Abstract
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy have greatly improved the prognosis of patients with metastatic melanoma, but resistance to these therapeutic modalities limits the percentage of patients with long-lasting responses. Accumulating evidence indicates that a persisting subpopulation of melanoma cells contributes to resistance to targeted therapy or immunotherapy, even in patients who initially have a therapeutic response; however, the root mechanism of resistance remains elusive. To address this problem, we propose a new model, in which dynamic fluctuations of protein expression at the single-cell level and longitudinal reshaping of the cellular state at the cell-population level explain the whole process of therapeutic resistance development. Conceptually, we focused on two different pivotal signalling pathways (mediated by microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) and IFNγ) to construct the evolving trajectories of melanoma and described each of the cell states. Accordingly, the development of therapeutic resistance could be divided into three main phases: early survival of cell populations, reversal of senescence, and the establishment of new homeostatic states and development of irreversible resistance. On the basis of existing data, we propose future directions in both translational research and the design of therapeutic strategies that incorporate this emerging understanding of resistance.
Introduction
Melanoma, the most deadly malignancy of the skin, has been associated with steadily decreasing mortality despite the rising incidence of this disease over the past few years1–4. The reason behind this encouraging phenomenon is the greatly improved prognosis of patients with stage IV (metastatic) melanoma owing to the two major therapeutic breakthroughs made within the past 10 years: targeted therapy5–7 and immunotherapy8–10. These two treatment options, however, are not curative for most patients with metastatic melanoma owing to the rapid development of acquired resistance to targeted therapy11 and the predominant innate resistance to immunotherapy8,12.
Accumulating evidence indicates the existence of two subpopulations of melanoma cells that contribute to resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy13–15, which are both characterized by slow cell cycle activity, a de-differentiated state and invasiveness16–19. The first insights into the presence of these cells precede the current era20,21. Accordingly, two different models have been developed to explain the biology of these subpopulations, namely, the cancer stem cell (CSC) model and the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF)-rheostat phenotype switching model.
In the CSC model, melanoma cells are hierarchically organized and can differentiate from CSCs to progenitor cells and then to terminally differentiated melanoma cells without the option of dedifferentiating in the opposite direction22,23. CSCs contribute to multidrug resistance, to cell survival under various stress conditions and to the establishment of a new drug-resistant heterogeneous melanoma cell population24,25. Thus, unique features of CSCs could be targeted to eradicate these cells and overcome resistance to therapies that successfully eliminate the more differentiated cell population. To date, early attempts to target one such marker, CD20, were terminated owing to lack of efficacy (NCT01032122 and NCT01376713).
In the MITF-rheostat model, melanoma cells are horizontally organized and their phenotypes, namely, proliferative with high levels of MITF expression (MITFhi) or invasive with low levels of MITF (MITFlow), are interchangeable26–28. In this model, senescent subclones with extremely high or low levels of MITF expression contribute to therapeutic resistance29. This MITF-centric model does not, however, intrinsically provide an obvious target for drug development.
To reconcile these two models and to direct the development of future therapies, we propose a new model that combines the dynamic oscillation of cell states at the single-cell level with constant reshaping of the cell ensemble at the population level. In this model, the dynamic fluctuation of cell states provides a reservoir of cells for tumour restructuring, which contributes to the development of therapeutic resistance.
Evidence obtained over the past few years supports a crucial role for IFNγ and its related pro-inflammatory cytokines (for example, TNF)30,31 in the therapeutic efficacy but also in the development of resistance to T cell-activating immunotherapies19,32,33. Indeed, cumulative data suggest that both IFNγ and TNF can induce therapy resistance via a persister cell state characterized by dedifferentiation34,35. Thus, we focus on IFNγ–JAK1/2–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1/STAT3 pathway (referred to herein as the IFNγ pathway) as the master regulator of the whole cytokine network36 in order to illustrate the dynamic fluctuating cell-state model in the development of resistance to immunotherapy. Furthermore, we integrate the modulation of melanoma biology by both MITF and IFNγ in a model that explains resistance to the major therapeutic modalities used to treat patients.
Dynamic fluctuation of protein expression
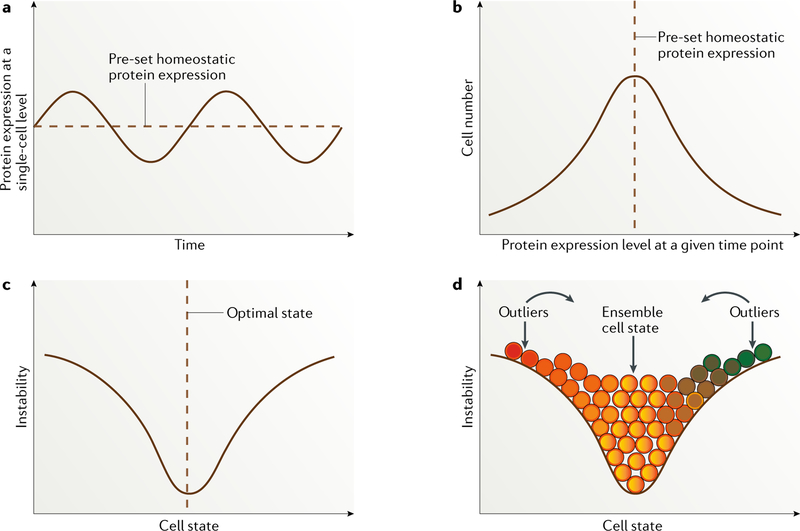
At the single-cell level, the expression of a given protein fluctuates dynamically around a predetermined homeostatic level37 (FIG. 1a), which is probably pre-set according to intrinsic epigenetic mechanisms, gene regulatory networks (a multiplicity of binary regulatory events) and extrinsic factors38. Protein expression levels vary substantially both longitudinally within the same cell (temporal variation) (FIG. 1a) and between different cells at a given time point (spatial variation)39 (FIG. 1b), contributing to the heterogeneity of the entire cell population.
Fig. 1 |. Dynamic fluctuation model.
a | Dynamically fluctuating expression pattern of a given protein longitudinally at the single-cell level. b | Cell distribution based on expression levels of a particular protein, with the vast majority of cells located around the predefined homeostatic protein expression level. c | Cell state defined by a particular protein or a group of correlated proteins entangled within a regulatory pathway, with the majority of cells located at the optimal ensemble state. The more distant from this pre-set state a cell is, the more unstable it is likely to be, with a strong tendency to switch back to the point of homeostatic balance. d | Distribution of cells of different states (depicted in different colours). Continuous colour changes indicate that cell-state transitions occur across a spectrum. Unlike the perfectly symmetric distribution shown, the cell-state curve varies for proteins that define different cell states. Immortalized melanoma cells are probably skewed towards one end of the spectrum in a context-dependent way. Importantly, unstable outliers are in a cell state that differs substantially from the majority of the cell population and are therefore expected to behave differently in a given situation, such as stress.
The reasons contributing to this highly dynamic variation in protein expression could be either stochastic (owing to noise) or deterministic40. Stochastic variability in protein expression can arise from random patterns of gene expression, gene location and randomness in transcription and translation, all resulting from differences in chromatin remodelling, the number of transcription factor binding sites and the availability of cofactors, as well as from intracellular biochemical fluctuations, such as cytoskeleton rearrangements, metabolic state, protein localization and interactions, natural variation in the concentrations of key reactants and post-translational modifications41–44. Variation in protein expression owing to noise alone is thought to be generally small and transient in non-malignant cells45,46 but is higher in malignant cells, especially at metastatic stages37,42,47, indicating that heterogeneity in protein expression is higher in tumour cells than in non-malignant cells. Deterministic protein variation occurs in response to signals from other cellular components of the microenvironment that are mediated by cytokines and cell signalling pathways38,45. The joint contribution of stochastic variation and deterministic variation can result in substantially increased variability in protein levels.
At the cell-population level, the expression of a given protein fits a log-normal distribution (FIG. 1b) and can be influenced by external factors, such as drug exposure43. This perturbed protein state can be transmitted from mother to daughter cells transiently, giving rise to temporally stable non-genetic, phenotypic switching41,44,48; however, stochastic single-cell variation promotes rapid phenotypic divergence between sister cells after several cell divisions41,44,48, leading to either the previous or a new heterogeneous homeostatic state, in an extracellular-dependent way49. The mechanisms driving the tendency towards a particular homeostatic state can include, but are not limited to, cell subclonal cooperativity, evolutionary advantage, cell–cell physical communication, paracrine effects and microenvironment remodelling40.
The state of a cell is mostly determined by the expression levels of different proteins50, which is a continuous quantitative variable. At any given time point, the cellular state is a continuous spectrum as opposed to fitting into artificially defined categories. This concept can be well illustrated by reversing the distribution of variation in protein expression at the cell-population level (FIG. 1b) along the horizontal axis, such that the cell state (determined by the levels of protein expression) is shown as a continuous variable along the x axis, whereas the likelihood of cells to fluctuate between a given temporary cell state and other cell states is plotted along the y axis (FIG. 1c). In this chart, differences in the state of an individual cell are directly related to instability: outlier cells are the most unstable and thus are most likely to revert back to the bulk-population cell state51 (FIG. 1d). Presumably, somatic genetic variances lead to the existence of a different spectrum of expression of given proteins, contributing to the massive heterogeneity of tumour cells.
MITF and resistance to targeted therapy
MITF plays a pivotal role in melanoma
MITF, which has been described to regulate the fluctuation between an invasive and a proliferative phenotype in melanoma cells26–28, illustrates how a single protein can serve as a marker of a particular cell state. Melanomas are derived from transformed melanocytes52, whose primary role is to produce melanin, a pigment that shields adjacent keratinocytes from ultraviolet radiation53. MITF is the master regulator of differentiation of neural crest cells into melanocytes and of the expression of pigmentation-related genes (encoding pigment-producing enzymes and other factors involved in the maturation and export of melanin), such as TYR, TYRP1 and DCT54 (Supplementary Fig. 1). Relative to melanocytes, MITF expression levels are maintained in most melanomas55, amplified in 5–20% and mutated in a subset of familial melanomas56. The results of an in vitro study suggest that MITF can be considered as a lineage-specific oncogene in most melanomas57,58. Pigmentation-related genes have been documented to be recognized by T cells59 and thus contribute, at least in part, to the highly immunogenic nature of melanoma. Accordingly, vitiligo has been observed as a sequela of effective immunotherapy in patients with melanoma60–62.
