Abstract
With the advent of the aging society, how to grow old healthily has become an important issue for the whole of society. Effective intervention strategies for healthy aging are most desired, due to the complexity and diversity of genetic information, it is a pressing concern to find a single drug or treatment to improve longevity. In this study, long-term administration of triterpenoids of Ganoderma lucidum (TGL) can mitigate brain physiological decline in normal aging mice. In addition, the age-associated pathological features, including cataract formation, hair loss, and skin relaxation, brown adipose tissue accumulation, the β-galactosidase staining degree of kidney, the iron death of spleen, and liver functions exhibit improvement. We used the APP/PS1 mice and 3 × Tg-AD mice model of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) to further verify the improvement of brain function by TGL and found that Ganoderic acid A might be the effective constituent of TGL for anti-aging of the brain in the 3 × Tg-AD mice. A potential mechanism of action may involve the regulation of sphingolipid metabolism, prolonging of telomere length, and enhance autophagy, which allows for the removal of pathological metabolites.
Keywords: Ganoderma lucidum, triterpenoids, aging, mTOR pathway, sphingolipid metabolism
Introduction
The physiological function of human organs gradually declines with aging, and the brain is no exception, as it shows a decline in learning ability, memory, attention, decision-making speed, sensory perception (i.e., vision, hearing, touch, smell, and taste), and motor coordination (Mattson and Arumugam, 2018). As individuals age, there is a decline in many cognitive skills, including executive function, working memory (especially task switching), and episodic memory (van Geldorp et al., 2015). It is hard for old people to understand fast language and complex sentences due to cognitive decline and hearing loss (Parker et al., 2006; Puvill et al., 2016; Maharani et al., 2018). Age-related decline in brain function occurs at about the same time as a decline in activity in other organs and then accelerates significantly after age 50 (Bowtell et al., 2017). Thus, keeping the brain in a normal physiological state is an important index used to evaluate healthy aging in terms of activities of daily living.
When individuals enter their 60, 70, and/or 80 s, physiological aging is accompanied by an increase in the potential for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Mattson and Arumugam, 2018; Jia et al., 2020). Aging is also a major risk factor for stroke (Mancino et al., 2018; Hou et al., 2019). The proportion of individuals over age 65 in most industrialized countries is increasing rapidly, and this age group is considered to be at the ‘risk period’ for higher rates of AD, PD, and stroke (Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018; Jia et al., 2020). It has been estimated that over 12 million Americans will be diagnosed with AD in the next 30 years. The number of deaths caused by AD has increased by 70% in the United States between 2000 and 2013 (Strydom et al., 2018). Currently, there are about 1 million people with PD in the United States (Abeliovich and Gitler, 2016; Marras et al., 2018), and every year, about 12 million people experience strokes while nearly 3 million people die (Sarraj et al., 2020). The aging process in China is much faster than we imagined, in which more than 249 million elderly people over the age of 60, which account for 17.88% of the total population and make China the country with the largest aging population in the world (Chen et al., 2019). In 2005, the prevalence of AD was reported to be 3.5% following a large-sample, population-based survey in four regions including rural and urban areas (Zhang et al., 2005). Two large-sample, multi-region studies have been performed: the first was in 2014 and the second in 2019. Studies have shown that the prevalence of dementia was 5.14% (95% confidence interval (CI) 4.71–5.57) in 2014 and 5.60% (95% CI 3.50–7.60) in 2019 for individuals aged 65 years or older (Jia et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2019). Due to the aging of Chinese society, the current incidence of dementia may be higher (Jia et al., 2020). The latest global burden of disease study in 2019 showed that the prevalence of age-standardized dementia in China increased by 5.6% from 1990 to 2016, and the global prevalence increased by 1.7% (Afshin et al., 2019; Feigin et al., 2019; Zhou et al., 2019). Therefore, effective intervention strategies for healthy aging are most desired, especially in China.
Thanks to the developments in science and technology, many characteristics of the aging brain have been identified at the cellular, molecular, and even global organ level, including the following: (1) mitochondrial dysfunction (A. Grimm and Eckert, 2017; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018; Stockburger et al., 2018); (2) protein, nucleic acid, and lipid damage and accumulation by oxidation in cells (A. Grimm and Eckert, 2017; Tse and Herrup, 2017; Zucca et al., 2017; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); (3) energy metabolism disorders (Yin et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018; Shetty et al., 2019); (4) impaired cellular “waste disposal” mechanisms (autophagy-lysosome and proteasome dysfunction) (Lipinski et al., 2010; Ling and Salvaterra, 2011; Yang et al., 2014; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); (5) impaired adaptive stress response signaling pathways (Yin et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018; Lautrup et al., 2019); (6) DNA repair impairments (Maynard et al., 2015; Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); (7) abnormal neural network activity (Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); (8) dysregulation of neuronal calcium ion levels (van Geldorp et al., 2015; Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); (9) stem cell depletion (Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018); and (10) increased inflammatory responses (Puvill et al., 2016; Mattson and Arumugam, 2018). Cell senescence and telomere wear are two markers of proliferative peripheral tissue senescence in humans and may occur in some types of glial cells in the brain (Conklin et al., 2018; Anitha et al., 2019), but this remains to be confirmed. Thus, any diet, exercises, medicines, interventions, and composite strategies on improving the indicators mentioned above are valuable as therapeutic interventions to be investigated.
Sun Simiao, a famous Chinese physician and considered the ancient pharmaceutical King of Chinese Medicine, sustained that for disease prevention, food intervention is to be the first approach, followed by the homology of medicine and food, and lastly drugs. Thus, the homology of medicine and food is one of the most popular choices in Asian countries. Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) is a traditional Chinese medicine with a history dating back thousands of years. As medicine and food homologous resource, it has been widely used in Asian countries, such as China, Japan, and Korea, for tranquilizing and prolonging life effects (Klupp et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2019). No serious toxic side effects of G. lucidum have been reported at present (Klupp et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2019), and some studies and reviews have indicated that G. lucidum is safe, tolerable, and free of toxic effects (Wachtel-Galor et al., 2004; Klupp et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2019; Zeng et al., 2019; Phu et al., 2020). However, additional well-designed, large-scale randomized control trials also need to be performed to evaluate its short- and long-term pharmacological and toxicological effects.
Ganoderma lucidum is rich in triterpenoids (Supplementary Table 1) and exerts pharmacological activities in the heart, liver, spleen, and brain (Supplementary Tables 2, 3). In this study, the effects of long-term administration of TGL were evaluated in 8-month normal aging mice and lasting for another 10 months, observing the effect of TGL on the brain of normal aging mice. Besides, this also includes age-associated physiological indices: eye function (cataract formation), hair loss and skin relaxation, brown adipose tissue accumulation, the β-galactosidase staining degree of the kidney, and the iron death of the spleen. The potential therapeutic effects of TGL on age related-diseases were evaluated in the APP/PS1 and 3 × Tg-AD transgenic mouse model to verify the mechanism of TGL to improve brain damage.
Materials and Methods
TGL Preparation
Triterpenoids of Ganoderma lucidum preparation was carried out as follows [refer to Supplementary Figure 1A for the extraction process; the Ganoderma triterpene (ganoderenic acids B, C, and D and ganoderic acids A, B, C2, D, G, and H) content of each compound is shown in Supplementary Figure 1B and Supplementary Table 1] (Lai et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021): we crushed the common feed for mice, mixed the 1 Kg feed with 2 g TGL extract evenly, added a small amount of pure water to dilute and rub, cut this into small pieces, and dried them at 60°C, and then the administered TGL feed was ready.
Animals and Treatments
Normal Aging
C57 BL/6 mice (aged 25 weeks) were obtained from the Center of Laboratory Animal of Guangdong Province (SCXK [Yue] 2008-0020, SYXK [Yue] 2008-0085) and were housed in plastic cages in a temperature-controlled (25 ± 2°C) colony room, exposed to a 12/12-h light/dark cycle. Food and water were available ad libitum. All experimental protocols were approved by the Center of Laboratory Animals of the Guangdong Institute of Microbiology.
We divided 100 mice into four groups evenly: Female control group, Female TGL group, Male control group, and Male TGL group. After 8 months of normal feeding, we began the administration of TGL. The mice of the control group were fed with a standard diet, and the mice of the TGL groups were fed a diet containing triterpenes of G. lucidum. Water was available ad libitum. These treatments lasted 10 months, some aging mice died in a 10-month experiment, thus the final number of mice and the specific grouping strategy depends on Figure 1A. The younger group (12 weeks, acclimate for at least 1 week) received no treatment and was used only for comparison in metabolomics analysis.
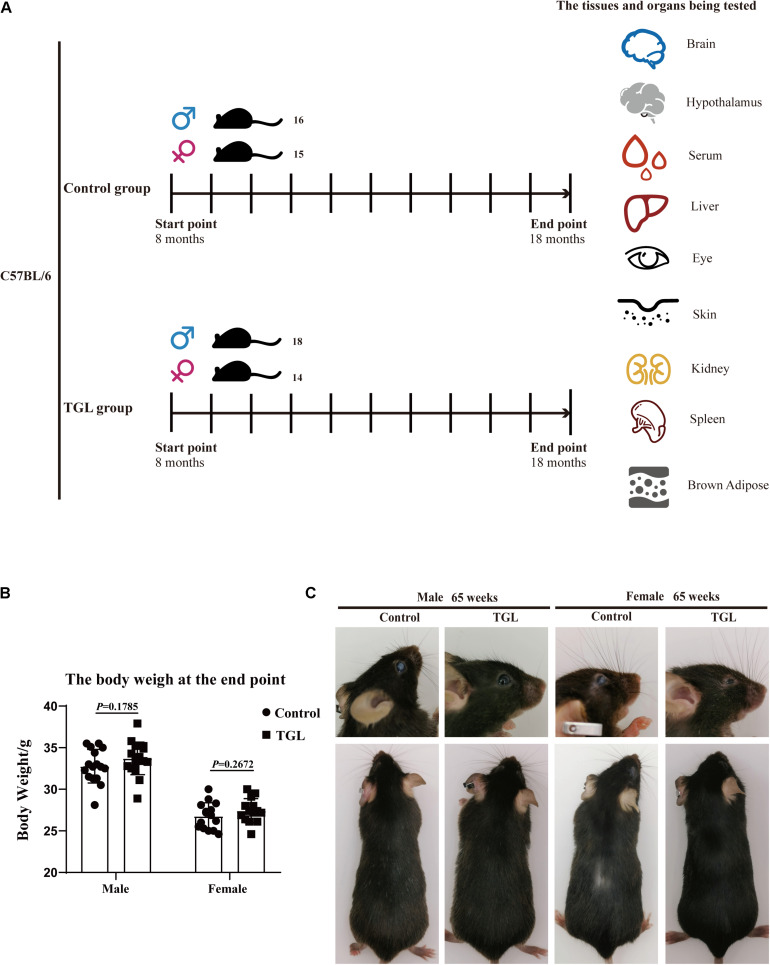
FIGURE 1.
Graphical abstract and Experimental procedure in normal aged mice. (A) Experimental procedure in normal aged mice; (B) TGL shows no significant effects on the bodyweight of normal aged mice; (C) TGL shows an improvement in eyes and hair in normal aged mice. n ≥ 14.
Blood was collected through the venous sinus of the eye-orbit after the animals were anesthetized. The blood was left at room temperature for 2 h, then centrifuged (3500 rpm, 10 min, 4°C), collected serum, equalized, and stored at −80°C. After blood sample collection, lacrimal gland, cornea, skin, brown adipose, spleen, and some brain tissue were removed, fixed in neutral formalin, dehydrated, and cleared. The samples were then mounted in paraffin and cut into sections for histological assessment; Kidney and liver tissue were stored at −80°C to prepare frozen sections; Besides 3 per group hypothalamus were placed in RNA protective solution; The remaining brain tissues were stored at −80°C after liquid nitrogen treatment.
APP/PS1 Double Transgenic Mouse Preparation and Treatment
Thirty male APP/PS1 transgenic mice (2 months of age) were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co., LTD. The mean bodyweight of the mice was 20 ± 5 g. Animals were allowed to acclimate for at least 4 weeks before the initiation of the experiment. APP/PS1 transgenic mice were randomly allocated into three groups of 10: AD model (Model, M), low-dose group (oral TGL at 25 mg/[kg/d]) (TGLL), and the high-dose group (oral TGL at 100 mg/[kg/d]) (TGLH). Then ten C57BL/6J male mice (9 months of age) purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co., LTD., was utilized as the control group (Normal, N). The Control group and Model group were treated with equal volumes of distilled water. TGL was suspended in distilled water, and i.g once a day for 24 weeks. The steps for blood collection and hypothalamus removal are the same as above.
3 × Tg-AD Mouse Preparation and Treatment
A total of 16 male 3 × Tg-AD mice (129-Tg (APPSwe, tauP301L)1Lfa Psen1tm1Mpm/Mmjax, 6 weeks of age) were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co., LTD. The mean bodyweight of the mice was 20 ± 5 g. Mice were randomly allocated into two groups of eight: Control group (Control), GA group (GA). A 10 mg/kg/d dose of ganodenic acid A, which was suspended in distilled water was administered to the GA group. The control group was treated with equal volumes of distilled water, and this lasted for 12 weeks. The steps for blood collection are the same as above, and brain tissues were stored at −80°C after liquid nitrogen treatment.
