Abstract
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer‐related death worldwide. As well as the identified role of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), its association with driver mutations has improved the therapeutics for patients with lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. These patients usually display shorter overall survival and a higher tendency to develop distant metastasis compared with those carrying the wild‐type EGFR. Nevertheless, the way to control mutated EGFR signaling remains unclear. Here, we performed membrane proteomic analysis to determine potential components that may act with EGFR mutations to promote lung cancer malignancy. Expression of transmembrane glycoprotein non‐metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) was positively correlated with the status of mutated EGFR in non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This protein was not only overexpressed but also highly glycosylated in EGFR‐mutated, especially EGFR‐L858R mutated, NSCLC cells. Further examination showed that GPNMB could activate mutated EGFR without ligand stimulation and could bind to the C‐terminus of EGFR, assist phosphorylation at Y845, turn on downstream STAT3 signaling, and promote cancer metastasis. Moreover, we also found that Asn134 (N134) glycosylation of GPNMB played a crucial role in this ligand‐independent regulation. Depleting N134‐glycosylation on GPNMB could dramatically inhibit binding of GPNMB to mutated EGFR, blocking its downstream signaling, and ultimately inhibiting cancer metastasis in NSCLC. Clarifying the role of N‐glycosylated GPNMB in regulating the ligand‐independent activation of mutated EGFR may soon give new insight into the development of novel therapeutics for NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR mutation, GPNMB, metastasis, N‐glycosylation, NSCLC
In this study, we used membrane proteomic analysis to identify that GPNMB is overexpressed and highly N‐glycosylated in the EGFR mutant, especially the EGFR‐L858R mutated, NSCLC. GPNMB could bind to mutated EGFR without ligand stimulation, activate its downstream signaling and promote cancer metastasis. N134 glycosylation of GPNMB also plays a crucial role in controlling this ligand‐independent regulation.
Abbreviations
- D+T
EGFR del19 plus T790M mutations
- Del19
exon 19 deletion
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- FDR
false discovery rate
- GPNMB
glycoprotein non‐metastatic melanoma protein B
- L+T
EGFR L858R plus T790M mutations
- L858R
leucine‐to‐arginine point mutation at position 858
- MAPK pathway
the Ras/Raf/mitogen‐activated kinase pathway
- MPF
malignant pleural effusion
- N134Q
mutation substitutes a asparagine (N) with a glutamine (Q) at position 134
- NSCLC
non‐small cell lung cancer
- STAT pathway
signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway
- T790M
mutation substitutes a threonine (T) with a methionine (M) at position 790 of exon 20
- TKI
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
1. INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer‐related deaths worldwide. 1 , 2 Although the identification of EGFR driver mutations has improved lung cancer therapeutics, patient 5‐y survival rates worldwide are still less than 25%. Patients with mutated EGFR usually display shorter overall survival time and a higher tendency to develop distant metastases compared with those individuals carrying wild‐type EGFR. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 To date, how mutated EGFR evades negative, activation‐dependent regulation and promotes distant metastasis is still unclear. Therefore, gaining deeper insight into the protein network of mutated EGFR would help us to understand details of this network and provide new ideas for lung cancer treatment.
EGFR is a transmembrane protein that belongs to the ErbB superfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). 9 , 10 When ligands bind, they form homodimers or heterodimers, autophosphorylate intracellular tyrosine residues, and trigger downstream signaling pathways such as the Ras/Raf/ MAPK pathway, PI3K‐Akt pathway, or STAT pathway, which affect many cellular activities. 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 Members of the ErbB family proteins have received much attention as a result of their strong association with cancer malignancy. 15 , 16 Retrospective analyses have shown that the expression levels of EGFR were increased in various cancers and were correlated with poor prognosis in patients. 7 , 17 , 18
In East Asia, EGFR is the most frequently mutated gene in NSCLC. 19 Deletion of exon 19 (Del19) and the leucine‐to‐arginine point mutation at position 858 (L858R) in exon 21 are the 2 most common mutations found in clinics. 20 , 21 , 22 These mutations may increase kinase activity of EGFR, leading to hyperactivation of its downstream signaling, and conferring oncogenic properties on EGFR‐mutated cells. 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 As such, EGFR TKIs have become first‐line treatment for patients with lung cancer and who have EGFR mutations. 9 Despite the good therapeutic response from EGFR TKIs, drug resistance and distant metastases are major clinical challenges. Whether any component exists that acts with mutated EGFR to trigger downstream signaling, and subsequently its metastatic behavior, is still a mystery. Therefore, investigating the protein network may help towards a greater understanding of the details of how mutated EGFR controls cancer malignancy in cells.
Glycoprotein non‐metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) is a type I transmembrane protein and is a highly N‐ or O‐linked glycosylated protein. 27 , 28 , 29 In humans, there are 2 splicing variants: one consists of 560 amino acids and the other has 572 amino acids. Both contain a large extracellular domain, a single transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. 27 Previous studies have shown that GPNMB is enriched on the cell surface and participates in many physiological processes such as cell‐cell adhesion, differentiation, and the immune response. 27 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 However, the role of GPNMB in cancers is ambiguous. Both anti‐tumorigenic and pro‐tumorigenic properties have been reported. 34 , 35 , 36 In breast cancer, GPNMB was first characterized as a tumor suppressor in normal mammary epithelial cells. 37 It was described as a mediator that promotes cancer metastasis in both melanoma and breast cancer. 33 , 38 Recently, a study has indicated that the phosphorylation events of GPNMB, tyrosine kinase 6 (BRK) and hypoxia‐induced factor 1α (HIF1α) could be used to predict the worse outcomes in patients with triple‐negative breast cancer. 39 However, the molecular mechanisms engaged by GPNMB in NSCLC malignancy are not clear.
In this study, we used membrane proteomic analyses to reveal potential components that interact with EGFR mutants on the cell surface to promote lung cancer malignancy. Compared with wild‐type EGFR lung cancer cells, membrane proteins with significantly increased expression in EGFR‐mutated lung cancer cells were selected and used to establish the connection with EGFR through systematic analysis. The data revealed that GPNMB was increased and highly glycosylated in EGFR‐mutant lung cancer cells. As the role of GPNMB in cancers is ambiguous, we explored the functional relationship between GPNMB and mutated EGFR in NSCLC in more detail.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plasmids, antibodies, primer sequences, and detailed protocols are listed in Data S1 and Table S1.
2.1. Cell lines and culture conditions
Human lung adenocarcinoma cells: CL1‐0, CL1‐5, CL68, CL97, CL100, and VL307 were kindly provided by Dr. Pan‐Chyr Yang, and PC9 was obtained from Dr. Chih‐Hsin Yang's laboratory in National Taiwan University. Cells A549 (ATCC® CCL‐185™), H1975 (ATCC® CRL‐5908™), H3255 (ATCC® CRL‐2882™), and H1299 (ATCC® CRL‐5803™) were purchased from the ATCC. Cell culture conditions are listed in the Data S1.
