Abstract
Objective
Infection of human hepatocytes by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a multistep process involving both viral and host factors. microRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. Given that miRNAs were indicated to regulate between 30% and 75% of all human genes, we aimed to investigate the functional and regulatory role of miRNAs for the HCV life cycle.
Design
To systematically reveal human miRNAs affecting the HCV life cycle, we performed a two-step functional high-throughput miRNA mimic screen in Huh7.5.1 cells infected with recombinant cell culture-derived HCV. miRNA targeting was then assessed using a combination of computational and functional approaches.
Results
We uncovered miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p as novel modulators of HCV assembly/release. We discovered that these miRNAs regulate O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase (OGT) protein expression and identified OGT and O-GlcNAcylation as regulators of HCV morphogenesis and infectivity. Furthermore, increased OGT expression in patient-derived liver tissue was associated with HCV-induced liver disease and cancer.
Conclusion
miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p and their target OGT are previously undiscovered regulatory host factors for HCV assembly and infectivity. In addition to its effect on HCV morphogenesis, OGT may play a role in HCV-induced liver disease and hepatocarcinogenesis.
Keywords: Hepatitis C, HCV, Hepatocyte, Molecular Mechanisms
Introduction
Chronic hepatitis C is a major cause of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Since the approval of pan-genotypic direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), it is considered a curable disease in more than 90% of treated patients. Nonetheless, an estimated 71 million individuals are still infected by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and several challenges remain; viral cure reduces but does not eliminate the HCC risk in patients with advanced fibrosis[3], the majority of infected patients has limited access to therapy and DAA failure/viral resistance has been reported in a subset of patients[4, 5]. To overcome these limitations, approaches to target host factors involved in HCV infection and pathogenesis are developed[6, 7]. Interestingly, defined host factors that contribute to the establishment of chronic HCV infection and represent potential antiviral targets, e.g. epidermal growth factor receptor[8], also play a role in liver disease pathogenesis and represent candidate targets for treatment of advanced liver disease and HCC prevention[9]. Thus, uncovering host factors usurped by HCV not only contributes to a better understanding of virus-host interactions underlying the HCV life cycle but also to the identification of potential targets for treatment of liver disease and prevention of HCC.
The establishment of various models to study HCV infection has shed light on the molecular mechanisms that govern the HCV life cycle, which can be subdivided into early steps, including viral entry, translation and replication as well as late steps, including assembly and release of new virions. Each step of the HCV replication cycle relies on specific virus-host interactions that involve host proteins and microRNAs (miRNAs)[7], small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. One miRNA can target numerous messenger RNAs (mRNAs) by base-pairing with a complementary site that is typically located within the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of the mRNA. Accumulating evidence indicates that miRNAs participate to HCV replication by exerting pro- or antiviral effects. The breakthrough discovery of the direct targeting of HCV by miR-122, the most abundant miRNA in the liver, revealed the crucial role of this miRNA for HCV translation/replication that contributes to progression to chronic HCV infection[1, 10]. miR-122 antisense oligonucleotides were subsequently developed as host-targeting antivirals[11, 12]. Other miRNAs can indirectly target HCV by regulating host factors that participate in antiviral responses and immune surveillance[2, 13, 14]. Since up to 60% of all human protein-coding genes were reported to be under miRNA-mediated regulation and miRNAs are involved in basically every biological process, we hypothesized that miRNAs provide a tool for loss-of-function approaches to uncover novel HCV host factors. We performed genome-wide high-throughput modulation of the human miRNome and analyzed their impact on HCV infection by combining computational and functional approaches.
Material and methods
Cells, cell culture conditions, viruses, virus purification, infectivity assays, miRNAs, antagomiRs, siRNAs, antibodies, immunoblot, immunocapture, electron microscopy analysis of viral particles and gene expression analysis in liver tissue are described in the Supplementary information.
Functional miRNA/siRNA screens
Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with the miRIDIAN human miRNA mimic library (mIRBase 19) comprising more than 2000 mature miRNAs or 28 ON-TARGETplus smart pool siRNAs (20 nM, Dharmacon) using Interferin HTS (Polyplus) in a 96-well format[8]. After 48h, a viability test (Presto Blue, Thermo Scientific) was performed prior to a two-step infection assay[15, 16, 17]. During part 1 of the protocol, 50 μL of HCV cell culture-derived particles (HCVcc, JcR2a) were incubated with cells during 4h. The inoculum was removed and cells were incubated with 150 μl of medium for 48h. In part 2, supernatants from part 1 cells were transferred onto naïve Huh7.5.1 cells and part 1 cells were lysed to determine luciferase activity[17, 18]. After 72h, part 2 cells were lysed to determine luciferase activity[17]. siCD81 (20 nM), antagomiR-122 (100 nM) and siApoE (20 nM) were used as positive controls[17]. A non-targeting siRNA with no sequence complementarity to any human gene or homology to any human miRNA was used as negative control.
Inhibitor treatment
Four hours following HCV RNA electroporation[8], Huh7.5.1 cells were incubated with vehicle or inhibitors of OGT (peracetylated 5-thio-N-acetylglucosamine (Ac45S-GlcNAc)[19]) or OGA (Thiamet G (Sigma))[20]. After 96h, supernatants were transferred onto naïve Huh7.5.1 cells for 72h prior to determination of luciferase activity while electroporated cells were lysed to determine luciferase activity.
Gene expression analyses
Total RNA was purified[17] and transcribed into cDNA using Maxima reverse transcriptase (Thermo Scientific). GAPDH and OGT mRNA was detected by real time qPCR using iTaq™ Universal Probes Supermix (Bio-Rad) and TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (Thermo Scientific). Relative OGT/GAPDH gene expression was calculated by the ΔΔCt method[21].
Dual luciferase reporter gene assay
The human OGT 3′UTR sequence was retrieved from NCBI (NM_181672.2) and Ensembl genome browser (ENST00000373719.3). A fragment of the OGT 3′UTR (positions 3380-3837, NM_181672.2) (Thermo Fisher Scientific GENEART) was cloned between the NotI and XhoI sites downstream of a Renilla luciferase cassette in a psiCHECK2 plasmid (Promega). A mutated version of this construct (9-bp substitution in the predicted miR-501-3p target site) was generated as described[22]. The functionality of the OGT 3′UTR was assessed as described[23]. The miRIDIAN mimic negative control 1 was used as control. Renilla and firefly luciferase activity was assessed 48h after transfection into HeLa cells using Dual-Luciferase Reporter assay (Promega).
Bioinformatic and statistical analysis
Data analysis and statistical treatment for the miRNA mimic screen were performed in R (www.r-project.org). Cell measurement data used in further analysis were cell viability and luciferase activity. In total 26 sets of plates (performed in triplicate) were tested. The presence of multiple wells with negative and positive controls on each plate allowed stepwise normalization intra- and inter-plate. First, intra-plate zonal bias was examined and a model of median effects across the entire screen determined using the median-polish algorithm[24] and all plates corrected accordingly. Then the dataset was examined for outlier plates, i.e. plates where all individual measurements correlate very poorly with the other remaining replicates. Three and 9 plates were excluded for part 1 and part 2 of the screen, respectively, based on poor median correlation (r < 0.7) so that the remaining plates correlation improved substantially (> 40%). Next, the plates were normalized inter replicates using the particularly robust quantile-quantile approach[25]. Finally, the data were tested using a moderated t-test (empirical Bayes shrinkage, R-package limma[26]) for the null-hypothesis of no change of a given miRNA compared to the negative control. The resulting p-values for independent testing of each miRNA where corrected for the multiple testing situation and expressed as local false discovery rate (lfdr, R-package fdrtool[27]). The testing was performed independently for part 1 and 2 of the screen and candidate miRNAs selected for each part. For data from part 1, a lfdr threshold of 0.00027 was used. Data from part 2 were subject to increase inherent stochastic noise and for this reason the minimum acceptable relative risk of false positives was increased to 0.1226 (i.e. maximum 15% risk for each of the retained hits).