Histopathology
Paraffin sections were gradually dewaxed to water. We strictly followed the procedures or instructions of HE staining, the Prussian blue iron staining Kit, and the Tunel Cell Apoptosis Detection Kit (which required repair in EDTA or sodium citrate solution at high temperature if the formalin soaking time is too long). Oil red O staining and β-galactosidase staining used frozen tissue sections. See the kit instructions on the Key resources table. Observe with the microscope and capture images, the images were analyzed by using ImageJ software (NIH).
Western Blot Analysis
We referred to the protocol described on the Thermo Fisher website1 or Affinity Biosciences website2. Global brain tissue was dissected from normal aging mice and 3 × Tg-AD mice, and proteins were extracted with radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (Thermo ScientificTM T-PERTM Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent, 78510). The proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes followed by incubation with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody (1:10000). The antibodies can be seen in the key resources table. Band intensity was quantified using ImageJ software.
Transcriptome Sequencing
We took the hypothalamus tissues of normal aging mice and APP/PS1 mice; total RNA was extracted with a TRIzol reagent kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). RNA concentration and purity were measured using NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, United States). RNA integrity was assessed using the RNA Nano 6000 Assay Kit of the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, United States). A total amount of 1 μg RNA per sample was used as input material for the RNA sample preparations. Sequencing libraries were generated using NEBNext UltraTM RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (NEB, United States) following manufacturer’s recommendations, and index codes were added to attribute sequences to each sample. The clustering of the index-coded samples was performed on a cBot cluster generation system using TruSeq PE Cluster Kit v4-cBot-HS (Illumina) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After cluster generation, the library preparations were sequenced on an Illumina platform and paired-end reads were generated. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis use KEGG database3.
Unsupervised Metabolomics Analysis
Sample Preparation
Volumes of 120 μL frozen serum aliquots were mixed with 480 μL extraction solution by mixing methanol and acetonitrile (2:1). The extraction solution contained two standards (2-chloro-L-phenylalanine and decanoic acid). Samples were vortexed for 120 s and then placed at 4°C for 30 min. Following centrifugation for 10 min at 14000 rpm, the supernatant was split into two aliquots (250 μL each aliquot), and one of the supernatant aliquots was used for analysis and one for backup. The aliquot to be analyzed was dried via evaporation in Labconco Centrivap Console and was then dissolved in 125 μL 50% methanol and centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was moved to 200 μL MicroSert Insert for analysis.
Brain tissue (100 mg) was homogenized in 1000 μL extraction solution by mixing methanol acetonitrile (2:1), then placed at 4°C for 30 min. The extraction solution contained two standards (2-chloro-L-phenylalanine and decanoic acid). Following centrifugation for 10 min at 14000 rpm, the supernatant was split into two aliquots (400 μL each aliquot), one of the supernatant aliquots was used for analysis and the other was stored for backup. The aliquot used for analysis was dried via evaporation in Labconco Centrivap Console and then was dissolved in 200 μL 50% methanol and centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was moved to 200 μL MicroSert Insert for analysis.
Mass Spectroscopy Analysis
Sample extraction and reconstitution were performed in solvents compatible with positive and negative ionization modes and all modes were run on a Thermo UltiMate 3000 RSLC and a Thermo Scientific Q-Exactive Focus high-resolution mass spectrometer. The heated electrospray ion source of mass spectroscopy (MS) was maintained at 300°C. The capillary temperature was maintained at 320°C for both positive and negative injections. The spray voltage was 3.5 KV for positive injections and 3.2 KV for negative injections. The flow rates of sheath gas and auxiliary gas for both positive and negative injections were 45 (arbitrary units) and 8 (arbitrary units), respectively. The scan model was Full MS/dd-MS2. The mass resolution of full-MS and dd-MS2 for both positive and negative injections were set to 35,000 and 17,500, respectively. MS/MS normalized collision energy was set to 20, 40, and 60 eV. The instrument scanned 70–1050 m/z. Both positive and negative ion modes were operated with a 2.7 μm particle using a 2.1 mm × 100 mm Waters CORTECS T3 column. The column temperature was maintained at 40°C. In the positive ion mode, the sample extracts were gradient-eluted at 400 μL/min using (A) 0.1% formic acid in water and (B) 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (2% B-25% B in 3.5 min, 25% B-100% B in 15 min, 100% B for 3 min). In the negative ion mode, the sample extracts were gradient-eluted at 400 μL/min using (A) water and (B) acetonitrile (2% B-25% B in 3.5 min, 25% B-100% B in 15 min, 100% B for 3 min).
Statistical Analysis
All data are described as the means ± standard deviations (SD) of at least three independent experiments. The significant differences between treatments were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or T-Test at p < 0.05. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, Abacus Concepts, Berkeley, CA, United States) and Prism 8 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, United States) software were used for all statistical analyses. The levels of significance were set at ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns means no significance.
Results
Weight and Appearance Changes
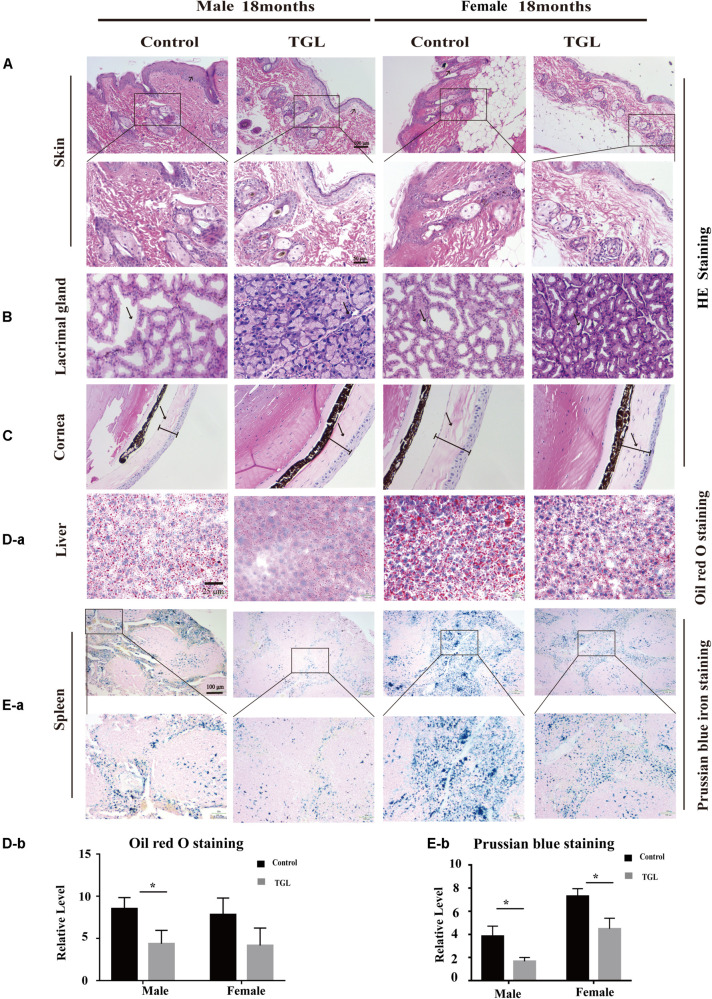
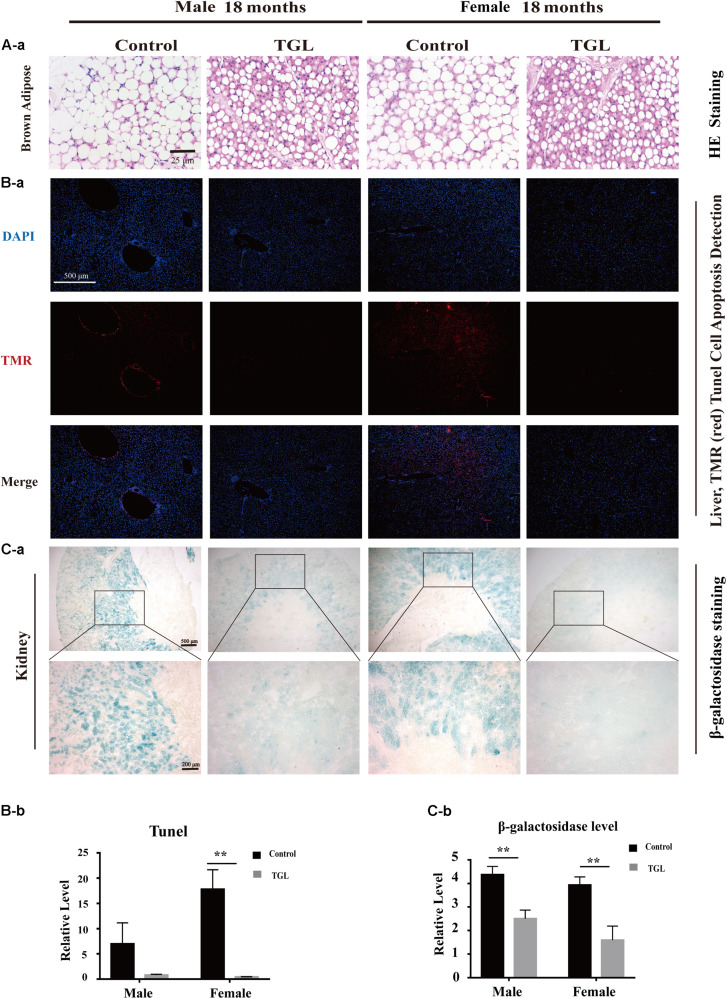
In this study, we found there were no significant differences in weight between the TGL-treated group and the control group, regardless of sex (Figure 1B), but the female TGL-treated group had a slender body shape. The condition of the skin is an important indicator of aging (Bonte et al., 2019), we found that the TGL-treated group has smoother fur after 10 months of TGL administration, the fur of the control group was more dry and sparse, females responded more robustly than males in terms of appearance in the gloss of the hair, and part of the control group showed shedding of senescent cells and skin diseases (Figure 1C), hints that TGL seems to have a more pronounced effect on female aging mice. H&E staining indicated that there exist thickening and distortion of the elastic fibers and the epidermal cell layer was arranged irregularly in the control group, while in the TGL-treated groups, these symptoms showed significant improvement (Figure 2A). Besides, some mice in the control group had cataracts, while in the TGL-treated groups no cataracts were found in either males or females (Figure 1C), cataracts occurred in 11.1% of males and 14.28% of females in the control groups. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lacrimal glands of the control group showed obvious acinar cavity expansion and flat epithelium, while TGL treatment significantly improved the function of lacrimal glands (Figure 2B). Besides, the corneal epithelium thickened and was arranged irregularly, and the collagenous fiber arrangement of the corneal stroma lost its original shape in the Control group (Figure 2C).
FIGURE 2.
Improvement of multiple organ aging after long-term administration of TGL. TGL shows an improvement in skin, eyes, liver, and spleen. (A) HE staining of the skin; (B) HE staining of the Lacrimal gland; (C) HE staining of the Cornea; (D) Oil red O staining of the liver; (E) Prussian blue iron staining of the spleen. Data are presented as the means ± SD of more than six independent experiments. *p < 0.05.
Enhanced Autophagy Effects of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on the Brain of Normal Aged Mice
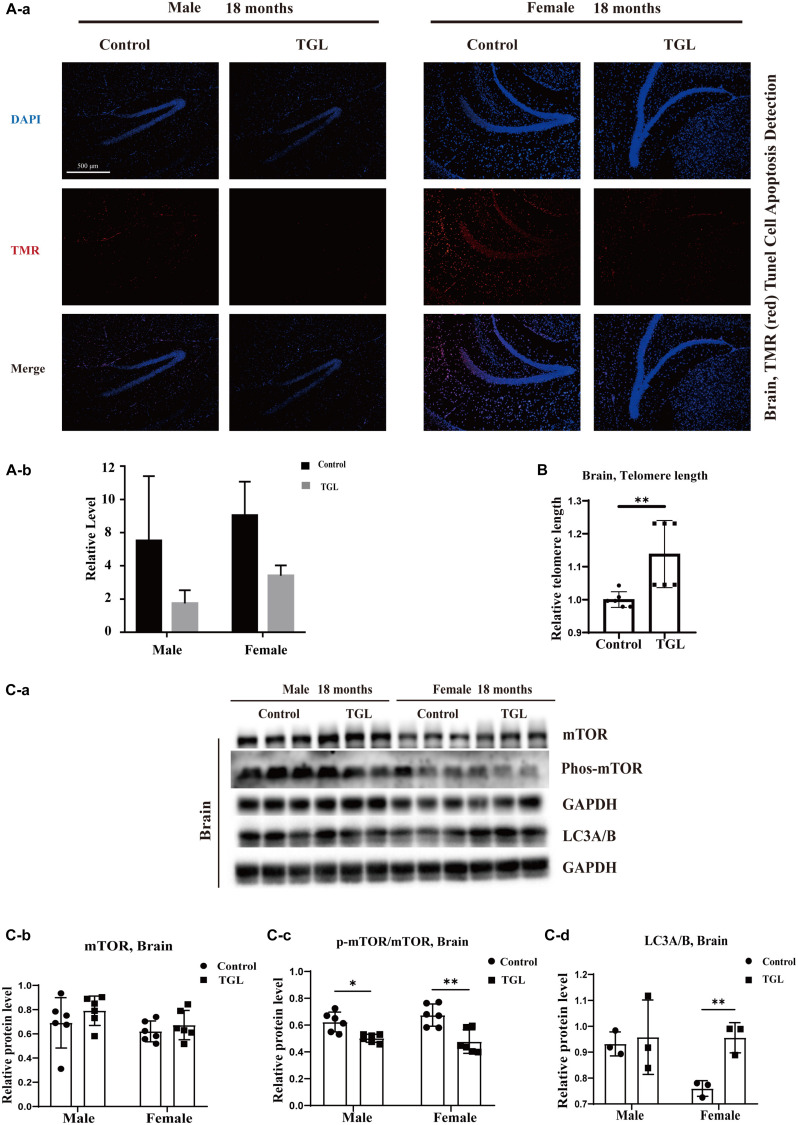
A mind-tranquilizing effect was the main function of G. lucidum in its traditional application, and in our previous study, we showed that alcohol extracts of G. lucidum could delay the progression of AD by regulating DNA methylation in rodents (Lai et al., 2019). Thus, we evaluated other potential effects and mechanisms of the aging brain. Tunnel assays for the detection of apoptotic cells showed there were fewer apoptotic cells in brain tissue samples in the TGL-treated groups than that in the control group (Figure 3A, p < 0.05). The telomere lengths in brain tissue samples were longer in the female TGL-treated group than that in the female control group (Figure 3B, p < 0.05). Then we found the expression of phosphorylated-mTOR and LC3A/B were upregulated in the TGL-treated groups (Figure 3C, p < 0.05). Indicate that triterpenoids of G. lucidum may delay brain aging by delaying telomere shortening, activating autophagy, and other functions.
