Abstract
Proteins are nature’s primary building blocks for the construction of sophisticated molecular machines and dynamic materials, ranging from protein complexes such as photosystem II and nitrogenase that drive biogeochemical cycles to cytoskeletal assemblies and muscle fibers for motion. Such natural systems have inspired extensive efforts in the rational design of artificial protein assemblies in the last two decades. As molecular building blocks, proteins are highly complex, both in terms of their three-dimensional structures and chemical compositions. To enable control over the self-assembly of such complex molecules, scientists have devised many creative strategies by combining tools and principles of experimental and computational biophysics, supramolecular chemistry, inorganic chemistry, materials science, and polymer chemistry, among others. Owing to these innovative strategies, what started as a purely structure-building exercise two decades ago has, in short order, led to artificial protein assemblies with unprecedented structures and functions and protein-based materials with unusual properties. Our goal in the Review is to give an overview of this exciting and highly interdisciplinary area of research, first outlining the design strategies and tools that have been devised for controlling protein self-assembly, then describing the diverse structures of artificial protein assemblies, and finally highlighting the emergent properties and functions of these assemblies.
Graphical Abstract

1. Introduction
Life likely emerged through the self-assembly and organization of a primordial mixture of ions, minerals and small, ångström-scale organic molecules.1–4 Yet, the complexity of living systems we know them today largely rests on the existence of extended biological polymers such as polypeptides, polynucleotides and polysaccharides, in which molecular components are covalently linked into linear arrays in a modular, genetically encoded fashion.5,6 The stable, covalent pre-arrangement of their components allows biopolymers to arrange into elaborate nano- and microscale architectures, endowing them with the ability to act as recognition elements and store energy (polysaccharides),7–11 maintain and transmit genetic information with high fidelity (polynucleotides),12–15 and record and transduce chemical, physical and mechanical information (polypeptides).16–27
From the point of chemical versatility, polypeptides reign supreme among biopolymers, as they are composed of twenty distinct amino acid components. The compositional complexity of these linear polymers with twenty different building blocks creates an incalculable number of chemical interactions between the building blocks and the environment surrounding them.28,29 Despite this, polypeptides have the ability to fold into discrete and often singular architectures with nanometer dimensions, namely proteins.30–32 Such a well-defined spatial organization of twenty functionalities in three-dimensional space enables proteins to interact with and act upon almost any other type of matter (organic or inorganic, biological or abiological) or external stimuli with high precision.16–27 Importantly, proteins can also associate with copies of themselves or of other proteins in a specific fashion to form larger complexes and assemblies.33–37 Protein-protein interactions are not only critical for the high-fidelity transmission of chemical information in a cell, but also for the construction of large (several nm’s to μm’s) protein assemblies that execute complex, multi-step biochemical processes or form structural materials that shape the cell and allow it to dynamically interact with the environment (Figure 1).38–49
Figure 1.
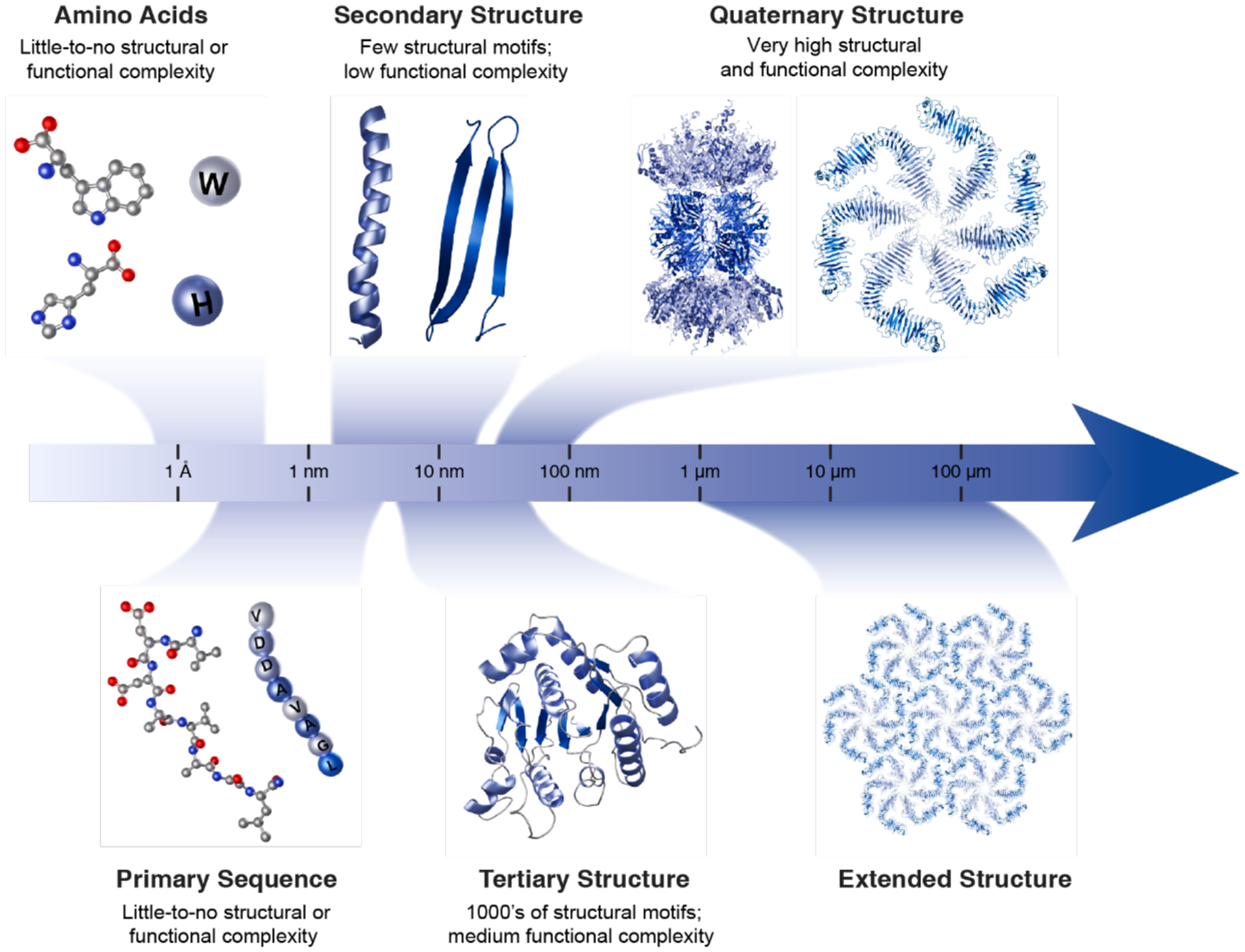
Complexification of protein assembly, from ångström-scale amino acids to extended, micron-scale protein structures. Individual amino acids are first covalently linked to form unstructured polymers, termed polypeptides. Polypeptides adopt secondary structure motifs, such as α-helices and β-strands, that combine to determine the tertiary structures of proteins. Discrete, folded polypeptides with either identical or distinct tertiary structures can assemble via non-covalent interactions into supramolecular complexes, termed quaternary structures. Further non-covalent interactions at the interfaces of symmetric quaternary structures can give rise to extended structures, exemplified here by a bacterial S-layer structure.
The scaling of structural and functional diversity with the increasing hierarchical organization and dimensions of proteins is illustrated in Figure 2. While the folding of polypeptide chains into tertiary protein structures engenders the essential functions of an autonomous cell (e.g., catalysis, recognition and binding, signaling, electron transport, etc.),50–53 it is the assembly of proteins into supramolecular and extended structures that provides organisms with the necessary functional complexity.41,45,46,49,54,55 Inspired by these sophisticated machines and materials, there has been great interest in the control of protein self-assembly by design. As we aim to capture in this Review, this exciting new field has witnessed tremendous advances in just over a decade, progressing from the construction of simple protein dimers to the design of 3D protein crystals, megadalton-scale protein cages, in vivo active enzymes and stimuli-responsive materials with unprecedented properties and functions.
Figure 2.

Protein evolution entails the incorporation of a small structural module into a larger, functional tertiary fold, which can then associate with other functional domains to form quaternary assemblies with diverse, multi-component functions. This process is exemplified here with the βαβ motif-containing Rossmann fold, which is part of protein complexes with functions spanning histone deacetylation (sirtuin), DNA repair (photolyase), and dinitrogen reduction (nitrogenase). In all three quaternary assemblies, the Rossmann fold functions as the nucleotide-binding domain.
At a first glance, protein self-assembly and protein folding may appear quite similar to one another in that they are driven by the same intermolecular forces: van der Waals, hydrophobic, electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, disulfide, solvation/desolvation, solvent and configurational entropy.28,29 Thus, one may be tempted to think that the task of rationally designing or predicting protein self-assembly is also similar to designing and predicting protein folding. However, the two processes are quite dissimilar. Folding of a polypeptide into a tertiary structure is a self-contained, intramolecular process that is largely independent of environmental parameters (at or near ambient conditions) or concentration (at low volume fractions). The process is self-specific (there is little cross-talk with other species in solution), almost always proceeds under thermodynamic control, and is dominated by rather stringent steric/dihedral constraints of the polypeptide backbone.31,32,56 These constraints, coupled with appropriate amino acid sidechain interactions, enable most polypeptide sequences to spontaneously fold into singular 3D structures, as postulated by Anfinsen.57,58 Indeed, the sequence-folding patterns contained within the immense repository of experimentally determined protein structures have been used to develop knowledge-based tools and deep-learning methods to predict 3D protein structures a priori from amino acid sequences with atomic-level accuracy.59–64 In parallel, it has also been possible to develop computational platforms based on the same empirical parameters to design novel protein folds from scratch.65–70
The challenge of designing protein assembly is an altogether different matter. Unlike folding, the self-assembly of a protein is both environment- and concentration-dependent, can be complicated by crosstalk with other species in solution, is not subject to any prescribed steric constraints and does not always operate under thermodynamic control, meaning that it can be pathway-dependent and lead to different structural outcomes under different environmental conditions.54,71–74 It is well-appreciated in nanoscience that most nanoparticles (such as proteins) that interact via strong, short-range attractive forces tend to form amorphous aggregations rather than ordered structures.75 Indeed, as anyone who has dabbled in protein crystallization can attest to, the most probable outcome of protein self-assembly is heterogeneous aggregation. At the same time, it is also frequently observed that a single protein can crystallize in several different space group symmetries, featuring various protein-protein contacts that can be hard to rationalize in terms of their thermodynamic favorability even a posteriori. This is because the free-energy landscape for the self-assembly of any protein is multidimensional, shallow and marked by many energy minima whose magnitudes are readily altered by external perturbations.
While such a complex energy landscape makes the prediction and design of protein self-assembly difficult, this complication is not unique to proteins. It also applies to the self-assembly and crystallization of small molecules, inorganic complexes, nanoparticles, and even large colloids, which have been extensively investigated over the last several decades.76–80 Consequently, there exists a knowledge base and a good understanding of how self-assembly can be controlled across different length scales through the manipulation of the intrinsic properties of objects (e.g., shape, charge, size), through the design of chemical/physical interactions between them, and through the use of concepts such as symmetry and templating. Indeed, these concepts of molecular/nanoscale self-assembly and supramolecular chemistry have been combined with the tools of protein design and engineering in many creative ways, fueling the rapid progress of the protein self-assembly by design.
There have been excellent reviews that have covered the topic of protein self-assembly and highlighted its broad reach across protein design and engineering, chemical and structural biology, bio- and nanotechnology and materials science.49,81–101 Our primary goal is not only to update those reviews with the most recent examples from literature, but to provide a logical framework that we believe aptly describes the progression of the field from structure-building to property- and function-building. Although we acknowledge the key importance of disordered or heterogeneous protein ensembles, our focus here will be entirely on the design and construction of structurally well-defined, compositionally uniform protein assemblies, which lend themselves more readily to establishing design-structure-property-function relationships. This review will also not include the topic of peptide engineering and assembly, which is a diverse field in its own right and has been extensively covered in many reviews, including one in this issue.102–109 Section 2 will start with a summary of modes of protein self-assembly in natural systems, followed by a description of different tools and strategies that have been employed to design artificial protein architectures. Section 3 will focus on the design and construction of different classes of structures using the tools described in Section 2. Pivoting from structure to property and function, Section 4 will focus on artificial protein assemblies with emergent physical, material and functional properties and dynamic behavior. We will conclude by giving an overview of the field of protein assembly by design and directions for future exploration.
2. Design principles and tools for protein assembly
2.1. Construction principles of natural protein assemblies
Natural evolution has created countless examples of functional protein assemblies that have inspired the design efforts covered in this Review. Before describing these examples, we will briefly summarize the general design parameters of natural protein assemblies, namely their shape/structure/dimensionality, symmetry, compositions, and connectivity, and how these relate to biological functions. We also note that by “protein assemblies” we refer exclusively to protein complexes that act as a unit and are sufficiently long-lived to be structurally characterized by conventional tools such as crystallography, electron microscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), atomic force microscopy (AFM), small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), etc.
Most generally, protein assemblies can be structurally characterized as closed/finite or open/extended.110 Finite protein assemblies (Figure 3a) are dimeric or oligomeric (i.e., consisting of three or more protein monomers) and physically bounded. Although the functions of finite protein assemblies are quite diverse, they are typically involved in the execution of biochemical processes such as signaling, catalysis and binding/recognition.110 Importantly, most of these biological functions derive explicitly from the formation of larger protein assemblies; in other words, they cannot be performed by the monomeric components in isolation. A classic example is hemoglobin (Figure 3a-ii), whose ability to bind O2 with positive cooperativity and in an allosterically controllable fashion (by pH, CO2 or 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)) is wholly dependent on its tetrameric assembly state and central to its biological role as a regulable O2 transporter.111 In contrast, the monomeric myoglobin is incapable of cooperativity and allosteric control and acts in O2 storage and delivery (rather than transport).112 Another inherent benefit of protein dimerization or oligomerization is the stabilization of the protein subunits through the formation of intermolecular bonds and the reduction of exposed protein surfaces.110
Figure 3.
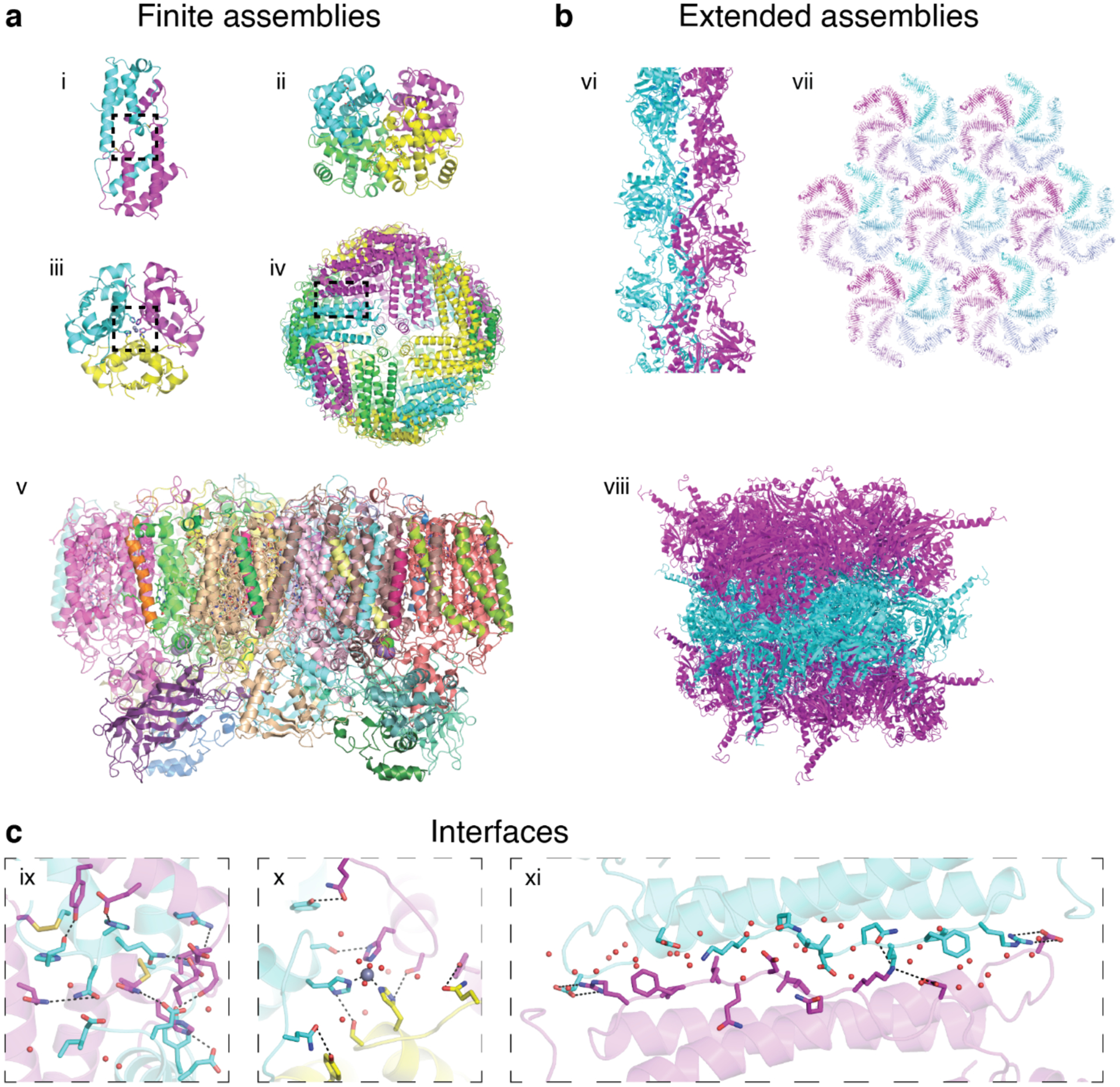
Finite and extended natural protein assemblies. a) Examples of finite protein assemblies: Interleukin-5 (i, PDB ID: 1HUL), hemoglobin (ii, PDB ID: 1HHO), insulin (iii, PDB ID: 1ZNI), human heavy chain ferritin (iv, PDB ID: 6B8F), and photosystem II (v, PDB ID: 1AXT). b) Examples of extended protein assemblies: 1D actin filament (vi, PDB ID: 6BNO), 2D S-layer (vii, PDB ID: 5N8P) and 3D infectious cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus protein crystal (viii, PDB ID: 2OH5). c) Close-up views of protein-protein interfaces of interleukin-5 (ix), insulin (x), and ferritin (xi) highlighting non-covalent, covalent, and metal-mediated interactions. In addition to these enthalpic contributions, the expulsion of waters upon the burial of interfacial amino acid residues (i.e., the “hydrophobic effect”) represents an important entropic contribution to interface stability.
Extended protein assemblies (Figure 3b) are polymeric (i.e., consisting of many monomers), usually possess crystalline order and are characterized by their dimensionalities, 1D, 2D or 3D, that span nm-to-μm length scales. Rather than performing biochemical tasks, extended protein assemblies serve as mechanical/architectural elements and in scaffolding/transport of other cellular components, commensurate with their dimensionalities. For example, 1D cytoskeletal filaments (e.g., actin (Figure 3b-vi), and microtubules)113–115 are involved in controlling cellular shape, movement and intracellular transport; 2D protein arrays (e.g., bacterial S-layers, Figure 3b-vii)116,117 act as protective layers or selective membranes; 3D protein lattices (e.g., crystals of insulin in pancreatic β-cells, cypovirus polyhedrin, Figure 3b-viii, peroxisomal alcohol oxidase)118–121 serve as stable platforms for storage, scaffolding and catalysis. A particular class of finite protein assemblies are 0D, cage-like architectures (e.g., ferritin (Figure 3a-iv), virus capsids).122,123 Although such assemblies are typically more “polymeric” rather than “oligomeric” in terms of component quantity and also primarily serve in scaffolding and encapsulation, they are physically bounded and thus categorized structurally as finite or closed.
Protein assemblies can also be classified according to whether they possess symmetry or not. Symmetry is a powerful design element that is ubiquitous in natural protein assemblies.110 It allows the formation of large protein complexes from a small number of building blocks while also minimizing the numbers of distinct contact types and associative surfaces between proteins.110,124 These advantages of symmetry are not only important for the natural evolution but also for the rational, bottom-up construction of protein assemblies, as they minimize the genetic and therefore the design burden. Consequently, the majority of natural protein assemblies are symmetric, with cyclic, dihedral or cubic point group symmetries in the case of closed architectures, helical or cyclic + translation symmetries in 1D structures, plane group symmetries in 2D assemblies and space group symmetries in 3D arrays.
Protein assemblies can be homomeric (i.e., composed of one type of protein monomer) (Figure 3a-i, iii and iv) or heteromeric (i.e., composed of two or more different types of protein monomers) (Figure 3a-ii and v). A large fraction of symmetrical protein assemblies is homomeric, while a much smaller fraction of symmetrical protein assemblies is heteromeric. The functional complexity of protein assemblies generally scales with their heteromeric composition, in that the different types of protein subunits within an assembly perform different functions. For example, photosystem II (PSII, itself a C2 symmetric heteromer, Figure 3a-v) consists of ~20 different protein subunits,125 enabling PSII to perform many coupled tasks (light-harvesting, long-distance energy and electron transfer, charge separation, water oxidation, generation of proton-motive force), which would be impossible to accomplish with a smaller or a homomeric protein assembly.
The key determinant of the structures, properties, and functions of protein assemblies are the connections between protein monomers. Along with the protein subunits themselves, protein-protein interfaces dictate the geometry/shape of an assembly, its rigidity or flexibility, if it can associate/dissociate or change its structure in response to a stimulus, or whether it contains a functional cofactor or an active site. Protein-protein interfaces (Figure 3c) in natural assemblies are mediated by the same non-covalent and covalent interactions that stabilize tertiary folds (e.g., electrostatic/polar, disulfide bonds (Figure 3c-ix), metal coordination (Figure 3c-x), hydrophobic (Figure 3c-xi), solvation/configurational entropy), but can vary widely in shape, composition and size.126 Although most interfaces tend to be flat (Figure 3c-xi), they can also have quite irregular, non-uniform shapes (Figure 3c-ix). Hydrophobic hot spots or extended patches are common features of stable protein-protein interfaces. Most protein-protein interfaces have buried surface areas of 1000–2000 Å2, yet some can be smaller (e.g., ~600 Å2 in the Zn-mediated dimer interface of Rad50), or much larger, with many dimeric interfaces burying more than 5000 Å2.37
2.2. Tools and strategies for the design of artificial protein assemblies
In a traditional engineering-based approach, a design task ideally starts with the questions “what function should the designed object serve? what properties should it have?”, followed by “what form should the object possess to fulfill the desired function or properties” and “what are the available building blocks and how should they be put together”? A look at the chemical and structural sophistication of natural protein assemblies (Figure 3) quickly reveals the challenges in posing the design questions in this order. First, the molecular interfaces that connect the protein subunits in natural assemblies are often too extensive and heterogeneous to be routinely designed from scratch. Second, we have a limited understanding of structure-property or structure-function relationships in proteins, though we have certainly learned that a static 3D picture of a protein or a protein assembly (even at atomic resolution) is hardly sufficient for predicting its properties and functions with great accuracy. Given these two ability/knowledge gaps, the majority of efforts in the area of designing protein assemblies have been directed at obtaining target structures or shapes (a great challenge in its own right) through the development of bottom-up construction strategies. Importantly, these strategies have not only yielded numerous examples of novel protein architectures (Section 3), but also lent themselves well to generating and discovering new functions and properties (Section 4). The latter point emphasizes the value of structure-building tools regardless of functional intent.
In this section, we will provide an overview of the different strategies that have been developed over the last two decades to control protein self-assembly and to construct supramolecular or extended protein architectures (Figure 4). Further details on these strategies will be provided when discussing specific examples in Section 3. There are two take-away points: 1) There has been tremendous progress in the rational and computational design of protein structures and protein-protein interfaces. 2) Rational design of protein assembly in the laboratory is not limited by the biochemical constraints of the cellular environment and an adherence to the construction strategies that nature uses. Thus, scientists have been able to adapt tools and materials from various disciplines (supramolecular and inorganic chemistry, reticular chemistry, inorganic and DNA nanotechnology, and polymer chemistry) to devise many innovative design approaches for protein assembly.
Figure 4.
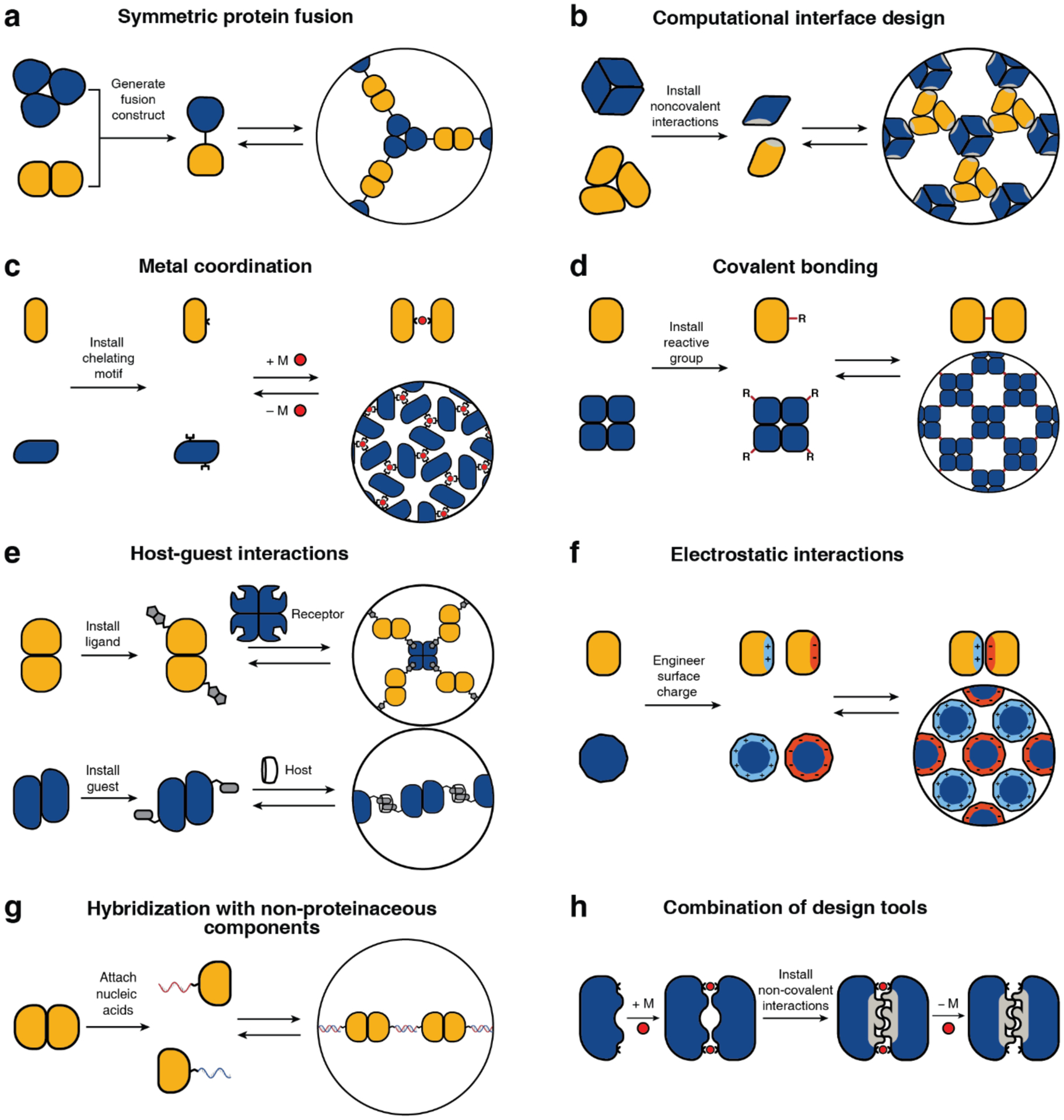
Schematic representation of the design tools and strategies for protein self-assembly, which encompass non-covalent, covalent, and metal-mediated interactions. Each strategy has been successfully used to construct both finite and extended assemblies with a wide array of protein building blocks. Selection of the design strategy is largely dictated by the desired stability, selectivity, and reversibility of the target assembly.
Regardless of the approach used, the concept of symmetry has featured prominently in the design of artificial protein assemblies, from protein cages to 1D, 2D and 3D protein crystalline arrays.127–130 Recently, Laniado and Yeates compiled a rule set for designing symmetric protein assemblies from oligomeric components and identified 124 distinct types of symmetry-combination materials.131 The readers are referred to this article and the many excellent reviews that articulate the importance of symmetry considerations in the design of ordered protein assemblies45,83,87,132–134 as well as in the synthesis of supramolecular and reticular materials.135–139
2.2.1. Symmetric protein fusion
Most approaches for constructing protein assemblies directly involve the design or modification of a protein-protein interface (vide infra). One of the earliest studies, wherein the rational design of protein assemblies was explicitly articulated, used an alternative approach, which we refer to as symmetric protein fusion. This method was introduced by the Yeates Group and exploits the natural, self-associative interfaces of oligomeric proteins to drive self-assembly. It is based on the principle that most symmetric objects and extended materials can be generated from the proper combination of two symmetry elements, as summarized by Padilla, Laniado and Yeates,127,131 and earlier in the supramolecular chemistry literature.135–139 In the symmetric protein fusion method, this combination is achieved by genetically fusing the monomeric subunits of natively oligomeric proteins that possess appropriate symmetries (Figure 4a). The proper orientation of subunits with respect to one another is central to obtaining the desired assembly geometry and requires a careful integration of a rigid peptide linker domain.
In the first demonstration of this strategy, Padilla et al. fused the monomeric components of C2 and C3 symmetric protein oligomers with an α-helical linker. This generated a construct that assembled into a tetrahedral cage, enabled by the fusion-enforced orientation of the resulting C2 and C3 symmetric interfaces at the desired angle (~54.7°).127 A second fusion constructed from the subunits of two C2 symmetric dimers (with non-intersecting symmetry axes) led to the formation of 1D protein filaments, further providing proof-of-principle.127 Using a similar strategy, Sinclair et al. combined protein building blocks with matching rotational symmetries to construct 1D and 2D crystalline arrays.128 Linker length and rigidity played central roles in determining whether or not fusion constructs would form assemblies with long range order.128 To make genetic protein fusion a more versatile tool for self-assembly, an increasing diversity of domains have been used as building blocks, including de novo designed coiled coils.140–142 Cannon et al. recently assembled an icosahedral cage using a doubly fused, three-component construct comprised of a dimer, pentamer, and trimer.143
An inherent challenge of the fusion approach is the linker design and the requirement to choose natively oligomeric protein building blocks with appropriate symmetries/topologies. To enable geometrically specific assembly, the linker must be of optimal length/rigidity and positioned accurately while the stability of the monomers is maintained. The high association constants of the native protein-protein interfaces may also increase the likelihood of kinetically trapped aggregates. The use of externally tunable (i.e., non-obligate) protein-protein interfaces along with algorithms that accurately model linker lengths/placement could greatly increase the scope of the symmetric protein fusion approach.
2.2.2. Computational interface design
The computational design of self-assembling supramolecular or extended protein architectures involves the modeling of the geometric arrangement of multiple protein units to form a desired architecture, followed by the design of energetically favorable protein-protein interfaces to stabilize that architecture (Figure 4b). All computational protein design calculations contain an energy function with which to evaluate a protein structure.144,145 Energy functions used in protein modeling can be molecular mechanics-based functions similar to those used in molecular dynamics simulations,146–151 or they can be statistical functions derived from rotamer configurations and sequence patterns obtained from a database of protein structures.152–154 The former is often too computationally expensive to reproducibly and accurately evaluate in protein design calculations, whereas the latter cannot effectively model unfamiliar structures that do not frequently appear in the structural database.144 As a result, energy functions used in protein design frequently use a combination of physical terms, such as electrostatic and van der Waals’ interactions, and statistical terms, such as torsion angle probabilities.155,156
In principle, an accurate energy function, combined with a method for traversing the energy landscape, is sufficient to predict a protein’s folded structure given its sequence. However, the protein design problem is in some ways the inverse of the protein folding problem.157 Rather than attempting to predict the lowest energy structure of a protein given its sequence, the aim of protein design is to predict a sequence that will stabilize a desired structure. Complicating matters is the fact that many amino acid side chains can adopt multiple conformations, or rotamers, and therefore the number of rotamers that must be sampled is much larger than just the number of natural amino acids. While most protein design calculations use discrete rotamer libraries that help limit the search space,158–164 even the smallest rotamer libraries are impossible to exhaustively sample except in the case of calculations involving only a few positions. There are several ways to address this problem.145 Most commonly, Monte Carlo methods are employed to randomly sample the design space and attempt to converge on a favorable sequence.165–170 Because of the inherent stochasticity of these searches, multiple iterations are frequently required to obtain the best sequence or sequences. Alternatives to Monte Carlo searches include dead-end elimination,171,172 in which physically incompatible rotamers are first identified and excluded and an exhaustive search is then performed with the remaining rotamers, and mean-field calculations,173,174 in which sequences are evaluated by considering the average positions of all possible rotamers of an amino acid. Dead-end elimination methods have been successfully used for small proteins,66,156,175,176 but are usually too computationally expensive for larger proteins, whereas mean-field calculations perform well with hydrophobic core residues but are less effective with surface residues.145,169
A protein’s sequence and tertiary structure can be designed with a suitable energy function and a method to explore the search space of possible rotamers. However, the design of supramolecular protein assemblies also requires the optimization of the rigid body orientations of the protein subunits. This can be accomplished by protein docking calculations, which attempt to predict the quaternary structure of two or more protein domains.177 Docking calculations typically start with a global search of the degrees of freedom of the system using simplified representations of the proteins, such as by excluding amino acid side chains. This low-resolution docking step is then followed by an all-atom, high resolution docking stage with finer perturbations.177 As with protein sequence design, protein docking calculations can be performed with a variety of energy functions and approaches to sample the degrees of freedom of the system. Notable examples include fast Fourier transform (FFT) docking,178 which largely assesses surface complementarity, docking with Monte Carlo methods,179 and docking based on biochemical interaction data.180 In addition, several servers that integrate multiple docking calculations to predict multimeric protein structures have been developed.181,182
As discussed above, multiple tools have been developed for each part of the computational protein design process, and different calculations have been combined to design protein oligomers.176 However, the most frequently used software for the computational design of protein assemblies is currently Rosetta183 which has been used to construct dimers,184 small oligomers,185 protein cages,186 1D helical filaments,187 and 2D protein arrays,188 which will be discussed in more detail in Section 3.
As evidenced by this large array of artificial protein structures, computational design has emerged as a powerful tool for designing and optimizing non-covalent protein-protein interactions. However, this approach still requires a considerable amount of trial-and-error and is inherently geared toward finding deep-energy minima primarily through hydrophobic/packing interactions, which is suitable for optimizing association energies and specificities, but not for dynamics. It is important to note that there has been steady progress in the computational design of polar/H-bonding interactions.189,190 With additional improvements in scoring functions and protocols to effectively model polar interactions, protein solvation and metal coordination, it will increasingly be possible to computationally design protein assemblies not only with desired structures but also with complex dynamic behavior and functions.
2.2.3. Metal coordination
Although natural protein-protein interfaces are primarily formed through non-covalent interactions, it is estimated that 5–10% of oligomeric proteins contain interfacial metal ions or metallocofactors.191 Such naturally occurring interfacial metal centers drive protein self-assembly or stabilize quaternary structures, mediate transient protein–protein interactions, and act as catalytic centers.192 From a structure-building perspective, metal coordination bonds are highly appealing, as they are considerably stronger than non-covalent interactions but reversible, enabling the formation of protein-protein interfaces on a small design footprint and under thermodynamic control.193 These criteria are satisfactorily met by mid-to-late first-row transition metal ions (Mn2+ to Zn2+), which are labile for ligand substitution, yet can form thermodynamically stable complexes. Metal-ligand bonds are highly directional, meaning that the stereochemical preferences of metal ions can dictate the symmetry and structures of protein assemblies.194 Furthermore, metals have inherent reactivities and their coordination bonds are inherently environment-sensitive (e.g., to solution pH, redox potential or the presence of extrinsic chelators), thus providing a facile means to control the thermodynamics and kinetics of protein self-assembly and to construct stimuli-responsive or reactive protein assemblies.195,196 Finally, metal-mediated protein-protein interactions can be designed using a variety of natural amino acids (predominantly, histidine (His), aspartic acid (Asp), glutamic acid (Glu), cysteine (Cys)) as well as synthetic, non-biological ligands (e.g., phenanthroline, hydroxyquinoline, bi- or terpyridine) to access diverse modalities of protein self-assembly (Figure 4c).197,198
The advantages of metal coordination have been widely exploited in molecular self-assembly,135–139 and were first adapted explicitly for the design of supramolecular protein assemblies in 2007 by the Tezcan Group.199 An obvious challenge in using metal coordination for controlling protein-protein interactions is the potential lack of selectivity that stems from the fact that the surface of any protein is replete with metal-binding amino acid sidechains. To circumvent this challenge, two pairs of metal-chelating, i/i+4 bis-His motifs were incorporated on the surface of cytochrome cb562 (cyt cb562), a monomeric, four-helix-bundle protein. Despite its minimal design footprint, the resulting construct (termed MBPC1) formed a discrete D2 symmetric tetramer upon binding four Zn2+ ions in a tetrahedral coordination geometry.199 Notably, the same building block self-assembled into two other discrete oligomers upon binding Ni2+ (a C3-symmetric trimer) and Cu2+ (a C2-symmetric dimer), as dictated by the stereochemical preferences of the metal ions194, thus showing the unique versatility of metal coordination in directing protein-protein interactions. Building up on these proof-of-principle experiments, the approach of Metal-Directed Protein Self-Assembly (MDPSA) has been broadly adopted to construct protein assemblies with a variety of structures and dimensionalities,129,200–202 as well as dynamic,202–204 stimuli-responsive195,204 and functional architectures,205–207 using both natural199,202 and non-natural metal-binding motifs208,209 installed on protein surfaces. These examples are discussed in detail in Sections 3 and 4.
Despite these advantages, the lack of selectivity in metal-protein interactions still represents an important hurdle in MDPSA, often requiring trial-and-error as part of the design process. This selectivity issue can be particularly exacerbated in the crowded and heterogeneous cellular environment (i.e., for in vivo applications) wherein metal concentrations are tightly controlled. These challenges can in part be ameliorated by combining the design of metal coordination on protein surfaces with the computational design of protein-protein interfaces. This combined approach has indeed been shown to yield metalloprotein oligomers that efficiently form in bacterial cells by selective binding of metal ions and catalyze enzymatic reactions in vivo.205,210 Another area of improvement for MDPSA is a better understanding of the energetics of metal-protein interactions. Compared to the relatively well-described hydrophobic packing interactions and, increasingly, polar interactions,211 there are still no accurate energy or scoring functions for the computational modeling of metal coordination in proteins,212 even for closed-shell metal ions such as Zn2+.213 Once such energy/scoring functions are established, MDPSA and computational design may provide a particularly powerful combination in the design of functional protein assemblies.
2.2.4. Covalent bonding
As in the case of metal coordination, covalent bonding offers a powerful tool for structure building, primarily in the form of disulfide bonds (Figure 4d). With bond dissociation energies of up to 60 kcal/mol,214 disulfide bonds are more than an order of magnitude stronger than typical non-covalent bonds, yet they are reversible through a two-electron redox equilibrium. This allows disulfides to stabilize protein structures on very small interaction footprints, while also enabling responsiveness to external stimuli (solution pH, redox potential/state) and enzymatic regulation.215 Although commonly found in cytosolic proteins for intrachain crosslinking of tertiary folds, disulfide bonds also frequently serve to stabilize quaternary or extended protein structures through interchain bonding (e.g., in antibodies and extracellular proteins).216–219
In analogy to metal coordination, the combination of high stability, reversibility, and stimuli-responsiveness of the disulfide bond has made it a popular tool in the self-assembly of synthetic supramolecular complexes and generation of dynamic covalent libraries.220–222 In terms of protein self-assembly, an important feature of disulfide bonding is its self-selectivity: a Cys sidechain will only couple with another Cys sidechain. Indeed, this can be exploited to readily generate disulfide-bonded protein homodimers. In one case, Banatao et al. prepared homodimers of three different single-Cys variants of lysozyme and demonstrated that these variants formed 3D crystals with morphologies inaccessible with the monomeric protein.223
Unlike homodimerization, however, the self-assembly of most oligomeric or extended protein architectures would necessitate the formation of more than a single disulfide bond, in turn requiring the building blocks to possess more than one surface Cys residue. In such cases, it is imperative that the multiple Cys residues be placed in precise positions to pair correctly and yield the desired assembly structures. This is relatively easily accomplished with toroidal building blocks, such as the homohexameric Hemolysin-coregulated protein 1 (Hcp1), whose top and bottom faces can be tailored with symmetry-related Cys residues to yield 1D nanotubes continuously linked by inter-hexamer disulfide bonds (see Section 3.4.2).224 Alternatively, building blocks that possess 2D or 3D symmetry, such as the C4 symmetric l-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase (RhuA) and the octahedral ferritin, can be engineered in their vertices with Cys residues to self-assemble into disulfide-mediated 2Dlattices (see Sections 3.5.2).225–228 Particularly, the 2D C98RhuA lattices, described in more detail in Section 3.5.2, illustrate the key importance of the reversibility of disulfide bonds in the formation of defect-free lattices, while also highlighting how the flexibility of these bonds can give rise to coherent lattice dynamics (Section 4.2.2).225–227 Other types of covalent linkages have also been used to drive protein self-assembly, such as native chemical ligation,229 Tyr dimerization,230 and sulfo-NHS/EDC coupling,231 however, the irreversibility of these linkages generally translates into a lack of order and structural homogeneity.
It is apparent that disulfide bonds provide unique advantages toward designing protein assemblies, but they also suffer from a lack of selectivity and a reliance on accurate geometric alignment. For example, in the case of non-symmetric protein building blocks, ensuring the geometrically specific formation of multiple disulfide bonds during protein self-assembly would require additional design elements. At least in one case (cyt cb562), such specificity was achieved through the simultaneous incorporation of metal-coordination and computationally designed non-covalent interactions, which yielded the formation of tetrameric architectures containing up to six interfacial disulfide bonds.210,232,233 Further specificity could potentially be attained through the implementation of abiological covalent bonds such as boronate esters, imines, and triazines,234–237 particularly if the relative instabilities of these bonds in aqueous media can be ameliorated.
2.2.5. Host-guest interactions
As amply demonstrated in natural systems and in supramolecular chemistry,238–241 “host–guest” interactions can be readily applied to drive protein self-assembly in a modular fashion. Generally, a “host” is defined as a large molecule or a macromolecule (even a protein) that specifically recognizes a smaller “guest” molecule through a synergy of non-covalent interactions.242–244 The high specificity and reversibility of host-guest interactions allow for self-assembly with high fidelity and readily lend themselves to the generation of dynamic, switchable, and stimuli-responsive complexes.245–249
Depending on the nature of chemical components, the host-guest pairs can be either biological or synthetic. The most common biological host-guest pairs for protein assembly are streptavidin-biotin and cytochrome/myoglobin-heme pairs, featuring high-affinity interactions between the host protein and cognate cofactor.250–256For example, Ringler and Schulz generated a quadratic network by mixing the C4-symmetric enzyme RhuA labeled with biotin with the D2-symmetric streptavidin.128 Similarly, the Hayashi Lab exploited heme-apocytochrome/apomyoglobin interactions to build various supramolecular protein assemblies.250,251 Synthetic host-guest pairs used for protein self-assembly often comprise macrocyclic hosts (e.g., cyclodextrins, cucurbiturils, calixarenes) and various small molecule guests, which are widely employed in the self-assembly of synthetic supramolecular complexes.257,258 The Brunsveld Group developed synthetic host-guest pairs for protein assembly, obtaining protein heterodimers stabilized exclusively by molecular recognition between cyclodextrin and lithocholic acid.259 Follow-up studies have expanded this strategy to obtain both discrete and extended assemblies driven by selective recognition between synthetic macrocycles and small molecule ligands.260–268
Host-guest interactions represent a versatile tool to drive protein self-assembly that does not require extensive interface design and often incorporates non-proteinaceous building blocks, yielding multi-component assemblies with relative ease (Figure 4e). One potential drawback of using this tool is its dependence on chemical modification of the protein with the host/guest molecules. The linkers that connect host/guest molecules to the protein building blocks are often long and flexible, which may preclude the formation of structurally ordered protein assemblies. To address these challenges, future work in host-guest recognition driven protein self-assembly could involve more widespread utilization of host-guest interactions between a synthetic host and native amino acid residues of a protein building block (e.g., sulfocalixarene-lysine), which would eliminate the need for bioconjugation.257,266–269 A particular advantage of synthetic host-guest pairs is their modularity, which can potentially allow the interprotein complexation affinities and specificities to be tuned by synthetic modifications to the guest or the host.270
2.2.6. Electrostatic interactions
Electrostatic interactions are widely utilized in both natural and designed protein assemblies,271–274 as they can be implemented both locally through salt bridges and globally between oppositely charged domains (Figure 4f). To drive assembly through local electrostatic interactions, researchers leverage amino acid residues with ionic side chains (i.e., Glu, Asp, arginine (Arg), and lysine (Lys)) to generate charge anisotropy across specific interfaces of the protein building block.275 To drive assembly through global electrostatic interactions, one can extend charge anisotropy across an entire protein surface or use charged protein spheres as macromolecular point charges.276,277 The Debye lengths of typical electrolyte solutions can extend well over several nm’s (i.e., on the same length scale as most protein building blocks),272 meaning that electrostatic interactions can exert a sizeable energetic influence on self-assembly thermodynamics and kinetics at long distances. In both a local and global context, the overall charge of the protein interface/surface (characterized by the isoelectric point) varies with pH, giving rise to assemblies whose affinity and association kinetics can be readily controlled by solution conditions.276 Researchers have generated protein assemblies of a wide structural variety, from discrete oligomers to superlattices, via local and global electrostatic interactions.272,276–281 These assemblies have incorporated multiple different protein building blocks and even non-proteinaceous building blocks like nanoparticles.272,277
Because the free energy of a salt bridge interaction is relatively small in well-solvated environments (3–4 kcal/mol),282 a multivalent display of oppositely charged residues or a high overall net charge may be required to exploit electrostatically driven self-assembly. In a recent example, Simon et al. found that positively and negatively “supercharged” variants of the asymmetric superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) assembled via electrostatic interactions to form discrete particles with eight-fold symmetry (Section 3.2.2).276 In this context, highly symmetric protein building blocks are particularly appealing, as they require fewer surface mutations to obtain highly charged states and can more readily arrange into desired assembly geometries due to their symmetry.272 These advantages are well illustrated by the electrostatically driven, binary 3D lattices of cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) capsid279 and ferritin.277 In addition to proteins, researchers have utilized RNA, nanoparticles, and dendrimers as building blocks for electrostatically stabilized lattices.272,274,277,278,280 Electrostatic interactions represent an intuitive and powerful tool for the design and construction of tunable, multicomponent assemblies.
2.2.7. Hybridization with non-proteinaceous components
The design strategies for artificial protein assemblies discussed thus far rely on optimizing the geometric arrangement of protein building blocks and/or engineering the protein-protein interfaces between subunits. Such protein-centered design approaches can be complemented by the incorporation of non-proteinaceous components to build hybrid assemblies (Figure 4g). As evident in many natural protein assemblies and biomaterials (e.g., nucleoprotein assemblies like the ribosome and nucleosome),283,284 and extensively demonstrated in nanotechnology, polymer chemistry, and supramolecular chemistry, hybrid systems are often synergistic.285,286 The combination of two different types of building blocks gives rise to emergent properties that would not be accessible using just one type of building block.287–289 Importantly, hybridization of proteins with non-proteinaceous components (e.g., nucleic acids, inorganic nanoparticles, synthetic polymers)290–294 expands the structural and functional scope of the proteins, creating new-to-nature functions295,296 and enabling access to self-assembly modes beyond what is possible based on a polypeptide-only composition.
Non-proteinaceous building blocks can be biological (i.e., nucleic acids, sugar) or abiological (i.e., synthetic polymers, metal nanoparticles, and carbon nanotubes),272,277,278,280,290,295,297–302 and impart a high degree of tunability in the control of protein self-assembly. In this regard, the high specificity of Watson-Crick base-pairing interactions is quite powerful, as highlighted by the remarkable structural diversity and programmability of artificial DNA-based nanostructures.303–306 In one of the earliest examples of DNA-dependent protein self-assembly, the Finn Group prepared CMPV-DNA conjugates, which could be tunably arranged into 2D hexagonal arrays and extended 3D aggregates by varying the assembly temperature (Section 3.6.4).307 More recently, the Mirkin Group demonstrated, through several examples, exquisite control over the 3D lattice arrangements of proteins covalently conjugated to single-stranded DNA sequences (Section 3.6.4).290,308 Like DNA, synthetic polymers and inorganic nanoparticles offer considerable structural tunability in terms of protein self-assembly, while also imparting novel mechanical and functional properties. As described in section 4.3.4, the Kostianen Group harnessed electrostatic interactions between spherical or cylindrical protein building blocks (ferritin, CCMV, tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)) and inorganic nanoparticles or polymeric dendrimers to mediate the assembly of hybrid 1D wires and 3D lattices with new optical, magnetic and mechanical features.296,309 As detailed in section 4.4, Zhang et al. integrated ferritin crystals with hydrogel networks to render 3D crystalline hybrid materials that were capable of isotropic expansion/contraction and self-healing.295
Potential size mismatches between the protein and non-proteinaceous building blocks and the inherent flexibility of protein-DNA or protein-polymer linkages can be an obstacle to the formation of ordered assemblies. Similarly, site-specific conjugation of DNA or polymers to proteins is often laborious and low-yielding. Nevertheless, as in the case of host-guest-interaction-driven self-assembly, the hybridization of proteinaceous and non-proteinaceous components brings the important advantage of modularity and the possibility of creating inherently multifunctional materials without extensive interface design and modification.
3. Finite and extended protein assemblies
3.1. Dimers
Dimeric proteins are the simplest and by far the most abundant form of protein assemblies in nature.310 The design of homo- and heterodimeric proteins is a stringent test of our understanding of the principles underlying protein-protein interactions. Importantly, the approaches developed for designing dimeric protein assemblies are relevant for higher-order protein assemblies, which inherently consist of binary protein interfaces. One widely used approach to designing dimeric assemblies, chemically induced dimerization, is exclusive to dimers and has been extensively covered in previous reviews.89,311,312 In this section, we will discuss the distinct design strategies for protein dimerization including domain swapping, computational design and metal-mediated assembly, which have also been applied to form protein oligomers and higher-order protein architectures.
3.1.1. Dimerization by domain swapping
Domain swapping is a mode of oligomerization found in natural proteins in which one protein domain is exchanged with the identical domain from a second copy of the same protein.313,314 In essence, the pre-existing intra-molecular interface between two domains within the monomeric protein is repurposed into a new inter-molecular interface between two proteins.315 As such, domain swapping typically requires minimal interface redesign and has been exploited to design new protein assemblies.
Early cases of domain swapping in engineered proteins involved stabilizing domain-swapped states that were discovered serendipitously. For example, a six-residue deletion in a surface loop of staphylococcal nuclease was found to result in a solution-stable dimer.316 A crystal structure revealed that the deletion strained the loop and forced an α-helix into an unfavorable extended conformation. This conformation was stabilized by a second copy of the protein, which, through domain swapping of the α-helix, allowed the helix to make native-like contacts with the second protein. Meanwhile, recombinant expression of the protein CD2 fused to glutathione S-transferase (GST) yielded a domain-swapped dimer of CD2.317 While mutations intended to stabilize the dimeric form of CD2 had little effect, mutations that destabilized the monomeric form significantly increased the fraction of protein that assembled into the domain-swapped dimer in solution. Similarly, a single-point mutation to the IgG-binding domain of protein L resulted in low yields of a domain-swapped dimer.318 To obtain an obligate dimer of protein L, the interface of the domain-swapped dimer was computationally re-designed to incorporate three mutations, which led to a dimer dissociation constant that was comparable to that of many naturally occurring protein dimers.
Geiger and coworkers have explored the domain swapping behavior of human Cellular Retinol Binding Protein II (hCRBPII) in detail and used it to design protein switches. Initially, they found that mutation of Tyr60 to hydrophobic residues produced domain-swapped dimers, with L60 and I60 variants producing 80–100% dimer.319 Crystal structures revealed that the orientations of Asn59 and residue 60 are reversed in the dimers compared to the monomers and that breaking a hydrogen bond between Tyr60 and Glu72 was key to promoting the domain-swapped state (Figure 5a-b). Because Asn59 partially occupies the hCRBPII ligand-binding site in the domain-swapped state, the authors then hypothesized that ligand binding could result in conformational changes in the domain-swapped state. They identified an additional residue, Thr51, where mutations to bulkier amino acids also resulted in domain-swapped dimers which, significantly, could be crystallized in both the apo and ligand-bound states (Figure 5c).320 Incorporation of a disulfide bond along the interface of the two domains led to two new apo and ligand-bound conformations, thus expanding the total number of available conformations. Finally, installing a His2Cys metal-binding site along the domain interface resulted in a Zn-binding site with micromolar Zn affinity in the apo state, but a five-fold lower affinity in the ligand-bound state.
Figure 5.