Other datasets were analyzed using the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, Wilcoxon test, Spearman correlation or the two-tailed unpaired t-test for data with normal distribution as assessed by D'Agostino and Pearson omnibus and Shapiro-Wilk normality tests (GraphPad Prism v.6 package).
Results
Genome-wide identification of human miRNAs affecting the HCV life cycle
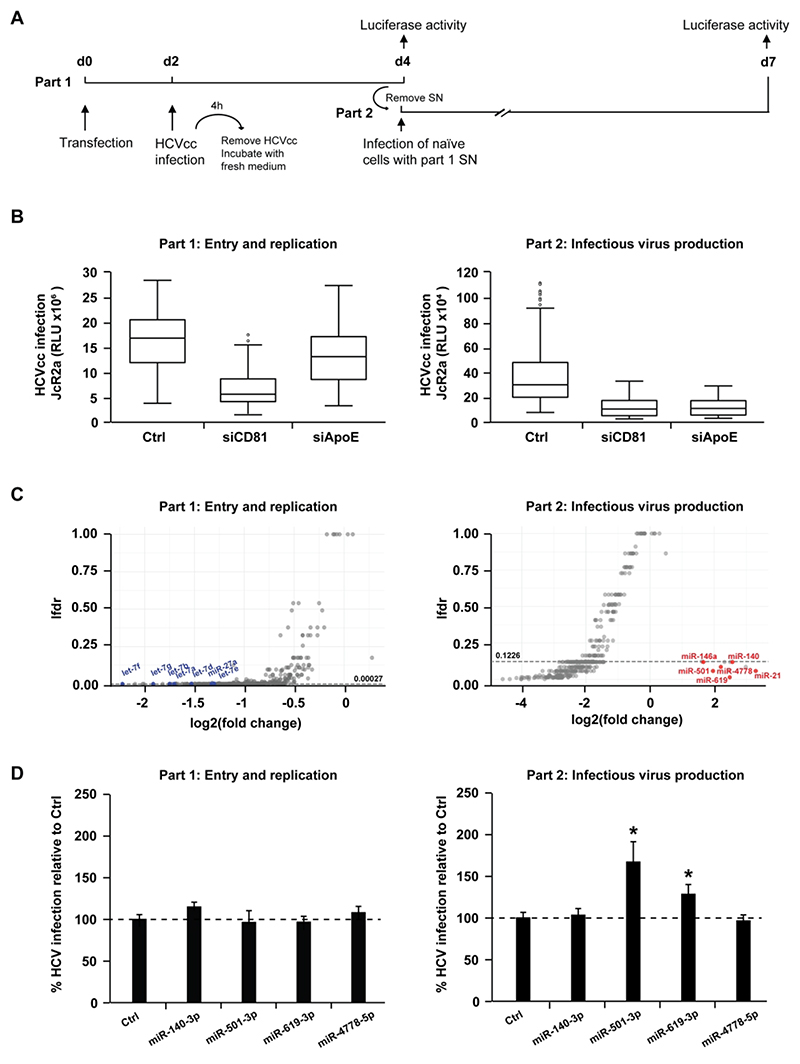
We performed a genome-wide screen in human hepatoma Huh7.5.1 cells using a genomic miRNA mimics library and a two-step infection assay[17] with a luciferase reporter virus (JcR2a), which allowed us to functionally assess the role of miRNAs during the early steps (part 1 - viral entry/translation/replication) and the late steps (part 2 - viral assembly/release/infectivity) of the HCV life cycle (Fig. 1A). Silencing of CD81 and ApoE, two essential host factors required for HCV entry or assembly, respectively, was performed in parallel using small interfering RNA (siRNA) as controls. Silencing of CD81 resulted in a reduction of HCV infection in part 1 and consequently in part 2 of the screen since reduced viral entry in the first part of the assay leads to a reduced production of viral particles (Fig. 1B)[17]. Silencing of ApoE resulted in a marked inhibition of HCV infection only in part 2 of the assay, consistent with the role of ApoE in HCV assembly (Fig. 1B)[17]. The screen identified 427 miRNAs (corresponding to about 16% of the library) that significantly modulated HCV infection (lfdr < threshold, Supplementary Table 1 and Fig. 1C): 186 miRNAs affected HCV infection in part 1, 309 miRNAs affected HCV infection in part 2, including 68 hits in part 1 and part 2. The limited number of part 1 and 2 hits may be due to the fact that a single miRNA may modulate the expression of several proteins, which may have different roles in the viral life cycle. Most hits were observed to dampen HCV infection independently of any significant alteration of cell viability (data not shown). The 186 miRNAs modulating the early steps of HCV infection all decreased viral infection. Among the 309 miRNAs that had an impact in part 2, 11 miRNAs increased HCV infection by at least 3-fold while 298 miRNAs inhibited HCV infection by at least 2.7-fold. Hits from the screen included the let-7 family[2, 28], miR-27a[29] and miR-29 family[30] that were already shown to inhibit HCV infection, as well as miR-21[31] and miR-146a-5p[17] that were shown to stimulate HCV infection thus supporting the relevance of our findings. Collectively, our screen identified a set of miRNAs whose overexpression overall impairs HCV infection by affecting viral entry/translation/replication and/or virion assembly/egress/infectivity.
Figure 1. High-throughput screen identifies human miRNAs that regulate the HCV life cycle.
(A) Schematic outline of the miRNA mimic screen strategy. Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with miRNA mimics or controls prior to infection with Renilla luciferase HCVcc (JcR2a) two days later (part 1). Cell supernatants of part 1 were used to inoculate naïve Huh7.5.1 cells (part 2). Cells from part 1 and part 2 were lysed at the end of each infection step (2 and 3 days post infection, respectively) to determine luciferase activity. (B) Modulation of HCV entry and replication (part 1) and/or assembly and infectivity (part 2) upon transfection of control non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl, negative control), siCD81 (inhibiting viral entry) or siApoE (inhibiting viral assembly). By inhibiting HCV entry, siCD81 impacts part 1 as well as part 2. In contrast, by specifically impairing late steps of HCV replication cycle, siApoE inhibits HCV infection only in part 2. The box plots show the sample lower quartile (25th percentile; bottom of the box), the median (50th percentile; horizontal line in box) and the upper quartile (75th percentile; top of the box) of relative light units (RLU) in each lysate. The whiskers indicate s.d. Data are from three independent experiments. (C) Effects of miRNA overexpression on each part of the HCV life cycle. Data were tested using a moderated t-test (empirical Bayes shrinkage, R-package limma[26]) for the null-hypothesis of no change of a given miRNA compared to the negative control. The resulting p-values for independent testing of each miRNA where corrected for the multiple testing situation and expressed as local false discovery rate (lfdr, R-package fdrtool[27]). miRNAs having a significant effect on either part 1 or 2 of the screen are below the thresholds indicated by dashed lines (lfdr < 0.00027 or 0.1226, respectively). miRNAs that were previously reported to impact on HCV infection as well as miR-140-3p, miR-501-3p, miR-619-3p and miR-4778-5p are highlighted in blue (Log2(FC) < 0) or red (Log2(FC) > 0). Data are from three independent experiments. (D) Effect of miR-140-3p, miR-501-3p, miR-619-3p and miR-4778-5p on the HCV life cycle. Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with siCtrl (Ctrl), miR-140-3p, miR-501-3p, miR-619-3p or miR-4778-5p and infection experiments were carried out as described in A. HCV infection was determined as luciferase activity. Results represent mean percentage ± s.d. from three independent experiments in triplicate. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test.
miR-619-3p, miR-501-3p and OGT play a role in late steps of the HCV life cycle
We focused our analysis on miRNAs that modulate late steps of the HCV life cycle, as the molecular mechanisms of HCV assembly/release remain only partially understood. Our screen identified 241 miRNAs that modulated late steps without affecting early steps of infection: 11 miRNAs increased HCV infection while 230 miRNAs decreased HCV infection. Among the miRNAs that increased HCV infection, miR-140-3p, miR-501-3p, miR-619-3p and miR-4778-5p have not yet been associated with HCV. Since they enhanced HCV infection in part 2 without affecting part 1, these miRNAs may target host genes that control virus assembly/egress/infectivity. We first confirmed the effect of these miRNAs in independent experiments using the same protocol as for the screen. Overexpression of miR-619-3p or miR-501-3p consistently led to an increase in the infection of progeny virions (Fig. 1D) while infection was decreased with progeny virions from antagomiR-transfected cells (Supplementary Figure S1A). miR-619-3p or miR-501-3p were thus selected for further investigation. To study the molecular mechanisms by which these miRNAs affect HCV infection, we generated a list of predicted miRNA targets using DIANA, TargetScan Human v6.2 and miRDB databases, and selected candidate targets based on their expression in our Huh7.5.1 cells as assessed by microarray (data not shown). Ingenuity Pathway Analysis enabled us to refine the gene list by selecting 28 genes involved in the following functional networks or pathways that contribute to the HCV life cycle[32, 33, 34]: lipid metabolism and cholesterol biosynthesis, protein maturation and processing at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), components of the endosomal sorting complex, adipocyte biogenesis, cellular morphology and cell inflammation (Table 1).
