Intraerythrocytic malaria parasites reside within a parasitophorous vacuolar membrane (PVM) generated during host cell invasion1. Erythrocyte remodeling and parasite metabolism respectively require export of effector proteins and transport of small molecules across this barrier between the parasite surface and host cell cytosol2,3. Protein export across the PVM is accomplished by the Plasmodium translocon of exported proteins (PTEX) consisting of three core proteins including the AAA+ ATPase HSP101 and two additional proteins known as PTEX150 and EXP24. Inactivation of HSP101 and PTEX150 arrests protein export across the PVM5,6, but the contribution of EXP2 to parasite biology is not well understood7. At the same time, a nutrient permeable channel in the PVM has been characterized electrophysiologically, but its molecular identity is unknown8,9. Here, using regulated gene expression, mutagenesis and cell-attached patch clamp measurements, we show that EXP2, the putative membrane-spanning channel of PTEX4,10–14, serves dual roles as a protein-conducting channel in the context of PTEX and as a channel able to facilitate nutrient passage across the PVM independent of HSP101. Our data suggest a dual functionality for a channel operating in its endogenous context.
To interrogate EXP2 function in the intraerythrocytic cycle of Plasmodium falciparum, we employed the recently developed TetR-DOZI-aptamer system15,16 to achieve conditional control of EXP2 translation in a clonal parasite line designated EXP2apt (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1). In the presence of anhydrotetracycline (aTc), EXP2apt parasites showed a ~60% reduction in basal EXP2 expression by western blot and displayed a growth defect relative to the parental line (Fig. 1b, c). Removal of aTc from the culture resulted in further reduction of EXP2 levels to less than 10% of the parent in 48 h and a complete block in replication, demonstrating an essential requirement of EXP2 for blood-stage survival. We also observed a correlation between the number of merozoites produced per infected red blood cell (RBC) and EXP2 expression levels (Supplementary Fig. 2), demonstrating EXP2 is important for fitness in the later stages of the parasite developmental cycle17.
Figure 1. EXP2 is essential for blood stage survival and protein export.
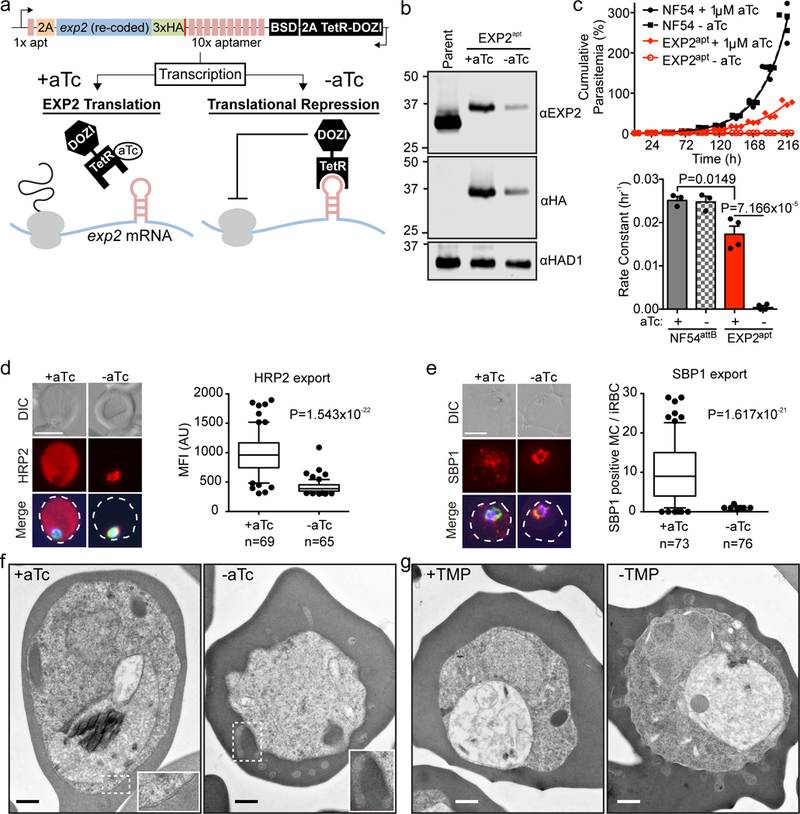
a, Schematic of TetR-DOZI-aptamers strategy for conditional translational repression of EXP2. 2A, thosea asigna virus 2A skip peptide; HA, haemagglutinin tag; BSD, blasticidin-S deaminase; TetR-DOZI, Tetracycline repressor-DOZI fusion. b, Western blot of parental NF54attB - aTc and EXP2apt parasites +/− aTc for 48 h. The cytosolic haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase protein HAD1 serves as a loading control. Predicted molecular weights after signal peptide cleavage: EXP2: 30.8 kDa; EXP2–3xHA: 34.1 kDa. Results are representative of three independent experiments. EXP2 levels are reduced to 42.74±9.49% +aTc and 6.49±3.95% -aTc relative to the parental line. Uncropped western blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11. c, Growth analysis of NF54attB and EXP2apt parasites +/− aTc. Results from one experiment with three technical replicates are shown and are representative of multiple independent experiments. Bar graph shows mean exponential growth rate constants (hr−1) derived from the fit of three (NF54attB) or four (EXP2apt) independent experiments. Error bars indicate s.e.m. d, e, Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) showing export of the Plasmodium Export Element (PEXEL)-containing protein HRP2 (d) and the PEXEL-negative exported protein (PNEP) SBP1 (e) in EXP2apt parasites (bearing a 3xFLAG tag on HSP101) synchronized to a 3 h invasion window and allowed to develop 24 h post invasion +/− aTc. Merge images include (d) Aldolase or (e) HSP101–3xFLAG in green and DAPI in blue. Scale bars, 5 μm. Quantification of HRP2 export to the host cytosol (d) or the number of SBP1-positive Maurer’s Clefts (MC) (e) is shown. Data are pooled from two independent experiments, n is the number of individual parasite-infected RBCs. Boxes and whiskers delineate 25th-75th and 10th-90th percentiles, respectively. All P values determined by an unpaired, two-sided t-test. DIC, differential interference contrast; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. f, g, PV morphological abnormalities following EXP2 knockdown (f) or HSP101 inactivation (g) visualized by transmission electron microscopy. The phenotype was visualized in three independent experiments by Giemsa stain (Supplementary Fig. 3) and in a single electron microscopy experiment. Scale bar, 500 nm.
Similar to other PTEX core components5,6, depletion of EXP2 resulted in a severe defect in export of effector proteins beyond the PVM (Fig. 1d, e). This was accompanied by abnormalities in PV morphology which could be visualized in Giemsa-stained thin smears (Supplementary Fig. 3) and revealed by transmission electron microscopy to be tubular distensions of the PVM projecting into the erythrocyte cytosol, in contrast to the normal tight apposition of the PVM to the parasite plasma membrane (PPM) (Fig. 1f). To test the impact on PV morphology of inactivating a distinct PTEX core component, we utilized a previously reported approach for post-translational conditional inactivation of HSP1015 which we regenerated in the NF54attB background used in the present study (Supplementary Fig. 4). In this system, a mutant, unstructured version of E. coli DHFR is fused to the endogenous C-terminus of HSP101. Normal function is maintained in the presence of trimethoprim (TMP) while withdrawal of this stabilizing ligand leads to rapid inactivation of HSP101. Similar PVM distensions were observed following conditional inactivation of HSP101 (Fig. 1g) and presumably arise from buildup of blocked exported proteins in the PV lumen that either directly expand the volume of the PV or alter the osmotic balance within the compartment, leading to swelling. Specificity of exported protein trafficking through PTEX has been hypothesized to occur either through recognition of unique export signals on cargo secreted into the PV lumen, or through dedicated export subcompartments to which PTEX has privileged access18. That PVM distension arise from discrete points rather than presenting as a uniform PVM swelling is better explained by the later model. We tested this possibility with a split GFP approach modeled after a previously reported sub-compartmental split GFP strategy in P. falciparum19. This system enabled us to monitor the PTEX accessibility of a soluble GFP1–10 reporter targeted to the PV lumen. Vacuolar GFP fluorescence was observed when a GFP11 tag was fused to the endogenous C-terminus of EXP2, PTEX150 or HSP101, indicating that PTEX components are freely accessible by diffusion of non-exported proteins in the PV lumen (Supplementary Fig. 5). This argues against export-dedicated subcompartments and suggests that other constraints, such as possible sites of PVM-PPM anchoring, contribute to the formation of the distensions observed upon EXP2 or HSP101 knockdown. These split GFP assays also indicate that the C-terminus of EXP2 resides within the PV lumen.