MITF also maintains the homeostasis of melanoma cells, in which it is a pivotal regulator of cell growth through mechanisms including upregulation of cell cycle-related genes (such as CDK2, CDKN1A and CDKN2A) and cell survival via upregulation of anti-apoptotic genes (such as BCL2 and BCL2A1) (Supplementary Fig. 1). MITF can also inhibit angiogenesis and a proliferative-to-invasive phenotypic switch, both of which are correlated with resistance to targeted therapy63–65. In general, the MITFhi subgroup of melanoma cells is considered to have a proliferative or differentiated phenotype, whereas MITFlow melanoma cells are invasive, dedifferentiated or senescent. Of note, melanoma cells with extremely high levels of MITF expression can lose their proliferative properties and revert to a senescent, paradoxically differentiated, status29,66.
MITF regulation in melanoma progression
Owing to its pivotal roles in melanoma, the expression of MITF is tightly regulated. A detailed description of the MITF-regulating network is beyond the scope of this article but is depicted in Supplementary Fig. 2 and has been described elsewhere29,67,68. Under the influence of extracellular signalling pathways (including those commonly activated by mutations in BRAF, the most commonly activated oncogene in melanoma29,69), natural selection and other factors, this elegant gene regulatory network maintains a predetermined homeostatic level of MITF expression70,71 during melanoma progression; this pre-set level ensures that the phenotype of most melanoma cells is optimally balanced between invasiveness and proliferation, and thus the cells thrive (FIGS 2,3). In this context, exposure to a BRAF-targeted agent can lead to rewiring of the MITF gene regulatory network, affecting its downstream network and leading to a new homeostasis (FIG. 3).
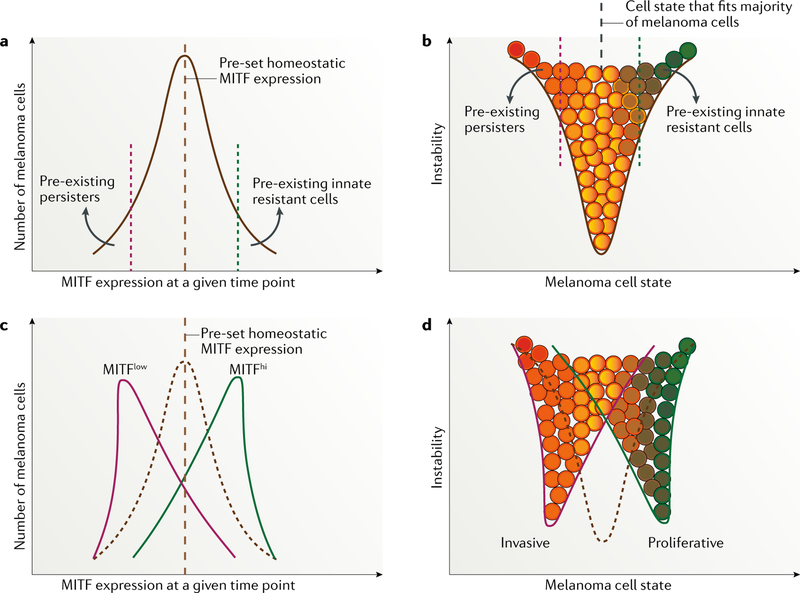
Fig. 2 |. MITF expression and phenotype switching in melanoma before and after treatment with targeted agents.
a,b | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) expression and melanoma cell-state pattern before exposure to targeted therapy, representing a unimodal distribution of MITF expression in the same population of melanoma cells. Of note, variations in predefined points exist between melanoma cell lines, mouse models and patient samples 72,225 owing to differences in melanoma initiation and in microenvironment selective pressure. c,d | Alterations in MITF expression and variation in cell state after starting therapy.
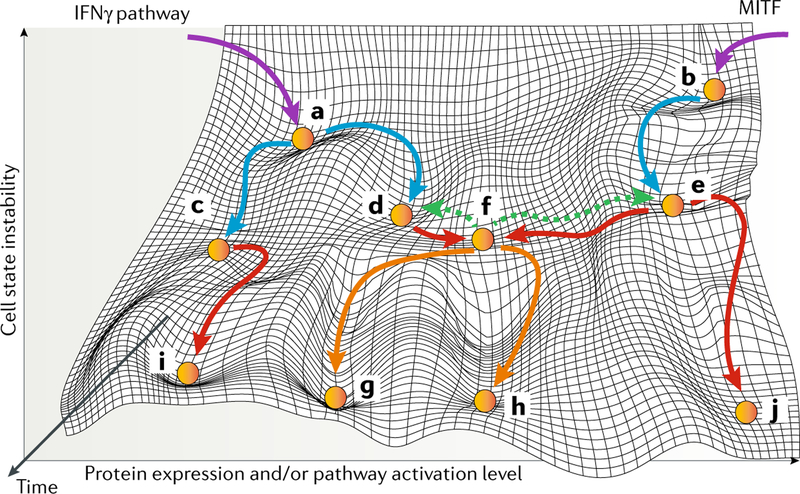
Fig. 3 |. Reshaping of cell states at different stages in melanoma.
The initiation, progression and development of initial and secondary therapy resistance are designated with purple, blue, red and orange arrows, respectively. Green dashed arrows demonstrate the complete reversibility of a cellular state soon after therapy initiation. Melanoma initiation can occur through an IFNγ-dependent and immunogenicity-dependent mechanism (part a) or a microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF)-related mechanism (part b). Through immune editing, melanoma cells bifurcate into different states characterized by IFNγ hypoactivation and low immunogenicity (part c) and IFNγ hyperactivation and high immunogenicity (part d). MITF-related cell state is maintained, with inter-individual variations, during disease progression (part e). A persister cell state is characterized by IFNγ hyperactivation, high immunogenicity, low expression of MITF and an invasive phenotype that contribute to resistance to both targeted agents and immunotherapy (part f). This persister state is not stable and will reverse back to that seen in part d or part e if therapy is withdrawn or, otherwise, through the accumulation of both epigenetic and genetic aberrations, will evolve into more stable states (parts g,h). Epigenetic and genetic alterations can lead to a cell state of IFNγ hypoactivation and low immunogenicity (part i) that contributes to resistance to immunotherapy and to a state with extremely high MITF expression and a senescent phenotype (part j) that contributes to resistance to targeted agents.
Development of resistance to targeted therapy
The conflicting CSC22,23 and MITF-rheostat phenotype-switching29 models were developed on the basis of bulk-cell analyses that reflected the ensemble cell phenotype and behaviour or averaged results of whole melanoma cell populations72, which differ from those of any individual cell73 (FIG. 1d). If we instead consider resistance from the single-cell perspective, these two theories can be reconciled.
Single-cell RNA sequencing data indicate that MITF expression levels vary continuously from cell to cell (spatial continuum)13, indicating the existence of a continuous spectrum of cells with different states at a given time point. In the absence of therapy, some melanomas have a skewed cell population in terms of MITF expression levels, generally with a predominance of MITFhi cells. The expression of MITF within a given single cell also follows the dynamic fluctuation model and varies longitudinally owing to either stochastic74 or deterministic mechanisms. In the entire melanoma cell population, owing to the exquisite gene regulatory network (Supplementary Fig. 2), MITF expression levels vary across a spectrum13 but are maintained within a narrow dynamic range in the vast majority of melanoma cells (FIG. 2a). Meanwhile, even before the initiation of therapy, stochastic or deterministic factors (extracellular signals or intracellular genetic alterations) enable melanoma cells to establish outlier phenotypes with extremely high or low expression of MITF, which are associated with cellular behaviours that differ from those of the bulk melanoma cell population and serve as reservoirs of fitness-enhanced cells that can resist eventual exogenous stress or adverse impacts, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapy14,29,45,46,75–79 (FIG. 2a,b). MITF levels have to be maintained at a certain level in order for melanoma cells to proliferate and, thus, the outlier cells are marked by senescence. Noticeably, owing to its complex regulating network, MITF can be autoregulated by counteracting extrinsic noise and return to homeostasis after induced stress46,80,81.
Heterogeneity in MITF expression exists even within outlier cells13,76, the most clear example being MITFlow cells, which generally have an invasive phenotype (persister cells). Historically, some of these persister cells were qualified as CSCs owing to high expression levels of certain CSC markers82–84. The expression of CSC markers tends to fit a bimodal log-normal distribution reflecting a population of stem-like cells with high expression of CSC markers and a different population of highly dedifferentiated cells that tend to express barely any known CSC or mature-melanocyte lineage markers34,66,85. Similar to MITF, the expression of CSC markers dynamically fluctuates, and thus CSCs do not constitute a static clone with hard-wired differences determined by unique somatic genetic alterations48 but rather reflect transcriptional states combined with underlying genetic heterogeneity that persist over time — that is, CSCs comprise a dynamic population of different individual cells at different time points86. This heterogeneity provides an explanation for the failure to prevent resistance in preclinical studies in which known CSC biomarkers (such as NGFR or KDM5B) were silenced17, along with other fruitless efforts to target CSCs in clinical studies in patients with melanoma (NCT01032122 and NCT01376713).
In general, spatial heterogeneity provides cell diversity that facilitates Darwinian selection during melanoma development and enables different cells to react differently to Lamarckian induction. Owing to longitudinal oscillation in the levels of different proteins, which contributes to the constant temporal fluctuation of cell states at the single-cell level39, this process is highly dynamic. As a result, even within the same cell subgroup, individual cells will have different states at different time points. Treatment with a targeted agent, for example, a MAPK inhibitor, will reset the MITF homeostatic point, leading to a MITF expression-defined cell distribution that shifts either towards lower levels, higher levels or both directions in a context-dependent manner87 (FIGS 2,3). The mechanisms driving this shift in MITF expression include Lamarckian induction (owing to BRAF being an upstream regulator of MITF; Supplementary Fig. 2) and/or Darwinian selection88,89. At the level of the whole-cell population, a phenotype switch takes place (FIG. 2c,d).
At the single-cell level, the level of MITF expression is an indicator of MAPK pathway dependency. Median levels of MITF expression indicate pathway dependency, whereas either extremely high or low levels are associated with resistance to MAPK inhibitors29,90,91. The MITFextremelyhi subset of melanoma cells is the most differentiated and least addicted to MAPK signalling and is, therefore, associated with intrinsic resistance to MAPK inhibitors, whereas the MITFlow population comprises dedifferentiated, invasive and apoptosis-resistant cells, programmed to be persisters capable of surviving harsh environmental conditions, such as hypoxia, a lack of nutrients, targeted therapy and/or immunotherapy17,75,92. A shift in the distribution of MITF expression levels results in an expansion of the therapy-resistant outlier populations (FIG. 2a,b versus FIG. 2c,d). During treatment with targeted therapy, those surviving outliers serve as a reservoir cell population in which de novo epigenetic and genetic aberrations lead to the development of irreversible resistance, ultimately giving rise to a new melanoma cell population resistant to targeted therapy92,93 (FIG. 3j,h). The results of preclinical studies suggest that even the persistence of only one single cell94 after different types of therapy can eventually give rise to a heterogeneous population and establish a new homeostasis93.
