Abstract
Background
Cocaine dependence is a severe disorder for which no medication has been approved. Like opioids for heroin dependence, replacement therapy with psychostimulants could be an effective therapy for treatment.
Objectives
To assess the effects of psychostimulants for cocaine abuse and dependence. Specific outcomes include sustained cocaine abstinence and retention in treatment. We also studied the influence of type of drug and comorbid disorders on psychostimulant efficacy.
Search methods
This is an update of the review previously published in 2010. For this updated review, we searched the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group Trials Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase and PsycINFO up to 15 February 2016. We handsearched references of obtained articles and consulted experts in the field.
Selection criteria
We included randomised parallel group controlled clinical trials comparing the efficacy of a psychostimulant drug versus placebo.
Data collection and analysis
We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane.
Main results
We included 26 studies involving 2366 participants. The included studies assessed nine drugs: bupropion, dexamphetamine, lisdexamfetamine, methylphenidate, modafinil, mazindol, methamphetamine, mixed amphetamine salts and selegiline. We did not consider any study to be at low risk of bias for all domains included in the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool. Attrition bias was the most frequently suspected potential source of bias of the included studies. We found very low quality evidence that psychostimulants improved sustained cocaine abstinence (risk ratio (RR) 1.36, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.05 to 1.77, P = 0.02), but they did not reduce cocaine use (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.16, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.33) among participants who continued to use it. Furthermore, we found moderate quality evidence that psychostimulants did not improve retention in treatment (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.06). The proportion of adverse event‐induced dropouts and cardiovascular adverse event‐induced dropouts was similar for psychostimulants and placebo (RD 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01; RD 0.00, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01, respectively). When we included the type of drug as a moderating variable, the proportion of patients achieving sustained cocaine abstinence was higher with bupropion and dexamphetamine than with placebo. Psychostimulants also appeared to increase the proportion of patients achieving sustained cocaine and heroin abstinence amongst methadone‐maintained, dual heroin‐cocaine addicts. Retention to treatment was low, though, so our results may be compromised by attrition bias. We found no evidence of publication bias.
Authors' conclusions
This review found mixed results. Psychostimulants improved cocaine abstinence compared to placebo in some analyses but did not improve treatment retention. Since treatment dropout was high, we cannot rule out the possibility that these results were influenced by attrition bias. Existing evidence does not clearly demonstrate the efficacy of any pharmacological treatment for cocaine dependence, but substitution treatment with psychostimulants appears promising and deserves further investigation.
Plain language summary
Efficacy of psychostimulant drugs for cocaine dependence
Review question
We investigated whether psychostimulant substitution was safe and effective for treating patients with cocaine dependence.
Background
Cocaine dependence is a frequent disorder for which no medication has been approved for treatment. Substitution therapy involves the replacement of the abused drug, which is often illegal and used several times a day, by a legal, orally administered and longer‐acting one. A substitute drug has to have similar effects as the abused one, but with a lower addictive potential, enabling drug abstinence and patient adherence to medical and psychological assistance. This strategy can increase the abstinence rate in patients with heroin and tobacco dependence. In this review, we investigated whether psychostimulant substitution with medications that have psychostimulant effect was effective for treating patients with cocaine dependence.
Search date: the evidence is current to 15 February 2016.
Studies and participants' characteristics
We reviewed the evidence about the effect of psychostimulants on cocaine abstinence, safety and retention to treatment in patients with cocaine dependence. We found 26 studies that had enrolled 2366 participants and investigated the effects of psychostimulants against placebo for cocaine abuse or dependence. Most participants were men (75%) in their middle age (mean age 39.6 years). About half (47.6%) were African American, and 39.3% were white. The most common way they used cocaine was smoking. All but two studies took place in the USA, and they studied the effects of nine medications with a psychostimulant effect: bupropion, dexamphetamine, lisdexamfetamine, methylphenidate, modafinil, mazindol, methamphetamine, mixed amphetamine salts and selegiline. All clinical trials provided psychotherapy. Study length ranged from 6 to 24 weeks.
Key results
Investigators assessed cocaine abstinence (determined by urinalysis) in participants receiving the study intervention versus those receiving placebo. Though some analyses found that cocaine abstinence was higher with psychostimulants than with placebo, we are uncertain whether psychostimulants decrease cocaine use among participants who continue to use it or if they increase the number of people who stay clean, as the quality of the evidence was very low.
We also investigated the effect of the interventions studied on treatment retention. This outcome is important because withdrawing treatment and scheduled visits can suggest relapse to cocaine use. Psychostimulants probably make little or no difference when compared with placebo (moderate quality of evidence)
Psychostimulants appear well tolerated and are not associated with serious adverse events. Furthermore, psychostimulants show more favourable outcomes for some groups of patients, such as methadone‐maintained, dual heroin‐cocaine addicts, for whom there were positive results on both cocaine and heroin use.
Quality of the evidence
We did not consider any study to be free from risk of bias. We judged the quality of evidence to be very low for the outcomes of cocaine use and sustained abstinence but moderate for retention in treatment.
University researchers performed all studies with public funding, although eight of them also had additional private funding.
Conclusions
The efficacy of psychostimulants for cocaine dependence is not entirely clear, but these treatments appear promising and deserve further investigation.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Psychostimulants for cocaine dependence.
| Psychostimulants for cocaine dependence | ||||||
|
Patient or population: people with cocaine dependence
Settings: outpatient
Intervention: psychostimulants Comparison: placebo | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Psychostimulants | |||||
| Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalysis across the study per participant | — | The mean cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) of the proportion of cocaine‐free urinalysis across the study per participant in the intervention groups was 0.16 standard deviations higher (0.02 lower to 0.33 higher) | — | 526 (8 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c | SMD 0.16 (−0.02 to 0.33) |
| Sustained cocaine abstinence | Study population | RR 1.36 (1.05 to 1.77) | 1549 (14 studies) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very lowa,b,c,d | — | |
| 164 per 1000 | 224 per 1000 (173 to 291) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 147 per 1000 | 200 per 1000 (154 to 260) | |||||
| Number of participants who finished the study | Study population | RR 1.00 (0.93 to 1.06) | 2205 (24 studies) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ Moderateb | — | |
| 566 per 1000 | 566 per 1000 (526 to 600) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 542 per 1000 | 542 per 1000 (504 to 575) | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across studies) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; RR: risk ratio; SMD: standardised mean difference. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: we are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
aAttrition bias was unclear or high for all the included studies. bThe pooled effect has been calculated after combining studies investigating a large number of different drugs, at different doses, in participants with relevant clinical differences (e.g. comorbid opioid dependence). c95% confidence interval was wide. Any new study could change the results significantly. dStatistical heterogeneity was moderate (28%).
Background
The overall prevalence of cocaine use disorders has been declining over the last several years after decades of uninterrupted increase. This is mainly a reflection of trends in Europe and the Americas (UNDOC 2015). In the USA, there were 1.5 million current cocaine users aged 12 or older (0.6% of the population) in 2013, and 855,000 people had experienced past year dependence or abuse (0.3% of the population) (SAMSHA 2014). In the European Union (EU), cocaine is the most commonly used illicit stimulant drug, although most users live in just a few member states. In 2014, EMCDDA 2015 estimated that about 15.6 million, or 4.6% of adults aged 15 to 64 years, had used cocaine at some point in their lifetime, and 3.4 million, or 1% of adults, had used cocaine in the previous year.
Cocaine also remained the primary drug of concern in Latin America and the Caribbean in 2013, and in Australia since 2004 more people have been using cocaine but with less frequency. Use in Asia is low, at a prevalence of 0.05% among the population aged 14 to 65 years. Thus, the estimated annual prevalence of cocaine use by region is 0.4% in Africa, 1.4% in the Americas, 0.05% in Asia, 0.7% in Europe and 1.6% in Oceania (UNDOC 2015).
In 2013, 584,000 Americans aged 12 or older reported receiving treatment for cocaine use in the previous year (SAMSHA 2014). In Europe, cocaine was cited as the primary drug for 13% of all people who entered specialised drug treatment in 2013 (55,000), and for 16% of those entering treatment for the first time (25,000). Spain, Italy and the United Kingdom were the EU countries treating most of the people (EMCDDA 2015).
The prevalence of cocaine use and cocaine use disorders is particularly high in vulnerable groups, such as people with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or opioid dependence. Prevalence studies in people with substance use disorders have shown ADHD rates of 23.1% (Van Emmerik‐Van Oortmerssen 2012). Among cocaine abusers seeking treatment, lifetime ADHD prevalence ranges from 9.9% to 34.6%, depending on the study (Van Emmerik‐Van Oortmerssen 2012). Dual dependence on both opiates and cocaine occurs in about 60% of people admitted to methadone maintenance treatment in the USA and negatively impacts prognosis (Kosten 2003). A broad range of people (24% to 66%) receiving office‐based buprenorphine treatment for opioid dependence are also cocaine users (Chinazo 2014). Furthermore, cocaine dependence is also prevalent in the needle exchange programs for opioid abusers (Kidorf 2004).
Description of the condition
Cocaine use disorders comprised two clinical entities in the fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV) (American Psychiatric Association 2000): cocaine abuse and cocaine dependence. While cocaine abuse was characterised by hazardous cocaine use, DSM‐IV defined cocaine dependence as compulsive drug use that could result in tolerance or withdrawal. In the current DSM‐5 classification (American Psychiatric Association 2013), no distinction exists between abuse and dependence, and cocaine use disorder – a pattern of cocaine use leading to significant impairment and distress – is included among other stimulant use disorders. Cocaine use can be accompanied by drug craving (strong desire or urge for consumption), tolerance and development of withdrawal symptoms. Clinicians specify how severe (mild, moderate and severe) the cocaine disorder is depending on the number of symptoms.
From a biological point of view, cocaine addiction appears as a dopaminergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic dysregulation. Cocaine is a dopamine (DA) and also a norepinephrine (NE) reuptake inhibitor, and thus it increases DA in the nucleus accumbens, a process that has been associated with drug‐reinforcing properties (Koob 1988; Volkow 1997a). With repeated cocaine use, studies have reported a down‐regulation of both DA release and DA2 receptors in striatum (Volkow 1990; Volkow 1996; Volkow 1997b; Volkow 2004). The dopaminergic dysfunction could explain the appearance of tolerance and withdrawal. Additionally, glutamate hyperactivity also takes place, mainly in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala, which have projections to nucleus accumbens (Kalivas 2005). This glutamatergic dysfunction could be involved in the two remaining cocaine dependence characteristics: a compulsive pattern of cocaine use and relapse to cocaine use after a cocaine‐free period (Kalivas 2005). Furthermore, the output from the accumbens to the ventral pallidum is GABAergic and peptidergic, and decreased GABA release in the ventral pallidum has been associated with cocaine‐seeking behaviour (Kalivas 2007).
Description of the intervention
Given that DA, glutamate and GABA are involved in the neurobiology of cocaine use disorders, drugs modulating the action of these neurotransmitters are reasonable candidates for treating the conditions. DA has a pivotal role in establishing addictive behaviour, so many studies have tested dopaminergic drugs for treating cocaine addiction, with diverse approaches targeting DA, ranging from administration of cocaine like‐drugs (replacement therapy) to treating people with agonist or antagonists of dopamine receptors (Kalivas 2007). Given the successful results of replacement therapy in heroin, described in Mattick 2009, and in nicotine dependence (Hartmann‐Boyce 2014), the use of cocaine like‐drugs, such as central nervous system (CNS) stimulants, could be the most promising strategy.
Replacement therapy involves substituting the abused, often illegal drug, which users take parenterally several times a day, with a legal, orally administered one with a longer half‐life. A substitute drug has a similar mechanism of action and behavioural effect as the abused one but has a lower addictive potential and blocks drug craving and withdrawal, leading to drug abstinence and favouring adherence to medical and psychological assistance (Gorelick 2004; Grabowski 2004b).
How the intervention might work
CNS stimulants indirectly increase DA, and if administered orally with long‐lasting compounds, they could normalise the DA dysfunction associated with cocaine addiction. Over the last decade, replacement therapy with CNS stimulants has been gaining support (Gorelick 2004). Studies have assessed several CNS stimulants for cocaine abuse, including in people with comorbid disorders such as ADHD or opioid dependence (Castells 2007; Cunill 2015; Perez de los Cobos 2014).
Why it is important to do this review
Different studies have investigated around 50 drugs for treating cocaine dependence, but none of them have clearly demonstrated efficacy (Kleber 2007; Minozzi 2015a; Minozzi 2015b; Pani 2011). Consequently, neither the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) nor the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved any medication for the treatment of cocaine use disorders. However, since promising results have been shown with CNS stimulants (Castells 2007), several clinical trials on these drugs are currently underway.
Objectives
To assess the effects of psychostimulants for cocaine abuse and dependence. Specific outcomes include sustained cocaine abstinence and retention in treatment. We also studied the influence of type of drug and comorbid disorders on psychostimulant efficacy.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included only randomised parallel group placebo‐controlled clinical trials.
Types of participants
Participants were community adults meeting DSM criteria (regardless of edition) for cocaine abuse or dependence. We also included studies enrolling patients with comorbid conditions (i.e. psychiatric comorbidity or opioid dependence).
Types of interventions
Experimental intervention
CNS stimulants for cocaine abuse. Because "psychostimulant" and "CNS stimulant" are not terms describing a pharmacological group but a pharmacological effect, there is not a single list of drugs with this effect. Instead, drug classification systems such as the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification and the American Hospital Formulary Service (AHFS) Pharmacologic‐Therapeutic Classification System divide CNS stimulants into several groups according to their main indication (AHFS 2014; ATC 2015). To identify a complete list of drugs with psychostimulant effect, we performed a search among all drugs belonging to groups or subgroups suspected of containing potential psychomotor stimulants. In the ATC classification, these pharmacological groups were N06BA (centrally acting sympathomimetics), A08AA (centrally acting antiobesity products), N06BC (xanthine derived), N06BX (other psychostimulants and nootropics), N07BA (drugs used in nicotine dependence) and R03DA (xanthines) from t. In the AHFS classification, the groups were 12:92 (miscellaneous autonomic drugs), 28:16.04.92 (antidepressants, miscellaneous), 28:20.04 (amphetamines), 28:20.92 (anorexigenic agents and respiratory and cerebral stimulants, miscellaneous) and 86:16 (respiratory smooth muscle relaxants). We also included drugs metabolised to a known psychostimulant such as selegiline, and we reviewed the World Anti‐Doping Agency (WADA) list (WADA 2016) and other sources of information in pharmacology and psychopharmacology (Brayfield 2014; Brunton 2011). From this list of potential CNS stimulants, we included only those drugs having at least one published study showing a CNS stimulant effect in our definitive list of psychostimulants. We defined a CNS stimulant effect as increased CNS activity resulting in fatigue relief, improved performance in simple tasks, increased locomotor activity and anorexia in healthy people.
Control intervention
Placebo.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Reduction of cocaine use, assessed by mean (standard deviation (SD)) proportion of negative urinalysis across the study per participant
Sustained cocaine abstinence (number of patients who achieved sustained cocaine abstinence)
Retention in treatment (number of patients who finished the study)
Secondary outcomes
Efficacy
Self‐reported cocaine use
Cocaine craving (assessed by a quantitative scale)
Survival
-
Clinical severity assessed by the Clinical Global Impression (investigator‐ and participant‐rated)
Endpoint severity
Improvement
Proportion achieving substantial clinical improvement
Depression symptoms assessed by a standardised instrument
For studies including dual opioid‐cocaine abusers
Heroin use assessed by mean (SD) proportion of negative urinalysis across the study per patient
Sustained heroin abstinence (number of participants who achieved sustained heroin abstinence)
Self‐reported heroin use
For studies including dual ADHD patients‐cocaine abusers
ADHD symptoms severity assessed by a standardised instrument
Safety outcomes
Number of patients who dropped out the study due to any adverse event
Number of patients who dropped out the study due to any cardiovascular adverse events
Number of patients who abused study medication
Number of patients experiencing any serious advers event
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
In Appendix 1, we have listed the search methods we used in the original review (Castells 2010).
For the update, we searched the following databases.
Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group (CDAG) Specialised Register (searched 21 January 2014 in CRSLive).
CENTRAL (2016, Issue 1) using the search strategy outlined in Appendix 3.
MEDLINE (PubMed) (from 2008 to 15 February 2016) using the search strategy outlined in Appendix 4.
Embase (Elsevier, EMBASE.com) (from 2008 to 15 February 2016) using the search strategy outlined in Appendix 5.
Web of Science (Thomson Reuters) (from 2008 to 15 February 2016) using the search strategy outlined in Appendix 6.
We searched and identified for ongoing clinical trials and unpublished studies via Internet searches on the following sites.
centerwatch.com (searched 15 February 2016).
clinicaltrials.gov (searched 15 February 2016).
www.isrctn.com (searched 15 February 2016).
www.who.int/ictrp (searched 15 February 2016).
Searching other resources
Personal contact
We asked the corresponding authors of all included studies, along with experts in the field and pharmaceutical companies, to identify other published, unpublished or ongoing trials.
Citations
We handsearched the reference lists of retrieved studies and relevant review articles to identify any further studies.
For each included study, we performed a citation search in the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) Web of Science to identify any later studies that may have cited it.
All searches included non‐English language literature and studies with English abstracts. When we considered that the reports were likely to meet inclusion criteria, we had them translated.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Three review authors (of XC, RC and CP) inspected abstracts of potentially relevant studies and retrieved the full text of those studies deemed to be relevant. When we identified unpublished trials, we contacted the coordinators to request data.
Data extraction and management
Three review authors (XC, RC, CP) inspected the full text of retrieved papers using a piloted data extraction sheet. We resolved any disagreement by consensus or appeal to a fourth author (DC). In case of missing information, we emailed authors to request missing data. If we did not receive an answer within a month of the first email, we made a second attempt.
We extracted the following data.
-
Study description and funding.
Author.
Year of publication.
Country.
Author affiliation: pharmaceutical industry (yes/no).
Study funding: pharmaceutical industry (yes/no).
-
Methods.
Sequence generation.
Allocation concealment.
Blinding of patients/clinicians/therapists/assessors.
Design: single site/multisite.
Study duration (from randomisation to treatment completion).
Number of participants.
Handling of drop‐outs (intention‐to‐treat (ITT) versus per protocol)
Instruments administered to assess study outcomes.
-
Participants.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria.
Sex.
Age (mean, SD).
Ethnicity (% white, % African American, % other).
Employment status (% unemployed).
Comorbid disorders (% with comorbid psychiatric disorders).
-
Intervention.
Type of CNS stimulant.
Dose.
Pharmaceutical presentation.
Adherence (by method used to assess treatment adherence).
Adjunc psychological interventions (description of the adjunct psychological interventions).
-
Outcomes.
Cocaine use by means of urine screen (mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalysis across the study per patient)
Sustained cocaine abstinence. The number of patients achieving sustained cocaine abstinence, assessed with urinalysis, regardless of the definition used for of the length of abstinence.
Number of patients who finished the study.
Self‐reported cocaine use (mean (SD) days of cocaine use across the study).
Cocaine craving (mean (SD) cocaine craving score at study conclusion).
Clinical impression (number of patients obtaining a clinical global impression (CGI) score of 1 or 2 at study conclusion)
Anxiety symptoms severity (mean (SD) cocaine anxiety score at study conclusion)
Depression symptoms severity (mean (SD) cocaine depression score at study conclusion)
Heroin use by means of urine screen (mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalysis across the study per patient)
Sustained heroin abstinence. The number of patients achieving sustained heroin abstinence (regardless how studies define length of abstinence), assessed with urinalysis.
Self‐reported heroin use (mean (SD) days of heroin use across the study).
ADHD severity (mean ADHD (SD) at study conclusion and number of patients achieving a 30% decrease in the ADHD severity score).
Participants who dropped out due to adverse events (number of patients who dropped out due to any adverse event, number of patients who dropped out due to cardiovascular adverse events).
Number of patients who had serious adverse events.
Number of patients who abused study medication.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
We assessed the risk of bias in this review using the criteria recommended in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011) (see Table 2). The recommended approach for assessing risk of bias in studies included in Cochrane reviews uses a two‐part tool, addressing seven specific domains, namely sequence generation, allocation concealment (both pertaining to selection bias), blinding of participants and providers (performance bias), blinding of outcome assessors (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective outcome reporting (reporting bias) and other sources of bias. The first part of the tool involves describing what investigators reported happening in the study. The second part of the tool involves assigning judgement of high, low or unclear the risk of bias for that entry. To make these judgments, we used the criteria indicated by Higgins 2011 and adapted it to the addiction field. See Table 2 for details.
1. Criteria for the assessment of the risk of bias in RCT.
| Item | Judgment | Description |
| 1. Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | The investigators describe a random component in the sequence generation process such as: random number table; computerised random number generator; coin tossing; shuffling cards or envelopes; throwing dice; drawing of lots; minimisation. |
| High risk | The investigators describe a non‐random component in the sequence generation process such as: odd or even date of birth; date (or day) of admission; hospital or clinic record number; alternation; judgement of the clinician; results of a laboratory test or a series of tests; availability of the intervention. | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information about the sequence generation process to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 2. Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Investigators enrolling participants could not foresee assignment because 1 of the following, or an equivalent method, was used to conceal allocation: central allocation (including telephone, web‐based, and pharmacy‐controlled, randomisation); sequentially numbered drug containers of identical appearance; sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes. |
| High risk | Investigators enrolling participants could possibly foresee assignments because 1 of the following methods was used: open random allocation schedule (e.g. a list of random numbers); assignment envelopes without appropriate safeguards (e.g. if envelopes were unsealed or nonopaque or not sequentially numbered); alternation or rotation; date of birth; case record number; any other explicitly unconcealed procedure. | |
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk. This is usually the case if the method of concealment is not described or not described in sufficient detail to allow a definite judgement. | |
| 3. Blinding of participants and providers (performance bias) Objective outcomes |
Low risk | No blinding or incomplete blinding, but the review authors judge that the outcome is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding; Blinding of participants and key study personnel ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken. |
| High risk | No blinding or incomplete blinding, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding; Blinding of key study participants and personnel attempted, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 4. Blinding of participants and providers (performance bias) Subjective outcomes |
Low risk | Blinding of participants and providers ensured and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| High risk | No blinding or incomplete blinding, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding; Blinding of key study participants and personnel attempted, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 5. Blinding of outcome assessor (detection bias) Objective outcomes |
Low risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, but the review authors judge that the outcome measurement is not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding Blinding of outcome assessment ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding; Blinding of outcome assessment, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 6.Blinding of outcome assessor (detection bias) Subjective outcomes |
Low risk | Blinding of outcome assessment ensured, and unlikely that the blinding could have been broken |
| High risk | No blinding of outcome assessment, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding; Blinding of outcome assessment, but likely that the blinding could have been broken, and the outcome measurement is likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 7. Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) For all outcomes except retention in treatment |
Low risk | No missing outcome data; Reasons for missing outcome data unlikely to be related to true outcome (for survival data, censoring unlikely to introduce bias); Missing outcome data balanced in numbers across intervention groups, with similar reasons for missing data across groups; For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on the intervention effect estimate; For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes not enough to have a clinically relevant impact on observed effect size; Missing data have been imputed using appropriate methods; All randomised participants are reported/analysed in the group they were allocated to by randomisation irrespective of non‐adherence and co‐interventions (intention‐to‐treat) |
| High risk | Reason for missing outcome data likely to be related to true outcome, with either imbalance in numbers or reasons for missing data across intervention groups; For dichotomous outcome data, the proportion of missing outcomes compared with observed event risk enough to induce clinically relevant bias in intervention effect estimate; For continuous outcome data, plausible effect size (difference in means or standardised difference in means) among missing outcomes enough to induce clinically relevant bias in observed effect size; 'As‐treated' analysis done with substantial departure of the intervention received from that assigned at randomisation. |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk (e.g. number randomised not stated, no reasons for missing data provided; number of dropouts not reported for each group) | |
| 8. Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | The study protocol is available and all of the study's pre‐specified (primary and secondary) outcomes that are of interest in the review have been reported in the pre‐specified way; The study protocol is not available but it is clear that the published reports include all expected outcomes, including those that were pre‐specified (convincing text of this nature may be uncommon). |
| High risk | Not all of the study’s pre‐specified primary outcomes have been reported; 1 or more primary outcomes is reported using measurements, analysis methods or subsets of the data (e.g. subscales) that were not pre‐specified; 1 or more reported primary outcomes were not pre‐specified (unless clear justification for their reporting is provided, such as an unexpected adverse effect); 1 or more outcomes of interest in the review are reported incompletely so that they cannot be entered in a meta‐analysis; The study report fails to include results for a key outcome that would be expected to have been reported for such a study. |
|
| Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement of low or high risk | |
| 9. Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
| High risk | There is at least 1 important risk of bias. For example, the study: Had a potential source of bias related to the specific study design used; Stopped early due to some data‐dependent process (including a formal‐stopping rule); Had extreme baseline imbalance; Has been claimed to have been fraudulent; or Had some other problem. |
|
| Unclear risk | There may be a risk of bias, but there is either: Insufficient information to assess whether an important risk of bias exists; or Insufficient rationale or evidence that an identified problem will introduce bias. |
The tool contains a single entry for the domains of sequence generation and allocation concealment (avoidance of selection bias) for each study. We considered blinding of participants, personnel and outcome assessors (avoidance of performance bias and detection bias) separately for objective outcomes (e.g. dropout, use of substance of abuse measured by urinalysis, participants relapsed at the end of follow‐up, participants engaged in further treatments) and subjective outcomes (e.g. duration and severity of signs and symptoms of withdrawal, craving, self‐reported use of substance, side effects, social functioning as integration at school or at work, family relationship). We considered incomplete outcome data (avoidance of attrition bias) for all outcomes except retention in treatment, which, by definition, is not affected by this source of bias.
