.0351 (12) | 0.0607 (13) | 0.0275 (13) |
| O4 | 0.0483 (6) | 0.0981 (10) | 0.0513 (8) | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0254 (5) | 0.0227 (7) |
| O5 | 0.0578 (6) | 0.0613 (7) | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0156 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0404 (5) | 0.0525 (6) | 0.0322 (6) | 0.0196 (4) | 0.0028 (4) | 0.0136 (5) |
| O7 | 0.0700 (8) | 0.1711 (16) | 0.0831 (11) | 0.0810 (10) | 0.0212 (8) | 0.0529 (11) |
| O8 | 0.0537 (7) | 0.1721 (16) | 0.0566 (9) | 0.0299 (9) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0359 (10) |
| O9 | 0.0770 (8) | 0.0950 (10) | 0.0308 (7) | 0.0267 (7) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0211 (7) |
| O10 | 0.0480 (7) | 0.0991 (10) | 0.0639 (9) | 0.0302 (6) | −0.0064 (6) | 0.0241 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0396 (7) | 0.0856 (11) | 0.0419 (9) | 0.0249 (7) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0084 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0458 (7) | 0.0405 (9) | 0.0147 (6) | −0.0044 (6) | 0.0138 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0346 (6) | 0.0281 (6) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0107 (5) | 0.0078 (5) | 0.0096 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0351 (6) | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0112 (5) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0104 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0330 (6) | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0079 (6) | 0.0108 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0454 (8) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0162 (6) | 0.0100 (6) | 0.0112 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0370 (7) | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0107 (5) | −0.0009 (6) | 0.0104 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0321 (6) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0124 (5) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0120 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0411 (7) | 0.0393 (8) | 0.0385 (9) | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0130 (6) | 0.0143 (7) |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O1 | 1.4228 (9) | C9—C10 | 1.491 (3) |
| S1—O2 | 1.4264 (13) | C10—H10a | 0.96 |
| S1—N2 | 1.6264 (14) | C10—H10b | 0.96 |
| O3—N3 | 1.402 (2) | C10—H10c | 0.96 |
| O3—C9 | 1.333 (2) | O4—C17 | 1.223 (2) |
| N1—C4 | 1.468 (2) | O5—C17 | 1.2827 (18) |
| N1—H1a | 1.0015 (14) | O5—H6a | 1.2945 (12) |
| N1—H1b | 0.7932 (11) | O6—C12 | 1.3010 (16) |
| N1—H1c | 0.8315 (15) | O6—H6a | 1.1837 (11) |
| N2—C7 | 1.391 (2) | O7—N4 | 1.211 (3) |
| N2—H2a | 0.9703 (12) | O8—N4 | 1.214 (2) |
| N3—C7 | 1.312 (2) | O9—N5 | 1.218 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3764 (15) | O10—N5 | 1.218 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.374 (2) | N4—C13 | 1.460 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.374 (2) | N5—C15 | 1.4638 (19) |
| C2—H2 | 0.93 | C11—C12 | 1.425 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.367 (2) | C11—C16 | 1.3841 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C11—C17 | 1.493 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3668 (15) | C12—C13 | 1.409 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.376 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.93 | C14—C15 | 1.372 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C7—C8 | 1.403 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.379 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.348 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.93 |
| C8—H8 | 0.93 | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 120.50 (6) | C8—C9—C10 | 133.88 (19) |
| O1—S1—N2 | 108.78 (6) | C9—C10—H10a | 109.47 |
| O2—S1—N2 | 104.15 (7) | C9—C10—H10b | 109.47 |
| N3—O3—C9 | 108.94 (14) | C9—C10—H10c | 109.47 |
| C4—N1—H1a | 102.59 (10) | H10a—C10—H10b | 109.47 |
| C4—N1—H1b | 107.06 (15) | H10a—C10—H10c | 109.47 |
| C4—N1—H1c | 107.83 (13) | H10b—C10—H10c | 109.47 |
| H1a—N1—H1b | 124.65 (16) | C17—O5—H6a | 105.28 (11) |
| H1a—N1—H1c | 103.41 (14) | C12—O6—H6a | 102.01 (10) |
| H1b—N1—H1c | 110.21 (14) | O7—N4—O8 | 123.34 (17) |
| S1—N2—C7 | 124.43 (12) | O7—N4—C13 | 118.74 (17) |
| S1—N2—H2a | 113.65 (11) | O8—N4—C13 | 117.91 (17) |
| C7—N2—H2a | 116.39 (12) | O9—N5—O10 | 124.03 (14) |
| O3—N3—C7 | 104.86 (14) | O9—N5—C15 | 118.56 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.38 (14) | O10—N5—C15 | 117.41 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.57 (16) | C12—C11—C16 | 120.99 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.22 | C12—C11—C17 | 118.93 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.22 | C16—C11—C17 | 120.07 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.68 (12) | O6—C12—C11 | 121.05 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.16 | O6—C12—C13 | 122.90 (13) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.16 | C11—C12—C13 | 116.03 (12) |
| N1—C4—C3 | 120.80 (10) | N4—C13—C12 | 120.40 (13) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 118.09 (15) | N4—C13—C14 | 116.57 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.09 (14) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.02 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.44 (16) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.50 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.28 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.75 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.28 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.75 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.80 (11) | N5—C15—C14 | 117.72 (14) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 | N5—C15—C16 | 120.43 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.82 (13) |
| N2—C7—N3 | 117.05 (14) | C11—C16—C15 | 119.61 (13) |
| N2—C7—C8 | 131.01 (14) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.19 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 111.93 (15) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.19 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 104.20 (16) | O4—C17—O5 | 124.29 (16) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 127.9 | O4—C17—C11 | 119.59 (13) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 127.9 | O5—C17—C11 | 116.11 (13) |
| O3—C9—C8 | 110.05 (18) | O5—H6a—O6 | 156.58 (6) |
| O3—C9—C10 | 116.07 (17) |
4-{[(5-Methylisoxazol-3-yl)amino]sulfonyl}anilinium 2-hydroxy-3,5-dinitrobenzoate (TUJPEV). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1a···O6i | 1.0015 (14) | 2.0683 (10) | 3.0655 (17) | 173.55 (7) |
| N1—H1b···N3ii | 0.7932 (11) | 2.2920 (11) | 3.0393 (15) | 157.33 (11) |
| N1—H1c···O4ii | 0.8315 (15) | 1.8318 (14) | 2.663 (2) | 177.12 (7) |
| N2—H2a···O5 | 0.9703 (12) | 1.8440 (10) | 2.7852 (15) | 162.64 (9) |
| O5—H6a···O6 | 1.2945 (12) | 1.1837 (11) | 2.4268 (16) | 156.58 (6) |
| O5—H6a···C12 | 1.2945 (12) | 1.9326 (15) | 2.7490 (19) | 115.40 (6) |
| O6—H6a···O5 | 1.1837 (11) | 1.2945 (12) | 2.4268 (16) | 156.58 (6) |
| O6—H6a···C17 | 1.1837 (11) | 2.0485 (15) | 2.8249 (19) | 119.42 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Crystal data
| C8H13N2O+·C7H3N2O7−·H2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 398.33 | F(000) = 416 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.497 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.6691 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 6994 reflections |
| b = 11.3831 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–31.6° |
| c = 12.2900 (5) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| α = 89.727 (2)° | T = 100 K |
| β = 76.771 (2)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 76.930 (2)° | 0.52 × 0.13 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 883.62 (6) Å3 |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4061 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3042 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.937, Tmax = 0.987 | k = −14→12 |
| 17014 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.038 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.086 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| S = 1.77 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| 4061 reflections | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| 258 parameters | (Δ/σ)max = 0.014 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmax = 0.46 e Å−3 |
| 52 constraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Number of fixed parameters: 15 |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.30546 (16) | −0.17099 (9) | 0.14963 (8) | 0.0232 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.56653 (17) | −0.35718 (9) | 0.01361 (9) | 0.0316 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.48656 (18) | −0.36691 (9) | −0.14697 (9) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.36254 (16) | −0.00313 (9) | −0.33889 (8) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.23753 (16) | 0.16995 (9) | −0.24573 (8) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| O6 | 0.07250 (15) | 0.19153 (8) | 0.16330 (8) | 0.0204 (4) | |
| O7 | 0.14533 (16) | 0.02234 (9) | 0.25238 (8) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| O8 | 0.31889 (16) | 0.38510 (9) | 0.41956 (8) | 0.0221 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.30174 (18) | 0.05930 (11) | −0.25094 (10) | 0.0185 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.48606 (19) | −0.31064 (11) | −0.06125 (10) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.11898 (17) | 0.64252 (10) | 0.66449 (9) | 0.0147 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.23841 (17) | 0.58259 (10) | 0.47936 (9) | 0.0144 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.3103 (2) | −0.11910 (12) | 0.05547 (11) | 0.0151 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.3895 (2) | −0.18160 (12) | −0.05145 (11) | 0.0154 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.3838 (2) | −0.12419 (13) | −0.15034 (12) | 0.0160 (5) | |