Peak expression of HSP101 and PTEX150 begins in late schizogony during merozoite formation and extends into the early ring stage shortly after invasion11,20, overlapping with the expression of many exported proteins early in intraerythrocytic development during a period of dramatic host cell remodeling21. In contrast, EXP2 transcription peaks later20, achieving higher transcript abundance than HSP101 and PTEX150 (Fig. 2a). Pulse-chase experiments indicated EXP2 synthesis also peaks later11 and time-resolved western blots of tightly synchronized parasites revealed increasing ratios of EXP2 relative to HSP101 as development proceeds (Fig. 2b). Furthermore, the majority of EXP2 was not co-purified with depleting immunoprecipitation of HSP101, particularly in the later part of the cycle when EXP2 levels are highest (Fig. 2c). These results suggest EXP2 may serve additional roles beyond PTEX-mediated protein export.
Figure 2. EXP2 expression differs from other PTEX components.
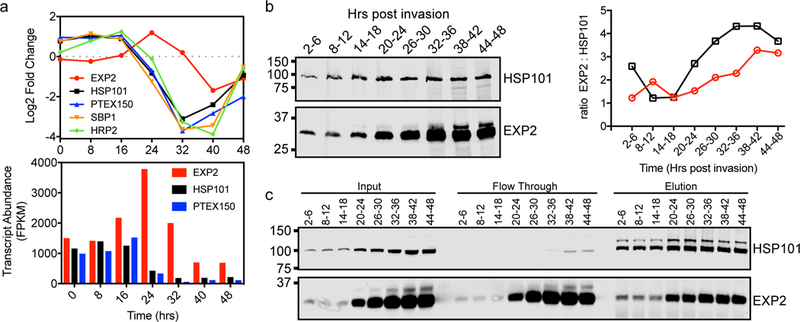
a, Transcript fold change of PTEX core components and exported proteins HRP2 and SBP1 throughout intraerythrocytic development gauged by RNA sequencing analysis of synchronized P. falciparum 3D7 parasites. Transcript abundance is shown for PTEX core components. Data from Otto et al dataset consisting of a single biological sample at each time point20. b, Time-resolved western blot detecting HSP101 and EXP2 in parasites with a 3xFLAG tag on the endogenous HSP101 C-terminus. Parasites were synchronized to a 4 h window by pulse-invasion. HSP101 and EXP2 were detected with anti-FLAG and anti-EXP2 antibodies, respectively. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Ratios of quantified EXP2 signal to HSP101 signal at each time point from two independent experiments (different symbols and colors) are given at right showing increasing levels of EXP2 relative to HSP101 in the second half of parasite development. c, Western blot of time-resolved immunoprecipitation of HSP101–3xFLAG and co-immunoprecipitation of EXP2. Parasites were synchronized as in b. Elution samples were not reduced to avoid release of anti-FLAG heavy and light chain from the beads and minor, higher molecular weight species of HSP101 are seen in these conditions. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Uncropped western blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 11.
Disruption of EXP2 orthologs in the related apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii results in a defect in small molecule transport (but not protein export) across the PVM that can be rescued by complementation with P. falciparum EXP213. The Toxoplasma PVM channel22 is thought to have similar characteristics to a nutrient-permeable PVM channel of unknown molecular identity in P. falciparum, which was characterized by on-cell patch clamp and is thought to play a crucial role in nutrient acquisition8,9. As EXP2 is thought to form the protein-conducting PVM channel in PTEX, we tested the hypothesis that EXP2 is also the PVM nutrient-permeable channel3,13,23. We found that after iso-osmotic bulk release from the host RBCs, parasites remained within their PVM available for patch clamp recording of membrane permeability, detected as ionic current24 (Fig. 3a, b). Application of voltage revealed a channel permeable to nutrient-sized ions such as N-Methyl-D-glucamine and glutamate (Fig. 3c). Conductance of the patched PVM was typically in the nanosiemens range and showed step-wise currents when ~ +30 or ~ −60 mV were applied to the pipette electrode (Fig. 3d, e). Observed step sizes were variable (mode ~190 pS); largest steps were ~230 pS (Supplementary Fig. 6), consistent with sub-conductance states described previously for the PVM when scaling conductance for ion concentration8. A full channel conductance (~300 pS) can be estimated from step-wise decrements in conductance (presumably channels diffusing out of the patch, Supplementary Fig. 7), comparable to previous reports9. The reversal potential, close to 0 mV, was estimated from the current response to a step of voltage (Fig. 3f). From these steps, a conductance-voltage (G-V) response was constructed for each patch (Fig. 3g). The G-V response was maximal near zero transmembrane potential and diminished with both positive and negative voltages (Vhalf-open, positive = 29±2 mV and Vhalf-open, negative = −63±2 mV), also consistent with previous reports9,25. No other discernable channels were observed here, i.e. in absence of the channel activity noted above, patches had a resistance of several gigaohms. Channel rundown and the lipid-glass interactions inherent to patch clamping26 prevented an estimate of channel densities; attempts at total channel count by accessing a “whole-vacuole” configuration were unsuccessful. Instead, relative PVM channel density was derived as the ‘frequency of channel detection’ (fchan): the probability of observing at least one PVM channel in a given patch as determined from a series of patches.
Figure 3. PVM channel characteristics and correlation with EXP2 levels.
