Key Points
Question
Are genes associated with obesity treatment success in children with obesity?
Findings
In this interventional genetic association study that included 1198 children with overweight or obesity, 5 of 56 obesity single-nucleotide variants were statistically significantly associated with changes in body weight, however, only to a minor degree.
Meaning
In this study, environmental, social, and behavioral factors seem to play a substantial role in obesity treatment strategies in children.
Abstract
Importance
Genome-wide association studies have identified genetic loci influencing obesity risk in children. However, the importance of these loci in the associations with weight reduction through lifestyle interventions has not been investigated in large intervention trials.
Objective
To evaluate the associations between various obesity susceptibility loci and changes in body weight in children during an in-hospital, lifestyle intervention program.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Long-term Effects of Lifestyle Intervention in Obesity and Genetic Influence in Children (LOGIC), an interventional prospective cohort study, enrolled 1429 children with overweight or obesity to participate in an in-hospital lifestyle intervention program. Genotyping of 56 validated obesity single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) was performed, and the associations between the SNVs and body weight reduction during the intervention were evaluated using linear mixed-effects models for each SNV. The LOGIC study was conducted from January 6, 2006, to October 19, 2013; data analysis was performed from July 15, 2015, to November 6, 2016.
Exposures
A 4- to 6-week standardized in-hospital lifestyle intervention program (daily physical activity, calorie-restricted diet, and behavioral therapy).
Main Outcomes and Measures
The association between 56 obesity-relevant SNVs and changes in body weight and body mass index.
Results
Of 1429 individuals enrolled in the LOGIC Study, 1198 individuals (mean [SD] age, 14.0 [2.2] years; 670 [56%] girls) were genotyped. A mean (SD) decrease was noted in body weight of −8.7 (3.6) kg (95% CI, −15.7 to −1.8 kg), and body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) decreased by −3.3 (1.1) (95% CI, −5.4 to −1.1) (both P < .05). Five of 56 obesity SNVs were statistically significantly associated with a reduction of body weight or body mass index (all P < 8.93 × 10−4 corresponding to Bonferroni correction for 56 tests). Compared with homozygous participants without the risk allele, homozygous carriers of the rs7164727 (LOC100287559: 0.42 kg; 95% CI, 0.31-0.53 kg, P = 4.00 × 10−4) and rs12940622 (RPTOR: 0.35 kg; 95% CI, 0.18-0.52 kg; P = 1.86 × 10−5) risk alleles had a lower reduction of body weight, whereas carriers of the rs13201877 (IFNGR1: 0.65 kg; 95% CI, 0.51-0.79 kg; P = 2.39 × 10−5), rs10733682 (LMX1B: 0.45 kg; 95% CI, 0.27-0.63 kg; P = 6.37 × 10−4), and rs2836754 (ETS2: 0.56 kg; 95% CI, 0.38-0.74 kg; P = 1.51 × 10−4) risk alleles were associated with a greater reduction of body weight after adjustment for age and sex.
Conclusions and Relevance
Genes appear to play a minor role in weight reduction by lifestyle in children with overweight or obesity. The findings suggest that environmental, social, and behavioral factors are more important to consider in obesity treatment strategies.
This genetic association study evaluates changes in weight and body mass index associated with single-nucleotide variants in children with overweight and obesity.
Introduction
The high prevalence of childhood obesity is a major health challenge. In high-income countries, almost 25% of boys and girls are overweight or obese.1 Obesity in childhood often carries over into adulthood, predisposing individuals to additional comorbidities, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and/or heart disease. Obesity is a multifactorial disease associated with environmental, social, behavioral, physiologic, psychological, and genetic factors.2 The interaction between genetics and unhealthy lifestyle contributes to the complex cause of obesity. Results from twin, family, and adoption studies have shown that the heritability of obesity ranges from 30% to 70%.3 Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several gene loci, which seem to be relevant for body weight regulation. The most recent large GWAS meta-analysis with outcome body mass index (BMI) by the Genetic Investigation of Anthropometric Traits Consortium included data from 339 224 individuals and 125 GWAS on BMI. The study identified 97 loci that are associated with a higher BMI.4 Associations between several of these genes and obesity have been identified among children.5,6,7,8
Evidence has shown a wide interindividual response to obesity treatment with inconsistent results regarding the role of genetics in successful weight loss during childhood and adolescence.9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18 Reasons for this inconsistency have been that most of these studies have (1) not strictly adhered to a standardized lifestyle program, but rather conducted the intervention in an outpatient setting; (2) focused on only a few candidate genes, such as the FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated protein [OMIM *610966]) gene or the MC4R (melanocortin 4 receptor [OMIM *155541]) gene; and (3) included only relatively small sample sizes. The study with the largest population included 684 individuals.18 The aim of this study was to investigate existing associations between various obesity susceptibility loci and changes in age- and sex-adjusted body weight during an inpatient, standardized lifestyle intervention program in a large cohort of children and adolescents with overweight or obesity. We hypothesized that children with a genetic predisposition for obesity would achieve an overall lower amount of weight lost than children without the predisposition.