| H3a | 0.432743 | −0.167918 | −0.218686 | 0.0192* | |
| C4 | 0.3044 (2) | −0.00126 (13) | −0.14615 (11) | 0.0150 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.2281 (2) | 0.06626 (13) | −0.04539 (11) | 0.0148 (5) | |
| H5a | 0.176964 | 0.149404 | −0.044656 | 0.0177* | |
| C6 | 0.2290 (2) | 0.00871 (12) | 0.05379 (11) | 0.0140 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.1429 (2) | 0.08121 (13) | 0.16123 (11) | 0.0159 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.2598 (2) | 0.45829 (12) | 0.49910 (12) | 0.0158 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.2070 (2) | 0.43367 (13) | 0.61582 (11) | 0.0160 (5) | |
| H9a | 0.221191 | 0.354014 | 0.636387 | 0.0192* | |
| C10 | 0.1376 (2) | 0.52320 (12) | 0.69587 (11) | 0.0157 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.1694 (2) | 0.67095 (12) | 0.55875 (11) | 0.0141 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.1445 (2) | 0.80006 (12) | 0.52928 (11) | 0.0153 (5) | |
| H12a | 0.110348 | 0.85057 | 0.598371 | 0.0184* | |
| C13 | −0.0374 (2) | 0.83589 (13) | 0.47019 (13) | 0.0224 (5) | |
| H13a | −0.054927 | 0.919318 | 0.452627 | 0.0335* | |
| H13b | −0.165759 | 0.824046 | 0.518462 | 0.0335* | |
| H13c | −0.005734 | 0.786763 | 0.402409 | 0.0335* | |
| C14 | 0.3509 (2) | 0.82298 (12) | 0.45745 (12) | 0.0195 (5) | |
| H14a | 0.461527 | 0.800548 | 0.496897 | 0.0292* | |
| H14b | 0.331515 | 0.907081 | 0.442205 | 0.0292* | |
| H14c | 0.389104 | 0.775688 | 0.38823 | 0.0292* | |
| C15 | 0.0772 (2) | 0.50600 (13) | 0.81821 (12) | 0.0221 (5) | |
| H15a | −0.068894 | 0.545223 | 0.847126 | 0.0332* | |
| H15b | 0.163895 | 0.540389 | 0.855439 | 0.0332* | |
| H15c | 0.097793 | 0.421295 | 0.830953 | 0.0332* | |
| O1w | 0.32852 (17) | 0.60955 (9) | 0.25340 (8) | 0.0272 (4) | |
| H1n3 | 0.061415 | 0.706878 | 0.722609 | 0.037 (5)* | |
| H1n4 | 0.270467 | 0.602234 | 0.406704 | 0.034 (5)* | |
| H2w1 | 0.339729 | 0.675124 | 0.210779 | 0.053 (6)* | |
| H1w1 | 0.381611 | 0.539911 | 0.20932 | 0.055 (6)* | |
| H7 | 0.211364 | −0.063754 | 0.220331 | 0.078 (7)* |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0185 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | −0.0018 (5) | 0.0031 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0431 (7) | 0.0219 (6) | 0.0232 (6) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0063 (5) | 0.0044 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0489 (7) | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0229 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0053 (5) | −0.0086 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0138 (6) | −0.0083 (5) | −0.0030 (5) | −0.0009 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0235 (6) | −0.0045 (5) | −0.0072 (5) | 0.0058 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0244 (6) | 0.0142 (6) | 0.0187 (6) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0029 (4) |
| O7 | 0.0284 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0140 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0003 (4) |
| O8 | 0.0321 (6) | 0.0137 (5) | 0.0176 (6) | −0.0026 (5) | −0.0027 (5) | −0.0025 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0182 (6) | 0.0202 (7) | 0.0186 (7) | −0.0071 (6) | −0.0047 (5) | 0.0034 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0161 (7) | 0.0198 (7) | −0.0035 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0136 (6) | −0.0024 (5) | −0.0017 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| N4 | 0.0172 (6) | 0.0117 (6) | 0.0129 (6) | −0.0026 (5) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0177 (8) | 0.0148 (7) | −0.0064 (6) | −0.0014 (6) | 0.0022 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0118 (7) | 0.0176 (8) | −0.0030 (6) | −0.0017 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0140 (8) | −0.0070 (6) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0029 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0146 (7) | 0.0196 (8) | 0.0125 (7) | −0.0073 (6) | −0.0030 (6) | 0.0033 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0121 (7) | 0.0137 (7) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0046 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0154 (7) | 0.0154 (7) | −0.0048 (6) | −0.0015 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0130 (7) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | −0.0048 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0132 (7) | 0.0193 (8) | −0.0022 (6) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0110 (7) | 0.0187 (8) | −0.0031 (6) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0137 (7) | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0182 (8) | −0.0033 (6) | −0.0041 (6) | 0.0029 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0106 (7) | 0.0152 (7) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0028 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | −0.0012 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0178 (7) | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0155 (7) | −0.0034 (6) | −0.0014 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0218 (8) | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0321 (9) | −0.0033 (6) | −0.0089 (7) | 0.0052 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0141 (8) | 0.0218 (8) | −0.0048 (6) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0047 (7) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0019 (6) |
| O1w | 0.0471 (7) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | −0.0043 (5) | −0.0005 (5) | 0.0003 (5) |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.2939 (17) | C4—C5 | 1.3881 (18) |
| O1—H7 | 1.4329 (9) | C5—H5a | 0.93 |
| O2—N2 | 1.2279 (17) | C5—C6 | 1.3816 (19) |
| O3—N2 | 1.2346 (17) | C6—C7 | 1.4844 (18) |
| O4—N1 | 1.2304 (15) | C8—C9 | 1.439 (2) |
| O5—N1 | 1.2321 (15) | C9—H9a | 0.93 |
| O6—C7 | 1.2355 (16) | C9—C10 | 1.3449 (19) |
| O7—C7 | 1.3040 (17) | C10—C15 | 1.4889 (19) |
| O7—H7 | 1.0191 (9) | C11—C12 | 1.4936 (19) |
| O8—C8 | 1.2198 (17) | C12—H12a | 0.98 |
| N1—C4 | 1.4597 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.531 (2) |
| N2—C2 | 1.4576 (17) | C12—C14 | 1.5318 (19) |
| N3—C10 | 1.3963 (18) | C13—H13a | 0.96 |
| N3—C11 | 1.3236 (17) | C13—H13b | 0.96 |
| N3—H1n3 | 0.9729 (11) | C13—H13c | 0.96 |
| N4—C8 | 1.4152 (18) | C14—H14a | 0.96 |
| N4—C11 | 1.3303 (17) | C14—H14b | 0.96 |
| N4—H1n4 | 0.9085 (11) | C14—H14c | 0.96 |
| C1—C2 | 1.4259 (18) | C15—H15a | 0.96 |
| C1—C6 | 1.4349 (19) | C15—H15b | 0.96 |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (2) | C15—H15c | 0.96 |
| C3—H3a | 0.93 | O1w—H2w1 | 0.9169 (10) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3763 (19) | O1w—H1w1 | 0.9146 (10) |
| C1—O1—H7 | 96.54 (8) | N4—C8—C9 | 113.60 (12) |
| C7—O7—H7 | 101.27 (9) | C8—C9—H9a | 119.24 |
| O4—N1—O5 | 124.04 (12) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.51 (13) |
| O4—N1—C4 | 118.12 (11) | H9a—C9—C10 | 119.24 |
| O5—N1—C4 | 117.84 (11) | N3—C10—C9 | 118.95 (12) |
| O2—N2—O3 | 123.42 (12) | N3—C10—C15 | 116.00 (11) |
| O2—N2—C2 | 119.16 (12) | C9—C10—C15 | 125.06 (13) |
| O3—N2—C2 | 117.39 (12) | N3—C11—N4 | 118.76 (12) |
| C10—N3—C11 | 122.45 (11) | N3—C11—C12 | 120.45 (12) |
| C10—N3—H1n3 | 118.37 (11) | N4—C11—C12 | 120.78 (12) |
| C11—N3—H1n3 | 119.14 (11) | C11—C12—H12a | 108.71 |
| C8—N4—C11 | 124.69 (12) | C11—C12—C13 | 109.61 (13) |
| C8—N4—H1n4 | 116.55 (11) | C11—C12—C14 | 111.42 (10) |
| C11—N4—H1n4 | 118.72 (12) | H12a—C12—C13 | 108.78 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 124.06 (12) | H12a—C12—C14 | 106.87 |
| O1—C1—C6 | 120.40 (11) | C13—C12—C14 | 111.36 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 115.53 (12) | C12—C13—H13a | 109.47 |
| N2—C2—C1 | 120.85 (12) | C12—C13—H13b | 109.47 |
| N2—C2—C3 | 116.56 (11) | C12—C13—H13c | 109.47 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.58 (12) | H13a—C13—H13b | 109.47 |
| C2—C3—H3a | 120.52 | H13a—C13—H13c | 109.47 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.97 (12) | H13b—C13—H13c | 109.47 |
| H3a—C3—C4 | 120.52 | C12—C14—H14a | 109.47 |
| N1—C4—C3 | 118.77 (12) | C12—C14—H14b | 109.47 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 119.38 (12) | C12—C14—H14c | 109.47 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.85 (13) | H14a—C14—H14b | 109.47 |
| C4—C5—H5a | 120.33 | H14a—C14—H14c | 109.47 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.34 (12) | H14b—C14—H14c | 109.47 |
| H5a—C5—C6 | 120.33 | C10—C15—H15a | 109.47 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.71 (12) | C10—C15—H15b | 109.47 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 119.30 (12) | C10—C15—H15c | 109.47 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.99 (12) | H15a—C15—H15b | 109.47 |
| O6—C7—O7 | 122.20 (12) | H15a—C15—H15c | 109.47 |
| O6—C7—C6 | 121.26 (12) | H15b—C15—H15c | 109.47 |
| O7—C7—C6 | 116.54 (12) | H2w1—O1w—H1w1 | 110.00 (10) |
| O8—C8—N4 | 119.14 (12) | O1—H7—O7 | 165.94 (7) |
| O8—C8—C9 | 127.26 (13) |
2-Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate monohydrate (VABZIJ). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12a···O7i | 0.98 | 2.42 | 3.3068 (15) | 151 |
| N3—H1n3···O6i | 0.9729 (11) | 1.7539 (9) | 2.7182 (14) | 170.48 (8) |
| N4—H1n4···O1w | 0.9085 (11) | 1.8401 (10) | 2.7348 (15) | 167.76 (8) |
| O1w—H2w1···O1ii | 0.9169 (10) | 1.8895 (10) | 2.7886 (14) | 166.21 (6) |
| O1w—H1w1···O3iii | 0.9146 (10) | 2.0399 (10) | 2.9352 (14) | 165.84 (7) |
| O7—H7···O1 | 1.0191 (9) | 1.4329 (9) | 2.4340 (13) | 165.94 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, y+1, z; (iii) −x+1, −y, −z.