2.2. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting
Cells were lysed on ice for 5‐10 min in 20 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 100 μM Na3VO4, 50 mM NaF, 30 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 0.5% NP‐40 (all from Sigma‐Aldrich) and complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The lysates were passed several times through a 21‐gauge needle and clarified by centrifugation at 12 000 rpm for 30 min at 4°C. The supernatants were taken as the total cell lysates and immunoprecipitated using anti‐FLAG, anti‐GPNMB, or anti‐myc antibodies and protein A‐Sepharose beads (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc). The precipitated proteins were separated using SDS‐PAGE and immunoblotting was performed in accordance with the standard procedures.
2.3. Wound‐healing assay
Cells were seeded into chamber wells and incubated at 37℃ in an humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 in air overnight. After removing the chamber, cells were washed with PBS and photographed at 0 and 8 h to observe their migratory abilities. Three independent experiments in triplicate were performed for each cell line.
2.4. Modified Boyden chamber invasion assay
Modified Boyden chambers with polycarbonate‐membrane inserts (pore size, 8 μm; Falcon; Becton Dickinson) coated with 30 μg of Matrigel (BD) were used for cell invasion assays. 41 Cells were suspended in medium containing 10% NuSerum (Thermo) and placed in the upper chambers, while 1 mL of medium was placed in each of the lower chambers. After 12 h incubation, cells were fixed with methanol and stained with 10% Giemsa stain solution (Sigma). Cell numbers were counted under a microscope at ×100 magnification. Experiments were performed at least twice, and each sample was assayed in triplicate.
2.5. Experimental metastasis in vivo
A single‐cell suspension containing 106 cells in 0.1 mL PBS was injected into the lateral tail veins of 6‐wk‐old SCID mice (National Laboratory Animal Center, Taiwan). 40 At 10 wk after injection, the mice were sacrificed and their lungs were examined for metastatic nodules (details in Data S1) All mouse experiments were performed with the approval of the Laboratory Animal Center, National Taiwan University College of Medicine.
2.6. Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Differences between the different groups were analyzed using Student t test or multiple comparison test. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (v.8.0) or SAS software, and a value of P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Membrane protein linkage map of mutated EGFR in NSCLC
To explore the potential cell surface partners that act with mutated EGFR to provide its oncogenic characteristics, we first investigated by quantitative membrane proteomic analyses the membrane profiling of 5 EGFR‐wild‐type (CL1‐0, CL1‐5, CL83, CL152, and CL142) and 3 EGFR‐mutant (CL25, CL97, and CL100) lung cancer cell lines. A list of 3796 proteins was identified (FDR < 1%) from the 8 cell lines, 3723 proteins of which were quantified by the MaxQuant package (v.1.6.11) with label‐free quantitation intensities in at least 1 cell line. Among these, 361 differentially expressed proteins were filtered with a P‐value < .05.
As Figure 1A shows, the differentially expressed proteins in EGFR‐mutant cells presented 2 separate clusters including 140 upregulated (average ratio > 1.45) and 221 downregulated (average ratio < 0.72) proteins. Functional analysis indicated that upregulated proteins in EGFR‐mutant cells were enriched in exocytosis, cell activation involved in the immune response, regulation of cell adhesion, carbohydrate derivative metabolic process, cytokine‐mediated signaling pathway, and membrane raft organization. In contrast, the downregulated proteins were mostly involved in peptidyl‐asparagine modification, protein targeting, lipid metabolic process, the response to endoplasmic reticulum stress, and the endoplasmic reticulum‐associated protein degradation (ERAD) pathways (Figure 1B).
FIGURE 1.
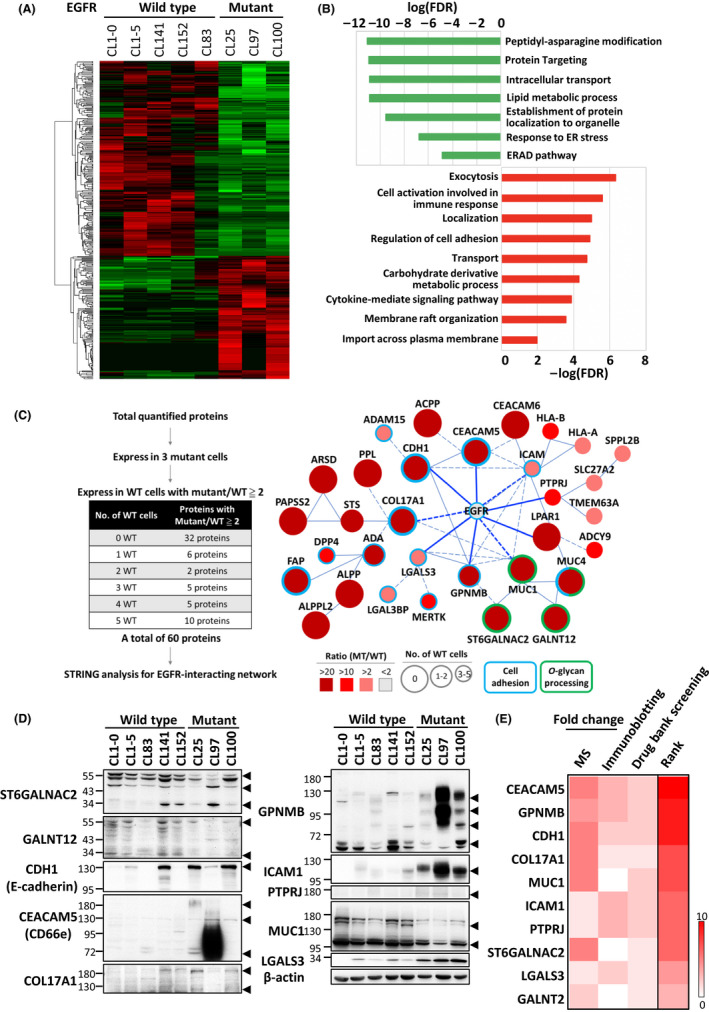
Altered membrane protein profiling associated with EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. A, Heat‐map and clustering analysis of 361 differentially expressed proteins in EGFR‐wild‐type and EGFR‐mutant NSCLC cells by membrane proteomic analysis. B, Functional analyses of the upregulated (red) and downregulated (green) proteins in mutated EGFR cells. C, Enriched network in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. Left: Filtering criteria of the input proteins to build a network of mutated EGFR. Right: The mutated EGFR network conducted using the STRING database (blue: cell adhesion; green: O‐glycan processing; solid line: interaction with experimental confirmation,;dotted line: predicted interaction). The area of each protein represents the number of wild‐type cancer cells in which the identified protein occurred; the color indicates the ratio of protein expression (mutant/wild‐type). D, Validation of 10 candidates randomly selected from Figure 1C. Arrowheads point to the bands of the indicated protein. E, Ranking of the 10 selected candidates
To select potential candidates, we used this profiling to establish a protein linkage map with EGFR. As Figure 1C shows, proteins expressed in all EGFR‐mutant cells, excluding not expressed or low expressed, with at least 2‐fold difference compared with EGFR‐wild‐type cells were first selected from the 3723 proteins identified by the MaxQuant package. Under these criteria, 60 proteins were chosen and their associations with EGFR explored using STRING (Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins) database analysis. Interestingly, 32 proteins interacted with EGFR, including 9 direct and 23 indirect interactions (Figure 1D). Most of these proteins were involved in cell adhesion regulation, and some were related to O‐glycan processing.