IFNγ and resistance to immunotherapy
IFNγ network in melanoma
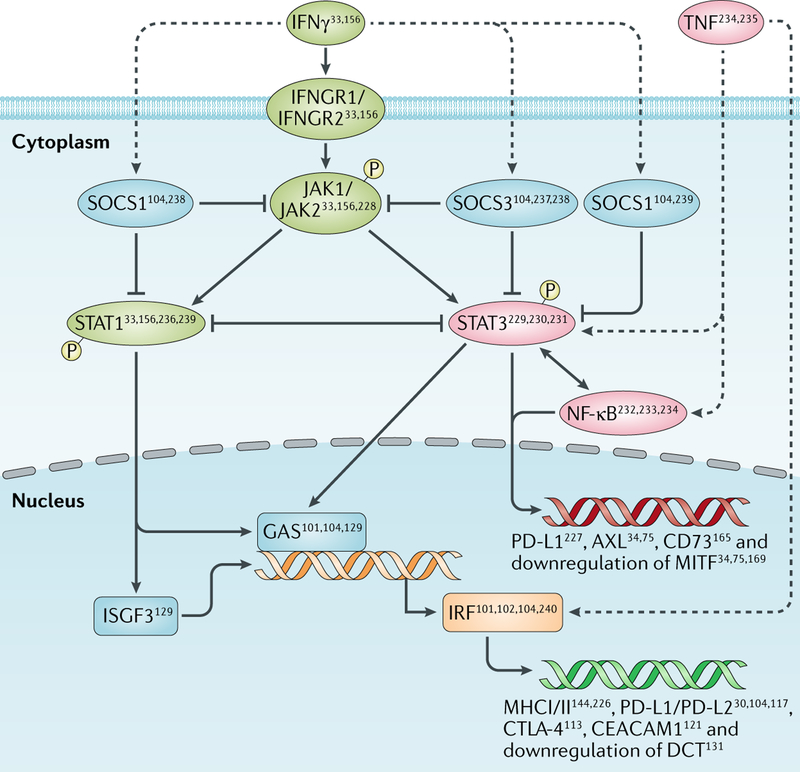
The crucial components of IFNγ signalling are context-dependent, varying greatly between different cancer types and between different mutational contexts even within the same tumour type95. Herein, we focus solely on melanoma cells and on a few elements of the JAK–STAT signalling network (IFNγ–JAK1/JAK2–STAT1/STAT3 in this article), which are essentially activated by IFNγ and TNF, both of which have been shown to be simultaneously released by immunotherapy-reinvigorated T cells31,96. A detailed description of IFNγ pathway components in melanoma is beyond the scope of this article but has been depicted in FIG. 4 (REFS97,98).
Fig. 4 |. IFNγ–JAK1/JAK2–STAT1/STAT3 pathway in melanoma.
Dashed lines represent positive regulation with no specific regulatory mechanism elucidated yet. Examples of regulated downstream molecules are provided. CEACAM1, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; GAS, growth arrest-specific protein; IFNGR, IFNγ receptor; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; ISGF, interferon-stimulated transcription factor; MITF, microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; P, phosphorylated molecule; PD-L, programmed cell death 1 ligand; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signalling; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.
IFNγ and immune response of melanoma
The IFNγ pathway is centrally involved in the regulation of diverse biological functions of melanoma cells, which could be roughly divided into immune-pertinent aspects (such as antigen processing and presentation, cytokine production and immune-checkpoint molecule expression) and those concerning the cell-autonomous functions of melanoma cells (for example, cell proliferation, growth, apoptosis and differentiation). IFNγ has long been considered as the primary mediator of the immune response to melanoma cells owing to its capacity to increase the expression of proteins involved in the antigen-processing machinery (such as components of the immunoproteasome99, MHC class Ia molecules, antigen peptide transporter 1 (TAP1), TAP2, several IFNγ-inducible proteasome subunits, tapasin and β2-microglobulin100–104), as well as pro-inflammatory cytokines that attract T cells, such as CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 (REF.100).
Counteracting the immune response
As the key regulator of immune response in melanoma, an important intrinsic function of IFNγ is to prevent severe immune overactivation by exerting immune inhibitory functions99. One of the inhibitory mechanisms regulated by the IFNγ pathway is the upregulation of non-classical MHC class Ib molecules105,106, most notably HLA-E and HLA-G, which inhibit both natural killer (NK) cells and T cells107. The expression of MHC class II molecules106,108–110, which are negatively correlated with melanoma cell differentiation111 and can protect melanoma cells from apoptosis through a lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3)-dependent mechanism112, is also upregulated upon IFNγ signalling. Very high levels of MHC class Ia molecules could also impair immune responses. In the B16 mouse model, the elimination of melanoma cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) targeting tyrosinase-related protein 2 is impaired in response to IFNγ-dependent induction of high levels of noncognate MHC class I molecules, which probably compete with cognate MHC molecules31. The IFNγ pathway also has an immunosuppressive role through the upregulation of immune-checkpoint molecules including cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4)105,113, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1)114–119, PD-L2 (REF.104), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)114,120, carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1)121 and possibly TIM3 (also known as HAVCR2) and LAG3 (REF.113). A third inhibitory mechanism involves STAT3-dependent inhibition of the production and sensing of inflammatory signals in melanoma cells, leading to the impairment of dendritic cell maturation122.
Cell-autonomous functions in melanoma
In most contexts, IFNγ exerts an antiproliferative effect on melanoma cells100,101,110,111,123–126 by inducing G1 cell cycle arrest through mechanisms related to the regulation of p27Kip1 (also known as CDKN1B), CDK6, cyclin A, cyclin E and miR-29 family members127–129. IFNγ-induced cell cycle arrest has long been known to be associated with increased invasiveness of melanoma cells. Early data showed that IFNγ successfully impairs the proliferation and increases the metastatic ability of B16 mouse melanoma cells124; this process was positively correlated with in vitro invasiveness27,130 and with downregulation of MITF and several downstream melanocyte differentiation antigens131 and leads to impaired recognition of melanoma cells by CTLs110,111,132,133. The mechanisms underlying this process include the inhibition of canonical WNT signalling and the activation of the JUN and p38 pathways132 (probably through activation of STAT1)134. These changes resemble those observed during the generation of persister cells in response to targeted therapy135.
Clinical evidence confirming the effect of IFNγ on the metastatic potential of melanoma cells came from a randomized phase III clinical trial of IFNγ as the adjuvant treatment of patients with high-risk melanoma, who had less favourable disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival outcomes than patients in the observation arm136. Correlative evidence was reported years later, indicating that the presence of detectable IFNγ levels in plasma was an independent prognostic factor of shorter DFS137.
IFNγ pathway reshaping in melanoma
IFNγ has important roles in melanomagenesis138, especially with regard to pro-survival and immune-evasion effects involved in ultraviolet radiation-induced melanomagenesis105,139. Thus, IFNγ pathway signalling needs to be maintained at a certain level in the vast majority of initially activated melanocytes and newly transformed melanoma cells (FIG. 3). Subsequently, a nascent melanoma undergoes constant interaction with the host immune system, which promotes multiple processes that favour immune escape during evolution to a clinically evident melanoma140,141.
As discussed, IFNγ acts as a double-edged sword in melanoma, and thus maximal melanoma fitness would favour the presence of either low or high levels of activity in order for melanoma cells to evade recognition and elimination by T cells. In any particular melanoma, the presence of one or both subgroups (hypoactivated and hyperactivated IFNγ pathway) and the dominance of one of them are context-dependent. Very low or no activation of the IFNγ pathway leads to a lack of MHC molecules and pro-inflammatory cytokines, favouring NK cell recognition while providing melanoma cells opportunities to evade T cell surveillance. Conversely, very high activation levels of this pathway lead to overexpression of both classical and non-classical MHC molecules, upregulation of immune checkpoints and melanoma cell dedifferentiation. Both situations (FIG. 3c,d) result in a lack of immune response, which provides survival fitness in the face of host immune surveillance99,126,142–147. This immune selection process leads to the bifurcation of the distribution curve of IFNγ activation status in melanoma cells148 (FIG. 3c,d).
Development of resistance to immunotherapy
Similar to the correlation between the bifurcation of MITF expression and resistance to targeted therapy, melanoma cells resistant to immunotherapy can be divided into two subcategories. The first one is associated with hypoactivation of the IFNγ pathway149,150, which thereby has a lack of immunogenicity that makes it innately resistant to immunotherapy. The second one has hyperactivation of the IFNγ pathway, which overlaps with a dedifferentiated and invasive phenotype; this population reflects a stress-induced persister status15,35. As with targeted therapy, resistance to immunotherapy is caused by both Darwinian selection and Lamarckian induction19,151–153. Overall, Darwinian selection primarily contributes to the enrichment of the IFNγ hypoactivation subgroup, whereas Lamarckian induction favours the hyperactivation state.
The cell subgroup with IFNγ hypoactivation can be divided into two subcategories on the basis of responsiveness to IFNγ released by T cells reinvigorated by immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI). The IFNγ-responsive subpopulation, in which ICI-induced activation of IFNγ increases immunogenicity, is recognized by T cells and then eliminated. The IFNγ-non-responsive subpopulation, which has previously been reported as being characterized by homozygous loss-of-function mutations in JAK1 and JAK2, genomic loss of IFNGR1 and/or IFNGR2 and amplification of SOCS1, is present before exposure to immunotherapy33,154–156, survives and is, therefore, enriched after initiation of therapy. In cells with genetic loss-of-function of IFNγ resulting in hypoactivation, the lack of reactive PD-L1 expression prevents ICI from activating T cells at all100. In addition, the lack of expression of MHC class I further enables melanoma cells to evade recognition by T cells33,101 and impairs T cell infiltration into melanomas, which is a prerequisite for a response to the currently available immunotherapies100. Importantly, the IFNγ pathway can also be silenced through epigenetic modifications, providing a rationale to explore combinations of epigenetic modulators with immunotherapy155,157. During the enrichment of melanoma cells with non-responsive hypoactive IFNγ signalling, both genetic and epigenetic aberrations continue to accumulate owing to chromosomal instability in melanoma cells, leading to a new homeostatic cell state (FIG. 3g). Of note, the mechanism underlying hypoactivation of IFNγ pathway that enables melanoma cells to escape immunotherapy aligns with the immunological roles of the IFNγ pathway; whether this subgroup of melanoma cells is proliferative and MITFhi (as anticipated) remains to be determined.
