Abstract
Background
Achieving robust responses with adoptive cell therapy for the treatment of the highly lethal pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) has been elusive. We previously showed that T cells engineered to express a mesothelin-specific T cell receptor (TCRMsln) accumulate in autochthonous PDA, mediate therapeutic antitumor activity, but fail to eradicate tumors in part due to acquisition of a dysfunctional exhausted T cell state.
Methods
Here, we investigated the role of immune checkpoints in mediating TCR engineered T cell dysfunction in a genetically engineered PDA mouse model. The fate of engineered T cells that were either deficient in PD-1, or transferred concurrent with antibodies blocking PD-L1 and/or additional immune checkpoints, were tracked to evaluate persistence, functionality, and antitumor activity at day 8 and day 28 post infusion. We performed RNAseq on engineered T cells isolated from tumors and compared differentially expressed genes to prototypical endogenous exhausted T cells.
Results
PD-L1 pathway blockade and/or simultaneous blockade of multiple coinhibitory receptors during adoptive cell therapy was insufficient to prevent engineered T cell dysfunction in autochthonous PDA yet resulted in subclinical activity in the lung, without enhancing anti-tumor immunity. Gene expression analysis revealed that ex vivo TCR engineered T cells markedly differed from in vivo primed endogenous effector T cells which can respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Early after transfer, intratumoral TCR engineered T cells acquired a similar molecular program to prototypical exhausted T cells that arise during chronic viral infection, but the molecular programs later diverged. Intratumoral engineered T cells exhibited decreased effector and cell cycle genes and were refractory to TCR signaling.
Conclusions
Abrogation of PD-1 signaling is not sufficient to overcome TCR engineered T cell dysfunction in PDA. Our study suggests that contributions by both the differentiation pathways induced during the ex vivo T cell engineering process and intratumoral suppressive mechanisms render engineered T cells dysfunctional and resistant to rescue by blockade of immune checkpoints.
Keywords: cell engineering, immunity, cellular, immunotherapy, adoptive, tumor microenvironment
Introduction
The incidence and mortality of the particularly lethal malignancy pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) is on the rise.1 The standard of care for advanced PDA is cytotoxic chemotherapy regimens of either FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine +abraxane, which both can be highly toxic and are not curative.2 Immunotherapies that depend on augmenting endogenous immune responses not only require expression of immunogenic tumor antigens, but can take several weeks to achieve a clinical benefit, an often-impractical time frame. Thus, effective therapeutic options are desperately needed.
Mesothelin (Msln) is overexpressed by PDA,3 4 is poorly expressed by normal cells, and is currently a clinical target for immunotherapies.5 We previously demonstrated that CD8 T cells engineered to express a mesothelin-specific T cell receptor (TCRMsln) preferentially accumulate in tumors in the autochthonous KrasLSLG12D/+; Trp53LSL-R172H/+; p48-Cre (KPC) PDA mouse model.4 The infused engineered T cells exhibited transient anti-tumor activity but rapidly became dysfunctional in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Repeated infusions of T cells every 2 weeks induced tumor shrinkage and significantly prolonged animal survival,4 results reproduced in a disseminated ovarian cancer model,6 but multiple infusions is labor intensive and clinically challenging. As we are preparing to translate this T cell therapy to cancer patients, we are actively seeking an approach to safely enhance their antitumor activity.
In the contexts of malignancy and chronic viral infection, antigen-specific T cells can become exhausted (TEX), which can be broadly defined as a dysfunctional state. Chronic antigen encounter leads to persistent TCR signaling and TEX formation. TEX express PD-1 and exhibit functional deficiencies, including diminished cytokine production following target recognition.7 Mechanistically, PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade can reinvigorate a subset of TEX, particularly a proliferative subset of ‘progenitor’ PD-1+ TEX that expresses T cell factor-1 (Tcf-1), a stem cell memory transcription factor.8–13 Tcf-1 sustains the TEX progenitor cells, which are dependent on expression of PD-1 to prevent differentiation to effector cells.14 The HMG-transcription factor Tox is a master regulator that restrains terminal differentiation of effector T cells15 and is critical for TEX formation.16–18 We have shown that systemic PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade can expand endogenous tumor-specific T cells with transient antitumor activity in a PDA animal model.19 However, the extent that this strategy can benefit in vitro activated, genetically modified, and expanded TCR engineered T cells is untested.
Here, we investigate if clinically available strategies could reverse the dysfunction engineered T cells acquire following treatment of autochthonous PDA in a mouse model. We show that TCRMsln cells infiltrating PDA rapidly acquire a marked TCR signaling defect. Disappointingly, neither the function nor quantity of TCRMsln cells infiltrating PDA were improved by monotherapy PD-L1 blockade, or even by a combination of antibodies blocking PD-L1, Tim-3 and Lag-3 concurrently. Molecular profiling showed that differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in intratumoral TCRMsln T cells were distinct from those identified in TEX described in other settings, and were not altered by PD-L1 blockade. Further, TCRMsln cells prior to transfer co-expressed Tcf-1 and Tox but lacked PD-1 suggesting a distinct differentiation program acquired during in vitro generation. Our study highlights the need for interventions beyond immune checkpoint blockade to overcome the acquired engineered T cell exhaustion in treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Results
Functional deficits in both PD-1+ and PD-1- cells TCR engineered T cells infiltrating PDA
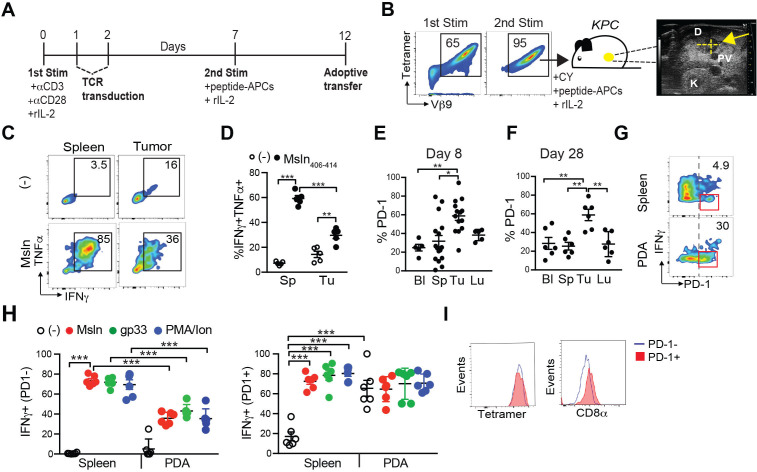
We previously developed an adoptive T cell therapy protocol that significantly prolonged survival of KPC mice.4 This protocol also resulted in long-lived functional memory T cells in normal tissues.4 Specifically, murine P14 CD8 T cells transduced to express a Msln406-414:H-2Db-specific TCR (clone 1045) infiltrate tumors and metastasis and mediate objective responses.4 However, the treatment was not curative because engineered T cells were rendered dysfunctional in the tumor microenvironment (TME), while retaining function in normal tissues.4 To investigate the factors contributing to intratumoral T cell dysfunction, T cells were stimulated with αCD3 + αCD28, transduced on days 1 and 2 with the 1045 retroviral vector and cultured with recombinant human IL-2 (rIL-2) for 7 days to promote T cell expansion and survival (figure 1A).4 On day 7, T cells were restimulated (second stim) with Msln406-414-pulsed, irradiated splenocytes and rIL-2 to obtain a pure population of engineered (TCRMsln) T cells (figure 1B). KPC mice with a 3–6 mm primary tumor mass, as determined by high-resolution ultrasound, received T cell therapy as described4 (figure 1B). At 8 days after transfer, intratumoral TCRMsln cells were defective in IFNγ and TNFα production compared with TCRMsln cells isolated from the spleen (figure 1C, D), consistent with our prior study.4 A higher proportion of intratumoral TCRMsln cells expressed PD-1 compared with blood, spleen, and lung at day 8 post-transfer (figure 1E). However, the proportion of PD-1+ TCRMsln cells did not increase further by 28 days postinfusion (figure 1F). As we previously showed TCRMsln cells fail to accumulate in lung via in situ staining4 and PD-1 levels were similarly low on both circulating and lung TCRMsln cells, the few TCRMsln cells detected in lung likely reflect blood contamination. Unexpectedly, PD-1-negative engineered T cells were defective in IFNγ production following peptide restimulation ex vivo, whereas the PD-1+ T cells exhibited a constitutive level of IFNγ production but were unresponsive to further stimulation through the TCR following Msln peptide restimulation (figure 1G, H). This was also the case when we used gp33 peptide, which stimulates the endogenous P14 TCR expressed by the engineered T cells (figure 1H). Thus, PD-1 does not appear to be a marker of exhausted T cells, and instead may identify T cells at their maximal activation. Since splenic TCRMsln cells remain highly functional and persist, our T cell therapy approach is sufficient to generate persistent T cells and tumor-mediated suppression is operative. Tetramer staining was similar between TCRMsln PD1 +and PD1- T cells whereas CD8α staining was marginally higher in TCRMsln PD1+ vs PD1- T cells (figure 1I). As CD8α coreceptor stabilizes TCR binding to peptide:MHC, these data suggest potentially stronger TCR signaling in the PD1 +population.
Figure 1.