Measures of treatment effect
We introduced treatment effect measures into Review Manager (RevMan) 5 to pool data. We calculated three different measures of treatment effect.
We calculated count data, such as the efficacy on drug use, as continuous data. We extracted the mean (SD) proportion of drug free‐urinalysis over the planned number of urinalyses per patient, comparing active treatment and placebo groups. We did not compare the proportion of negative urinalysis between active intervention and placebo. We calculated the standardised mean difference (SMD) for each comparison to allow combination.
For categorical efficacy outcomes, such as sustained drug abstinence, we calculated the risk ratio (RR) for each comparison.
For categorical safety outcomes, such as the number of patients who dropped out of the study due to any adverse event, we calculated the risk difference (RD). We preferred RD to RR because several studies had no events for either the active or control interventions, preventing us from calculating the RR for these studies, which would have resulted in an overestimation of the intervention effect on adverse event‐induced dropouts. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (CI) for each measure of treatment effect.
Unit of analysis issues
We handled studies with multiple comparisons as follows. When several independent comparisons were available, for example, methylphenidate + psychotherapy versus placebo + psychotherapy versus methylphenidate + fake psychotherapy versus placebo + fake psychotherapy, we included them as two independent studies (methylphenidate + psychotherapy versus placebo + psychotherapy, on the one hand, and methylphenidate + fake psychotherapy versus placebo + fake psychotherapy, on the other). In studies with multiple and correlated interventions (for example, methylphenidate 20 mg versus methylphenidate 40 mg versus placebo), we combined experimental groups into a single group and included it in the meta‐analysis as a single comparison. For binary data, we added sample sizes and the number of participants with the event across groups. We combined continuous data using the formulae described in section 7.7.3.8, 'Combining groups' of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011).
There were no unit of analysis issues regarding the inclusion of cross‐over clinical trials because we excluded such trials from the review.
Dealing with missing data
We used the ITT sample size as a denominator for categorical variables, such as the number of patients achieving sustained cocaine abstinence.
For continuous data, we entered the sample size used in the calculations of the mean and SD into RevMan.
We did not impute missing data.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We investigated heterogeneity by means of the I2 and Chi2 statistic.
Assessment of reporting biases
We constructed funnel plots to investigate any relationship between effect size and study precision (closely related to sample size). Such a relationship could be due to publication or related biases or due to systematic differences between small and large studies. If we identified a relationship, we examined clinical diversity of the studies as a possible explanation (Egger 1997).
If we found a statistically significant result, we calculated the number of negative studies with an average sample size needed to neutralise this effect.
Data synthesis
We used the random‐effects model to calculate weighted averages and 95% CIs.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
Regardless of the existence of statistical heterogeneity, we planned the following subgroup analyses.
Type of CNS stimulant: amphetamine derivative, bupropion, modafinil, etc.
Clinical definition of cocaine use disorder: are cocaine abusers included? Yes/no.
Comorbidities: was the presence of a comorbidity (opioid dependence, ADHD) an inclusion criterion? Yes/no.
Study quality and risk of bias: high and unclear risk of bias versus low.
Type of administered scales: self‐ versus hetero‐administered.
Single site versus multisite.
Funding: with versus without pharmaceutical industry funding.
We performed subgroup analyses only when results from at least two studies were available.
We did not perform the analysis of the influence of the type of administered scale because there were too few studies reporting suitable outcomes for this subanalysis (depression symptoms and ADHD severity).
Likewise, we did not undertake the analysis of the impact of the source of funding because all studies were publicly funded, and pharmaceutical industry funding only involved the supply of study medication in a few studies.
Sensitivity analysis
We carried out a sensitivity analysis for safety outcomes. We calculated the RR instead of the RD used in the primary analyses.
Summary of findings table
We assessed the overall quality of the evidence for the primary outcomes using the GRADE system, which takes into account issues not only related to internal validity but also to external validity, such as directness of results (GRADE 2004; Guyatt 2008; Guyatt 2011; Schunemann 2006). The 'Summary of findings' tables present the main findings of a review in a transparent and simple tabular format, providing key information concerning the quality of evidence, the magnitude of effect of the interventions examined and the sum of available data on the main outcomes.
The GRADE system uses the following criteria for assigning grades of evidence.
High: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect.
Moderate: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate.
Low: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate.
Very low: any estimate of effect is very uncertain.
The following reasons merit the downgrading of evidence: serious (−1) or very serious (−2) limitation to study quality; important inconsistency (−1); some (−1) or major (−2) uncertainty about directness; imprecise or sparse data (−1); and high probability of reporting bias (−1).
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2010 (Castells 2010). In the first version of this review, we retrieved 32 full‐text articles for more detailed evaluation; we excluded half of them, thus including 16 trials that satisfied all the criteria for inclusion in the review.
In the present update, we identified 488 reports, 3 of which were ongoing studies, 10 were awaiting classification and 439 were excluded on the basis of title and abstract. We inspected the full text of 36 studies and excluded 26. Thus, we identified and included 10 new studies in this update, in addition to the 16 studies included in the previous version (see Figure 1).
1.
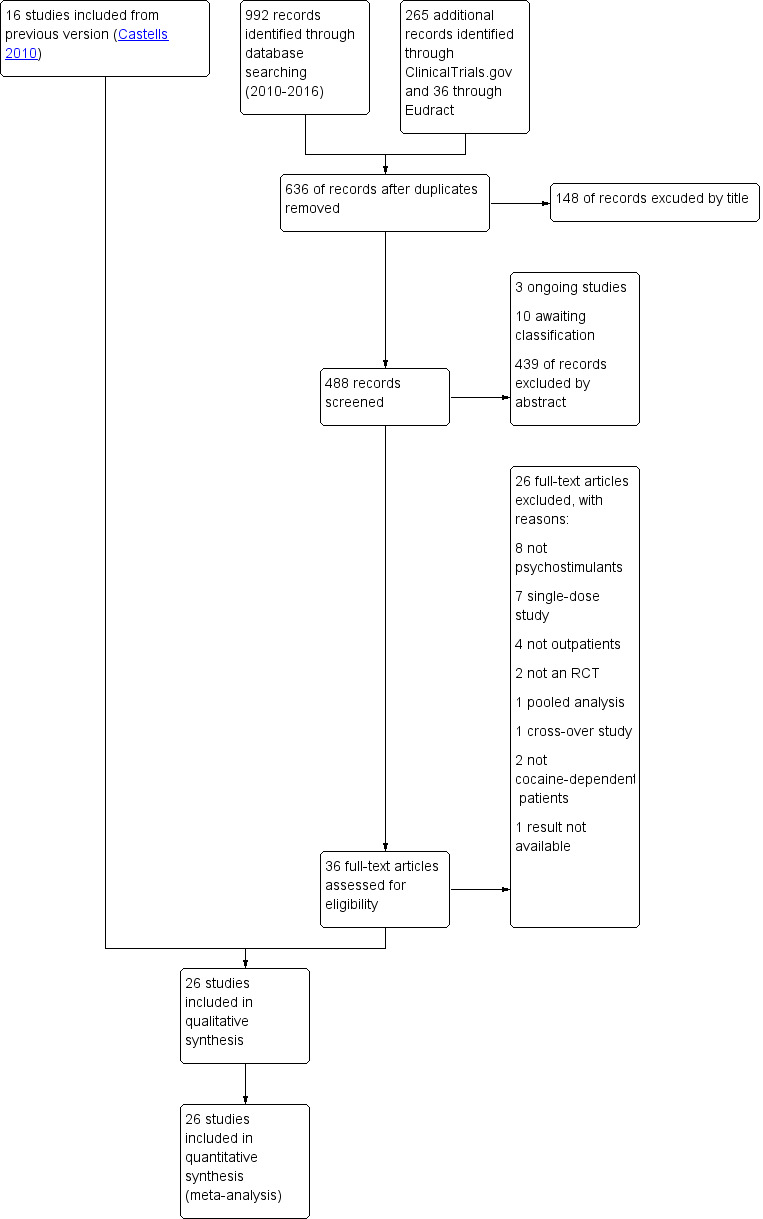
Study flow diagram.
Included studies
Twenty‐six studies met the inclusion criteria of this review. All studies investigated a psychostimulant drug intervention, but two had a factorial design and also assessed the efficacy of a behavioural intervention (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Poling 2006). One study compared two CNS stimulants against placebo (Schmitz 2012). In eleven studies, the presence of a comorbid psychiatric disorder was an inclusion criteria: opioid dependence in six (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Grabowski 2004a; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Poling 2006), ADHD in three (Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Schubiner 2002), and alcohol dependence and schizophrenia in one each (NCT00142818; Perry 2004). University researchers performed all studies, 17 with public funding (Anderson 2009; Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Elkashef 2006; Grabowski 1997; Grabowski 2001; Grabowski 2004a; Kampman 2015; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Mooney 2009; Mooney 2015; Morgan 2016; Poling 2006; Schmitz 2012; Schmitz 2014; Schubiner 2002; Shoptaw 2008), and 8 with both public and private funding (Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Perry 2004; Shearer 2003; Stine 1995). One study did not describe the funding source (NCT00142818).
Participants
The included studies randomised 2366 participants, mostly middle aged (mean age 39.6 years) men (74.7%). About half (47.6%) were African American, and 39.3% were white. Mean lifetime cocaine use ranged from 7.7 to 22.4 years. Thirteen studies reported the route of cocaine use, with inhalation being the most common (60.8%). See Table 3 for details on additional participant characteristics.
2. Baseline characteristics of the patients included in the clinical trials of the meta‐analysisa.
| Sample size (N) | 2366 |
|
Sex % female |
25.3 |
|
Age Mean age (years) |
39.6 |
|
Ethnicity % white % black % other |
39.3 47.6 13.1 |
|
Employment status % currently employed |
39.3 |
|
Days of cocaine use/month Range |
10.6‐17.8 |
|
Length of cocaine use Range of mean lifetime cocaine use (years) |
7.7‐22.4 |
|
Route of cocaine use % intranasal % intrapulmonary % intravenous |
23.8 60.8 14.7 |
|
Comorbidities % opioid dependence % alcohol dependence |
21.4 10.4 |
aBaseline patient characteristics are presented for trials reporting this information. Sex was available for all studies; age for all studies but one; ethnicity, for 22 studies; the presence of opioid and alcohol dependence, for 24 and 19, respectively; lifetime cocaine use, for 17; days of cocaine use in a month, for 15; employment, for 9; and route of cocaine use, for 13.
Interventions and settings
Investigators assessed nine drugs: bupropion in three studies (Margolin 1995a; Poling 2006; Shoptaw 2008), dexamphetamine in four (Grabowski 2001; Grabowski 2004a; Schmitz 2012; Shearer 2003), lisdexamfetamine in one (Mooney 2015), methylphenidate in four (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Grabowski 1997; Levin 2007; Schubiner 2002), modafinil in eight (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Kampman 2015; Morgan 2016; NCT00142818; Schmitz 2012; Schmitz 2014), mazindol infour (Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Perry 2004; Stine 1995), methamphetamine in one (Mooney 2009), mixed amphetamine salts in one (Levin 2015), and selegiline in one (Elkashef 2006).
Participants received psychotherapy in addition to the studied intervention in all studies: in 13, they received cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT); in 5, counselling; in 1, CBT + counselling; in 3, CBT + contingency management (CM); in 1, modified CBT + motivational intervention; in 1, psychoeducation + relapse prevention therapy + CBT; and in 1, case management + behavioural contingency + group psychotherapy. One study randomised participants to CBT or to CM in addition to pharmacological treatment with methylphenidate or placebo.
Eight studies were multicentre trials (Anderson 2009; Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Elkashef 2006; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995a; Shearer 2003; Stine 1995), seventeen single‐centre (Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Grabowski 1997; Grabowski 2001; Grabowski 2004a; Kampman 2015; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Mooney 2009; Mooney 2015; Morgan 2016; Perry 2004; Poling 2006; Schmitz 2012; Schmitz 2014; Schubiner 2002; Shoptaw 2008), and one did not specify the number of study sites (NCT00142818). All studies took place in the USA except Shearer 2003 and Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013, which were performed in Australia and Switzerland, respectively.
Study length ranged from 6 to 24 weeks, with an average length of 12.6 weeks.
Excluded studies
We excluded 38 studies from this review (See Characteristics of excluded studies and Figure 1). Eleven were not randomised, placebo‐controlled clinical trials, eight were RCTs that investigated pharmacological interventions other than psychostimulants, seven were RCTs that administered a single dose of psychostimulants, four were RCTs that included only inpatients, four did not include cocaine‐dependent patients, one was an RCT with a cross‐over design, another was a pooled analysis of RCTs, another did not report the results, and a final one was a laboratory study without outpatient follow‐up.
Risk of bias in included studies
We present a comprehensive description of the risk of bias for each study in the Characteristics of included studies and a summary in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
2.
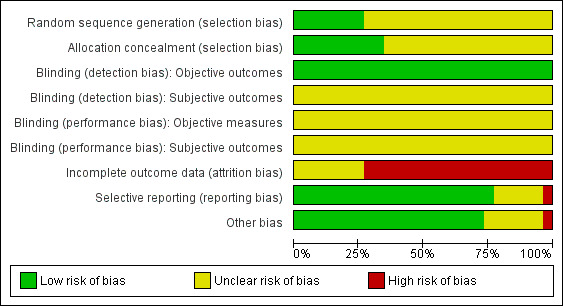
Methodological quality graph: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item presented as percentages across all included studies.
3.
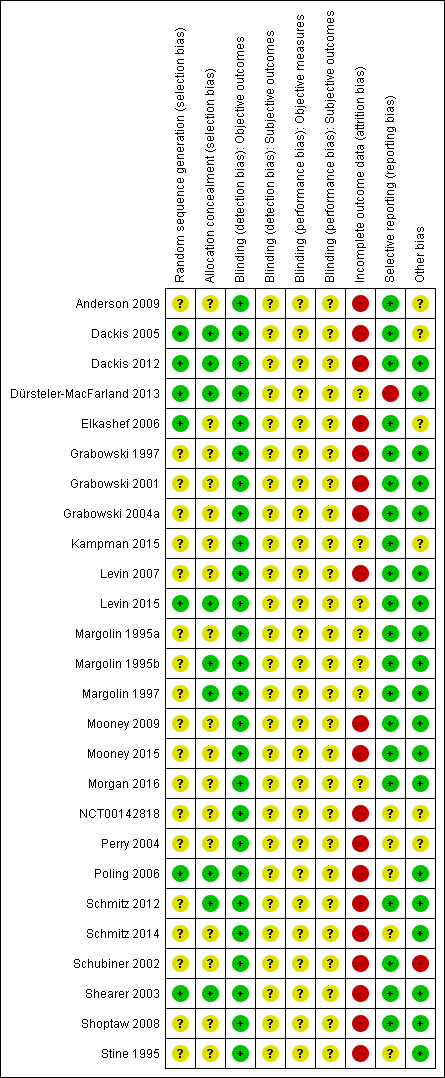
Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgements about each methodological quality item for each included study.
Allocation
We deemed sequence generation and allocation concealment to be adequate in seven studies (Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Elkashef 2006; Levin 2015; Poling 2006; Shearer 2003) and nine studies (Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Poling 2006; Schmitz 2012; Shearer 2003), respectively. In the remaining studies, the risk of bias due to sequence generation and allocation concealment was unclear.
Blinding
Since the pharmacological interventions studied have powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned intervention, we could not rule out the risk of performance and detection bias on subjective outcomes. For the same reason, we rated performance bias on objective outcomes to be unclear. Conversely, we considered the risk of detection bias to be low for objective outcomes because the measure of this type of outcomes is unlikely to be influenced by the awareness of the studied intervention.
Incomplete outcome data
We assessed 19 studies as being at high risk of attrition bias (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Elkashef 2006; Grabowski 1997; Grabowski 2001; Grabowski 2004a; Levin 2007; Mooney 2009; Mooney 2015, NCT00142818; Perry 2004; Poling 2006; Schmitz 2012; Schmitz 2014; Schubiner 2002; Shearer 2003; Shoptaw 2008; Stine 1995) and 7 as being at unclear risk (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Kampman 2015; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Morgan 2016).
Selective reporting
We considered the risk of reporting bias to be low in 20 studies (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Elkashef 2006; Grabowski 1997; Grabowski 2001; Grabowski 2004a; Kampman 2015; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Mooney 2009; Mooney 2015; Morgan 2016; Schmitz 2012; Schubiner 2002; Shearer 2003; Shoptaw 2008), high in 1 (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013), and unclear in the remaining five.
Other potential sources of bias
Seventeen studies were free of other biases. Schubiner 2002 excluded patients from the analysis, so we considered it to be at high risk of bias. Five had unbalanced participantcharacteristics at baseline, so we considered the risk of bias to be unclear (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Elkashef 2006; Kampman 2015; Perry 2004). NCT00142818 did not provided sufficient information to permit judgment, so we also considered it to be at unclear risk.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
We compared any psychostimulant versus placebo, and we present primary outcomes in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and in the Table 1.
4.
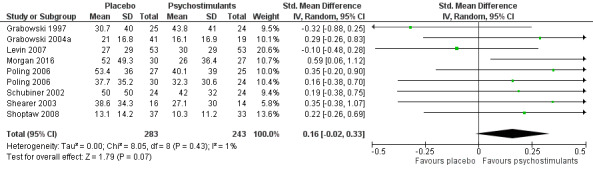
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
5.
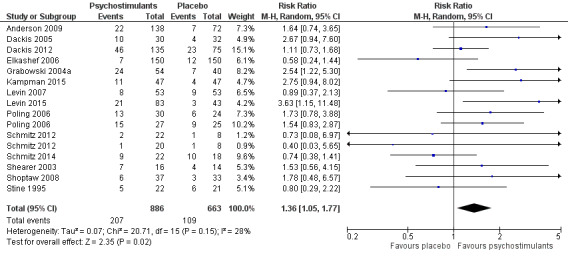
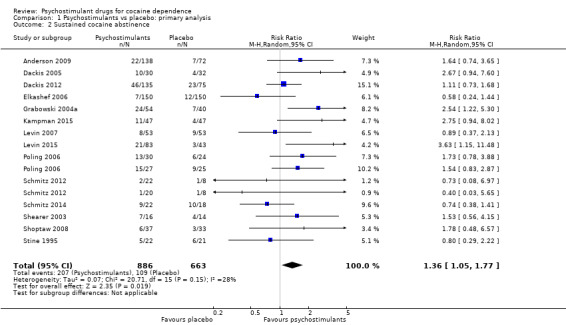
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
6.
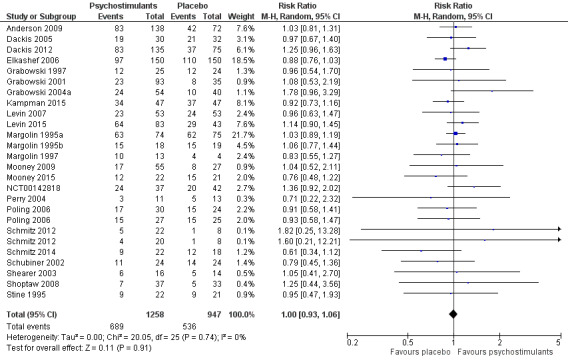
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.3 Number of patients who finished the study.
Primary outcomes
Cocaine use
The mean cocaine use across the study was infrequently reported. Eight studies involving 526 participants assessed cocaine use by measuring the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalysis across the study per patient (Grabowski 1997; Grabowski 2004a; Levin 2007; Morgan 2016; Poling 2006; Schubiner 2002; Shearer 2003; Shoptaw 2008). We did not find any significant difference between groups (SMD 0.16, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.33; Analysis 1.1, Figure 4) nor any heterogeneity.
1.1. Analysis.
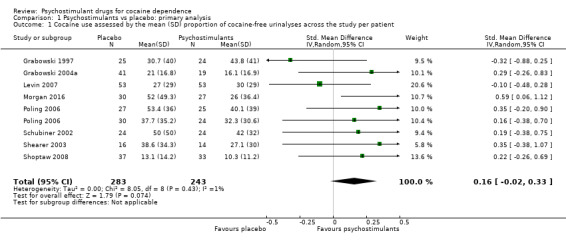
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
Sustained cocaine abstinence
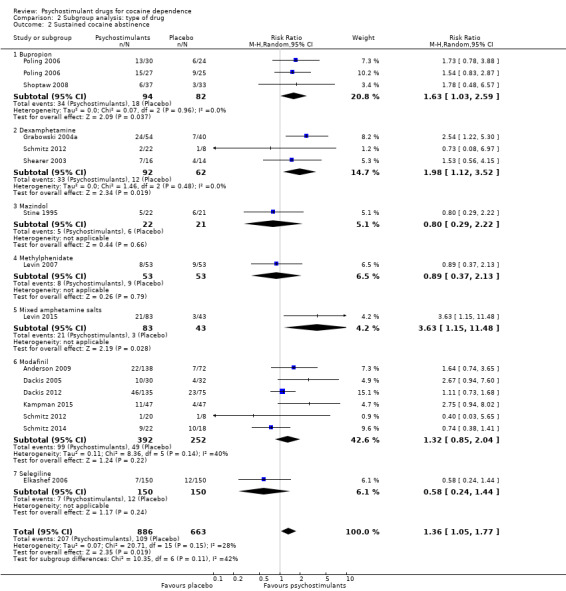
Fourteen studies involving 1549 participants reported the effect of the studied intervention on sustained cocaine abstinence (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Dackis 2012; Elkashef 2006; Grabowski 2004a; Kampman 2015; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Poling 2006; Schmitz 2012; Schmitz 2014; Shearer 2003; Shoptaw 2008; Stine 1995). Investigators considered three weeks to be 'sustained' abstinence in all but Levin 2007, which used a two‐week definition. The result of the meta‐analysis favoured the psychostimulant group (RR 1.36, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.77, P = 0.02; Analysis 1.2, Figure 5). We found no significant heterogeneity. To further analyse the efficacy of psychostimulants for achieving sustained cocaine abstinence, we calculated the RD and the number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB). The RD was 0.07 (P = 0.02), and the NNTB was 14.
1.2. Analysis.
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
Number of participants who finished the study (retention in treatment)
This outcome was available for all studies but two (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Morgan 2016), and data from 2205 participants contributed to the meta‐analysis (see Analysis 1.3, Figure 6). We did not find a significant difference between groups (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.06), nor did we find any heterogeneity.
1.3. Analysis.
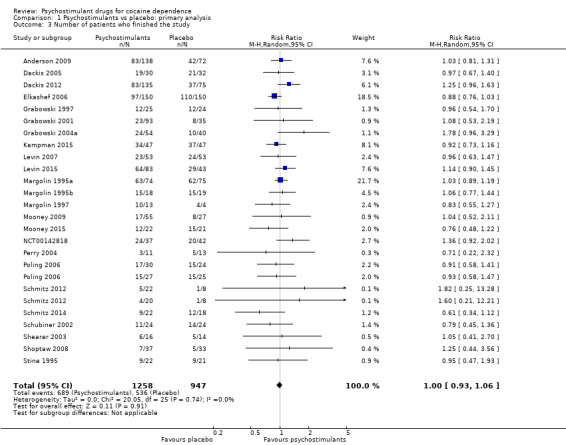
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 3 Number of patients who finished the study.