The mechanism underlying effective ICI involves the use of immune checkpoints against immune clearance in melanomas with a hyperactivated IFNγ pathway; the blockade of these checkpoints reinvigorates certain groups of T cells to initiate an immune response against melanoma. As described, treatment with anti-programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) antibodies induces the expansion of CD8+ T cell populations with an exhausted phenotype, whereas anti-CTLA-4 treatment induces an additional expansion of an ICOS+ T helper 1 (TH1) cell-like CD4+ (activated) T cell population158. Meanwhile, immunosuppressive regulatory T (Treg) cells are also inhibited primarily by CTLA-4 blockade159–161. The activated effector T cells release large amounts of IFNγ and TNF96,156,162, inducing apoptosis, antigen processing and presentation, secretion of various chemokines and upregulation of PD-L1 and/or PD-L2 (REF.104), which can then be neutralized by ICI155, further facilitating melanoma cell clearance. Accumulating preclinical evidence has shown that, in some scenarios, this additional release of IFNγ and TNF (which has stress-related effects101) will push the already IFNγ-hyperactivated cells into more extreme states, thus leading to the induction of a persister status in melanoma cells152,155,163.
Early evidence suggested that recombinant IFNγ could stimulate shedding and suppress expression of nevus-associated antigens164. Further evidence came from adoptive cell transfer strategies targeting melanocytic differentiation antigens (MART-1 or PMEL (commonly referred to as gp100)), which predominantly inhibited tumour growth via cytostatic effects induced by increased secretion of IFNγ and TNF (REFS35,127). An inflammation-associated reversible, invasive, senescence-like dedifferentiation phenotype was induced by in vitro treatment with IFNγ and TNF (REF.34), together with the upregulation of NGFR and genes associated with an invasive phenotype, such as AXL, JUN, WNT5A and EZH2 (REFS127,165–170). Similar phenomena have been reported in the context of resistance to ICI160,168,171. Data from studies reported over the past few years reinforce this phenomenon by showing that inhibition of JAK1/JAK2 by ruxolitinib overcomes resistance of immunotherapy in a mouse model of melanoma155.
Three phases of therapeutic resistance
We propose a model in which therapeutic resistance to both targeted agents and ICI comprises three different phases: early survival of cells with innate resistance or induced persister cells, reversal of senescence and, finally, establishment of irreversible resistance. These three phases overlap with the dynamics of the bulk-cell population, yet the single-cell characteristics are enriched — and will become dominant — over time. On the basis of current knowledge, drawing a clear boundary between different resistance phases is difficult, in part owing to the very limited amount of tumour samples obtained throughout the course of therapy and the paucity of studies in animal models using single-cell fate mapping technologies. A deeper characterization of these resistance phases would facilitate in vivo monitoring in animals and patients, an understanding of the influence of different cell populations on one another and mechanistic studies aimed at identifying novel vulnerabilities.
Phase 1: early survival
Two subgroups of melanoma cells resistant to targeted therapy and immunotherapy, respectively, exist: innate resistant ones, namely, MITFextremelyhi cells that are resistant to targeted therapy and cells with IFNγ hypoactivation that are resistant to immunotherapy (FIG. 3i,j); in addition, two groups of induced persisters that express senescence markers172–175 exist: MITFlow cells that are resistant to targeted therapy and cells with IFNγ hyperactivation that are resistant to immunotherapy34,77 (FIG. 3f).
During the early survival phase, which lasts from days to weeks in vitro, no new epigenetic or genetic aberrations occur17,176. Instead, this phase is mainly driven by dynamically fluctuating gene and protein expression in both persisters and cells with innate resistance. Accordingly, drug resistance in persisters has been shown to be completely reversible. Indeed, a transiently pre-resistant cell state matching our definition of persister was proved to exist in studies that used Luria–Delbrück fluctuation analysis176, but whether innate resistant cells can be shifted towards drug-sensitive states remains to be determined.
To target cell subpopulations with innate resistance to either targeted therapy or immunotherapy, switching to another therapeutic modality is a reasonable choice. For persisters, however, accumulating data suggest that this cellular state is a pre-programmed senescent state that enables cells to survive multiple stresses including hypoxia177, oxidative stress178, nutrient deprivation179, inflammation180, radiotherapy181, chemotherapy182,183, targeted therapy173,184 and T cell-activating immunotherapy152, thus contributing to cross-resistance to different therapies. A detailed description of the rewiring of key signal transduction pathways in persisters is beyond the scope of this article; briefly, the main characteristics of this senescent persister subpopulation are the activation of MAPK bypass pathways34 as well as induction of an inflammatory network. More specifically, the activation of JAK1–STAT3 is commonly observed in persister cells and leads to the further upregulation of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and other bypass signalling pathways34,64, as well as the activation of multiple pro-inflammatory molecules (including TNF (REF.185), NF-κB, TGFβ and IFNγ) with MITF-inhibitory effects (Supplementary Fig. 2) — thus, this population has a dedifferentiated, MITFlow, invasive phenotype.
During the early survival phase, the persister cell population does not remain constant but expands over time through induced subpopulation-specific secretome changes, which stimulate cell outgrowth and dissemination186 by turning adjacent melanoma cells into persisters187. The mutual positive feedback between melanoma cells, particularly mediated by the secretome of persister cells, and other cells in the tumour microenvironment (TME)188,189 is also important. The paradoxical MAPK inhibitor-induced activation of tumour-promoting cellular components within the TME190–192 reshapes the TME into a resistance-promoting niche; in turn, this niche induces drug resistance by activating MAPK bypass pathways in melanoma cells (such as PI3K–AKT193 or STAT3 (REF.187)) or by releasing supportive cytokines (such as IL-1β, IL-6 and CCL2)194–197. This process facilitates the existence of spatially clustered resistant persister cell populations, which serve as a cell reservoir for the future development of clones with irreversible therapeutic resistance. Although less dominant in the resistant subpopulation of melanoma cells in patient samples obtained early after initiation of targeted therapy198, persisters become more prevalent in samples obtained during clinical disease progression79.
To summarize, after the initial hit of targeted therapy or immunotherapy, three different subgroups of melanoma cells can remain: MITFextremelyhi cells with innate resistance to targeted therapy, cells with IFNγ hypoactivation and innate resistance to immunotherapy and MITFlow persisters with IFNγ hyperactivation (FIG. 3), although only one or two subgroups might exist within a given tumour. As the external stress of therapy persists, these three different subgroups gradually enter the second phase of resistance development.
Phase 2: reversal of senescence
In this section, we focus on MITF to depict the changes that persister cells undergo during the second phase of therapy resistance because MITF-related epigenetic and genetic rewiring has been better described than IFNγ-related mechanisms. Similar phenomena could be depicted by describing the activation of the IFNγ pathway in response to immunotherapy but are beyond the scope of this article.
The MITFextremelyhi subgroup, which remains senescent during phase 1 (REF.199), will similarly develop reactivation of the MAPK pathway to restore proliferation during phase 2 (REF.34). As discussed, MITF levels have a tendency to revert back to their heterogeneous homeostatic range. In this phase, after a persistent exposure to MAPK inhibitors, de novo epigenetic and genetic aberrations start to occur and accumulate in a time-dependent manner14,79, enabled by a drug tolerance-facilitating TME191 and leading to a rewiring of the MITF-regulating system, which in turn gradually leads to a new MITF homeostatic status. As MITF expression shifts from the extremes back towards a new homeostatic point, melanoma cells with a senescent phenotype gradually subside and are substituted by a new subgroup with a proliferative phenotype — these changes are associated with the phenomenon of clinical progression79. Of note, senescent persisters and/or MITFextremelyhi cells do not disappear but rather remain present in small numbers.
This phase is the transitory period of time that leads to the establishment of a new homeostasis (phase 3). In terms of targeted therapy, in vitro, this phase generally starts after several weeks of exposure to MAPK inhibitors and probably after a longer time in the setting of immunotherapy, but no clear end time boundary exists. In general, phase 2 is highly dynamic, and persister-related resistance is mostly reversible in the early stage200 and mostly irreversible at later stages.
Phase 3: new homeostasis
In phase 3 of our model of drug resistance, after months to years of exposure to MAPK inhibitors or T cell-activating immunotherapy, the accumulation of both epigenetic and genetic aberrations and the modulation of the TME and melanoma cell secretome186 finally result in the establishment of a new homeostasis and of irreversible resistance, which has been shown in vitro to be associated with a high degree of tumour heterogeneity201. One of the most conspicuous features of heterogeneity is that persisters induced by targeted therapy and immunotherapy seem to follow different trajectories (FIG. 3g,h). Specifically, patients with disease progression on targeted therapies tend to have less durable remissions and more prompt disease progression than those receiving immunotherapy, some of whom gain durable benefit after reaching a maximal response202. This difference might result from the persistent immune-activating effect of immunotherapy or, rather, from the reshaping of the TME, which probably reduced the fitness of persisters cells, limiting their ability to switch towards a proliferative phenotype by accumulating both genetic and epigenetic aberrations. Thus, although the persister subgroups induced by targeted therapy and immunotherapy initially overlap (as indicated by dedifferentiation, a mesenchymal phenotype, angiogenic features, interferon and inflammatory features and increased expression of CSC biomarkers, immune checkpoints and multiple RTKs)15,79,88,166,203–207, the trajectories of development of further resistance eventually separate. In the clinic, different progression patterns can be observed when comparing the Kaplan–Meier curves of both progression-free survival and overall survival of patients treated with targeted therapy208 or immunotherapy209, implying that the persister stage might be more vulnerable to therapeutic intervention than that of cells attaining irreversible resistance, which have higher heterogeneity.
In phase 3, some melanoma cells become addicted to MAPK inhibitors and, thus, drug withdrawal provides a new stress204,210,211, which can lead to the inhibition of cell growth and proliferation. This rationale supports the discontinuation of and rechallenge with targeted therapies in patients with melanoma after weeks or months of therapy; however, a concern that remains with this approach is that the increased stress of treatment discontinuation could enrich for persistent cells with higher levels of heterogeneity212, diminishing the responsiveness of the remaining cell population to drug rechallenge. Indeed, therapeutic rechallenge following the development of acquired resistance and a treatment break has been shown to lead to responses of lower magnitude and shorter duration than those reported for the initial treatment213, and thus this strategy should be generally reserved for patients with disease progression on targeted therapy in which irreversible cell states are likely to predominate.
Whether some melanoma cells become addicted to immunotherapy-enhanced expression of both IFNγ and TNF remains to be determined. Preliminary clinical evidence indicates that a substantial group of patients remain free from disease progression after immunotherapy discontinuation and for long periods of time, which might result from the near complete elimination of melanoma cells by immunotherapy. Other potential explanations for this observation include the known long half-life of immunotherapy agents, the persistent pharmacodynamic effects long after clearance of these agents (for example, mediated by memory T cells) and remodelling of the TME that limits the proliferation of melanoma cells, among others.