Conformational changes in domain-swapped hCRBPII. a) Structure of the W60 hCRBPII domain-swapped dimer. b) Overlay of the hCRBPII monomer (red) and the W60 hCRBPII domain-swapped dimer (cyan). c) Comparison of the apo (green) and holo (magenta) states of the D51 hCRBPII domain-swapped dimer. Binding of retinal results in significant conformational changes. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref. 319. Copyright 2016 Elsevier. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref. 319. Copyright 2016 Elsevier. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref. 320. Copyright 2019 ACS.
The Loh Group developed an approach to induce domain swapping termed “mutually exclusive folding”, which involves inserting a small protein domain, called the “lever”, into a surface loop of a second protein, called the “assembler” (Figure 6).321 If the distance between the N- and C-termini of the lever is greater than the distance between the ends of the selected loop, then the lever in its folded state exerts strain on the assembler, disfavoring its monomeric state. While this was initially predicted to lead to unfolding of the “assembler”, insertion of ubiquitin (“lever”) into barnase (“assembler”) instead resulted in a mixture of oligomers, of which the purified dimers were structurally confirmed to assemble via domain swapping.321 The same approach was applied with several other proteins as either the “lever” or “assembler”. Insertion of ubiquitin in to any one of four loops in ribose binding protein (RBP) led to domain swapping and partial re-activation of a de-activated RBP for ribose binding.322 Replacement of ubiquitin with the protein FKBP, which transfers from a partially unfolded apo state to a folded state upon the binding of the ligand FK506.9, enabled FK506-dependent activation of RBP, as well as staphylococcal nuclease, upon insertion of FKBP into a loop.323
Figure 6.

Domain swapping by mutually exclusive folding. a) Insertion of Ub into a loop in RBP. b) Schematic of domain swapping by mutually exclusive folding. c) Activation of protein function by domain swapping. Adapted with permission from Ref.322. Copyright 2015 Elsevier.
In addition to the mutually exclusive folding strategy above,321 a second domain-swap approach that has been applied to multiple proteins was reported by Gosavi and coworkers.324 This approach utilizes a hydrophobic QVVAG hinge loop that has been implicated in domain swapping of the natural protein stefin B (Figure 7a).324 The authors first created three variants of single-chain monellin, a protein which does not domain-swap, where each variant had a different loop replaced by the QVVAG motif. All three loops in question connected two β-strands. Of the three variants, two gave a mixture of monomers and dimers, while a third resulted in pure dimers. A crystal structure of the most successful variant revealed that it did indeed dimerize via domain swapping, as the inserted motif formed an extended β-strand instead of a loop (Figure 7b). The authors then created an additional variant of monellin in which two of the loops were replaced by the QVVAG motif and obtained a double domain-swapped dimer in high yield (Figure 7c). Finally, the motif was engineered into a loop in the proteins MK0293, Sso7d, and ubiquitin, which yielded solely dimers, dimers with a small fraction of monomers, and a mixture of oligomeric states, respectively. Thus, the QVVAG motif can be engineered into loops to induce domain swapping in a variety of proteins, though it does not always yield a single oligomeric state.
Figure 7.

Domain swapping by insertion of a QVVAG motif. a) Cartoon depiction of domain swapping via the QVVAG hinge loop. b) Structure of the MNEI single domain-swapped dimer. c) Structure of the MNEI double domain-swapped dimer. Adapted with permission from Ref.324. Copyright 2019 NPG.
3.1.2. Dimerization through computational interface design
One approach to designing a dimeric protein complex involves grafting a structural motif from one member of an existing protein-protein interface onto a new, evolutionarily unrelated protein. While the resulting protein-protein interface should mimic the pre-existing interface, the new protein scaffold can provide benefits over the natural protein scaffolds, such as increased stability. In general, motif grafting involves several steps (Figure 8). First, a starting protein scaffold is selected, which can be done by choosing a certain protein fold (e.g., a three-helix bundle)325 or by searching the Protein Data Bank (PDB) for proteins with similar backbone structures to the motif to be transplanted.326–329 Next, the desired motif is computationally inserted into the selected scaffold. The insertion process can be carried out in a number of ways. Initial approaches involved grafting just the amino acid side chains of the structural motif onto regions of the scaffold protein with similar backbone structures to the initial motif.326,327 Later approaches enabled the entire structural motif, including both the side chains and the backbone conformations, to be transplanted into the scaffold, either by deleting segments of the target scaffold and replacing them with the motif328,329 or by folding simple protein topologies around the motif.325 Once the motif has been inserted into the new protein scaffold, residues around the motif are computationally designed to optimize the scaffold for the incorporation of the motif. Finally, the top-scoring designs are selected for experimental validation. Any variants that are able to bind the target can be further optimized by generating libraries and performing phage display or related high-throughput binding assays. Motif grafting has been used to design proteins capable of binding HIV326–329 and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)325 monoclonal antibodies, as well as cancer-associated pro-survival proteins.330,331 The designed antibody-binding proteins recapitulate the native antibody-antigen interface and have the potential to lead to new vaccine candidates.
Figure 8.
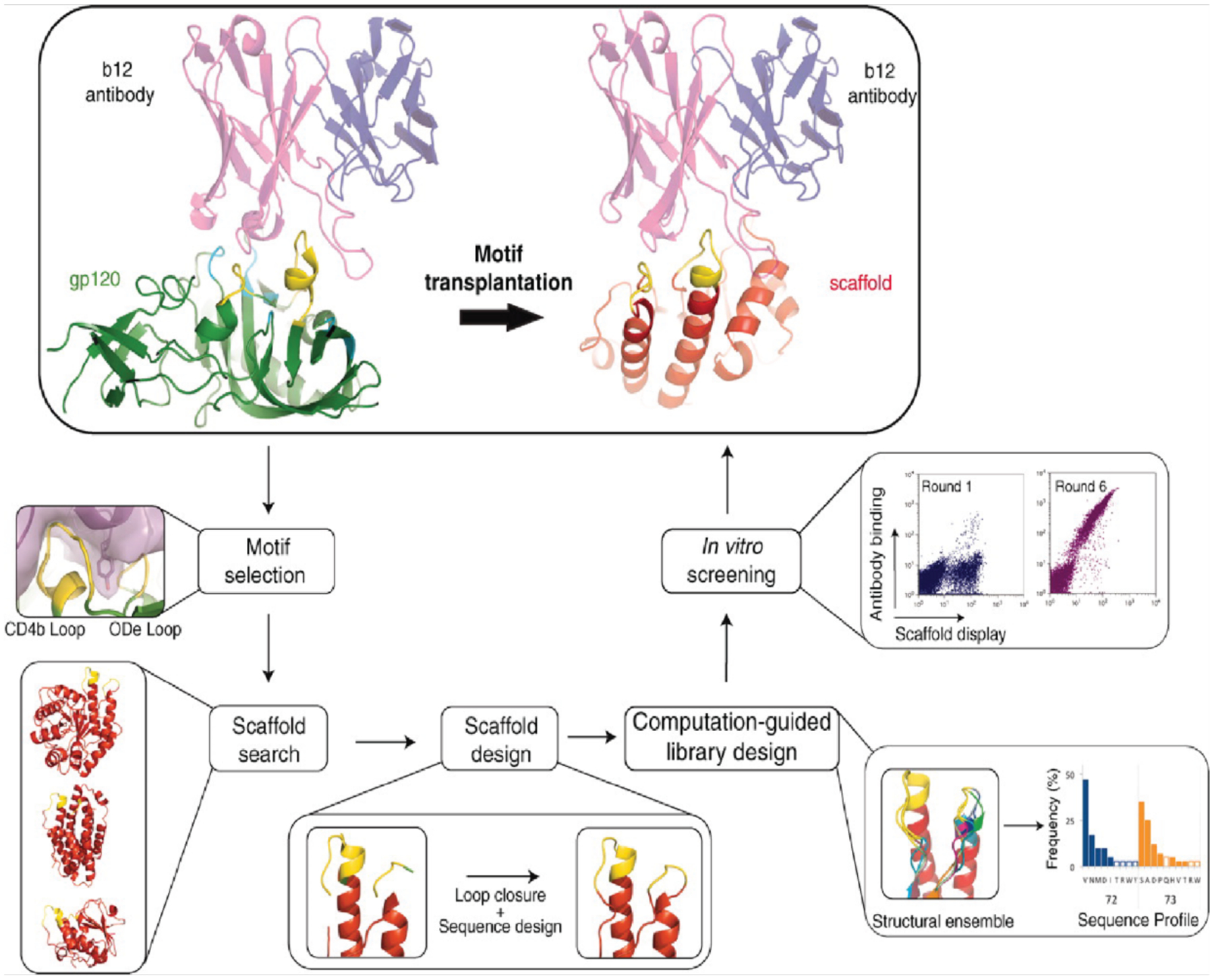
Computational and experimental steps for the transplantation of a structural motif to a new scaffold. Scaffolds can either be chosen by searching the PDB for existing structures or by designing a desired fold around the motif using ab initio folding calculations. Adapted with permission from Ref.328. Copyright 2011 AAAS.
Motif grafting can be an effective approach in part because it relies on a pre-existing protein-protein interface. Designing protein-protein interactions from scratch presents a more difficult challenge. Several groups have demonstrated the redesign of monomeric proteins to generate solution-stable homodimers. Kuhlman and coworkers took advantage of β-strand pairing to redesign the γ-adaptin appendage domain into a symmetric homodimer via the formation of an intermolecular β-sheet.332 Of the four computationally designed candidates that were experimentally tested, one expressed well and formed a homodimer in solution. The crystal structure of that dimeric variant closely matched the design model. Mayo and coworkers redesigned the engrailed homeodomain into a symmetric homodimer by designing an α-helical interface instead.176 Following library generation and screening, they obtained a variant that formed a dimer in solution, and an NMR structure of the dimer aligned well with the design model.
In designing new protein-protein interfaces from scratch, researchers have frequently attempted to recapitulate general properties of natural interfaces. Most protein-protein interfaces feature some degree of shape complementarity between the constituent proteins’ backbones, which contributes to the burial of large portions of solvent-exposed surface area along the interface. Therefore, protein docking calculations are often an important first step in designing new protein-protein interfaces. Once backbone-complementary orientations of the two proteins are found, residues along the nascent interface can be designed to stabilize the dimeric conformation. Several groups have used protein docking calculations followed by computational sequence design to generate heterodimeric complexes, though these have not been thoroughly structurally characterized.333,334
More recently, Baker and coworkers have used computational docking and interface design calculations, followed by affinity maturation, to develop Ankyrin repeat proteins capable of binding Frizzled subtypes with high affinity and selectivity for certain subtypes over others.335 Key to the selectivity of the binding proteins was the computational docking (Figure 9), which allowed for the design of large interfaces that included both the highly conserved Frizzled lipid-binding site and regions with less conservation among Frizzled subtypes. Maly and coworkers also used docking, interface design, and affinity maturation to develop designed helical repeat proteins that selectively bind to different drug-bound states of the NS3a protease.336 These different dimeric complexes could subsequently be used to translate drug inputs into diverse outputs.
Figure 9.
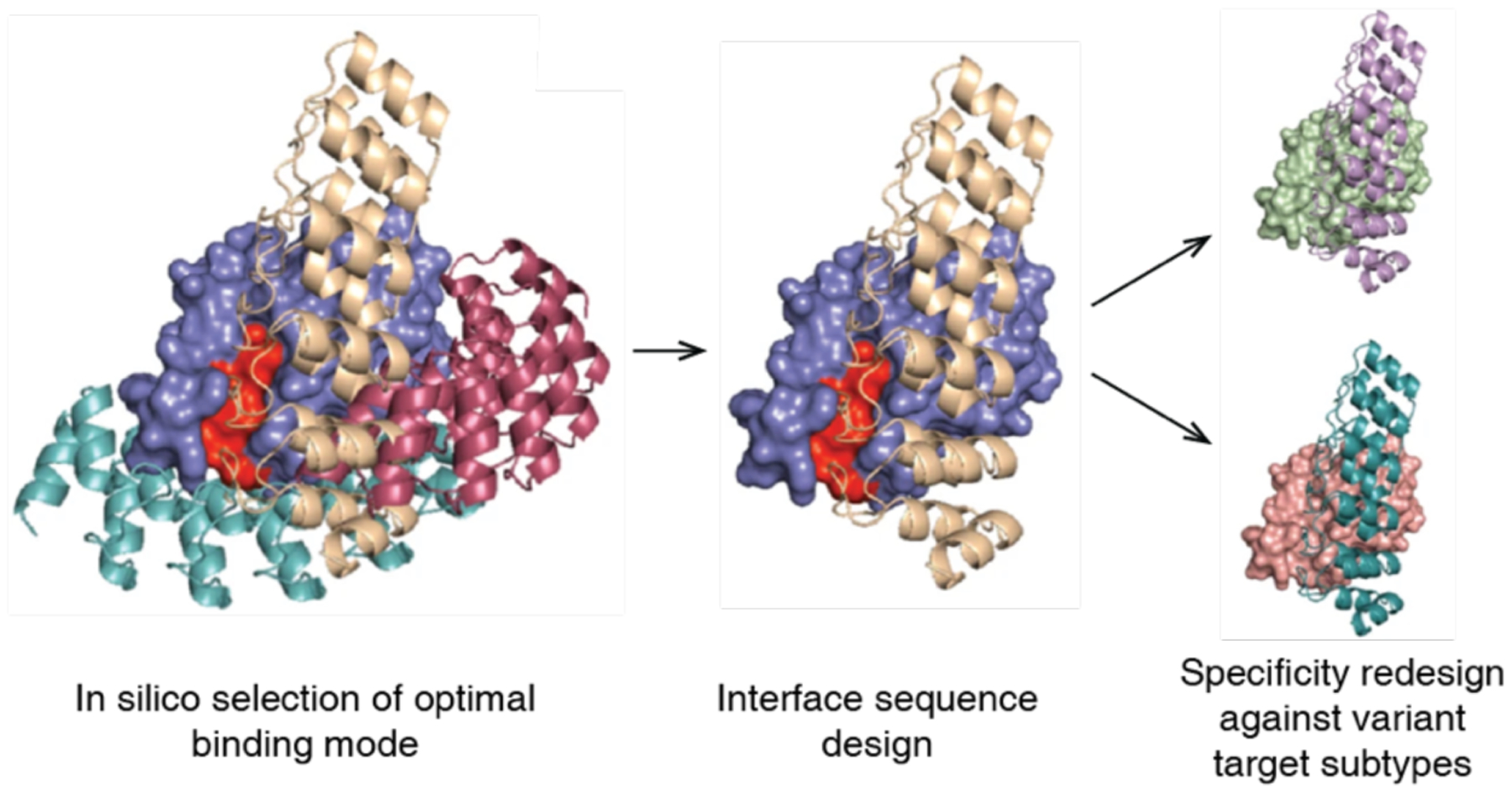
Computational docking calculations can be used to sample possible binding modes, from which the resulting protein-protein interface can be designed to obtain dimeric complexes. Adapted with permission from Ref.335. Copyright 2019 NPG.
In addition to shape complementarity, natural protein-protein interfaces typically contain several “hot-spot” residues that contribute a large fraction of the total binding energy.337 To exploit this concept, a protocol for designing protein-protein interfaces was developed. It first places disembodied amino acids to form such key interactions with a target protein (Figure 10).338 The PDB is then searched for suitable scaffolds, which are docked against the target protein to identify binding modes that can accommodate the hot-spot residues. Once the hot-spot residues are incorporated into the scaffold protein, the remaining residues around the interface are redesigned and the best designs are selected for experimental characterization and affinity maturation, as necessary. Using this protocol, Baker and coworkers designed proteins with nanomolar affinity toward the conserved stem region of influenza hemagglutinin,338 a heterodimeric complex between an Ankyrin repeat protein and the protein PH1109,184 as well as proteins capable of binding to and inhibiting hen egg lysozyme.339 In all three studies, affinity maturation was used to obtain the final, optimized proteins. A crystal structure of a complex of influenza hemagglutinin and one of the evolved binders revealed good agreement with the computational model,338 as did a crystal structure of the designed hen egg lysozyme inhibitor.339 Structural characterization of the Ankyrin repeat-PH1109 complex, however, revealed that, following affinity maturation, the relative orientation of the two proteins was flipped 180° compared to the computational model.184 Nonetheless, many of the designed hot-spot interactions along the protein-protein interface were preserved. The diversity of targets for which new binding proteins have been designed via this approach demonstrates the importance of hot-spot residues in the design of new protein-protein interfaces.
Figure 10.
Overview of protein-protein interface design via “hot-spot” residues as applied to the design of proteins that bind to influenza hemagglutinin. Adapted with permission from Ref.338. Copyright 2011 AAAS.
3.1.3. Dimerization through metal-coordination
The relatively low success rate of individual computational designs and frequent need for affinity maturation to obtain high-affinity protein complexes underscores the challenges of designing protein-protein interfaces strictly through non-covalent interactions. An alternative approach is to use metal-ligand interactions, which are stronger than non-covalent interactions and capable of driving protein self-assembly without requiring an extensively designed interface.198,340,341 The resulting interfaces can then be redesigned to stabilize the oligomeric assembly with or without metal ions.193
Tezcan and coworkers have applied metal-mediated assembly to design homodimeric protein complexes, along with other homo-oligomeric states, using the four-helix bundle hemoprotein cyt cb562 as a scaffold protein. In one study, two i/i+4 bis-His motifs were designed on the surface of helix 3 of cyt cb562 to yield a variant termed MBPC1.194 Addition of Cu2+ resulted exclusively in the dimerization of MBPC1 in solution, and a crystal structure of the copper-bound protein revealed an antiparallel dimer held together by two Cu2+:His4 sites with square planar geometries (Figure 11a).194 In another study, metal-mediated oligomerization was expanded to include the use of non-natural ligands.197 A cyt cb562 variant was designed with a single His residue and a hydroxyquinoline chelate covalently attached to a Cys residue in an i/i+7 arrangement. The addition of half-molar equivalents of the divalent metal ions Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ resulted in the formation of dimeric species in solution, with dissociation constants on the order of 10−9 M or lower. A crystal structure of the nickel-bound dimeric complex revealed a V-shaped dimer with a single Ni2+ ion bound to the His and hydroxyquinoline moieties of the two monomers in a distorted octahedral geometry (Figure 11b).
Figure 11.

Metal-mediated dimerization of cyt cb562 via a) Cu2+ binding to a pair of i/i+4 bis-His motifs or b) Ni2+ binding to a His residue and a hydroxyquinoline chelate in an i/i+7 arrangement. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.194. Copyright 2009 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.197. Copyright 2010 ACS.
Kuhlman and coworkers designed a homodimeric assembly by incorporating metal-binding functionalities into the computational interface design process.342 Rosetta was used to place pairs of His residues on the surface of α-helical scaffold proteins. The second copy of each monomer was then placed to form C2-symmetric dimers with two tetrahedral metal-binding sites, and the resulting dimeric interfaces were re-designed. Of eight tested computational designs, one design, termed MID1, expressed well and formed a dimer with or without Zn2+, though Zn-binding significantly increased the affinity of two monomers for each other. Crystal structures revealed that the overall conformation of the Zn-bound dimer closely resembled the design model, although only three out of four His residues coordinated to Zn2+ (Figure 12). Though unanticipated, these coordinatively unsaturated Zn sites enabled the design and evolution of enzymatic activity toward hydrolysis and Diels-Alder reactions, as discussed in more detail in Section 4.207,343,344
Figure 12.

Design model and structure of MID1. a) Computational design model of MID1. b) Comparison of the MID1 design model (tan) and crystal structure (cyan). Adapted with permission from Ref.342. Copyright 2012 ACS.
The function of most natural metalloenzymes relies on a stable protein scaffold that exerts control over the metal coordination environment and tunes metal reactivity.345,346 Such a metal-independent, highly preorganized architecture is challenging to achieve via metal-mediated protein self-assembly, because in this approach the structure of the protein scaffold tends to be directed by the coordination preferences of the metal ions instead. To overcome this challenge, Rittle et al. developed a simple approach, termed Metal Active Sites by Covalent Tethering (MASCoT), in which two proteins are first covalently tethered by the formation of a disulfide bond between single Cys residues on their surfaces (Figure 13a).347 Incorporation of metal binding residues subsequently allows the conformation of the nascent protein-protein interface to be locked into place upon addition of metal. Using this approach, the researchers made a suite of metal-binding proteins with tunable primary and secondary coordination spheres (Figure 13b–e). These metal binding sites featured unusual asymmetric coordination environments due to constraints imposed by the disulfide bond and bound all first-row transition metals from Mn2+ to Zn2+ with unusually high affinities for designed proteins. Furthermore, a variant with a penta-His metal binding site was able to bind nitric oxide, suggesting that metal binding sites developed through the MASCoT approach have the potential to bind ligands and act as active sites for catalysis.
Figure 13.
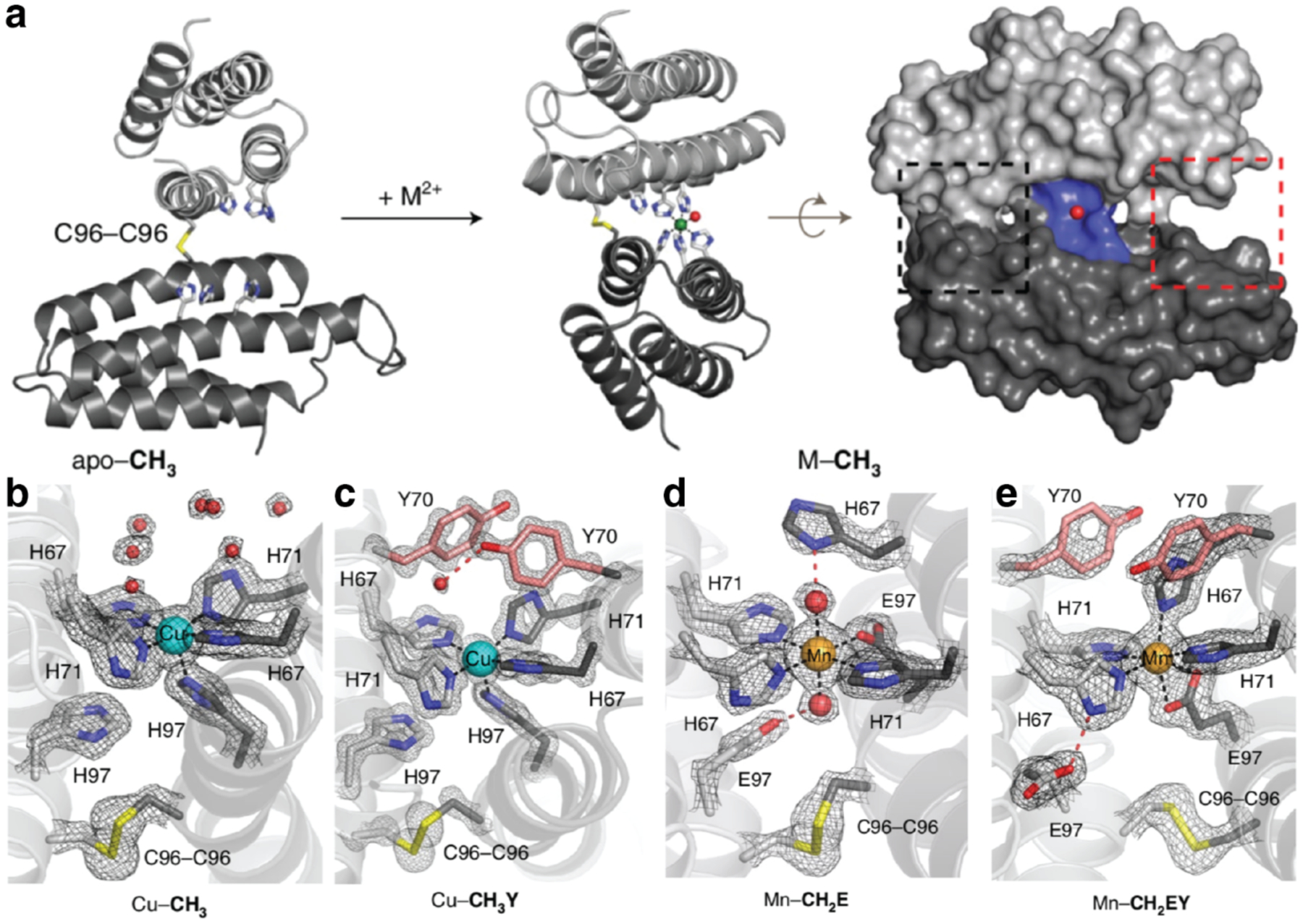
Metal Active Sites by Covalent Tethering (MASCoT). a) Implementation of MASCoT. The C96-C96 disulfide bond covalently tethers two proteins, forming a nascent protein-protein interface that is locked into place upon metal addition. b-e) Formation of metal binding sites with different primary and secondary coordination spheres. Adapted with permission from Ref.347. Copyright 2019 NPG.
3.2. Small oligomers
Nature uses protein oligomerization to generate structural and functional complexity through the self-assembly of individual protein domains into larger protein oligomers.45,54 From an engineering perspective, designing new oligomeric protein assemblies is beneficial for (1) increasing the intrinsic stability of proteins, (2) controlling shape, composition and size of protein complexes for target function, and (3) creating novel inter-molecular interfaces for new enzymatic active sites or allosteric regulation of supramolecular structures.110 In this section, we will focus on protein oligomerization aided by computational design, based on the generation of genetic fusion and domain swapping constructs, and mediated by electrostatic interactions and protein-metal interactions.
3.2.1. Oligomerization through computational interface design
Symmetry enables the formation of large architectures from simple building blocks through the design of a small number of associative surface patches.348 Schulz and coworkers took advantage of symmetry by rationally designing protein-protein interfaces between homo-oligomeric protein building blocks, which enabled the formation of larger homo-oligomers with only a few mutations.349 The researchers first attempted to build dimers out of the monomeric protein 6-phospho-β-galactosidase (Pga) by stabilizing two different crystallographic interfaces through the introduction of additional large, non-polar residues (i.e., Phe, Trp, Met). This resulted in four variants with dimer yields between 3% and 56%, although none of the dimers yielded crystals for structure determination. The researchers then set out to generate tetramers out of the homodimeric proteins O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase (Oas) and urocanase (Uro), and construct octamers out of the homotetrameric protein RhuA. In each case, the researchers aligned two copies of the protein building block along its molecular symmetry axis (two-fold rotational axis for the dimers, four-fold rotational axis for the tetramer) and performed a one-dimensional search along the relative rotation angle to find suitable orientations for the two copies of the protein to form a new protein-protein interface. Mutations were then rationally made to stabilize the interface. Three variants of the Oas dimer yielded only small amounts of tetramer in solution and failed to crystallize. In contrast, a variant of the Uro dimer yielded a tetramer in 80% yield, with the crystal structure revealing that the tetramer was similar to the designed assembly. However, a slight shift in the relative orientation of the monomers broke the designed D2 symmetry and instead resulted in four local C2 symmetries. Meanwhile, three variants of the tetramer RhuA, which had only one or two mutations, all resulted in quantitative yields of the octamer in solution, and crystal structures indicated that one formed the octamer as designed, whereas another formed an octamer with displaced fourfold axes. This example illustrated the possibility of designing higher-order homo-oligomers with only a small number of mutations through the use of symmetric building blocks.349
Many natural proteins contain modular, monomeric structures and are believed to have evolved by the duplication of structural elements to form symmetric homooligomers, followed by the fusion of these domains to form a monomeric protein.350,351 This process can be reverse engineered by designing symmetric proteins, then breaking them into smaller monomers that assemble to form oligomeric analogues of the original monomer. Meiler and coworkers used this approach to design a perfectly symmetrical eight-stranded βα-barrel protein.352 The researchers took half of an asymmetric (βα)8-barrel protein, HisF, and connected two copies of the half-protein to reform the full (βα)8-barrel, but with perfect two-fold symmetry (Figure 14a). They then used the Rosetta suite to optimize the protein sequence and sidechain packing and expressed the variant with the best score according to Rosetta energy units. A monomer consisting of half of the designed protein assembled into a dimer whose crystal structure closely matched that of both the single-chain (βα)8-barrel and the design model.352 Similarly, Voet et al. designed a perfectly symmetrical β-propeller protein.353 Starting with a six-bladed β-propeller protein, the sensor domain of a protein kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the researchers replaced each blade with the third blade of the protein to form a perfectly symmetrical template. They optimized the sequence of the blade using Rosetta and fused the identical blades to form two, three, and six-bladed monomers, named Pizza2, Pizza 3, and Pizza 6. All monomers expressed well, and the two and three-bladed proteins assembled into six-bladed oligomers whose structures almost exactly matched the six-bladed monomer (Figure 14b).
Figure 14.
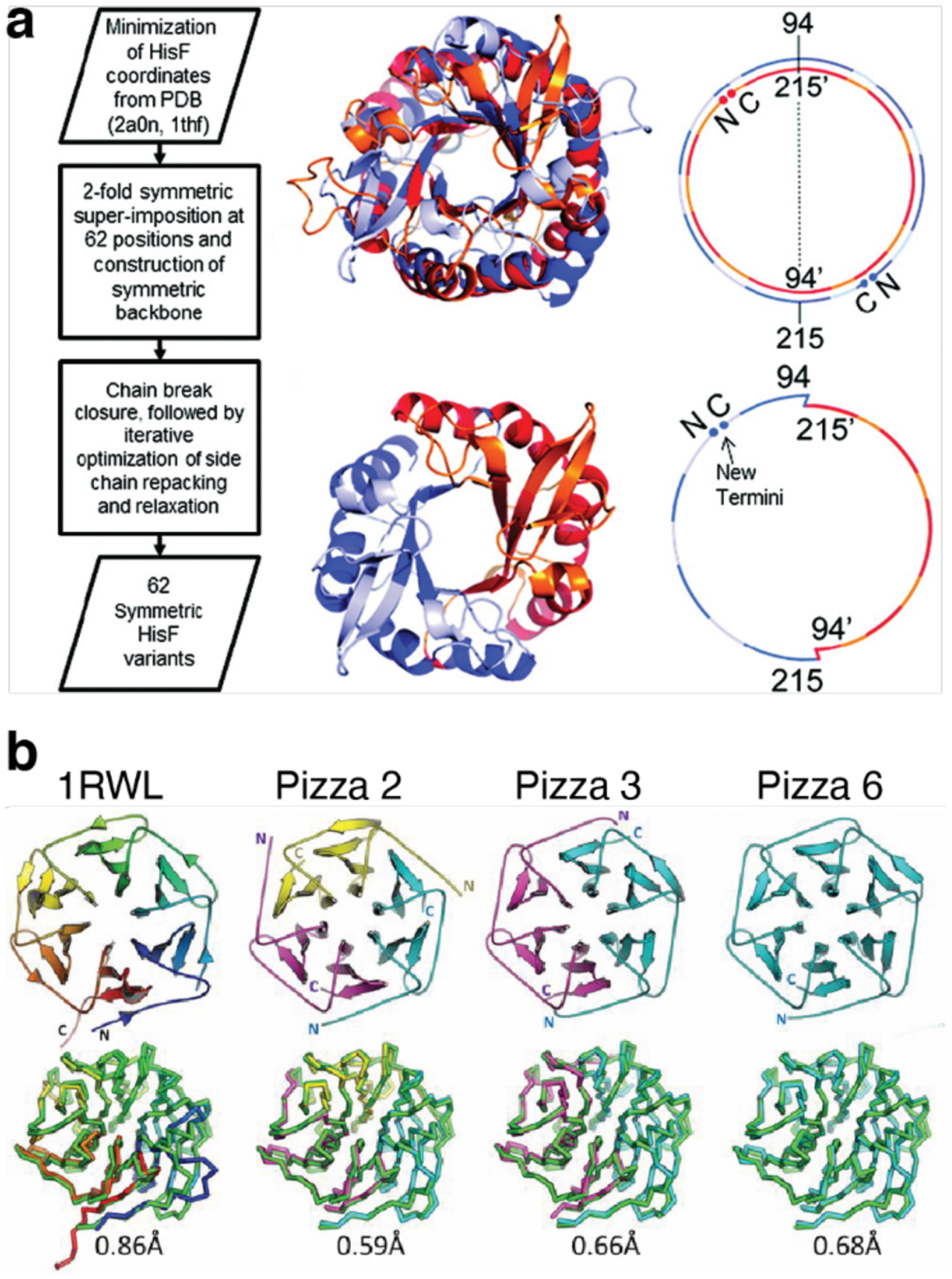
Design of symmetric homo-oligomers from proteins with repeating units. a) Design of a two-fold symmetric (βα)8-barrel. The two halves are soluble as monomeric proteins that assemble into a dimeric barrel. b) Crystal structures of Pizza6 proteins with different oligomeric states. From left to right: wild-type protein used as a template for Pizza6 design, Pizza2 (trimer), Pizza3 (dimer), Pizza6 (monomer). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.352. Copyright 2011 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.353. Copyright 2014 National Academy of Sciences.
While both of the previous examples used pre-existing proteins as building blocks, Bradley and coworkers developed a computational strategy (Figure 15) for the de novo design of symmetrical proteins consisting of repeating structural motifs that form closed, toroidal structures.185 The protocol first defined the secondary structure of the repeat motif, as well as the number of repeats of that motif and the geometrical parameters of the final structure (inter-repeat rise and curvature). Ab initio folding calculations were then performed to generate backbone conformations that match those criteria and determine the amino acid sequence to yield each backbone conformation. The resulting protein candidates were filtered to remove poor designs and clustered to identify recurring packing arrangements. Finally, low-energy designs from those clusters were further assessed by re-predicting their structures based on their sequences. The researchers applied this protocol to design left-handed α-helical repeat proteins that formed closed toroids of various sizes.185 Variants corresponding to four toroidal architectures were crystallized and revealed structures that closely matched the design models. A 9-repeat design was then split into a 3-repeat fragment that was expected to assemble into a 9-repeat trimer. Instead, the fragment formed a 12-repeat tetramer, suggesting that the repeat sequence was compatible with both 9- and 12-repeat structures.
Figure 15.

Computational design of α-helical toroids. The protocol consists of a) ab initio folding to generate backbone conformations, b) sequence design of conformations, c) filtering to remove poor designs, d) clustering of results to identify recurring packing arrangements, e) resampling of structures from the clusters, and f) a final assessment of results by re-predicting the designed structures from their sequences. Adapted with permission from Ref.185. Copyright 2015 NPG.
The aforementioned studies involved the design of oligomeric assemblies by breaking a symmetric protein into smaller monomers that assemble to re-form the initial protein. In an alternative approach, Baker and coworkers sought to design cyclic homo-oligomers by starting with de novo-designed αβ-proteins354 or monomeric repeat proteins.355 Although oligomers based on αβ-protein building blocks formed multiple oligomeric species in solution, several monodisperse oligomers were formed with the repeat protein scaffolds. The researchers began by docking the selected scaffold proteins in cyclic geometries using a low-resolution docking protocol. Because low-resolution docking ignores side chains, predicting which docked geometries yielded the most readily designable interfaces presented a challenge. This challenge was addressed by precompiling a database of favorable interactions between pairs of residues and binning them based on the rigid-body orientations of the pairs of residues. For a pair of residues along a nascent interface in a docked model, their side-chain-independent orientations were used to find the Rosetta energy of the most favorable potential interaction in the database, and the sum of these energies over all pairs of residues along the nascent interface was used to score the docking geometry (Figure 16). The best scoring geometries were then subjected to sequence design to optimize the protein-protein interfaces, and ~100 circularly symmetric, homo-oligomeric designs (ranging from dimers to hexamers) were selected for experimental characterization. A large fraction of these variants was soluble, and ~20 % had oligomeric states that matched the design model as determined by SEC-MALS. Furthermore, crystal structures and SAXS patterns of several designs were consistent with computed models. Mohan and coworkers then used this approach to design dimers of an Ankyrin repeat protein that could bind to the cytokine receptor EpoR, which dimerizes in response to its protein-ligand.356 By modifying the size and orientation of the Ankyrin repeat dimers, the researchers were able to examine and tune the cellular response induced by EpoR dimerization.
Figure 16.

