Abstract
Background
Electronic cigarettes (ECs) are handheld electronic vaping devices which produce an aerosol formed by heating an e‐liquid. Some people who smoke use ECs to stop or reduce smoking, but some organizations, advocacy groups and policymakers have discouraged this, citing lack of evidence of efficacy and safety. People who smoke, healthcare providers and regulators want to know if ECs can help people quit and if they are safe to use for this purpose. This is an update of a review first published in 2014.
Objectives
To examine the effectiveness, tolerability, and safety of using electronic cigarettes (ECs) to help people who smoke achieve long‐term smoking abstinence.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group's Specialized Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO to 1 February 2021, together with reference‐checking and contact with study authors.
Selection criteria
We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and randomized cross‐over trials in which people who smoke were randomized to an EC or control condition. We also included uncontrolled intervention studies in which all participants received an EC intervention. To be included, studies had to report abstinence from cigarettes at six months or longer and/or data on adverse events (AEs) or other markers of safety at one week or longer.
Data collection and analysis
We followed standard Cochrane methods for screening and data extraction. Our primary outcome measures were abstinence from smoking after at least six months follow‐up, adverse events (AEs), and serious adverse events (SAEs). Secondary outcomes included changes in carbon monoxide, blood pressure, heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, lung function, and levels of known carcinogens/toxicants. We used a fixed‐effect Mantel‐Haenszel model to calculate the risk ratio (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) for dichotomous outcomes. For continuous outcomes, we calculated mean differences. Where appropriate, we pooled data from these studies in meta‐analyses.
Main results
We included 56 completed studies, representing 12,804 participants, of which 29 were RCTs. Six of the 56 included studies were new to this review update. Of the included studies, we rated five (all contributing to our main comparisons) at low risk of bias overall, 41 at high risk overall (including the 25 non‐randomized studies), and the remainder at unclear risk.
There was moderate‐certainty evidence, limited by imprecision, that quit rates were higher in people randomized to nicotine EC than in those randomized to nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) (risk ratio (RR) 1.69, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.25 to 2.27; I2 = 0%; 3 studies, 1498 participants). In absolute terms, this might translate to an additional four successful quitters per 100 (95% CI 2 to 8). There was low‐certainty evidence (limited by very serious imprecision) that the rate of occurrence of AEs was similar) (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.19; I2 = 0%; 2 studies, 485 participants). SAEs occurred rarely, with no evidence that their frequency differed between nicotine EC and NRT, but very serious imprecision led to low certainty in this finding (RR 1.37, 95% CI 0.77 to 2.41: I2 = n/a; 2 studies, 727 participants).
There was moderate‐certainty evidence, again limited by imprecision, that quit rates were higher in people randomized to nicotine EC than to non‐nicotine EC (RR 1.70, 95% CI 1.03 to 2.81; I2 = 0%; 4 studies, 1057 participants). In absolute terms, this might again lead to an additional four successful quitters per 100 (95% CI 0 to 11). These trials mainly used older EC with relatively low nicotine delivery. There was moderate‐certainty evidence of no difference in the rate of AEs between these groups (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.11; I2 = 0%; 3 studies, 601 participants). There was insufficient evidence to determine whether rates of SAEs differed between groups, due to very serious imprecision (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.15 to 2.44; I2 = n/a; 4 studies, 494 participants).
Compared to behavioral support only/no support, quit rates were higher for participants randomized to nicotine EC (RR 2.70, 95% CI 1.39 to 5.26; I2 = 0%; 5 studies, 2561 participants). In absolute terms this represents an increase of seven per 100 (95% CI 2 to 17). However, this finding was of very low certainty, due to issues with imprecision and risk of bias. There was no evidence that the rate of SAEs differed, but some evidence that non‐serious AEs were more common in people randomized to nicotine EC (AEs: RR 1.22, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.32; I2 = 41%, low certainty; 4 studies, 765 participants; SAEs: RR 1.17, 95% CI 0.33 to 4.09; I2 = 5%; 6 studies, 1011 participants, very low certainty).
Data from non‐randomized studies were consistent with RCT data. The most commonly reported AEs were throat/mouth irritation, headache, cough, and nausea, which tended to dissipate with continued use. Very few studies reported data on other outcomes or comparisons and hence evidence for these is limited, with confidence intervals often encompassing clinically significant harm and benefit.
Authors' conclusions
There is moderate‐certainty evidence that ECs with nicotine increase quit rates compared to ECs without nicotine and compared to NRT. Evidence comparing nicotine EC with usual care/no treatment also suggests benefit, but is less certain. More studies are needed to confirm the size of effect, particularly when using modern EC products. Confidence intervals were for the most part wide for data on AEs, SAEs and other safety markers, though evidence indicated no difference in AEs between nicotine and non‐nicotine ECs. Overall incidence of SAEs was low across all study arms. We did not detect any clear evidence of harm from nicotine EC, but longest follow‐up was two years and the overall number of studies was small.
The evidence is limited mainly by imprecision due to the small number of RCTs, often with low event rates. Further RCTs are underway. To ensure the review continues to provide up‐to‐date information, this review is now a living systematic review. We run searches monthly, with the review updated when relevant new evidence becomes available. Please refer to the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews for the review's current status.
Plain language summary
Can electronic cigarettes help people stop smoking, and do they have any unwanted effects when used for this purpose?
What are electronic cigarettes?
Electronic cigarettes (e‐cigarettes) are handheld devices that work by heating a liquid that usually contains nicotine and flavorings. E‐cigarettes allow you to inhale nicotine in a vapor rather than smoke. Because they do not burn tobacco, e‐cigarettes do not expose users to the same levels of toxins that we know can cause smoking‐related diseases in people who use conventional cigarettes.
Using an e‐cigarette is known as 'vaping'. Many people use e‐cigarettes to help them to stop smoking tobacco.
Why we did this Cochrane Review
Stopping smoking lowers your risk of getting lung cancer and other diseases. Many people find it difficult to quit. We wanted to find out if using e‐cigarettes could help people to stop smoking, and if people using them for this purpose experienced any unwanted effects.
What did we do?
We searched for studies that looked at the use of e‐cigarettes to help people stop smoking.
We looked for randomized controlled trials, in which the treatments people received were decided at random. This type of study usually gives the most reliable evidence about the effects of a treatment. We also looked for studies in which everyone received an e‐cigarette treatment.
We were interested in finding out:
· how many people stopped smoking for at least six months; and · how many people had unwanted effects, reported on for at least one week.
Search date: We included evidence published up to 1st February 2021.
What we found
We found 56 studies in 12,804 adults who smoked. The studies compared e‐cigarettes with:
· nicotine replacement therapy, such as patches or gum;
· varenicline (a medicine to help people stop smoking); · nicotine‐free e‐cigarettes; · behavioral support, such as advice or counseling; or · no support, for stopping smoking.
Most studies took place in the USA (24 studies), the UK (9), and Italy (7).
What are the results of our review?
More people probably stop smoking for at least six months using nicotine e‐cigarettes than using nicotine replacement therapy (3 studies, 1498 people), or nicotine‐free e‐cigarettes (4 studies, 1057 people).
Nicotine e‐cigarettes may help more people to stop smoking than no support or behavioral support only (5 studies, 2561 people).
For every 100 people using nicotine e‐cigarettes to stop smoking, 10 or 11 might successfully stop, compared with only six of 100 people using nicotine‐replacement therapy or nicotine‐free e‐cigarettes, or four of 100 people having no support or behavioral support only.
We are uncertain if there is a difference between how many unwanted effects occur using nicotine e‐cigarettes compared with nicotine replacement therapy, no support or behavioral support only. There was some evidence that non‐serious unwanted effects were more common in groups receiving nicotine e‐cigarettes compared to no support or behavioral support only. Similar low numbers of unwanted effects, including serious unwanted effects, were reported for other comparisons. There is probably no difference in how many non‐serious unwanted effects occur in people using nicotine e‐cigarettes compared to non‐nicotine e‐cigarettes.
The unwanted effects reported most often with nicotine e‐cigarettes were throat or mouth irritation, headache, cough and feeling sick. These effects reduced over time as people continued using nicotine e‐cigarettes.
How reliable are these results?
Our results are based on a small number of studies, and in some the measured data varied widely.
We are moderately confident that nicotine e‐cigarettes help more people to stop smoking than nicotine replacement therapy or nicotine‐free e‐cigarettes. However, these results might change if further evidence becomes available.
We are less confident about how nicotine e‐cigarettes compare with no support, or behavioral support, to stop smoking.
Most of our results for the unwanted effects are likely to change when more evidence becomes available.
Key messages
Nicotine e‐cigarettes probably do help people to stop smoking for at least six months. They probably work better than nicotine replacement therapy and nicotine‐free e‐cigarettes.
They may work better than no support, or behavioral support alone, and they may not be associated with serious unwanted effects.
However, we need more, reliable evidence to be confident about the effects of e‐cigarettes, particularly the effects of newer types of e‐cigarettes that have better nicotine delivery.
Summary of findings
Background
Throughout this review, we discuss (1) conventional cigarettes and; (2) electronic cigarettes, defined as handheld electronic vaping devices that produce aerosol for inhalation formed by heating an e‐liquid. In this review, all mention of smoking, smoking cessation, cigarette use, smoke intake, etc. concern combustible tobacco cigarettes. When the text concerns electronic cigarettes we use the abbreviation 'ECs'. EC users are sometimes described as vapers, and EC use as vaping. We refer to ECs that do not contain nicotine as non‐nicotine ECs; these can also be conceptualized as placebo ECs, but we are using the term non‐nicotine EC, as they can be conceptualized as an intervention in themselves. This review does not address the use of vaping devices to inhale substances other than nicotine, such as cannabis.
Description of the condition
Stopping smoking is associated with large health benefits. Despite most people who smoke wanting to quit, many find it difficult to succeed in the long term. Almost half who try to quit without support will not manage to stop for even a week, and fewer than five per cent remain abstinent at one year after quitting (Hughes 2004).
Behavioral support and medications such as nicotine patches or gum increase the chances of quitting through providing nicotine to help alleviate withdrawal symptoms, but even with this additional support long‐term quit rates remain low (Cahill 2016; Hartmann‐Boyce 2018b; Hartmann‐Boyce 2019). One of the limitations of current treatments is that, despite substituting nicotine delivery, none adequately addresses the sensory, behavioral and social aspects of smoking that ex‐smokers miss when they stop smoking (e.g. holding a cigarette in their hands, taking a puff, enjoyment of smoking, feeling part of a group). ECs may offer a way to overcome this limitation (Notley 2018b).
There is no doubt that people become dependent on tobacco, and find it difficult to stop smoking, primarily because of nicotine and its actions on the brain's reward system (Balfour 2004). However, other factors also contribute to tobacco dependence (Benowitz 2010; Rose 2006). Sensory and behavioral cues provide additional reinforcement of smoking behavior (Rose 1993; Rose 2000) and over time become almost as rewarding as nicotine. There are several lines of evidence to support this. Firstly, people who smoke appear to have a preference for cigarette smoke compared to other forms of nicotine delivery. This is partly related to the speed of nicotine delivery through smoke inhalation. However, even when nicotine is administered intravenously it does not provide the same level of satisfaction or reward as smoking (Rose 2000; Westman 1996). Secondly, the local sensory effects of smoking (e.g. the ‘scratch’ in the back of the throat) may be important for enjoyment and reward. Numbing the sensations of cigarette smoke by anaesthetizing the upper and lower respiratory tract leads to less enjoyment of smoking (Rose 1985). Conversely, products that mimic the sensory effects of smoking on the mouth and throat (such as citric acid, black pepper, and ascorbic acid) reduce craving and some withdrawal symptoms, at least in the short term (Levin 1993; Rose 1994; Westman 1995). Thirdly, very low nicotine content cigarettes (VLNCs) which have a very low content of nicotine (e.g. 0.08 mg instead of the normal 1 mg) and so have negligible or no central effects, have also been investigated for their role in aiding smoking cessation (Przulj 2013). Despite delivering low levels of nicotine, VLNCs are satisfying over the initial few days of abstinence from nicotine (Donny 2007; Donny 2015; Pickworth 1999; Rose 2000). They also reduce tobacco withdrawal symptoms, including urges to smoke and low mood (Barrett 2010; Donny 2009; McRobbie 2016; Perkins 2010; Rose 2000), and have been shown to improve long‐term continuous abstinence rates in one study (Walker 2012). Social aspects of smoking, such as feeling part of a like‐minded group, or including smoking behavior as part of one's social identity are also key elements of cigarette smoking that people who smoke report to be key aspects of cigarette dependence (Notley 2018a).
Considering the other factors that contribute to tobacco dependence, there is interest in developing smoking‐cessation products that would not only help relieve the unpleasant effects of nicotine withdrawal but would also act as an effective substitute for smoking behavior and the rituals and sensations that accompany smoking, without the health risks associated with the inhalation of tobacco smoke. Until recently the only pharmaceutical treatments available that had some of these characteristics were the nicotine inhalator and nicotine oral spray. However, these do not have greater cessation efficacy than the other nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) products (Hajek 1999; Hartmann‐Boyce 2018a). This may in part be due to the considerable effort (e.g. 20 minutes of continuous puffing) needed to provide nicotine blood concentrations consistent with other NRTs (Schneider 2001). Adherence to correct use of the inhalator is low compared to other NRTs (Hajek 1999). It is therefore possible that any advantage of sensorimotor replacement is diminished by low nicotine delivery and limited similarities between inhalator use and sensations of smoking (Bullen 2010). A nicotine inhaler using pressurized air has recently been approved as a smoking cessation aid in the UK. The nicotine delivery is substantially lower than from cigarettes, and also lower than from the nicotine inhalator (Romeu 2020).
Description of the intervention
ECs are electronic vaping devices that are handheld and produce an aerosol formed by heating an e‐liquid, designed for inhalation by the user (E‐cigarette ontology 2021). The e‐liquid, usually comprising propylene glycol and glycerol, with or without nicotine and flavors, is stored in disposable or refillable cartridges or a reservoir or 'pod'. The commonly‐used term for this aerosol is vapor, which we use throughout the review. In many countries, ECs are marketed as consumer products. Although routes are in place for licensing them as a medicine in some areas, no country yet has a licensed, medicinal EC.
ECs provide sensations similar to smoking a cigarette. They provide taste and throat sensations that are closer to smoking than those provided by the nicotine inhalator (Barbeau 2013). The vapor that looks like tobacco smoke is only visible when the user exhales after drawing on the mouthpiece, not when the device is being held. In qualitative studies users report a sense of shared identity with other users, similar to tobacco smoking identity, and also report pleasure and enjoyment of use, suggesting that ECs may be viewed less as a medical cessation aid but rather as an acceptable alternative to tobacco smoking (Cox 2017; Notley 2018a).
There are many different brands and models of EC available. Variation exists both in the device ('product') and consumable (e‐liquid used). There is a wide variation in the composition of e‐liquids (nicotine content, flavors and other components) (Goniewicz 2012; Goniewicz 2014), with some users choosing to mix their own e‐liquids (Cox 2019b). Initial studies showed that early models of EC delivered very low amounts of nicotine to naïve users (Bullen 2010; Eissenberg 2010; Vansickel 2010). Later studies that have measured nicotine pharmacokinetics in both experienced and naïve EC users have found that some EC users can achieve blood nicotine levels similar to those achieved with smoking, albeit more slowly, and that their ability to do so often improves over time (Hajek 2015b; Vansickel 2012; Vansickel 2013; Yingst 2019a; Yingst 2019b).
Early on in their development, ECs looked like cigarettes and used disposable cartridges. These models were often called 'cig‐a‐likes'. The nicotine delivery from these products was low, and even the modern versions of EC devices that use pre‐filled cartridges, generally produced by the tobacco industry, for the most part have only low nicotine delivery (Hajek 2017). The later refillable, or 'tank', products have a larger battery and a transparent container that users fill with an e‐liquid of their choice, and usually provide faster and more efficient nicotine delivery, allow a wider choice of flavors and nicotine concentrations, and are typically used by experienced vapers who manage to switch to vaping completely (ASH 2019; Dawkins 2013b; Farsalinos 2014). Observational evidence suggests people who smoke are more likely to successfully quit using tank models than with cig‐a‐likes (Chen 2016; Hitchman 2015). EC types are also often grouped by 'generation': first‐generation devices are typically cig‐a‐likes; second‐generation devices are usually tank models, sometimes referred to as 'vape pens'; and third‐generation devices are tank models which, unlike second‐generation devices, allow users to adjust the power (wattage) level of the product (see NCSCT EC briefing for further information and images of different product types). More recently, smaller 'pod' devices, such as Juul, appeared that use nicotine salt. This nicotine formulation reduces irritant effects and allows the delivery of higher nicotine levels that closely mimic the pharmacokinetic profile of nicotine delivery from cigarettes, despite the low battery power of the device (Hajek 2020). Juul has now become the most popular EC in the USA (Huang 2019). The EU Tobacco Products Directive (European Parliament 2014) does not allow sales of e‐liquids with nicotine content higher than 20 mg/ml, and so the US version of Juul (59 mg/nl nicotine) is not available within the EU (Huang 2019; Talih 2020).
The different device types (cig‐a‐like, refillable and pods using high nicotine content salts) may differ significantly in their efficacy in helping people who smoke to quit, as they differ in delivery of nicotine, the active ingredient. Nicotine itself, when delivered through mechanisms and doses similar to that delivered in traditional NRT, is not considered harmful (Hartmann‐Boyce 2018a). The safety profile of the different types of EC may be similar as they use the same constituents, although within the generic range of EC types, there is some evidence to suggest EC providing less nicotine may pose higher risks. This is because low‐nicotine delivery devices need to be puffed with higher intensity to provide users with the nicotine levels that they seek, and more intensive puffing is accompanied by increased inhalation of potential toxicants (Dawkins 2016; Dawkins 2018; Smets 2019). Throughout this review we refer to a nicotine‐containing EC as ‘nicotine EC’ and to nicotine‐free EC as 'non‐nicotine EC', which can also be considered 'placebo EC'. The 'placebo' comparison is a test just of the nicotine effect and not of the potential sensorimotor or behavioral and social replacement that the EC may provide.
There is no one agreed classification system for EC devices, and product development has moved so quickly that the definitions used within trials of the devices tested may no longer be necessarily fit for purpose. In this review, the definitions used are based on those drawn from the included trials. We currently label three different types of EC as 'cartridges' for devices with disposable cartridges and ‐ typically, but not always ‐ low nicotine delivery (e.g. cig‐a‐likes); refillable ECs for devices that vapers fill with their own choice of e‐liquids; and pods for the small devices that use nicotine salts. We may review this categorization system in future versions of the review as new trials and devices emerge.
Why it is important to do this review
Since ECs appeared on the market in 2006 there has been a steady increase in their use. In the UK the ASH 2019 survey found 19.4% of the adult population have ever tried vaping, but only 7.2% were current vapers. EC use remains slightly more common among men compared with women, although the difference is small. EC use is most prevalent in current (19.9%) and former (11.6%) smokers. Less than one per cent of never‐smokers report regular EC use. Prevalence data from the USA in 2019 showed that 4.4% of adults were current EC users (Du 2020). Data from lower‐income countries suggest similar levels of EC use and awareness (Besaratinia 2019; Jiang 2016; Palipudi 2016).
Particular concern has been raised about the increased use of EC in young people, especially among never‐smokers. Data for 2019 from Canada, England, and the USA show regular use (≥ 20 days in the last 30 days) among 16‐ to 19‐year‐olds to be 5.7%, 2.7% and 6.7%, respectively. There appear to be some regional differences in the change in the prevalence of EC use. For example, in North America the rates of regular EC use among 16‐ to 19‐year‐old never‐smokers has significantly increased between 2017 and 2019, compared to England where there has not been any significant change (0.2% to 0.3%) (Hammond 2020). However, as with adults, regular use is greatest among those who are also smoking and lowest among never‐smokers (1.0%, 0.3%, and 1.8% for Canada, England and USA, respectively).
Regulatory approaches being used for ECs currently vary widely, from no regulation to partial and complete bans (McNeill 2021). Within the USA, for example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified them as tobacco products and there are a range of laws that include prohibition of EC use indoors, require retailers to have a license to sell, and prohibit sales to minors. Laws prohibiting sales to minors apply nationwide, but other laws vary by state (Du 2020). The European Union includes ECs in their Tobacco Products Directive, except where therapeutic claims are made or in instances where they contain over 20 mg/nl of nicotine, when they will require medicines authorization (European Parliament 2014).
Categorical statements about the toxicity of ECs are not possible because of the large number of devices and liquids available and the frequent addition of new products to the market. In 2019, cases of severe lung injury associated with EC use were reported in the USA, and by February 2020 there were around 2800 hospitalized cases or deaths (CDC 2020). This illness was termed E‐cigarette or Vaping‐Associated Lung Injury (EVALI) and caused concern throughout the world (Hall 2020), and a negative change in people's perception of the risks of EC use compared to smoking (Tattan‐Birch 2020). These cases were somewhat at odds with data from trials and cohort studies, and it was later found that these injuries were related to use of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)‐containing EC, and in particular THC products adulterated with vitamin E acetate (Blount 2020; Hartnett 2020). Among those brands of nicotine EC that have been tested, levels of toxins have been found to be substantially lower than in cigarettes (Hajek 2014; McNeill 2021). Long‐term effects beyond 12 months are unknown, although based on what is known about liquid and vapor constituents and patterns of use, a report from the UK's Royal College of Physicians has concluded that using an EC is likely to be considerably safer than smoking (RCP 2016). The US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) concluded that ECs are likely to be far less harmful than continuing to smoke cigarettes, with the caveat that the long‐term health effects of e‐cigarette use are not yet known (NASEM 2018).
Despite general acknowledgement that EC use exposes the user to fewer toxicants and at lower levels than smoking cigarettes (McNeill 2021; NASEM 2018; RCP 2016), there remains some hesitancy in making these products available to people who smoke as a harm reduction tool or smoking cessation aid (e.g. McDonald 2020). Lack of quality control measures, possible harms of second‐hand EC vapor inhalation, concerns that the products may be a gateway to smoking initiation or may prolong continued dual‐use of tobacco, concerns that ECs may undermine smoke‐free legislation if used in smoke‐free spaces, concerns about the involvement of the tobacco industry, and concerns that the long‐term effects of EC use on health are not yet known are often cited. Recently, a report from the US Preventive Services Taskforce concluded "that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of electronic cigarettes (e‐cigarettes) for tobacco cessation in adults" (USPFTS 2021). However, others suggest that potential benefits outweigh potential disadvantages (Farsalinos 2014; Hajek 2014; McNeill 2021; NASEM 2018; RCP 2016).
People who smoke, healthcare providers and regulators are interested to know if ECs can help smokers quit and if it is safe to use them to do so. In particular, healthcare providers have an urgent need to know what they should recommend for people who want to stop smoking. The largest health gains are achieved from stopping smoking completely, as opposed to reducing cigarette consumption, and as such this review focuses on the effectiveness of ECs in aiding smoking cessation.
This review was first published in 2014, and updated in 2016 and 2020.
Following the publication of the 2020 update of this review, we are maintaining it as a living systematic review (Brooker 2019). This means we are continually running searches and incorporating new evidence into the review. For more information about the living systematic review methods being used, see Appendix 1. A living systematic review approach is appropriate for this review, for three reasons. First, the review addresses an important public health issue; the role of ECs in enabling people who smoke to stop smoking, with potential for substantial ongoing individual and societal benefits if effective. Secondly, there remains uncertainty in the existing evidence; more studies are needed to confirm the degree of benefit for different comparisons and product types, and there is considerable uncertainty about adverse events and other markers of safety. Thirdly, we are aware of multiple ongoing trials on this topic that are likely to have an important impact on the conclusions of the review.
Objectives
To examine the safety, tolerability and effectiveness of using electronic cigarettes (ECs) to help people who smoke achieve long‐term smoking abstinence.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We include randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and randomized cross‐over trials in which people who smoke are randomized to ECs or to a control condition. RCTs are the best available primary evidence, but the continued paucity of RCTs in this area requires that we also include uncontrolled intervention studies in which all participants are given an EC intervention.
We include studies regardless of their publication status or language of publication.
Types of participants
People defined as currently smoking cigarettes at enrolment into the studies. Participants could be motivated or unmotivated to quit.
Types of interventions
Any type of EC or intervention intended to promote EC use for smoking cessation, including studies which did not measure smoking cessation but provided ECs with the instruction they be used as a complete substitute for cigarette use. ECs may or may not contain nicotine.
Types of comparators
We compare nicotine ECs with non‐nicotine ECs, ECs versus alternative smoking cessation aids, including NRT or no intervention, and ECs added to standard smoking cessation treatment (behavioral or pharmacological or both) with standard treatment alone.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Cessation at the longest follow‐up point, at least six months from the start of the intervention, measured on an intention‐to‐treat basis using the strictest definition of abstinence, preferring biochemically‐validated results where reported
Number of participants reporting adverse events or serious adverse events at one week or longer (as defined by study authors)
Secondary outcomes
Changes in the following measures at one week or longer:
Carbon monoxide (CO), as measured through breath or blood
Blood pressure
Heart rate
Blood oxygen saturation
Lung function measures
Known toxins/carcinogens, as measured through blood or urine (toxicant names and abbreviations are listed in Appendix 2)
Studies had to report one of the primary or secondary outcomes above to be eligible for inclusion.
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
For this update we searched the following databases on 1st February 2021:
Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group Specialized Register
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
MEDLINE (OVID SP)
Embase (OVID SP)
PsycINFO (OVID SP)
ClinicalTrials.gov
WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP: www.who.int/ictrp/en/)
At the time of the search, the Register included the results of searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled trials (CENTRAL), issue 1, 2021; MEDLINE (via OVID) to update 20210104; Embase (via OVID) to week 202101; PsycINFO (via OVID) to update 20201228. See the Tobacco Addiction Group website for full search strategies and a list of other resources searched.
For the first version of the review we also searched CINAHL (EBSCO Host) (2004 to July 2014). We did not search this database from 2016 onwards as it did not contribute additional search results to the first version of the review. The search terms were broad and included e‐cig$ OR elect$ cigar$ OR electronic nicotine. The search for the 2016 update added the terms vape or vaper or vapers or vaping. The 2020 searches added further terms, including the MESH heading 'Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems' and terms to limit by study design. Our search strategy for MEDLINE (Ovid SP) is listed in Appendix 3. The previously‐used search strategy is shown in Appendix 4. The search date parameters of the original searches were limited to 2004 to the present, due to the fact that ECs were not available before 2004.
Searching other resources
We searched the reference lists of eligible studies found in the literature search and contacted authors of known trials and other published EC studies.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors (for this update from: JHB, NL, CN, RB, PH, NR, ARB, HMR) independently prescreened all titles and abstracts obtained from the search, using a screening checklist, and then independently screened full‐text versions of the potentially relevant papers for inclusion. We resolved any disagreements by discussion or with a third review author.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (for this update from: CN, ARB, AT, HMR) extracted data from the included studies using a pre‐piloted data extraction form, and checked them against each other. We resolved any disagreements by discussion or with a third review author. We extracted data on:
Author
Date and place of publication
Study dates
Study design
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Setting
Summary of study participant characteristics
Summary of intervention and control conditions
Number of participants in each arm
Smoking cessation outcomes
Type of biochemical validation (if any)
Adverse events (AEs), serious adverse events (SAEs), and relevant biomarkers
Assessment time points
Study funding source
Author declarations of interest
Risk of bias in the domains specified below
Additional comments
We adopted a broad focus to detect a variety of adverse events.
One review author (JHB) then entered the data into Review Manager 2020 software for analyses, and another checked them (AB for this update).
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (for this update from: CN, ARB, AT, HMR) independently assessed the risks of bias for each included study, using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' Tool v1 (Higgins 2011). This approach uses a domain‐based evaluation that addresses seven different areas: random sequence generation; allocation concealment; blinding of participants and providers; blinding of outcome assessment; incomplete outcome data; selective outcome reporting; and other potential sources of bias. We assigned a grade (low, high, or unclear) for risk of bias for each domain. We resolved disagreements by discussion or by consulting a third review author.
Specific considerations about judgments for individual domains in this review are outlined below:
Random sequence generation/allocation concealment: We rated all non‐randomized studies at high risk in these domains;
Blinding of participants and personnel: We did not evaluate this domain for non‐randomized studies, as we considered it not to be applicable. For randomized studies which did not use blinding, we considered studies to be at low risk in this domain if the intervention was compared to an active control of similar intensity, as we judged performance bias to be unlikely in this circumstance. If studies were unblinded and the comparator group was a minimal‐intervention control or of lower intensity than the intervention group, we considered the study to be at high risk of bias in this domain;
Following standard methods of the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Review Group, we considered studies to be at low risk of detection bias (blinding of outcome assessment) if our primary outcome was objectively measured or if the intensity of intervention was similar between groups, or both. For studies where cessation was measured, our judgment was based on whether cessation was biochemically verified. For other studies, we judged this domain based on adverse or serious adverse events;
Again following standard methods of the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group, we rated studies at high risk of attrition bias if loss to follow‐up was greater than 50% overall or if there was a difference in follow‐up rates of more than 20% between study arms.
We judged studies to be at high risk of bias overall if they were rated at high risk in at least one domain, and at low risk of bias overall if they were judged to be at low risk across all domains evaluated. We judged the remaining studies to be at unclear risk of bias overall.
Measures of treatment effect
We analyzed dichotomous data by calculating the risk ratio (RR). For cessation, we calculated the RR as ((number of events in intervention condition/intervention denominator) / (number of events in control condition/control denominator)) with a 95% confidence interval (CI), using data at the longest follow‐up period reported.
We analyzed continuous data (other measures of tobacco exposure) by comparing the difference between the mean change from baseline to follow‐up in the intervention and comparator groups. For outcomes other than cessation where data were reported at multiple time points, we used data at the longest follow‐up point at which ECs were still being provided.
Unit of analysis issues
In the case of trials with multiple arms, we do not combine data between arms unless this is the way it has been presented by study authors. We note in our analyses where this is the case.
For all but one study, the unit of assignment was the individual. Dawkins 2020 assigned condition based on homeless support service; this was a small pilot study with very few events and hence we judged clustering to have very little impact on our overall result. If larger cluster‐randomized trials are eligible in the future, we will assess whether study authors have adjusted for this clustering, and whether this had an impact on the overall result. When clustering appears to have had little impact on the results, we will use unadjusted quit‐rate data; however when clustering does appear to have an impact on results, we will adjust for this using the intraclass correlation (ICC).
For randomized cross‐over trials, we report results at the end of the first assignment period where available and where sufficiently long to meet our inclusion criteria for outcomes. All other outcomes from randomized cross‐over trials are reported narratively. We offer a narrative synthesis of data from non‐randomized studies, and where possible use effect direction plots as described in the Cochrane Handbook (Higgins 2021).
Dealing with missing data
For smoking cessation, we used a conservative approach, as is standard for the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group, treating participants with missing data as still smoking. We based the proportion of people affected by adverse events on the number of people available for follow‐up, and not the number randomized. For other outcomes, we use complete‐case data and do not attempt to impute missing values.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We assessed the clinical and methodological diversity between studies to guide our decision as to whether data should be pooled. We were also guided by the degree of statistical heterogeneity, assessed by calculating the I2 statistic (Higgins 2003), and considering a value greater than 50% as evidence of substantial heterogeneity. We did not present pooled results where I2 values exceeded 75%.
Assessment of reporting biases
Reporting bias can be assessed using funnel plots, where 10 or more RCTs contribute to an outcome. However, there are currently insufficient studies to support this approach.
Data synthesis
We provide a narrative summary of the included studies. Where appropriate, we have pooled data from these studies in meta‐analyses. For dichotomous data, we used a fixed‐effect Mantel‐Haenszel model to calculate the RR with a 95% confidence interval, in accord with the standard methods of the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group for cessation studies.
For continuous outcomes, we pooled mean differences (or standardized mean differences for studies using different measures for the same construct), using the inverse variance approach (also with a 95% CI).
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We had planned to undertake subgroup analyses to investigate differences between studies, such as:
Intensity of behavioral support used;
Type of EC (cartridge; refillable; pod);
Instructions for EC use (e.g. study provision, length of provision, whether participants had a role in product choice);
Type of participants (e.g. experience of EC use).
However, there were too few studies to conduct such analyses. Should further studies become available in future, we will follow this approach. For safety outcomes, we present subgroups by length of follow‐up for descriptive purposes.
In the absence of sufficient data for subgroup analyses on EC type, in the text we specify the type of nicotine EC when reporting pooled results for cessation.
Sensitivity analysis
We conducted sensitivity analyses to detect whether pooled results were sensitive to the removal of studies judged to be at high risk of bias.
Summary of findings and assessment of the certainty of the evidence
Following standard Cochrane methodology, we created 'Summary of findings' tables for our three main comparisons using GRADEpro GDT: nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC; nicotine EC versus NRT; and nicotine EC versus behavioral support only/no support. We selected these comparisons a priori as being the most clinically relevant. In the 'Summary of findings' tables, we present data on our primary outcomes (cessation, adverse events, serious adverse events) for these main comparisons. Also following standard Cochrane methodology, we used the five GRADE considerations (study limitations, consistency of effect, imprecision, indirectness and publication bias) to assess the certainty of the body of evidence for each outcome, and to draw conclusions about the certainty of evidence within the text of the review.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
For this update, our bibliographic database searches identified 825 non‐duplicate records (Figure 1). We screened all records and retrieved the full‐text papers of 100 potentially relevant articles. After screening and checking the full‐text of 100 papers, we included 26 records, representing six studies new for this update (Czoli 2019; Ikonomidis 2020; Ozga‐Hess 2019; Pulvers 2020; Scheibein 2020; Yingst 2020), nine new articles linked to studies already identified, and 11 new references to ongoing studies (see Characteristics of ongoing studies). Secondary study reports, commentaries, and correspondence relating to included studies are linked to studies in the reference section. Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 present PRISMA flow charts for previous versions of this review.
1.
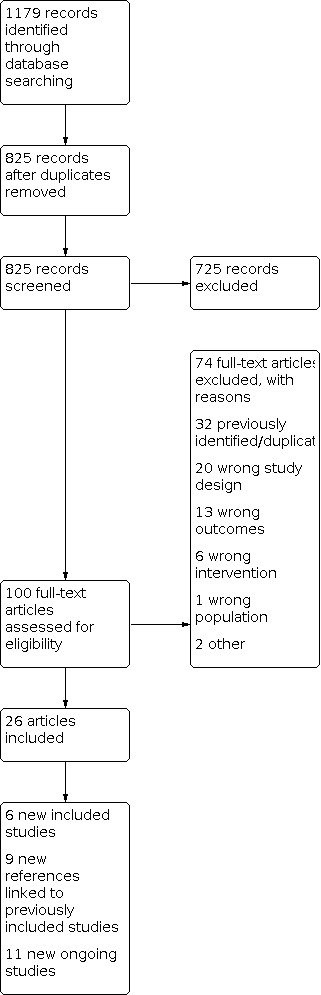
2021 update flow diagram
2.
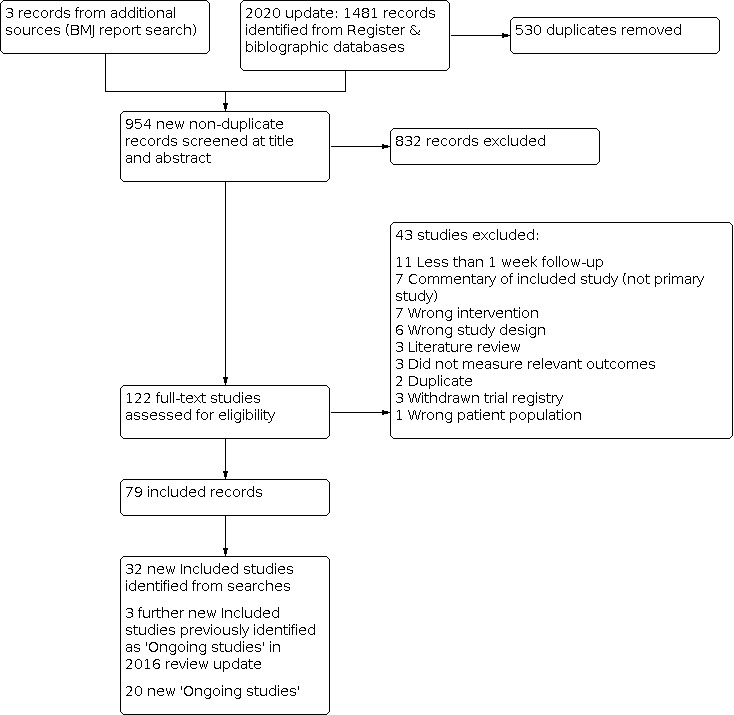
2020 update flow diagram
3.
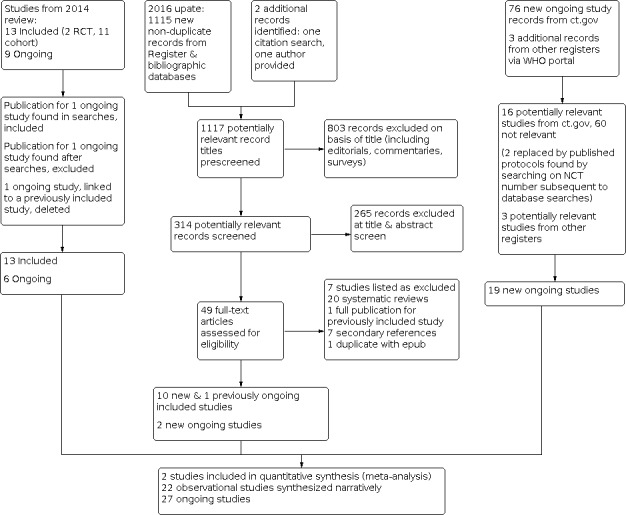
2016 update flow diagram
4.
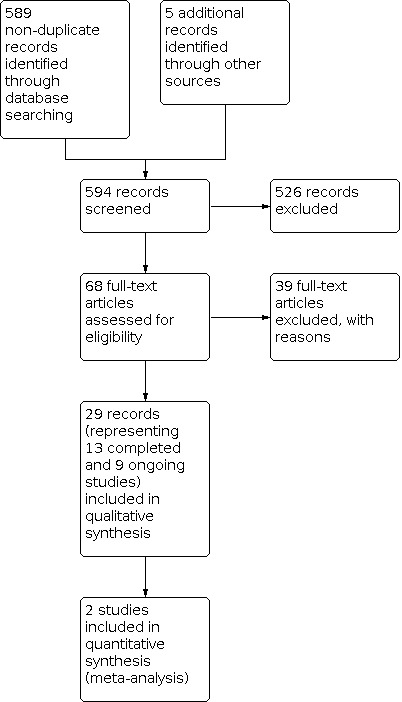
2014 flow diagram
Included studies
In total, we include 56 studies, six new included studies and 50 eligible included studies identified in previous versions of the review. Key features of the included studies are summarized below. Further details on each included study can be found in the Characteristics of included studies tables.
Participants
The 56 included studies represented 12,804 participants. Twenty‐four studies were conducted in the USA, nine were conducted in the UK, seven in Italy, three in Greece, two each in Australia, New Zealand, and Canada, and one each in Belgium, Ireland, Poland, the Republic of Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, and Turkey. All studies were conducted in adults who smoke. Seventeen studies exclusively recruited participants who were not motivated to quit smoking, and 29 studies exclusively recruited participants motivated to quit; motivation was not specified for the other studies. Eighteen studies recruited from specific population groups; these included six studies which recruited participants based on physical health condition (heart attack, cancer, HIV, periodontitis, awaiting surgery), three studies which recruited participants with serious mental illness, and three studies which recruited participants in treatment or having recently completed treatment for alcohol or other drug use. Two studies recruited people accessing homeless centres or using supported temporary accomodation. One study each recruited: people aged 55 or older, young adults, and black and latinx participants.
Interventions and comparators
All but one study provided nicotine EC, either alone (50 studies) or in conjunction with NRT or varenicline (five studies). One study recruited dual users at baseline, and instructed them to continue using their own EC devices (Czoli 2019). In two studies where nicotine EC was provided on its own, nicotine levels were judged to be so low as to be clinically comparable to non‐nicotine EC (Lee 2019; Van Staden 2013); we include these studies in non‐nicotine EC comparisons. Eight studies compared nicotine EC with non‐nicotine EC, 16 studies compared nicotine EC to behavioral support only or to no support, and eight studies compared nicotine EC to NRT. One study directly compared a cig‐a‐like with a refillable (tank) device (Yingst 2020). Results from these studies are reported by comparison in Effects of interventions. Further details on the intervention and comparator groups (where applicable) for each study can be found in the Characteristics of included studies tables.
Where reported in the primary research publications, details on the devices tested can also be found in the Characteristics of included studies tables. Of the studies with sufficient data with which to judge, 26 used cartridge devices (only one of which had high nicotine delivery), 21 used refillable devices, three used both types, one used a pod device, and the remainder did not report device type.
Outcomes
Of the 56 included studies:
22 reported data on abstinence
39 reported data on adverse events
24 reported data on serious adverse events
36 reported data on carbon monoxide
9 reported data on heart rate
12 reported data on blood pressure
2 reported data on blood oxygen saturation
9 reported data on at least one known toxin/carcinogen
5 reported data on at least one measure of lung function
Study types and funding
Twenty‐nine studies were RCTs, 13 of which contributed to cessation analyses. Five studies used randomized cross‐over designs, and the remainder were uncontrolled cohort studies. Of the 46 studies which reported funding information, 32 had no EC industry funding or support.
Excluded studies
We list 92 studies excluded at full‐text stage, along with reasons for exclusion, in the Characteristics of excluded studies table. The most common reason for exclusion was that studies were short‐term, following up participants for periods of less than one week.
Risk of bias in included studies
Overall, we judged five studies (Bullen 2013; Eisenberg 2020; Hajek 2019; Lee 2018; Lee 2019) to be at low risk of bias, ten to be at unclear risk, and the remaining 41 at high risk of bias (note, this includes the non‐randomized studies, which we deemed to be at high risk due to this lack of randomization).
Details of 'Risk of bias' judgments for each domain of each included study can be found in the Characteristics of included studies table. Figure 5 illustrates judgments for each included study.
5.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
We judged 23 studies to be at high risk of selection bias; for 22, this is because the studies were not randomized. We also rated a pilot cluster‐randomized trial at high risk as randomization was not carried out as intended for pragmatic reasons (Dawkins 2020). We judged 14 studies to be at low risk of selection bias, and the remainder to be at unclear risk as there was insufficient information with which to judge.
Blinding
Of the 35 studies assessed for these domains, we judged 16 to be at low risk for both performance and detection bias. We rated 14 at high risk for performance or detection bias, or both. In these studies, blinding was not used and different levels of support were provided; this alone or in conjunction with the outcome measures being used (subjective rather than objective measures) meant we thought there was a high risk of bias being introduced. We judged the rest to be at unclear risk.
Incomplete outcome data
We judged most studies (40 out of 56) to be at low risk of attrition bias. We rated six studies with substantial loss to follow‐up at high risk of attrition bias. The remainder did not provide sufficient data on which to judge, and hence we judged them to be at unclear risk.
Selective reporting
Of the 56 studies, we considered that 29 were at low risk of reporting bias, as all prespecified/expected outcomes were reported. We rated four at high risk, as data were not presented as specified in the original protocols. We judged the rest to be at unclear risk, due to insufficient information with which to make a judgment.
Other potential sources of bias
We considered Ioakeimidis 2018 to be at high risk of other bias; data were from a conference poster and the associated abstract, and quit rates in the intervention arm differed between the two sources.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1; Table 2; Table 3
Summary of findings 1. Nicotine EC compared to NRT for smoking cessation.
| Nicotine EC compared to NRT for smoking cessation | ||||||
| Patient or population: People who smoke Setting: New Zealand, UK, USA Intervention: Nicotine EC Comparison: NRT | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | № of participants (studies) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with NRT | Risk with Nicotine EC | |||||
| Smoking cessation at 6 months to 1 year Assessed with biochemical validation |
Study population | RR 1.69 (1.25 to 2.27) | 1498 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ MODERATEa | ‐ | |
| 6 per 100 | 10 per 100 (8 to 14) | |||||
| Adverse events at 4 weeks to 6 months Assessed by self‐report |
Study population | RR 0.98 (0.80 to 1.19) | 485 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWb | ‐ | |
| 45 per 100 | 44 per 100 (36 to 53) | |||||
| Serious adverse events at 4 weeks to 1 year Assessed via self‐report and medical records |
Study population | RR 1.37 (0.77 to 2.41) | 727 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWb | One study reported no events; effect estimate based on the one study in which events were reported | |
| 5 per 100 | 7 per 100 (4 to 13) | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). For cessation, the assumed risk in the control group is based on assumed quit rates for NRT assuming receipt of limited behavioral stop‐smoking support (as per Hartmann‐Boyce 2018a). The assumed risk for adverse events and serious adverse events is a weighted mean average of quit rates across control groups in contributing studies. CI: Confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: Risk ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High certainty: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate certainty: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low certainty: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low certainty: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | ||||||
aDowngraded one level due to imprecision; small number of events (< 300 overall). bDowngraded two levels due to imprecision; confidence intervals encompass clinically‐important harm as well as clinically important benefit.
Summary of findings 2. Nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC for smoking cessation.
| Nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC for smoking cessation | ||||||
| Patient or population: People who smoke cigarettes Setting: Canada, Italy, New Zealand, UK, USA Intervention: Nicotine EC Comparison: Non‐nicotine EC | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | № of participants (studies) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with non‐nicotine EC | Risk with Nicotine EC | |||||
| Smoking cessation at 6‐12 months Assessed with biochemical validation |
Study population | RR 1.70 (1.03 to 2.81) | 1057 (4 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ MODERATEa, b | ‐ | |
| 6 per 100 | 10 per 100 (6 to 17) | |||||
| Adverse events at 1 week to 6 months Assessed via self‐report |
Study population | RR 1.01 (0.91 to 1.11) | 601 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ MODERATEc | ‐ | |
| 35 per 100 | 35 per 100 (31 to 38) | |||||
| Serious adverse events at 1 week to 1 year Assessed via self‐report and medical records |
Study population | RR 0.60 (0.15 to 2.44) | 494 (4 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWd | 3 studies reported no events; effect estimate based on the one study in which events were reported | |
| 2 per 100 | 1 per 100 (0 to 4) | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). For cessation, the assumed risk in the control group is based on receipt of moderate‐intensity behavioral stop‐smoking support. The assumed risk for adverse events and serious adverse events is a weighted mean average of quit rates across control groups in contributing studies. CI: Confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: Risk ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High certainty: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate certainty: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low certainty: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low certainty: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | ||||||
aNot downgraded for risk of bias. One of three studies considered high risk of bias; removing this study increased the direction of the effect in favor of the intervention. bDowngraded one level due to imprecision; confidence intervals incorporate no clinically‐significant difference as well as clinically‐significant benefit. cDowngraded one level due to imprecision: though confidence intervals are narrow, only 3 studies with 601 participants contribute data. dDowngraded two levels due to imprecision: confidence intervals encompass clinically‐significant harm as well as clinically‐significant benefit.
Summary of findings 3. Nicotine EC compared to behavioral support only/no support for smoking cessation.
| Nicotine EC compared to behavioral support only/no support for smoking cessation | ||||||
| Patient or population: People who smoke Setting: Canada, Italy, UK, USA Intervention: Nicotine EC Comparison: Behavioral support only/no support | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | № of participants (studies) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with behavioral support only/no support | Risk with Nicotine EC | |||||
| Smoking cessation at 6 to 12 months Assessed using biochemical validation |
Study population | RR 2.70 (1.39 to 5.26) | 2561 (5 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOWa, b | ‐ | |
| 4 per 100 | 11 per 100 (6 to 21) | |||||
| Adverse events at 12 weeks to 6 months Assessed via self‐report |
Study population | RR 1.22 (1.12 to 1.32) | 765 (4 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWa | ‐ | |
| 60 per 100 | 73 per 100 (67 to 79) | |||||
| Serious adverse events at 4 weeks to 6 months Assessed via self‐report and medical records |
Study population | RR 1.17 (0.33 to 4.09) | 1011 (6 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOWa, c | 4 of the 6 studies reported no SAEs; MA is based on pooled results from 2 studies | |
| 1 per 100 | 1 per 100 (0 to 5) | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). For cessation, the assumed risk in the control group is based on receipt of limited stop‐smoking support. The assumed risk for adverse events and serious adverse events is a weighted mean average of quit rates across control groups in contributing studies. CI: Confidence interval; RCT: randomized controlled trial; RR: Risk ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High certainty: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate certainty: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low certainty: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low certainty: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | ||||||
aDowngraded two levels due to risk of bias. Due to lack of blinding and differential support between arms, judged to be at high risk of bias. bDowngraded one level due to imprecision; although confidence intervals are consistent with clinically‐ important difference, event count is very low (< 100). cDowngraded two levels due to imprecision; confidence intervals incorporate clinically‐significant benefit and clinically‐significant harm.
Data on our outcomes of interest are summarized below. Due to the volume of data available, some relevant information is hosted on a companion repository; these data are open‐access and can be found at https://doi.org/10.5287/bodleian:dX4Dgp7dJ. They are referred to below as supplemental tables. Forest plots are available through 'analysis' links; for some outcomes, benefit is plotted on the right, for others on the left. This is due to direction of effect, e.g. an increase in cessation is a benefit, whereas an increase in a carcinogen is not.
Direct comparisons between nicotine EC and other pharmacotherapies
Comparisons reported here include cartridge and refillable nicotine ECs versus NRT, and cartridge nicotine ECs versus varenicline. Only randomized controlled trials contribute data.
Cessation
Pooled data from three studies (2 cartridge, 1 refillable), all of which we rated at low risk of bias, showed higher quit rates in people randomized to nicotine EC than to NRT (RR 1.69, 95% CI 1.25 to 2.27; I2 = 0%; 1498 participants; Analysis 1.1). One study (Ioakeimidis 2018), available as a conference presentation only and considered at high risk of bias due to inconsistencies in the data reported and an unclear definition of abstinence, found lower quit rates in people allocated to nicotine EC (cartridge) compared to those allocated to varenicline (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.82; 54 participants; Analysis 2.1).
1.1. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
2.1. Analysis.