Future directions
The model we have proposed was developed on the basis of observations made in vitro, although attempts have been made to find analogy between the distinct three phases in mouse models and patient samples79. These attempts have been limited, however, by the overlapping epigenomic and genomic signatures observed during early survival, reversal of senescence and irreversible resistance, as well as the challenge of obtaining patient samples at time points in relation to the start of therapy when tumour volumes are at a minimum.
Translational research
Correlation between MITF and IFNγ pathway.
One of the most intriguing questions for which answers remain elusive is the direct correlation between the MITF network, the most clearly depicted network in development of resistance to targeted therapy, and IFNγ, its counterpart in resistance to immunotherapy. To date, most of the correlative evidence has been generated indirectly by analysing the properties of persister cells. Whether mechanistic intersections exist between the MITF network and immunotherapy resistance, beyond the involvement of pigmentation-related antigens, remains to be determined. The effect of the IFNγ pathway on the MITF network (excluding regulation of the persister state) is also elusive. Understanding these interactions will be key to addressing the overlap between cells with innate resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Ongoing single-cell RNA sequencing analyses of patients with ICI-treated melanoma, in particular, of tumour cells, should provide the required resolution to establish more direct links between IFNγ and MITF.
Description of different phases of development of therapeutic resistance.
One of the conundrums regarding longitudinal surveillance during therapy with targeted agents or immunotherapy is the failure to correlate different observations from preclinical studies using in vitro assays, animals models and patient samples. The tumour specimens described in the vast majority of published on-therapy analyses are collected in the first few weeks of treatment or at the time of clinical progression. This approach relates to the fact that patients with a clinical response have tumours that have regressed compared with baseline measurements and are less feasibly and safely biopsied for research purposes. To circumvent these limitations, some researchers have tried to describe the evolving phenotypes over longer periods of drug exposure using both in vitro and mouse models66,88. The characteristics and potential therapeutic vulnerabilities of melanomas for which early on-treatment samples have been obtained (when patients are in the midst of a clinical response) cannot be established. Similarly, we do not know what impedes infiltrating CD8+ cells (that have effectively contributed to a response in the case of targeted therapy or directly mediated this response in the case of immunotherapies) from being able to eliminate persister cells. Additional challenges face the use of peripheral blood samples to gain these insights. In the near future, the development of more human-relevant, immune-competent mouse models might provide new insights on the dynamics of persisters and the possibility of tracking their resistant biology in peripheral blood. Studies should be carried out with the aim of monitoring cell state switching as well as addressing uncertainties regarding the optimal time points of assessment (for example, 1–2 days, 1–2 weeks, 1–2 months or later time points after initiation of therapy with MAPK inhibitors). Samples from different time points might reflect very different disease biology: simultaneous elimination of sensitive cells and enrichment of resistant populations.
Epigenetic and genetic aberrations are accumulated during long-term exposure to immunotherapy, leading to irreversible resistance and, thus, whether cell subgroups with different IFNγ activation states have a tendency to acquire particular aberrations needs to be understood. Additionally, establishing the relationship between MITF, IFNγ and markers of the MITF and IFNγ-defined states in tumour cells with TME-related factors (such as shed RTKs or exosomes) would facilitate monitoring of patients and guide therapeutic interventions as relevant changes in cell state emerge. Lastly, further characterization of cells with innate resistance to both targeted therapy and immunotherapy is needed to elucidate novel therapeutic strategies.
Therapeutic strategy
Implications from a dynamic fluctuation model.
According to our dynamic fluctuation model, two properties of melanoma cells are important: heterogeneity and the existence of distinct homeostatic states. Certain therapeutic strategies need to be considered with caution owing to the potential shortcoming of increasing particular resistance mechanisms. A continuous oscillation in drug exposure with standard doses of agents such as MAPK inhibitors might increase genomic complexity during ‘drug holidays’ (interruptions of treatment lasting days or weeks for reasons other than toxicity management). This strategy is distinct from pulsatile dosing strategies, in which doses much higher than those that can be tolerated continuously are administered. If pulsatile dosing results in more tumour cell elimination, an inherent benefit will be the restriction of the survivor cell subpopulation. In addition, strategies deployed against minority cell populations are unlikely to generate clinical, radiographic evidence of single-agent efficacy; for this reason, therapies targeting CSC biomarkers are not efficacious as monotherapies. Melanoma CSCs, however, must not be considered a static subpopulation and might not be amenable to elimination; instead, prevention of the transition from tumour cell to CSC might be more advantageous.
We consider several strategies to be supported by the emerging understanding of the dynamics of therapy resistance. First, to counteract heterogeneity, the combination of targeted agents or immunotherapies with epigenetic modulators, stress response inhibitors or metabolic agents (for example, inhibitors of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator 1α (PGC-1α), steroid hormone receptor-α (ERRα) or oxidative phosphorylation) warrants investigation38,214,215. This higher-order combination therapy might enable a thorough eradication of both subpopulations with innate resistance and persisters at very early stages of therapy, limiting the potential of these cells to serve as reservoirs for future epigenetic and genetic aberrations.
A second potential strategy is predicated on exploiting tumour heterogeneity using a dosing schedule for targeted agents that maintains therapy-sensitive cells within the melanoma cell population, with the rationale that these cells will compete with and prevent the outgrowth of certain resistant subpopulations216–218. On the other hand, the possibility that cooperation might occur between different subgroups of cells40,186,219 is a concern and needs to be further investigated. These competing hypotheses highlight the dire need for better monitoring of the resistant cell states and their evolution.
Third, the ability of cells to shift between or remain in certain homeostatic states might be amenable to disruption. A key element of this strategy is to prevent MITF and IFNγ expression from reverting back to the predefined homeostatic or activation status set points, such that persisters and/or innate resistant cells remain in cell cycle arrest. To achieve this goal, novel drug combinations are needed; agents that target cell cycle would seem to be leading candidates220 and should be explored on the backbone of targeted therapies and immunotherapies. Of note, CDK4 and/or CDK6 inhibitors are available, whereas CDK2 inhibitors remain a less well-developed drug class.
Implications of melanoma evolution.
Different tumour cell states arise during melanoma progression and the subsequent development of therapeutic resistance (FIG. 3). Those cell states remain heterogeneous but can be distinguished on the basis of certain properties. By depicting cell states and their properties more clearly, new therapeutic strategies can be devised.
In terms of therapeutic resistance, the longer the duration of therapeutic exposure, the greater the degree of tumour heterogeneity (FIG. 3f–j). This observation implies that combination therapy regimens, applied after a short initial period of single-agent targeted therapy or immunotherapy, might be able to eradicate cells with innate resistance or persister cells. The collection of serial biopsy samples at an early on-treatment time point will help discriminate which cell subpopulations dominate early during therapeutic resistance and which combination regimens should be prioritized.
The currently available data indicate that one of the most promising strategies is to target persister cells221,222: owing to the heterogeneous epigenetic and genetic aberrations accumulated during both the reversal of senescence and irreversible resistance phases, the persister cell phase seems to be more vulnerable to intervention194. Among direct targeting strategies that should be considered, JAK inhibitors, metabolic modulators, multiple RTK inhibitors and epigenetic modulators222 (to block phenotype switching) have promise; these strategies aim to prevent or reverse the epithelial–mesenchymal transition221. Nevertheless, caution should be taken regarding combination therapies, especially those involving candidates that might have a negative impact on immune system. Indeed, a pilot clinical trial of combination therapy with a JAK inhibitor and an anti-PD-1 antibody was closed early owing to a lack of differences in intratumoural T cell subsets (CD8+ T cells and Treg cells) and no effect on tumour cells despite a statistically significant reduction in peripheral T cell activation223.
Reshaping of the tumour microenvironment.
Persister cells that survive targeted therapy or immunotherapy follow different evolutionary trajectories, with a more rapid and widespread outbreak described for targeted therapy than for immunotherapy. This behaviour might relate to the different TME-modulating effects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Thus, when considering the addition of an agent to a targeted therapy or immunotherapy backbone, we need to consider and assess its effects on the cellular components of the TME — both tumour-related and immune-related.
A second TME-related aspect worth considering is treatment with agents that remodel the either non-cellular or cellular components of the TME. These agents include those that can limit the invasive behaviour of the persister cells by inhibiting extracellular proteolytic proteins or that can make the TME more hostile to melanoma cells by inhibiting angiogenesis or reducing the accessibility of essential nutrients to melanoma cells. Another category includes agents that eliminate immune inhibitory cells. Examples include the depletion of melanoma-promoting B cells using an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody188,224 (NCT01307267) and the further release T cells or other immune stimulatory cellular components from immune inhibitory signals by combining anti-PD-1 antibodies with other immune-checkpoint inhibitors (such as anti-TIM3 antibodies), antagonists of other immune inhibitory signals (such as TGFβ inhibitors) or T cell agonists.
Conclusions
The advances in melanoma therapy have resulted in the current combinations of two agents from the same therapeutic modality. Ongoing investigations seek to build higher-order combination strategies on a backbone of targeted therapy or immunotherapy. Beyond clinical end points, the mechanisms driving resistance in each individual patient need to be ascertained with great precision in order to understand whether they will be address by the novel therapeutic approaches and thus develop a precision medicine-based principle driving the subsequent development and application of novel regimens. Our improving understanding of melanoma cells, at both the single-cell level and the cell-subpopulation level, is crucial to achieving this goal.
Supplementary Material
Key points.
In any particular cell, the expression of a given protein fluctuates dynamically around a pre-set homeostatic level, contributing to temporal heterogeneity. At the cell-population level, the expression of a given protein fits a log-normal distribution, contributing to spatial heterogeneity.
Cell state is mostly determined by the expression levels of different proteins, which is a continuous quantitative variable and can be perturbed by extrinsic stress, such as drug exposure.
The development of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy can be divided into three phases, namely, early survival (including persister cells and innate resistant cells), reversal of senescence and new homeostasis; along these phases, resistance gradually changes from reversible to irreversible.
The persister cell subpopulation is programmed to tolerate cell death and capable of surviving harsh environmental conditions, such as hypoxia, lack of nutrients and exposure to targeted therapy and/or immunotherapy.
Future therapeutic developments should take into account the highly dynamic heterogeneity and the existence of distinct homeostatic states of tumour cells.
Acknowledgements
D.E.F. acknowledges grant support from the NIH (5P01 CA163222 and 2R01 AR043369) and the Dr Miriam and Sheldon G. Adelson Medical Research Foundation. K.T.F. acknowledges grant support from the Dr Miriam and Sheldon G. Adelson Medical Research Foundation.
X.B. declares no competing interests.