Next, 10 candidates were selected at random to re‐examine by immunoblotting their expression in the tested cells. The results showed that the expression levels of GPNMB, ICAM1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1), PTPRJ (protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type J), LGALS3 (lectin, galactoside‐binding, soluble, 3), CDH1 (cadherin 1), and CEACAM5 (carcinoembryonic antigen‐related cell adhesion molecule 5) in EGFR‐mutant cells were significantly higher than in the wild‐type cells. However, the expression levels of MUC1 (mucin 1) and COL17A1 (collagen type XVII alpha 1 chain) did not present any dramatic difference between wild‐type and mutant cells (Figure 1D).
To enhance the application for lung cancer treatment, using Drug Bank screening, we further investigated whether any drugs could target the selected candidates. Following the above criteria, we ultimately obtained a ranking of 10 candidates (Figure 1E) that showed that the expression levels of CEACAM5, GPNMB, and CDH1 were related more to mutated EGFR signaling. As GPNMB has a dual function in various cancers and its expression also correlates with cancer metastasis, we choose it for further study.
3.2. GPNMB is highly expressed and promotes cell migration in EGFR‐mutated NSCLC
To confirm that highly expressed GPNMB is a general occurrence in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC, we further detected the expression of GPNMB in 10 more NSCLC cell lines, including 2 wild‐type (A549 and Hop62) and 8 EGFR‐mutant (H3255, VL307, H1975, PC9, HCC827, H1650, PE089, and CL68) cell lines. The data showed that GPNMB is not only highly expressed but is also more prone to post‐translational modification in EGFR‐mutant cells than in the wild‐type cells (Figure 2A, upper panel).
To determine if the increased expression of GPNMB in EGFR‐mutant cells was through transcriptional or translational regulation, we further detected mRNA expression of GPNMB, including variant 1 (v1) and variant 2 (v2), in NSCLC cells. Interestingly, the expression of GPNMB v1 was significantly different among EGFR‐wild‐type and EGFR‐mutant cells (Figure 2B, bottom left). Although the expression of GPNMB v2 also displayed a similar trend in cells, the difference was not significant (Figure 2B, bottom right). Moreover, that GPNMB was highly expressed in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC was further confirmed by gene set enrichment analysis of RNA‐Seq data (GSE40419) 42 (Figure 2C and Table 1) and proteomic data by Chen et al 43 (Figure 2D and Table 2). Collectively, these data suggested that higher GPNMB expression may be related to mutated EGFR oncogenic characteristics in NSCLC.
FIGURE 2.
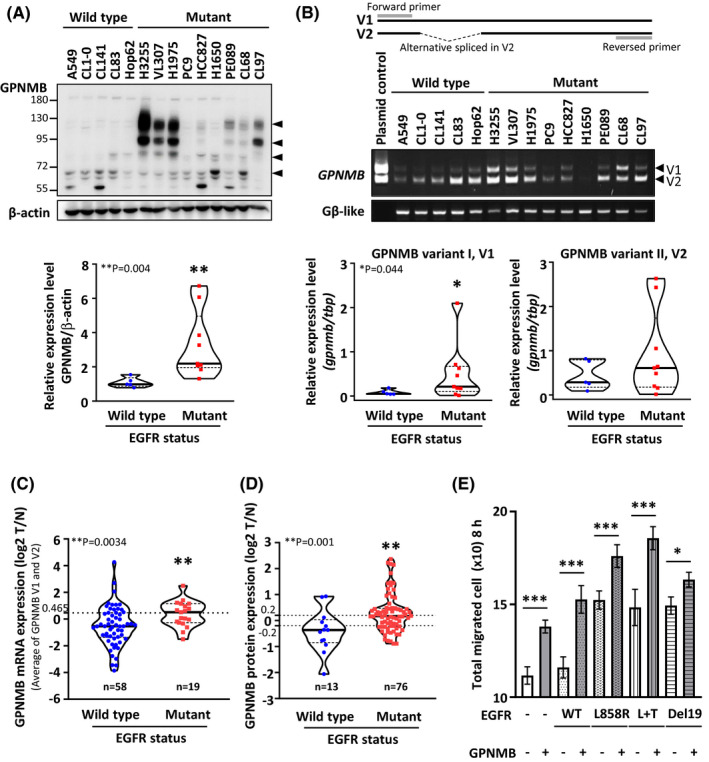
GPNMB is highly expressed and promotes cell migration in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC cells. A, B, Top: Protein and mRNA expression of GPNMB in 5 EGFR‐wild‐type and 9 EGFR‐mutant NSCLC cells were determined by immunoblotting and RT‐PCR. Bottom: Quantification of GPNMB protein (arrowheads) and mRNA expression using ImageJ software normalized to the internal control, β‐actin and Gβ‐like, of each cell. Top: PCR primer design (P = .004 for protein expression and .044 for mRNA expression; solid line: mean; dotted line: 25th or 75th percentiles). C, GPNMB mRNA expression (average of v1 and v2) in 77 patients with lung adenocarcinoma from the GSE40419 database42. High and low GPNMB expression groups were separated using the average expression level as the cut‐off (dotted line: 0.465, P = .0034). D, GPNMB protein expression in 89 patients with lung cancer from Chen et al. 43 High and low GPNMB expression groups were selected using log2 = ±0.2 as the cut‐off value (P = .001). E, Effects of various EGFR combined with or without GPNMB expression on cell migration. WT: wild‐type and L + T: L858R + T790 M (n = 3 experiments, * P < .05 and *** P < .001, nonparametric multiple comparison test)
TABLE 1.
| Characteristics | No. of patients (%) |
Low GPNMB* expression Patient no. (%) |
High GPNMB* expression Patient no. (%) |
P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77 | 52 (68%) | 25 (32%) | ||
| EGFR | ||||
| Wild‐type | 58 (75%) | 43 (83%) | 15 (60%) | |
| All mutants | 19 (25%) | 9 (17%) | 10 (40%) | .0267b |
| L858R | 12 (16%) | 4 (8%) | 8 (32%) | |
| Del19 | 6 (8%) | 4 (8%) | 2 (8%) | |
| Others | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Age | 64.03 ± 9.52 | 63.31 ± 9.39 | 65.52 ± 9.80 | .3521a |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 33 (43%) | 22 (42%) | 11 (44%) | >.999b |
| Male | 44 (57%) | 30 (58%) | 4 (56%) | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| I‐II | 61 (79%) | 42 (81%) | 19 (76%) | .5308c |
| III‐IV | 14 (18%) | 8 (15%) | 6 (24%) | |
| Unclear | 2 (3%) | 2 (4%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 43 (56%) | 29 (56%) | 14 (56%) | >.999b |
| No | 34 (44%) | 23 (44%) | 11 (44%) | |
P‐value by a: Student t test, b: Fisher's exact test, c: Chi‐square test; *Cut‐off value: log2 T/N = 0.465.