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Crystal data
| C9H17N2+·C7H3N2O7− | F(000) = 800 |
| Mr = 380.35 | Dx = 1.489 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yabc | Cell parameters from 1891 reflections |
| a = 6.1537 (3) Å | θ = 3.5–26.6° |
| b = 19.1541 (14) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 14.5527 (11) Å | T = 200 K |
| β = 98.343 (6)° | Needle, yellow |
| V = 1697.2 (2) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.13 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer | 3339 independent reflections |
| Graphite monochromator | 1976 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.067 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.034 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.920, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −23→23 |
| 7800 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0004I2) |
| S = 1.33 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.005 |
| 3339 reflections | Δρmax = 0.36 e Å−3 |
| 268 parameters | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Extinction correction: B-C type 1 Lorentzian isotropic (Becker & Coppens, 1974) |
| 98 constraints | Extinction coefficient: 2200 (700) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.Number of fixed parameters : 10 |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O2b | 0.8418 (3) | 0.56169 (11) | 0.78950 (14) | 0.0440 (8) | 0.727 (4) |
| H61b | 0.852107 | 0.560819 | 0.76707 | 0.0359* | 0.273 (4) |
| O21b | 0.7735 (8) | 0.6569 (3) | 0.4912 (4) | 0.048 (2) | 0.273 (4) |
| H6b | 0.805712 | 0.644967 | 0.507207 | 0.0328* | 0.727 (4) |
| O11b | 0.5083 (2) | 0.68884 (8) | 0.59278 (11) | 0.0444 (6) | |
| O12b | 0.5447 (2) | 0.64534 (8) | 0.73586 (12) | 0.0524 (7) | |
| O31b | 1.1108 (3) | 0.45706 (10) | 0.81717 (14) | 0.0829 (9) | |
| O32b | 1.4073 (3) | 0.47245 (10) | 0.75770 (13) | 0.0775 (8) | |
| O51b | 1.3288 (3) | 0.55869 (9) | 0.44602 (12) | 0.0603 (7) | |
| O52b | 1.0707 (3) | 0.63212 (10) | 0.39870 (12) | 0.0680 (8) | |
| N3b | 1.2111 (3) | 0.48284 (10) | 0.76049 (14) | 0.0472 (8) | |
| N5b | 1.1654 (3) | 0.59180 (10) | 0.45701 (14) | 0.0418 (7) | |
| C1b | 0.8002 (3) | 0.60956 (10) | 0.63903 (15) | 0.0264 (7) | |
| C2b | 0.9062 (3) | 0.56604 (11) | 0.70954 (15) | 0.0299 (7) | |
| C3b | 1.0952 (3) | 0.53063 (10) | 0.69140 (15) | 0.0309 (7) | |
| C4b | 1.1814 (3) | 0.53946 (10) | 0.61042 (15) | 0.0309 (7) | |
| C5b | 1.0736 (3) | 0.58234 (10) | 0.54290 (14) | 0.0271 (7) | |
| C6b | 0.8810 (3) | 0.61681 (10) | 0.55538 (15) | 0.0273 (7) | |
| C11b | 0.6030 (3) | 0.65080 (11) | 0.65583 (18) | 0.0351 (8) | |
| N1a | −0.1521 (2) | 0.82026 (8) | 0.63826 (12) | 0.0293 (6) | |
| N8a | 0.1721 (2) | 0.76019 (9) | 0.67283 (12) | 0.0373 (7) | |
| C2a | −0.3261 (3) | 0.85089 (11) | 0.57022 (15) | 0.0370 (8) | |
| C3a | −0.2602 (3) | 0.91805 (11) | 0.52679 (15) | 0.0401 (8) | |
| C4a | −0.1188 (3) | 0.90791 (11) | 0.45061 (16) | 0.0417 (8) | |
| C5a | 0.0933 (3) | 0.86805 (11) | 0.48032 (14) | 0.0401 (8) | |
| C6a | 0.0611 (3) | 0.79367 (11) | 0.51423 (14) | 0.0344 (8) | |
| C7a | 0.0226 (3) | 0.79087 (10) | 0.61288 (14) | 0.0268 (7) | |
| C9a | 0.1394 (8) | 0.7480 (3) | 0.7694 (4) | 0.0377 (17) | 0.687 (4) |
| C10a | 0.0234 (5) | 0.8112 (2) | 0.8006 (2) | 0.0388 (12) | 0.687 (4) |
| C11a | −0.1865 (3) | 0.82334 (13) | 0.73606 (16) | 0.0375 (8) | |
| C13a | 0.192 (2) | 0.7733 (6) | 0.7752 (10) | 0.0377 (17) | 0.313 (4) |
| C12a | −0.0453 (12) | 0.7700 (5) | 0.7962 (6) | 0.0388 (12) | 0.313 (4) |
| H4b | 1.313123 | 0.516393 | 0.601144 | 0.0371* | |
| H8a | 0.304017 | 0.743029 | 0.652706 | 0.073 (8)* | |
| H10a | 0.119515 | 0.852593 | 0.800333 | 0.0466* | 0.686 |
| H21a | −0.458393 | 0.859249 | 0.600103 | 0.0444* | |
| H22a | −0.373911 | 0.816372 | 0.520773 | 0.0444* | |
| H31a | −0.393523 | 0.944805 | 0.502041 | 0.0481* | |
| H32a | −0.182575 | 0.948658 | 0.575716 | 0.0481* | |
| H41a | −0.084564 | 0.95395 | 0.425285 | 0.0501* | |
| H42a | −0.20539 | 0.883982 | 0.397103 | 0.0501* | |
| H51a | 0.180506 | 0.866759 | 0.428286 | 0.0482* | |
| H52a | 0.186838 | 0.894538 | 0.52943 | 0.0482* | |
| H61a | 0.191356 | 0.765112 | 0.506561 | 0.0413* | |
| H62a | −0.063947 | 0.77162 | 0.474177 | 0.0413* | |
| H91a | 0.046176 | 0.706149 | 0.772504 | 0.0452* | 0.687 (4) |
| H92a | 0.283833 | 0.74265 | 0.808712 | 0.0452* | 0.687 (4) |
| H11a | −0.009873 | 0.803439 | 0.864351 | 0.0466* | 0.686 |
| H12a | −0.318 (2) | 0.7965 (9) | 0.7425 (13) | 0.045* | |
| H13a | −0.230 (3) | 0.8711 (6) | 0.7485 (13) | 0.045* | |
| H14a | −0.105082 | 0.7226 | 0.782436 | 0.0466* | 0.313 (4) |
| H15a | −0.047311 | 0.780768 | 0.862598 | 0.0466* | 0.313 (4) |
| H16a | 0.27893 | 0.735519 | 0.809131 | 0.0452* | 0.313 (4) |
| H17a | 0.251697 | 0.820686 | 0.789237 | 0.0452* | 0.313 (4) |
| H21b | 0.621837 | 0.678052 | 0.538628 | 0.082 (11)* | 0.273 (4) |
| H2b | 0.702896 | 0.598291 | 0.774475 | 0.082 (11)* | 0.727 (4) |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O2b | 0.0481 (12) | 0.0570 (16) | 0.0296 (15) | 0.0087 (11) | 0.0152 (10) | 0.0091 (11) |
| O21b | 0.045 (3) | 0.053 (4) | 0.046 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.023 (3) |
| O11b | 0.0369 (8) | 0.0391 (10) | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0136 (7) | 0.0102 (8) | 0.0073 (9) |
| O12b | 0.0488 (9) | 0.0643 (12) | 0.0488 (12) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0232 (8) | −0.0030 (9) |
| O31b | 0.0796 (13) | 0.0853 (16) | 0.0753 (16) | −0.0256 (11) | −0.0175 (11) | 0.0533 (13) |
| O32b | 0.0728 (12) | 0.0903 (16) | 0.0642 (14) | 0.0483 (11) | −0.0074 (10) | 0.0050 (11) |
| O51b | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0650 (12) | 0.0694 (13) | 0.0077 (9) | 0.0350 (9) | −0.0110 (10) |
| O52b | 0.0926 (13) | 0.0722 (14) | 0.0455 (12) | 0.0171 (11) | 0.0314 (10) | 0.0241 (10) |
| N3b | 0.0575 (13) | 0.0347 (13) | 0.0432 (15) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0137 (11) | −0.0004 (10) |
| N5b | 0.0476 (11) | 0.0400 (13) | 0.0414 (13) | −0.0046 (10) | 0.0193 (10) | −0.0067 (10) |
| C1b | 0.0265 (10) | 0.0220 (11) | 0.0303 (13) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0024 (9) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C2b | 0.0337 (11) | 0.0267 (12) | 0.0294 (14) | −0.0061 (10) | 0.0050 (10) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C3b | 0.0361 (11) | 0.0233 (12) | 0.0304 (14) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0053 (10) | 0.0025 (10) |
| C4b | 0.0257 (10) | 0.0240 (12) | 0.0413 (15) | −0.0013 (9) | −0.0005 (10) | −0.0053 (11) |
| C5b | 0.0295 (10) | 0.0254 (12) | 0.0274 (13) | −0.0052 (9) | 0.0073 (9) | −0.0017 (10) |
| C6b | 0.0298 (10) | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0290 (13) | −0.0028 (9) | −0.0003 (9) | 0.0007 (10) |
| C11b | 0.0297 (11) | 0.0296 (13) | 0.0464 (16) | −0.0042 (10) | 0.0070 (11) | −0.0061 (12) |