Footnotes
Competing interests
X.B. declares no competing interests. D.E.F. has a financial interest associated with Soltego, which was reviewed and is currently managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. K.T.F. serves on the Board of Directors of Clovis Oncology, Loxo Oncology, Strata Oncology and Vivid Biosciences; serves on the Corporate Advisory Boards of PIC Therapeutics and X4 Pharmaceuticals; serves on the Scientific Advisory Boards of Adaptimmune, Aeglea, Amgen, Apricity, Arch Oncology, Array BioPharma, Asana, Fog Pharma, Fount, Neon Therapeutics, Oncoceutics, Sanofi, Shattuck Labs, Tolero and Tvardi; and is a consultant to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boston Biomedical, Cell Medica, Checkmate, Debiopharm, Genentech, Merck, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, Takeda and Verastem.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0204-6
RELATED LINKS
Publisher's Disclaimer: This Author Accepted Manuscript is a PDF file of an unedited peer-reviewed manuscript that has been accepted for publication but has not been copyedited or corrected. The official version of record that is published in the journal is kept up to date and so may therefore differ from this version.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 5–29 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 7–30 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 67, 7–30 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Siegel RL, Miller KD & Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68, 7–30 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Flaherty KT et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 809–819 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Flaherty KT et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 1694–1703 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Larkin J. et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 1867–1876 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hodi FS et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 711–723 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Robert C. et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 320–330 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Robert C. et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 372, 2521–2532 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sullivan RJ & Flaherty KT Resistance to BRAF-targeted therapy in melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 49, 1297–1304 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ribas A. et al. Association of pembrolizumab with tumor response and survival among patients with advanced melanoma. JAMA 315, 1600–1609 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tirosh I. et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 352, 189–196 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hugo W. et al. Non-genomic and immune evolution of melanoma acquiring MAPKi resistance. Cell 162, 1271–1285 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hugo W. et al. Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell 165, 35–44 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fallahi-Sichani M. et al. Adaptive resistance of melanoma cells to RAF inhibition via reversible induction of a slowly dividing de-differentiated state. Mol. Syst. Biol. 13, 905 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ravindran Menon D. et al. A stress-induced early innate response causes multidrug tolerance in melanoma. Oncogene 34, 4448–4459 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen L, Heymach JV, Qin FX & Gibbons DL The mutually regulatory loop of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and immunosuppression in cancer progression. Oncoimmunology 4, e1002731 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA & Ribas A. Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168, 707–723 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mani SA et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells Cell 133, 704–715 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gupta PB, Chaffer CL & Weinberg RA Cancer stem cells: mirage or reality? Nat. Med. 15, 1010–1012 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF & Weissman IL Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 414, 105–111 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zabierowski SE & Herlyn M. Melanoma stem cells: the dark seed of melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 2890–2894 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schatton T. et al. Identification of cells initiating human melanomas. Nature 451, 345–349 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schatton T, Frank NY & Frank MH Identification and targeting of cancer stem cells. Bioessays 31, 1038–1049 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kemper K, de Goeje PL, Peeper DS & van Amerongen R. Phenotype switching: tumor cell plasticity as a resistance mechanism and target for therapy. Cancer Res. 74, 5937–5941 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hoek KS et al. Metastatic potential of melanomas defined by specific gene expression profiles with no BRAF signature. Pigment Cell Res. 19, 290–302 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zipser MC et al. A proliferative melanoma cell phenotype is responsive to RAF/MEK inhibition independent of BRAF mutation status. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 24, 326–333 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wellbrock C & Arozarena I. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in melanoma development and MAP-kinase pathway targeted therapy. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 28, 390–406(2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ribas A & Wolchok JD Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359, 1350–1355 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cho HI, Lee YR & Celis E. Interferon gamma limits the effectiveness of melanoma peptide vaccines. Blood 117, 135–144 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nowicki TS, Hu-Lieskovan S & Ribas A. Mechanisms of Resistance to PD-1 and PD-L1 Blockade. Cancer J. 24, 47–53 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sucker A. et al. Acquired IFNgamma resistance impairs anti-tumor immunity and gives rise to T cell-resistant melanoma lesions. Nat. Commun. 8, 15440 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tsoi J. et al. Multi-stage differentiation defines melanoma subtypes with differential vulnerability to drug-induced iron-dependent oxidative stress. Cancer Cell 33, 890–904 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mehta A. et al. Immunotherapy resistance by inflammation-induced dedifferentiation. Cancer Discov. 8, 935–943 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zha Z. et al. Interferon-gamma is a master checkpoint regulator of cytokine-induced differentiation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E6867–E6874 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Buszczak M, Signer RA & Morrison SJ Cellular differences in protein synthesis regulate tissue homeostasis. Cell 159, 242–251 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huang S. Genetic and non-genetic instability in tumor progression: link between the fitness landscape and the epigenetic landscape of cancer cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32, 423–448 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brock A & Huang S. Precision oncology: between vaguely right and precisely wrong. Cancer Res. 77, 6473–6479 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou H, Neelakantan D & Ford HL Clonal cooperativity in heterogenous cancers. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 64, 79–89 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Raj A & van Oudenaarden A. Nature, nurture, or chance: stochastic gene expression and its consequences. Cell 135, 216–226 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Frank SA & Rosner MR Nonheritable cellular variability accelerates the evolutionary processes of cancer. PLOS Biol. 10, e1001296 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Niepel M, Spencer SL & Sorger PK Non-genetic cell-to-cell variability and the consequences for pharmacology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 13, 556–561 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Spencer SL, Gaudet S, Albeck JG, Burke JM & Sorger PK Non-genetic origins of cell-to-cell variability in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Nature 459, 428–432 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Losick R & Desplan C. Stochasticity and cell fate. Science 320, 65–68 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sigal A. et al. Variability and memory of protein levels in human cells. Nature 444, 643–646 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Marusyk A, Almendro V & Polyak K. Intra-tumour heterogeneity: a looking glass for cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 323–334 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brock A, Chang H & Huang S. Non-genetic heterogeneity—a mutation-independent driving force for the somatic evolution of tumours. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 336–342 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Huang S, Ernberg I & Kauffman S. Cancer attractors: a systems view of tumors from a gene network dynamics and developmental perspective. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 869–876 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cohen AA et al. Dynamic proteomics of individual cancer cells in response to a drug. Science 322, 1511–1516 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Huang S & Kauffman S. How to escape the cancer attractor: rationale and limitations of multi-target drugs. Semin. Cancer Biol. 23, 270–278 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shain AH & Bastian BC From melanocytes to melanomas. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 345–358 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen H, Weng QY & Fisher DE UV signaling pathways within the skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 134, 2080–2085 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Liu JJ & Fisher DE Lighting a path to pigmentation: mechanisms of MITF induction by UV. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 23, 741–745 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.King R, Googe PB, Weilbaecher KN, Mihm MC Jr & Fisher DE Microphthalmia transcription factor expression in cutaneous benign, malignant melanocytic, and nonmelanocytic tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 25, 51–57 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yokoyama S. et al. A novel recurrent mutation in MITF predisposes to familial and sporadic melanoma. Nature 480, 99–103 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Garraway LA et al. Integrative genomic analyses identify MITF as a lineage survival oncogene amplified in malignant melanoma. Nature 436, 117–122 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ugurel S. et al. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor gene amplification in metastatic melanoma is a prognostic marker for patient survival, but not a predictive marker for chemosensitivity and chemotherapy response. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 6344–6350 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Jager E. et al. Inverse relationship of melanocyte differentiation antigen expression in melanoma tissues and CD8+ cytotoxic-T cell responses: evidence for immunoselection of antigen-loss variants in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 66, 470–476 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gogas H. et al. Prognostic significance of autoimmunity during treatment of melanoma with interferon. N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 709–718 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Freeman-Keller M. et al. Nivolumab in resected and unresectable metastatic melanoma: characteristics of immune-related adverse events and association with outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 22, 886–894 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lo JA, Fisher DE & Flaherty KT Prognostic significance of cutaneous adverse events associated with pembrolizumab therapy. JAMA Oncol. 1, 1340–1341 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fane ME et al. NFIB mediates BRN2 driven melanoma cell migration and invasion through regulation of EZH2 and MITF. EBioMedicine 16, 63–75 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Kim H. et al. Downregulation of the ubiquitin ligase RNF125 underlies resistance of melanoma cells to BRAF inhibitors via JAK1 deregulation. Cell Rep. 11, 1458–1473 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Slominski A. et al. The role of melanogenesis in regulation of melanoma behavior: melanogenesis leads to stimulation of HIF-1alpha expression and HIF-dependent attendant pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 563, 79–93 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rambow F. et al. Toward minimal residual disease-directed therapy in melanoma. Cell 174, 843–855 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hartman ML & Czyz M. MITF in melanoma: mechanisms behind its expression and activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 1249–1260 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Koludrovic D & Davidson I. MITF, the Janus transcription factor of melanoma. Future Oncol. 9, 235–244 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Davies H. et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417, 949–954 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rose AA et al. MAPK pathway inhibitors sensitize BRAF-mutant melanoma to an antibody-drug conjugate targeting GPNMB. Clin. Cancer Res. 22, 6088–6098 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.van Lanschot CG, Koljenovic S, Grunhagen DJ, Verhoef C & van Akkooi AC Pigmentation in the sentinel node correlates with increased sentinel node tumor burden in melanoma patients. Melanoma Res. 24, 261–266 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Widmer DS et al. Systematic classification of melanoma cells by phenotype-specific gene expression mapping. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 25, 343–353 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Altschuler SJ & Wu LF Cellular heterogeneity: do differences make a difference? Cell 141, 559–563 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bennett DC Mechanisms of differentiation in melanoma cells and melanocytes. Environ. Health Perspect. 80, 49–59 (1989). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Konieczkowski DJ et al. A melanoma cell state distinction influences sensitivity to MAPK pathway inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 4, 816–827 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Pearl Mizrahi S, Gefen O, Simon I & Balaban NQ Persistence to anti-cancer treatments in the stationary to proliferating transition. Cell Cycle 15, 3442–3453 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Smith MP et al. Inhibiting drivers of non-mutational drug tolerance is a salvage strategy for targeted melanoma therapy. Cancer Cell 29, 270–284 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Muller J. et al. Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma. Nat. Commun. 5, 5712 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Song C. et al. Recurrent tumor cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic alterations during MAPKi-induced melanoma regression and early adaptation. Cancer Discov. 