FIGURE 3.
Effects of triterpenoids of G. lucidum on the brain of normal aged mice. (A) TGL shows an improvement in brain cells apoptosis rate using TUNEL staining; (B) TGL shows inhibition of telomere shortening in the brain; (C) TGL shows an impact on the mTOR pathway to enhance the autophagy. Data are presented as the means ± SD of more than six independent experiments, and more than three independent experiments in Western blot. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
Effect of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on the Hypothalamus of Normal Aged Mice
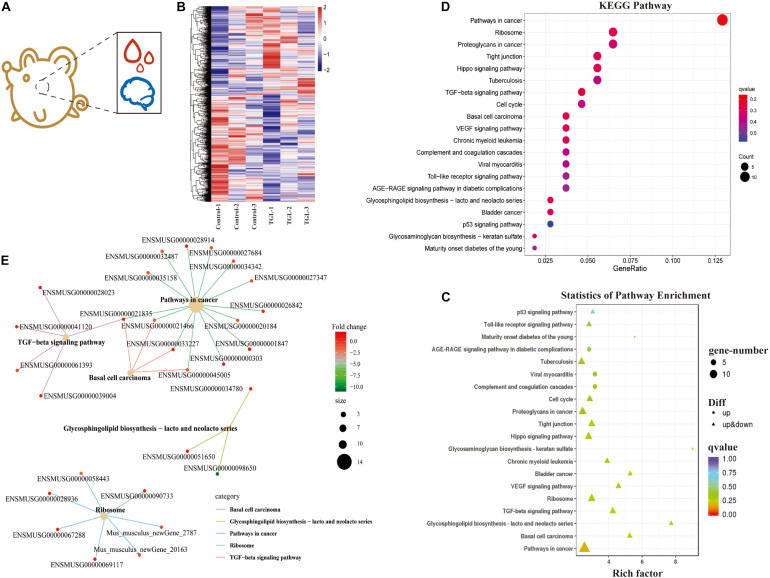
In our previous study, we demonstrated that alcohol extracts of the G. lucidum fruit body could improve the microbiome-gut-liver axis, improve the microbiome-gut-brain axis, and could regulate the CNS, and improve metabolic regulation in high sugar and fat diet mice (Diling et al., 2020). Thus, we explored the mechanism of TGL involvement in metabolic regulation using RNA sequencing of extracts from hypothalamus tissue samples (Figure 4A). As shown in Figure 4B, there were about 366 differentially expressed mRNAs detected, among which 190 mRNAs were up-regulated and 176 mRNAs were down-regulated (Figure 4B and Table 1). Enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes using KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway analysis is shown in Figures 4C,D. The main pathways involved included pathways in cancer, the TGF-beta signaling pathway, and biosynthesis of the glycosphingolipid Lacto/neolacto series. The network interaction of DEGs is shown in Figure 4E. Previous studies have revealed that sphingolipid metabolism could be involved in galactosylceramide and glycosphingolipid biosynthesis, and TGL may thus target sphingolipid metabolism.
FIGURE 4.
Effect of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on hypothalamus RNA sequencing of normal aged mice. (A) Schematic diagram of test index; (B) Heatmap of differently expressed mRNAs; (C,D) Enrichment analysis of differentially expressed gene KEGG pathway. Note: The x-coordinate is GeneNum, indicating the number of genes of interest in this entry, and the Y-coordinate is each Pathway entry. The color of the column represents the p-value of the hypergeometric test. (E) KEGG enrichment network diagram of differentially expressed genes. The network diagram of differentially expressed genes and the KEGG pathway. The color of edges represents different pathways, and the color of gene nodes represents multiple differences. The larger the pathway node, the more genes enriched in the pathway.
TABLE 1.
RNA sequencing of hypothalamus (Top 100 different expressed mRNAs).
| Symbol | C1_FPKM | C2_FPKM | C3_FPKM | TGL-1_FPKM | TGL-2_FPKM | TGL-3_FPKM | p-value | log2FC | Regulated |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_12923 | 3.889608 | 3.290139 | 3.234409 | 0.053785 | 0 | 0.056914 | 1.66E-73 | −6.57187 | down |
| Gm43720 | 0.669973 | 0.584832 | 0.734276 | 0.02567 | 0 | 0.000223 | 3.09E-32 | −5.97605 | down |
| Taok1 | 11.70314 | 12.37501 | 10.5112 | 2.730262 | 3.997773 | 3.198907 | 1.02E-26 | −1.80556 | down |
| Gm28048 | 8.712056 | 9.694984 | 0.431736 | 0 | 0.000306 | 0 | 9.32E-20 | −10.7704 | down |
| Bcl2l2 | 39.69579 | 38.87336 | 37.57313 | 17.4676 | 15.38983 | 18.45921 | 1.03E-19 | −1.31449 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_14522 | 0.24126 | 0.611931 | 0.31302 | 0.059981 | 0.021117 | 0.060201 | 9.12E-11 | −3.02239 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_1511 | 15.50723 | 36.33932 | 11.57809 | 5.083674 | 5.985105 | 3.695479 | 1.97E-10 | −2.09377 | down |
| Ngp | 0.969112 | 0.835183 | 1.236629 | 0.114383 | 0.183466 | 0.145172 | 7.08E-10 | −2.74507 | down |
| Phc3 | 10.24863 | 6.610594 | 8.556628 | 2.537218 | 4.992046 | 3.632396 | 2.53E-09 | −2.21105 | down |
| Cpne1 | 4.453808 | 4.480745 | 5.728442 | 11.16032 | 7.617339 | 11.39168 | 8.88E-09 | 1.320762 | up |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_15486 | 2.116321 | 1.838757 | 1.799755 | 0.587295 | 0.122823 | 0.275683 | 1.03E-08 | −2.551 | down |
| Anp32e | 18.27329 | 21.48529 | 21.3954 | 34.10668 | 30.15924 | 32.04015 | 2.00E-08 | 0.846808 | up |
| Lypd6 | 6.339828 | 2.896344 | 8.136196 | 1.943519 | 2.299223 | 2.859215 | 2.15E-08 | −1.8172 | down |
| Ptch1 | 18.11132 | 12.92783 | 19.11014 | 8.431311 | 10.36519 | 7.254182 | 3.49E-08 | −1.03398 | down |
| Gatad2b | 8.531223 | 3.290149 | 7.480017 | 1.829689 | 2.707072 | 2.368215 | 1.57E-07 | −1.62155 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_7451 | 0.47321 | 0.715459 | 0.900427 | 2.064423 | 2.864607 | 2.115137 | 4.46E-07 | 1.732702 | up |
| Rnf13 | 34.83294 | 27.26737 | 21.82686 | 62.65552 | 44.34845 | 84.607 | 4.99E-07 | 1.316054 | up |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_13835 | 81.60193 | 110.9614 | 135.5357 | 301.9333 | 246.8458 | 182.6184 | 6.97E-07 | 1.12706 | up |
| Adam1a | 11.58916 | 10.89115 | 6.950538 | 5.682081 | 5.252263 | 5.009995 | 7.52E-07 | −1.05363 | down |
| Nfat5 | 4.938496 | 6.347 | 3.062845 | 5.670891 | 7.865202 | 7.090772 | 1.24E-06 | 0.997967 | up |
| Pcdhga8 | 4.389451 | 2.866374 | 6.223647 | 2.032655 | 1.719958 | 2.082496 | 2.49E-06 | −1.20561 | down |
| Aldh1a2 | 1.697769 | 1.582407 | 1.882824 | 3.327981 | 3.696433 | 7.531053 | 2.77E-06 | 1.494426 | up |
| Osbpl6 | 10.07962 | 9.967105 | 8.61995 | 7.226177 | 7.813877 | 6.724273 | 3.45E-06 | −0.71505 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_17313 | 5.096818 | 4.661171 | 7.446638 | 2.252344 | 1.991808 | 2.109914 | 3.55E-06 | −1.30573 | down |
| Rac1 | 15.45162 | 15.58981 | 16.55221 | 16.1087 | 68.20964 | 69.8126 | 4.17E-06 | 1.700827 | up |
| Ptgds | 329.8186 | 344.9323 | 408.1165 | 571.3699 | 600.5531 | 1385.647 | 4.87E-06 | 1.211963 | up |
| Slc13a4 | 0.532723 | 0.965426 | 0.480298 | 1.330932 | 1.848271 | 4.333051 | 7.00E-06 | 1.923232 | up |
| Azi2 | 14.78044 | 16.10542 | 16.87702 | 21.2957 | 20.55793 | 19.16221 | 7.32E-06 | 0.700732 | up |
| Rab27a | 6.94201 | 8.103768 | 8.159093 | 3.867649 | 5.128242 | 3.996698 | 8.69E-06 | −0.83788 | down |
| Slc22a6 | 0.244441 | 0.273731 | 0.12178 | 0.411466 | 0.796756 | 2.216438 | 1.08E-05 | 2.419438 | up |
| Myl12a | 8.356751 | 8.685487 | 9.705156 | 15.42321 | 14.62305 | 19.54725 | 1.15E-05 | 0.804032 | up |
| Tmem9b | 25.18691 | 27.73696 | 28.4351 | 32.74496 | 62.38393 | 67.81904 | 1.21E-05 | 1.014054 | up |
| Pitx2 | 13.58033 | 12.01773 | 7.359167 | 18.30537 | 21.04272 | 22.4479 | 1.23E-05 | 0.900374 | up |
| Spp1 | 4.563857 | 5.579025 | 4.672519 | 7.785845 | 9.797311 | 15.03454 | 1.29E-05 | 1.13448 | up |
| Paqr7 | 41.38397 | 22.08821 | 48.21004 | 18.52836 | 18.22971 | 16.8107 | 1.33E-05 | −0.90075 | down |
| Pcdhgb5 | 2.167199 | 1.730722 | 21.07459 | 0.801004 | 1.31047 | 0.959021 | 1.51E-05 | −3.01305 | down |
| Fmod | 1.767021 | 1.258097 | 1.14861 | 2.087399 | 3.682632 | 5.977344 | 1.57E-05 | 1.502393 | up |
| Rhof | 18.47653 | 12.44221 | 13.31581 | 11.19265 | 8.337795 | 8.465769 | 1.61E-05 | −0.70898 | down |
| Pcdhgc4 | 13.13775 | 7.538917 | 65.98213 | 5.727133 | 6.518003 | 5.458537 | 1.75E-05 | −1.69952 | down |
| Igfbp2 | 6.671881 | 5.23182 | 4.62881 | 9.806509 | 9.538176 | 18.76624 | 1.88E-05 | 1.204219 | up |
| Ogn | 1.283395 | 1.324278 | 0.958192 | 1.870447 | 3.054949 | 5.543355 | 2.08E-05 | 1.551819 | up |
| Tfdp2 | 5.926766 | 4.901073 | 3.93437 | 1.605638 | 3.78065 | 4.35234 | 2.28E-05 | −1.30098 | down |
| Serping1 | 3.146913 | 3.479642 | 3.593491 | 6.167186 | 6.26718 | 6.881413 | 2.43E-05 | 0.913624 | up |
| Atp8a1 | 37.30142 | 43.92654 | 15.52566 | 13.62472 | 16.1126 | 13.84528 | 2.45E-05 | −1.16087 | down |
| Gpc2 | 0.125598 | 0.25074 | 0.30578 | 0.612154 | 0.624173 | 1.115076 | 2.74E-05 | 1.756986 | up |
| Grm2 | 7.521406 | 6.845249 | 4.812198 | 12.11454 | 11.00831 | 9.703672 | 2.76E-05 | 0.783435 | up |
| Sco2 | 5.863888 | 6.247402 | 0.984866 | 1.153106 | 0.606637 | 0.815138 | 2.89E-05 | −2.22673 | down |
| Pcdhgc5 | 5.084746 | 4.174581 | 9.834584 | 3.219718 | 3.519621 | 2.560906 | 5.76E-05 | −1.09671 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_20163 | 19.93332 | 22.75848 | 17.98565 | 11.65688 | 9.074512 | 9.381307 | 5.87E-05 | −1.00875 | down |
| Trim2 | 47.02116 | 41.57854 | 12.90792 | 11.70039 | 14.17824 | 12.64701 | 6.02E-05 | −1.20445 | down |
| Clec3b | 1.548666 | 1.612173 | 2.81814 | 5.829777 | 4.277997 | 4.631124 | 6.96E-05 | 1.288496 | up |
| Fxyd3 | 0.885017 | 0.274696 | 0.365057 | 1.192751 | 1.504817 | 2.304581 | 7.73E-05 | 1.694682 | up |