Methods
The Long-term Effects of Lifestyle Intervention in Obesity and Genetic Influence in Children (LOGIC) study was conducted from January 6, 2006, to October 19, 2013, and included 1429 individuals aged 6 to 19 years who were referred to a German rehabilitation center for inpatient weight loss treatment. Exclusion criteria for the LOGIC Study were secondary obesity; monogenetic diseases, such as Prader-Willi syndrome; and early withdrawal from the inpatient program (<3 weeks). The study design has been described in detail elsewhere.19 Previous publications reported on cardiometabolic risk parameters,20 quality of life and physical activity,21 adipokines,22 and physical fitness.23 In a subgroup of 310 children, the association of the melatonin receptor 1 B (MTNR1B [OMIM *600804]) variant with weight reduction during the inpatient therapy was examined. MTNR1B is a protein coding gene, which is associated with fasting glucose level and type 2 diabetes.10 All parents provided written informed consent for their children and adolescents for study participation. The participants did not receive financial compensation. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki24 and approved by the ethics committee of the School of Medicine of the Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany. The study was followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Genetic Association Studies (STREGA) reporting guideline.
In brief, the standardized, nonpharmacologic weight loss program was conducted for 4 to 6 weeks, depending on health insurance allowances, and was performed identically and standardized during the whole study period. The program focused on a calorie-restricted diet, increases in the level of physical activity, and behavior therapy. The intervention was conducted according to the German guidelines for inpatient weight loss programs.25
Anthropometric Examinations
All clinical examinations were conducted by trained medical staff according to standardized procedures. At the baseline examination, body height was measured barefoot, with minimal clothing, to the nearest 0.5 cm using a rigid scale. At baseline and once weekly during the intervention, body weight was measured with minimal clothing to the nearest 0.1 kg using a digital scale (Tanita BC-420 P MA Profi; Tanita Europe BV). Owing to personnel or logistical reasons, the weekly weight measurements were not performed in every participant at every time point. Body mass index was calculated as the individual’s body weight in kilograms divided by the square of body height in meters. Overweight was defined as a BMI above the 90th percentile and obesity was defined as a BMI above the 97th percentile, using population-specific data.26,27 The degree of obesity was additionally described using the least-square means method developed by Cole,28 which normalizes the BMI-skewed distribution and expresses BMI as an SD score (SDS), in combination with national German reference data.27
Genotyping and Quality Control
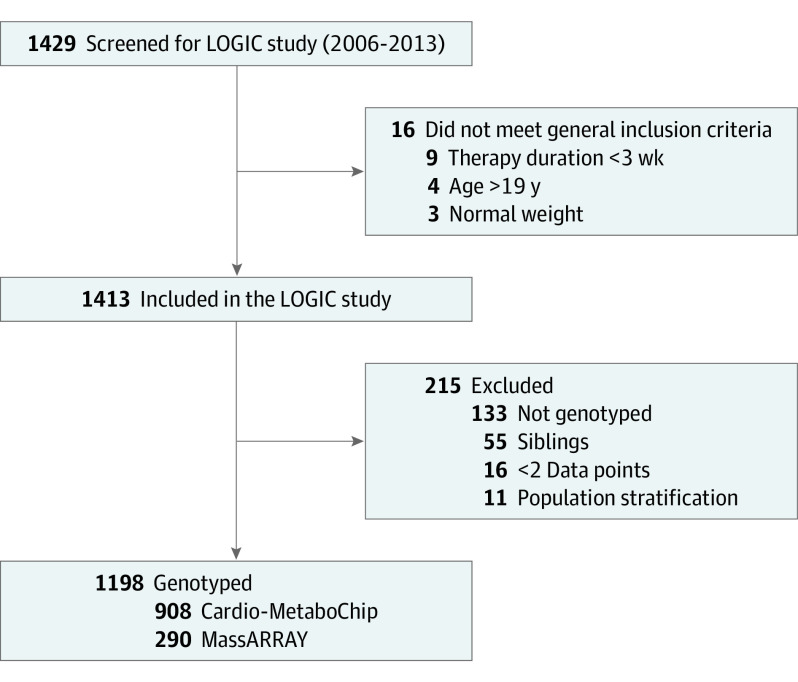
Genomic DNA for all participants had been extracted from EDTA blood samples following a standard protocol. For the genetic analysis, only children who were overweight or obese were included. If siblings were enrolled, the child with complete genotyped data or, if that was not possible, the youngest sibling, was included. From 1429 children enrolled into the program, 908 were genotyped with a custom-designed SNV chip that allows for an array-wide analysis of lipid and other metabolic and cardiovascular traits (Cardio-MetaboChip; Illumina).29 Furthermore, owing to later recruitment, an additional 290 children were genotyped (MassARRAY system with iPLEX chemistry; Agena) (Figure 1). To investigate population stratification, SNVs that are related to the QT interval were selected, and a joint principal component analysis on the 1000 genomes and LOGIC data was performed. The QT interval SNVs were chosen because they provide a set of SNVs that are not associated with the analysis traits of interest, in contrast to most of the genotypes on the Cardio-MetaboChip. QT interval SNVs that violate the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P < .05) were excluded. Children who were identified as population outliers based on visual inspection were removed from the analysis to avoid population stratification. To study the genetic variants that are known to affect body weight and body mass, we defined a candidate pool of 97 SNVs from previous publications.4
Figure 1. Flowchart.