Computational design of cyclic homo-oligomers. a) Monomers are first docked in cyclic geometries using low-resolution, symmetric docking. b) Docked oligomers are then scored using a residue-pair transform (RPX) method which models side-chain interactions implicitly. c) The best scoring geometries are finally subjected to interface design. Adapted with permission from Ref.355. Copyright 2016 NPG.
There has also been progress in designing oligomeric assemblies by focusing on hydrogen bond networks, which can impart specificity in protein-protein interactions. However, hydrogen bond networks can be challenging to design due to the precision with which polar residues must be placed and the energetic penalties associated with buried, unsatisfied hydrogen bond donors or acceptors. Boyken et al. therefore developed a computational sequence design method, HBNet, which precomputes all possible hydrogen bonding interactions between all possible polar residues at a given set of positions and is thus more efficient at identifying possible hydrogen bonding networks than traditional sequence design methods.211 To design homo-oligomers with HBNet, the researchers first generated a large number of α-helical, coiled-coil backbone arrangements consisting of multiple copies of two-helix monomeric subunits. They then used HBNet to identify backbone arrangements capable of accommodating hydrogen bond networks spanning the protein-protein interface(s) and involving at least three residues. Finally, traditional Rosetta sequence design was employed to optimize the remaining residues outside of the hydrogen bond networks (Figure 17). Of the >100 top-ranked designs that were experimentally tested (including dimers, trimers, and tetramers), more than half formed the designed oligomeric state. Furthermore, the crystal structures and solution SAXS scattering patterns of several variants confirmed that most of the hydrogen bond networks closely matched their corresponding design models. This study demonstrated that it is possible to computationally design a wide range of hydrogen bonding networks at protein-protein interfaces to achieve different assembly geometries, which is reminiscent of the sequence-dependent programmability of DNA. HBNet has since been applied to design a set of orthogonal heterodimers that can be used to make pH switchable assemblies and protein logic gates.189,190,357
Figure 17.
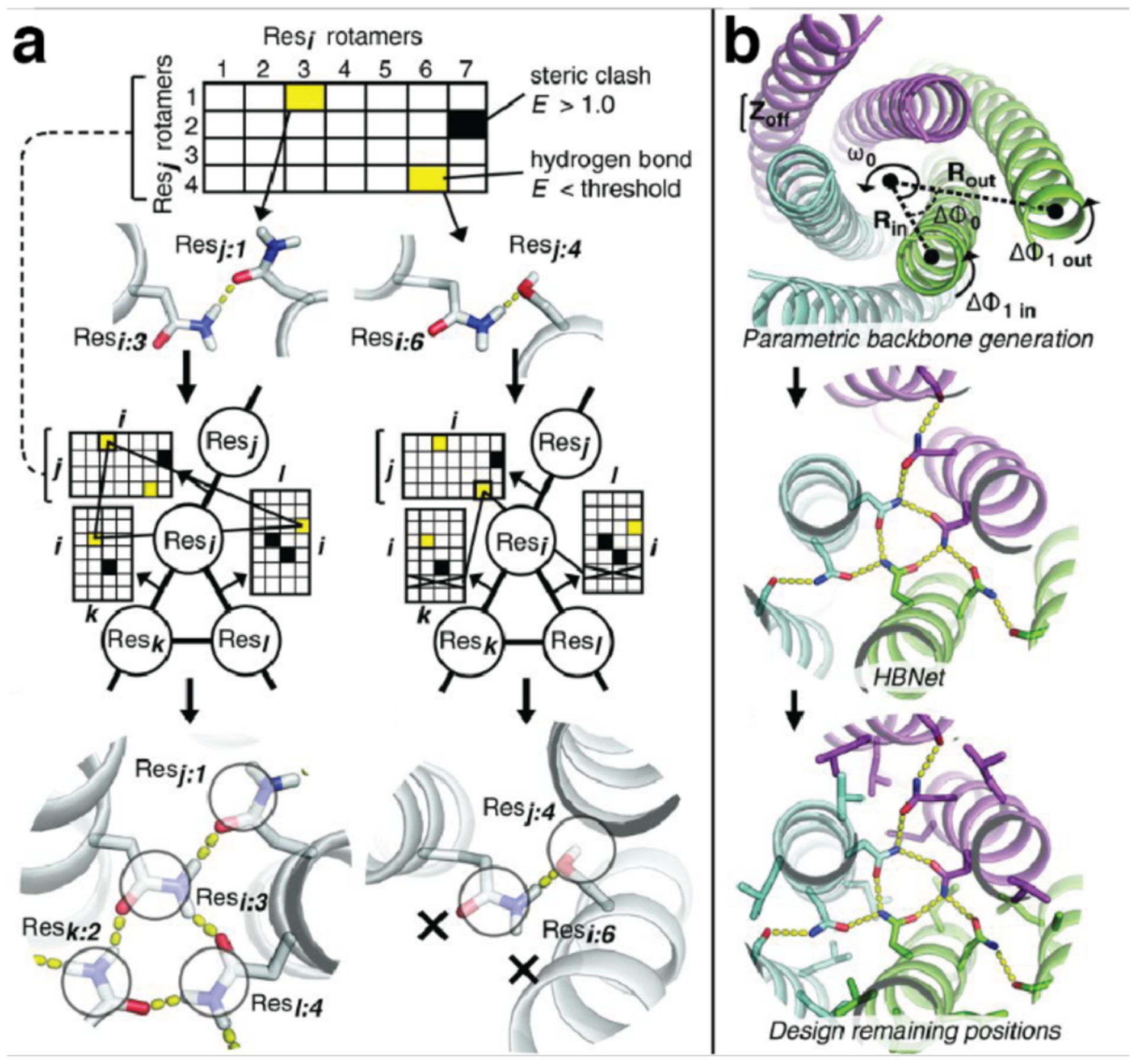
Design of coiled-coil oligomers via HBNet. a) HBNet precomputes the hydrogen bond and repulsive interaction energies between side chains for all possible rotamers at a set of selected positions. This information is stored in a graph structure; traversing the graph reveals the combinations of hydrogen-bonding rotamers that form a hydrogen bond network. b) Design of homo-oligomers by sequentially designing coiled-coil backbones, using HBNet to identify hydrogen bonding networks that connect two-helix monomers, and designing the remaining residues around the hydrogen bonding network to accommodate the network. Adapted with permission from Ref.211. Copyright 2016 AAAS.
Having developed a method for computationally designing hydrogen bond networks, Lu et al. surmised that they could use the method to design transmembrane proteins.358 Because of the hydrophobicity of the lipid bilayer, specific protein-protein interactions in transmembrane proteins cannot be designed by burying hydrophobic residues along the interface. Instead, buried hydrogen bonds can play a key role in determining protein interaction specificity in the membrane environment. The researchers therefore used HBNet to create buried hydrogen bond networks in four-helix bundles and subsequently added a ring of amphipathic aromatic residues to define the extracellular side and a ring of positively charged residues to define the cytoplasmic side. Hydrophobic residues were then placed at surface-exposed positions between the amphipathic and positively charged rings to generate transmembrane regions. The researchers expressed the four-helix bundles as either monomers or as dimers of two-helix monomers. Dimers with longer transmembrane regions and a monomer expressed well, localized to the membrane of cells, had high thermal stability and exhibited the expected oligomeric state. The crystal structure of one of the dimers closely resembled the design model (Figure 18a–b). Additionally, the researchers used the same approach to design a six-helix transmembrane trimer and a transmembrane tetramer with eight membrane-spanning helices (Figure 18c), both of which were expressed and formed the expected oligomeric state.
Figure 18.
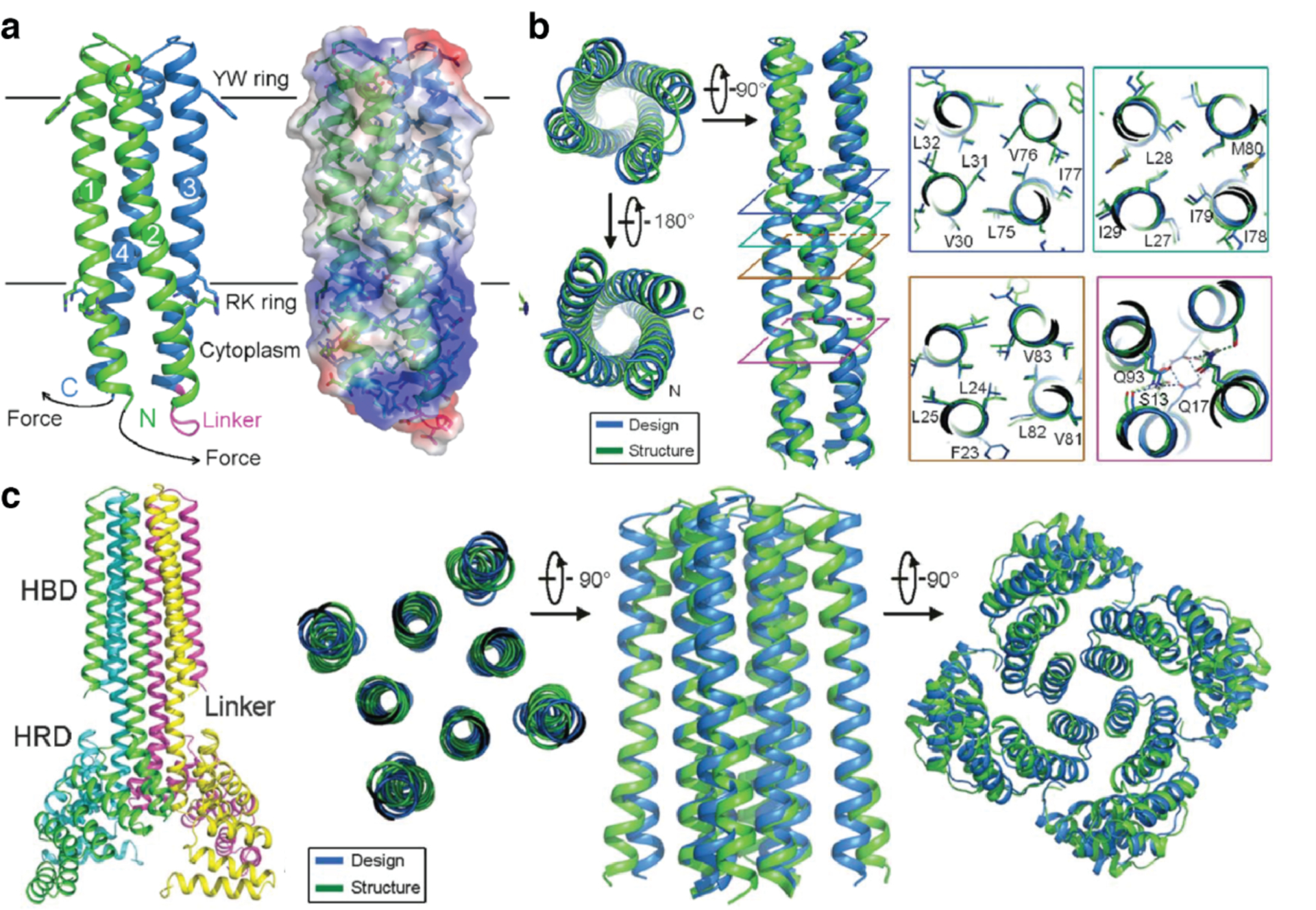
Crystal structures of de novo designed transmembrane oligomers. a) Model of the dimeric transmembrane protein, indicating the position of the amphipathic (YW) and positively charged (RK) rings. b) Comparison between the crystal structure and design model of a transmembrane dimer. c) Crystal structure and design model of the transmembrane tetramer. Adapted with permission from Ref.358. Copyright 2018 AAAS.
Building on these studies, Xu et al. designed α-helical proteins that assemble into transmembrane pores.359 Using HBNet and protocols they had previously developed for the design of α-helical oligomers, the researchers started by designing water-soluble two-helix proteins that assembled into hexamers or octamers with central solvent channels. They experimentally tested three hexameric and fifteen octameric designs and found one hexameric and two octameric variants that formed homogeneous assemblies with the correct oligomeric state. Crystal structures of the hexameric variant (Figure 19a) and one of the two successful octameric variants (Figure 19b) confirmed that the structures of the assemblies closely matched the design models. The researchers then converted the structurally characterized, water-soluble oligomers into transmembrane pores by replacing solvent-exposed residues in the intended transmembrane region with hydrophobic residues. Both the hexameric variant and the octameric variant were expressed and purified from the membrane fraction of E. coli cells, and the hexameric variant formed the correct oligomeric state. Meanwhile, the oligomeric state of the transmembrane version of the octameric variant was ambiguous, but a tetrameric version formed by linking two monomers more clearly formed the correct oligomeric state (Figure 19c).
Figure 19.
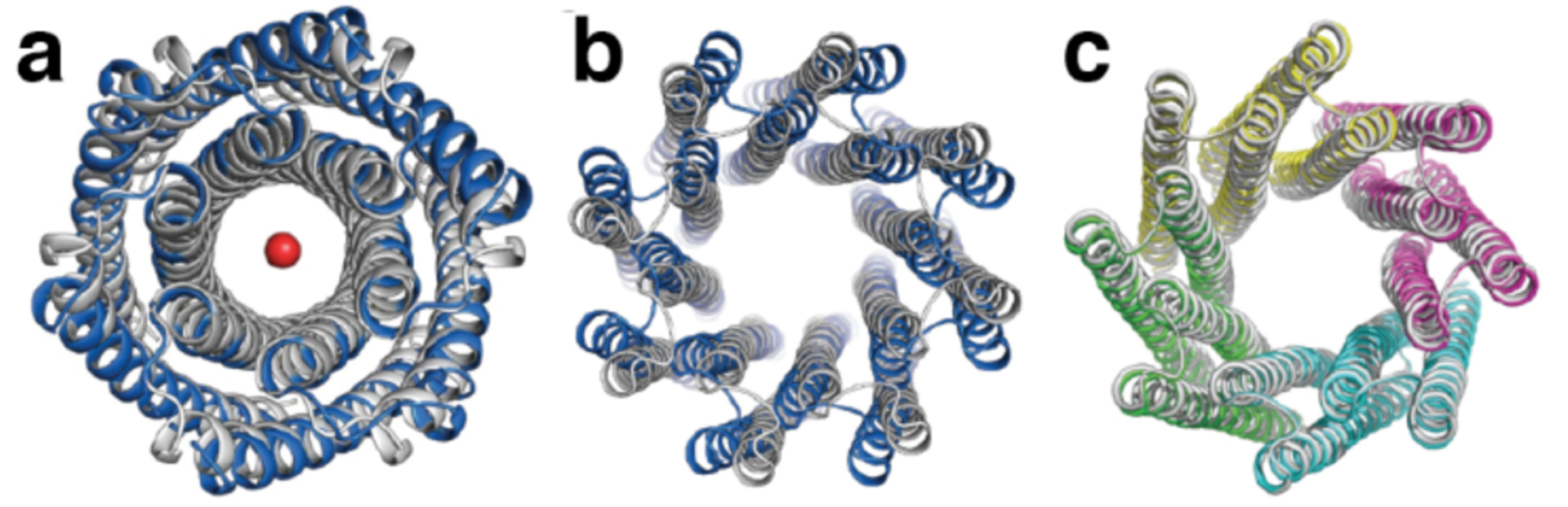
Computationally designed, oligomeric transmembrane pores. a) Overlay between the crystal structure (blue) and design model (grey) of the water-soluble hexamer. b) Overlay between the crystal structure (blue) and design model (grey) of the water-soluble octamer. A slight tilt in the monomers results in a greater deviation from the design model than in the hexameric case. c) Cryo-EM structure of the tetrameric transmembrane pore. Adapted with permission from Ref.359. Copyright 2020 NPG.
3.2.2. Oligomerization through electrostatic interactions
Forming oligomeric protein assemblies strictly through non-covalent interactions typically requires the design of extensive protein-protein interfaces. By contrast, Ellington, Glotzer and coworkers demonstrated that discrete oligomers can also be formed simply by combining pairs of oppositely supercharged proteins.276 Using GFP as a model system, the researchers observed that various pairs of oppositely charged GFP variants, such as Ceru+32 and GFP-17 (with total charges of +32 and −17, respectively), formed large oligomeric species when combined in solution (Figure 20a–b). The sizes of these species depended on solution conditions. At high salt concentrations and/or low pH, the predominant species were either monomeric with a diameter of ~6 nm or formed oligomers with a diameter of 12 nm. In contrast, at low salt concentrations and pH 7.4, the predominant species were large, 1,300-nm diameter oligomers. These solution behaviors suggested that the oligomers formed by supercharged GFP variants assembled via specific intermolecular interactions, even though no such interactions were explicitly designed. A high-resolution cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the ~12 nm oligomer revealed a D4 symmetric oligomer consisting of two stacked octameric rings (Figure 20c). The researchers hypothesized that the large number of charged residues on the monomers provide an abundance of potential interaction sites, enabling the monomers to find modes of interaction that mediated the formation of larger assemblies. The ability of multiple supercharged GFP variants to form oligomeric assemblies when paired with monomers of the opposite charge, along with the fact that supercharging has been demonstrated for various proteins in addition to GFP, suggest that supercharging could serve as a simple, broadly applicable method to obtain non-covalent oligomers.
Figure 20.
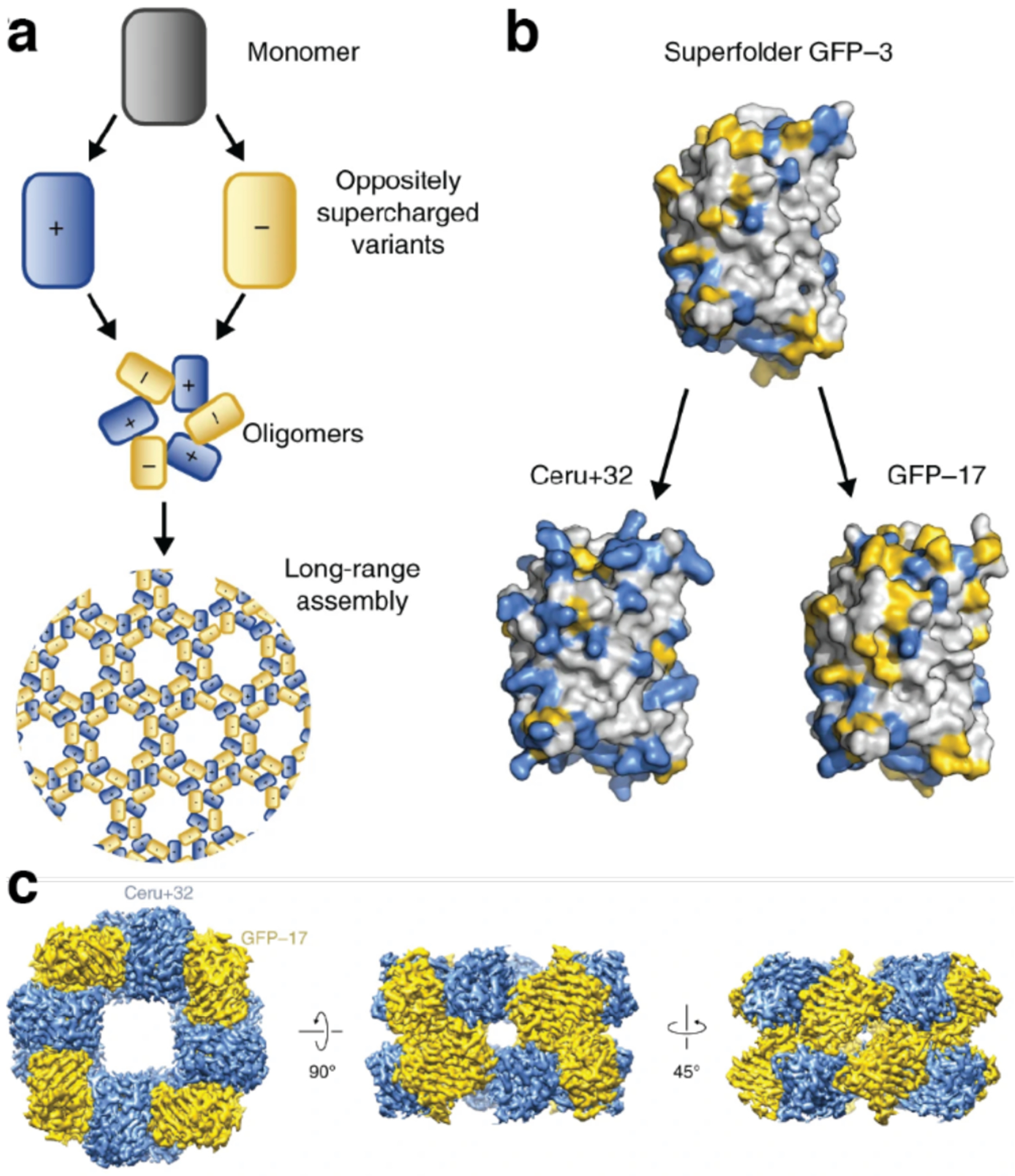
Oligomerization of oppositely supercharged Cerulean (Ceru) and GFP variants mediated by electrostatic interactions. a) Hypothesized model of symmetric oligomers and long-range assembly of oppositely supercharged monomeric proteins. b) Supercharged GFP variants engineered by mutating the surface residues of sfGFP to basic (blue) or acidic (yellow) residues. c) Cryo-EM reconstruction of the Ceru+32/GFP−17 16-mer at 3.47 Å resolution in three different orientations. Adapted with permission from Ref.276. Copyright 2019 NPG.
3.2.3. Oligomerization by genetic fusion and domain swapping
Globular proteins have evolved both intramolecular and intermolecular interactions (with other biomolecules) to stabilize and maintain the rigidity of their 3D structures.157 From the perspective of artificial protein self-assembly design, the intra/intermolecular interactions of pre-existing motifs/domains can be repurposed to form new assembly interfaces between protein building blocks. In this subsection, we will discuss how genetic fusion can be used to this effect.
The genetic fusion strategy for designing artificial protein assemblies is based on introducing connectivity between two independent domains. Arai and coworkers used WA20-Foldon fusion proteins as a building block: the WA-20 unit served as the main framework in the homodimeric state and Foldon was a connector to mediate homotrimer assembly (Figure 21).360 Trimerization of monomeric Foldon in the fusion protein induced the self-assembly of the building blocks into four unique nanostructures: S (6-mer), M (12-mer), L (18-mer), and H (24-mer). Solution SAXS results indicated that S-form oligomers had a barrel shape, while M-form oligomers formed a tetrahedron. The same research group also utilized the homodimer assembly of WA20 to construct both closed and open structures.361 Two WA20 monomers were linked by two types of peptide linkers whose amino acid sequences prefer the formation of an α-helix or random coils. Such fusion dimers preferentially formed cyclized, chain-like homo-oligomers ranging from dimer to pentamer regardless of linker types. Conversely, when the fusion WA20 dimer was mixed with the original WA20 dimer as a stopper and all intermolecular interactions were reconstituted, the fusion WA20 dimers preferentially formed extended, chain-like assemblies. Furthermore, shape analysis of the repeating units using SAXS indicated that the conformational details of the chains depend on the types of linkers used at the fusion point. The fusion dimer with the helix-favoring linker showed a linear alignment whereas the random coil-favoring linker showed a compact alignment.
Figure 21.
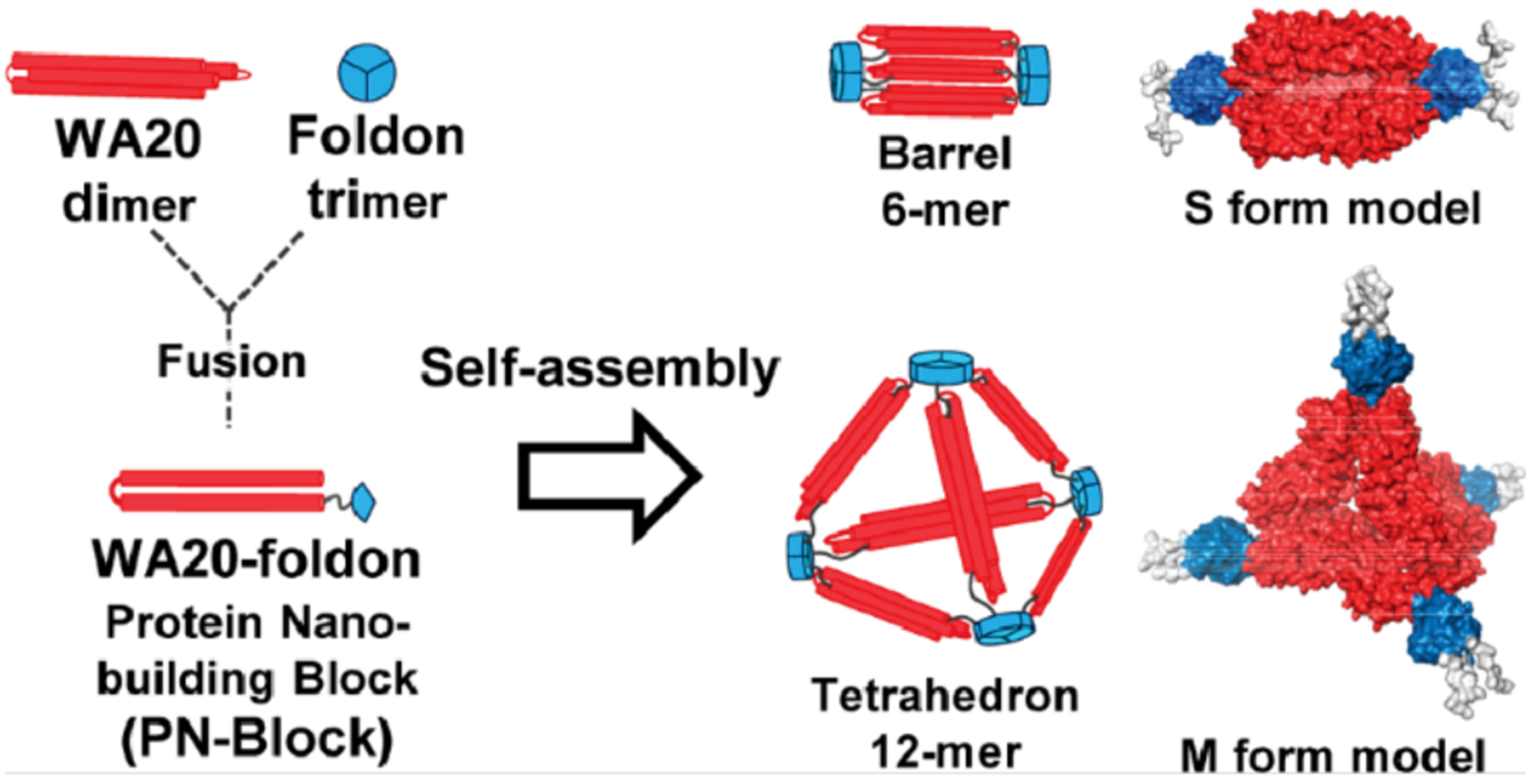
Genetic fusion strategy for self-assembly of WA20-Foldon fusion protein using native trimerization of Foldon. Adapted with permission from Ref.360. Copyright 2015 ACS.
Taking advantage of the high stability and folding efficiency of green fluorescent protein (GFP), Jung and colleagues utilized the sfGFP protein as a building block for designed protein oligomers inside cells (Figure 22).362 The 11 β-strand GFP was first split to two fragments: β-strand 11 of GFP (GFP11, residues 215–330) and the rest of the GFP structure (GFP1–10, residues 1–214). Then, GFP11 was transplanted to the N-terminus of GFP 1–10 via a short peptide linker, which did not allow the intramolecular association between GFP11 and GFP1–10 within the same monomer. This genetic fusion construct underwent intermolecular incorporation of the β-strand from GFP11 into the empty space in the β-barrel of GFP10, thereby forming polygonal GFP assemblies ranging from dimer to decamer (Figure 22). The linker length was the most critical factor to promote cellular self-assembly. This strategy was further developed to stabilize the polygonal GFP assemblies by incorporating negative charges on the GFP surface, and to control polygonal morphologies by adding a functional fusion pair to the N- and C-termini of GFP or co-expressing capping GFP, which suppressed circular oligomerization of the fusion constructs. This study demonstrated that genetic fusion could be used to reengineer a protein monomer to promote self-assembly into oligomeric states with defined structures or varied higher-order assemblies inside cells.
Figure 22.
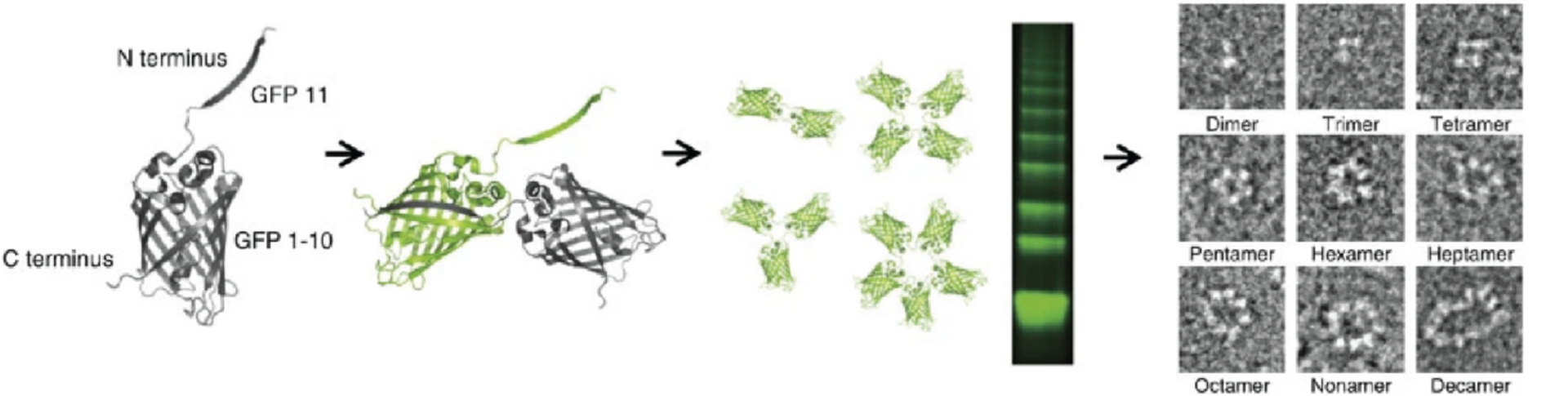
Discrete formation of GFP polygons by GFP1–10 with N-terminal-fused GFP11. The intermolecular incorporation of β-strand 11 into the β-barrel of GFP 1–10 guides stable oligomerizations from dimeric to decameric structures. Adapted with permission from Ref.362. Copyright 2015 NPG.
Muñoz and coworkers designed a variant of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2) to assemble into a hexameric ring upon fold switching.363 They began by noticing that CI2 always crystallized in a hexagonal space group, and that some crystallization conditions resulted in domain-swapped dimers. The researchers therefore set out to engineer a variant of CI2 that destabilized the native fold in the hope that a change in the fold of the protein would expose new residues that could stabilize the hexameric conformation. The resulting protein, CI2eng, was largely monomeric at low concentrations but formed mostly hexameric and some dodecameric species at high concentrations. Circular dichroism (CD) and solution NMR experiments strongly implicated a fold switch in the CI2eng monomer as being responsible for its assembly into the larger oligomers, and a cryo-EM structure of the dodecamer revealed that the alternate fold of CI2eng exposed a previously buried hydrophobic patch that formed a new interface with an adjacent monomer in the assembly. Further mutagenesis increased the yield of hexameric and dodecameric species in solution, and the researchers could take advantage of the conformational changes involved in oligomerization to reversibly assemble and disassemble the oligomers (see also Section 4.2.1).363
3.2.4. Metal-mediated oligomerization
Metal-binding interactions are considerably stronger than common non-covalent interactions, and metal-mediated oligomerization can capture many salient features of non-covalent protein-protein interactions (e.g., stability, directionality, symmetry, reversibility) on a much smaller surface area than that required for stable non-covalent interfaces.88,198 Various research groups have utilized metal-mediated oligomerization to create novel protein assemblies.364,365 In particular, the Tezcan Group has extensively studied metal-mediated oligomerization design principles using cyt cb562, a four-helix bundle hemoprotein with high stability and solubility, as a scaffold.84,193,194,196,199,205,208,210,232,366,367 Cyt cb562 is natively monomeric even in the mM concentration range, implying that, with regards to protein self-assembly, its surface is evolutionarily naïve. Tezcan and coworkers have developed two complementary approaches for the design of metal-mediated oligomers. In the first approach, metal-directed protein self-assembly (MDPSA), metal-chelating motifs are installed on the surface of a target protein. Upon metal addition, the strength, directionality, and selectivity of the resulting metal-ligand interactions help guide protein self-assembly (Figure 23). Metal-directed cyt cb562 assemblies can be further modified using a second approach, metal-templated interface redesign (MeTIR), in which metal-directed protein assemblies are redesigned using non-covalent interactions and covalent linkers along the protein-protein interface(s). Sequential interface design through MDPSA and MeTIR results in stable, metal-independent oligomers, mimicking the time course of a hypothetical evolutionary pathway for the formation of stable protein assemblies from an initial metal-templated structure.368–370
Figure 23.
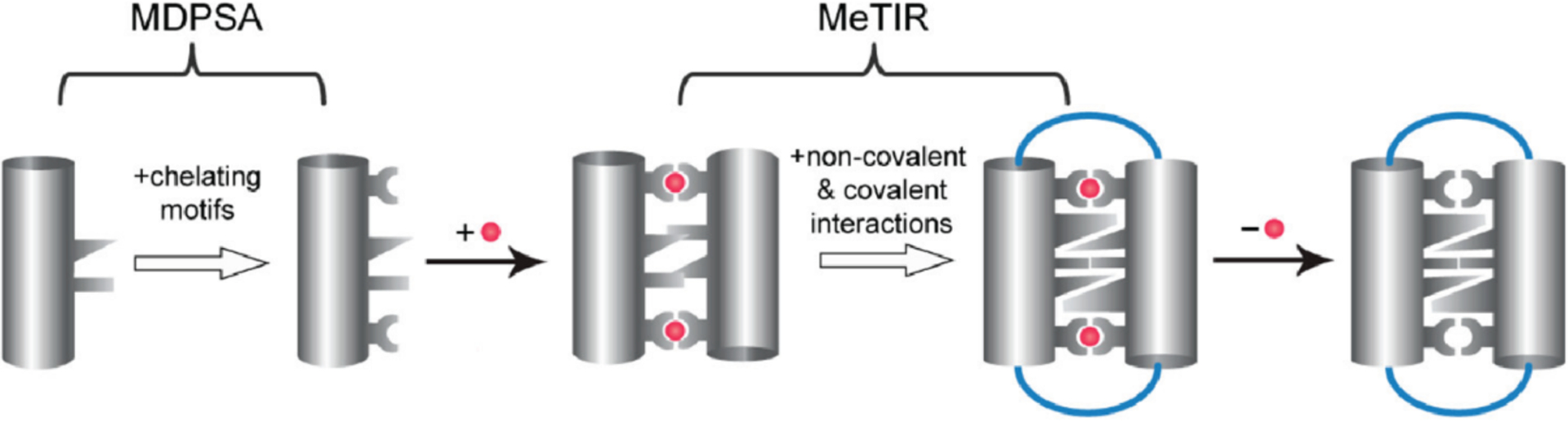
MDPSA and MeTIR strategies for metal-mediated oligomerization. In MDPSA, metal-chelating motifs are installed on the surface of target proteins, thereby guiding protein self-assembly through metal-coordination. In MeTIR strategy, metal-directed protein assemblies are redesigned using non-covalent interactions and a covalent linker at the protein-protein interface. The sequential design approach through MDPSA and MeTIR results in the formation of stable oligomers without the aid of metal ions. Adapted with permission from Ref. 83. Copyright 2016 Elsevier.
Using MDPSA, Salgado et al. demonstrated that the installation of two bis-His motifs (H59/H63, H73/H77) on helix 3 of cyt cb562 guides protein self-assembly mediated by various first-row transition metal ions (Figure 24a). The resulting construct, MBPC1, self-assembled into various oligomeric states dictated by the coordination preferences of nucleating metal ions. For example, due to its preference for a tetrahedral coordination geometry, Zn2+ induced D2 symmetric tetramerization of MBPC1 (i.e., Zn4 : MBPC14) by forming four 3His/1Asp coordination sites, His73/His77 from one protomer, His62 from a second, and Asp74 from a third.199,366 Meanwhile, Ni2+ induced C3 symmetric trimerization of MBPC1 (i.e., Ni2 : MBPC13) via octahedral 6His coordination, while Cu2+ mediated C2 symmetric dimerization (i.e., Cu2 : MBPC12) via the formation of square planar 4His coordination sites.194
Figure 24.
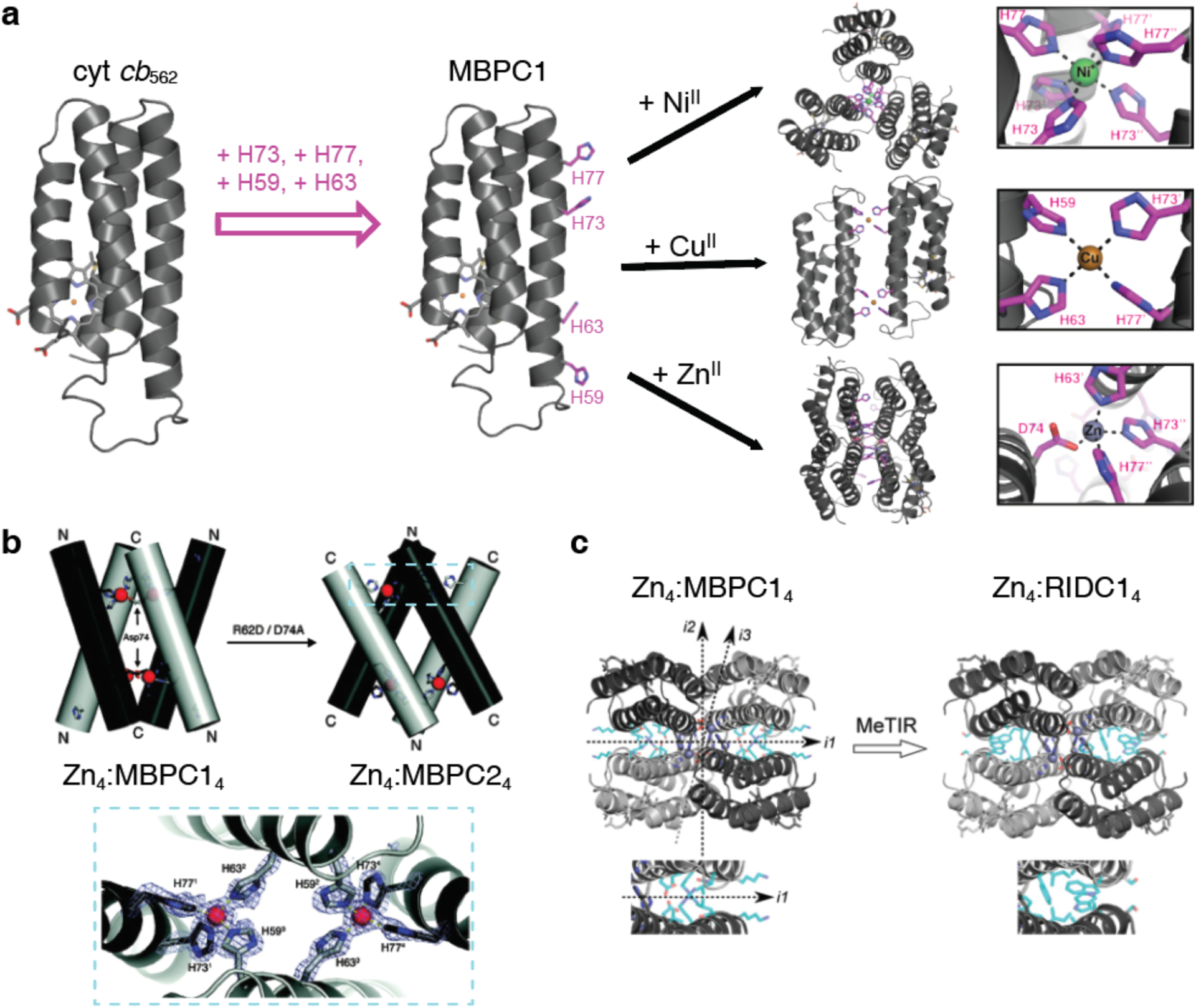
Metal-mediated protein oligomers based on cyt cb562 as a building block. a) Design of cyt cb562 oligomers using the MDPSA approach. In the MBPC2 variant, surface-exposed bis-His clamps are located at residues 59/63 and 73/77. Depending on the metal ion coordination preferences, different oligomerization states are achieved – Ni2:MBPC13 trimer (top), Cu2:MBPC12 dimer (middle), and Zn4:MBPC14 tetramer (bottom). b) In the MBPC2 variants, the R62D and D74A mutations give rise to the Zn4:MBPC24 tetramer where the orientation of the protein monomers is inverted. c) MeTIR strategy for redesigning the interface of Zn4:MBPC14. i1 interface of Zn4:MBPC14 tetramer is redesigned to install hydrophobic residues and create the stabilized Zn4:RIDC14 tetramer. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.366. Copyright 2008 ACS. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.88. Copyright 2019 ACS.
Close examination of the tetrameric Zn4:MBPC14 complex revealed an extensive buried surface area within the architecture (~5000 Å2). To examine how the surface interactions between the protomers collectively influence the assembly, Salgado et al. made a small modification to the metal coordination sphere.366 Within Zn4:MBPC14, Zn2+ coordination to the Asp74 residue was instrumental for crosslinking the MBPC1 monomers at the helix 3 C-termini to give rise to V-shaped dimers. Assuming a negligible effect from non-covalent interactions within the interface, the authors developed the variant MBPC2, where the coordinating Asp residue was moved from the C-terminal His73/His77 clamp to the N-terminal His59/His63 clamp, predicting that the modification would invert the crosslinking position in the assembly. MBPC2, characterized by the mutations R62D/D74A indeed formed a Zn4:MBPC24 complex characterized by ultracentrifugation and crystallography, wherein the V-shaped dimers were linked at the N-terminus rather than the C-terminus (Figure 24b). However, Asp62 was revealed not to participate in coordination. Instead, the Zn2+ coordination environment was composed of the 73/77 bis-His clamp from one protomer, His59 from a second and His63 from a third. These results revealed that the coordination environment alone did determine the outcome of metal-mediated protein assembly. Upon closer examination of MBPC1 and MBPC2 Zn-mediated tetramers, salt bridging interactions involving Arg34 were shown to be critical in guiding the precise geometry of the self-assembled architectures.366
These studies demonstrated that it was feasible to mediate protein self-assembly simply through installation of a small number of metal coordination motifs on a protein’s surface. Recognizing that such metal-directed protein assemblies possessed extensive buried interfaces between the protein monomers, Salgado et al. developed the MeTIR strategy to obtain stable protein assemblies wherein the metal-templated interfaces were further engineered for installation of favorable interactions. Based on the structure of Zn4:MBPC14, which has three different sets of C2 symmetric interfaces (i1, i2, and i3), the researchers redesigned the surface of MBPC1 using rotamer optimization based on Rosetta (Figure 24c).193 The computational analysis of i1 identified six mutations (R34A/L38A/Q41W/K42S/D66W/V69I) that were incorporated to yield the construct Rosetta Interface Design Cytochrome1 (RIDC1) with a well-packed hydrophobic core. This was followed by the computational redesign of i2, which included six more mutations (I67L/Q71A/A89K/Q93L/T96A/T97I) and produced the second-generation variant RIDC2. Based on crystal structures, both RIDC1 and RIDC2 constructs formed tetrameric assemblies with the same supramolecular geometry as Zn4:MBPC14, while sedimentation velocity/analytical ultracentrifugation (SV-AUC) measurements showed that the interfacial mutations in RIDC1 and RIDC2 led to the stabilization Zn-induced tetramer by nearly two orders of magnitude (i.e., tetramerization at ~100-fold lower protein/Zn concentrations) compared with the parent MBPC1 in solution. The extensive hydrophobic interactions in RIDC1 also sustained stable monomer-monomer interactions in the absence of metal ions, with a dissociation constant of ~25 μM for RIDC1. As an indirect means to evaluate the increase in Zn-binding affinity/specificity, the authors investigated the oligomerization behavior of RIDC1 with the addition of Cu2+, which prefers a square planar rather than tetrahedral coordination geometry. The crystal structure of Cu2:RIDC12 indeed demonstrated that Cu2+ was bound in an unfavored, distorted coordination configuration, which suggests that the “memory” of tetrahedral Zn-coordination had been programmed onto the RIDC1 surface.
The researchers observed that the incorporation of hydrophobic interactions into i2 did not considerably stabilize the Zn-induced tetramer, which they ascribed to the large intermonomer separation in this interface, preventing efficient hydrophobic packing. Thus, Brodin et al. added a covalent linkage in the form of a disulfide bond (C96-C96) to the i2 interface of RIDC1 which, along with the redesigned non-covalent interactions in i1, further stabilized the tetrameric assembly.367 Such stabilization of the both the i1 and i2 interfaces enabled the formation of a stable tetramer (C96RIDC14) even in the absence of metal ions. As intended with Zn templating, C96RIDC14 exhibited nanomolar binding affinities for Zn2+ and selective Zn2+ coordination over other divalent metal ions (except Cu2+). In a follow-up study, Salgado et al. demonstrated that RIDC1 variants crosslinked with flexible, bis-maleimide crosslinkers could also form highly stable tetramers with high selectivity for Zn2+ coordination.371
Both MDPSA and MeTIR approaches have been expanded to develop metal-mediated protein oligomers with broad functionalities such as stable metalloprotein assembly in vivo,210 artificial metalloenzyme activity,205 allosteric metalloprotein activity,88,232 and chemically switchable metalloprotein design.196 Medina-Morales et al. demonstrated that metal-mediated oligomers designed by MDPSA and MeTIR approaches could self-assemble upon Zn2+ complexation in bacterial cells. When a C81 mutation was applied to C96RIDC1 (C81/C96RIDC1), the resulting variant showed Zn2+-induced self-assembly in the periplasmic environment of E. coli.210 Inspired by in vivo metal-mediated oligomerization, Song et al. modified the surface of the Zn2+-complexed C96RIDC1 tetramer with a tripodal Zn2+ binding site to generate the tetramer AB3, which exhibited β-lactamase-like activity in prokaryotic cells (Figure 25a–b).205 This tetramer had four structural Zn2+ sites which stabilized the protein self-assembly (Figure 25c), and four catalytic Zn2+ sites which promoted the hydrolysis of para-nitrophenyl acetate (pNPA) and ampicillin, a commonly used selection marker. Based on this observation, directed evolution of the AB3 tetramer was carried out to improve the catalytic efficiency of ampicillin hydrolysis, which will be further discussed in Section 4.5.3.
Figure 25.
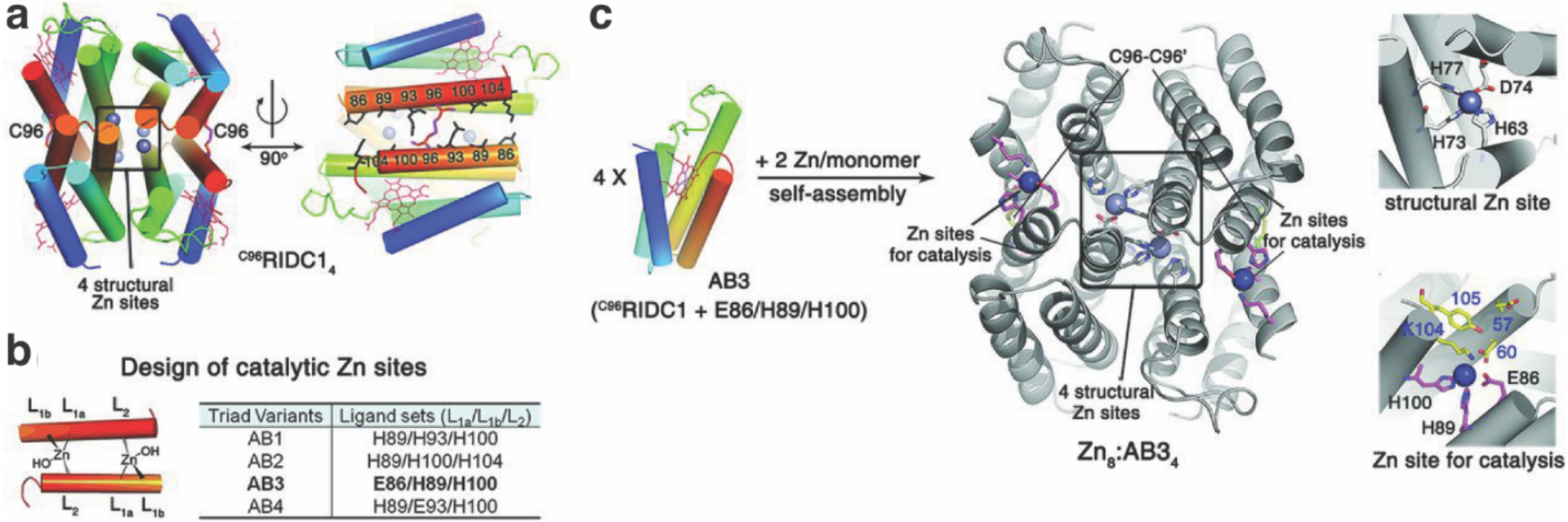
Overview of a designed supramolecular protein assembly with catalytic metal sites. a) Tetrameric structure of Zn2+-bound C96RIDC14. b) List of C96RIDC14 variants with potential catalytic Zn2+-binding sites on the outer surface of the tetramer. c) Crystal structure of AB3 which forms the stable tetramer with catalytic Zn2+ binding sites. Adapted with permission from Ref.205. Copyright 2014 AAAS.
Kakkis et al. modified MBPC-1, one of the early variants created using the MDPSA approach, to yield a new metal-mediated trimer architecture through three generations of interface redesign.196 In the first generation, TriCyt1, G70W and D66N mutations in the interface of MBPC1 induced metal-mediated trimerization in which hexa-His residues (H73/H77) ligate mid-to-late first row transition metal ions from Mn2+ to Zn2+ (Figure 26a). The yields of trimerization were highly metal-dependent: Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ showed high trimer populations whereas the trimer abundance was reduced in the presence of Mn2+ and Fe2+. In the second generation, TriCyt2, Rosetta sequence design was used to add hydrophobic patches and hydrogen bonding interactions to the trimer interface, increasing the trimer abundance following association with all first-row metal ions (Figure 26b–d). In TriCyt3, the third-generation variant, additional hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions were incorporated into the trimer interface, generating a stable metal-independent trimer (Figure 26e–g). This stepwise “titration” of interfacial interactions into metal-templated interfaces (1) provided tunable coupling between protein quaternary structure and metal coordination, and (2) enabled the construction of high-affinity metal-binding sites.
Figure 26.
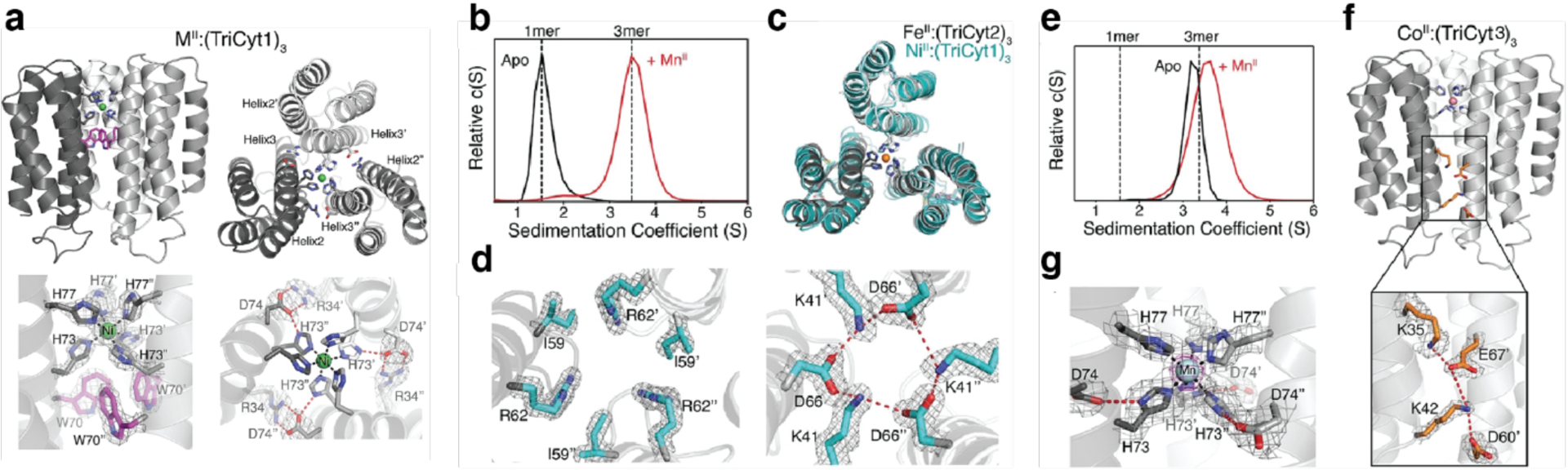
TriCyt series of metal-mediated protein trimers. a) Crystal structure of Ni2+:(TriCyt1)3. b) Sedimentation coefficient distributions of apo-TriCyt2 (black) and Mn2+:(TriCyt2)3. c) Crystal structure of Fe2+:(TriCyt2)3 superimposed to Ni2+:(TriCyt1)3. d) Hydrophobic packing and electrostatic interaction newly added to the trimer interface of Fe2+:(TriCyt2)3. e) Sedimentation coefficient distributions of apo-TriCyt3 (black) and Mn2+:(TriCyt3)3. f) Crystal structure of Co2+:(TriCyt3)3 and hydrogen-bonding networks in the trimer interface. g) Hexa-his coordination environment of Mn2+ in Mn2+:(TriCyt3)3. Adapted with permission from Ref.196. Copyright 2020 Wiley.
Overall, metal-mediated oligomerization has led to significant advances in the design of artificial protein self-assemblies. This approach can be further expanded to build novel protein assemblies whose shapes and dimensions are predictable in a rational manner, and to construct diverse functional metal centers within these assemblies.
3.3. Protein cages
Cage-like proteins are hollow, well-defined nanoparticles that carry out functions that relate to encapsulation and delivery, sequestration, and containment.94,372–374 Inspired by the highly symmetric and aesthetically pleasing structures of these assemblies as well as their diverse functions, protein engineers have developed various strategies to build artificial protein cages, ranging from de novo designed structures to reengineered natural assemblies.
There are many comprehensive reviews focusing on the modification of natural protein assemblies such as virus-like particles (VLPs), chaperonin barrels, and ferritin without altering the overall architectures.85,94,375 In this section, we will focus on artificial or semisynthetic protein cages with new structures that have been obtained by de novo design or the reengineering of natural protein cages. We also note that many of these artificial protein cages display intriguing functional properties, which are discussed in Section 4.
3.3.1. Protein cages through genetic fusion
Natural protein cages are generally characterized by polyhedral symmetries (e.g., tetrahedral, octahedral, icosahedral). They are typically composed of one (or two) monomeric subunits which present several self-associative surfaces that simultaneously fulfill the multiple symmetry requirements of polyhedral assembly geometries. Guided by the principles of natural protein cage assemblies, researchers have used symmetric protein fusion to design protein cages of a wide structural variety.87,132,133 As described in Section 2.2.1, the fused protein constructs are obtained by linking two protein oligomers with α-helical peptides.127 They are usually semirigid, contain naturally evolved surface patches with high selectivity for non-covalent interactions and satisfy the symmetry requirements for the target structure. Moreover, the length and sequence of the peptide linker between different domains need to be optimized so that the fused proteins are flexible enough to avoid clashes during self-assembly and rigid enough to prevent structural heterogeneity.83
To meet the symmetry requirement of target structures, protein fusion exploits the symmetry arising from the quaternary structures of the fused domains. One approach is to fuse two oligomeric proteins such that the resulting building block possesses appropriate symmetries and takes advantage of their native interfacial interactions to drive the formation of higher-order assemblies. α-helical peptides have been preferred linkers for forming rigid fusion structures and to meet the geometric design rules for target cage assemblies (Figure 27a). The Yeates Group was the first to apply this strategy to construct a tetrahedral protein cage.127 Two natural oligomeric domains, dimeric M1 matrix protein from the influenza virus and trimeric bromoperoxidase, were joined through a semirigid helical linker in a predetermined orientation based on computational models. To fulfill the geometric design rules for a tetrahedral structure, symmetry axes of the trimeric and dimeric domains need to intersect at an angle of 54.7°. Achieving this specific angle is dependent on the structural rigidity of the linker. The fused protein building blocks self-assembled into a 12-subunit tetrahedral cage with a molecular weight of 550 kDa, although minor components larger or smaller than 12-subunits were also detected, reflecting possible flexibility or polymorphism in the assembled particles. To resolve the cage-like assembly in atomic detail, the design was later improved by mutating two critical residues on the trimeric component to increase the homogeneity and crystallizability of the cage. These efforts culminated in a crystal structure of a tetrahedral protein cage with a 16-nm diameter (Figure 27b).376 To further understand the origin of structural flexibility and heterogeneity, the authors prepared a double and a triple mutant of the initially designed sequence, which crystallized in five distinct forms as tetrahedral cages.377 After examining the oligomeric interfaces and the helical linkers in the crystal structures, the researchers found that the interfaces between the trimeric components of the fusion proteins were strictly conserved while the dimer interfaces were heterogeneous. The α-helical linkers also potentially contributed to the structural flexibility.377
Figure 27.