TABLE 2.
Clinical characteristics of 69 patients with lung adenocarcinoma by Chen et al 43
| Characteristics | No. of patients (%) |
Low GPNMB* expression Patient no. (%) |
High GPNMB* expression Patient no. (%) |
P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 69 | 30 (43%) | 39 (57%) | ||
| EGFR | ||||
| Wild‐type | 11 (16%) | 9 (30%) | 2 (5%) | |
| All mutants | 58 (84%) | 21 (70%) | 37 (95%) | .0074b |
| L858R | 28 (40%) | 12 (40%) | 16 (41%) | |
| Del19 | 22 (32%) | 6 (20%) | 16 (41%) | |
| Others | 8 (12%) | 3 (10%) | 5 (13%) | |
| Age | 63.58 ± 10.62 | 65.37 ± 9.92 | 62.20 ± 11.06 | .2296a |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 40 (58%) | 15 (50%) | 25 (64%) | .3528b |
| Male | 29 (42%) | 15 (50%) | 14 (36%) | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| I‐II | 60 (87%) | 24 (80%) | 36 (92%) | .1324c |
| III‐IV | 9 (13%) | 6 (20%) | 3 (8%) | |
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 10 (14%) | 8 (27%) | 2 (5%) | .0164b |
| No | 59 (86%) | 22 (73%) | 37 (95%) | |
P‐value by a: Student t test, b: Fisher's exact test, c: Chi‐square test; *Cut‐off value: log2 T/N = ±0.2.
In clinics, patients with mutated EGFR have a higher tendency to develop distant metastases. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 This led us wonder if overexpression of GPNMB was related to the metastatic abilities of cells with EGFR mutants. To this end, various EGFR mutants were transfected with or without the GPNMB plasmid into H1299 cells, a EGFR‐wild‐type cell line with lower levels of GPNMB, to evaluate cell migratory ability by wound‐healing assay. The results showed that cell migratory abilities were dramatically improved when EGFR mutants or GPNMB were expressed in cells. Moreover, synergistic effects occurred when cells co‐expressed the EGFR mutant, especially the EGFR‐L858R, and GPNMB plasmids (Figures 2E and S1, overall P < .001, nonparametric multiple comparison test). These results suggested that GPNMB may act as a mediator to promote cell migration in EGFR‐mutated NSCLC.
3.3. GPNMB activates EGFR downstream signaling through ligand‐independent regulation
As GPNMB was overexpressed in EGFR‐mutated lung cancer cells, we were curious about the role of GPNMB in regulating mutant EGFR downstream signaling. Here, EGFR mutants were co‐transfected with or without GPNMB into H1299 cells, and EGFR downstream signaling was examined by immunoblotting. Unexpectedly, overexpressing GPNMB could dramatically enhance EGFR‐Y845 and its downstream STAT3‐Y705 phosphorylation without ligand stimulation (Figure 3A). Next, H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB cells were treated with stattic, a STAT3 activation inhibitor, and cell migratory abilities were examined by wound‐healing assays. The results showed that the migration abilities of H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB cells were inhibited in a dose‐dependent manner when cells were treated with stattic (Figure S2), suggesting that GPNMB‐mediated cell migration in EGFR‐mutant cells is through STAT3 regulation.
FIGURE 3.
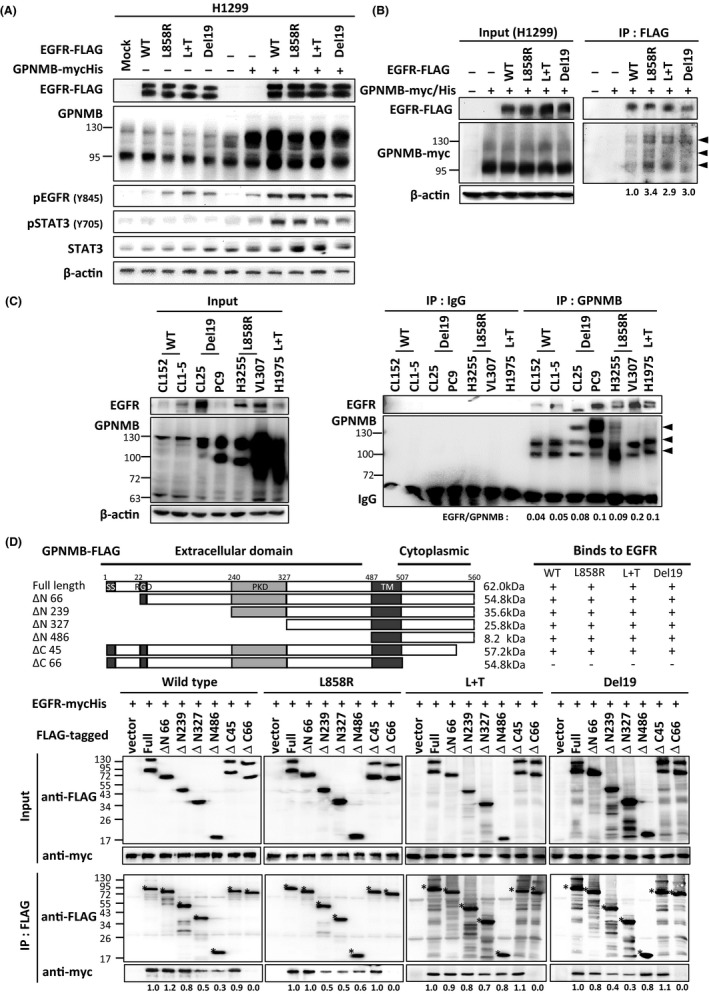
GPNMB preferentially binds to mutated EGFR and facilitates its downstream signaling without ligand stimulation. A, Various EGFR were co‐transfected with or without GPNMB into H1299 cells, and the downstream signaling of EGFR was examined by immunoblotting. “Mock” represents cells without any manipulation, “–” indicates vector control. B, FLAG‐tagged EGFR mutants and myc/His‐tagged GPNMB were co‐transfected into H1299 and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti‐FLAG antibodies. The precipitated amounts of EGFR and GPNMB were examined by immunoblotting (arrowheads: the precipitated product). C, Total lysates from NSCLC cells with different EGFR status were used to perform immunoprecipitation with anti‐GPNMB or IgG antibodies and the bindings between EGFR and GPNMB were examined by immunoblotting. Left: Input proteins. Right: The precipitated amounts of various EGFR and GPNMB (arrowheads) were determined and quantification shown under the blot. D, Domain mapping of GPNMB with wild‐type and mutated EGFR. Top: FLAG‐tagged GPNMB deletion mutants, the interactions of each fragment are shown on the right. Bottom: The resulting blots of domain mapping (*, indicates the band of each truncated GPNMB)
Then, we explored whether GPNMB could bind to EGFR mutants without ligand stimulation in cells. FLAG‐tagged EGFR mutants were co‐transfected with GPNMB‐myc/His‐tagged plasmids into H1299 cells, and the interactions between these 2 proteins were examined by immunoprecipitation assays. The data revealed that binding of GPNMB to EGFR mutants was stronger than for the wild‐type EGFR (Figure 3B). Similar data were obtained from endogenous binding experiments using several lung cancer cells with different EGFR statuses (Figure 3C). Next, the reciprocal binding domain of GPNMB for mutated EGFR was analyzed. FLAG‐tagged GPNMB truncated mutants were co‐transfected with wild‐type or mutated EGFR‐myc/His (including L858R, L858R + T790 M and Del19) plasmids into HEK293T cells. The binding domains of GPNMB for various types of EGFR were determined by co‐immunoprecipitation. Interestingly, we found that EGFR wild‐type or different mutants could not interact with the cytoplasmic region of GPNMB (ΔC66) (Figure 3D). This finding implied that, as well as protein‐protein interaction, other factors may exist that control this ligand‐independent regulation of GPNMB and mutated EGFR.