LOGIC indicates Long-term Effects of Lifestyle Intervention in Obesity and Genetic Influence in Children.
For the MassARRAY system with iPLEX chemistry, the blood samples were analyzed in a matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonik GmbH). The resulting mass spectra were analyzed automatically for peak identification using the SpectroTYPER RT, version 4.0 software (Sequenom). For quality control, the spectra were checked by 2 independent persons.
After quality control inspection and combining quality-controlled genotype data covered by Cardio-MetaboChip (90 SNVs) and by MALDI-TOF from the MassARRAY (60 SNVs), 56 SNVs remained for analysis in the whole cohort. A schematic outline of the SNV selection is provided in the eFigure in the Supplement.
Statistical Analysis
The distributions of body weight, BMI, and BMI-SDS at the different study time points were investigated using quantile-quantile plots and found to be approximately normal. Single-nucleotide variant associations were modeled as effect per risk allele (additive genetic model). All analyses were performed with R, version 3.1.1 (R Core Team, 2014). Data analysis was performed from July 15, 2015, to November 6, 2016. Genes were provided according to Illumina annotation.30
To assess the associations of known obesity SNVs and changes in body weight, BMI, and BMI-SDS in the LOGIC Study, we fitted a linear mixed-effect model with random participant-specific intercept for each SNV:
| weightij = β0 + β1 × timeij + β2 × SNVi + β3 × timeij × SNV + bi0 + εij, |
| BMIij = β0 + β1 × timeij + β2 × SNVi + β3 × timeij × SNV + bi0 + εij, and |
BMI-SDSij = β0 + β1 × timeij + β2 × SNVi + β3 × timeij × SNV + bi0 + εij, where time denotes the number of weeks in therapy when BMI was measured; bi0, a subject-specific intercept; and εij, the error term for participant i at time point j. Restricted maximum likelihood estimation was used.
Since changes in body weight and BMI also depend on age and sex, we fitted 2 additional models with adjustment for age and sex at baseline:
| weightij = β0 + β1 × timeij + β2 × SNVi + β3 × agei + β4 × sexi + β5 × timeij × SNVi + β6 × timeij × agei + β7 × timeij × sexi + bi0 + εij, and |
| BMIij = β0 + β1 × timeij + β2 × SNVi + β3 × agei + β4 × sexi + β5 × timeij × SNV + β6 × timeij × agei + β7 × timeij × sexi + bi0 + εij. |
P values were subjected to multiple testing correction using the Bonferroni method, resulting in a significance threshold of 0.000893 for 56 tests.
Results
Of 1429 individuals enrolled in the LOGIC Study, 1198 children (mean [SD] age, 14.0 (2.2) years; 670 [56%] girls) were genotyped (Figure 1). There were no statistically significant differences between the included and excluded children regarding sex or anthropometric characteristics (eTable 1 in the Supplement).
The characteristics of the study sample at baseline and at the different time points are reported in Table 1. Thirty percent of the participants completed the treatment after 4 weeks, according to the therapy plan. Mean (SD) reductions were noted from baseline to the end of the intervention in body weight (−8.7 [3.6] kg; 95% CI, −15.7 to −1.8 kg), BMI (−3.3 [1.1]; 95% CI, −5.4 to −1.1), and BMI-SDS (−0.38 [0.14]; 95% CI, −0.65 to −0.11) (all P < .05).
Table 1. Characteristics of the Study Participants Before the Start of the Intervention and at the Weekly Measurement Time Pointsa.
| Time | No. | Sex, No. (%) | Mean (SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girls | Boys | Body weight, kg | BMI | BMI-SDS | ||
| Baseline | 1198 | 670 (56) | 528 (44) | 92.2 (23.1) | 33.8 (5.8) | 2.76 (0.54) |
| Week 1 | 1179 | 660 (56) | 519 (44) | 88.7 (22.3) | 32.6 (5.7) | 2.60 (0.57) |
| Week 2 | 1170 | 657 (56) | 513 (44) | 87.2 (21.9) | 32.0 (5.6) | 2.56 (0.58) |
| Week 3 | 1157 | 651 (56) | 506 (44) | 86.1 (21.5) | 31.6 (5.5) | 2.50 (0.59) |
| Week 4 | 1131 | 644 (57) | 487 (43) | 84.8 (21.3) | 31.2 (5.4) | 2.45 (0.60) |
| Week 5 | 825 | 484 (59) | 341 (41) | 85.4 (20.5) | 31.2 (5.4) | 2.45 (0.61) |
| Week 6 | 820 | 474 (58) | 346 (42) | 84.3 (20.1) | 30.8 (5.2) | 2.40 (0.61) |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); BMI-SDS, BMI-standard deviation score.
Mean (SD) age at baseline was 14.0 (2.2) years.