Functional deficits in both PD-1+ and PD-1- TCR engineered T cells infiltrating PDA. (A) Generation of murine TCRMsln T cells for adoptive cell therapy. Congenic P14 CD8 +T cells are activated with anti-CD3 +anti-CD28 (first Stim), transduced with the high affinity TCRMsln (1045), and restimulated (second Stim) in vitro with irradiated peptide-pulsed splenocytes, and transferred on day 12. T cells are supplemented with recombinant human IL-2 (rIL-2) every other day. (B) Representative staining for Msln406-414:H-2Db tetramer and Vβ9 staining in TCRMsln cells 5 days following the first Stim, or 5 days following the second Stim in vitro according to figure 1A. T cells are infused into KPC mice bearing a 3–6 mm pancreas mass detected by high-resolution ultrasound. The T cell therapy protocol consists of Cytoxan (CY) 6 hours prior to T cell infusion and T cells administered with irradiated peptide-pulsed splenocytes (peptide-APCs) and IL-2. Arrow, hypoechoic pancreas tumor; D, duodenum. PV, portal vein; K, kidney. (C) Cytokine production by CD8+ Thy1.1+ TCRMsln T cells following ex vivo restimulation ± Msln406-414 peptide on day 8. Representative of 5 mice. (D) Proportion of TCRMsln T cells coproducing IFNγ and TNFα was determined by intracellular cytokine staining. Each dot is an independent animal. Data are mean±SEM *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, one-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s post-test. Proportion of TCRMsln cells that express PD-1 at day 8 (E) and day 28 (F) post-transfer. Bl, blood; Sp, spleen; Tu, tumor; Lu, Lung. Each dot is an independent mouse. Data are mean±SEM one-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s post-test. *P<0.05; **p<0.01. (G) PD-1 and IFNγ gated on TCRMsln cells at 8 days postinfusion and following a 4 hour ex vivo restimulation with Msln406-414 peptide. (H) Proportion of PD-1- (left graph) and PD-1+ (right graph) TCRMsln cells producing IFNγ at 8 days post-transfer following the indicated stimulations: Msln406-414 peptide (triggers the transduced TCR), gp33 peptide (triggers the endogenous TCR), and a positive control PMA +Ionomycin (PMA/Ion). Each dot is an independent mouse. Data are mean±SEM. Note that the left graph is cytokine production by PD-1-negative TCRMsln cells and the right graph is cytokine production by PD-1 +TCRMsln cells and do not reflect the percentages shown in the plots in figure 1G which are gated on total TCRMsln cells. One-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s post-test. ***P<0.001. (I) CD8α staining on intratumoral PD-1+ (red) and PD-1- (blue) TCRMsln cells on day 8 post-transfer. ANOVA, analysis of variance; PDA, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PMA, phorbyl-12 myristate 13-acetate.
TCR engineered T cells fail to respond to PD-L1 blockade
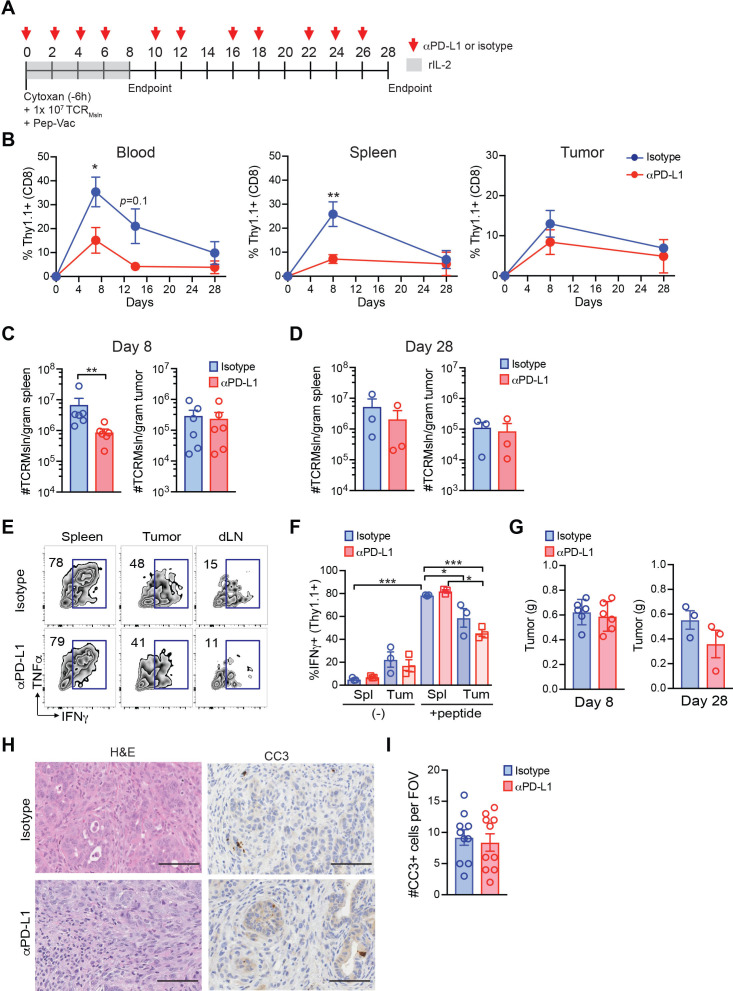
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade can reinvigorate a subpopulation of PD-1+ T cells in hosts with chronic virus infection or cancer.7 9–11 20 To investigate the effect of PD-1 blockade on engineered T cell dysfunction in PDA, KPC mice with a 3–6 mm primary tumor mass were enrolled to receive TCRMsln cell therapy ±αPD-L1 or isotype control (figure 2A). αPD-L1 significantly decreased the proportion of circulating and splenic engineered T cells at day 8 postinfusion, while not significantly impacting the frequency of engineered T cells intratumorally (figure 2B). αPD-L1 decreased splenic TCRMsln cell number at day 8 (figure 2C), while not impacting the number of engineered T cells that persisted in the spleen or tumor at day 28 (figure 2C, D). αPD-L1 failed to significantly rescue the diminished cytokine production by intratumoral TCRMsln T cells already evident by day 8 (figure 2E, F). We observed a trend for decreased endogenous CD8+ T cells in spleen and tumor, and a significant decrease in circulating endogenous CD8 T cell frequency following αPD-L1 (online supplemental figure 1A). However, overall number of endogenous CD8 T cells was not changed by αPD-L1 at either time point (online supplemental figure 1B, C). αPD-L1 also did not change tumor weight (figure 2G) or alter tumor cell apoptosis (figure 2H, I). Thus, αPD-L1 was insufficient to reinvigorate exhausted engineered T cells in autochthonous PDA.
Figure 2.
TCR engineered T cells fail to respond to PD-L1 blockade. (A) T cell therapy protocol following αPD-L1 or isotype in KPC mice. (B) Proportion of TCRMsln of total CD8+ T cells in blood, spleen, or tumor. Data are mean±SEM Student’s t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Number of TCRMsln cells per gram spleen or tumor at day 8 (C) or day 28 (D). Each dot is an independent mouse. Data are mean±SEM Student’s t-test. **P<0.01. (E) Representative FACs plots gated on TCRMsln cells following ex vivo restimulation with antigen at day eight post-transfer ±αPD-L1 or isotype. Numbers in graphs are the frequency of TCRMsln cells producing IFNγ. dLN, pancreatic draining lymph nodes. (F) Proportion of TCRMsln cells producing IFNγ at day 8 post-transfer. Each dot is an independent mouse. Spl, spleen; Tum, tumor. Data are mean±SEM. (-), no peptide. One-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s post-test among the no peptide (-), or the +peptide groups. *P<0.05; ***p<0.001. (G) Tumor weights in grams (g) at day 8 or day 28 post-therapy. Each dot is an independent animal. Data are mean±SEM. (H) Histology and cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) staining of representative tumors following TCRMsln cell therapy and indicated antibodies at day 28. (I) Number of CC3 +cells per field of view (FOV) at day 28 post-therapy. Data are mean±SEM. ANOVA, analysis of variance.