Secondary outcomes
Efficacy
Self‐reported cocaine use
One study involving 28 participants reported this outcome (Stine 1995). We did not find any significant difference between groups (SMD 0.00, 95% CI −0.74 to 0.74; Analysis 1.4).
1.4. Analysis.
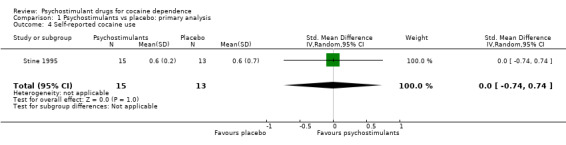
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 4 Self‐reported cocaine use.
Cocaine craving
Six studies involving 532 participants reported cocaine craving (Elkashef 2006; Margolin 1995a; Mooney 2015; Perry 2004; Shoptaw 2008; Stine 1995). There was no significant difference between groups (SMD −0.12, 95% CI −0.40 to 0.17; Analysis 1.5). We found moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 43%).
1.5. Analysis.
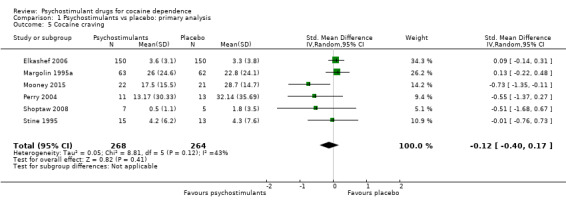
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 5 Cocaine craving.
Survival
No study reported survival outcomes.
Addiction severity (participant‐rated CGI‐severity scale)
One study involving 300 participants reported on participant‐rated addiction severity (Elkashef 2006). The result of the meta‐analysis favoured psychostimulants (SMD 0.28, 95% CI 0.05 to 0.50; P = 0.02; Analysis 1.6).
1.6. Analysis.
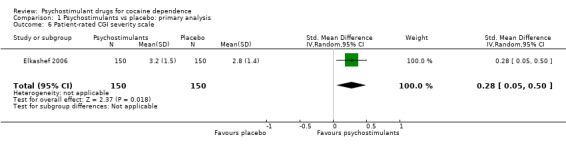
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 6 Patient‐rated CGI severity scale.
Addiction severity (investigator‐rated CGI‐severity scale)
One study involving 300 participants reported on investigator‐rated addiction severity (Elkashef 2006). There was no significant difference between groups (SMD 0.07, 95% CI −0.15 to 0.30; Analysis 1.7).
1.7. Analysis.
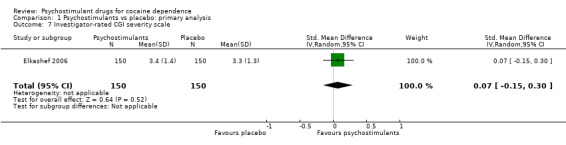
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 7 Investigator‐rated CGI severity scale.
Addiction severity improvement (participant‐rated CGI‐improvement scale)
One study involving 300 participants reported participant‐rated addiction severity improvement (Elkashef 2006).The result favoured psychostimulants (SMD 0.27, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.50; P = 0.02; Analysis 1.8).
1.8. Analysis.
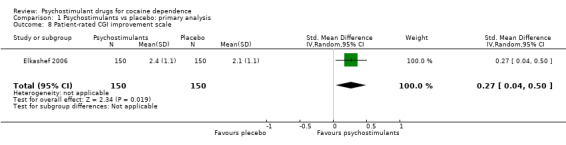
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 8 Patient‐rated CGI improvement scale.
Addiction severity improvement (investigator‐rated CGI‐improvement scale)
One study involving 300 participants reported investigator‐rated addiction severity improvement (Elkashef 2006). There was no significant difference between groups (SMD 0.00, 95% CI −0.23 to 0.23; Analysis 1.9).
1.9. Analysis.
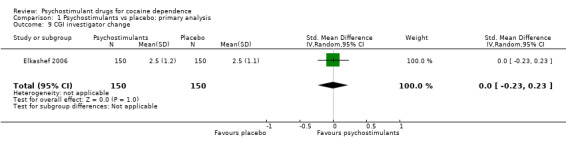
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 9 CGI investigator change.
Substantial addiction severity improvement (investigator‐rated CGI‐improvement scale = 1 or 2)
One study involving 106 participants reported the proportion of participants achieving substantial addiction severity improvement (Levin 2007). There was no significant difference between groups (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.15; Analysis 1.10).
1.10. Analysis.
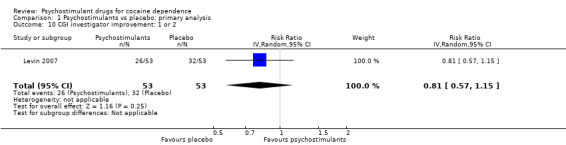
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 10 CGI investigator improvement: 1 or 2.
Global activity functioning
No study reported this outcome, so we could not analyse it.
Depression symptoms
Two studies involving 90 participants reported on symptoms of depression (Poling 2006; Stine 1995). We found no significant difference between groups (SMD −0.07, 95% CI −0.48 to 0.34; Analysis 1.11), nor did we find any heterogeneity.
1.11. Analysis.
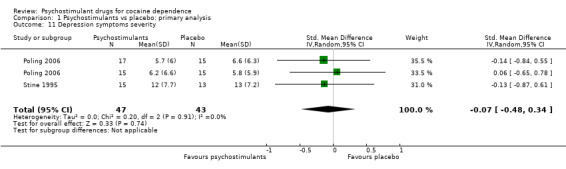
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 11 Depression symptoms severity.
For studies including dual opioid‐cocaine abusers
Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalysis across the study per participant
Two studies involving 167 participants reported on heroin use (Grabowski 2004a; Poling 2006). We found no significant difference between experimental and control groups (SMD 0.29, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.61; P = 0.07; Analysis 1.12), nor did we find any heterogeneity.
1.12. Analysis.
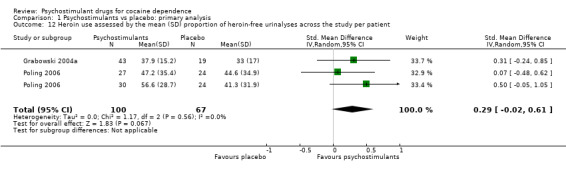
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 12 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
Sustained heroin abstinence
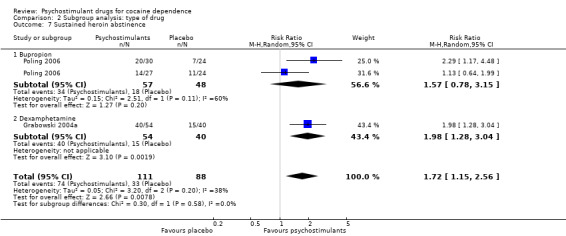
Two studies involving 199 participants reported on sustained heroin abstinence (Grabowski 2004a; Poling 2006). The result of the meta‐analysis favoured psychostimulants (RR 1.77, 95% CI 1.31 to 2.40; P = 0.0002; Analysis 1.13). We found moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 38%).
1.13. Analysis.
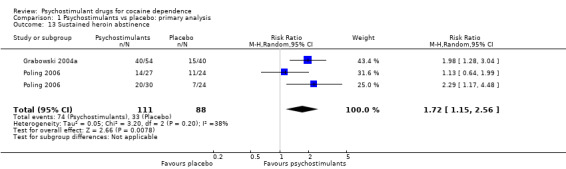
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 13 Sustained heroin abstinence.
Self‐reported heroin use
No study reported on self‐reported heroin use, so we could not analyse the outcome.
For studies including dual ADHD patients‐cocaine abusers
ADHD severity
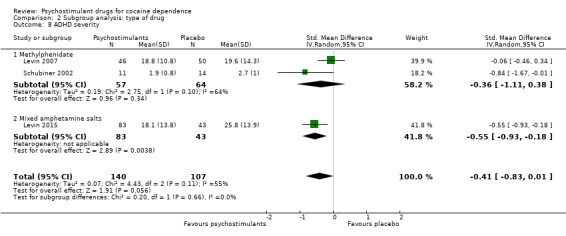
Three studies involving 247 participants reported on ADHD severity (Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Schubiner 2002). We did not find a significant difference between groups (SMD −0.41, 95% CI −0.83 to 0.01; P = 0.06; Analysis 1.14). There was high heterogeneity (I2 = 55%).
1.14. Analysis.
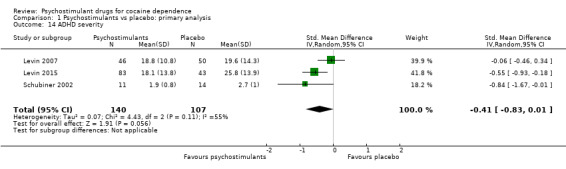
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 14 ADHD severity.
Safety
Dropouts due to any adverse event
Eighteen studies involving 1601 participants reported on dropouts due to adverse events (Anderson 2009; Dackis 2005; Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Elkashef 2006; Grabowski 2001; Kampman 2015; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1995b; Margolin 1997; Mooney 2009; Mooney 2015; Perry 2004; Schmitz 2014; Schubiner 2002; Shearer 2003; Stine 1995). The meta‐analysis did not show any significant difference between groups (RD 0.00, 95% CI −0.01 to 0.01; Analysis 1.15). We did not find any heterogeneity.
1.15. Analysis.
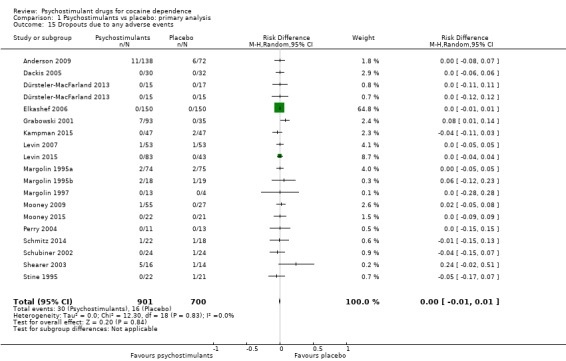
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 15 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse event
Eleven studies involving 688 participants reported on dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events (Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013; Levin 2007; Levin 2015; Margolin 1995a; Margolin 1997; Mooney 2015; Perry 2004; Schmitz 2014; Schubiner 2002; Shearer 2003; Stine 1995). The meta‐analysis did not show any significant difference between groups (RD 0.00, 95% CI −0.02 to 0.01; Analysis 1.16). We did not find any heterogeneity.
1.16. Analysis.
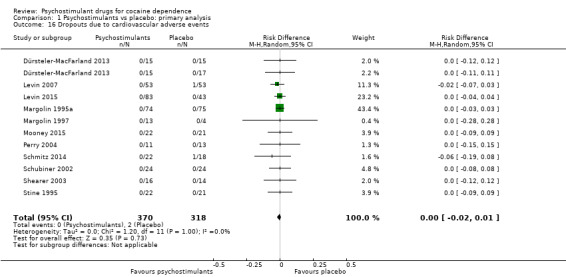
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 16 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
Medication abuse
This outcome was not available from any study, so we could not analyse it.
Serious adverse events
Six studies involving 444 participants reported on serious adverse events (Dackis 2005; Kampman 2015; Levin 2015; Mooney 2015; NCT00142818; Schmitz 2014). The meta‐analysis did not show any significant difference between groups (RD: −0.02, 95% CI −0.06 to 0.01; Analysis 1.17). We did not find any heterogeneity
1.17. Analysis.
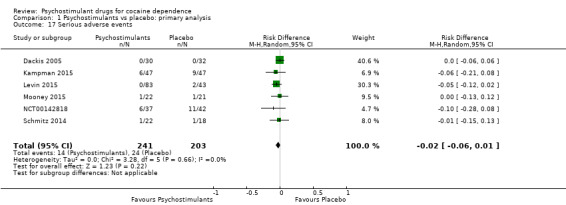
Comparison 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, Outcome 17 Serious adverse events.
Subgroup analyses
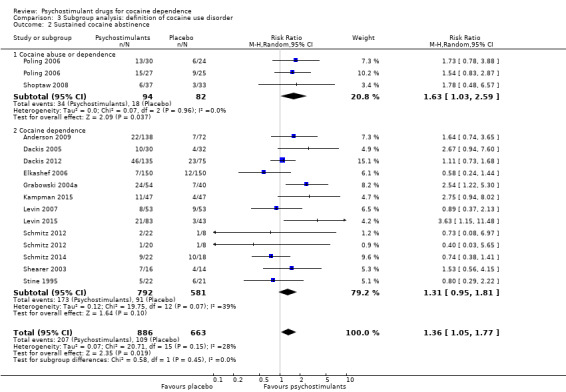
We did not find any between‐subgroup differences for any subgroup analyses. Nevertheless, these analyses identified some subgroups within which the interventions studied were more efficacious than placebo. Modafinil was more efficacious than placebo for reducing cocaine use (Analysis 2.1), bupropion, dexamphetamine and mixed amphetamine salts were more efficacious than placebo for achieving sustained cocaine abstinence (Analysis 2.2), dexamphetamine was found to improve heroin abstinence in participants with a comorbid heroin dependence (Analysis 2.7), and mixed amphetamine salts improved ADHD symptom severity in participants with comorbid ADHD (Analysis 2.8). Psychostimulants were more efficacious than placebo for achieving sustained cocaine abstinence in studies that included participants with cocaine abuse and cocaine dependence (Analysis 3.2). Psychostimulants reduced cocaine use and increased sustained cocaine abstinence in studies in which ADHD was not an inclusion criterion (Analysis 4.1). Psychostimulants increased sustained cocaine abstinence in studies in which heroin dependence was an inclusion criterion (Analysis 5.2).
2.1. Analysis.
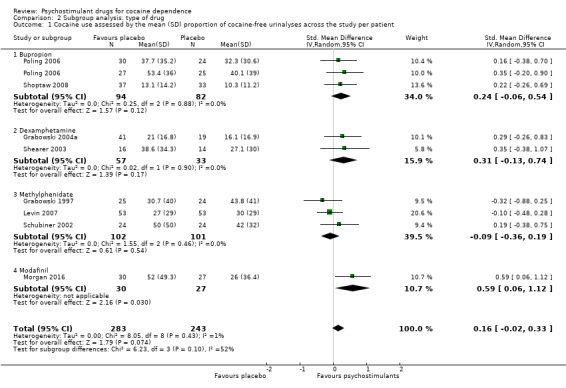
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
2.2. Analysis.
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
2.7. Analysis.
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 7 Sustained heroin abstinence.
2.8. Analysis.
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 8 ADHD severity.
3.2. Analysis.
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
4.1. Analysis.
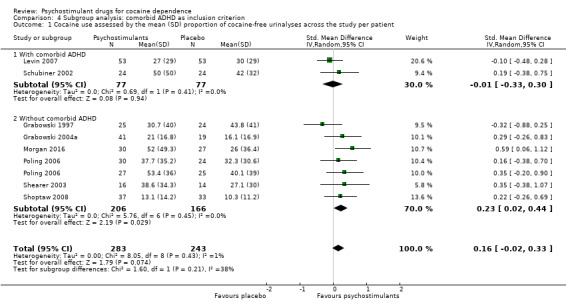
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
5.2. Analysis.
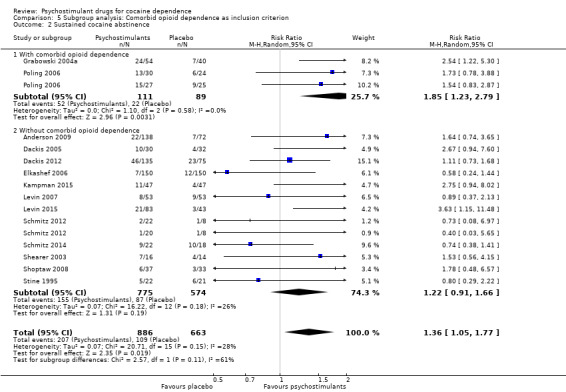
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
We performed subgroup analyses for risk of bias as stated in the protocol, but none of them showed a statistically significant difference between subgroups.
Reporting bias analysis
We constructed funnel plots of the three primary outcome variables, and none were suggestive of reporting bias (see Figure 7; Figure 8; Figure 9).
7.
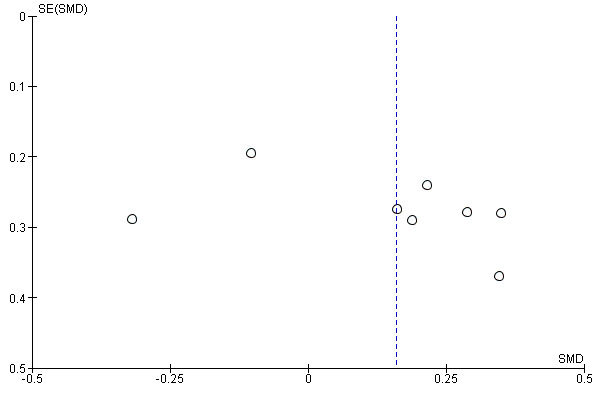
Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.1 Cocaine use by means of urine screen.
8.
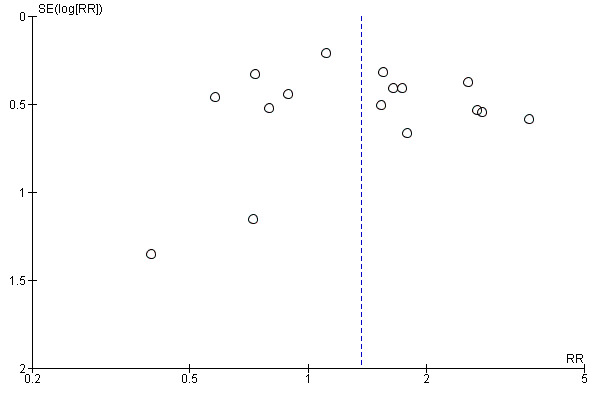
Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
9.
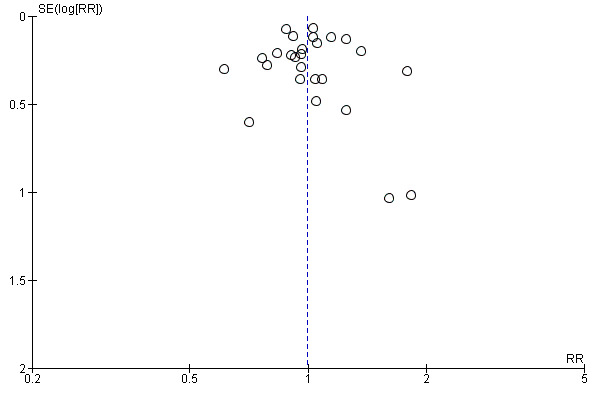
Funnel plot of comparison: 1 Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis, outcome: 1.3 Number of patients who finished the study (retention).
Sensitivity analysis
We carried out a sensitivity analysis for safety outcomes, calculating RR instead of RD.
For dropouts due to AEs, we did not obtain a significant result (RR 1.11, 95% CI 0.60 to 2.02; P = 0.74; Analysis 6.1). We did not find any heterogeneity.
6.1. Analysis.
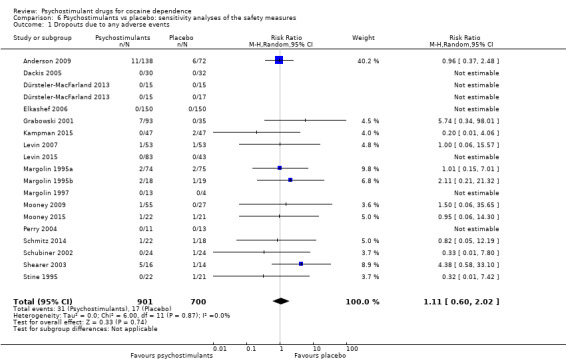
Comparison 6 Psychostimulants vs placebo: sensitivity analyses of the safety measures, Outcome 1 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
For dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events, we did not obtain a significant result (RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.09 to 2.70; P = 0.41; see Analysis 6.2). We found no heterogeneity.
6.2. Analysis.
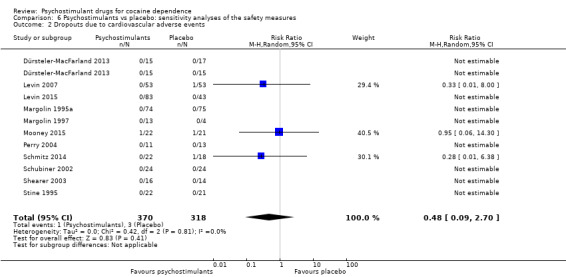
Comparison 6 Psychostimulants vs placebo: sensitivity analyses of the safety measures, Outcome 2 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
Discussion
Summary of main results
This review of the effects of psychostimulants for cocaine dependence showed mixed results on the primary outcomes. We found very low quality evidence that psychostimulants did not decrease cocaine use among participants who continue to take it and moderate quality evidence that they do not improve treatment retention in comparison to placebo. Nevertheless, we found very low quality evidence that a higher proportion of participants achieved sustained cocaine abstinence with psychostimulants than with placebo. However, while the relative improvement of sustained cocaine abstinence was notable, the absolute benefit was relatively small. In consonance with reviews such as Mattick 2009 showing the efficacy of substitute treatment for heroin use and Hartmann‐Boyce 2014 showing improvements for nicotine dependence, the findings of this review suggest that psychostimulants are a promising treatment for cocaine dependence.
Psychostimulants did not improve cocaine craving or symptoms of depression. Although the effect of psychostimulants on depression symptoms was only available for a handful of studies, it is worth highlighting the negative result on this outcome because it could suggest that the positive effects that these drugs appear to have on sustained cocaine abstinence were not accompanied by similar effects on mood. Psychostimulants showed acceptable short‐term safety, and we found no differences with placebo on the rate of dropouts due to adverse events or cardiovascular adverse events or the incidence of serious adverse eventss. Nevertheless, this review focused on serious adverse events and on adverse events that were serious enough to deserve study withdrawal. Thus, a comprehensive review of psychostimulant safety, including mild and long‐term adverse events, is still necessary.
The included studies evaluated nine drugs with psychostimulant effects or metabolised to a psychostimulant drug: bupropion, dexamphetamine, mazindol, methamphetamine, methylphenidate, mixed amphetamine salts, lisdexamfetamine, modafinil and selegiline. For some of them, we found statistically significant effects. Bupropion, dexamphetamine and mixed amphetamine salts appeared to be more efficacious than placebo in achieving sustained cocaine abstinence. Modafinil appeared to be more efficacious than placebo in reducing cocaine use. Lisdexamfetamine significantly improved cocaine craving compared to placebo. Dexamphetamine was more efficacious than placebo in achieving sustained heroin abstinence in participants with both cocaine and opioid dependence. Mixed amphetamine salts significantly improved ADHD severity compared to placebo in participants with comorbid ADHD. Selegiline appeared to improve CGI, but only when it was investigator‐rated. Readers should interpret these findings with caution because the number of studies investigating each type of drug was small and therefore it is not possible to conclude that there are specific drug effects depending on the type of psychostimulant.
It is important to note that some of the included drugs, such as bupropion, modafinil or selegiline, are not usually considered psychostimulants nor classified within the psychostimulant section in drug classification systems (ATC 2015; AHFS 2014). Selegiline is not a psychostimulant itself, but it is metabolised to amphetamine and methamphetamine (Shin 1997). However, its psychostimulant and reinforcing effects appear to be stereoselective, being more pronounced with D‐selegiline than with the L‐isomer that is used in the clinical practice (Yasar 2006a). Moreover, the therapeutic dose of selegiline is lower than that administered in laboratory studies that have assessed its psychostimulant and reinforcing effects (Engberg 1991; Mahmood 1997; Yasar 2006b). Unlike selegiline, modafinil and bupropion appear to have psychostimulant properties by themselves. Indeed, some studies show that they, like cocaine and other psychostimulants, block the dopamine transporter (Dwoskin 2006; Learned‐Coughlin 2003; Madras 2006; Volkow 2009; Zolkowska 2009), and others demonstrate their locomotor‐stimulating effects (Cousins 2001; Makris 2007; Redolat 2005; Zolkowska 2009). In addition, both drugs have some substitute properties for cocaine and for other prototypical CNS stimulants in discriminative stimulus studies (Craft 1996; Dopheide 2007; Evans 1987; Katz 2000). At the same time, it is worth noting that some people misuse both bupropion and modafinil (Jasinski 2000; Langguth 2009; McCormick 2002; Welsh 2002).