There were no statistically significant cross-sectional associations between obesity-related SNVs and body weight, BMI, or BMI-SDS at baseline. Table 2 reports the statistically significant longitudinal associations between obesity-related SNVs and changes in body weight, BMI, and BMI-SDS. eTables 2, 3, and 4 in the Supplement present the associations with all of the investigated SNVs.
Table 2. Statistically Significant Associations Between SNVs and Changes in Body Weight, BMI, and BMI-SDS per Week During the Intervention.
| SNV | Chr | Position | Effect allelea | Other allele | β Coefficient (95% CI)b | P value | Corr P value | Effect allele frequency | Gene30,c | No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNV association with body weight change | ||||||||||
| rs13201877 | 6 | 137.717.234 | G | A | −0.073 (−0.106 to −0.039) | 2.39 × 10−5 | .001 | 0.210 | IFNGR1 | 1184 |
| rs10733682 | 9 | 128.500.735 | A | G | −0.041 (−0.065 to −0.018) | 6.37 × 10−4 | .04 | 0.516 | LMX1B | 1194 |
| rs7164727 | 15 | 70.881.044 | T | C | 0.047 (0.021 to 0.073) | 4.02 × 10−4 | .02 | 0.633 | LOC100287559 | 1194 |
| rs12940622 | 17 | 76.230.166 | G | A | 0.054 (0.029 to 0.078) | 1.86 × 10−5 | .001 | 0.565 | RPTOR | 1194 |
| rs2836754 | 21 | 39.213.610 | C | T | −0.047 (−0.072 to −0.023) | 1.51 × 10−4 | .01 | 0.575 | ETS2 | 1190 |
| SNV association with BMI change | ||||||||||
| rs13201877 | 6 | 137.717.234 | G | A | −0.022 (−0.034 to −0.011) | 1.48 × 10−4 | .01 | 0.210 | IFNGR1 | 1184 |
| rs2836754 | 21 | 39.213.610 | C | T | −0.015 (−0.024 to −0.007) | 2.84 × 10−4 | .02 | 0.575 | ETS2 | 1190 |
| SNV association with BMI-SDS change | ||||||||||
| rs13078960 | 3 | 85.890.280 | G | T | 0.003 (0.002 to 0.005) | 2.52 × 10−5 | .001 | 0.268 | CADM2 | 1047 |
| rs13107325 | 4 | 103.407.732 | T | C | 0.004 (0.002 to 0.006) | 1.67 × 10−4 | .01 | 0.139 | SLC39A8 | 1191 |
| rs11170468 | 12 | 37.716.315 | A | C | 0.003 (0.001 to 0.004) | 1.05 × 10−4 | .01 | 0.700 | CPNE8 | 1197 |
| rs9925964 | 16 | 31.037.396 | A | G | −0.002 (−0.003 to −0.001) | 3.48 × 10−4 | .02 | 0.584 | KAT8 | 1186 |
Abbreviations: A, adenosine; BMI, body mass index; C, cytosine; Chr, chromosome; Corr, corrected; G, guanine; SDS, standard deviation score; SNV, single-nucleotide variant; T, thymine.
Provides the effect estimates against the other alleles, which serves as reference.
Standardized regression coefficient.
Genes were provided according to Illumina annotation.
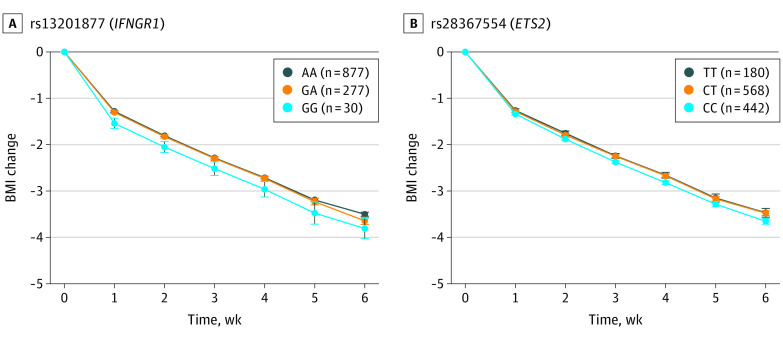
To illustrate these associations, Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the mean changes in body weight or BMI between weeks 0 and 6 for carriers of the different genotypes of the SNVs rs13201877, rs10733682, rs7164727, rs12940622, and rs2836754. The nearest genes of these are IFNGR1 (interferon γ receptor 1 [OMIM *107470]) for rs13201877, LMX1B (LIM homeobox 14 transcription factor 1, beta [OMIM *602575]) for rs10733682, LOC100287559 [no OMIM ID available] for rs7164727, RPTOR (regulatory-associated protein of MTOR, complex 1 [OMIM *607130]) for rs12940622, and ETS2 (ETS proto-oncogene 2, transcription factor [OMIM *164740]) for rs2836754. Compared with homozygous participants without the risk allele, homozygous carriers of the rs7164727 (LOC100287559: 0.42 kg; 95% CI, 0.31-0.53 kg; P = 4.00 × −4) and the rs12940622 (RPTOR: 0.35 kg; 95% CI, 0.18-0.52 kg; P = 1.86 × 10−5) risk alleles had a lower reduction of body weight, whereas carriers of the rs13201877 (IFNGR1: 0.65 kg; 95% CI, 0.51-0.79 kg; P = 2.39 × −5), rs10733682 (LMX1B: 0.45 kg; 95% CI, 0.27-0.63 kg; P = 6.37 × −4), and rs2836754 (ETS2: 0.56 kg; 95% CI, 0.38-0.74 kg; P = 1.51 × −4) risk alleles had a greater reduction of body weight after adjustment for age and sex (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Changes in Body Weight and Genotypes.