7, 1248–1265 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hensel Z. et al. Stochastic expression dynamics of a transcription factor revealed by single-molecule noise analysis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 797–802 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hoek KS et al. In vivo switching of human melanoma cells between proliferative and invasive states. Cancer Res. 68, 650–656 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kumar D, Gorain M, Kundu G & Kundu GC Therapeutic implications of cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma. Mol. Cancer 16, 7 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Brinckerhoff CE Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in melanoma: there’s smoke, but is there fire? J. Cell. Physiol. 232, 2674–2678 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Murphy GF, Wilson BJ, Girouard SD, Frank NY & Frank MH Stem cells and targeted approaches to melanoma cure. Mol. Aspects Med. 39, 33–49 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Holzel M, Bovier A & Tuting T. Plasticity of tumour and immune cells: a source of heterogeneity and a cause for therapy resistance? Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 365–376 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Pisco AO & Huang S. Non-genetic cancer cell plasticity and therapy-induced stemness in tumour relapse: ‘what does not kill me strengthens me’. Br. J. Cancer 112, 1725–1732 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Litvin O. et al. Interferon alpha/beta enhances the cytotoxic response of MEK inhibition in melanoma Mol. Cell 57, 784–796 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Su Y. et al. Single-cell analysis resolves the cell state transition and signaling dynamics associated with melanoma drug-induced resistance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 13679–13684 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Pisco AO et al. Non-Darwinian dynamics in therapy-induced cancer drug resistance. Nat. Commun. 4, 2467 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Johannessen CM et al. A melanocyte lineage program confers resistance to MAP kinase pathway inhibition. Nature 504, 138–142 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ji Z. et al. MITF modulates therapeutic resistance through EGFR signaling. J. Invest. Dermatol. 135, 1863–1872 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Hata AN et al. Tumor cells can follow distinct evolutionary paths to become resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Nat. Med. 22, 262–269 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Ramirez M. et al. Diverse drug-resistance mechanisms can emerge from drug-tolerant cancer persister cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 10690 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Quintana E. et al. Efficient tumour formation by single human melanoma cells. Nature 456, 593–598 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Yu H, Pardoll D & Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 798–809 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kammertoens T. et al. Tumour ischaemia by interferon-gamma resembles physiological blood vessel regression. Nature 545, 98–102 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Parker BS, Rautela J & Hertzog PJ Antitumour actions of interferons: implications for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 131–144 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ivashkiv LB IFNgamma: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 18, 545–558 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Minn AJ Interferons and the immunogenic effects of cancer therapy. Trends Immunol. 36, 725–737 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Shin DS et al. Primary resistance to PD-1 blockade mediated by JAK1/2 mutations. Cancer Discov. 7, 188–201 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Respa A. et al. Association of IFN-gamma signal transduction defects with impaired HLA class I antigen processing in melanoma cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 2668–2678 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Sucker A. et al. Genetic evolution of T cell resistance in the course of melanoma progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 6593–6604 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.White CA et al. Constitutive transduction of peptide transporter and HLA genes restores antigen processing function and cytotoxic T cell-mediated immune recognition of human melanoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 75, 590–595 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Garcia-Diaz A. et al. Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. 19, 1189–1201 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zaidi MR et al. Interferon-gamma links ultraviolet radiation to melanomagenesis in mice. Nature 469, 548–553 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Spranger S. et al. Density of immunogenic antigens does not explain the presence or absence of the T cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment in melanoma. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, E7759–E7768 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Wischhusen J, Waschbisch A & Wiendl H. Immune-refractory cancers and their little helpers—an extended role for immunetolerogenic MHC molecules HLA-G and HLA-E? Semin. Cancer Biol. 17, 459–468 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Brocker EB, Zwadlo G, Holzmann B, Macher E & Sorg C. Inflammatory cell infiltrates in human melanoma at different stages of tumor progression. Int. J. Cancer 41, 562–567 (1988). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Rodriguez T. et al. Patterns of constitutive and IFN-gamma inducible expression of HLA class II molecules in human melanoma cell lines. Immunogenetics 59, 123–133 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mortarini R, Belli F, Parmiani G & Anichini A. Cytokine-mediated modulation of HLA-class II, ICAM-1, LFA-3 and tumor-associated antigen profile of melanoma cells. Comparison with anti-proliferative activity by rIL1-beta, rTNF-alpha, rIFN-gamma, rIL4 and their combinations. Int. J. Cancer 45, 334–341 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Garbe C. et al. Antitumor activities of interferon alpha, beta, and gamma and their combinations on human melanoma cells in vitro: changes of proliferation, melanin synthesis, and immunophenotype. J. Invest. Dermatol. 95 (Suppl. 6), 231–237 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Hemon P. et al. MHC class II engagement by its ligand LAG-3 (CD223) contributes to melanoma resistance to apoptosis. J. Immunol. 186, 5173–5183 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mo X. et al. Interferon-gamma signaling in melanocytes and melanoma cells regulates expression of CTLA-4. Cancer Res. 78, 436–450 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Spranger S. et al. Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and T(regs) in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8+ T cells. Sci. Transl Med. 5, 200ra116 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Taube JM et al. Colocalization of inflammatory response with B7-h1 expression in human melanocytic lesions supports an adaptive resistance mechanism of immune escape. Sci. Transl Med. 4, 127ra137 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tumeh PC et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 515, 568–571 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Seo SK et al. Attenuation of IFN-gamma-induced B7-H1 expression by 15-deoxy-delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 via downregulation of the Jak/STAT/IRF-1 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 112, 82–89 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dong H. et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat. Med. 8, 793–800 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Minn AJ & Wherry EJ Combination cancer therapies with immune checkpoint blockade: convergence on interferon signaling. Cell 165, 272–275 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Brody JR et al. Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in metastatic malignant melanoma recruits regulatory T cells to avoid immune detection and affects survival. Cell Cycle 8, 1930–1934 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Markel G. et al. Dynamic expression of protective CEACAM1 on melanoma cells during specific immune attack. Immunology 126, 186–200 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Wang T. et al. Regulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses by Stat-3 signaling in tumor cells. Nat. Med. 10, 48–54 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Bahrambeigi V. et al. PhiC31/PiggyBac modified stromal stem cells: effect of interferon gamma and/or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) on murine melanoma. Mol. Cancer 13, 255 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Taniguchi K. et al. Interferon gamma induces lung colonization by intravenously inoculated B16 melanoma cells in parallel with enhanced expression of class I major histocompatibility complex antigens. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3405–3409 (1987). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Brown TJ, Lioubin MN & Marquardt H. Purification and characterization of cytostatic lymphokines produced by activated human T lymphocytes. Synergistic antiproliferative activity of transforming growth factor beta 1, interferon-gamma, and oncostatin M for human melanoma cells. J. Immunol. 139, 2977–2983 (1987). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zaidi MR & Merlino G. The two faces of interferon-gamma in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 6118–6124 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Matsushita H. et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes block tumor growth both by lytic activity and IFNgamma-dependent cell-cycle arrest. Cancer Immunol. Res. 3, 26–36 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Kortylewski M. et al. Interferon-gamma-mediated growth regulation of melanoma cells: involvement of STAT1-dependent and STAT1-independent signals. J. Invest. Dermatol. 122, 414–422 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Schmitt MJ et al. Interferon-gamma-induced activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) up-regulates the tumor suppressing microRNA-29 family in melanoma cells. Cell Commun. Signal 10, 41 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Raz A. Actin organization, cell motility, and metastasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 233, 227–233 (1988). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Natarajan VT et al. IFN-gamma signaling maintains skin pigmentation homeostasis through regulation of melanosome maturation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 2301–2306 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Gollob JA, Sciambi CJ, Huang Z & Dressman HK Gene expression changes and signaling events associated with the direct antimelanoma effect of IFN-gamma. Cancer Res. 65, 8869–8877 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Le Poole IC et al. Interferon-gamma reduces melanosomal antigen expression and recognition of melanoma cells by cytotoxic T cells. Am. J. Pathol. 160, 521–528 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Schultz J. et al. Tumor-promoting role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat)1 in late-stage melanoma growth. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 27, 133–140 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ramsdale R. et al. The transcription cofactor c-JUN mediates phenotype switching and BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Sci. Signal 8, ra82 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Meyskens FL Jr. et al. Randomized trial of adjuvant human interferon gamma versus observation in high-risk cutaneous melanoma: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 87, 1710–1713 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Porter GA et al. Significance of plasma cytokine levels in melanoma patients with histologically negative sentinel lymph nodes. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 8, 116–122 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.He YF et al. Sustained low-level expression of interferon-gamma promotes tumor development: potential insights in tumor prevention and tumor immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 54, 891–897 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Chhabra Y. et al. Genetic variation in IRF4 expression modulates growth characteristics, tyrosinase expression and interferon-gamma response in melanocytic cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 31, 51–63 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ & Schreiber RD Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 3, 991–998 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Dunn GP et al. Interferon-gamma and cancer immunoediting. Immunol. Res. 32, 231–245 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Kaplan DH et al. Demonstration of an interferon gamma-dependent tumor surveillance system in immunocompetent mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7556–7561 (1998). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Kovarik J. et al. Malignant melanoma associates with deficient IFN-induced STAT 1 phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 12, 335–340 (2003). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Osborn JL & Greer SF Metastatic melanoma cells evade immune detection by silencing STAT1 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 4343–4361 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Benci JL et al. Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 167, 1540–1554 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Zhao C. et al. Feedback activation of STAT3 as a cancer drug-resistance mechanism. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 37, 47–61 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Li Z. et al. Expression of SOCS-1, suppressor of cytokine signalling-1, in human melanoma. J. Invest. Dermatol. 123, 737–745 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Jager E. et al. Immunoselection in vivo: independent loss of MHC class I and melanocyte differentiation antigen expression in metastatic melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 71, 142–147 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Patel SJ et al. Identification of essential genes for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 548, 537–542 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Manguso RT et al. In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target. Nature 547, 413–418 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Restifo NP, Smyth MJ & Snyder A. Acquired resistance to immunotherapy and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer 16, 121–126 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Ribas A. Adaptive immune resistance: how cancer protects from immune attack. Cancer Discov. 