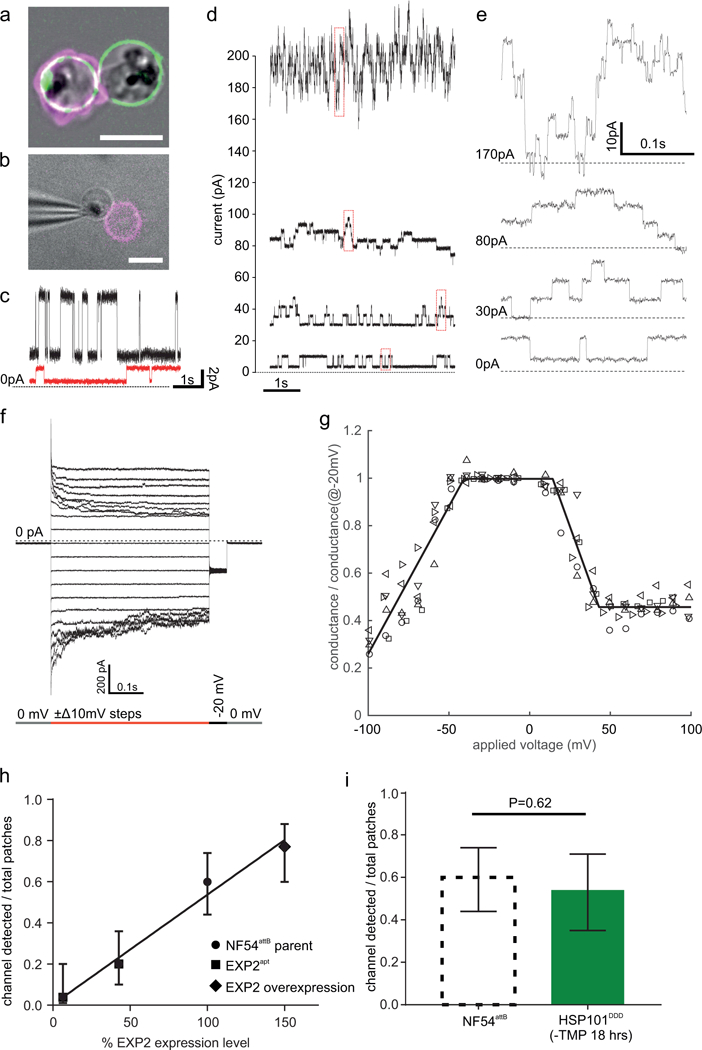
a, Parasite liberation from the RBC within an intact PVM using a high potassium buffer shown with NF54attB::EXP2-mNeonGreen parasites24. Green: EXP2-mNeonGreen marks the PVM. Magenta: Phalloidin-Alexa633 marks the RBC F-actin cytoskeleton. A double infected cell is shown where one parasite was released and the other remained within the host RBC. Zeiss 880 Airyscan image. b, The PVMs of released parasites (here NF54attB) are patch clamped in an on-cell configuration. Magenta: Phalloidin-Alexa488 (epifluorescence). Gray: bright field. c, Single channel flickering with a command voltage of 30 mV applied to the pipette using either small inorganic ions (black trace, buffer A and B in bath and pipette respectively) or amino acid and glucose-derived charge carriers (red trace, buffer O containing glutamic acid and N-methyl-D-glucamine in bath and pipette). Buffer O has a 3.6x lower conductivity and a ~30x reduced concentration of inorganic ions compared to the average of buffer A&B. The step size reduction shown here is 4.4x (6.54 pA to 1.47 pA) demonstrating that the PVM channel passes the nutrient ions of buffer O. d, Range of typical current fluctuations at 30 mV. e, Zoom in on the boxed (red) current recordings in d. f, Voltage response of a PVM channel ensemble. g, Conductance-voltage plot derived from the current-voltage response. Different symbols denote the 6 individual experiments used to create the plot. Solid line is a piecewise linear fit to all the data points. h, Correlation of the mean probability by which at least one channel is found in an experiment (fchan) with the EXP2 abundance by western blot (solid line: linear regression R2=0.98). The error bars denote the 95% CI calculated after Wilson44. i, fchan in NF54attB::HSP101DDD 18h after TMP washout to inactivate HSP101 compared to NF54attB parent line used in h. Error bars calculated after Wilson44. P value calculation detailed in Statistics and Reproducibility section. Scale bars in a, b are 5 μm. Current traces are filtered with a 500 Hz 8-pole Bessel filter for display. See the Statistics and Reproducibility section for information on the sample size.
If EXP2 constitutes the PVM channel, then fchan should depend upon EXP2 expression. We compared parasites expressing a second copy of EXP2 (~150% wild-type EXP2 levels by western blot, Supplementary Fig. 2), the parental strain (100%), EXP2apt +aTc (~40%) and EXP2apt -aTc (~10%). There was a tight correlation between fchan and expression of EXP2 (Fig. 3h, R=0.98). In contrast, conditional inactivation of HSP101 did not change fchan (Fig. 3i), nor the PVM channel sub-conductance states and voltage response (Supplementary Fig. 8), suggesting that EXP2 function in the PVM channel is independent of its role in the PTEX complex.
If EXP2 is a component of the PVM channel, changes to the EXP2 sequence should alter the electrophysiological characteristics of the channel. The C-terminal 54 residues of EXP2 (S234-E287) are highly charged (Supplementary Fig. 9, 28 negatively charged residues and 6 positively charged residues) and are poorly conserved among apicomplexans outside the Plasmodium genus, suggesting that alternation of this region of EXP2 may not altogether compromise function13. Indeed, complementation of EXP2apt with full length EXP2 or a truncated version lacking residues 234–287 both rescued growth and export following aTc washout (Supplementary Fig. 9). The charged truncated region comprising residues 234–287 is predicted to be in the aqueous space outside the lipid bilayer (Supplementary Fig. 5). Rather than sensing the trans-membrane potential, those charges can be expected to sense the potential gradient created by the access resistance of the channel27,28 (Fig. 4a). Indeed, following aTc washout to deplete endogenous EXP2, EXP2apt::Δ234–287 parasites displayed a PVM channel with altered voltage response. The half-open state with positive and negative voltages was substantially shifted away from 0 mV compared to the parent line, consistent with a diminished voltage response (Fig. 4 b-d). Single step conductance was not changed (Supplementary Fig. 10). When expression of full-length EXP2 was induced by the presence of aTc, a heterogeneous voltage response was recorded, consistent with mixed oligomers of full length and truncated EXP2 forming the PVM channel (Supplementary Fig. 10). The slope value of the voltage response was altered significantly for positive applied voltages (Fig. 4 e, f), consistent with a reduction in apparent gating charge (Fig. 4 g, h), in accordance with the concept of charge coupling in the region of pore access resistance.
Figure 4. Altered voltage response of the PVM channel in EXP2apt::Δ234–287 parasites.
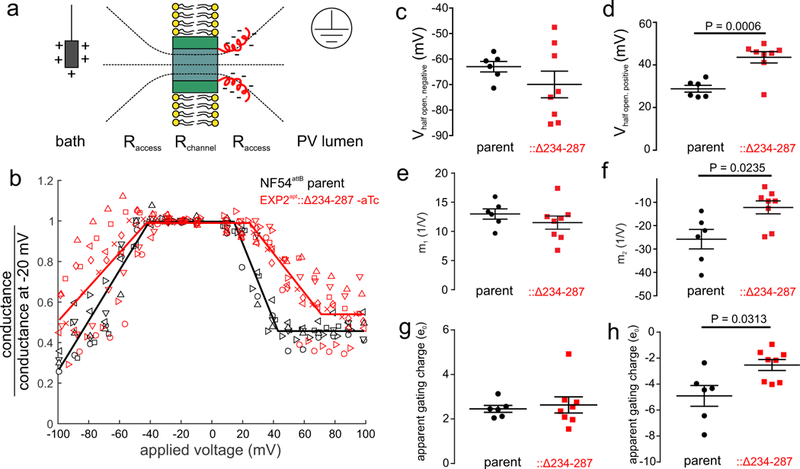
a, Model for PVM channel gating by EXP2. Residues 234–287 (red), though not embedded in the bilayer (yellow) due to high charge, sense the electric field in the PV lumen due to the access resistance of the channel. This charge-sidedness can explain the asymmetry in the voltage response (Fig. 3g). Positive potential applied on the pipette electrode (gray box) would pull the C-terminus toward the bilayer while negative voltages would push the same residues away. As the electric field (dashed) drops non-linearly with distance from the channel mouth, it is to be expected that positive voltages pulling the C-terminus couple stronger than negative voltages pushing it away. Qualitatively this is consistent with the GV curve being asymmetric and responding stronger to positive voltages, as well as the increased variability in the statistics of the voltage response with the direction of the field. b, Conductance voltage plot of EXP2apt::Δ234–287 (red, N=8 experiments) and the NF54attB parent (black, N=6 experiments). Symbols distinguish experiments. Solid line is a piecewise linear fit to all combined experiments. c, d, Half-open voltage for negative voltages (c) and for positive voltages (d). e, f, Slopes at negative (e) and at positive (f) voltages. g, h, Apparent gating charges derived from the voltage response slope at negative voltages (g) and positive voltages (h). c-h, points are calculated from fits to individual traces of (b), P values are from an unpaired two-sided t-test, lines are mean±s.e.m.
The altered voltage response of the truncation mutant directly indicates EXP2 gates the PVM channel. Together with the dependence of fchan on EXP2 expression and the observation that EXP2 forms a heptameric PVM pore in the context of PTEX29, the most likely explanation of the data is that EXP2 is the nutrient-permeable PVM channel. Taken together, our results indicate critical functions of EXP2 as the PTEX protein-translocating pore and the nutrient-permeable channel of the PVM. There is no precedent for a channel protein performing such dual functions. While other PTEX components are unique to Plasmodium spp.4, EXP2 is conserved amongst vacuole-dwelling apicomplexans13 and appears to have been further adapted to function as a protein conducting channel by PTEX150/HSP101 in blood-stage malaria parasites. It remains to be seen if the nutrient-permeable PVM channel is formed in the context of PTEX, by EXP2 alone or by EXP2 with non-PTEX co-factors. Of these possibilities, the latter two seem to fit with the observations of the expression mismatch between EXP2 and the other PTEX components and the independence of the PVM channel from HSP101 function.