| Slc6a13 | 1.984694 | 1.538029 | 1.57059 | 2.857289 | 3.160465 | 6.928728 | 7.80E-05 | 1.346279 | up |
| Atxn7l3 | 12.59657 | 11.37764 | 10.24654 | 32.68215 | 11.73012 | 26.14544 | 8.59E-05 | 1.080079 | up |
| H3f3b | 44.60186 | 46.38337 | 51.33964 | 126.2611 | 105.5351 | 48.37488 | 9.20E-05 | 0.973486 | up |
| Rprm | 41.61818 | 37.74937 | 33.05315 | 64.0092 | 55.17521 | 51.14713 | 9.35E-05 | 0.598208 | up |
| Synj1 | 50.21541 | 57.96886 | 66.0465 | 37.84828 | 45.0888 | 31.57636 | 0.000101 | −0.66404 | down |
| H2-Q1 | 0.267972 | 0.243174 | 0.096663 | 0.530357 | 0.631109 | 0.99056 | 0.000101 | 1.732081 | up |
| Rps28 | 68.00393 | 47.808 | 80.13228 | 127.8886 | 92.81004 | 118.9684 | 0.000103 | 0.79234 | up |
| Ppp1r9a | 22.42754 | 28.30584 | 24.18876 | 14.83328 | 12.26083 | 5.461852 | 0.00011 | −1.30678 | down |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_14521 | 1.072404 | 1.001249 | 0.873793 | 0.245256 | 0.512898 | 0.27324 | 0.000112 | −1.47976 | down |
| Foxb1 | 8.975046 | 8.292566 | 5.090877 | 15.56052 | 12.96705 | 11.33847 | 0.000122 | 0.831645 | up |
| Prg4 | 0.147244 | 0.419417 | 0.344384 | 0.436722 | 1.142215 | 1.880561 | 0.000124 | 1.91222 | up |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_21979 | 11.31698 | 7.821126 | 8.214593 | 5.56862 | 5.952519 | 5.044618 | 0.000134 | −0.69488 | down |
| Galnt16 | 25.79815 | 34.77434 | 28.3016 | 70.09834 | 30.49534 | 63.24136 | 0.000135 | 0.943713 | up |
| Sphk1 | 0.273167 | 0.304012 | 0.224675 | 0.893284 | 0.770787 | 0.883149 | 0.000149 | 1.531377 | up |
| Wdr77 | 17.27344 | 8.842787 | 16.67199 | 7.451219 | 8.619811 | 7.844271 | 0.000152 | −0.88545 | down |
| Fsd1l | 3.294207 | 2.83381 | 2.810097 | 3.65967 | 3.366155 | 2.839395 | 0.000153 | 1.390214 | up |
| Gm28036 | 9.417948 | 4.500991 | 1.961159 | 2.505359 | 1.595868 | 0.785525 | 0.000174 | −1.92552 | down |
| Myh4 | 0.208298 | 0.222836 | 0.151057 | 0.376344 | 0.54702 | 0.467163 | 0.0002 | 1.244447 | up |
| Slc6a12 | 0.264733 | 0.227287 | 0.104826 | 0.448564 | 0.611936 | 1.848077 | 0.000254 | 1.896547 | up |
| Aspg | 1.854029 | 1.874206 | 1.906641 | 3.251615 | 2.427306 | 4.529861 | 0.000278 | 0.924055 | up |
| Tmem267 | 11.66432 | 9.798137 | 9.689703 | 13.23979 | 15.95576 | 12.43407 | 0.000332 | 0.789803 | up |
| Fbln1 | 3.253842 | 3.430193 | 3.274527 | 4.951525 | 5.160303 | 6.023687 | 0.000332 | 0.71697 | up |
| Ahcyl2 | 42.43559 | 15.24158 | 37.83194 | 15.79211 | 16.5671 | 17.91718 | 0.000343 | −1.00208 | down |
| Slc47a1 | 0.559734 | 0.964785 | 0.483391 | 1.174253 | 1.650622 | 2.769661 | 0.000356 | 1.342388 | up |
| Nbl1 | 11.12559 | 13.55878 | 14.09049 | 18.49148 | 19.99199 | 19.77541 | 0.000401 | 0.587494 | up |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_21883 | 4.859227 | 8.03323 | 3.822363 | 1.438963 | 2.150494 | 2.388066 | 0.000427 | −1.34507 | down |
| Adora1 | 11.45976 | 18.19518 | 11.52225 | 18.63551 | 24.41292 | 24.19367 | 0.00044 | 0.615842 | up |
| Bmp6 | 1.181217 | 1.537264 | 1.419002 | 2.106625 | 2.299605 | 3.440335 | 0.00048 | 0.924294 | up |
| Gabpb2 | 4.133897 | 3.729611 | 3.128166 | 2.178008 | 1.648487 | 2.656451 | 0.000485 | −0.74112 | down |
| Mdfic | 0.375961 | 0.644931 | 0.561184 | 0.803601 | 1.025879 | 0.863842 | 0.000498 | 1.100109 | up |
| Dyrk1a | 7.841053 | 9.030653 | 8.404052 | 12.67455 | 7.112959 | 14.23365 | 0.000499 | 0.808919 | up |
| Mindy3 | 13.38096 | 14.45982 | 14.52083 | 9.082119 | 10.74618 | 12.46219 | 0.000504 | −0.61554 | down |
| Gal3st4 | 1.207063 | 1.027611 | 1.531161 | 3.433771 | 1.888287 | 2.814491 | 0.000541 | 0.905185 | up |
| Mus_musculus_newGene_15009 | 2.9457 | 2.854937 | 2.396335 | 1.353186 | 1.805244 | 2.001115 | 0.000559 | −0.67321 | down |
| Col25a1 | 9.488102 | 13.3002 | 9.942588 | 5.493827 | 8.633615 | 6.928233 | 0.000633 | −0.68212 | down |
| Fgfr1op | 6.256988 | 5.914114 | 2.999508 | 2.878672 | 2.939719 | 2.694882 | 0.000636 | −0.97513 | down |
| Macrod2 | 12.08988 | 9.510841 | 4.441681 | 4.298766 | 6.074126 | 7.414225 | 0.000716 | −1.18296 | down |
| Aebp1 | 3.095477 | 4.318746 | 3.966831 | 4.587501 | 7.083368 | 6.949616 | 0.000748 | 0.733223 | up |
| Rprd1b | 10.78543 | 3.070225 | 3.991385 | 2.486718 | 2.939771 | 2.373803 | 0.000752 | −1.26824 | down |
| Eya2 | 0.684411 | 0.734553 | 0.746447 | 1.221404 | 1.403488 | 1.807 | 0.000796 | 1.031067 | up |
| Sumo2 | 49.4363 | 25.06764 | 10.82903 | 11.17719 | 8.213712 | 15.44789 | 0.000802 | −1.32669 | down |
| Pcdhgb1 | 1.822618 | 3.238295 | 1.178243 | 8.429773 | 3.888132 | 2.899032 | 0.000838 | 1.277849 | up |
| Cap1 | 56.2933 | 33.90784 | 30.66407 | 61.58003 | 65.04071 | 62.07548 | 0.00087 | 0.667503 | up |
| Fam131b | 3.792873 | 4.024515 | 5.314095 | 6.649393 | 6.251654 | 7.349866 | 0.000906 | 0.624582 | up |
| Gstm2 | 1.168082 | 1.128437 | 1.425652 | 2.788445 | 2.056896 | 3.038896 | 0.000912 | 1.068272 | up |
| Bbx | 4.801812 | 5.454796 | 4.683867 | 3.618744 | 3.809623 | 3.062787 | 0.000914 | −0.85461 | down |
| Ankfn1 | 3.826081 | 5.374508 | 3.561852 | 2.733567 | 2.333025 | 1.04414 | 0.000936 | −1.00005 | down |
| AL732309.1 | 0.205796 | 0.447086 | 0.47556 | 1.433138 | 0.179026 | 5.598956 | 0.000994 | 2.662847 | up |
Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that the cellular components, including the extracellular exosome, the integral component of plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, the perinuclear region of cytoplasm, protein complex, and proteinaceous extracellular matrix, were significantly influenced (Supplementary Figure 2A). The biological processes of negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules, cell-cell signaling, synapse organization, cellular response to oxidative stress, neurotransmitter transport, insulin secretion, and regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway were influenced (Supplementary Figure 2B). Besides, the molecular functions of calcium ion binding, protein homodimerization activity, heparin-binding, ligase activity, calmodulin-binding, histone binding, neurotransmitter: sodium symporter activity, anion: anion antiporter activity, calcium channel regulator activity, and galactosylceramide sulfotransferase activity were influenced (Supplementary Figure 2C).
Long-Term Intake of TGL Delays the Age-Related Physiological Changes in Various Organs
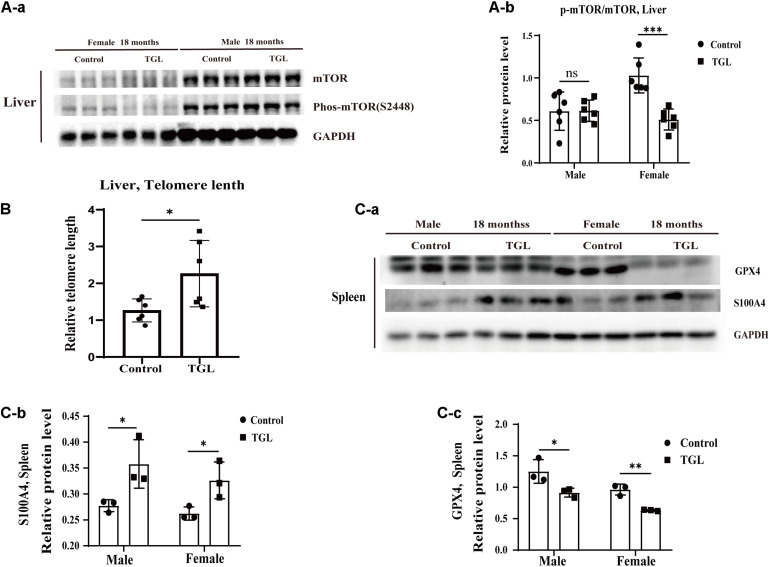
The anti-aging effect of G. lucidum on mice is comprehensive, and, overall, in addition to regulating the brain, it also improves the damage of various organs and common aging indicators. In this study, compared to the control group, Oil red O staining of the liver in the TGL-treated group was significantly better (Figure 2D, p < 0.05), and the number of apoptosis cells was reduced (Figure 5B, p < 0.05), mTOR pathway is also activated in female liver tissue (Figure 6A, p < 0.05). Meanwhile, liver tissue had a longer telomere length in the TGL group (Figure 6B, p < 0.05). Brown adipose tissue depot contribute to improving glucose metabolism, weight loss, and reversing insulin resistance, and consumption of excess fat (Villarroya et al., 2017; Singh et al., 2018), TGL significantly improved the brown adipose tissue levels around the scapula, while adipocytes in the control group were greater and larger (Figure 5A). A feature of cellular senescence is the activity of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) (Jurk et al., 2012), The β-galactosidase staining of kidney tissues in the control group was significantly higher than that in the TGL-treated group (Figure 5C, p < 0.05), which indicated that TGL could reduce the senescence marker β-galactosidase. Accumulation of iron coupled with impaired ferritinophagy and inhibition of ferroptosis, ferritin (iron storage) levels are becoming biomarkers of cellular senescence (Masaldan et al., 2018). Iron metabolism is tightly regulated in organisms, keeping cells in iron homeostasis. Excessive Fe2+ in cells is toxic, which can induce the body to produce large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This leads to further attack by ROS and also oxidization of lipids in the cell membrane, causing cell death and aging (Cutler et al., 2014). In this study, Prussian blue iron staining was deeper and more extensive in the spleen of the control group than that in the TGL-treated group (Figure 2E, p < 0.05); Western blotting assays showed that the expressions of GPX4 and S100A4 were significantly upregulated in the female TGL-treated group (Figure 6C, p < 0.05), which indicated that the ferroptosis would be inhibited or delayed by TGL in aging.