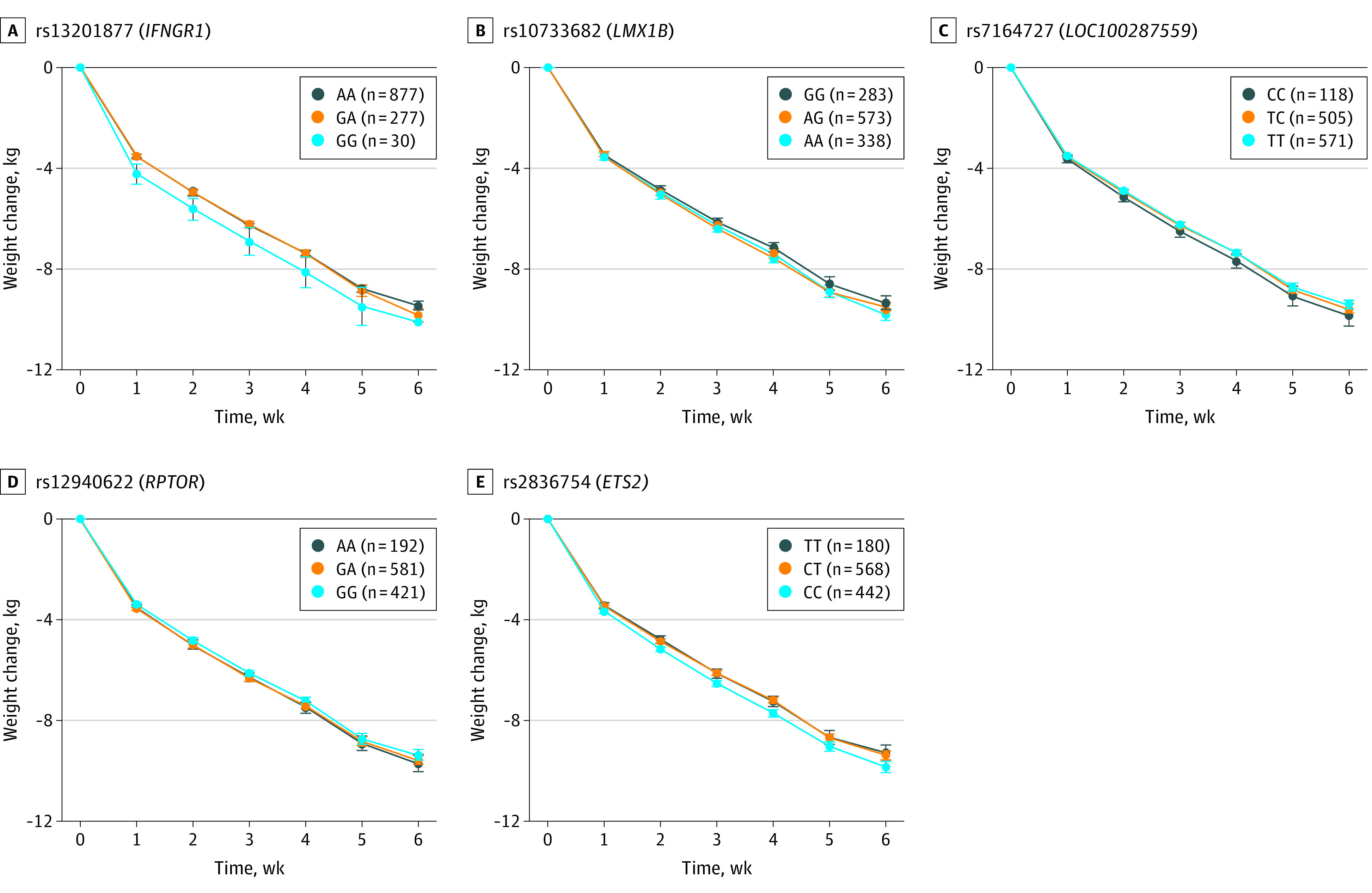
Mean change in age- and sex-adjusted body weight between weeks 0 and 6 and week 0 for carriers of the different genotypes of the SNVs rs13201877 (A), rs10733682 (B), rs7164727 (C), rs12940622 (D) and rs 2836754 (E). A indicates adenosine; C, cytosine; G, guanine; and T, thymine. Parenthetical values indicate the number of children included in the analysis. Error bars indicate the 95% CI.
Figure 3. Changes in Body Mass Index (BMI) and Genotypes.