| N1a | 0.0249 (8) | 0.0327 (11) | 0.0305 (11) | 0.0026 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | 0.0000 (9) |
| N8a | 0.0332 (9) | 0.0493 (12) | 0.0291 (12) | 0.0137 (9) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0056 (9) |
| C2a | 0.0243 (10) | 0.0400 (14) | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0063 (10) | −0.0002 (10) | −0.0020 (12) |
| C3a | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0465 (16) | 0.0071 (10) | −0.0044 (11) | 0.0000 (11) |
| C4a | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0397 (15) | 0.0370 (15) | −0.0028 (11) | −0.0060 (11) | 0.0087 (11) |
| C5a | 0.0368 (11) | 0.0526 (16) | 0.0319 (14) | −0.0008 (11) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0091 (12) |
| C6a | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0411 (15) | 0.0262 (13) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0032 (9) | −0.0057 (11) |
| C7a | 0.0283 (10) | 0.0224 (12) | 0.0291 (13) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0025 (9) | −0.0030 (10) |
| C9a | 0.040 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.0304 (18) | −0.001 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C10a | 0.049 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0270 (17) | −0.0043 (18) | 0.0083 (15) | −0.0029 (19) |
| C11a | 0.0367 (12) | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0364 (15) | 0.0003 (11) | 0.0161 (11) | −0.0056 (12) |
| C13a | 0.040 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.0304 (18) | −0.001 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
| C12a | 0.049 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.0270 (17) | −0.0043 (18) | 0.0083 (15) | −0.0029 (19) |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O2b—C2b | 1.285 (3) | C2a—H22a | 0.99 |
| O2b—H2b | 1.103 (2) | C3a—C4a | 1.518 (3) |
| H61b—C2b | 0.95 | C3a—H31a | 0.99 |
| O21b—C6b | 1.311 (6) | C3a—H32a | 0.99 |
| O21b—H21b | 1.303 (6) | C4a—C5a | 1.520 (3) |
| H6b—C6b | 0.95 | C4a—H41a | 0.99 |
| O11b—C11b | 1.248 (3) | C4a—H42a | 0.99 |
| O11b—H21b | 1.1454 (16) | C5a—C6a | 1.530 (3) |
| O12b—C11b | 1.272 (3) | C5a—H51a | 0.99 |
| O12b—H2b | 1.3846 (15) | C5a—H52a | 0.99 |
| O31b—N3b | 1.205 (3) | C6a—C7a | 1.490 (3) |
| O32b—N3b | 1.230 (3) | C6a—H61a | 0.99 |
| O51b—N5b | 1.219 (3) | C6a—H62a | 0.99 |
| O52b—N5b | 1.230 (3) | C9a—C10a | 1.508 (6) |
| N3b—C3b | 1.466 (3) | C9a—C13a | 0.581 (13) |
| N5b—C5b | 1.456 (3) | C9a—C12a | 1.323 (10) |
| C1b—C2b | 1.407 (3) | C9a—H91a | 0.99 |
| C1b—C6b | 1.387 (3) | C9a—H92a | 0.99 |
| C1b—C11b | 1.497 (3) | C9a—H16a | 0.9922 |
| C2b—C3b | 1.404 (3) | C10a—C11a | 1.501 (4) |
| C3b—C4b | 1.371 (3) | C10a—C13a | 1.358 (14) |
| C4b—C5b | 1.375 (3) | C10a—H10a | 0.99 |
| C4b—H4b | 0.95 | C10a—H11a | 0.99 |
| C5b—C6b | 1.392 (3) | C10a—H15a | 1.207 |
| N1a—C2a | 1.471 (2) | C11a—C12a | 1.530 (8) |
| N1a—C7a | 1.313 (2) | C11a—H12a | 0.977 (15) |
| N1a—C11a | 1.470 (3) | C11a—H13a | 0.978 (13) |
| N8a—C7a | 1.311 (2) | C13a—C12a | 1.534 (16) |
| N8a—C9a | 1.467 (6) | C13a—H92a | 0.9083 |
| N8a—C13a | 1.498 (15) | C13a—H16a | 0.99 |
| N8a—H8a | 0.9604 (17) | C13a—H17a | 0.99 |
| C2a—C3a | 1.514 (3) | C12a—H14a | 0.99 |
| C2a—H21a | 0.99 | C12a—H15a | 0.99 |
| H6b—O21b—H21b | 102.88 | N8a—C9a—C13a | 81.6 (16) |
| C11b—O12b—H2b | 98.61 (14) | N8a—C9a—C12a | 118.3 (5) |
| O31b—N3b—O32b | 124.0 (2) | N8a—C9a—H91a | 109.47 |
| O31b—N3b—C3b | 118.6 (2) | N8a—C9a—H92a | 109.47 |
| O32b—N3b—C3b | 117.4 (2) | N8a—C9a—H14a | 114.78 |
| O51b—N5b—O52b | 123.6 (2) | N8a—C9a—H16a | 111.65 |
| O51b—N5b—C5b | 118.57 (18) | C10a—C9a—H91a | 109.47 |
| O52b—N5b—C5b | 117.83 (18) | C10a—C9a—H92a | 109.47 |
| C2b—C1b—C6b | 120.82 (17) | C13a—C9a—C12a | 99.9 (15) |
| C2b—C1b—C11b | 119.6 (2) | C13a—C9a—H91a | 168.74 |
| C6b—C1b—C11b | 119.51 (18) | C13a—C9a—H14a | 137.56 |
| O2b—C2b—C1b | 121.84 (19) | C12a—C9a—H92a | 126.91 |
| O2b—C2b—C3b | 120.77 (19) | C12a—C9a—H16a | 127.82 |
| H61b—C2b—C1b | 121.37 | H91a—C9a—H92a | 111.59 |
| H61b—C2b—C3b | 121.37 | H14a—C9a—H16a | 126.91 |
| C1b—C2b—C3b | 117.3 (2) | H14a—C9a—H17a | 129.78 |
| N3b—C3b—C2b | 120.4 (2) | H16a—C9a—H17a | 77.55 |
| N3b—C3b—C4b | 117.12 (18) | C9a—C10a—C11a | 109.8 (3) |
| C2b—C3b—C4b | 122.44 (18) | C11a—C10a—C13a | 122.2 (6) |
| C3b—C4b—C5b | 118.75 (18) | C11a—C10a—H10a | 109.47 |
| C3b—C4b—H4b | 120.62 | C11a—C10a—H11a | 109.47 |
| C5b—C4b—H4b | 120.62 | C11a—C10a—H17a | 132.02 |
| N5b—C5b—C4b | 118.74 (17) | C13a—C10a—H11a | 116.43 |
| N5b—C5b—C6b | 119.80 (17) | C13a—C10a—H15a | 108.54 |
| C4b—C5b—C6b | 121.5 (2) | C12a—C10a—H17a | 124.07 |
| O21b—C6b—C1b | 118.4 (3) | H10a—C10a—H11a | 109.16 |
| O21b—C6b—C5b | 122.4 (3) | H10a—C10a—H15a | 132.06 |
| H6b—C6b—C1b | 120.41 | H11a—C10a—H17a | 117.48 |
| H6b—C6b—C5b | 120.41 | H15a—C10a—H17a | 127.34 |
| C1b—C6b—C5b | 119.17 (18) | N1a—C11a—C10a | 111.6 (2) |
| O11b—C11b—O12b | 123.9 (2) | N1a—C11a—C12a | 112.2 (4) |
| O11b—C11b—C1b | 119.4 (2) | N1a—C11a—H12a | 108.1 (11) |
| O12b—C11b—C1b | 116.70 (19) | N1a—C11a—H13a | 107.3 (12) |
| C2a—N1a—C7a | 121.83 (17) | C10a—C11a—H12a | 120.7 (10) |
| C2a—N1a—C11a | 116.29 (16) | C10a—C11a—H13a | 105.2 (10) |
| C7a—N1a—C11a | 121.87 (16) | C12a—C11a—H13a | 131.8 (11) |
| C7a—N8a—C9a | 121.9 (2) | H12a—C11a—H13a | 102.9 (15) |
| C7a—N8a—C13a | 122.3 (5) | N8a—C13a—C9a | 75.8 (15) |
| C7a—N8a—H8a | 119.53 (19) | N8a—C13a—C10a | 114.0 (9) |
| C9a—N8a—C13a | 22.6 (5) | N8a—C13a—C12a | 104.5 (8) |
| C9a—N8a—H8a | 118.5 (2) | N8a—C13a—H10a | 113.12 |
| C13a—N8a—H8a | 114.3 (5) | N8a—C13a—H92a | 112.32 |
| N1a—C2a—C3a | 114.01 (15) | N8a—C13a—H16a | 109.47 |
| N1a—C2a—H21a | 109.47 | N8a—C13a—H17a | 109.47 |
| N1a—C2a—H22a | 109.47 | C9a—C13a—H10a | 130.08 |
| C3a—C2a—H21a | 109.47 | C9a—C13a—H17a | 167.66 |
| C3a—C2a—H22a | 109.47 | C10a—C13a—H92a | 129.79 |
| H21a—C2a—H22a | 104.52 | C10a—C13a—H16a | 129.35 |
| C2a—C3a—C4a | 114.39 (18) | C12a—C13a—H92a | 113.84 |
| C2a—C3a—H31a | 109.47 | C12a—C13a—H16a | 109.47 |
| C2a—C3a—H32a | 109.47 | C12a—C13a—H17a | 109.47 |
| C4a—C3a—H31a | 109.47 | H10a—C13a—H91a | 126.53 |
| C4a—C3a—H32a | 109.47 | H10a—C13a—H92a | 130.35 |
| H31a—C3a—H32a | 104.05 | H10a—C13a—H16a | 135.32 |
| C3a—C4a—C5a | 114.58 (18) | H92a—C13a—H17a | 107.21 |
| C3a—C4a—H41a | 109.47 | H16a—C13a—H17a | 114.05 |
| C3a—C4a—H42a | 109.47 | C9a—C12a—C11a | 119.1 (6) |
| C5a—C4a—H41a | 109.47 | C9a—C12a—H11a | 111.16 |
| C5a—C4a—H42a | 109.47 | C9a—C12a—H15a | 119.13 |
| H41a—C4a—H42a | 103.83 | C10a—C12a—H91a | 125.59 |
| C4a—C5a—C6a | 114.44 (16) | C10a—C12a—H14a | 169.66 |
| C4a—C5a—H51a | 109.47 | C11a—C12a—C13a | 109.6 (7) |
| C4a—C5a—H52a | 109.47 | C11a—C12a—H91a | 130.75 |
| C6a—C5a—H51a | 109.47 | C11a—C12a—H14a | 109.47 |
| C6a—C5a—H52a | 109.47 | C11a—C12a—H15a | 109.47 |
| H51a—C5a—H52a | 104 | C13a—C12a—H14a | 109.47 |
| C5a—C6a—C7a | 112.99 (17) | C13a—C12a—H15a | 109.47 |
| C5a—C6a—H61a | 109.47 | H91a—C12a—H11a | 130.35 |
| C5a—C6a—H62a | 109.47 | H91a—C12a—H15a | 118.71 |