FIGURE 5.
Improvement of multiple organ aging after long-term administration of TGL. TGL shows an improvement in brown adipose, liver, and kidney. (A) HE staining of brown adipose tissue; (B) Apoptosis rate of Liver using TUNEL staining; (C) TGL shows an improvement on aging in kidney using β-galactosidase staining. Data are presented as the means ± SD of more than six independent experiments. **p < 0.01.
FIGURE 6.
Improvement of multiple organ aging after long-term administration of TGL. TGL shows an improvement in the liver and spleen. (A) TGL shows inhibition of the expressions in mTOR and p-mTOR of the liver. (B) The expression of GPX4 and S100A4. (C) TGL shows inhibition of telomere shortening in the liver. Data are presented as the means ± SD of more than six independent experiments and more than three independent experiments in Western blot. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns, not statistically significant.
Regulation of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on Sphingolipid Metabolism in Normal Aged Mice
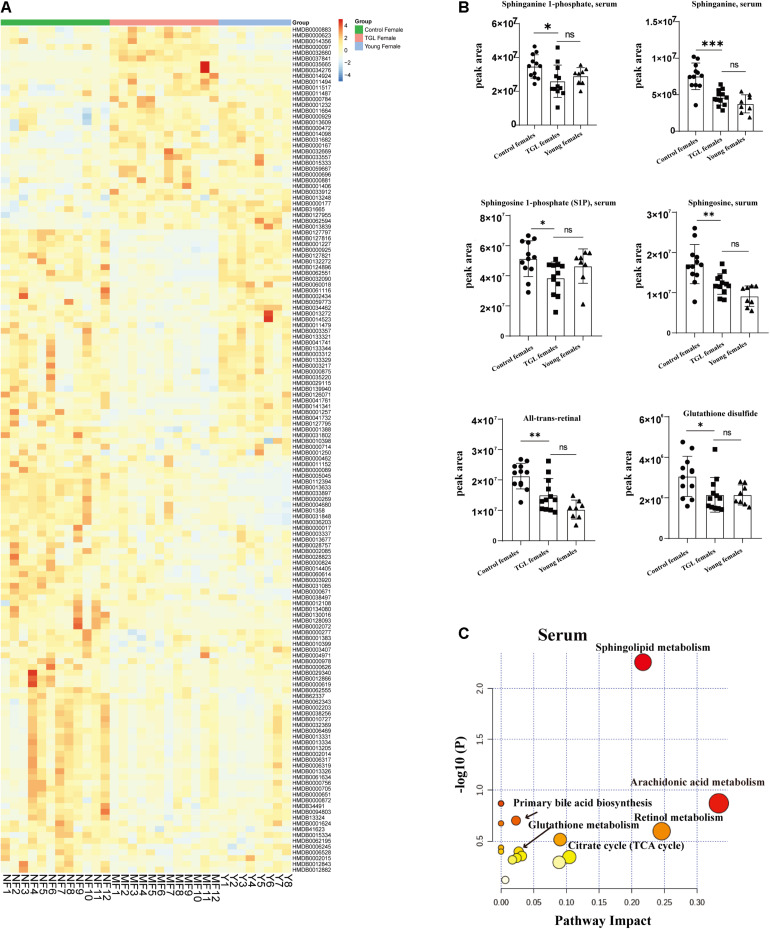
Based on the more significant improvements of TGL on female aging mice, to determine whether TGL targeted sphingolipid metabolism to exert its role in delaying aging, metabolomics analysis of serum was performed. At the same time, we added young female C57BL/6 mice (12 weeks) as a reference to observe whether the TGL group tends to the younger group. We found that the serum metabolites were significantly different between the TGL-treated groups and the control group and the young control group (Figure 7A and Supplementary Figures 3A,B). Most sphingolipid metabolites, including sphinganine 1-phosphate, sphinganine, sphingosine 1-phoshphate (S1P), sphingosine, all-trans-retinal, and glutathione disulfide, differed in the TGL-treated groups compared to the control group (Figure 7B, p < 0.05), while there were no differences in the TGL-treated groups and young control group (Figure 7B, p > 0.05). And metabolites of the brain can also be clearly distinguished between the control group and the TGL group (Supplementary Figures 2C,D). The results of serum and brain metabolism using KEGG pathway analysis showed that sphingolipid metabolism and arachidonic acid metabolism are the mainly influenced pathways (Figure 7C, Supplementary Figure 2E, and Tables 2, 3). Previous studies (Van Liew et al., 1993; Cutler et al., 2014; Hannun and Obeid, 2018; Trayssac et al., 2018; Jesko et al., 2019) indicated that sphingolipid metabolism could regulate development, lifespan, and age-related diseases, and the mTOR signaling pathway could also be modulated by bioactive sphingolipids (Jesko et al., 2019). In this study, we found that phosphorylated-mTOR was activated in the brain (Figure 3C, p < 0.05) and liver (Figure 6A, p < 0.05) of TGL-treated groups, and especially in females. These results indicated that the TGL may target sphingolipid metabolism to improve the lifespan and age-related diseases, and the mTOR signal pathway.
FIGURE 7.
Effect of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on sphingolipid metabolism of normal aged mice. (A) Heatmap of serum metabolites; (B) Effects on sphingolipid metabolites, including the sphinganine 1-phosphate, sphinganine, sphingosine 1-phoshphate (S1P), sphingosine, all-trans-retinal, and glutathione disulfide; (C) results of serum metabolomics using KEGG pathway analysis showed that sphingolipid metabolism and arachidonic acid metabolism are the mainly influenced pathways after treatment of TGL; n ≥ 14. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns, not statistically significant.
TABLE 2.
Metabolites pathway analysis of serum differences metabolites between control group and TGL-treated group.
| ID Annotation | Set | In set | Background | In background | p-value |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 39 | 5 | 3584 | 25 | 5.31E-06 |
| Metabolic pathways | 39 | 24 | 3584 | 1455 | 6.41E-03 |
| Calcium signaling pathway | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 10 | 1.04E-01 |
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 128 | 4.09E-01 |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 8 | 8.39E-02 |
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 99 | 6.67E-01 |
| Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 8 | 8.39E-02 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 75 | 1.96E-01 |
| Fructose and mannose metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 48 | 4.11E-01 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 39 | 3 | 3584 | 49 | 1.55E-02 |
| Valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 28 | 3.65E-02 |
| Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 126 | 4.01E-01 |
| Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 39 | 5 | 3584 | 75 | 1.16E-03 |
| Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 39 | 9 | 3584 | 1023 | 8.25E-01 |
| ABC transporters | 39 | 5 | 3584 | 90 | 2.62E-03 |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 46 | 8.85E-02 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 82 | 2.24E-01 |
| beta-Alanine metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 31 | 4.40E-02 |
| Glutathione metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 38 | 6.35E-02 |
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 44 | 8.20E-02 |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 41 | 3.63E-01 |
| Propanoate metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 36 | 3.27E-01 |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 27 | 2.57E-01 |
| Histidine metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 44 | 3.84E-01 |
| Riboflavin metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 21 | 2.06E-01 |
| Retinol metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 24 | 2.32E-01 |
| Phototransduction | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 8 | 8.39E-02 |
| Tryptophan metabolism | 39 | 5 | 3584 | 81 | 1.64E-03 |
| Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 27 | 2.57E-01 |
| alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 40 | 6.95E-02 |
| Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 54 | 1.16E-01 |
| Vitamin B6 metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 32 | 2.96E-01 |
| Purine metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 92 | 6.39E-01 |
| Phenylalanine metabolism | 39 | 2 | 3584 | 46 | 8.85E-02 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 56 | 4.61E-01 |
| Butanoate metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 40 | 3.56E-01 |
| D-Glutamine and D-glutamate metabolism | 39 | 1 | 3584 | 12 | 1.23E-01 |
Use online software MBROLE (version 2.0) (csbg.cnb.csic.es/mbrole2/index.php) for differences metabolites pathway analysis.
TABLE 3.
Metabolites pathway analysis of differences metabolites of brain tissue between control group and TGL-treated group.
| Pathway | Total Cmpd | Hits | Holm adjust | FDR | Impact |
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 36 | 2 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0.17539 |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 1 | 1 | 0.69273 | 0.15416 |
| Lysine degradation | 25 | 1 | 0.35624 | 0.10178 | 0.14085 |
| Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | 18 | 1 | 0.005943 | 0.005943 | 0.11429 |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 33 | 1 | 0.14592 | 0.063101 | 0.10446 |
| Histidine metabolism | 16 | 1 | 0.89835 | 0.14374 | 0.09016 |
| Purine metabolism | 66 | 3 | 0.45432 | 0.10904 | 0.06093 |
| Pyruvate metabolism | 22 | 1 | 1 | 0.19028 | 0.0591 |
| Glycerolipid metabolism | 16 | 1 | 1 | 0.28982 | 0.04361 |
| Primary bile acid biosynthesis | 46 | 1 | 0.79466 | 0.12465 | 0.02285 |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | 40 | 2 | 1 | 0.36274 | 0.02264 |
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis | 77 | 1 | 0.5312 | 0.11183 | 0.02188 |
| Fatty acid biosynthesis | 47 | 1 | 1 | 0.44825 | 0.01473 |
| Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 48 | 2 | 0.17353 | 0.063101 | 0 |
| Retinol metabolism | 16 | 1 | 0.69798 | 0.12465 | 0 |
| Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 8 | 1 | 0.79466 | 0.12465 | 0 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | 36 | 1 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0 |
| Linoleic acid metabolism | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0 |
| alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | 13 | 1 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0 |
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis | 8 | 1 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0 |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0.28258 | 0 |
| Fatty acid elongation | 39 | 1 | 1 | 0.44825 | 0 |
| Fatty acid degradation | 39 | 1 | 1 | 0.44825 | 0 |
| Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 36 | 1 | 1 | 0.44825 | 0 |
Improvements of TGL on APP/PS1 Mice
To further evaluate improvement by TGL on aging, and to verify the pathway of TGL improving brain injury, we performed a combined analysis of metabolomics and transcriptome data of TGL-treated APP/PS1 mice. The metabolites present in the serum of TGL-treated APP/PS1 mice had changed (Figure 8A), and the KEGG pathway analysis of these metabolites showed that there were about 117 metabolites enriched in glycerophospholipid metabolism, 27 metabolites enriched in glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis, and 2 metabolites enriched in the sphingolipid metabolism and the sphingolipid signaling pathway (see Figure 8B for additional details).
FIGURE 8.
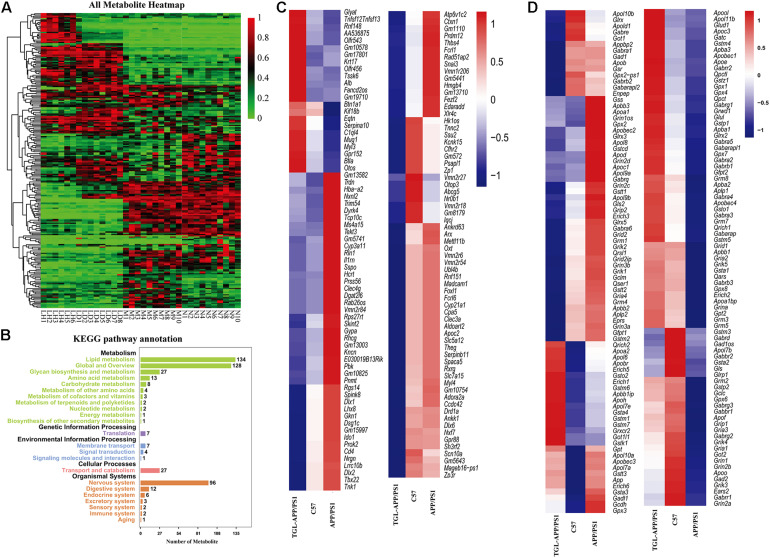
Improvements of triterpenoids of G. lucidum in APP/PS1 mice. (A) Heatmap of serum metabolites; (B) KEGG analysis of serum metabolites; (C,D) Different expressed mRNA of brain tissues. More than six independent experiments in Serum metabolomics and more than three independent experiments in Transcriptome sequencing.
RNA sequencing of global brain tissues indicated that most mRNAs expressed belonged to genes involved in the secretion and metabolism of neurotransmitters (Figures 8C,D) and ion channel for potassium, sodium, and calcium (Figures 8C,D), and this involved genes in synaptic regulation (Figures 8C,D), histone modification (Figures 8C,D), and electrolytes regulation (Figures 8C,D), which recovered to levels similar to those expressed in healthy controls. KEGG enrichment analysis of the differentially expressed mRNA sequences showed similar patterns to that of a previously published paper (Cutler et al., 2014). The IPA (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis) analysis indicated that the function and diseases, including carbohydrate metabolism and lipid metabolism, were influenced (Supplementary Table 4) and that differentially expressed mRNAs were enriched for the sphingolipid metabolism pathway (Supplementary Table 5). The above evidence indicated that TGL exerted multi-system, multi-target, multi-directional comprehensive regulation on the brain, including improvement in metabolism, immunity, neurotransmitters, electrolyte balance, synaptic transmission, and histone methylation. Together with our previous study that alcohol extracts of G. lucidum could improve the system of AD (Lai et al., 2019), all of this demonstrates that TGL has multiple biological activities that could target the gut–brain axis to stimulate the CNS in a manner that regulates host metabolism, the immune response, and other key signaling pathways.