Comparison 2: Nicotine EC versus varenicline, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
Adverse events
Pooled data from two studies (both considered at low risk of bias) showed no evidence of a difference in the number of participants reporting adverse events (AEs) between nicotine EC and NRT arms (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.19; I2 = 0%; 485 participants; Analysis 1.2). Hajek 2019 did not contribute data to this analysis due to the way in which events were recorded; of their prespecified adverse reactions of interest, nausea was more frequent in the NRT group, throat/mouth irritation was more frequent in the nicotine EC group, and there was little difference in other reactions (see Supplemental Table 1 for more detail).
1.2. Analysis.
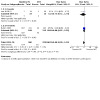
Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 2: Adverse events
In Ioakeimidis 2018, reports of sleep disorders were evenly distributed between groups, and nausea was more common in the varenicline arm than in the nicotine EC arm (see Supplemental Table 1 for more detail).
Serious adverse events
Two studies comparing nicotine ECs with NRT provided data on SAEs; in one (Lee 2018) none occurred in either arm. In Hajek 2019 (n = 698), more events occurred in the nicotine EC arm than in the NRT arm, but the confidence interval was wide and included no difference as well as the possibility of more events in the NRT arm (RR 1.37, 95% CI 0.77 to 2.41; Analysis 1.3). As noted above, Bullen 2013, which compared nicotine EC, non‐nicotine EC, and NRT, only reported that no serious adverse events (SAEs) occurred that were considered related to study treatment. No events occurred in Ioakeimidis 2018 (Analysis 2.2).
1.3. Analysis.
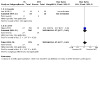
Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
2.2. Analysis.

Comparison 2: Nicotine EC versus varenicline, Outcome 2: Serious adverse events
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Pooled data from two studies (Hatsukami 2020; Lee 2018; neither considered at high risk of bias) comparing nicotine EC with NRT found that CO levels decreased more in those randomized to nicotine EC, but the point estimate was small, confidence intervals were wide, and statistical heterogeneity was substantial (MD −0.66 ppm, 95% CI −1.94 to 0.62; I2 = 69%; 136 participants; Analysis 1.4).
1.4. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 4: Carbon monoxide (ppm)
Heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation
Only Hatsukami 2020 contributed data for these outcomes. A small benefit in favor of EC was found for change in heart rate (Analysis 1.5). No difference was found for blood pressure or blood oxygen saturation, although confidence intervals were wide (Analysis 1.6; Analysis 1.7).
1.5. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 5: Heart rate (bpm)
1.6. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 6: Systolic blood pressure
1.7. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 7: Blood oxygen saturation
Toxicants
Again, only Hatsukami 2020 contributed data for these outcomes. For 3‐HPMA, 2‐HPMA, HMPMA, PheT, and CEMA, point estimates favored EC but confidence intervals included no difference (Analysis 1.8; Analysis 1.10; Analysis 1.11; Analysis 1.12; Analysis 1.13). Both AAMA and NNAL decreased more in NRT than in EC groups, with confidence intervals excluding no difference (Analysis 1.9; Analysis 1.14).
1.8. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 8: 3‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
1.10. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 10: 2‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
1.11. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 11: HMPMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
1.12. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 12: PheT (pmol/mg creatinine)
1.13. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 13: CEMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
1.9. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 9: NNAL (pmol/mg creatinine))
1.14. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 14: AAMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
Lung function
Lee 2018 measured change in FEV1 and FEV1/FVC; for both outcomes, point estimates favored EC over NRT; confidence intervals excluded no difference for FEV1 (Analysis 1.15; Analysis 1.16).
1.15. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 15: FEV1 (ml)
1.16. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 16: FEV1/FVC (%)
Nicotine EC alone or versus control
Comparisons reported here include nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, and nicotine EC compared to behavioral support only or to no support. In this section, we also report results from studies in which all participants received nicotine EC (cohort studies and randomized studies which did not differ across arms in EC provision, device generation, or nicotine content).
Cessation
Randomized controlled trials
At six months or longer, quit rates were higher in nicotine EC groups than in comparator groups. Compared to EC without nicotine (placebo EC), pooled results showed nicotine EC produced higher quit rates (RR 1.70, 95% CI 1.03 to 2.81; I2 = 0%; 3 studies of cartridge devices, 1 refillable, 1057 participants; Analysis 3.1). The effect size increased when we removed the one study at high risk of bias (Lucchiari 2020). The effect was more pronounced when comparing nicotine EC to behavioral support only or to no support (RR 2.70, 95% CI 1.39 to 5.26; I2 = 0%; 5 studies (3 refillable, 2 cartridge), 2561 participants; Analysis 4.1). As this involved unblinded comparisons with unequal levels of support, we judged all data contributing to this outcome to be at high risk of bias.
3.1. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
4.1. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
Pulvers 2020 (pod device) measured cessation at six months in the intervention group only, using self‐report. As they did not measure cessation at six months in the comparator group we could not include these data in meta‐analysis. At six months, 23 (24%) of intervention participants were exclusively using EC and 10 (10.4%) reported using neither EC nor combustible cigarettes (making a combined quit rate of 34.4% in the intervention arm at six months).
Data from other studies
Eight studies provided all participants with nicotine EC and assessed abstinence at six months or longer (Table 4; 1 refillable, 6 cartridge, 1 not specified). The highest proportion of quitters was observed in Ely 2013 (cartridge), in which all participants (n = 48) used EC and 18 used additional pharmacotherapy: 44% of participants were abstinent at six months. The lowest quit rates were seen in two studies where participants were not motivated to quit at baseline: in Caponnetto 2013b, 14% of participants were abstinent at 12 months, and in Polosa 2011 23% of participants were abstinent at six months, but this fell to 13% at 24 months (both studies used cartridge devices).
1. Summary of proportion of participants abstinent from smoking at 6+ months follow‐up: cohort studies of nicotine EC.
| Study | Motivated or unmotivated to quit smoking? | % abstinent | ||||
| Cohort studies | 6‐month | 12‐month | 18‐month | 24‐month | Notes | |
| Adriaens 2014a | Unmotivated to quit | 19.6% (10/51) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | Data from 8‐month follow‐up |
| Bell 2017 | "Willing to attempt to quit" | 26.6% (8/30) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Caponnetto 2013b | Unmotivated to quit | ‐ | 14% (2/14) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Ely 2013b | Motivated to quit | 44% (21/48) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Pacifici 2015 | Unmotivated to quit | ‐ | 53% (18/34) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Polosa 2011 | Unmotivated to quit | 23% (9/40) | ‐ | 15% (6/40) | 13% (5/40) | ‐ |
| Polosa 2014b | Unmotivated to quit | 36% (18/50) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
| Polosa 2015 | Not defined | 42% (30/71) | 41% (29/71) | ‐ | ‐ | ‐ |
aTechnically an RCT but observational for purposes of EC analysis. bAll participants (N = 48) used an EC, but 16 also used bupropion and 2 used varenicline.
Adverse events
Randomized controlled trials
Pooled data from three studies (none at high risk of bias) showed no evidence of a difference in the number of participants experiencing adverse events when comparing nicotine EC to non‐nicotine EC (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.11; I2 = 0%; 601 participants; Analysis 3.2). When comparing nicotine EC to behavioral support only or to no support, more people in the groups randomized to nicotine EC reported experiencing adverse events (RR 1.22, 95% CI 1.12 to 1.32; I2 = 41%; 4 studies, 765 participants; Analysis 4.2). As this involved unblinded comparisons with unequal levels of support, we judged all data contributing to this outcome to be at high risk of bias.
3.2. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 2: Adverse events
4.2. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 2: Adverse events
A further seven randomized controlled trials provided adverse event or related data for this comparison, but could not be included in the meta‐analysis due to the way in which data were presented (see Supplemental Table 1). In the studies comparing nicotine EC to non‐nicotine EC, one found similar event rates across arms (Caponnetto 2013a), and two reported more events in the nicotine EC arms (Felicione 2019; Tseng 2016). In a further study comparing nicotine to non‐nicotine EC, events were reported by type, with an increase in some seen in the nicotine group and an increase in others seen in the non‐nicotine group (Lucchiari 2020). In the three studies comparing nicotine EC to behavioral support only or traditional cigarettes, Kumral 2016 found an increase in sinonasal symptoms in the group receiving nicotine EC compared to behavioral support only, and Ozga‐Hess 2019 found that throat irritation, cough, and dry mouth increased in the e‐cigarette group relative to the traditional cigarette group. By contrast, Pulvers 2020 found a reduction in respiratory symptoms in the e‐cigarettes compared to the traditional cigarettes group.
Data from other studies
Seventeen studies provided all participants with nicotine EC and assessed adverse events at one week or longer (see Supplemental Table 1). In the seven studies which tracked event rates over time, six showed adverse events reducing over time (Bell 2017; Caponnetto 2013b; Goniewicz 2017; Polosa 2011; Polosa 2014b; Pratt 2016). Hickling 2019 showed no change. The most commonly‐reported adverse events were throat/mouth irritation, headache, cough, and nausea.
Serious adverse events
Randomized controlled trials
Four studies compared nicotine EC with non‐nicotine EC and reported data on SAEs; in three of these, no events occurred, so results could not contribute to the meta‐analysis, although they are included in the forest plots for descriptive purposes. In the one study (Eisenberg 2020, n = 255 for this comparison) where events occurred, more were reported in the non‐nicotine arm (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.15 to 2.44; Analysis 3.3). We rated this study at low risk of bias.
3.3. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Six studies compared nicotine EC with behavioral support only or no support and reported data on SAEs; in four of these, no events occurred. Pooled results from the two studies in which events occurred showed more events occurring in the nicotine EC arm, but confidence intervals were wide and encompassed clinically significant benefit and clinically significant harm (RR 1.17, 95% CI 0.33 to 4.09; I2 = 5%; 2 studies, 1011 participants; Analysis 4.3).
4.3. Analysis.
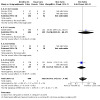
Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Bullen 2013, which compared nicotine EC, non‐nicotine EC, and NRT, only reported that no SAEs occurred that were considered to be related to study treatment. In a study in people experiencing homelessness (Dawkins 2020), SAEs were not reported, but authors report that four to seven participants in the usual‐care arm and five to seven participants in the nicotine EC arm visited Accident & Emergency services at a hospital. Further detail can be seen in Supplemental Table 2.
Data from other studies
Seven studies provided all participants with nicotine EC and reported SAEs at a week or longer (Supplemental Table 2). In five of these (Bell 2017; Caponnetto 2013b; Humair 2014; Polosa 2011; Valentine 2018), authors report that no SAEs occurred. In NCT02648178 (19 participants), one death occurred (no further detail provided). Hickling 2019 (50 participants) recruited participants from mental health settings; five SAEs were recorded during the study, all of which were psychiatric hospitalizations. None were considered related to study treatment.
Carbon monoxide
Randomized controlled trials
Pooled data from two trials (neither considered at high risk of bias) comparing nicotine EC with non‐nicotine EC found lower exhaled CO levels in people randomized to nicotine EC (MD −2.44 ppm, 95% CI −3.91 to −0.97; 171 participants; Analysis 3.4). Although statistical heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 71%), point estimates in both studies favored nicotine EC. Three further randomized studies measured CO levels in those assigned to nicotine EC and those assigned to non‐nicotine EC, but did not present data in a way that could be pooled: George 2019 did not compare data by group; Tseng 2016 reports no between‐group differences; and Meier 2017 found a slightly higher CO reading in those using nicotine EC, but the clinical and statistical significance of this difference was not clear (see Supplemental Table 3 for more detail). These data are from all study participants based on group randomized, not on subsequent EC or cigarette use.
3.4. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 4: Carbon monoxide (ppm)
Pooled data from six studies comparing nicotine EC to behavioral support alone or no support resulted in a high I2 value (92%); pooled results are not presented here (see Analysis 4.4 for individual study data). Heterogeneity was primarily driven by magnitude rather than direction of effect, with results generally favoring nicotine EC. Three further trials reported data which could not be included in a meta‐analysis. Walele 2018 compared nicotine EC to cigarettes and found CO levels declined in the EC group and remained similar to baseline in the cigarette group. Veldheer 2019 compared nicotine EC with a cigarette substitute (non‐pharmacological); change in CO was similar between groups. Czoli 2019 instructed baseline dual users to spend periods only using EC or only using traditional cigarettes; CO measured during sole EC use was lower than baseline and lower than during cigarette‐only periods. Further detail can be seen in Supplemental Table 3.
4.4. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 4: Carbon monoxide (ppm)
Data from other studies
Eighteen studies provided all participants with nicotine EC and reported data on CO at one week or longer. In the 17 studies that presented change over time, CO declined from baseline, although in Ikonomidis 2018 CO levels were equivalent to baseline again at 24 weeks, and in Polosa 2014b a decline was observed in people who quit smoking or reduced cigarette consumption by at least half, but not in those who continued smoking at least half as many cigarettes as they had from baseline.
Heart rate
Randomized controlled trials
One RCT (Caponnetto 2013a) provided data on heart rate and compared nicotine EC with non‐nicotine EC; there was a greater decrease in heart rate in the nicotine EC arm (MD −2.80, 95% CI −3.85 to −1.74; 141 participants; Analysis 3.5). This was comparable with findings from the one RCT (Hatsukami 2020) comparing nicotine EC with no pharmacotherapy, which also found a greater reduction in the EC arm (MD −2.70, 95% CI −4.25 to −1.15; 90 participants; Analysis 4.5).
3.5. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 5: Heart rate
4.5. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 5: Heart rate (bpm)
A further three RCTs provided data on heart rate which could not be included in a meta‐analysis. George 2019 compared nicotine to non‐nicotine EC and found no difference in heart rate between arms; Walele 2018 compared a nicotine EC with a traditional cigarette and reported "no clinically significant changes", and Veldheer 2019 found decreases in both the nicotine EC and QuitSmart cigarette substitute groups, with the decrease being slightly greater in the latter group. See Supplemental Table 4 for further information.
Data from other studies
Five studies in which all participants received a nicotine EC also reported data on heart rate; changes were minimal and directions of effect were mixed (see Supplemental Table 4).
Blood pressure
Caponnetto 2013a found no difference in the change in systolic blood pressure (BP) between nicotine EC and non‐nicotine EC arms (MD 0.60, 95% CI −0.99 to 2.19;1 41 participants; Analysis 3.6). Similarly, Hatsukami 2020 and Ikonomidis 2018 found no difference in the change in blood pressure when comparing nicotine EC to cigarettes. However, Pulvers 2020 found a benefit in favor of the EC arm; pooling data from these three studies resulted in high levels of statistical heterogeneity (I2 = 82%), so pooled results are not presented (Analysis 4.6). Three further RCTs measured change in blood pressure but presented results in such a way that they could not be pooled. George 2019 compared nicotine EC and non‐nicotine EC and combined data from both groups; BP declined over time. Compared to a QuitSmart cigarette substitute, Veldheer 2019 found EC led to a greater reduction in BP. Walele 2018 found "no clinically significant changes" when comparing nicotine EC to a conventional cigarette at two weeks. Further data can be found in Supplemental Table 5.
3.6. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 6: Systolic blood pressure
4.6. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 6: Systolic blood pressure
Five studies which provided nicotine EC to all participants reported change in blood pressure; results were mixed and small (Hickling 2019; Ikonomidis 2018; Oncken 2015; Van Staden 2013; Walele 2018; see Supplemental Table 5).
Oxygen saturation
Hatsukami 2020 found a small increase in blood oxygen saturation when comparing nicotine EC to cigarettes (MD 0.50%, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.69; 89 participants; Analysis 4.7). Van Staden 2013, a short‐term pre‐post study which measured outcomes after two weeks of EC use, found that people who smoked who switched to ECs had significant improvement in blood oxygen saturation (96.2% (SD 1.8) to 97.5% (SD 1.3); 1.3% increase, 95% CI 0.6 to 2.1; P = 0.002).
4.7. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 7: Blood oxygen saturation
Toxicants
All randomized controlled trials measuring these outcomes compared nicotine EC with no pharmacotherapy.
Two trials measured change in 3‐HPMA (one at high risk of bias). In both, the point estimate favored the EC arm, but statistical heterogeneity was substantial (I2 = 97%), reflecting differences in magnitude of effect. We therefore do not present a pooled result, but data from the studies can be seen in Analysis 4.8. Four further studies in which all participants were given nicotine EC measured 3‐HPMA; all found reductions over time (Supplemental Table 6).
4.8. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 8: 3‐HPMA (SMD)
Four trials measured change in NNAL (three at high risk of bias; Analysis 4.9). Three of the four studies found results favoring nicotine EC, but for the fourth the point estimate went in the opposite direction; statistical heterogeneity was again high (I2 = 95%), so pooled results are not presented. Pulvers 2018, which provided all participants with nicotine EC, found a reduction in NNAL over time, and Czoli 2019, which was a cross‐over trial, found NNAL decreased when using nicotine EC compared to using traditional cigarettes (Supplemental Table 6).
4.9. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 9: NNAL (SMD)
One trial found reductions in 2‐HPMA and AAMA compared to control (Analysis 4.10; Analysis 4.14), and a further two studies in which all participants received nicotine EC found reductions in both of these measures over time (Supplemental Table 6).
4.10. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 10: 2‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
4.14. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 14: AAMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
One trial found reductions in S‐PMA compared to control (Analysis 4.15); this was consistent with the one study (Goniewicz 2017) in which all participants received nicotine EC that measured S‐PMA, where levels declined over time (Supplemental Table 6).
4.15. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 15: S‐PMA (nanograms)
In single trials, changes favored EC for reductions in HMPMA (Analysis 4.11), PheT (Analysis 4.12), and CEMA (Analysis 4.13). Of the 19 remaining measurements in studies where all participants received an EC, 14 reduced over time and five increased (Supplemental Table 6).
4.11. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 11: HMPMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
4.12. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 12: PheT (pmol/mg creatinine)
4.13. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 13: CEMA (pmol/mg creatinine)
Lung function
Caponnetto 2013a measured a number of lung function parameters. FeNO increased more in the nicotine EC than the non‐nicotine EC group (MD 2.35, 95% CI 1.78 to 2.92; 90 participants; Analysis 3.7). No difference was found between nicotine and non‐nicotine EC for FEV1, FVC, or FEV1/FVC (Analysis 3.8; Analysis 3.9; Analysis 3.10).
3.7. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 7: FeNO (ppb)
3.8. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 8: FEV1 (l)
3.9. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 9: FVC (l)
3.10. Analysis.

Comparison 3: Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC, Outcome 10: FEV1/FVC
Compared to behavioral support only/no support, Walele 2018 found improvements in FVC favoring nicotine EC (Analysis 4.16), and no difference in FEV1 or PEF 25‐75 (Analysis 4.17; Analysis 4.19). Pooled data from Walele 2018 and Pulvers 2020 showed no difference in FEF 25‐75, with substantial levels of statistical heterogeneity (MD −0.06, 95% CI −0.18 to 0.06, I2 = 72%; 2 studies, 555 participants; Analysis 4.18).
4.16. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 16: FVC (litres)
4.17. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 17: FEV1 (litres)
4.19. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 19: PEF 25‐75 (litres/minute)
4.18. Analysis.

Comparison 4: Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 18: FEF 25‐75 (litres/second))
Veldheer 2019, which randomized participants to nicotine EC or the QuitSmart cigarette substitute, measured change in a number of lung function parameters: direction of effect was mixed across these, with no statistically or clinically significant between‐group differences at 12 weeks (Supplemental Table 7).
Two studies which provided all participants with nicotine EC measured change in lung function over time: Hickling 2019 found an increase in peak flow, and Oncken 2015 "no significant differences" in airway function (Supplemental Table 7).
Combination therapy: nicotine EC and NRT
This section covers two comparisons: studies in which all arms received NRT and participants were randomized to nicotine EC or non‐nicotine EC, and studies in which all participants received NRT and one arm was randomized to nicotine EC in addition. All studies contributing data are randomized controlled trials. No studies in this group reported data on heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen, or toxicants.
Cessation
Two trials (both at high risk of bias, both testing refillable devices) in which all participants received NRT compared nicotine EC to non‐nicotine EC; pooled results favored nicotine EC (RR 1.77, 95% CI 1.07 to 2.94; I2 = 0%; 1039 participants; Analysis 5.1). Walker 2020 also compared nicotine EC + NRT to NRT alone; the point estimate favored nicotine EC but the confidence interval was wide and included no difference (Analysis 6.1).
5.1. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
6.1. Analysis.

Comparison 6: Nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
Adverse events
The two trials (both at high risk of bias) in which nicotine ECs were compared to non‐nicotine ECs in participants receiving NRT found no evidence of a difference in the number of people experiencing AEs between arms; data from Walker 2020 can be seen in Analysis 5.2; Baldassarri 2018 reported results combined across groups but noted "no significant differences by treatment group" (Supplemental Table 1).
5.2. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 2: Adverse events
The two trials comparing nicotine EC + NRT to NRT alone that contributed data to this outcome were both at high risk of bias. Statistical heterogeneity was high when combining data (I2 = 79%) and hence we do not present pooled results. In one study (Walker 2020), AEs were lower in the EC group and the confidence interval excluded no difference, while in the other study (Guillaumier 2018) AEs were higher in the EC group but the confidence interval was wide (Analysis 6.2).
6.2. Analysis.

Comparison 6: Nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 2: Adverse events
Serious adverse events
Walker 2020, comparing nicotine EC with non‐nicotine EC as adjuncts to NRT, had fewer SAEs in the nicotine EC group than in the non‐nicotine EC group, but the confidence interval includes no difference (Analysis 5.3).
5.3. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Three studies provided data on SAEs and compared nicotine EC + NRT to NRT alone. The pooled estimate favored the NRT‐alone group, but again the confidence interval was wide and included no difference (RR 1.26, 95% CI 0.46 to 3.42: I2 = 0; 682 participants; Analysis 6.3).
6.3. Analysis.
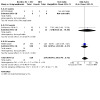
Comparison 6: Nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Carbon monoxide
Walker 2020 (which compared nicotine EC + NRT, non‐nicotine EC + NRT, and NRT alone) measured change in CO levels but did not report data in a way that could be pooled. CO declined over time, with the greatest reduction seen in the nicotine EC group (see Supplemental Table 3). Baldassarri 2018, comparing nicotine and non‐nicotine EC as adjuncts to NRT, found a slightly greater reduction in CO in the nicotine EC group, but the confidence interval included no clear evidence of a difference (Analysis 5.4) between groups.
5.4. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 4: Carbon monoxide (ppm)
Lung function
Baldassarri 2018, which compared nicotine EC to non‐nicotine EC and in which both groups received NRT, found no between‐group differences in FeNO, FEV1, or FVC (Analysis 5.5; Analysis 5.6; Analysis 5.7); confidence intervals were wide for all outcomes.
5.5. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 5: FeNO (ppb)
5.6. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 6: FEV1 (%)
5.7. Analysis.

Comparison 5: Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT, Outcome 7: FVC (%)
Comparisons based on nicotine dose
Two trials provided data comparing different doses of nicotine in EC (although other studies provided a range of doses, these were not randomly assigned). In Caponnetto 2013a, where different concentrations were available via the same device, cessation and adverse event data were not available. No serious adverse events were reported in either arm (Analysis 7.1). There were no clinical or statistically significant differences between arms for carbon monoxide, heart rate, blood pressure, or lung function measures (Analysis 7.2 to Analysis 7.8). In Yingst 2020 (cross‐over, comparing different doses and different devices) exhaled CO and reported nausea were not different between devices; self‐reported dizziness was low overall but slightly higher in the higher‐dose arm. Further detail can be found in Supplemental Table 1 and Supplemental Table 3.
7.1. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 1: Serious adverse events
7.2. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 2: Carbon monoxide (ppm)
7.8. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 8: FEV1/FVC
Non‐nicotine EC
Although non‐nicotine ECs serve as a 'control group' in our primary analysis, due to their behavioral properties they can also be considered an intervention in and of themselves. Comparisons included here are: non‐nicotine EC versus NRT; non‐nicotine EC versus usual care; and non‐nicotine EC as an adjunct to NRT. All contributing data are from randomized controlled trials. None of these studies reported data on change in CO, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, toxicants, or lung function.
Cessation
When comparing non‐nicotine EC to behavioral support only, pooled results from two studies (n = 388) found higher quit rates in participants randomized to non‐nicotine EC, but the confidence interval included the possibility of no difference (RR 1.74, 95% CI 0.76 to 3.96; I2 = 0%; Analysis 8.1). When evaluating non‐nicotine EC as an adjunct to NRT, Walker 2020 also found higher quit rates in participants randomized to non‐nicotine EC, although again the confidence interval included no difference (Analysis 9.1).
8.1. Analysis.

Comparison 8: Non‐nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
9.1. Analysis.

Comparison 9: Non‐nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
Lee 2019 compared non‐nicotine EC with NRT; the point estimate favored NRT but the confidence interval included no difference (Analysis 10.1).
10.1. Analysis.

Comparison 10: Non‐nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 1: Smoking cessation
Adverse events
Eisenberg 2020 found a higher rate of adverse events in the EC arm than in behavioral support only, with the confidence interval excluding no difference (Analysis 8.2). By contrast, Walker 2020 found fewer adverse events in participants receiving non‐nicotine EC + NRT compared to NRT alone, with the confidence interval excluding no difference (Analysis 9.2). Lee 2019 also found that fewer participants receiving non‐nicotine EC reported adverse events than those receiving NRT, with the confidence interval excluding no difference (Analysis 10.2).
8.2. Analysis.

Comparison 8: Non‐nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 2: Adverse events at 12 weeks
9.2. Analysis.

Comparison 9: Non‐nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 2: Adverse events
10.2. Analysis.

Comparison 10: Non‐nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 2: Adverse events
Serious adverse events
Eisenberg 2020 found a higher rate of SAEs in the EC arm than in the behavioral support‐only arm, but confidence intervals were wide and incorporated clinically significant benefit and clinically significant harm (Analysis 8.3). In Walker 2020, more SAEs occurred in the group randomized to non‐nicotine EC + NRT than in the NRT‐alone group, but the confidence interval included no difference as well as the potential for a clinically significant difference in favor of the intervention (Analysis 9.3). No SAEs were reported in either arm of Lee 2019 (non‐nicotine EC versus NRT).
8.3. Analysis.

Comparison 8: Non‐nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events at 24 weeks
9.3. Analysis.