Methods
Parasite culture
For electrophysiology and IMF experiments parasites were cultured in human red blood cells obtained from donors participating in the NIH IRB-approved Research Donor Program in Bethesda, MD. Red blood cells were separated from other blood cells and serum by spinning it down 4x in RPMI 1640. Parasites were cultured in 5% hematocrit at 1–5% parasitemia in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with with 25 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM hypoxanthine, 25 μg/ml gentamicin, 0.5% Albumax II (all from Gibco, Waltham, MA), and 4.5 mg/ml glucose (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). For all other experiments, de-identified, IRB-exempt expired RBCs were obtained from the blood bank at the St. Louis Children’s Hospital or directly from the American Red Cross and parasite culture was performed as described with the exception that RPMI was supplemented with 0.5% Albumax I30. Mutant lines were kept under selection drug pressure while cultured.
Genetic modification of P. falciparum
Cloning was carried out by Infusion (Clontech) unless otherwise noted. For editing the exp2 genomic locus, the pre-single guide RNA (sgRNA) expression cassette was cut from the plasmid pAIO31 by digestion with NotI and ligated into the NotI site in the plasmid pUF-132. The Cas9–2xNLS-FLAG coding sequence was then amplified from pAIO with primers CCACATTTCGAATAAACTCGAGATGGACAAGAAGTACAGCATCGGCC and GACCTGCAGGGTACCCCCGGGTTACTTGTCGTCGTCGTCCTTGTAGTCCACTTTCCGCTTTTTCTTAGG and inserted between XhoI and XmaI in the pUF-1-pre-sgRNA plasmid, replacing the yFCU marker and placing Cas9 under control of the hsp86 promoter and PbDT 3’ UTR, resulting in the plasmid pUF-Cas9-pre-sgRNA. A Cas9 target was chosen downstream of the exp2 stop codon (ATATTATGTACAGTATCTGA) and the guide RNA seed sequence was synthesized as a sense and anti-sense primer pair (sense shown) TAAGTATATAATATTATATTATGTACAGTATCTGAGTTTTAGAGCTAGAA. The primers were annealed and inserted into the BtgZI site of pUF-Cas9-pre-sgRNA to yield the plasmid pUF-Cas9-EXP2-CT-gRNA. For installation of aptamers at the exp2 locus, a 5’ homology flank was amplified with primers TTCAAACTTCATTGACTGTGCCCAAGTTGAGAACAAAAAATATTCTATACATGTTACTTC and GAGCTCCGGCAAATGACAAGGGCCGGCCCAAACTACAGTGTTTGTATTTTTATATACGAAGAATAACAAAAAAAAGGAAAATATATAACTGACTTTAATTTTAAAA from NF54attB genomic DNA and by inserted by Gibson assembly (NEB) into a pJAZZ-based plasmid carrying the necessary TetR-DOZI-aptamer components16 at FseI. A 3’ flank beginning just downstream of the gRNA target site was amplified with primers TACGGTACAAACCCGGAATTCGAGCTCGGGTACAGTATCTGATGGAGAAACAATCTTTTA and ATTGGGTATTAGACCTAGGGATAACAGGGTAATTCATAAGGAGAGTACATAAATAAAATAATCAAAC and inserted at I-SceI with Gibson assembly. The exp2 coding sequence (without introns) was recoded to a Saccharomyces cerevisiae codon bias and synthesized as a gene block (IDT) with a 3xHA tag (lower case indicates Gibson assembly overhangs): ggtgatgttgaagaaaatccaggtccaATGAAAGTAAGCTATATCTTTTCCTTTTTTCTGTTGTTCTTTGTCTATAAGAATACAAACACGGTTGTGTGTGATAACGGTTATGGGGATTTAGCGGCAACTTCAGCCTTAACTACCGTCATAAAGGACCCAATCTCCTTGACGATAAAAGACATCTATGAACACGGTGTCAAAAATCCTTTTACTAAAATCATTCATAAGTTGAAGAAATTTATCAGGTATAGAAAAGTATTAAGATGGTCTAGAATGTGGTGGGTATTGCTTGTTCGTGAGATTGTTGGAGATAATACGATTGAAAAGAAGACAGAGAAGGCATTAAGAGAAATTTGGGACCAATGCACAATTGCCGTTTACAATAATACCCTTAATGCTGTAGAATCCAAACCATTATTGTTCCTGCATGGTATACTAAATGAATGTAGAAATAATTTCGCCACAAAACTACGTCAAGACCCTTCTCTAATTGTGGCAAAGATCGACCAAATCATAAAATCCCAAATTTACAGGTTCTGGGTTTCCGAACCATATCTAAAAATCGGTAGAAGCCATACTCTATACACCCACATAACCCCAGATGCTGTTCCTCAATTGCCTAAGGAATGTACTCTGAAACATTTGAGTTCTTACATGGAAGAGAAGTTAAAAAGTATGGAATCTAAAAAGAACATTGAAAGTGGTAAGTACGAATTTGACGTAGATTCCTCTGAGACCGATTCAACAAAAGACGATGGAAAGCCTGACGATGATGATGATGATGACGACAACTTTGACGATGATGACAATTTTGATGATGACACGGTAGAGGAGGAAGACGCCAGTGGGGATCTGTTCAAGAATGAGAAGAAGGATGAAAATAAAGAGTACCCTTATGACGTTCCAGACTACGCTTATCCTTACGACGTCCCCGACTACGCGTATCCCTACGACGTTCCTGATTACGCTTGAgcgatcgcggattataaagatgatgat. This gene block was inserted into the AsiSI site in the modified pJAZZ vector using Gibson assembly, resulting in the plasmid pEXP2apt. The plasmid was co-transfected into NF54attB parasites33 with pUF-Cas9-EXP2-CT-gRNA. 1 μM aTc was maintained in the medium from the time of transfection and selection was applied with 2.5 μg/ml Blasticidin-S 24 h post transfection. After parasites returned from selection, proper integration was confirmed with the following primers (A, B, C and D respectively in Supplementary Fig. 1): GATCATCTCTTATATTAATAGGAATATATGATTTTTCACT, GCTCCGGCAAATGACAAGGG, CGGTCTCAGTGGTGTACGGTA, and TCACTTATGTTGTATAGAGACACAATTCGT. A clonal line was derived by limiting dilution and designated EXP2apt.
For generation of the HSP101DDD fusion in the NF54attB parasite background, a gRNA target site was chosen just upstream of the hsp101 stop codon (TAATAGTAAAGCTAAAAACT) and the gRNA seed sequence was synthesized as a sense and anti-sense primer pair (sense shown) TAAGTATATAATATTTAATAGTAAAGCTAAAAACTGTTTTAGAGCTAGAA, annealed and inserted into the BtgZI site of the plasmid pAIO, resulting in the plasmid pAIO-HSP101-CT-gRNA. To integrate the DHFR-based destabilization domain (DDD) at the 3’ end of hsp101, a 5’ homology flank (up to but not including the stop codon) was amplified from NF54attB genomic DNA using primers GACGCGAGGAAAATTAGCATGCATCCTTAAGGAGATTCTGGTATGCCACTTGGTTC and CGTATGGGTACCTAGGGGTCTTAGATAAGTTTATAACTAAGTTTTTAGCTTTACTATT, incorporating a synonymous shield mutation in the protospacer adjustment motif of the gRNA target site within the hsp101 coding sequence. A 3’ homology flank (beginning 3 bp downstream of the stop codon) was amplified using primers CACTATAGAACTCGAGAATTACGCATATATATATATATATATATATATAACATGGGTTG and GAACCAAGTGGCATACCAGAATCTCCTTAAGGATGCATGCTAATTTTCCTCGCGTC. The flank amplicons were assembled in a second PCR reaction using primers CACTATAGAACTCGAGAATTACGCATATATATATATATATATATATATAACATGGGTTG and CGTATGGGTACCTAGGGGTCTTAGATAAGTTTATAACTAAGTTTTTAGCTTTACTATT and inserted between XhoI and AvrII in pPM2GT-3xHA-DDD5, resulting in the plasmid pPM2GT-HSP101–3xHA-DDD. The 3xHA sequence was then replaced with a 3xFLAG sequence using a QuikChange Lightning Multi Site Directed Mutagenesis kit (Agilent) and the primer CTTAGTTATAAACTTATCTAAGACCCCTAGGGACTACAAGGACGACGACGACAAGGATTATAAAGATGATGATGATAAAGATTATAAAGATGATGATGATAAAATCAGTCTGATTGCGGCGTTAG, resulting in the plasmid pPM2GT-HSP101–3xFLAG-DDD. This plasmid was linearized at the AflII site between the 3’ and 5’ homology flanks and co-transfected with pAIO-HSP101-CT-gRNA into NF54attB and selection was applied with 10 μM trimethoprim 24 h post-transfection. A clonal line was isolated by limiting dilution after parasites returned from selection and designated NF54attB::HSP101DDD.