Ganodenic Acid A Improved Regulation of Sphingolipid Metabolism in 3 × Tg-AD Mice
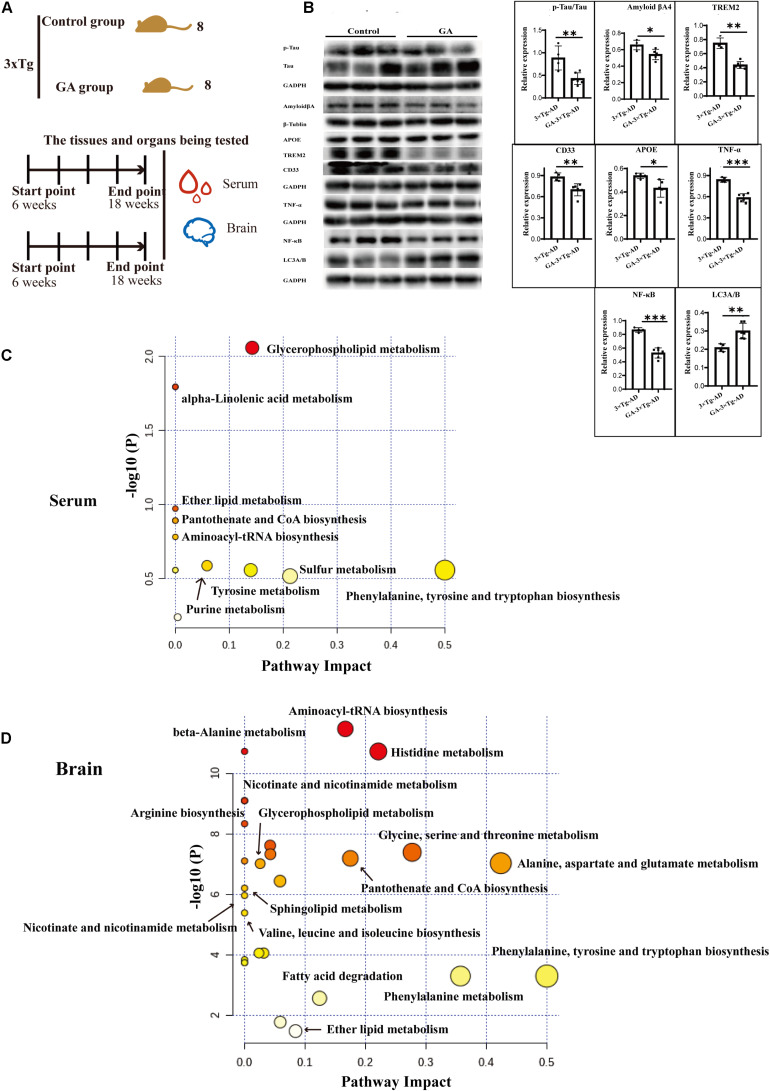
Based on previous pharmacological investigations of G. lucidum (Kalvodova et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2007; Maceyka et al., 2012; Teekachunhatean et al., 2012; Cheng et al., 2013; Guo et al., 2013; Miura et al., 2014; Hirano-Sakamaki et al., 2015; Chakrabarti et al., 2016; Cao et al., 2017; Lin et al., 2017; MOW Grimm et al., 2017; Pera et al., 2017; Angelopoulou and Piperi, 2019; Fabiani and Antollini, 2019; Jesko et al., 2019; Kurz et al., 2019; Magistretti et al., 2019; Crivelli et al., 2020), as shown in Figure 9A, after the 10 weeks treatment of TGL, serum and brain tissue were used to evaluate the regulation of Ganoderma triterpenes on sphingolipid metabolism. First, the expression of AD biomarkers p-Tau, β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides, APOE, TREM2, CD33 in brain tissues were reduced (Figure 9B, p < 0.05), the inflammatory cytokines of TNF-α and NF-κB p65 were inhibited (Figure 9B, p < 0.05), and the level of the autophagy-associated gene LC3A/B was upregulated (Figure 9B, p < 0.05). These results indicated that ganodenic acid A might be the effective constituent improving the systems of AD.
FIGURE 9.
Ameliorate effects of Ganodenic acid A by regulating sphingolipid metabolism in 3 × Tg-AD mice. (A) Experimental procedure in 3 × Tg-AD mice; (B) The AD biomarkers of p-Tau, Aβ, APOE, TREM2, CD33, the inflammatory cytokines of TNF-α and NF-κB p65 and the autophagy level of LC3A/B were measured in brain tissues; (C) KEGG analysis of serum metabolites; (D) KEGG analysis of brain metabolites. Data are presented as the means ± SD of more than six independent experiments and six independent experiments in Western blot. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.
Next, an unsupervised metabolome analysis of serum and brain samples was used to define the mechanism of action involved in ganodenic acid A activity. The analysis showed that glycerophospholipid metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, pantothenate, and CoA biosynthesis were influenced (Figures 9C,D) by exposure to ganodenic acid A, which indicated that it is active in sphingolipid metabolism to reduce the biomarkers of AD.
Discussion
Our data provide further evidence that long-term administration of TGL could mitigate the age-associated physiological decline in the normal aging mice, including cataract formation, hair loss and skin relaxation, brown adipose tissue accumulation, the β-galactosidase staining degree of the kidney, and the iron death of spleen and brain function. Testing using the APP/PS1 mice model showed that TGL could also improve brain function in AD (Lai et al., 2019), and measurements in the 3 × Tg-AD mice showed that ganoderic acid A might be the effective constituent involved in delaying brain aging in AD. A likely mechanism of brain improvement may involve the regulation of sphingolipid metabolism, prolonging telomere length, enhancing autophagy to remove pathological metabolites.
Although the relationships between telomere shortening, aging, and disease are still not entirely clear, it can be affirmed that normal aging is dependent on telomere shortening (Blackburn et al., 2015). Studies have demonstrated that a reduction in telomere length leads to the cessation of cell division; thus cellular senescence, apoptosis, exposure to antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory activity can attenuate the degree of shortening of telomere length during aging (Blackburn et al., 2015). In this study, we found that telomere lengths in the liver and brain in the TGL-treated groups were longer than in the normal group, which indicated that TGL could slow the telomere shortening to anti-aging and reduce susceptibility to cancer.
The results in this study showed that TGL had effects on delaying aging, and the TGL-treated female group generally showed a more obvious improvement concerning all these aging-associated changes. Unsupervised metabolomics analysis showed that different sphingolipid metabolites were present in serum and brain samples in normal aged mice following TGL treatment. The relative KEGG pathway analysis indicated that the sphingolipid metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism pathways were enriched (Figure 6 and Table 2), which indicated that the TGL could target sphingolipid metabolism. Sphingolipid metabolism and glutathione metabolism play important roles in senescence and age-related diseases (Maher, 2005; Trayssac et al., 2018). Sphingolipids are a highly conserved class of lipids. They were discovered in the brain more than a century ago, and are known as cerebral glycosides (Yeh, 1984; Sonnino and Prinetti, 2016). Members of this diverse and ubiquitous lipid family share a common structural feature of a long chain backbone skeleton and are important components of the lipid bilayer, where they contribute to the structure and function of membranes, the interconversion of vesicle transport, and membrane dynamics (Olsen and Faergeman, 2017). Ceramide is the central molecule of all sphingomyelin metabolism (Brodowicz et al., 2018). Its formation begins with the condensation of two common cellular metabolites, serine and palmitoyl CoA, in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The other metabolites of the products are 3-ketosphingominol, dihydro-sphingominol (known as sphingominol), and glycolipids (GSL), including gangliosides containing sialic acid and lactosylceramides (LacCer), ceramide 1-phosphate, and more complex sphingolipids, such as GSL and sphingolipids. Increasing studies have shown these membrane sphingolipids, composed of sphingolipids and ceramides and sphingolipases and its enzymes, exert important roles in signal transduction, especially in regulating the central nervous system (CNS) physiology (Yeh, 1984; Hirabayashi, 2012; Assi et al., 2013; Sonnino and Prinetti, 2016; Olsen and Faergeman, 2017; Brodowicz et al., 2018; Vutukuri et al., 2018; Hussain et al., 2019). In our study, levels of sphingolipid metabolites, including the sphinganine 1-phosphate, sphinganine, S1P, sphingosine, all-trans-retinol, and glutathione disulfide, were altered in the TGL-treated groups and the control group of the normal-aged mice (Figure 6). Retinol metabolism has been associated with an increased risk of cataract development (Nourmohammadi et al., 2008), our analysis showed that TGL could reduce the incidence rate of cataracts.
Over the past few decades, studies have revealed that abnormal sphingolipid metabolism is involved in the pathology of AD (Dinkins et al., 2016; Martinez and Mielke, 2017; Toledo et al., 2017; Czubowicz et al., 2019). The increased de novo synthesis of ceramide accelerated neuronal differentiation, while high levels of ceramide were detected in AD and other neurodegenerative diseases (Lin et al., 2017). As ceramide levels in cerebrospinal fluid and white matter are also elevated, especially in the milder symptoms of AD dementia (Czubowicz et al., 2019; Kurz et al., 2019), several other clinical studies have revealed that plasma ceramide levels are associated with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and memory loss in AD patients. High plasma ceramide levels have been associated with hippocampal volume loss, thus the changes in brain and plasma ceramide levels could be used as a biomarker of the early stages of AD (Chakrabarti et al., 2016; Dinkins et al., 2016; MOW Grimm et al., 2017).
Other potential targets of ceramide metabolism, such as sphingomyelin, sphingomyelin, sphingomyelinase, and sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1), have also been identified (Martinez and Mielke, 2017; Olsen and Faergeman, 2017; Hussain et al., 2019). Studies have shown that higher levels of sphingolipids can inhibit the γ-secretase activity during amyloid precursor protein (APP) decomposition, thereby reducing the accumulation of Aβ (Pera et al., 2017; Fabiani and Antollini, 2019). Ceramide, in turn, stabilizes BACE-1, which helps cleave the Aβ (Kalvodova et al., 2005). As ceramides can be converted to sphingosine, levels of sphingosine are also increased in the brain of patients with AD. Since sphingosine can be phosphorylated to form S1P (which is reduced in AD), this pathway may be of interest in studying potential pharmacological targets for AD (Maceyka et al., 2012; Czubowicz et al., 2019). Gilenya is an S1P receptor agonist approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and has been shown to modulate the neuroinflammatory pathway in mice with AD (Angelopoulou and Piperi, 2019; Jesko et al., 2019; Crivelli et al., 2020). Since almost all nerve cells express the S1P receptor, it has been proposed as an interesting target for drug treatment of AD (Angelopoulou and Piperi, 2019; Jesko et al., 2019; Crivelli et al., 2020). More complex changes in GSL were observed in AD, and high GM1 levels appear to be associated with Aβ. Specifically, the ganglioside GM1 was enriched in lipid rafts, leading to the toxic accumulation and aggregation of Aβ (Miura et al., 2014; Hirano-Sakamaki et al., 2015; Magistretti et al., 2019), suggesting that there was a strong association between the steady-state ganglioside levels and AD. In this study, we found that the sphingolipid metabolites, including the sphinganine-1-phosphate, sphinganine, S1P, sphingosine, and all-trans-retinal and glutathione disulfide, were altered in TGL-treated groups and control groups in the APP/PS1 and 3 × Tg-AD mice models (Figures 7, 8). Furthermore, ganoderic acid A could be detected in the brain after intravenously dosing using UFLC-MS/MS, which suggested triterpenoids could cross the blood–brain barrier (Supplementary Table 2; Cao et al., 2017). In addition, considering that G. lucidum also exerts different pharmacological activities in the heart, liver, spleen, and brain (Supplementary Tables 2, 3), this indicates that TGL may improve brain function likely by delaying the brain aging in AD through the regulation of sphingolipid metabolism, and ganoderic acid A might represent active constituent.
Limitation of the Study
Because of the long period required to obtain the normal aged mice and the COVID-19 pandemic, we failed to complete the survival curve experiment, so we cannot fully determine whether triterpenoids of G. lucidum can prolong the life span. Due to the complexity of the chemical constituents of G. lucidum and the high costs of isolation and purification of single components, the present and previous studies have mostly focused on the study of mixtures. Thus, it is difficult to conduct in-depth conduct investigations into the pharmacological mechanisms involved. In this study of potential pharmacological activities of triterpenoids from G. lucidum, behavioral experiments were performed only in APP/PS1 mice (Lai et al., 2019), and only the effects of ganoderic acid A have been evaluated in the 3 × Tg-AD mouse model.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics Statement
The animal protocols used in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use committee of the Center of Laboratory Animals of the Guangdong Institute of Microbiology.
Author Contributions
MZe, LQ, YG, XT, and XZ carried out most of the experiment. MZe, YG, LQ, XT, and XZ perfomed the histopathology and molecular biology experiments. LQ completed the metabolomics-related experiments. YX, QW, DC, and MZh led the progress of the whole experiment and reviewed the manuscript. All authors designed the study, wrote the manuscript, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Sequencing services were provided by Biomarker Technologies Co., Ltd., Beijing, China.