| C7a—C6a—H61a | 109.47 | H11a—C12a—H14a | 133.54 |
| C7a—C6a—H62a | 109.47 | H14a—C12a—H15a | 109.31 |
| H61a—C6a—H62a | 105.71 | O21b—H21b—O11b | 167.3 (3) |
| N1a—C7a—N8a | 121.93 (19) | H6b—H21b—O11b | 152.98 |
| N1a—C7a—C6a | 120.45 (16) | O2b—H2b—O12b | 166.81 (13) |
| N8a—C7a—C6a | 117.59 (17) | H61b—H2b—O12b | 150.18 |
| N8a—C9a—C10a | 107.3 (3) |
1-Aza-8-azoniabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 4-aminobenzoate (WADXOR). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N8a—H8a···O11b | 0.9604 (17) | 1.9329 (15) | 2.864 (2) | 162.83 (11) |
| C10a—H10a···O32bi | 0.99 | 2.44 | 3.248 (4) | 138 |
| C2a—H21a···O31bii | 0.99 | 2.48 | 3.275 (3) | 137 |
| C6a—H62a···O21biii | 0.99 | 2.44 | 3.152 (6) | 128 |
| C10a—H11a···O21biv | 0.99 | 2.47 | 3.033 (7) | 116 |
| O21b—H21b···O11b | 1.303 (6) | 1.1454 (16) | 2.433 (6) | 167.3 (3) |
| O11b—H21b···O21b | 1.1454 (16) | 1.303 (6) | 2.433 (6) | 167.3 (3) |
| O12b—H2b···O2b | 1.3846 (15) | 1.103 (2) | 2.471 (2) | 166.81 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Crystal data
| C26H29N2+·C7H3N2O7− | F(000) = 1256 |
| Mr = 596.63 | Dx = 1.341 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 383 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 14.5648 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 9909 reflections |
| b = 12.9374 (3) Å | θ = 2.3–28.3° |
| c = 16.1619 (3) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 103.900 (1)° | T = 200 K |
| V = 2956.22 (11) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.51 × 0.26 × 0.17 mm |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 7344 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5724 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.015 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −19→19 |
| Tmin = 0.932, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −17→17 |
| 29552 measured reflections | l = −21→15 |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F > 3σ(F)] = 0.054 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F) = 0.190 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.80 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/(σ2(I) + 0.0063999998I2) |
| 7344 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.044 |
| 399 parameters | Δρmax = 0.63 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| 120 constraints |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Special details
| Refinement. Number of fixed parameters 6 |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.25627 (8) | 0.71181 (9) | 0.31343 (7) | 0.0246 (3) | |
| H71 | 0.30128 | 0.669474 | 0.349979 | 0.035 (4)* | |
| N2 | 0.10023 (8) | 0.56683 (9) | 0.26575 (7) | 0.0233 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.29865 (11) | 0.95151 (12) | 0.41661 (10) | 0.0334 (5) | |
| H1a | 0.245898 | 0.980932 | 0.377422 | 0.0401* | |
| C2 | 0.33463 (11) | 0.86695 (12) | 0.39170 (10) | 0.0322 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.386765 | 0.835478 | 0.430202 | 0.0386* | |
| C3 | 0.29839 (12) | 0.81754 (12) | 0.30656 (10) | 0.0333 (5) | |
| H3a | 0.350521 | 0.811391 | 0.27725 | 0.04* | |
| H3b | 0.250048 | 0.862741 | 0.270514 | 0.04* | |
| C4 | 0.17112 (10) | 0.71678 (11) | 0.34935 (9) | 0.0281 (4) | |
| H4a | 0.123241 | 0.762704 | 0.313566 | 0.0337* | |
| H4b | 0.189039 | 0.745897 | 0.40767 | 0.0337* | |
| C5 | 0.12943 (10) | 0.61031 (11) | 0.35226 (9) | 0.0271 (4) | |
| H5a | 0.07387 | 0.614805 | 0.377337 | 0.0326* | |
| H5b | 0.177161 | 0.564522 | 0.388386 | 0.0326* | |
| C6 | 0.18571 (10) | 0.55563 (11) | 0.23345 (9) | 0.0262 (4) | |
| H6a | 0.231171 | 0.509606 | 0.271816 | 0.0315* | |
| H6b | 0.168931 | 0.5233 | 0.176272 | 0.0315* | |
| C7 | 0.23149 (10) | 0.65944 (12) | 0.22789 (9) | 0.0282 (4) | |
| H7a | 0.289537 | 0.649813 | 0.207068 | 0.0338* | |
| H7b | 0.187639 | 0.703827 | 0.186493 | 0.0338* | |
| C8 | 0.05326 (9) | 0.46528 (10) | 0.26756 (8) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.099282 | 0.417266 | 0.304542 | 0.0276* | |
| C11 | 0.33145 (11) | 1.00535 (12) | 0.49876 (10) | 0.0326 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.41578 (13) | 0.97941 (14) | 0.55685 (10) | 0.0391 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.454927 | 0.926517 | 0.543205 | 0.047* | |
| C13 | 0.44278 (15) | 1.03053 (17) | 0.63457 (11) | 0.0502 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.499799 | 1.011658 | 0.674094 | 0.0603* | |
| C14 | 0.38752 (17) | 1.10810 (17) | 0.65451 (12) | 0.0554 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.40688 | 1.143158 | 0.707495 | 0.0665* | |
| C15 | 0.30389 (15) | 1.13552 (16) | 0.59798 (13) | 0.0516 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.265849 | 1.18931 | 0.61197 | 0.0619* | |
| C16 | 0.27570 (13) | 1.08400 (13) | 0.52053 (11) | 0.0397 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.217882 | 1.102436 | 0.481949 | 0.0476* | |
| C21 | −0.03166 (9) | 0.47504 (10) | 0.30647 (8) | 0.0240 (4) | |
| C22 | −0.04272 (11) | 0.40385 (12) | 0.36763 (10) | 0.0315 (5) | |
| H22 | 0.003276 | 0.351198 | 0.385315 | 0.0378* | |
| C23 | −0.12077 (12) | 0.40899 (13) | 0.40333 (11) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| H23 | −0.127745 | 0.359826 | 0.445056 | 0.0466* | |
| C24 | −0.18805 (12) | 0.48544 (13) | 0.37818 (11) | 0.0385 (5) | |
| H24 | −0.241677 | 0.488365 | 0.401911 | 0.0461* | |
| C25 | −0.17687 (11) | 0.55719 (12) | 0.31859 (11) | 0.0351 (5) | |
| H25 | −0.222711 | 0.610174 | 0.301738 | 0.0421* | |
| C26 | −0.09910 (10) | 0.55304 (11) | 0.28271 (9) | 0.0286 (4) | |
| H26 | −0.091899 | 0.603396 | 0.241958 | 0.0344* | |
| C31 | 0.02520 (10) | 0.41880 (11) | 0.17810 (9) | 0.0248 (4) | |
| C32 | 0.06690 (11) | 0.32720 (12) | 0.16027 (10) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| H32 | 0.112496 | 0.2938 | 0.204043 | 0.0397* | |
| C33 | 0.04254 (13) | 0.28416 (13) | 0.07918 (11) | 0.0392 (5) | |
| H33 | 0.071842 | 0.221893 | 0.067798 | 0.047* | |
| C34 | −0.02351 (12) | 0.33108 (13) | 0.01557 (10) | 0.0379 (5) | |
| H34 | −0.039638 | 0.301886 | −0.039979 | 0.0455* | |
| C35 | −0.06672 (12) | 0.42142 (14) | 0.03267 (10) | 0.0385 (5) | |
| H35 | −0.113709 | 0.453238 | −0.01092 | 0.0461* | |
| C36 | −0.04162 (11) | 0.46550 (12) | 0.11316 (10) | 0.0321 (5) | |
| H36 | −0.070483 | 0.528311 | 0.123929 | 0.0386* | |
| O1 | 0.63327 (8) | 0.37352 (10) | 0.53505 (8) | 0.0392 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.58197 (10) | 0.44006 (14) | 0.67133 (9) | 0.0614 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.43608 (10) | 0.48129 (12) | 0.65684 (9) | 0.0549 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.19464 (9) | 0.32143 (13) | 0.44743 (10) | 0.0569 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.22764 (11) | 0.24248 (13) | 0.34091 (10) | 0.0631 (6) | |
| O6 | 0.54745 (10) | 0.23529 (12) | 0.30214 (8) | 0.0518 (5) | |