To generate an endogenous 3xFLAG tag at the HSP101 C-terminus of NF54attB and EXP2apt parasites, the DDD was removed from the plasmid pPM2GT-HSP101–3xFLAG-DDD using a QuikChange Lightning Multi Site Directed Mutagenesis kit and the primer GGATTATAAAGATGATGATGATAAAGATTATAAAGATGATGATGATAAATGACGGCCGCGTCGAGTTATATAATATATTTATG, resulting in the plasmid pPM2GT-HSP101–3xFLAG. This plasmid was linearized at the AflII site between flanks and co-transfected with pAIO-HSP101-CT-gRNA into NF54attB and EXP2apt parasites. Selection was applied with 10 nM WR99210 24 h post-transfection and clonal lines were isolated by limiting dilution after parasites returned from selection, resulting in the lines NF54attB::HSP101–3xFLAG and EXP2apt::HSP101–3xFLAG.
To facilitate integration of complementing second copies of EXP2 into the benign cg6 locus of NF54attB through integrase mediated attB x attP recombination33, the attP sequence was first inserted into the plasmid pyEOE34 using a QuikChange Lightning Multi Site Directed Mutagenesis kit and the primer GGTCGACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCGAGCTCGAATTCTGGTTTGTCTGGTCAACCACCGCGGTCTCAGTGGTGTACGGTACAAACCCGAATTCTGGTTTGTCTGGTCAACCACCGCGGTCTCAGTGGTGTACGGTACAAACCCGGAATTCTAGATTTAATAAATATGTTCTTATATATAATG resulting in the plasmid pyEOE-attP. The full length exp2 coding sequence without introns was amplified from NF54attB cDNA with primers CGAATAAACACGATTTTTTCTCGAGATGAAAGTCAGTTATATATTTTCCTTTTTTTTGTTATTCTTCG and TAACTCGACGCGGCCGCTCACAGGTCCTCCTCGGA GATCAGCTTCTGCTCCTCGGCCCTAGCACCGTTCAAGTCTTCCTCGGAGATTAGCTTTTGTTCACCGTTCAAATCTTCTTCAGAAATCAACTTTTGTTCGCTAGCTTCTTTATTTTCATCTTTTTTTTCATTTTTAAATAAATCTCCACTG to introduce a 3xMYC tag and inserted into pyEOE-attP between XhoI and EagI, resulting in the plasmid pyEOE-attP-EXP2–3xMYC. A truncated version of the exp2 coding sequence ending at codon position 233 was subsequently amplified with primers CGAATAAACACGATTTTTTCTCGAGATGAAAGTCAGTTATATATTT TCCTTTTTTTTGTTATTCTTCG and AATCAACTTTTGTTCGCTAGCATCTACATCAAACTCATATTTTCCACTTTC and inserted into this vector between XhoI and NheI, resulting in the plasmid pyEOE-attP-EXP2Δ234–287-3xMYC. These plasmids and the pyEOE-attP empty vector were each co-transfected with pINT35 into EXP2apt::HSP101–3xFLAG parasites or NF54attB at the mature schizont stage using program U-033 on a Nucleofector 2b and Basic Parasite Nucleofector kit 2 (Lonza). Selection with 2μM DSM132 was applied 24 h post transfection (in addition to 2.5 μg/ml Blasticidin-S and 1 μM aTc for maintenance of endogenous EXP2 control by the aptamer system). Following return from selection, parasites were cloned by limiting dilution and expression of EXP2 second copies was confirmed by western blot.
For split GFP assays, the GFP1–10 sequence containing the SERA5 signal peptide for secretion into the PV was synthesized as a gene block (signal peptide in lowercase): atgaagagttatatttcgctcttctttatcttgtgcgtcatcttcaataagaatgtcatcaaatgtactggcgagagtATGAGCAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTCACTGGAGTTGTCCCAATTCTTGTTGAATTAGATGGTGATGTTAATGGGCACAAATTTTCTGTCAGAGGAGAGGGTGAAGGTGATGCTACAATCGGAAAACTCACCCTTAAATTTATTTGCACTACTGGAAAACTACCTGTTCCATGGCCAACACTTGTCACTACTCTGACCTATGGTGTTCAATGCTTTTCCCGTTATCCGGATCACATGAAAAGGCATGACTTTTTCAAGAGTGCCATGCCCGAAGGTTATGTACAGGAACGCACTATATCTTTCAAAGATGACGGGAAATACAAGACGCGTGCTGTAGTCAAGTTTGAAGGTGATACCCTTGTTAATCGTATCGAGTTAAAGGGTACTGATTTTAAAGAAGATGGAAACATTCTCGGACACAAACTCGAGTACAACTTTAACTCACACAATGTATACATCACGGCAGACAAACAAAAGAATGGAATCAAAGCTAACTTCACAGTTCGCCACAACGTTGAAGATGGTTCCGTTCAACTAGCAGACCATTATCAACAAAATACTCCAATTGGCGATGGCCCTGTCCTTTTACCAGACAACCATTACCTGTCGACACAAACTGTCCTTTCGAAAGATCCCAACGAAAAGTAA. The gfp1–10 sequence was PCR amplified with or without the sera5 signal peptide using forward primers AAATATATCACCTAGGATGAAGAGTTATATTTCGCTCTTCTTTATCTTGTGC or AAATATATCACCTAGGATGAGCAAAGGAGAAGAACTTTTC, respectively, and the reverse primer ATAACTCGACCTTAAGTTACTTTTCGTTGGGATCTTTCGAAAGGACAG and each amplicon was inserted between AvrII and AflII in the plasmid pLN-ENR-GFP35. The resulting plasmids pLN-spGFP1–10 and pLN-cytGFP1–10, respectively (which also contain the attP sequence), were co-transfected with pINT into NF54attB parasites and selection with 2.5 μg/ml Blasticidin-S was applied 24 h post transfection. A clone was derived by limiting dilution from each resulting parasite population and designated spGFP1–10 or cytGFP1–10, respectively. For tagging endogenous PTEX components with GFP11, the 3xHA-GFP11 sequence was synthesized as the gene block CCTAGGTACCCGTACGACGTCCCGGACTACGCTGGCTATCCCTATGATGTGCCCGATTATGCGTATCCTTACGATGTTCCAGATTATGCCGATGGAGGGTCTGGTGGCGGATCAACAAGTCGTGACCACATGGTCCTTCATGAGTACGTAAATGCTGCTGGGATTACATAACGGCCG, PCR amplified with primers GATGAAAATAAAGAACCTAGGTACCCGTACGACGTCCCG and TAACTCGACGCGGCCGTTATGTAATCCCAGCAGCATTTACG and inserted between AvrII and EagI in pyPM2GT-EXP2-mNeonGreen24, replacing mNeonGreen and resulting in the plasmid pyPM2GT-EXP2–3xHA-GFP11. Flanks targeting the 3’ end of hsp101 were PCR amplified from pPM2GT-HSP101–3xFLAG using primers CACTATAGAACTCGAGAATTACGCATATATATATATATATATATATATAACATGGGTTG and GACGTCGTACGGGTACCTAGGGGTCTTAGATAAGTTTATAACTAAGTTTTTAGC and inserted between XhoI and AvrII in pyPM2GT-EXP2–3xHA-GFP11, resulting in the plasmid pyPM2GT-HSP101–3xHA-GFP11. To edit the 3’ end of ptex150, a gRNA target site was chosen just downstream of the ptex150 stop codon (TGGGAACCTCTTGTGTTTTA) and the gRNA seed sequence was synthesized as a sense and anti-sense primer pair (sense shown) TAAGTATATAATATTTGGGAACCTCTTGTGTTTTAGTTTTAGAGCTAGAA, annealed and inserted into the BtgZI site of pAIO, resulting in the plasmid pAIO-PTEX150-CT-gRNA. A 5’ homology flank (up to but not including the stop codon) was amplified from NF54attB genomic DNA using primers GCCTTATAATCGTTCCTTTTGAGAACCTTAAGCTTCTTAGGACAAAATGGTACATATC and GACGTCGTACGGGTACCTAGGGTTATCATCTTCTTCTTCGTCTAATTCTTCTTCATC. A 3’ homology flank beginning just downstream of the gRNA target site was amplified using primers CACTATAGAACTCGAGGGTATAGAAAAAATATATAATATTTATATGCTTTTCTGCC and GATATGTACCATTTTGTCCTAAGAAGCTTAAGGTTCTCAAAAGGAACGATTATAAGGC. The flank amplicons were assembled in a second PCR reaction using primers CACTATAGAACTCGAGGGTATAGAAAAAATATATAATATTTATATGCTTTTCTGCC and GACGTCGTACGGGTACCTAGGGTTATCATCTTCTTCTTCGTCTAATTCTTCTTCATC and inserted between XhoI and AvrII in pyPM2GT-EXP2–3xHA-GFP11, resulting in the plasmid pyPM2GT-PTEX150–3xHA-GFP11. These GFP11 tagging plasmids were each linearized at the AflII site introduced between the 3’ and 5’ homology flanks and co-transfected with their respective EXP2, HSP101 or PTEX150 Cas9/gRNA plasmids into spGFP1–10 and cytGFP1–10 parasites. Selection was applied with 2μM DSM1 24 h post-transfection and clonal lines were isolated by limiting dilution after parasites returned from selection.