Design of protein cages by genetic fusion using α-helical peptides as linkers. a) Illustration of the geometric design principle of genetic fusion. Crystal structure of designed 12-mer tetrahedral cage (b) and 24-mer cubic cage (c). Natural oligomers used as building blocks (left) and genetically fused components, assembled into symmetric cage structures (right). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.376. Copyright 2012 AAAS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.376. Copyright 2012 AAAS. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.378. Copyright 2014 NPG.
In another study, the same group reported a porous cubic protein structure obtained using a different trimer and dimer. Trimeric KDPGal (2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogalacto) aldolase and dimeric N-terminal domain of FkpA protein were genetically fused at an angle of 35.3°.378 A crystal structure revealed that the designed 24-subunit cubic cage (Figure 27c) was highly porous with openings of ~10 nm to a central cavity with a diameter of 13 nm. Such a large porous protein scaffold was proposed to serve as a container for macromolecules or a chaperone for crystallization. Notably, two additional protein structures, a 12-subunit tetrahedron and an 18-subunit triangular prism, were also observed in solution by native mass spectrometry (MS) and negative stain transmission electron microscopy (ns-TEM). These results demonstrated that while it was feasible to design protein cages of a specific shape/size, it was still challenging to achieve structural homogeneity due to the flexibility of fused protein building blocks. To comprehensively understand how solution environment influences the structural features of designed cages, Lai et al. carried out high-throughput SAXS measurements to characterize protein cages in solution. They subsequently developed force plots to measure based on their SAXS data how cage conformations varied in response to solution conditions, such as pH and salt concentration.379 Along with crystallography and EM, these tools offer promise in analyzing and optimizing solution behavior of designed protein assemblies.
Increasing the versatility of protein building blocks can enhance the geometric diversity of polyhedral protein assemblies. Cannon et al. designed a symmetric fusion comprised of dimer-, trimer- and pentamer-forming domains to create a self-assembling icosahedral protein cage built from sixty copies of the protein subunit (Figure 28).143 The three-component protein building block was generated from a rigid dimer-pentamer α-helical fusion and a flexibly-linked dimer-trimer fusion (Figure 28). After the computational screening of suitable oligomeric components, a construct with favorable design properties was tested and successfully formed a 60-subunit icosahedral cage with a 2.5 MDa mass and a 30 nm diameter. Cryo-EM and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses suggested substantial degrees of flexibility and asymmetric deformation of the assembled cages in solution, which is not unexpected given the hollow nature of the cage and the flexibility within the double-fusion protein. This study was the first to report a designed protein cage built from components containing three different rotational symmetry elements.
Figure 28.
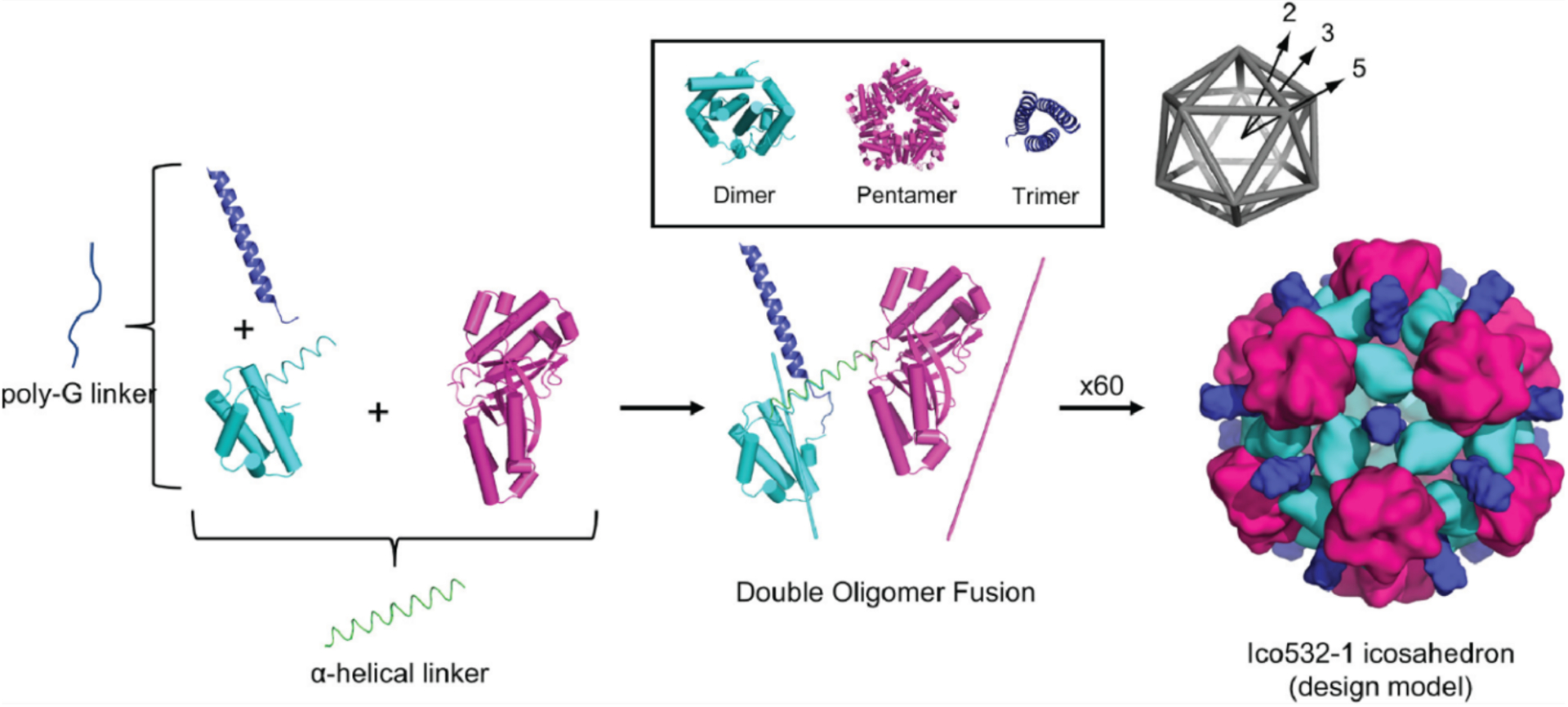
Design of protein icosahedral cage by a double-fusion protein with three symmetry components. Adapted from Ref.143. Copyright 2020 ACS.
An alternative to using helical linkers to connect two oligomeric proteins is fusing one protein domain with a de novo designed coiled-coil peptide domain, as introduced by the Marsh Group.380 The utilization of coiled-coils as building blocks for cage assembly has significant advantages.103,381 First, coiled-coil domains are stable, highly modular and offer access to a wide variety of modalities for oligomerization and symmetrization.103,381–386 Second, in the intended designs, coiled-coil domains are mainly distributed on the outer surface of the cage. With one end of the coiled-coil peptide fused to the oligomerizing protein and the other end remaining free, an extra handle is available to link a second protein on the exterior of the cage for target applications. Finally, the length of the coiled-coil domain can be adjusted, enabling the facile construction of cages with different dimensions. However, the inherent flexibility of the coiled-coil/oligomer linkages can also lead to high flexibility, precluding crystal formation and high-resolution structure determination by X-ray crystallography. In early studies, Marsh fused a trimeric KDGP-aldolase and a pair of designed complementary peptide sequences that adopt an antiparallel heterodimeric coiled-coil structure (Figure 29a). Upon mixing the trimeric building block fused to the positively charged peptide with its negatively charged fusion counterpart, the researchers obtained a heterodimer and a heterotetramer as determined by SEC and DLS analyses. Analysis by ns-TEM and analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) further indicated the presence of several oligomeric states, including dimeric, tetrameric and octameric complexes.380,387
Figure 29.
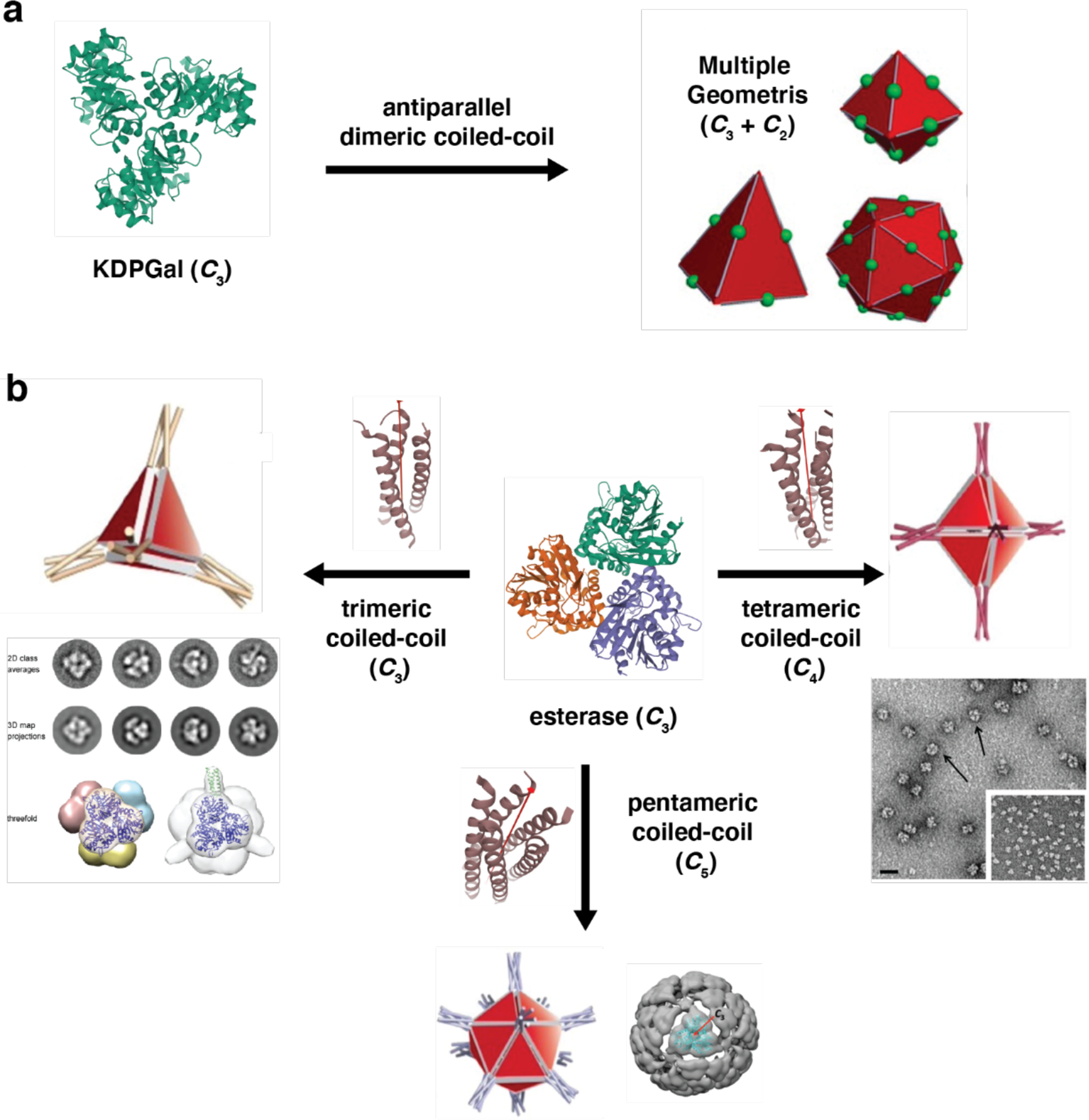
Design scheme of protein cages by genetic fusion using oligomers and coiled-coil domains. a) Trimeric KDGP-aldolase building blocks connected with antiparallel coiled-coil domains self-assemble into heterogeneous structures. b) Different combinations of symmetry elements are obtained by fusing the C-terminus of a trimeric protein to coiled-coil-forming peptides with different oligomerization states. Protein cages of different geometry are observed by ns-TEM or cryo-EM. (a-b) Adapted with permission from Ref.141. Copyright 2017 Wiley. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.140. Copyright 2016 National Academy of Science. Adapted with permission from Ref.142. Copyright 2019 ACS.
Following the proof-of-principle studies with KDGP-aldolase, the Marsh Group also employed a C3-symmetric esterase trimer as a building block for protein cage construction (Figure 29b) through fusion with a C4-symmetric coiled-coil domain.140 A screening of different linker lengths led to the discovery of a construct with a four-Gly linker that yielded the desired octahedral cage (Oct-4). The architecture of the 24-subunit assembly was verified using AUC, native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and ns-TEM, but its flexibility precluded the determination of a high-resolution structure by cryo-EM.140 In later studies, the researchers demonstrated the modularity of their design strategy by combining the esterase domain with trimeric and pentameric coiled-coil motifs, which yielded the desired 12-subunit tetrahedral (Tet8-5H) and a 60-subunit icosahedral cage (Ico8), respectively.142,388 As described in more detail in Section 4.1, Ico8 displayed very high thermal stability.142
3.3.2. Computationally designed protein cages
As summarized in Sections 3.1.2. and 3.2.1, powerful methodologies have been developed for the computational design of binary protein-protein interfaces as well as symmetric oligomeric architectures. These methodologies have also led to several successful examples of de novo designed protein cages.
The Baker Group has developed a general computational approach for designing self-assembling protein cages that consists of two steps: 1) Symmetrical docking of protein building blocks in a target symmetric architecture; 2) Design of low-energy protein-protein interfaces between the protomers to drive self-assembly. Oligomeric proteins that share an element of symmetry with the target architecture have been used to reduce the number of new protein-protein interactions that need to be designed and the number of distinct new interactions that are required to overcome the entropic cost of self-assembly. They first employed natural trimeric protein building blocks to form a 24-subunit, 13 nm diameter octahedral cage (O3–33) and a 12-subunit, 11-nm diameter tetrahedral cage (T3–08/T3–10).186 Based on the crystal structures of O3–33 and T3–10, the designed materials adopt the target models with high accuracy and the designed interfaces are responsible for driving self-assembly.
A subsequent study expanded the structural and functional range of designed protein architectures by using two distinct protein building blocks as subunits.389 A new simulation protocol related to symmetric docking was introduced and enabled the different protein components to be arranged and moved independently according to distinct sets of symmetry operators. Specifically, two distinct tetrahedral architectures (T33 and T32) were constructed from five pairs of designed proteins (Figure 30). In T33, the three-fold symmetry axes of two different trimeric building blocks (four copies of each) were aligned along the three-fold symmetry axes of a tetrahedron (Figure 30a–c), which placed one set of trimers at the vertices of the tetrahedron and the other at the face centers. Similarly, in the T32 architecture, four trimeric and six dimeric proteins were aligned along the three-fold and two-fold symmetry axes passing through the vertices and edges of a tetrahedron, respectively (Figure 30e–h). Subsequently, the amino acid sequences were designed by Rosetta at the new interface to stabilize the modeled tetrahedron and drive co-assembly of the two building blocks (Figure 30d). The structural characterization of designed structures (XRD and ns-TEM) revealed that the inter-building-block interfaces closely match with the computational models.
Figure 30.

Overview of two-component tetrahedral protein cages developed by computational design. a) Symmetric docking of two distinct trimeric proteins to design a tetrahedral cage (T33). Atomic structure (b) and ns-TEM images (c) of T33–15. Two-fold and three-fold views are shown. d) Redesign of protein-protein interfaces between two trimers. e) The T32 cage is constructed with one trimeric and one dimeric building blocks. Crystal structure (f) and ns-TEM results (h) are shown. Insets in (c) and (h) show projections calculated from the computationally designed model (left) and class averages of the particles from microscopy (right). Adapted with permission from Ref.389. Copyright 2014 NPG.
Although the computational design of novel interfaces between oligomeric units has led to many successful outcomes, this method generally requires screening many candidate variants, as computationally designed interfaces, which mainly rely of hydrophobic interactions, often produce poorly soluble proteins. Yeates and coworkers used the preliminary HBNet protocol (section 3.2.1) that favors the formation of hydrogen-bonding networks over exclusively hydrophobic interactions to stabilize the designed protein-protein interfaces.390 Two tetrahedral cages (T33–51 and T33–53) were formed from a pair of trimeric building blocks in solution and characterized by ns-TEM. Uniform particles of ~13-nm diameter were observed for both tetrahedral cages. However, the crystal structures revealed that the interfaces of the tetrahedral cages are somewhat different from the designed models, illustrating the challenges of developing computational methods for polar interface design.
With the idea that protein cages with diameters above 25 nm are desirable as carriers for cargo packaging and delivery, computational methods have also been applied to construct large two-component cages (I53, I52 and I32) with icosahedral point group symmetries.391,392 As demonstrated in Figure 31a, the I53 model was formed from a combination of 12 pentameric building blocks and 20 trimeric building blocks aligned along five-fold and three-fold icosahedral symmetry axes, respectively.391 Similarly, the I52 architecture (Figure 31d) consisted of 12 pentamers and 30 dimers, and the I32 architecture (Figure 31g) comprised 20 trimers and 30 dimers. After screening based on symmetrical docking, 71 designs of type I53, 44 of type I52, and 68 of type I32 were selected for experimental characterization. Ten designs formed stable assemblies based on SAXS and negative-stain EM and three complexes were characterized by single-crystal XRD (I53–40, I52–32 and I32–28) (Figure 31). It is worth noting that the I52 and I32 architectures were structurally different from any natural protein complexes characterized to date. A follow-up study investigating the assembly process of two icosahedral cages using a combination of biochemical, biophysical, and theoretical methods, revealed the dominance of cooperative assembly of two components at various stoichiometries.393
Figure 31.
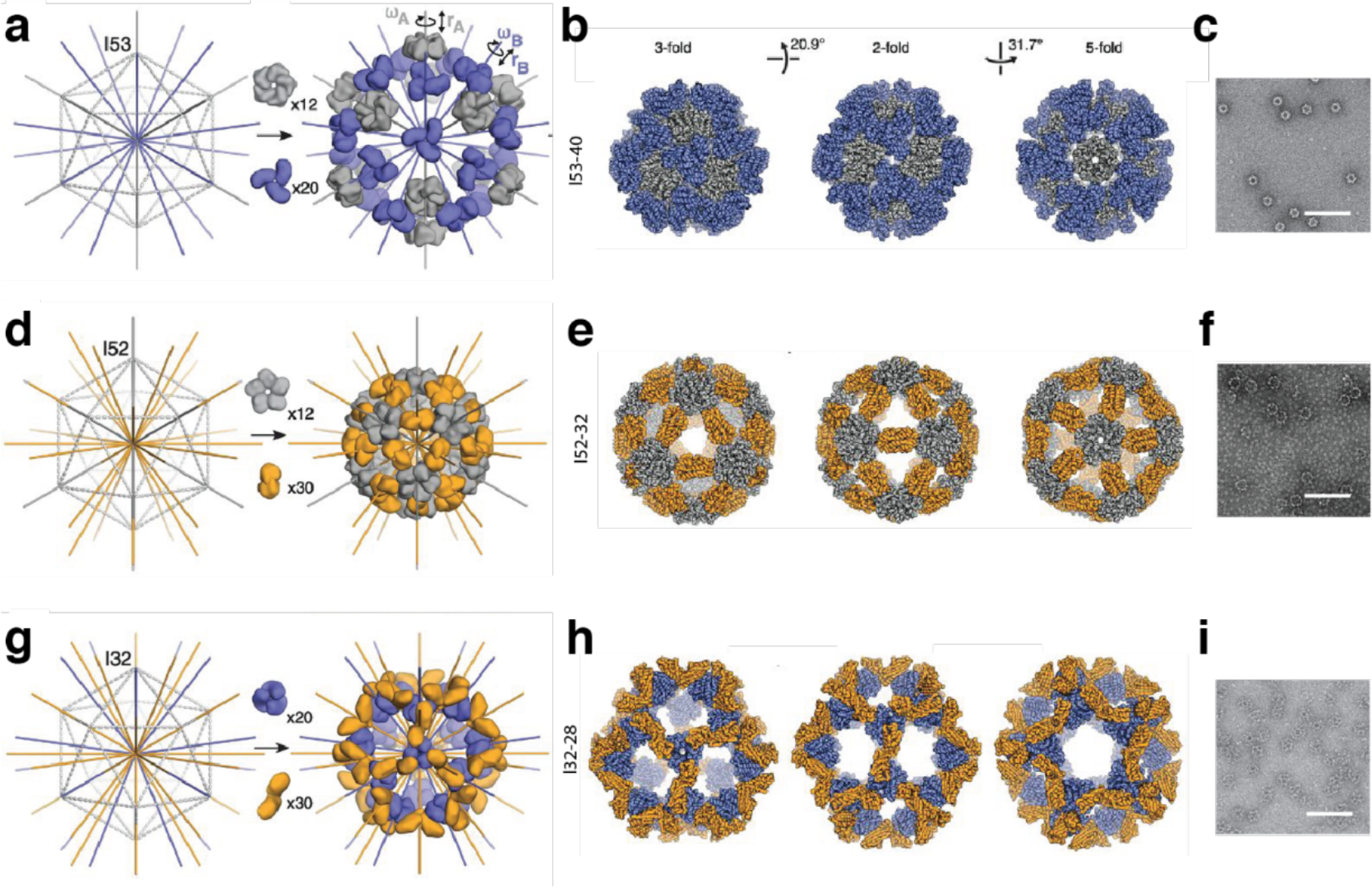
Overview of two-component icosahedral protein cages constructed through a computational design method. Icosahedral cages created by combining building blocks with different rotational symmetry were designed: I53–40 (a-c), I52–32 (d-f) and I32–28 (g-i). (a, d, g) show icosahedra outlined in gray dashed lines with three different combinations of symmetry axes (left). Models created by aligning pentameric, trimeric and dimeric proteins along target symmetry axes. Translational and rotational parameters are optimized by systematic screening. (b, e, h) Crystal structures of the designed cages. Views are shown along three-fold, two-fold and five-fold axes. (c, f, i) ns-TEM characterization of the designed cages (100 nm scale bar). Adapted with permission from Ref.391. Copyright 2016 AAAS.
Along with the two-component icosahedral architectures, Hsia et al. also reported a 60-subunit protein icosahedron (I3–01) built from a single trimeric protein. The design strategy started with aligning the three-fold axes of the trimers with the three-fold axes of an icosahedron, followed by protein-protein interface optimization to drive the assembly (Figure 32). The resulting icosahedral cage demonstrated high stability, as further discussed in Section 4.1.392
Figure 32.
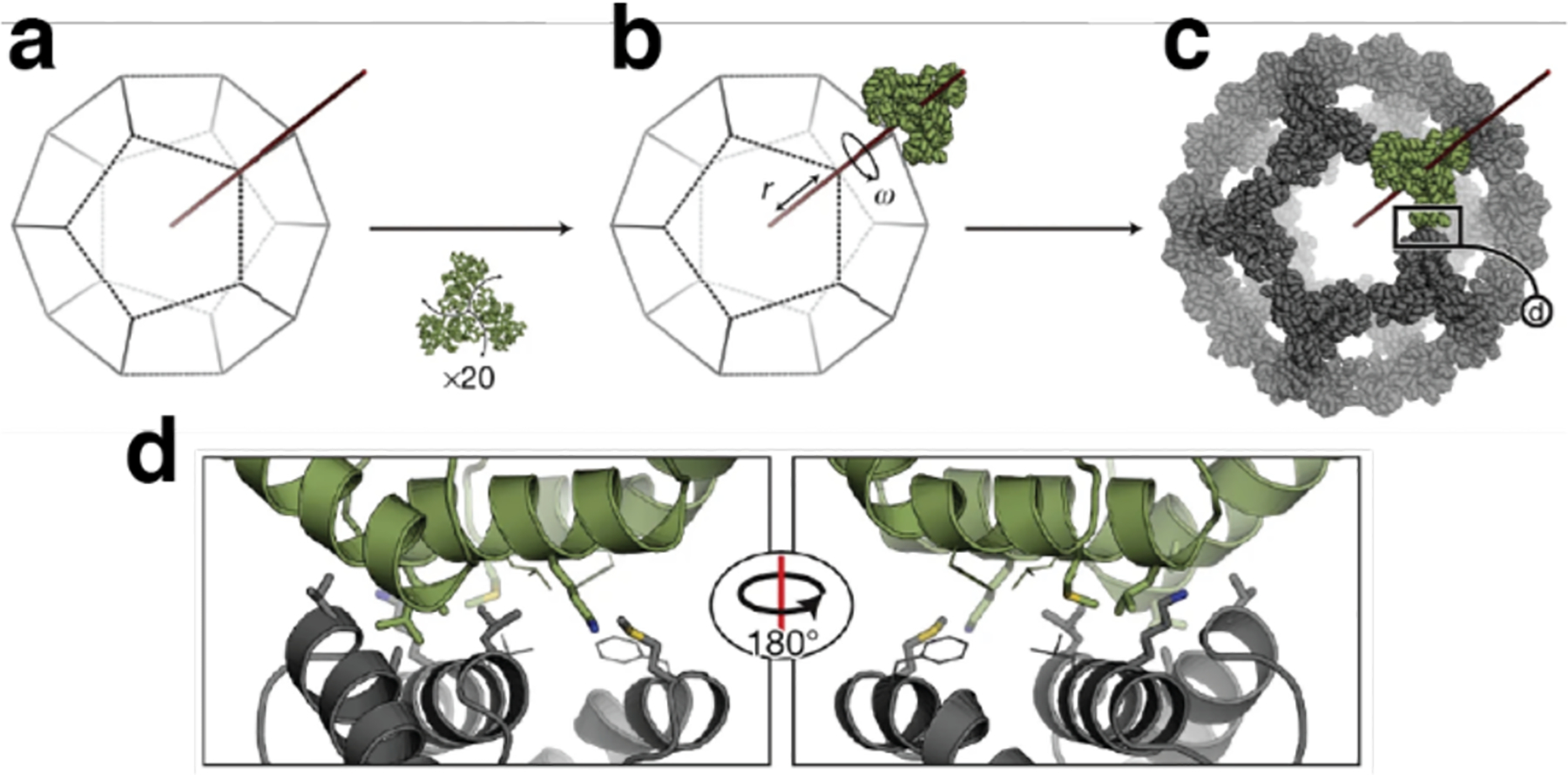
Design of an icosahedral cage based on single component. a-c) Symmetric docking of trimeric building block to an icosahedral structure. d) Sequence design yields low-energy interfaces after mutation on five residues. Adapted with permission from Ref.392. Copyright 2016 NPG.
The library of two-component protein nanocages has been further expanded with emergent functions by using antibodies as building blocks. Divine et al. constructed a series of antibody nanocages (AbCs) including dihedral, tetrahedral, octahedral and icosahedral architectures using two structural components, in which one building block was an antibody and the second a designed antibody-binding homo-oligomer (Figure 33).394 For all the target architectures, dimeric IgG antibodies served as the two-fold symmetric protein to fulfill the geometry requirement of the designed nanocages. The designed homo-oligomers were prepared by rigidly fusing antibody Fc-binding domains, helical repeat connectors, and cyclic oligomer-forming modules together. Depending on the point symmetry of the desired architectures, the symmetries of the homo-oligomer could be varied between C2, C3, C4 and C5. The fused helices were tuned to optimize the intersection angles between the two-fold axis of the antibody and the principal symmetry axis of the homo-oligomers to drive the formation of desired nanocages. The biological activity of AbCs on cell signaling and viral neutralization was investigated, as further discussed in Section 4.5.1.
Figure 33.