jitc-2021-003525supp001.pdf (6MB, pdf)
As antibody blockade may be incomplete, we next evaluated engineered T cell that were genetically deficient in PD-1. We cotransferred congenic Thy1.1+/Thy1.2+ Pdcd1+/+ and Thy1.1+/Thy1.1+ (Thy1.2-) Pdcd1-/- TCRMsln T cells into the same KPC recipients at 1:1 ratio (online supplemental figure 2A). At day 8 post-transfer, the proportion of Pdcd1-/- TCRMsln T cells was elevated compared with Pdcd1+/+ TCRMsln cells in tumors and other tissues (online supplemental figure 2B), resulting in a 2.3-fold increase in intratumoral Pdcd1-/- TCRMsln T cell number. However, complete loss of PD-1 expression failed to increase the fraction of intratumoral TCRMsln cells that produce IFNγ (online supplemental figure 2C). Ki67 expression, which identifies T cells in all phases of cell cycle except G0 were also not different at day 8 among the Pdcd1+/+ and Pdcd1-/- engineered T cells (online supplemental figure 2D). At day 28 postinfusion, the proportion of Pdcd1-/- TCRMsln cells was significantly lower compared with Pdcd1+/+ TCRMsln cells, which was also reflected by a>1 log decrease in donor Pdcd1-/- T cell number (online supplemental figure 2E). These data support that PD-1 promotes memory T cell formation21 and maintains Tcf-1+ TEX progenitor cells.14
jitc-2021-003525supp002.pdf (2MB, pdf)
Molecular profiling of TCRMsln cells infiltrating PDA
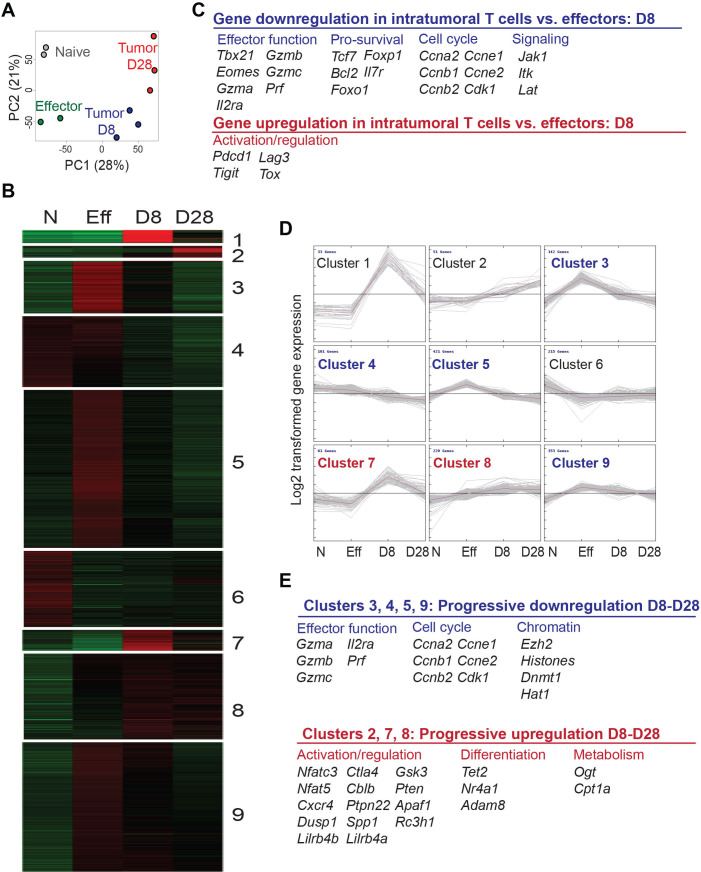
To probe the molecular basis of engineered T cell dysfunction in PDA, we performed a comparative whole-genome transcriptomic analysis of engineered TCRMsln T cells sorted from autochthonous KPC tumors at day 8 (D8) and day 28 (D28) post-transfer, to naïve CD8+ T cells (N) and engineered effector T cells prior to transfer (Eff). Naïve CD8+ T cells clustered based on principal component analysis (PCA) separately from all the other TCRMsln cells groups (figure 3A). TCRMsln cells isolated from tumors clustered together, and D8 intratumoral TCRMsln cells clustered separately from D28 intratumoral TCRMsln cells. Purified splenic TCRMsln cells also clustered distinctly from intratumoral TCRMsln cells isolated from the same KPC animals (online supplemental figure 3A). Despite rigorous gating and flow sorting to obtain high purity of donor T cells (>95% CD8+Thy1.1+ T cells), we detected rare pancreas-associated genes (eg, Cpb1, Amy2b, Try4, Dmbt1, Ctrb1) in the intratumoral T cell preparations in Cluster 1 (figure 3B, online supplemental tables S1 and S2). These transcripts were most abundant at D8 (online supplemental figure 3B) and may reflect rare contaminating pancreatic tumor cells from the dissociated tumor mass that highly express a small subset of genes. Alternatively, trogocytosis as described for CD19-specific CAR T cells T cells encountering tumor cells,22 might be responsible, but if nucleic acids are included in this process is unknown. Intratumoral TCRMsln cells downregulated effector T cell transcription factors and effector molecules compared with splenic TCRMsln cells (eg, Tbx2, Eomes, Il2ra, Gzma, Gzmb, Gzmc, Pfn) (figure 3C), consistent with defective cytokine production (figure 1C, D).4 Genes involved in T cell longevity/survival (eg, Tcf7, Bcl2, Foxo1, Foxp1, Il7r), cell cycle (eg, Ccna2, Ccnb1, Ccnb2, Ccne1, Ccne2, Cdk1) and signaling molecules (Lat, Jak1, Itk) in intratumoral TCRMsln cells were also significantly decreased (figure 3C–D, online supplemental tables S1 and S2). Cluster analyses revealed a progressive upregulation of genes involved in regulation of lymphocyte function and signaling (Ctla4, Cblb, Ptpn22, Dusp1, Pten, Apaf1, Rc3h1, Cxcr4, Nfatc3), differentiation (Tet2b, Nr4a1, Adam8), and metabolism (Ogt, Cpt1a) (figure 3D, E). Lilr4b, recently shown to be elevated on CD8+ T cells that express multiple coinhibitory molecules in a melanoma mouse model,23 was also progressively elevated in intratumoral TCRMsln cells. At D28, Pdcd1, Ctla4, Tigit and Lag3 were elevated on intratumoral TCRMsln cells (online supplemental table 2), similar to T cells in human PDA.24 Ezh2, which is a regulator of repressive chromatin states and transcriptional quiescence,25 was elevated in effector and progressively reduced in intratumoral TCRMsln cells.
Figure 3.
Molecular profiling of TCRMsln cells infiltrating PDA. (A) Principle component analysis of naïve splenic CD8+ T cells (Naïve, n=2), TCRMsln effector T cells prior to transfer (Effector D12, n=2), TCRMsln cells sorted from PDA at day 8 (tumor D8, n=3) or at day 28 (tumor day 28, n=3). (B) Heat map of DEGs and indicated clusters of genes based on K-means clustering of transcript levels. Data are log2-transformed expression intensities and probes were mean-centered. (C) Selected DEGs in TCRMsln cells infiltrating tumors vs spleens of KPC mice. (D) K-means clustering of transcript levels for nine clusters. Data are log2-transformed expression intensities and probes were mean-centered. (E) Selected genes associated with stemness or terminal differentiation from selected K-means clusters. Progressively downregulated genes and progressively upregulated genes relevant to T cell functionality. The accession number to access the raw and processed data at Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) is GSE196435. See also online supplemental tables S2 and S3. DEGs, differentially expressed genes; PDA, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
We next compared DEGs from adoptively transferred TCRMsln T cells to exhausted CD8 T cells studied in other model systems. DEGs in intratumoral TCRMsln cells showed minimal overlap to T cells that first encounter an endogenous liver tumor antigen (SV40) in vivo26 (online supplemental figure 3C). However, both intratumoral TCRMsln and SV40-specific T cells exhibited elevated expression of Pdcd1, Lag3 and Ctla4 and decreased Il7r and Tcf7 (online supplemental table 2). Exhausted SV40-specific T cells and TEX isolated from chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection upregulate Cd160, Ezh2, 2b4, Blimp1, Id2 and Il10rb and downregulate Smad1 and Cd107,26 and these genes were not significantly altered in intratumoral TCRMsln cells. In addition, genes controlling nucleosome and chromatin assembly progressively decreased in TCRMsln cells, including histone acetyltransferases and DNA methyltransferases (Hat1, Dnmt3b, Dnmt1), which are increased in SV40-specific T cells on day 8 and then decrease by day 30.26 Thus, while some of these differences may reflect time from the initial priming event and the context of that priming, they may also reflect distinct in vivo situations in which the T cells are chronically encountering antigen.
Engineered T cells acquire molecular characteristics distinct from TEX in chronic infection
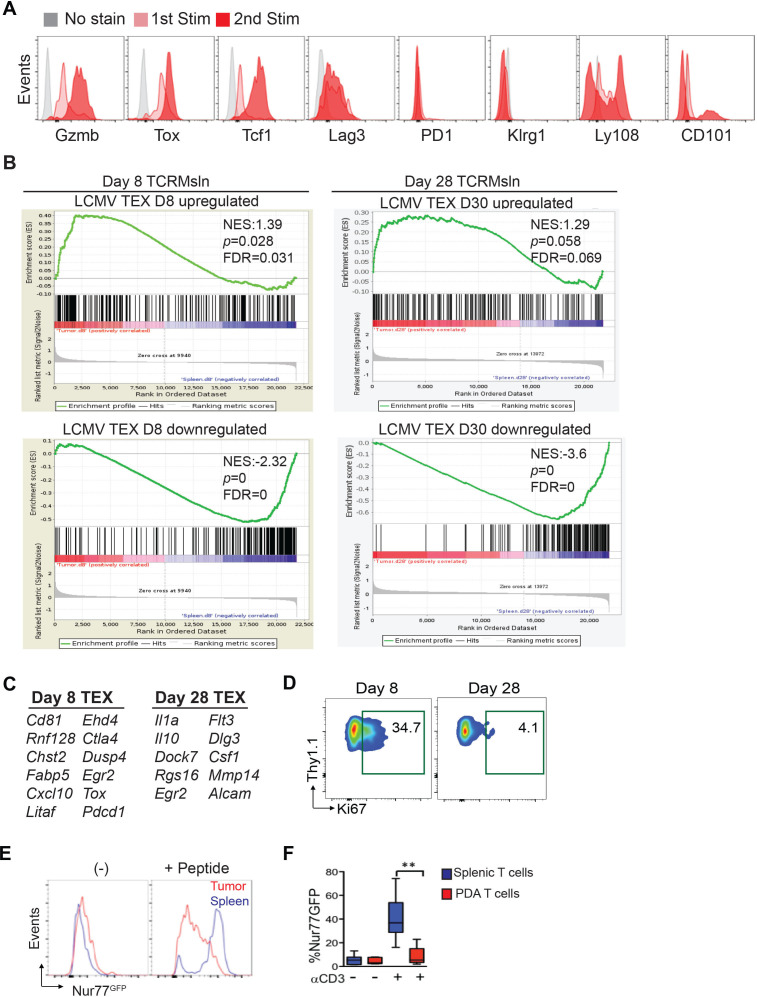
We next stained engineered T cells following the first in vitro stimulation with transduction (1st Stim) and following the second in vitro restimulation (2nd Stim) to enrich and expand transduced cells prior to infusion for assessment of Tox and Tcf-1, factors known to impact TEX and responsiveness to PD-L1 blockade. The engineered T cells did not express PD-1, did express Lag3, and co-expressed both Tox and Tcf-1 that were further increased following the second stimulation (figure 4A). These data suggest a distinct differentiation program acquired during the generation of engineered T cells in vitro. We next compared the molecular signature of intratumoral TCRMsln cells to prototypical TEX that arise in vivo during persistent LCMV infection using gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). A subset of upregulated and DEGs overexpressed in intratumoral TCRMsln cells significantly overlapped with prototypical early TEX (isolated from mice with chronic viral infection27) at D8 (figure 4B, online supplemental table 3). These include Cd81, Pdcd1, Ctla4, Dusp4, Cxcl10, Egr2, Tox, and Fabp (figure 4C). By D28, a subset of different DEGs in intratumoral TCRMsln cells again overlapped with prototypical TEX at D30 (figure 4B) such as Il1a, Il10 and Csf1 (figure 4C), but did not quite reach statistical significance. Endogenous TEX that are rescued by PD-1 pathway blockade are proliferating.11 19 Although TCRMsln cells proliferate early after transfer, by D28 most intratumoral transferred engineered T cells no longer express Ki67 (figure 4D). To investigate if elements in the TME might be interfering with TCR signaling, we expressed TCRMsln in Nur77GFP reporter T cells, in which the observed GFP signal intensity is directly proportional to the TCR signal strength.28 Both intratumoral TCRMsln cells (figure 4E) and endogenous intratumoral CD8 T cells (figure 4F) exhibited reduced Nur77GFP expression following incubation with Msln peptide or αCD3 ex vivo, consistent with an acquired TCR signaling defect. Thus, the program of engineered TEX in PDA may be distinct from endogenous TEX that arise during chronic viral infection. Future studies using additional Msln+ cancer models or a different TCR antigen specificity will help identify how the pancreatic TME contributes to TEX differentiation.