Funding. The present work was supported by financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701086), GDAS’ Project of Science and Technology Development (2018GDASCX-0102 and 2020GDASYL-20200103020), and Guangdong Province Innovation Team Construction Program on Modern Agriculture Industrial Technology System (The Edible Fungus) (No. 2020KJ103).
Key Resources
| Antibodies | ||||
| Reagent or Resource | Source | Identifier | Working concentration (primary antibodies) | Official website |
| GAPDH | ProteinTech | 60004-1-Ig | 1:10000 | http://www.ptgcn.com/ |
| mTOR | ProteinTech | 20657-1-Ap | 1:1000 | http://www.ptgcn.com/ |
| Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) | Affinity | AF3308 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| LC3A/B | Abcam | ab128025 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| Goat-Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L)HRP | Affinity | S0001 | 1:10000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| Goat-Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L)HRP | Affinity | S0002 | 1:10000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| GPX4 | Affinity | DF6701 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| S100A4 | Affinity | S100A4 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| p-Tau | Affinity | AF3308 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| Tau | Abcam | Ab32057 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| Amyloid β | Affinity | AF6084 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| APOE | Abcam | Ab204112 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| TREM2 | Affinity | DF12529 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| CD33 | Affinity | DF6789 | 1:1000 | http://www.affbiotech.com/ |
| TNF-α | Abcam | ab9579 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| NF-κB | Abcam | ab16502 | 1:1000 | https://www.abcam.com/ |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||||
| Reagent or Resource | Source | Identifier | ||
| RNAiso Plus | Takara | 9109 | ||
| DNAiso Reagent | Takara | 9770Q | ||
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||||
| Reagent or Resource | Source | Identifier | Official website | |
| Detection kit for β-galactosidase (β-Gal) activity | Solarbio | BC2580 | http://www.solarbio.com/ | |
| TMR (Red) Tunel Cell Apoptosis Detection Kit | Servicebio | G1502 | https://www.servicebio.cn/ | |
| TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus) | Takara | RR820A | https://www.takarabiomed.com.cn/ | |
| Prussian blue staining kit | Servicebio | G1029 | http://www.servicebio.cn/ | |
| Relative Mouse Telomere Length Quantification qPCR Assay Kit | ScienCell | #M8908 | https://www.sciencellonline.com/ | |
| Deposited Data | ||||
| RNA sequencing data | This paper | PRJNA669847 | ||
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2021.628860/full#supplementary-material
The specific content of each compound in triterpenoids of G. lucidum. (A) Separation and purification process of triterpenoids of G. lucidum; (B) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of triterpenoids of G. lucidum.
Effect of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on hypothalamus RNA sequencing of normal aged mice. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis (A) Cellular component; (B) Biological process; (C) Molecular function.
Effect of triterpenoids of G. lucidum on serum and brain metabolism of normal aged mice. (A) Hierarchical Clustering Heatmaps of serum metabolite (Distance Measure: Euclidean; Clustering Algorithm: Ward); (B) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of serum metabolite; (C) Hierarchical Clustering Heatmaps of brain tissue metabolite (Distance Measure: Euclidean; Clustering Algorithm: Ward); (D) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of brain tissue metabolite; (E) Metabolites pathway analysis of brain tissue differences metabolites between the control group and TGL-treated group. Use online software MetaboAnalyst (version 4.0) (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca/) for differences in metabolites pathway analysis; n ≥ 14.
The main active substance of triterpenoids of G. lucidum.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of triterpenes of G. lucidum. Tmax, time to peak; Cmax, Peak blood concentration; Vd, apparent volume of distribution; t1/2α, Distribution half-life; t1/2β, Elimination half-time; ig, intragastric administration; iv, intravenous immunoglobulin; per os, oral administration; #, mL min–1 kg–1; ∗, L h–1 kg–1.
G. lucidum and its effects (Phu et al., 2020).
The IPA analysis showed that the function and diseases, including carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, were influenced (APP/PS1).
The different expressed mRNAs enriched into the sphingolipid metabolism (APP/PS1).
References
- Abeliovich A., Gitler A. D. (2016). Defects in trafficking bridge Parkinson’s disease pathology and genetics. Nature 539 207–216. 10.1038/nature20414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Afshin A., Sur P. J., Fay K. A., Cornaby L., Ferrara G., Salama J. S., et al. (2019). Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 393 1958–1972. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30041-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulou E., Piperi C. (2019). Beneficial effects of fingolimod in Alzheimer’s disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Neuromol. Med. 21 227–238. 10.1007/s12017-019-08558-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anitha A., Thanseem I., Vasu M. M., Viswambharan V., Poovathinal S. A. (2019). Telomeres in neurological disorders. Adv. Clin. Chem. 90 81–132. 10.1016/bs.acc.2019.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assi E., Cazzato D., De Palma C., Perrotta C., Clementi E., Cervia D. (2013). Sphingolipids and brain resident macrophages in neuroinflammation: an emerging aspect of nervous system pathology. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013:309302. 10.1155/2013/309302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H., Epel E. S., Lin J. (2015). Human telomere biology: a contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science 350 1193–1198. 10.1126/science.aab3389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonte F., Girard D., Archambault J. C., Desmouliere A. (2019). Skin changes during ageing. Subcell Biochem. 91 249–280. 10.1007/978-981-13-3681-2_10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell J. L., Aboo-Bakkar Z., Conway M. E., Adlam A. R., Fulford J. (2017). Enhanced task-related brain activation and resting perfusion in healthy older adults after chronic blueberry supplementation. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 42 773–779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodowicz J., Przegalinski E., Muller C. P., Filip M. (2018). Ceramide and its related neurochemical networks as targets for some brain disorder therapies. Neurotox. Res. 33 474–484. 10.1007/s12640-017-9798-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao F. R., Xiao B. X., Wang L. S., Tao X., Yan M. Z., Pan R. L. (2017). Plasma and brain pharmacokinetics of ganoderic acid A in rats determined by a developed UFLC-MS/MS method. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 1052 19–26. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S. S., Bir A., Poddar J., Sinha M., Ganguly A., Chakrabarti S. (2016). Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-phosphate in cell death pathways: relevance to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 13 1232–1248. 10.2174/1567205013666160603004239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Xu P., Song P., Wang M., He J. (2019). China has faster pace than Japan in population aging in next 25 years. Biosci. Trends 13 287–291. 10.5582/bst.2019.01213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. R., Yang M., Guan S. H., Wu X. H., Pang X. Y., Wang Y. (2013). Pharmacokinetics of ganoderic acid D and its main metabolite by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 930 1–6. 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.04.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. M., Hui W. S., Chu P. W., Chiu S. W., Ip N. Y. (2000). Ganoderma extract activates MAP kinases and induces the neuronal differentiation of rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 486 291–296. 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02317-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang M. H., Chiou S. H., Huang C. H., Yang W. B., Wong C. H. (2009). The lifespan-promoting effect of acetic acid and Reishi polysaccharide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 7831–7840. 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin Q. A., King B. G., Zanesco A. P., Lin J., Hamidi A. B., Pokorny J. J. (2018). Insight meditation and telomere biology: the effects of intensive retreat and the moderating role of personality. Brain Behav. Immun. 70 233–245. 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crivelli S. M., Giovagnoni C., Visseren L., Scheithauer A. L., de Wit N., den Hoedt S. (2020). Sphingolipids in Alzheimer’s disease, how can we target them? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 159 214–231. 10.1016/j.addr.2019.12.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuong V. T., Chen W., Shi J., Zhang M., Yang H., Wang N. (2019). The anti-oxidation and anti-aging effects of Ganoderma lucidum in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 117 99–105. 10.1016/j.exger.2018.11.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. G., Thompson K. W., Camandola S., Mack K. T., Mattson M. P. (2014). Sphingolipid metabolism regulates development and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 143-144 9–18. 10.1016/j.mad.2014.11.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czubowicz K., Jesko H., Wencel P., Lukiw W. J., Strosznajder R. P. (2019). The role of ceramide and Sphingosine-1-phosphate in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 56 5436–5455. 10.1007/s12035-018-1448-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Alshareef M., Henderson F. J., Martinez S. J., Vandergrift W. R., Lindhorst S. M. (2020). Ganoderic acid A/DM-induced NDRG2 over-expression suppresses high-grade meningioma growth. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 22 1138–1145. 10.1007/s12094-019-02240-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diling C., Yinrui G., Longkai Q., Xiaocui T., Yadi L., Jiaxin F. (2020). Metabolic regulation of Ganoderma lucidum extracts in high sugar and fat diet-induced obese mice by regulating the gut-brain axis. J. Funct. Foods 65:103639. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103639 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dinkins M. B., Enasko J., Hernandez C., Wang G., Kong J., Helwa I. (2016). Neutral Sphingomyelinase-2 deficiency ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and improves cognition in the 5XFAD mouse. J. Neurosci. 36 8653–8667. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1429-16.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiani C., Antollini S. S. (2019). Alzheimer’s disease as a membrane disorder: spatial cross-talk among beta-amyloid peptides, nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and lipid rafts. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:309. 10.3389/fncel.2019.00309 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin V. L., Nichols E., Alam T., Bannick M. S., Beghi E., Blake N. (2019). Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 18 459–480. 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm A., Eckert A. (2017). Brain aging and neurodegeneration: from a mitochondrial point of view. J. Neurochem. 143 418–431. 10.1111/jnc.14037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm M., Michaelson D. M., Hartmann T. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids, lipids, and apoE lipidation in Alzheimer’s disease: a rationale for multi-nutrient dementia prevention. J. Lipid Res. 58 2083–2101. 10.1194/jlr.R076331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W. L., Pan Y. Y., Li L., Li T. T., Liu B., Lv X. C. (2018). Ethanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates lipid metabolic disorders and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Funct. 9 3419–3431. 10.1039/c8fo00836a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo X. Y., Liu D., Ye M., Han J., Deng S., Ma X. C. (2013). Structural characterization of minor metabolites and pharmacokinetics of ganoderic acid C2 in rat plasma by HPLC coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 75 64–73. 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.11.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha D. T., Oh J., Khoi N. M., Dao T. T., Dung L. V., Do T. N. (2013). In vitro and in vivo hepatoprotective effect of ganodermanontriol against t-BHP-induced oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 150 875–885. 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. (2018). Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19 175–191. 10.1038/nrm.2017.107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y. (2012). A world of sphingolipids and glycolipids in the brain–novel functions of simple lipids modified with glucose. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 88 129–143. 10.2183/pjab.88.129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano-Sakamaki W., Sugiyama E., Hayasaka T., Ravid R., Setou M., Taki T. (2015). Alzheimer’s disease is associated with disordered localization of ganglioside GM1 molecular species in the human dentate gyrus. FEBS Lett. 589 3611–3616. 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.09.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y., Dan X., Babbar M., Wei Y., Hasselbalch S. G., Croteau D. L. (2019). Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 15 565–581. 10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y., Wang Y., Wang H., Liu Z., Yu X., Yan J. (2019). Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 6 211–224. 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30511-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain G., Wang J., Rasul A., Anwar H., Imran A., Qasim M. (2019). Role of cholesterol and sphingolipids in brain development and neurological diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 18:26. 10.1186/s12944-019-0965-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesko H., Wencel P. L., Lukiw W. J., Strosznajder R. P. (2019). Modulatory effects of fingolimod (FTY720) on the expression of sphingolipid metabolism-related genes in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 56 174–185. 10.1007/s12035-018-1040-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia J., Wang F., Wei C., Zhou A., Jia X., Li F. (2014). The prevalence of dementia in urban and rural areas of China. Alzheimers Dement. 10 1–9. 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia L., Quan M., Fu Y., Zhao T., Li Y., Wei C. (2020). Dementia in China: epidemiology, clinical management, and research advances. Lancet Neurol. 19 81–92. 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30290-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurk D., Wang C., Miwa S., Maddick M., Korolchuk V., Tsolou A. (2012). Postmitotic neurons develop a p21-dependent senescence-like phenotype driven by a DNA damage response. Aging Cell 11 996–1004. 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00870.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalvodova L., Kahya N., Schwille P., Ehehalt R., Verkade P., Drechsel D. (2005). Lipids as modulators of proteolytic activity of BACE: involvement of cholesterol, glycosphingolipids, and anionic phospholipids in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 280 36815–36823. 10.1074/jbc.M504484200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klupp N. L., Kiat H., Bensoussan A., Steiner G. Z., Chang D. H. (2016). A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of Ganoderma lucidum for the treatment of cardiovascular risk factors of metabolic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 6:29540. 10.1038/srep29540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz J., Parnham M. J., Geisslinger G., Schiffmann S. (2019). Ceramides as novel disease biomarkers. Trends Mol. Med. 25 20–32. 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.10.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. S., Yu M. S., Yuen W. H., So K. F., Zee S. Y., Chang R. C. (2008). Antagonizing beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity of the anti-aging fungus Ganoderma lucidum. Brain Res. 1190 215–224. 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai G., Guo Y., Chen D., Tang X., Shuai O., Yong T. (2019). Alcohol extracts from ganoderma lucidum delay the progress of Alzheimer’s disease by regulating DNA methylation in rodents. Front. Pharmacol. 10:272. 