Model designs and structural characterizations of AbCs by cryo-EM. a) D2 Dihedral d2.7; b) T32 tetrahedral t32.4; c) O42 octahedral o42.1; d) I52 icosahedral i52.3. Combination of building blocks into a target cage geometry (left) and cryo-EM reconstructions (right). Adapted with permission from Ref.394. Copyright 2021 AAAS.
3.3.3. Metal-directed protein cages
Although computational design provides a powerful means for the de novo design of heterogeneous, non-covalent protein-protein interactions, accurate replication of multiple, extensive, self-associative surface patches, as found in natural protein assemblies, remains challenging.390 Strong, reversible and directional metal-coordination interactions can be used to bypass the necessity of designing large, non-covalent protein interfaces while leveraging symmetry-directed assembly. Such strategies have enabled the construction of synthetic protein cages with unique structural, functional, and dynamic properties without depending on extensive computational and experimental work.
In early studies, Ni et al. reported tetrahedral protein cages that were assembled via Zn2+ coordination from monomeric cyt cb562 building blocks in the crystal lattice.395,396 A variant of cyt cb562 (CFMC1) was originally designed to form dimers through Zn2+ coordination and computationally designed hydrophobic interactions. While this targeted dimer structure was indeed confirmed through solution studies, the crystal structure of the Zn-adduct revealed tetrahedral, cage-like units with diameters of 8 nm, composed of twelve monomers and thirty metal ions (Zn30:CFMC112). While serendipitous, this tetrahedral cage formed within an ordered lattice (Figure 34) and was used as a host to immobilize large and flexible targets such as microperoxidase for X-ray crystallographic structural interrogation (see Section 4.3.2 for more details).395 Notably, the Zn30:CFMC112 cage was subsequently used as a structural template to design new cyt cb562 variants that could stably assemble into dodecameric cage-like assemblies through the simultaneous coordination of Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions in solution (vide infra).195 In a related example, Hirota and colleagues designed a domain-swapped cyt cb562 dimer which formed a cage-like structure in crystal lattices through metal coordination. This pseudo-D3-symmetric, 6-nm diameter structure consisted of three domain-swapped dimers and was formed through coordination of several acidic residues to a Zn-SO4 cluster encapsulated inside the cage cavity.396 The cage-like assemblies were further stabilized by the connection of the protein subunits via a hinge loop in the domain-swapped dimers.
Figure 34.
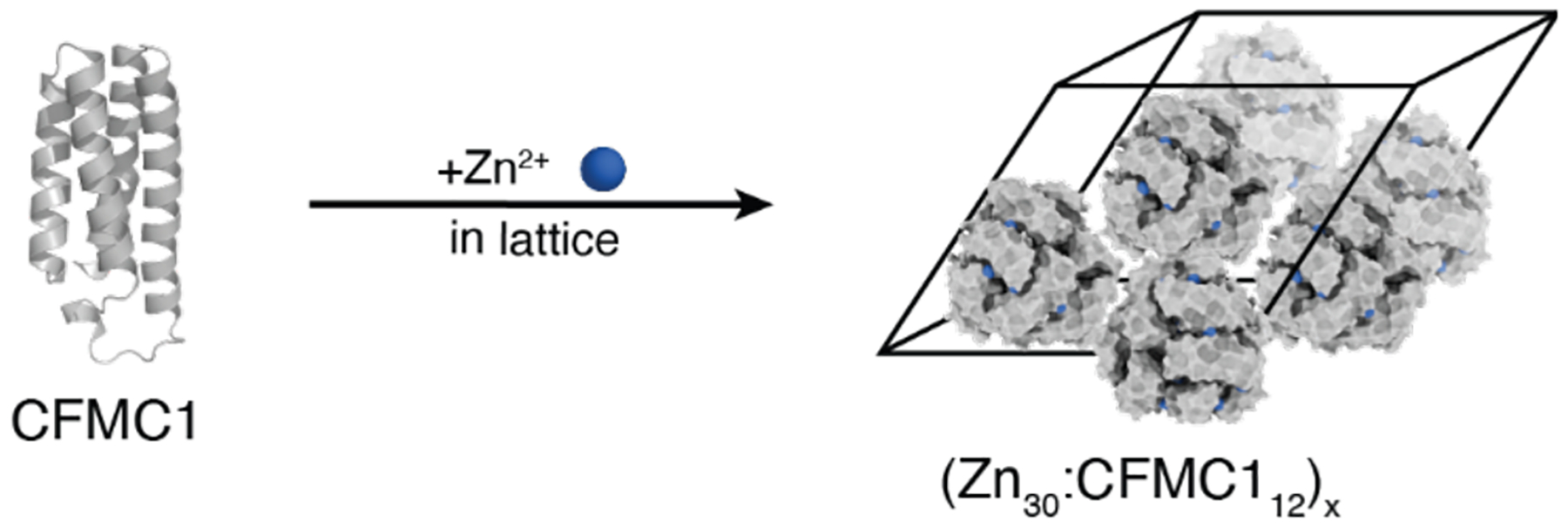
Zn2+-mediated tetrahedral protein cage in ordered lattice. Adapted with permission from Ref.195. Copyright 2020 NPG.
Beyond the formation of protein cages within a crystal lattice, metal ion-dependent assembly of protein polyhedra in solution has been pursued by several research groups. Building on their protein oligomer-coiled-coil fusion strategy (Section 3.3.1), the Marsh Group reported a tetrahedral protein cage assembled from four copies of a trimeric esterase building block fused to a peptide sequence for metal-dependent coiled-coil formation (Tet8-M).397 The addition of divalent metal ions, in particular Ni2+, led to the self-assembly of Tet8-M into dodecameric assemblies in solution. Although the yield for the formation of the cages was not quantitative, the assembly process could be reversed through metal chelation or the acidification of the solution, providing a first example of stimuli-responsive protein cages obtained fully by design.
More recently, the Heddle Group reported a highly stable, Au-directed protein cage.200 In this work, a toroidal protein, tryptophan RNA-binding attenuation protein (TRAP), was used as the building block (Figure 35a). With the addition of a gold(I)-triphenylphosphine compound (Figure 35b), the Cys-substituted 11-mer TRAP ring assembled into monodisperse cage structures (Figure 35c–d) with masses greater than 2 MDa. Detailed cryo-EM analyses revealed that the TRAP-cages were held together by 120 S-Au+-S staples between 24 uniform rings. Notably, the TRAP cages existed in two different chiral forms (Figure 35e–f). The geometry of these structures is based on the Archimedean snub cube and belongs to a class of “paradoxical geometries”, considering that C11-symmetric building blocks are precluded from assembling into regular polyhedra. Additionally, the Au-mediated TRAP-cage assembly displayed high efficiency, with a yield over 80%, as well as high chemical and thermal stability. Meanwhile, it could also be disassembled into the capsomer units by addition of reducing agents. Such a stable yet reversible structure highlighted the utility of metal-mediated protein-protein interactions in constructing assemblies with externally controllable assembly and disassembly behavior, making them suitable for packing and releasing cargo molecules as potential delivery platforms.
Figure 35.
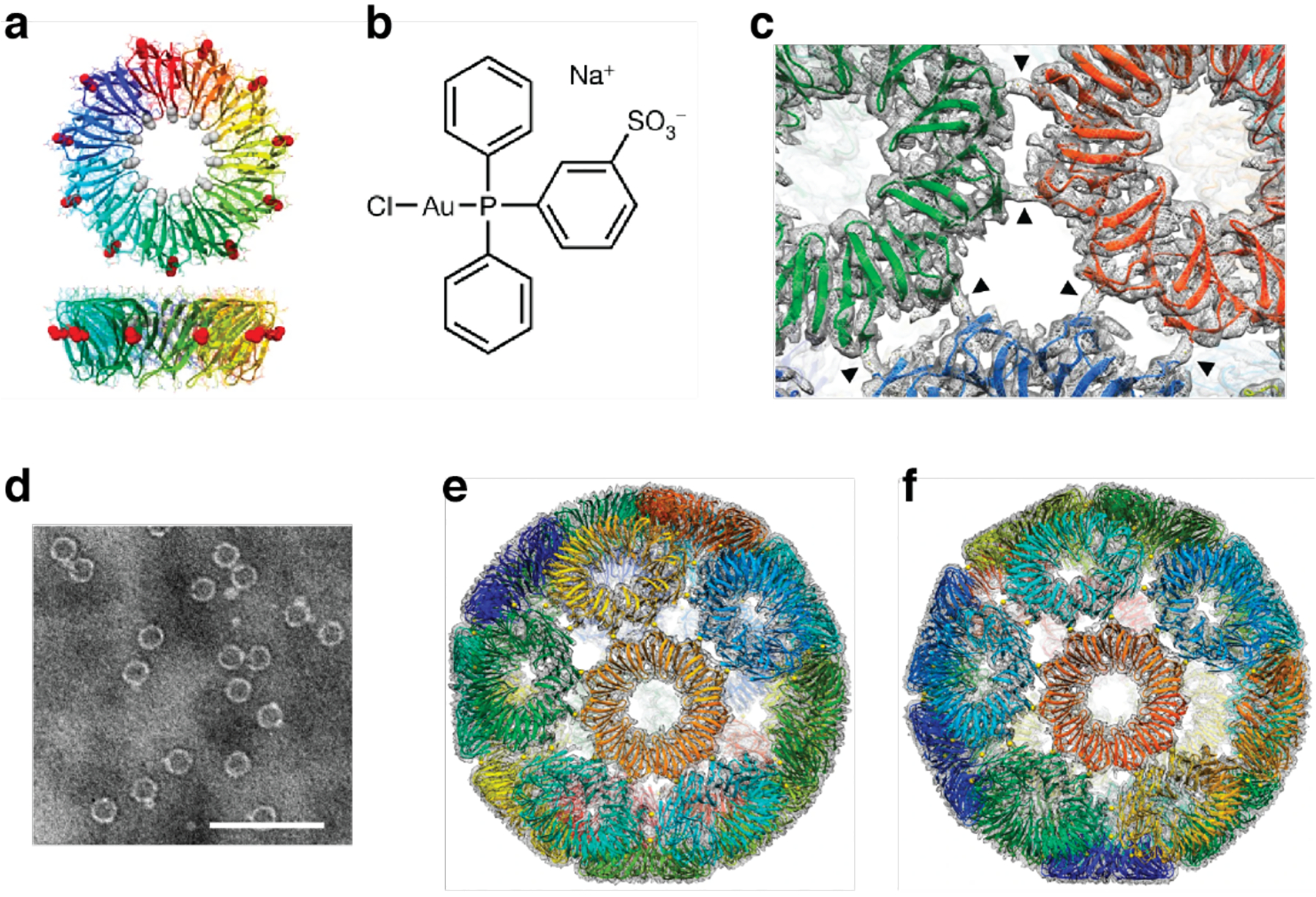
Metal-mediated TRAP-cage assembly. a) Cys-substituted 11-mer TRAP ring. b) Au-TPPMS structure. c) Left-handed TRAP-cage model and electron density map. The arrowheads indicate density bridges connecting neighboring TRAP rings. d) ns-TEM images of cages purified by SEC after incubating TRAP with Au-TPPMS for 3 days. Overall fits of the final TRAP-cage models onto their respective density maps: left-handed (e) and right-handed (f) structures. Adapted with permission from Ref.200. Copyright 2019 NPG.
As it can be gleaned from the examples of artificial protein cages described thus far, all design approaches have certain limitations. For example, the computational design or protein fusion approaches exclusively depend on the use of natively oligomeric proteins, which eventually restricts the structural scope of the assemblies obtained and typically yields highly porous architectures that are not stimuli-responsive. Despite providing facile access to responsive behavior, metal-mediated protein self-assembly also often relies on inherently symmetric building blocks. Importantly, metal coordination does not provide sufficient selectivity for the simultaneous formation of different protein-protein interfaces which is necessary for the formation of high-symmetry architectures like protein cages. This is due to the fact that the typical metal-coordinating amino acid residues on protein surfaces (e.g., His, Cys, Glu and Asp) are considered as soft (or intermediate-soft) according to Pearson’s Hard-Soft Acid-Base (HSAB) classification398 and have considerable overlap in terms of their coordination preferences for soft transition metal ions (e.g., Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+). Owing to this lack of chemical discrimination, it has been challenging to design a heterometallic protein complex whose self-assembly is selectively guided by multiple metal ions that mediate different protein-protein interactions.
To address this challenge, Golub et al. turned to a “hard” bidentate chelating motif, hydroxamate (HA, the conjugate base of hydroxamic acid), a common functional group found in bacterial siderophores to enable exceptionally stable coordination of the “hard” metal ion (e.g., Fe3+).399,400 HA groups preferentially form octahedral Fe3+ complexes with an inherent C3 symmetry that the researchers sought to impose on protein oligomerization.195 Importantly, the formation constants of Fe3+:(HA)3 complexes (>1028 M−3) are vastly higher than those of HA-complexes of any other metal ion such that they can be considered as orthogonal to the aforementioned soft metal-ligand combinations.399,400 For protein derivatization, a small reagent, iodo-hydroxamic acid (IHA), was synthesized for site-selective attachment to Cys residues. The resulting Cys-HA sidechain is isosteric with that of Arg, furnishing a pseudo-natural amino acid functionality with the unique ability to chelate hard metal ions and induce C3 symmetry on a single-residue footprint. With the IHA reagent in hand, the researchers engineered the monomeric building block cyt cb562 such that it could self-assemble into a polyhedron through simultaneous coordination of Zn2+ (soft) and Fe3+ (hard) ions to generate C2 and C3 symmetries, respectively. For this, they used the structure of the aforementioned Zn30:CFMC112 crystalline cage assemblies as a template (Figure 34)395 and strategically placed Zn-coordinating His/Asp motifs and Fe-coordinating Cys-HA groups on the cyt cb562 surface to create the construct BMC3 (Figure 36a–b).195
Figure 36.
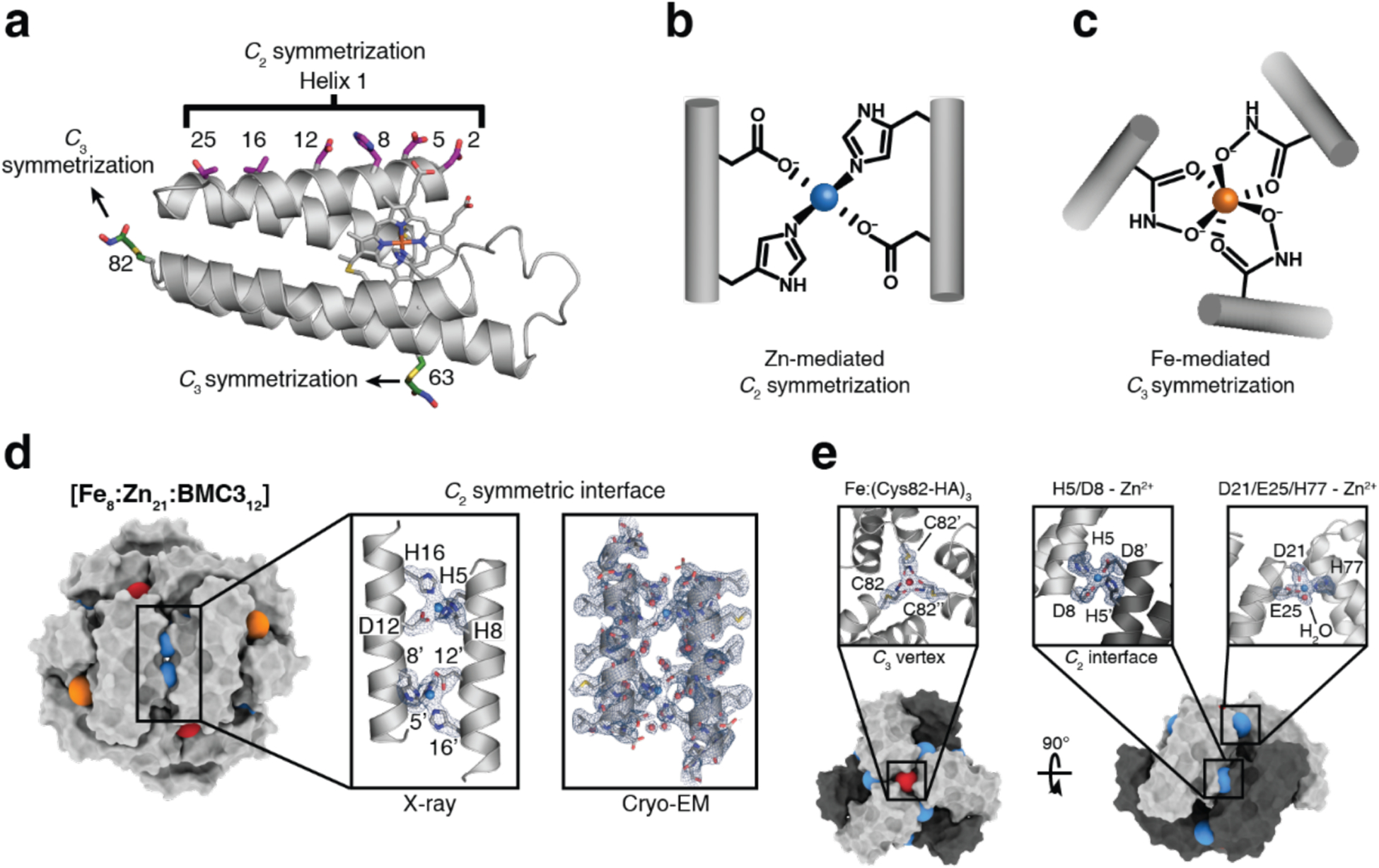
Metal-mediated protein cage via orthogonal chemical interactions. a) Structural overview of the cyt cb562 scaffold. Salient structural elements are shown as sticks. b) C2-symmetric protein dimerization induced by tetrahedral Zn2+ coordination of native amino acid side chains. c) C3-symmetric protein trimerization induced by octahedral Fe3+-tris-hydroxamate coordination. Surface representations of the BMC3 cage (d) and BMC4 cage (e), with metal ions shown as colored spheres. Insets show atomic details of each metal coordination site, with the mFo − DFc electron density omit map (blue mesh) contoured at 3σ. Adapted with permission from Ref.195. Copyright 2020 NPG.
BMC3 was found by ns-TEM to self-assemble into 9-nm dodecameric cages with tetrahedral symmetry in the presence of Zn2+ and Fe3+. Importantly, AUC experiments showed that the self-assembly of the dodecameric cages in solution required the simultaneous presence of both Zn2+ and Fe3+. The crystal structure of resulting cage protomers (Fe8:Zn21:BMC312) confirmed the formation of the desired tetrahedral architecture through selective Fe3+:(HA)3 coordination at the C3 symmetric vertices and Zn2+-(His)3(Asp)1 coordination in the C2 symmetric edges (Figure 36d–e). A 2.6-Å cryo-EM structure revealed that the solution structure was nearly identical to that observed in the solid state. The researchers further showed that a modification of the Zn-mediated interfaces yielded a second variant (BMC4), which formed Fe/Zn-mediated hexameric cages, enabled by the flexibility of Fe3+:(HA)3 mediated vertices.195 In contrast to the typically porous structures of many artificial protein assemblies, the polyhedral BMC3 cages have tightly packed shells without large apertures and are responsive to diverse stimuli such as EDTA and chemical reductants due to the reversible nature of the assembly process (see Section 4.2.1). These assemblies also represent the first examples of artificial protein cages constructed from simple, asymmetric building blocks like their natural counterparts.
3.3.4. Reengineering of natural cages
Constructing cage-like protein assemblies is not limited to bottom-up design. In a complementary approach, natural cage-forming proteins can be reengineered to obtain protein architectures with alternative structures and/or new properties.
Huard et al. reported a protein-protein interface engineering strategy called “Reverse Metal-Templated Interface Redesign” (rMeTIR), which transforms a natural protein-protein interface into one that only engages in selective response to a metal ion (Figure 37a).401 As shown in Figure 37b, an obligate protein complex (ferritin in this case) was used as a starting species and targeted for conversion into a form that requires metal binding for self-assembly. The first step of rMeTIR was to graft metal-coordination sites that possess the right geometry to fit into one of the three types of symmetrical (C2, C3 or C4) ferritin interfaces in an unstrained fashion. The next step involved the elimination of key interfacial interactions to destabilize the interface so that the formation of the cage could only be triggered by the addition of the appropriate metal ion. The authors applied rMeTIR to the C2 interface of ferritin to engineer a Cu-dependent protein cage.401 Specifically, a ferritin variant was first engineered with two pairs of His residues at the C2-symmetric interface to enable the formation of square-planar Cu coordination sites upon cage formation. The successful grafting of two interfacial Cu centers was confirmed by XRD. Subsequently, the researchers engineered the C2-interfacial surfaces of ferritin monomers with destabilizing mutations to create a variant that would exclusively form the cage upon Cu2+ binding (Figure 37c). The resulting variant MIC1 was indeed monomeric when isolated, but self-assembled efficiently into spherical cages upon selective binding of Cu2+. Other divalent metal ions, which do not favor square-planar geometries, could not induce cage formation, illustrating the requisite geometric specificity of Cu coordination (Figure 37d). Notably, Cu2+ ions acted as structural templates for cage formation, as they could be removed post-assembly without disrupting the cage architecture. The resulting apo-MIC1 cage was characterized by XRD, AUC, and ns-TEM (Figure 37). This example provided a convenient strategy to convert obligate protein assemblies into stimuli-responsive architectures and enabled the study of the monomeric assembly components in isolation.401
Figure 37.
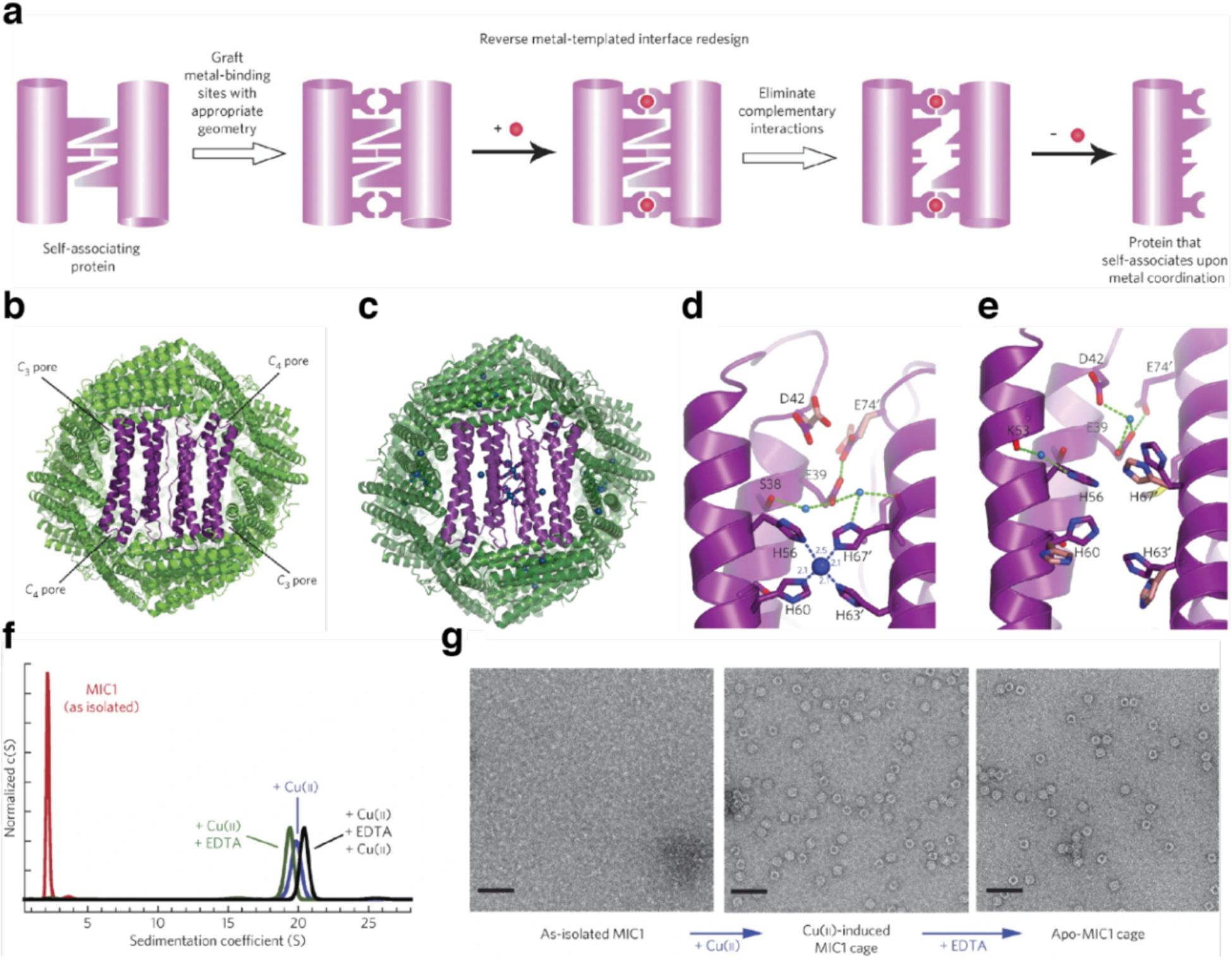
Copper-inducible ferritin cage assembly. a) Schematic illustration of the reverse metal-templated interface redesign (rMeTIR) process. b) Ferritin cage viewed down the C2 symmetry axis. c) The crystal structure of Cu2+-bound MIC1 cage. d) Close-up view of the C2 interface of the Cu2+-bound MIC1 cage. e) Close-up view of the C2 interface of the MIC1 cage (apo-MIC1) obtained after the chelation of copper ions with EDTA. f) Sedimentation velocity profile of MIC1 in the different states: as-isolated, monomeric; Cu2+-induced cage; EDTA-treated cage; Cu2+-reconstituted cage. g) ns-TEM images of MIC1 in different states: monomeric, Cu2+-induced cage, and apo-cage. Scale bars, 50 nm. Adapted with permission from Ref.401. Copyright 2013 NPG.
In a similar vein, Zhao and coworkers reported an engineering strategy named Key Subunit Interface Redesign (KSIR) to control the geometry of natural protein cages.402 KSIR alters natural protein-protein interactions by selectively deleting a small number of “silent” amino acid residues which are not involved in interfacial interactions. Specifically, this reengineering process was carried out in three steps: 1) Determination of the key subunit interfaces in a target symmetrical protein architecture based on the crystal structure; 2) Identification of silent amino acid residues (SAAR) that were located at the key subunit interfaces; 3) Deletion of SAAR and redesign the key subunit interface, which drove the formation of new protein architecture.402 The KSIR approach was applied to the C3-C4 interface of the octahedral ferritin cage. Through the selective deletion of six amino acid residues, the researchers converted the native 24-meric ferritin cage with a 12-nm diameter into an non-native 48-mer nanocage with a 17-nm diameter, whereas the insertion of six residues led to a 16-meric lenticular cage.403
The same group demonstrated that complete elimination of an inter-subunit interface (C3-C4 interface) in ferritin cages resulted in the formation of 8-meric nanorings in solution. In the crystal lattice, these nanorings were observed to stack in a face-to-tail pattern through hydrogen bonding to form nanotubes, which staggered with each other to form porous 3D protein materials as shown in Figure 38a.404 In a follow-up study, the 8-mer nanoring was further engineered to generate a set of discrete protein cages with different sizes and geometries via disulfide bond formation (Figure 38b).405 Specifically, the deletion of an intra-subunit disulfide bond in the octameric protein architecture yielded 24meric, ferritin-like nanocages in solution, while selective insertion of an inter-subunit disulfide bonds into the octamers triggered its conversion into 16-meric lenticular nanocages. Deleting the intra-subunit disulfide bond and inserting the inter-subunit disulfide bond at the same time promoted the formation of 48-mer protein cages in solution. Taken together, the examples using the KSIR strategy demonstrate the diverse protein architectures that could be obtained by altering the assembly modes of the highly associative components of natural cages.
Figure 38.

Ferritin cage reengineering into structures with different sizes and geometries. a) Conversion of the 24-mer ferritin cage into 8-mer nanorings with D4 symmetry and a 3D porous protein lattice. b) Conversion of the 8-mer bowl-like nanoring into higher-order structures via disulfide bond formation. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.404. Copyright 2018 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.405. Copyright 2019 NPG.
Circular permutation is a widely used strategy to change the connectivity of secondary structure elements in a protein while maintaining the overall three-dimensional shape.406 Conceptually, this type of sequence rearrangement allows for relocation of the N and C termini of capsid subunits and can lead to morphology alternation of natural protein cages. Inspired by naturally permuted assemblies, the Yeates Group reengineered PduA, a major shell component of the propanediol-utilization (Pdu) bacterial microcompartment, by circular permutation.407 The modification caused a dramatic change in the quaternary structure of the capsomer subunits from symmetric cyclic hexamers to pentamers. Consequently, the higher-order assemblies of PduA varied from an outer shell of the microcompartment with thousands of hexamers to a dodecahedral cage with icosahedral symmetry made of pentamers.407
The Hilvert Group reported a circularly permuted variant of Aquifex aeolicus lumazine synthase (cpAaLS) that self-assembled into spherical and tubular cage structures with morphologies that could be controlled by the length of the linker connecting the native termini.408 Specifically, for cpAaLS, new chain termini were inserted into a loop that faced the luminal cavity via a flexible peptide linker between residues 119 and 120 (Figure 39a). The authors found that peptide length could be used to alter the cone angle of the capsomer. Shorter linkers favored the formation of larger spherical structures and 1D tubular assemblies, while longer linkers promoted the assembly of smaller spheres (Figure 39b). Moreover, combining the cpAaLs variant with wild type AaLS and other engineered variants enabled the co-assembly of patchwork cages in E. coli cells. This approach enabled encapsulation of guest proteins (GFP) in the lumen, modification of the interior and exterior surfaces of the cage via genetic fusion, and the tuning of the size and electrostatics of the particles. These studies highlight the utility of circular permutation as a potentially general strategy for tailoring the properties of cage-forming proteins and altering the self-assembly of natural protein cages.
Figure 39.
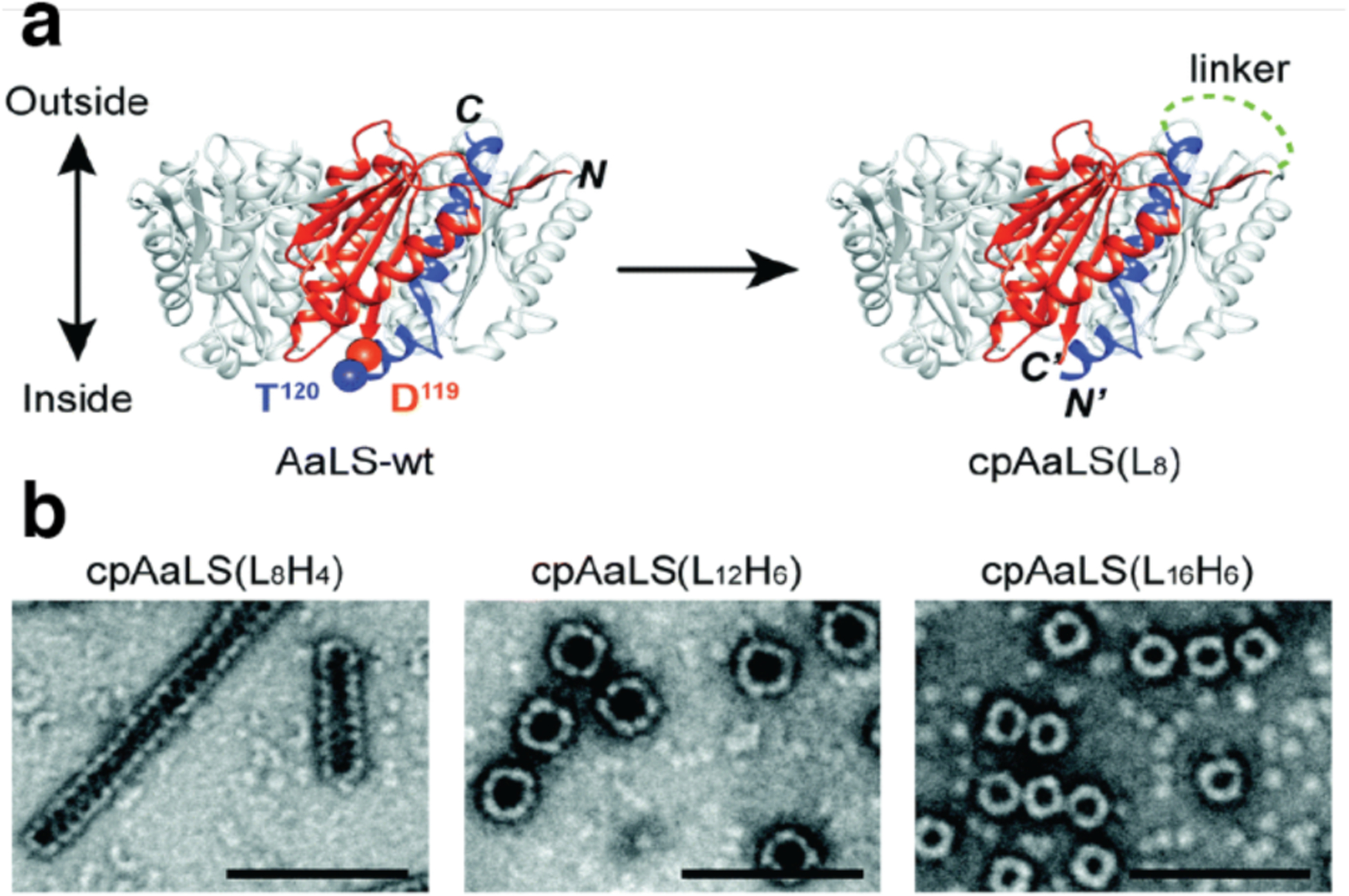
Circular permutation of Aquifex aeolicus lumazine synthase (AaLS). a) Design of circularly permuted AaLS (cpAaLS). b) ns-TEM images of cpAaLS with linkers of varying length, cpAaLS(LxHy), where x and y represent the number of total amino acids and His residues, respectively (100 nm scale bar). Adapted from Ref.409. Copyright 2018 RSC.
3.4. Extended 1D assemblies
The self-assembly of proteins into extended filaments is essential for the formation of natural cytoskeletal structures (e.g., actin filaments and microtubules) in all domains of life. In nature, extended 1D assemblies have diverse functions, serving as structural supports, transport highways for molecular cargo and containers of genetic material.410,411 On the other hand, uncontrolled fibrillation can contribute to disease states.412 At a first glance, 1D structures may appear like readily accessible assembly design targets due to simpler design requirements than other higher-order structures with multiple symmetry elements. However, rational construction of 1D assemblies, which involves control over length, width and assembly dynamics, remains a significant challenge. Extended 1D assemblies encompass several common morphologies, from flexible filaments and nanowires260,291,413–416 to nanotube structures.202,224,270,417 There are also several subtypes of nanotubes, as they can be composed of stacked protein rings,417,418 assembled through the association of helical filaments,270 or formed when nascent 2D sheets roll up into a hollow structure due to inherent curvature or kinetic effects.202,419 Potential applications for extended 1D assemblies vary with morphology. They span broad functions across different length scales, from scaffolding and encapsulation of functional moieties at the nanoscale to bulk material such as gelation. It should be noted that the discussion below focuses on ordered protein assembly generated de novo and does not touch on modification of naturally occurring 1D protein scaffolds such as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) and M13 bacteriophage rods,374,420,421 or the extensive literature in the field of peptide filament assembly.104,422–430
Runaway domain swapping and end-to-end domain stacking are the two main structural mechanisms leading to the emergence of protein filaments that have been categorized in nature.431 In the context of protein assembly engineering, domain swapping, discussed in Section 3.1.1 in the context of protein dimer design, is also relevant to the development of protein materials formed by fibrilization.432 Genetic protein fusion is another strategy that relies on existing protein interfaces for assembly design (Sections 2.2.1 and 3.2.3). Fused constructs capable of forming filaments were among early examples of designed 1D assemblies, developed as proof-of-principle illustrations toward more complex structures like designed cages and 2D protein arrays which are described in Sections 3.3.1 and 3.4.1.127,128 The discussion on extended 1D assemblies below focuses on protein filaments, nanowires, nanotubes, and microtubules assembled via host-guest or receptor-ligand interactions, covalent bonding, metal coordination, electrostatic interactions, and computational interface design.
3.4.1. 1D assemblies mediated by host-guest and receptor-ligand interactions
Hayashi and coworkers have used hemoproteins reconstituted with artificial heme analogs as functional and structural units in protein assemblies. Taking an approach based essentially on host-guest association, the group exploited apoprotein-cofactor interactions to generate various types of protein fibers, networks and clusters by removing the native heme cofactor and replacing it with an artificial heme cofactor covalently linked to the protein surface.251 The building blocks were produced from cyt b562250,414,415,433 and myoglobin.415,434,435 The two heme b (protoporphyrin IX iron complex) containing hemoproteins were modified by site-selective mutagenesis to introduce a Cys residue for the covalent attachment of heme via iodoacetamide or maleimide reactive groups (Figure 40a). The reversible head-to-tail assembly of these building blocks gave rise to oligomeric clusters, nanorings, and fibrils depending on the length of the linker between the protein surface and appended heme. Alternatively, synthetically generated heme dimers415 and trimers250 were used to change the connectivity between the protein subunits. Oohora et al. extended this strategy by combining heme-directed assembly with the orthogonal biotin-streptavidin ligand-receptor pair, obtaining heteromeric fibrillar co-assemblies where myoglobin and streptavidin take on alternating alignments (Figure 40b).435
Figure 40.
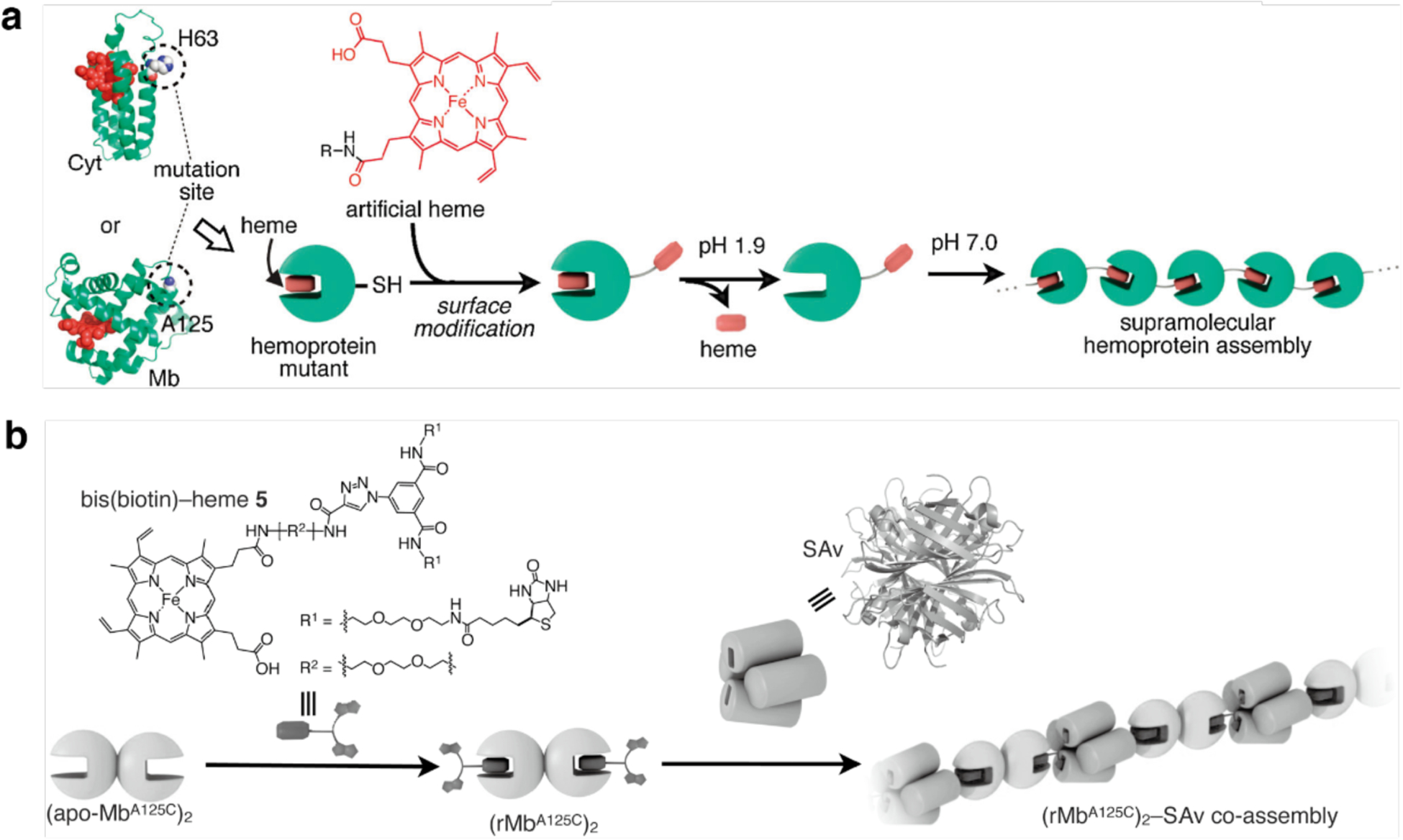
Fibrillar protein self-assembly through apo-hemoprotein/heme interactions. a) H63C and A125C mutations are incorporated into cytochrome b562 (Cyt) and myoglobin (Mb) respectively to position Cys residues on the protein surface for further conjugation to artificial heme derivatives. Under low pH conditions, the native heme cofactor is removed from the heme pocket. After reconstitution at physiological pH conditions, hemoprotein assemblies are obtained via artificial heme-heme pocket interactions. b) Heterotypic co-assembly of dimerized apomyoglobin (apo-MbA125C)2 and streptavidin (Sav) is achieved using a bis(biotin)-heme bifunctional ligand. Adapted with permission from Ref.251. Copyright 2012 RSC.
The ability of macrocyclic host cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8]) to form a 1:2 complex with peptide tags such as Trp-Gly-Gly (WGG) or Phe-Gly-Gly (FGG) with binding constants on the order of 109–1011 M−2 has also been exploited to generate protein nanowires (Figure 41). The Liu Group combined CB[8] with the dimeric glutathione-S-transferase (GST) protein fused to the FGG tripeptide at the N-termini to obtain uniform nanowires up to ~120 nm in length from an equimolar mixture of the two components.413 The assembly strategy was extended to generate nanowires with spring-like response to Ca2+ addition.264 The protein building block was modified to incorporate a recoverin domain, which adopts a contracted conformation in the absence of Ca2+ and an extended conformation upon binding to Ca2+. The FGG-recoverin-GST construct underwent assembly into nanowires with CB[8] as expected and the conformational change triggered by Ca2+ addition produced a reversible extension of fiber length by as much as 50%.
Figure 41.

Formation of GST homodimer nanowires via host-guest interactions. The phenylalanine-glycine-glycine (FGG) motifs fused to the N-termini of GST serve as guest molecules binding to the cucurbit[8]uril (CB[8]) macrocyclic host. Adapted with permission from Ref.413. Copyright 2013 Wiley.
Yang et al. combined the specific affinity of a protein building block to a ligand with π-π stacking interactions to develop well-defined helical microtubules.270 Each monomer of their homotetrameric building block, soybean agglutinin (SBA), has a site that binds to N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine (GalNAc) or α-D-galactopyranoside (Gal) in the presence of Ca2+ or Mn2+. Within the tetramer, the sites are not oriented in the same plane, preventing the formation of 1D fibrillar structures. Instead, when combined with equimolar concentrations of designed ligands composed of (1) GalNAc or Gal, (2) a variable-length oligo(ethylene oxide) spacer and (3) a Rhodamine B (RhB) moiety that induces ligand dimerization by π-π stacking, SBA assembled into regular micron-scale tubular structures with a 26 nm diameter (Figure 42a). A 7.9-Å resolution cryo-EM reconstruction revealed that the tetramers adopted a left-handed helical structure within the tubules, which were composed of 3 proto-filaments wound around a hollow, with each helical repeat being composed of nine SBA tetramers (Figure 42b). Ligand dimerization through RhB stacking was only observed along the length of the protofibers, while interactions between protofibers occurred between two pairs of ligands. The formation of the microtubules was reversible through the addition of β-cyclodextrin (βCD), a competing ligand that complexes with RhB, while subsequent addition of adamantane, a stronger βCD binder, led to nanotube recovery. In addition, the kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of the assembly indicated that growth proceeded in a directional, pseudo-1D fashion.
Figure 42.