Though several studies support the notion that no pharmacological intervention is efficacious for all cocaine dependent patients but only for some subgroups with specific clinical characteristics (Kampman 2004; Kosten 2005; McDowell 2005), the subgroup analyses of this review did not identify any such characteristics, as there were no between‐subgroup statistically significant differences. Given that the number of studies within each subgroup was low, we cannot rule out the possibility that true differences were not identified in this review due to lack of statistical power.
Psychostimulants were more efficacious than placebo for achieving both sustained cocaine and heroine abstinence in methadone‐maintained participants with comorbid heroin dependence. This finding may suggest the possibility of an underlying interaction between opioids and psychostimulants (Castells 2009; Leri 2003). These hopeful findings must be interpreted with the utmost care because they were based on only two out of five published clinical trials, for which data were available in a way that allowed statistical meta‐analysis.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
The external validity of this review is limited by the inclusion/exclusion criteria of the included studies. Most studies took place in the USA, hampering the generalisability of the findings to other regions. Besides, there is an overrepresentation of dual opioid‐cocaine dependent participants in comparison to clinical samples. Conversely, the studies usually excluded participants with comorbid alcohol dependence or major depressive disorder, which are frequent comorbid disorders.
Quality of the evidence
It is important to assess clinical trial quality and its influence on meta‐analysis results because it is associated with biased results, with lower quality studies showing more favourable outcomes to the studied intervention (Jüni 2001). In our review, we did not consider any study to be at a low risk of bias for all domains, therefore we cannot rule out the possibility that the main results are biased. Nevertheless, we stress that we did not find any statistically significant differences in any subgroup analysis between studies with a high or unclear risk of bias and those with a low risk of bias. Such a finding would demonstrate that the results of the meta‐analysis could be biased.
We could not analyse the influence of attrition bias because all included studies had a high dropout rate and were therefore at a high or unclear risk of having biased results because of the incompleteness of the analysed data. Nevertheless, attrition bias does not affect all study outcomes. Since no missing data exist for study retention or adverse event‐induced dropout, these outcomes are free from this source of bias. With the exception of 'sustained cocaine abstinence' and 'retention', the number of studies included in the meta‐analyses was small. Therefore the precision of the calculated effects is low. This is particularly true for many subgroup analyses.
Another factor that can affect the quality of the evidence in this review is the fact that we pooled the results of studies investigating drugs with different mechanisms of action, and we did not control for the influence of their dose. To do so, we would have had to understand the pharmacodynamic equivalence between these drugs, and to our knowledge, this information is not available.
For some subgroup analyses, the number of studies and participants included is low and so is the statistical power. This is the case for studies investigating mazindol, which took place more than 20 years ago and had sample sizes that ranged form 17 to 43 participants.
There were also limitations affecting the external validity of the studies. Study duration was short, in contrast with the chronic course of cocaine dependence. Furthermore, the majority of studies used three‐week uninterrupted cocaine abstinence as the definition of sustained abstinence. This definition is arguable because three weeks of cocaine abstinence has little clinical significance.
We deemed the quality of the evidence to be very low for the efficacy of psychostimulants on 'cocaine use across the study' and 'sustained cocaine abstinence' mainly because treatment dropout was high, there was a possibility of attrition bias, and the pooled effects calculated were rather imprecise. Conversely, the quality of the evidence for the effect of psychostimulants on 'retention in treatment' was moderate because this outcome is not influenced by attrition bias, and the pooled effect calculated was reasonably precise.
Potential biases in the review process
Reporting bias can jeopardise the validity of any meta‐analysis. We have tried to limit the influence of reporting bias by screening several data sets and requesting unpublished results from the corresponding authors. This process resulted in a substantial increase in the available data. We created funnel plots to determine whether reporting bias occurred, and none were suggestive of biased results.
A limitation of this review is that the findings of the subgroup analysis may yield confounded results as a consequence of its bivariate nature. For instance, we found that the achievement of sustained cocaine abstinence was associated with the type of studied psychostimulant (bupropion and dexamphetamine were the only psychostimulants with statistically significant results on this outcome) and with the presence of a comorbid opioid dependence (psychostimulants were efficacious in dual opioid‐cocaine dependent participants but not in participants without comorbid opioid dependence). Nevertheless, the clinical trials with dual opioid‐cocaine dependent participants used bupropion and dexamphetamine as psychostimulants. Thus, we cannot disentangle the effect of a comorbid opioid dependence from that of the studied psychostimulant without more clinical trials allowing for multiple subgroup analyses.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Several reviews using a narrative methodology are available (Grabowski 2004a; Karila 2008; Moeller 2008). Two systematic reviews and meta‐analyses are also available, including the first version of this updated review (Castells 2007; Castells 2010). Our review agrees with these previously published studies in that psychostimulants appear efficacious for achieving sustained cocaine abstinence, but our results are statistically more consistent. As in the previous version of this review, we found that bupropion and dexamphetamine are the most promising stimulants and that the patients who would most benefit from psychostimulant replacement might be those with a comorbid opioid dependence treated with methadone.
One disagreement exists between this and a previously published meta‐analysis regarding adverse event‐induced dropouts (Castells 2007). That report found that adverse event‐induced dropouts were more prevalent amongst participants treated with psychostimulants than in those taking a placebo, while the present review does not support this finding. Differences regarding the number of included studies (the previous review included 9 RCTs and this one has 26) together with methodological differences (the previous review used a Fisher test while the present review employed meta‐analytical procedures to calculate the effects of the intervention on adverse event induced dropouts) may explain the discrepancy found on this outcome.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Replacement therapy with opiates or nicotine has shown to be efficacious for the treatment of tobacco and heroin dependence, respectively. Though the results of this review do not fully support the use of psychostimulant replacement for cocaine dependence, there is some room for optimism in the finding of a small improvement of sustained cocaine abstinence. The drugs most supported by existing data include bupropion, dexamphetamine and mixed amphetamine salts. Finally, dual opioid‐cocaine dependent patients as well as those without a comorbid ADHD seem to be the most suitable candidates for agonist therapy with psychostimulants.
Implications for research.
This review shows that some psychostimulants may be promising medications for the treatment of cocaine dependence, mainly in patients with comorbid opoid dependence and without comorbid ADHD. This therapeutic approach is expected to attract intense future research activity. Given the high attrition characteristic of cocaine dependence studies, which hampers the validity of any clinical trial, future studies should address incomplete outcome data with suitable methods.
We have identified some niches for future research; for instance, psychostimulants should be studied in geographical areas other than the USA. Studies should also assess the efficacy of psychostimulants in patients with comorbid mood disorders or alcohol dependence. In addition, given the promising results of indirect dopamine drugs like disulphiram in Carroll 2004 or levodopa in Schmitz 2008, researchers could also investigate the possibility of synergy between two groups of drugs acting on the dopamine system at different levels.
One methodological finding of this systematic review is that the way studies report abstinence has changed over time. In the past, trials frequently reported this outcome as the mean cocaine‐free urinalysis across the study, but in recent years, they analyse cocaine abstinence as the probability of remaining cocaine‐negative over time using complex statistical methods such as generalised estimating equation models or generalised linear mixed models. Conversely, studies still frequently report the proportion of patients attaining sustained cocaine abstinence, and thus this outcome may be the preferred primary drug abstinence outcome in future meta‐analyses. Finally, several studies included in this review have a small sample size, with limited statistical power to show differences on cocaine abstinence.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9 August 2016 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | 10 new studies included |
| 15 February 2016 | New search has been performed | New literature search run. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 4, 2008 Review first published: Issue 2, 2010
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 15 February 2010 | Amended | correction of minimal errors |
| 18 December 2009 | Amended | minor amendments |
| 25 July 2008 | Amended | protocol first published in issue 4, 2008 |
| 24 July 2008 | New citation required and major changes | Change the status: from registered title to protocol |
Acknowledgements
We would like to give special thanks to Marta Roqué and Ivan Solà, from the Iberoamerican Cochrane Centre in Barcelona, and to Laura Amato, Silvia Minozzi and Zuzana Mitrova, from the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group in Rome, for the many helpful comments and suggestions that we have received while we were conducting this review.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Search strategies January 2010
Relevant randomised trials were identified by searching the following electronic databases:
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library 2008, issue 4 )
MEDLINE (January 1966 to January 2009)
Embase (January 1988 to January 2009)
PsycINFO (1985 to January 2009)
CENTRAL (The Cochrane Library 2008, issue 4) (09 January 2009)
| #1. Cocaine‐Related Disorders:mesh |
| 2. (cocaine OR crack) AND (abuse* OR dependen* OR misuse OR addict*) |
| 3. #1 OR #2 |
| 4. Amphetamines:mesh |
| 5. (amphetamine OR amfetamine OR acefylline piperazine OR adrafinil OR amfebutamone OR amfepramone OR aminorex OR aminophylline OR bamifylline OR benzphetamine OR bufylline OR bupropion OR caffeine OR cathine OR cathinone OR choline theophyllinate OR clobenzorex OR dexamphetamine OR dexanfetamine OR dexmethylphenidate OR diethylpropion OR diprophylline OR doxofylline OR dyphylline OR ephedrine OR etamiphylline OR ethylamphetamine OR fencamfamine OR fenetylline OR fenozolone OR lisdexanfetamine OR mazindol OR mefenorex OR mesocarb OR methamphetamine OR methylenedioxymethamphetamine OR methylphenidate OR modafinil OR nicotine OR norpseudoephedrine OR pemoline OR phentermine OR pipradrol OR prolintane OR propentofylline OR proxyphylline OR selegiline OR sydnocarb OR theobromine OR theophylline):TI;AB |
| 6. #4 or #5 |
| 7. #3 AND #6 |
MEDLINE search strategy (via OVID) (08 January 2009)
| 1. Cocaine‐related disorders[MeSH] |
| 2. (cocaine OR crack) AND (abuse* OR dependen* OR misuse OR addict* OR disorder*).ti,ab |
| 3. 1 or 2 |
| 4. Amphetamine[mesh] |
| 5. (amphetamine* OR amfetamine OR acefylline piperazine OR adrafinil OR amfebutamone OR amfepramone OR aminorex OR aminophylline OR bamifylline OR benzphetamine OR bufylline OR bupropion OR caffeine OR cathine OR cathinoneOR choline theophyllinate OR clobenzorex OR dexamphetamine OR dexanfetamine OR dexmethylphenidate OR diethylpropion OR diprophylline OR doxofylline OR dyphylline OR ephedrine OR etamiphylline OR ethylamphetamine OR fencamfamine OR fenetylline OR fenozolone OR lisdexanfetamine OR mazindol OR mefenorex OR mesocarb* OR methamphetamine OR methylenedioxymethamphetamine* OR methylphenidate OR modafinil OR nicotine OR norpseudoephedrine OR pemoline OR phentermine OR pipradrol OR prolintane OR propentofylline OR proxyphylline OR selegiline OR sydnocarb OR theobromine OR theophylline).ti,ab |
| 6. 4 OR 5 |
| 7. 3 AND 6 |
| 8. randomized controlled trial.pt. |
| 9. controlled clinical trial.pt. |
| 10. randomized.ab. |
| 11. placebo.ab. |
| 12. drug therapy.fs. |
| 13. randomly.ab. |
| 14. trial.ab. |
| 15. groups.ab. |
| 16. 8 OR 9 OR 10 OR 11 OR 12 OR 13 OR 14 OR 15 |
| 17. exp animals/ not humans.sh.¬ |
| 18. 16 NOT 17 |
| 19. 7 AND 18 |
Embase search strategy (Ovid) (08 January 2009)
| 1. exp Cocaine Dependence |
| 2. ((cocaine or crack) ADJ (abuse* or dependen* or misuse or addict* or disorder*)).ti,ab. |
| 3. 1 or 2 |
| 4. (amphetamine or amfetamine or acefylline piperazine or adrafinil or amfebutamone or amfepramone or aminorex or aminophylline or bamifylline or benzphetamine or bufylline or bupropion or caffeine or cathine or cathinone or choline theophyllinate or clobenzorex or dexamphetamine or dexanfetamine or dexmethylphenidate or diethylpropion or diprophylline or doxofylline or dyphylline or ephedrine or etamiphylline or ethylamphetamine or fencamfamine or fenetylline or fenozolone or lisdexanfetamine or mazindol or mefenorex or mesocarb or methamphetamine or methylenedioxymethamphetamine or methylphenidate or modafinil or nicotine or norpseudoephedrine or pemoline or phentermine or pipradrol or prolintane or propentofylline or proxyphylline or selegiline or sydnocarb or theobromine or theophylline).ti,ab. |
| 5. 4 OR 5 |
| 6. Clinical Trials/exp |
| 7. Randomized controlled trials/ |
| 8. Random Allocation/ |
| 9. Single‐Blind Method/ |
| 10. Double‐Blind Method/ |
| 11. Cross‐Over Studies/ |
| 12. Placebos/ |
| 13 Randomi?ed controlled trial$.tw. |
| 14 RCT.tw. |
| 15 Random allocation.tw. |
| 16 Randomly allocated.tw. |
| 16. Double blind$.tw. |
| 17 Allocated randomly.tw. |
| 18 (allocated adj2 random).tw. |
| 19 Single blind$.tw. |
| 20 Double blind$.tw. |
| 21 ((treble or triple) adj blind$).tw. |
| 22 Placebo$.tw. |
| 23 Prospective Studies |
| 24 11 or 21 or 7 or 17 or 22 or 18 or 23 or 16 or 13 or 6 or 9 or 12 or 14 or 15 or 20 or 8 or 10 or 19 |
| 25. Case study/ |
| 26. Case report.tw. |
| 27. Abstract report/ or letter/ |
| 28 27 or 25 or 26 |
| 29 24 not 28 |
| 30. animal/ not human/¬ |
| 31. 24 NOT 28 |
| 32. 31 AND 5 |
PsycINFO (Ovid) (09 January 2009)
| 1. exp Cocaine |
| 2 ((cocaine or crack) and (abuse* or dependen* or misuse or addict*)).ti,ab. |
| 3. 1 or 2 |
| 4. (amphetamine or amfetamine or acefylline piperazine or adrafinil or amfebutamone or amfepramone or aminorex or aminophylline or bamifylline or benzphetamine or bufylline or bupropion or caffeine or cathine or cathinone or choline theophyllinate or clobenzorex or dexamphetamine or dexanfetamine or dexmethylphenidate or diethylpropion or diprophylline or doxofylline or dyphylline or ephedrine or etamiphylline or ethylamphetamine or fencamfamine or fenetylline or fenozolone or lisdexanfetamine or mazindol or mefenorex or mesocarb or methamphetamine or methylenedioxymethamphetamine or methylphenidate or modafinil or nicotine or norpseudoephedrine or pemoline or phentermine or pipradrol or prolintane or propentofylline or proxyphylline or selegiline or sydnocarb or theobromine or theophylline).ti,ab. |
| 5. 4 OR 5 |
| 6 randomi*.mp. |
| 7 ((singl$ or doubl$ or trebl$ or tripl$) adj10 (blind$ or mask$)).mp. |
| 8 (clin$ adj10 trial$).mp. |
| 9 placebo$.mp. or placebo/ or crossover.mp. or treatment‐effectiveness‐evaluation/ or mental‐health‐program‐evaluation/ |
| 10 (random$ adj10 (assign$ or allocate$)).mp. |
| 11 8 or 6 or 7 or 10 or 9 |
| 12 11 and 5 |
Appendix 2. CDAG Specialised Register search strategy
| #1 (amphetamine* OR amfetamine OR "acefylline piperazine" OR adrafinil OR amfebutamone OR amfepramone OR aminorex OR aminophylline OR bamifylline OR benzphetamine OR bufylline OR bupropion OR caffeine OR cathine OR cathinone OR "choline theophyllinate" OR clobenzorex OR dexamphetamine OR dexanfetamine OR dexmethylphenidate OR diethylpropion OR diprophylline OR doxofylline OR dyphylline OR ephedrine OR etamiphylline OR ethylamphetamine OR fencamfamine OR fenetylline OR fenozolone OR lisdexanfetamine OR mazindol OR mefenorex OR mesocarb* OR methamphetamine OR methylenedioxymethamphetamine* OR methylphenidate OR modafinil OR nicotine OR norpseudoephedrine OR pemoline OR phentermine OR pipradrol OR prolintane OR propentofylline OR proxyphylline OR selegiline OR sydnocarb OR theobromine OR theophylline) AND (INREGISTER) |
| #2 cocaine:AB OR (cocaine):TI OR (cocaine):XDI |
| #1 AND #2 |
Appendix 3. CENTRAL search strategy (15 February 2016)
| 1. MESH DESCRIPTOR Cocaine‐Related Disorders EXPLODE ALL TREES |
| 2. ((cocaine or crack) and (abuse* or dependen* or misuse or addict* or disorder*)):TI,AB,KY |
| 3. #1 OR #2 |
| 4. MESH DESCRIPTOR Amphetamines EXPLODE ALL TREES |
| 5. ((amphetamine or amfetamine or acefylline piperazine or adrafinil or amfebutamone or amfepramone or aminorex or aminophylline or armodafinil or bamifylline or benzphetamine or bufylline or bupropion or caffeine or cathine or cathinone or choline theophyllinate or clobenzorex or dexamphetamine or dexanfetamine or dexmethylphenidate or diethylpropion or diprophylline or doxofylline or dyphylline or ephedrine or etamiphylline or ethylamphetamine or fencamfamine or fenetylline or fenozolone or lisdexanfetamine or mazindol or mefenorex or mesocarb or methamphetamine or methylenedioxymethamphetamine or methylphenidate or modafinil or nicotine or norpseudoephedrine or pemoline or phentermine or pipradrol or prolintane or propentofylline or proxyphylline or radafaxine or selegiline or sydnocarb or theobromine or theophylline)):TI,AB,KY |
| 6. #4 OR #5 |
| 7. #3 AND #6 |
Appendix 4. MEDLINE search strategy (via PubMed, 15 February 2016)
| (((("Cocaine‐Related Disorders"[Mesh]) OR ((cocaine[tiab] OR crack[tiab]) AND (abuse*[tiab] OR dependen*[tiab] OR misuse[tiab] OR addict*[tiab])))) AND (((amphetamine[tiab] OR amphetamine[tiab] OR acefylline piperazine[tiab] OR adrafinil[tiab] OR amfebutamone[tiab] OR amfepramone[tiab] OR aminorex[tiab] OR aminophylline[tiab] OR armodafinil[tiab] OR bamifylline[tiab] OR benzphetamine[tiab] OR bufylline[tiab] OR bupropion[tiab] OR caffeine[tiab] OR cathine[tiab] OR cathinone[tiab] OR choline theophyllinate[tiab] OR clobenzorex[tiab] OR dexamphetamine[tiab] OR dexanfetamine[tiab] OR dexmethylphenidate[tiab] OR diethylpropion[tiab] OR diprophylline[tiab] OR doxofylline[tiab] OR dyphylline[tiab] OR ephedrine[tiab] OR etamiphylline[tiab] OR ethylamphetamine[tiab] OR fencamfamine[tiab] OR fenetylline[tiab] OR fenozolone[tiab] OR lisdexanfetamine[tiab] OR mazindol[tiab] OR mefenorex[tiab] OR mesocarb[tiab] OR methamphetamine[tiab] OR methylenedioxymethamphetamine[tiab] OR methylphenidate[tiab] OR modafinil[tiab] OR nicotine[tiab] OR norpseudoephedrine[tiab] OR pemoline[tiab] OR phentermine[tiab] OR pipradrol[tiab] OR prolintane[tiab] OR propentofylline[tiab] OR proxyphylline[tiab] OR radafaxine[tiab] OR selegiline[tiab] OR sydnocarb[tiab] OR theobromine[tiab] OR theophylline[tiab])) OR Amphetamines[MeSH])) AND (((((((((randomized controlled trial[pt]) OR controlled clinical trial[pt]) OR randomized[tiab]) OR placebo[tiab]) OR clinical trials as topic[mesh:noexp]) OR randomly[tiab]) OR trial[ti])) NOT ((animals[mh] NOT humans[mh]))) AND (("2008/06/30"[PDat] : "3000/02/07"[PDat])) |
Appendix 5. Embase search strategy (15 February 2016)
| 1. 'cocaine dependence'/exp |
| 2. (cocaine OR crack NEAR/6 (abuse* OR dependen* OR misuse OR addict* OR disorder*) |
| 3. #1 OR #2 |
| 4. 'amphetamine derivative'/exp |
| 5. (amphetamine:ab,ti OR amfetamine:ab,ti OR acefylline:ab,ti OR piperazine:ab,ti OR adrafinil:ab,ti OR amfebutamone:ab,ti OR amfepramone:ab,ti OR aminorex:ab,ti OR aminophylline:ab,ti OR armodafinil:ab,ti OR bamifylline:ab,ti OR benzphetamine:ab,ti OR orbufylline:ab,ti OR bupropion:ab,ti OR caffeine:ab,ti OR cathine:ab,ti OR cathinone:ab,ti OR choline:ab,ti OR theophyllinate:ab,ti OR clobenzorex:ab,ti OR dexamphetamine:ab,ti OR dexanfetamine:ab,ti OR dexmethylphenidate:ab,ti OR diethylpropion:ab,ti OR ordiprophylline:ab,ti OR doxofylline:ab,ti OR dyphylline:ab,ti OR ephedrine:ab,ti OR etamiphylline:ab,ti OR ethylamphetamine:ab,ti OR fencamfamine:ab,ti OR fenetylline:ab,ti OR fenozolone:ab,ti OR lisdexanfetamine:ab,ti OR mazindol:ab,ti OR mefenorex:ab,ti ORormesocarb:ab,ti OR methamphetamine:ab,ti OR methylenedioxymethamphetamine:ab,ti OR methylphenidate:ab,ti OR modafinil:ab,ti OR nicotine:ab,ti OR norpseudoephedrine:ab,ti OR pemoline:ab,ti OR phentermine:ab,ti OR pipradrol:ab,ti OR prolintane:ab,ti OR orpropentofylline:ab,ti) OR proxyphylline:ab,ti OR radafaxine:ab,ti OR selegiline:ab,ti OR sydnocarb:ab,ti OR theobromine:ab,ti OR theophylline:ab,ti) |
| 6. #4 OR #5 |
| 7. 'crossover procedure'/exp OR 'double blind procedure'/exp OR 'single blind procedure'/exp OR 'controlled clinical trial'/exp OR 'clinical trial'/exp OR 'randomized controlled trial'/exp OR placebo:ab,ti OR 'double blind':ab,ti OR 'single blind':ab,ti OR assign*:ab,ti OR allocat*:ab,ti OR volunteer*:ab,ti OR random*:ab,ti OR factorial*:ab,ti OR crossover:ab,ti OR (cross:ab,ti AND over:ab,ti)) |
| 8. #3 AND #6 AND #7 AND [embase]/lim AND [30‐6‐2008]/sd |
Appendix 6. Web of Science search strategy (15 February 2016)
| 1. TOPIC: (((cocaine OR crack) NEAR/6 (abuse* OR dependen* OR addict* OR disorder*))) |
| 2. TOPIC: (((amphetamine or amfetamine or acefylline piperazine or adrafinil or amfebutamone or amfepramone or aminorex or aminophylline or armodafinil or bamifylline or benzphetamine or bufylline or bupropion or caffeine or cathine or cathinone or choline theophyllinate or clobenzorex or dexamphetamine or dexanfetamine or dexmethylphenidate or diethylpropion or diprophylline or doxofylline or dyphylline or ephedrine or etamiphylline or ethylamphetamine or fencamfamine or fenetylline or fenozolone or lisdexanfetamine or mazindol or mefenorex or mesocarb or methamphetamine or methylenedioxymethamphetamine or methylphenidate or modafinil or nicotine or norpseudoephedrine or pemoline or phentermine or pipradrol or prolintane or propentofylline or proxyphylline or radafaxine or selegiline or sydnocarb or theobromine or theophylline))) |
| 3. #2 AND #1 |
| 4. TS= clinical trial* OR TS=research design OR TS=comparative stud* OR TS=evaluation stud* OR TS=controlled trial* OR TS=follow‐up stud* OR TS=prospective stud* OR TS=random* OR TS=placebo* OR TS=(single blind*) OR TS=(double blind*) |
| 5. #4 OR #3 Indexes=SCI‐EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI Timespan=2008‐2016 |
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Psychostimulants vs placebo: primary analysis.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 8 | 526 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.02, 0.33] |
| 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence | 14 | 1549 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [1.05, 1.77] |
| 3 Number of patients who finished the study | 24 | 2205 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.06] |
| 4 Self‐reported cocaine use | 1 | 28 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.74, 0.74] |
| 5 Cocaine craving | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 6 Patient‐rated CGI severity scale | 1 | 300 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.28 [0.05, 0.50] |
| 7 Investigator‐rated CGI severity scale | 1 | 300 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [‐0.15, 0.30] |
| 8 Patient‐rated CGI improvement scale | 1 | 300 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.27 [0.04, 0.50] |
| 9 CGI investigator change | 1 | 300 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.23, 0.23] |
| 10 CGI investigator improvement: 1 or 2 | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.57, 1.15] |
| 11 Depression symptoms severity | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 12 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 13 Sustained heroin abstinence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 14 ADHD severity | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 15 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 16 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 11 | 688 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 17 Serious adverse events | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
Comparison 2. Subgroup analysis: type of drug.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 8 | 526 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.02, 0.33] |
| 1.1 Bupropion | 2 | 176 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [‐0.06, 0.54] |
| 1.2 Dexamphetamine | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.31 [‐0.13, 0.74] |
| 1.3 Methylphenidate | 3 | 203 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.09 [‐0.36, 0.19] |
| 1.4 Modafinil | 1 | 57 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.59 [0.06, 1.12] |
| 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence | 14 | 1549 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [1.05, 1.77] |
| 2.1 Bupropion | 2 | 176 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.63 [1.03, 2.59] |
| 2.2 Dexamphetamine | 3 | 154 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.98 [1.12, 3.52] |
| 2.3 Mazindol | 1 | 43 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.80 [0.29, 2.22] |
| 2.4 Methylphenidate | 1 | 106 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.37, 2.13] |
| 2.5 Mixed amphetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.63 [1.15, 11.48] |
| 2.6 Modafinil | 6 | 644 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.32 [0.85, 2.04] |
| 2.7 Selegiline | 1 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.24, 1.44] |
| 3 Number of patients who finished the study | 24 | 2205 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.06] |
| 3.1 Bupropion | 3 | 325 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.89, 1.15] |
| 3.2 Dexamphetamine | 4 | 282 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.37 [0.91, 2.05] |
| 3.3 Mazindol | 4 | 121 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.76, 1.21] |
| 3.4 Methamphetamine | 1 | 82 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.52, 2.11] |
| 3.5 Methylphenidate | 3 | 203 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.68, 1.21] |
| 3.6 Mixed amphetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.90, 1.45] |
| 3.7 Modafinil | 7 | 723 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.89, 1.21] |
| 3.8 Selegiline | 1 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.76, 1.03] |
| 3.9 Lisdexamfetamine | 1 | 43 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.48, 1.22] |
| 4 Cocaine craving | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 4.1 Bupropion | 2 | 137 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.07 [‐0.30, 0.44] |
| 4.2 Mazindol | 2 | 52 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.81, 0.30] |
| 4.3 Selegiline | 1 | 300 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.09 [‐0.14, 0.31] |
| 4.4 Lisdexamfetamine | 1 | 43 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.73 [‐1.35, ‐0.11] |
| 5 Depression symptoms severity | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 5.1 Bupropion | 1 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.04 [‐0.54, 0.46] |
| 5.2 Mazindol | 1 | 28 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.87, 0.61] |
| 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 6.1 Bupropion | 1 | 105 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.13, 0.71] |
| 6.2 Dexamphetamine | 1 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.31 [‐0.24, 0.85] |
| 7 Sustained heroin abstinence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.1 Bupropion | 1 | 105 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.57 [0.78, 3.15] |
| 7.2 Dexamphetamine | 1 | 94 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.98 [1.28, 3.04] |
| 8 ADHD severity | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 8.1 Methylphenidate | 2 | 121 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐1.11, 0.38] |
| 8.2 Mixed amphetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.55 [‐0.93, ‐0.18] |
| 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 9.1 Bupropion | 1 | 149 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.05, 0.05] |
| 9.2 Dexamphetamine | 2 | 158 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.12 [‐0.06, 0.30] |
| 9.3 Mazindol | 4 | 121 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.09, 0.07] |
| 9.4 Methamphetamine | 1 | 82 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.02 [‐0.05, 0.08] |
| 9.5 Methylphenidate | 3 | 216 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.05, 0.03] |
| 9.6 Selegiline | 1 | 300 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 9.7 Modafinil | 4 | 406 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.05, 0.02] |
| 9.8 Mixed amphetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.04, 0.04] |
| 9.9 Lisdexamfetamine | 1 | 43 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.09, 0.09] |
| 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 11 | 688 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 10.1 Bupropion | 1 | 149 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.03, 0.03] |
| 10.2 Dexamphetamine | 1 | 30 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.12, 0.12] |
| 10.3 Mazindol | 3 | 84 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.07, 0.07] |
| 10.4 Methylphenidate | 3 | 216 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.05, 0.03] |
| 10.5 Modafinil | 1 | 40 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.06 [‐0.19, 0.08] |
| 10.6 Mixed amphetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.04, 0.04] |
| 10.7 Lisdexamfetamine | 1 | 43 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.09, 0.09] |
| 11 Serious adverse events | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
| 11.1 Mixed amfetamine salts | 1 | 126 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.12, 0.02] |
| 11.2 Modafinil | 4 | 275 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.08, 0.04] |
| 11.3 Lisdexamfetamine | 1 | 43 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.13, 0.12] |