Figure 4.
Engineered T cells acquire molecular characteristics distinct from TEX in chronic infection. (A) Histogram overlays of T cell activation and exhaustion molecules in TCRMsln cells on day 5 following stimulation with αCD3+αCD28 and rIL-2 (first Stim), and on day 12, 5 days following the second in vitro restimulation with peptide-pulsed irradiated splenocytes and IL-2 (second Stim), which is the time point prior to T cell infusion. The gray histograms are gated on CD8α+Thy1.1+engineered T cells without the indicated stain. (B) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) in day 8 (left) or day 28 (right) of TCRMsln isolated from PDA as compared with day 8 (left) or day 30 (right) exhaustion profiles of virus specific T cells isolated from spleens during chronic LCMV infection. Left plot: GSEA plot of D8 intratumoral TCRMsln cells (vs D8 splenic TCRMsln effectors) of genes previously identified to be upregulated (left) in exhausted LCMV virus-specific CD8+ T cells at day 8 after chronic LCMV clone 13 infection (compared with effectors, 8 days after acute infection; GEO:GSE30962). Right plot: GSEA plot of D28 TCRMsln (vs D28 splenic TCRMsln effectors) of genes previously identified to be upregulated (top) or downregulated (bottom) in exhausted LCMV virus-specific CD8+ T cells at day 30 after chronic LCMV clone 13 infection (compared with memory T cells, day 30 after acute infection; GEO:GSE9650). NES, Normalized Enrichment Score. FDR q≤0.031 (left) and FDR q value=0 (right). (C) Selected D8 genes enriched in both intratumoral TCRMsln cells and virus-specific TEX cells. See also online supplemental table S4. (D) Representative Ki67 staining in TCRMsln cells isolated from KPC PDA at day 8 or day 28 post-transfer. (E) P14 Nur77GFP T cells were transduced with TCRMsln and transferred into tumor bearing KPC mice and analyzed for GFP expression ±peptide at day 22 postinfusion. Representative of n=3 mice. Data are gated on donor CD8+Thy1.1+ T cells. (F) Endogenous CD8+ T cells isolated from Nur77GFP B6 mice bearing orthotopic tumors ±αCD3. n=3 mice. Data are mean±SEM Student’s t-test. **P<0.01. The accession number to access the raw and processed data from TCRMsln cells at GEO is GSE196435. FDR, false discovery rate; LCMV, lymphocytic chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; PDA, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Effector gene expression in engineered T cells is not altered by αPD-L1
We next assessed if αPD-L1 changed the molecular profile of engineered T cells by analyzing DEGs by splenic and intratumoral TCRMsln cells ±αPD-L1 treatment. We observed substantial variability in DEGs in TCRMsln cells from different αPD-L1 treated KPC mice at both D8 and D28 post T cell transfer (online supplemental figure S4, GEO:GSE196435). Using an adjusted p<0.15, a subset of T cell effector genes were down-regulated at D8 following αPD-L1 including Eomes, Ly108, Cd5, Sell, Klf3 and mTOR in splenic T cells (table S4), but no longer differentially expressed at D28 (online supplemental table S5). Intratumorally, αPD-L1 had minimal effect on well-characterized effector genes at D8 or D28 but increased small nuclear RNAs and olfactory genes in TCRMsln cells. In contrast to endogenous TEX19 29 αPD-L1 did not enhance Ifng or Tnfa, expression of other immune checkpoints, or cell cycle genes (online supplemental tables 6 and 7). Our data suggest that the molecular program acquired during generation of in vitro engineered T cells may interfere with establishment of a population of T cells responsive to PD-1 blockade.
In vitro-generated effector T cells differ from in vivo-generated effector CD8 T cells
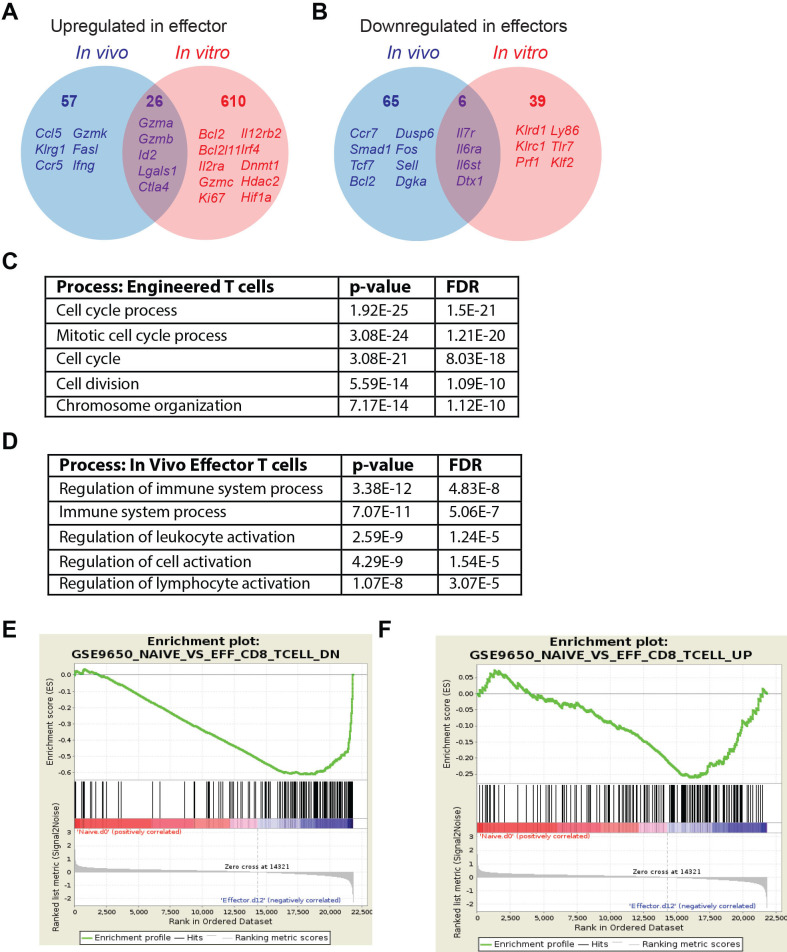
We next compared gene expression of in vitro-generated engineered T cells prior to T cell infusion to effector T cells that arise physiologically during acute viral infection. DEGs from both datasets were identified based on comparison to sorted naïve CD8 T cells. As anticipated from the distinct conditions, there were many DEGs from in vitro-generated and TCR engineered TEFF from in vivo-generated TEFF (figure 5A, B). Genes similarly upregulated included Gzma, Gzmb, Lgals1, Ctla2b, Id2, Casp3, and Ctla4 (online supplemental table 8). T cells generated in vitro uniquely upregulated Mki67, IL2ra, Gzmc, and Irf4 and decreased Prf, Klr1c, Klr1d and Klf2. In contrast, in vivo-generated effector T cells uniquely upregulated Gzmk, Klrg1, Ccl5, Ccr5, Ccr2, Fasl and Ifng while uniquely downregulating Ccr7, Tcf7, Sell and Socs3. Pathway analysis showed that the primary biological processes altered in engineered T cells were related to cell cycle and cell division (figure 5C), consistent with expansion of T cells in IL-2. In contrast, the top biological processes in the in vivo-derived TEFF included regulation of immune cell activation (figure 5D). GSEA of in vitro-generated TEFF did not significantly overlap with in vivo-generated TEFF (figure 5E, F). Thus, engineered T cells undergo distinct transcriptional programming as compared with in vivo primed T cells which may imprint altered T cell differentiation and/or susceptibility to immune checkpoint blockade.
Figure 5.
In vitro-generated effector T cells differ from in vivo-generated effector CD8 T cells. (A) Venn diagrams of genes significantly upregulated in the in vitro-generated engineered CD8 +effector T cells vs day 8 effector CD8 +T cells that arise during acute LCMV infection. All data is normalized to naïve CD8 +T cells. (B) Venn diagrams of genes significantly downregulated in in vitro-generated engineered CD8 +effector T cells vs day 8 effector CD8 +T cells that arise during acute LCMV infection. All data is normalized to naïve CD8 +T cells. (C) Top five biological processes based on DEGs in vivo-derived effector T cells was determined by Gorilla (http://cbl-gorilla.cs.technion.ac.il/). (D) Top five biological processes based on DEGs in vitro-derived engineered T cells was determined by Gorilla (http://cbl-gorilla.cs.technion.ac.il/)/. (E) GSEA of genes downregulated in naïve T cells compared with day 8 in vivo-generated effector T cells vs day 12 in vitro-generated engineered T cells normalized to naïve T cells (GEO:GSE30962). NES, −3.044; p=0; FDR=0. (F) GSEA of genes upregulated in naïve T cells compared with day eight in vivo-generated effector T cells vs day 12 in vitro-generated engineered T cells normalized to naïve T cells (GEO:GSE30962). NES, −1.299; p=0.0578; FDR=0.064. The accession number for microarray data for TCRMsln cells is GSE196435. DEGs, differentially expressed genes; FDR, false discovery rate; GSEA, gene set enrichment analysis; LCMV, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; NES, Normalized Enrichment Score.
Many genes upregulated in murine TCR engineered T cells were also elevated in human TCR engineered T cells generated using the same T cell expansion conditions (eg, αCD3+αCD28+IL-2).30 Similar genes involved in cell proliferation and survival (Mki67, Top2a, Plk1, Ccnb1, Mybl2, Cdkn1a, Bax, Bak1), effector function or chromatin modification (Tbet, Satb1, Gzmb, Il2ra, Il2rb, Il12rb, Ifngr1, Hdac1), costimulatory molecules (Cd28, Tnfrsf9/41BB), activation and regulatory molecules (Lag3, Ctla4, Cblb, Havrc2/Tim3, Tgfb1), but not Pdcd1/PD-1, were enriched in both mouse and human TCR engineered T cells.