Antibodies
The following antibodies were used for IFA and western blot at the indicated dilutions: rabbit polyclonal anti-HA SG77 (ThermoFisher) (WB: 1:1000); mouse anti-FLAG mAb clone M2 (Sigma) (IFA: 1:500, WB 1:500); rabbit mAb anti-FLAG 8H8L17 (ThermoFisher) (WB: 1:500); mouse anti-EXP2 mAb clone 7.736 (WB: 1:1000); mouse anti-HRP2 mAb 2G1237 (IFA 1:500); rabbit polyclonal anti-SBP138 (IFA: 1:500); rabbit polyclonal anti-PfHAD139 (WB: 1:500); mouse anti-cMYC mAb 9E10 (ThermoFisher) (WB: 1:300); rabbit polyclonal anti-Plasmodium Aldolase ab38905 (Abcam) (IFA: 1:1000).
Parasite growth assays
Following extensive aTc washout, parasites were plated with or without 1μM aTc in triplicate at an initial parasitemia of 1%. Media was changed every 48 h and 1:1 subculture was performed as needed (generally every other day beginning at 96 h) to avoid culture overgrowth. Parasitemia (percent of total RBCs infected) was measured every 24 h by flow cytometry on a FACSCanto (BD Biosciences) by nucleic acid staining of cultured RBCs with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) containing 0.8 μg/ml acridine orange (gating strategy is shown in Supplemental Fig. 13). Cumulative parasitemias were back calculated based on the subculture schedule and data were fit to an exponential growth equation to determine rate constants using Prism (Graphpad).
IFA and quantification of protein export
For evaluation of protein export by IFA, mature schizonts were purified on an LD column using a QuadroMACs magnetic separator (Miltenyi Biotech) and allowed to invade fresh, uninfected RBCs with shaking for 3 hours before treatment with 5% w/v D-sorbitol to destroy unruptured schizonts. Pulse-invaded cells were washed extensively to remove aTc and then plated with or without 1 μM aTc and allowed to develop 24 h post invasion. Cells were fixed with PBS containing 4% paraformaldehyde and 0.0075% glutaraldehyde (for detection of HRP2) or cold 100% acetone (for detection of SBP1) and processed for IFA as described5. Primary antibody solutions contained either mouse anti-HRP2 and rabbit anti-Plasmodium aldolase (to mark the parasite and PV, see below) or rabbit anti-SBP1 and mouse anti-FLAG (detecting HSP101–3xFLAG to mark the PVM). After washing, secondary antibody incubation was carried out for one hour with Alexa Fluor anti-mouse 594 and anti-rabbit 488 IgG antibodies (for HRP2 experiments) or anti-rabbit 594 and anti-mouse 488 IgG antibodies (for SBP1 experiments) (Life Technologies), each diluted 1:2000. After final washing, coverslips were mounted using Pro-long antifade Gold with DAPI (Life Technologies). Images were collected with an ORCA-ER CCD camera (Hamamatsu) using AxioVision software on an Axio Imager.M1 microscope (Zeiss) with a 100x oil immersion objective using the same exposure times for each image (100 ms for HRP2–594 and 150 ms for Aldolase-488 for HRP2 experiments or 300 ms for SBP1–594 and 150 ms for FLAG-488 for SBP1 experiments). Ten images were acquired for each condition using the DAPI channel for field selection to avoid bias. Images were then analyzed using Volocity 6.3 (PerkinElmer).
The border of each single-infected erythrocyte was traced using the DIC channel as a guide to define a region of interest (ROI). In HRP2 export experiments, the parasite was marked using the “find objects” measurement tool for the strong cytosolic signal from the Plasmodium aldolase-488 channel (automatic threshold setting with threshold offset set to −40% and minimum object size set to 0.5 μm2). Given the intimate apposition of the PVM to the PPM, the aldolase signal was found to be suitable for marking both compartments. The signal corresponding to exported HRP2 was determined for each infected erythrocyte by removing the HRP2 signal within the aldolase object boundary in each ROI using the “subtract” tool and the mean fluorescence intensity of the HRP2 signal remaining in each ROI was collected. In SBP1 experiments, the PVM was marked using the “find objects” measurement tool for the HSP101–3xFLAG-488 channel (automatic threshold setting with threshold offset set to −30% and minimum object size set to 0.5 μm2). Individual Maurer’s clefts were identified using the “find spots” measurement tool for the SBP1–594 channel (offset minimum spot intensity set to 40% and brightest spot within radius set to 0.5 μm). All spots within the PVM object boundary were then removed using the “subtract” measurement tool and the number and fluorescent intensity of the remaining spots in each ROI were collected. Six independent experiments were performed. Two representative experiments were quantified and the data were pooled and plotted with Prism.
Transmission electron microscopy
For ultrastructural analyses, infected RBCs were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde/2.5% glutaraldehyde (Polysciences) in 100 mM sodium cacodylate buffer, pH 7.2 for 1 h at room temperature. Samples were washed in sodium cacodylate buffer at room temperature and postfixed in 1% osmium tetroxide (Polysciences) for 1 h. Samples were then rinsed extensively in dH20 prior to en bloc staining with 1% aqueous uranyl acetate (Ted Pella) for 1 h. Following several rinses in dH20, samples were dehydrated in a graded series of ethanol and embedded in Eponate 12 resin (Ted Pella). Sections of 95 nm were cut with a Leica Ultracut UCT ultramicrotome (Leica Microsystems), stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate, and viewed on a JEOL 1200 EX transmission electron microscope (JEOL USA) equipped with an AMT 8-megapixel digital camera and AMT Image Capture Engine V602 software (Advanced Microscopy Techniques).