2.3. Analysis.
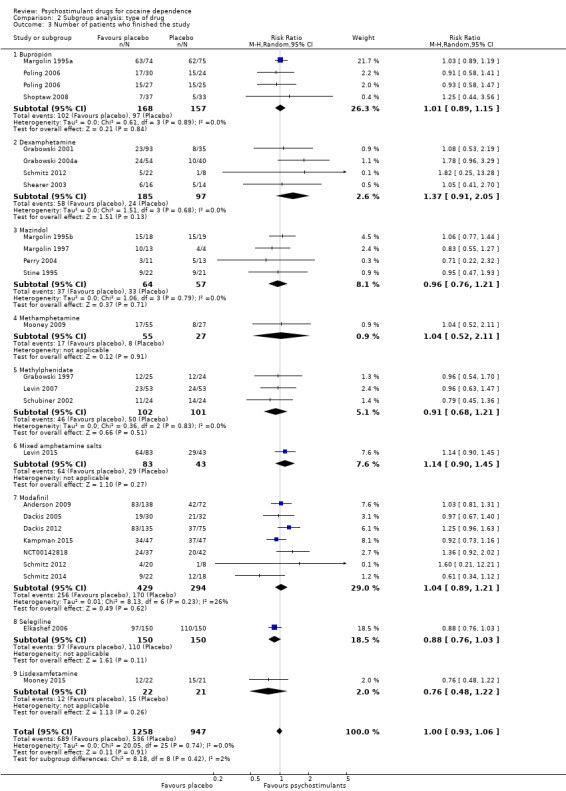
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 3 Number of patients who finished the study.
2.4. Analysis.
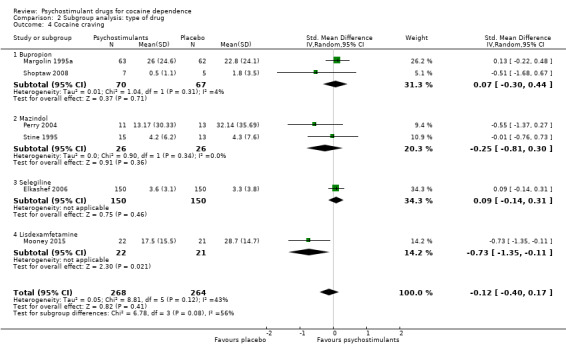
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 4 Cocaine craving.
2.5. Analysis.
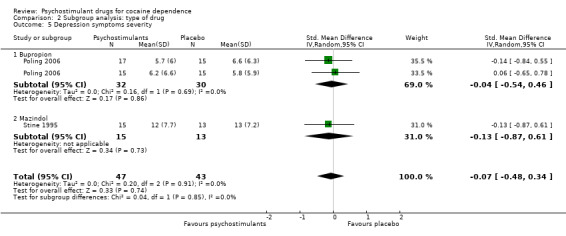
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 5 Depression symptoms severity.
2.6. Analysis.
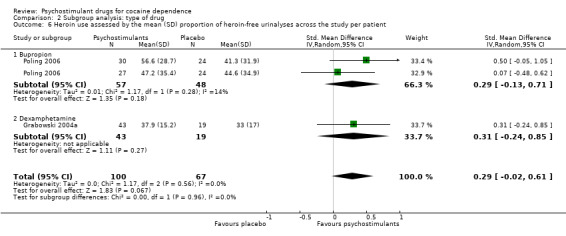
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
2.9. Analysis.
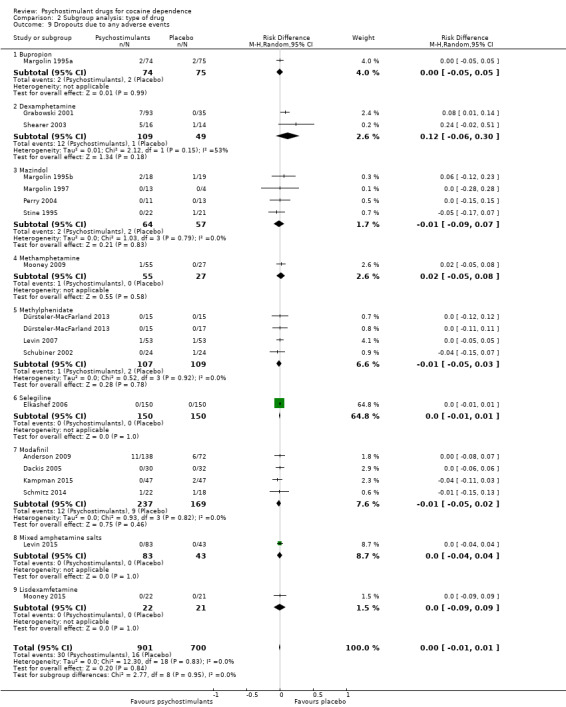
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
2.10. Analysis.
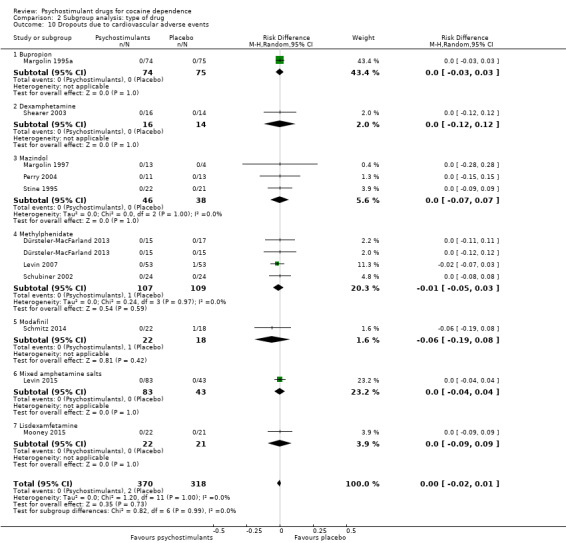
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
2.11. Analysis.
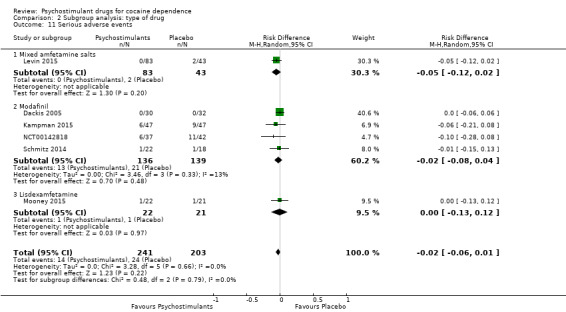
Comparison 2 Subgroup analysis: type of drug, Outcome 11 Serious adverse events.
Comparison 3. Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 8 | 526 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.02, 0.33] |
| 1.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 2 | 176 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.24 [‐0.06, 0.54] |
| 1.2 Cocaine dependence | 6 | 350 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.14 [‐0.13, 0.40] |
| 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence | 14 | 1549 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [1.05, 1.77] |
| 2.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 2 | 176 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.63 [1.03, 2.59] |
| 2.2 Cocaine dependence | 12 | 1373 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.31 [0.95, 1.81] |
| 3 Number of patients who finished the study | 24 | 2205 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.06] |
| 3.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 3 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.69, 1.24] |
| 3.2 Cocaine dependence | 21 | 2005 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.07] |
| 4 Cocaine craving | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 4.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 2 | 36 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.53 [‐1.21, 0.14] |
| 4.2 Cocaine dependence | 4 | 496 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.05 [‐0.36, 0.26] |
| 5 Depressive symptoms severity | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 5.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 1 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.04 [‐0.54, 0.46] |
| 5.2 Cocaine dependence | 1 | 28 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.87, 0.61] |
| 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 6.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 1 | 105 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.13, 0.71] |
| 6.2 Cocaine dependence | 1 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.31 [‐0.24, 0.85] |
| 7 Sustained heroin abstinence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.2 Cocaine dependence | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8 ADHD severity | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 8.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8.2 Cocaine dependence | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 9.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 1 | 24 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.15, 0.15] |
| 9.2 Cocaine dependence | 17 | 1577 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 10 | 645 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 10.1 Cocaine abuse or dependence | 1 | 24 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.15, 0.15] |
| 10.2 Cocaine dependence | 9 | 621 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 11 Serious adverse events | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
| 11.1 Cocaine abuse and dependence | 0 | 0 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11.2 Cocaine dependence | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
3.1. Analysis.
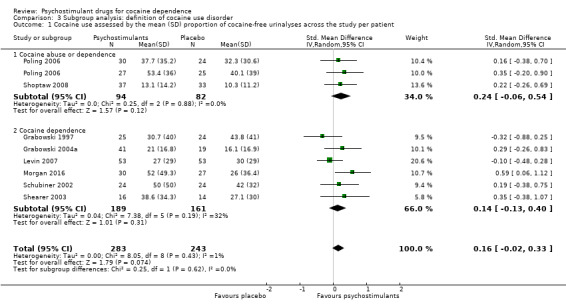
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
3.3. Analysis.
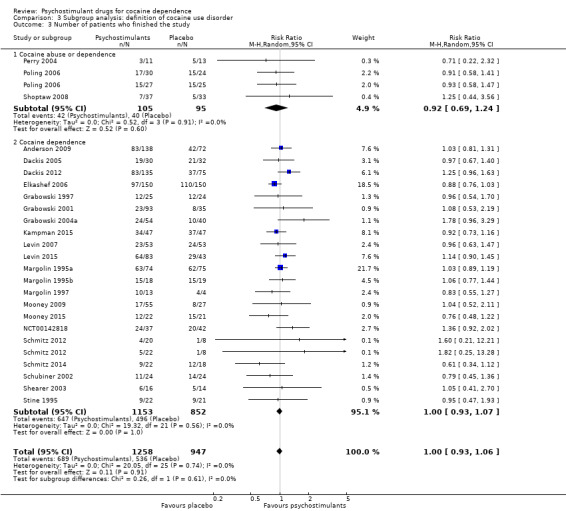
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 3 Number of patients who finished the study.
3.4. Analysis.
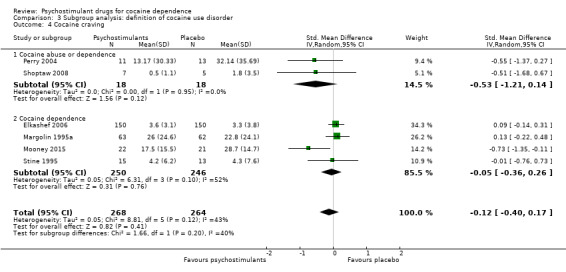
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 4 Cocaine craving.
3.5. Analysis.
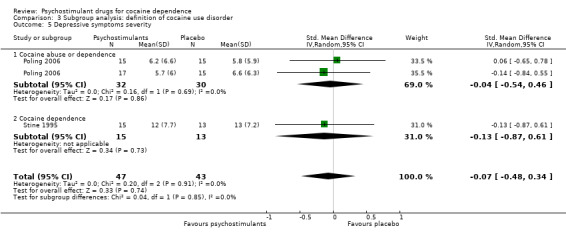
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 5 Depressive symptoms severity.
3.6. Analysis.
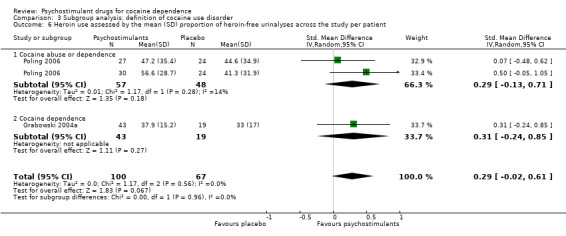
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
3.7. Analysis.
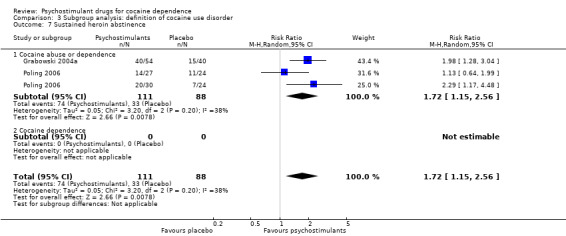
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 7 Sustained heroin abstinence.
3.8. Analysis.
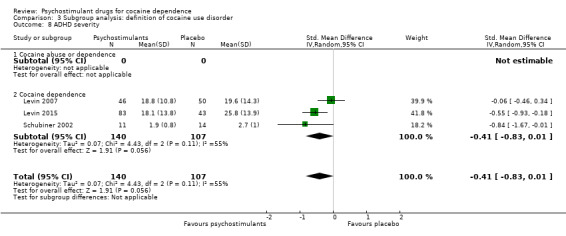
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 8 ADHD severity.
3.9. Analysis.
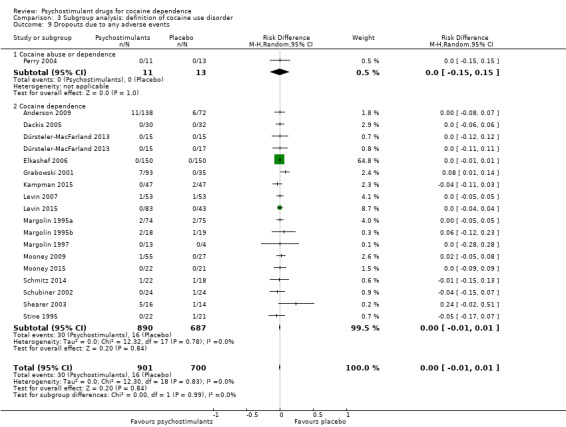
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
3.10. Analysis.
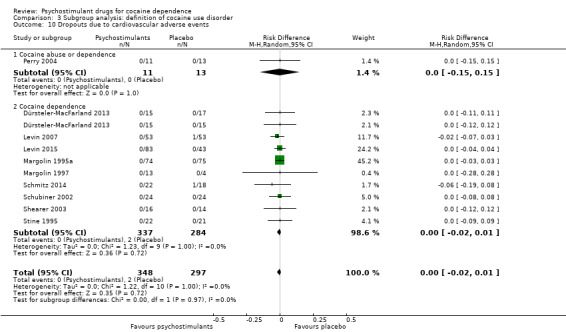
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
3.11. Analysis.
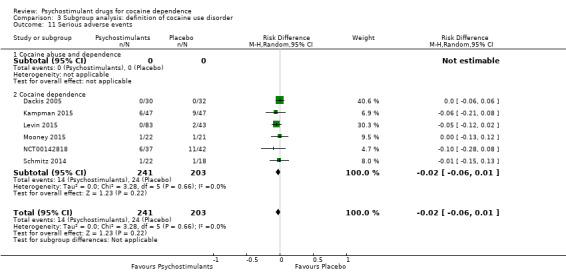
Comparison 3 Subgroup analysis: definition of cocaine use disorder, Outcome 11 Serious adverse events.
Comparison 4. Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 8 | 526 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.02, 0.33] |
| 1.1 With comorbid ADHD | 2 | 154 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.33, 0.30] |
| 1.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 6 | 372 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.23 [0.02, 0.44] |
| 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence | 14 | 1549 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [1.05, 1.77] |
| 2.1 With comorbid ADHD | 2 | 232 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.71 [0.42, 6.98] |
| 2.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 12 | 1317 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.34 [1.03, 1.74] |
| 3 Number of patients who finished the study | 24 | 2205 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.06] |
| 3.1 With comorbid ADHD | 3 | 280 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.87, 1.28] |
| 3.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 21 | 1925 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.92, 1.06] |
| 4 Cocaine craving | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 4.1 With comorbid ADHD | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 5 Depressive symptoms severity | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 5.1 With comorbid ADHD | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 6.1 With comorbid ADHD | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 7 Sustained heroin abstinence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.1 With comorbid ADHD | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7.2 Withou comorbid ADHD | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 8 ADHD severity | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 8.1 With comorbid ADHD | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 8.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 9.1 With comorbid ADHD | 3 | 280 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.03, 0.03] |
| 9.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 15 | 1321 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 11 | 688 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 10.1 With comorbid ADHD | 3 | 280 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.03, 0.02] |
| 10.2 Without comorbid ADHD | 8 | 408 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.02] |
| 11 Serious adverse events | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
| 11.1 With ADHD | 0 | 0 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11.2 Without ADHD | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
4.2. Analysis.
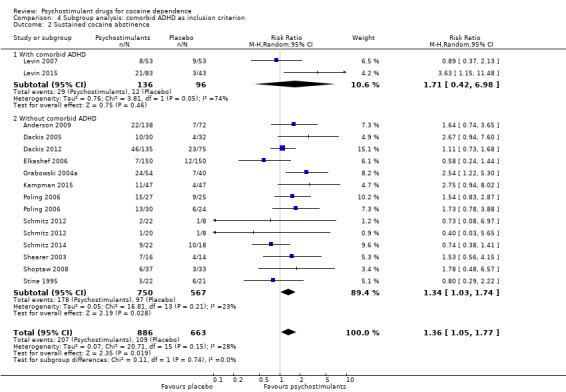
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence.
4.3. Analysis.
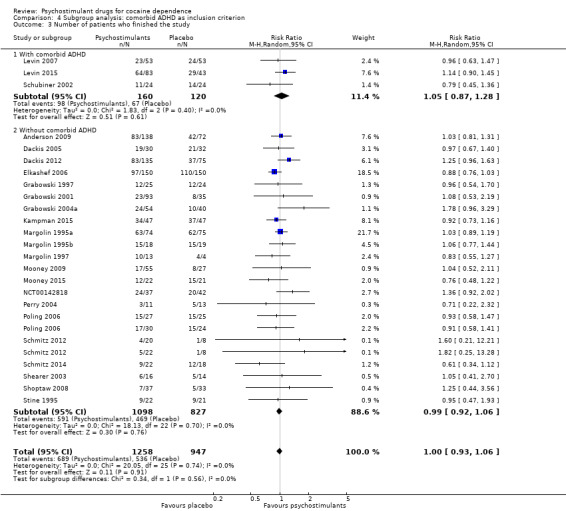
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 3 Number of patients who finished the study.
4.4. Analysis.
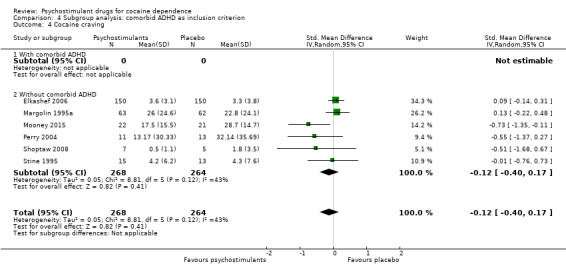
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 4 Cocaine craving.
4.5. Analysis.
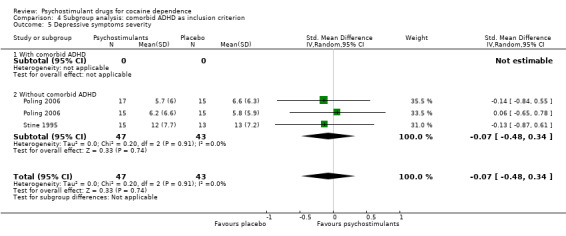
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 5 Depressive symptoms severity.
4.6. Analysis.
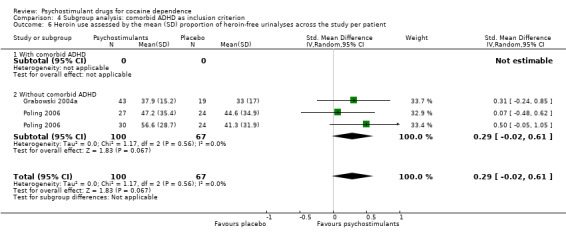
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
4.7. Analysis.
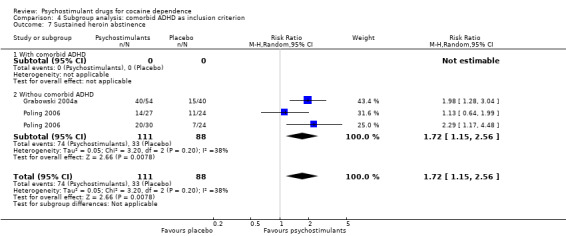
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 7 Sustained heroin abstinence.