3.4. N‐linked glycosylation of GPNMB is critical for regulating the downstream signaling of mutated EGFR
As Figure 2A shows, GPNMB was modified in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC cells compared with wild‐type cells. This led us to ask whether modifications of GPNMB were related to ligand‐independent regulation of the mutated EGFR signaling. As GPNMB is a well known glycosylated protein, we first examined the possibility of N‐glycosylation. Lysates from 5 EGFR‐wild‐type and 4 EGFR‐mutant cells were treated with or without PNGase F for 3 h to cleave the N‐linked oligosaccharides on asparagine residues; cells were then analyzed for GPNMB expression patterns by immunoblotting. The results showed that the highly modified GPNMB proteins in EGFR‐mutant cells displayed a dramatic band shift from high molecular weight to 64 kDa (Figure 4A), suggesting that GPNMB proteins are highly N‐glycosylated in these cells. Next, we tried to clarify whether N‐linked glycosylation of GPNMB was related to the ligand independently of activation of mutated EGFR. Therefore, 11 GPNMB mutants with changes in the glycosylation sites (N93Q, N134Q, N146Q, N200Q, N249Q, N275Q, N306Q, N312Q, N459Q, and N467Q [N: Asn and Q: Gln]) were constructed and transfected into H1299 cells to evaluate the effects on EGFR downstream signaling. Interestingly, expression of GPNMB N93Q, N134Q, N146Q, and N200Q mutants could significantly downregulate Y845 phosphorylation of EGFR, and the phosphorylation status of STAT3 was also compromised in cells that expressed N93Q, N134Q, and N146Q changes (Figure 4B).
FIGURE 4.
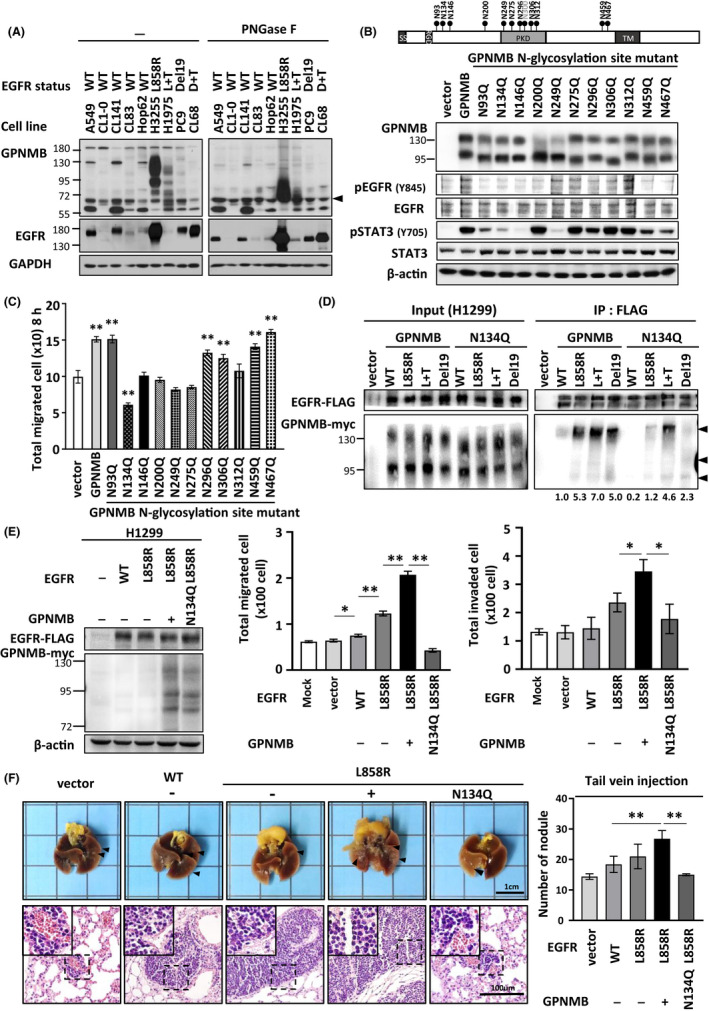
N134‐glycosylated GPNMB controls the oncogenic properties of mutated EGFR in vitro and in vivo. A, Lysates from different NSCLC cells with various EGFR status were treated with or without PNGase F, and both GPNMB and EGFR expressions were examined by immunoblotting (arrowhead: the unmodified GPNMB). B, Top: Localization of 11 glycosylation sites in the GPNMB gene structure. Bottom: Plasmids of 11 GPNMB glycosylated mutants were transfected into H1299 and EGFR downstream signaling was examined by immunoblotting. C, Effects of 11 GPNMB glycosylated mutants on cell migration by wound‐healing assay (n = 3 experiments, ** P < .01). D, Different EGFR mutants were co‐transfected with GPNMB‐wild‐type or N134Q plasmids into H1299 cells and immunoprecipitated with anti‐FLAG antibodies to detect the effects on the binding affinities between GPNMB‐wild‐type/N134Q and various EGFR mutants (arrowheads: the precipitated GPNMB quantified under the blot). E, H1299 cells were transfected with the indicated EGFR and GPNMB mutant plasmids, and the effects on cell migratory and invasive abilities were examined (*P < .05 and ** P < .001). Protein expression of transfected EGFR and GPNMB are shown on the left. F, Tail‐vein metastatic assay in vivo. Left: the growth (top) and H&E staining (bottom) of lung tissues from each group. Right: number of tumor nodules of each group (** P < .01)
3.5. N134 glycosylation of GPNMB controls the oncogenic properties of mutated EGFR in vitro and in vivo
As N‐linked glycosylation of GPNMB, especially at the N93, N134, and N146 sites, could interfere with downstream signaling of EGFR, we further explored these effects on GPNMB‐induced metastasis in NSCLC. First, we transfected various GPNMB mutants into H1299 cells and examined cell migratory ability using wound‐healing assays. Interestingly, migratory ability was significantly inhibited when cells expressed the GPNMB‐N134Q mutation compared with the control cells (Figures 4C and S3; P < .0001). Next, binding of GPNMB‐wild‐type or N134Q to various EGFR mutants was examined through co‐immunoprecipitation assays. As expected, GPNMB wild‐type strongly interacted with EGFR mutants compared with wild‐type EGFR. Interactions, especially that of EGFR‐L858R, were significantly decreased in cells that expressed the GPNMB‐N134Q plasmid (Figure 4D). This result suggested that N134 glycosylation of GPNMB may play a crucial role in controlling mutated EGFR oncogenic characteristics.