Mean change in age- and sex-adjusted BMI (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) between weeks 0 and 6 and week 0 for carriers of the different genotypes of the SNVs rs13201877 (A) and rs2836754 (B). A indicates adenosine; C, cytosine; G, guanine; and T, thymine. Parenthetical values indicate the number of children included in the analysis. Error bars indicate the 95% CI.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the largest interventional study in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity investigating the association of genetics with the outcome of a standardized lifestyle intervention program. Our findings suggest that 5 of 56 obesity-related SNVs are associated with body weight and/or BMI reduction during the intervention. We were able to support our hypothesis of the presence of obesity risk alleles, which were associated with lower body weight reduction for 2 SNVs (rs12940622 and rs7164727); however, the effect size was low. Our data revealed that 3 obesity-associated SNVs (rs13201877, rs10733682, and rs2836754) were instead associated with greater weight reductions. We could not find any associations between weight loss and the most widely investigated obesity susceptibility loci MC4R, TMEM-18 (OMIM *613220), or FTO. However, this lack of association refers especially for FTO caused by low coverage because the tag SNVs (defined as an SNV that proxies for a set of SNVs in 4 linkage disequilibriums with itself) of FTO were not available in our data set owing to technical reasons. Nevertheless, in the Cardio-MetaboChip subset we could analyze other FTO SNVs (rs17817449 and rs3751812) and noted no association with weight loss. Of SNVs, that have been reported as having genome-wide significance in children with overweight or obesity,6 only one could be confirmed in our sample. This SNV was located in the protein coding gene LMX1B, which functions as a transcription factor and is essential, among others, for the dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons. Hypodopaminergic function is related to abnormal eating behavior, which might explain the association of LMX1B with weight change in our study.31 Likewise, the function of the RPTOR gene could explain the observed associations. This gene encodes a component of a signaling pathway that regulates cell growth in response to nutrient and insulin levels, which in turn influence body weight.32 However, the other SNVs that showed statistically significant associations with weight changes in our study do not have a clearly defined role explaining why they might affect body weight, as is the case for most obesity-related genes identified by GWAS. For example, genetic variants in IFNGR1 are associated with susceptibility to mycobacterial disease.33 The gene ETS2 encodes a transcription factor, which regulates genes involved in development and apoptosis.34 Overall knowledge about the gene LOC100287559 is scarce.
Our data are in accordance with previous observations implying that gene variations associated with body weight (ie, obesity genes) do not necessarily influence longitudinal changes in body weight.35,36,37,38 In this context, our study revealed different results regarding the use of BMI-SDS compared with the age- and sex-adjusted body weight or BMI. BMI z-scores, also called BMI-SDS, are measures of body weight adjusted for children’s age and sex. Even though z-scores are optimal for assessing adiposity on a single occasion, it is not necessarily the best scale for measuring change in adiposity, as the within-child variability over time depends on the child’s level of adiposity. Therefore, the use of BMI is recommended for longitudinal analyses instead of BMI-SDS39 and this might also be the reason for the different results in our study.
Several studies have also examined the associations between obesity-related SNVs and lifestyle interventions in children and adolescents.9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18 All of these studies analyzed only a few SNVs on selected candidate genes, mostly FTO and MC4R. Only 3 studies involved more than 2 genes in their analysis,9,11,15 the largest number being 12 loci.9 Most of these studies were performed in an outpatient setting with limited sample sizes ranging from 207 to 401 individuals.9,11,12,13,14,15,16 Only 2 studies were conducted in an inpatient, and thereby more controlled, setting.10,17,18 In 357 Czech children with overweight or obesity, statistically significant associations between the SNVs rs17817449 of the FTO gene and rs17782313 of the MC4R gene and a reduction of BMI was observed after a 1-month inpatient lifestyle intervention program.17 A recent investigation within the same study showed no association between the SNVs rs6971091 of the NYD-SP18 gene or rs4854344 of the TMEM18 gene and weight reduction in 684 children.18 A previous investigation conducted within our LOGIC study examined associations between an MTNR1B variant and weight loss in 310 children with overweight or obesity during the 4- to 6-week inpatient therapy program and could not find statistically significant associations with regard to short-term weight loss.10
Overall, all previous association studies have shown inconsistent results. For the obesity-related polymorphism rs17817449 of the FTO gene, statistically significant associations were found with regard to weight loss during the weight loss intervention in a study by Zlatohlavek et al.17 However, 7 studies reported no statistically significant associations9,11,12,14,15,18 or only a trend regarding a genetic predisposition to weight loss.14 In 2 studies involving 10 or more SNVs, variants of SDCCAG8 (OMIM *613524) were associated with reduced weight loss during an outpatient lifestyle intervention.9,15 Likewise, there is inconsistency regarding acute weight loss vs weight maintenance after follow-up. Reinehr et al14 did not find an association between FTO and weight loss during 1 year of outpatient intervention, but observed an association with weight regain over 1 year of follow-up. Similarly, Hinney et al9 reported that variants of SDCCAG8 were associated with reduced weight loss during an outpatient lifestyle intervention, but there were no associations with weight regain after 1 year of follow-up.