Table 1. Computational analysis of miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p targets and pathway enrichment.
| miRNA ID | Target gene symbol | Pathway or network |
|---|---|---|
| miR-501-3p | MEF2A; PPP3CA; PPP3CC | Calcium signaling |
| HMGCS1 | Cholesterol biosynthesis | |
|
AFF4; CHMP1B; CUX1; DCLK1; LMX1A; PTBP2; RBMS1; RC3H1; SCN2A; SEC63; ZFHX4 |
Inflammatory response, dermatological diseases and conditions, inflammatory disease | |
|
CDK6; CSDE1; GLI2; HOXD10; LSM5; MEF2A; MYCN; OGT; PPP2R2C; PPP2R5E; SEMA3C; TFDP2 |
Cellular development, nervous system development and function; organ morphology | |
|
CIT; COL10A1; FNBP1L; GAN;
HERC1; KPNA4; NONO; SHPRH; STRN; TARDBP; UBE2H; USP37 |
Cell death and survival; cellular compromise; free radical scavenging | |
|
ATXN1; CBLL1; CEBPA; DCC;
PEX5L; RCC2; RNF144A; ZC3H12C |
Cell morphology, cellular assembly and organization; cellular function and maintenance | |
| miR-619-3p | RUNX1T1; SMAD3 | Adipocyte biogenesis |
|
FOXG1; GPBP1; MID1; MKL2; MSI1; PCBP2; WDFY3 |
Cell cycle; organismal injury and abnormalities; cancer | |
|
ACVR2B; DCX; ESRRG; MAPK9;
OGT; PCBP1; PDE3B; SMAD3; SMARCC1; TGFB3; PAPOLA |
Carbohydrate metabolism, energy production; small molecule biochemistry |
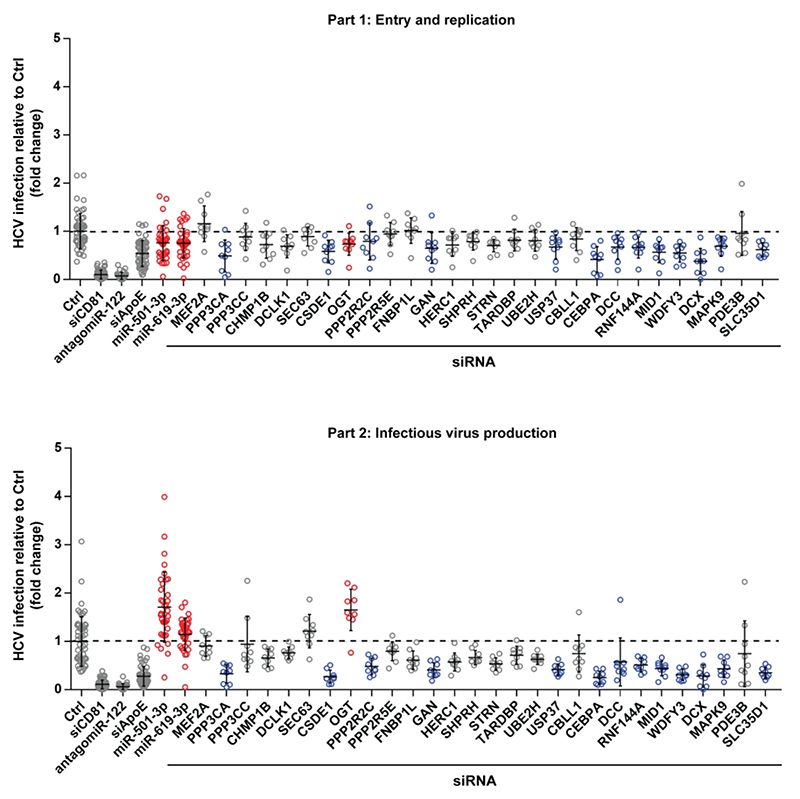
To assess whether knock-down of these 28 candidate targets affects virus production, we performed a siRNA-based screen using siRNA pools exhibiting strong silencing without cytotoxicity (Fig. 2). Silencing of CD81 and antagomiR-122 served as controls for part 1; knock-down of ApoE served as control for part 2 (Fig. 2). Hits were defined as genes whose knock-down modulated HCV infection in at least one part of the screen with high significance (Fig. 2, p-value < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney U-test). HCV entry/translation/replication was significantly modulated by silencing of PPP3CA, CEBPA, MID1, WDFY3, DCX and SLC35D1. HCV assembly/egress/infectivity was significantly modulated by knock-down of PPP3CA, CSDE1, GAN, USP37, CEBPA, MID1, WDFY3, DCX, MAPK9, SLC35D1, DCC, RNF144A, PPP2R2C and OGT. Strikingly, only the silencing of OGT was associated with an enhancement of HCV assembly/release/infectivity (p-value = 0.0002), while that of the other hits was associated with reduced HCV infection (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. OGT is a novel host cell factor involved in the late steps of the HCV life cycle.
Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with a set of siRNAs against 28 predicted targets of miR-501-3p and/or miR-619-3p, and infected with HCVcc JcR2A according to the two-step protocol depicted in Fig. 1A. siCD81, antagomiR-122 and siApoE were used as loss-of-function controls to perturb HCV entry, translation/replication and assembly, respectively. miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p, which were ineffective in part 1 of the screen but enhanced HCV infection in part 2, were transfected in parallel. HCV infection was quantified as fold change of luciferase activity with respect to negative control (siCtrl). Results for different replicates are shown as individual points. For each gene, median fold change of luciferase activity ± s.d. is shown as black horizontal lines. The dashed line indicates a fold change of 1. Data are from three independent experiments in triplicate. Results for miR-501-3p, miR-619-3p and siOGT that increase HCV infection in part 2 are depicted in red. Results for siRNA targeting PPP3CA, CEBPA, MID1, WDFY3, DCX, SLC35D1, CSDE1, GAN, USP37, MAPK9, DCC, RNF144A, or PPP2R2C that significantly modulated HCV infection in part 1 and/or part 2 but did not phenocopy the effect of miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p are depicted in blue.
These results indicate that the down-regulation of OGT phenocopies the effect of miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p on HCV infection (Fig. 2) and suggest OGT as a novel player in the HCV life cycle.