Comparison 9: Non‐nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Discussion
Summary of main results
This update includes a further six studies compared with the previously published version. Our three main comparisons, nicotine EC compared to NRT, nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC, and nicotine EC compared to behavioral support only/no support still show increased quit rates in people assigned to nicotine EC arms; this is moderate‐certainty for the first two comparisons, and very low certainty for the latter (Table 1; Table 2; Table 3). In absolute terms, pooled data suggest an additional four people for every 100 would quit smoking with nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC or to NRT, and that an additional seven people per 100 would quit if offered a nicotine EC compared to being offered behavioral support alone or no support. Most data come from studies of cartridge devices which deliver relatively little nicotine in comparison to newer device models. However, within newer device models with better nicotine delivery, this update includes the first included study of a pod device (Pulvers 2020).
The certainty of the evidence for adverse events in nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC has been upgraded from low‐ to moderate‐certainty evidence of no difference. Evidence on adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs) was of low to very low certainty across all other comparisons, due to a paucity of data. SAEs were rare, in both intervention and comparator arms, with many of the studies which measured SAEs reporting no such events in either study arm. For nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC, pooled data suggest no difference in the number of people experiencing AEs and one fewer person per 100 experiencing SAEs with nicotine EC compared to non‐nicotine EC arms, but confidence intervals include no difference. Conversely, data from comparisons between nicotine EC and behavioral support alone or no support suggest an additional 13 people per 100 assigned to nicotine EC may experience AEs, with no difference in the number experiencing SAEs. As with AEs from other smoking cessation treatments (e.g. NRT, Hartmann‐Boyce 2018a), these events typically related to irritation at site (e.g. dry mouth, cough) and resolved over time. Compared to NRT, one fewer person per 100 might be expected to experience an AE if assigned to nicotine EC, and two additional people per 100 might be expected to experience an SAE. These figures should be treated with caution, due to large confidence intervals encompassing no clinically significant difference. The small amount of contributing data, and the variation in 'control group' risk across comparisons, reflect different methods of collecting data and different lengths of follow‐up. No studies in any of the different comparison conditions detected serious harms considered to be related to EC use.
Beyond AEs and SAEs, we consider data on a range of safety‐ and health‐related outcomes, including carbon monoxide and other toxins, lung function, blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen levels. Data on all of these outcome measures are limited; for most outcomes within most comparisons, only one study currently contributes data. Pooled data from two studies in which all participants received nicotine replacement therapy showed that nicotine EC led to higher quit rates than non‐nicotine EC, but we judged both studies to be at high risk of bias, meaning the effect remains uncertain.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
This field of research and EC devices themselves continue to evolve rapidly. This is the first update conducted as part of our 'living systematic review' approach, with which we will proceed for at least the next 12 months, meaning we can continue to rapidly incorporate new evidence (see Appendix 1). This is important, as all of our analyses currently suffer from imprecision.
This update captures data from the past year, up to February 2021. Subsequent monthly searches will keep this review current. Although studies predominantly came from the USA and UK, overall this review covers data from 14 countries; geographical range in studies may be particularly important in this area, due to the marked differences in EC regulation between countries; for example, studies conducted in countries that limit nicotine dose in EC or allow only certain EC devices to be tested may observe less pronounced effects on quitting. This review includes studies in some 'harder to reach' populations, including people not motivated to quit smoking, people with substance misuse disorders, and people experiencing homelessness. Quit rates in these groups are traditionally lower, which may make it more difficult to detect effects of interventions. However, it could be that these groups may particularly stand to benefit from EC if they are effective, because in absolute terms conventional cessation methods are often not as effective for them.
As well as the rapid pace of research in this field, EC technology itself continues to evolve, which poses a challenge when considering the applicability of our evidence to the present. We had downgraded the certainty of our data in the 2016 update, as the devices tested in the trials were first‐generation 'cig‐a‐like' devices which did not deliver nicotine well, meaning the studies may have yielded more conservative estimates than would be seen with newer models, as newer devices and models have tended towards improved nicotine delivery. Nicotine delivery is also relevant to the comparator NRT arms tested; use of both a shorter‐ and a longer‐acting form of NRT shows the highest success, and it is important that where possible this be the comparator chosen for such trials (Lindson 2019).
Regarding EC device type, in the 2020 update and now in this update, we have more data from newer devices, although there will always be a time lag between current devices and the research evidence available. None of the analyses of our primary outcomes signified substantial levels of statistical heterogeneity, despite the fact that different devices were used in the included studies. However, this could be because confidence intervals were wide for individual studies, and does not rule out clinically significant differences in effects between EC types. As further data emerge, we hope to be able to formally test for differences in subgroup analyses, and ideally over time in head‐to‐head comparisons of different device types. Our review now includes one study of a pod device (Pulvers 2020) and one study directly comparing device types (Yingst 2020). However, neither contributes data to our cessation outcomes.
The adverse effects described in both the RCT and cohort studies continue to look similar, regardless of the brand of EC used or nicotine content, with placebo and nicotine‐containing ECs showing similar numbers and types of adverse events in direct comparisons. They also reflect what is reported in survey data (Dawkins 2013b; Etter 2011), so we believe that they are broadly applicable to most EC brands.
There has been concern raised that the dual use of cigarettes and EC may expose people to greater health risks, including higher nicotine levels. However, given that people who smoke like to maintain relatively stable blood nicotine levels (Russell 1990), receiving nicotine from an alternative source (i.e. EC) is likely to reduce nicotine intake from cigarettes, which should be accompanied by a reduction in smoke and toxin intake (Fagerström 2004). In a study assessing biochemical changes exclusively in dual‐users, there was a significant decrease in exhaled carbon monoxide levels and urinary 3‐HMPA (McRobbie 2015). In this update, we found one new study conducted in dual‐users. Similar to McRobbie 2015, Czoli 2019 found that levels of biomarkers of exposure to toxicants were significantly lower when participants exclusively used EC compared to dual use; by contrast, biomarkers of exposure increased when participants exclusively smoked as compared to dual use. These results are supported by longer‐term studies in people who smoke and were provided with ECs, which found decreases in exhaled carbon monoxide among dual‐users (Adriaens 2014; Pacifici 2015; Polosa 2011; Polosa 2014b).
The structure of our analyses follows standard practice of the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group, i.e. evaluating outcomes on an intention‐to‐treat basis, meaning our pooled results represent the effect of offering an EC intervention. This is different from evaluating the per protocol effect, or the effect only in those who use the EC to quit smoking entirely, or continue to smoke whilst also using EC. Some of our included studies have also assessed data using these groupings and we have attempted to note this in the supplemental tables. Although pragmatic and hopefully of use to those designing and delivering interventions, we acknowledge that our intention‐to‐treat approach limits the ability to use the data presented here to draw conclusions about biomarkers in subgroups of participants based on subsequent EC use/smoking profiles.
Certainty of the evidence
We consider the certainty of the evidence below as it relates to primary outcomes for our three main comparisons: nicotine EC versus NRT; nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC; nicotine EC versus behavioral support only/no support (Table 1; Table 2; Table 3). The certainty of evidence for all other comparisons and outcomes should be considered very low due to a paucity of data.
Our 'Summary of findings' tables and assessments of certainty are based on the evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The cohort studies that we include were all deemed to have high risks of bias, which is inherent in the study design. Data presented from these studies need to be interpreted with caution. However, data from cohort studies were reassuringly consistent with data from RCTs.
Risk of bias did not impact on the certainty of evidence for comparisons between nicotine and non‐nicotine EC, or between nicotine EC and NRT. For the latter, we judged all three studies to be at low risk of bias overall. For the former, removing the one study at high risk of bias increased the effect estimate for our efficacy outcome. Risk of bias decreased our certainty in the effect estimates for our nicotine EC versus behavioral support only/no support comparison, as due to the nature of the comparison, blinding was not possible and differential levels of support could lead to bias. All but one of our main comparisons were downgraded for imprecision, due to wide confidence intervals and few events. Other than risk of bias and imprecision, we identified no other issues which decreased the certainty of the primary outcomes for our main comparisons. In the previous version of this review we had downgraded cessation outcomes for indirectness, due to the included studies testing devices that were no longer available due to poor nicotine delivery (we therefore judged it plausible that our analyses could be underestimating the effect of devices available at the time the review was published). In this version, we no longer downgrade on this basis, as this update includes a wider range of EC models, including more recent devices, and heterogeneity in outcomes remains low.
Cessation
All three comparisons found effect estimates favoring nicotine EC for smoking cessation. For nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC and for nicotine EC versus NRT, we judged the evidence to be of moderate certainty, meaning we think the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of effect. For nicotine EC versus behavioral support only/no support, we judged the evidence to be of very low certainty, meaning we have very little confidence in the effect estimate. Another way to look at this, however, is to consider that nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC comparisons isolate the effect of nicotine as provided by an EC, and nicotine EC versus NRT comparisons isolate the effect of the sensorimotor elements provided by an EC. Given that both of these comparisons find a benefit of nicotine EC for smoking cessation, it might logically follow that the comparison between nicotine EC and behavioral support only/no support would find a benefit in favor of nicotine EC, since this comparison would capture both pharmacological and sensorimotor mechanisms of effect. This increases our confidence in the effect of nicotine EC when compared to behavioral support alone or to no support.
Adverse and serious adverse events
In this update, we have upgraded the certainty of evidence for adverse events in the nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC comparison; the addition of new data has led to narrower confidence intervals, and as a result we have upgraded the evidence from low to moderate certainty of no difference. For our other comparisons and adverse effect outcomes, effect estimates of adverse events and serious adverse events were judged to be of low or very low certainty, with the main problem being imprecision. This means the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. None of the analyses signaled serious harm, nor did complementary data from cohort studies, but unlike our cessation analyses, many of the confidence intervals encompassed the possibility of both clinically significant harm and clinically significant benefit. This uncertainty should reduce as more studies become available.
Potential biases in the review process
We consider the review process we used to be robust. For outcome assessment, we followed the standard methods used for Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Review Group cessation reviews. Our search strategy included the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group Specialized Register and we were able to capture a number of ongoing studies. However, there may be unpublished data that our searches did not uncover. We also considered participants lost to follow‐up as continuing to smoke, which is standard practice in this field. There are concerns that frequently updating meta‐analyses can lead to issues with multiple testing; we followed Cochrane guidance in conducting this living systematic review and hence do not adjust for multiple testing (Brooker 2019).
Three of our review authors are authors of included studies. These authors were not involved in the decisions about inclusion of their studies, or in data extraction or 'Risk of bias' assessment for these studies.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
This Cochrane Review aligns with but updates the conclusions of the 2018 U.S. National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine‘s Consensus Study Report, Public Health Consequences of E‐cigarettes (NASEM 2018), which reviewed literature published through August 2017 to address the question, “Do e‐cigarettes help smokers quit smoking combustible tobacco cigarettes?”. Focusing on RCTs and existing systematic reviews, it used a prespecified Level of Evidence framework to develop conclusions. The report’s overall conclusion was that there was “limited evidence that e‐cigarettes may be effective aids to promote smoking cessation.” Based on the RCTs available, it concluded that there was “moderate evidence” that e‐cigarettes containing nicotine were more effective for cessation than e‐cigarettes without nicotine, but “insufficient evidence” about the effectiveness of e‐cigarettes compared to no treatment or to FDA‐approved smoking cessation treatments. Our review contradicts this latter point, as we now find moderate‐certainty evidence of benefit when comparing nicotine EC with NRT; this is primarily due to a large RCT published after NASEM 2018. A 2021 review from Public Health England, which cites the 2020 version of this Cochrane Review, concludes that, compared to their 2018 review, there is now stronger evidence that nicotine vaping products are effective for smoking cessation (McNeill 2021).
Findings are also broadly consistent with those from other reviews published in the past year, with some exceptions. Amato 2020 did not evaluate effectiveness and focused only on safety; consistent with our review, they found very low‐ to moderate‐certainty evidence on a range of possible adverse effects, with the most frequently reported being cough, dry mouth, shortness of breath, irritation of the mouth and throat, and headache. Akiyama 2021 reviewed biomarker findings from clinical studies and concluded that the use of EC could lead to a significant reduction in exposure to harmful substances compared to traditional cigarettes; this is again consistent with findings from our review. Martinez‐Morata 2021 reviewed blood pressure findings and concluded that EC may result in short‐term elevations, but that more data are needed; our review also lacks sufficient data to draw any conclusions about blood pressure at one week or longer.
Zhang 2021 conducted a rapid review; while their pooled analysis also suggested that EC increased quit rates compared to NRT or non‐nicotine EC, they judged the evidence to be of low certainty according to GRADE. As with us, they downgraded by one level due to inconsistency, but unlike us they also downgraded by one level for statistical heterogeneity. Zhang 2021 combined studies with NRT comparators and those with non‐nicotine EC comparators in the same analysis and found moderate statistical heterogeneity; we evaluated these two comparisons separately and did not find evidence of statistical heterogeneity. Patnode 2021 reviewed evidence on tobacco cessation interventions for the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPFTS 2021). They state that none of their included EC trials suggested higher rates of serious adverse events; this is in line with our analyses. However, they report that findings across EC trials were inconsistent for effectiveness, with some finding statistically significant evidence of benefit and some finding no statistically significant difference. They did not conduct statistical meta‐analyses and include five trials, all of which are included in our cessation meta‐analyses. None of our cessation meta‐analyses, which include these trials, detected levels of heterogeneity beyond what would be expected from chance alone. Wang 2021 reviewed data both from observational studies and from randomized controlled trials; in the trials, e‐cigarettes were associated with increased smoking cessation (as with our review). In observational studies, ECs were not associated with increased smoking cessation. As discussed in Methods, although we included non‐randomized studies in which an EC intervention is provided in this review, we do not include observational studies in which no EC intervention is provided, due to known issues with confounding.
Reviews of ECs for policymaking are often broader in scope than our review, which focuses exclusively on their role in supporting smoking cessation in people who smoke. Outside of smoking cessation, there remain unanswered questions about the impact of EC availability and use on young people; we hope to evaluate this in a separate review.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Evidence suggesting nicotine EC can aid in smoking cessation is consistent across several comparisons. There was moderate‐certainty evidence, limited by imprecision, that EC with nicotine increased quit rates at six months or longer compared to non‐nicotine EC and compared to NRT. There was very low‐certainty evidence (limited by risk of bias as well as imprecision) that EC with nicotine increased quit rates compared to behavioral support alone or to no support.
The effect of nicotine EC when added to NRT was unclear.
None of the included studies (short‐ to mid‐term, up to two years) detected serious adverse events considered possibly related to EC use. The most commonly‐reported adverse effects were throat/mouth irritation, headache, cough, and nausea, which tended to dissipate with continued use. In some studies, reduced toxin concentrations and biomarkers of harm were observed in people who smoked and switched to vaping, consistent with reductions seen in smoking cessation.
Implications for research.
Further randomized controlled trials of nicotine EC are needed, following up participants at six months or longer. Studies with active comparators (i.e. comparing nicotine EC to frontline smoking cessation pharmacotherapies) are likely to be of particular use to decision‐makers. All studies (including uncontrolled intervention cohort studies) should aim to assess the safety profile of electronic cigarettes for as long as possible (the current review only includes data up to two years), and ideally be powered to detect differences in safety outcomes, including adverse events and serious adverse events. Evidence from one well‐conducted RCT suggests that people who quit smoking using EC may continue to use EC longer than they might use other stop‐smoking pharmacotherapies, making assessments of their long‐term safety profile particularly important. Safety results should be presented in both absolute and relative risk terms (in comparison to the risks of continuing to smoke tobacco).
Studies should offer recent devices to participants, to be most representative of what will be on the market at the time results are released. Data on pod‐type EC are particularly lacking, though we now include one trial. Protocols and statistical analysis plans should be registered in advance and openly available.
Further RCTs need to be adequately powered. Further trials of pod devices would be of particular value, as would RCTs providing EC in a way that would be used in real‐world settings (e.g. taking into account individual preferences for strengths and flavors of e‐liquids and even EC devices, and also allowing for changes in preferences over time).
Further reviews, using best available methods, need to be conducted to evaluate the possible relationships between EC use and availability and youth uptake of EC and conventional cigarettes.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 5 August 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 2nd August 2021. In addition to the studies identified from March to July 2021, we found two new ongoing studies and one report linked to a study already in the review. We will incorporate these into the review as part of a future update. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 11, 2012 Review first published: Issue 12, 2014
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 7 July 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 1st July 2021. In addition to the studies identified from March to June 2021, we found two new included studies and two reports linked to studies already in the review. DOIs for the two new included studies are as follows: Myers‐Smith 2021: https://doi.org/10.1111/add.15628 & Kimber 2021: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106909. We will incorporate these into the review as part of a future update. |
| 9 June 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 1st June 2021. In addition to the studies identified from March to May 2021, we found one report linked to a study already in the review, one ongoing study, and one potentially new study that we are looking into further. We will incorporate these into the review as part of a future update. As part of this new update we will also include a new outcome ‐ proportion of people still using e‐cigarettes or other pharmacotherapy at longest follow‐up. |
| 12 May 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 4th May 2021. In addition to the studies identified from March and April 2021, we found four new ongoing studies. We will incorporate these into the review as part of a future update. |
| 15 April 2021 | New search has been performed | Updated with six new included studies and new data from one previously included study. Most recent search 1 Feb 2021. |
| 15 April 2021 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | 6 new included studies added (Czoli 2019; Ikonomidis 2020; Ozga‐Hess 2019; Pulvers 2020; Scheibein 2020; Yingst 2020), certainty in finding of no difference in adverse events between nicotine EC and non‐nicotine EC updated to moderate (from low). First study of pod EC device included. |
| 1 April 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 1st April 2021. In addition to the studies identified from March 2021 we found two new ongoing studies and one paper linked to a study already included in the review. We will incorporate these into the review as part of a future update. |
| 17 March 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 1st March 2021. Studies identified in March are not included in this version of the review, but will be incorporated into a subsequent version. We found four new included studies, five new ongoing studies and five papers linked to studies already included in the review. The four new included studies were all conference abstracts; three of which were identified from the SRNT 2021 abstract book (SYM2A, SYM2B, PH‐353; www.srnt.org/page/2021_Meeting). The fourth is available here: dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.07.1091. |
| 4 February 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. We run and screen searches monthly. Last search date 1st February 2021. In addition to the studies identified from our December 2020 and January 2021 searches we found one paper linked to a study already included in the review (Lucchiari 2020), and have preliminary results from a study listed as ongoing (Begh 2019). We will incorporate this paper and data into the review as part of a future update. |
| 20 January 2021 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. Searches are run and screened monthly. Last search date 4th January 2021. In addition to the studies identified from our December 2020 searches we found four new completed studies, one new ongoing study and one paper linked to a study already included in the review. These studies and papers will be incorporated into the review at the next update. DOIs for the four new included studies are as follows: Ozga‐Hess et al. 2019: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106105; Pulvers et al. 2020: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.26324; Scheibein 2020: 10.1186/s12954-020-00406-y; Yingst et al. 2020: 10.1080/09540121.2019.1687835 |
| 15 December 2020 | Amended | This is a Living Systematic Review. Searches are run and screened monthly. Last search date 1st December 2020. Searches found 3 new completed studies, 11 new ongoing studies and 9 papers linked to studies already included in the review. These studies and papers will be incorporated into the review at the next update. DOIs for the three new included studies are as follows: Czoli et al:10.1093/ntr/nty174; Bonevski et al: 10.1093/ntr/ntaa143; Eisenberg et al: 10.1001/jama.2020.18889. |
| 20 July 2020 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Strength of evidence increased for existing comparisons; new comparisons added |
| 20 July 2020 | New search has been performed | New searches run January 2020. 35 new studies added. Living systematic review protocol incorporated |
| 14 December 2016 | Amended | Clarification on outcome data from Adriaens ‐ no changes to conclusions |
| 23 June 2016 | New search has been performed | Update search run January 2016, 11 new included studies added. Reduction removed as outcome, now covered in Harm Reduction review. |
| 23 June 2016 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | 11 new included studies added; no changes to conclusions. |
Acknowledgements
The 2020 update was supported by the Cochrane Incentives Award Scheme and the University of Oxford Returning Carer's Fund, as well as through core infrastructure funding from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) for the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Review Group. This update and the 2020 update have also been supported through a Tobacco Advisory Group Cancer Research UK Project Grant. The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Systematic Reviews Programme, NIHR, National Health Service (NHS) or the Department of Health.
We thank Dr Jonathan Livingstone‐Banks for running monthly searches.
We would like to thank Assistant Professor Stephen R. Baldassarri, Drs Pasquale Caponnetto, Fabio Cibella and Professor Riccardo Polosa, Professor Matthew Carpenter, Bruce R. Lindgren and Professor Dorothy Hatsukami, Assistant Professor Tracy Smith, Assistant Professor Susan Veldheer, Lauren Hickling, Stephanie K. Bell, Associate Professor Coral Gartner, Professor Billie Bonevski, Karolien Adriaens, Dr Sharon Cox, Professor Lynne E. Dawkins, Professor Mark Eisenberg, Andrea Hebert‐Losier, Kris Filion, Dr Ignatios Ikonomidis, Dr Kim Pulvers, Florian Scheibein, Dr Markos Klonizakis, Dr Scott Sherman, Dr Kylie Morphett, Dr Ivan Berlin, Marzena Orzol, Dr Katie Myers Smith and Christine Czoli for providing additional data or information. We would like to thank Dr Sharon Cox and Professor Lynne E. Dawkins for performing peer review for this update, and Dr Debbie Robson for performing editorial review for this update.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Protocol for living systematic review
Justification for ‘Living Review’ status
Living systematic reviews (LSRs) offer a new approach to updating reviews, in which the review is continually updated by incorporating relevant new evidence as it becomes available (Brooker 2019). Previous versions of this Cochrane Review of electronic cigarettes (ECs) for smoking cessation have informed policy worldwide (Hartmann‐Boyce 2016; McRobbie 2014). This update has found high degrees of uncertainty (low‐ and very low‐certainty evidence) for most outcomes, due to the small number of included randomized controlled trials, and the resulting imprecision in effect estimates. This means that some conclusions are likely to change substantially as new evidence emerges.
On average, Cochrane Reviews are updated every three to four years. For EC, where the evidence base is rapidly evolving, this schedule impedes the ability of the review to provide the most up‐to‐date evidence to decision‐makers. As EC use, availability, and design changes, policymakers are frequently drawing on this review to inform decisions, so it is imperative that it is up‐to‐date to ensure decisions are being made on the basis of the entirety of the evidence. Regular updates have the potential to strengthen the existing conclusions of the review or to change conclusions where conflicting evidence or evidence on new outcomes emerges (e.g. comparisons between EC and other interventions; longer‐term safety data).
Objective of the change to ‘Living Review’ status
To implement approved Cochrane LSR methods to provide an up‐to‐date, accessible, engaging and unbiased review of the evidence on the effect and safety of using EC to quit smoking.
LSR methodological considerations
The methods outlined below are specific to maintaining this review of Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation as an LSR on the Cochrane Library. These methods will be ‘active’ immediately upon publication of this update. Core review methods, such as the criteria for considering studies in the review and assessment of risks of bias, are unchanged and are detailed in the main body of the review. Below we outline the methods for which specific considerations apply as a result of the change to ‘living’ status.
Search methods for identification of studies
We will conduct database searches monthly, beginning December 2020. These searches will be of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, and clinical trial registries, as detailed in the main body of the review. The funders of this LSR – Cancer Research UK (CRUK) ‐ already run monthly searches of the EC evidence and so we will work alongside their health information officer to ensure that we are identifying all the relevant literature with our searches. We will review our search strategies on an ongoing basis every 12 months, as indexing terms and keywords may change, and new search filters may be published. Such changes will be managed by input from experienced information specialists.
Selection of studies
We will immediately screen any new citations retrieved by the monthly searches using Covidence, undertaking dual screening of title and abstract, and then full text, by independent review authors. Where we find multiple citations of the same study we will group them into one study record with a single study ID. One review author (AB) will contact corresponding authors of potentially relevant ongoing studies as they are identified and ask them to advise when results are available, or to share early or unpublished data. Based on the information and projected timescales shared, we will contact corresponding authors on an ongoing basis to retrieve new evidence as it becomes available.
Data synthesis
Whenever we identify new studies relevant to the review, we will extract the relevant data and assess risks of bias as detailed in the main body of the review. We will highlight availability of this new evidence on both the Cochrane Library and on our own dedicated website. We will incorporate the new data into meta‐analyses and tables in the Revman (Review Manager 2020) and supplementary data files, and carry out GRADE assessments (GRADEpro GDT). We will conduct a full update of the review (full incorporation and interpretation of all new data within the review and re‐publishing) when the accumulating evidence leads to changes in any one of:
The direction of effect or clinical significance of the findings for one or more outcomes;
The certainty (e.g. GRADE rating) of one or more outcomes;
The availability of studies investigating new settings, populations, interventions, comparisons or outcomes.
Formal sequential meta‐analysis approaches will not be used for updated meta‐analyses, in line with Cochrane guidance for LSRs.
Future updates of review methods
The LSR approach acknowledges that reviews may cease to need to be ‘living’ over time, as the review findings become stable, or the question is no longer a priority for decision‐makers (Brooker 2019). Eighteen months into this review’s ‘living’ status (March 2022) we will evaluate the LSR approach, including the likely benefits of and challenges to continuing this methodology for this evidence base, and whether such an approach remains warranted. If the evidence is high certainty for all outcomes and all comparisons at that point, meaning further studies are judged very unlikely to impact the effect estimate, we would consider ceasing living mode for this review. If, as is more likely, some or all outcomes are not yet certain, we will facilitate discussions within the author team and Cochrane, as well as engaging with a wider PPI panel and key decision‐makers, e.g. policymakers, in order to determine next steps. If the decision is made to continue in living mode, we will review, and if necessary revise, the living review methods described in this Appendix before continuing.
Appendix 2. Toxins/carcinogen names and abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Name |
| ‐ | 1‐Hydroxyfluorene |
| ‐ | 1‐Hydroxyphenanthrene |
| ‐ | 1‐Hydroxypyrene |
| 2‐HPMA | 2‐hydroxypropylmercapturic acid |
| ‐ | 2‐Hydroxyfluorene |
| ‐ | 2‐Hydroxyphenanthrene |
| ‐ | 2‐Naphthol |
| ‐ | 3‐, 4‐Hydroxyphenanthrenes |
| 3‐HPMA | 3‐hydroxypropylmercapturic acid |
| ‐ | 3‐Hydroxyfluorene |
| AAMA | N‐acetyl‐S‐(carbamoylethyl)‐L‐cysteine (synonym: 2‐carbamoylethylmercapturic acid) |
| CEMA/CNEMA | 2‐cyanoethylmercapturic acid; referred to as 'acrylonitrile' in Pulvers 2018 |
| ‐ | Formic acid |
| HEMA | 2‐hydroxyethylmercapturic acid |
| HMPMA/HPMMA | 3‐hydroxy‐1‐methyl propylmercapturic acid |
| MHBMA | 2‐hydroxy‐3‐buten‐1‐ylmercapturic acid |
| MMA | N‐nitrosodimethyamine |
| NNAL | 4‐(methylnitrosamino)‐1‐(3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanol |
| PheT | Phenanthrene tetraol |
| PMA | phenylmercapturic acid; referred to as 'benzene' in Pulvers 2018 |
| S‐PMA | S‐phenylmercapturic acid |
Appendix 3. MEDLINE search strategy ‐ 2020 update
1. exp case control studies/ or exp cohort studies/ or Case control.tw. or (cohort adj (study or studies)).tw. or Cohort analy$.tw. or (Follow up adj (study or studies)).tw. or (observational adj (study or studies)).tw. or Longitudinal.tw.
2. (e‐cig$ or ecig$ or electr$ cigar$ or electronic nicotine).mp. or (vape or vapes or vaporizer or vapourizer or vaporiser or vapouriser or vaper or vapers or vaping).ti,ab. or exp Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems/
3. (randomized controlled trial or controlled clinical trial).pt. or randomized.ab. or placebo.ab. or clinical trials as topic.sh. or randomly.ab. or trial.ti.
4. exp animals/ not humans.sh.
5. 3 not 4
6. 2 and 5
7. 1 and 2
8. 6 or 7
9. smoking cessation.mp. or exp Smoking Cessation/
10. tobacco cessation.mp. or "Tobacco‐Use‐Cessation"/
11. (nicotine dependence or tobacco dependence).mp.
12. exp Smoking/th
13. "Tobacco‐Use‐Disorder"/
14. Smoking reduction/ or Smoking reduction.mp.
15. exp Pipe smoking/ or exp Tobacco smoking/ or exp Tobacco Products/
16. ((quit$ or stop$ or ceas$ or giv$ or abstain* or abstinen*) adj5 (smoking or smoke* or tobacco)).ti,ab.
17. exp Tobacco/ or exp Nicotine/
18. 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17
19. 8 and 18
Appendix 4. MEDLINE search strategy ‐ pre‐2020
e‐cig$.mp. [mp=title, abstract, original title, name of substance word, subject heading word, protocol supplementary concept, rare disease supplementary concept, unique identifier]
electr$ cigar$.mp.
electronic nicotine.mp.
(vape or vaper or vapers or vaping).ti,ab.
1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4
Identical terms used for other databases.
Line 4 added to search strategy for 2016 update.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Nicotine EC versus NRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 Smoking cessation | 3 | 1498 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.69 [1.25, 2.27] |
| 1.2 Adverse events | 2 | 485 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.80, 1.19] |
| 1.2.1 4 weeks | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.31, 1.73] |
| 1.2.2 6 months | 1 | 456 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.81, 1.22] |
| 1.3 Serious adverse events | 2 | 727 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.37 [0.77, 2.41] |
| 1.3.1 4 weeks | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 1.3.2 1 year | 1 | 698 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.37 [0.77, 2.41] |
| 1.4 Carbon monoxide (ppm) | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Subtotals only | |
| 1.4.1 8 weeks | 2 | 136 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.66 [‐1.94, 0.62] |
| 1.5 Heart rate (bpm) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.5.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.6 Systolic blood pressure | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.6.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.7 Blood oxygen saturation | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.7.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.8 3‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.8.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.9 NNAL (pmol/mg creatinine)) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.9.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.10 2‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.10.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.11 HMPMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.11.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.12 PheT (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.12.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.13 CEMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.13.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.14 AAMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.14.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.15 FEV1 (ml) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.15.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.16 FEV1/FVC (%) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 1.16.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 2. Nicotine EC versus varenicline.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.1 Smoking cessation | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 2.2 Serious adverse events | 1 | 54 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 2.2.1 12 weeks | 1 | 54 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
Comparison 3. Nicotine EC versus non‐nicotine EC.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 Smoking cessation | 4 | 1057 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.70 [1.03, 2.81] |
| 3.2 Adverse events | 3 | 601 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.91, 1.11] |
| 3.2.1 1 week | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.50 [0.27, 8.19] |
| 3.2.2 6 months | 1 | 298 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.71, 1.34] |
| 3.2.3 12 weeks | 1 | 255 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.01 [0.94, 1.08] |
| 3.3 Serious adverse events | 4 | 494 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.60 [0.15, 2.44] |
| 3.3.1 1 week | 1 | 48 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 3.3.2 4 weeks | 1 | 74 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 3.3.3 24 weeks | 1 | 255 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.60 [0.15, 2.44] |
| 3.3.4 1 year | 1 | 117 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 3.4 Carbon monoxide (ppm) | 2 | 171 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐2.44 [‐3.91, ‐0.97] |
| 3.4.1 2 weeks | 1 | 25 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.40 [‐3.00, 2.20] |
| 3.4.2 12 weeks | 1 | 146 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐3.40 [‐5.18, ‐1.62] |
| 3.5 Heart rate | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.5.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.6 Systolic blood pressure | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.6.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.7 FeNO (ppb) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.7.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.8 FEV1 (l) | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.8.1 12 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.9 FVC (l) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.9.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.10 FEV1/FVC | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 3.10.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 4. Nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.1 Smoking cessation | 5 | 2561 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.70 [1.39, 5.26] |
| 4.2 Adverse events | 4 | 765 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.22 [1.12, 1.32] |
| 4.2.1 12 weeks | 2 | 657 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.20 [1.11, 1.30] |
| 4.2.2 16 weeks | 1 | 50 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.18 [0.67, 2.07] |
| 4.2.3 6 months | 1 | 58 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 11.00 [0.64, 190.26] |
| 4.3 Serious adverse events | 6 | 1011 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.33, 4.09] |
| 4.3.1 4 to 6 weeks | 2 | 246 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 4.3.2 12 weeks | 1 | 408 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.69 [0.21, 66.17] |
| 4.3.3 16 weeks | 1 | 50 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 4.3.4 6 months | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.71 [0.16, 3.10] |
| 4.4 Carbon monoxide (ppm) | 8 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.4.1 3 to 4 weeks | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.4.2 6 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.4.3 8 weeks | 2 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.4.4 4 months | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.4.5 6 months | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.5 Heart rate (bpm) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.5.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.6 Systolic blood pressure | 3 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.6.1 6 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.6.2 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.6.3 4 months | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.7 Blood oxygen saturation | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.7.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.8 3‐HPMA (SMD) | 2 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.8.1 8 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.8.2 12 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.9 NNAL (SMD) | 4 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.9.1 3 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.9.2 8 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.9.3 12 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.9.4 6 weeks | 1 | Std. Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.10 2‐HPMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.10.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.11 HMPMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.11.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.12 PheT (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.12.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.13 CEMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.13.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.14 AAMA (pmol/mg creatinine) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.14.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.15 S‐PMA (nanograms) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.15.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.16 FVC (litres) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.16.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.17 FEV1 (litres) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.17.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.18 FEF 25‐75 (litres/second)) | 2 | 555 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.06 [‐0.18, 0.06] |
| 4.18.1 6 weeks | 1 | 168 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.14 [‐0.28, 0.00] |
| 4.18.2 12 weeks | 1 | 387 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [‐0.10, 0.30] |
| 4.19 PEF 25‐75 (litres/minute) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 4.19.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 5. Nicotine EC + NRT versus non‐nicotine EC + NRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1 Smoking cessation | 2 | 1039 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.77 [1.07, 2.94] |
| 5.2 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.2.1 12 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.3 Serious adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.3.1 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.4 Carbon monoxide (ppm) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.4.1 8 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5.5 FeNO (ppb) | 1 | 30 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐7.23, 6.51] |
| 5.5.1 6 months | 1 | 30 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.36 [‐7.23, 6.51] |
| 5.6 FEV1 (%) | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [‐0.01, 0.10] |
| 5.6.1 6 months | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [‐0.01, 0.10] |
| 5.7 FVC (%) | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.03, 0.09] |
| 5.7.1 6 months | 1 | 32 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.03 [‐0.03, 0.09] |
Comparison 6. Nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.1 Smoking cessation | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.2 Adverse events | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.2.1 12 weeks | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 6.3 Serious adverse events | 3 | 682 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.26 [0.46, 3.42] |
| 6.3.1 5 weeks | 1 | 7 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 6.3.2 12 weeks | 1 | 50 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.00 [0.13, 70.30] |
| 6.3.3 6 months | 1 | 625 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.12 [0.39, 3.27] |
Comparison 7. Higher versus lower nicotine content.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.1 Serious adverse events | 1 | 72 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 7.1.1 1 year | 1 | 72 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 7.2 Carbon monoxide (ppm) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.2.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.3 Heart rate | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.3.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.4 Systolic blood pressure | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.4.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.5 FeNO (ppb) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.5.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.6 FEV1 (l) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.6.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.7 FVC (l) | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.7.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.8 FEV1/FVC | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 7.8.1 12 weeks | 1 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
7.3. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 3: Heart rate
7.4. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 4: Systolic blood pressure
7.5. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 5: FeNO (ppb)
7.6. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 6: FEV1 (l)
7.7. Analysis.

Comparison 7: Higher versus lower nicotine content, Outcome 7: FVC (l)
Comparison 8. Non‐nicotine EC versus behavioural support only/no support.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.1 Smoking cessation | 2 | 388 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.74 [0.76, 3.96] |
| 8.2 Adverse events at 12 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 8.3 Serious adverse events at 24 weeks | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 9. Non‐nicotine EC + NRT versus NRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.1 Smoking cessation | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.2 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.3 Serious adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 9.3.1 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected |
Comparison 10. Non‐nicotine EC versus NRT.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.1 Smoking cessation | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.2 Adverse events | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.2.1 6 months | 1 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 10.3 Serious adverse events | 1 | 132 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 10.3.1 6 months | 1 | 132 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
10.3. Analysis.