Time-resolved western blot and immunoprecipitation
For time-resolved analysis of EXP2 and HSP101 by western blot, magnet purified terminal schizonts were allowed to pulse-invade fresh RBCs with shaking for 4 hours before treatment with 5% w/v D-sorbitol to destroy unruptured schizonts. Synchronized cultures were harvested every 6 hours for the duration for the developmental cycle and the erythrocyte cytosol was released by treatment with cold PBS containing 0.025% saponin (Sigma). Pellets were stored at −80°C until all samples were collected and then processed in parallel for western blot. Pellets were lysed in RIPA buffer containing EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche), briefly bath sonicated and then centrifuged to pellet hemozoin. Supernatants were lysed in sample buffer containing DTT and boiled before separation by SDS-PAGE. For immunoprecipitation, time-resolved samples were similarly prepared and pellets were lysed in PBS containing 0.4% Triton X-100 and EDTA-free protease inhibitory cocktail. Hemozoin was cleared and lysates were rotated overnight at 4°C with anti-FLAG M2 agarose (Sigma) equilibrated in the lysis buffer. After extensive washing, agarose beads were eluted by boiling in sample buffer without DTT (to minimized release of anti-FLAG IgG heavy and light chains) before separation by SDS-PAGE. Western blot imaging was carried out with an Odyssey infrared imaging system (Li-COR Biosciences). Detection of primary antibodies was achieved with IRDye 680- or 800-conjugated secondary antibodies (Li-COR Biosciences) used at 1:10,000. Signal quantification was performed with Image Studio software (Li-COR Biosciences).
Electrophysiology
Late stage parasites were liberated in their PVM after percoll isolation40. Briefly, 0.5 ml of culture (5% hematocrit, <5% parasitemia) was layered on 65% percoll. After a brief spin down cells were collected from the interface. The cells were washed 3x in culture medium and incubated in 200 μl isotonic “high-potassium” buffer (140 mM KCl, 5 mM NaCl, 0.4 mM CaCl2, 0.4 mM MgCl2, 25 mM HEPES, 4.5 mg/ml glucose, 0.5% Albumax II) for 1 hour. To confirm liberation from the host RBC, that often stays attached to the parasite, 66 nM phalloidin-Alexa488 (Invitrogen) was used in the “high-potassium” buffer to label the attached RBC. 50 μl of this cell suspension were added to 3 ml of buffer A in the observation dish (fluorodish, WPI). The dish was mounted on the stage of a Zeiss Observer D200, equipped with a 100× 1.45NA oil objective, a filter-set for Alexa 488 (excitation 450–490 nm, emission 500–550 nm) and a Coolsnap EZ2 camera (Photometrics). Images were recorded using Micro Manager 1.4.21 and 1.4.22 [REF 41]. Pipettes were pulled using a Sutter instrument (Novato, CA) pipette puller from Borosilicate glass capillaries (outer diameter: 1.5 mm, inner diameter: 0.86mm, in factory fire-polished, Sutter instrument). As bath buffer 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.4 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 20 mM HEPES NaOH (pH 7.4), 4.5 mg/ml glucose (buffer A) and as pipette buffer 155 mM CsCl, 1.4 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 20 mM HEPES NaOH (pH 7.4) (buffer B) were used, similar to Desai et al8. Permeability of the PVM channel to nutrient-sized molecules was tested with 155 mM N-Methyl-D-glucamine, 155 mM L-Glutamic acid, 1.4 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM HEPES NaOH (pH 7.4) (buffer O). Concentration of small inorganic charge carriers is thus ~30x reduced in buffer O compared to buffer A and B. Conductivities of buffers were measured at 24°C with a CDM230 Conductivity Meter (Radiometer Analytica): buffer A 17.3 mS/cm, buffer B 20.7 mS/cm, buffer O 5.23 mS/cm.
Electrophysiology data was recorded in pClamp10 using an Axopatch 200B, filtered at 10kHz (8-pole Bessel) and digitized at 50kHz using a digidata 1332A or 1550B4 (all Molecular Devices). Command voltage denotes the voltage dialed on the amplifier. Applied voltage is the voltage reduced by the product of current and access resistance (15–20 MOhm), necessary to plot the conductance voltage response correctly. Voltage convention for the data presented is bath to ground and voltages applied to the pipette. Data was analyzed using ClampFit10 and custom matlab scripts. Error for data shown in Fig. 3h, i was calculated in Excel (version 2016, Microsoft), P value in Fig. 3i was calculated in R (version 3.5.0, R core Team) with the fisher.test function, otherwise Prism was used.
Unless otherwise noted, sub-conductance steps were identified as the peaks (‘findpeaks’ function of matlab) in a derivative (dt = 200 us) of the current trace filtered offline with a 500 Hz 8-pole Bessel filter. The difference of current before and after the step were recorded as step size.
The rapid voltage response of the PVM channel makes it difficult to reliably find the maximum current for the normalization of the current using a voltage step protocol. As an alternative, conductance normalized to the conductance at −20 mV was plotted here to reflect on the open probability of the channel. The mean current on the second half of the voltage step was subtracted by the mean current at 0 mV to adjust for drift and divided by the applied voltage. Normalization is done with the mean current of the second half of the step to −20 mV at the end of each sweep.
The conductance voltage curves were fit to a piecewise linear function in the form
where V is the voltage applied to the membrane and G is the conductance, m1, m2, b1, b2, c1, c2, c3 are free fit parameters.
The plateau conductance around 0 mV (p1) and at positive voltages (p2) follow as:
That allows the definition of a half-open conductance as:
The half-open voltages (Vhalf-open, positive and Vhalf-open, negative for the two arms) follow from that:
Apparent Gating charges (zi) were calculated from the slopes m1 and m2 by comparing to the slope of the expression for the open probability po [REF 42]:
Where kb is the Boltzmann constant, T the absolute temperature (298K), w the work needed to change conformation, and e0 the elementary charge. Since the model assumes two states (open and closed) the conductance curves need to be rescaled such that the plateaus p1 and p2 represent open and closed. The slopes mi thus become:
The derivative of the expression at the half-open voltage gives:
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Code Availability Statement
Matlab R2015b (Mathworks) scripts as described in methods are available upon request.
Statistics and Reproducibility
Figure 1c-e and Supplementary Figure 9d: Exact P values < 0.001 were calculated using the T.DIST.2T function in Excel for Mac (version 15.38, Microsoft).
Figure 3a: Presence of PVM around released parasite was observed in 3 independent experiments. The observation was published previously with the same technique24. Approximately 100 parasites were inspected and found to be retained in their PVM. A representative example was imaged and chosen for the figure.
Figure 3b: The RBC membrane attached to the released parasite was generally visualized to verify the pipette was approaching the parasite. A representative image was chosen to demonstrate this approach.
Figure 3c: Organic ion permeability was observed in 4 of 8 independent patch clamp experiments. Of the 4 experiments with channel activity one showed single channel activity, shown in the figure, and was compared to an example of single channel activity seen with the salt solutions used in the rest of the work.
Figure 3d, e: Examples of channel activity were chosen to reflect the range of patch conductances found in the experiments (as shown in Supplementary Figure 6).
Figure 3f: The example was chosen from the recordings that were used to generate Figure 3g.
Figure 3h: fchan is calculated from a series of independent patch clamp experiments, n = 25, 35, 35 and 31 for 10%, 40%, 100% and 150% EXP2 expression respectively.
Figure 3i: Bars denote fchan calculated from independent patch clamp experiments, n=35 and 28 for NF54attB and NF54attB::HSP101DDD –TMP, respectively. P value was calculated after Fisher43 in R (version 3.5.0, R core Team) with the fisher.test function.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NIH grant HL133453 to J.R.B and in part by the Division of Intramural Research of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health. We thank Svetlana Glushakova for the creation and performance of the technique of vacuolar liberation, the performance of the IMF experiment, and many helpful conversations throughout the course of this project. We thank J. McBride, D. Cavanagh and EMRR for EXP2 antibody, D. Taylor for HRP2 antibody, C. Braun-Breton for SBP1 antibody, W. Beatty for assistance with electron microscopy, P. Gurnev for the buffer conductivity measurement, Paul Blank for helpful suggestions for the statistical treatment of the patch clamp data and B. Vaupel for technical assistance.