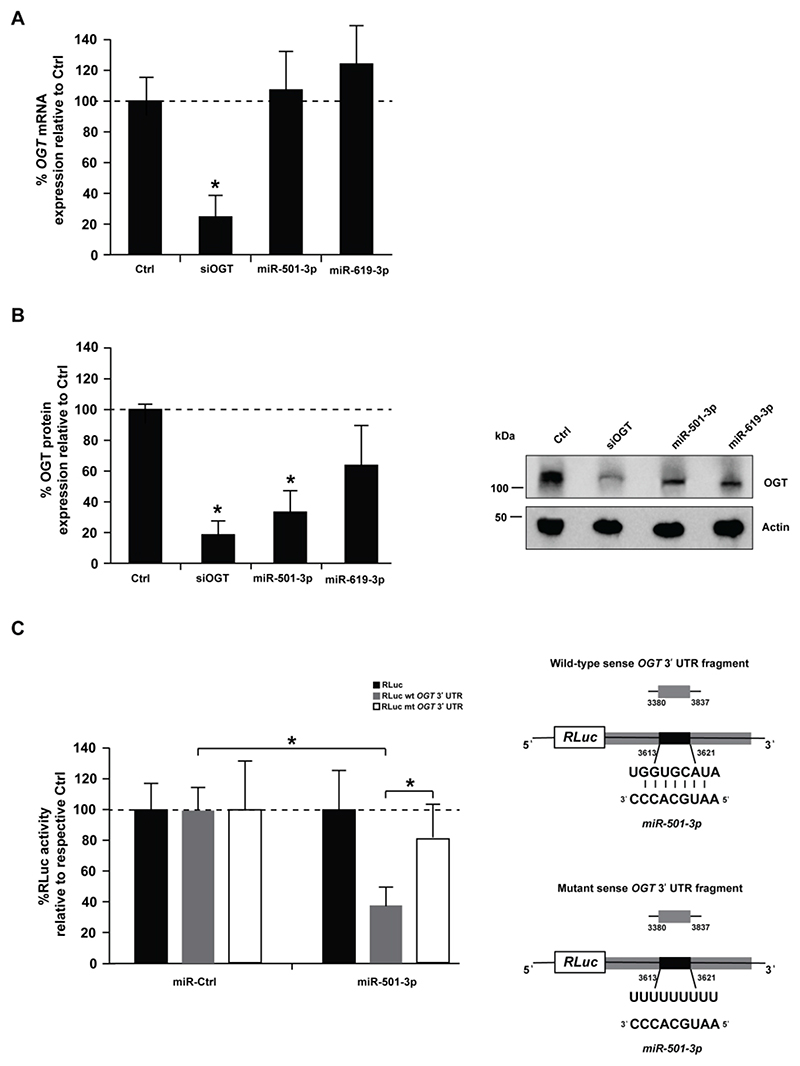
miR-501-3p post-transcriptionally regulates OGT expression
To study whether miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p target OGT, we analyzed OGT RNA and protein levels in Huh7.5.1 cells following overexpression of miR-501-3p or miR-619-3p. While neither miRNA had an impact on OGT RNA levels (Fig. 3A), up-regulation of miR-501-3p significantly decreased OGT protein expression by ~65% (Fig. 3B, p-value < 0.05, t-test). miR-619-3p also decreased OGT expression but less robustly than miR-501-3p (Fig. 3B), prompting us to focus our investigation on miR-501-3p. To assess whether OGT is a functional target of miR-501-3p, we subcloned a fragment of the OGT mRNA 3′UTR that harbors the predicted miR-501-3p target site in the Renilla luciferase expression cassette (RLuc) of a dual luciferase reporter construct. Co-transfection of miR-501-3p mimic with the wild-type 3’UTR reporter (RLuc wt OGT 3’UTR) significantly decreased luciferase activity as compared to the empty vector (Fig. 3C, p-value < 0.05, t-test). In contrast, the repression of luciferase expression was lost when the reporter with mutated miR-501-3p binding site (RLuc mt OGT 3’UTR) was used (Fig. 3C). These data are consistent in indicating that miR-501-3p mediates post-transcriptional regulation of OGT.
Figure 3. miR-501-3p mediates post-transcriptional regulation of OGT by decreasing its expression at the protein level.
Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with siCtrl (Ctrl), a pool of siRNA against OGT, miR-501-3p or miR-619-3p. After 96h, RNA and proteins were purified, and OGT expression analyzed by RT-qPCR and Western blot. (A) Percentage of OGT mRNA expression in miRNA-transfected cells as compared to negative control. Results are presented as mean ± s.d. and are from three independent experiments in triplicate. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, t-test (B) OGT protein expression. Left: percentage of OGT protein expression in siRNA- or miRNA-transfected cells as assessed by quantification of Western blots. OGT levels were normalized to actin levels using ImageLab™ 5.2.1 software (BioRad). Results are presented as mean ± s.d. and are from three independent experiments. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, t-test. Right: representative Western blot analysis. (C) Analysis of miRNA targeting of OGT expression by dual luciferase reporter assay. Left: HeLa cells were co-transfected with a miR-501-3p mimic and a dual luciferase reporter plasmid containing either wild type miR-501-3p (RLuc wt OGT 3’UTR) or mutated miR-501-3p binding site (RLuc mt OGT 3’UTR) to modulate RLuc expression. Co-transfection of the miR-501-3p mimic and empty RLuc vector was used as control. Data are expressed as mean percentage of Renilla luciferase activity ± s.d. normalized to firefly luciferase, and relative to co-transfection of the vectors with non-targeting miRNA (miR-Ctrl). Results are from three independent experiments in triplicate. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, t-test. Right: Schematic representation of the used constructs.
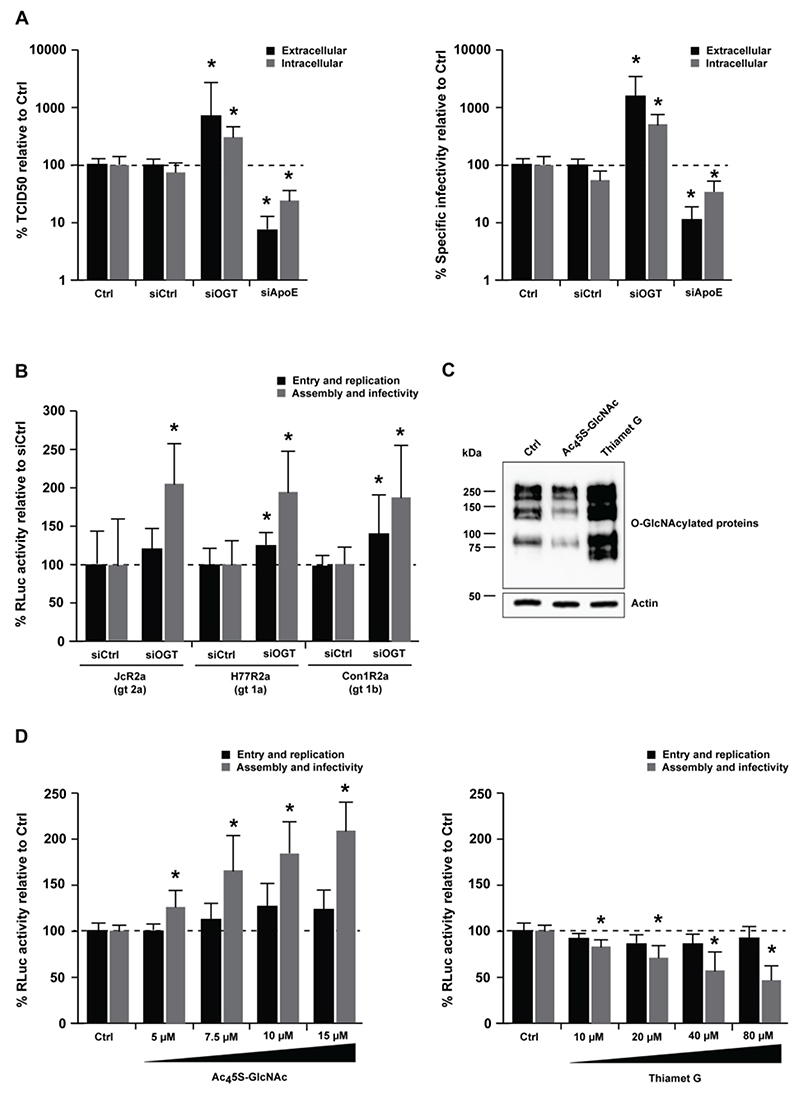
O-GlcNAcylation modulates HCVcc infectivity
To investigate whether OGT modulates HCV assembly and/or infectivity, we determined infectious virus titer (TCID50) and HCV RNA levels to calculate the specific infectivity of HCVcc particles generated in OGT-silenced Huh7.5.1 cells. Interestingly, OGT-silencing led to a significant increase in the TCID50 and the specific infectivity of HCVcc (Fig. 4A, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test). Noteworthy, the effect of OGT on HCVcc infectivity was genotype-independent as demonstrated by increased infectivity of HCVcc bearing the envelope glycoproteins of genotypes 1a, 1b and 2a upon OGT-silencing (Fig. 4B). We next sought to investigate how OGT could modulate HCVcc infectivity. OGT is the only enzyme that catalyzes the addition of N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) to serine and threonine residues of proteins. Moreover, OGT has a scaffold function and promotes binding of proteins in multiprotein complexes[35]. To assess whether the enzymatic activity of OGT modulates HCVcc infectivity, we used pharmacological inhibitors of OGT (Ac45S-GlcNAc) or O-GlcNAcase (OGA) (Thiamet G), the OGT counterpart that removes O-GlcNAc (Fig. 4C). Ac45S-GlcNAc led to a significant enhancement of HCVcc infectivity in a dose-dependent manner, while the opposite effect was observed with Thiamet G (Fig. 4D, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test). Collectively, these results demonstrate that O-GlcNAcylation modulates HCVcc infectivity.