Impact of multiple coinhibitory receptor blockade during engineered T cell therapy
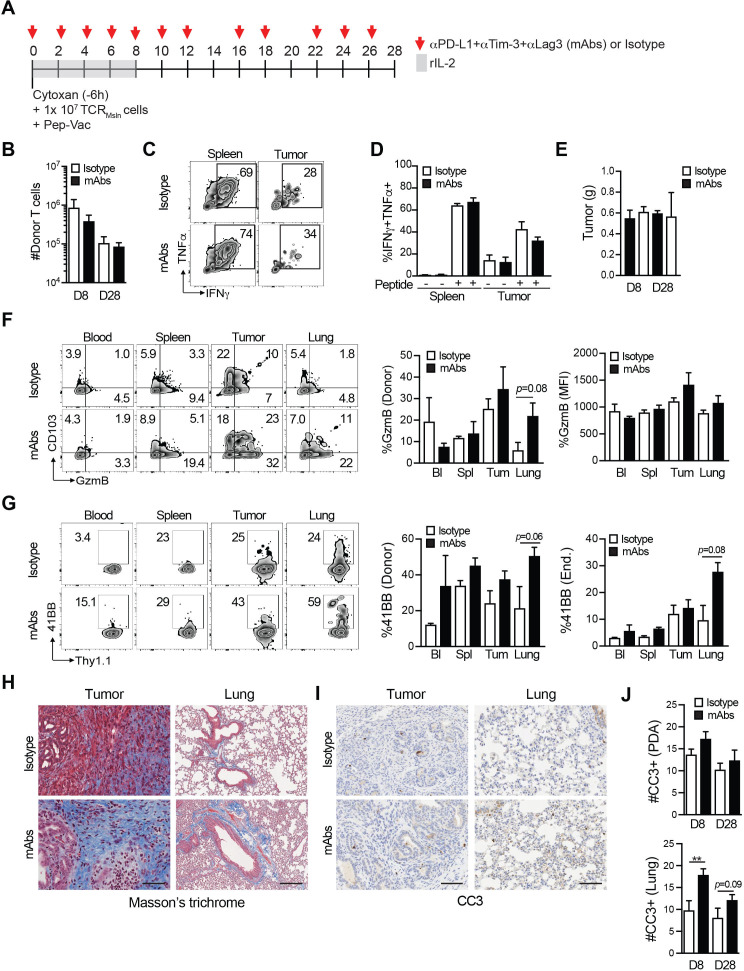
We next considered that additional coinhibitory molecules elevated on intratumoral TCRMsln cells4 may be contributing to T cell dysfunction. We therefore treated KPC mice with TCRMsln cell therapy ± a combination of αPD-L1, αTim-3 and αLag3 for 8 or 28 days (figure 6A). Combination blockade did not significantly impact TCRMsln cell accumulation or persistence in PDA (figure 6B). The antibody treatments did not enhance cytokine production by intratumoral TCRMsln cells (figure 6C, D). Tumor weights at endpoints were not significantly different between treated cohorts (figure 6E). Antibody blockade modestly increased granzyme B in intratumoral engineered T cells yet did not achieve statistical significance (figure 6F). We did note an increase in CD103 in TCRMsln cells in tumors, independent of coinhibitory blockade (figure 6F), which may reflect increased TGFβ.31 We observed a small increase in 41BB expression by both donor and endogenous CD8+ T cells in the lung in combination antibody treated mice, which could reflect a sub-clinical increase in recognition of mesothelin in normal tissues (figure 6G). Collagen deposition was unchanged in tumors following the combination therapy at day 28 (figure 6H). However, collagen deposition was increased in lungs from combination antibody treated animals, a sign of pathological damage (figure 6H). Blockade of multiple coinhibitory receptors failed to significantly increase tumor cell apoptosis yet did significantly increase the number of CC3+ cells in lungs at day 8 (figure 6I, J). Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular CC3 in tumor cells was similar between KPC mice that received engineered T cells and isotype mAbs as compared with KPC mice that received engineered T cells with the checkpoint mAbs (online supplemental figure 5A, B), consistent with the immunohistochemical staining. Thus, the combination of interfering with three coinhibitory molecules was insufficient to overcome engineered T cell dysfunction in PDA and increase antitumor activity. However, a trend for increased 41BB by both endogenous and donor T cells, increased collagen deposition, and increased apoptosis in the lungs of combination antibody-treated mice suggests sub-clinical reactivity to healthy tissue without enhancing antitumor immunity.
Figure 6.
Impact of multiple coinhibitory receptor blockade during engineered T cell therapy. (A) T cell therapy protocol ±αPD-L1, αTIM-3, αLag3 (mAbs) or isotype controls in KPC mice. (B) Number of TCRMsln cells normalized to tumor gram at 8 and 28 days postinfusion. Data are mean±SEM. (C) Representative flow cytometry plots of intracellular cytokine staining gated on TCRMsln cells. (D) Proportion of TCRMsln cells producing cytokines following ±4 hour ex vivo restimulation with Msln406-414 peptide. Data are mean±SEM and n=3–4 mice per group. (E) Tumor weights at endpoint. Data are mean±SEM and n=3–4 mice per group. (F) Representative flow cytometry plots of Granzyme B and CD103 gated on donor T cells. Graphs are the proportion of TCRMsln cells expressing Granzyme B ex vivo and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Granzyme B per donor T cell. Data are mean±SEM and n=3–4 mice per group. (G) Representative flow cytometry plots of 41BB expression by engineered T cells. Graphs are the proportion of TCRMsln cells (left) or endogenous CD8+ T cells (right) that express 41BB at 8 days post infusion. Data are mean±SEM and n=3–4 mice per group. (H) Masson’s trichrome of tumor and lung tissue from representative treated mice. Scale bar, 50 µm. (I) Representative cleaved caspase 3 (CC3) staining of tumor and lung at 8 days post infusion. n=3–4 mice per group. (J) Number of CC3+ cells in tumor or lung at day 8 or day 28 post T cell infusion. Data are mean±SEM. **P<0.01 (unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test). n=3–4 mice per group and 3–4 10×field of views per tissue section.
Discussion
Here, we identify a disconnection between PD-1 expression by engineered T cells and responsiveness to PD-L1 blockade. Our findings in an autochthonous preclinical PDA model, demonstrate that PD-1 pathway blockade fails to sustain engineered T cell activity or prevent acquisition of a dysfunctional state in tumors. Further, blockade of a combination of multiple T cell coinhibitory receptors still failed to enhance intratumoral cytokine production or anti-tumor activity of engineered T cells. TCRMsln cells upregulate markers of antigen recognition in PDA and have transient antitumor activity in KPC mice4 and in an ovarian cancer model6 affirming that antigen is being presented at the tumor site, which is further supported by our previous finding that serial infusions of TCRMsln cells mediate objective responses in both tumor models.
While it remains to be determined the extent our results in the murine model will be applicable to the clinic, we have attempted to faithfully model TCR adoptive T cell therapy trials in humans. First, we assessed TCR engineered T cells specific to a murine Msln epitope that permits assessments of both antitumor activity and safety, as murine Msln is expressed similar to human Msln in tumors and at lower levels in normal tissues.32 33 Second, the engineered T cells were tested in a syngeneic, immunocompetent and autochthonous genetically-engineered PDA mouse model that recapitulates the hallmark features of human PDA including the genetics, histopathology, fibroinflammatory response, and has been predictive of clinical responses to cytotoxic and immune-based therapies.34 Thus, the fact that combination immune checkpoint blockade failed to enhance the activity of a defined antigen-specific T cell population in PDA is consistent with factors other than an insufficient quantity of tumor-reactive T cells contribute to the failure of immune checkpoint blockade in PDA patients.35–38 A limitation of our study is the limited analysis of human TCR engineered T cells that have been similarly expanded and assessed at the same time point as murine TCR engineered T cells. While we observed some overlap in genes expressed when we compared the murine T cells to available data on human TCR engineered T cells cultured with αCD3+αCD28 and IL-2,30 human T cell gene expression was assessed at 48 hours post activation, whereas our murine T cell gene expression was assessed on day 12, which is the day of T cell transfer. Thus, additional experiments beyond the scope of this study will be critical to document similarities and potential differences between in vitro-activated murine T cells and human T cells.