Strengths and Limitations
In contrast to the studies involving 168 to 684 children,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18 our sample size exceeded 1000 children. In addition, we assessed a large number of obesity-related SNVs based on the results of current GWAS instead of selected candidate genes. Moreover, the highly controlled inpatient standardized setting of our intervention is optimal for investigating the associations between genetics and body weight changes.
This study has limitations. It was not a randomized clinical trial because such a trial was believed to be ethically questionable by randomizing treatment-seeking overweight and obese individuals into a no-treatment group or wait-list control group. Thus, the results cannot determine causality. Owing to technical reasons we had to limit our main analysis to 56 SNVs which were analyzed in the whole cohort. Because FTO variants were covered in three-quarters of our study, we cannot exclude an association with this locus. However, the associations with weight loss seem weak, as we saw no indication for an association in the available data. Furthermore, 2 different systems were used for genotyping. For about one-quarter of the participants the Cardio-MetaboChip was not applicable for genotyping at that time because production had been stopped. However, the error rate was assumed to be similar between the 2 systems, especially when applying strict quality control thresholds. Both technologies are reliable, well-established genotyping methods. The MALDI MassARRAY system has been developed as a diagnostic tool, which is used to determine specific disease-causing SNVs.40
Conclusions
Our study offers evidence showing that genes susceptible to obesity play a minor role in treatment success in children who are overweight or obese. Further studies are needed to determine whether other non–obesity-related genes may impact weight reduction. This study suggests that environmental, social, and behavioral factors play the most important role in obesity treatment strategies in children, whereas genetics are secondary.
eTable 1. Comparison of the Included and Excluded Participants
eTable 2. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in Body Weight Adjusted for Age and Sex During the Intervention
eTable 3. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in BMI Adjusted for Age and Sex During the Intervention
eTable 4. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in BMI-SDS During the Intervention
eFigure. Selection and Genotyping of SNPs
References
- 1.Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766-781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Han JC, Lawlor DA, Kimm SY. Childhood obesity. Lancet. 2010;375(9727):1737-1748. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60171-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chesi A, Grant SFA. The genetics of pediatric obesity. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26(12):711-721. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.08.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, et al. ; LifeLines Cohort Study; ADIPOGen Consortium; AGEN-BMI Working Group; CARDIOGRAMplusC4D Consortium; CKDGen Consortium; GLGC; ICBP; MAGIC Investigators; MuTHER Consortium; MIGen Consortium; PAGE Consortium; ReproGen Consortium; GENIE Consortium; International Endogene Consortium . Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518(7538):197-206. doi: 10.1038/nature14177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bradfield JP, Taal HR, Timpson NJ, et al. ; Early Growth Genetics Consortium . A genome-wide association meta-analysis identifies new childhood obesity loci. Nat Genet. 2012;44(5):526-531. doi: 10.1038/ng.2247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Felix JF, Bradfield JP, Monnereau C, et al. ; Bone Mineral Density in Childhood Study (BMDCS); Early Genetics and Lifecourse Epidemiology (EAGLE) consortium; Early Growth Genetics (EGG) Consortium; Bone Mineral Density in Childhood Study BMDCS . Genome-wide association analysis identifies three new susceptibility loci for childhood body mass index. Hum Mol Genet. 2016;25(2):389-403. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv472 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scherag A, Dina C, Hinney A, et al. Two new Loci for body-weight regulation identified in a joint analysis of genome-wide association studies for early-onset extreme obesity in French and German study groups. PLoS Genet. 2010;6(4):e1000916. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang HJ, Hinney A, Song JY, et al. Association of common variants identified by recent genome-wide association studies with obesity in Chinese children: a case-control study. BMC Med Genet. 2016;17:7. doi: 10.1186/s12881-016-0268-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hinney A, Wolters B, Pütter C, et al. No impact of obesity susceptibility loci on weight regain after a lifestyle intervention in overweight children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2013;26(11-12):1209-1213. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2013-0179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holzapfel C, Siegrist M, Rank M, et al. Association of a MTNR1B gene variant with fasting glucose and HOMA-B in children and adolescents with high BMI-SDS. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;164(2):205-212. doi: 10.1530/EJE-10-0588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moleres A, Rendo-Urteaga T, Zulet MA, et al. ; EVASYON Study Group . Obesity susceptibility loci on body mass index and weight loss in Spanish adolescents after a lifestyle intervention. J Pediatr. 2012;161(3):466-470.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Müller TD, Hinney A, Scherag A, et al. “Fat mass and obesity associated” gene (FTO): no significant association of variant rs9939609 with weight loss in a lifestyle intervention and lipid metabolism markers in German obese children and adolescents. BMC Med Genet. 2008;9:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-9-85 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Reinehr T, Hinney A, Toschke AM, Hebebrand J. Aggravating effect of INSIG2 and FTO on overweight reduction in a one-year lifestyle intervention. Arch Dis Child. 2009;94(12):965-967. doi: 10.1136/adc.2008.147652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reinehr T, Wolters B, Roth CL, Hinney A. FTO gene: association to weight regain after lifestyle intervention in overweight children. Horm Res Paediatr. 