4.8. Analysis.
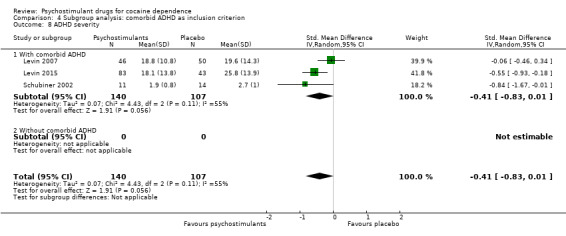
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 8 ADHD severity.
4.9. Analysis.
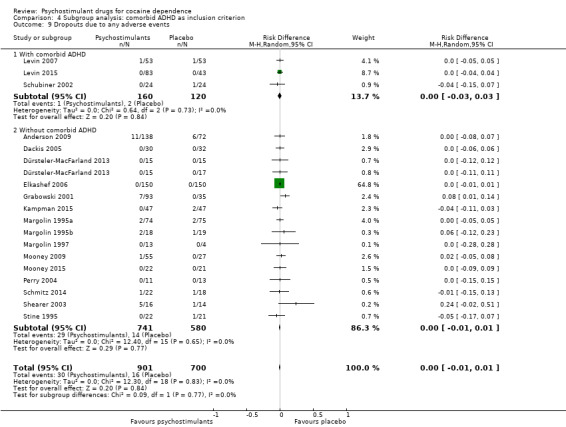
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
4.10. Analysis.
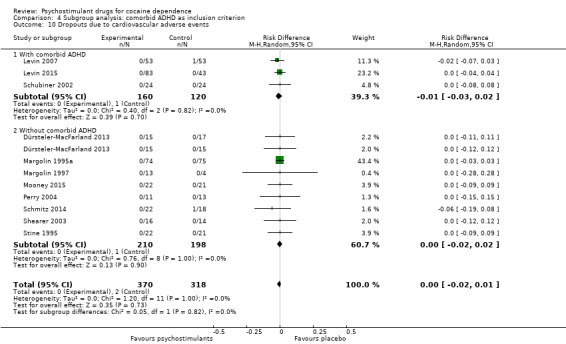
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
4.11. Analysis.
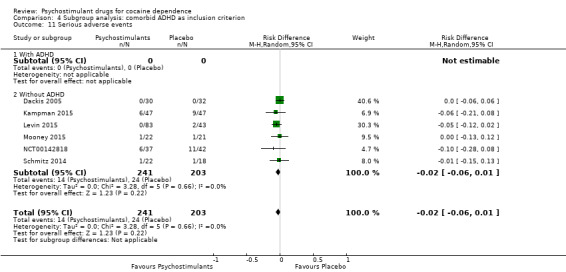
Comparison 4 Subgroup analysis: comorbid ADHD as inclusion criterion, Outcome 11 Serious adverse events.
Comparison 5. Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 8 | 526 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.16 [‐0.02, 0.33] |
| 1.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 2 | 166 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.26 [‐0.05, 0.58] |
| 1.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 6 | 360 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [‐0.13, 0.38] |
| 2 Sustained cocaine abstinence | 14 | 1549 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.36 [1.05, 1.77] |
| 2.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 2 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.85 [1.23, 2.79] |
| 2.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 12 | 1349 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.22 [0.91, 1.66] |
| 3 Number of patients who finished the study | 24 | 2205 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.93, 1.06] |
| 3.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 5 | 403 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.91, 1.14] |
| 3.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 19 | 1802 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.91, 1.07] |
| 4 Cocaine craving | 6 | 532 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.12 [‐0.40, 0.17] |
| 4.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 1 | 125 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.13 [‐0.22, 0.48] |
| 4.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 5 | 407 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.25 [‐0.65, 0.14] |
| 5 Depression symptoms severity | 2 | 90 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.07 [‐0.48, 0.34] |
| 5.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 1 | 62 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.04 [‐0.54, 0.46] |
| 5.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 1 | 28 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.13 [‐0.87, 0.61] |
| 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 6.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 2 | 167 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.29 [‐0.02, 0.61] |
| 6.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 7 Sustained heroin abstinence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 2 | 199 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.72 [1.15, 2.56] |
| 7.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8 ADHD severity | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 8.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 0 | 0 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 3 | 247 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.41 [‐0.83, 0.01] |
| 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 9.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 4 | 265 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.04, 0.05] |
| 9.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 14 | 1336 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.00 [‐0.01, 0.01] |
| 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 11 | 688 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.00 [‐0.02, 0.01] |
| 10.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 3 | 228 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [‐0.02, 0.02] |
| 10.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 8 | 460 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.01 [‐0.03, 0.02] |
| 11 Serious adverse events | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
| 11.1 With comorbid opioid dependence | 0 | 0 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11.2 Without comorbid opioid dependence | 6 | 444 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | ‐0.02 [‐0.06, 0.01] |
5.1. Analysis.
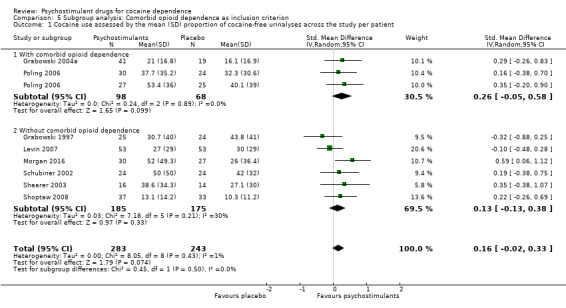
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 1 Cocaine use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of cocaine‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
5.3. Analysis.
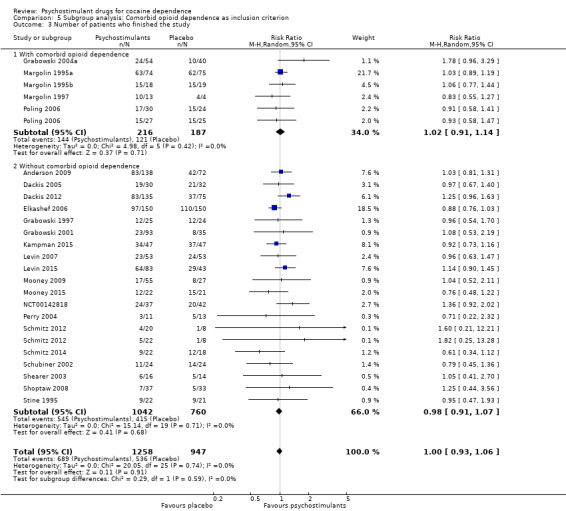
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 3 Number of patients who finished the study.
5.4. Analysis.
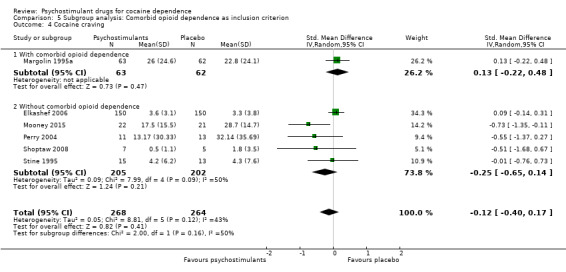
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 4 Cocaine craving.
5.5. Analysis.
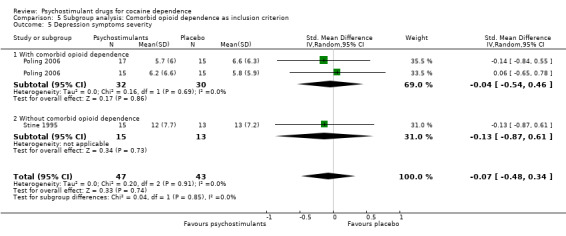
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 5 Depression symptoms severity.
5.6. Analysis.
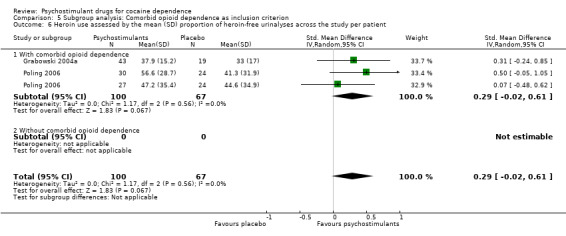
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 6 Heroin use assessed by the mean (SD) proportion of heroin‐free urinalyses across the study per patient.
5.7. Analysis.
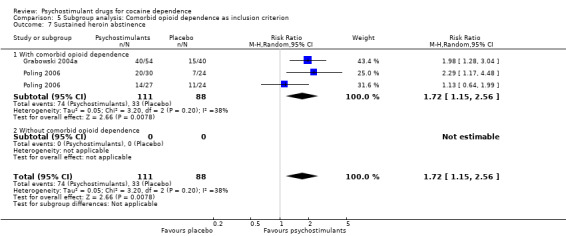
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 7 Sustained heroin abstinence.
5.8. Analysis.
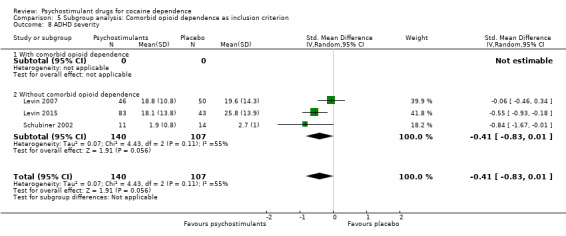
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 8 ADHD severity.
5.9. Analysis.
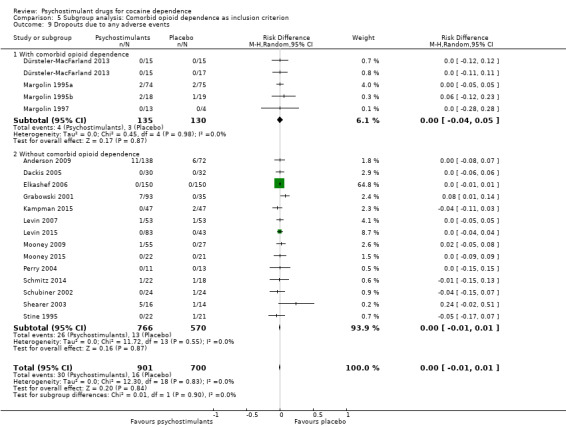
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 9 Dropouts due to any adverse events.
5.10. Analysis.
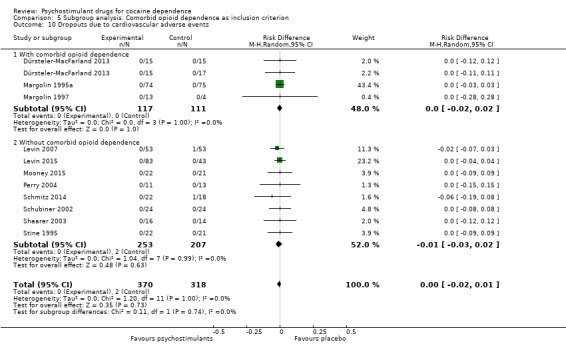
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 10 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events.
5.11. Analysis.
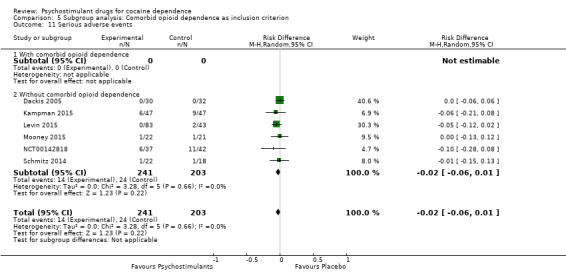
Comparison 5 Subgroup analysis: Comorbid opioid dependence as inclusion criterion, Outcome 11 Serious adverse events.
Comparison 6. Psychostimulants vs placebo: sensitivity analyses of the safety measures.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Dropouts due to any adverse events | 18 | 1601 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.11 [0.60, 2.02] |
| 2 Dropouts due to cardiovascular adverse events | 11 | 688 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.48 [0.09, 2.70] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Anderson 2009.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, multicentre clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 210 participants with cocaine dependence (DSM‐IV) who provided at least 1 positive urinalysis during the 3 week screening/baseline period. Alcohol‐dependent participants were excluded. Mean age: 42.4 years Sex: 148 men Ethnicity: African American: 116, white: 81, other: 9 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 16.6, mean lifetime cocaine use: 15.5 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants received CBT. Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Percentage of cocaine non‐use days (self‐reported and confirmed by urinalysis) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention to treatment Severity of cocaine dependence assessed by means of Addiction Severity Index (ASI‐Lite), Brief Substance Craving Scale (BSCS), Cocaine Craving Questionnaire (CCQ), self‐reported and observer reported CGI. |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: self‐report of use and pill count |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (40%) in all the study groups. Reasons for participant dropout were not reported, and it is unclear whether they differed between active and placebo groups. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was generalised estimating equations (GEE), which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Imbalanced baseline characteristics regarding ethnicity. The modafinil 200 mg group included more African Americans and fewer whites than the modafinil 400 mg and placebo groups. African Americans showed a modestly higher weekly percentage of cocaine use days than did whites. In addition, there was a nearly significant difference among groups in the number of years using cocaine. Again, the modafinil 200 mg group had used cocaine 2.5‐3 years longer than the other study groups.These differences could indicate that the sample receiving modafinil had a more severe cocaine addiction, which could result in biased results. |
Dackis 2005.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 62 cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV) who had used at least USD 200 worth of cocaine in the past 30 days. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 44.5 years Sex: 44 men Ethnicity: African American: 50, white: NR, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 10.6, mean lifetime cocaine use: 12.5 years Route of cocaine use: 54 intrapulmonary |
|
| Interventions | 2 parallel groups:
All participants received CBT (16 sessions). Duration: 8 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with BSCS and CCQ Depression symptoms assessed with the BDI and Ham‐D |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: blister pack return |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Computer generated code" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Research pharmacist was the only person aware of the medication assignment code" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (33%) in both study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not exhaustively reported and it is unclear whether they differed between active and placebo groups. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes was not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Imbalanced baseline characteristics regarding history of cocaine use. The modafinil group had fewer days of cocaine use per week, weekly cocaine cost and longer years of cocaine use than the placebo group, with a statistical trend of significance. These differences could indicate that the sample receiving modafinil had a less severe cocaine addiction, which could result in biased results. |
Dackis 2012.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 210 cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV) who had used at least USD 200 worth of cocaine in the past 30 days and with at least 1 positive urinalysis during screening period. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 44.5 years Sex: 157 men Ethnicity: African American: 165, white: NR, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last week: 2.68, mean lifetime cocaine use: 13.8 years Route of cocaine use: 129 (78.4%) intrapulmonary |
|
| Interventions | 3 parallel groups:
All participants received CBT. Duration: 8 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Participant‐reported cocaine severity (CGI) Physician‐rated cocaine severity (CGI) Cocaine craving assessed with BSCS and CCQ Depression symptoms assessed with the BDI and Ham‐D |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public (medication provided by pharmaceutical company) Assessment of adherence: pill count |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer generated randomisation |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Study pharmacist generated random sequence, which was kept concealed to the remaining study personnel |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (75%) in both study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not exhaustively reported, and it is unclear whether they differed between active and placebo groups. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes was not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method uses was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in the study protocol (NCT00128285) are reported in the article. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, multicentre clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: Switzerland N = 62 cocaine and heroin dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV) receiving diacetylmorphine maintenance. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 35.9 years Sex: 40 men Ethnicity: NR Employed: 38 History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 14.8, mean lifetime cocaine use: 10.9 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received diacetylmorphine. Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine‐free urinalysis Self‐reported cocaine use (frequency and amount) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with BSCS and CCQ Depression symptoms assessed with the BDI |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: medication was administered under supervision |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | The randomisation list was kept concealed until the end of the data collection period |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, as study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance.Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Number of participants who discontinued treatment was not reported for each study intervention. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Results on treatment dropout not reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Elkashef 2006.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, multicentre clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA n = 300 cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded Mean age: 40.7 years Sex: 234 men Ethnicity: African American: 188, white: 80, other: 32 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 17.6, mean lifetime cocaine use: 13.6 years Route of cocaine use: 257 intrapulmonary, 12 other |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received individualised counselling, 1 h session per week Duration: 8 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with BSCS Depressive symptoms assessed with Ham‐D Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: NR |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Adaptive randomizations using a biased coin procedure" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (31%) in both study groups. Most participants did not complete the study due to failure to return to clinic. It is unclear how missing data of objective and subjective outcomes were imputed. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Imbalanced baseline characteristics regarding history of cocaine use. The selegiline group had longer years of cocaine use than the placebo group. This difference could indicate that the sample receiving selegiline had a more severe cocaine addiction, which could result in biased results. |
Grabowski 1997.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: not ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 49 cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM‐III‐R). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 34.3 years Sex: 38 male Ethnicity: African American:28, white :17, other: 4 Employed: 23 History of cocaine use: NR Cocaine route of use: 41 intrapulmonary, 4 intranasal, 4 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received psychosocial therapy (11 sessions) Duration: 13 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of twice weekly urinalysis (provided by author) Retention in treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: MEMS bottles |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (51%) in both study groups. Reasons for dropping out in each study group were not reported. Missing data were not imputed. Nevertheless, the maximum likelihood statistical method was used, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Grabowski 2001.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 101 days' duration; 3 parallel groups, placebo‐controlled, single‐site trial Statistical analysis: ITT and also a post hoc analyses with 112 participants (after exclusion of 16 participants without positive urinalysis at baseline) |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 128 cocaine‐dependent participants (DSM‐IV). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded Mean age: 36 years Sex: 101 male Ethnicity: African American: 74, white: 40, other: 14 Employed: 49 History of cocaine use: mean lifetime cocaine use: 12.2 years Route of cocaine use: 103 intrapulmonary, 23 intranasal, 3 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT (13 sessions) Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of with twice weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Dropouts due to adverse events Depression symptoms assessed with the BDI |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: Rivoflavin and MEMS bottles |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (76%) in all study groups. Reasons for dropping out in each study group were not reported. Missing data were not imputed. The statistical method was not described; nevertheless authors state that the method used did not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Grabowski 2004a.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: not ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 94 dual opioid‐cocaine dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 36.7 years Sex: 63 male Ethnicity: African American:10, white: 71, other: 13 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: 44 intrapulmonary, 30 intranasal, 20 intravenous (20 speedball users) |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT and relapse prevention (1 h each week) plus methadone 1.1 mg/kg/d Duration: 24 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of twice weekly urinalysis (provided by author) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention in treatment Depression symptoms assessed with the BDI |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: Riboflavin, MEMS bottles, urine screen drug metabolite |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcome or the outcome measurement were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, since the study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (64%) in both study groups. Reasons for dropping out in each study group were not reported. Missing data were not imputed. The statistical method was not described; nevertheless, authors stated that the method used did not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Kampman 2015.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 94 cocaine dependent patients (DSM‐IV), using cocaine at least 8 days in a consecutive 30‐day period over the 60days immediately preceding study entry and having a negative urinalysis during screening and a negative urinalysis on the day of randomisation. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 46.5 Sex: 76 men Ethnicity: African American: 70, white: 24, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 12, mean lifetime cocaine use: 12.5 Route of cocaine use: 79 intrapulmonary, 13 intranasal, 2 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CM for attendance and weekly CBT Duration: 8 weeks Single site trial (USA) |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by self‐report and confirmed by twice weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Cocaine craving assessed by means of BSCS Cocaine withdrawal symptoms assessed by means of CSSA Retention in treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcome or the outcome measurement were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since the study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Attririon was moderate (25%) in both groups. Reasons for dropping out were described. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Missing data of subjective outcomes were not imputed because the statistical method was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in study protocol (NCT00368290) are reported in the article. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | The modafinil group had more severe addiction‐related problems than the placebo group. |
Levin 2007.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre clinical trial Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 106 cocaine‐dependent (DSM‐IV) participants with adult ADHD. Participants with physiologic dependence on alcohol were excluded. Mean age: 37 years Sex: 88 male Ethnicity: African American: 21, white: 64, other: 15 Employed: 80 History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 13.5, mean lifetime cocaine use: 16.5 years Route of cocaine use: 36 intrapulmonary, 64 intranasal, 5 other |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT weekly sessions Duration: 11 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 2 weeks of continuous abstinence) Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Craving assessed with a VAS ADHD severity assessed with ASRS Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: riboflavin |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, since the study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (56%). Most patients in both groups dropped out due to lack of interest. Missing data were not imputed. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in study protocol (NCT0013673) are reported in the article. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Levin 2015.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre clinical trial Analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA Participants had to meet DSM‐IV criteria for current cocaine dependence and adult ADHD (DSM‐IV‐TR). Used cocaine at least 4 days in the past month Mean age: 36.4 years Sex: 106 men Ethnicity: African American: 22, white: 72, other: 28 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during the last 28 days: 11.7, mean lifetime cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT Duration: 14 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by self‐report and confirmed by 3 time weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: urine quantification of amphetamines (not available to study staff) and urine riboflavin fluorescence |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Participants, investigators, and study staff were blind to allocation". |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since the study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear that blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Attrition was moderate (26%). Reasons for dropping out were described. Missing urine samples were not imputed. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in study protocol (NCT00553319) are reported in the article. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Margolin 1995a.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre clinical trial Allocation stratified by the presence of antisocial personality disorder Statistical analysis: unspecified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 149 methadone maintained dual heroin‐cocaine dependent outpatients (DSM‐IIIR). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 37.2 Sex: 93 male Ethnicity: African American: 64, white: 67, other: 18 Employed: 10 History of cocaine use: mean lifetime cocaine use: 7.7 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received methadone plus counselling Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with a VAS Depression symptoms assessed with Ham‐D Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: bupropion and metabolites every 2 weeks |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Attrition was moderate (16%) in both groups. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes was not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method uses was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Margolin 1995b.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: unspecified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 37 methadone maintained dual heroin‐cocaine dependent outpatients who were cocaine abstinent for 2 weeks. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 34.1 Sex: 16 men Ethnicity: African American: 9, white: 25, other: 3 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean lifetime cocaine use: 11 years, mean amount of cocaine use: 2.51 g/week Route of cocaine use: 7 intrapulmonary, 7 intranasal, 23 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received methadone, plus case management, behavioural contingency and weekly psychotherapy group Duration: 12 weeks Single site trial (USA) |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Depression symptoms assessed with BDI Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: unspecified |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Pharmacy controlled. "All study personnel were blind to subject assignment" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcome or the outcome measurement were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Attrition was moderate (19%) in both groups. Imputation of missing urine samples was performed by means of worst possible scenario. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes, if any, was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Margolin 1997.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: unspecified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 17 methadone maintained dual heroin‐cocaine (DSM‐IIIR) dependent outpatients Mean age: 36 years Sex: 9 men Ethnicity: African American:4, white: 11, other: 2 Employed: 2 History of cocaine use: lifetime cocaine use: 9.6 years. Route of cocaine use: 11 intrapulmonary, 1 intranasal, 5 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received methadone plus weekly counselling session Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: unspecified |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "All study personnel, with exception of the pharmacist were blind to treatment assignment" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Attrition was moderate (18%) in all study groups. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Mooney 2009.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Analysis: ITT Post hoc analysis focused on 25 participants finishing the trial |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 82 cocaine dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 36.4 years Sex: 54 men Ethnicity: African American: 49, white: 23, other: 10 Employed: 39 History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 11.7, mean lifetime cocaine use: 10.1 years Route of cocaine use: 58 intrapulmonary |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT (1 h session weekly) and CM (implemented in weeks 6‐9, fixed‐ratio schedule with benzoylecgonine negative urine samples reinforced with a USD 20 payment) Duration: 9 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Depression symptoms assessed with BDI Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: riboflavin |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (70%) in all the study groups. Protocol violations followed by loss to follow‐up were the most frequent reasons for dropping out in all study groups. Missing data were not imputed. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Mooney 2015.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 43 cocaine dependent participants (DSM‐IV) Mean age: 45.7 years Sex: 35 men Ethnicity: African American: 26, white: 11, other: 4 Employed: 9 History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 14.3, mean lifetime cocaine use: 10.5 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received weekly CBT Duration: 14 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of urinalysis Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Depression symptoms assessed with BDI‐II Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: riboflavin |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (37%) in both groups. Reasons for dropout were reported. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes, if any, was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in study protocol (NCT00958282) are reported in the article |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Morgan 2016.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Analysis: not specified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 57 participants with DSM‐IV cocaine dependence (with a score on the severity of dependence scale ≥ than 3 and self‐reported use of cocaine in at least 9 of the past 12 months) Mean age: 43 Sex: 44 men Ethnicity: African American: NR, white: NR, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: days of cocaine use during last month: NR, lifetime cocaine use: 22,4 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received psycho‐education and relapse prevention therapy (5 sessions per week during inpatient treatment) and CBT (weekly during outpatient treatment), in addition to contingency management Duration: 12 days inpatient + 6 weeks outpatient |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by self‐report and confirmed by 3 times weekly urinalysis | |
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: diary and riboflavin |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | Unclear risk | Number of participants who discontinued treatment was not reported for each study intervention. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
NCT00142818.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled clinical trial Statistical analysis: not specified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = participants with DSM‐IV cocaine (sed ≥ USD 200 worth of cocaine in the past 30 days) and alcohol dependence (drank within 30 days of intake day + report a minimum of 48 standard alcoholic drinks in a consecutive 30‐day period over the 90‐day period prior to starting intake + has 2 or more days of heavy drinking + 72 hours of consecutive abstinence from alcohol determined by self‐report and confirmed by a negative breathalyser test and CIWA‐Ar score < 8) Mean age: NR Sex: 58 men Ethnicity: African American: NR, white: NR, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: days of cocaine use during last month: NR, lifetime cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
Duration: 13 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by self‐report and confirmed by urinalysis at week 14 (results not reported yet) Reduction in cocaine use measured by number of negative urinalysis (results not reported yet) Retention in treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: NR Assessment of adherence: NR |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (46%). Reasons for dropping out were described. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | This item cannot be scored because the study has not been published yet. Little information is published in this preliminary report. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | This bias cannot be ruled out because reported data are scarce. |