Formation of helical microtubules based on dual interactions. a) Soybean agglutinin (SBA) tetramers (left) associate with dual-function ligands to form microtubules via protein-sugar binding and π-π stacking. The ligand (middle) is composed of a protein-binding sugar moiety, a variable-length linker and a dimerizing RhB moiety. Microtubule cryo-EM micrograph (right), scale bar: 25 nm. b) Model of microtubule based on cryo-EM reconstruction. Three helical filaments compose the microtubule, where each helical turn consists of nine tetramer units. Adapted with permission from Ref.270. Copyright 2016 ACS.
3.4.2. 1D assemblies through covalent bonding
Several studies have used Cys modifications on the faces of toroidal or ring-shaped building blocks to build covalently linked protein nanotubes. Ballister et al. applied this approach to Hcp1 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a homohexameric ring structure with a height of 4.4 nm and outer and inner diameters of 9 and 4 nm, respectively (Figure 43a).224 While under physiological conditions the rings do not undergo self-association, they stack (non-helically) into extended tubular structures upon crystallization into a P6 honeycomb lattice (Figure 43b). After examining the ring-ring interfaces within the crystal structure, the researchers targeted residues Gly90 and Arg157 for mutation to Cys. These residues were selected because they are located on opposite sides of the ring in a suitable orientation to accommodate disulfide bond formation. Covalently linked nanotubes corresponding to the design (Figure 43c) were obtained both from purified protein and in vivo, although their lengths were limited to a few connected units and aggregates were also observed in vivo. Optimization of in vitro assembly conditions through pH and ionic strength screening, as well as addition of chaotropic polyethylene glycol (PEG) and reductant, led to the growth of longer tubes that consisted of more than 10 subunits and up to 100 nm in length. Additional controls over nanotube structure were enacted by using end-differentiation capping units, rings bearing reactive Cys residues only on one side, or pore-plugging polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers functionalized with bifunctional maleido-NHS-ester linkers, which were designed to react with inward-facing Q54C residues. Both the length-control and pore-plugging features were designed in view of potential drug encapsulation applications of the covalently linked Hcp1 nanotubes.
Figure 43.
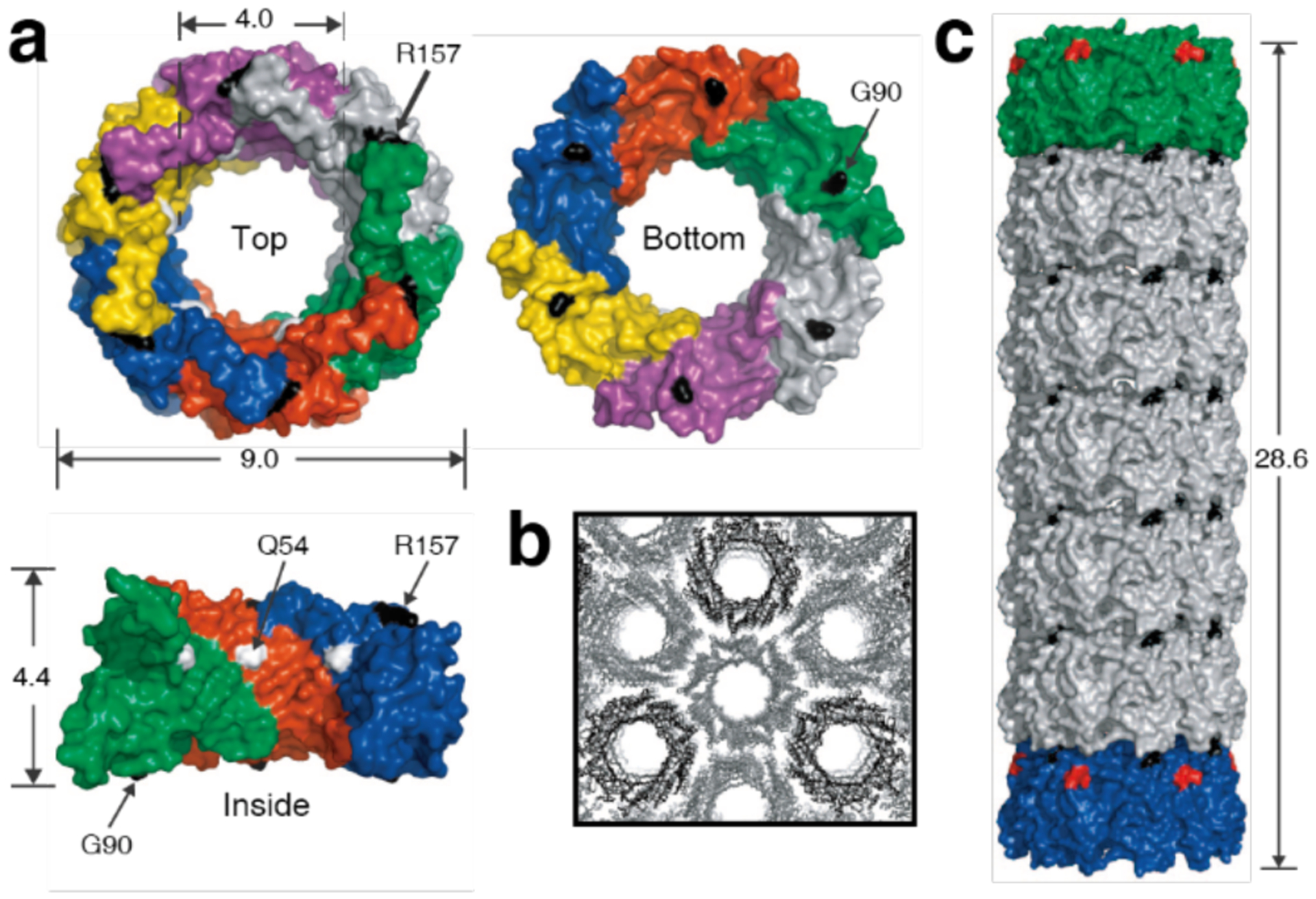
Design of covalently linked Hcp1 nanotube based on crystal packing. a) Structure of the Hcp1 hexameric ring viewed from top, bottom, and in cross-section exposing the interior surface of the pore. b) The honeycomb lattice packing of Hcp1 crystal viewed from the z-axis, showing stacking of Hcp1 rings into nanotubes. c) Side view of the nanotube formed by five G90C/R157CHcp1 rings (grey) and two capping units (green and blue) modified with Cys residues only on one side. Adapted with permission from Ref.224. Copyright 2008 National Academy of Sciences.
Similar to the design process for Hcp1 nanotubes, Miranda et al. installed V69C and E50C mutations on the opposing faces of TRAP from Bacillus stearothermophilus, an 11-subunit homooligomeric ring, with the goal of assembling nanotubes through multivalent disulfide bond formation between the ring faces.418 The construct, bearing additional mutations for improved solubility and future biomineralization of the cavity, was found to form nanotubes hundreds of nanometers in length in the presence of dithiothreitol (DTT) or dimercapto-1-propanol (DMP). DTT or DMP addition was essential for tube formation, as the use of alternative reducing agents β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME) and tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) did not promote nanotube formation. This finding suggested that DTT or DMP, which both bear dual thiol functionalities, might be integrated into the nanotubes as crosslinkers. The authors proposed a mechanism for nanotube formation wherein the rings first self-associated in a head-to-head fashion via hydrophobic surface burial, and the resulting dimers then underwent DTT-mediated covalent crosslinking to form nanotubes. A follow-up study by Nagano et al.436 confirmed the proposed mechanism through molecular modeling, particle reconstruction from ns-TEM micrographs and control experiments performed with TRAP mutants displaying Cys residues only on one face of the ring. This study demonstrated that the C50 residues were not required for crosslinking due to stable association between ring surfaces through hydrophobic packing, while C69 residues did participate in DMP-mediated crosslinking.
Whereas the previous examples used crystal packing of ring-shaped proteins to determine the position of potential crosslinking residues but carried out nanotube assembly in solution, the Ueno Group has used protein crystals as non-equilibrium scaffolds for the formation of protein nanotubes which cannot be obtained from solution.437 The crystal provides a controlled microenvironment for site-specific crosslinking, ensuring uniform orientation and precise connectivity between building blocks. The covalently linked nanotubes are then recovered upon crystal dissolution. This approach was applied to generate nanotubes based on P3121 crystals of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase type III (RubisCO) from the archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1. RubisCO is a homodecamer composed of double pentameric rings with C5 symmetry. It was modified with a single mutation, I419C, located face-to-face on the decamer surfaces such that the Cα-Cα distance for the Cys residues was expected to be 6.5 Å, or within range for bridging by a disulfide bond. Nanotube formation was carried out by co-oxidation of the I149CRubisCO crystals with the crosslinkers 1,2-ethanedithiol (ED) triggered by the addition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The addition of H2O2 alone was not effective for nanotube elongation, as mostly monomeric rings and stacks composed of up to five rings were recovered under these conditions. On the other hand, the treatment with DTT or ED yielded nanotubes up to 400 nm in length. The necessity of using flexible crosslinkers could be explained by the constrained conformation of Cys side chains within the crystal.
Abe et al. later used a similar approach to isolate covalently linked protein filaments from Trypanosoma brucei cysteine protease cathepsin B (TbCatB) crystals, formed by overexpression of R92C/T223CTbCatB in baculovirus-infected insect cells upon oxidation (Figure 44a).416 Monomers form 1D arrays within the P42212 crystals of TbCatB assembled in vivo. The mutant R92C/T223C was selected because the 5.9 Å Cα-Cα distance for the residues in the wildtype crystal was deemed appropriate for disulfide bond formation by oxidation (Figure 44b). Due to the reducing conditions within the cell, filament formation did not occur in vivo. However, the oxidation reaction took place during crystal isolation under aerobic conditions, as confirmed by the structural characterization of purified crystals by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The covalently linked filaments were recovered following crystal dissolution under acidic conditions. Notably, the purified protein crystallized in vitro in the P21 space group, wherein the monomer orientation did not allow for C92-C223 crosslinking. Interestingly, the extended 1D structures recovered upon dissolution were bundles of two designed filaments with a zigzag arrangement of proteins (Figure 44c). The two filaments stayed bound together due to the large contact surface area between subunits, with interface stabilization provided by non-polar contacts and hydrogen bonding.
Figure 44.
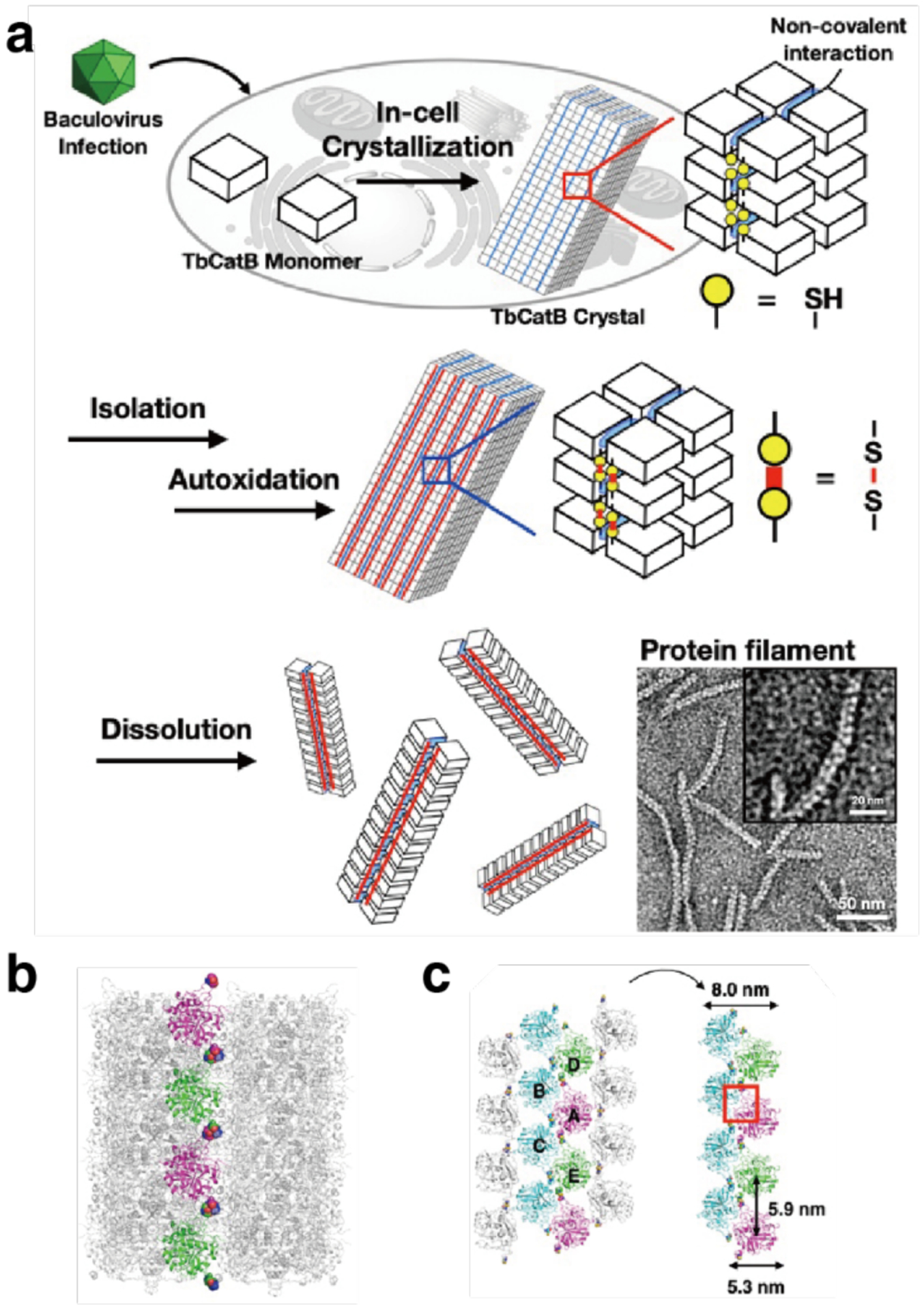
Covalently linked protein filaments based on the TbCatB protein. a) Illustration of the process to generate covalently linked R91C/T223CTbCatB protein filament bundles. Overexpression of TbCatB gives rise to protein crystals in vivo. During isolation, the crystals undergo autoxidation which links monomers by disulfide bonding into filaments that can be recovered by dissolving the crystals. b) Design of R91C/T223CTbCatB filament based on the P42212 crystal structure. c) Zig-zag protein arrangement in the two-filament bundle isolated upon crystal dissolution. Adapted with permission from Ref.416 Copyright 2021 Wiley.
3.4.3. Metal-directed 1D assemblies
Building 1D protein assemblies directed by metal-protein interactions is an appealing method due to, among other reasons, the small footprint of the required protein modification, the directionality of the metal-protein interactions, and the inherent modularity of the approach. In an early example, the Ward Group was inspired by metal-mediated assembly of coordination polymers and networks to design a protein fiber composed of streptavidin and a linear biotin-bearing metal-binding linker.209 The selected bis-biotinylated terpyridine (Biot2-terpy) ligand was combined with Fe2+ to form the complex [Fe(Biot2-terpy)2]2+, a preorganized linear connector bearing two pairs of biotin moieties at either end. With the addition of Ca2+, the mixture of streptavidin and the connector yielded 1D polymerized assemblies that bundled into fibers with diameters and lengths on the micron and millimeter-scale, respectively. The bundles also acted as template for CaCO3 biomineralization in the presence of CO2 vapor.
In another example of metal-mediated protein nanowires, Liu and coworkers took advantage of the homodimerization of glutathione S-transferase from Schitosoma japonicum (SjGST) and the metal-affinity of His-tags to generate self-assembled nanofibers.260 The building block SjGST-6His was generated by fusing a 6His tag at the N-terminus of the monomer. The homodimerization of the protein gave rise to C2 symmetric building blocks presenting the His-tag arms at opposing ends, and thus serving as two-way linear units that can be connected by the addition of His-coordinating Ni2+ ions. Mixtures of SjGST-6His and NiSO4 yielded flexible nanowires with a broad size distribution and a uniform height of 4.9 nm as measured by AFM. Notably, the self-assembled wires retained the enzymatic activity of the native SjGST and were able to scavenge the cytotoxic compound 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) in the presence of reduced glutathione (GSH). In a related study, Bai et al. introduced an alternative metal-chelating motif on the SjGST surface in order to produce metal-mediated protein nanorings with a highly controlled size distribution.438 By positioning the chelating bis-His clamp at residues 137 and 138, they created a Ni2+ coordination environment and a new protein-protein interface that was further stabilized by a network of electrostatic interactions and a hydrogen bond. This stable interface connected protein building blocks at a consistent geometry with respect to each other, such that the resulting nanoring assemblies formed within a narrow size distribution. The strength of the non-covalent interactions within the protein-protein interface was tunable with ionic strength in solution, which in turn could be used to control nanoring diameter.
The chaperonin GroEL has proved to be a versatile and functional building block for the construction of protein nanotubes.201,203,292,417,439,440 GroEL is a barrel-shaped complex with D7 symmetry composed of two stacked heptameric rings. In nature, it assists the process of refolding denatured proteins. The Aida Group has developed a metal-mediated approach to produce GroEL nanotubes by modifying the barrel entrance with Cys residues conjugated to photochromic spiropyran (SP) via maleimide chemistry.417 In solution, SP undergoes isomerization to merocyanine (MC), which is known to coordinate divalent metal ions in a 2:1 ratio (Figure 45a). In the presence of divalent metal ions (Mg2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Co2+, Zn2+), the modified GroEL barrels stacked into micron-scale nanotubes through multivalent interactions mediated by metal ions and the isomerized MC units exposed on the apical surfaces of the GroEL building blocks (Figure 45b). The 15 nm width of the nanotubes was consistent with the protein barrel’s outer diameter. It is important to note that monovalent cations (Na+, K+, Cs+) did not induce assembly, while trivalent cations (Fe3+, In3+, Ce3+, Eu3+) gave rise to ill-defined aggregates. The metal-mediated GroEL nanotubes were further shown to have switchable assembly properties (Section 4.2.1).203,439 Furthermore, a C7, single ring-layer GroEL mutant was used to create nanotube capping units. This mutant was originally designed by attenuating the salt bridges between the ring surfaces.441 Using the same SP/MC conjugation and metal-mediated assembly strategy, Sim et al. produced nanotubes of controllable length between 40 and 320 nm by varying the ratio of the single-layer capping and double-layer polymerizing GroEL units.201 The switchability and length control properties of the GroEL nanotubes make them an interesting candidate for use as drug delivery vehicles as detailed in section 4.3.1.
Figure 45.
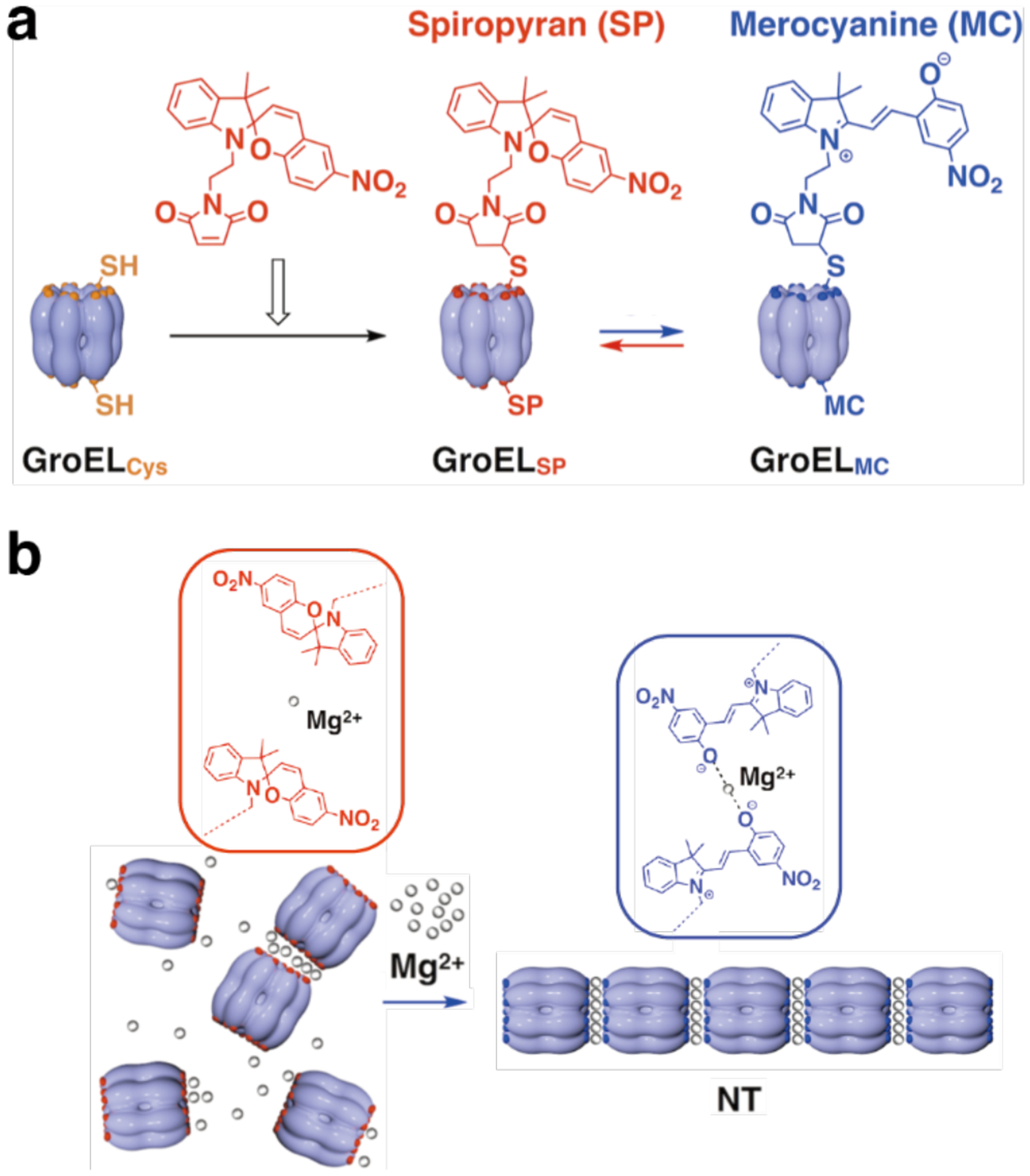
Mg2+-mediated assembly of GroEL nanotubes. a) The apical domains of GroEL are labeled with spiropyran (SP) which undergoes spontaneous isomerization to merocyanine (MC) in solution. b) GroELMC nanotube formation induced by Mg2+. Adapted with permission from Ref.439. Copyright 2013 ACS.
In an alternative strategy for GroEL nanotube assembly, Kashiwagi et al. conjugated the Cys-modified GroEL barrels to DNA strands, which enabled nanotube formation through multivalent strand complementarity.440 The DNA-mediated assembly strategy was also applied to generate GroEL-DNA Janus nanoparticles bearing strands with different sequences at either end of the barrel.442 Rather than forming discrete nanotubes, these constructs polymerized into extended structures with lamellar periodic features. The GroEL barrels were presumed to adopt a hexagonal packing when combined with additional DNA strands.
The Tezcan Group extended their metal-mediated interface design approach, in combination with computational interface design tools, to develop a protein building block capable of reconfigurable metal-mediated assembly into 1D nanotubes, 2D sheets, and 3D crystals.202 This building block, termed Rosetta Interface Designed Cytochrome 3 (RIDC3), is based on an earlier metal-binding variant of cyt cb562 and forms a C2-symmetric dimer through Zn2+ coordination at a “high affinity” site composed of three His residues, H73/H77 on one monomer and H63 on the other. In this arrangement, a further “low affinity” site at the N-terminal Ala and Asp residue (A1 and D39) is available for metal coordination (Figure 46a). Brodin et al. screened assembly outcomes while varying pH (5.5 to 8.5) and [Zn2+]:[RIDC3] ratios, obtaining nanotubes with a diameter in the range of 80 nm and length up to 15 μm and micron-scale 2D arrays under different conditions (Figure 46b). The nanotubes were observed at pH 8.5 and 100:1 [Zn2+]:[RIDC3], while 2D sheets were observed at lower [Zn2+]:[RIDC3] ratios and more acidic pH, closer to the RIDC3 pI (~5.3). Based on these findings and lattice packing parameters, the authors proposed a Zn-dependent nucleation/growth mechanism for RIDC3 assemblies, where both 1- and 2D assemblies originate from small 2D nuclei. Under fast nucleation conditions (high [Zn2+]:[RIDC3] ratio or high pH, where high affinity sites are fully deprotonated), the large number of small nuclei preferentially form helical nanotubes. In contrast, when nucleation is slowed down, nuclei grow into large 2D sheets. The reconfigurable properties of the assembly are further discussed in section 4.2.2.
Figure 46.
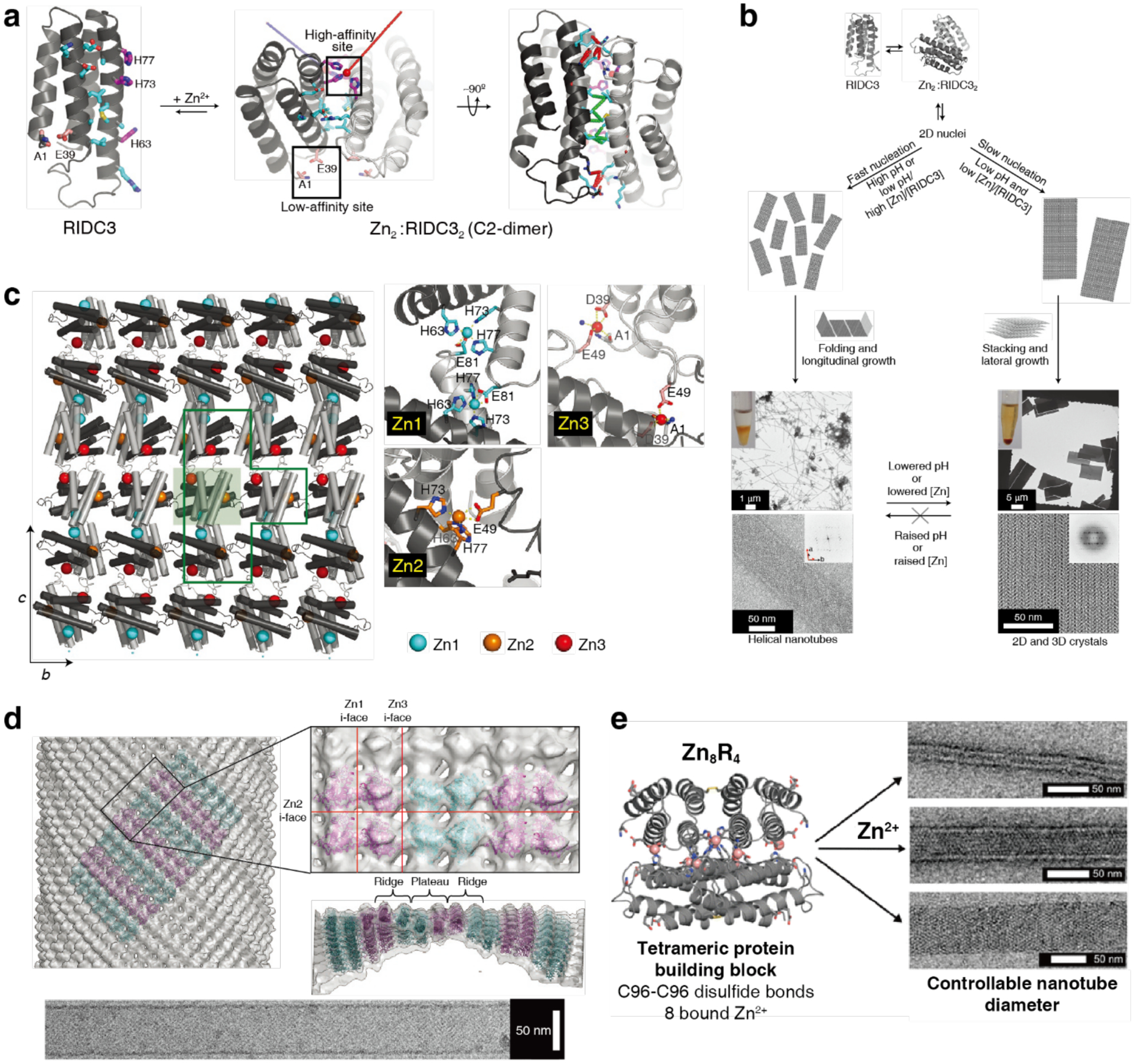
Zn2+-mediated assembly of RIDC3, a metal-binding cyt cb562 variant. a) The RIDC3 monomer undergoes dimerization upon Zn2+ coordination at the high affinity site. Amino acids that stabilize the interface in the C2-symmetric dimer are shown in cyan, the high- and low-affinity Zn binding sites are depicted in magenta and pink, respectively. b) Zn-mediated RIDC3 self-assembly into different morphologies under fast and slow nucleation conditions. High pH or high [Zn]:[RIDC3] ratio enables fast nucleation, giving rise to more nuclei which form the helical nanotubes. Low pH and low [Zn]:[RIDC3] give rise to fewer nuclei that grow into 2D and 3D crystals. c) Zn-mediated packing of RIDC3 monomers in the 2D crystal plane based on XRD (left). Close-up views of the three different Zn2+ binding environments found in the 2D RIDC3 crystals (right). d) RIDC3 nanotube reconstruction from cryo-EM micrographs (left). Zoomed-in representation of the packing of RIDC3 molecules highlighting interaction planes where different Zn2+ coordination environments are found (right). Cryo-EM micrograph of an RIDC3 nanotube (bottom). e) Structure of the tetrameric H59/C96RIDC3 building block formed via disulfide bonding and Zn coordination (left). Three classes of nanotubes with controllable diameters form under different solution conditions. (a-d) Adapted with permission from Ref.202. Copyright 2012 NPG. (e) Adapted with permission from Ref.419. Copyright 2015 ACS.
Characterization of the nanotubes by cryo-EM using helical, real-space reconstruction methods revealed that the hollow structures have C9 helical symmetry. The surfaces of the nanotubes show a pattern of ridges and plateaus that is also seen in the 2D layers of the 3D RIDC3 crystals studied by XRD (PDB ID: 3TOM) (Figure 46d), supporting the mechanistic insights mentioned above. The conversion of nascent crystalline 2D sheets into helical nanotubes depends on curvature being induced along both lattice vectors within the sheet. While the coordination geometries at the Zn1 and Zn2 sites in the 2D plane (Figure 46c) appear to be maintained during the conversion, the coordination environment at the Zn3 site seems to deviate from the Zn3-Glu492 coordination observed in XRD due to the participation of adjacent acidic residues Asp2 and Asp50. Finally, the researchers also demonstrated that the stacking of the 2D layers into 3D crystals could be promoted by π-π interactions between site-specifically attached rhodamine functionalities. Collectively, the metal-directed RIDC3 arrays provided the first example for the externally tunable self-assembly of a designed protein building block into 1, 2 and 3D arrays with well-defined structures.202
Following the insight that RIDC3 nanotubes are derived from anisotropic rectangular 2D sheets, Brodin et al. redesigned the building block to generate a D2-symmetric tetramer that was used for metal-mediated formation of nanotubes with different diameters under kinetic control (Figure 46e).419 They introduced residue C96 to generate covalently linked RIDC3 dimers, and residue H59 to stabilize the Zn2+ coordination environment that locks in the formation of the Zn-mediated tetramer (8 Zn2+: 4 H59/C96RIDC3). The tetramers have additional Zn-binding sites with different affinities that were exploited to generate three different classes of nanotubes with different diameters (20, 48, or 68 nm) by changing pH and Zn2+ addition conditions in solution. The arrangement of tetramers within all nanotube types was the same, in addition to the identical structure of the tetramer monomers found in the nanotubes and 3D crystals. These results indicated that the same Zn-mediated contacts ensured the formation of all nanotube types. However, these contacts were also flexible enough to accommodate the range of curvatures that are associated with nanotubes of different diameters.419
3.4.4. Electrostatically directed 1D assemblies
Electrostatic interactions between protein building blocks and oppositely charged effector molecules have been widely employed in the design of extended protein assemblies, especially to generate ordered 3D lattices (Section 3.6.3), as well as for the assembly of 1D nanowires. Stable protein 1 (SP1) has been a choice protein building block for the formation of nanowires following early observations that it naturally undergoes stacking, a property that was exploited by Shoseyov and coworkers to form functionalized extended SP1 structures.443–445 SP1 is a homooligomeric dodecamer isolated from aspen (Populus tremula) plants. It is composed of two rings that stack by hydrophobic association into a double-layer structure with six-fold symmetry. The exposed ring surfaces are highly negatively charged due to the distribution of acidic residues (Figure 47a).
Figure 47.

Assembly of SP1 nanowires via multivalent electrostatic interactions. a) Top and side views of the SP1 ring with structure with charge distribution on the surface. The color scale goes from negative (red) to positive (blue) charge. b) Illustration of a generation 5 PAMAM dendrimer (PD5) (left) and co-assembly of PD5 and SP1 into nanowires (right). c) Illustration of SP1 nanowire formation mediated by multivalent interactions with ethylenediamine. (a-b) Adapted with permission from Ref. 52. Copyright 2015 ACS. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.231. Copyright 2016 RSC.
This structural property was exploited by the Liu Group in a series of reports to generate ordered SP1 nanowires by combining the negatively charged rings with non-proteinaceous building blocks bearing positively charged surfaces, including quantum dots (QDs),291 soft nanoparticle PAMAM dendrimers (Figure 47b)281,446 and core-crosslinked micelles (CCMs).447 Such combinations of heterologous elements yielded nanowires formed by “sandwiching” the positively charged nanoparticles between SP1 rings through multivalent electrostatic interactions. The size match between protein ring and nanoparticle was a determinant factor in the structural outcomes,291 an effect that has also been observed in the case of Cys-modified Hcp1 rings co-assembled with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) of various sizes (section 4.3.4).448
Miao et al. also showed that ethylenediamine (EDA) added to SP1 in 1:1 ratio with the exposed carboxyl groups on the top and bottom faces of the rings mediated multivalent electrostatic interactions that stabilize ordered nanotubes hundreds of nanometers in length (Figure 47c).231 The authors further used a “zero-length” crosslinking strategy to covalently link the proteins to EDA by adding EDC and sulfo-NHS to the nanowires.
3.4.5. Computationally designed 1D assemblies
Nucleoprotein architectures, although ubiquitous and highly functional in nature,449–452 remain somewhat rare among rationally designed protein assemblies. The Mayo Group applied computational protein interface design to generate co-assembling protein-DNA nanowires.299 The wires are composed of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and a protein building block that has the dual functions to bind to a dsDNA and homodimerize (Figure 48a). They selected engrailed homeodomain (ENH) from Drosophila melanogaster as the protein building block due to its high binding affinity to a dsDNA motif (TAATNN). Moreover, ENH, a three-helix protein, has a surface (the exterior faces of helices 1 and 2) amenable to computational homodimer interface design, as it is oriented opposite to the DNA-binding helix (helix 3). Fast Fourier transform-based docking was used to generate C2-symmetric ENH homodimer models that underwent computational redesign to minimize the energy of the interface and were iteratively screened and improved using a molecular dynamics protocol. The designed homodimer retained high, specific affinity to the target dsDNA sequence and oriented the binding domains opposite to each other. To generate linear wires from the co-assembly, the dsDNA component was designed to position two protein-binding sites 180° apart on the double helix. When imaged by AFM, the nanowires had lengths on the order of 300 nm, corresponding to ~60 repeat units. The co-crystal structure was also solved by X-ray diffraction, revealing that the wires indeed form following the proposed mechanism. However, two different protein-DNA binding configurations were observed, causing the infinitely repeated protein-DNA wires to be slightly kinked (Figure 48b). The strategy of combining the design of protein oligomers with DNA binding could be expanded to give rise to more complex and diverse ordered co-assemblies in 2D and 3D.
Figure 48.
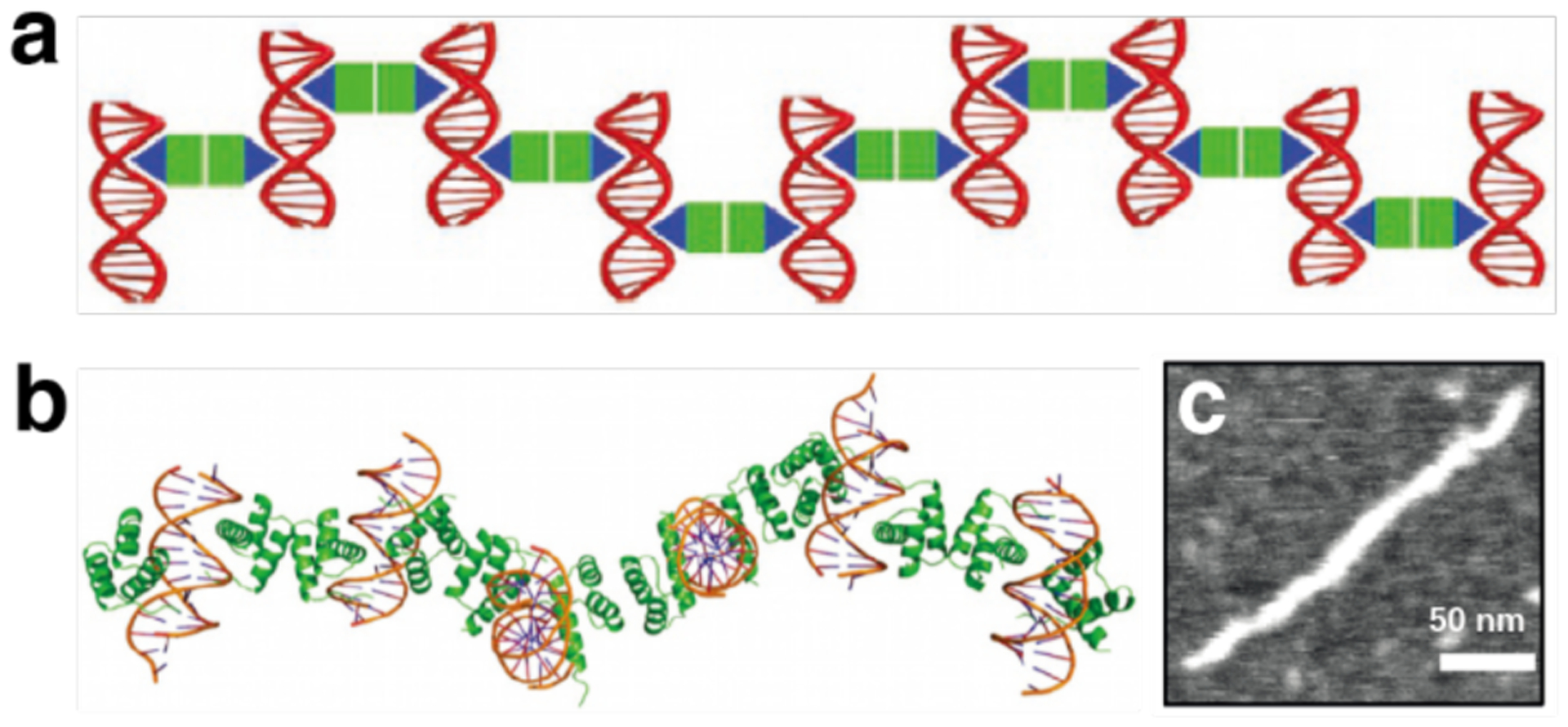
Protein-DNA nanowires. a) Illustration of the co-assembly of computationally designed ENH dimers and dsDNA into a linear nanowire. b) Co-crystal structure shows that kinked wires are formed. c) AFM image of the protein-DNA nanowire. Adapted with permission from Ref.299. Copyright 2015 NPG.
More recently, the Baker Group described a general computational approach for the design of self-assembled helical protein filaments with controllable geometries and diameters based on de novo designed, idealized helical repeat protein building blocks.187 Typically the protein interface design process is simplified by using building blocks with internal symmetry to reduce the number of interfaces that require redesign. However, reversibly forming protein filaments found in nature tend to be composed of asymmetric building blocks and thus have multiple interfaces. This problem was simplified by considering that helical symmetry originates from repeated application of a single rigid-body transform (six degrees of freedom) and accounting for cyclic symmetry. The design approach (Figure 49a) started with an asymmetric protein monomer structure and generated a second randomly oriented copy in physical contact with the first. This was accomplished by applying random rotation, choosing a direction, and sliding the second copy into contact with the first. The filaments considered were generated not only by the rigid-body transform relating the two contacting monomers, but also by the nth root of this transform (where n = 2 – 5), and with cyclic symmetry generated by the application of cyclic symmetry operations (Cn) around the superhelical axis. In all cases, the next step generated several repeating turns of the full filament by re-applying the rigid-body transformation and cyclic symmetry operations, eliminating clashing geometries, and making sure that there is at least an additional interface beyond the one generated in the initial sliding-into-contact step. Filament architectures were selected based on low predicted energy at multiple interfaces, and Rosetta combinatorial sequence optimization was carried out on a central monomer, propagating the sequence to all other monomers.
Figure 49.
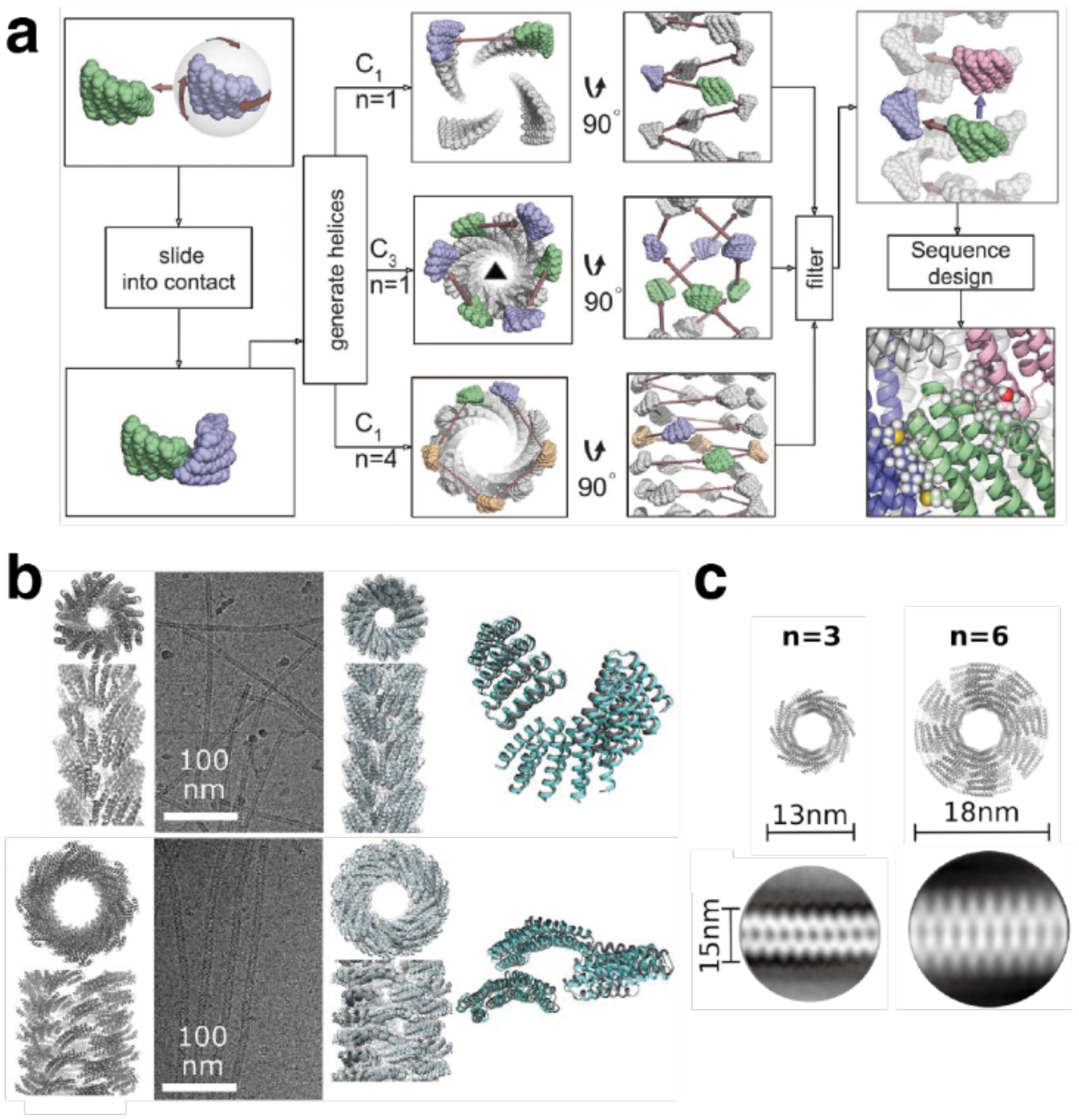
Computationally designed helical protein filaments. a) Computational protocol to design self-assembling protein filaments. A copy of an asymmetric protein monomer is randomly rotated and moved, then slid into contact with the first monomer. The operation is repeated to generate helices. Cyclic symmetry and the ordering of contacting units are screened, and sequence of the monomer is redesigned to optimize the interfaces. b) From left to right: Computationally designed models, cryo-EM micrographs, cryo-EM structures, and overlay of designed model and cryo-EM structure for the C3 symmetric DHF91 (top) and the C1 symmetric DHF79 (bottom) designs. c) Fibers with variable diameter can be generated by changing the number of repeat units within the monomer. Computationally designed models (top) and 2D class average structures (bottom) are shown for two variants of the DHF58 filament. Adapted with permission from Ref.187. Copyright 2018 AAAS.
The resulting designs were filtered for high shape complementarity, low monomer-monomer interaction energy and few or no buried unsatisfied hydrogen bonds. Following this design process, 124 designs were selected for experimental testing. Of these designs, 34 were found to form 1D assemblies and six were studied by cryo-EM. Among the six designs spanning a range of architectures, good correspondence was found between the designed model and experiment in terms of monomer orientations and packing in the filament. However, interfacial interactions varied considerably. While four of the designs had an excellent match to the model, monomers in another filament, designed with C1 symmetry, shifted to produce a C3 symmetric structure (Figure 49b).187 Furthermore, a series of filaments with variable diameters were produced by changing the number of repeat units within the monomer (Figure 49c). The filament assembly dynamics were monitored both in vitro and in living cells. In addition, seeded fiber growth was achieved from a surface, and capping units were used to control growth and induce disassembly. The nucleating and terminating units were designed by selectively eliminating interaction interfaces.187
3.5. Extended 2D assemblies
Two-dimensional protein lattices are common in nature, particularly in association with cellular membranes. Bacteria and archaea produce protective surface layers (S-layers) consisting of proteins or glycoproteins.117,453 Bacteriorhodopsin forms 2D patches, known as purple membranes, covering nearly half of the surface area of the archaeal cell to harvest light and pump protons.454 Other examples of naturally formed 2D protein lattices include gap-junction plaques455 and water channels.456 This section describes the efforts which, inspired by nature, have taken advantage of different design strategies to construct ordered 2D protein arrays. As in the case of other types of supramolecular and extended structures, symmetry takes on an important role in building block selection and array design, as 2D crystals are restricted to 17 possible plane group symmetry configurations.457 Certain lattice arrangements are more amenable to design than others, as they require fewer unique interfaces or symmetry element combinations to be realized.458 In general, building blocks with two-, three- and four-fold symmetry have been highly represented in the area of 2D protein assembly so far. Given the technological relevance of self-assembled 2D materials459,460 and the functional diversity of proteins, ordered 2D protein assemblies built from the bottom up represent a highly sought-after platform that could find diverse applications, encompassing sensing, catalysis, light-harvesting, and nanomedicine.
For reviews of natural 2D assemblies functionalized for application development, or 2D materials based on peptides and proteins readers are encouraged to consult other recent publications.117,423,461–463 The section below reports on recent developments in 2D protein assembly design by way of diverse strategies such as genetic protein fusion, covalent bonding, metal coordination, receptor-ligand interactions, computational design, and interface-assisted assembly.
3.5.1. 2D protein assemblies through genetic fusion
It is essential to consider the symmetries of the protein building blocks and the linkages between them to tile them into ordered 2D lattices. For example, square lattices are generated by combining a four-fold symmetric building block with a linking strategy that yields two-fold symmetry, as articulated by Yeates and colleagues.131 This simple combination can be achieved by several different approaches. The Noble Group proposed linking native protein assembly elements that have different rotational symmetries by genetic protein fusion. The elements are connected into a fusion construct at their termini along a shared symmetry axis, thus promoting a given assembly outcome by eliminating degrees of freedom from the fused building blocks.128 The assembly elements can originate from homologous or heterologous systems. Using this strategy, the authors demonstrated the formation of ordered 1D and 2D protein arrays.128 Specifically, two different sets of constructs were tested to produce 2D arrays. Aminolevulinic acid dehydrogenase (ALAD) was used as a homologous D4 component in both cases. It was fused either to Streptag I peptide and assembled with streptavidin (heterologous assembly motif), or with the coiled-coil forming peptides Lac21E and Lac21K (heterologous assembly motif) for co-assembly into a 2D lattice with variable cell dimensions enabled by changing the length of the peptide (Figure 50). The authors noted that the length and flexibility of the linker, as well as the alignment of the fusion point to the shared symmetry axis along which the assembly is designed to grow, are all important parameters to promote formation of the desired 2D structures.
Figure 50.

Genetic fusion approach to 2D protein assembly. Self-assembly of binary 2D arrays along the C2 symmetry axis shared by the components. The homologous D4-symmetric protein building block ALAD is combined with a) a heterologous D2-symmetric assembly motif (Streptavidin/Streptag I) or b) a heterologous C2-symmetric assembly motif (Lac21E/Lac21K). Adapted with permission from Ref.128. Copyright 2011 NPG.
Poulos et al. implemented a genetic fusion strategy to design a crystalline 2D lattice464 by combining the concept of rotational symmetry matching described above128 with the polymer-driven crystallization approach reported by Bowie and coworkers.465 They created a TTT-FUR fusion construct composed of three Tel-SAM domains (TTT) and the ferric uptake regulator (FUR) domain.464 Tel-SAM domains formed one dimensional fibers with a 21 screw axis under pH control, while the FUR domains underwent homodimerization. This combination allowed TTT-FUR fusion proteins to form 2D sheets with the FUR domains stabilizing contacts between polymerized TTT fibers. Screening of crystallization conditions yielded 3D crystals, where the 2D layers showed stacking one on top of the other. As described earlier (Section 2.2.1), the protein fusion strategy takes advantage of naturally evolved protein-protein interfaces, combining them into building blocks designed for a target structure based on symmetry considerations. In extended assemblies, just as in finite assemblies built by genetic fusion, controlling the rigidity of the fusion construct and optimizing the orientation of different domains through linker design are important challenges as these parameters determine assembly outcomes.
3.5.2. 2D assemblies through covalent bonding
In addition to imposing two-fold rotational symmetry, the formation of covalent bonds between building blocks provides a facile means to create stable protein arrays while only incorporating a minimal number of mutations into the building blocks. Tessellation of the C4-symmetric RhuA building block, first employed by Ringler and Schulz (section 3.4.4),466 inspired Suzuki et al. to take advantage of strategically positioned Cys residues to create C2-symmetric linkages for a straightforward path toward generating 2D protein lattices. The four corners of the RhuA tetramer were identified as appropriate positions to install a single Cys residue (C98) for lattice assembly via disulfide bond formation under slow oxidation conditions (Figure 51a).225 An octameric D4-symmetric RhuA variant (F88/C98) was also investigated. Both building blocks formed extensive, highly regular 2D arrays with p4212 plane group symmetry. Notably, the self-assembly process was reversible under reducing conditions. An additional RhuA variant bearing a bis-His motif (H63/H98) at the four corners was shown to form p4 lattices through metal coordination, an alternative C2-symmetric linkage (Figure 51b). The formation of this RhuA assembly could also be reversed by EDTA addition. Among the three variants, the C98RhuA lattices connected through a single disulfide linkage at the corners exhibited the largest array size, the lowest defect frequency, and dynamic lattice behavior, as discussed further in Section 4.2.2.
Figure 51.