5, 915–919 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Schumacher TN & Schreiber RD Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 348, 69–74 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Zaretsky JM et al. Mutations associated with acquired resistance to PD-1 blockade in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 375, 819–829 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Bellone M & Elia AR Constitutive and acquired mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in human cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 36, 17–24 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Gao J. et al. Loss of IFN-gamma pathway genes in tumor cells as a mechanism of resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Cell 167, 397–404 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Chang CC et al. Multiple structural and epigenetic defects in the human leukocyte antigen class I antigen presentation pathway in a recurrent metastatic melanoma following immunotherapy. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 26562–26575 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Wei SC et al. Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell 170, 1120–1133 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Pardoll D. Cancer and the immune system: basic concepts and targets for intervention. Semin. Oncol. 42, 523–538 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Twyman-Saint Victor C. et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature 520, 373–377 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Overacre-Delgoffe AE et al. Interferon-gamma drives treg fragility to promote anti-tumor immunity. Cell 169, 1130–1141 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Topalian SL, Drake CG & Pardoll DM Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 27, 450–461 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Zhao X & Subramanian S. Intrinsic resistance of solid tumors to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Res. 77, 817–822 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Herlyn M, Guerry D & Koprowski H. Recombinant gamma-interferon induces changes in expression and shedding of antigens associated with normal human melanocytes, nevus cells, and primary and metastatic melanoma cells. J. Immunol. 134, 4226–4230 (1985). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Reinhardt J. et al. MAPK signaling and inflammation link melanoma phenotype switching to induction of CD73 during immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 77, 4697–4709 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Landsberg J. et al. Melanomas resist T cell therapy through inflammation-induced reversible dedifferentiation. Nature 490, 412–416 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Braumuller H. et al. T-Helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence. Nature 494, 361–365 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Zingg D. et al. The histone methyltransferase Ezh2 controls mechanisms of adaptive resistance to tumor immunotherapy. Cell Rep. 20, 854–867 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Riesenberg S. et al. MITF and c-Jun antagonism interconnects melanoma dedifferentiation with pro-inflammatory cytokine responsiveness and myeloid cell recruitment. Nat. Commun. 6, 8755 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Sanchez-Perez L. et al. Potent selection of antigen loss variants of B16 melanoma following inflammatory killing of melanocytes in vivo. Cancer Res. 65, 2009–2017 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Falletta P. et al. Translation reprogramming is an evolutionarily conserved driver of phenotypic plasticity and therapeutic resistance in melanoma. Genes Dev. 31, 18–33 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Haferkamp S. et al. Vemurafenib induces senescence features in melanoma cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 133, 1601–1609 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Webster MR et al. Wnt5A promotes an adaptive, senescent-like stress response, while continuing to drive invasion in melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 28, 184–195 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Tsao H, Fukunaga-Kalabis M & Herlyn M. Recent advances in melanoma and melanocyte biology. J. Invest. Dermatol. 137, 557–560 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Giuliano S. et al. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor controls the DNA damage response and a lineage-specific senescence program in melanomas. Cancer Res. 70, 3813–3822 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Shaffer SM et al. Rare cell variability and drug-induced reprogramming as a mode of cancer drug resistance. Nature 546, 431–435 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Mo J. et al. Hypoxia-induced senescence contributes to the regulation of microenvironment in melanomas. Pathol. Res. Pract. 209, 640–647 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.La Porta CA, Zapperi S & Sethna JP Senescent cells in growing tumors: population dynamics and cancer stem cells. PLOS Comput. Biol. 8, e1002316 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Giampietri C. et al. Cancer microenvironment and endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 417281 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Li Y & Laterra J. Cancer stem cells: distinct entities or dynamically regulated phenotypes? Cancer Res. 72, 576–580 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Zhang X. et al. Both complexity and location of DNA damage contribute to cellular senescence induced by ionizing radiation. PLOS ONE 11, e0155725 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Collado M & Serrano M. Senescence in tumours: evidence from mice and humans. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10, 51–57 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Sun X. et al. Senescence-associated secretory factors induced by cisplatin in melanoma cells promote non-senescent melanoma cell growth through activation of the ERK1/2-RSK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9, 260 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Liu Y. et al. Targeting aurora kinases limits tumour growth through DNA damage-mediated senescence and blockade of NF-kappaB impairs this drug-induced senescence. EMBO Mol. Med. 5, 149–166 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Gray-Schopfer VC, Karasarides M, Hayward R & Marais R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocks apoptosis in melanoma cells when BRAF signaling is inhibited. Cancer Res. 67, 122–129 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Obenauf AC et al. Therapy-induced tumour secretomes promote resistance and tumour progression. Nature 520, 368–372 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Ohanna M. et al. Secretome from senescent melanoma engages the STAT3 pathway to favor reprogramming of naive melanoma towards a tumor-initiating cell phenotype. Oncotarget 4, 2212–2224 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Somasundaram R. et al. Tumor-associated B cells induce tumor heterogeneity and therapy resistance. Nat. Commun. 8, 607 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Hsu MY et al. Notch3 signaling-mediated melanoma-endothelial crosstalk regulates melanoma stem-like cell homeostasis and niche morphogenesis. Lab Invest. 97, 725–736 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Wang T. et al. BRAF inhibition stimulates melanoma-associated macrophages to drive tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 21, 1652–1664 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Hirata E. et al. Intravital imaging reveals how BRAF inhibition generates drug-tolerant microenvironments with high integrin beta1/FAK signaling. Cancer Cell 27, 574–588 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Flach EH, Rebecca VW, Herlyn M, Smalley KS & Anderson AR Fibroblasts contribute to melanoma tumor growth and drug resistance. Mol. Pharm. 8, 2039–2049 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Fedorenko IV, Wargo JA, Flaherty KT, Messina JL & Smalley KSM BRAF inhibition generates a host-tumor niche that mediates therapeutic escape. J. Invest. Dermatol. 135, 3115–3124 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Young HL et al. An adaptive signaling network in melanoma inflammatory niches confers tolerance to MAPK signaling inhibition. J. Exp. Med. 214, 1691–1710 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Acosta JC et al. Chemokine signaling via the CXCR2 receptor reinforces senescence. Cell 133, 1006–1018 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Ohanna M. et al. Senescent cells develop a PARP-1 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B-associated secretome (PNAS). Genes Dev. 25, 1245–1261 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Jobe NP et al. Simultaneous blocking of IL-6 and IL-8 is sufficient to fully inhibit CAF-induced human melanoma cell invasiveness. Histochem. Cell Biol. 146, 205–217 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Frederick DT et al. BRAF inhibition is associated with enhanced melanoma antigen expression and a more favorable tumor microenvironment in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 1225–1231 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Smith MP et al. Effect of SMURF2 targeting on susceptibility to MEK inhibitors in melanoma. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 105, 33–46 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Sharma SV et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141, 69–80 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Sharma R. et al. Activity-based protein profiling shows heterogeneous signaling adaptations to BRAF inhibition. J. Proteome Res. 15, 4476–4489 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Brahmer J. et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 373, 123–135 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Titz B. et al. JUN dependency in distinct early and late BRAF inhibition adaptation states of melanoma. Cell Discov. 2, 16028 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Sun C. et al. Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition in melanoma. Nature 508, 118–122 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Riaz N. et al. Tumor and microenvironment evolution during immunotherapy with nivolumab. Cell 171, 934–949 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Mak MP et al. A patient-derived, pan-cancer EMT signature identifies global molecular alterations and immune target enrichment following epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Clin. Cancer Res. 22, 609–620 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Maccalli C, Parmiani G & Ferrone S. Immunomodulating and immunoresistance properties of cancer-initiating cells: implications for the clinical success of immunotherapy. Immunol. Invest. 46, 221–238 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Schachter J. et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet 390, 1853–1862 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Long GV et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib versus dabrafenib monotherapy in patients with metastatic BRAF V600E/K-mutant melanoma: long-term survival and safety analysis of a phase 3 study. Ann. Oncol. 28, 1631–1639 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Das Thakur M. et al. Modelling vemurafenib resistance in melanoma reveals a strategy to forestall drug resistance. Nature 494, 251–255 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Kong X. et al. Cancer drug addiction is relayed by an ERK2-dependent phenotype switch. Nature 550, 270–274 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Dagogo-Jack I & Shaw AT Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15, 81–94 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Valpione S. et al. Rechallenge with BRAF-directed treatment in metastatic melanoma: a multi-institutional retrospective study. Eur. J. Cancer 91, 116–124 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.De Luca A. et al. Mitochondrial biogenesis is required for the anchorage-independent survival and propagation of stem-like cancer cells. Oncotarget 6, 14777–14795 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Duellman SJ et al. A novel steroidal inhibitor of estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERR alpha). Biochem. Pharmacol. 80, 819–826 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Bardini M. et al. Clonal variegation and dynamic competition of leukemia-initiating cells in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia with MLL rearrangement. Leukemia 29, 38–50 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Keats JJ et al. Clonal competition with alternating dominance in multiple myeloma. Blood 120, 1067–1076 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Charles JP et al. Monitoring the dynamics of clonal tumour evolution in vivo using secreted luciferases. Nat. Commun. 5, 3981 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Cleary AS, Leonard TL, Gestl SA & Gunther EJ Tumour cell heterogeneity maintained by cooperating subclones in Wnt-driven mammary cancers. Nature 508, 113–117 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Miller DM & Flaherty KT Cyclin-dependent kinases as therapeutic targets in melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 27, 351–365 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Wan L, Pantel K & Kang Y. Tumor metastasis: moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nat. Med. 19, 1450–1464 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Roesch A. et al. Overcoming intrinsic multidrug resistance in melanoma by blocking the mitochondrial respiratory chain of slow-cycling JARID1B(high) cells. Cancer Cell 23, 811–825 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Kirkwood JM et al. Effect of JAK/STAT or PI3Kδ plus PD-1 inhibition on the tumor microenvironment: biomarker results from a phase Ib study in patients with advanced solid tumors [abstract]. Cancer Res. 78 (Suppl. 13), CT176 (2018). [Google Scholar]
- 224.Winkler JK, Schiller M, Bender C, Enk AH & Hassel JC Rituximab as a therapeutic option for patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 67, 917–924 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Lauss M. et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in melanoma reveals the importance of CpG methylation in MITF regulation. J. Invest. Dermatol. 135, 1820–1828 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Chatterjee-Kishore M, Kishore R, Hicklin DJ, Marincola FM & Ferrone S. Different requirements for signal transducer and activator of transcription 1alpha and interferon regulatory factor 1 in the regulation of low molecular mass polypeptide 2 and transporter associated with antigen processing 1 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16177–16183 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Gowrishankar K. et al. Inducible but not constitutive expression of PD-L1 in human melanoma cells is dependent on activation of NF-κB. PLOS ONE 10, e0123410 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Platanias LC. Nat Rev Immunol, 2005; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Lee H, et al. Nat Med, 2010; [Google Scholar]
- 230.Kreis S, et al. Mol Cancer Res, 2007; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Nam S. Mol Oncol, 2012; [Google Scholar]
- 232.Sims JT, et al. Plos One, 2013; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Lee H, et al. Cancer Res, 2011; [Google Scholar]
- 234.Lee H, et al. Cancer Cell, 2009; [Google Scholar]
- 235.Zhang L, et al. IUBMB Life, 2015; [Google Scholar]
- 236.Wong LH, et al. J Immunol, 1998; [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Kovarik A, et al. Melanoma Res, 2005; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Lesinski GB, et al. BMC Cancer, 2010; [Google Scholar]
- 239.Huang FJ, et al. Cancer Res, 2008; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Murtas D, et al. Br J Cancer, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.