| O7 | 0.66627 (9) | 0.28940 (12) | 0.40564 (9) | 0.0507 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.49861 (10) | 0.43835 (11) | 0.63197 (9) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.25133 (10) | 0.29121 (12) | 0.40756 (10) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.57563 (13) | 0.27360 (13) | 0.37128 (12) | 0.0398 (6) | |
| C41 | 0.54458 (10) | 0.35627 (11) | 0.50735 (10) | 0.0298 (4) | |
| C42 | 0.50987 (11) | 0.30564 (12) | 0.42622 (10) | 0.0314 (5) | |
| C43 | 0.41587 (11) | 0.28489 (12) | 0.39522 (10) | 0.0329 (5) | |
| H43 | 0.395087 | 0.249901 | 0.342348 | 0.0394* | |
| C44 | 0.35106 (10) | 0.31453 (12) | 0.44039 (10) | 0.0313 (4) | |
| C45 | 0.37850 (10) | 0.36477 (12) | 0.51759 (10) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| H45 | 0.332901 | 0.38543 | 0.547596 | 0.0366* | |
| C46 | 0.47336 (11) | 0.38456 (11) | 0.55054 (9) | 0.0290 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.676841 | 0.321683 | 0.458063 | 0.030 (4)* |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0282 (6) | 0.0236 (5) | −0.0039 (4) | 0.0055 (4) | −0.0028 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0227 (5) | −0.0035 (4) | 0.0063 (4) | −0.0032 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0314 (7) | −0.0037 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0308 (7) | 0.0334 (7) | −0.0076 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0304 (7) | 0.0318 (7) | −0.0113 (6) | 0.0111 (6) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0331 (7) | 0.0302 (7) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0075 (5) | −0.0076 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0241 (6) | −0.0051 (5) | 0.0082 (5) | −0.0053 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0232 (6) | 0.0304 (7) | 0.0265 (6) | −0.0032 (5) | 0.0088 (5) | −0.0047 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0285 (7) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0223 (6) | −0.0060 (6) | 0.0073 (5) | −0.0045 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0245 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0010 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0306 (7) | 0.0307 (7) | −0.0080 (6) | 0.0064 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0398 (9) | 0.0415 (9) | 0.0337 (8) | −0.0067 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0523 (11) | 0.0604 (12) | 0.0319 (8) | −0.0142 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | 0.0005 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0691 (14) | 0.0629 (13) | 0.0354 (9) | −0.0230 (10) | 0.0149 (9) | −0.0159 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0584 (12) | 0.0455 (10) | 0.0562 (11) | −0.0106 (9) | 0.0242 (10) | −0.0151 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0392 (9) | 0.0350 (8) | 0.0444 (9) | −0.0049 (7) | 0.0090 (7) | −0.0039 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0213 (6) | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0255 (6) | −0.0020 (5) | 0.0050 (5) | −0.0024 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0329 (8) | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0046 (6) |
| C23 | 0.0426 (9) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0413 (9) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0228 (7) | 0.0058 (7) |
| C24 | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0493 (9) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0245 (7) | −0.0078 (7) |
| C25 | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0336 (8) | 0.0447 (9) | 0.0044 (6) | 0.0104 (6) | −0.0058 (6) |
| C26 | 0.0269 (7) | 0.0271 (7) | 0.0323 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0079 (6) | 0.0002 (5) |
| C31 | 0.0226 (6) | 0.0253 (6) | 0.0282 (6) | −0.0049 (5) | 0.0093 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C32 | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0367 (8) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0076 (6) | −0.0021 (6) |
| C33 | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0463 (9) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0154 (8) | −0.0097 (7) |
| C34 | 0.0452 (9) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0313 (8) | −0.0104 (7) | 0.0109 (7) | −0.0090 (6) |
| C35 | 0.0387 (9) | 0.0451 (9) | 0.0283 (7) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C36 | 0.0316 (8) | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0310 (7) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0073 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0242 (6) | 0.0466 (7) | 0.0449 (6) | −0.0022 (5) | 0.0046 (5) | 0.0065 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0954 (12) | 0.0457 (8) | 0.0021 (7) | −0.0029 (6) | −0.0243 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0459 (8) | 0.0698 (9) | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0153 (7) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0171 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0239 (6) | 0.0732 (10) | 0.0713 (9) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0067 (6) | −0.0008 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0465 (8) | 0.0774 (11) | 0.0531 (8) | −0.0103 (7) | −0.0120 (7) | −0.0150 (7) |
| O6 | 0.0595 (9) | 0.0612 (9) | 0.0400 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | 0.0226 (6) | −0.0026 (6) |
| O7 | 0.0391 (7) | 0.0619 (9) | 0.0567 (8) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0223 (6) | −0.0035 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0405 (8) | 0.0347 (7) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0023 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0466 (8) | 0.0442 (8) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0056 (6) | 0.0040 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0352 (8) | 0.0491 (10) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0095 (7) |
| C41 | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0277 (7) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0099 (6) |
| C42 | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0049 (6) | 0.0133 (6) | 0.0074 (6) |
| C43 | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0059 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C44 | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0334 (8) | 0.0333 (7) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C45 | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0333 (7) | 0.0060 (6) | 0.0067 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C46 | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0017 (6) | 0.0016 (5) |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N1—H71 | 0.9448 (11) | C16—H16 | 0.95 |
| N1—C3 | 1.5141 (19) | C21—C22 | 1.388 (2) |
| N1—C4 | 1.492 (2) | C21—C26 | 1.3962 (19) |
| N1—C7 | 1.5036 (18) | C22—H22 | 0.95 |
| N2—C5 | 1.4718 (17) | C22—C23 | 1.395 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.4682 (19) | C23—H23 | 0.95 |
| N2—C8 | 1.4848 (17) | C23—C24 | 1.383 (2) |
| C1—H1a | 0.95 | C24—H24 | 0.95 |