Assembly of 2D crystals based on C4-symmetric RhuA modified at the corners to enable C2 connectivity between building blocks. a) C98RhuA forms a p4212 lattice following oxidation. b) H63/H98RhuA forms a p4 lattice following divalent metal coordination. TEM characterization of 2D crystals of RhuA variants: (I) Low-magnification views of RhuA crystals, (II) high-magnification views of RhuA crystals with the Fast Fourier transforms (inset), (III) reconstructed 2D images, and (IV) structural models based on (III). Adapted with permission from Ref.225. Copyright 2016 NPG.
Zhao et al. exploited oxidative coupling of tyrosine residues as an alternative strategy to produce covalently crosslinked 2D protein arrays.230 They selected the ring-shaped building block SP1, discussed above (Section 3.4.4) in the context of extended 1D assemblies, as a building block. Previously, Shoseyov and coworkers had observed the formation of long-range 2D arrays from wild type445 and polyHis-tagged467 SP1 rings following assembly at an air-phospholipid and an air-water interface, respectively. In contrast, Zhao et al. carried out the assembly in bulk solution after installing an S98Y mutation at the SP1 ring periphery (Figure 52). They reported an enzymatic crosslinking strategy using either a single enzyme (horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in the presence of H2O2), or a cooperative dual enzyme system (HRP and glucose oxidase (GOx) in the presence of glucose).230 In both cases, hexagonally packed sheets, hundreds of nanometers in size, were formed following the crosslinking reaction. Sheet stacking into multilayered structures could be controlled by adjusting pH, with lower pH conditions closer to SP1 pI (~4.3) favoring stacking due to reduced repulsion between the charged sheet surfaces. In a follow-up study, the authors demonstrated that S98YSP1 could be rapidly converted to covalently linked nanosheets with light-controlled oxidative crosslinking of tyrosine residues by using [Ru(bipy)3]2+ as a photosensitizer in the presence of ammonium persulfate (APS).468
Figure 52.
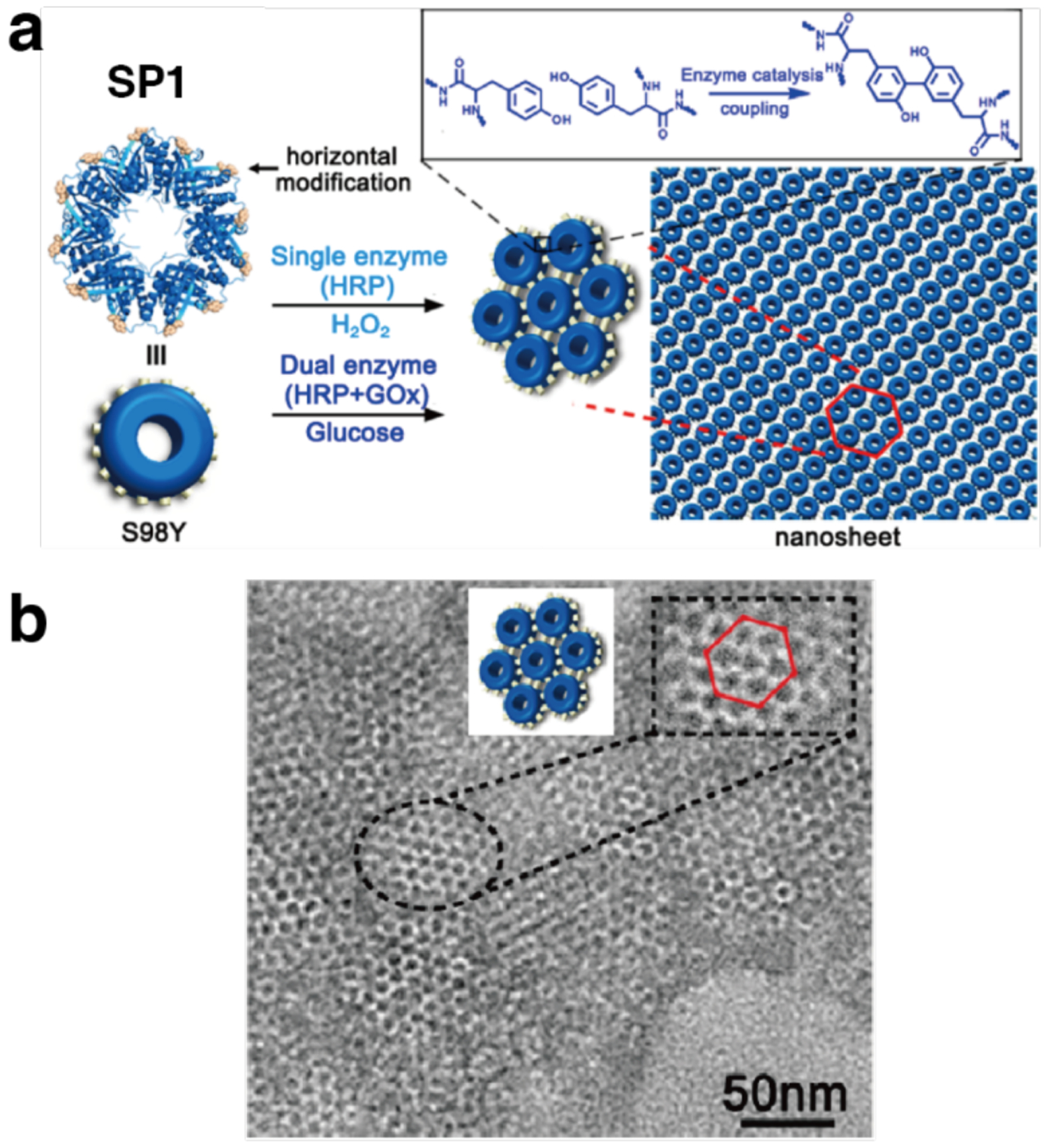
Covalently linked protein nanosheets based on the S98Y variant of cricoid stable protein 1 (SP1). a) Tyrosine crosslinking at the periphery of the SP1 disk can be carried either via a single enzyme pathway with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and H2O2, or a dual enzyme pathway with HRP, glucose oxidase (GOx) and glucose. b) TEM characterization of the protein nanosheets with inset showing an enlarged area of the micrograph and a model of hexagonal packing of the SP1 disks. Adapted with permission from Ref.230. Copyright 2017 ACS.
Later, Li et al. used small molecule tethers for the preparation of covalently linked 2D nanosheets. The authors employed bis-maleimide-terminated PEG linkers of variable length to generate nanosheets composed of EBFP2 and EGFP, fluorescent proteins that constitute a Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) pair.469 In this template-free system, the β-barrel-shaped proteins, modified with Cys residues at equatorial positions lying close to the C4 rotational axes, were mixed with the thiol-reactive linkers to yield a covalently linked 2D monolayer. The length of the PEG linker significantly impacted nanosheet size, with longer linkers giving rise to larger sheets due to reduced electrostatic repulsion between adjacent proteins. Notably, the proteins adopted a fixed orientation and even distribution within the nanosheets, which exhibited light-harvesting properties.
Ferritin, a protein cage composed of 24 subunits, has been a popular building block for the formation of extended protein-based lattices due to its octahedral structure that exhibits 432 point group symmetry. Ferritin’s robustness and tolerance to genetic and chemical modification have made it an ideal scaffold to test a broad range of assembly design strategies. It has arguably proven to be the most versatile building block available in the design and construction of protein assemblies, as demonstrated by the broad range of ferritin-based ordered 2D and 3D lattices reported just in the last decade. The Zhao Group employed several types of modifications at the C4 axis of the ferritin cage to enable the formation of square 2D lattices.228,273,470,471 Zhou et al. applied a disulfide bonding strategy to make covalently linked 2D lattices from homo-oligomeric human heavy chain ferritin (HuHF) by installing Cys residues near the C4 axes of the cage (C162).228 This single mutation positioned four Cys residues in close proximity to each other, created a “hot spot” for interactions, to construct a superlattice upon slow oxidation in the presence of β-ME (Figure 53).
Figure 53.

Covalently linked 2D HuHF arrays. a) A single mutation near the C4 axis positions four Cys residues in close proximity to each other. Slow oxidation yields ordered 2D HuHF arrays through multivalent disulfide bond formation at the “hot spots”. b) ns-TEM characterization of the square lattice. Adapted with permission from Ref.228. Copyright 2019 RSC.
The tobacco mosaic virus coat protein (TMVCP) has a rich phase behavior that is intricately controlled by pH, salt concentration, and temperature.472–474 The double-layer TMVCP “20S” disk structure, composed of 34 subunits arranged into two stacked 17-mer rings, has an 18 nm outer diameter, a 4.7 nm height and 4 nm-wide central pore. Blum and coworkers observed that TMVCP disks bearing a C-terminal His-tag form dense hexagonally packed 2D arrays at pH 5.5–6.0, a behavior that markedly differs from the observations made with wildtype TMVCP.475
In the last few years, the Wang Group has used strategies such as disulfide bond- and metal-mediated assembly to generate ordered 2D and 3D lattices based on TMVCP. Notably, Zhang et al. reported that a variant bearing three Cys mutations (C1 and C3 at the periphery of the disk designed to promote in-plane assembly, and C103 on the inner surface of the central pore) exhibited four distinctive assembly behaviors depending on pH and ionic strength.476 The observed structures included rods, rod-bundles, and 2D arrays. The 2D arrays were observed in conditions ranging roughly from pH 6.0 to 8.0 with phosphate buffer concentration maintained below 200 mM. The same C1/C3/C103 mutant was later used to generate large monolayered nanosheets tens of microns in size upon Cys oxidation with Cu2+ (Figure 54).477 Triclinic and hexagonal close-packed TMVCP 3D crystals were also assembled based on a C1/C3/C103 variant assembled through disulfide bonding and a C-terminal 4-His tagged variant (also bearing the C103 mutation on the inner pore surface) via Zn-binding respectively.478 Most recently, the C103/C-terminal 4-His variant was used to generate ordered 2D co-assemblies of TMVCP and various functional nanoparticles such as AuNPs and QDs as discussed further in section 4.3.4.479
Figure 54.
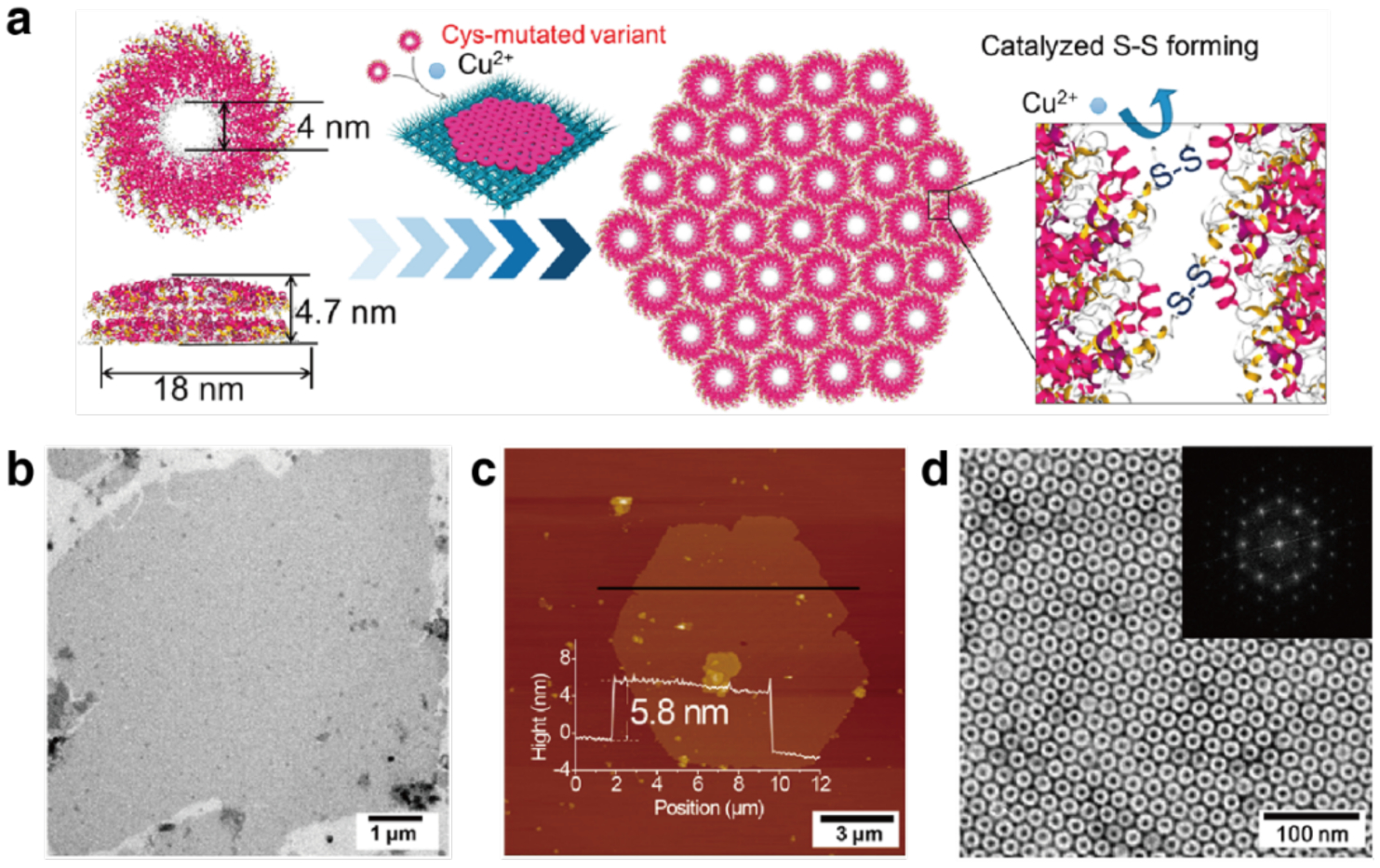
Covalently crosslinked TMVCP nanosheets. a) A schematic diagram of the formation of TMVCP 2D nanosheets upon oxidation of the peripheral Cys residues by Cu2+. Characterization of the nanosheets by b) ns-TEM, c) AFM, and d) high resolution ns-TEM. Inset shows the corresponding FFT. Adapted with permission from Ref.477. Copyright 2018 ACS.
3.5.3. Metal-mediated 2D assemblies
Metal coordination is a powerful tool to build interfaces between protein building blocks in large part due to the strong and directional nature of the interaction. As noted earlier, metal-mediated assemblies can be designed by introducing metal-binding motifs composed of natural amino acids on the protein surface, by conjugating metal-chelating functionalities, or by introducing non-canonical metal-binding amino acids. The Tezcan Group extended their metal-mediated interface design approach to generate periodic protein arrays based on a metal-binding variant of cyt cb562.202 As outlined in Section 3.4.3, the variant RIDC3 assembles into extended 2D crystals under the slow nucleation conditions of low [Zn2+]:[RIDC3] ratios and acidic pH, close to the pI of RIDC3 (~5.3). The crystal structure of the 3D crystal, determined at 2.3 Å, revealed the central role of Zn2+ coordination in the assembly and confirmed that the 3D crystals form through stacking of the 2D layers at pH conditions where inter-layer repulsion is minimized. As shown in Figure 46c in Section 3.4.3, the assembly of the 2D crystals occured through the tiling of antiparallel RIDC3 dimers mediated by the coordination of two Zn2+ ions (Zn1) at the high affinity sites described previously. The key determinants of crystal growth were orthogonal coordination vectors at Zn1 and Zn2, where inter-dimer connections within the plane occur through Zn1-E81 and Zn2-E49, producing an infinite chain along one axis. Finally, a second set of interactions at the lower affinity site with Zn3 and another E49 residue connected the chains along the orthogonal axis.
Subramanian et al. later developed an artificial DNA-protein hybrid architecture based on the RIDC3 building block, which displayed intricate assembly behavior that depended on the synergistic effects of Watson-Crick base pairing, protein-metal coordination, and nucleic acid-protein interactions.298 A Cys residue (C21) was first installed on RIDC3 for site-specific bioconjugation to short DNA strands. Protein-DNA chimeras bearing complementary 10 base-long DNA strands were prepared (Figure 55a) and their co-assembly was screened under a range of conditions where temperature, pH, protein-DNA conjugate concentration, and [Zn2+]:[RIDC3-DNA] ratio were varied. In contrast to the metal-mediated assemblies based on unmodified RIDC3 discussed above, protein-DNA chimeras formed ordered arrays only in a very narrow parameter window owing to the delicate balance of contributing interactions. Structural characterization of the arrays was carried out through a combination of AFM, SAXS, cryo-EM and molecular dynamics modeling to reveal that the layered architecture consisted of V-shaped dimeric modules linked through Watson-Crick base-pairing and a four-coordinate Zn-binding motif (two E27/E31 pairs). The dimers were further linked in an antiparallel fashion to four neighbouring modules through tridentate Zn2+ coordination (E8/D12/H63). The resulting arrangement created a corrugated 2D sheet where the dsDNA domains served as staples between the proteins above and below the plane (Figure 55b). The sheets were capable of stacking in register, such that the DNA domains fit into the open protein-protein interfaces of the sheets above and below where they form non-covalent contacts with the protein surfaces (Figure 55c). This unique, sophisticated architecture illustrated the complexity in the interplay of diverse interactions that contribute to the intricate association of biopolymers in natural nucleoprotein structures such as the ribosome.298
Figure 55.
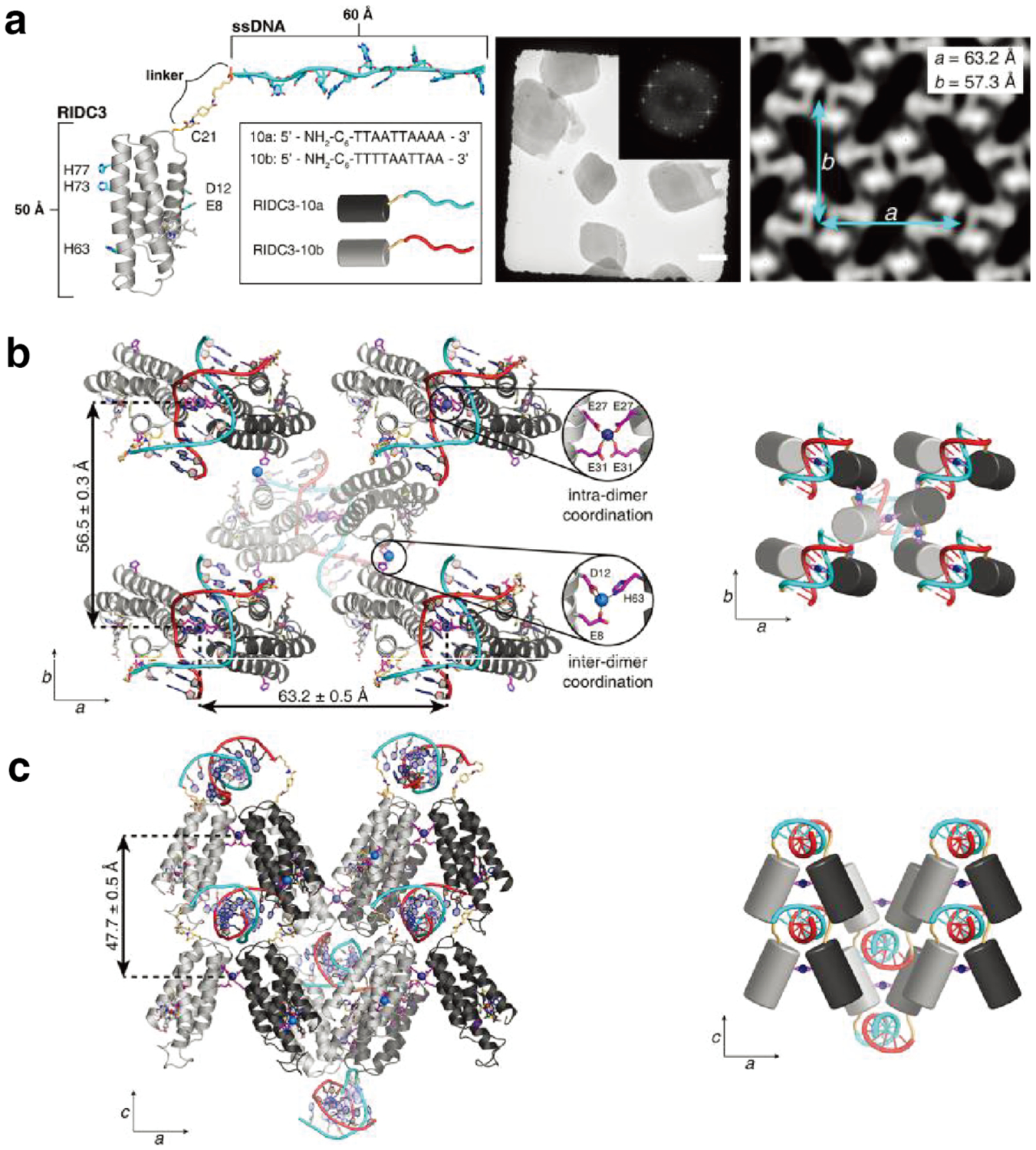
Artificial metal-dependent nucleoprotein assemblies based on a chimeric RIDC3-DNA building block. a) RIDC3-DNA hybrids (left). TEM characterization (middle) and reconstructed 2D cryo-EM map (right) of the RIDC3-DNA 2D crystals. MD-minimized models and cartoon illustrations of b) a single 2D RIDC3–DNA layer and c) the 3D stacking of two RIDC3–DNA layers. Adapted with permission from Ref.298. Copyright 2018 ACS.
In a related approach, Qiao et al. reported the Zn2+-mediated assembly of SMAC, a homodimeric V-shaped building block, into nanowires and wavy 2D layers.480 They installed two bis-His motifs on each monomer (H75/H79 and H137/H141), which adopted a quadrilateral in-plane orientation upon SMAC dimerization. As observed in the case of RIDC3, the two metal coordination sites on SMAC had different binding affinities to Zn2+ ions. Upon metal addition, the H75/H79 sites became saturated first, leading to the formation of zig-zag nanowires, while higher Zn2+ concentrations were required to occupy the orthogonally oriented H137/H141 sites and induce the formation of wavy 2D sheets.
Recently, Yang and Song reported on the genetic incorporation of the unnatural chelating amino acid bipyridine-alanine (bipy-Ala) to drive assembly of various extended structures in 1D and 2D through the selective formation of [Ni(bipy-Ala)2] complexes.481 Acetyltransferase from Bacillus antharsis, a D3 symmetric homohexamer, was selected as a building block for this study based on a number of criteria, including its symmetry being amenable to multidirectional assembly. Amber codon and orthogonal aminoacyl tRNA synthases/tRNA pairs were used to incorporate bipy-Ala at several positions on the top/bottom faces and the lateral faces of the hexamer to screen for 1D and 2D assemblies respectively. Ni2+ was chosen as the target metal ion to drive assembly for its high affinity to bipy chelating groups and its preference for selective formation of [Ni(bipy)2]2+ complexes. Ordered 1D and crystalline 2D assemblies were achieved with optimization of assembly conditions, in addition to combinatorial and hierarchical structures. The incorporation of unnatural chelating amino acids promises to be a powerful approach to expand the repertoire of metal-dependent protein assembly motifs and, by the same token, to diversify the repertoire of orthogonal interaction types available to tune and control protein assembly.
3.5.4. 2D assemblies mediated by protein-ligand interactions
The first example of a designed 2D protein assembly harnessed the specific recognition between streptavidin and biotin, a natural receptor-ligand pair with exceptionally high affinity. Ringler and Schulz combined the C4-symmetric, tetrameric RhuA, and a C2-symmetric linker (streptavidin), to design a 2D array with square geometry.466 RhuA was mutated at three positions (N133C, K261C, and C126S), and the newly installed Cys residues were further labeled with biotin (bR) to enable directional binding of one RhuA molecule to four streptavidin units, producing a cross-shaped construct (bRS4) (Figure 56). Further association of RS4 with bR yielded small 2D arrays limited to roughly 50 × 50 nm in size. Tethering the bR building block to a lipid monolayer interface enabled the growth of arrays up to 200 nm in width. Furthermore, addition of bis-biotinylated streptavidin spacers (bbS) was used to increase spacing between bRS4 hubs, thus controlling mesh size. This early example of 2D protein assembly achieved modest domain sizes, which can be attributed to the low potential for reconfigurability of the associations between proteins due to high biotin-streptavidin affinity and the rigidity of the building blocks. These limitations have since been circumvented through various protein assembly design approaches, as described throughout Section 3.5.
Figure 56.
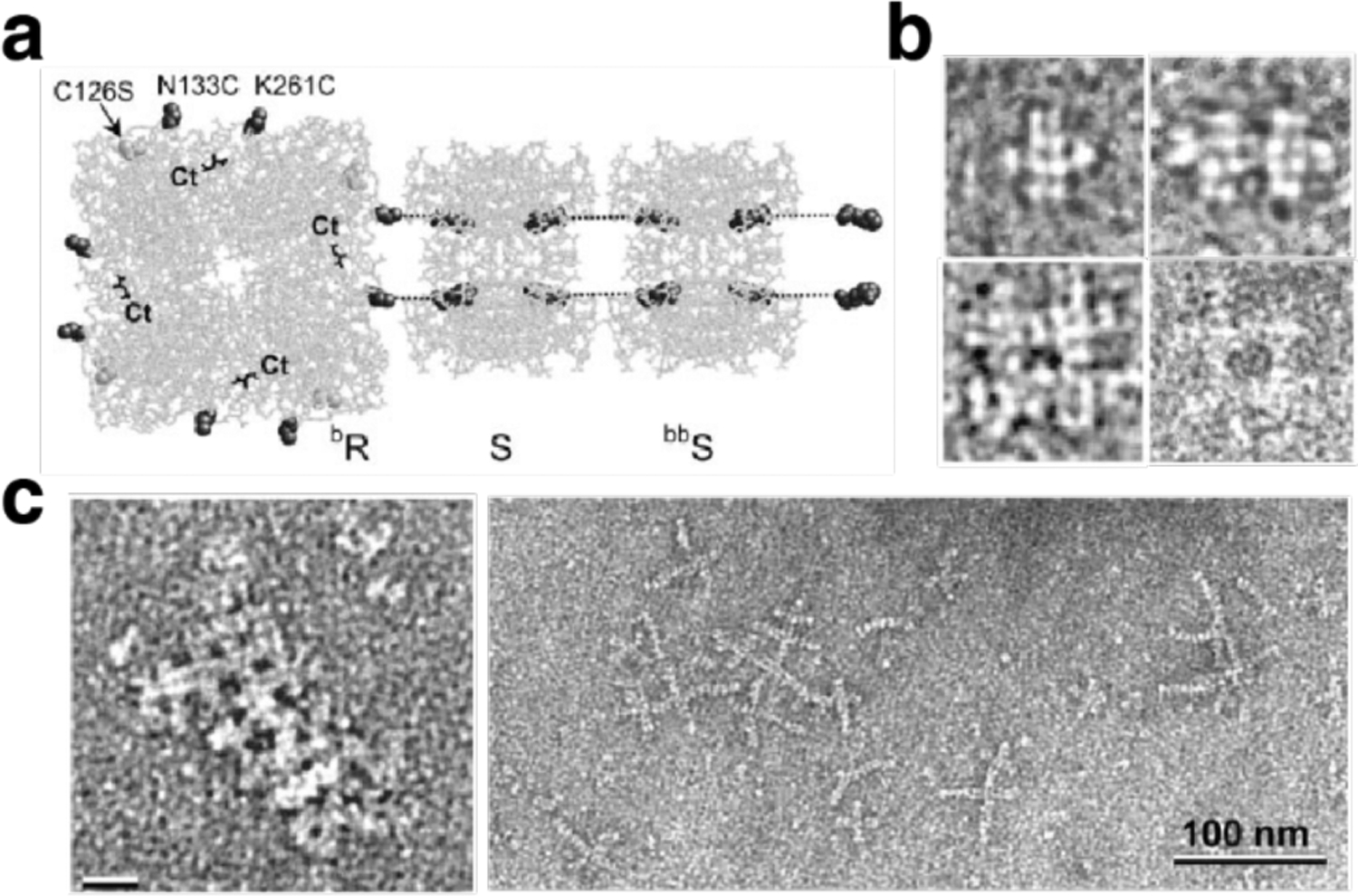
Assembly of biotin-labeled RhuA with streptavidin. a) Schematic representation of the C4-symmetric enzyme RhuA with point mutation for biotin labeling (bR). Streptavidin (S) binds to two biotin labels on each side of bR, to form the building block bR•S. bbS, S bound to bis-biotin linkers, is further bound to bR•S. b) Association of bR and S building blocks imaged by ns-TEM. Clockwise from top left: bR•S4, bR2•S7, bR4•S16•bbS12, and bR4•S12. c) Self-assembled networks produced from bR with bR•S4 (left) and bR•S4 with (bbS•S)x (right) imaged by ns-TEM. Adapted with permission from Ref.466. Copyright 2003 AAAS.
The high affinity of many natural protein-ligand interactions and precise positioning of receptors within the protein architecture provide an attractive means to design protein assemblies by combining native proteins with multivalent ligand mimics. Over the past few years, Chen and coworkers have exploited the specific protein-ligand interactions of sugar-binding lectin proteins in combination with π-π stacking-driven dimerization of RhB to build a range of extended protein assemblies. Following earlier success using dimerizing sugar-RhB conjugates as linkers in the design of 3D crystals (section 3.6.2.2)482 and 1D microtubules (section 3.4.1),270 they have targeted more diverse structures spanning multiple dimensions in recent years. In the first study seeking to diversify the types of assemblies achieved using this linking strategy from a single building block, Yang et al. selected lectin A (LecA) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa as the protein component, a cuboid homotetramer that specifically binds to galactose, and varied the length of the oligo-(ethylene oxide) tether within the sugar-RhB assembly-inducing ligand (Figure 57a).483 They were able to obtain three different LecA packing patterns (Figure 57b) depending on the length of the tether, which corresponded to extended assemblies such as 1D nanoribbons, 2D sheets, and 3D layered structures on the extended assembly scale. 2D sheets were observed with linkers containing 2, 4 or 5 ethylene oxide repeat units within the inducing ligand and arose from a diagonal-diagonal protein packing scheme (Figure 57c).
Figure 57.
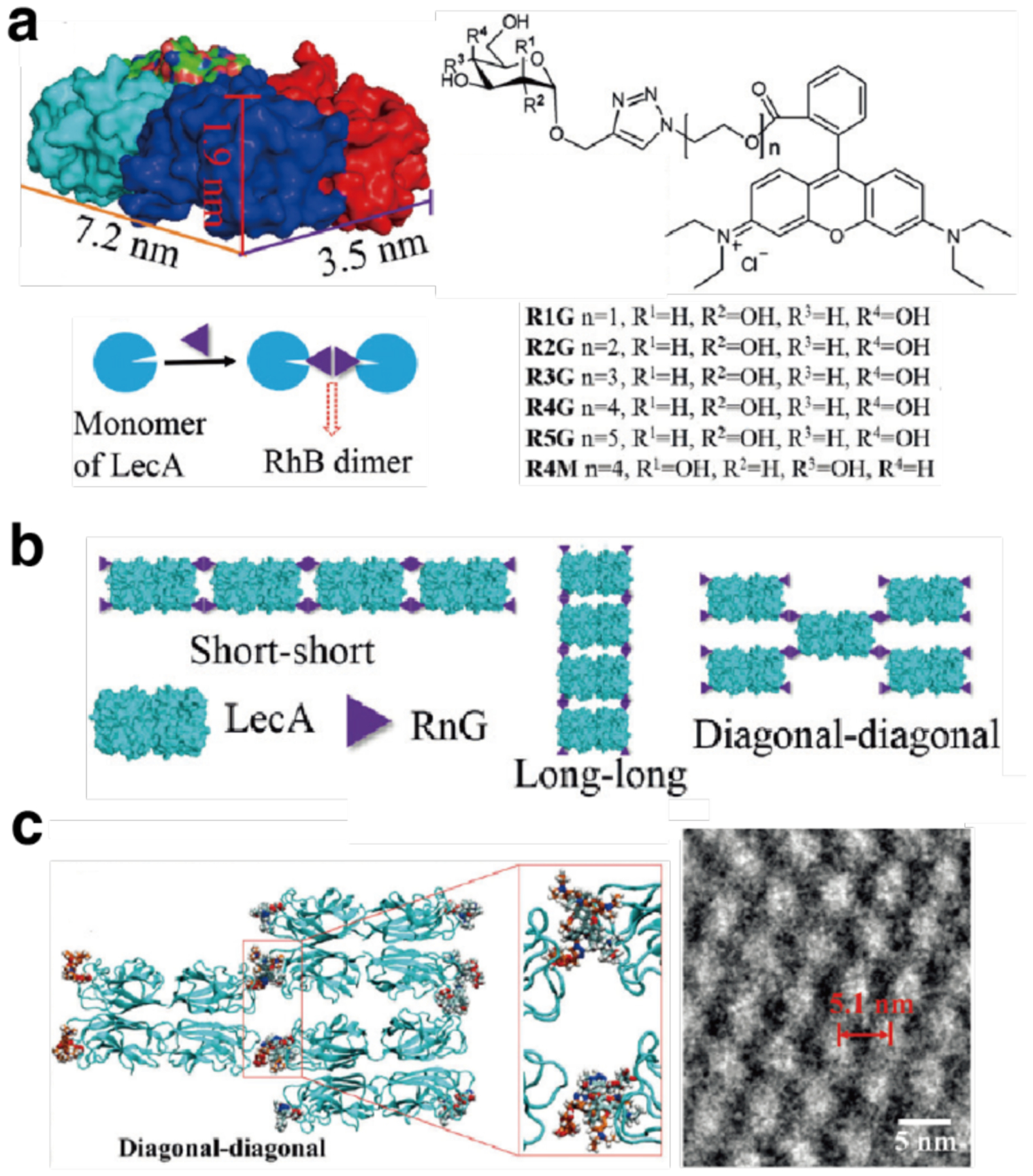
Assembly of LecA via a combination of ligand binding and RhB dimerization. a) Structure of the tetrameric protein, LecA and inducing ligand RnG (n = 1 to 5). Cartoon representation of LecA/RnG dimerization. b) The three packing patterns of LecA/RnG based on the dimerization of RnG. c) Schematic representation of diagonal-diagonal packing of LecA/R2G (left) and enlarged cryo-EM images of a LecA/R5G 2D lattice. Adapted with permission from Ref.483. Copyright 2017 Wiley.
In a further study, the researchers targeted the formation of a Pascal triangle lattice using wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) as the building block and sialyllactoside-RhB conjugate as the assembly-inducing ligand (Figure 58a–b).484 WGA is an anisotropic, horse-shoe-shaped homodimer that bears eight independent carbohydrate-binding sites. The four sites on the top face of the dimer have at least two-fold stronger binding affinity to the carbohydrate ligand than the sites on the bottom face. The anisotropic shape of the WGA dimer, the disparity in ligand affinity, and RhB dimerization all contributed to the success of the design. Triangular units formed first through dimerization of ligands bound to high affinity sites. This was followed by formation of clusters and in-plane polymerization into 2D lattices via the ligands bound to weaker sites in a subsequent step, yielding the targeted periodic Pascal triangle lattice structure at equimolar concentrations of WGA and inducing ligand (Figure 58c–e). Stoichiometric excess of the inducing ligand eventually led to the formation of 3D crystals through saturation of the available binding sites, where both intralayer and interlayer contacts were mediated by RhB dimerization.
Figure 58.
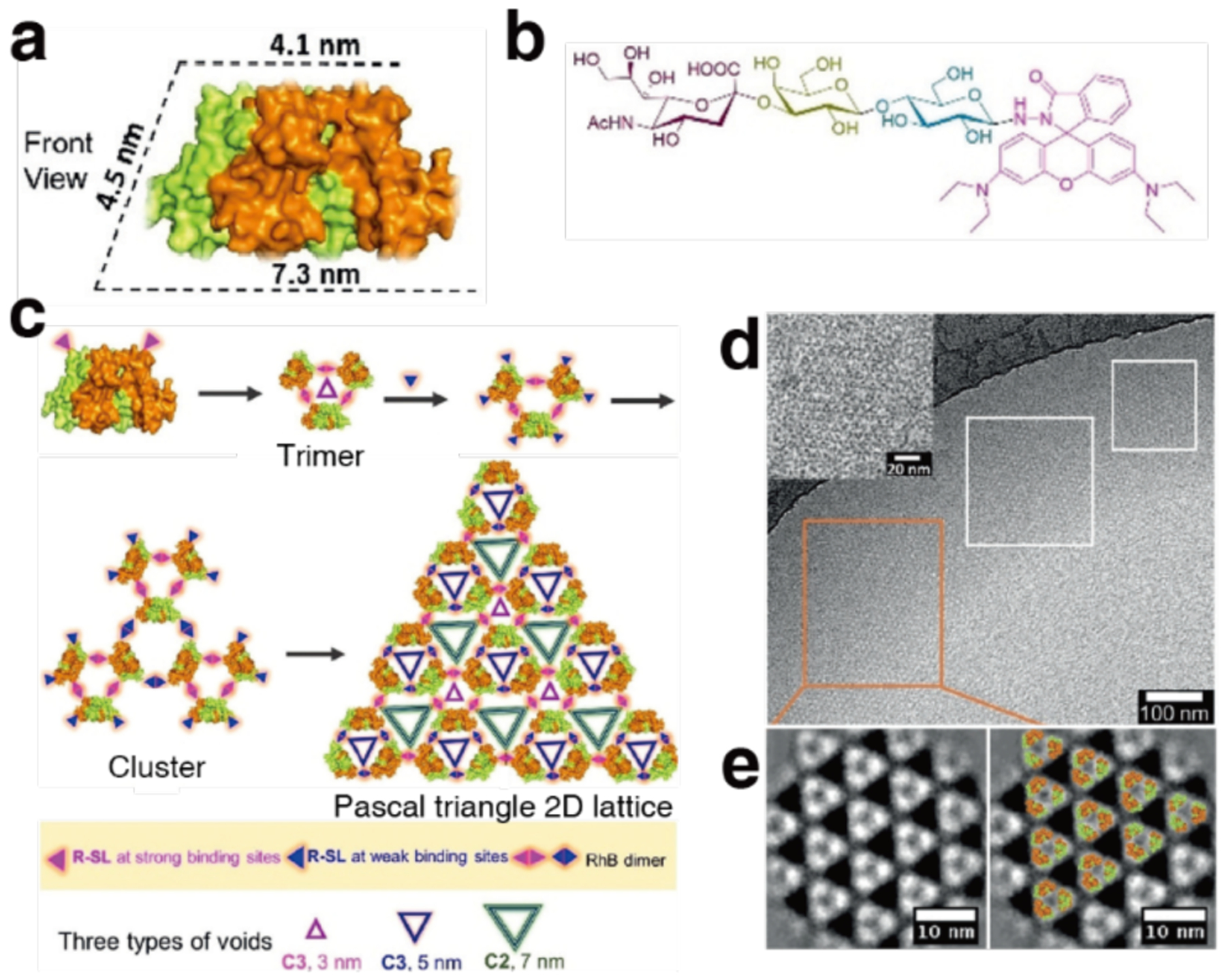
Pascal triangle lattice formation from wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and sialyllactoside-RhB (R-SL). a) Structure of the WGA dimer. b) Structure of assembly-inducing ligand (R-SL). c) Proposed mechanism of WGA assembly with R-SL. d) Cryo-EM characterization of the WGA 2D lattices. Inset: enlarged image. e) Cryo-EM images of the 2D lattice (left), and the overlay of the structural model (right). Adapted with permission from Ref.484. Copyright 2020 Wiley.
In a departure from the typical structurally stable and immutable protein building blocks used in extended assembly, Xu et al. recently exploited the allosteric ligand binding properties of adenylate kinase (AKe) to design a ligand-dependent assembly system that switches from 1D to 2D configuration.485 AKe contains dual recognition domains for ATP and AMP, bisubstrates that induce a conformational change in the enzyme from an open to closed state upon association and undergo a phosphotransfer reaction (ATP + AMP → 2 ADP) (Figure 76c in section 4.2.1). The dynamic protein assembly was designed by converting AKe to an amphiphile through the conjugation of a maleimide-terminated poly-L-valine tail to C77. In the open conformation, the AKe amphiphile assembled into extended 1D fibers of uniform diameter above its critical aggregation concentration under the influence of the hydrophobic effect. Upon addition of equimolar diadenosine-5-pentaphosphate (Ap5A), a tethered unreactive substrate mimicking the dual binding of ATP and AMP, the 1D assemblies were converted to ordered 2D sheets following the conformational shift of AKe from the relaxed open state to the rigidified closed conformation. This study highlights the knowledge gaps in the protein assembly design field when it comes to inherently dynamic building blocks. This area is ripe for investigation toward the development of active protein-based materials and artificial devices based on active building blocks.
Figure 76.
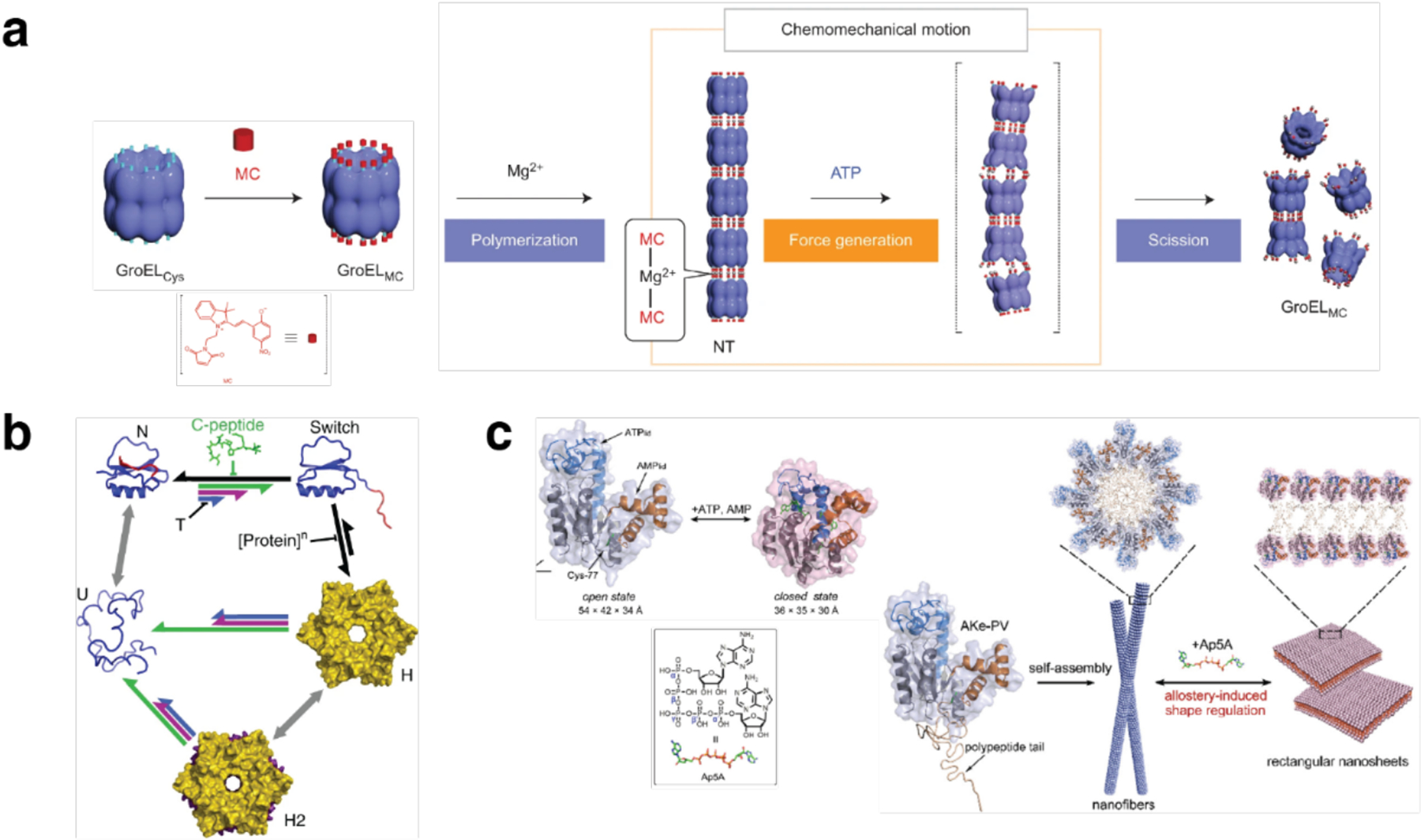
Stimuli-responsive, switchable protein assemblies. a) Mg2+-mediated GroELMC nanotube formation and ATP-triggered chemomechanical nanotube scission. b) Thermodynamic model for allosteric assembly of the engineered Cl2 variants controlled by temperature and C-peptide concentration. All the engineered variants populate the same five species: native monomer (N), fold-switched monomer (switch), hexamer (H), dodecamer (H2) and unfolded monomer (U). c) Adenylate kinase (AKe) in open and closed state (left) and structural transition of AKe-based protein amphiphile assembly from 1D nanofilament to 2D rectangular nanosheet upon Ap5A binding. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.203. Copyright 2013 NPG. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.363. Copyright 2019 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.485. Copyright 2019 ACS.
3.5.5. Computationally designed 2D assemblies
As outlined previously (Section 2.1), natural protein assemblies are characterized by extensive non-covalent interfacial contacts. Along these lines, the Baker Group focused on a general computational approach to design ordered 2D protein arrays mediated by non-covalent interactions.188 To simplify the design process, Gonen et al. targeted layer group symmetries requiring only two unique interfaces between identical, homo-oligomeric building blocks (6 of the 17 possible layer group symmetries). Furthermore, the scope of potential building blocks was limited to proteins with internal point symmetry, as they already contain one of the two required interfaces, and cyclic rather than dihedral symmetry, because of a greater abundance of candidate proteins possessing this characteristic in the PDB. A symmetric docking procedure was applied in Rosetta to first position the cyclic oligomers into the target layer groups. Monte Carlo trajectories for protein orientations were generated and the most shape-complementary solutions with the largest number of contacting residues and the fewest steric clashes were selected. After successive minimization and optimization sequence design steps, 62 candidates were selected for experimental investigation. Three of the designs were reported to form extended, regular, planar arrays, which could be produced both in vitro and in vivo. High resolution structural characterization of these arrays with p321, p4212, and p6 layer group symmetries was carried out by cryo-EM (Figure 59).
Figure 59.

Computationally designed 2D lattices with p321, p4212, and p6 layer group symmetry (designs p3Z_42, p4Z_i9, p6_9H). a) Packing of the designed lattices with the representation of the unit cells. b) Schematic representations of the designed 2D arrays. c) Designed interfaces between protein building blocks. d) ns-TEM characterization of the designed 2D lattices. Inset: enlarged image and FFT of the ns-TEM image. e) Projection map calculated from (d), and the overlay of the designed model on the projection map. Adapted with permission from Ref.188. Copyright 2015 AAAS.
Matthaei et al. combined symmetry docking calculations with a fusion strategy to generate a tiled 2D surface based on naturally-occurring oligomeric proteins with a central pore.486 Following screening of oligomeric proteins from the PDB according to symmetry, shape, termini orientation, and additional criteria, a homohexameric protein (STM4215) was selected for fusion via a flexible hexaglycine linker and interface redesign for a tighter arrangement within the lattice. Addition of Ca2+ ions, which naturally binds to the monomers, rendered the designed fused dimers competent for 2D assembly. Large sheets, typically in the 1 to 10 μm range, but as large as 100 μm, were observed by fluorescence microscopy and ns-TEM allowed to characterize the designed p3 lattice. In a follow-up study, the building block was modified with different functional tags (e.g., hexa-His tag, gold-binding peptide, biotinylation tag) and, upon Ca2+-triggered assembly, was used as a 2D scaffold for the fabrication of hybrid materials by binding AuNPs and proteins to the functionalized array surface.487
Chen et al. later extended the 2015 study188 to a general method for developing 2D protein assemblies based on de novo designed pseudosymmetric protein building blocks.488 The homodimeric de novo designed helical bundle protein was first connected into a single chain. Possible 2D lattices with pseudo-C12 symmetry were screened based on lattice dimensions and rotation of the building block around its central axis. Surface redesign of the de novo protein was then carried out in Rosetta using a standard fixed backbone approach. After identifying a promising design capable of forming extended ordered 2D assemblies that contained exclusively hydrophobic residues at the interface, an effort to improve binding specificity and reduce non-specific aggregation was made by applying the Rosetta HBNet algorithm (see Section 3.2.1) to introduce buried hydrogen bonds at the interface. A design selected after this procedure indeed formed more extended regular assemblies than the fully hydrophobic design.
Most recently, the co-assembly of two protein building blocks into binary two-dimensional layers was achieved by Ben-Sasson et al. by using computational redesign of rigid interfaces between pairs of dihedral protein building blocks.489 Although it required sampling of more degrees of freedom, proteins with dihedral rather than cyclic symmetry were chosen to take advantage of the additional in-plane two-fold rotation axes present in the dihedral structures, which intrinsically corrected for any deviation from the design model that might cause out-of-plane curvature. After arranging the two protein building blocks with their symmetry axes aligned to the 2D layer group, the spacing between them and their orientations were sampled to identify arrangements with contact regions meeting a 400 Å2 surface area threshold and composed mainly of aligned helices. Subsequently, the amino acid sequences at the interfaces were optimized with Rosetta combinatorial sequence design to give low-energy interfaces with a hydrophobic center surrounded by polar residues. Screening experiments led to the discovery of a successful design, a system composed of D3 and D2 homo-oligomers that formed p6m symmetric two-dimensional lattices (Figure 60). In isolation, the building blocks were soluble in the millimolar concentration range. However, once combined at concentrations as low as 10 nM, they quickly assembled into ordered arrays. Assemblies could be formed both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, when interfaced with cell surfaces, the arrays exhibited properties with therapeutic relevance (Section 4.5.2).
Figure 60.