2014;81(6):391-396. doi: 10.1159/000358328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Scherag A, Kleber M, Boes T, et al. ; NUGENOB Consortium . SDCCAG8 obesity alleles and reduced weight loss after a lifestyle intervention in overweight children and adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012;20(2):466-470. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vogel CI, Boes T, Reinehr T, et al. Common variants near MC4R: exploring gender effects in overweight and obese children and adolescents participating in a lifestyle intervention. Obes Facts. 2011;4(1):67-75. doi: 10.1159/000324557 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zlatohlavek L, Vrablik M, Motykova E, et al. FTO and MC4R gene variants determine BMI changes in children after intensive lifestyle intervention. Clin Biochem. 2013;46(4-5):313-316. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.11.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zlatohlavek L, Maratka V, Tumova E, et al. Body adiposity changes after lifestyle intervention in children/adolescents and the NYD-SP18 and TMEM18 variants. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:7493-7498. doi: 10.12659/MSM.907180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rank M, Siegrist M, Wilks DC, et al. Long-term effects of an inpatient weight-loss program in obese children and the role of genetic predisposition-rationale and design of the LOGIC-trial. BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-30 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rank M, Siegrist M, Wilks DC, et al. The cardio-metabolic risk of moderate and severe obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2013;163(1):137-142. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.01.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rank M, Wilks DC, Foley L, et al. Health-related quality of life and physical activity in children and adolescents 2 years after an inpatient weight-loss program. J Pediatr. 2014;165(4):732-7.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.05.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Siegrist M, Rank M, Wolfarth B, et al. Leptin, adiponectin, and short-term and long-term weight loss after a lifestyle intervention in obese children. Nutrition. 2013;29(6):851-857. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.12.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wilks DC, Rank M, Christle J, Langhof H, Siegrist M, Halle M. An inpatient lifestyle-change programme improves heart rate recovery in overweight and obese children and adolescents (LOGIC Trial). Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2014;21(7):876-883. doi: 10.1177/2047487312465691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310(20):2191-2194. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Reinehr T, Holl RW, Wabitsch M. The German Working Group of Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence (AGA): improving the quality of care for overweight and obese children in Germany. Obes Facts. 2008;1(1):26-32. doi: 10.1159/000113405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000;320(7244):1240-1243. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kromeyer-Hauschild K, Wabitsch M, Geller F, Ziegler A, Geiß H, Hesse V.. Perzentilenfür den Body Mass Index für das Kindes- und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde. 2001;149:11. doi: 10.1007/s001120170107 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cole TJ. The LMS method for constructing normalized growth standards. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1990;44(1):45-60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Voight BF, Kang HM, Ding J, et al. The metabochip, a custom genotyping array for genetic studies of metabolic, cardiovascular, and anthropometric traits. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002793. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002793 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Illumina. Metabochip gene annotation. Accessed October 24, 2016. https://support.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/downloads/productfiles/cardio-metabochip/metabochip_gene_annotation.zip
- 31.GeneCards. LMX1B gene (protein coding). Accessed March 4, 2020. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LMX1B
- 32.GeneCards. gene RPTOR. (protein coding). Accessed March 4, 2020. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=RPTOR
- 33.GeneCards. IFNGR1 gene (protein coding). Accessed March 4, 2020. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=IFNGR1
- 34.GeneCards. ETS2 gene (protein coding). Accessed March 4, 2020. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=ETS2
- 35.Cuypers KF, Loos RJ, Kvaløy K, Kulle B, Romundstad P, Holmen TL. Obesity-susceptibility loci and their influence on adiposity-related traits in transition from adolescence to adulthood—the HUNT study. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046912 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hjelmborg JV, Fagnani C, Silventoinen K, et al. Genetic influences on growth traits of BMI: a longitudinal study of adult twins. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16(4):847-852. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ortega-Alonso A, Sipilä S, Kujala UM, Kaprio J, Rantanen T. Genetic influences on change in BMI from middle to old age: a 29-year follow-up study of twin sisters. Behav Genet. 2009;39(2):154-164. doi: 10.1007/s10519-008-9245-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sandholt CH, Allin KH, Toft U, et al. The effect of GWAS identified BMI loci on changes in body weight among middle-aged Danes during a five-year period. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014;22(3):901-908. doi: 10.1002/oby.20540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cole TJ, Faith MS, Pietrobelli A, Heo M. What is the best measure of adiposity change in growing children: BMI, BMI %, BMI z-score or BMI centile? Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005;59(3):419-425. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602090 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vogel N, Schiebel K, Humeny A. Technologies in the whole-genome age: MALDI-TOF-based genotyping. Transfus Med Hemother. 2009;36(4):253-262. doi: 10.1159/000225089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable 1. Comparison of the Included and Excluded Participants
eTable 2. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in Body Weight Adjusted for Age and Sex During the Intervention
eTable 3. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in BMI Adjusted for Age and Sex During the Intervention
eTable 4. Associations Between the 56 SNPs and Changes in BMI-SDS During the Intervention
eFigure. Selection and Genotyping of SNPs