| C1—C2 | 1.317 (2) | C24—C25 | 1.375 (3) |
| C1—C11 | 1.474 (2) | C25—H25 | 0.95 |
| C2—H2 | 0.95 | C25—C26 | 1.392 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.494 (2) | C26—H26 | 0.95 |
| C3—H3a | 0.99 | C31—C32 | 1.393 (2) |
| C3—H3b | 0.99 | C31—C36 | 1.3867 (19) |
| H3a—H3b | 1.5869 | C32—H32 | 0.95 |
| C4—H4a | 0.99 | C32—C33 | 1.389 (2) |
| C4—H4b | 0.99 | C33—H33 | 0.95 |
| C4—C5 | 1.511 (2) | C33—C34 | 1.370 (2) |
| H4a—H4b | 1.6058 | C34—H34 | 0.95 |
| C5—H5a | 0.99 | C34—C35 | 1.386 (3) |
| C5—H5b | 0.99 | C35—H35 | 0.95 |
| H5a—H5b | 1.6091 | C35—C36 | 1.387 (2) |
| C6—H6a | 0.99 | C36—H36 | 0.95 |
| C6—H6b | 0.99 | O1—C41 | 1.2810 (17) |
| C6—C7 | 1.512 (2) | O2—N3 | 1.2281 (18) |
| H6a—H6b | 1.6016 | O3—N3 | 1.215 (2) |
| C7—H7a | 0.99 | O4—N4 | 1.227 (2) |
| C7—H7b | 0.99 | O5—N4 | 1.224 (2) |
| H7a—H7b | 1.6014 | O6—C9 | 1.201 (2) |
| C8—H8 | 1 | O7—C9 | 1.319 (2) |
| C8—C21 | 1.522 (2) | O7—H7 | 0.9238 (15) |
| C8—C31 | 1.5282 (19) | N3—C46 | 1.456 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.396 (2) | N4—C44 | 1.453 (2) |
| C11—C16 | 1.399 (3) | C9—C42 | 1.512 (3) |
| C12—H12 | 0.95 | C41—C42 | 1.444 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.390 (2) | C41—C46 | 1.430 (2) |
| C13—H13 | 0.95 | C42—C43 | 1.367 (2) |
| C13—C14 | 1.372 (3) | C43—H43 | 0.95 |
| C14—H14 | 0.95 | C43—C44 | 1.379 (2) |
| C14—C15 | 1.382 (3) | C44—C45 | 1.378 (2) |
| C15—H15 | 0.95 | C45—H45 | 0.95 |
| C15—C16 | 1.390 (3) | C45—C46 | 1.380 (2) |
| H71—N1—C3 | 109.70 (10) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.61 |
| H71—N1—C4 | 107.37 (11) | C8—C21—C22 | 118.95 (12) |
| H71—N1—C7 | 106.90 (11) | C8—C21—C26 | 122.30 (13) |
| C3—N1—C4 | 112.27 (12) | C22—C21—C26 | 118.75 (14) |
| C3—N1—C7 | 110.59 (11) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.72 |
| C4—N1—C7 | 109.82 (10) | C21—C22—C23 | 120.56 (14) |
| C5—N2—C6 | 107.42 (10) | H22—C22—C23 | 119.72 |
| C5—N2—C8 | 110.41 (11) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.9 |
| C6—N2—C8 | 110.71 (11) | C22—C23—C24 | 120.20 (16) |
| H1a—C1—C2 | 116.52 | H23—C23—C24 | 119.9 |
| H1a—C1—C11 | 116.52 | C23—C24—H24 | 120.2 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 126.96 (14) | C23—C24—C25 | 119.60 (17) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 118.03 | H24—C24—C25 | 120.2 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 123.95 (13) | C24—C25—H25 | 119.64 |
| H2—C2—C3 | 118.03 | C24—C25—C26 | 120.72 (15) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 112.26 (13) | H25—C25—C26 | 119.64 |
| N1—C3—H3a | 109.47 | C21—C26—C25 | 120.16 (14) |
| N1—C3—H3b | 109.47 | C21—C26—H26 | 119.92 |
| C2—C3—H3a | 109.47 | C25—C26—H26 | 119.92 |
| C2—C3—H3b | 109.47 | C8—C31—C32 | 119.98 (11) |
| H3a—C3—H3b | 106.54 | C8—C31—C36 | 121.61 (13) |
| N1—C4—H4a | 109.47 | C32—C31—C36 | 118.41 (13) |
| N1—C4—H4b | 109.47 | C31—C32—H32 | 119.64 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 110.53 (12) | C31—C32—C33 | 120.73 (13) |
| H4a—C4—H4b | 108.39 | H32—C32—C33 | 119.64 |
| H4a—C4—C5 | 109.47 | C32—C33—H33 | 119.85 |
| H4b—C4—C5 | 109.47 | C32—C33—C34 | 120.30 (16) |
| N2—C5—C4 | 110.21 (12) | H33—C33—C34 | 119.85 |
| N2—C5—H5a | 109.47 | C33—C34—H34 | 120.18 |
| N2—C5—H5b | 109.47 | C33—C34—C35 | 119.65 (15) |
| C4—C5—H5a | 109.47 | H34—C34—C35 | 120.18 |
| C4—C5—H5b | 109.47 | C34—C35—H35 | 119.87 |
| H5a—C5—H5b | 108.72 | C34—C35—C36 | 120.25 (14) |
| N2—C6—H6a | 109.47 | H35—C35—C36 | 119.88 |
| N2—C6—H6b | 109.47 | C31—C36—C35 | 120.65 (15) |
| N2—C6—C7 | 110.93 (12) | C31—C36—H36 | 119.67 |
| H6a—C6—H6b | 107.97 | C35—C36—H36 | 119.68 |
| H6a—C6—C7 | 109.47 | C41—O1—H7 | 101.64 (10) |
| H6b—C6—C7 | 109.47 | C9—O7—H7 | 112.68 (16) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 110.95 (12) | O2—N3—O3 | 123.16 (15) |
| N1—C7—H7a | 109.47 | O2—N3—C46 | 118.72 (15) |
| N1—C7—H7b | 109.47 | O3—N3—C46 | 118.10 (13) |
| C6—C7—H7a | 109.47 | O4—N4—O5 | 122.91 (15) |
| C6—C7—H7b | 109.47 | O4—N4—C44 | 118.79 (14) |
| H7a—C7—H7b | 107.95 | O5—N4—C44 | 118.29 (16) |
| N2—C8—H8 | 108.39 | O6—C9—O7 | 122.64 (19) |
| N2—C8—C21 | 111.04 (11) | O6—C9—C42 | 122.44 (16) |
| N2—C8—C31 | 110.45 (11) | O7—C9—C42 | 114.91 (15) |
| H8—C8—C21 | 107.41 | O1—C41—C42 | 120.00 (15) |
| H8—C8—C31 | 108.03 | O1—C41—C46 | 125.00 (14) |
| C21—C8—C31 | 111.38 (10) | C42—C41—C46 | 115.00 (13) |
| C1—C11—C12 | 122.33 (15) | C9—C42—C41 | 121.64 (14) |
| C1—C11—C16 | 119.24 (13) | C9—C42—C43 | 116.80 (14) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 118.42 (15) | C41—C42—C43 | 121.55 (16) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.81 | C42—C43—H43 | 119.87 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.37 (17) | C42—C43—C44 | 120.27 (14) |
| H12—C12—C13 | 119.81 | H43—C43—C44 | 119.87 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.82 | N4—C44—C43 | 120.01 (14) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 120.37 (17) | N4—C44—C45 | 118.40 (15) |
| H13—C13—C14 | 119.82 | C43—C44—C45 | 121.59 (13) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 | C44—C45—H45 | 120.57 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.40 (18) | C44—C45—C46 | 118.86 (15) |
| H14—C14—C15 | 119.8 | H45—C45—C46 | 120.57 |
| C14—C15—H15 | 120.17 | N3—C46—C41 | 120.55 (13) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 119.7 (2) | N3—C46—C45 | 116.73 (14) |
| H15—C15—C16 | 120.17 | C41—C46—C45 | 122.71 (13) |
| C11—C16—C15 | 120.77 (16) | O1—H7—O7 | 148.96 (9) |
| C11—C16—H16 | 119.61 |
4-(Diphenylmethyl)-1-(3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl)piperazin-1-ium 2-carboxy-4,6-dinitrophenolate (YAXPOE). Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H71···O1i | 0.9448 (11) | 1.9544 (11) | 2.8126 (15) | 150.01 (8) |
| N1—H71···O2i | 0.9448 (11) | 2.3020 (16) | 3.032 (2) | 133.62 (8) |
| C3—H3a···O6ii | 0.99 | 2.40 | 3.340 (2) | 159 |
| C5—H5a···C21 | 0.99 | 2.47 | 2.8777 (19) | 104 |
| C6—H6b···C31 | 0.99 | 2.50 | 2.8974 (19) | 104 |
| O7—H7···O1 | 0.9238 (15) | 1.6675 (13) | 2.505 (2) | 148.96 (9) |
| O7—H7···C41 | 0.9238 (15) | 2.2985 (16) | 2.827 (2) | 115.91 (9) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Ministerstvo Školství, Mládeže a Tělovýchovy grant NPU I – LO1603.
References
- Childs, S. L., Stahly, G. P. & Park, A. (2007). Mol. Pharm. 4, 323–338. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dayananda, A. S., Yathirajan, H. S., Gerber, T., Hosten, E. & Betz, R. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1165–o1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dean, J. A. (1987). Handbook of Organic Chemistry, pp. 8–46 New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Book Co.
- Fu, X., Liu, X., Sun, P., Zhang, S., Yang, Q., Wei, Q., Xie, G., Chen, S. & Fan, X. (2015). J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 114, 79–90.
- Gao, X., Zhang, H., Wen, X., Liu, B., Jin, S. & Wang, D. (2015). J. Mol. Struct. 1093, 82–95.