Perry 2004.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Statistical analysis: unspecified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 24 cocaine dependent/abuser outpatients (DSM‐III‐R) with schizophrenia. It was unclear whether participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 37.8 years Sex: 23 men Ethnicity: African American:19, white: 4, other: 1 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received antipsychotics (933 ± 764 mg/d chlorpromazine equivalent dose), limited CBT and motivational enhancement Duration: 6 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of once weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment (provided by author) Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: unspecified |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (67%). Reasons for dropouts were not reported. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was GEE, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The efficacy outcomes reported correspond to those one expects from this type of study, but safety data are poor. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement because the study did not describe participants' baseline characteristics |
Poling 2006.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Randomisation was stratified by sex and ethnicity Statistical analysis: unspecified |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 106 methadone‐maintained, dual heroin‐cocaine dependent/abusers (DSM‐IV). Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. 30 participants had major depressive disorder. Mean age: 34.6 years Sex: 74 men Ethnicity: African American: 11, white: 80, other: 15 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 16.6, mean lifetime cocaine dependence: 94 Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received:
Duration: 24 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis (provided by author) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention in treatment Depression symptoms assessed with Ham‐D and CES‐D |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: check mouth |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Urn randomisation technique" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Only research pharmacist was aware of the medication condition" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (42%). Reasons for dropping out were not reported. Missing data were not imputed. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM), which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the efficacy outcomes reported correspond to those one expects from this type of study. Nevertheless, safety data are poor. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Schmitz 2012.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Randomisation was stratified by sex and cocaine addiction Statistical analysis: randomised participants who received the first dose of medication |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 73 cocaine dependent participants (DSM‐IV), with at least 1 positive urinalysis during screening. Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 42.9 years Sex: 51 men Ethnicity: African American: 37, white: 15, other: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 17.8 days, mean lifetime cocaine dependence: 13 years Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
Duration: 16 weeks of treatment |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine positive urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention to treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: riboflavin and self‐reported number of pills per day |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "All investigators and staff, except the pharmacist were blind to medication assignment" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (81%) in all study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not reported, and it is unclear whether they differed between active and placebo groups. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. Nevertheless, the statistical method used was Generalised Linear Mixed Model (GLMN), which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes stated in the study protocol (NCT00218062) are reported in the article. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Schmitz 2014.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial. Before randomisation, participants entered a 4‐week non‐medicated phase during which they received motivational interviewing and contingency management. Abstinent participants (those achieving 2 consecutive cocaine abstinent weeks: 6 consecutive cocaine‐negative urinalysis) were identified and randomised separately from those that did not achieve abstinence. Statistical analysis: unclear |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 81 cocaine dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV).Participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 42.5 years Sex: 61 men Ethnicity: African American: 56, white: 14, other: 11 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received motivational interviewing and contingency management targeting cocaine abstinence before randomisation, followed by contingency management targeting treatment adherence and CBT (weekly 1 h individual sessions) after randomisation. Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use asssessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention in treatment |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: riboflavin |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (48%) in all study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not reported, and it is unclear whether they differed between active and placebo groups. Missing urine samples were not imputed. Nevertheless, the statistical method use was GLMM, which does not require imputation of missing data to perform an ITT analysis. Imputation method for missing data of subjective outcomes, if any, was not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Efficacy outcomes stated in the study protocol (NCT00218023) are reported in the article. Nevertheless, information on safety is poor. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Schubiner 2002.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Stratified by sex; men were further stratified by antisocial personality disorder and women by borderline personality disorder. Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 59 cocaine‐dependent participants with comorbid ADHD (DSM‐IV). it was unclear wether participants with comorbid alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 37.1 years Sex: 43 men Ethnicity: white: 34 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean days of cocaine use during last month: 13.5 Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT (24 group sessions for cocaine dependence and individual sessions for ADHD with comorbid SUD) Duration: 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis Retention in treatment Craving assessed with the Tiffany Cocaine Craving Scale ADHD symptoms assessed with ADHD Symptom Checklist Depression symptoms assessed with BDI Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: computerised questionnaire on the number of pills taken |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure was not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (48%) in all study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not reported for any study group. Imputation methods, if any, were not reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | High risk | 1 study group (Pemoline) was withdrawn during the course of the study because of recruitment difficulties. |
Shearer 2003.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre clinical trial Stratification by sex Analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: Australia N = 30 cocaine‐dependent (DSM‐IV). 24 participants had a comorbid opioid dependence. It was unclear whether participants with alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 28 years Sex: 16 men Ethnicity: NR Employed: NR History of cocaine use: mean frequency of cocaine use: 6 times a day Route of cocaine use: 30 intravenous |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received drug and alcohol counselling, and 24 received methadone. Duration: 14 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of urinalysis every 2 weeks (provided by author) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) (provided by author) Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Self‐reported cocaine use Depression symptoms assessed with the Brief Symptom Inventory |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding private and public Assessment of adherence: unspecified |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | "Using randomisation schedules" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | "Pharmacy controlled" |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (63%) in all study groups. Reasons for dropping out were not described for each study group. Missing urine samples were imputed as positive. Missing data of subjective outcomes were imputed from baseline using a 'worst case scenario' assumption of no change. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Shoptaw 2008.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, single‐site clinical trial Stratification by sex Statistical analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 70 cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM IV). Participants with alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 36.9 years Sex: 59 men Ethnicity: African American 38, white 2, other 30 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: last month cocaine use: 11.1 days, lifetime cocaine use: 8.2 years Route of cocaine use: 59 intrapulmonary, 7 intranasal, 1 intravenous, 2 oral, 1 NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT (3 sessions a week) and counselling (once a week) Duration: 16 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of 3 times weekly urinalysis (provided by author) Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Cocaine craving assessed with VAS Depression symptoms assessed with BDI |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: public Assessment of adherence: pill count |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, since study medication has behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Study medication and matched placebo had an identical appearance. Nevertheless, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (83%) in all study groups. Failure to return was the most frequent reason for dropping out in both study groups. Missing data were not imputed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Though the study protocol was not available, the outcomes reported are those that one expects from this type of study. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
Stine 1995.
| Methods | Double‐blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre clinical trial Analysis: ITT |
|
| Participants | Country: USA N = 43 cocaine‐dependent (DSM‐III‐R) outpatients, reporting cocaine use of at least 12 g in the 3 months prior to entering the study. 15 participants had a comorbid major depressive disorder and 4 an antisocial personality disorder. Participants with alcohol dependence were excluded. Mean age: 34.5 years Sex: 37 men Ethnicity: African American: 22, white: 17, other: 4 Employed: NR History of cocaine use: NR Route of cocaine use: NR |
|
| Interventions |
All participants also received counselling (6 sessions) Duration: 6 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use assessed by means of once weekly urinalysis Sustained cocaine abstinence (defined as at least 3 weeks of continuous abstinence) Retention in treatment Self‐reported cocaine use Cocaine craving assessed with a 5‐point Analogue Scale Depression symptoms severity assessed with Ham‐D and BDI Dropouts due to adverse events |
|
| Notes | Author's affiliation: university Study funding: co‐funding public and private Assessment of adherence: self‐report or failure to pick up |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Insufficient information to permit judgement |
| Blinding (detection bias) Objective outcomes | Low risk | The outcomes or the outcome measurements were not likely to be influenced by lack of blinding. |
| Blinding (detection bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, since study medication has powerful behavioural effects, it is unclear whether blinding can be achieved when it is compared to placebo. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Objective measures | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Blinding (performance bias) Subjective outcomes | Unclear risk | Blinding procedure is not described. Furthermore, study medication has powerful behavioural effects that may reveal the assigned medication, which may lead treating clinicians to provide co‐intervention, thereby biasing the final outcome. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) Objective and subjective measures except retention and dropouts | High risk | Attrition was high (58%) in all study groups. Missing urine samples were as imputed as positive. Missing data of subjective outcomes was imputed using LOCF. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Though the study protocol was not available the efficacy outcomes reported correspond to those one expects from this type of study. Nevertheless, safety data are poor. |
| Other bias | Low risk | The study appears to be free from other sources of bias. |
ADHD: attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder; ASRS: adult ADHD self‐reported scale; BDI: Beck depression inventory; BSCS: brief substance craving scale; CBT: cognitive behavioural therapy; CCQ: cocaine craving questionnaire; CES‐D: Centre for Epidemiologic Studies depression scale; CGI: clinical global impression; CIWA‐Ar: Clinical Institute withdrawal assessment for alcohol; CM: contingency management; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; GEE: generalised estimating equations; GLMM: generalized linear mixed model; Ham‐D: Hamilton depression scale; IR: instant release; ITT: intention to treat; LOCF: last observation carried forward; MEMS: medication event monitoring system; NR: not reported; SR: slow release; SUD: substance use disorder; VAS: visual analogue scale; VC: voucher control; XR: extended release.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Afshar 2012 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Avants 1998 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Berger 1989 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Cannavan 2014 | Inpatients |
| Goldstein 2010 | Single methylphenidate dose |
| Goldstein 2011 | Single methylphenidate dose |
| Herin 2010 | Full text with results not available |
| Kalechstein 2011 | Inpatients |
| Kaleschtein 2013 | Inpatients |
| Kampman 1997 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Levin 1998 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Levin 1999 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Levin 2006 | Cocaine dependence or abuse was not an inclusion criteria |
| Levin 2008 | Pooled analysis of 3 RCTs |
| Magee 2015 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Magee 2016 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Margolin 1991 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Mariani 2012 | Intervention other than psychostimulants (mixed amphetamine salts plus topiramate); ongoing in the version of the review (NCT00421603) |
| Moeller 2011 | Single dose of d‐amphetamine |
| Moeller 2014 | Single dose of methylphenidate |
| Montoya 1994 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Mooney 2008 | Cocaine abuse or dependence was not an inclusion criteria |
| Morgan 2010 | Inpatients |
| Nuitjen 2015 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Ollo 1996 | Laboratory study without an outpatient follow‐up |
| Peirce 2009 | Cocaine abuse or dependence was not an inclusion criteria |
| Poling 2010 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Rush 2010 | Cross‐over randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Seibyl 1992 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Shearer 2010 | Cocaine and methamphetamine dependent patients together |
| Shorter 2013 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Tennant 1990 | Not a randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Vansickel 2008 | Single dose of methylphenidate and modafinil |
| Volkow 2010 | Not randomised placebo controlled clinical trial |
| Vosburg 2010 | Single dose of modafinil |
| Wang 2010 | Single dose of methylphenidate |
| Winhusen 2013 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
| Winhusen 2014 | Intervention other than psychostimulants |
RCT: randomised controlled trial.
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
EudraCT 2013‐004024‐11.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 12‐week duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled |
| Participants | Participants with cocaine and opioid dependence (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Self‐reported cocaine use Negative urinalysis |
| Notes | Completed |
NCT00015223.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; placebo controlled |
| Participants | Participants with cocaine dependence and ADHD (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Not specified |
| Notes | Completed (last updated June 2015) |
NCT00218348.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 25‐weeks duration; 4 parallel groups, placebo‐controlled. Phase II. |
| Participants | Cocaine dependent participants (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Substance use Retention |
| Notes | Completed (January 2008, last updated: January, 2009) |
NCT00218387.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 8‐week duration; 3 parallel groups, placebo‐controlled. Phase II. Mesures of interest: Benzoylecgonine presence in urine 3 times a week |
| Participants | Cocaine‐dependent participants (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT |
| Outcomes | Number of cocaine non‐use days Consecutive cocaine non‐use days |
| Notes | Completed (July 2010, last updated: November 2011) |
NCT00344565.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 12‐week duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase II. |
| Participants | Cocaine‐dependent outpatients (DSM‐IV) that used cocaine at least 8 days in the last month or report episodic binges of large amounts of cocaine |
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT‐RP |
| Outcomes | Treatment retention outcome Cocaine use Cognitive functioning Cocaine withdrawal symptoms throughout the study |
| Notes | Completed (March 2007, last updated: November 2012) |
NCT00495092.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 23‐weeks duration; 3 parallel groups, placebo controlled |
| Participants | Participants with cocaine dependence, according to DSM‐IV‐TR criteria |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine abstinence symptoms Cocaine craving Study retention Cocaine use |
| Notes | Completed October 2010 (last updated February 2012) |
NCT00514202.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 12‐week duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase II |
| Participants | Cocaine‐dependent and ADHD participants |
| Interventions |
All participants also received CBT. |
| Outcomes | Substance use ADHD symptoms Treatment retention Cocaine craving |
| Notes | Completed (October 2008; last updated February 2012) |
NCT00701532.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 90‐day duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase III |
| Participants | Participants with cocaine dependence (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | PET‐decreased dopamine transporter occupation rates Clinical efficacy of modafinil during cocaine withdrawal Tolerance and safety of high modafinil doses |
| Notes | Completed (January 2013, last updated April 2013) |
NCT00733993.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 3 weeks' duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase I/II. |
| Participants | Cocaine‐dependent participants (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine positive urine at 3 weeks of treatment Cue reactivity at 3 weeks of treatment |
| Notes | Completed (October 2011, last updated January, 2016) |
NCT00838981.
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 24 weeks' duration; parallel groups, placebo controlled |
| Participants | Participants with cocaine and opioid dependence |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Cocaine use |
| Notes | Completed (March 2014, last updated July 2015) |
ADHD: attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder; CBT: cognitive behavioural therapy; CBT‐RP: CBT and relapse prevention; CM: contingency management; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; PET: positron emission tomography; SR: slow release.
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
NCT00218036.
| Trial name or title | Pharmacotherapy dosing regimen in cocaine and opiate dependent individuals |
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 24‐week duration; 5 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase II. |
| Participants | Cocaine abuse or dependence participant (SCID) and Opiate dependence (SCID) |
| Interventions |
All participants also received methadone |
| Outcomes | Confirmed abstinence of cocaine Retention Medication adherence |
| Starting date | July 2006 |
| Contact information | Jan Lindsay jan.a.lindsay@uth.tmc.edu |
| Notes | — |
NCT02111798.
| Trial name or title | Bupropion‐enhaced contingency management for cocaine dependence |
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 30‐week duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled |
| Participants | Methadone‐maintained cocaine dependent participants |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Number of cocaine negative urines Latency to first cocaine positive urine |
| Starting date | May 2014 |
| Contact information | Maxine Stitzer mstiitzer@jhmi.edu Kelly Dunn kdun@jhmi.edu |
| Notes | Recruiting |
NTC00123383.
| Trial name or title | Randomised placebo controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence |
| Methods | Random allocation; double‐blind; 10‐week duration; 2 parallel groups, placebo controlled. Phase II. |
| Participants | Cocaine‐dependent participants (DSM‐IV) |
| Interventions |
All participants also received Tailored CBT |
| Outcomes | Urinalysis negative for cocaine over 10 weeks Adverse events adherence Retention |
| Starting date | July 2005 |
| Contact information | — |
| Notes | Unknown (last updated April 2007) |
CBT: cognitive behavioural therapy; CM: contingency management; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders;SCID: structured clinical interview for DSM‐IV.
Differences between protocol and review
We introduced two changes to this update since the first review (Castells 2010). Firstly, we added a new outcome: number of participants experiencing any serious adverse event. Secondly, we created a 'Summary of Findings' table.
Contributions of authors
All authors contributed to the protocol design.
XC wrote the protocol.
XC, RC and CP performed the selection of the studies.
XC, RC and CP carried out the data extraction.
XC did the statistical analysis.
All authors participated in the discussion and drafting of the final report.
Sources of support
Internal sources
The authors received no funding for this project, Other.
External sources
The authors received no funding for this project, Other.
Declarations of interest
XC: none known.
RC: none known.
CP: none known.
XV: none known.
DC: none known.
New search for studies and content updated (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Anderson 2009 {published and unpublished data}
- Anderson AL, Reid MS, Li SH, Holmes T, Shemanski L, Slee A, et al. Modafinil for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2009;104(1‐2):133‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dackis 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Dackis CA, Kampman KM, Lynch KG, Pettinati H, O'Brien CP. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005;30(1):205‐11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starosta AN, Rha C, Whitingham T. Factors involved in predicting the success of modafinil for the treatment of cocaine‐dependent subjects. 68th Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence 2006 June 17‐22:www.cpdd.org/Pages/Meetings/Meetings_PDFs/2006abstractbook.pdf: College on Problems of Drug Dependence, 2006:186. [Google Scholar]
Dackis 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Dackis CA, Kampman KM, Lynch KG, Plebani JG, Pettinati HM, Sparkman T, et al. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2012;43(3):303‐12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dürsteler‐MacFarland 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Dürsteler‐MacFarland KM, Farronato NS, Strasser J, Boss J, Kuntze MF, Petitjean SA, et al. A randomized, controlled, pilot trial of methylphenidate and cognitive‐behavioral group therapy for cocaine dependence in heroin prescription. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2013;33(1):104‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Elkashef 2006 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Elkashef A, Fudala PJ, Gordon L, Li S‐H, Kahn R, Chiang N, et al. Double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of selegiline transdermal system (STS) for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2006;85(3):191‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grabowski 1997 {published and unpublished data}
- Grabowki J, Schmitz J, Roache JD, Rhoades H, Elk R, Creson DL. Methylphenidate (MP) for initial treatment of cocaine dependence and a model for medication evaluation. NIDA Research Monograph 1994;141:436. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski J, Roache JD, Schmitz JM, Rhoades H, Creson D, Korszun A. Replacement medication for cocaine dependence: methylphenidate. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1997;17(6):485‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grabowski 2001 {published and unpublished data}
- Grabowski J, Rhoades H, Schmitz J, Stotts A, AnnDaruzska L, Creson D, et al. Dextroamphetamine for cocaine‐dependence treatment:a double‐blind randomised clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2001;21(5):522‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grabowski 2004a {published and unpublished data}
- Grabowski J, Rhoades H, Scotts A, Cowan K, Kopecky C, Dougherty A, et al. Agonist‐like or antagonist‐like treatment for cocaine dependence with methadone for heroin dependence: two double‐blind randomized clinical trials. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004;29(5):969‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kampman 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Kampman KM, Lynch KG, Pettinati HM, Spratt K, Wierzbicki MR, Dackis C, et al. A double blind, placebo controlled trial of modafinil for the treatment of cocaine dependence without co‐morbid alcohol dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;155(Oct):105‐10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 2007 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Aharonovich E, Garawi F, Bisaga A, Brooks D, Raby WN, Rubin E, et al. Concurrent cannabis use during treatment for comorbid ADHD and cocaine dependence effects on outcome. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2006;32(4):629‐35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin FR, Evans SM, Brooks DJ, Garawi F. Treatment of cocaine dependent treatment seekers with adult ADHD: double‐blind comparison of methylphenidate and placebo. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2007;87(1):20‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 2015 {published data only}
- Levin FR, Mariani JJ, Specker S, Mooney M, Mahony A, Brooks DJ, et al. Extended‐release mixed amphetamine salts vs placebo for comorbid adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder and cocaine use disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015;72(6):593‐602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Margolin 1995a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Margolin A, Kosten TR, Avants SK, Wilkins J, Ling W, Beckson M, et al. A multicenter trial of bupropion for cocaine dependence in methadone‐maintained patients. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1995;40(2):125‐31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Margolin 1995b {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Margolin A, Avants SK, Kosten TR. Mazindol for relapse prevention to cocaine abuse in methadone‐maintained patients. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1995;21(4):469‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Margolin 1997 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Margolin A, Avants K, Malison RT, Kosten TR. High‐ and low‐dose mazindol for cocaine dependence in methadone‐maintained patients:a preliminary evaluation. Substance Abuse 1997;18(3):125‐31. [Google Scholar]
Mooney 2009 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Mooney ME, Herin DV, Schmitz JM, Moukaddam N, Green CE, Grabowski J. Effects of oral methamphetamine on cocaine use: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2009;101(1‐2):34‐41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mooney 2015 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Mooney ME, Herin DV, Specker S, Babb D, Levin FR, Grabowski J. Pilot study of the effects of lisdexamfetamine on cocaine use: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;153(Aug):94‐103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Morgan 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Morgan PT, Angarita GA, Canavan S, Pittman B, Oberleitner L, Malison RT, et al. Modafinil and sleep architecture in an inpatient‐outpatient treatment study of cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2015;160(Mar):49‐56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NCT00142818 {published data only}
- NCT00142818. Modafinil and naltrexone to reduce cocaine and alcohol dependence (Mod‐Nal). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00142818 (first received 1 September 2005).