10.3389/fphar.2019.00272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautrup S., Sinclair D. A., Mattson M. P., Fang E. F. (2019). NAD (+) in brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Cell Metab. 30 630–655. 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.09.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. H., Kim J. H., Song C. H., Jang K. J., Kim C. H., Kang J. S. (2016). Ethanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum augments cellular anti-oxidant defense through activation of Nrf2/HO-1. J. Pharmacopuncture 19 59–69. 10.3831/KPI.2016.19.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Lee D. S., Kang Y., Yao N. Q., An R. B., Kim Y. C. (2013). Protective effect of ganodermanondiol isolated from the Lingzhi mushroom against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzymes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 53 317–324. 10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C., Tian D., Liu Y., Li H., Zhu J., Li M. (2019). Review of the molecular mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids: ganoderic acids A, C2, D, F, DM, X and Y. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 174 130–141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Z., Yuan Z., Li G., Fu F., Shan Y. (2018). Hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic effects of polysaccharides extracted from Reishi Mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (Leysser: Fr) Karst, in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Med. Food 21 1218–1227. 10.1089/jmf.2018.4182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Zhang J., Liu Y., Wu R., Yang H., Hu X. (2017). Studies on diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease through metabolomics and hippocampal proteomics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 105 119–126. 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling D., Salvaterra P. M. (2011). Brain aging and Abeta(1)(-)(4)(2) neurotoxicity converge via deterioration in autophagy-lysosomal system: a conditional Drosophila model linking Alzheimer’s neurodegeneration with aging. Acta Neuropathol. 121 183–191. 10.1007/s00401-010-0772-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M. M., Zheng B., Lu T., Yan Z., Py B. F., Ng A. (2010). Genome-wide analysis reveals mechanisms modulating autophagy in normal brain aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107 14164–14169. 10.1073/pnas.1009485107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Lai G., Guo Y., Tang X., Shuai O., Xie Y. (2021). Protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum spore extract in Trimethylamine-N-oxide-induced cardiac dysfunction in rats. J. Food Sci. 86 546–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maceyka M., Harikumar K. B., Milstien S., Spiegel S. (2012). Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 22 50–60. 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.09.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magistretti P. J., Geisler F. H., Schneider J. S., Li P. A., Fiumelli H., Sipione S. (2019). Gangliosides: treatment avenues in neurodegenerative disease. Front. Neurol. 10:859. 10.3389/fneur.2019.00859 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maharani A., Dawes P., Nazroo J., Tampubolon G., Pendleton N. (2018). Visual and hearing impairments are associated with cognitive decline in older people. Age Ageing 47 575–581. 10.1093/ageing/afy061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. (2005). The effects of stress and aging on glutathione metabolism. Ageing Res. Rev. 4 288–314. 10.1016/j.arr.2005.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancino R., Martucci A., Cesareo M., Giannini C., Corasaniti M. T., Bagetta G. (2018). Glaucoma and Alzheimer disease: one age-related neurodegenerative disease of the brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 16 971–977. 10.2174/1570159X16666171206144045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marras C., Beck J. C., Bower J. H., Roberts E., Ritz B., Ross G. W. (2018). Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 4:21. 10.1038/s41531-018-0058-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. P., Mielke M. M. (2017). Sphingolipids in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. J. Alzheimers Dis. 60 753–756. 10.3233/JAD-170735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaldan S., Clatworthy S., Gamell C., Meggyesy P. M., Rigopoulos A. T., Haupt S. (2018). Iron accumulation in senescent cells is coupled with impaired ferritinophagy and inhibition of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 14 100–115. 10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Arumugam T. V. (2018). Hallmarks of brain aging: adaptive and pathological modification by metabolic states. Cell Metab. 27 1176–1199. 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.05.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard S., Fang E. F., Scheibye-Knudsen M., Croteau D. L., Bohr V. A. (2015). DNA damage, DNA repair, aging, and neurodegeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 5:a025130. 10.1101/cshperspect.a025130 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura Y., Miyaji K., Chai Y. L., Chen C. L., Lai M. K., Yuki N. (2014). Autoantibodies to GM1 and GQ1balpha are not biological markers of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 42 1165–1169. 10.3233/JAD-140474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourmohammadi I., Modarress M., Khanaki K., Shaabani M. (2008). Association of serum alpha-tocopherol, retinol and ascorbic acid with the risk of cataract development. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 52 296–298. 10.1159/000148189 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen A., Faergeman N. J. (2017). Sphingolipids: membrane microdomains in brain development, function and neurological diseases. Open Biol. 7:170069. 10.1098/rsob.170069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. G., Bechinger-English D., Jagger C., Spiers N., Lindesay J. (2006). Factors affecting completion of the SF-36 in older people. Age Ageing 35 376–381. 10.1093/ageing/afl003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pera M., Larrea D., Guardia-Laguarta C., Montesinos J., Velasco K. R., Agrawal R. R. (2017). Increased localization of APP-C99 in mitochondria-associated ER membranes causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. EMBO J. 36 3356–3371. 10.15252/embj.201796797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phu H. T., Thuan D., Nguyen T., Posadino A. M., Eid A. H., Pintus G. (2020). Herbal medicine for slowing aging and aging-associated conditions: efficacy, mechanisms and safety. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 18 369–393. 10.2174/1570161117666190715121939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvill T., Lindenberg J., Gussekloo J., de Craen A. J., Slaets J. P., Westendorp R. G. (2016). Associations of various health-ratings with geriatric giants, mortality and life satisfaction in older people. PLoS One 11:e0163499. 10.1371/journal.pone.0163499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarraj A., Savitz S., Pujara D., Kamal H., Carroll K., Shaker F. (2020). Endovascular thrombectomy for acute ischemic strokes: current US access paradigms and optimization methodology. Stroke 51 1207–1217. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.028850 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shetty A. K., Upadhya R., Madhu L. N., Kodali M. (2019). Novel insights on systemic and brain aging, stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis. 10 470–482. 10.14336/AD.2019.0330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Aryal B., Chaube B., Rotllan N., Varela L., Horvath T. L. (2018). Brown adipose tissue derived ANGPTL4 controls glucose and lipid metabolism and regulates thermogenesis. Mol. Metab. 11 59–69. 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.03.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnino S., Prinetti A. (2016). The role of sphingolipids in neuronal plasticity of the brain. J. Neurochem. 137 485–488. 10.1111/jnc.13589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockburger C., Eckert S., Eckert G. P., Friedland K., Muller W. E. (2018). Mitochondrial function, dynamics, and permeability transition: a complex love triangle as a possible target for the treatment of brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 64 S455–S467. 10.3233/JAD-179915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom A., Coppus A., Blesa R., Danek A., Fortea J., Hardy J. (2018). Alzheimer’s disease in Down syndrome: an overlooked population for prevention trials. Alzheimers Dement. (N Y) 4 703–713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teekachunhatean S., Sadja S., Ampasavate C., Chiranthanut N., Rojanasthien N., Sangdee C. (2012). Pharmacokinetics of ganoderic acids a and f after oral administration of ling zhi preparation in healthy male volunteers. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2012:780892. 10.1155/2012/780892 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng B. S., Wang C. D., Zhang D., Wu J. S., Pan D., Pan L. F., et al. (2012). Hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of a proteoglycan from Ganoderma lucidum on streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 16 166–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo J. B., Arnold M., Kastenmuller G., Chang R., Baillie R. A., Han X. (2017). Metabolic network failures in Alzheimer’s disease: a biochemical road map. Alzheimers Dement. 13 965–984. 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.01.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayssac M., Hannun Y. A., Obeid L. M. (2018). Role of sphingolipids in senescence: implication in aging and age-related diseases. J. Clin. Invest. 128 2702–2712. 10.1172/JCI97949 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse K. H., Herrup K. (2017). DNA damage in the oligodendrocyte lineage and its role in brain aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 161 37–50. 10.1016/j.mad.2016.05.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Geldorp B., Heringa S. M., van den Berg E., Olde R. M., Biessels G. J., Kessels R. P. (2015). Working memory binding and episodic memory formation in aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s dementia. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 37 538–548. 10.1080/13803395.2015.1037722 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Liew J. B., Davis P. J., Davis F. B., Bernardis L. L., Deziel M. R., Marinucci L. N. (1993). Effects of aging, diet, and sex on plasma glucose, fructosamine, and lipid concentrations in barrier-raised Fischer 344 rats. J. Gerontol. 48 B184–B190. 10.1093/geronj/48.5.b184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroya F., Cereijo R., Villarroya J., Giralt M. (2017). Brown adipose tissue as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 13 26–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vutukuri R., Brunkhorst R., Kestner R. I., Hansen L., Bouzas N. F., Pfeilschifter J. (2018). Alteration of sphingolipid metabolism as a putative mechanism underlying LPS-induced BBB disruption. J. Neurochem. 144 172–185. 10.1111/jnc.14236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel-Galor S., Szeto Y. T., Tomlinson B., Benzie I. F. (2004). Ganoderma lucidum (‘Lingzhi’); acute and short-term biomarker response to supplementation. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 55 75–83. 10.1080/09637480310001642510 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Zhou Z., Ren X., Wang Y., Yang R., Luo J. (2015). Effect of Ganoderma lucidum spores intervention on glucose and lipid metabolism gene expression profiles in type 2 diabetic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 14:49. 10.1186/s12944-015-0045-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Liu R., Sun J., Guan S., Yang M., Bi K. (2007). HPLC method for the determination and pharmacokinetic studies of four triterpenoids in rat plasma after oral administration of Ganoderma lucidum extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. 21 389–396. 10.1002/bmc.768 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao C., Wu Q., Zhang J., Xie Y., Cai W., Tan J. (2017). Antidiabetic activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides F31 down-regulated hepatic glucose regulatory enzymes in diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 196 47–57. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao C., Wu Q. P., Cai W., Tan J. B., Yang X. B., Zhang J. M. (2012). Hypoglycemic effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in type 2 diabetic mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35 1793–1801. 10.1007/s12272-012-1012-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Chu X., Yin M., Liu X., Yuan H., Niu Y. (2014). mTOR and autophagy in normal brain aging and caloric restriction ameliorating age-related cognition deficits. Behav. Brain Res. 264 82–90. 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Wu F., He Y., Zhang Q., Zhang Y., Zhou G. (2018). A novel PTP1B inhibitor extracted from Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates insulin resistance by regulating IRS1-GLUT4 cascades in the insulin signaling pathway. Food Funct. 9 397–406. 10.1039/c7fo01489a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y. Y. (1984). Biosynthesis of phospholipids and sphingolipids from acetoacetate and glucose in different regions of developing brain in vivo. J. Neurosci. Res. 11 383–394. 10.1002/jnr.490110406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F., Sancheti H., Patil I., Cadenas E. (2016). Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 100 108–122. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng P., Chen Y., Zhang L., Xing M. (2019). Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide used for treating physical frailty in China. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 163 179–219. 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2019.02.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. N., Lin Z. B. (2004). Hypoglycemic effect of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 25 191–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. X., Zahner G. E., Roman G. C., Liu J., Hong Z., Qu Q. M. (2005). Dementia subtypes in China: prevalence in Beijing, Xian, Shanghai, and Chengdu. Arch. Neurol. 62 447–453. 10.1001/archneur.62.3.447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou M., Wang H., Zeng X., Yin P., Zhu J., Chen W. (2019). Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 394 1145–1158. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucca F. A., Segura-Aguilar J., Ferrari E., Munoz P., Paris I., Sulzer D. (2017). Interactions of iron, dopamine and neuromelanin pathways in brain aging and Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 155 96–119. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The specific content of each compound in triterpenoids of G. lucidum. (A) Separation and purification process of triterpenoids of G. lucidum; (B) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of triterpenoids of G. lucidum.
Effect of Triterpenoids of G. lucidum on hypothalamus RNA sequencing of normal aged mice. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis (A) Cellular component; (B) Biological process; (C) Molecular function.
Effect of triterpenoids of G. lucidum on serum and brain metabolism of normal aged mice. (A) Hierarchical Clustering Heatmaps of serum metabolite (Distance Measure: Euclidean; Clustering Algorithm: Ward); (B) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of serum metabolite; (C) Hierarchical Clustering Heatmaps of brain tissue metabolite (Distance Measure: Euclidean; Clustering Algorithm: Ward); (D) Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of brain tissue metabolite; (E) Metabolites pathway analysis of brain tissue differences metabolites between the control group and TGL-treated group. Use online software MetaboAnalyst (version 4.0) (http://www.metaboanalyst.ca/) for differences in metabolites pathway analysis; n ≥ 14.
The main active substance of triterpenoids of G. lucidum.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of triterpenes of G. lucidum. Tmax, time to peak; Cmax, Peak blood concentration; Vd, apparent volume of distribution; t1/2α, Distribution half-life; t1/2β, Elimination half-time; ig, intragastric administration; iv, intravenous immunoglobulin; per os, oral administration; #, mL min–1 kg–1; ∗, L h–1 kg–1.
G. lucidum and its effects (Phu et al., 2020).
The IPA analysis showed that the function and diseases, including carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, were influenced (APP/PS1).
The different expressed mRNAs enriched into the sphingolipid metabolism (APP/PS1).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.