- Gilli, G., Bellucci, F., Ferretti, V. & Bertolasi, V. (1989). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111, 1023–1028. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gilli, G. & Gilli, P. (2009). The Nature of the Hydrogen Bond, pp. 81–147. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Gilli, P., Pretto, L., Bertolasi, V. & Gilli, G. (2009). Acc. Chem. Res. 34, 34–44. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hemamalini, M. & Fun, H.-K. (2010a). Acta Cryst. E66, o1194–o1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hemamalini, M. & Fun, H.-K. (2010b). Acta Cryst. E66, o2950–o2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hemamalini, M. & Fun, H.-K. (2010c). Acta Cryst. E66, o2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hosmane, R. S. & Liebman, J. F. (2009). Struct. Chem. 20, 693–697.
- Huang, F., Song, W.-D. & Li, S.-D. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m388–m389.
- Jeffrey, G. A. (1995). Crystallogr. Rev. 4, 213–254.
- Jin, S., Lin, Z., Wang, D., Chen, G., Ji, Z., Huang, T. & Zhou, Y. (2015a). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 45, 159–168.
- Jin, S., Wang, D., Linhe, Q., Fu, M., Wu, S. & Ren, J. (2013). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 43, 258–265.
- Jin, S., Zhang, H., Liu, H., Wen, X., Li, M. & Wang, D. (2015b). J. Mol. Struct. 1096, 157–170.
- Jones, C. L., Wilson, C. C. & Thomas, L. H. (2014). CrystEngComm, 16, 5849–5858.
- Khan, I. M., Ahmad, A. & Ullah, M. F. (2013). Spectrochim. Acta A, 102, 82–87. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Malathy, S., Nirmalram, J. S. & Muthiah, P. T. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 618–620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Müller, P. (2009). Crystallogr. Rev. 15, 57–83.
- Ng, S. W., Naumov, P., Drew, M. G. B., Wojciechowski, G. & Brzezinski, B. (2001). J. Mol. Struct. 595, 29–37.
- Petříček, V., Dušek, M. & Palatinus, L. (2014). Z. Kristallogr. 229, 345–352.
- Rajkumar, M. & Chandramohan, A. (2017). J. Mol. Struct. 1134, 762–769.
- Senthil Kumar, V. S., Kuduva, S. S. & Desiraju, G. R. (1999). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 1069–1074.
- Senthil Kumar, V. S., Kuduva, S. S. & Desiraju, G. R. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, o865–o866.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Singh, N., Khan, I. M., Ahmad, A. & Javed, S. (2014). J. Mol. Liq. 191, 142–150.
- Smith, G., Bott, R. C. & Wermuth, U. D. (2001a). Acta Cryst. E57, o640–o642.
- Smith, G. & Lynch, D. E. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 382–386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Lynch, D. E., Byriel, K. A. & Kennard, C. H. L. (1995). Aust. J. Chem. 48, 1133–1149.
- Smith, G. & Wermuth, U. D. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, 430–434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Bott, R. C., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2002a). Aust. J. Chem. 55, 349–356.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Bott, R. C., White, J. M. & Willis, A. C. (2001b). Aust. J. Chem. 54, 165–170.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2002b). Acta Cryst. E58, o845–o847.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2005a). Acta Cryst. E61, o746–o748. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & Healy, P. C. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o610–o613.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2003a). Aust. J. Chem. 56, 707–713.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2007). Aust. J. Chem. 60, 264–277.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2011). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 41, 1649–1662.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & White, J. M. (2001c). Acta Cryst. E57, o1036–o1038.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & White, J. M. (2003b). Acta Cryst. E59, o1977–o1979.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & White, J. M. (2005b). Acta Cryst. E61, o1836–o1838.
- Sobczyk, L., Grabowski, S. J. & Krygowski, T. M. (2005). Chem. Rev. 105, 3513–3560. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-D., Guo, X.-X. & Yu, L. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1890–o1891.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, B., Nanubolu, J. B. & Ravikumar, K. (2013). Acta Cryst. C69, 1164–1169. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Subashini, A., Samuel, E., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-T., Che, G.-B., Liu, C.-B., Wang, X. & Liu, L. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, m76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wei, S., Jin, S., Hu, Z., Zhou, Y. & Zhou, Y. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yamuna, T. S., Kaur, M., Anderson, B. J., Jasinski, J. P. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o318–o319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.-L. & Jian, F.-F. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J., Jin, S., Tao, L., Liu, B. & Wang, D. (2014). J. Mol. Struct. 1072, 208–220.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, DUJZAK, JEVNAA, NUQVEB, QIQJAD, SEDKET, VABZIJ, WADXOR, YAXPOE, LUDFUL, SAFGUD, TIYZIM, TUJPEV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IIIsup4.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IV. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IVsup5.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) V. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Vsup6.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIsup7.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VII. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIIsup8.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) VIII. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VIIIsup9.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) IX. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452IXsup10.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) X. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452Xsup11.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) XI. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452XIsup12.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452NUQVEBsup13.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452QIQJADsup14.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452SEDKETsup15.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452TIYZIMsup16.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452TUJPEVsup17.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452VABZIJsup18.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452WADXORsup19.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452YAXPOEsup20.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989018011544/su5452sup21.pdf
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report