Figure 4. Silencing of OGT affects HCV morphogenesis and infectivity.
(A) Analysis of HCV infectivity. Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with siCtrl, a pool of siRNA against OGT or ApoE as a loss-of-function control to perturb HCV assembly, prior to infection with HCVcc (Jc1) two days later (entry and replication). Mock-transfected cells were used as control (Ctrl). After another 48h, intra- and extracellular HCVcc particles were used to infect naïve Huh7.5.1 cells (assembly and infectivity). Virus supernatants of Huh7.5.1 cells were assayed by (left) endpoint dilution assay (TCID50). Intra- and extracellular HCV RNA was purified and analyzed by RT-qPCR to calculate (right) the specific infectivity (TCID50/RNA). Data are expressed as mean percentage as compared to control ± s.d. Results are from four independent experiments in triplicate. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test. (B) Genotype-independent effect of OGT on HCV infection. Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with siCtrl or siOGT prior to infection with HCVcc JcR2a (genotype 2a), H77R2a (genotype 1a) or Con1R2a (genotype 1b). Experiments were carried out and analyzed as described in A. Data are expressed as mean percentage of Renilla luciferase activity as compared to control ± s.d. Results are from three independent experiments in quadruplicate. The dashed line indicates values from control-transfected cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test. (C) Activity of OGT/OGA inhibitors on O-GlcNAcylation. The activity of Ac45S-GlcNAc (OGT inhibitor) or Thiamet G (OGA inhibitor) on O-GlcNAcylation of proteins in Huh7.5.1 cells was demonstrated by Western blot as described in Supplementary Methods. (D) Effect of O-GlcNAcylation on HCV infectivity. Huh7.5.1 cells were electroporated with HCVcc (JcR2a), prior to treatment with increasing concentrations of Ac45S-GlcNAc (OGT inhibitor, left) or Thiamet G (OGA inhibitor, right) 4h later. After 96h, supernatants were transferred onto naïve Huh7.5.1 cells and electroporated cells were lysed to determine luciferase activity. Luciferase activity in infected Huh7.5.1 cells was assessed 72h later. Data are expressed as mean percentage as compared to control ± s.d. Results are from three independent experiments in quadruplicate. The dashed line indicates values from vehicle-treated cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test.
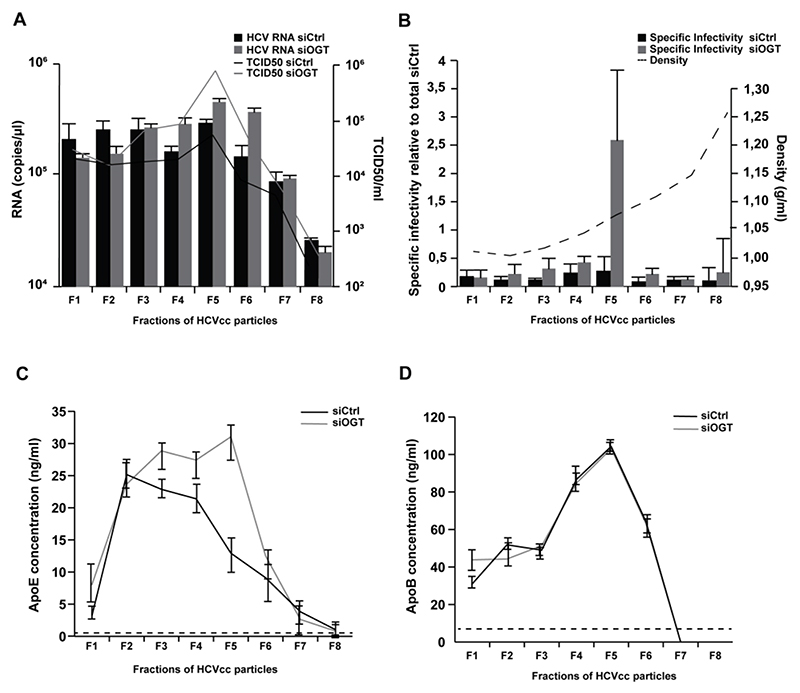
OGT-silencing affects HCVcc biophysical properties and size distribution
To further assess how OGT may impact HCVcc morphogenesis, we analyzed the structural and biophysical properties of HCVcc produced in siCtrl- and siOGT-transfected Huh7.5.1 cells following iodixanol gradient ultracentrifugation. Silencing of OGT led to the production of more infectious HCVcc with higher density (Fig. 5A-B) as well as higher ApoE concentrations (Fig. 5C) suggesting that OGT/O-GlcNAcylation affects the biophysical properties of HCVcc. No change in apoB concentrations were observed between HCVcc produced from siCtrl- or siOGT-transfected cells (Fig. 5D), in line with the model that HCV lipoviroparticles contain several exchangeable ApoE molecules and one non-exchangeable apoB[36]. We also visualized HCVcc by electron microscopy (EM) following anti-E2 antibody immunocapture[36] to assess whether OGT-silencing had an impact on HCVcc size. Particle size distribution was assessed from a series of randomly acquired electron micrographs. A shift towards bigger sizes was observed for sucrose-cushion purified HCVcc generated in OGT-silenced Huh7.5.1 cells as compared to control HCVcc (Fig. 6A-B). This shift was also observed in different fractions of iodixanol gradient-separated HCVcc (Fig. 6C-F) in line with the higher infectivity and ApoE concentrations of HCVcc generated in OGT-silenced Huh7.5.1 cells (Fig. 5A-C). These data suggest that OGT-silencing affects the lipidation of HCVcc.
Figure 5. Silencing of OGT modulates HCVcc biophysical properties.
(A) Separation of HCVcc by iodixanol density gradient ultracentrifugation. HCVcc were produced in non-targeting siRNA control- or siOGT-transfected Huh7.5.1 cells. After overlaying HCVcc (JcR2A) on a 4%-40% iodixanol step gradient and ultracentrifugation for 16h, fractions of HCV particles were used to infect naïve Huh7.5.1 cells in order to determine TCID50. HCV RNA of each fraction was purified and analyzed by RT-qPCR. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. (B) Specific infectivity (TCID50/RNA) was calculated and the density was determined by weighting each fraction. Specific infectivity of each fraction is expressed as fold change as compared to the total infectivity of the control. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. (C-D) ApoE and ApoB concentrations in the individual fractions were determined by ELISA. The dashed lines indicate limits of quantification of the assays. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments.
Figure 6. Silencing of OGT increases the size of HCVcc.
(A) Representative pictures of HCV particles generated in Huh7.5.1 cells transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or siOGT. (B-F) Comparative analysis of particle size distribution for immunocapture (IC) from HCV particles produced in Huh7.5.1 cells transfected with siCtrl or siOGT prior to infection with HCVcc (JcR2a) following sucrose-cushion purification (B) or iodixanol gradient fractionation (C-F) of HCVcc. HCVcc were transferred via anti-E2 antibody AR3A on electron microscopy (EM) grids through IC. Particle size distribution was assessed from a series of randomly acquired electron micrographs with Image-J software (NIH). Results from one of three (A-B) or two (C-F) independent experiments are shown. Black lines: size distribution of immunocaptured HCVcc produced in siCtrl-transfected cells. Grey lines: size distribution of immunocaptured HCVcc produced in siOGT-transfected cells.