Comparison 10: Non‐nicotine EC versus NRT, Outcome 3: Serious adverse events
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Adriaens 2014.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: 3‐armed RCT; with all participants then assigned to nicotine EC (treated as cohort in this review) Recruitment: Advertisement on university website, flyers on university campuses, emails to personnel and advertisement in local newspaper Setting: Community and laboratory, Belgium Study start date/end date: Not stated |
|
| Participants | Total N: 48 provided data Randomized to: EC1 16; EC2 17; control 17 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
56% women, mean age 44, mean cpd 19, mean FTCD 5.79, all unwilling to quit with no baseline EC use |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Intervention: 2 intervention groups (EC1 and EC2) provided with EC and instructed to use EC or smoke ad libitum (EC1 group provided with Joyetech eGO‐C, EC2 group provided with Kanger T2‐CC) and provided guidance on EC use. For both types, provided 30 mL bottles of tobacco‐flavored e‐liquid (Dekang “Turkish Blend”), containing 18 mg/mL of nicotine. 4 bottles at baseline replenished at 4 weeks, keep any remaining after 8 weeks Control: 6 bottles for 2 months at week 8 (half offered EC1, half offered EC2); no guidance on use |
|
| Outcomes | 3 lab sessions over 2 months (weeks 1, 4 and 8), plus online questionnaires, further follow‐up at 3 and 6 m after last lab session Cessation: measured but definition not provided, validated with eCO 5 ppm or less Adverse events and biomarkers: eCO, salivary cotinine measured during lab sessions. Also collected craving and withdrawal symptoms via lab sessions, “benefits and complaints”, mood, EC usage |
|
| Study funding | "No external funding for this study was obtained. Electronic cigarettes and e‐liquids were purchased at E‐cig4U (`t Rond 10, 4285 DE Woudrichem, The Netherlands; http://www.e‐cig4u.nl/) with balances of previous research funds obtained by Frank Baeyens." | |
| Author declarations | The authors declare no conflict of interest | |
| Notes | Randomization was for short‐term outcomes only Additional data provided from authors |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Block randomization was performed by using a randomization tool available on the website www.randomizer.org |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Unblinded but as this review only includes data on objective measurements and not cessation judged unlikely to affect outcomes |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Unblinded but as this review only includes data on objective measurements and not cessation judged unlikely to affect outcomes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 36 out of 48 completed follow‐up (11/16 in EC1 group, 12/17 in EC2 group, 13/17 in control group) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Outcome reporting somewhat non‐traditional; for example, collecting complaints but not explicitly adverse events, and incidence of AEs not reported. Unable to find prospectively‐registered protocol |
Baldassarri 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized parallel‐assignment double‐blind trial Recruitment: outpatient pulmonary and primary care clinics, Tobacco Treatment Service, referrals from medical providers Setting: Hospital outpatient and primary care clinics, USA Study start date: October 2014; Study end date: June 2014 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 40 N per arm: Non‐Nicotine: 20; Nicotine EC: 20 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Women: 52.5%; Mean age: 53 Mean cpd: 17 Mean FTND: 5.9; motivated to quit E cigarette use at baseline: Not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Both groups received standard care (8 weeks nicotine patch and counseling) and were randomized to nicotine EC or non‐nicotine EC. EC: eGO style EC (650 mAh battery, EVOD clearomizer, 3.7 V, 1.8 Ω single bottom coil), provided with e‐liquid purchased from an online vape shop (0 mg/ml or 24 mg/ml nicotine strength, 70/30 propylene glycol/vegetable glycerin, tobacco flavor); Instructed to use it as needed as a substitute for tobacco to try to satisfy cravings to smoke. If the patch alone proved adequate to prevent withdrawal and smoking cravings, the participant was advised not to use the EC. Additional EC devices, replacement coils, and liquid were provided as needed for the first 8 weeks of the study |
|
| Outcomes | Questionnaires and CO measurements taken at baseline, treatment visits at week 2, 4, 6, 8 and follow‐up at week 24 Cessation: 7‐day point prevalence abstinence, eCO ≤ 6 ppm Adverse events and biomarkers: Side effects were measured although it is unclear whether a questionnaire with prespecified symptoms was used Spirometry and FeNO at baseline and 6‐month follow‐up Other outcomes: Change in reported number of cpd at weeks 8 and 24; Change in per cent predicted FEV1 and FVC from baseline to week 24, and EC use patterns |
|
| Study funding | "Funding for this study was provided by the Yale School of Medicine, Section of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant T32HL007778. NHLBI had no role in the study design, collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data, writing the manuscript, or the decision to submit the paper for publication." | |
| Author declarations | "Dr. Toll received a grant from Pfizer for medicine only for a research study, and he receives funding as an expert witness in litigation filed against the tobacco industry. Dr. Chupp received grants from NIH, Genetech, Glaxo Smith Kline, Astra Zeneca/Medimmune and Boston Scientific. He received consulting/speaking fees from Genetech, Astra Zeneca/Medimmune, Mannkind, and Boston Scientific. There are no other conflicts of interest for the remaining authors." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Study listed as ongoing study NCT02498145 in 2016 review update Additional data provided from authors |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Participants were randomized using a random number generator with 1:1 blocked randomization (block size n= 8).” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Both groups received standard care (nicotine patch and counseling) and were randomized to: nicotine EC or non‐nicotine EC (no further detail given) |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “Treatment assignment was blinded to both the investigators and participants” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | CO biochemically validated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: “The study had a modest loss to follow‐up (20%) at week 24.” Number lost to follow‐up in each group is not reported in the paper Week 24 retention rate: Nicotine EC group: 19/20 (95%); Non‐nicotine EC group: 13/20 (65%); > 20% difference between groups |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Outcomes reported align with those listed in the clinicaltrials.gov record. (registered 2015; prior to study completion in 2016) |
Bell 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Pragmatic, uncontrolled, mixed‐methods trial Recruitment: Targeted settings for people with HIV Setting: Community, Brisbane, Australia Study start date: 21 February 2017; Study end date: 26 October 2017 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 30 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: People living with HIV 29 participants identified as male, and 1 participant did not identify as male or female; Mean age: 42; Mean cpd: 18 EC use at baseline: 46.7% (n = 14) Never tried; 50% (n = 15) Tried, never used for an extended period; 3.3% (n = 1) Used on a regularly (weekly) basis Willing to attempt to quit |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Single‐arm study. Print materials to help quit smoking. Provided booklet with instructions on how to use, store and handle EC; copies of device user manuals. Given Innokin Endura T18® vaporiser kit, Innokin Endura T22® vaporiser kit, 4 spare coils, 1 wall charger, 10 x 10‐mL bottles of Nicophar® 12 mg nicotine e‐liquid. Supplies to last 12 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks 1, 4, 8, 12, 24; Self‐report and semistructured interviews Cessation: 7 days point prevalence at weeks 4, 8, 12 and 24. Continuous abstinence at weeks 12 and 24. No biochemical validation Adverse events Other outcomes: Acceptability and use of trial products; Number of quit attempts |
|
| Study funding | "This work was supported by the HIV Foundation Queensland. The funder will play no role in the analysis and interpretation of results. All trial products were purchased and the suppliers have no involvement in the conduct of the trial or the interpretation or reporting of the results." | |
| Author declarations | "No other authors declare conflicts of interest. Mark Boyd has received research grant funding (paid to the institution) from AbbVie, Gilead and Merck and received honoraria for participation in HIV Advisory Boards and for the preparation and delivery of educational materials from AbbVie, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen‐Cilag, Merck and ViiV Healthcare." | |
| Notes | Additional data provided from authors. New for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled study |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled study |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “At Week 24, 26 of the 30 participants who enrolled in the study were followed up.” (confirmed by authors) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Study not published at time of data extraction, but study protocol published |
Bullen 2013.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: 3 parallel groups RCT Recruitment: People who smoke recruited from the community, via newspaper advertisements Setting: Research Unit, New Zealand Study start date: 6 September 2011; Study end date: 5 July 2013 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 657. 289 nicotine EC (NEC), 295 patch, 73 non‐nicotine EC (PEC) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
62% women, mean age 42, ⅓ NZ Maori, smoking 18 cpd, mean FTND score 5.5 Motivated to quit E cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Randomized to NEC, PATCH or PEC use for 13 weeks (from 1 week prior to TQD)
All participants referred to Quitline and received an invitation to access phone‐ or text‐based support. This was accessed by < 10% |
|
| Outcomes | Sustained (≤ 5 cigarettes allowed) validated (exhaled breath CO < 10 ppm) abstinence at 6 months ≥ 50% self‐reported reduction in baseline cigarettes at 6 months Participants reporting any adverse events Proportion of AEs that were serious Proportion of unrelated AEs |
|
| Study funding | Health Research Council of New Zealand | |
| Author declarations | "We declare that we have received no support from any companies for the submitted work and have no non‐financial interests that might be relevant to the submitted work. ML, via his company Health New Zealand, previously did research funded by Ruyan (an e‐cigarette manufacturer). CB and HM have done research on Ruyan e‐cigarettes funded by Health New Zealand, independently of Ruyan. HM has received honoraria for speaking at research symposia, has received benefits in kind and travel support from, and has provided consultancy to, the manufacturers of smoking cessation drugs. NW has provided consultancy to the manufacturers of smoking cessation drugs, received honoraria for speaking at a research meeting and received benefits in kind and travel support from a manufacturer of smoking cessation drugs. JW has provided consultancy to the manufacturers of smoking cessation medications." | |
| Notes | Accessed support: NEC: 115/289; PATCH: 106/295; PEC: 26/73 | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computerized block randomization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Computerized via study statistician |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | NEC and PEC were blind to treatment condition in relation to one another. No blinding for NEC/PEC vs PATCH conditions, but as NEC and PATCH were both active treatments performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation used |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | LTFU 22% (all considered to be smoking). Patch group had a higher LTFU and withdrawal than EC (loss to follow‐up 17% NEC, 27% patches, 22% PEC). However, minimal difference in per‐protocol and ITT analyses |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All prespecified outcomes reported |
Caponnetto 2013a.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: 3‐arm double‐blind randomized controlled trial: EC with 7.2 mg nicotine for 12 weeks; same for 6 weeks followed by 5.2 mg for 6 weeks: EC with no nicotine for 12 weeks Recruitment: Newspaper advertisements Setting: Outpatient clinic, Italy Study start date: April 2010; Study end date:April 2012 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 300 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
36% women, mean age 44 (SD 12.5), mean cpd 20 (IQR: 15 ‐ 25) Not currently or intending to quit smoking in the next 30 days E cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like EC presented as a healthier alternative to tobacco smoke and could be freely used, ad libitum (up to 4 cartridges a day) for 12 weeks, as a tobacco substitute EC used: 'Categoria' (model 401) with disposable cartridges
Baseline visit and up to 7 follow‐up visits to receive more cartridges, hand‐in diaries, measure CO and vital signs |
|
| Outcomes | Abstinence at 12 months (complete self‐reported abstinence from tobacco smoking since previous visit at 6 months, confirmed with CO < 7 ppm at 12 months) ≥ 50% reduction in baseline cigarettes at 12 months Recorded AEs thought to be related to tobacco smoking and EC at baseline and at each study visit (7 follow‐up visits over 12 weeks, plus at 24 and 52 weeks) |
|
| Study funding | "This research was supported by a grant‐in‐aid from Lega Italiana AntiFumo. The study sponsor had no involvement in the study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. RP and PC are currently funded by the University of Catania, Italy. The e‐cigarette supplier had no involvement in the study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication." | |
| Author declarations | "RP has received lecture fees and research funding from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline, manufacturers of stop smoking medications. He has served as a consultant for Pfizer and Arbi Group Srl, the distributor of the CategoriaTM e‐Cigarette. The other authors have no relevant conflict of interest to declare in relation to this work." | |
| Notes | Additional data provided from authors | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated, block size 15 (5:5:5 ratio) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization carried out by pharmacy, who did not have direct contact with the participants |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Double‐blind. Quote: “Blinding was ensured by the identical external appearance of the cartridges. The hospital pharmacy was in charge of randomization and packaging of the cigarettes” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation used |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 211 (70.3%) and 183 (61%) attended 6‐ and 12‐month follow‐up (at 12 m, 35% lost in 7.2 group; 37% lost in 5.4 group; 45% lost in no‐nicotine group) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear if original intention was to combine groups A+B or not. In sample size calculation they compared A+B with C, but results are not always reported in this way |
Caponnetto 2013b.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment and setting: Inpatients at a psychiatric institution in Italy Study start date/end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 14 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
57% women, mean age 44.6 (SD 12.5), mean pack years smoked 28.8 (SD 12.9) Motivated to quit: Not specified E cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Seen at baseline, given EC ('Categoria' brand) with an initial 4‐week supply of 7.4 mg nicotine cartridges. Instructed to use ad libitum up to 4 cartridges a day. EC cartridges supplied at months 1, 2, and 3 No instruction on cessation or reduction was provided. |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up at 1, 2, 3, 6 and 12 months where cigarette consumption, CO, AEs and positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia were measured Sustained reduction of ≥ 50% for at least 30 days at 12 months 30‐day point prevalence CO‐validated abstinence at 12 months Adverse events |
|
| Study funding | "We wish to thank Arbi Group Srl (Milano, Italy) for the free supplies of “Categoria” e‐cigarette kits and nicotine cartridges as well as their support. We would also like to thank LIAF (Lega Italiana AntiFumo) for the collaboration." | |
| Author declarations | "Pasquale Caponnetto, Roberta Auditore, Cristina Russo and Giorgio Carlo Cappello declare no conflict of interest. Riccardo Polosa has received lecture fees and research funding from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline, manufacturers of stop smoking medications. He has served as a consultant for Pfizer and Arbi Group Srl (Milano, Italy), the distributor of the CategoriaTM e‐cigarette." | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort; no randomization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 0/14 lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Carpenter 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized parallel‐assignment open‐label trial Recruitment: Recruitment from local urban community in southeastern USA, using various media outlets Setting: Community, southeastern USA Study start date: November 2014; Study end date: May 2016 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 68 N per arm: Control group: 22; ENDS group: 46 (split into 2 non‐randomized groups: BluCig 16 mg: 25; BluCig 24 mg: 21) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Women: 59.7%; Mean age: 42.2; Mean cpd: 15.3; Heaviness of smoking (0 ‐ 6): 2.9 EC use: Control: 9%; ENDS 16 mg group: 4%; ENDS 24mg group: 33% Motivation to quit smoking in next month (0 – 10): Control: 4.0; ENDS 16 mg: 5.0; ENDS 24 mg: 4.4 |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Intervention: At study start, choice of tobacco or menthol flavor Blu Starter Pack EC, with 16 mg/mL nicotine. Midway through study, the manufacturer of Blu altered the product and discontinued availability of the device, replaced with BluPlusþ, with 24 mg/mL nicotine. 3‐week sampling period, given up to 7 cartridges at each of 3 weekly visits. Instructions on usage "kept minimal to preserve naturalistic intent." The study team suggested that ENDS could be used "as you wish, to cut down or quit smoking, help manage smoking restrictions, or both." Control: own brand of cigarettes |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks 2, 3, 4, 8, 12 and 16 Carbon monoxide, NNAL Other outcomes: cessation (< 6 months), product evaluation, EMA |
|
| Study funding | "Support was provided by NIH R21 DA037407 (to M.J. Carpenter), P01 CA200512 (to K.M. Cummings, M.J. Carpenter, and M.L. Goniewicz), UL1 TR001450, and P30 CA138313. M.L. Goniewicz's laboratory is supported via P30 CA016056. B.W. Heckman is supported via K12 DA031794 and K23 DA041616. T.L. Wagener's effort is partially supported by the Oklahoma Tobacco Research Center, which is funded by the Oklahoma Tobacco Settlement Endowment Trust." | |
| Author declarations | "M.L. Goniewicz is a consultant/advisory board member for Johnson & Johnson. K.M. Cummings reports receiving a commercial research grant from and is a consultant/advisory board member for Pfizer Inc., and has provided expert witness testimony for various plaintiffs in lawsuits involving cigarette manufacturers. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Listed as ongoing study NCT02357173 in 2016 review update. Additional data provided from authors In all, 25 participants (54%) received the Blu Starter Pack (16 mg), and 21 participants (46%) received BluPlusþ (24 mg); no switches were made within participants. Note: this is not included in our analysis of higher v lower as assignment to nicotine dose was not done at random; 24 mg and 16 mg merged in our main analysis |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “Randomization to group was stratified by motivation to quit in the next 30 days (0–6 vs. 7–10 on a VAS scale) but proportioned 2:1 (ENDS:control) to increase precision estimates for e‐cigarette uptake and usage.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not blinded and includes non‐active control |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | CO biochemically verified but abstinence not used as outcome in this review, so rated based on adverse event reporting. Self‐report, no blinding of participants. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Retention rate: Week 4: Control:19/22 (86%); ENDS 16 mg: 23/25 (92%); ENDS 24 mg: 20/21 (95%) Week 16: Control: 16/22 (73%); ENDS 16 mg: 19/25 (76%); ENDS 24 mg: 15/21 (71%) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Other bias | Low risk | Midway through the study, the manufacturer of Blu altered the product and discontinued availability of the device, replaced with BluPlusþ, with 24 mg/mL nicotine, again offered in both tobacco and menthol flavorings, and with improved battery duration (4‐watt battery for both devices). In all, 25 participants (54%) received the Blu Starter Pack (16 mg), and 21 participants (46%) received BluPlusþ (24 mg); no switches were made within participants. The change in product (IRB approved) allowed us the unexpected opportunity to assess what impact, if any, the change in product design had on study outcomes. Note that the manufacturer, style of device, and packaging did not change, nor did our messaging to participants. The only difference was the strength of product. Thus, trial outcomes are reported across 3 groups: control versus 16 mg versus 24 mg ENDS. We have not rated this as high risk of bias as our analyses do not compare on nicotine strength and both nicotine arms are combined in our main analysis |
Czoli 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Nonblinded within‐participants cross‐over Recruitment: advertisements placed in newspapers, online, and in local vape shops, and received CAD 295 for participating in the study Setting: Kitchener−Waterloo and Toronto, Ontario, Canada Study start date: September 2015. Study end date: NR |
|
| Participants | Total N: 48 29.2% female; mean age 35.9 (SD 11.7); mean cpd NR; dual EC users at baseline; not motivated to quit Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: own choice (mainly tank) 3 consecutive 7‐day periods in which the use of tobacco cigarettes and e‐cigarettes was experimentally manipulated 4 study conditions: Dual use (e‐cigarette and tobacco cigarette); Tobacco cigarette; E‐cigarette; No product use Virtually all dual users reported using tank systems (92%) and e‐cigarettes with nicotine (94%) To control for order effects, participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 condition orders, A or B Following the baseline condition of dual use: Group A participants switched to E‐cigarette use, then to Tobacco cigarette use, and finally to No product use Group B participants switched to Tobacco cigarette use, then to E‐cigarette use, and finally to No product use |
|
| Outcomes | Baseline (visit 1) and after each of the 7‐day periods (visit 2 (week 1), visit 3 (week 2), visit 4 (week 3)) Carbon monoxide Urinary concentration of cotinine Urinary concentrations of 1‐hydroxypyrene (1‐HOP) and 4‐(methylnitrosamino)‐1‐(3‐pyridyl)‐1‐butanol (NNAL) |
|
| Study funding | This research was supported by an Ontario Ministry of Health and LongTerm Care Health System Research Fund grant (#06697 awarded to DH). Additional support was provided by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), the Vanier Canada Graduate Scholarship (CDC), a CIHR and Public Health Agency of Canada, Applied Public Health Chair (DH), and an Ontario Institute for Cancer Research Investigator Award (GTF) | |
| Author declarations | MLG reports grants from and served as an advisory board member to pharmaceutical companies that manufacture smoking cessation drugs. DH has provided paid expert testimony in tobacco litigation on behalf of governments and class‐action plaintiffs on issues related to tobacco product science and regulation. The other authors have no competing interests to declare | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details of randomization method given |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | No blinding |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All followed up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence of selective reporting |
Dawkins 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort 4‐center pragmatic cluster feasibility trial Recruitment: At homeless centers Setting: 4 homeless centers in the UK Study start date: 1 October 2018; Study end date: 31 March 2020 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 80 N per arm: EC 48; UC 32 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: people accessing homeless centers 35% women; mean age 42.7; mean cpd 20; mean FTND: FTCD 5.51 Motivated to quit: “varied considerably; large majority expressed a desire to quit smoking in the near future” E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Usual care: Written information on quitting smoking (adapted from NHS Choices); signposting to the local stop‐smoking service (SSS) by center staff Intervention: as usual care, plus refillable EC provided once with e‐liquid provided 1 x wk for 4 weeks, Aspire PockeX (tank style), choice of 3 flavors (fruit, menthol, tobacco) and 2 nicotine strengths (12 mg/mL or 18 mg/mL). Written info for EC use and support from center staff, who met once a week to provide e‐liquid and troubleshoot EC use |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks: 4, 12, 24; Clinic visits and self‐report Cessation: CO‐validated sustained at 24 weeks Adverse events and biomarkers: Self‐reported negative effects in EC arm only – each participant asked to rate on scale so cannot meta‐analyse; exhaled CO; unintended consequences Other outcomes measured: Qualitative process evaluation; costs; self‐reported positive and negative affects; recruitment rates; retention; EC/other tobacco/nicotine product use at study end; HRQoL; healthcare service utilization; other drug use/dependence; unintended consequences |
|
| Study funding | This study is funded by the National Institute for Health Research Public Health (project reference: 17/44/29) | |
| Author declarations | SC, AF, JL, CB, AT, DR, IU, LB, SP have no competing interests. PH has received research grant from and provided consultancy to Pfizer. LD has provided consultancy for the pharmaceutical industry relating to the development of smoking cessation products | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update. Authors provided information prior to peer review | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Intention was to randomize but were unable to due to practical constraints Quote: “Thus the actual allocation of centres to each arm was a pragmatic decision based on centre readiness and staff/researcher availability though we balance potential confounders and differences in environment by ensuring each cluster (EC and UC) contained one day centre and one residential unit.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “Participants joined after cluster randomisation… Allocation was concealed to participants until after the baseline assessment.” Comment: But unclear if allocation was concealed for those recruiting, and allocation would have been known to new participants |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not blinded and different levels of support between arms, so performance bias cannot be ruled out |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Cessation (primary outcome) biochemically‐validated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | 13/48 (27.1%) lost to follow‐up in the intervention arm and 20/32 (62.5%) lost to follow‐up in the control arm at 24 weeks |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All anticipated outcomes reported |
Eisenberg 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: 3‐arm RCT Recruitment: Community Setting: Canada Study start date: November 2016. Study end date: September 2019. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 376; Nicotine e‐cigarettes = 128; Non‐nicotine e‐cigarettes = 127; Counselling (control) = 121 47% female; mean age 52.66; mean cpd 21; mean FTND 6 (SD 2). Motivated to quit ‐ Yes Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Nicotine e‐cigarettes plus counseling: 12 weeks of e‐cigarettes. Rechargeable base with prefilled, disposable, tobacco‐flavored liquid cartridges (15 or 0 mg nicotine/mL), which were produced specifically for use in clinical studies (purchased from NJOY Inc, Scottsdale, Arizona). 21 cartridges at baseline with additional cartridges supplied as needed. Nicotine and nonnicotine e‐cigarettes were identical in appearance. Instructed to be used as desired. No schedule for e‐cigarette tapering, but participants were aware that they would return their e‐cigarettes after 12 weeks Participants received individual smoking cessation and relapse prevention counseling (minimum 30 minutes at baseline, 10 minutes during telephone follow‐ups, and 15 ‐ 20 minutes at clinic visits). Individualized quit plans Non‐nicotine e‐cigarettes plus counseling: As above with 0 mg nicotine/mL in liquid cartridge Counseling (control): Participants received individual smoking cessation and relapse prevention counseling (minimum 30 minutes at baseline, 10 minutes during telephone follow‐ups, and 15 ‐ 20 minutes at clinic visits). Individualized quit plans |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up was conducted by telephone at weeks 1, 2, 8, and 18, and at clinic visits at weeks 4, 12, 24, and 52 Self‐reported smoking (7‐day recall), adherence, and adverse events (AEs) were assessed during follow‐up contacts Biochemically‐validated 7‐day point prevalence smoking abstinence at 4, 12 and 24 weeks, defined as self‐reported abstinence in the past 7 days with exhaled carbon monoxide < 11 ppm At baseline: cpd; FTND; Glover‐Nilsson Smoking Behavioral Questionnaire (to assess behavioral dependence on smoking); and Beck Depression Inventory II (BDI‐II; to assess depressive symptoms) |
|
| Study funding | This trial was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR; funding reference No. 133727 and 155969). Both nicotine e‐cigarettes and nonnicotine e‐cigarettes were purchased from NJOY Inc (Scottsdale, Arizona) | |
| Author declarations | Dr Eisenberg reported receiving educational grants from Pfizer Inc for providing continuing medical education in cardiology. Dr Wilderman reported receiving financial compensation from Pfizer Inc for his involvement in a smoking cessation study using varenicline. Dr Filion reported receiving salary support from the Fonds de Recherche du Quebec, a William Dawson Scholar award from McGill University, and personal fees from Institut National D’excellence en Santé et Services Sociaux. No other disclosures were reported | |
| Notes | New cessation and adverse event data for 2021 update. Previously listed as NCT02417467 (included with SAE data only) | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Eligible participants were randomized via an online central randomization system. The system used a computer‐generated randomization list containing permuted blocks of 6 and 9, stratified by center |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Participants, investigators, and study personnel were blinded to nicotine content in the e‐cigarette groups |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Participants, investigators, and study personnel were blinded to nicotine content in the e‐cigarette groups |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Participants, investigators, and study personnel were blinded to nicotine content in the e‐cigarette groups |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Low numbers lost to follow‐up, treated as ITT |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Due to a prolonged and unforeseen delay in e‐cigarette manufacturing, enrolment was paused on 27 September 2019, and then terminated on 14 November 2019. Given reduced power, the timing of the primary endpoint was changed from 52 weeks to 12 weeks on 04 December 2019. No 12‐month follow‐up but this was for manufacturing reasons and was reported |
Ely 2013.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment: Letter sent to family practice patients who currently smoked Setting: Single family practice, Colorado USA Study start date: 14 April 2013; Study end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Letters sent to 640 patients, 48 chose to participate and 44 completed the program, 4 were lost to follow‐up Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Of the 44 participants, 66% women, all non‐Hispanic/white, aged 20 ‐ 75 (30% were age 51 ‐ 60), 57% had a high school education or less Motivated to quit: Want to quit or switch from tobacco cigarettes to ECs E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like The 6‐month smoking cessation program was based on The '5 A's' model and transtheoretical model. Options for treatment were discussed with each participant at the start of the program. All used an EC, with 16 using bupropion and 2 using varenicline as well Participants were provided with written information on “blu cig” and “smoke tip” ECs, about cost, availability, nicotine dosage options |
|
| Outcomes | Phone follow‐ups at 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months At completion of program (using ITT) Abstinence from smoking and EC use Abstinence from smoking but not EC use ≥ 50% reduction of baseline cigarette consumption (still using ECs) |
|
| Study funding | Not specified | |
| Author declarations | Not specified | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 4/48 lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No definition of abstinence provided Not clear if 'completed program' was at 6 months. |
Felicione 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Double‐blind RCT Recruitment: People who smoke were recruited from an outpatient opioid‐maintenance clinic in West Virginia, USA Setting: Outpatient opioid‐maintenance clinic in West Virginia, USA Study start date/Study end date: Not reported |
|
| Participants | Total N: 25; N per arm: Placebo (non‐nicotine): 11; Active (18 mg/ml nicotine): 14 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: People who smoke who were currently receiving a buprenorphine/naloxone combination in sublingual form, and had maintained sobriety from opioids and all other illicit substances for at least 90 consecutive days as verified via urinalysis 73.0% women; mean age 32.5; mean cpd 22; mean FTND 5.8 Motivated to quit: Quit ladder Score (range 1 ‐ 10): 5.6 average |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Compared nicotine (18 mg/ml) to non‐nicotine EC. Second‐generation EC consisted of the eGo‐T battery (900mAh, 3.3 V constant output) (Joyetech; Irvine, CA) and the Kanger mini Protank‐II, 1.5 ml Pyrex glass tank with a drip tip and atomizer head coils (KangerTech; China), choice between tobacco (n = 15) and menthol (n = 10) flavored liquid (2‐week supply). Participants were then trained in EC device operation, including assembly, liquid filling, manual battery operation, and cleaning/storage. Practised puffing on EC in the presence of a team member, and asked questions if needed. Participants instructed to use their ECIG ad libitum every day for 2 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Baseline (day 1), 14 days, 28 days for clinic measures. Data also collected via text‐messages over 2‐week intervention period Withdrawal/side effects: Every evening during the 2‐week intervention period, participants rated a variety of effects possibly experienced as a result of nicotine/tobacco withdrawal and/or use of the ECIG: nausea, dizziness, throat irritation/soreness, cough, dry mouth, headache, shortness of breath, irritability/frustration/anger, craving/urge to smoke, and other. Each item was rated on a continuous scale that ranged from 0 (not at all) to 100 (extremely) Expired air CO Other outcomes: Self‐reported cigarette and EC use; readiness to quit at day 1, 14 and 28 |
|
| Study funding | Not reported | |
| Author declarations | Not reported | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “Using a mixed factorial, simple randomization, double‐blind study design, participants were assigned to one of two ECIG conditions…” (No further details given) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details on allocation given. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: “double‐blind study design”, no further detail given |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Quote: “double‐blind study design”, no further details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “…80.6% completed the two‐week intervention (n=14 active; n=11 placebo), and 70.9% also completed the follow‐up session (n=13 active; n=9 placebo).” Active follow‐up completion rate: 13/14 = 93%; Placebo follow‐up completion rate: 9/11= 82% N.B. 6 participants were disqualified post‐randomization: Quote: “Of those individuals who were screened for the study, 93.9% were enrolled (n = 18 active; n = 13 placebo); two individuals who were ineligible provided an expired air CO level < 10 ppm. Six of the enrolled participants (n = 4 active and n = 2 placebo; n = 5 tobacco flavor and n = 1 menthol flavor) were disqualified for responding to 7 or fewer days of text messages.” |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | All measures listed were reported: Self‐reported cigarette use, text message‐based cigarette use, e‐cig use, expired air CO, readiness to quit ladder, withdrawal/side effect; No study protocol or clinical trial record available to confirm all intended outcome measures were reported |
George 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective, randomized controlled trial with a parallel, nonrandomized preference cohort Recruitment: Participants were recruited from local advertisements, smoking cessation databases, and visits to local businesses, as well as via the Scottish Primary Care Research Network Setting: Single tertiary research centre, UK Study start date: August 2016; Study end date: July 2018 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 114 in “final evaluable dataset” (145 recruited into the trial) N per arm: Tobacco cigarettes (TC): 40; EC nicotine (16 mg): 37; EC‐Nicotine‐free: 37 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
65.4% women; mean age 46.9; mean cpd 18.7 Motivated to quit: TC group: No; EC nicotine (16 mg): Yes; EC‐Nicotine‐free: Yes. |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like EC nicotine (16 mg) arm: EC containing 16 mg nicotine (Vapourlites Starter Kit with XR5 16 mg nicotine cartomizer; Vapourlites, Peterlee, United Kingdom) EC‐Nicotine‐free arm: Nicotine‐free EC plus nicotine flavoring (Vapourlites Starter Kit with 0 mg nicotine cartomizer) (non‐randomized) TC arm: continued their usual daily smoking habits and did not use EC for the 4‐week period of the trial |
|
| Outcomes | Week 4 Adverse events and biomarkers: BP, heart rate, adverse events Other outcomes measured: Endothelial function, oxidized low‐density lipoprotein, high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein, tissue plasminogen activator, and platelet activation inhibitor‐1 |
|
| Study funding | "The VESUVIUS (Vascular Effects of Regular Cigarettes Versus Electronic Cigarette Use) trial was funded by the British Heart Foundation (grant PG/15/64/31681); and supported by Immunoassay Biomarker Core Laboratory, University of Dundee, the Tayside Medical Sciences Centre, and the NHS Tayside Smoking Cessation Service. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, writing of the report, or in the decision to submit for publication." | |
| Author declarations | "Dr. Donnan has received research grants from AbbVie, Shire, and Gilead Sciences. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Consented participants who were willing to quit smoking were randomized to one of the EC arms in a 1:1 fashion using a centrally controlled web‐based good clinical practices– compliant randomization system to either: 1) EC containing 16 mg nicotine; or 2) nicotine‐free EC plus nicotine flavoring because it was considered by the institutional ethics committee as ethically unacceptable to randomize those who were willing to quit smoking into a smoking arm. Those unwilling to consider quitting smoking continued in the parallel preference TC cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central randomization |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not blinded and AE/SAE data are self‐report only. For other outcomes, low risk as objectively measured: Quote: “Patients fasted overnight and measurements were conducted at baseline and 1 month according to the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force guidelines (19) by a single operator (M.H.) blinded to study allocation at a single site.” “Pulse wave velocity and augmentation index were measured at baseline and 1 month by a single operator (M.H.) blinded to study allocation.” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Number randomized not provided per group. Quote: “A total of 145 patients were recruited into the trial (Figure 1). A final number of 114 patients (40 TC, 37 EC‐nicotine, 37 EC‐nicotine‐free) completed both visits.” |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Clinical trial record lists: Change in FMD; Change in oxidized LDL; Change in PAI‐1; Change in hs‐CRP; Change in Pulse Wave Velocity; Change in tPA; Change in Augmentation Index@75bpm All reported in the paper |
Goniewicz 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Longitudinal within‐subjects observational Recruitment: Advertisements in the media, the internet, posted advertisements in clinics and offices, and by word of mouth Setting: University, Poland Study start date: March 2011; Study end date: June 2011 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 22 started out and 2 dropped out in the first week due to an adverse event (nausea) and inability to commit to clinic visits. This resulted in analytic sample of 20 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
60% women; mean age 31; mean cpd 16; mean FTND 3.9 Motivated to quit: At the time of screening, 95% of participants (n = 19) reported planning to quit smoking, with 80% (n = 16) reporting that they have made at least 1 quit attempt prior to involvement in the study E cigarette use at baseline: Not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Pen‐style M201 e‐cigarettes for 2 weeks, with an automatically‐operated battery with an output power of 4.6 Volts (280 mAh) and the heating element resistance of 3.6 – 3.8 Ohms. At baseline, provided with EC (M201 Mild, Poland) with 20 tobacco‐flavored cartridges a week containing 11.0 ± 1.5 mg of nicotine in a mixture of propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin (50:50). Encouraged to substitute their regular cigarettes with the e‐cigarette for 2 weeks and refrain from smoking |
|
| Outcomes | Day 7, Day 14 Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Poland (grant number N N404 025638). Instrumentation and analytical chemistry at UCSF was supported by the National Institutes of Health, P30 DA012393 and S10 RR026437. The study sponsor had no involvement in the study design, collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.” | |
| Author declarations | "MLG was a faculty member of the Medical University of Silesia, Poland during the study. He received a research grant from Pfizer, a pharmaceutical company that markets smoking cessation medications. MLG and NLB have been consultants to pharmaceutical companies that market smoking cessation medications. NLB has been an expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. The other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 dropouts – 1 for nausea, 1 could not complete clinic visits. Analysis based on 20 completers |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes reported |
Guillaumier 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Pragmatic, open‐label, single‐centre, 2‐arm randomized controlled trial Recruitment: Withdrawal service in Melbourne, Australia Setting: Substance use disorder treatment setting, and following discharge, community setting, Melbourne, Australia Study start date: 1 August 2017; Study end date: April 2019. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 100 N per arm: EC intervention = 50; NRT Control = 50 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Participants were discharged from a smoke‐free alcohol or other drugs (AOD) residential withdrawal service 32% women; mean age 40.9; mean cpd 21 Motivated to quit: Median (SD) = 7.3 (2.4) of 1 to 10 scale with 10 "highly motivated" |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable. Up to an hours training session, information pack. Innokin Endura T22 starter kit and refill liquid (Nicophar). 4‐week supply of liquid nicotine, with further supplies of liquid nicotine mailed twice at 4‐ week intervals. Dosing schedule of e‐liquid dependent nicotine dependence score: high‐nicotine‐dependence category assigned initial 4‐week e‐liquid supply (total 8 × 10 ml bottles) consisting of: 2 × 10 ml bottles of 18 mg e‐liquid and 6 × 10 ml bottles of 12 mg e‐liquid. The second and third batches = 8 × 10 ml bottles of 12 mg e‐liquid only. Participants scoring in the moderate‐ and low‐dependence categories: three 4‐week supplies of 8 × 10 ml bottles of 12 mg e‐liquid. Participants given 1‐week supply of nicotine patches for use while getting used to the EC. NRT control: Information pack, 12 weeks NRT on the same schedule as for ENDs. 4‐week supply of patches plus a nicotine spray and inhaler, followed by refills including patches plus inhaler, gum and lozenges. Both groups received proactive referral to quitline counseling (call‐back service), which provides calls at pre‐discharge and on days 1, 3, 7, 14 and 28 post‐discharge, with an emphasis on relapse prevention. Counsellors trained on the use of ENDs. |
|
| Outcomes | Week 6, 12; self‐report. Adverse events collected Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | "The study is supported by a VicHealth Innovation Research Grant (2016–0096). AG is supported by a post‐doctoral fellowship from the Heart Foundation. ALB is supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) senior research fellowship and a Faculty of Health and Medicine, University of Newcastle Gladys M Brawn senior research fellowship. BB is supported by an Australian NHMRC career development fellowship (GNT1063206) and a Faculty of Health and Medicine, University of Newcastle Gladys M Brawn career development fellowship." "This study was supported by a VicHealth Innovation Research Grant (2016‐0096)." |
|
| Author declarations | "The authors declare that they have no competing interests." "None to declare." |
|
| Notes | New for 2020 update; additional data originally provided by authors and subsequently published | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Upon completing the baseline survey, participants were randomised 1:1 to an intervention via a computer‐sequenced 4–6 block randomisation embedded in the tablet device software.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “At the end of the baseline survey, participants will be randomised 1:1 to an intervention via a computer‐sequenced 4–6 block randomisation embedded in the iPad.” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: “Participants were informed of their intervention group by the RA and provided with a training session of up to one hour.” “Due to the nature of the intervention, neither participants nor staff can be blinded to allocation. However, the data safety monitoring committee and the statistician responsible for the data analysis will be blinded.” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | No biochemical validation, self‐report data |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “At 6 and 12‐weeks, 63 participants (63%) and 50 participants (50%) were followed up, respectively. While slightly higher retention rates were evidence in the VNP group at 6‐weeks (68% vs 58% in NRT group; p=0.300); there were no differences between groups at 12‐weeks (25 recontacted in both arms; i.e., 50%).” |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Unpublished findings provided by authors report on all outcomes mentioned in the protocol |
Hajek 2015a.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort, intervention provided Recruitment: People who smoke attending stop‐smoking service Study start date: March 2014; Study end date: March 2015 Setting: Stop‐smoking service, London, UK |
|
| Participants | Total N: 100 (69 of whom accepted offer of EC) Inclusion criteria:
38% women (those who accepted) 55% women (those who declined), mean age 41, mean cpd 14, all motivated to quit. EC use at baseline not specified but some who declined EC offer had used EC in the past Motivated to quit: Yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like and refillable EC: offered to all people who smoke joining service; offered choice of ‘cig‐a‐like’ (Gamucci, 1.6% or 2.2% nicotine per ml) product or tank model (EVOD, 1.8%; later replaced with Aspire product due to leakage issues). 69% of those offered received an EC on TQD Medication: Offered stop‐smoking medications including NRT and varenicline as in standard protocol. Of EC users 33% opted to also use NRT, 29% varenicline, 38% nothing Support: weekly, as in standard protocol |
|
| Outcomes | Adverse events collected throughout, method for collection unclear Also collected: 4‐week biochemically‐validated abstinence, participant feedback, cost |
|
| Study funding | "The pilot study was sponsored by City of London Corporation." | |
| Author declarations | "Peter Hajek received research funds from and provided consultancy to manufacturers of smoking cessation medications. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare." | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | 26% lost in EC group, dropout rate in EC decliners not reported. Reasons for dropout not stated |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear which outcomes authors set out to collect, no protocol available |
Hajek 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Multicentre pragmatic randomized controlled trial to examine the efficacy of e‐cigarettes compared with nicotine replacement therapy Recruitment: participants attending UK stop‐smoking service and via social media Setting: U.K. National Health Service stop‐smoking services Study start date: 1 April 2015; Study end date: 31 March 2018 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 886 N per arm: EC: 439; NRT: 447 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
48% women; median age 41; median cpd 15 ; mean FTND 4.6; 41.5% reported past use of ECs Motivated to quit: Not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable NRT: Informed of range of NRT products and selected preferred product, encouraged to use combination. Participants free to switch products. Supplies provided for up to 3 months EC: Starter pack (1 Kit, Aspire UK) provided along with 30 ml bottle of Tobacco Royale flavor e‐liquid, concentration 18 mg/ml. Participants showed how to use and asked to purchase future e‐liquid online or from local vape shops and to buy different EC device if the 1 provided did not meet their needs. Enouraged to experiment with e‐liquids of different strengths and flavors. If unable to obtain own supply, provided with further 10‐ml bottle (not proactively offered). Oral and written info on how to operate EC Both arms received multi‐session behavioral support as per UK stop‐smoking service practice (one‐to‐one sessions weekly with local clinicians, exhaled CO monitored for at least 4 weeks post‐TQD); signed behavioral contract not to use other therapy for at least 4 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks 4, 26 and 52 Cessation: Sustained and biochemically‐validated CO < 8 ppm Adverse events and biomarkers: “adverse reactions”: presence or absence of nausea, sleep disturbance and throat and mouth irritation, and respiratory symptoms (presence or absence of shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and phlegm), death Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “Supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Health Technology Assessment Programme (project number, 12/167/135) and by a grant (A16893) from the Cancer Research UK Prevention Trials Unit.” | |
| Author declarations | From ICJME disclosure forms: “Miss Natalie Bisal has nothing to disclose. Dr. Dawkins reports personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work; Dr. Goniewicz reports personal fees from Johnson and Johnson, outside the submitted work; Dr. Hajek reports grants and personal fees from Pfizer, outside the submitted work; Ms. Li reports grants from NCCHTA, during the conduct of the study; Dr. McRobbie reports grants from NIHR HTA program, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work; Dr. Myers Smith has nothing to disclose. Dr. Parrott has nothing to disclose. Dr. Pesola has nothing to disclose. Mrs Anna Phillips‐Waller has nothing to disclose. Dr. Przulj reports grants from Pfizer, outside the submitted work; Dr. Ross has nothing to disclose. Dr. Sasieni has nothing to disclose. Ms. Wu has nothing to disclose." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update, listed as ongoing study ISRCTN60477608 in 2016 review update Note higher use of allocated product at 12 m in intervention group compared to control group: “Among participants with 1‐year abstinence, 80% (63 of 79) were using e‐cigarettes at 52 weeks in the e‐cigarette group and 9% (4 of 44) were using nicotine replacement in the nicotine‐replacement group.” |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Randomization took place on the quit date to limit differential dropout. Randomization sequences (1:1 ratio in permuted blocks of 20, stratified according to trial site) were generated with the use of a pseudorandom number generator in Stata software and were embedded into an application that only revealed the next treatment assignment once a participant had been entered into the database.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Refer to 'Random sequence generation'. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded, but as both arms contained active interventions performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation used |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | At 12 months: EC Arm: 356/439 NRT Arm: 342/447 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All prespecified outcomes reported |
Halpern 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized clinical trial Recruitment: Eligible participants were employees and their spouses at 54 companies that used Vitality wellness programs Setting: Online resources via workplace setting (54 companies), USA Study start date: First phase of recruitment October 2014, second phase November 2015 (to meet recruitment target); Study end date: 20 April 2017 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 6006 N per arm: Usual care: 813; Free e‐cigarettes: 1199; Free cessation aids: 1588; Reward incentives plus free cessation aids: 1198; Redeemable deposit plus free cessation aids: 1208. Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
51.1% women; median age 44; median cpd 10 Ecig use at baseline: 10.7% current use; 23.1% past but not current use; 39.7% never used ECs Motivated to quit: Unselected sample (total sample): 9.2% no plan to quit; 61.6% want to quit later; 27.7% want to quit/need help |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like a) Usual care: Standardized Vitality program aimed at promoting tobacco cessation. This program includes existing employee benefits for quitting and the use of text/email messages to encourage tobacco cessation b) as (a), plus free EC: Free NJOY e‐cigarettes (including battery sticks, a USB charger, and up to 20 chambers with 1.0 to 1.5% nicotine per week in participants’ chosen flavors). Use of all products was free until 6 months after the quit date c) as (b) plus access to free NRT, bupropion or varenicline d) as (c) plus incentives across 6 m for testing negative for tobacco use e) as (c) plus provide money at start and lose money from this fund if they do not test negative across 6 m |
|
| Outcomes | Months 1, 3, 6 and 12 Cessation: Sustained smoking abstinence for 6 months, biochemical validation (urine cotinine, anabasine and blood carboxyhemoglobin) Other outcomes measured: Costs |
|
| Study funding | "Supported by a grant from the Vitality Institute to the University of Pennsylvania Center for Health Incentives and Behavioral Economics." | |
| Author declarations | "Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text of this article at NEJM.org. Check these and: Dr. Troxel reports other from VAL Health, outside the submitted work. Dr. Volpp reports grants and personal fees from CVS Health, personal fees from VAL Health, grants from Humana, grants from Merck, grants from Weight Watchers, grants from Hawaii Medical Services Association, grants from Oscar Health Insurance, outside the submitted work. All of the other authors state that they have nothing to disclose." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Study listed as ongoing study NCT02328794 in 2016 review update Only arms (a) and (b) included in our analyses. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not blinded and different amounts of support given to each group |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | At 12 months very low numbers completed biochemical validation. Submitted a sample n = CG:1, free e‐cigs;4, free cessation:5, rewards: 14, deposits:16 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Expected outcomes reported and checked with trial registration |
Hatsukami 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: randomized trial Recruitment: Media advertisements Setting: Clinic visits in community, USA Study start date: 25 November 2014; Study end date: 2 December 2018 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 264 N per arm: Usual brand: 36; AD‐E: 76; CS‐E: 76; CS‐NRT: 76. Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