To examine this idea, we established several stable cell lines including H1299/mock, H1299/EGFR‐wild‐type, H1299/EGFR‐L858R, H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB‐wild‐type, and H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB‐N134Q to evaluate the effects of GPNMB‐N134 glycosylation on cancer metastasis. The migratory and invasive abilities of these cells were first examined in vitro. Results showed that the expression of EGFR‐L858R increased cell migratory and invasive abilities, and the presence of GPNMB had an additive effect on EGFR‐L858R‐induced cell migration and invasion. However, these effects were significantly compromised in cells that co‐expressed EGFR‐L858R and GPNMB‐N134Q (Figures 4E and S4; P < .05). This effect was also seen when cells co‐expressed GPNMB‐wild‐type/N134Q and EGFR‐L858R + T790 M plasmids. Although a similar trend occurred in cells that co‐expressed EGFR‐del19 and GPNMB plasmids, the result still did not reach significance; this may be because EGFR‐Y845 cells were less phosphorylated (Figure S5). Next, we chose stable cells with EGFR‐L858R mutations to evaluate the inhibitory effects of depleting GPNMB N134 glycosylation on mutated EGFR‐induced metastasis in vivo. As expected, mice injected intravenously with H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB‐wild‐type and EGFR‐L858R cells developed more pulmonary nodules than those injected with H1299/mock and EGFR‐wild‐type cells (mean numbers of nodules: 14.4 ± 0.93 for H1299/vector, 18.4 ± 2.66 for H1299/EGFR‐wild‐type, 21.0 ± 4.04 for H1299/EGFR‐L858R, and 26.8 ± 2.71 for H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB; all P < .001). The synergistic effects of GPNMB on promoting EGFR‐L858R‐induced cancer metastasis were dramatically reduced when N134 glycosylation was reduced (mean number of nodules, 15 ± 0.32 for H1299/EGFR‐L858R + GPNMB‐N134Q, P < .001; Figure 4F). Collectively, N134 glycosylation of GPNMB is critical for controlling mutated EGFR‐induced cancer metastasis in vitro and in vivo.
4. DISCUSSION
In recent years, EGFR TKIs have become the first‐line treatment for patients with NSCLC with EGFR mutations; drug resistance and distant metastases are the big clinical challenges. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 46 To date, how mutant EGFR activates downstream signaling without ligand stimulation and promotes metastasis is still unclear. Whether any factors exist that can help the activation of mutated EGFR signaling is still an unanswered question in lung cancer studies.
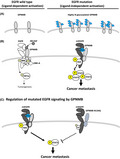
By membrane proteomic analysis, we identified that GPNMB can interact with mutated EGFR, activate its downstream signaling and had a synergistic effect on promoting cancer metastasis. As Figure 5A shows, GPNMB is not only overexpressed but also highly glycosylated in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. Binding of GPNMB to mutated EGFR, especially EGFR‐L858R, is much stronger than that of wild‐type EGFR. This interaction could assist EGFR‐Y845 and its downstream STAT3‐Y705 phosphorylation through ligand‐independent regulation and promote cancer malignancy (Figure 5B, right). These findings differ from those reported by Lin et al who stated that GPNMB could form complexes with LINK‐A, BRK, HIF1α and EGFR under HB‐EGF stimulation and promote tumorigenesis in triple‐negative breast cancer 39 (Figure 5B, left). Finally, we were excited to find a critical role for GPNMB‐N134 glycosylation in EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. Depleting N134 glycosylation could compromise the interaction between GPNMB and mutated EGFR, significantly inhibiting cell migration, invasion, and cancer metastasis (Figure 5C). These findings suggest that N134 glycosylation of GPNMB plays a critical role in ligand‐independent activation of mutated EGFR signaling in NSCLC.
FIGURE 5.
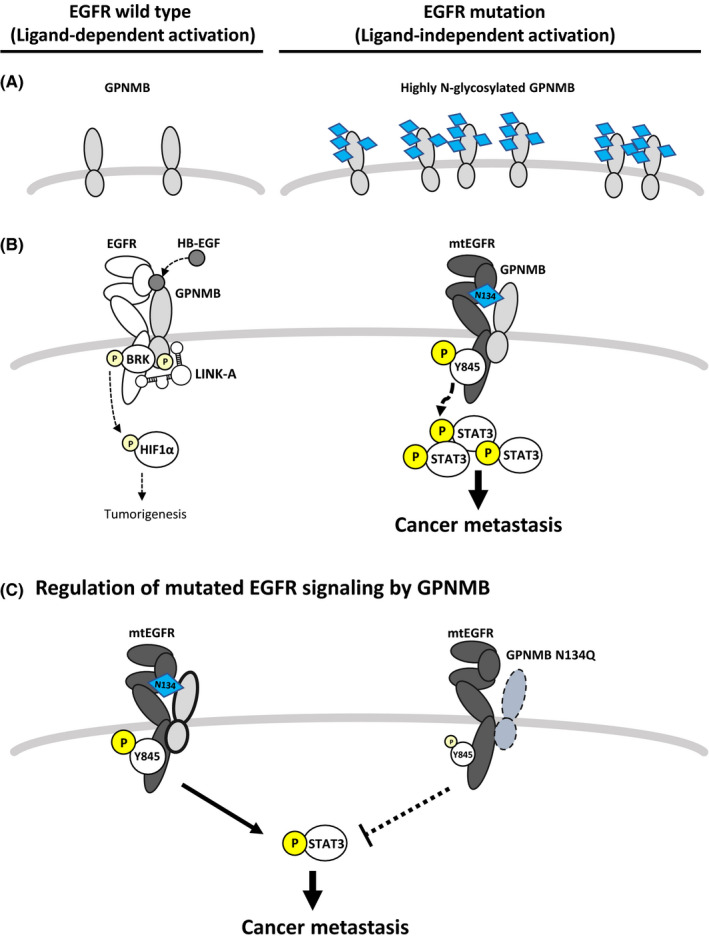
Provisional model of GPNMB ligand that independently activates mutated EGFR in NSCLC. A, GPNMB is overexpressed and highly N‐glycosylated in the EGFR‐mutant NSCLC cells. B, Left:Ligand‐dependent activation of EGFR by GPNMB. GPNMB could form complexes with LINK‐A, BRK, HIF1α and EGFR under HB‐EGF stimulation to promote tumorigenesis (presented by Yang et al 39 ). Right: Ligand‐independent activation of mutated EGFR signaling by GPNMB. N‐glycosylated GPNMB interacts with mutated EGFR facilitates the phosphorylation of both EGFR Y845 and its downstream STAT3 Y705 without ligand stimulation, and promotes cancer metastasis. C, Depleting the N134 glycosylation of GPNMB compromised the binding between GPNMB and mutated EGFR, blocked the activity of mutated EGFR, and inhibited cancer metastasis in NSCLC
The advances in high‐accuracy mass spectrometry has led proteomics to be a powerful tool for unveiling complex protein network in cells. 47 Researchers generally use the total proteome or phospho‐proteome to extract disease‐related protein networks, such as explored here for EGFR‐mutant NSCLC. 48 , 49 Recently, Nishimura et al analyzed 36 FFPE tissues of lung adenocarcinomas using semi‐quantitative shotgun proteomics. Combined with analysis of variance and weighted gene co‐expression network analysis, they identified 13 co‐expressed modules and their eigen proteins that were affected by EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. 50 Accordingly, we could find that most of the significant modules, including SUMOylation and the ERK/MAPK pathway, belonged to cytosolic regulation, which is less than ideal for novel therapeutics development. Therefore, membrane proteomic analysis might be a solution for solving this problem. Here, we successfully integrated the membrane proteome with STRING analysis and Drug Bank screening to identify that GPNMB may act with mutated EGFR to promote lung cancer metastasis. To our knowledge, this report is the first using this strategy to explore how mutated EGFR evades negative activation‐dependent regulation in NSCLC. The findings for N134‐glycosylated GPNMB provide a new target for diagnosis or therapeutics in NSCLC.