Most studies of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade have assessed the impact on endogenous tumor-specific CD8 T cells that are primed by cross-presenting dendritic cells in secondary lymphoid niches that provide a variety of costimulatory signals. In contrast, engineered T cells are primed artificially in vitro by stimulation with αCD3 and αCD28 to induce proliferation for transduction of the TCR genes, and then further expanded by peptide-pulsed irradiated antigen-presenting cells, which includes sustained culture in IL-2 for 12 days. Our gene expression analysis revealed that in vitro-generated engineered effector T cells at the time of transfer have a transcriptional program that differs markedly from in vivo-generated effector T cells. One contributing factor to the programming of in vitro generated effector T cells may be the sustained exposure to IL-2, which supports in vitro survival and expansion but can promote terminal differentiation of effector T cells and disfavor memory T cell differentiation.39–41 Altering T cell culture conditions by including IL-7, IL-15 and/or IL-21,39 42 enhancing wingless-related integration site (Wnt) signaling,43 or genetically enforcing selected transcriptional pathways, may promote the generation of engineered T cells responsive to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition. Thus, while it is possible that optimizing culture conditions may generate a PD-1/PD-L1 responsive population of engineered T cells, here we selected to use the identical T cell engineering protocol that we previously showed promotes long-lived and functional memory T cells in normal tissues and elicits significant antitumor benefits in KPC PDA.4
TEX have been well defined in settings of persistent virus and in a subset of PD-1 responsive malignancies.7 TEX express PD-1 and represent a distinct epigenetically regulated differentiation state driven by repetitive TCR signaling. Notably, PD-1 is not a unidimensional marker of TEX and is also transiently expressed on functional T cells undergoing activation, and blockade during such activation can interfere with CD8 T cell differentiation and persistence.21 Future studies, that delay the timing after adoptive transfer of PD-1 blockade in vivo to not begin concurrent with the T cell infusion may reveal a window when beneficial effects might be achieved. A subpopulation of PD-1highTcf1- TEX is commonly perceived as terminally differentiated and retains some beneficial though limited effector functions. A distinct PD-1intermediateTcf1+ progenitor subset lacks effector functions but retains proliferative and self-renewal capacity, and the ability to generate cells that differentiate to highly functional effector T cells following PD-1 blockade.8–13 The ‘reinvigorated’ effector T cells, while capable of mediating therapeutic activity, will also become terminally differentiated if antigen is not cleared. It is the in vivo presence of this PD-1intermediateTcf1+TEX progenitor population capable of generating new effectors that correlates with clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition.10 11 The Tcf7 gene encoding Tcf1, was significantly decreased in intratumoral TCRMsln cells, which would suggest that TCRMsln cells are refractory to PD-1 blockade due to a differentiation program that is defective in the generation of cells capable of forming this putative progenitor subpopulation. However, as Tcf1+TEX progenitor cells are generally rare even in responsive settings,44 our current analysis may have failed to detect a rare subpopulation, though such cells apparently still appear unresponsive. Since PD-1 signaling appears protective of the PD-1intermediate Tcf1+ TEX progenitor subset,14 the absence of PD-1 expression by the infused cells and/or our treatment strategy of blocking PD-L1 signaling, which was initiated at the time of T cell transfer, may have interfered with the differentiation pathway needed to establish this progenitor subpopulation. Elevated Lag3 levels on the engineered T cells prior to infusion also suggests an altered differentiation program compared with physiologically in vivo primed T cells. PD-1 blockade failed to enhance the efficacy of adoptively transferred melanoma-reactive CD8 T cells in a mouse model, but the combination of administering a CD27 agonist with PD-1 blockade did synergize with adoptive T cell therapy.45 Although it is not clear if this combination targets a distinct subset of the transferred T cells, or if the beneficial results are unique for the transplanted melanoma model, the results highlight the need to identify engineering strategies and/or therapeutic combinations that are safe and beneficial, and to define the settings and cancer types in which such approaches can be effectively applied.
In distinction to the findings here with engineered T cells, endogenous tumor-specific T cells can transiently respond to PD-L1 blockade in an orthotopic PDA animal model.19 Notably, this did not appear to result from reinvigorating intratumoral TEX. Instead, PD-L1 blockade induced the expansion of tumor-specific T cells in spleen and blood, and T cell trafficking from the periphery into the tumor was required for antitumor activity.19 This study is consistent with T cell clonal replacement following PD-1 pathway inhibition in human skin carcinoma.46 The fact that PD-L1 blockade is insufficient to reinvigorate intratumoral engineered or endogenous tumor-reactive T cells is consistent with a role for the TME impeding establishment of a niche for Tcf-1+ progenitor cells. There are numerous potential suppressive mechanisms reported in PDA including suppressive cytokines such as TGFβ47 and many immunosuppressive cells including Foxp3+ Tregs and myeloid cells.24 48 49 Thus, developing strategies to modify the TME to recruit the cells needed to create an intratumoral niche that can sustain a Tcf1+ T cell progenitor population may prove beneficial.50
PD-L1 is variably expressed by tumor epithelial cells in human and murine PDA24 44 51 and further increased in tumor cells following exposure to IFNγ.19 Although PD-L2 is expressed on some non-tumor cells in PDA,52 PD-L1 blockade was sufficient to enhance anti-tumor activity of endogenously primed tumor-specific T cells in an orthotopic PDA mouse model19 indicating that this pathway is relevant in limiting endogenous T cell antitumor activity. Since PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade failed to enhance engineered T cell function in PDA, our results are consistent with a model in which PD-1 is not the dominant driver of engineered T cell dysfunction.
In addition to persistent TCR signaling, immunoregulatory cytokines in the TME can contribute to TEX development in part by increasing expression of coinhibitory molecules.23 IL-27 promotes Blimp-1, c-MAF, coinhibitory receptor expression and T cell terminal exhaustion in melanoma model.23 While we detected elevated Tox in TCRMsln cells prior to transfer, and increased Tox in intratumoral TCRMsln cells by gene expression analysis, we did not detect enrichment of Blimp-1 or Cmaf in intratumoral TCRMsln cells. These data suggest that TCRMsln cells are not merely terminally differentiated exhausted T cells, but potentially may instead be suppressed.
Together, our study demonstrates that blocking multiple inhibitory T cell checkpoints fail to enhance the antitumor activity of adoptive T cell therapy for pancreatic cancer and may instead lead to increased risk for off-tumor toxicity. The subclinical reactivity in the lung during adoptive T cell therapy following blockade of multiple coinhibitory receptors will require further investigation of the long-term consequences and to identify the independent contributions of blocking PD-1, Tim3 and/or Lag3. Two non-mutually exclusive hypotheses that could explain our findings are the suppressive mechanisms operative in the TME and the way T cells are generated in vitro for therapy. A previous study reported that culturing T cells in IL-2 can lead to generation of terminally differentiated effector T cells that mediate suboptimal tumor control,39 suggesting that altering our T cell culturing conditions might generate cells more responsive to checkpoint blockade. While further studies will be required to determine if altering culture conditions can generate T cells that are responsive to immune checkpoint blockade in PDA, our study suggests that the current combination of adoptive T cell therapy with immune checkpoint inhibition may be more deleterious than beneficial and redirects our efforts to test combinations that overcome TME-induced immunosuppression and engineering strategies that can sustain T cell survival and function despite persistent antigen stimulation.
Materials and methods
Study design
The aim of this study was to determine if immune checkpoint blockade is a safe and beneficial approach to enhance the antitumor efficacy of TCR engineered T cell therapy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. We conducted an analysis of T cells, tumors and normal tissues following transfer of mesothelin-specific TCR engineered T cells in combination with blocking PD-L1 or multiple immune checkpoints using an autochthonous PDA mouse model. We conducted histopathology of tumors and normal tissues. We performed RNAseq and flow cytometry on engineered T cells prior to transfer, infiltrating PDA and spleens and following PD-L1 blockade. DEGs in exhausted engineered T cells were compared with exhausted T cells defined in other disease models. Experiments were conducted with biological replicates as outlined in the figure legends. No outliers were removed.
Animals
KrasLSL-G12D+;Trp53LSL-R172H/+;p48Cre (KPC) mice on the C57Bl/6J background (The Jackson Laboratory, 00664) were >99.6% identical to C57Bl/6J mice as determined by SNP analyses and have previously been described.4 P14 mice53 were bred to the Thy1.1+ congenic strain (The Jackson Laboratory, 000406), to generate P14 Cd90.1+/+ or P14 CD90.1+/- T cells as a source for T cell engineering. C57Bl/6 Pdcd1-/- mice were generously provided by Dr. Tasuku Honjo (Kyoto University) via Dr. Thomas Gajewski (University of Chicago) and were crossed to P14 CD90.1+ mice.
Murine mesothelin TCR retroviral vector
A retroviral vector containing the murin high-affinity mesothelin-specific TCR (1045) was generated as previously described.4 Briefly, 2.2×106 Platinum-E (Plat-E, ATCC) retroviral packaging cells were plated on 10 cm tissue culture-treated plates in Plat-E media (Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, Gibco), 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco), 2% L-glutamine (Sigma), 1% Pen/strep (Sigma), blasticidin (10 µg/mL, Sigma), puromycin (1 µg/mL, Sigma) for 24 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. On day 2, Plat-E cells were transfected with the MIGRI-TCR1045aP2A-TCR1045a plasmid using Effectene (Qiagen). The MIGRI plasmid has been previously described.54 On day 3, Plat-E media was replaced with T-cell media (DMEM, 10% FBS, 2% L-glutamine, 1% Pen/strep, β-mercaptoethanol), and cells were further incubated at 32°C, 5% CO2. On days 4 and 5, viral supernatants were harvested and passed through a 0.45 µM filter (Sigma) for immediate use.
Generation of TCRMsln engineered T cells
Single cell suspensions of mononuclear cells from female P14 Thy1.1+ spleens were generated by mechanical disruption and red blood cell lysis (ACK), and then transduced and expanded for therapy similar to the methods we use to generate engineered human T cells for therapy. Briefly, mononuclear cells were stimulated in vitro with 1 µg/mL αCD3 (clone 145–2 C11)+1 µg/mL αCD28 (clone 37.51) in 10 mL of complete T cell media containing 50 U/mL of recombinant human IL-2 (rIL-2) upright in T25 flasks at 37°C, 5% CO2. On day 1 and day 2 poststimulation, activated T cells were transduced with the MIGRI-TCR1045aP2A-TCR1045a retrovirus by spinfection in 12-well plates+10 µg/mL polybrene +50 U/mL rIL-2 for 90 min at 1000 G at 30° as described.4 On day 5, T cells were screened for transduction efficiency by flow cytometric staining with αCD8-e450 (clone 53–6.7; BD Biosciences), αThy1.1-PerCP (clone OX-7; BD Biosciences), αVβ9-PE (clone MR10-2; BD Biosciences) and/or a Msln406-414-H-2Db-APC tetramer generated by the Fred Hutch Immune monitoring core. On day 7 post in vitro stimulation, transduced T cells were restimulated in vitro with peptide-pulsed, irradiated (3500 R) splenocytes from B6 mice at a 5:1 APC to T-cell ratio in the presence of rIL-2 (50 U/mL). All T-cell cultures were supplemented with rIL-2 (50 U/mL) every other day for the duration of in vitro culture. On day 5 post the second stimulation in vitro,>90% of the CD8+Thy1.1+ T cells expressed TCRMsln as determined by flow cytometric analysis. The T cells were harvested and resuspended in sterile saline and infused into mice as described below.