49% women; mean age 45.2; mean cpd 15.2; mean FTND 3.4 E cigarette use at baseline: Not reported Motivated to quit: Initially uninterested |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like, but the only cig‐a‐like product with high nicotine content Usual brand arm: Purchased their own usual brand of cigarettes; at end of clinical trial phase (week 8), offered ECs or NRT for up to 8 weeks, with a choice of product and no specific instructions for use EC AD‐E arm: Use EC whenever you like instead of a cigarette; can smoke as many or as few cigarettes as you want EC CS‐E arm: Complete substitution with e‐cigarettes (i.e. “you will stop smoking cigarettes and use only e‐cigarettes”) The primary e‐cigarette product was Vuse Solo (4.8% nicotine, manufactured by RJ Reynolds, Inc). Initially a choice of Blu cigarettes (cartridge‐based system, marketed previously by Lorillard) and Fin (prefilled tanks system, manufactured by Fin Branding Group) was offered; but because Vuse attained the highest market share during the early phase of the study, switched exclusively to Vuse. Participants could choose 1 of 4 flavors: tobacco, mint, menthol, and berry. Participants were provided 7 cartridges a week with the option of returning to the clinic before their next visit to obtain additional cartridges if needed. All products provided free to the participants. All unused products and used EC cartridges were collected at each visit CS‐NRT arm: Complete substitution with 4 mg nicotine gum or lozenge, with the participant choosing what product they would like to use (i.e. “you will stop smoking cigarettes and use only nicotine gum or lozenge”). The 4 mg was down‐titrated to 2 mg if adverse side effects were experienced. Nicotine gum came in mint, cinnamon, and fruit flavors, while the nicotine lozenge was mint or cherry flavors. All these products were provided free to the participants and unused products were collected at each visit Behavioural support: CS‐E arm and CS‐NRT arm: received brief counseling on how to avoid smoking cigarettes |
|
| Outcomes | 2‐week baseline period (weeks −1 and 0); Week 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 8 Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | "supported by grants U19CA157345 from the National Cancer Institute (DKH/PS), UL1 TR000062 and UL1 TR002494 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science of the National Institutes of Health, and T32 DA007097 from the National Institute of Drug Abuse (EM). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies" | |
| Author declarations | "RJC is a member of the FDA Tobacco Products Scientific Advisory Committee. PGS serves or has served as an expert witness in tobacco company litigation on behalf of plaintiffs" | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. AD‐E arm not included in this review Additional data provided from authors. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not blinded and some interventions contained different levels of support |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded but all relevant outcomes for our analyses were objective |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “There was a significant difference in dropout rates across groups following study entry (p = .041), with the highest dropout rates observed in the complete substitution groups, particularly in the NRT group…” AD‐E: Week 1 = 73/76; Week 2 = 73/76; Week 4 = 69/76; Week 6 = 66/76; Week 8 = 65/76 = 85% CS‐E: Week 1 =69/76; Week 2 = 67/76; Week 4 = 66/76; Week 6 = 61/76; Week 8 = 58/76 = 69.7% CS‐NRT: Week 1 =72/76; Week 2 = 65/76; Week 4 = 60/76; Week 6 = 57/76; Week 8 = 53/76 = 69.7% UB: Week 1 = 35/36; Week 2 = 35/36; Week 4 = 33/36; Week 6 = 33/36; Week 8 = 32/36 = 88.8% |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Table in supplementary section describes that heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen levels were measured, but findings not reported in paper; however, provided by authors upon request |
Hickling 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Single‐group assignment – pre‐test post‐test pilot study Recruitment: Participants were referred from community mental health teams within the South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust. Setting: Healthcare setting, UK. Study start date: 24 September 2014; Study end date: 2 May 2017 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 50 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: People who smoke tobacco with a psychotic disorder (established clinical diagnosis of schizophreniform, schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder or bipolar disorder, or attending an early detection service in a high‐risk state) 24% women; mean age 38.96; mean cpd 17.94; mean FTND not reported Motivated to quit: “unwilling to quit soon” E‐cigarette use at baseline: Must not have used e‐cigarettes on more than 2 occasions in the past 30 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Participants provided with free tobacco‐flavored NJOY traditional bold disposable e‐cigarette (4.5% nicotine) in an "amount equivalent to 150% of their daily tobacco use (as recommended by the manufacturer)" for 6 weeks. Participants were instructed in the use EC; not required to stop smoking tobacco, but were encouraged to replace it with EC as much as possible. Followed up at 4 weeks and encouraged to continue EC use, informed about EC types and where these could be purchased |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 24 Self‐reported and biochemical validation Cessation: Tobacco use, as measured by the Time Line Follow Back. Tobacco cigarette use was also indexed weekly by measuring exhaled CO levels with a Smokerlyzer ED50 CO meter (Bedfont Instruments, UK) Adverse events and biomarkers:
In a subsample of participants (N = 8), 3‐hydroxypropylmercapturic acid (3‐HPMA, a measure of the toxicant acrolein) and formic acid were measured at baseline and week 6. These participants were chosen as their tobacco intake had decreased by more than 50% in this period. The measurement of 3‐HPMA and formic acid was also performed by validated LC‐MS/MS assays Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | "This work was funded by the Maudsley Charity (grant number 715); and supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London." | |
| Author declarations | "R.P‐I. has received honoraria and speaker support from Lundbeck. L.D. has provided consultancy for the pharmaceutical industry (Johnson & Johnson 2015, 2017) and acted as an expert witness for an e‐cigarette patent infringement case (Porzio, Bromberg & Newman Attorneys at Law, 2015). Between 2011 and 2013, she conducted research for several independent electronic cigarette companies (Totally Wicked, SKYCIGS and E‐Lites) for which the University of East London received funds. The e‐cigarette companies involved had no input into the design, conduct or write up of these projects and she has not received any funds from e‐cigarette companies in the last 4 years. She has no links with, and has not received any funds from, the tobacco industry, although two e‐cigarette companies that she worked with in 2013 were subsequently acquired by the tobacco industry (SKYCIGs and E‐Lites). L.H., T.R., K‐V.S., J.M., A.M. and P.M. have no conflicts of interest." | |
| Notes | Study listed as ongoing study NCT02212041 in the 2016 review update Additional data provided from authors |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled study |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled study |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Follow‐up: Week 6: 46/50; Week 10: 42/50; Week 24: 40/50 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Report all outcomes listed on http://clinical trials.gov except NNAL. Authors confirmed that they had intended to test for NNAL but had major issues with the assays |
Holliday 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Pilot RCT Recruitment: Recruited via the Newcastle Dental Hospital and by primary care practitioners working in the north‐east England region Setting: Dental clinical research facility (DCRF), located in the Newcastle Dental Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. Study start date: 20 September 2016; Study end date: 31 July 2018 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 80 N per arm: Intervention group: 40; Control group: 40 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Periodontitis 52.5% women; mean age 44.36; mean cpd 17.4; mean FTND 5 Motivated to quit: Not selected on motivation and not reported E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not currently using an e‐cigarette, or not having used 1 for more than 2 days in the last 30 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable All participants given standard stop‐smoking advice (10 ‐ 15 minutes in duration) and offer of referral to stop‐smoking services Intervention: given EC starter kit (Vype eTank clearomizer) and brief training on its use by a dentist. Provided with an approximately 2‐week supply of e‐liquid (20 ml) with a choice of flavor (Blended Tobacco, Crisp Mint, Dark Cherry and Vpure (flavorless)) and nicotine strength (0 mg/ml, 6 mg/ml, 12 mg/ml, 18 mg/ml) and information on where to buy more. EC intervention delivered directly following the standard stop‐smoking advice and was expected to be 10 ‐ 15 minutes in duration Control group: no further intervention |
|
| Outcomes | Months 1 and 6; Self‐report and biochemical validation of smoking status Cessation: Rates of continuous eCO‐verified smoking abstinence at 6 months were calculated following the Russell Standard (RS6) Adverse events and biomarkers: expired air CO, adverse events monitored at each study visit Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | "Richard Holliday is funded by a National Institute for Health Research Doctoral Research Fellowship (DRF‐2015‐08‐077). This paper presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care." | |
| Author declarations | "The authors declare that they have no competing interests." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization was performed using a secure password‐protected web‐based system |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "The randomisation allocation schedule will be generated by a statistician with no other involvement in the study to achieve concealment of allocation." |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Nature of study precluded blinding; different levels of support across intervention arms |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Attrition < 50% |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All prespecified outcomes are reported |
Humair 2014.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment: People attending an outpatient clinic Setting: University hospital outpatient clinic, Switzerland Study start date/end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 17 Inclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No Mean 23 cpd, 82% had a psychiatric illness Motivated to quit: Yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Offered an EC with nicotine 59% also reported using NRT or varenicline in addition to EC |
|
| Outcomes | Smoking cessation and reduction by at least 30% at 12 months (self‐report) Adverse events No significant side effects |
|
| Study funding | Not specified | |
| Author declarations | Not specified | |
| Notes | Abstract only, hence little detail available Not clear if EC was provided by clinic or if participants had to buy their own |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Numbers lost to follow‐up not reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Ikonomidis 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: (acute phase) Randomized cross‐over assignment (outcomes measured within hours of the intervention and hence do not meet the criteria of 1 week or more); chronic phase: non‐randomized, single‐group assignment Recruitment: Hospital smoking cessation unit Setting: Hospital smoking‐cessation unit, Greece Study start date: 31 January 2017; Study end date: Estimated completion date: December 2021 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 90 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 54% women; mean age 50.2; mean cpd 23.4; mean FTND: Not reported Motivated to quit: Yes – recruited from smoking cessation unit E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: not clear E cigarette details: In the chronic phase, all 70 participants were instructed to replace their conventional cigarettes (con‐cig) with an e‐cig containing nicotine (12 mg/dL (e‐cig fluid with nicotine concentration of 12 mg/mL (propylene glycol 74.3%, glycerin 20%, flavoring 4.5%, nicotine 1.2%))) for 1 month |
|
| Outcomes | 1 month; Self‐report and objective measures Cessation: Self‐report cessation at 1 month. CO measured at 1 month. Cessation data not used as < 6 months Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | This study was supported by a grant from the Hellenic Cardiology Society and Hellenic Society of Lipidiology and Atherosclerosis. | |
| Author declarations | None | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Acute phase of trial not relevant for the review as very short‐term outcomes | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not blinded and differential levels of support given |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Objective measures used for all outcomes reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 70 participants and 20 controls recruited – no dropout |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | NCT record states that chronic endothelial integrity, platelet aggregation and high‐shear stress‐dependent platelet function would be assessed but is not reported in this research letter – however study estimated completion date is December 2021, so perhaps data not ready for publication or limited capacity in the research letter – not the primary publication |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Few details – written as commentary. Trial registration suggests this is an ongoing study |
Ikonomidis 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | RCT Recruitment: Smoking cessation clinic of second cardiology department of National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Attikon General Hospital Setting: Hospital smoking‐cessation unit, Greece Study start date: NS |
|
| Participants | N = 40; Arm 1 E‐cigarette n = 20; Arm 2 conventional tobacco cigarette n = 20 80% female; mean age 44.8 (SD 11.3); mean cpd: 25.8 (C‐cig 25.5 SD 9.3. E‐cig: 26.2 SD 9.1) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable E‐cig: second‐generation e‐cig device and popular in Greek Market e‐liquid (NOBACCO eGo Epsilon BDC 1100, eGo battery, 1100 mAh, operating at 3.9 V ‐ propylene glycol 74.3%, glycerin 20%, flavoring 4.5%, nicotine 1.2%/12 mg/ml) |
|
| Outcomes | Baseline, 4 months: Exhaled CO concentration; blood pressure Also, cpd; Ppatelet function by Platelet Function Analyzer PFA‐100 and Light Transmission Aggregometry; Pulse wave velocity; Plasma malondialdehyde levels as oxidative stress index |
|
| Study funding | "There was no funding for this study" | |
| Author declarations | "The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper." | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Table of random numbers as reproduced from the online randomization software www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/index |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not possible |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Only CO outcomes used here, which are objectively measured |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All followed up (confirmed via contact with authors) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No protocol or clinical trial record available to confirm whether all prespecified criteria were reported |
Ioakeimidis 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized controlled trial Recruitment: Not specified Setting: Hospital, Greece. Study start date/Study end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 54 N per arm: Arm 1: 27; Arm 2: 27 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: People who have experienced acute coronary syndrome 65% women; mean age 52; mean cpd 21; mean FTND 5.6 Motivated to quit: Yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: No prior EC use |
|
| Interventions |
EC: information on whether cig‐a‐like or refillable not provided Both arms given "low intensity counselling" Intervention 1: 12‐week use of EC 12 mg/ml nicotine Intervention 2: 12‐week varenicline |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks: 4, 12, 24 Cessation: 7‐day PP at 24 weeks, self‐report Adverse events and biomarkers: Unclear how these were reported. Abstract says no SAEs, poster implies this may have just been CV or neuropsychiatric SAEs. Abstract says nothing about AEs but nausea and sleeping disorders given in table in poster. Implies (S)AEs collected during treatment period only Other outcomes measured: Not specified |
|
| Study funding | Not reported | |
| Author declarations | Not reported | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Abstract and poster only; limited data available | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not specified but equal amounts of contact and support between arms so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Self‐report only but equal amounts of contact between arms, no reason to suspect differential misreport |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Abstract/poster only so not able to judge |
| Other bias | High risk | Abstract and poster only. Two different figures presented for quit rate in EC arm (no difference in those presented in varenicline arm) between abstract and poster. Poster percentage aligns with figure, so using that (16.5%) as opposed to abstract figure (32.5%). Contacted authors but no reply. Calculated n quit based on percentages but unclear what denominators were; EC calculates back to whole number for EC but not for varenicline |
Kumral 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective randomized clinical trial Recruitment: All patients admitted to a smoking cessation clinic at the Department of Otorhinolaryngology‐Head and Neck Surgery, Okmeydanı Training and Research hospital Setting: Smoking cessation clinic, Turkey Study start date: March 2013; Study end date: November 2013 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 98 but analysis excludes 16 from intervention and 10 from control who did not stop smoking; thus 72 analyzed N per arm: EC: 58 (42 ana lysed); Non‐EC 40 (30 ana lysed) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 44% women; mean age 36; mean cpd and mean FTND not specified Motivated to quit: “All patients were willing to quit smoking” E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Unclear EC arm: “used EC to quit smoking” – allowed to select brand and flavor, used “medium density” liquid (11 ‐ 12 mg/ml) (no further detail given) Non‐EC arm: Received cognitive behavioral therapy (no further detail given) |
|
| Outcomes | 3 Months Sino‐nasal outcome test (SNOT‐22) via self‐administered questionnaire, to evaluate changes in subjective symptoms. Saccharin transit test to evaluate nasal mucociliary clearance (MCC) function which authors state is “an important defence mechanism” |
|
| Study funding | Not specified | |
| Author declarations | Not specified | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “Patients participating in the study were randomly divided into two groups; EC smokers (group 1) and non‐EC smokers (group 2).” No further detail provided |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information given |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Participants were not blinded. The trial is described as single‐blinded and outcome assessors were blinded. No placebo used |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Self‐reported outcome data, participants not blinded and unequal amounts of support between arms |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Dropout rate not clear. Only ana lysed people who quit |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Lee 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomized parallel‐assignment double‐blind pilot trial Setting: San Francisco Veterans Affairs Medical Center (SFVAMC), USA Recruitment: veterans awaiting surgery Recruitment: In VA hospital presenting for surgery Study start date: August 2015; Study end date: May 2016 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 50 N per arm: NRT: 30; END: 20 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Patients awaiting elective surgery 10% women; mean age 54; mean cpd 14; mean FTND 3.3 Motivated to quit: Not specified E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified but excluded daily users |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Both groups receive: i) referral to the California Smokers' Helpline, ii) brief advice lasting less than 2 minutes, iii) a brochure from the ASA about quitting smoking before surgery EC arm: 6‐week supply of NJOY e‐cigarettes (disposable, first generation). Instructed to use Bold (4.5%) ad lib for 3 weeks, then Gold (2.4%) ad lib for 2 weeks and then study (0%) ad lib for final week. Number of ECs issued corresponded to baseline cpd, assuming 1 EC = 10 cigarettes. Asked to refrain from the use of all study products at the end of 6 weeks NRT arm: 5‐week Nicoderm CQ patches, 1 week placebo patches. Dose based on cpd at baseline: ≥ 10 cpd, 21 mg/day for 3 weeks, 14 mg/day for 1 week, 7 mg/day for 1 week, 0 mg/day for 1 week. < 10 cpd at baseline: 14 mg/day for 3 weeks, 7 mg/day for 2 weeks, 0 mg/day for 1 week |
|
| Outcomes | 30 Days (phone), 8 Weeks (in person), 6 Months (phone) Cessation: 7‐day PP at 30 days (not validated), 8 weeks (CO‐validated), 6 months (not validated). Smoking cessation for at least 48 hours on day of surgery (CO‐validated) Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “This work was funded by internal UCSF Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Care funds (San Francisco, California, United States of America) and the UCSF Resource Allocation Program grant, administered by the Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center developmental funds from the National Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA 82103‐16). E‐cigarettes were purchased from NJOY using these funds. NJOY had no involvement in the design, execution, or analysis of the study. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.” | |
| Author declarations | “The authors declare there are no competing interests” | |
| Notes | 3 NRT participants used EC, 2 EC participants used nicotine patch Study listed as ongoing study NCT02482233 in the 2016 review update |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Randomization was computer‐generated, with randomly permuted block sizes of 3 or 6, in a 2:1 ratio using the ralloc program” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Allocation was concealed by consecutively numbered, sealed, opaque envelopes” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded but both interventions active with equal amounts of support so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Self‐report only at 6 months and participants not blinded to condition, but similar level of support given to both groups so differential misreport judged unlikely |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 1 NRT and 1 ENDs loss to follow‐up at 6 months |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Lee 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized controlled trial Recruitment: Recruited from motor company. Setting: Motor company, medical office in Korea Study start date: 5 January 2012; Study end date: 31 August 2012 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 150 N per arm: EC: 75; NRT: 75 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 0% women; mean age 42.3; mean cpd: Not reported, 1.01 packs per day; mean FTND 4.05 Motivated to quit: Yes, or to reduce E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Both arms received 50 mins education session on smoking cessation and use of smoking cessation aids in medical office (no further detail given). Asked to return to medical office every 4 weeks (to 24 weeks?) for “evaluation and counseling by an independent health practitioner” Arm 1: 50‐min education sessions on smoking cessation and the use of smoking‐cessation aids, instructed to visit the medical office each month for evaluation and counseling by a health practitioner who was unaffiliated with the study. Participants supplied with eGo‐CTM EC (nicotine 0.01 mg/mL) from Ovale in 12‐wk supply Arm 2: As (1) but instead of EC given 2 mg nicotine gum in 12‐wk supply |
|
| Outcomes | 12, 24 weeks (in person) Cessation: continuous abstinence from 9 ‐ 24 weeks, exhaled CO < 10 ppm, negative urine cotinine Adverse events and biomarkers: Yes but just note ‘adverse events’ Other outcomes measured: 7‐day PPA, cigarette reduction |
|
| Study funding | “none” | |
| Author declarations | “none declared” | |
| Notes | Study listed as ongoing study KCT0001277 in the 2016 review update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “computer‐generated randomization sequence with a block size of 2” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “The enrolment and assignment of all subjects were performed by a clinical research coordinator not involved in the study” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded but both interventions active with equal amounts of support, so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Participants not blinded but results biochemically validated |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 61/75 NRT and 71/75 EC FU at 24 weeks |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All prespecified outcomes reported |
Lucchiari 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized parallel‐assignment double‐blind trial Recruitment: Participants enrolled in lung cancer‐screening program Setting: Early lung cancer detection program (Cosmos II) at European Institute of Oncology, Italy Study start date: September 2014; Study end date: January 2016 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 210 N per arm: 70 participants per arm Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: 55 years of age or older 37% women; mean age 62.8; mean cpd 19.38; mean FTND 4.37 Motivated to quit: yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Excluded people who smoke who had ever regularly used e‐cigarettes for more than 1 week alone or in combination with tobacco cigarettes |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Both arms received “low intensity counseling” – phone at week 1, 4, 8 and 12, approx. 10 mins each Nicotine EC arm: e‐cigarette kit and 12 10‐mL liquid cartridges (8 mg/mL nicotine concentration). During the first week, participants could use the e‐cigarette ad libitum. At the end of the first week, asked to use only EC for the next 11 weeks Nicotine‐free EC (placebo) arm: Nicotine‐free EC – same as above but with nicotine‐free EC |
|
| Outcomes | Months 3, 6 and 12 (but only 3‐ and 6‐month data available) Cessation: Continuous abstinence for previous month, CO ≤ 7 ppm Adverse events and biomarkers: FOR EC ARMS ONLY:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | This study was supported by a grant from Fondazione Umberto Veronesi (FUV) | |
| Author declarations | The authors declare no conflicts of interest | |
| Notes | Listed as ongoing study Lucchiari 2016 (NCT02422914) in 2016 review; new for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “A randomization list using a permuted block design (40 blocks of 6 subjects randomly assigned to 1 of the 3 treatment arms) had been previously prepared by independent personnel.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Double‐blind, active and placebo e‐cigarettes labeled by independent personnel, researcher and participants blind |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | “double blind” for nicotine vs no nicotine EC but limited info given; however, as similar levels of support across arms performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation used |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Approx. 73% followed up in each group at 6 months, very little difference between groups |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Paper states data also collected at 12 m but this is not presented and unclear why. Paper states CO collected but data not presented |
Martner 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: A nonconcurrent multiple baseline across participants design. Three phases were included: Baseline, EC, and EC + CM. Half the participants received the EC phase following baseline; the other half received EC + CM following baseline Recruitment: Community Setting: Set‐up meetings occurred at the University of Florida Behavioral Health and Technology Research Clinic, USA Study start date/Study end date: Not specified. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 12 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
58.3% women; mean age 37.5; mean cpd 16.25; mean FTND 5 Motivated to quit: Expressed a desire to quit smoking. E‐cigarette use at baseline: 3 participants never tried an EC prior to the study; 2 owned an EC but quit using it more than a month prior to the study; remaining 7 had tried an EC more than a year prior to the study but never owned one |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable All participants provided with smokio electronic cigarettes (second‐generation ECs) and V2 e‐liquid with a concentration of 24 mg/ml (2.4%) of nicotine. Researchers provided participants with a copy of the National Cancer Institute’s brochure Clearing the Air (http://smokefree. gov). Then researchers and participants read through a manual that described the study procedures, and showed participants how to use the software to measure CO and how to use the EC Participants initially received EC without contingency for a period of 14 days following the quit attempt. If participants failed to reduce CO levels during this phase, they received contingency management in addition to EC |
|
| Outcomes | 4 weeks Adverse events and biomarkers: Adverse events collected in 4‐day smoking behavior questionnaires; eCO Other outcomes measured: acceptability and use of EC; overall experience of study |
|
| Study funding | "The study was supported in part by crowd‐sourced funding enabled by Experiment.com. Preparation of this paper was supported in part by Grant P30DA029926." | |
| Author declarations | "The authors declare no conflicts of interest." | |
| Notes | N of 1 (within‐participants randomized design, not between groups). New for 2020 update. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No details provided. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | AEs measured in behavioral change questionnaire but not reported |
McRobbie 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment: advertisements in free London newspapers Setting: Smokers' clinic, East London, UK Study start date: February 2013; Study end date: September 2013 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 40 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
45% women, mean age 47 (SD 12), mean cpd 19 (SD 10), mean FTND 5.2 (SD 2.8), 65% in full‐time employment Motivated to quit: Yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Excluded those who had used EC for more than 1 week in the past |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Participants attended baseline session 1 week prior to their TQD. On the TQD, participants were provided with an EC (Green Smoke, 1st generation device, 2.4% nicotine cartridges). 2 cartridges a day were supplied initially, with the supply adjusted to actual use later. Attended 4 weekly follow‐up sessions and received standard behavioral support |
|
| Outcomes | Cigarette consumption and CO readings collected at each session. Urine sample for cotinine and 3‐HPMA analysis collected at baseline and 4 weeks post‐TQD Change in urinary 3‐HPMA (ng/mg creatinine) at 4 weeks Change in urinary cotinine (ng/mg creatinine) at 4 weeks Change in CO at 4 weeks |
|
| Study funding | "This study was funded by a grant given to P. Hajek, H. McRobbie, and M.L.Goniewicz from the UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact." | |
| Author declarations | "H. McRobbie is Clincal Director at The Dragon Institute; reports receiving commercial research grant from Pfizer; and has received speakers bureau honoraria from Johnson&Johnson and Pfizer. M.L. Goniewicz reports receiving commercial research grant from Pfizer. P. Hajek has received speakers bureau honoraria from and is a consultant/advisory board member for the manufacturers of stop‐smoking medications. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors." | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 7/40 participants were lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All predefined outcomes reported |
Meier 2017.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized cross‐over trial (e‐cig vs placebo) Recruitment: via local media outlets Setting: Community, USA Study start date/Study end date: Not specified. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 24 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 25% women; mean age 48.5; mean cpd 16.3; FTND not reported Motivated to quit: No (eligibility criteria was to not want to quit in next 30 days) E‐cigarette use at baseline: 8/24 (33%) had previously tried an EC, avg 9.4 months since last use, avg length of use 3.6 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like
Smoked “as usual” for 1 week followed by 2 weeks of either placebo or active 1st generation EC BluCig starter kit with up to 7 cartridges (prefilled, with either active 16 mg or 0 mg nicotine solution) Participants were instructed “this e‐cig may or may not contain nicotine; we ask that you try it at least once, but use it however you like; smoke regular cigarettes as you wish.” Shown how to charge the device and sampled the product during the visit. Provided a handout on how to use the product (e.g., switching cartridges) and general information about ECs |
|
| Outcomes | 1 week in each condition, in person Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “..supported by grants P01 CA138389, P30 CA138313 (Hollings Cancer Center Support Grant) from the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health and UL1 TR000062 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science of the National Institutes of Health. BWH was supported by K12DA031794” | |
| Author declarations | “KMC has received grant funding from the Pfizer, Inc., to study the impact of a hospital‐based tobacco cessation intervention. He also receives funding as an expert witness in litigation filed against the tobacco industry. We have no other declarations of interests to declare” | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “Participants were randomized to receive either an active or placebo EC first”, no further information provided. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Refer to 'Random sequence generation'. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “Participants and research staff conducting sessions were blinded to dose. All cartridges were pre‐loaded by the manufacturer. Labeling was removed by a research team member not involved in participant contact to mask placebo versus active ECs. We restricted flavor options to regular tobacco flavor or menthol to most closely match usual cigarette brand flavor profile and reduce unwanted variance in product” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “Participants and research staff conducting sessions were blinded to dose. All cartridges were pre‐loaded by the manufacturer. Labeling was removed by a research team member not involved in participant contact to mask placebo versus active ECs. We restricted flavor options to regular tobacco flavor or menthol to most closely match usual cigarette brand flavor profile and reduce unwanted variance in product” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
NCT02648178.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Setting: Medical centre, USA Recruitment: People with cancer Design: Non‐randomized single‐group assignment trial Recruitment: Clinical settings, including outpatient clinics and the infusion suite Study start date: June 2016; Study end date: May 2018 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 19 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Patients with stage I ‐ IV aerodigestive tract cancers or bladder cancer who smoke daily 42.1% women; mean age: not reported ‐categories 18 ‐ 65 years: N = 9, > 65 years: N = 10; cpd and FTND: not reported. Motivated to quit: No (inclusion criterion) E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified but EC use within 30 days is an exclusion criterion |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like and refillable Instructed on use of EC, and given a supply that is "approximately equivalent to their current nicotine intake". Given Halo Triton EC (leak‐proof refillable tank system) or Halo G6 leak proof prefilled cartomizers. Began participants with 18 mg/ml and moved nicotine content up or down based on participant preference. Choice of flavors, provided for 9 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Weeks 3, 6, 9, 12. Self‐report at clinic visits Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | Not reported – data extracted from clinical trial registry record | |
| Author declarations | Not reported – data extracted from clinical trial registry record | |
| Notes | Study listed as ongoing study in the 2016 review update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized, single‐group assignment |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized, single‐group assignment |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 19 enrolled; 10 participants followed up at 12 weeks |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | The following measures were not reported: exhaled carbon dioxide; urine propylene glycol; urine nicotine, cotinine, NNAL and 1‐ hydroxy naphthalene (1‐HOP), and Timeline Follow‐Back Questionnaire (TLFB). Data at 6, 12 months also not reported |
NCT02918630.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: RCT Recruitment: Clinics Setting: SMI clinics, USA Study start date: October 2016; Study end date: August 2017 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 7 N per arm: NRT: 4; EC+NRT 3 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Yes ‐ SMI (schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, or PTSD) 43% women; mean age 48.3; mean cpd: NR; mean FTND: NR Motivated to quit: Wanted to quit or reduce their cigarette smoking but did not want to quit in the immediate future (this was an exclusion criterion) NB – trial registry states wanted to reduce and protocol states wanted to quit or reduce as inclusion criteria E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Both arms received a nicotine patch 21 mg for 4 weeks EC + NRT: 4 weeks: 1) a 3.3 V, 1000 mAh battery; and 2) a 1.5 Ohm, dual‐coil cartomizer (SmokTech; Shenzhen, China). Nicotine concentrations 36 mg/ml. Verbal and written instructions on how to use and maintain the e‐cigarettes at Week 1 visit NRT arm: NRT only |
|
| Outcomes | 5 weeks Cessation: n/a but “change in smoking” Adverse events and biomarkers: Breath CO, COPD‐related symptoms, EC side effects (e‐cig side effects questionnaire), AEs, SAEs Other outcomes measured: Urinary cotinine, cpd, tobacco dependence, craving, withdrawal symptoms, desire to quit, confidence to quit, EC dependence, EC use, satisfaction with EC, nicotine dependence, schizophrenia symptoms (brief psychiatric rating scale), cognitive domains associated with schizophrenia (MATRICS consensus cognitive battery), changes in positive symptoms of schizophrenia (scale for the assessment of positive symptoms), changes in negative schizophrenia symptoms (scale for the assessment of negative symptoms), suicide ideation (Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale) |
|
| Study funding | Not reported | |
| Author declarations | Not reported | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. Information from http://clinical trials gov registry and unpublished protocol; discrepancies between the two in terms of trial methods. Feasibility for future NIH grant application. Intended to recruit 20 participants but only 7 started and completed | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | “double‐blind” but “open‐label” elsewhere, no further info given |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Schizophrenia and COPD outcomes not reported. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Some discrepancies between clinicaltrials record and protocol linked to from record, including when NRT started and inclusion criteria (just schizophrenia or all SMI). Target sample size was 20 but only 7 people recruited |
Nides 2014.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Open‐label non‐comparative study Recruitment: Study site database and community advertisements Setting: Clinical Trials Unit, USA Study start date: April 2013; Study end date: 10 July 2013 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 29 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Exclusion criterion: EC within the previous 14 days; use of NRT in last 30 days 44% women; mean age 43; mean cpd 20.1; mean FTND 4.5 Motivated to quit: no E‐cigarette use at baseline |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Participants attended 3 clinic visits at 1‐week intervals Visit 1: Baseline Visit 2: Provided with 1st generation type ‐ 'NJOY® King Bold' (NJOY, Inc. Scottsdale, AZ), with 26 mg nicotine. Used ad libitum for 20 minutes in the clinic, then ad libitum use over the next week. Recorded use of regular cigarettes and puffs on EC Visit 3: Participants abstained from all sources of nicotine for 12 hours prior to visit |
|
| Outcomes | Adverse events | |
| Study funding | Funding for this study was provided by NJOY, Inc., Scottsdale, AZ | |
| Author declarations | Dr Nides has received compensation from NJOY, Inc. and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr Leischow has received compensation from GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, and Cypress Bioscience. Mr Simmons and Ms Bhatter have no conflict of interest to report | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 participants dropped out between visits 1 and 2 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Planned comparisons reported |
Oncken 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized cross‐over study Recruitment: Newspaper advertisements, radio announcements, and from local general medicine practices Setting: Lab‐based study, Connecticut, USA Study start date: October 2012; Study end date: June 2015 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 27 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
45% women; mean age 42; 70% white; 15% Hispanic, 15% black; mean cpd 16; 45% had tried EC at baseline, 50% smoked menthol cigarettes Motivated to quit: No E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Prescribed Joye eGo‐C (www.joyetech.com) and e‐Juice (18 mg/mL nicotine) procured from American eLiquid (www.americanliquid.com) Cross‐over study between menthol‐flavored and non‐menthol tobacco‐flavored EC. Requested not to smoke their regular cigarettes during study period, but most (60%) reported intermittently smoking cigarettes during study |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up at 1 wk and 2 weeks BP, heart rate, body plethysmography, static lung volumes and airways resistance (Raw) and specific conductance (sGaw) – taken at lab visits after abstaining from EC for at least 2 hrs, then taken again after inhaling EC and repeated 5 mins later Adverse events also reported but method for measuring not stated Also measured nicotine concentrations, rates of cigarette and EC use |
|
| Study funding | This project was supported by Academic Enhancement funds from the Department of Medicine at the University of Connecticut Health Center (to CO) and the Clinical Research Center at the University of Connecticut Health Center | |
| Author declarations | CO is currently receiving study medication (nicotine inhaler and placebo) from Pfizer pharmaceuticals for an NIH funded of nicotine inhaler for smoking cessation during pregnancy | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Method not stated; Quote: "Subjects were then randomly assigned to use the menthol or plain e‐cigarette cartridge for one week, switching to the other cartridge for the second week" |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No detail given |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No detail given on blinding but equal levels of support between arms, so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Some subjective outcomes but equal levels of support between arms so differential misreport judged unlikely |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 20/27 followed up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Ozga‐Hess 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: RCT Recruitment: Cigarette smokers were recruited from the community via fliers, online postings, and word of mouth Setting: Morgantown, West Virginia, USA Study start date: Not reported. Study end date: Not reported |
|
| Participants | Total N: 60; E‐cigarette plus own brand = 30. Own brand cigarette (control) = 30 38.3% female; mean age completers 35.1 (SD 11) (N = 34) non‐completers 36.8 (SD 12.9) (N = 26); mean cpd completers 16.7 (SD 4.9), non‐completers 19.6 (SD 6.1); mean FTND completers 5.3 (SD 1.8), non‐completers 5.9 (SD 1.9) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable E‐cigarette (18 mg/ml ) plus own brand cigarette. Kanger mini Protank‐II, which is a 1.5 ml Pyrex glass tank with a drip tip and atomizer head coils (KangerTech; China), and a 3.3 V constant output, 900 mAh, eGo‐T battery (Joyetech; Irvine, CA). The liquid (The Vapor Room, Sky Vapors LLC, Frostburg, MD) was labeled as 70% propylene glycol and 30% vegetable glycerin, with a nicotine concentration requested of 18 mg/ml. Participants could choose tobacco, menthol or wild berry flavor and could switch between sessions. Ad libitum use for 4 weeks Own brand cigarette ad libitum use for 4 weeks |
|
| Outcomes | Daily for salivary cotinine samples. Daily self‐monitoring device to log e‐cigarette and cigarette use. Collected used cigarette filters Weekly CO breath test Attended the laboratory weekly for assessments (Days 8, 15, 22, and 29). Then completed a follow‐up visit 1‐month post‐intervention self‐reported withdrawal symptoms Reported experience of specific symptoms rated using a visual analog scale with a range from 0 (not at all) to 100 (extremely). e.g. craving, irritability, dry mouth, throat irritation, and cough |
|
| Study funding | Financial support provided to MDB and GAD by WVU Senate Grant for Research, and to GAD, MDB, and NAT by Cooperative Agreement Number 1‐U48‐DP‐005004 from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to the West Virginia Prevention Research Center. Support provided to NJF and JEOH by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS T32 GM081741). Additional support provided by WV Tobacco Cessation QuitLine | |
| Author declarations | Author SGF has consulted for various pharmaceutical companies on matters relating to smoking cessation. All other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "Using a simple randomized design" Comment: not adequately explained |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not adequately described in the paper |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Participants and investigators were not blind |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | 40% retention, but no difference between groups |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes reported |
Pacifici 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Uncontrolled pre‐post pilot study Recruitment: Word of mouth Setting: Hospital‐based smoking cessation clinic, Italy Study start date/end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 34 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 47.1% women, mean age 40.6, mean cpd 21.5 no EC use at baseline, not motivated to quit |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Participants were given commercially‐available EC (AVATAR device, Battery 550 mAh/3.9 V, W: 7.8, cartomizer with 2, 2 ohm resistance, tank capacity 1.5 mL, temperature of the aerosol: 55/65 degrees), 2 different chargers for each EC and PUFFIT e‐liquids with nicotine content matching the individual nicotine daily intake and tobacco and/or other flavors freely chosen by each participant W1: nicotine‐free e‐liquid W2&3: Own EC with personal nicotine dosage, encouraged to use as substitute for traditional cigarettes W4: Encouraged to forego all traditional cigarettes Throughout: assistance at any time of day from centre staff with any EC‐related problem, plus follow‐up group sessions and smartphone messaging application Behavioural support: Multi‐component medically‐assisted training program with monitoring of nicotine intake as a biomarker of correct EC use, including Information about general working principles, safety and risks of EC, together with medically‐assisted face‐to‐face training on how to correctly use the device to absorb nicotine vapor |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up at 1, 4 and 8 m Cessation (measure not defined) Adverse events Exhaled CO, COT, 3‐HCOT concentration cpd |
|
| Study funding | The authors thank Renata Solimini, Adele Minutillo, Emilia Marchei and Maria Concetta Rotolo for their technical assistance. This work was supported by the Department of Therapeutic Research and Medicines Evaluation Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Roma, Italy | |
| Author declarations | The authors declare no conflict of interest | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All participants followed up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | AEs measured but not reported |
Polosa 2011.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment: Advertisments in local hospital in Catania, Italy Setting: not specified Study start date: February 2010; Study end date: June 2010 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 40, hospital staff Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
35% women, mean age 42.9 (SD 8.8), median cpd 25 (IQR 20 ‐ 30), median FTND 6.0 (IQR 6 ‐ 8) Motivated to quit: No E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Seen at baseline, given EC ('Categoria' brand) with an initial 4‐week supply of 7.4 mg nicotine cartridges. Instructed to use ad libitum up to 4 cartridges per day. EC cartridges supplied at months 1, 2, and 3 No instruction on cessation or reduction was provided |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up at 1, 2, 3, 6, 18 and 24 months where cigarette consumption, CO, and AEs were measured, incl. 30‐day PP CO‐validated abstinence at 6 months and CO‐validated abstinence at 18 and 24 months (not otherwise defined) Adverse events |
|
| Study funding | "We wish to thank Arbi Group Srl (Milano, Italy) for the free supplies of ‘Categoria’ e‐Cigarette kits and nicotine cartridges as well as their support. We would also like to thank the study participants for all their time and effort and LIAF (Lega Italiana AntiFumo) for the collaboration" | |
| Author declarations | "None of the authors have any competing interests to declare, but RP has received lecture fees from Pfizer and, from Feb 2011, he has been serving as a consultant for Arbi Group Srl.Arbi Group Srl (Milano, Italy), the manufacturer of the e‐Cigarette supplied the product, and unrestricted technical and customer support. They were not involved in the study design, running of the study or analysis and presentation of the data" | |
| Notes | Smoking cessation services provided to those who spontaneously asked for assistance with quitting. These participants were excluded from the study protocol | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 13/40 were lost to follow‐up, but used ITT analysis |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Polosa 2014b.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort study Recruitment: Volunteers, leaflets, cessation service kiosk in hospital Setting: Smoking cessation clinic, Italy Study start date: January 2013; Study end date: November 2013 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 50 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
40% women, mean age 41, mean cpd 25, mean FTND 6.0 No EC use at baseline, not motivated to quit |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable 2nd generation devices (personal vaporisers ‐ PVs): EGO/CE4 model, filled with tobacco aroma e‐Liquid containing 9 mg/ml nicotine; instructed to use the study products ad libitum (up to a maximum of 5 ml/day; i.e. half vial) Behavioural support: Participants were instructed how to charge, fill, activate and use the EC. Key troubleshooting was addressed and phone numbers were supplied for assistance. “No emphasis on encouragement, motivation and reward for the smoking cessation‐related efforts were provided during the study.” |
|
| Outcomes | 4, 8, 12 and 24 weeks 30‐day PP verified by CO ≤ 10 ppm Adverse events Cpd, exhaled CO, reduction rates, product usage, and opinions of the EC products |
|
| Study funding | "The authors wish to thank FlavourArt (Oleggio, NO, Italy; www.flavourart.it). Authors wish to thank LIAF, Lega Italiana Anti Fumo (Italian acronym for Italian Anti Smoking League) for supporting this research" | |
| Author declarations | "RP has received lecture fees and research funding from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline, manufacturers of stop smoking medications. He has also served as a consultant for Pfizer and Arbi Group Srl, an Italian distributor of e‐Cigarettes. RP is currently scientific advisor for LIAF, Lega Italiana Anti Fumo (Italian acronym for Italian Anti Smoking League). PC, MM, JBM, and CR have no relevant competing interest to declare in relation to this work" |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 76% followed up, ITT analysis used, no significant differences in baseline characteristics between completers and those lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Polosa 2015.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Prospective cohort Recruitment: Professional retail staff in participating vape shops Setting: 7 vape shops in Catania province, Italy Study start date/end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 71 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
38% women, mean age 41.7, mean cpd 24.9, mean FTND 5 No EC use at baseline |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Instructed how to charge, fill, activate and use EC; key troubleshooting advice provided; phone number available for technical support “Encouraged to use these products in anticipation of reducing the number of cig/day smoked” |
|
| Outcomes | 6 and 12 m follow‐up 30‐day PPA via self‐report Details of product purchase Sustained 50% and 80% reduction in cpd from baseline |
|
| Study funding | Authors wish to thank the local participating Vape Shops and LIAF, Lega Italiana Anti Fumo (Italian acronym for the Italian Anti‐Smoking League) for supporting this research | |
| Author declarations | Riccardo Polosa has received lecture fees and research funding from Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline, manufacturers of stop smoking medications. He has also served as a consultant for Pfizer and Arbi Group Srl, an Italian distributor of e‐Cigarettes. Riccardo Polosa is currently scientific advisor for LIAF, Lega Italiana Anti Fumo (Italian acronym for Italian Anti‐Smoking League). Jacques Le‐Houezec is a consultant for Johnson & Johnson France, a manufacturer of nicotine replacement therapy, and was reimbursed for travel and accommodation to present at a conference in Shenzhen (China) organized by the e‐cig manufacturer association (CECMOL). Pasquale Caponnetto and Fabio Cibella have no relevant conflict of interest to declare in relation to this work | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not controlled |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 69% follow‐up at 12 m. Participants lost to follow‐up considered as continuing smokers |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Pratt 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Observational study – uncontrolled experimental study Recruitment: community mental health centre through self‐referral and clinician referrals Setting: community mental health centre (USA) Study start date: October 2013; Study end date: June 2014 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 19 (21 originally recruited, however 2 participants did not return for any weekly visits so 19 analyzed) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Psychiatrically stable, in‐treatment, people who smoke with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder or bipolar disorder 68% women; mean age 42; mean cpd: Only cigarettes per week reported: 192 (SD = 159.3). This would be an average of 27 cpd; mean FTND 5.5 Motivated to quit: “None of the participants was actively engaged in a quit attempt during the study” E‐cigarette use at baseline: E‐cig use was an exclusion criterion |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like E‐cigarette details: (NJOY brand) based on each participant's level of use of combustible tobacco. Each e‐cigarette cartridge was approximately equivalent to 2 packs of combustible cigarettes. Trained research interviewers instructed participants on the proper use of e‐cigarettes |
|
| Outcomes | Week 1, 2, 3, 4 Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “Financial support to purchase the e‐cigarettes and pay small stipends to the participants in this unfunded pilot study came from Dr. Mary Brunette's discretionary reserve account.” | |
| Author declarations | “All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest” | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 dropouts (9.5%) failed to return to clinic. Analysis based on 19 participants |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Pulvers 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Observational uncontrolled experimental study Recruitment: Community Setting: Visits took place in University labs, USA Study start date: January 2015; Study end date: April 2015 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 40 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No 27% women; mean age 30.08; mean cpd 8.76; FTND not reported Motivated to quit: over half either did not intend to quit at all or did not intend to quit in the next 6 months 22/40 (55%) E‐cigarette use at baseline: Inclusion criteria included the following:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable 2nd generation EC starter kit with 2 e‐Go C batteries (3.7 volts/650 MaH), a USB connection cord, an AC adapter, and a carrying case, and a supply of Saturn V4i atomizers (2.4 ohms) filled with liquid in their preferred flavor (28 atomizers total; 2/day). Provided 24 mg/mL dosage vegetable glycerin liquid in a tester sample to all participants. Those who reported the 24 mg was too strong were provided 12 mg/mL dosage liquid. The first session included brief education, training, action planning for making a complete switch to EC. A referral to the California Smokers’ Helpline was made at the final visit (week 4). |