EGFR is a well known RTK and acts as a key regulator in dictating many cellular processes. 51 , 52 , 53 In lung adenocarcinoma, especially in Asia, somatic mutations of EGFR can activate constitutively its downstream signaling without ligand stimulation and result in tumorigenesis. 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Therefore, understanding the ligand‐independent regulation of mutated EGFR is important for lung cancer studies. As EGFR is a heavily glycosylated protein, several studies have focused on whether the glycan on EGFR itself can regulate the function of EGFR. Lau et al found that the N‐glycan number and branching degree can interfere with the expression of EGFR on the cell surface. 54 Previous studies have also shown that glycosylation at Asn420 and 579 of EGFR is crucial for preventing ligand‐independent dimerization. 55 , 56 Moreover, Yen et al demonstrated that the extracellular sialylation of EGFR could attenuate the interaction of EGFR with EGF, suppress its dimerization, and inhibit EGFR phosphorylation. 53 Recently, N‐glycosylation of integrin α5β1 was reported to suppress EGFR‐Y1068 phosphorylation. 57 In this study, we discovered that GPNMB is highly N‐glycosylated in the EGFR mutant, especially EGFR‐L858R NSCLC cells and that N134 glycosylation of GPNMB is important for Y845 phosphorylation of mutated EGFR. Y845 is a Src‐induced transphosphorylation site on EGFR, which is in an activation loop, influences kinase activity, and is also recognized as a key for EGFR oncogenic properties. 58 Previous publications have shown that the phosphorylation status of Y845 in EGFR‐del19 cells is less than that in EGFR‐L858R mutant cells. 23 This may be the reason why we observed that the synergistic effect of GPNMB on mutated EGFR‐induced cancer malignancy was much more obvious in cells harboring the EGFR‐L858R mutation rather than cells with the del19 mutation. To our knowledge, this report is the first to show that specific N‐glycosylation of EGFR‐associated partners could promote ligand‐independent activation of EGFR and affect cancer metastasis. Whether depleting the N‐glycosylation status of GPNMB could cause conformational change and interfere with the hetero‐dimerization of GPNMB and EGFR should soon be further clarified. Moreover, inhibiting extracellular N‐linked glycosylation of GPNMB may cause harmful effects on biological function. Therefore the development of therapeutic targeting to a specific N‐glycosylation site (like N134 of GPNMB) may in the future instigate new ideas for developing novel lung cancer therapeutics.
DISCLOSURE
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Supporting information
Figure S1
Figure S2
Figure S3
Figure S4
Figure S5
Table S1
Data S1
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the following individuals for material and technical supports: Dr. Pan‐Chyr Yang, Dr. Chih‐Hsin Yang (Department of Medicine, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University), Dr. Kay‐Hooi Khoo (Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica), Dr. Yu‐Ju Chen (Institute of Chemistry, Academia Sinica), Dr. Chia‐Yi Lin (Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica) and Ms Tzu‐Yu Chen (Graduate Institute of Medical Genomics and Proteomics, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University). This research was funded by National Taiwan University (NTU‐105R7879) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (Taiwan) (MOST 105‐2628‐B‐002‐007‐MY3, 108‐3114‐Y‐001‐002, 108‐2314‐B‐002‐191‐MY3, 109‐2113‐M‐038‐002).
Han C‐L, Chen X‐R, Lan A, et al. N‐glycosylated GPNMB ligand independently activates mutated EGFR signaling and promotes metastasis in NSCLC. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:1911–1923. 10.1111/cas.14872
Chia‐Li Han and Xuan‐Ren Chen are equally contributed to this project.
REFERENCES
- 1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(1):7‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Zappa C, Mousa SA. Non‐small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Treatment and Future Advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016;5(3):288‐300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Pines G, Köstler WJ, Yarden Y. Oncogenic Mutant Forms of EGFR: Lessons in Signal Transduction and Targets for Cancer Therapy. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(12):2699‐2706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Tsai MF, Chang TH, Wu SG, et al. EGFR‐L858R mutant enhances lung adenocarcinoma cell invasive ability and promotes malignant pleural effusion formation through activation of the CXCL12‐CXCR4 pathway. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Wu SG, Yu CJ, Tasi MF, et al. Survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients with malignant pleural effusion. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(6):1409‐1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Li WY, Zhao TT, Xu HM, et al. The role of EGFR mutation as a prognostic factor in survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in non‐small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. BMC Cancer. 2019;19(1):145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wu SG, Liu YN, Yu CJ, Yang JCH, Shih JY. Driver mutations of young lung adenocarcinoma patients with malignant pleural effusion. Genes, Chromosomes Cancer. 2018;57(10):513‐521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Li L, Luo S, Lin H, et al. Correlation between EGFR mutation status and the incidence of brain metastases in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2017;9(8):2510‐2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(3):169‐181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Sasaki T, Hiroki K, Yamashita Y. The Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Cancer Metastasis and Microenvironment. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:546318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Alroy I, Yarden Y. The ErbB Signaling Network in Embryogenesis and Oncogenesis: Signal Diversification Through Combinatorial Ligand‐Receptor Interactions. FEBS Lett. 1997;410(1):83‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ferguson KM, Berger MB, Mendrola JM, Cho HS, Leahy DJ, Lemmon MA. EGF Activates Its Receptor by Removing Interactions That Autoinhibit Ectodomain Dimerization. Mol Cell. 2003;11(2):507‐517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Avraham R, Yarden Y. Feedback Regulation of EGFR Signalling: Decision Making by Early and Delayed Loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(2):104‐117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lewis TS, Shapiro PS, Ahn NG. Signal Transduction Through MAP Kinase Cascades. Adv Cancer Res. 1998;74:49‐139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2010;141(7):1117‐1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Herbst RS. Review of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Biology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;59(2 Suppl):21‐26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB Receptors and Cancer: The Complexity of Targeted Inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(5):341‐354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Krause DS, Etten RAV. Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(2):172‐187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Prabhakar CN. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non‐small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4(2):110‐118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Fang S, Wang Z. EGFR mutations as a prognostic and predictive marker in non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:1595‐1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Gazdar AF, Shigematsu H, Herz J, Minna JD. Mutations and addiction to EGFR: the Achilles 'heal' of lung cancers? Trends Mol Med. 2004;10(10):481‐486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Pao W, Miller VA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, small‐molecule kinase inhibitors, and non‐small‐cell lung cancer: current knowledge and future directions. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(11):2556‐2568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J. Gefitinib‐sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti‐apoptotic pathways. Science. 