Adoptive T cell therapy
We previously developed a protocol optimized to promote the expansion of TCR-engineered cells in mice.4 Briefly, KPC mice were enrolled for treatment studies when they achieved 3–6 mm pancreatic tumors as determined by serial monitoring with high-resolution ultrasound (Vevo 2100). Enrolled mice received cyclophosphamide (Cy, 180 mg/kg ip, UW Pharmacy), and 6 hours later received ip 1×107 congenic (Thy1.1+) CD8+ transduced to express the high-affinity TCRMsln + 5×107 irradiated and peptide-pulsed (Msln406-414, GQKMNAQAI) syngeneic splenocytes. Engineered T cells were stimulated 2× in vitro prior to transfer (described above), and recipients also received recombinant human IL-2 (rIL-2, 2×104 U by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection every other day for 8 days after each T cell infusion.
In vivo antibody treatments
KPC mice with 3–6 mm tumors as determined by high-resolution ultrasound were treated with the adoptive T cell therapy protocol as described above +isotype control (clone 2A8) or purified αPD-L1 (clone 10F.9G2, Bioxcell, 200 µg ip) every other day for a maximum of 3 injections per week for the entire treatment period as shown in figure 2. For studies assessing blockade of multiple inhibitory pathways, mice were treated with anti-Lag-3, anti-PD-1 and anti-Tim-3, at 200 µg ip of each 3× per week for 8 or 28 days. These monoclonal antibodies were generously provided by TESARO.
Mouse tissue preparation
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected prior to organ harvest. Blood was collected in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 20 mM EDTA, then lysed with 1X ACK Lysis buffer (Thermo Fisher) at room temperature and centrifuged at 10 000 rpm for 1 min. PBMCs were then resuspended in 1 mL complete media (DMEM containing 10% FBS +1% pen/strep), stored on ice for <2 hour and subsequently stained with antibodies for flow cytometric analyses. Tumor, pancreas, spleen, metastases, and/or lung were also collected and placed into ice cold media (DMEM containing 10% FBS +1% pen/strep). Tissues were subsequently divided for analyses including RNA (flash frozen), immunohistochemistry (formalin fixed), and immunofluorescence (OCT compound). For flow cytometric analyses of single cells, tissues were weighed, minced, and then incubated for 20 min in collagenase (1 mg/mL; Sigma) at 37°C, filtered (70 µm filters, Sigma), and washed 2× in complete media. Live cells were counted by Trypan blue exclusion
Flow cytometry
Mononuclear cells were stained with fluorophore-conjugated monoclonal antibodies specific to murine CD45 (Ly5), Thy1.1 (OX-7), CD8α (53–6.7), PD-1 (J43), Granzyme B (NGZB), IFNγ (XMG1.2), TNFα (MP6-XT22), CD101 (Moushi101, eBiosciences), Slamf6 (330-AJ), Lag3 (C9B7W, Biolegend), KLRG1 (2F1, Biolegend) at a 1:100 dilution in PBS+2.5% FBS. Antibodies were purchased from BD Biosciences unless otherwise noted. To measure intracellular cytokine production, engineered T cells ± Msln406-414 peptide were incubated in vitro for 5 hours in the presence of GolgiPlug (BD Biosciences), stained for surface antigens, fixed and permeabilized (BD Biosciences Fixation/Permeabilization kit), and then stained with appropriate antibodies. For transcription factor analysis, cells were fixed using Foxp3 staining kit (Tonbo) for 30 min at 4°C, and stained with anti-Tox (TXRX10, Invitrogen) and anti-Tcf1 (C63D9, Cell signaling) at a 1:50 dilution in PBS+2.5% FBS overnight, and washed with perm/wash buffer. To quantify the frequency of cells proliferating, cells were surface stained as above followed by eBioscience Foxp3 Fixation/Permeabilization solutions prior to nuclear staining with anti-Ki67 (SolA15). Data were acquired on an LSRII, FacsCanto, or Fortessa and analyzed using FlowJo V.10.3 (BD Biosciences). Cell numbers infiltrating tissues were normalized to tumor weight.
Cell sorting and RNA isolation for gene expression
Mononuclear cells isolated from tumors or spleens from KPC recipient mice at 8 or 28 days after engineered T cell transfer were stained with fluorescently-conjugated monoclonal antibodies specific to CD45 (Ly5, BD Biosciences), Thy1.1 (OX-7, BD Biosciences), CD8α (53–6.7, BD Biosciences) and CD4 (GK1.5, BD Biosciences) at 1:100 diluted in PBS+2.5% FBS for 30 min on ice. Cells were washed 2X in PBS+2.5% FBS for 5 min at 1350 rpm at 4°C. Cells were resuspended in complete media at ~10–30 x 106 /mL, filtered using a 70 µm mesh filter tubes (Falcon), and engineered T cells (live, CD45 +CD8+Thy1.1+) were sorted in 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes containing 1.0 mL of complete media to >95% purity using a FACS Aria (BD Biosciences). For isolation of naïve mouse T cell RNA, we sorted CD45 +CD8+CD44lowCD62Lhigh splenic T cells from two independent P14 mice. For isolation of effector T cell RNA prior to T cell infusion, we transduced naïve P14 CD8 +T cells with the high affinity 1045 TCRMsln identically to the methods used to generate TCRMsln cells for adoptive T cell therapy. At day 7, TCRMsln were restimulated with syngeneic, irradiated Msln406-414 peptide-pulsed splenocytes in complete media+rIL-2 at 50 U/mL. At day 5, effector TCRMsln cells (>95% of the T cell culture as determined by flow cytometry) were prepared for RNA isolation in TRIZol (Thermo Fisher) according to manufacturer’s protocols.
Microarrays
Microarray analyses of total RNA isolated from mouse T cells was processed at Affymetrix. Total RNA was quantified using an RNA Quantification Kit (Affymetrix). We performed duplicate analysis using 100 pg input RNA and 1 ng input RNA and samples were processed using the mouse Clariom D Pico Assay. Quality of 100 pg and 1 ng samples and gene expression overall was compared using the SST-RMA algorithm1 in Affymetrix Expression Console Software. The ‘Within Bounds/Outside Bounds’ metrics were initially determined using Affymetrix Expression Console Software. A sample was marked outside bounds if it fell outside of the expected threshold set, and one outlier was removed from further downstream analysis based on this screening. All raw and processed microarray data reported in this study is available at GEO: GSE196435.
Gene expression analyses
Affymetrix CEL files were RMA normalized using the Bioconductor package oligo.55 The dataset was initially filtered by discarding transcript clusters without gene symbols and flagging transcript clusters whose signal intensity values were below a low signal threshold, which was defined as the median signal intensity of the ‘antigenomic’ control samples within each array. For each pairwise comparison (using naïve as the reference), a transcript cluster was retained only if all of the samples in at least one condition weren’t flagged by the signal intensity filter. Differential gene expression was determined using the Bioconductor package limma56 employing a false discovery rate (FDR) to correct for multiple testing.57 Significant differential gene expression was defined as |log2 (ratio)|>=1 (±2 fold) with the FDR set to 5%. K-means cluster analysis was performed using the union of the genes identified as differentially expressed in one or more condition. Normalized log2 signal intensities were mean-centered at the transcript cluster level prior to clustering. The number of clusters was selected using the figure of merit method.58 K-means clustering was performed and a heat map of the clusters was generated using the TM4 microarray software suite MultiExperiment Viewer.59 PCA plots were generated using R.60 GSEA61 was performed using GSEA software (http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp).
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad software. All mouse experiments reflect n=3–6 mice per group. Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to compare two-group data. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey post-test were used for multiple comparisons. Pearson r was used to determine correlational significance. Data were expressed as mean±SEM p<0.05 was considered significant, and *, p<0.05; **p<0.005; ***, p<0.0005.
Acknowledgments
We thank Megan Larmore and Brian Johnson at the University of Washington HIC/Comparative Pathology Program for assistance with immunohistochemical staining. We thank TESARO for graciously providing murine monoclonal antibodies. We thank the University of Minnesota and Fred Hutch flow cytometry cores. We thank the team at Affymetrix for assistance with protocol development.
Footnotes
Contributors: IMS, AH, MRR, PB performed experiments. IMS, MRR and ALB analyzed the data. MRR, ALB, RSB and SRH provided feedback on manuscript drafts. RSB and JD performed the bioinformatics analysis. SRH provided expertise on the KPC mouse model and supervised studies. IMS and PDG designed and supervised the studies and wrote the manuscript. IMS and PDG are responsible for the overall content and the guarantor of the study.
Funding: MRR is supported by NIH T32 AI007313 and the Dennis W. Watson fellowship. ALB was supported by an American Association of Immunologists (AAI) postdoctoral fellowship. IMS received support from the American Cancer Society Institutional Research Grant (124166-IRG-58-001-55-IRG65), Randy Shaver Cancer Research Fund, and pilot awards from the Masonic Cancer Center (University of Minnesota Medical School). Support was also provided by the National Cancer Institute, CA255039 and CA249393 (IMS), CA018029 and CA033084 (PDG), and CA161112 and CA224193 (SRH), and Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, 16-65-GREE (PDG), 17-85-HING (SRH), 17-20-25-STRO (IMS), and 19-35-STRO (IMS). PDG is also supported by a Stand up to Cancer Lustgarten grant as well as received support from Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene company.
Competing interests: PDG was a consultant for and received support from Juno Therapeutics (a Celgene/BMS Company) during the performance of the study, and is a consultant for RAPT Therapeutics, Elpiscience, Celsius, and NexTech. SRH was a consultant for Halozyme Therapeutics. IMS is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Luminary Therapeutics and Immunogenesis and receives research support from Genocea, not related to studies here. PDG and IMS hold patents in T cell receptors for cancer immunotherapy
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. All raw and processed microarray data from this study is available at Gene Expression Omnibus: GSE196435.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, University of Washington, and University of Minnesota approved all animal studies.