|
| Outcomes | 3 lab visits (baseline, week 2, and week 4) and 2 phone visits (week 1 and week 3). Biological samples were taken at all 3 in‐person visits (baseline, week 2, and week 4). However, due to budgetary restrictions, only the baseline and week 4 biological data were analyzed Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured: Cotinine, change in tobacco consumption (cpd using TLFB interview), change in frequency of EC use, change in nicotine dependence and attitudes/behavior, change in 30‐day nicotine exposure |
|
| Study funding | “This study was funded by the University of Minnesota (JSA), P30 DA012393 (NLB), P50 CA180890 (NLB), and California State University San Marcos (KP).” | |
| Author declarations | “Benowitz is a consultant to pharmaceutical companies that market smoking cessation medications and has been an expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. The other authors have no conflicts of interest.” | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 37/40 provided follow‐up data |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All outcomes reported |
Pulvers 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: RCT. Unblinded. 2:1 ratio Recruitment: Participants were recruited from the San Diego, California, and Kansas City, Missouri and Kansas, metropolitan areas Setting: USA Study start date: May 2018. Study end date: May 2019 |
|
| Participants | Total N = 186; Electronic‐cigarettes = 125. Own brand cigarette = 61 40.3% female; mean age 43.3 (SD 12.5); mean cpd 12.1 (SD 7.2). E‐cigarettes use at baseline: 0.05 (0.3%) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: pod Electronic‐cigarettes: JUUL (5% nicotine); Choice of flavors (Menthol, Mango, Cool Mint, Virginia Tobacco); Given 1 pod per pack of cigarettes; Given a 2‐week supply at baseline and then a further 4‐week supply at week‐2 visit. At each follow‐up appointment (week 1, telephone call; week 2, in‐person visit; and week 4, telephone call), barriers and benefits of switching to e‐cigarette were discussed and action planning for exclusive switching was revisited. Compensated on a schedule of USD 20 at baseline, USD 40 at week 2 and USD 60 at week 6 Own brand cigarettes: Compensated on a schedule of USD 20 at baseline, USD 40 at week 2 and USD 60 at week 6 |
|
| Outcomes | Baseline, week 2 and week 6. Telephone survey at 6 months Change in past 7‐day combustible cigarette use measured by 7‐day timeline follow‐back interview 30‐day point prevalence at 6 months (EC group only)
Lung function; Pulmonary function test of small airway disease that is most sensitive to effects of cigarette smoking; mean midexpiratory phase of forced expiratory (FEF25%‐75%); respiratory symptoms as measured with the American Thoracic Society Questionnaire (scores range from 0 ‐ 32, with higher scores indicating greater respiratory symptoms) Blood pressure Adverse events: respiratory symptoms |
|
| Study funding | Drs Pulvers and Nollen and Ms Rice were supported by grant No. 5SC3GM122628 from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Drs Schmid and Ahluwalia were supported in part by grant No. P20GM130414, from the NIH‐funded Center of Biomedical Research Excellence (COBRE). Dr Schmid was partially supported by Institutional Development Award No. U54GM115677 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the NIH, which funds Advance Clinical and Translational Research (Advance‐CTR) | |
| Author declarations | Dr Schmid reported serving as a consultant for legal firms representing Eli Lilly, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, and Gilead outside the submitted work. Dr Benowitz reported receiving personal fees from Pfizer and Achieve Life Sciences and serving as a consultant to pharmaceutical companies that market smoking cessation medications and as an expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies outside the submitted work. Dr Ahluwalia reported receiving personal fees from Lucy Goods outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update. Additional data provided by authors | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomization sequence was generated with an Excel (Microsoft) random number formula applied to each site (2:1 ratio) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Allocation was placed into sealed individual envelopes labeled with participant identification numbers for each site, retrieved from a locked cabinet monitored by the project manager, and opened individually following consent of each participant |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Could not be blinded |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Carbon monoxide validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | E‐cig: 115/126 OB: 54/61 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Per protocol reporting |
Scheibein 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Non‐randomized single‐arm Recruitment: From supported temporary accommodation (STA) service STA project workers and support staff identified potential study participants who smoked and wished to quit Setting: Dublin Simon Community, Ireland Study start date: Recruitment February 2019 (overall trial start date March 2018). Study end date: June 2019 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 23 but only report baseline for the 9 that completed the study. % female 8.7% (2/23) at baseline, (22.2% 2/9) completed and reported; mean age 43.89 (SD 7.36); mean cpd 25.22 (SD 7.77); mean FTND 7.89 (SD 1.2); mean CO 21.89 (SD 14.4 corresp) E‐cigarettes use at baseline: no Motivated to quit: yes Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Electronic‐cigarette: Endura T22e Electronic Nicotine Delivery System and 2 10 ml bottles of fluid strengths (0, 6, 11, 18 and 20 mg/ml) and flavors ('Purple Berry', 'Ice Menthol', 'Regular Blend' and 'American Tobacco') |
|
| Outcomes | Baseline (‘week 1’), week 4, week 8, week 12: CO, adverse events Also number of cigarettes smoked; Fagerström Test Scores |
|
| Study funding | This study was completed as part of a Tobacco Harm Reduction Scholarship funded by Knowledge Action Change | |
| Author declarations | FS was a recipient of a Tobacco Harm Reduction Scholarship provided by Knowledge Action Change. He is currently the recipient of an Enhanced Scholarship from the same organization. AM and KM acted as mentors for both the Tobacco Harm Reduction Scholarship and Enhanced Scholarship. AM is an associate of New Nicotine Alliance. KM is a recipient of a grant from the Foundation for a Smoke Free World. JW declares no interests. WR declares no interests |
|
| Notes | New for 2021 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Only 1 arm |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Not randomized |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Self‐reported adverse events |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | 9/23 completed. Reason was many people moved away so not linked to unacceptability of the study. Incomplete paperwork to enable to be followed |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol published afterwards |
Smith 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Double‐blind randomized controlled trial Recruitment: Recruited from the local area via advertising on craigslist social media Setting: Laboratory and electronic diaries, USA Study start date/Study end date: Not specified. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 30 N per arm: PG/VG ratio 70/30 = NR; PG/VG ratio 50/50 = NR; PG/VG ratio 0/100 = NR Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
30% women; mean age 43.7; mean cpd 18.5; mean FTND 5.4 Motivated to quit: Not specified E‐cigarette use at baseline: Participants had used an e‐cigarette an average of 1.6 times in their life, and no one reported use in the last 30 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like EC provided for 1 week. All aspects of the ENDS device and e‐liquid were held constant between groups with the exception of PG/VG ratio: PG/VG ratio 70/30; PG/VG ratio 50/50; PG/VG ratio 0/100. Ego‐T 1100 mAh battery and disposable cartomizers (510 Smoketech, 1.5‐Ω dual coil). E‐liquid was tobacco‐flavored (Classic Tobacco, American E‐liquid) and contained 18 mg nicotine/ml |
|
| Outcomes | 1 week; 2 lab visits pre and post and participant diaries Adverse events and biomarkers: Participants provided a CO sample at each visit Other outcomes measured: cpd, ENDS puffs |
|
| Study funding | Funding for this project was provided by pilot funding from the National Cancer Institute (P01CA200512 to K.M.C.). Salary support provided by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (K12DA031794 to T.T.S., K23DA041616 to B.W.H.) | |
| Author declarations | M.J.C. has received consulting honoraria from Pfizer. K.M.C. has received payment as a consultant to Pfizer, Inc., for service on an external advisory panel to assess ways to improve smoking cessation delivery in health care settings. He also has served as paid expert witness in litigation filed against the tobacco industry | |
| Notes | Additional data provided from authors. New for 2020 update. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “At the conclusion of the lab visit, participants were randomized and assigned to take home one of the three e‐liquids to use at home for a 1‐week sampling period (10 participants/ratio).” Quote: “Participants were randomly assigned to receive one e‐liquid to take home for 1 week.” (no further detail given) |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “PG/VG ratio was blinded from participant and staff members who conducted experimental sessions.” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Number of participants at follow‐up not reported, but this may be due to the 1‐week follow‐up and it seems that all participants (excluding 1 participant who was not randomized) were followed up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No protocol. Few details for CO measurements, just percentage change for each group, but mean CO data provided by author on request |
Stein 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Non‐controlled open‐label experimental study Recruitment: A flyer posted at a large methadone maintenance treatment program Setting: Methadone maintenance treatment program, USA Study start date: April 2015; Study end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 12 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: People receiving MMT for opoid use disorder 50% women; mean age 45.9; mean cpd 17.8; mean FTND: Not reported Motivated to quit: yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Had not used e‐cigarettes for more than 2 of the past 30 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like 2 week supply of NJOY e‐cigarettes at week 1 (quit day), consisting of 5 packs of NJOY e‐cigarettes (15 in total). Participants could request an additional 5 pack (20 in total) for the following 2‐week study period, if they ran out before a study visit. Participants instructed to use EC exclusively for a total of 6 weeks (end of treatment). They were referred to the state telephone QuitLine for supportive counseling at the quit‐day visit (week 1) |
|
| Outcomes | Participants quit and received e‐cigs at week 1. Assessments were carried out at week 3, 5, 7 and 9 Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “MDS is a recipient of National Institute on Drug Abuse Award K24 DA000512. This award funded the project described here.” | |
| Author declarations | “None declared.” | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | No randomization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | No randomization |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “One individual dropped out after week 3 and did not return; another completed all follow‐up assessments except week 7.” |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Strasser 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized, factorial trial (Participants were randomized to one of the 5 brands of e‐cigarettes – although only 4 brands analyzed) Recruitment: Media ads Setting: Recruitment from the community, study took place at University, USA. Study start date/Study end date: Not specified. |
|
| Participants | Total N: Analysis based on 24 (28 originally recruited, but the first 4 participants enrolled experienced malfunctioning NJOY e‐cigs and withdrew – the project was removed from the market before the 5th participant was randomized) N per arm: blu: 6; Green Smoke: 6; V2: 6; White Cloud: 6 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Not applicable 29% women; mean age 43.3; mean cpd 17; mean FTND 3.7 Motivated to quit: Participants had no current plans to try to quit smoking (eligibility criterion) E‐cigarette use at baseline: No more than 3 previous episodes of use and not currently using (eligibility criterion) |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like All participants received nicotine EC and were instructed to use them exclusively for 9 days The 5 brands selected, including brand reported nicotine levels, were: (1) NJOY (18mg nicotine) – this brand was discontinued and not analyzed as the e‐cigs provided malfunctioned; (2) V2, 18 mg nicotine; (3) Green Smoke, 18.9 ‐ 20.7 mg nicotine; (4) blu, 20 ‐ 24mg nicotine; and (5) White Cloud, 23 ‐ 24 mg nicotine. Each brand advertised the delivery of the same level of nicotine (appropriate for about a pack/day smoker), provided the standard tobacco flavor (no other flavors made available), and used a disposable cigarette‐like device |
|
| Outcomes | Day 10 is the only testing point of interest for us but participants were also tested at days 1 and 5 Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and FDA Center for Tobacco Products (CTP) under Award Number P50CA179546, as well as grants from the National Cancer Institute (P50 CA143187, P30 CA16520, and P30 DA12393)” | |
| Author declarations | “Dr Benowitz has served on scientific advisory boards for Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline related to smoking cessation medications and has been an expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. Dr Schnoll receives medication and placebo free of charge from Pfizer and has provided consultation to Pfizer and GlaxoSmithKline. These companies had no involvement in this study. Dr Strasser has received funding through the Pfizer GRAND program, an independent peer‐reviewed grant program funded through Pfizer (2008‐2011); all investigators have received funding from the United States National Institutes of Health” | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Although participants were randomized to different brands of EC, no description on how randomization was carried out |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not specified |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No description of whether groups were blind to other conditions, but given similar levels of support between arms, so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Unclear whether any blinding took place, some outcomes were measured using objective measures and there was no difference in contact between arms |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | For blu, Green Smoke, and V2 groups, 83% of participants completed the 10‐day study; only 33% of participants randomized to White Cloud completed the 10‐day study; meaning loss to follow‐up was considerably higher in this group |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Tseng 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: 2‐arm; double‐blind placebo‐controlled RCT Recruitment: Advertisements placed in Craigslist as well as flyers distributed on the street and placed in New York City venues with details for how to contact study staff. Setting: Community, USA Study start date: July 2014 – 2015 (month unclear); Study end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 99 (100 were randomized but 1 participant randomized to the control arm was found to be ineligible between randomization and baseline) N per arm: Nicotine EC: 50; Placebo EC: 49 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Young adults 32.3% women; mean age 28.43; mean cpd 14.33; FTND not measured but time to first cigarette was measured categorically. The mode category was 6 ‐ 30 mins (39/99; 41.5%) Smoking behavioral dependence scale (11 items): mode category ‘Moderate’ (51/99; 51.5%) Motivated to quit: Readiness to quit (1 – 10 scale, 1 – 8 apply to current people who smoke): 5.57 ± 1.49 E‐cigarette use at baseline: No use of e‐cigs in past 14 days (eligibility criterion) |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like E‐cigarette details: 3 weeks of disposable 4.5% nicotine NJOY, King Bold (NJOY, Inc, Scottsdale, AZ) which resemble conventional cigarettes. NJOY also manufactured the non‐nicotine placebo EC. Both nicotine and placebo ECs were tobacco‐flavored. The products were purchased by the investigators and provided to the participants free of charge Other stop‐smoking pharmacotherapies: None Behavioural support: Prior to receiving the ECs, participants were required to complete a 20‐ to 30‐minute telephone counseling session with a trained tobacco cessation Counsellor. The purpose of the telephone counseling was to review current smoking patterns and offer behavioral and environmental change strategies. These included specific smoking reduction options, such as eliminating cigarettes at work and in the home, carrying only those cigarettes needed for that day, dropping cigarettes associated with less intense triggers first, avoiding smoking triggers, and other strategies to manage urges.18 participants were asked to reduce the number of cigarettes smoked daily by at least 50% of the total number of cigarettes smoked per day at baseline. To mimic real‐life EC use, minimum EC use instruction was provided. Participants were encouraged to replace cigarettes with as much or as little use of an EC as needed in order to reduce nicotine withdrawal symptoms |
|
| Outcomes | Week 1, 3 Cessation: Not applicable Adverse events and biomarkers: adverse events and symptoms related to EC use Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | “This work was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences at the National Institutes of Health (grant number UL1TR000038).” | |
| Author declarations | “None declared” | |
| Notes | Study listed as ongoing study NCT02628964 in the 2016 review update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “computer generated” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: “…was concealed from research assistants. Blinding of the allocation of nicotine or placebo EC was ensured by the identical appearance of the ECs”. However, not enough information given on how allocation was concealed at the point of randomization |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: “Blinding of the allocation of nicotine or placebo EC was ensured by the identical appearance of the ECs” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Quote: "Blinding of the allocation of nicotine or placebo EC was ensured by the identical appearance of the ECs” |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Nicotine EC ltfu: 10/50; Placebo EC ltfu: 10/49 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Valentine 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Open‐label prospective cohort study Recruitment: Recruited from within the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Connecticut Healthcare System by word of mouth Setting: Receiving psychiatric services from Department of Veterans Affairs healthcare system, USA Study start date/Study end date: Not specified. |
|
| Participants | Total N: 50 (sample analyzed for primary outcomes on week 1 completers – N = 43) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: Military veteran people who smoke who had no immediate intention to stop smoking and were currently receiving psychiatric services from the Department of Veterans Affairs healthcare system. 7% women; mean age 56.9; mean cpd 16.6; mean FTND 4.9 Motivated to quit: Had no immediate intention to stop smoking E‐cigarette use at baseline: E‐cigarettes or smokeless tobacco products may have been used for less than 2 of the past 30 days |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable All given eVic Supreme (Joyetech), "a commercial, variable‐power, tank‐type device". 6.5 mL tank (Delta 23, Joyetech) and a C3 triple coil atomizer head (Joyetech) with a total resistance of 1.8 ohms. Participants could choose flavor (menthol or tobacco) and nicotine concentration (12 or 24 mg/mL). Participants taught how to use EC, with additional materials dispensed as needed. Participants were informed that they could use the study e‐cigarette or regular tobacco cigarettes, or both, ad libitum during study participation |
|
| Outcomes | Week 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 (Weekly lab visits and 1 month follow‐up) Adverse events and biomarkers: Alveolar (breath) CO levels (ppm) Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | "This research was supported by the New England Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Statistical analyses, biochemical assays, and analyses of e‐cigarette solutions were supported by the Administrative and Laboratory cores of P50DA036151 (Yale TCORS) from the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Tobacco Products. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration." | |
| Author declarations | "Ralitza Gueorguivea, PhD, discloses consulting fees for Palo Alto Health Sciences and Mathematica Policy Research and a provisional patent submission by Yale University: Chekroud, A. M., Gueorguieva, R., & Krystal, K. H. “Treatment Selection for Major Depressive Disorder” (filing date June 3, 2016, USPTO docket number Y0087.70116US00). The authors report no other financial relationships with commercial interests." | |
| Notes | New for 2020 update. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled cohort study |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Uncontrolled cohort study |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Follow‐up: 31/50 at week 8 |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No protocol or clinical trial record. |
Van Staden 2013.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Single‐group within‐subject design Recruitment: Participants from a military hospital in South Africa Setting: South Africa Study start date/ end date: Not specified |
|
| Participants | Total N: 15, mean age 38 years, smoked 20 cpd (range 10 ‐ 30), for an average of 17 years (range 5 ‐ 27) Total N: 13 completed the study (5 women) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Inclusion based on specific population characteristic: No Motivated to quit: Not specified E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Participants were asked to use an EC only for 2 weeks (i.e. no cigarettes) EC: 'Twisp eGo' cartridge 0.8 ml containing 0.0144 mg of nicotine |
|
| Outcomes | The following measurements were taken at baseline and 2‐week follow‐up:
|
|
| Study funding | "We are grateful for the sponsorship of the eGo e‐cigarette packs by Twisp and also for the valuable advice and laboratory assistance given by Col. (Dr) J Lubbe, Chemical Pathologist, 1 Military Hospital, Pretoria with regard to the measurement of the cotinine levels. We also wish to acknowledge Professor Martin Veller for his insightful contributions during the preparation of this manuscript and also Dr Richard van Zyl‐Smith for his assistance and review." | |
| Author declarations | "The sponsor of the Twisp e‐cigarette had no role in the design and conduction; the collection, analysis and interpretation of the study; or in the preparation, review or approval of the manuscript." | |
| Notes | Dropouts (N = 2) were due to illness (headache and fever) and undertaking a military course associated with high stress and exposure to others smoking, making it difficult to abstain from cigarettes The paper states that the EC cartridge contained 0.8 ml of solution with 0.0144 mg of nicotine. This would be an unusually low concentration of nicotine and we have assumed an error in units where milligrams should have been grams (0.0144 grams of nicotine would make the concentration 18 mg/ml) |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Prospective cohort |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Not randomized |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2/15 lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unable to determine prespecified outcomes |
Veldheer 2019.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Randomized parallel‐assignment double‐blind trial Setting: USA (2 sites) Recruitment: Community advertisements Study start date: June 2015; Study end date: June 2018. |
|
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 520 Total N: 263 in this analysis (520 planned overall; THIS INCLUDES ONLY THOSE FOLLOWED UP AT 1 AND 3 MONTHS) N per arm: sub: 72; EC: 191 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
58% women; mean age 47; mean cpd 18; mean FTND: Not specified Motivated to quit: Interested in reducing cigarette intake but not planning to quit in next 6 months E‐cigarette use at baseline: None |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like For 24 weeks: 1) Cigarette substitute: QuitSmart cigarette substitute ‐ plastic tube looks like a real cigarette, designed to provide the same draw resistance as a smoker's usual cigarette. No drug delivery. 2 cigarette substitutes and a product manual are provided to participants following randomization and replacement products are provided throughout the intervention period (24 weeks). At baseline, associated user manual, research staff explain how to use product. Reduction goal to 50% at weeks 0 and 1, 75% at weeks 2 and 4, continue reducing onwards from there 2) EC with no nicotine: EGO e‐cigarette. Cartomizers containing 0 mg/ml nicotine provided throughout the intervention period (24 weeks) Associated user manual, research staff explain how to use product. 3) As (2) but 8 mg/ml nicotine 4) As (2) but 36 mg/ml nicotine |
|
| Outcomes | Months 1, 3, 6, 9; (only 1 and 3 month available at time of extraction) Cessation: Conventional tobacco product use measured but measures not clear Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under Award Number P50DA036105. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the views of the NIH or FDA. The project [publication] was supported by CTSA award No. UL1TR000058 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent official views of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences or the National Institutes of Health. | |
| Author declarations | JF has done paid consulting for pharmaceutical companies involved in producing smoking cessation medications, including GSK, Pfizer, Novartis, J&J, and Cypress Bioscience. TE is a paid consultant in litigation against the tobacco industry and is named on a patent application for a device that measures the puffing behavior of electronic cigarette users. There are no competing interests to declare for other authors | |
| Notes | Preliminary data from RCT; full results not yet available EC arms pooled in preliminary data available to us at time of writing Authors provided outcome data; Study listed as ongoing study Lopez 2016 in the 2016 review update |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “the assignment codes are made from separate randomization lists created in advance by the statistician for each site stratum.” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Once a participant has been confirmed eligible for randomization, a computer procedure will assign the participant to the next condition on the list automatically.” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded for non‐EC arms but given similar level of support/product, so performance bias judged unlikely |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not blinded for non‐EC arms but given similar level of support/product, so differential misreport judged unlikely |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Dataset only includes those followed up at 1 and 3 months, which excludes 140 participants; breakdown by arm not provided |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Results paper just preliminary results with all EC arms collapsed. Protocol and NCT record list different outcomes and study lengths. |
Wadia 2016.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Uncontrolled experimental study Recruitment: Dental hospital staff were recruited – not specified how Setting: Dental hospital, UK Study start date: April 2015; Study end date: December 2015 |
|
| Participants | Total N: 20 (18 of the 20 attended the reassessment visit) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
% women, age, cpd and FTND: not specified. Motivated to quit: enrolled people who smoke who did not intend to quit smoking, but were prepared to attempt to substitute smoking with the use of e‐cigarettes for 2 weeks E‐cigarette use at baseline: not specified |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Participants provided with a blu PROTM e‐cigarette kit (Electric Tobacconist®), an extra bottle of blu PRO Tobacco™ e‐Liquid (Electric Tobacconist) and written instructions. The e‐Liquid was Classic Tobacco‐flavoured and contained 18 mg of nicotine (medium strength). The participants agreed to substitute their regular smoking habits with the use of e‐cigarettes for 2 weeks. They were asked to make a note of any cigarette smoking during the 2 weeks if complete abstinence was unsuccessful |
|
| Outcomes | 2 weeks Adverse events and biomarkers: adverse effects Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | Not specified | |
| Author declarations | Not specified | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | No randomization |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | No randomization |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 lost to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | All expected outcomes reported |
Walele 2018.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: RCT (short‐term, Cravo 2016) followed by cohort study (Walele 2018) in which all participants were given nicotine EC Recruitment: Community Setting: 2 centres in the UK (Covance Clinical Research Unit Ltd, Leeds and Simbec Research Ltd, Wales) Study start date: December 2013; Study end date: December 2016 |
|
| Participants | 420 participants Inclusion criteria differ per study phase: Cravo 2016 (short‐term RCT):
Additional criteria for Walele 2018 (participants from Cravo 2016):
Exclusion criteria: Cravo 2016:
Walele 2018 (participants from Cravo 2016):
Cravo 2016 Total N: 419 randomized, 408 analyzed (excludes 11 who were excluded prior to any product use) N per arm: EVP: 306; Control: 102 45% women; mean age 34.6; Mean cpd: most 11 ‐ 20 cpd (56% int, 62% control); Mean FTND: most moderate (57% int, 54% cont) Motivated to quit: No E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not excluded based on prior EC use Walele 2018 Total N: 209 (147 pre‐EVP group; 62 pre‐CC group) 45% women; mean age 36.6; mean cpd 2.6 (data from figure): Not reported; FTND: Not reported Motivated to quit: As reported for Cravo 2016 E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like Cravo 2016 EC: EVP prototype (2.0% nicotine), developed by Fontem Ventures B.V. (Amsterdam, the Netherlands). Instructed to only use EVP for study period. It consisted of a rechargeable battery (voltage range of 3.0e4.2 V), an atomiser and a capsule (small cartridge) containing e‐liquid. The capsules were replaceable and the battery and atomiser were reusable. Could choose between two different e‐liquids, which differed solely in their flavor: a menthol‐flavored e‐liquid with 2.0% nicotine (2.7 mg nicotine/capsule) and a tobacco‐flavored e‐liquid with 2.0% nicotine (2.7 mg nicotine/capsule) Control: Used their own usual conventional cigarette brand Walele 2018 E‐cigarette details: Commercially available Puritane™ (closed system EVP) consists of a lithium‐ion rechargeable battery and a replaceable cartomiser comprising of an e‐liquid reservoir pre‐filled by the manufacturer, a heating element and a mouthpiece; 1.6% nicotine (16 mg/g) Available in tobacco or menthol. 2 weeks before baseline, participants had a familiarization session with Puritane™, where they could see and try the EVP |
|
| Outcomes |
Cravo 2016: Weeks 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12 Walele 2018: starting on the last day of the previous trial): Months 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21 and 24 Study centre visits for assessments Adverse events and biomarkers:
Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding |
Cravo 2016 "This work was funded and supported by Fontem Ventures B.V. Imperial Brands plc is the parent company of Fontem Ventures B.V. the manufacturer of the EVP prototype used in this study" Walele 2018 "This work was funded and supported by Fontem Ventures B.V. Imperial Brands Group plc is the parent company of Fontem Ventures B.V., the manufacturer of the EVP used in this study" |
|
| Author declarations |
Cravo 2016 "Dr. Cravo has nothing to disclose. Mrs Martin reports personal fees from Fontem Ventures B.V. during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tobacco and pharmaceutical industries outside the submitted work. Dr. Sharma reports other from Fontem Ventures B.V. during the conduct of the study. Dr. Bush reports other from Fontem Ventures B.V. during the conduct of the study. Mrs Savioz reports personal fees from Fontem Ventures B.V. during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tobacco and pharmaceutical industries outside the submitted work. Mr Craige has nothing to disclose. Mr Walele has nothing to disclose." Walele 2018 (copied from Transparency documents) "Dr. Koch reports other from Fontem Ventures B.V., during the conduct of the study; Dr. Martin reports personal fees from Fontem Ventures B.V., during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tobacco and pharmaceutical industries, outside the submitted work; Dr. O'Connell has nothing to disclose. Dr. Bush reports other from Fontem Ventures B.V., during the conduct of the study; Dr. Savioz reports personal fees from Fontem Ventures B.V., during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tobacco and pharmaceutical industries, outside the submitted work; Dr. Walele has nothing to disclose." |
|
| Notes | Sponsor: Imperial Tobacco Group PLC Study listed as ongoing studies NCT02029196 and NCT02143310 in 2016 review update. Treated as single study in this review due to including the same participants, and no time lag between studies "The same subjects who participated in our previous clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov, #NCT02029196) conducted in the same centres, with another EVP (Cravo et al., 2016), were invited to participate the study by Walele 2018. All volunteering subjects were assigned to switch to using Puritane™, a closed system EVP, for two years, starting on the last day of the previous trial (End of Study [EoS] visit), which corresponded to the baseline visit of Walele 2018." |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “Randomisation was performed using an Interactive Web Response System (IWRS; Almac Clinical Technologies)” |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: "Randomisation was performed using an Interactive Web Response System (IWRS; Almac Clinical Technologies)” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Open‐label, no blinding, differential levels of support/product use so performance bias cannot be ruled out |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Open‐label, no blinding, with differential levels of support/product use and subjective outcomes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Cravo: 286/306 int (4.5% ltfp) and 101/102 (1% ltfp) control completed study but all who received product included in analysis. In EVP group, 14 withdrew consent, 2 experienced AEs, 1 death, 3 “other”. CC group 1 AE Walele 2018: High 209/387 enrolled for study Walele 2018. A total of 102 participants (48.8%; EVP: 75/145 (51%); CC: 27/61 (43.5%) completed the study |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | Cravo 2016: Low All anticipated outcomes reported (study registered prior to study completion) Walele 2018: Low All anticipated outcomes reported (study registered prior to study completion) |
Walker 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: RCT Recruitment: National media advertising Setting: Community based, New Zealand Study start date: Recruitment between March 2016; Study end date: Aug 2018 |
|
| Participants | N per arm: Patches‐only group: 125; Patches plus nicotine e‐cigarette group: 500; Patches plus nicotine‐free e‐cigarette group: 499 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
69% women; mean age 41.6; mean cpd 17.3; mean FTND 5.2 Motivated to quit: yes E‐cigarette use at baseline: Not reported but use of an e‐cigarette for smoking cessation for more than 1 week anytime in the past year was an exclusion criterion |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Refillable Moderate‐intensity behavioral support was available for all participants immediately after randomization, then once a week for 6 weeks. This support consisted of 10 – 15 mins of withdrawal‐oriented behavioral support and advice on using their allocated treatment, delivered proactively over the phone by researchers who had received standardized training in delivery of such support. Assigned to: 1) Nicotine patch for 14 weeks including 2 week prequit. 21 mg, 24‐hr nicotine patch (Habitrol) 2) Nicotine patch and nicotine‐free EC for 14 weeks. As 1, plus 14‐week supply at no cost. A 2nd generation eVOD (Kangertech, Shenzhen GuangDong, China) starter kit, with a choice of 1 of 2 tobacco e‐liquid flavors. Advised to start using the e‐cigarette 2 weeks before their quit date, as and when necessary or desired, and in accordance with the manufacturer’s written instructions, to become familiar with its use Participants were instructed to stop smoking from their quit date and continue with their allocated treatment for 12 weeks (ad libitum use of the e‐cigarette), irrespective of any lapses to smoking 3) Nicotine patch and nicotine EC for 14 weeks. As above, but 18 mg/mL nicotine |
|
| Outcomes | Quit date, 1, 3, 6 and 12 months Continuous abstinence at 6 months with CO validation Adverse events and biomarkers: Known side‐effects associated with e‐cigarette use and nicotine patch use; SAEs Other outcomes measured:
|
|
| Study funding | Funding: Health Research Council of New Zealand. "The sponsor of the study had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication." | |
| Author declarations | NW, CB, MV, GL, ML, and VP report grants from the Health Research Council of New Zealand, during the conduct of the study. NW, CB, MV, and VP report grants from Pfizer, outside of the submitted work. GL chairs the organization End Smoking New Zealand, which advocates for harm reduction approaches to tobacco control. E‐cigarettes were purchased from a New Zealand e‐cigarette online retailer (NZVAPOR, https://www.nzvapor.com/), e‐liquid was purchased from Nicopharm, Australia (https://www.nicopharm.com.au/), and nicotine patches were supplied by the New Zealand Government via their contract with Novartis (Sydney, Australia). NZVAPOR also provided, at no cost to participants, on‐line and phone support regarding use of the e‐cigarettes. Neither NZVAPOR nor Nicopharm have links with the tobacco industry. None of the above parties had any role in the design, conduct, analysis, or interpretation of the trial findings, or writing of this publication. | |
| Notes | Study listed as ongoing study NCT02521662 in the 2016 review update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated randomization sequence |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Quote: “We ensured allocation concealment because the statistician who generated the random allocation was not the person randomising participants.” |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Quote: “Participants and researchers collecting outcome data were masked to the nicotine content of the e‐liquid” but those allocated to patch only would be aware they did not have an E‐cigarette Quote: “Third, while we attempted to minimise detection bias by masking the nicotine content of the e‐liquid, we were only 30% successful, and thus some bias in favour of nicotine e‐cigarettes could have occurred.” |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Biochemical validation |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | < 50% lost to follow‐up, similar rates of attrition between groups (within 20%) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | CO‐verified abstinence at 12 months stated as a secondary outcome but data are not reported in the main text. However, state in the appendix that too few people in each group were followed up to 12 months (36/1124) so no data are presented for this time point |
Yingst 2020.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Design: Cross‐over study Recruitment: Participants were recruited from people living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) (who smoked) seeking care at the Penn State Health HIV Comprehensive Care Program Setting: USA Study start date:Not reported |
|
| Participants | Total N: 17; 41.2% female; mean age 49.1 (SD 8.8); mean cpd 16.9 (SD 7.9); mean CO 22.4 (13.1) E‐cigarettes use at baseline: not reported Motivated to quit: No Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria: not reported |
|
| Interventions |
EC: Cig‐a‐like; Refillable Cig‐a‐like device (Blu), nicotine concentration 24 mg/ml. Propylene glycol/ vegetable glycerin ratio 70/30. Nicotine delivery 4.56 ng/ml after 20 puffs in 10 minutes Button‐operated device (eGO), nicotine concentration 36 mg/ml. Propylene glycol/ vegetable glycerin ratio 70/30. Nicotine delivery 6.9 ng/ml after 10 puffs in 5 minutes (refillable) |
|
| Outcomes | Visits: baseline, day 7, day 14, day 21 CO measured (day 0, 7, 14, 21); adverse events (nausea, dizziness) Also: Number of tobacco cigarettes smoked per day (self‐report); EC puffs per day (self‐report) |
|
| Study funding | This study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number P50DA036107 and the Center for Tobacco Products of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. JY is also funded by the Penn State Cancer Institute (PSCI) and TE is also supported by U54DA036105. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or the Food and Drug Administration | |
| Author declarations | JF has done paid consulting for pharmaceutical companies involved in producing smoking cessation medications, including GSK, Pfizer, Novartis, J&J, and Cypress Bioscience. TE is a paid consultant in litigation against the tobacco industry and the electronic cigarette industry and is named on a patent application for a device that measures the puffing behavior of electronic cigarette users | |
| Notes | New for 2021 update | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Used 2 ENDS in a random order – not enough information |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Unable to blind, but interventions judged equally intensive |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Objective outcome‐ CO monitoring (CO < 10 ppm) |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No loss to follow‐up |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear what outcomes were prespecified |
AE: adverse event; BMI: body mass index; CO: carbon monoxide; COT: cotinine; cpd: cigarettes per day; EC: electronic cigarette; ENDS: electronic nicotine delivery system; FTND: Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence; HRQoL: health‐related quality of life; IQR: interquartile range; ITT: intention‐to‐treat; LTFU: lost to follow‐up; MMT: methadone maintenance treatment; NEC: nicotine electronic cigarette; NRT: nicotine replacement therapy; PEC: placebo electronic cigarette; PP(A): point prevalence (abstinence); ppm: parts per million; SAE: serious adverse event; SD: standard deviation; SMI: serious mental illness; TQD: target quit date; UC: usual care
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Adkison 2013 | Although this study uses a prospective cohort design, no data on EC use were collected at baseline, with EC use data only being available at follow‐up |
| Al‐Delaimy 2015 | Observational study with no intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Anonymous 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Battista 2013 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Bianco 2019 | Ineligible intervention |
| Biener 2015 | Cohort study, but EC use evaluated retrospectively only |
| Biondi‐Zoccai 2019 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Biondi‐Zoccai 2020 | Acute EC use only |
| Borderud 2014 | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Brose 2015 | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Brown 2014a | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Bullen 2010 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Bullen 2018 | Withdrawn trial registry |
| Caponnetto 2019 | Ineligible intervention |
| Cavarretta 2019 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Chaumont 2018 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Chaumont 2019 | Ineligible intervention |
| Chausse 2015 | Ineligible study design |
| Choi 2014 | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Chorti 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Collins 2019 | Ineligible intervention |
| Cook 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Cox 2019a | Short‐term abstinence only (< 6 months) |
| Czogala 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| D'Ruiz 2017 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Dawkins 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Dawkins 2013a | Short‐term EC use only |
| Dawkins 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Douptcheva 2013 | Longitudinal study, but no data are reported for smoking cessation or reduction or for adverse events |
| Dutra 2014 | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Eissenberg 2010 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Etter 2014 | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Farsalinos 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Farsalinos 2013a | Included people that had already stopped smoking conventional cigarettes |
| Farsalinos 2013b | Short‐term EC use only |
| Farsalinos 2013c | Short‐term EC use only |
| Farsalinos 2013d | Short‐term EC use only |
| Flouris 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Flouris 2013 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Gmel 2016 | Cohort study, but EC use only evaluated retrospectively |
| Gottlieb 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Grana 2014b | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| James 2016 | Follow‐up at 12 weeks, AE data not collected |
| Kasza 2013 | Longitudinal study, but no data are reported for smoking cessation or reduction or for adverse events |
| Kouretas 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Kousta 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Lechner 2015 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Lee 2014 | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Manzoli 2015 | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Marini 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Mayor 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Meltzer 2017 | Ineligible intervention |
| Miura 2015 | Tests a device which is not an EC |
| NCT02487953 | Withdrawn trial registry |
| NCT03036644 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| NCT03575468 | Ineligible intervention |
| NCT04107779 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Nolan 2016 | Short‐term abstinence only (< 6 months) |
| NTR6224 | Study terminated early, no usable results. Previously listed as ongoing |
| Palamidas 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Pearson 2012 | Longitudinal study, but no data are reported for smoking cessation or reduction or for adverse events |
| Pokhrel 2013 | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Polosa 2014a | Observational study with no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Popova 2013 | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Prochaska 2014 | RCT but no EC intervention provided ‐ included in previous versions, but excluded from 2020 |
| Russo 2018 | Ineligible study design |
| Schober 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Siegel 2011 | Retrospective survey of 222 EC users that responded to a survey sent to 5000 new users of the 'Blu' EC. Likely to be a self‐selected sample |
| Song 2020 | Ineligible patient population |
| St.Helen 2020 | Wrong intervention |
| Stein 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
| Stower 2019 | Ineligible study design |
| Tsikrika 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Tucker 2018 | Short‐term abstinence only (< 6 months) |
| Tzatzarakis 2013 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Vakali 2014 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Valentine 2016 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Van Heel 2017 | Ineligible study design |
| Vansickel 2010 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Vansickel 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Vansickel 2013 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Vardavas 2012 | Short‐term EC use only |
| Vickerman 2013 | Cross‐sectional survey |
| Voos 2019 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Voos 2020 | Ineligible study design |
| Wagener 2014 | EC use for up to 1 week, but does not report on any adverse events |
| Walele 2016a | RCT but follow‐up too short |
| Walele 2016b | RCT but follow‐up too short |
| Yan 2015 | Ineligible study design |
| Yuki 2017 | Less than 1 week follow‐up |
| Zhang 2019 | Commentary of included study (not primary study) |
EC: electronic cigarette
Characteristics of ongoing studies [ordered by study ID]
ACTRN12617001324303.
| Study name | Vaporised nicotine products versus oral forms of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) products for tobacco smoking cessation among low‐socioeconomic status (low‐SES) people who smoke |
| Methods | Parallel, single‐blinded, randomized controlled trial Setting: Australia Recruitment: Not stated. |
| Participants | Target sample size: 868 Inclusion criteria:
The term “current smoker” in this trial will refer to those who use either factory‐made or roll‐own cigarettes. Exclusion criteria:
People will also be excluded if they report any of the following medical conditions in the previous 3 months: serious chronic lung diseases, arrhythmia, heart attack, stroke, or severe angina |
| Interventions | Vaporised nicotine product (VNP) arm:
Oral nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) arm:
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: Carbon monoxide‐verified six‐month continuous abstinence (smoking not more than 5 cigarettes) from the quit date (8 months from baseline) Secondary outcomes measured at 2‐week and 6‐week check‐in calls and 8‐month follow‐up
Weekly text message surveys and check‐in calls 2 weeks and 6 weeks into the treatment period. These check‐in calls will also assess smoking status, short‐term outcomes, and adverse events at these time points |
| Starting date | Anticipated start date: 30 April 2019 |
| Contact information | Richard P Mattick, r.mattick@unsw.edu.au Alexandra Aiken, a.aiken@unsw.edu.au |
| Notes |
ACTRN12618000408280.
| Study name | A pragmatic randomized partial cross‐over clinical trial of nicotine vaporizers added to standard care for smoking cessation and relapse prevention (CARP) among priority populations with comorbidities |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial Setting: Australia Recruitment: Not stated |
| Participants | Target sample size: 810 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes:
Secondary outcomes:
Abstinence is assessed through study‐specific survey questions in Module CS Combustible Smoking Questions – administered through electronic survey or structured telephone interview. Participants that self‐report abstinence from smoking will be asked for a urine specimen for bioconfirmation. Urine specimens will be batch‐tested for anabasine and cotinine at 6,12 and 21 month time points |
| Starting date | 5 June 2018 |
| Contact information | Malcolm Brinn, m.brinn@uq.edu.au Coral Gartner, c.gartner@uq.edu.au |
| Notes |
ACTRN12619001787178.
| Study name | Project NEAT: nicotinE As Treatment for tobacco smoking following discharge from residential withdrawal services |
| Methods | RCT Project NEAT: A randomized controlled trial to examine the efficacy of vaporised nicotine products and telephone quit line support compared with nicotine replacement therapy and telephone quit line support when used following discharge from a residential withdrawal services Setting: Australia (New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria) Recruitment 4 hospitals sites: Belmont Hospital, Belmont; St Vincent's Hospital, Darlinghurst; Turning Point Drug and Alcohol Centre, Richmond; Royal Brisbane & Womens Hospital, Herston |
| Participants | Target sample size: 926 Inclusion criteria: • Aged 18 or over • Daily tobacco smoker (10 or more cigarettes) on entering withdrawal unit • Accessing treatment from participating services • Want to quit smoking in the next 30 days • Has capacity to consent and able to understand the participant materials and follow the study instructions and procedure (e.g. sufficient English language ability and not too unwell as judged by medical staff). Exclusion criteria: • Pregnant or breast‐feeding • Enrolled in another study • Scheduled to be transferred to a long‐term residential rehabilitation service following discharge from the withdrawal unit • Used VNP (containing nicotine) in the last 30 days • Currently engaged in Quitline’s call‐back services • No ready access to a phone |
| Interventions | Condition One: Vaporised Nicotine Products and Quitline Condition Two: Current Best Practice Treatment for Tobacco Smoking (Combination Nicotine Replacement Therapy and Quitline) |
| Outcomes | 9 months after inpatient withdrawal unit discharge: Self‐reported 7 months continuous abstinence from tobacco smoking Biochemically‐verified 7‐month continuous abstinence from tobacco smoking 3 and 9 months after inpatient withdrawal unit discharge: 30‐day point prevalence abstinence 7‐day point prevalence abstinence Abstinence from all nicotine/ tobacco products |
| Starting date | Anticipated enrolment: 19 December 2019. Anticipated date last data collection 19 September 2022 |
| Contact information | Prof Billie Bonevski, Billie.Bonevski@newcastle.edu.au |
| Notes | Funding: National Health and Medical Research Council (grant number: G1800272), Canberra ACT 2601. |
Begh 2019.
| Study name | Examining the effectiveness of general practitioner and nurse promotion of electronic cigarettes versus standard care for smoking reduction and abstinence in hardcore smokers with smoking‐related chronic disease: protocol for a randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | Individually randomized, blinded, 2‐arm trial Setting: General practices, England Recruitment: Primary care registries |
| Participants | Target sample: 320 (160 per arm) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Months 2, 8 Primary outcomes:
Secondary outcomes:
|
| Starting date | November 2016 |
| Contact information | Rachna Begh, rachna.begh@phc.ox.ac.uk |
| Notes |
Berlin 2019.
| Study name | Randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, double‐dummy, multicentre trial comparing electronic cigarettes with nicotine to varenicline and to electronic cigarettes without nicotine: the ECSMOKE trial protocol |
| Methods | 3‐arm randomized, placebo‐controlled, multicentre, double‐blind, double‐dummy, parallel groups, phase III type trial Setting: Smoking cessation clinics of both academic and community hospitals Recruitment is either local (a) directly by the centres or centralized (b) using a web page and a centralized study‐specific phone number and email address
|
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 650 participants Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | A) EC without nicotine (ECwoN) plus placebo tablets of varenicline (0.50mg) administered by oral route: placebo condition; B) EC with nicotine (ECwN) plus placebo tablets of varenicline: ECwN condition. V C) Reference: ECwoN plus 0.5 mg varenicline tablets: varenicline condition. Varenicline administered according to the marketing authorization E‐cigarette details:
Behavioural support:
Treatment duration: 1 week + 3 months |
| Outcomes | Week 2, 4, 8, 10, 12, 24 after target quit day Primary outcome:
Secondary outcomes:
|
| Starting date | 17 October 2018 |
| Contact information | Ivan Berlin, ivan.berlin@aphp.fr |
| Notes |
Caponnetto 2014.
| Study name | Smoking cessation and reduction In schizophrenia (the SCARIS study) |
| Methods | 3‐arm prospective 12‐m randomized controlled trial investigating efficacy and safety of EC Setting: psychiatric and smoking cessation centres, Italy Recruitment: local newspapers and radio/television advertisements |
| Participants | 153 participants Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
|
| Interventions | 12‐wk supply of:
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up visits at 4, 8, 12, 24 and 52 weeks Outcome measures:
|
| Starting date | September 2014 |
| Contact information | Pasquale Caponnetto, p.caponnetto@unict.it |
| Notes |
Caponnetto 2020.
| Study name | Non‐inferiority trial comparing cigarette consumption, adoption rates, acceptability, tolerability, and tobacco harm reduction potential in smokers switching to Heated Tobacco Products or electronic cigarettes: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | RCT 12 weeks |
| Participants | 220 healthy people who smoke tobacco cigarettes |
| Interventions | Arm 1 ‐ Heated Tobacco Products (HTPs) Arm 2 ‐ E‐cigarettes (ECs) |