Perry 2004 {published and unpublished data}
- Perry EB, Gil R, Miles D, Brenner L, MacDougall L, Johson R, et al. Mazindol augmentation of antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenic patients with comorbid cocaine abuse or dependence: a preliminary double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Dual Diagnosis 2004;1(1):37‐47. [Google Scholar]
Poling 2006 {published and unpublished data}
- Poling J, Oliveto A, Petry N, Sofuoglu M, Gonsai K, Gonzalez G, et al. Six‐month trial of bupropion with contingency management for cocaine dependence in a methadone‐maintained population. Archives of General Psychiatry 2006;63(2):219‐28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schmitz 2012 {published and unpublished data}
- Schmitz JM, Rathnayaka N, Green CE, Moeller FG, Dougherty AE, Grabowski J. Combination of modafinil and d‐amphetamine for the treatment of cocaine dependence: a preliminary investigation. Frontiers in Psychiatry/Frontiers Research Foundation 2012;3(Aug):77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schmitz 2014 {published and unpublished data}
- Schmitz JM, Green CE, Stotts AL, Lindsay JA, Rathnayaka NS, Grabowski J, et al. A two‐phased screening paradigm for evaluating candidate medications for cocaine cessation or relapse prevention: modafinil, levodopa‐carbidopa,naltrexone. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2014;136(Mar):100‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schubiner 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Downey KK, Schubiner H, Schuster CR. Double‐blind placebo controlled stimulant trial for cocaine dependent ADHD adults. NIDA Research Monograph 2000;180:116. [Google Scholar]
- Schubiner H, Saules KK, Arfken CL, Johanson CE, Schuster CR, Lockhart N, et al. Double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of methylphenidate in the treatment of adult ADHD patients with comorbid cocaine dependence. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 2002;10(3):286‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shearer 2003 {published and unpublished data}
- Shearer J, Wodak A, Beek I, Mattick RP, Lewis J. Pilot randomized double blind placebo‐controlled study of dexamphetamine for cocaine dependence. Addiction 2003;98(8):1137‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shoptaw 2008 {published and unpublished data}
- Shoptaw S, Heinzerling KG, Rotheram‐Fuller E, Kao UH, Wang P‐C, Bholat MA, et al. Bupropion hydrochloride versus placebo, in combination with cognitive behavioral therapy, for the treatment of cocaine abuse/dependence. Journal of Addictive Diseases 2008;27(1):13‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stine 1995 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Stine SM, Krystal JH, Kosten TR, Charney DS. Mazindol treatment for cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1995;39(3):245‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Afshar 2012 {published data only}
- Afshar M, Knapp CM, Sarid‐Segal O, Devine E, Colaneri LS, Tozier L, et al. The efficacy of mirtazapine in the treatment of cocaine dependence with comorbid depression. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2012;38(2):181‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Avants 1998 {published data only}
- Avants SK, Margolin A, DePhilippis D, Kosten TR. A comprehensive pharmacologic‐psychosocial treatment program for HIV‐seropositive cocaine‐and‐opioid‐dependent patients. Preliminary findings. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 1998;15(3):261‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Berger 1989 {published data only}
- Berger P, Gawin F, Kosten TR. Treatment of cocaine abuse with mazindol. Lancet 1989;1(8632):283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cannavan 2014 {published data only}
- Canavan SV, Forselius EL, Bessette AJ, Morgan PT. Preliminary evidence for normalization of risk taking by modafinil in chronic cocaine users. Addict Behaviors 2014;39(6):1057‐61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goldstein 2010 {published data only}
- Goldstein RZ, Woicik PA, Moeller SJ, Telang F, Jayne M, Wong C, et al. Liking and wanting of drug and non‐drug rewards in active cocaine users: the STRAP‐R questionnaire. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2010;24(2):257‐66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goldstein 2011 {published data only}
- Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND. Oral methylphenidate normalizes cingulate activity and decreases impulsivity in cocaine addiction during an emotionally salient cognitive task. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36(1):366‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Herin 2010 {published data only}
- Herin DV. Agonist‐like medications for cocaine dependence treatment: clinical studies. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;35(Supplement):S21. [Google Scholar]
Kalechstein 2011 {published data only}
- Kalechstein A, Mahoney J, Bennett R, Shah RS, Yoon J, Chang LC, et al. Short‐term modafinil administration improves working memory and sustained attention in cocaine‐dependent volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36(Supplement):S176. [Google Scholar]
Kaleschtein 2013 {published data only}
- Kalechstein AD, Mahoney JJ 3rd, Yoon JH, Bennett R, Garza R 2nd. Modafinil, but not escitalopram, improves working memory and sustained attention in long‐term, high‐dose cocaine users. Neuropharmacology 2013;64(Jan):472‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kampman 1997 {published data only}
- Kampman KM, Volpicelli J. Combination of the dopaminergic agent, phentermine, and the serotoninergic agent, fenfluramine, in the treatment of cocaine dependence. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 1997;14(4):401‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 1998 {published data only}
- Levin FR, Evans SM, McDowell DM, Kleber HD. Methylphenidate treatment for cocaine abusers with adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a pilot study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1998;59(6):300‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 1999 {published data only}
- Levin FR, Evans SM, Kleber HD. Methylphenidate treatment for cocaine abusers with adult attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. NIDA Research Monograph 1999;179:39. [Google Scholar]
Levin 2006 {published data only}
- Levin FR, Evans SM, Brooks DJ, Kalbag AS, Garawi F, Nunes EV. Treatment of methadone‐maintained patients with adult ADHD: double‐blind comparison of methylphenidate, bupropion and placebo. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2006;81(2):137‐48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 2008 {published data only}
- Levin FR, Bisaga A, Raby W, Aharonovich E, Rubin E, Mariani J, et al. Effects of major depressive disorder and attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder on the outcome of treatment for cocaine dependence. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2008;34(1):80‐9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Magee 2015 {published data only}
- Magee JC, Lewis DF, Winhusen T. Evaluating nicotine craving, withdrawal, and substance use as mediators of smoking cessation in cocaine‐ and methamphetamine‐dependent patients. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;18(5):1196‐201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Magee 2016 {published data only}
- Magee JC, Winhusen T. The coupling of nicotine and stimulant craving during treatment for stimulant dependence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2016;84(3):230‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Margolin 1991 {published data only}
- Margolin A, Kosten T, Petrakis I, Avants SK, Kosten T. Bupropion reduces cocaine abuse in methadone‐maintained patients. Archives of Geneneral Psychiatry 1991;48(1):87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mariani 2012 {published data only}
- Mariani JJ, Pavlicova M, Bisaga A, Nunes EV, Brooks DJ, Levin FR. Extended‐release mixed amphetamine salts and topiramate for cocaine dependence: a randomized controlled trial. Biological Psychiatry 2012;72(11):950‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moeller 2011 {published data only}
- Moeller FG, Steinberg JL, Lane SD, Ma L, Kosten TR, Narayana PA. Pharmacological MRI of d‐amphetamine: effects of a go‐no/go task in cocaine dependent subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36(Supplement):S285. [Google Scholar]
Moeller 2014 {published data only}
- Moeller SJ, Honorio J, Tomasi D, Parvaz MA, Woicik PA, Volkow ND, et al. Methylphenidate enhances executive function and optimizes prefrontal function in both health and cocaine addiction. Cerebral Cortex 2014;24(3):643‐53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Montoya 1994 {published data only}
- Montoya ID, Preston KL, Rothman R, Cone E, Gorelick DA. Safety and efficacy of bupropion in combination with bromocriptine for treatment of cocaine dependence. NIDA Research Monograph 1994;153:304. [Google Scholar]
Mooney 2008 {published data only}
- Mooney ME, Poling J, Gonzalez G, Gonsai K, Kosten T, Sofluoglu M. Preliminary study of buprenorphine and bupropion for opioid dependent smokers. American Journal on Addictions 2008;17(4):287‐92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Morgan 2010 {published data only}
- Morgan PT, Pace‐Schott E, Pittman B, Stickgold R, Malison RT. Normalizing effects of modafinil on sleep in chronic cocaine users. American Journal of Psychiatry 2010;167(3):331‐40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nuitjen 2015 {published data only}
- Nuijten M, Blanken P, Brink W, Hendriks V. Modafinil in the treatment of crack‐cocaine dependence in the Netherlands: Results of an open‐label randomised controlled feasibility trial. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2015;29(6):678‐87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ollo 1996 {published data only}
- Ollo C, Alim TN, Rosse RB, Lindquist T, Green T, Gillis T, et al. Lack of neurotoxic effect of diethylpropion in crack‐cocaine abusers. Clinical Neuropharmacology 1996;19(1):52‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Peirce 2009 {published data only}
- Peirce JM, Petry NM, Roll JM, Kolodner K, Krasnansky J, Stabile PQ, et al. Correlates of stimulant treatment outcome across treatment modalities. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2009;35(1):48‐53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Poling 2010 {published data only}
- Poling J, Rounsaville B, Gonsai K, Severino K, Sofuoglu M. The safety and efficacy of varenicline in cocaine using smokers maintained on methadone: a pilot study. The American Journal on Addictions 2010;19(5):401‐8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rush 2010 {published data only}
- Rush CR, Stoops WW, Sevak RJ, Hays LR. Cocaine choice in humans during D‐amphetamine maintenance. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2010;30(2):152‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Seibyl 1992 {published data only}
- Seibyl JP, Brenner L, Krystal JH, Johson R, Charney DS. Mazindol and cocaine addiction in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 1992;31(11):1179‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shearer 2010 {published data only}
- Shearer J, Shanahan M, Darke S, Rodgers C, Beek I, McKetin R, et al. A cost‐effectiveness analysis of modafinil therapy for psychostimulant dependence. Drug and Alcohol Review 2010;39(3):235‐42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shorter 2013 {published data only}
- Shorter D, Lindsay JA, Kosten TR. The alpha‐1 adrenergic antagonist doxazosin for treatment of cocaine dependence: a pilot study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2013;131(1):66‐70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tennant 1990 {published data only}
- Tennant F. Clinical trial of multiple treatment agents for cocaine dependence: a placebo‐controlled elimination study. NIDA Research Monograph 1990;105:512‐3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vansickel 2008 {published data only}
- Vansickel AR, Fillmorex MT, Hays LR, Rush CR. Effects of potential agonist‐replacement therapies for stimulant dependence on inhibitory control in cocaine abusers. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2008;34(3):293‐305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 2010 {published data only}
- Volkow N. Decreased motivation in ADHD is associated with deficit in dopamine reward pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;35(Supplement):S39. [Google Scholar]
Vosburg 2010 {published data only}
- Vosburg SK, Hart CL, Haney M, Rubin E, Foltin RW. Modafinil does not serve as a reinforcer in cocaine abusers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2010;15(2):233‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wang 2010 {published data only}
- Wang GJ, Volkow N, Telang F, Tomasi D, Logan J, Wong C, et al. Decreased striatal and prefrontal dopaminergic responses in active cocaine dependent subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;35(Supplement):S372. [Google Scholar]
Winhusen 2013 {published data only}
- Winhusen T, Lewis D, Adinoff B, Brigham G, Kropp F, Donovan DM, et al. Impulsivity is associated with treatment non‐completion in cocaine‐ and methamphetamine‐dependent patients but differs in nature as a function of stimulant‐dependence diagnosis. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2013;44(5):541‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Winhusen 2014 {published data only}
- Winhusen TM, Brigham GS, Kropp F, Lindblad R, Gardin JG 2nd, Penn P, et al. A randomized trial of concurrent smoking‐cessation and substance use disorder treatment in stimulant‐dependent smokers. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2014;75(4):336‐43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
EudraCT 2013‐004024‐11 {published data only}
- EudraCT 2013‐004024‐11. New pharmacotherapeutic treatment options for crack‐cocaine dependent people in the Netherlands: A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled randomized feasibility study of sustained release dexamphetamine. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=2013‐004024‐11 (first received 1 September 2014).
NCT00015223 {published data only}
- NCT00015223. Methylphenidate in the treatment of cocaine dependent patients with adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00015223 (first received 18 April 2001).
NCT00218348 {published data only}
- NCT00218348. Treatment of cocaine dependence: comparison of three doses of dextro‐amphetamine sulfate and placebo. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00218348 (first received 15 September 2005).
NCT00218387 {published data only}
- NCT00218387. Modafinil combined with cognitive behavior therapy to treat cocaine addiction. clinicaltrials.gov/show/study/NCT00218387 (first received 16 September 2005).
NCT00344565 {published data only}
- NCT00344565. A placebo‐controlled double‐blind combined treatment of modafinil and CBT for cocaine dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00344565 (first received 26 June 2006).
NCT00495092 {published data only}
- NCT00495092. Efficacy of caffeine, with and without biperiden, in the detoxification of cocaine dependent patients. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00495092 (first received 29 June 2007).
NCT00514202 {published data only}
- NCT00514202. Pilot study examining effect for dextroamphetamine to treat cocaine dependence plus attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00514202 (first received 07 August 2007).
NCT00701532 {published data only}
- NCT00701532. Brain imaging study of the effects of modafinil in cocaine addiction. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00701532 (First received: 18 June 2008).
NCT00733993 {published data only}
- NCT00733993. Caffeine and cocaine. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00733993 (first received 12 August 12 2008).
NCT00838981 {published data only}
- NCT00838981. Pharmacotherapy and CM for opioid and cocaine dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00838981 (first received 6 February 2009).
References to ongoing studies
NCT00218036 {published data only}
- NCT00218036. Pharmacotherapy dosing regimen in cocaine and opiate dependent individuals ‐ 8 [Pharmacotherapy dosing regimen in cocaine and opiate dependent individuals]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00218036 (first received 16 September 2005).
NCT02111798 {published data only}
- NCT02111798. Bupropion‐enhanced contingency management for cocaine dependence [Bupropion‐enhanced CM for cocaine dependence]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02111798 (first received 28 March 2014).
NTC00123383 {published data only}
- NTC00123383. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence [Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NTC00123383 (first received 21 July 2005).
Additional references
AHFS 2014
- American Society of Health‐System Pharmacists. AHFS. American Hospital Formulary Service. Drug Information 2009. Bethesda: American Society of Health‐System Pharmacists, 2014. [Google Scholar]
American Psychiatric Association 2000
- American Psychiatry Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2000. [Google Scholar]
American Psychiatric Association 2013
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013. [Google Scholar]
ATC 2015
- World Health Organization. ATC/DDD Index. www.whocc.no/atcddd/indexdatabase/ (accessed prior to 25 August 2016).
Brayfield 2014
- Brayfield A. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. 38. Pharmaceutical Press, 2014. [Google Scholar]
Brunton 2011
- Brunton L, Chabner B. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th Edition. McGraw Hill, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Carroll 2004
- Carroll KM, Fenton LR, Ball SA, Nich C, Frankforter TL, Shi J, et al. Efficacy of disulfiram and cognitive behavior therapy in cocaine‐dependent outpatients: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Archives of General Psychiatry 2004;61(3):264‐72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Castells 2007
- Castells X, Casas M, Vidal X, Bosch R, Roncero C, Ramos‐Quiroga JA, et al. Efficacy of central nervous system stimulant treatment for cocaine dependence: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled clinical trials. Addiction 2007;1002(12):1871‐87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Castells 2009
- Castells X, Kosten TR, Capellà D, Vidal X, Colom J, Casas M. Efficacy of opiate maintenance therapy and adjunctive interventions for opioid dependence with comorbid cocaine use disorders: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of controlled clinical trials. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 2009;35(5):339‐49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chinazo 2014
- Cunningham CO, Giovanniello A, Kunins HV, Roose RJ, Fox AD, Sohler NL. Buprenorphine treatment outcomes among opioid‐dependent cocaine users and non‐users. American Journal of Addictions 2013;22(4):352‐357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cousins 2001
- Cousins MS, Stamat HM, Wit H. Acute doses of d‐amphetamine and bupropion increase cigarette smoking. Psychopharmacology 2001;157(3):243‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Craft 1996
- Craft RM, Stratmann JA. Discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in female versus male rats. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1996;42(1):27‐37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cunill 2015
- Cunill R, Castells X, Tobias A, Capellà D. Pharmacological treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder with co‐morbid drug dependence. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2015;29(1):15‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dopheide 2007
- Dopheide MM, Morgan RE, Rodvelt KR, Schachtman TR, Miller DK. Modafinil evokes striatal [(3)H]dopamine release and alters the subjective properties of stimulants. European Journal of Pharmacology 2007;568(1‐3):112‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dwoskin 2006
- Dwoskin LP, Rauhut AS, King‐Pospisil KA, Bardo MT. Review of the pharmacology and clinical profile of bupropion, an antidepressant and tobacco use cessation agent. CNS Drug Reviews 2006;12(3‐4):178‐207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Egger 1997
- Egger M, Davey‐Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta‐analysis detected by a simple graphical test. BMJ 1997;315(7109):629‐34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
EMCDDA 2015
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European Drug Report. Trends and developments. www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_239505_EN_TDAT15001ENN.pdf (accessed prior to 25 August 2016).
Engberg 1991
- Engberg G, Elebring T, Nissbrandt H. Deprenyl (selegiline), a selective MAO‐B inhibitor with active metabolites; effects on locomotor activity, dopaminergic neurotransmission and firing rate of nigral dopamine neurons. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1991;259(2):841‐47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Evans 1987
- Evans SM, Johanson CE. Amphetamine‐like effects of anorectics and related compounds in pigeons. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1987;241(3):817‐25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gorelick 2004
- Gorelick DA, Gardner EL, Xi ZX. Agents in development for the management of cocaine abuse. Drugs 2004;64(14):1547‐73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grabowski 2004b
- Grabowski J, Shearer J, Merrill J, Negus SS. Agonist‐like, replacement pharmacotherapy for stimulant abuse and dependence. Addictive Behaviors 2004;29(7):1439‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADE 2004
- The GRADE Working Group. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004;328(7454):149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guyatt 2008
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck‐Ytter Y, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008;336(7650):924‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guyatt 2011
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartmann‐Boyce 2014
- Hartmann‐Boyce J, Stead LF, Cahill K, Lancaster T. Efficacy of interventions to combat tobacco addiction: Cochrane update of 2013 reviews. Addiction 2014;109(9):1414‐25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jasinski 2000
- Jasinski DR, Kovacević‐Ristanović R. Evaluation of the abuse liability of modafinil and other drugs for excessive daytime sleepiness associated with narcolepsy. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2000;23(3):149‐56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jüni 2001
- Jüni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Assessing the quality of clinical trials. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care. Meta Analysis in Context. London: BMJ publishing group, 2001:87‐108. [Google Scholar]
Kalivas 2005
- Kalivas PW, Volkow ND. The neural basis of addiction: a pathology of motivation and choice. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(8):1403‐13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kalivas 2007
- Kalivas PW. Neurobiology of cocaine addiction: implications for new pharmacotherapy. American Journal on Addictions 2007;16(2):71‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kampman 2004
- Kampman KM, Pettinati H, Lynch KG, Dackis C, Sparkman T, Weigley C, et al. A pilot trial of topiramate for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2004;75(3):233‐40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Karila 2008
- Karila L, Gorelick D, Weinstein A, Noble F, Benyamina A, Coscas S, et al. New treatments for cocaine dependence: a focused review. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2008;11(3):425‐38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Katz 2000
- Katz JL, Izenwasser S, Terry P. Relationships among dopamine transporter affinities and cocaine‐like discriminative‐stimulus effects. Psychopharmacology 2000;148(1):90‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kidorf 2004
- Kidorf M, Disney ER, King VL, Neufeld K, Beilenson PL, Brooner RK. Prevalence of psychiatric and substance use disorders in opioid abusers in a community syringe exchange program. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2004;74(2):115‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kleber 2007
- Kleber HD, Weiss RD, Anton RF Jr, George TP, Greenfield SF, Kosten TR, et al. American Psychiatric Association Steering Committee on Practice Guidelines. Treatment of patients with substance use disorders, second edition. American Journal of Psychiatry 2007;164(4 Suppl):5‐123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Koob 1988
- Koob GF, Bloom FE. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of drug dependence. Science 1988;242(4879):715‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kosten 2005
- Kosten T, Sofuoglu M, Poling J, Gonsai K, Oliveto A. Desipramine treatment for cocaine dependence in buprenorphine‐ or methadone‐treated patients: baseline urine results as predictor of response. American Journal on Addictions 2005;14(1):8‐17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Langguth 2009
- Langguth B, Hajak G, Landgrebe M, Unglaub W. Abuse potential of bupropion nasal insufflation: a case report. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2009;29(6):618‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Learned‐Coughlin 2003
- Learned‐Coughlin SM, Bergström M, Savitcheva I, Ascher J, Schmith VD, Långstrom B. In vivo activity of bupropion at the human dopamine transporter as measured by positron emission tomography. Biological Psychiatry 2003;54(8):800‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Leri 2003
- Leri F, Bruneau J, Stewart J. Understanding polydrug use: review of heroin and cocaine co‐use. Addiction 2003;98(1):7‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Madras 2006
- Madras BK, Xie Z, Lin Z, Jassen A, Panas H, Lynch L, et al. Modafinil occupies dopamine and norepinephrine transporters in vivo and modulates the transporters and trace amine activity in vitro. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2006;319(2):561‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mahmood 1997
- Mahmood I. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of selegiline. An update. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 1997;33(2):91‐102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Makris 2007
- Makris AP, Rush CR, Frederich RC, Taylor AC, Kelly TH. Behavioral andsubjective effects of d‐amphetamine and modafinil in healthy adults. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 2007;15(2):123‐33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mattick 2003
- Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mattick 2009
- Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue CD002209. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McCormick 2002
- McCormick J. Recreational bupropion abuse in a teenager. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2002;53(2):214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McDowell 2005
- McDowell D, Nunes EV, Seracini AM, Rothenberg J, Vosburg SK, Ma GJ, et al. Desipramine treatment of cocaine‐dependent patients with depression: a placebo‐controlled trial. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2005;80(2):209‐21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Minozzi 2015a
- Minozzi S, Amato L, Pani PP, Solimini R, Vecchi S, Crescenzo F, et al. Dopamine agonists for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003352.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Minozzi 2015b
- Minozzi S, Cinquini M, Amato L, Davoli M, Farrell MF, Pani PP, et al. Anticonvulsants for cocaine dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006754.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moeller 2008
- Moeller FG, Schmitz JM, Herin D, Kjome KL. Use of stimulants to treat cocaine and methamphetamine abuse. Current Psychiatry Reports 2008;10(5):385‐91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pani 2011
- Pani PP, Trogu E, Vecchi S, Amato L. Antidepressants for cocaine dependence and problematic cocaine use. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 12. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002950.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perez de los Cobos 2014
- Pérez de los Cobos J, Siñol N, Pérez V, Trujols J. Pharmacological and clinical dilemmas of prescribing in comorbid adult attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and addiction. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2014;77(2):337‐56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Redolat 2005
- Redolat R, Vidal J, Gomez MC, Carrasco MC. Effects of acute bupropion administration on locomotor activity in adolescent and adult mice. Behavioral Pharmacology 2005;16(1):59‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
SAMSHA 2014
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMSHA). Results from the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings, NSDUH Series H‐48, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 14‐4863. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 2014. Available from: www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/NSDUHresultsPDFWHTML2013/Web/NSDUHresults2013.pdf (accessed prior to 25 August 2016).
Schmitz 2008
- Schmitz JM, Mooney ME, Moeller FG, Stotts AL, Green C, Grabowski J. Levodopa pharmacotherapy for cocaine dependence: choosing the optimal behavioral therapy platform. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2008;94(1):142‐50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schunemann 2006
- Schunemann HJ, Fretheim A, Oxman AD. Improving the use of research evidence in guideline development: 13. Applicability, transferability and adaptation. Health Research Policy & Systems 2006;4(1):26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shin 1997
- Shin HS. Metabolism of selegiline in humans. Identification, excretion, and stereochemistry of urine metabolites. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 1997;25(6):657‐62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
UNDOC 2015
- United Nations Office on Drug and Crime. World Drug Report. www.unodc.org/documents/wdr2015/World_Drug_Report_2015.pdf (accessed prior to 25 August 2016).
Van Emmerik‐Van Oortmerssen 2012
- Emmerik‐Van Oortmerssen K, Glind G, Brink W, Smit F, Crunelle CL, Swets M, et al. Prevalence of attention‐deficit hyperactivity disorder in substance use disorder patients: a meta‐analysis and meta‐regression analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2012;122(1‐2):11‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 1990
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Schlyer D, Shiue CY, Alpert R, et al. Effects of chronic cocaine abuse on postsynaptic dopamine receptors. American Journal of Psychiatry 190;147(6):719‐24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 1996
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Hitzemannn R, Gatley SJ, et al. Cocaine uptake is decreased in the brain of detoxified cocaine abusers. Neuropsychopharmacology 1996;14(3):159‐68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 1997a
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fischman MW, Foltin RW, Fowler JS, Abumrad NN, et al. Relationship between subjective effects of cocaine and dopamine transporter occupancy. Nature 1997;386(6627):827‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 1997b
- Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J, Gatley SJ, Hitzemann R, et al. Decreased striatal dopaminergic responsiveness in detoxified cocaine‐dependent subjects. Nature 1997;386(6627):830‐3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 2004
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Swanson JM. Dopamine in drug abuse and addiction: results from imaging studies and treatment implications. Molecular Psychiatry 2004;9(6):557‐69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Volkow 2009
- Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F, et al. Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. Journal of the American Medical Association 2009;301(11):1148‐54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
WADA 2016
- World Anti‐Doping Agency. List of Prohibited Substances and Methods (available from: http://list.wada‐ama.org/). Internet resource 2016.
Welsh 2002
- Welsh CJ, Doyon S. Seizure induced by insufflation of bupropion. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(12):951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yasar 2006a
- Yasar S, Justinova Z, Lee SH, Stefanski R, Goldberg SR, Tanda G. Metabolic transformation plays a primary role in the psychostimulant‐like discriminative‐stimulus effects of selegiline [(R)‐(‐)‐deprenyl]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2006;317(1):387‐94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yasar 2006b
- Yasar S, Gaál J, Panlilio LV, Justinova Z, Molnár SV, Redhi GH, et al. A comparison of drug‐seeking behavior maintained by D‐amphetamine, L‐deprenyl (selegiline), and D‐deprenyl under a second‐order schedule in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 2006;183(4):413‐21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zolkowska 2009
- Zolkowska D, Jain R, Rothman RB, Partilla JS, Roth BL, Setola V, et al. Evidence for the involvement of dopamine transporters in behavioral stimulant effects of modafinil. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2009;329(2):738‐46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Castells 2010
- Castells X, Casas M, Pérez‐Mañá C, Roncero C, Vidal X, Capellà D. Efficacy of psychostimulant drugs for cocaine dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue CD007380. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007380.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