OGT expression increases in liver disease
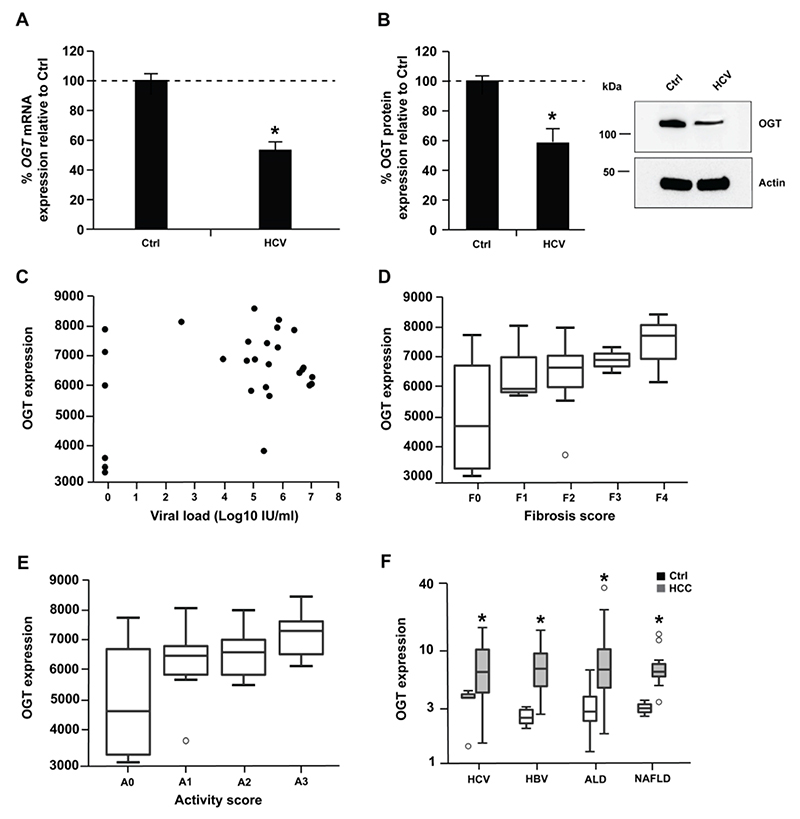
Since silencing of OGT promotes HCV infectivity, we assessed whether HCV infection in turn had an effect on miR-501-3p and OGT expression. In Huh7.5.1 cells, HCV infection lead to small but significant increase of miR-501-3p and decrease of OGT levels (Fig. 7A-B and Supplementary Fig. 1B; p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test), which may promote viral infection given the pro- and antiviral roles of miR-501-3p and O-GlcNAcylation, respectively (Fig. 1C-D and 4D). In contrast, no significant difference of OGT expression was observed between the livers of HCV transgenic and wildtype mice[37] (data not shown) suggesting that HCV proteins do not directly modulate OGT expression. In liver tissue from HCV-infected patients, HCV RNA levels were not correlated with OGT expression (Fig. 7C, Spearman correlation: 0.06004019, p-value = 0.7661) suggesting that in patients there is likely no direct effect of HCV on OGT expression.
Figure 7. OGT expression increases in HCC.
(A-B) Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with HCV (JcR2a). After 72h, RNA and proteins were purified, and OGT expression analyzed by RT-qPCR and Western blot. (A) Percentage of OGT mRNA expression relative to uninfected Huh7.5.1 cells (Ctrl). Results are presented as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments in duplicate. The dashed line indicates values from uninfected Huh7.5.1 cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test. (B) OGT protein expression. Left: percentage of OGT protein expression relative to uninfected Huh7.5.1 cells (Ctrl) following quantification of Western blots as described in Supplementary Methods. Results are presented as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The dashed line indicates values from uninfected Huh7.5.1 cells set at 100%. Statistics: *, p-value < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test. Right: representative Western blot analysis of OGT and actin. (C) OGT expression and viral load in liver tissue from 22 HCV-infected patients and 6 patients not infected with HCV described in[55]. Spearman correlation: rho = 0.06004019, p-value = 0.77. (D-E) OGT expression in liver tissue from 22 HCV-infected patients and 6 patients not infected with HCV according to fibrosis (D) or activity (E) scores described in[55]. Wilcoxon test: F1 vs F0 p-value = 0,38; F2 vs F0 p-value = 0,18; F3 vs F0 p-value = 0,43; F4 vs F0 p-value = 0,17; A1 vs A0 p-value = 0,28; A2 vs A0 p-value = 0,23; A3 vs A0 p-value = 0,09. (F) OGT expression in tumor (HCC) and non-tumor (Ctrl) liver tissue from 39 HCV-infected patients, 83 HBV-infected, 80 patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and 13 patients with non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD) as described in Supplementary Methods. *, p-value < 0.05, Wilcoxon test.
O-GlcNAcylation has been associated with a variety of cancers, including HCC recurrence linked to increased O-GlcNAcylation after liver transplantation[38]. We therefore investigated OGT expression in chronic liver disease and HCC. While there was a trend for increased OGT expression in liver tissue from HCV-infected patients with fibrosis and inflammation (Fig. 7D-E), OGT levels were markedly and significantly elevated in the tumor liver tissue of patients chronically infected with HCV or hepatitis B virus and patients with alcoholic liver disease or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as compared to non-tumor tissue (Fig. 7F, p-value < 0.05, Wilcoxon test). These data suggest that OGT expression increases in HCC in an etiology-independent manner. Collectively, these results suggest that OGT expression is likely increased in HCV-induced liver disease and cancer through inflammation and fibrosis rather than by HCV itself.
Discussion
By focusing on miRNAs affecting late steps of the viral life cycle, we uncovered that i) miR-501-3p regulates the expression of OGT; ii) silencing of OGT expression or inhibition of its enzymatic activity increases the infectivity of HCV particles; and iii) OGT knock-down leads to the release of bigger HCV particles. Our data suggest that O-GlcNAcylation affects HCV morphogenesis and infectivity.
While we were characterizing the role of OGT/O-GlcNAcylation for HCV morphogenesis, Li and colleagues published their functional genomics study of HCV-miRNA interactions[2]. By conducting genome wide miRNA mimic and hairpin inhibitor screens, they identified a set of miRNAs exhibiting a pro- or antiviral effect on HCV. Characterization of the underlying molecular processes showed that miR-25, let-7 and miR-130 families restrict viral infection by decreasing the expression of cellular HCV co-factors[2]. Despite similarities in the cell type and HCV infection models used here and by Li and colleagues, our screen only displays a small overlap with their study (9% common miRNA hits). This is not surprising given the small overlap between previous siRNA screens to uncover HCV host factors[8, 15] and is likely due i) to the different sizes of miRNA mimic libraries as the library used here was more than 2-times larger than the one used by Li and co-workers, and ii) to the markedly distinct pipelines for hit selection that were used in the two studies. Nonetheless, both screens were consistent in confirming the proviral role of miR-146a-5p in promoting HCV assembly/egress that we previously reported[17] and the global multistep inhibitory effects of the let-7 family on HCV infection[28], further corroborating the involvement of these miRNAs in fine-tuning the HCV life cycle. Both studies also consistently indicated that miR-518a-5p, miR-517-3p, miR-185 and members of the miR-302 family inhibit early steps of HCV infection, while miR-586, miR-620 and members of the miR-200 family inhibit late steps of viral infection. Since none of these miRNAs except miR-185 has been previously associated with HCV infection[39], it might be interesting to further characterize the involvement of these miRNAs in HCV-host interactions. Interestingly, an overall proviral effect of miR-501-3p was also observed by Li and colleagues[2], however the mechanism of action was not studied. By characterizing the role of miR-501-3p in the HCV life cycle, we uncovered OGT as a miR-501-3p target in liver-derived cells and showed for the first time a link between O-GlcNAcylation and HCV infection. These results indicate that genome-wide miRNA functional screens represent a powerful strategy to dissect the role of miRNAs in pathogen-host interactions.