| Outcomes | 12‐week study. Follow‐up 24 weeks Biochemically‐verified self‐reported continuous abstinence at 12 weeks from the previous visit Secondary outcomes will include: smoking reduction from baseline, adoption rates and product acceptability, tolerability, changes in step test values and in the level of selected biomarkers of exposure in exhaled breath (i.e. eCO) and in spot urine samples A follow‐up visit at 24 weeks to review product usage and smoking behavior under naturalistic condition of use |
| Starting date | Recruitment May 2019, enrolment is expected to be completed in November 2019 Results to be reported in 2020 |
| Contact information | Pasquale Caponnetto, p.caponnetto@unict.it |
| Notes |
NCT03569748 Funded by Philip Morris |
Fraser 2015.
| Study name | An open‐label randomized pragmatic policy trial examining effectiveness of short‐term use of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) vs short‐ or long‐term use of NRT vs short‐ or long‐term use of NRT or electronic nicotine delivery systems for smoking cessation in cigarette smokers |
| Methods | Phase 3 blinded RCT Setting: Australia Recruitment: commercial market research panel |
| Participants | Target sample size: 1600
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | 6 m and 12 m, self‐report
|
| Starting date | February 2014 |
| Contact information | Coral Gartner, c.gartner@uq.edu.au |
| Notes |
ISRCTN13288677.
| Study name | Can electronic cigarettes and nicotine replacement treatment help reduce smoking in smokers who struggle to quit? |
| Methods | Pilot single‐centre randomized control trial Setting: Queen Mary University of London, UK Recruitment method not specified. |
| Participants | Target sample size: 200 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | 1) NRT arm:
2) EC arm:
|
| Outcomes | Participants contacted by phone at 1 week, 4 weeks and 24 weeks after the initial screening session Primary outcomes:
Secondary outcomes:
|
| Starting date | January 2017 |
| Contact information | Marzena Orzol, m.orzol@qmul.ac.uk Katie Myers‐Smith, katie.smith@qmul.ac.uk |
| Notes |
ISRCTN61193406.
| Study name | Do e‐cigarettes help smokers quit when not accompanied by intensive behavioral support? A multi‐center randomized controlled trial |
| Methods | RCT Setting: UK Multicenter. Participants will be recruited mainly from hospitals and GP practices across the UK by the Clinical Research Network. The study is being organized by Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) Researchers from QMUL will provide the study treatment and conduct follow‐up calls |
| Participants | 1170 people who smoke tobacco cigarettes Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | 1. Control: NHS Quit Now program (QN) 2. E‐cigarette starter pack with no ongoing support (EC) 3. EC starter pack with helpline support (EC+) The study will aim to use a refillable EC that is similar to the type used in a previous EC trial (One Kit ‐ Innokin, UK Ecig Store), and one that is compliant with UK regulations, and not produced by a tobacco company |
| Outcomes | Follow‐up at 4 weeks, 6 months and 12 months. CO at 6 and 12 months Primary outcome measure: Sustained smoking cessation at 6 months post‐TQD. This is measured by asking participants if they have smoked since their TQD at the 6‐month follow‐up. To be counted as a 'quitter', participants must report smoking no more than 5 cigarettes since 2 weeks post‐TQD with no smoking in the previous week, validated by carbon monoxide (CO) reading of < 8 ppm. Participants lost to follow‐up will be counted as smokers Secondary outcome measures:
|
| Starting date | Overall trial start date: 01 September 2020 Trial end date: 31 May 2024 Not yet recruiting. Last edited 12 August 2020 |
| Contact information | Dr Katie Myers Smith, katie.smith@qmul.ac.uk |
| Notes |
Klonizakis 2017.
| Study name | Smokers making a quit attempt using e‐cigarettes with or without nicotine or prescription nicotine replacement therapy: impact on cardiovascular function (ISME‐NRT) ‐ a study protocol |
| Methods | Pragmatic, 3‐group, randomized, assessor‐blinded, single‐centre trial Setting: Centre for Sport and Exercise Science (CSES) of Sheffield Hallam University, UK Recruitment: From the community in the wider Sheffield area will be by: i) low‐cost newspaper and post‐office advertisement, ii) posters in local pharmacies, libraries, mosques, churches, and clubs, iii) social media or search engine advertisement (Facebook, Google ads) iv) notices in newsletters or participation in outreach events of community organizations (such as Sheffield U3A and AGE UK), iv) a study website, and v) out‐reach events in local ethnic community centres or places of worship |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 258 participants (86 participants arm) Inclusion Criteria:
Exclusion Criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up: Within 3 days of “quit date”, 3 and 6 months past quit date Outcome measures:
|
| Starting date | 24 April 2017 |
| Contact information | Markos Klonizakis, m.klonizakis@shu.ac.uk |
| Notes |
Murray 2020.
| Study name | Yorkshire Enhanced Stop Smoking (YESS) study: a protocol for a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of adding a personalized smoking cessation intervention to a lung cancer screening program |
| Methods | RCT Setting: Yorkshire, UK |
| Participants | Anticipated recruitment: 1040 people who smoke tobacco cigarettes Participants are aged 55 – 80, registered with a general practitioner (GP) in the Leeds Clinical Commissioning Group area and registered as a current or ex‐smoker in primary care databases Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | Arm 1: enhanced, personalized smoking cessation (SC) support package, including CT scan images. SC support over 4 weeks comprising behavioral support, pharmacotherapy and/or a commercially‐available e‐cigarette Arm 2: continued standard best practice. |
| Outcomes | Follow‐up contact will be requested at 4 weeks, 3 months and 12 months, with a 2‐week window to accommodate participant availability The primary objective is to measure 7‐day point prevalent carbon monoxide (CO)‐validated SC after 3 months Secondary outcomes include CO‐validated cessation at 4 weeks and 12 months, self‐reported continuous cessation at 4 weeks, 3 months and 12 months, attempts to quit smoking and changes in psychological variables, including perceived risk of lung cancer, motivation to quit smoking tobacco, confidence and efficacy beliefs (self and response) at all follow‐up points |
| Starting date | January 2019 and December 2020 with follow‐up data collection ending December 2021 |
| Contact information | Professor Rachael L Murray; rachael.murray@nottingham. ac.uk |
| Notes |
NCT01842828.
| Study name | Spain‐UK‐Czech E‐cigarette Study (SUKCES) |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial, open‐label pilot study Setting: smoking cessation clinics in London, Madrid and Prague Recuitment: via smoking cessation clinics |
| Participants | 220 people who smoke, seeking help to quit Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes |
|
| Starting date | December 2013 |
| Contact information | Peter Hajek, p.hajek@qmul.ac.uk |
| Notes |
NCT01989923.
| Study name | Smoking cessation in women with gynecological conditions |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial, open‐label feasibility study Setting: hospital clinic, USA Recruitment: in clinic |
| Participants | 30 women who smoke with cervical dysplasia Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
Both groups receive identical cessation counseling |
| Outcomes | At 6 and 12 weeks via survey:
|
| Starting date | June 2013 |
| Contact information | Laura A Beebe, laura-beebe@ouhsc.edu |
| Notes |
NCT02004171.
| Study name | Electronic cigarettes or nicotine inhaler for smoking cessation |
| Methods | Randomized controlled trial, open‐label safety/efficacy study Setting and recruitment not specified, USA |
| Participants | 40 participants Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | 4 weeks:
|
| Outcomes | Over 4 weeks:
|
| Starting date | December 2013 |
| Contact information | Barney Vaughan, vaughan@nyspi.columbia.edu |
| Notes |
NCT02124187.
| Study name | Smoking cessation and reduction in depression (SCARID) |
| Methods | 3‐arm prospective 12‐m randomized controlled trial investigating efficacy and safety of ECs |
| Participants | 129 participants Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | 12‐wk supply of:
|
| Outcomes | Follow‐up visits at 4, 8, 12, 24 and 52 weeks Outcome measures:
|
| Starting date | February 2015 |
| Contact information | Pasquale Caponnetto p.caponnetto@unict.it |
| Notes |
NCT02398487.
| Study name | Head‐to‐head comparison of personal vaporizers versus cig‐a‐like: prospective 6‐month randomized control design study (VAPECIG 2) |
| Methods | Randomized parallel‐assignment open‐label trial Setting: Italy, community |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 200 Inclusion criteria:
Exclude if:
|
| Interventions | Comparison between 2 types of EC; 'personal vaporizers' and 'cig‐a‐like' |
| Outcomes | 24 weeks:
|
| Starting date | October 2014 |
| Contact information | Riccardo Polosa |
| Notes |
NCT02527980.
| Study name | E‐cigarettes: dynamic patterns of use and health effects |
| Methods | Prospective observational study Setting: community, USA Recruitment: People who smoke and dual EC and cigarette users |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 450 Inclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | "We will conduct a 2‐year longitudinal cohort study comprising participants who smoke exclusively CCs (n = 175) and dual users of e‐cigs and CCs (n = 275)" |
| Outcomes | "We will use state‐of‐the‐art ecological momentary assessments to determine: 1) dynamic patterns of e‐cig and CC use and related outcomes (e.g. dependence, withdrawal symptoms, CC quit attempts and quitting success); 2) episodic (affective, contextual, social) and stable person‐factor (lifestyle factors, demographics) variables that covary meaningfully with e‐cig and CC use and related outcomes; 3) biomarkers of tobacco and carcinogen exposure as well as other health‐related outcomes (e.g. reduced pulmonary function)." |
| Starting date | September 2015 |
| Contact information | PI Megan Piper |
| Notes |
NCT02590393.
| Study name | The role of nicotine and non‐nicotine alkaloids in e‐cigarette use and dependence |
| Methods | Randomized parallel‐assignment double‐blind trial Setting: Smoking research clinic, USA Recruitment: volunteers |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 375 Inclusion criteria:
Exclude if: multiple, related to baseline health status |
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Primary:
Secondary:
|
| Starting date | May 2016 |
| Contact information | Jed Rose |
| Notes | "This is not a smoking cessation study; People who smoke will not be asked to quit smoking, and e‐cigarettes will not be used as a medical device or therapy." |
NCT02635620.
| Study name | Changes in lung function parameters, bronchial reactivity, state of health and smoking behavior associated with changing from conventional smoking to electronic cigarettes |
| Methods | Prospective observational study Setting: Community, Germany Recruitment: Vape shops and smoking cessation clinics |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 80 Inclusion criteria:
Exclude if:
|
| Interventions | Comparison between:
|
| Outcomes | Primary:
|
| Starting date | October 2015 |
| Contact information | Tobias Rüther |
| Notes |
NCT03589989.
| Study name | The ESTxENDS Trial‐ Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E‐cigarette) as an aid for smoking cessation. (ESTxENDS) |
| Methods | Randomized, parallel‐assignment, open‐label trial Setting: Switzerland Recruitment: Not specified |
| Participants | Estimated Enrolment: 1172
Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcome: Continuous smoking abstinence at 6 months post‐quit date measured by:
Seconday outcomes:
|
| Starting date | 16 July 2018 |
| Contact information | Reto Auer, reto.auer@biham.unibe.ch Anna Schöni, anna.schoeni@biham.unibe.ch |
| Notes | Linked trials: NCT03603340; NCT03603353; NCT03612336; NCT03612375; NCT03612453; NCT03612544; NCT03632421; NCT03938298 |
NCT03700112.
| Study name | An open‐label, randomized cross‐over study comparing nicotine pharmacokinetics of seven electronic cigarette products and one traditional cigarette across two delivery (10 puff and ad‐libitum) conditions, in healthy adult smokers. |
| Methods | Open‐label, randomized cross‐over trial Setting and recruitment not specified, New Zealand |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 24 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Day 48 Outcomes:
|
| Starting date | 7 December 2018 |
| Contact information | Study director: Concetta Carbonaro Responsible party: Juul Labs, Inc. |
| Notes |
NCT03962660.
| Study name | Harm reduction for tobacco smoking with support of tobacco‐replacing electronic nicotine delivery systems (HaRTS‐TRENDS) |
| Methods | Parallel, randomized controlled trial Setting: USA Recruitment: from prominent Housing First programs serving chronically homeless people who are often multiply affected by psychiatric, medical and substance‐use disorders. The proposed sample will be recruited from a highly vulnerable and marginalized population in a tight‐knit urban community |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 94 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion Criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes, measured across the 12‐month follow‐up:
Secondary outcomes, measured across the 12‐month follow‐up:
Other outcomes:
|
| Starting date | 9 May 2019 |
| Contact information | Tatiana M Ubay, tatiubay@uw.edu |
| Notes |
NCT04063267.
| Study name | Electronic cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy in individuals with substance use disorder |
| Methods | Parallel, randomized trial Recruitment/Setting: Not specified |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 240 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
E‐cigarettes arm:
Nicotine Replacement Therapy arm:
|
| Outcomes | Proportion of participants who achieve 50% reduction in cpd at 3 weeks |
| Starting date | 15 September 2019 |
| Contact information | NYU Langone Health, Scott.Sherman@nyulangone.org |
| Notes |
NCT04231838.
| Study name | A randomized controlled international multicentre study evaluating changes in metabolic syndrome in smokers with type 2 diabetes mellitus after switching from tobacco cigarettes to combustion‐free nicotine delivery systems: DIASMOKE Study Short title: Metabolic syndrome in diabetic smokers using cigarettes & combustion‐free nicotine delivery systems (DIASMOKE) |
| Methods | RCT Setting: Italy |
| Participants | 576 participants Inclusion criteria: Participants will be required to satisfy all of the following criteria at the screening visit, unless otherwise stated: • Participants will be: 1.1. over 23 years of age • T2DM Patients will have: 2.1. body mass index (BMI) between 17.6 and 32.0 kg/m2, inclusive 2.2. body weight exceeding 50 kg (men) or 40 kg women 2.3 6.5 < HbA1C < 10 3.2. completion of proforma (CRF) 3.3. lab assessment as outlined in the CRF
Exclusion Criteria: Participants will be excluded at the screening visit based on the following criteria:
At screening and prior to enrolment, all patients will be offered a locally‐available free smoking cessation program as per local guidelines. Those who express the intention of booking for the cessation program together with those who, at screening, are planning to quit smoking in the next 6 months, will not be recruited into the study. Patients taking part in the study will be informed that they are free to quit smoking and withdraw from the study at any time. Any person who decides to quit smoking will be directed to local stop smoking services. |
| Interventions | Arm A: tobacco cigarettes (continuing smoking their own tobacco cigarette brand) Arm B: switching to using combustion‐free nicotine delivery systems (C‐F NDS) |
| Outcomes | Time frame: 3 months, 6 months, 1 year and 2 years Change in metabolic syndrome prevalence Change in plasma glucose Change in triglycerides Change in high‐density lipoprotein (HDL) Change in waist circumference |
| Starting date | Estimated start date: 17 September 2020. Estimated primary completion September 2021. Estimated study completion March 2025 |
| Contact information | Daniela Saitta, PhD, daniela.saitta@eclatrbc.it Riccardo Polosa, PhD, polosa@unict.it |
| Notes |
NCT04238832.
| Study name | Impact of non‐cigarette tobacco product formulation on reinforcement value and use in current smokers Short title: Salt‐Based E‐cigarette |
| Methods | RCT Setting: USA, South Carolina |
| Participants | 30 participants Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | Salt base nicotine Free base nicotine |
| Outcomes | Most preferred product [ Time Frame: Lab Visit 2, occurring approximately 1 week after the initial screening/baseline visit ] Participants complete a preference assessment in which they choose between the salt liquid, free‐base liquid, or a traditional cigarette in a series of trials. The outcome of this assessment is the product chosen most often by each participant Cigarettes per day [ Time Frame: Week 2 of study ] The average number of cigarettes smoked per day during the 1 week sampling period. Biomarkers (i.e. expired CO, cotinine) will corroborate self‐reported indices of use |
| Starting date | 23 June 2020. Estimated completion August 2021 |
| Contact information | Tracy Smith, smithtra@musc.edu |
| Notes |
NCT04452175.
| Study name | Official title: Cigarette consumption after switchinG to high or low Nicotine strENght E‐cigaretteS In Smokers with Schizophrenia spectrum disorders: a 12‐month randomized, double‐blind multicentre trial Brief title: Cigarette consumption after switchinG to high or low nicotine strENght E‐cigaretteS In Smokers with Schizophrenia (GENESIS) |
| Methods | RCT Multicenter: Italy, Russia, Ukraine, UK Collaborators:
|
| Participants | Estimated enrolment: 260 Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions |
|
| Outcomes | Primary outcomes:
Secondary outcomes
|
| Starting date | October 2020. Estimated completion date March 2022 |
| Contact information | Pasquale Caponnetto, p.caponnetto@unict.it |
| Notes |
NCT04649645.
| Study name | International randomized controlled trial evaluating changes in oral health in smokers after switching to combustion‐free nicotine delivery systems (SMILE) |
| Methods | RCT Setting: multicenter: Italy, Moldova, Poland, UK and Indonesia |
| Participants | Estimated enrolment 606 participants Inclusion criteria:
For Arms A and B, participants have to be:
For Arm C, participants have to be:
Exclusion criteria:
|
| Interventions | Standard Arm (Arm A): own tobacco cigarette brand Intervention Arm (Arm B): combustion‐free nicotine delivery system (C‐F NDS) Control Arm (Arm C): no smoking or use of any nicotine/tobacco products |
| Outcomes | Oral health parameters and teeth appearance, comparing short‐ and long‐term impact on periodontal health between smokers continuing with conventional cigarette smoking, those switching to combustion‐free nicotine delivery systems (C‐F NDS), and never‐smokers over 18 months |
| Starting date | Not yet recruiting (last updated February 2021) Estimated study start date Feb 2021. Primary completion date Feb 2023. Completion April 2023 |
| Contact information | Principal investigator: Antonio Pacino, DDS, Addendo srl, Catania, Italy info@addendo.net |
| Notes |
BMI: body mass index; CAR: continuous abstinence rate; CO: carbon monoxide; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; cpd: cigarettes per day; CVD: cardiovascular disease; EC: electronic cigarette; ECG: electrocardiogram; FTND: Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence; NNAL: carcinogen found in tobacco smoke; NRT: nicotine replacement therapy; PP(A): point prevalence (abstinence); QoL: quality of life; TQD: target quit date; wk: week; yr: year
Differences between protocol and review
The protocol did not specify a minimum follow‐up period for data on adverse events. As of the 2016 update, we have changed the Methods section to clarify that we will exclude follow‐up data at less than a week.
The original version of this review included reduction as a secondary outcome. The 2016 update removed reduction as an outcome, to bring the review into line with other reviews of cessation treatments produced by the Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group and to prevent substantial overlap with the update of the Group's review of interventions for harm reduction.
As prespecified in the 2016 update, in the 2020 update we excluded non‐intervention studies. In the 2020 update, we also added in an appendix with a protocol setting out our plans to convert this review into a living systematic review in the future.
Contributions of authors
All authors contributed to the writing of this review. For this update, JHB, NL, CN, RB, PH, NR, ARB, HMR screened studies and/or extracted data. JHB and ARB entered data for analysis.
Sources of support
Internal sources
-
Queen Mary University of London, UK
provides salary, office space and library resources for HM and PH
-
The University of Auckland, New Zealand
provides salary, office space and library resources for CB
-
University of Oxford, UK
Support from Returning Carers' Fund
External sources
-
NIHR, UK
Infrastructure award for Cochrane Tobacco Addiction Group and Cochrane Incentive Award
-
Cancer Research UK, UK
Cancer Research UK project award funding to support living systematic review
Declarations of interest
RB holds an NIHR grant, however this did not directly fund this current work. She is principal investigator of an ongoing study listed in this review.
CB was principal investigator on the ASCEND e‐cigarette trial reported in the Cochrane review and a co‐investigator on the ASCEND II trial and several other studies included in the review. CB has provided consultancy for J&J KK (Japan) on NRT products. CB reports research grants from the Health Research Council of NZ, the Heart Foundation of NZ and the NZ Ministry of Health. He has recently led a project funded by Pfizer (NZ) on chronic disease management.
ARB's work on this review has been supported by Cancer Research UK Project Award funding. This is not deemed a conflict of interest.
PH provided consultancy for and received research funding from Pfizer, a manufacturer of stop‐smoking medications. He was principal investigator on one of the trials included in this review and co‐investigator on other relevant studies.
JHB has received support for this work from the Cochrane Review Support Programme and the University of Oxford's Returning Carer's Fund. Neither of these are deemed conflicts of interest.
NL has received payment for lectures on systematic review methodology, and has been an applicant on project funding to carry out priority setting and systematic reviews in the area of tobacco control (NIHR funded). None of this is deemed a conflict of interest.
HM has received honoraria for speaking at smoking cessation educational events and sitting on an advisory board organized by Pfizer.
CN has no known conflicts of interest.
NR has received royalties from UpToDate, Inc., for chapters on electronic cigarettes and occasional fees from academic hospitals or professional medical societies for lectures on smoking cessation that include discussion of electronic cigarettes. Dr. Rigotti was an member of the committee that produced the 2018 National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine's Consensus Study Report on the Public Health Benefits of E‐cigarettes. She was unpaid for this work. Outside the topic of e‐cigarettes, Dr. Rigotti has received honoraria from Achieve Life Sciences for consulting about cytisine. NR is a consultant for Achieve LifeSciences, which is developing an investigational smoking cessation medication for FDA approval (cytisine) and her institution (MGH) receives a grant from the company as a site for a clinical trial testing the safety and efficacy of cytisine. NR has received travel reimbursement (but no honoraria) from Pfizer for attending advisory boards regarding varenicline. NR holds grants from NIH for research work.
AT's work on this review has been supported by the Cochrane Review Support Programme and the University of Oxford's Returning Carer's Fund. Neither of these are deemed conflicts of interest.
TT has no known conflicts of interest.
Edited (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Adriaens 2014 {published data only}
- Adriaens K, Van Gucht D, Declerck P, Baeyens F. Effectiveness of the electronic cigarette: an eight-week Flemish study with six-month follow-up on smoking reduction, craving and experienced benefits and complaints. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2014;11(11):11220-48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Baldassarri 2018 {published data only}
- Baldassarri SR, Bernstein SL, Chupp GL, Slade MD, Fucito LM, Toll BA. Electronic cigarettes for adults with tobacco dependence enrolled in a tobacco treatment program: a pilot study. Addictive Behaviors May 2018;80:1-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02498145. Short term effects of electronic cigarettes in tobacco dependent adults. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02498145 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Bell 2017 {unpublished data only}
- ACTRN12616001641482. Tobacco harm reduction with vaporised nicotine (THRiVe): feasibility study. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?ACTRN=12616001641482 (first received 28 November 2016).
- Bell S, Dean J, Gilks C, Boyd MA, Fitzgerald L, Mutch A, et al. Tobacco harm reduction with vaporised nicotine (THRiVe): the study protocol of an uncontrolled feasibility study of novel nicotine replacement products among people living with HIV who smoke. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2017;14(7):799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bullen 2013 {published data only}
- Bullen C, Howe C, Laugesen M, McRobbie H, Parag V, Williman J, et al. Electronic cigarettes and smoking cessation: a quandary? - Authors' reply. Lancet 2014;383(9915):408-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen C, Howe C, Laugesen M, McRobbie H, Parag V, Williman J, et al. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2013;382(9905):1629-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen C, Howe C, Laugesen M, McRobbie H, Parag V, Williman J. Do electronic cigarettes help smokers quit? Results from a randomised controlled trial [Abstract]. In: European Respiratory Society Annual Congress, 2013 September 7 - 11, Barcelona, Spain. Vol. 42. 2013:215s-[P1047].
- Bullen C, Williman J, Howe C, Laugesen M, McRobbie H, Parag V, et al. Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial of electronic cigarettes versus nicotine patch for smoking cessation. BMC Public Health 2013;13:210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien B, Knight-West O, Walker N, Parag V, Bullen C. E-cigarettes versus NRT for smoking reduction or cessation in people with mental illness: secondary analysis of data from the ASCEND trial. Tobacco Induced Diseases 2015;13(1):5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Caponnetto 2013a {published data only}
- Campagna D, Cibella F, Caponnetto P, Amaradio MD, Caruso M, Morjaria JB, et al. Changes in breathomics from a 1-year randomized smoking cessation trial of electronic cigarettes. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2016;46(8):698-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caponnetto P, Campagna D, Cibella F, Morjaria JB, Caruso M, Russo C, et al. EffiCiency and Safety of an eLectronic cigAreTte (ECLAT) as tobacco cigarettes substitute: a prospective 12-month randomized control design study. PlOS One 2013;8(6):e66317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cibella F, Campagna D, Caponnetto P, Amaradio MD, Caruso M, Russo C, et al. Lung function and respiratory symptoms in a randomized smoking cessation trial of electronic cigarettes. Clinical Science 2016;130(21):1929–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsalinos K, Cibella F, Caponnetto P, Campagna D, Morjaria JB, Battaglia E, et al. Effect of continuous smoking reduction and abstinence on blood pressure and heart rate in smokers switching to electronic cigarettes. Internal and Emergency Medicine 2016;11(1):85-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT01164072. Efficacy and safety of an electronic nicotine delivery device (e-cigarette). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01164072 (first received 16 July 2010).
- NCT01194583. Efficacy and safety of an electronic nicotine delivery device (e-cigarette) without nicotine cartridges. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01194583 (first received 3 September 2010).
- Russo C, Cibella F, Caponnetto P, Campagna D, Maglia M, Frazzetto E, et al. Evaluation of post cessation weight gain in a 1-year randomized smoking cessation trial of electronic cigarettes. Scientific Reports 2016;6:18763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Caponnetto 2013b {published data only}
- Caponnetto P, Auditore R, Russo C, Cappello GC, Polosa R. Impact of an electronic cigarette on smoking reduction and cessation in schizophrenic smokers: a prospective 12-month pilot study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2013;10(2):446-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minutolo G, Caponnetto P, Auditore R, Russo C, Polosa R. Management of smoking reduction and cessation in inpatients with schizophrenia: Impact of electronic cigarettes. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;23:S581-2. [Google Scholar]
Carpenter 2017 {published data only}
- Carpenter MJ, Heckman BW, Wahlquist AE, Wagener TL, Goniewicz ML, Gray KM, et al. A naturalistic, randomized pilot trial of e-cigarettes: uptake, exposure, and behavioral effects. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 2017;26(12):1795-803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02357173. A trial of e-cigarettes: natural uptake, patterns and impact of use. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02357173 (accessed 17 February 2016).
- Smith TT, Wahlquist AE, Heckman BW, Cummings KM, Carpenter MJ. Impact of e-cigarette sampling on cigarette dependence and reinforcement value. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2020;22(2):297-301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Czoli 2019 {published data only}
- Czoli CD, Fong GT, Goniewicz ML, Hammond D. Biomarkers of exposure among "dual users" of tobacco cigarettes and electronic cigarettes in Canada. Nicotine and Tobacco Research 2019;21(9):1259-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2020 {published and unpublished data}
- Dawkins L, Bauld L, Ford A, Robson D, Hajek P, Parrott S, et al. A cluster feasibility trial to explore the uptake and use of e-cigarettes versus usual care offered to smokers attending homeless centres in Great Britain. PLOS One 2020;15(10):e0240968. [ISRCTN14140672] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISRCTN14140672. Exploring the use and uptake of e-cigarettes for homeless smokers. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN14140672 (first received 7 November 2018).
Eisenberg 2020 {published data only}
- Eisenberg MJ, Hébert-Losier M, Windle SB, Greenspoon T, Brandys T, Fülöp T. Effect of e-cigarettes plus counseling vs counseling alone on smoking cessation: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2020;324(18):1844-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert-Losier A, Filion KB, Windle SB, Eisenberg MJ. A randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of e-cigarette use for smoking cessation in the general population: E3 trial design. Canadian Journal of Cardiology Open 2020;2(3):168-75. [NCT02417467] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02417467. Evaluating the efficacy of e-cigarette use for smoking cessation (E3) trial. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02417467 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Ely 2013 {published data only}
- Ely J. Evaluation of the use of electric cigarettes in a rural smoking cessation program. Available online at: digitalunc.coalliance.org/fedora/repository/cogru:4161 [no longer available] 2013 (accessed 1st November 2014).
Felicione 2019 {published data only}
- Felicione NJ, Enlow P, Elswick D, Long D, Sullivan CR, Blank MD. A pilot investigation of the effect of electronic cigarettes on smoking behavior among opioid-dependent smokers. Addictive Behaviors 2019;91:45-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
George 2019 {published data only}
- George J, Hussain M, Vadiveloo T, Ireland S, Hopkinson P, Struthers AD, et al. Cardiovascular effects of switching from tobacco cigarettes to electronic cigarettes. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2019;74(25):3112-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02878421. Vascular EffectS of regUlar cigarettes Versus electronIc cigarette USe (VESUVIUS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02878421 (first received 25 August 2016).
Goniewicz 2017 {published data only}
- Goniewicz ML, Gawron M, Smith DM, Peng M, Jacob P 3rd, Benowitz NL. Exposure to nicotine and selected toxicants in cigarette smokers who switched to electronic cigarettes: a longitudinal within-subjects observational study. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2017;19(2):160-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guillaumier 2018 {unpublished data only}
- ACTRN12617000849392. The QuitNic Study: a pilot study of electronic nicotine devices for smoking cessation with drug and alcohol clients. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=372198 (first received 8 June 2017).
- Bonevski B, Manning V, Wynne O, Gartner C, Borland R, Baker A, et al. QuitNic: A pilot randomised controlled trial comparing nicotine vaping products with nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation following residential detoxification. Nicotine and Tobacco Research 2021;23(3):462-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillaumier A, Manning V, Wynne O, Gartner C, Borland R, Baker AL, et al. Electronic nicotine devices to aid smoking cessation by alcohol- and drug-dependent clients: protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial. Trials 2018;19:415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2015a {published data only}
- Hajek P, Corbin L, Ladmore D, Spearing E. Adding e-cigarettes to specialist stop-smoking treatment: City of London pilot project. Journal of Addiction Research & Therapy 2015;6(244):(online ahead of print). [DOI: 10.4172/2155-6105.1000244] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2019 {published and unpublished data}
- Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, Pesola F, Myers Smith K, Bisal N, et al. A randomized trial of e-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380(7):629-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajek P, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, Pesola F, Smith KM, Bisal N, et al. E-cigarettes compared with nicotine replacement therapy within the UK Stop Smoking Services: the TEC RCT. Health Technology Assessment 2019;23(43):1-82. [ISRCTN60477608] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISRCTN60477608. The efficacy of e-cigarettes compared with nicotine replacement therapy, when used within the UK stop smoking service. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN60477608 2014 (first received 2 April 2015).
- Li J, Hajek P, Pesola F, Wu Q, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D, et al. Cost-effectiveness of e-cigarettes compared with nicotine replacement therapy in stop smoking services in England (TEC study): a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 2020;115(3):507-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Halpern 2018 {published data only}
- Halpern SD, Harhay MO, Saulsgiver K, Brophy C, Troxel AB, Volpp KG. A pragmatic trial of e-cigarettes, incentives, and drugs for smoking cessation. New England Journal of Medicine 2018;378(24):2302-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02328794. Randomized clinical trial to reduce harm from tobacco. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02357173 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Hatsukami 2020 {published and unpublished data}
- Hatsukami D, Meier E, Lindgren BR, Anderson A, Reisinger S, Norton K, et al. A randomized clinical trial examining the effects of instructions for electronic cigarette use on smoking-related behaviors, and biomarkers of exposure. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2020;22(9):1524-32. [DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntz233] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Hickling 2019 {published data only}
- Hickling LM, Perez-Iglesias R, McNeill A, Dawkins L, Moxham J, Ruffell T, et al. A pre-post pilot study of electronic cigarettes to reduce smoking in people with severe mental illness. Psychological Medicine 2019;49(6):1033-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02212041. Acceptability, patterns of use and safety of electronic cigarette in people with mental illness: a pilot study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02212041 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Holliday 2019 {published data only}
- Holliday R, Preshaw PM, Ryan V, Sniehotta FF, McDonald S, Bauld L, et al. A feasibility study with embedded pilot randomised controlled trial and process evaluation of electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation in patients with periodontitis. Pilot and Feasibility Studies 2019;5:74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISRCTN17731903. Feasibility study of e-cigarettes in periodontitis. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN17731903 (first received 27 September 2016).
Humair 2014 {published data only}
- Humair J-P, Tango R. Can e-cigarette help patients to reduce or stop smoking in primary care practice? Journal of General Internal Medicine 2014;29:S480. [Google Scholar]
Ikonomidis 2018 {published data only}
- Ikonomidis I, Vlastos D, Kourea K, Kostelli G, Varoudi M, Pavlidis G, et al. Electronic cigarette smoking increases arterial stiffness and oxidative stress to a lesser extent than a single conventional cigarette: an acute and chronic study. Circulation 2018;137(3):303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT03039920. The effects of electronic cigarette smoking on the arterial wall and endothelial glycocalyx properties of smokers. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03039920 (first received 1 February 2017).
Ikonomidis 2020 {published data only}
- Ikonomidis I, Katogiannis K, Kostelli G, Kourea K, Kyriakou E, Kypraiou A, et al. Effects of electronic cigarette on platelet and vascular function after four months of use. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2020;141:111389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ioakeimidis 2018 {published data only}
- Ioakeimidis N, Vlachopoulos C, Georgakopoulos C, Abdelrasoul M, Skliros N, Katsi V, et al. Smoking cessation rates with varenicline and electronic cigarettes in relapsed smokers with a history of acute coronary syndrome. European Heart Journal 2018;39(Suppl_1):242. [Google Scholar]
Kumral 2016 {published data only}
- Kumral TL, Saltürk Z, Yildirim G, Uyar Y, Berkiten G, Atar Y, et al. How does electronic cigarette smoking affect sinonasal symptoms and nasal mucociliary clearance? B-ENT 2016;12(1):17-21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lee 2018 {published data only}
- Lee SM, Tenney R, Wallace A, Arjojmandi M. The end perioperative smoking pilot study: a randomized trial comparing e-cigarettes versus nicotine patch. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2017;64(1 Supplement 1):S48-S49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee SM, Tenney R, Wallace AW, Arjomandi M. E-cigarettes versus nicotine patches for perioperative smoking cessation: a pilot randomized trial. PeerJ 2018;6(9):e5609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02482233. A pilot randomized controlled clinical trial - "Electronic nicotine delivery device (e-cigarette) for perioperative smoking cessation in veterans". clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02482233 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Lee 2019 {published data only}
- KCT0001277. Effect of an electronic cigarette for smoking reduction and cessation in Korean male smokers: a randomized, controlled study. KCT0001277 2014 (accessed 15 August 2016). [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lee SH, Ahn SH, Cheong YS. Effect of electronic cigarettes on smoking reduction and cessation in Korean male smokers: a randomized controlled study. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine 2019;32(4):567-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lucchiari 2020 {published data only}
- Lucchiari C, Masiero M, Mazzocco K, Veronesi G, Maisonneauve P, Jemos C, et al. Benefits of e-cigarettes in smoking reduction and in pulmonary health among chronic smokers undergoing a lung cancer screening program at 6 months. Addictive Behaviours 2020;103:106222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchiari C, Masiero M, Veronesi G, Maisonneuve P, Spina S, Jemos C, et al. Benefits of e-cigarettes among heavy smokers undergoing a lung cancer screening program: randomized controlled trial protocol. JMIR Research Protocols 2016;5(1):e21. [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiero M, Lucchiari C, Mazzocco K, Veronesi G, Maisonneuve P, Jemos C, et al. E-cigarettes may support smokers with high smoking-related risk awareness to stop smoking in the short run: preliminary results by randomized controlled trial. Nicotine and Tobacco Research 2019;21(1):119-126. [NCT02422914] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiero M, Lucchiari C, Mazzocco K, Veronesi G, Maisonneuve P Jemos C, et al. Corrigendum: E-cigarettes may support smokers with high smoking-related risk awareness to stop smoking in the short run: preliminary results by randomized controlled trial. Nicotine and Tobacco Research 2020;22(4):594-5. [NCT02422914] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02422914. Benefits of tobacco free cigarette among heavy smokers undergoing a lung cancer screening program: a randomized controlled study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02422914 (accessed 17 February 2016).
Martner 2019 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
- Martner SG, Dallery J. Technology-based contingency management and e-cigarettes during the initial weeks of a smoking quit attempt. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis 2019;52(4):928-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McRobbie 2015 {published data only}
- McRobbie H, Goniewicz M, Phillips A, Myers-Smith K, West O, Hajek P. Effects of the use of electronic cigarettes with and without concurrent smoking on acrolein delivery POS4-33. In: Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco, 20th Annual Meeting, Seattle, Washington. 2014:13. [www.srnt.org/conferences/2014/pdf/SRNT_2014_Rapids_C.pdf]
- McRobbie H, Phillips A, Goniewicz ML, Smith KM, Knight-West O, Przulj D, et al. Effects of switching to electronic cigarettes with and without concurrent smoking on exposure to nicotine, carbon monoxide, and acrolein. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2015;8(9):873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT01714778. Toxins and Delivery in E-cigarette USers (TADEUS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01714778 (first received 26 October 2012).
Meier 2017 {published data only}
- Meier E, Wahlquist AE, Heckman BW, Cummings KM, Froeliger B, Carpenter MJ. A pilot randomized crossover trial of electronic cigarette sampling among smokers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2017;19(2):176-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NCT02648178 {published data only}
- NCT02648178. Evaluation of appeal and impact of e-cigarettes among chronic smokers with smoking-related cancers. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02648178 (accessed 17 February 2016).
NCT02918630 {published data only}
- NCT02918630. E-cigarettes to promote smoking reduction among individuals with schizophrenia. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02918630 (first received 5 July 2018).
Nides 2014 {published data only}
- NCT01898169. Evaluation of short-term safety and use patterns of an electronic nicotine delivery system. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01898169 (first received 12 July 2013).
- Nides MA, Leischow SJ, Bhatter M, Simmons M. Nicotine blood levels and short-term smoking reduction with an electronic nicotine delivery system. American Journal of Health Behavior 2014;38(2):265-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Oncken 2015 {published data only}
- NCT01775787. Effects of Electronic Cigarettes on Nicotine Concentrations (ECIG). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01775787 (first received 25 January 2013).
- Oncken CA, Litt MD, McLaughlin LD, Burki NA. Nicotine concentrations with electronic cigarette use: effects of sex and flavor. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;17(4):473-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedeh MA, Oncken C, Burki NK. Acute effects of electronic cigarettes on airway function in human subjects. In: American Thoracic Society International Conference Abstracts. Vol. 189. 2014:A4089.
Ozga‐Hess 2019 {published data only}
- Ozga-Hess JE, Felicione NJ, Ferguson SG, Dino G, Elswick D, Whitworth C, et al. Piloting a clinical laboratory method to evaluate the influence of potential modified risk tobacco products on smokers' quit-related motivation, choice, and behaviour. Addictive Behaviors 2019;99:106105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pacifici 2015 {published data only}
- Pacifici R, Pichini S, Graziano S, Pellegrini M, Massaro G, Beatrice F. Successful nicotine intake in medical assisted use of e-cigarettes: a pilot study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2015;12(7):7638-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Polosa 2011 {published data only}
- NCT01195597. Smoking cessation and reduction with an electronic nicotine delivery device (ENDD). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01195597 (first received 6 September 2010).
- Polosa R, Caponnetto P, Morjaria JB, Papale G, Campagna D, Russo C. Effect of an electronic nicotine delivery device (e-cigarette) on smoking reduction and cessation: a prospective 6-month pilot study. BMC Public Health 2011;11:786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polosa R, Morjaria JB, Caponnetto P, Campagna D, Russo C, Alamo A, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of electronic cigarette in real-life: a 24-month prospective observational study. Internal and Emergency Medicine 2014;9(5):537-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Polosa 2014b {published data only}
- NCT02124200. High Cessation Rates in Smokers Using Personal Vaporizers (VAPECIG). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02124200 (first received 28 April 2014).
- Polosa R, Caponnetto P, Maglia M, Morjaria JB, Russo C. Success rates with nicotine personal vaporizers: a prospective 6-month pilot study of smokers not intending to quit. BMC Public Health 2014;14:1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Polosa 2015 {published data only}
- Polosa R, Caponnetto P, Cibella F, Le-Houezec J. Quit and smoking reduction rates in vape shop consumers: a prospective 12-month survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2015;12(4):3428-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pratt 2016 {published data only}
- Pratt SI, Sargent J, Daniels L, Santos MM, Brunette M. Appeal of electronic cigarettes in smokers with serious mental illness. Addictive Behaviors 2016;59:30-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pulvers 2018 {published data only}
- Pulvers K, Emami AS, Nollen NL, Romero DR, Strong DR, Benowitz NL, et al. Tobacco consumption and toxicant exposure of cigarette smokers using electronic cigarettes. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2018;20(2):206-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pulvers 2020 {published data only}
- Pulvers K, Nollen NL, Rice M, Schmid CH, Qu K, Benowitz NL, et al. Effect of pod e-cigarettes vs cigarettes on carcinogen exposure among African American and Latinx smokers: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw0rk Open 2020;3(11):e2026324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Scheibein 2020 {published data only}
- Scheibein F, McGirr K, Morrison A, Roche, Wells JS. An exploratory non-randomized study of a 3-month electronic nicotine delivery system (ENDS) intervention with people accessing a homeless supported temporary accommodation service (STA) in Ireland. Harm Reduction Journal 2020;17(1):73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smith 2020 {published and unpublished data}
- Smith TT, Heckman BW, Wahlquist AE, Cummings KM, Carpenter MJ. The impact of e-liquid propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin ratio on ratings of subjective effects, reinforcement value, and use in current smokers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2020;22(5):791-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stein 2016 {published data only}
- Stein MD, Caviness C, Grimone K, Audet D, Anderson BJ, Bailey GL. An open trial of electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation among methadone-maintained smokers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016;18(5):1157-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Strasser 2016 {published data only}
- Strasser AA, Souprountchouk V, Kaufmann A, Blazekovic S, Leone F, Benowitz NL, et al. Nicotine replacement, topography, and smoking phenotypes of e-cigarettes. Tobacco Regulatory Science 2016;2(4):352-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tseng 2016 {published data only}
- NCT02628964. Assessing the use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) as a harm reduction strategy. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02628964 (accessed 17 February 2016).
- Tseng TY, Ostroff JS, Campo A, Gerard M, Kirchner T, Rotrosen J, et al. A randomized trial comparing the effect of nicotine versus placebo electronic cigarettes on smoking reduction among young adult smokers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016;18(10):1937-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Valentine 2018 {published data only}
- Valentine GW, Hefner K, Jatlow PI, Rosenheck RA, Gueorguieva R, Sofuoglu M. Impact of e-cigarettes on smoking and related outcomes in veteran smokers with psychiatric comorbidity. Journal of Dual Diagnosis 2018;14(1):2-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Van Staden 2013 {published data only}
- Van Staden SR, Groenewald M, Engelbrecht R, Becker PJ, Hazelhurst LT. Carboxyhaemoglobin levels, health and lifestyle perceptions in smokers converting from tobacco cigarettes to electronic cigarettes. South African Medical Journal 2013;103(11):865-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Veldheer 2019 {published and unpublished data}
- Lopez AA, Cobb CO, Yingst JM, Veldheer S, Hrabovsky S, Yen MS, et al. A transdisciplinary model to inform randomized clinical trial methods for electronic cigarette evaluation. BMC Public Health 2016;16(1):217. [PMCID:: PMC4778292] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02342795. Randomized controlled trial methods for novel tobacco products evaluation. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02342795 (accessed 17 February 2016).
- Veldheer S, Yingst J, Midya V, Hummer B, Lester C, Krebs N, . Pulmonary and other health effects of electronic cigarette use among adult smokers participating in a randomized controlled smoking reduction trial. Addictive Behaviors 2019;91:95-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yingst J, Foulds J, Veldheer S, Cobb CO, Yen M, Hrabovsky S, et al. Measurement of electronic cigarette frequency of use among smokers participating in a randomized controlled trial. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2020;22(5):699-704. [NCT02342795] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wadia 2016 {published data only}
- Wadia R, Booth V, Yap HF, Moyes DL. A pilot study of the gingival response when smokers switch from smoking to vaping. British Dental Journal 2016;221(11):722-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walele 2018 {published data only}
- Cravo AS, Bush J, Sharma G, Savioz R, Martin C, Craige S, et al. A randomised, parallel group study to evaluate the safety profile of an electronic vapour product over 12 weeks. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2016;81:S1-S14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT02029196. A randomised, parallel group, multi-centre study to evaluate the safety profile of the ITG EVP G1 product. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02029196 (accessed 16 July 2014).
- NCT02143310. A multi-centre study to evaluate the safety of use of electronic vapour products for two years. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02143310 (accessed 16 July 2014).
- Walele T, Bush J, Koch A, Savioz R, Martin C, O'Connell G. Evaluation of the safety profile of an electronic vapour product used for two years by smokers in a real-life setting. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2018;92:226-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walker 2020 {published data only}
- NCT02521662. A randomised-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of combining nicotine patches with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) plus behavioural support, on smoking abstinence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02521662 (accessed 17 February 2016).
- Walker N, Parag V, Verbiest M, Laking G, Laugesen M, Bullen C. Nicotine patches used in combination with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) for smoking cessation: a pragmatic, randomised trial. Lancet. Respiratory Medicine 2020;8(1):54-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker N, Verbiest M, Kurdziel T, Laking G, Laugesen M, Parag V, et al. Effectiveness and safety of nicotine patches combined with e-cigarettes (with and without nicotine) for smoking cessation: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2019;9(2):e023659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yingst 2020 {published data only}
- Yingst J, Foulds J, Zurlo J, Steinberg MB, Eissenberg T, Du P. Acceptability of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) among HIV positive smokers. AIDS Care 2020;32(10):1224-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Adkison 2013 {published data only}
- Adkison SE, O'Connor RJ, Bansal-Travers M, Hyland A, Borland R, Yong HH, et al. Electronic nicotine delivery systems: international tobacco control four-country survey. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2013;44(3):207-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Al‐Delaimy 2015 {published data only}
- Al-Delaimy WK, Myers MG, Leas EC, Strong DR, Hofstetter CR. E-cigarette use in the past and quitting behavior in the future: a population-based study. American Journal of Public Health 2015;105(6):1213-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donzelli A. E-cigarettes may impair ability to quit, but other explanations are possible. American Journal of Public Health 2015;105(11):e1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Anonymous 2019 {published data only}
- Anonymous. E-cigarettes best other cessation tools. Cancer Discovery 2019;9(4):OF3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Battista 2013 {published data only}
- Battista L, Di Iorio M, Tancredi M, Acconcia MC, Torromeo C, Barilla F, et al. Cardiovascular effects of electronic cigarettes. Circulation 2013;128:A16755. [Google Scholar]
Bianco 2019 {published data only}
- Bianco CL, Pratt SI, Ferron JC, Brunette MF. Electronic cigarette use during a randomized trial of interventions for smoking cessation among Medicaid beneficiaries with mental illness. Journal of Dual Diagnosis 2019;15(3):184-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Biener 2015 {published data only}
- Biener L, Hargraves JL. A longitudinal study of electronic cigarette use among a population-based sample of adult smokers: association with smoking cessation and motivation to quit. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;17(2):127-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Biondi‐Zoccai 2019 {published data only}
- Biondi-Zoccai G, Sciarretta S, Bullen C, Nocella C, Violi F, Loffredo L, et al. Acute effects of heat-not-burn, electronic vaping, and traditional tobacco combustion cigarettes: the Sapienza University of Rome-Vascular Assessment of Proatherosclerotic Effects of Smoking ( SUR - VAPES ) 2 randomized trial. Journal of the American Heart Association 2019;8(6):e010455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Biondi‐Zoccai 2020 {published data only}
- Biondi-Zoccai G, Carnevale R, Vitali M, Tritapepe L, Martinelli O, Macrina F, et al. A randomized trial comparing the acute coronary, systemic, and environmental effects of electronic vaping cigarettes versus heat-not-burn cigarettes in smokers of combustible cigarettes undergoing invasive coronary assessment: rationale and design of the SUR-VAPES 3 trial. Minerva Cardioangiologica 2020;68(6):548-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Borderud 2014 {published data only}
- Barton MK. Electronic cigarettes did not help patients with cancer stop smoking. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2015;65(2):85-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borderud SP, Li Y, Burkhalter JE, Sheffer CE, Ostroff JS. Electronic cigarette use among patients with cancer: characteristics of electronic cigarette users and their smoking cessation outcomes. Cancer 2014;120(22):3527-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillon M. Electronic cigarettes might not help cancer patients quit smoking. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2015;107(1):496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brose 2015 {published data only}