References
- 1.Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, et al. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014;74:2913–21. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Adel N. Current treatment landscape and emerging therapies for pancreatic cancer. Am J Manag Care 2019;25:S3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Argani P, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Ryu B, et al. Mesothelin is overexpressed in the vast majority of ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas: identification of a new pancreatic cancer marker by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE). Clin Cancer Res 2001;7:3862–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stromnes IM, Schmitt TM, Hulbert A, et al. T cells engineered against a native antigen can Surmount immunologic and physical barriers to treat pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2015;28:638–52. 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hassan R, Thomas A, Alewine C, et al. Mesothelin immunotherapy for cancer: ready for prime time? J Clin Oncol 2016;34:4171–9. 10.1200/JCO.2016.68.3672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anderson KG, Voillet V, Bates BM, et al. Engineered adoptive T-cell therapy prolongs survival in a preclinical model of advanced-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 2019;7:1412–25. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0258 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McLane LM, Abdel-Hakeem MS, Wherry EJ. CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer. Annu Rev Immunol 2019;37:457–95. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Paley MA, Kroy DC, Odorizzi PM, et al. Progenitor and terminal subsets of CD8+ T cells cooperate to contain chronic viral infection. Science 2012;338:1220–5. 10.1126/science.1229620 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Siddiqui I, Schaeuble K, Chennupati V, et al. Intratumoral TCF1 +PD-1+CD8+ T cells with stem-like properties promote tumor control in response to vaccination and checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Immunity 2019;50:195–211. 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Im SJ, Hashimoto M, Gerner MY, et al. Defining CD8+ T cells that provide the proliferative burst after PD-1 therapy. Nature 2016;537:417–21. 10.1038/nature19330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Miller BC, Sen DR, Al Abosy R. Subsets of exhausted CD8+ T cells differentially mediate tumor control and respond to checkpoint blockade. Nat Immunol 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Utzschneider DT, Charmoy M, Chennupati V, et al. T cell factor 1-expressing memory-like CD8(+) T cells sustain the immune response to chronic viral infections. Immunity 2016;45:415–27. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu T, Ji Y, Moseman EA, et al. The TCF1-Bcl6 axis counteracts type I interferon to repress exhaustion and maintain T cell stemness. Sci Immunol 2016;1 10.1126/sciimmunol.aai8593 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Z, Ji Z, Ngiow SF, et al. TCF-1-centered transcriptional network drives an effector versus exhausted CD8 T cell-fate decision. Immunity 2019;51:840–55. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.09.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Page N, Klimek B, De Roo M, et al. Expression of the DNA-binding factor TOX promotes the encephalitogenic potential of microbe-induced autoreactive CD8+ T cells. Immunity 2018;48:937–50. 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alfei F, Kanev K, Hofmann M, et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature 2019;571:265–9. 10.1038/s41586-019-1326-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Khan O, Giles JR, McDonald S, et al. TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Nature 2019;571:211–8. 10.1038/s41586-019-1325-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Scott AC, Dündar F, Zumbo P, et al. TOX is a critical regulator of tumour-specific T cell differentiation. Nature 2019;571:270–4. 10.1038/s41586-019-1324-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Burrack AL, Spartz EJ, Raynor JF, et al. Combination PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade promotes durable Neoantigen-Specific T cell-mediated immunity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cell Rep 2019;28:2140–55. 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang Y, Hu J, Li Y, et al. The transcription factor TCF1 preserves the effector function of exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Front Immunol 2019;10:169. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Odorizzi PM, Pauken KE, Paley MA, et al. Genetic absence of PD-1 promotes accumulation of terminally differentiated exhausted CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med 2015;212:1125–37. 10.1084/jem.20142237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hamieh M, Dobrin A, Cabriolu A, et al. CAR T cell trogocytosis and cooperative killing regulate tumour antigen escape. Nature 2019;568:112–6. 10.1038/s41586-019-1054-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chihara N, Madi A, Kondo T, et al. Induction and transcriptional regulation of the co-inhibitory gene module in T cells. Nature 2018;558:454–9. 10.1038/s41586-018-0206-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stromnes IM, Hulbert A, Pierce RH, et al. T-Cell localization, activation, and clonal expansion in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 2017;5:978–91. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Viré E, Brenner C, Deplus R, et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 2006;439:871–4. 10.1038/nature04431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schietinger A, Philip M, Krisnawan VE, et al. Tumor-Specific T cell dysfunction is a dynamic antigen-driven differentiation program initiated early during tumorigenesis. Immunity 2016;45:389–401. 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wherry EJ, Ha S-J, Kaech SM, et al. Molecular signature of CD8+ T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection. Immunity 2007;27:824. 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.006 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Moran AE, Holzapfel KL, Xing Y, et al. T cell receptor signal strength in Treg and iNKT cell development demonstrated by a novel fluorescent reporter mouse. J Exp Med 2011;208:1279–89. 10.1084/jem.20110308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koyama S, Akbay EA, Li YY, et al. Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun 2016;7:10501. 10.1038/ncomms10501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Singh P. Transcriptional profiles of mart-1(27-35) epitope specific TCReng human CD8+ and CD4+ T cells upon epitope encounter as elucidated by RNASeq. Immunome Res 2014;01. 10.4172/1745-7580.S2.004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.El-Asady R, Yuan R, Liu K, et al. TGF-β-dependent CD103 expression by CD8(+) T cells promotes selective destruction of the host intestinal epithelium during graft-versus-host disease. J Exp Med 2005;201:1647–57. 10.1084/jem.20041044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bera TK, Pastan I. Mesothelin is not required for normal mouse development or reproduction. Mol Cell Biol 2000;20:2902–6. 10.1128/MCB.20.8.2902-2906.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Inaguma S, Wang Z, Lasota J, et al. Comprehensive immunohistochemical study of mesothelin (MSLN) using different monoclonal antibodies 5B2 and MN-1 in 1562 tumors with evaluation of its prognostic value in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2017;8:26744–54. 10.18632/oncotarget.15814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stromal re-engineering to treat pancreas cancer. Carcinogenesis 2014;35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.O'Reilly EM, Oh D-Y, Dhani N, et al. Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab for patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 2019;5:1431–8. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.1588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Royal RE, Levy C, Turner K, et al. Phase 2 trial of single agent ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Immunother 2010;33:828–33. 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181eec14c [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQM. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med 2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hu ZI, Hellmann MD, Wolchok JD. Acquired resistance to immunotherapy in MMR-D pancreatic cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gattinoni L, Klebanoff CA, Palmer DC, et al. Acquisition of full effector function in vitro paradoxically impairs the in vivo antitumor efficacy of adoptively transferred CD8+ T cells. J Clin Invest 2005;115:1616–26. 10.1172/JCI24480 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kalia V, Sarkar S, Subramaniam S, et al. Prolonged interleukin-2Ralpha expression on virus-specific CD8+ T cells favors terminal-effector differentiation in vivo. Immunity 2010;32:91–103. 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pipkin ME, Sacks JA, Cruz-Guilloty F, et al. Interleukin-2 and inflammation induce distinct transcriptional programs that promote the differentiation of effector cytolytic T cells. Immunity 2010;32:79–90. 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hinrichs CS, Spolski R, Paulos CM, et al. Il-2 and IL-21 confer opposing differentiation programs to CD8+ T cells for adoptive immunotherapy. Blood 2008;111:5326–33. 10.1182/blood-2007-09-113050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gattinoni L, Zhong X-S, Palmer DC, et al. Wnt signaling arrests effector T cell differentiation and generates CD8+ memory stem cells. Nat Med 2009;15:808–13. 10.1038/nm.1982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Stromnes IM, Burrack AL, Hulbert A, et al. Differential effects of depleting versus programming tumor-associated macrophages on engineered T cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 2019;7:977–89. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Buchan SL, Fallatah M, Thirdborough SM, et al. PD-1 blockade and CD27 stimulation activate distinct transcriptional programs that synergize for CD8+ T-cell-driven antitumor immunity. Clin Cancer Res 2018;24:2383–94. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yost KE, Satpathy AT, Wells DK, et al. Clonal replacement of tumor-specific T cells following PD-1 blockade. Nat Med 2019;25:1251–9. 10.1038/s41591-019-0522-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shen W, Tao G-qing, Zhang Y, et al. TGF-β in pancreatic cancer initiation and progression: two sides of the same coin. Cell Biosci 2017;7. 10.1186/s13578-017-0168-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Clark CE, Hingorani SR, Mick R. Dynamics of the immune reaction to pancreatic cancer from inception to invasion. Cancer Res 2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stromnes IM, Brockenbrough JS, Izeradjene K, et al. Targeted depletion of an MDSC subset unmasks pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to adaptive immunity. Gut 2014;63:1769–81. 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Jansen CS, Prokhnevska N, Master VA, et al. An intra-tumoral niche maintains and differentiates stem-like CD8 T cells. Nature 2019;576:465–70. 10.1038/s41586-019-1836-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lu S-W, Pan H-C, Hsu Y-H, et al. IL-20 antagonist suppresses PD-L1 expression and prolongs survival in pancreatic cancer models. Nat Commun 2020;11:4611. 10.1038/s41467-020-18244-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang Y, Xu J, Hua J, et al. A PD-L2-based immune marker signature helps to predict survival in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 2019;7:233. 10.1186/s40425-019-0703-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pircher H, Bürki K, Lang R, et al. Tolerance induction in double specific T-cell receptor transgenic mice varies with antigen. Nature 1989;342:559–61. 10.1038/342559a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pui JC, Allman D, Xu L, et al. Notch1 expression in early lymphopoiesis influences B versus T lineage determination. Immunity 1999;11:299–308. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80105-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Carvalho BS, Irizarry RA. A framework for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics 2010;26:2363–7. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Smyth GK. Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and bioconductor, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Reiner A, Yekutieli D, Benjamini Y. Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics 2003;19:368–75. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btf877 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yeung KY, Haynor DR, Ruzzo WL. Validating clustering for gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2001;17:309–18. 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.4.309 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.4.309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, et al. Tm4: a free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. Biotechniques 2003;34:374–8. 10.2144/03342mt01 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.R. R development core team, R: a language and environment for statistical computing 2011.
- 61.Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:15545–50. 10.1073/pnas.0506580102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
jitc-2021-003525supp001.pdf (6MB, pdf)
jitc-2021-003525supp002.pdf (2MB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. All raw and processed microarray data from this study is available at Gene Expression Omnibus: GSE196435.