While N-glycosylation of HCV envelope glycoproteins plays an important role for escape from virus-neutralizing antibodies[40], so far no functional association between HCV and O-glycosylation has been reported. In contrast to N-linked glycosylation that consists of the attachment of a glycan to a nitrogen of an asparagine residue of proteins in the ER/Golgi prior to their trafficking to the plasma membrane and/or their secretion, the glycosylation of serine and threonine residues with O-GlcNAc is a post-translational modification (PTM) of intracellular proteins that are localized in the nucleus, cytoplasm or mitochondria. The O-glycosylation/deglycosylation of proteins is catalyzed by a single pair of nucleo-cytoplasmic enzymes, OGT/OGA. O-GlcNAcylation is complementary to protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, another more broadly known abundant protein PTM that involves numerous kinases/phosphatases. OGT/OGA are often found in protein complexes that also include kinases/phosphatases and a protein can be either O-GlcNAcylated or phosphorylated on a same residue to fine-tune cellular signaling[41]. O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation on the same or neighboring serine or threonine residue is known as yin yang site[42].
O-GlcNAcylation plays a major role in the regulation of metabolic pathways in the liver, including insulin signaling, bile acid metabolism and lipogenesis[35]. The large number of OGT/OGA substrates and cellular pathways regulated by O-GlcNAcylation hampers a detailed characterization of the role of these proteins in HCV infection. Since i) HCV assembly takes place at ER-derived membranes, ii) OGT/OGA are not known to localize in the ER lumen, and iii) O-GlcNAcylation of extracellular proteins containing EGF-like domains is catalyzed by EGF domain-specific OGT (EOGT) in the ER lumen in an OGT-independent manner[43]), OGT/OGA most likely modulate HCV infection by post-translationally modifying one or several cellular factors required for HCV morphogenesis rather than by affecting viral proteins, although HCV glycoproteins contain putative O-GlcNAcylation sites as determined using OGlcNAcScan, OGTsite and YingOYang1.2 bioinformatics tools (data not shown).
Regarding HCV host factors that may be regulated by OGT/OGA, O-GlcNAcylation sites have been predicted in human CLDN1[44] and OCLN at serine sites that can also be phosphorylated and this has been suggested to potentially play a role for HCV entry[45]. However, in our experimental setting we did not observe a significant effect of OGT-silencing on the early steps of HCV infection, suggesting that O-GlcNAcylation of CLDN1 and/or OCLN likely does not play a major role in HCV infection. Other host factors important for the HCV life cycle are well-known O-GlcNAcylated proteins, as for example various nuclear pore complex proteins (Nups) including Nup98, Nup153 and Nup155 that are involved in HCV replication and assembly and/or may be associated with viral particles[46, 47, 48]. However, since depletion of Nups was reported to alter HCV replication and/or assembly but to have no impact on the specific infectivity of HCV particles[46] in contrast to the depletion of OGT as shown here, it is unlikely that a modulation of Nup O-GlcNAcylation accounts for the effects of OGT-silencing and/or OGT/OGA inhibitors on HCVcc infectivity observed in our study. This is in line with our observation that OGT knock-down had no effect on Dengue virus (DENV) replication and infectivity (unpublished observations KH, MZ and Evelyne Schaffer, IBMC, Strasbourg), although Nup98 had been suggested to potentially play a role for DENV infection[46]. These data suggest that OGT does not broadly modulate the infectivity of viruses of the Flaviviridae family.
However, OGT and/or O-GlcNAcylation have been reported to play a role in the infection with other viruses[49, 50, 51]. Interestingly, while OGT expression modulates the levels of human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16) oncoproteins E6 and E7[52], E6 in turn can up-regulate OGT to increase O-GlcNAcylation and the oncogene activities of HPV[53], suggesting that OGT/O-GlcNAcylation could play a role in virus-induced cancer. In cell culture, HCV infection appeared to be associated with a minor decrease in OGT expression in line with an antiviral role of O-GlcNAcylation. In contrast, an increased OGT expression was observed in HCC tissues of HCV-infected patients. Since OGT has been suggested to activate oncogenic signaling pathways in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related HCC[54] and O-GlcNAcylation has been associated with HCC recurrence linked to increased O-GlcNAcylation after liver transplantation[38], these data suggest that in addition to their effect on the HCV life cycle, OGT/O-GlcNAcylation may also play a role in HCV-induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
Supplementary Material
Significance of this study.
What is already known about this subject?
To establish chronic infection, the hepatitis C virus (HCV) hijacks cellular factors including microRNAs (miRNAs), known to post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression.
miRNAs may positively or negatively modulate HCV infection either by directly targeting the viral genome or indirectly by regulating virus-associated cellular pathways[1, 2].
What are the new findings?
A functional miRNA mimic screen uncovered miR-501-3p and miR-619-3p to enhance late steps of HCV infection.
miR-501-3p regulates the expression of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) at the protein level.
Silencing of OGT expression or inhibition of O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation (O-GlcNAcylation) leads to an increase in the infectivity and size of HCV particles.
OGT expression increases in patient-derived liver tissue during liver disease progression and cancer.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
As upregulation of OGT and increased O-GlcNAcylation of proteins have been associated with various forms of cancer, OGT may play a dual role in HCV morphogenesis as well as pathogenesis of HCV-induced liver disease and carcinogenesis.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Gerald W. Hart and Stéphan Hardivillé, the CardioPEG CoreC4 (NHLBI P01 HL107153) for providing AL24 and for useful technical discussions. We are grateful to David Vocadlo (Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, Canada) for the gift of Ac45S-GlcNAc. We also thank Ralf Bartenschlager (University of Heidelberg, Germany) for providing the plasmids for production of HCVcc and Frank Chisari (The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA) for the gift of Huh7.5.1 cells. We acknowledge Evelyne Schaeffer (CNRS UPR3572, IBMC, Strasbourg) for the DENV experiment, Charlotte Bach and Christine Thumann (Inserm, U1110, Strasbourg) for excellent technical work during the functional miRNA mimic screen, as well as Armando A. Roca-Suarez (Inserm, U1110, Strasbourg), Hussein El Saghire (Inserm, U1110, Strasbourg), Arnaud Kopp (IGBMC, Department of Functional Genomics and Cancer) and Erika Girardi (UPR 9002, IBMC, Strasbourg) for helpful discussions. We thank the INGESTEM infrastructure for access to the IGBMC high-throughput screening workstation.
Financial support
This work was supported by the European Union (INTERREG-IV-Rhin Supérieur-FEDER-Hepato-Regio-Net 2012 to T.F.B. and M.B.Z., ERC-AdG-2014-671231-HEPCIR, EU H2020-667273-HEPCAR to T.F.B), ANRS (2012/239 to T.F.B., M.B.Z. and L.B.), ARC, Paris and Institut Hospitalo-Universitaire, Strasbourg (TheraHCC IHUARC IHU201301187 to T.F.B.), the Impulsion Program of the IDEXLYON (to M.B.Z.), Ligue contre le cancer (to M.B.Z.), Inserm, and University of Strasbourg. This work has been published under the framework of the LABEX ANR-10-LABX-0028_HepSYS, ANR-10-LABX-36 NetRNA and Inserm Plan Cancer 2019-2023 and benefits from funding from the state managed by the French National Research Agency as part of the Investments for the future program. S.P. and K.H. were supported by PhD fellowships from the French Ministry of Research and the IdEx program of the University of Strasbourg, respectively.
Footnotes
Competing interests: The authors do not have competing interest.