- Brose LS, Hitchman SC, Brown J, West R, McNeill A. Is the use of electronic cigarettes while smoking associated with smoking cessation attempts, cessation and reduced cigarette consumption? A survey with a 1-year follow-up. Addiction 2015;110(7):1160-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J, West R, Beard E, Michie S, Shahab L, McNeill A. Prevalence and characteristics of e-cigarette users in Great Britain: Findings from a general population survey of smokers. Addictive Behaviors 2014;39(6):1120-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchman SC, Brose LS, Brown J, Robson D, McNeill A. Associations between e-cigarette type, frequency of use, and quitting smoking: findings from a longitudinal online panel survey in Great Britain. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;17(10):1187-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brown 2014a {published data only}
- Brown J, Beard E, Kotz D, Michie S, West R. Real-world effectiveness of e-cigarettes when used to aid smoking cessation: a cross-sectional population study. Addiction 2014;109(9):1531-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bullen 2010 {published data only}
- Bullen C, McRobbie H, Thornley S, Glover M, Lin R, Laugesen M. Effect of an electronic nicotine delivery device (e cigarette) on desire to smoke and withdrawal, user preferences and nicotine delivery: randomised cross-over trial. Tobacco Control 2010;19(2):98-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bullen 2018 {published data only}
- Bullen C, Verbiest M, Galea-Singer S, Kurdziel T, Laking G, Newcombe D, et al. The effectiveness and safety of combining varenicline with nicotine e-cigarettes for smoking cessation in people with mental illnesses and addictions: study protocol for a randomised-controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2018;18(1):596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Caponnetto 2019 {published data only}
- Caponnetto P, Maglia M, Polosa R. Efficacy of smoking cessation with varenicline plus counselling for e-cigarettes users (VAREVAPE): a protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications 2019;15:100412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cavarretta 2019 {published data only}
- Cavarretta E, Sciarretta S, Nocella C, Peruzzi M, Marullo AG, Loffredo L, et al. Subjective smoking satisfaction between heat-not-burn, electronic vaping, and traditional tobacco combustion cigarettes: a sub-analysis of the SUR-VAPES 2 trial. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology 2019;26(Supplement 1):S114. [Google Scholar]
Chaumont 2018 {published data only}
- Chaumont M, Becker B, Zaher W, Culie A, Deprez G, Melot C, et al. Differential Effects of E-Cigarette on Microvascular Endothelial Function, Arterial Stiffness and Oxidative Stress: a Randomized Crossover Trial. Scientific reports 2018;8(1):10378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chaumont 2019 {published data only}
- Chaumont M, El Channan M, Bernard A, Lesage A, Deprez G, Van Muylem A, et al. Short-term high wattage e-cigarette cessation improves cardiorespiratory outcomes in regular users: a randomized crossover trial. Journal of Hypertension 2019;Conference: 29th European Meeting on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Protection, ESH 2019. Italy. 37(Supplement 1):e8-9. [Google Scholar]
Chausse 2015 {published data only}
- Chausse P, Naughton G, Dutheil F. Electronic cigarettes: the resistance value of the heating filament could be the key to lung toxicity. Chest 2015;148(1):e29-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Choi 2014 {published data only}
- Choi K, Forster JL. Beliefs and experimentation with electronic cigarettes: a prospective analysis among young adults. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2014;6(2):175-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K Forster JL. Authors' Response to: Context on use is needed before public health recommendations are made about e-cigarettes. Americal Journal of Preventive Medicine 2014;46(6):e58-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chorti 2012 {published data only}
- Chorti M, Poulianiti K, Jamurtas A, Kostikas K, Tzatzarakis M, Vynias D, et al. Effects of active and passive electronic and tobacco cigarette smoking on lung function (P08-02). Toxicology Letters 2012;211:S64. [Google Scholar]
Collins 2019 {published data only}
- Collins SE, Nelson LA, Stanton J, Mayberry N, Ubay T, Taylor EM, et al. Harm reduction treatment for smoking (HaRT-S): findings from a single-arm pilot study with smokers experiencing chronic homelessness. Substance Abuse 2019;40(2):229-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cook 2019 {published data only}
- Cook R, Davidson P, Martin R. E-cigarettes helped more smokers quit than nicotine replacement therapy. BMJ 2019;365:l2036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cox 2019a {published data only}
- Cox S, Dawkins L, Doshi J, Cameron J. Effects of e-cigarettes versus nicotine replacement therapy on short-term smoking abstinence when delivered at a community pharmacy. Addictive Behaviors Reports 2019;10:100202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Czogala 2012 {published data only}
- Czogala J, Cholewinski M, Kutek A, Zielinska-Danch W. Evaluation of changes in hemodynamic parameters after the use of electronic nicotine delivery systems among regular cigarette smokers. Przeglad Lekarski 2012;69(10):841-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
D'Ruiz 2017 {published data only}
- D'Ruiz CD, O'Connell G, Graff DW, Yan XS. Measurement of cardiovascular and pulmonary function endpoints and other physiological effects following partial or complete substitution of cigarettes with electronic cigarettes in adult smokers. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2017;87:36-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2012 {published data only}
- Dawkins L, Turner J, Hasna S, Soar K. The electronic-cigarette: effects on desire to smoke, withdrawal symptoms and cognition. Addictive Behaviors 2012;37(8):970-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2013a {published data only}
- Dawkins L, Turner J, Crowe E. Nicotine derived from the electronic cigarette improves time-based prospective memory in abstinent smokers. Psychopharmacology 2013;227(3):377-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2014 {published data only}
- Dawkins L, Corcoran O. Acute electronic cigarette use: nicotine delivery and subjective effects in regular users. Psychopharmacology 2014;231(2):401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Douptcheva 2013 {published data only}
- Douptcheva N, Gmel G, Studer J, Deline S, Etter JF. Use of electronic cigarettes among young Swiss men. Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health 2013;67(12):1075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dutra 2014 {published data only}
- Dutra LM, Glantz SA. Electronic cigarettes and conventional cigarette use among U.S. adolescents: a cross-sectional study. JAMA Pediatrics 2014;168(7):610-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Eissenberg 2010 {published data only}
- Eissenberg T. Electronic nicotine delivery devices: ineffective nicotine delivery and craving suppression after acute administration. Tobacco Control 2010;19(1):87-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Etter 2014 {published data only}
- Etter JF, Bullen C. A longitudinal study of electronic cigarette users. Addictive Behaviors 2014;39(2):491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2012 {published data only}
- Farsalinos K, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Savvopoulou M, Avramidou E, Vasilopoulou D, et al. Acute effects of using an electronic nicotine-delivery device (e-cigarette) on myocardial function: comparison with the effects of regular cigarettes. European Heart Journal 2012;33:203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsalinos KE, Romagna G, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Voudris V. Acute effects of using an electronic nicotine-delivery device (electronic cigarette) on myocardial function: comparison with the effects of regular cigarettes. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders 2014;14:78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2013a {published data only}
- Farsalinos KE, Romagna G, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Voudris V. Evaluating nicotine levels selection and patterns of electronic cigarette use in a group of "vapers" who had achieved complete substitution of smoking. Substance Abuse: Research and Treatment 2013;7:139-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2013b {published data only}
- Farsalinos KE, Romagna G, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Spyrou A, Voudris V. Impact of flavour variability on electronic cigarette use experience: an internet survey. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 2013;10(12):7272-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2013c {published data only}
- Farsalinos K, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Stefopoulos C, Spyrou A, Tsakalou M, et al. Immediate effects of electronic cigarette use on coronary circulation and blood carboxyhemoglobin levels: comparison with cigarette smoking. European Heart Journal 2013;34(Suppl 1):13. [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2013d {published data only}
- Farsalinos K, Tsiapras D, Kyrzopoulos S, Spyrou A, Stefopoulos C, Romagna G, et al. Effects of electronic cigarette use on the elastic properties of the ascending aorta in healthy subjects: comparison with the effects of tobacco cigarettes. European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging 2013;14(Suppl 2):ii203. [Google Scholar]
Flouris 2012 {published data only}
- Flouris AD, Poulianiti KP, Chorti MS, Jamurtas AZ, Kouretas D, Owolabi EO, et al. Acute effects of electronic and tobacco cigarette smoking on complete blood count. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2012;50(10):3600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Flouris 2013 {published data only}
- Flouris AD, Chorti MS, Poulianiti KP, Jamurtas AZ, Kostikas K, Tzatzarakis MN, et al. Acute impact of active and passive electronic cigarette smoking on serum cotinine and lung function. Inhalation Toxicology 2013;25(2):91-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gmel 2016 {published data only}
- Gmel G, Baggio S, Mohler-Kuo M, Daeppen JB, Studer J. E-cigarette use in young Swiss men: is vaping an effective way of reducing or quitting smoking? Swiss Medical Weekly 2016;146:w14271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gottlieb 2019 {published data only}
- Gottlieb MA. E-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy for smoking cessation. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380(20):1974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grana 2014b {published data only}
- Grana RA, Popova L, Ling PM. A longitudinal analysis of electronic cigarette use and smoking cessation. JAMA Internal Medicine 2014;174(5):812-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
James 2016 {published data only}
- James SA, Meier EM, Wagener TL, Smith KM, Neas BR, Beebe LA. E-Cigarettes for immediate smoking substitution in women diagnosed with cervical dysplasia and associated disorders. International Journal of Environmental Health Research 2016;13(3):E288. [DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13030288] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT01842828. E-Cigarettes as an addition to multi-component treatment for tobacco dependence: a pilot study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01842828 (accessed 16 July 2014).
Kasza 2013 {published data only}
- Kasza KA, Bansal-Travers M, O'Connor RJ, Compton WM, Kettermann A, Borek N, et al. Cigarette smokers' use of unconventional tobacco products and associations with quitting activity: findings from the ITC-4 U.S. cohort. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2013;16(6):672-81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kouretas 2012 {published data only}
- Kouretas D, Poulianiti K, Chorti M, Jamurtas A, Kostikas K, Tzatzarakis M, et al. Effects of electronic cigarette and tobacco cigarette smoking on complete blood count (P08-03). Toxicology Letters 2012;211:S64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kousta 2019 {published data only}
- Kousta S. E-cigarettes for smoking cessation. Nature Human Behaviour 2019;3:322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lechner 2015 {published data only}
- Lechner WV, Meier E, Wiener JL, Grant DM, Gilmore J, Judah MR, et al. The comparative efficacy of first- versus second-generation electronic cigarettes in reducing symptoms of nicotine withdrawal. Addiction 2015;110(5):862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lee 2014 {published data only}
- Lee S, Grana RA, Glantz SA. Electronic cigarette use among Korean adolescents: a cross-sectional study of market penetration, dual use, and relationship to quit attempts and former smoking. Journal of Adolescent Health 2014;54(6):684-90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Manzoli 2015 {published data only}
- Manzoli L, Flacco ME, Fiore M, La Vecchia C, Marzuillo C, Gualano MR, et al. Electronic cigarettes efficacy and safety at 12 months: cohort study. PLOS One 2015;10(6):e0129443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoli L, La Vecchia C, Flacco ME, Capasso L, Simonetti V, Boccia S, et al. Multicentric cohort study on the long-term efficacy and safety of electronic cigarettes: study design and methodology. BMC Public Health 2013;13(1):883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT01785537. The efficacy and safety of electronic cigarettes: a 5-year follow-up study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01785537 (first received 7 February 2013).
Marini 2014 {published data only}
- Marini S, Buonanno G, Stabile L, Ficco G. Short-term effects of electronic and tobacco cigarettes on exhaled nitric oxide. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2014;278(1):9-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mayor 2019 {published data only}
- Mayor S. E-cigarettes help twice as many smokers quit as nicotine replacement therapy, trial finds. BMJ 2019;364:l473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Meltzer 2017 {published data only}
- Meltzer LR, Simmons VN, Sutton SK, Drobes DJ, Quinn GP, Meade CD, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a smoking cessation self-help intervention for dual users of tobacco cigarettes and e-cigarettes: intervention development and research design. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2017;60:56-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Miura 2015 {published data only}
- Miura N, Yuki D, Minami N, Kakehi A, Futama Y. A study to investigate changes in the levels of biomarkers of exposure to selected cigarette smoke constituents in Japanese adult male smokers who switched to a non-combustion inhaler type of tobacco product. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2015;71(3):498-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NCT02487953 {published data only}
- NCT02487953. Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) as a smoking cessation treatment. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02487953 (first received 2 July 2015).
NCT03036644 {published data only}
- NCT03036644. Comparison of electronic cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes on cardiovascular function and oxidative stress. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03036644 (first received 30 January 2017).
NCT03575468 {published data only}
- NCT03575468. Enhanced e-cigarette coaching intervention for dual users of cigarettes and e-cigarettes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03575468 (first received 2 July 2018).
NCT04107779 {published data only}
- NCT04107779. Changes in biomarkers of cigarette smoke exposure after switching either exclusively or partly to JUUL ENDS. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04107779 (first received 27 September 2019).
Nolan 2016 {published data only}
- Nolan M, Leischow S, Croghan I, Kadimpati S, Hanson A, Schroeder D, et al. Feasibility of electronic nicotine delivery systems in surgical patients. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016;18(8):1757-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NTR6224 {published data only}
- NTR6224. Electronic cigarettes: an intervention for dual-users. www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=NTR6224 (first received 12 January 2017).
Palamidas 2014 {published data only}
- Palamidas A, Gennimata SA, Kaltsakas G, Tsikrika S, Vakali S, Gratziou C, et al. Acute effect of an e-cigarette with and without nicotine on lung function. Tobacco Induced Diseases 2014;12(Suppl 1):A34. [Google Scholar]
Pearson 2012 {published data only}
- Pearson JL, Richardson A, Niaura RS, Vallone DM, Abrams DB. E-cigarette awareness, use, and harm perceptions in US adults. American Journal of Public Health 2012;102(9):1758-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pokhrel 2013 {published data only}
- Pokhrel P, Fagan P, Little MA, Kawamoto CT, Herzog TA. Smokers who try e-cigarettes to quit smoking: findings from a multiethnic study in Hawaii. American Journal of Public Health 2013;103(9):e57-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Polosa 2014a {published data only}
- Polosa R, Morjaria J, Caponnetto P, Caruso M, Strano S, Battaglia E, et al. Effect of smoking abstinence and reduction in asthmatic smokers switching to electronic cigarettes: evidence for harm reversal. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health 2014;11(5):4965-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Popova 2013 {published data only}
- Ling PM, Popova L. Novel "Tobacco" product use and association with smoking cessation: a national study. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2012;27(2 Suppl):S254. [Google Scholar]
- Popova L, Ling PM. Alternative tobacco product use and smoking cessation: a national study. American Journal of Public Health 2013;103(5):923-30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Prochaska 2014 {published data only}
- Prochaska JJ, Grana RA. E-cigarette use among smokers with serious mental illness. PLOS One 2014;9(11):e113013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Russo 2018 {published data only}
- Russo C, Cibella F, Mondati E, Caponnetto P, Frazzetto E, Caruso M, et al. Lack of substantial post-cessation weight increase in electronic cigarettes users. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018;15(4):581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schober 2014 {published data only}
- Schober W, Szendrei K, Matzen W, Osiander-Fuchs H, Heitmann D, Schettgen T, et al. Use of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) impairs indoor air quality and increases FeNO levels of e-cigarette consumers. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health 2014;217(6):628-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Siegel 2011 {published data only}
- Siegel MB, Tanwar KL, Wood KS. Electronic cigarettes as a smoking-cessation tool: results from an online survey. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2011;40(4):472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Song 2020 {published data only}
- Song M-A, Reisinger SA, Freudenheim JL, Brasky TM, Mathe EA, McElroy JP, et al. Effects of electronic cigarette constituents on the human lung: a pilot clinical trial. Cancer Prevention Research 2020;13(2):145-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
St.Helen 2020 {published data only}
- StHelen G, Nardone N, Addo N, Dempsey D, Havel C, Jacob P, et al. Differences in nicotine intake and effects from electronic and combustible cigarettes among dual users. Addiction 2020;115(4):757-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stein 2019 {published data only}
- Stein JH, Korcarz CE. E-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy for smoking cessation. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380(20):1973-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Stower 2019 {published data only}
- Stower H. E-cigarettes to help smoking cessation. Nature Medicine 2019;25(3):358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tsikrika 2014 {published data only}
- Tsikrika S, Vakali S, Gennimata SA, Palamidas A, Kaltsakas G, Koulouris N, et al. Short term use of an e-cig: influence on clinical symptoms, vital signs and eCO levels. Tobacco Induced Diseases 2014;12(Suppl 1):A30. [Google Scholar]
Tucker 2018 {published data only}
- Tucker MR, Laugesen M, Bullen C, Grace RC. Predicting short-term uptake of electronic cigarettes: effects of nicotine, subjective effects, and simulated demand. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2018;20(10):1265-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tzatzarakis 2013 {published data only}
- Tzatzarakis MN, Tsitoglou KI, Chorti MS, Poulianiti KP, Jamurtas AZ, Koutedakis Y, et al. Acute and short term impact of active and passive tobacco and electronic cigarette smoking on inflammatory markers. Toxicology Letters 2013;221(Suppl):S86. [Google Scholar]
Vakali 2014 {published data only}
- Vakali S, Tsikrika S, Gennimata SA, Kaltsakas G, Palamidas A, Koulouris N, et al. E-cigarette acute effect on symptoms and airway inflammation: comparison of nicotine with a non-nicotine cigarette. Tobacco Induced Diseases 2014;12(Suppl 1):A35. [Google Scholar]
Valentine 2016 {published data only}
- Valentine GW, Jatlow PI, Coffman M, Nadim H, Gueorguieva R, Sofuoglu M. The effects of alcohol-containing e-cigarettes on young adult smokers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2016;159:272-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Van Heel 2017 {published data only}
- Van Heel M, Van Gucht D, Vanbrabant K, Baeyens F. The importance of conditioned stimuli in cigarette and e-cigarette craving reduction by e-cigarettes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2017;14(2):193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vansickel 2010 {published data only}
- Vansickel AR, Cobb CO, Weaver MF, Eissenberg TE. A clinical laboratory model for evaluating the acute effects of electronic "cigarettes": nicotine delivery profile and cardiovascular and subjective effects. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 2010;19(8):1945-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vansickel 2012 {published data only}
- Vansickel AR, Weaver MF, Eissenberg T. Clinical laboratory assessment of the abuse liability of an electronic cigarette. Addiction 2012;107(8):1493-500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vansickel 2013 {published data only}
- Vansickel AR, Eissenberg T. Electronic cigarettes: effective nicotine delivery after acute administration. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2013;15(1):267-70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vardavas 2012 {published data only}
- Vardavas CI, Anagnostopoulos N, Kougias M, Evangelopoulou V, Connolly GN, Behrakis PK. Short-term pulmonary effects of using an electronic cigarette: Impact on respiratory flow resistance, impedance, and exhaled nitric oxide. Chest 2012;141(6):1400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vickerman 2013 {published data only}
- Vickerman KA, Carpenter KM, Altman T, Nash CM, Zbikowski SM. Use of electronic cigarettes among state tobacco cessation quitline callers. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2013;15(10):1787-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Voos 2019 {published data only}
- Voos N, Kaiser L, Mahoney MC, Bradizza CM, Kozlowski LT, Benowitz NL, et al. Randomized within-subject trial to evaluate smokers' initial perceptions, subjective effects and nicotine delivery across six vaporized nicotine products. Addiction 2019;114(7):1236-48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Voos 2020 {published data only}
- Voos N, Smith D, Kaiser L, Mahoney MC, Bradizza CM, Kozlowski LT, et al. Effect of e-cigarette flavors on nicotine delivery and puffing topography: results from a randomized clinical trial of daily smokers. Psychopharmacology 2020;237(2):491-502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wagener 2014 {published data only}
- Wagener TL, Meier E, Hale JJ, Oliver ER, Warner ML, Driskill LM, et al. Pilot investigation of changes in readiness and confidence to quit smoking after e-cigarette experimentation and 1 week of use. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2014;16(1):108-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walele 2016a {published data only}
- Walele T, Sharma G, Savioz R, Martin C, Williams J. A randomised, crossover study on an electronic vapour product, a nicotine inhalator and a conventional cigarette. Part A: Pharmacokinetics. Regulatory Toxicity 2016;74:187-92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Walele 2016b {published data only}
- Walele T, Sharma G, Savioz R, Martin C, Williams J. A randomised, crossover study on an electronic vapour product, a nicotine inhalator and a conventional cigarette. Part B: Safety and subjective effects. Regulatory Toxicity 2016;74:193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yan 2015 {published data only}
- Yan XS, D'Ruiz C. Effects of using electronic cigarettes on nicotine delivery and cardiovascular function in comparison with regular cigarettes. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2015;71(1):24-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yuki 2017 {published data only}
- Yuki D, Sakaguchi C, Kikuchi A, Futamura Y. Pharmacokinetics of nicotine following the controlled use of a prototype novel tobacco vapor product. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2017;87(2):30-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zhang 2019 {published data only}
- Zhang Y, Upson D. E-cigarettes versus nicotine-replacement therapy for smoking cessation. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380(20):1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12617001324303 {published data only}
- ACTRN12617001324303. Vaporised nicotine products versus oral forms of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) products for tobacco smoking cessation among low-socioeconomic status (low-SES) smokers. anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12617001324303.aspx (first received 15 September 2017).
ACTRN12618000408280 {published data only}
- ACTRN12618000408280. Cessation and Relapse Prevention (CARP) Trial: Nicotine vaporisers compared to standard nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation among people with co-morbidities. www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12618000408280.aspx (first received 21 March 2018).
ACTRN12619001787178 {published data only}
- ACTRN12619001787178. Project NEAT: nicotinE As Treatment for tobacco smoking following discharge from residential withdrawal services. www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ACTRN12619001787178 (first received 18 November 2019).
Begh 2019 {published data only}
- Begh R, Coleman T, Yardley L, Barnes R, Naughton F, Gilbert H, et al. Examining the effectiveness of general practitioner and nurse promotion of electronic cigarettes versus standard care for smoking reduction and abstinence in hardcore smokers with smoking-related chronic disease: protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2019;20(1):659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISRCTN59404712. GP/nurse promotion of e-cigarettes in supporting reduced smoking and cessation in smokers. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN59404712 (first received 28 November 2017).
Berlin 2019 {published data only}
- Berlin I, Dautzenberg B, Lehmann B, Palmyre J, Liégey E, De Rycke Y, et al. Randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, double-dummy, multicentre trial comparing electronic cigarettes with nicotine to varenicline and to electronic cigarettes without nicotine: the ECSMOKE trial protocol. BMJ Open 2019;9(5):e028832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT03630614. Randomized trial of electronic cigarettes with or without nicotine in smoking cessation (ECSMOKE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03630614 (first received 15 August 2018).
Caponnetto 2014 {published data only}
- Caponnetto P, Polosa R, Auditore R, Minutolo G, Signorelli M, Maglia M, et al. Smoking cessation and reduction in schizophrenia (SCARIS) with e-cigarette: study protocol for a randomized control trial. Trials [electronic resource] 2014;15:88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT01979796. Antismoking effects of rlectronic cigarettes in subjects with schizophrenia and their potential influence on cognitive functioning: design of a randomized trial. Smoking Cessation And Reduction In Schizophrenia (The SCARIS Study). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01979796 (accessed 16 July 2014).
Caponnetto 2020 {published data only}
- Caponnetto P, Caruso M, Maglia M, Emma R, Saitta D, Busa B, et al. Non-inferiority trial comparing cigarette consumption, adoption rates, acceptability, tolerability, and tobacco harm reduction potential in smokers switching to Heated Tobacco Products or electronic cigarettes: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications 2020;8:17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fraser 2015 {unpublished data only}
- ACTRN12612001210864. An open-label randomised pragmatic policy trial examining effectiveness of short-term use of Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) vs short- or long-term use of NRT vs short- or long-term use of NRT or electronic nicotine delivery systems for smoking cessation in cigarette smokers. ACTRN12612001210864 (accessed 15 August 2016).
- Fraser D, Borland R, Gartner C. Protocol for a randomised pragmatic policy trial of nicotine products for quitting or long-term substitution in smokers. BMC Public Health 2015;15:1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ISRCTN13288677 {published data only}
- ISRCTN13288677. Can electronic cigarettes and nicotine replacement treatment help reduce smoking in smokers who struggle to quit? www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN13288677 (first received 17 March 2017).
ISRCTN61193406 {published data only}
- ISRCTN61193406. Do e-cigarettes help smokers quit when not accompanied by intensive behavioural support? www.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=ISRCTN61193406 2020 (first received 11 August 2020). [Google Scholar]
Klonizakis 2017 {published data only}
- Klonizakis M, Crank H, Gumber A, Brose LS. Smokers making a quit attempt using e-cigarettes with or without nicotine or prescription nicotine replacement therapy: Impact on cardiovascular function (ISME-NRT) - a study protocol. BMC Public Health 2017;17(1):293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCT03061253. E-cigarettes and cardiovascular function (ISME-NRT). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03061253 (first received 23 February 2017).
Murray 2020 {published data only}
- Murray RL, Brain K, Britton J, Quinn-Scoggins HD, Lewis S, McCutchan GM, et al. Yorkshire Enhanced Stop Smoking (YESS) study: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial to evaluate the effect of adding a personalised smoking cessation intervention to a lung cancer screening programme. BMJ Open 2020;10(9):e037086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NCT01842828 {published data only}
- NCT01842828. E-Cigarettes as an addition to multi-component treatment for tobacco dependence: a pilot study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01842828 (accessed 16 July 2014).
NCT01989923 {published data only}
- NCT01989923. Immediate smoking cessation for patients at risk for cervical dysplasia, cervical cancer and lower genital tract dysplasia and cancer - a feasibility study comparing nicotine replacement therapy with the electronic nicotine delivery system. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01989923 (accessed 16 July 2014).
NCT02004171 {published data only}
- NCT02004171. Electronic nicotine delivery devices (ENDDs) or nicotine inhaler for smoking cessation. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02004171 (accessed 16 July 2014).
NCT02124187 {published data only}
- NCT02124187. Smoking cessation and reduction in depression (SCARID). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02124187 (accessed 16 July 2014).
NCT02398487 {published data only}
- NCT02398487. Head-to-head comparison of personal vaporizers versus cigalike: prospective 6-month randomized control design study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02398487 (accessed 17 February 2016).
NCT02527980 {published data only}
- NCT02527980. E-cigarettes: dynamic patterns of use and health effects. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02527980 (accessed 17 February 2016).
NCT02590393 {published data only}
- NCT02590393. The role of nicotine and non-nicotine alkaloids in e-cigarette use and dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02590393 (accessed 17 February 2016).
NCT02635620 {published data only}
- NCT02635620. Changes in lung function parameters, bronchial reactivity, state of health and smoking behaviour associated with changing from conventional smoking to electronic cigarettes. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02635620 (accessed 17 February 2016).
NCT03589989 {published data only}
- NCT03589989. The ESTxENDS Trial- Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cigarette) as an aid for smoking cessation. (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03589989 (first received 18 July 2018).
- NCT03603340. The ESTxENDS Trial- Effects of using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) on depression (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03603340 (first received 27 July 2018).
- NCT03603353. The ESTxENDS Trial- Effects of using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) on sleep quality. (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03603353 (first received 27 July 2018).
- NCT03612336. The ESTxENDS Trial- Metabolic effects of using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03612336 (first received 2 August 2018).
- NCT03612375. ESTxENDS Trial-Oxidative stress induced by Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) measured in urine (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03612375 (first received 2 August 2018).
- NCT03612453. ESTxENDS Trial- Oxidative stress induced by Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) measured in EBC (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03612453 (first received 2 August 2018).
- NCT03612544. The ESTxENDS Trial- Toxins from using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03612544 (first received 2 August 2018).
- NCT03632421. The ESTxENDS Trial-effects of using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) on respiratory symptoms (ESTxENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03632421 (first received 15 August 2018).
- NCT03938298. The ESTxENDS Trial: Pulmonary function substudy (PulmENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/nct03938298 (first received 6 May 2019).
- NCT04236791. The ESTxENDS Trial- Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems as an aid for smoking cessation-extension of follow-up. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04236791 2020 (first received 22 January 2020). [Google Scholar]
- NCT04244773. ESTxENDS Trial: MN Substudy - Micronuclei in buccal epithelium, a surrogate measure of future cancer risk, induced by Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04244773 (first receved 28 January 2020). [Google Scholar]
- NCT04617444. The ESTxENDS Trial- Effects of using Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS/Vaporizer/E-cig) on olfactory function. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04617444 (first received 05 November 2020). [Google Scholar]
NCT03700112 {published data only}
- NCT03700112. Clinical study comparing 7 ENDS products and 1 combustible cigarette using 2 delivery methods. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03700112 (first received 7 December 2018).
NCT03962660 {published data only}
- NCT03962660. Harm Reduction for Tobacco Smoking with support of Tobacco-Rreplacing Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (HaRTS-TRENDS). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT03962660 (first received 24 May 2019).
NCT04063267 {published data only}
- NCT04063267. Electronic cigarettes as a harm reduction strategy in individuals with substance use disorder. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04063267 (first received 21 August 2019).
NCT04231838 {published data only}
- NCT04231838. Metabolic syndrome in diabetic smokers using cigarettes & combustion-free nicotine delivery systems. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04231838 (first received 18 January 2020). [Google Scholar]
NCT04238832 {published data only}
- NCT04238832. Salt-based e-cigarette and IQOS Study. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04238832 (firs treceived 18 January 2020). [Google Scholar]
NCT04452175 {published data only}
- NCT04452175. Cigarette consumption after switchinG to high or low nicotine strENght E-cigaretteS In Smokers With Schizophrenia (GENESIS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04452175 2020 (first received 30 June 2020). [Google Scholar]
NCT04649645 {published data only}
- NCT04649645. International randomized controlled trial evaluating changes in oral health in smokers after switching to combustion-free nicotine delivery systems. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04649645 (first received 02 December 020). [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Akiyama 2021
- Akiyama Y, Sherwood N. Systematic review of biomarker findings from clinical studies of electronic cigarettes and heated tobacco products. Toxicology Reports 2021;8:282-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Amato 2020
- Amato L, Cruciani F, Solimini R, Barca A, Pacifici R, Davoli M. Effects of electronic cigarettes on health: a systematic review of the available evidence. Recenti Progressi in Medicina 2020;111(1):30-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
ASH 2019
- Action on Smoking and Health. Use of electronic cigarettes (vapourisers) among adults in Great Britain. ash.org.uk/information-and-resources/fact-sheets/statistical/use-of-e-cigarettes-among-adults-in-great-britain-2019/ (accessed 21 July 2020).
Balfour 2004
- Balfour D. The neurobiology of tobacco dependence: a preclinical perspective on the role of dopamine projections to the nucleus. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2004;6(6):899-912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barbeau 2013
- Barbeau AM, Burda J, Siegel M. Perceived efficacy of e-cigarettes versus nicotine replacement therapy among successful e-cigarette users: a qualitative approach. Addiction: Science & Clinical Practice 2013;8(1):5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Barrett 2010
- Barrett SP. The effects of nicotine, denicotinized tobacco, and nicotine-containing tobacco on cigarette craving, withdrawal, and self-administration in male and female smokers. Behavorial Pharmacology 2010;21(2):144-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Benowitz 2010
- Benowitz NL. Nicotine addiction. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;362(24):2295-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Besaratinia 2019
- Besaratinia A, Tommasi S. Vaping: a growing global health concern. EClinicalMedicine 2019;17:100208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Blount 2020
- Blount BC, Karwowski MP, Shields PG, Morel-Espinosa M, Valentin-Blasini L, Gardner M, et al. Vitamin E acetate in bronchoalveolar-lavage fluid associated with EVALI. New England Journal of Medicine 2020;382(8):697-705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Brooker 2019
- Brooker J, Synnot A, McDonald S, Elliott J, Turner T, et al. Guidance for the production and publication of Cochrane living systematic reviews: Cochrane Reviews in living mode;December 2019. community.cochrane.org/sites/default/files/uploads/inline-files/Transform/201912_LSR_Revised_Guidance.pdf (accessed 30 July 2020).
Cahill 2016
- Cahill K, Lindson-Hawley N, Thomas K, Fanshawe TR, Lancaster T. Nicotine receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 5. Art. No: CD006103. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006103.pub7] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
CDC 2020
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. Outbreak of lung injury associated with the use of e-cigarette, or vaping, products. www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/e-cigarettes/severe-lung-disease.html#latest-outbreak-information Feb 2020 (accessed 12 Aug 2020).
Chen 2016
- Chen C, Zhuang YL, Zhu SH. E-cigarette design preference and smoking cessation: a U.S. population study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2016;51(3):356-63. [DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2016.02.002] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Covidence [Computer program]
- Veritas Health Innovation Covidence. Version accessed 30 July 2020. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation. Available at covidence.org.
Cox 2017
- Cox S, Jakes S. Nicotine and e-cigarettes: rethinking addiction in the context of reduced harm. International Journal of Drug Policy 2017;44:84-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cox 2019b
- Cox S, Leigh NJ, Vanderbush TS, Choo E, Goniewicz ML, Dawkins L. An exploration into "do-it-yourself" (DIY) e-liquid mixing: sers' motivations, practices and product laboratory analysis. Addictive Behaviors Reports 2019;9:100151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2013b
- Dawkins L, Turner J, Roberts A, Soar K. 'Vaping' profiles and preferences: an online survey of electronic cigarette users. Addiction 2013;108(6):1115-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2016
- Dawkins LE, Kimber CF, Doig M, Feyerabend C, Corcoran O. Self-titration by experienced e-cigarette users: blood nicotine delivery and subjective effects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2016;233(14-16):2933-41. [DOI: 10.1007/s00213-016-4338-2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dawkins 2018
- Dawkins L, Cox S, Goniewicz M, McRobbie H, Kimber C, Doig M, et al. 'Real-world' compensatory behaviour with low nicotine concentration e-liquid: subjective effects and nicotine, acrolein and formaldehyde exposure. Addiction 2018;113(10):1874-82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donny 2007
- Donny EC, Houtsmuller E, Stitzer ML. Smoking in the absence of nicotine: behavioral, subjective and physiological effects over 11 days. Addiction 2007;102(2):324-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donny 2009
- Donny EC, Jones M. Prolonged exposure to denicotinized cigarettes with or without transdermal nicotine. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2009;104(1-2):23-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Donny 2015
- Donny EC, Denlinger RL, Tidey JW, Koopmeiners JS, Benowitz NL, Vandrey RG, et al. Randomized trial of reduced-nicotine standards for cigarettes. New England Journal of Medicine 2015;373(14):1340-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Du 2020
- Du Y, Liu B, Xu G, Rong S, Sun Y, Wu Y, et al. Association of electronic cigarette regulations with electronic cigarette use among adults in the United States. JAMA Network Open 2020;3(1):e1920255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
E‐cigarette ontology 2021
- E-cigarette v1. Qeios. [URL: www.qeios.com/read/0WX80U]
Etter 2011
- Etter JF, Bullen C. Electronic cigarette: users profile, utilization, satisfaction and perceived efficacy. Addiction 2011;106(11):2017-28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
European Parliament 2014
- European Parliament and Council of the European Union. Directive 2014/40/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 3 April 2014 on the approximation of the laws, regulations and administrative provisions of the Member States concerning the manufacture, presentation and sale of tobacco and related products and repealing Directive 2001/37/EC. 2014 (accessed 25th November 2014). [PubMed]
Fagerström 2004
- Fagerström KO, Hughes JR. Nicotine concentrations with concurrent use of cigarettes and nicotine replacement: a review. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2004;4(Suppl 2):S73-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Farsalinos 2014
- Farsalinos KE, Polosa R. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of electronic cigarettes as tobacco cigarette substitutes: a systematic review. Therapeutic Advances in Drug Safety 2014;5(2):67-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goniewicz 2012
- Goniewicz ML, Kuma T, Gawron M, Knysak J, Kosmider L. Nicotine levels in electronic cigarettes. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2012;15(1):158-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Goniewicz 2014
- Goniewicz ML, Hajek P, McRobbie H. Nicotine content of electronic cigarettes, its release in vapour and its consistency across batches: regulatory implications. Addiction 2014;109(3):500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 30 July 2020. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). Available at gradepro.org.
Hajek 1999
- Hajek P, West R, Foulds J, Nilsson F, Burrows S, Meadow A. Randomized comparative trial of nicotine polacrilex, a transdermal patch, nasal spray, and an inhaler. Archives of Internal Medicine 1999;159(17):2033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2014
- Hajek P, Etter J-F, Benowitz N, Eissenberg T, McRobbie H. Electronic cigarettes: review of use, content, safety, effects on smokers and potential for harm and benefit. Addiction 2014;109(11):1801-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2015b
- Hajek P, Goniewicz ML, Phillips A, Myers Smith K, West O, McRobbie H. Nicotine intake from electronic cigarettes on initial use and after 4 weeks of regular use. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;17(2):175-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2017
- Hajek P, Przulj D, Phillips A, Anderson R, McRobbie H. Nicotine delivery to users from cigarettes and from different types of e-cigarettes. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2017;234(5):773-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hajek 2020
- Hajek P, Pittaccio K, Pesola F, Myers Smith K, Phillips-Waller A, Przulj D. Nicotine delivery and users' reactions to Juul compared with cigarettes and other e-cigarette products. Addiction 2020;115(6):1141-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hall 2020
Hammond 2020
- Hammond D, Rynard VL, Reid JL. Changes in prevalence of vaping among youths in the United States, Canada, and England from 2017 to 2019. JAMA Pediatrics 2020;174(8):797-800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartmann‐Boyce 2018a
- Hartmann-Boyce J, Chepkin SC, Ye W, Bullen C, Lancaster T. Nicotine replacement therapy versus control for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 5. Art. No: CD000146. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000146.pub5] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartmann‐Boyce 2018b
- Hartmann-Boyce J, Fanshawe TR, Lindson N, Livingstone-Banks J, Ordonez-Mena J, Aveyard P. Behavioural interventions for smoking cessation: an overview and network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 12. Art. No: CD013229. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013229] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartmann‐Boyce 2019
- Hartmann-Boyce J, Hong B, Livingstone-Banks J, Wheat H, Fanshawe TR. Additional behavioural support as an adjunct to pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 6. Art. No: CD009670. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009670.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartnett 2020
- Hartnett KP, Kite-Powell A, Patel MT, Haag BL, Sheppard MJ, Dias TP, et al. Syndromic surveillance for e-cigarette, or vaping, product use-associated lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 2020;382(8):766-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003;327(7414):557-60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Higgins 2021
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2021. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hitchman 2015
- Hitchman SC, Brose LS, Brown J, Robson D, McNeill A. Associations between e-cigarette type, frequency of use, and quitting smoking: findings from a longitudinal online panel survey in Great Britain. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2015;17(10):1187-94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Huang 2019
- Huang J, Duan Z, Kwok J, Binns S, Vera LE, Kim Y, et al. Vaping versus JUULing: how the extraordinary growth and marketing of JUUL transformed the US retail e-cigarette market. Tobacco Control 2019;28(2):146-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hughes 2004
- Hughes JR, Keely J, Naud S. Shape of the relapse curve and long-term abstinence among untreated smokers. Addiction 2004;99(1):29-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jiang 2016
- Jiang N, Chen J, Wang MP, McGhee SM, Kwong AC, Lai VW, et al. Electronic cigarette awareness and use among adults in Hong Kong. Addictive Behaviors 2016;52:34-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Levin 1993
- Levin ED, Behm F, Carnahan E, LeClair R, Shipley R, Rose JE. Clinical trials using ascorbic acid aerosol to aid smoking cessation. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1993;33(3):211-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lindson 2019
- Lindson N, Chepkin SC, Ye W, Fanshawe TR, Bullen C, Hartmann-Boyce J. Different doses, durations and modes of delivery of nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 4. Art. No: CD013308. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013308] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Martinez‐Morata 2021
- Martinez-Morata I, Sanchez TR, Shimbo D, Navas-Acien A. Electronic cigarette use and blood pressure endpoints: a systematic review. Current Hypertension Reports 2021;23(1):1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McDonald 2020
- McDonald CF, Jones S, Beckert L, Bonevski B, Buchanan T, Bozier J, et al. Electronic cigarettes: a position statement from the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand. Respirology 2020 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
McNeill 2021
- McNeill A, Brose LS, Calder R, Bauld L, Robson D. Vaping in England: an evidence update including vaping for smoking cessation, February 2021: a report commissioned by Public Health England London, UK: Public Health England. assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/962221/Vaping_in_England_evidence_update_February_2021.pdf 2021.
McRobbie 2016
- McRobbie H, Przulj D, Smith KM, Cornwall D. Complementing the standard multicomponent treatment for smokers with denicotinized cigarettes: a randomized trial. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016;18(5):1134-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
NASEM 2018
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, Health and Medicine Division, Board on Population Health and Public Health Practice. Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US), 2018. [Google Scholar]
Notley 2018a
- Notley C, Colllins R. Redefining smoking relapse as recovered social identity - secondary qualitative analysis of relapse narratives. Journal of Substance Use 2018;23(6):660-6. [Google Scholar]
Notley 2018b
- Notley C, Ward E, Dawkins L, Holland R. The unique contribution of e-cigarettes for tobacco harm reduction in supporting smoking relapse prevention. Harm Reduct J 2018;15(1):31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Palipudi 2016
- Palipudi KM, Mbulo L, Morton J, Bunnell R, Blutcher-Nelson G, Kosen S, et al. Awareness and current use of electronic cigarettes in Indonesia, Malaysia, Qatar, and Greece: findings from 2011–2013 global adult tobacco surveys. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2016;18(4):501-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Patnode 2021
- Patnode CD, Henderson JT, Coppola EL, Melnikow J, Durbin S, Thomas RG. Interventions for tobacco cessation in adults, including pregnant persons: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2021;325(3):280-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perkins 2010
- Perkins KA, Karelitz JL, Conklin CA, Sayette MA, Giedgowd GE. Acute negative affect relief from smoking depends on the affect situation and measure but not on nicotine. Biological Psychology 2010;67(8):707-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pickworth 1999
- Pickworth WB, Fant RV, Nelson RA, Rohrer MS, Henningfield JE. Pharmacodynamic effects of new de-nicotinized cigarettes. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 1999;1(4):357-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Przulj 2013
- Przulj D, McRobbie H, Hajek P. The effect of sensorimotor replacement on smoking cessation and craving. Open Addiction Journal 2013;5:41-50. [Google Scholar]
RCP 2016
- Tobacco Advisory Group of the Royal College of Physicians. Nicotine Without Smoke—Tobacco Harm Reduction. London: Royal College of Physicians, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Romeu 2020
- Romeu ER. Voke® nicotine inhaler for smoking cessation and reduction. ntag.nhs.uk/docs/app/NTAG-Apprasial-Voke-nicotine-inhalator-Feb-2020-final-for-web.pdf 2020.
Rose 1985
- Rose JE, Tashkin DP, Ertle A, Zinser MC, Lafer R. Sensory blockade of smoking satisfaction. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior 1985;23(2):289-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rose 1993
- Rose JE, Behm FM, Levin ED. Role of nicotine dose and sensory cues in the regulation of smoke intake. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior 1993;44(4):891-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rose 1994
- Rose JE, Behm FM. Inhalation of vapor from black pepper extract reduces smoking withdrawal symptoms. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1994;34(3):225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rose 2000
- Rose JE, Behm FM, Westman EC, Johnson M. Dissociating nicotine and nonnicotine components of cigarette smoking. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior 2000;67(1):71-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rose 2006
- Rose JE. Nicotine and nonnicotine factors in cigarette addiction. Psychopharmacology 2006;184(3-4):274-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Russell 1990
- Russell MA. Nicotine intake and its control over smoking. In: Wonnacott S, Russell MA, Stolerman I, editors(s). Nicotine Psychopharmacology: Molecular, Cellular and Behavioural Aspects. London: Oxford University Press, 1990:374-418. [Google Scholar]
Schneider 2001
- Schneider NG, Olmstead RE, Franzon MA, Lunell E. The nicotine inhaler: clinical pharmacokinetics and comparison with other nicotine treatments. Clinical Pharmcokinetics 2001;40(9):661-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smets 2019
- Smets J, Baeyens F, Chaumont M, Adriaens K, Van Gucht D. When less is more: vaping low-nicotine vs. high-nicotine e-liquid is compensated by increased wattage and higher liquid consumption. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019;16(5):723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Talih 2020
- Talih S, Salman R, El-Hage R, Karam E, Salam S, Karaoghlanian N, et al. A comparison of the electrical characteristics, liquid composition, and toxicant emissions of JUUL USA and JUUL UK e-cigarettes. Scientific Reports 2020;10(1):7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tattan‐Birch 2020
- Tattan-Birch H, Brown J, Shahab L, Jackson SE. Association of the US outbreak of vaping-associated lung injury with perceived harm of e-cigarettes compared with cigarettes. JAMA Network Open 2020;3(6):e206981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
USPFTS 2021
Walker 2012
- Walker N, Howe C, Bullen C, Grigg M, Glover M, McRobbie H, et al. The combined effect of very low nicotine content cigarettes, used as an adjunct to usual Quitline care (nicotine replacement therapy and behavioural support), on smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 2012;107(10):1857-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wang 2021
- Wang RJ, Bhadriraju S, Glantz SA. E-Cigarette Use and Adult Cigarette Smoking Cessation: A Meta-Analysis. American Journal of Public Health 2021;111:230-46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Westman 1995
- Westman EC, Behm FM, Rose JE. Airway sensory replacement combined with nicotine replacement for smoking cessation. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial using a citric acid inhaler. Chest 1995;107(5):1358-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Westman 1996
- Westman EC, Behm FM, Rose JE. Dissociating the nicotine and airway sensory effects of smoking. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior 1996;53(2):309-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yingst 2019a
- Yingst JM, Foulds J, Veldheer S, Hrabovsky S, Trushin N, Eissenberg TT, et al. Nicotine absorption during electronic cigarette use among regular users. PLOS One 2019;14(7):e0220300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yingst 2019b
- Yingst JM, Hrabovsky S, Hobkirk A, Trushin N, Richie JP Jr, Foulds J. Nicotine absorption profile among regular users of a pod-based electronic nicotine delivery system. JAMA Network Open 2019;2(11):e1915494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Zhang 2021
- Zhang YY, Bu FL, Dong F, Wang JH, Zhu SJ, Zhang XW, et al. The effect of e-cigarettes on smoking cessation and cigarette smoking initiation: an evidence-based rapid review and meta-analysis. Tobacco Induced Diseases 2021;19(4). [DOI: 10.18332/tid/131624] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Hartmann‐Boyce 2016
- Hartmann-Boyce J, McRobbie H, Bullen C, Begh R, Stead LF, Hajek P. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 9. Art. No: CD010216. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hartmann‐Boyce 2020
- Hartmann-Boyce J, McRobbie H, Lindson N, Bullen C, Begh R, Theodoulou A, et al. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 10. Art. No: CD010216. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub4] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McRobbie 2012
- McRobbie H, Bullen C, Hajek P. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation and reduction. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 11. Art. No: CD010216. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
McRobbie 2014
- McRobbie H, Bullen C, Hartmann-Boyce J, Hajek P. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation and reduction. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 12. Art. No: CD010216. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010216.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