2004;305(5687):1163‐1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Jiang J, Greulich H, Jänne PA, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Griffin JD. Epidermal growth factor‐independent transformation of Ba/F3 cells with cancer‐derived epidermal growth factor receptor mutants induces gefitinib‐sensitive cell cycle progression. Cancer Res. 2005;65(19):8968‐8974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Taya M, Hammes SR. Glycoprotein Non‐Metastatic Melanoma Protein B (GPNMB) and Cancer: A Novel Potential Therapeutic Target. Steroids. 2018;133:102‐107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Guo G, Gong K, Wohlfeld B, Hatanpaa KJ, Zhao D, Habib AA. Ligand‐independent EGFR signaling. Cancer Res. 2015;75(17):3436‐3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Maric G, Rose AA, Annis MG, Siegel PM. Glycoprotein non‐metastatic b (GPNMB): A metastatic mediator and emerging therapeutic target in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;6:839‐852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Selim AA. Osteoactivin bioinformatic analysis: prediction of novel functions, structural features, and modes of action. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15(2):MT19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Tomihari M, Hwang SH, Chung JS, Cruz PD, Ariizumi K. Gpnmb is a melanosome‐associated glycoprotein that contributes to melanocyte/keratinocyte adhesion in an RGD‐dependent fashion. Exp Dermatol. 2009;18(7):586‐595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sheng MHC, Wergedal JE, Mohan S, Lau KHW. Osteoactivin is a novel osteoclastic protein and plays a key role in osteoclast differentiation and activity. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(10):1451‐1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Chung JS, Dougherty I, Cruz PD Jr, Ariizumi K. Syndecan‐4 mediates the coinhibitory function of DC‐HIL on T cell activation. J Immunol. 2007;179(9):5778‐5784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Chung JS, Sato K, Dougherty II, Cruz PD Jr, Ariizumi K. DC‐HIL is a negative regulator of T lymphocyte activation. Blood. 2007;109(10):4320‐4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Rose AA, Pepin F, Russo C, Abou Khalil JE, Hallett M, Siegel PM. Osteoactivin promotes breast cancer metastasis to bone. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(10):1001‐1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Ramani V, Teshima T, Tamura K, et al. Melanoma‐Derived Soluble DC‐HIL/GPNMB Promotes Metastasis by Excluding T‐Lymphocytes from the Pre‐Metastatic Niches. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138(11):2443‐2451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Fiorentini C, Bodei S, Bedussi F, et al. GPNMB/OA protein increases the invasiveness of human metastatic prostate cancer cell lines DU145 and PC3 through MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 activity. Exp Cell Res. 2014;323(1):100‐111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Metz RL, Patel PS, Hameed M, Bryan M, Rameshwar P. Role of human HGFIN/nmb in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(5):R58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Tse KF, Jeffers M, Pollack VA, et al. CR011, a fully human monoclonal antibody‐auristatin E conjugate, for the treatment of melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(4):1373‐1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Qian X, Mills E, Torgov M, LaRochelle WJ, Jeffers M. Pharmacologically enhanced expression of GPNMB increases the sensitivity of melanoma cells to the CR011‐vcMMAE antibody‐drug conjugate. Mol Oncol. 2008;2(1):81‐93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Lin A, Li C, Xing Z, et al. The LINK‐A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signaling in triple‐negative breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(2):213‐224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Pan SH, Chao YC, Hung PF, et al. The ability of LCRMP‐1 to promote cancer invasion by enhancing filopodia formation is antagonized by CRMP‐1. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(8):3189‐3205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wang CC, Hsu YL, Chang CJ, Wang CJ, Hsiao TH, Pan SH. Inhibitor of DNA‐Binding Protein 4 Suppresses Cancer Metastasis through the Regulation of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(12):2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Seo JS, Ju YS, Lee WC, et al. The transcriptional landscape and mutational profile of lung adenocarcinoma. Genome Res. 2012;22(11):2109‐2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Chen YJ, Roumeliotis TI, Chang YH, et al. Proteogenomics of Non‐smoking Lung Cancer in East Asia Delineates Molecular Signatures of Pathogenesis and Progression. Cell. 2020;182(1):226‐244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. North‐East Japan Study Group. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2380‐2388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first‐line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG‐0802): a multicentre, open‐label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(8):735‐742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(27):3327‐3334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Nishimura T, Nakamura H, Végvári Á, Marko‐Varga G, Furuya N, Saji H. Current status of clinical proteogenomics in lung cancer. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2019;16(9):761‐772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Fehniger TE, Marko‐Varga G. Proteomics and disease revisited: the challenge of providing proteomic tools into clinical practice. J Proteome Res. 2010;9(3):1191‐1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Buljan M, Ciuffa R, van Drogen A, et al. Kinase Interaction Network Expands Functional and Disease Roles of Human Kinases. Mol Cell. 2020;79(3):504‐520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Nishimura T, Nakamura H, Yachie A, et al. Disease‐related cellular protein networks differentially affected under different EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Dawson JP, Berger MB, Lin CC, Schlessinger J, Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM. Epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization and activation require ligand‐induced conformational changes in the dimer interface. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(17):7734‐7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Lemmon MA. Ligand‐induced ErbB receptor dimerization. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(4):638‐648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Yen HY, Liu YC, Chen NY, et al. Effect of sialylation on EGFR phosphorylation and resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(22):6955‐6960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Lau KS, Partridge EA, Grigorian A, et al. Complex N‐glycan number and degree of branching cooperate to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell. 2007;129(1):123‐134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Whitson KB, Whitson SR, Red‐Brewer ML, et al. Functional effects of glycosylation at Asn‐579 of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 2005;44(45):14920‐14931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Yokoe S, Takahashi M, Asahi M, et al. The Asn418‐linked N‐glycan of ErbB3 plays a crucial role in preventing spontaneous heterodimerization and tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 2007;67(5):1935‐1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Hou S, Hang Q, Isaji T, Fukuda T, Gu J. Identification of the minimal N‐glycosylation on integrin α5β1 required for its inhibitory effect on EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(1):226‐232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Song H, Huang L, Zhang M, Wang X, Song S, Yang L. Transphosphorylation of EGFR at Y845 plays an important role in its autophosphorylation and kinase activity. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(5):2393‐2398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1
Figure S2
Figure S3
Figure S4
Figure S5
Table S1
Data S1