References
- 1.Jopling CL, Yi M, Lancaster AM, et al. Modulation of hepatitis C virus RNA abundance by a liver-specific MicroRNA. Science. 2005;309:1577–81. doi: 10.1126/science.1113329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li Q, Lowey B, Sodroski C, et al. Cellular microRNA networks regulate host dependency of hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1789. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01954-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baumert TF, Juhling F, Ono A, et al. Hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of new generation antivirals. BMC Med. 2017;15:52. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0815-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pawlotsky JM. Hepatitis C Virus Resistance to Direct-Acting Antiviral Drugs in Interferon-Free Regimens. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:70–86. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dietz J, Susser S, Vermehren J, et al. Patterns of Resistance-Associated Substitutions in Patients With Chronic HCV Infection Following Treatment With Direct-Acting Antivirals. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:976–88.:e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zeisel MB, Baumert TF. Clinical development of hepatitis C virus host-targeting agents. Lancet. 2017;389:674–5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30043-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zeisel MB, Crouchet E, Baumert TF, et al. Host-Targeting Agents to Prevent and Cure Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Viruses. 2015;7:5659–85. doi: 10.3390/v7112898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lupberger J, Zeisel MB, Xiao F, et al. EGFR and EphA2 are host factors for hepatitis C virus entry and possible targets for antiviral therapy. Nature Medicine. 2011;17:589–95. doi: 10.1038/nm.2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fuchs BC, Hoshida Y, Fujii T, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition attenuates liver fibrosis and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;59:1577–90. doi: 10.1002/hep.26898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Masaki T, Arend KC, Li Y, et al. miR-122 stimulates hepatitis C virus RNA synthesis by altering the balance of viral RNAs engaged in replication versus translation. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17:217–28. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.12.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1685–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.van der Ree MH, de Vree JM, Stelma F, et al. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a phase 1B, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:709–17. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31715-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bandiera S, Pfeffer S, Baumert TF, et al. miR-122--a key factor and therapeutic target in liver disease. J Hepatol. 2015;62:448–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li H, Jiang JD, Peng ZG. MicroRNA-mediated interactions between host and hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:1487–96. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li Q, Brass AL, Ng A, et al. A genome-wide genetic screen for host factors required for hepatitis C virus propagation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:16410–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907439106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Poenisch M, Metz P, Blankenburg H, et al. Identification of HNRNPK as regulator of hepatitis C virus particle production. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1004573. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bandiera S, Pernot S, El Saghire H, et al. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Upregulation of MicroRNA miR-146a-5p in Hepatocytes Promotes Viral Infection and Deregulates Metabolic Pathways Associated with Liver Disease Pathogenesis. J Virol. 2016;90:6387–400. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00619-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Da Costa D, Turek M, Felmlee DJ, et al. Reconstitution of the entire hepatitis C virus life cycle in non-hepatic cells. J Virol. 2012;86:11919–25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01066-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gloster TM, Zandberg WF, Heinonen JE, et al. Hijacking a biosynthetic pathway yields a glycosyltransferase inhibitor within cells. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:174–81. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yuzwa SA, Macauley MS, Heinonen JE, et al. A potent mechanism-inspired O-GlcNAcase inhibitor that blocks phosphorylation of tau in vivo. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:483–90. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc. 2008;3:1101–8. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jin Y, Chen Z, Liu X, et al. Evaluating the microRNA targeting sites by luciferase reporter gene assay. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;936:117–27. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-083-0_10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Van Renne N, Roca Suarez AA, Duong FHT, et al. miR-135a-5p-mediated downregulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor delta is a candidate driver of HCV-associated hepatocarcinogenesis. Gut. 2018;67:953–62. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mosteller F, Tukey J. Data Analysis and Regression. Addison-Wesley; Reading, MA: 1977. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Amaratunga D, Cabrera J. Analysis of Data from Viral DNA Microchips. Journal of the American Statistical Association. 2001;96:1161. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Smyth GK. Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology. 2004;3 doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1027. Article 3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Strimmer K. fdrtool: a versatile R package for estimating local and tail area-based false discovery rates. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:1461–2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheng M, Si Y, Niu Y, et al. High-throughput profiling of alpha interferon- and interleukin-28B-regulated microRNAs and identification of let-7s with anti-hepatitis C virus activity by targeting IGF2BP1. J Virol. 2013;87:9707–18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00802-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shirasaki T, Honda M, Shimakami T, et al. MicroRNA-27a regulates lipid metabolism and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in human hepatoma cells. J Virol. 2013;87:5270–86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03022-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bandyopadhyay S, Friedman RC, Marquez RT, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection and hepatic stellate cell activation downregulate miR-29: miR-29 overexpression reduces hepatitis C viral abundance in culture. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:1753–62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen Y, Chen J, Wang H, et al. HCV-induced miR-21 contributes to evasion of host immune system by targeting MyD88 and IRAK1. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003248. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ariumi Y, Kuroki M, Maki M, et al. The ESCRT system is required for hepatitis C virus production. PLoS One. 2011;6:e14517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Paul D, Madan V, Bartenschlager R. Hepatitis C virus RNA replication and assembly: living on the fat of the land. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;16:569–79. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Meyers NL, Fontaine KA, Kumar GR, et al. Entangled in a membranous web: ER and lipid droplet reorganization during hepatitis C virus infection. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016;41:117–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2016.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang X, Qian K. Protein O-GlcNAcylation: emerging mechanisms and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18:452–65. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Piver E, Boyer A, Gaillard J, et al. Ultrastructural organisation of HCV from the bloodstream of infected patients revealed by electron microscopy after specific immunocapture. Gut. 2017;66:1487–95. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lerat H, Honda M, Beard MR, et al. Steatosis and liver cancer in transgenic mice expressing the structural and nonstructural proteins of hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:352–65. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.31001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.de Queiroz RM, Carvalho E, Dias WB. O-GlcNAcylation: The Sweet Side of the Cancer. Front Oncol. 2014;4:132. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Singaravelu R, O’Hara S, Jones DM, et al. MicroRNAs regulate the immunometabolic response to viral infection in the liver. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11:988–93. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lavie M, Hanoulle X, Dubuisson J. Glycan Shielding and Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus Neutralizing Antibodies. Front Immunol. 2018;9:910. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G, et al. Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:825–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060608-102511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hart GW, Greis KD, Dong LY, et al. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine: the “yin-yang” of Ser/Thr phosphorylation? Nuclear and cytoplasmic glycosylation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;376:115–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sakaidani Y, Nomura T, Matsuura A, et al. O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine on extracellular protein domains mediates epithelial cell-matrix interactions. Nat Commun. 2011;2:583. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Butt AM, Khan IB, Hussain M, et al. Role of post translational modifications and novel crosstalk between phosphorylation and O-beta-GlcNAc modifications in human claudin-1, -3 and -4. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:1359–69. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0870-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Butt AM, Feng D, Nasrullah I, et al. Computational identification of interplay between phosphorylation and O-beta-glycosylation of human occludin as potential mechanism to impair hepatitis C virus entry. Infect Genet Evol. 2012;12:1235–45. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Neufeldt CJ, Joyce MA, Levin A, et al. Hepatitis C virus-induced cytoplasmic organelles use the nuclear transport machinery to establish an environment conducive to virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003744. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lussignol M, Kopp M, Molloy K, et al. Proteomics of HCV virions reveals an essential role for the nucleoporin Nup98 in virus morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:2484–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1518934113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhu Y, Liu TW, Madden Z, et al. Post-translational O-GlcNAcylation is essential for nuclear pore integrity and maintenance of the pore selectivity filter. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8:2–16. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjv033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jochmann R, Thurau M, Jung S, et al. O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation of Sp1 inhibits the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter. J Virol. 2009;83:3704–18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01384-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Groussaud D, Khair M, Tollenaere AI, et al. Hijacking of the O-GlcNAcZYME complex by the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein facilitates viral transcription. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006518. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Angelova M, Ortiz-Meoz RF, Walker S, et al. Inhibition of O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase Reduces Replication of Herpes Simplex Virus and Human Cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 2015;89:8474–83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01002-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kim M, Kim YS, Kim H, et al. O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase promotes cervical cancer tumorigenesis through human papillomaviruses E6 and E7 oncogenes. Oncotarget. 2016;7:44596–607. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zeng Q, Zhao RX, Chen J, et al. O-linked GlcNAcylation elevated by HPV E6 mediates viral oncogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:9333–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606801113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Xu W, Zhang X, Wu JL, et al. O-GlcNAc transferase promotes fatty liver-associated liver cancer through inducing palmitic acid and activating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Hepatol. 2017;67:310–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Boldanova T, Suslov A, Heim MH, et al. Transcriptional response to hepatitis C virus infection and interferon-alpha treatment in the human liver. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9:816–34. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201607006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.