References
- 1.Lingelbach K & Joiner KA The parasitophorous vacuole membrane surrounding Plasmodium and Toxoplasma: an unusual compartment in infected cells. J Cell Sci 111 ( Pt 11), 1467–1475 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Desai SA Ion and nutrient uptake by malaria parasite-infected erythrocytes. Cellular microbiology 14, 1003–1009, doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01790.x (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sherling ES & van Ooij C Host cell remodeling by pathogens: the exomembrane system in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40, 701–721, doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw016 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.de Koning-Ward TF et al. A newly discovered protein export machine in malaria parasites. Nature 459, 945–949, doi: 10.1038/nature08104 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beck JR, Muralidharan V, Oksman A & Goldberg DE PTEX component HSP101 mediates export of diverse malaria effectors into host erythrocytes. Nature 511, 592–595, doi: 10.1038/nature13574 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Elsworth B et al. PTEX is an essential nexus for protein export in malaria parasites. Nature 511, 587–591, doi: 10.1038/nature13555 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kalanon M et al. The Plasmodium translocon of exported proteins component EXP2 is critical for establishing a patent malaria infection in mice. Cellular microbiology 18, 399–412, doi: 10.1111/cmi.12520 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Desai SA, Krogstad DJ & McCleskey EW A nutrient-permeable channel on the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite. Nature 362, 643–646, doi: 10.1038/362643a0 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Desai SA & Rosenberg RL Pore size of the malaria parasite’s nutrient channel. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94, 2045–2049 (1997). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnson D et al. Characterization of membrane proteins exported from Plasmodium falciparum into the host erythrocyte. Parasitology 109 ( Pt 1), 1–9 (1994). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bullen HE et al. Biosynthesis, localization, and macromolecular arrangement of the Plasmodium falciparum translocon of exported proteins (PTEX). The Journal of biological chemistry 287, 7871–7884, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.328591 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hakamada K, Watanabe H, Kawano R, Noguchi K & Yohda M Expression and characterization of the Plasmodium translocon of the exported proteins component EXP2. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 482, 700–705, doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.097 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gold DA et al. The Toxoplasma Dense Granule Proteins GRA17 and GRA23 Mediate the Movement of Small Molecules between the Host and the Parasitophorous Vacuole. Cell host & microbe 17, 642–652, doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.003 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mesen-Ramirez P et al. Stable Translocation Intermediates Jam Global Protein Export in Plasmodium falciparum Parasites and Link the PTEX Component EXP2 with Translocation Activity. PLoS pathogens 12, e1005618, doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005618 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ganesan SM, Falla A, Goldfless SJ, Nasamu AS & Niles JC Synthetic RNA-protein modules integrated with native translation mechanisms to control gene expression in malaria parasites. Nature communications 7, 10727, doi: 10.1038/ncomms10727 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nasamu AS et al. Plasmepsins IX and X are essential and druggable mediators of malaria parasite egress and invasion. Science 358, 518–522, doi: 10.1126/science.aan1478 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Glushakova S et al. Hemoglobinopathic erythrocytes affect the intraerythrocytic multiplication of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. The Journal of infectious diseases 210, 1100–1109, doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu203 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goldberg DE & Cowman AF Moving in and renovating: exporting proteins from Plasmodium into host erythrocytes. Nature reviews . Microbiology 8, 617–621, doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2420 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kulzer S, Petersen W, Baser A, Mandel K & Przyborski JM Use of self-assembling GFP to determine protein topology and compartmentalisation in the Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocyte. Molecular and biochemical parasitology 187, 87–90, doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2012.11.004 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Otto TD et al. New insights into the blood-stage transcriptome of Plasmodium falciparum using RNA-Seq. Molecular microbiology 76, 12–24, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.07026.x (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boddey JA & Cowman AF Plasmodium nesting: remaking the erythrocyte from the inside out. Annual review of microbiology 67, 243–269, doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155730 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schwab JC, Beckers CJ & Joiner KA The parasitophorous vacuole membrane surrounding intracellular Toxoplasma gondii functions as a molecular sieve. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91, 509–513 (1994). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Charpian S & Przyborski JM Protein transport across the parasitophorous vacuole of Plasmodium falciparum: into the great wide open. Traffic 9, 157–165, doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00648.x (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Glushakova S et al. Exploitation of a newly-identified entry pathway into the malaria parasite-infected erythrocyte to inhibit parasite egress. Scientific reports 7, 12250, doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12258-x (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ito D, Schureck MA & Desai SA An essential dual-function complex mediates erythrocyte invasion and channel-mediated nutrient uptake in malaria parasites. eLife 6, doi: 10.7554/eLife.23485 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Garten M et al. Whole-GUV patch-clamping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114, 328–333, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609142114 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Levadny V, Aguilella VM & Belaya M Access resistance of a single conducting membrane channel. Biochim Biophys Acta 1368, 338–342 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hyun C, Rollings R & Li J Probing Access Resistance of Solid-state Nanopores with a Scanning Probe Microscope Tip. Small 8, 385–392, doi: 10.1002/smll.201101337 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ho C et al. CryoEM Reveals Translocation Mechanism in Malaria Parasite Effector Export. Nature. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Klemba M, Beatty W, Gluzman I & Goldberg DE Trafficking of plasmepsin II to the food vacuole of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. The Journal of cell biology 164, 47–56, doi: 10.1083/jcb200307147 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Spillman NJ, Beck JR, Ganesan SM, Niles JC & Goldberg DE The chaperonin TRiC forms an oligomeric complex in the malaria parasite cytosol. Cellular microbiology 19, doi: 10.1111/cmi.12719 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ganesan SM et al. Yeast dihydroorotate dehydrogenase as a new selectable marker for Plasmodium falciparum transfection. Molecular and biochemical parasitology 177, 29–34, doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2011.01.004 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Adjalley SH et al. Quantitative assessment of Plasmodium falciparum sexual development reveals potent transmission-blocking activity by methylene blue. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108, E1214–1223, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112037108 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Muralidharan V, Oksman A, Pal P, Lindquist S & Goldberg DE Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 110 stabilizes the asparagine repeat-rich parasite proteome during malarial fevers. Nature communications 3, 1310, doi: 10.1038/ncomms2306 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nkrumah LJ et al. Efficient site-specific integration in Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes mediated by mycobacteriophage Bxb1 integrase. Nature methods 3, 615–621, doi: 10.1038/nmeth904 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hall R et al. Antigens of the erythrocytes stages of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum detected by monoclonal antibodies. Molecular and biochemical parasitology 7, 247–265 (1983). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rock EP et al. Comparative analysis of the Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich proteins HRP-I, HRP-II and HRP-III in malaria parasites of diverse origin. Parasitology 95 ( Pt 2), 209–227 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Blisnick T et al. Pfsbp1, a Maurer’s cleft Plasmodium falciparum protein, is associated with the erythrocyte skeleton. Molecular and biochemical parasitology 111, 107–121 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Guggisberg AM et al. A sugar phosphatase regulates the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway in malaria parasites. Nature communications 5, 4467, doi: 10.1038/ncomms5467 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Glushakova S, Yin D, Li T & Zimmerberg J Membrane transformation during malaria parasite release from human red blood cells. Curr Biol 15, 1645–1650, doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.067 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Edelstein AD et al. Advanced methods of microscope control using muManager software. J Biol Methods 1, doi: 10.14440/jbm.2014.36 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hodgkin AL & Huxley AF A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117, 500–544 (1952). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fisher RA On the Interpretation of χ2 from Contingency Tables, and the Calculation of P. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 85, 87–94, doi: 10.2307/2340521 (1922). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wilson EB Probable Inference, the Law of Succession, and Statistical Inference. Journal of the American Statistical Association 22, 209–212, doi: 10.1080/01621459.1927.10502953 (1927). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.