Computationally designed binary 2D protein arrays. a) Orientation of the D3 and D2 symmetric protein building blocks to form a heterogeneous p6m protein assembly (left). Top view of the p6m symmetry operators and the lattice spacing degree of freedom, d (middle). A plausible arrangement of D3 and D2 symmetric building blocks to form p6m lattices (right). b) Interface between the two protein building blocks. c) ns-TEM characterization of p6m arrays formed in E.coli upon co-expression of the two protein building blocks. Adapted with permission from Ref.489. Copyright 2021 NPG.
3.5.6. 2D protein assembly at interfaces
In the 2D protein assemblies described above, the formation of protein arrays was mostly carried out in bulk solution. However, the potential for extensive 2D protein organization through their assembly at interfaces has long been recognized. For example, 2D protein crystallization at lipid-water interfaces has been investigated as early as the 1970s.490,491 More recently, the assembly of SP1 at air-water interfaces, with or without the presence of phospholipids, has yielded large, ordered, hexagonally packed arrays of SP1, a ring-shaped protein that has proved to be a versatile building block for the design of extended protein assemblies (Sections 3.3.4 and 3.5.2).445,467 The 2D crystallization of membrane proteins is also an important goal for investigating this class of protein that can be recalcitrant to forming 3D crystals.492,493 General conditions favoring 2D crystallization at an interface include: 1) the ability of molecules to stay in plane, which reduces translational degrees of freedom and increases local concentration, 2) the mobility of molecules within the plane to enable sampling of possible bonding configurations and correct lattice defects, and 3) the identical orientation of all molecules to favor regular contacts.494
A pair of recent studies have examined the potential of using a solid-liquid interface for programmable control over protein assembly and access to structures that cannot be obtained from bulk solution. Specifically, these studies were carried out on muscovite mica (m-mica) (001), an atomically flat mineral substrate which exhibits pseudo-hexagonal tessellation of charged cavities. These cavities bind to K+ and other cations, an association which affords control over the charge state of the substrate depending on cation concentration.495 Baker, De Yoreo and coworkers were inspired by the carboxylate-rich nature of proteins that interact with minerals and the lattice matching property of ice-binding proteins to investigate the design of protein-inorganic mineral interfaces where the locations of carboxylate residues match the electrostatic and structural features of the m-mica lattice for optimal binding and control of assembly.496 The de novo designed helical repeat protein DHR10, which possesses a flat surface and a regular repeating backbone with spacing equal to a multiple of 5.2 Å, or the nearest-neighbor distance between K+ sites on m-mica, was the chosen protein scaffold. The surface of DHR10 was redesigned with either Glu or Ala residues to match the pattern of K+ ions occupying cavities on m-mica, thus enhancing protein binding to the mineral template (Figure 61a). By changing the length of the protein building block and the mobility of the proteins on the substrate by adjusting salt concentration, the orientational order and patterning of proteins on the surface could be tightly controlled (Figure 61b–c). At low K+ concentrations, individual proteins were observed to bind independently to the surface in designed orientation, whereas at high K+ concentrations, liquid-ordered protein lattices that line up with the m-mica sublattice were obtained, exhibiting ordering over a length scale of many millimeters. Protein interface redesign was used to stabilize different monomer arrangements, allowing formation of 1D wires and 2D honeycomb lattices (Figure 61d–f). Overall, matching protein to substrate structure and tuning the charge state of the substrate allowed the authors to manipulate 2D assembly at the interface with respect to orientation, morphology, and size.
Figure 61.
Assembly of de novo designed helical repeat proteins at the muscovite mica interface. a) Schematic representation of DHR10-mica18 protein binding to the mica substrate through the modulation of a layer of K+ sublattice. b) The protein-mica interface design model predicted the orientation of DHR10-mica18 on K+-saturated mica surface. c) The three predominant orientations of DHR10-mica18 bound to the mica surface with the layer of K+ sublattice characterized by AFM. Assemblies of different variants of de novo designed helical proteins observed by AFM on mica treated with 3 M KCl: d) DHR10-mica18, e) DHR-mica6-NC and f) DHR-mica6-H. Adapted with permission from Ref.496. Copyright 2019 NPG.
In a collaboration with the De Yoreo Group, Tezcan and coworkers revisited the disulfide-linked C98RhuA lattices described above (section 3.5.2)225 to explore their assembly behavior at the m-mica interface.227 The surface of RhuA has a highly anisotropic charge distribution: the flat C-terminal surface is enriched in negatively charged residues, while the N-terminal side (which has a four-legged profile) is more positive (Figure 62a). This distribution endows the protein with a sizeable dipole moment (~1200 D) and simulations show that long-range interactions between the protein dipoles control the symmetry of the p4212 lattice that is observed in solution-grown crystals. By tuning the charge state of the m-mica surface with K+ concentration, this charge anisotropy was harnessed to control the outcome of surface-templated C98RhuA assembly (Figure 62b). At low K+ concentrations (5 mM) both faces of the protein were seen binding to the surface and formed p4, or all parallel, lattices with small domain sizes. In contrast, at high K+ concentrations (3 M), large ordered monolayered p4 arrays were obtained with the C-terminal side interacting with the surface. At increased protein monomer concentrations and 3 M K+, protein bilayer lattices formed under the influence of a salting-out effect. This rich phase behavior (Figure 62c) emerged under the influence of interactions that operate at different length scales. Access to the new p4-symmetric lattice prompted an examination of the properties emerging from an all-parallel arrangement of protein dipoles in the crystal. These properties are further discussed in section 4.4.
Figure 62.
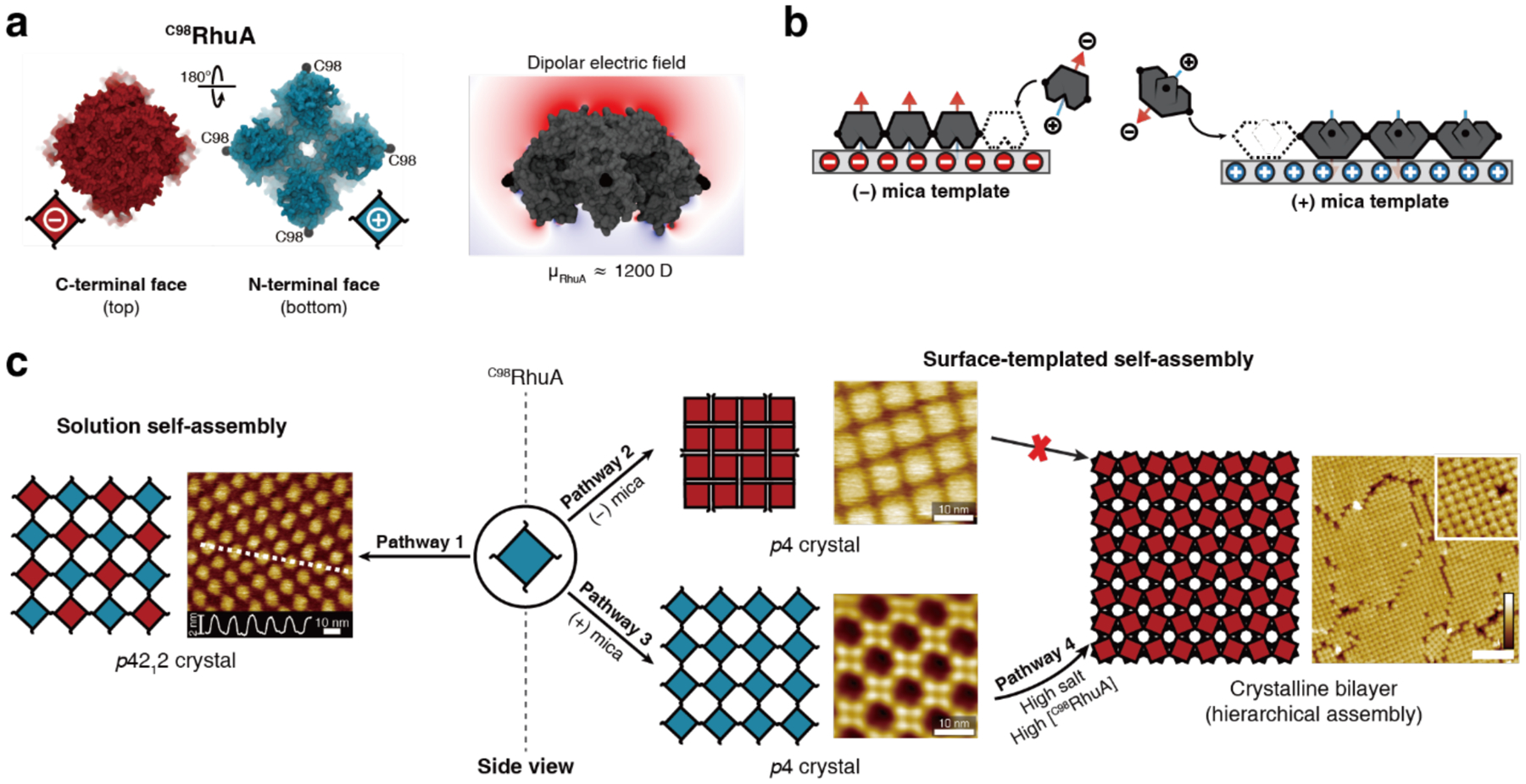
C98RhuA assembly at the mica interface. a) Schematic diagram of the negatively charged C-terminal face and partially positively charged N-terminal face of the C98RhuA tetramer (left), and the large dipole moment of the tetrameric protein (right). b) Preferential adsorption of either the N-terminal or the C-terminal face of RhuA depends on the charge state of the mica template. c) C98RhuA tetramer assembly pathways in solution and templated by the mica surface. Adapted with permission from Ref.227. Copyright 2020 NPG.
3.6. Extended 3D protein assemblies
Current approaches for the design of ordered 3D protein assemblies are largely informed by decades of effort to understand and improve protein crystallization. For a long time, obtaining large, high-quality single crystals to elucidate protein structure by X-ray diffraction was the primary motivation for optimizing protein crystal growth. Conventionally, researchers have varied the physical, chemical, and biological parameters involved in crystallization mixtures (e.g., temperature, pH, ionic strength, addition of ligands) to obtain well-diffracting protein crystals. However, the advent of recombinant DNA technology and the accumulation of structural information from homologous proteins has allowed researchers to better design rational modifications to the protein structure (e.g., improve crystal contacts or induce symmetry that promotes crystallization).497 Protein modification approaches that have improved protein crystallization success rates include: systematic truncation of the primary sequence, removal of post-translational modifications, screening of homologous proteins, or co-crystallization of the target protein with binding proteins or antibodies.498
In recent years, the design of 3D protein assemblies has proceeded mainly through two paths: rational mutagenesis of protein surface residues and addition of effector molecules that promote ordered assembly. The section below briefly surveys the approaches to rationally design protein surfaces and assembly strategies that incorporate different types of intermolecular interactions mediated by small molecules, nanoparticles, or polymeric effectors to drive ordered 3D protein assembly. With the wealth of available protein crystallization approaches, the field of 3D protein assembly has evolved to build ordered materials with potential applications that include storage, nanoreactor development, and control of soft matter properties.
3.6.1. 3D protein assemblies through rational design of protein surfaces
Rational mutagenesis of protein surface residues has been a fruitful approach to improve protein crystallization efforts and enable designed 3D protein assembly. The methods employed broadly target the design of intermolecular interfaces or the symmetrization of the building blocks.
One of the first examples of protein engineering studies to generate 3D crystals was the work of Lawson et al., who mutated HuHF to install metal ion-mediated contacts that facilitate crystal formation.499 Inspired by the propensity of horse spleen ferritin to readily crystallize upon the addition of divalent metals, the authors sought to reproduce the metal-mediated interface in HuHF.500 Specifically, the K86Q mutation, in combination with native D84, led to the formation of large single crystals of HuHF through Ca2+-mediated interactions (Figure 63).
Figure 63.

HuHF crystallization facilitated by Ca2+ contacts at K86Q residues.
Chemical modification approaches have similarly been employed to facilitate protein crystallization. For example, reductive methylation of Lys residues on lysozyme enabled Rypniewski and coworkers to obtain a 1.8 Å resolution crystal structure in 1993.501 Soon after, Rayment et al. reported the first crystal structure of the head portion of myosin by implementing a methylation approach.502 Surface entropy reduction is a related approach which replaces flexible surface residues such as Lys, Glu, or Gln with less flexible residues like Ala to promote crystallization.503
Whether by introducing protein point mutations or bulk modifications, these early mutagenesis approaches are still active areas of research today and have informed subsequent innovations in the development of 3D protein assemblies.497,504 Inspired by a leucine-zipper sequence known to promote formation of a stable protein-protein interaction, Yamada et al. reported the first crystal structure of a mutant human pancreatic ribonuclease 1 (RNase 1) protein.505 Using a strategy termed ‘crystal lattice engineering’, they installed four leucine residues on helix 2 of RNase 1, which promoted interfacial interactions via the designed hydrophobic leucine patches. Based on the 1.7 Å resolution crystal structure, they showed that human RNase 1 was structurally similar to bovine RNase A.
In a recent study, Du et al. took advantage of the symmetry of RhuA to build 3D arrays of different morphologies with minimal sequence modification.506 RhuA has a C4 symmetry axis, with Pro residues located at the C4-symmetric nodes. Notably, its N- and C-terminal faces (or top and bottom faces) have different morphologies and surface charge distributions, conferring anisotropic character to the protein. Upon installing His residues at the N- and C-termini, the RhuA mutants formed ribbons and sheets that assembled into directional 3D arrays. Specifically, the accessible His residues on the top and bottom of RhuA were able to form π-π interactions along the c-dimension to facilitate the stacking of RhuA molecules. Perpendicularly, the Pro residues at the corners of RhuA formed the edge-to-edge contacts along the a- and b-dimensions. By implementing selective point mutations, the researchers were able to obtain a range of 3D constructs that assembled through synergistic interactions, with minimal perturbation to the initial amino acid sequence.
Mutations at specific residues and patches along protein surfaces have led to the successful design of 3D assemblies. In contrast, the Beck Group has relied on changes to the global surface charge of ferritin cages to direct assembly.277 By enriching the surface of HuHF with Arg/Lys or Glu/Asp residues, they created positively and negatively charged ferritin cages, respectively. Mixing the oppositely charged cages led to the self-assembly of binary protein crystals. One unit cell of the resulting tetragonal crystal lattice was composed of four positively and one negatively charged ferritin cages (Figure 64). In a follow-up study, the team explored the impact of divalent Mg2+ on 3D assembly.507 While the binary lattices were maintained at low Mg2+ concentrations, high concentrations of Mg2+ led to the preferential formation of unitary cubic lattices composed solely of the negatively charged ferritin cages with Mg2+-mediated interfaces. These unitary lattices were used as a protein scaffold for the organization of metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized within the cages prior to crystal formation (Section 4.3.4).
Figure 64.
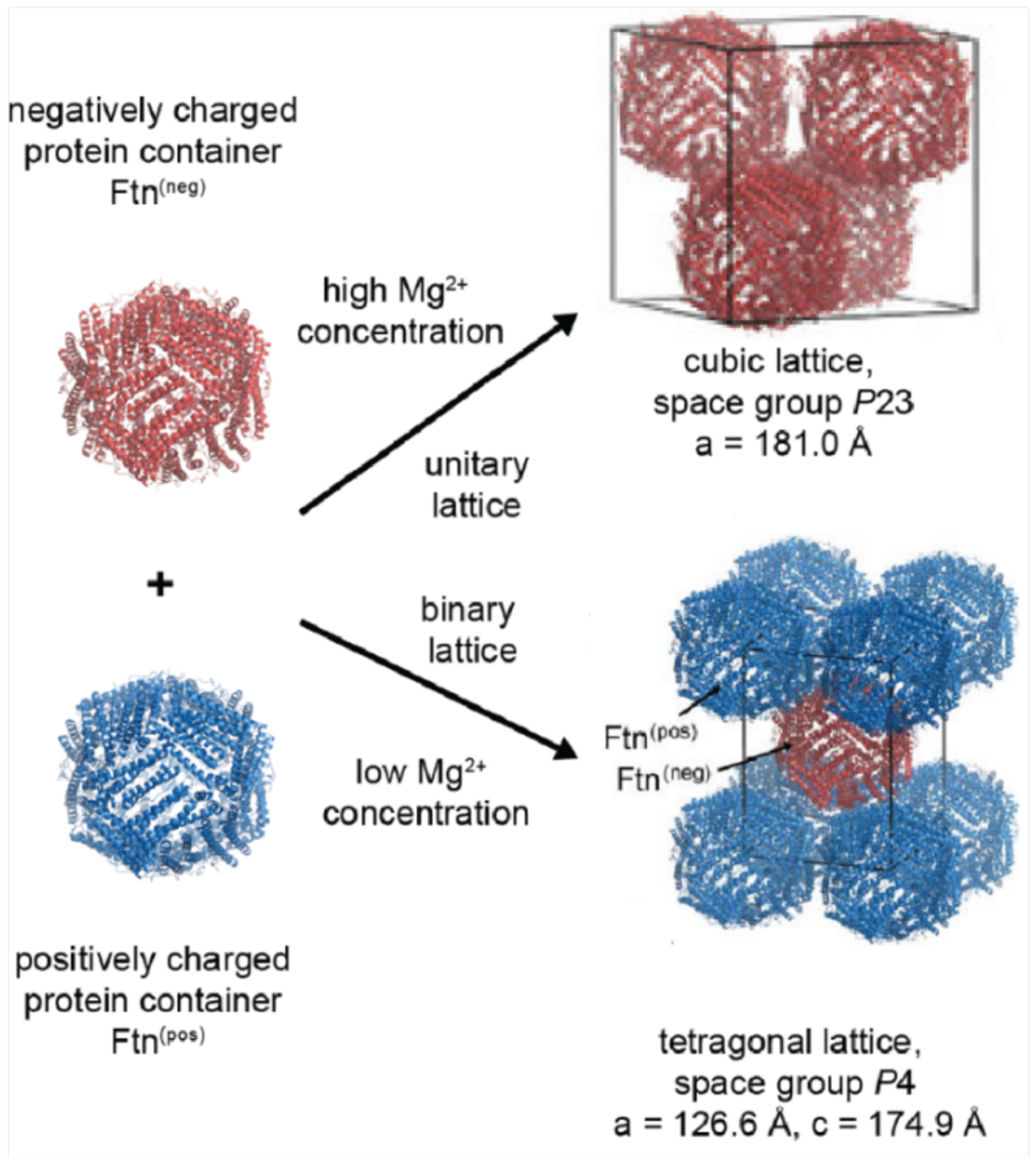
Assembly of charged HuHF lattices. Under low Mg2+ concentration conditions, the mixture of positively and negatively charged HuHF forms a tetragonal binary lattice, whereas when Mg2+ concentration is raised, cubic lattices composed only of the negatively charged variants and mediated by Mg2+ contacts are observed. Adapted with permission from Ref.507. Copyright 2018 ACS.
Design of 3D protein assemblies can be simplified by using symmetric building blocks, which are more likely to form long-range, ordered protein assemblies than asymmetric building blocks. Yeates and coworkers have proposed a “synthetic symmetrization” strategy (Figure 65a) motivated by the observation that protein oligomers tend to crystallize into space groups that support the point group symmetry of the oligomer.223 Synthetic symmetrization involves installing residues that promote self-association on the surface of asymmetric proteins to promote their crystallization. Accordingly, the researchers installed Cys residues at various positions on lysozyme to enable the formation of covalently-linked dimers.223 The lysozyme dimers were then screened for crystallization, leading to the isolation of six crystal morphologies that had not been previously observed in lysozyme crystals. This work demonstrated that protein symmetrization did not only improve protein crystallization but also expanded the list of accessible crystal morphologies. In a follow-up study, the monomeric protein CelA, known to be a difficult crystallization target, was subjected to the same disulfide bond-mediated dimerization approach (Figure 65b–d).508 This method of creating synthetic homodimers enabled the crystallization of CelA and structure determination at 2.4 Å resolution.
Figure 65.
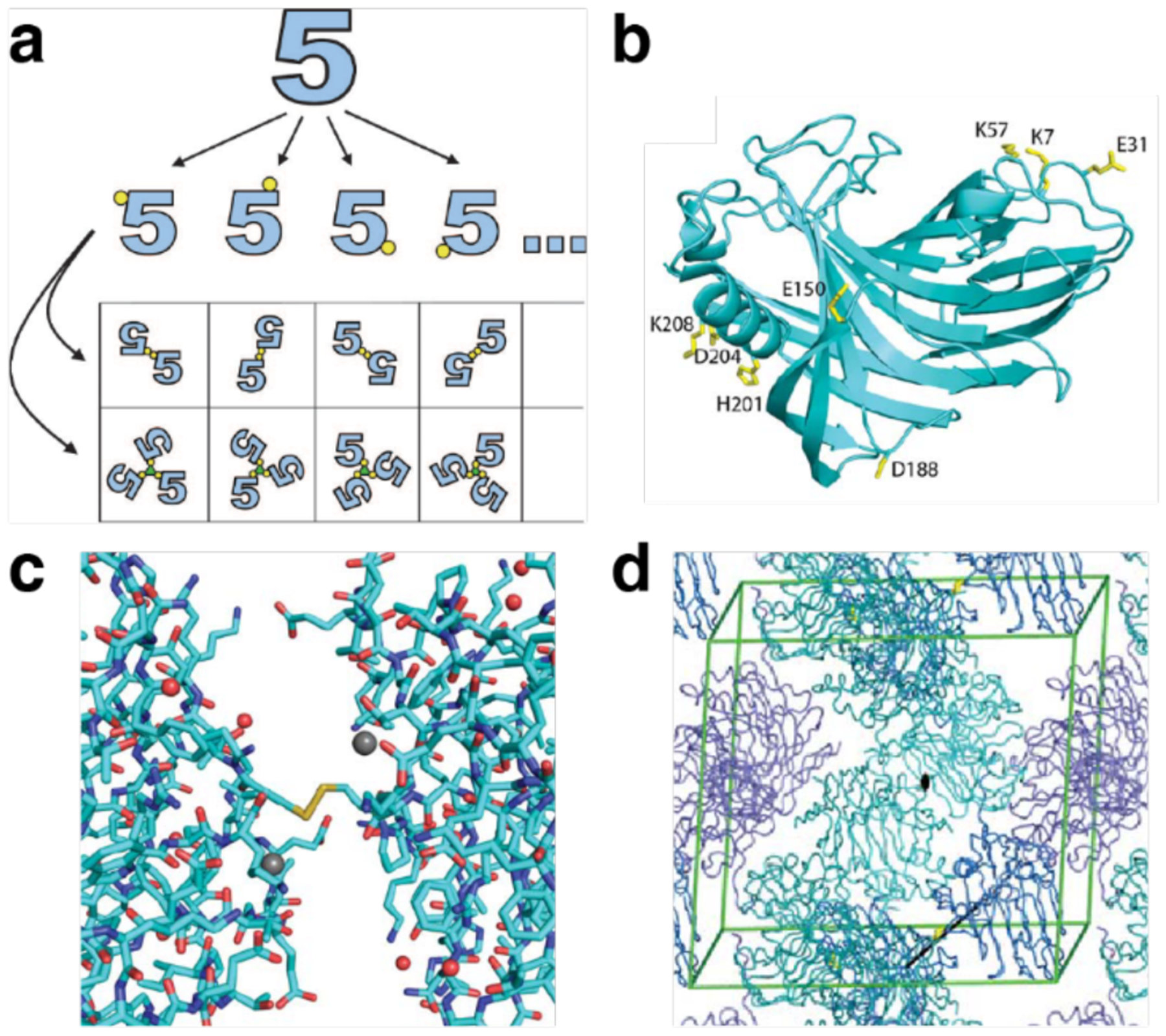
Synthetic symmetrization via Cys residues introduced by mutagenesis. a) Illustration of synthetic symmetrization. An asymmetric protein monomer is represented by the figure “5.” Cys residues introduced at different positions on the surface are shown in yellow. Dimerization is achieved via disulfide bond formation. Trimerization requires a trivalent mediator. b) Illustration of the approach using CelA. Eight positions were selected for mutation to Cys. c) Interface for disulfide-bonded monomers of the D188C variant obtained by XRD. Very few contacts, other than the disulfide bond, are observed. d) Crystal packing of the D188C dimer. Adapted with permission from Ref.508. Copyright 2011 Wiley.
The synthetic symmetrization approach was expanded to use discrete metal-binding to promote self-association of asymmetric protein building blocks into ordered assemblies. Using T4 lysozyme (T4L) and maltose-binding protein (MBP) as model systems, Laganowsky et al. installed His and Cys residues and incubated the mutants with metal ions (Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+) to form 3D protein crystals.509 The metal-binding sites were placed near the ends of the helices to form accessible binding sites and reduce steric hindrance. Upon metal addition, the proteins crystallized into 3D architectures featuring metal-ligand interactions between the exogenous metal and metal-binding amino acid residues at the protein surfaces (His, Glu, Asp). Notably, the metal-ligand complexes had octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar coordination geometries.
A related example of synthetic symmetrization via metal binding was reported by Brodin et al., who developed ordered metal-mediated assemblies in 1D, 2D and 3D based on RIDC3, a variant of the asymmetric building block cyt cb562.202 As detailed in Sections 3.4.3 and 3.5.3, in this assembly system, the strong Zn2+ binding site first promoted association of two RIDC3 molecules into an antiparallel dimer (symmetrization of an asymmetric building block), and the dimers further underwent long-range assembly through additional Zn2+-mediated interactions.
The Zhao Group has used HuHF surface modifications to generate 2D and 3D square arrays. By installing aromatic residues – phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr), or tryptophan (Trp) – at the 162 position of HuHF, Zhou et al. converted the C4 axis “hot spots” to hydrophobic patches prone to self-association via π-π interactions (Figure 66).470 The Phe mutant gave rise to 2D assemblies, while both the Tyr and Trp variants underwent further assembly into cubic 3D superlattices. The authors attributed the difference in assembly outcome on altered configuration of the π-π contacts depending on the aromatic ring substituents. The assembly process was reversible and sensitive to pH and salt concentration, parameters which influenced π-π stacking interactions and contributed to the screening of ferritin surface charges.
Figure 66.

2D and 3D arrays based on HuHF bearing aromatic residues at the C4 axes. a) The three 4-fold symmetry axes of the HuHF nanocage, Glu162 near the axis is shown in red. b) HuHF cages bearing aromatic residues at the 162 position undergo assembly into 2D nanosheets (R = Phe) or 3D superlattices (R = Tyr or Trp). c) ns-TEM characterization of 2D arrays formed by Phe162 HuHF variant. d) Unit cell obtained by SAXS and ns-TEM micrograph of 3D superlattices formed from Tyr162 HuHF. Adapted with permission from Ref.470. Copyright 2018 ACS.
In a further study, Zheng et al. explored the pH-dependent formation of 2D and 3D arrays based on HuHF modification with the amyloidogenic “GLMVG” peptide motif at the C4 symmetry axis.471 The hydrophobic motif was installed by replacing the native residues 159–163 in a solvent-exposed region around the C4 axes with the amyloidogenic sequence. At pH 9.0, the modified cages remained dispersed in solution. However, under more acidic conditions (pH 5.7), just above the theoretical pI for ferritin (~5.3), they quickly formed 2D sheets. With further incubation, the 2D assemblies first increased in size and later transformed into cubic 3D arrays. The same structures were observed at pH 6.5, albeit the assembly proceeded at a much slower rate.
With the diversification of approaches to protein surface engineering, the pace of growth of the protein assembly field has accelerated, producing an expanding range of ordered 3D assemblies. In addition to augmenting the protein units themselves, symmetrization of protein building blocks has been a useful means to drive long-range, ordered assembly.
3.6.2. Effector-mediated 3D protein assembly
The addition of external functionalities as effectors to facilitate 3D protein assembly has been a widely studied method. Small molecules, nanoparticles, or polymers, whether added as part of a physical mixture or covalently conjugated to the protein of interest, widen the scope of potential interactions and symmetry elements available to mediate the contacts between proteins in ordered, extended assemblies.
3.6.2.1. Metal-directed 3D assemblies
The introduction of metal-binding groups on protein surfaces is a common approach to promote ordered protein assembly. In addition to providing small-footprint binding motifs for developing protein-protein interfaces, metal-coordination enables the introduction of directionality and symmetry that promotes organization.202,509 Although selective mutagenesis of the protein surface has proven to be successful for assembly design, conventional methods employing only the canonical amino acids are limited in terms of accessible metal-binding functionality and geometric diversity.
To combat this limitation, researchers have harnessed post-synthetic protein modification through conjugation of small-molecule ligands onto the protein surface. In an early study, Radford and Tezcan conjugated a Cys-specific iodoacetamide derivative of phenanthroline (IA-Phen) ligand onto Cys59 of a cyt cb562 variant to form MBP-Phen1.208 Titration studies with first-row transition metals indicated that Ni(II) tightly associated with MBP-Phen1 to form quaternary structures. The MBP-Phen1 mixture with Ni(II), yielded crystals with two different space groups, P21 and P6322. Specifically, MBP-Phen1 assembled into unique triangular structures with each vertex formed through the coordination of a Ni atom to the phenanthroline ligand from one protein monomer and His77 from another (Figure 67a), whereby three Ni atoms were positioned in the same plane to form a Ni3:MBP-Phen13 triangle. These trimers then stacked into a hexagonal geometry to form the P21 and P6322 crystals (Figure 67b). A closer examination of the crystal structures revealed that the Phen groups fit into a small hydrophobic crevice covered by a flexible loop and were further stabilized by a H-bond between the Cys59 amide nitrogen and the Pro53 backbone carbonyl. These interactions stabilized MBP-Phen1 and favored the open configuration of the Ni3:MBP-Phen13 complex, as the hydrophobic crevice sterically hindered a second Phen group from coordinating to Ni and allowed only one other monomer to coordinate through His77. In a follow up study, the researchers investigated the influence of the hydrophobic environment on the Phen group and whether alternative protein oligomers/frameworks can be achieved.510 In a similar study, Douglas and coworkers conjugated phenanthroline ligands onto DNA binding protein from starved cells (DPS) cages and induced iron-mediated assembly.511 Although the obtained assemblies were not crystalline, this study represented another early example of integrating exogenous metal-binding ligands on the protein surface.
Figure 67.

Ni-mediated assembly of phenanthroline-modified cyt cb562 variant MBP-Phen1. a) Ni3:MBP-Phen13 assembly (left) and coordination environment of Ni-PhenC59 (right). b) Ni3:MBP-Phen13 lattice packing arrangement in the P21 and P6322 crystal forms. Adapted with permission from Ref.208. Copyright 2009 ACS.
Sontz et al. applied MDPSA to create 3D crystalline protein frameworks akin to metal organic frameworks (MOF) (Figure 68).129 Specifically, by exploiting the inherent symmetries of octahedral (432) HuHF cages and C2-symmetric ditopic organic linkers, the researchers successfully formed large, modular crystalline frameworks that were termed protein-MOFs. They prepared the T122HHuHF variant, positioning His residues at the C3 rotation axes of the cage, to generate tripodal coordination motifs for Zn2+ ions. Incubation of T122HHuHF with Zn2+ yielded crystals with face-centered cubic (fcc) packing, where Zn2+ ions located at the C3 axis pores adopted near-ideal tetrahedral geometries between the three His122 residue ε-N’s and a water molecule. Characterization of the mixture in solution by DLS suggested that the Zn ions did not drive solution-phase assembly. In contrast, addition of the rigid ditopic linker benzene-1,4-dihydroxamic acid gave rise to rhombic dodecahedral crystals in solution. Structure determination at 3.8 Å resolution revealed a body-centered cubic (bcc) lattice (I432 space group) with electron density at the expected organic linker position. This work introduced a new class of hybrid protein framework materials composed of a ternary mixture of proteins, metals and organic linkers, where the proteins acted as large nodes bridged by metal ions and organic linkers.129 In follow-up studies, Bailey et al. expanded the library of protein-MOFs. By screening different dihydroxamate linkers with various metal ions (Zn2+, Ni2+, and Co2+), they obtained an array of lattice arrangements (15 ferritin-MOFs), demonstrating the modularity of the system.512,513 One of the permutations led them to fdh-Ni-HuHF, a protein-MOF with unusual thermomechanical properties detailed in Section 4.4.
Figure 68.
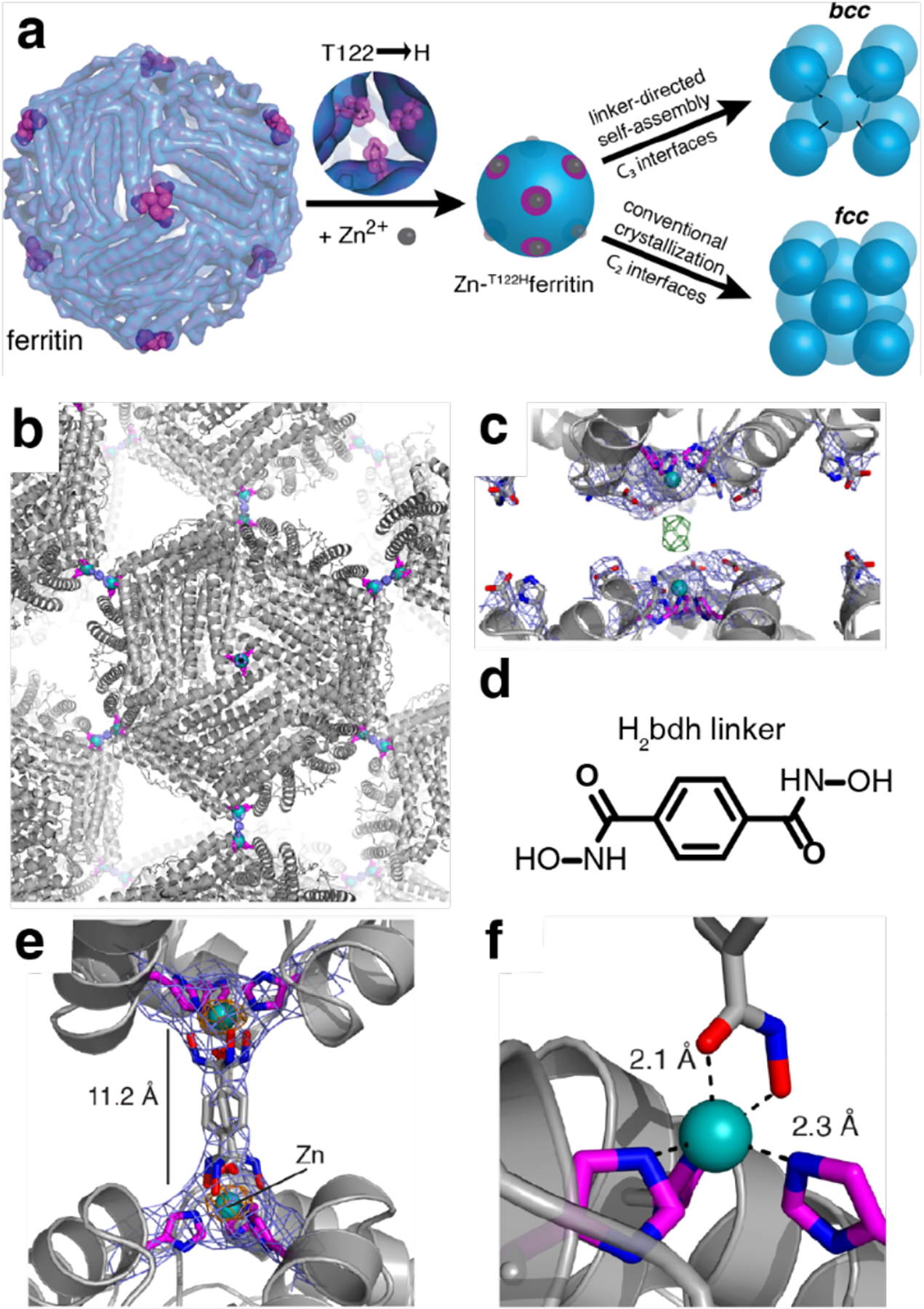
Protein-MOF assembly. a) Metal/linker-directed self-assembly of ferritin into 3D crystals. b) The bcc packing of the bdh-Zn-T122Hferritin lattice, mediated by bdh2− bridges across the C3 symmetric ferritin interfaces. c) View of C3 symmetric interfaces between neighboring ferritin molecules, showing the lack of direct protein–protein contacts and the presence of electron density between Zn2+ ions (2Fo−Fc map: blue-1σ; Fo−Fc map: green-3σ). d) Structure of H2bdh linker. e) Closeup view of the three crystallographically related bdh2− rotamers that bridge neighboring ferritin cages. f) Modeled bdh-Zn coordination. Adapted with permission from Ref.129. Copyright 2015 ACS.
3.6.2.2. 3D assemblies through receptor-ligand interactions
In addition to metal-binding organic linkers, receptor-ligand interactions have also been employed to mediate 3D protein assemblies. Early works by Sacchettini and Brewer investigated the sugar-mediated assembly of the lectin protein soybean agglutinin (SBA).514,515 SBA is a tetrameric protein that specifically binds to GalNAc/Gal sugars. In the presence of bivalent saccharides, SBA is crosslinked and forms a hexagonal lattice with a P6422 space group, which differs from the crystals of the free protein.514 In a related study, different ligands were used to crosslink SBA, which gave rise to crystals with the same P6422 space group, but different unit cell dimensions.515 A subsequent study by Dotan et al. described the formation of 3D protein assemblies exploiting another tetrameric lectin protein, concanavalin A (ConA).516 Similarly to the work by Sacchettini and Brewer, Dotan et al. used a bivalent saccharide with C2 symmetry to rationally connect ConA units. Interestingly, the quaternary structure of ConA is almost tetrahedral, and the researchers surmised that the addition of a symmetric ligand would yield a diamond-like lattice. Bismannopyranoside, a bismannoside (bis-Man) unit with a C2 spacer, was synthesized and incubated with ConA to form a protein crystal. Analysis of the 6-Å resolution structure revealed a pseudo-cubic orthorhombic unit cell (F222 space group). Results from single crystal XRD and auxiliary electron microscopy observations confirmed that ConA formed a diamond-like lattice as intended by rational design. These investigations of sugar-binding proteins provide some of the earliest examples of 3D protein crystals whose lattice arrangements were dictated by synthetic effector molecules.
In a more recent study, Sakai et al. displayed added control over ConA Man-mediated assembly.482 Rather than using symmetric bis-Man linkers, the researchers conjugated RhB onto Man, with an oligo(ethylene glycol) spacer, and relied on the π-π stacking-mediated dimerization of RhB to drive protein assembly. Control of the spacing between the sugar groups and RhB, enabled the assembly of ConA into interpenetrating and non-interpenetrating lattices. When three repeating units of ethylene glycol ware used as the spacer, ConA formed lattices with P21 packing, a non-interpenetrating protein crystalline framework. However, extending the linker to four repeating units led to the formation of an P21212 interpenetrated lattice (Figure 69). As discussed in Sections 3.4.1 and 3.5.4, the coupling of protein-ligand binding and dimerization of RhB moieties by π-π interactions has been a versatile approach to generate ordered protein assemblies in 1D, 2D and 3D.270,483,484
Figure 69.

Molecular packing of the Concanavalin A (ConA) and Mannopyranoside-RhB ligands in the 3D crystal. a) Packing in one layer of the crystal. b) Simplified packing model. ConA units shown in red and blue. Molecules of the same color are crosslinked via dimerizing ligands. c) The conformation of the ligand at the dimerization interface. Adapted with permission from Ref.482. Copyright 2014 NPG.
3.6.3. Electrostatically directed 3D protein assembly
3.6.3.1. 3D assemblies mediated by small molecules
Electrostatic charge complementarity between the protein surfaces and effectors is one of the most accessible approaches for forming ordered 3D assemblies. Kostiainen and coworkers have used incubation of ferritin with various cationic molecules toward this end.309,517 In one study, Mikkila et al. used zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) and pyrene derivatives to induce co-crystallization of a ferritin variant.309 Specifically, the pyrene and ZnPc small molecules formed a supramolecular complex carrying a positive charge, which acted as a molecular glue to facilitate protein-protein contacts between the negatively charged patches on the ferritin surface to mediate the formation of co-crystals. The resulting ternary lattices displayed fcc packing and retained the optical properties of the dye molecules. In a conceptually related study, upon screening the co-assembly of apoferritin from Pyrococcus furiosus with a library of cationic macrocyclic cyclophane hosts, Beyeh et al. found that by optimizing the number and orientation of electrostatic interactions between the protein cage and host molecule it was possible to generate porous cyclophane-cage networks.517 A pillar[5]arene with ten protonatable amines was shown to be an optimal host, giving rise to porous framework structures containing large interconnected voids between the protein cages. The macrocycles were located at the C3 axes of ferritin, electrostatically bridging the proteins to form a fcc lattice. The authors envisioned the use of the frameworks in heterogeneous catalysis by using the cyclophanes to trap guest molecules in close proximity to catalytic sites on the biomolecules, or for the development of water remediation materials.
Similar studies of protein-small molecule assemblies were carried out by Crowley and coworkers with the protein cytochrome c (cyt c) and the sulfonato-calix[8]arene (sclx8) macrocycle.518 Upon screening different crystallization conditions, the researchers found that sclx8 acted like a molecular glue by facilitating the formation of cyt c-sclx8 complexes in three different crystal forms (corresponding to the space groups P31, H3, and P43212). Under various conditions, sclx8 adopted similar extended conformations and was sandwiched between two cyt c units. Specifically, two double cone calixarenes were closely packed around the K4 residues of the protein (Figure 70). In a follow-up study, Engilberge et al. demonstrated that crystal porosity can be modulated with another positively charged small molecule, spermine.519 Taking advantage of the host-guest interactions between spermine and sclx8, the researchers could modulate sclx8-mediated protein self-assembly by spermine addition and obtain four additional crystal structures. Applying a similar approach, in combination with metal-dependent interactions, Guagnini et al. were able to control the crystal lattice formation of Penicillium chrysogenum antifungal protein B (PAFB), an anionic protein rich in His residues.520 On its own, PAFB has been shown to crystallize into a C2-symmetric lattice with 1.1 nm wide pores. Upon the co-crystallization of PAFB with Zn2+ and sclx8, crystals of H32 symmetry with 2.2 nm wide pores were formed. The Zn2+ ions formed trinuclear metal clusters and mediated protein assembly. Both supramolecular interactions – sclx8 complexation and zinc coordination – worked in synergy to alter the resulting crystal lattice. Similarly relying on electrostatic contacts between protein and effector, Voet and colleagues used polyoxometalate clusters that carry a negative charge with de novo designed oligomeric proteins Pizza-6s and Tako8 to generate cocrystals with various packing geometries.521,522
Figure 70.

Co-crystallization of cyt c and sulfonato-calix[8]arene (sclx8). Crystal packing in space groups a) P31 b) H3, and c) P43212. Cyt c, sclx8 and unit cell axes are depicted in gray, green and blue, respectively. d-f) The sclx8 mediated protein-protein interaction for each lattice. Adapted with permission from Ref.518. Copyright 2018 Wiley.
3.6.3.2. 3D assemblies through interactions with nanoparticles
Further taking advantage of the tunable effective net charge on protein surfaces, researchers have exploited the complementary electrostatic interactions between proteins and nanoparticles of different composition (metal, polymer, other proteins) to control protein self-assembly. For example, Kostiainen et al. incubated positively charged, 7−9 nm AuNPs with CCMV or ferritin, protein cages that carry patches of negative charge, to form ordered binary 3D lattices.272 The mixture of CCMV and AuNPs produced AB8fcc lattices, a lattice type that had only previously been observed for large colloidal polymer particles and did not have a known atomic or molecular crystal counterpart. On the other hand, the mixture of ferritin and AuNPs gave rise to interpenetrating simple cubic AB lattices akin to CsCl crystals. This study illustrated the potential of using small inorganic particles to organize patchy proteins into ordered 3D assemblies.272 Further examples of functional 3D protein assemblies incorporating metal nanoparticles are described in Section 4.3.4.
Liljestrom et al. furthered this design approach by using a protein as the oppositely charged counterpart to the larger protein cages instead of AuNPs. Upon incubating CCMV with avidin, they observed self-assembly of binary 3D lattices integrating both protein types.279 Avidin is a 7.5-nm wide protein with an isoelectric point of ~10.5. Both the size and charge of avidin work synergistically to facilitate the co-assembly of a binary lattice with CCMV cages. The resulting lattice could be modified pre- and post-assembly through the binding of biotinylated fluorescent dyes to the avidin molecules incorporated in the lattice (Figure 71). The same biotinylation strategy was used to immobilize HRP or AuNPs within the lattice. This work represents another example of exploiting global electrostatic interactions between protein particles to form ordered 3D arrays.279
Figure 71.
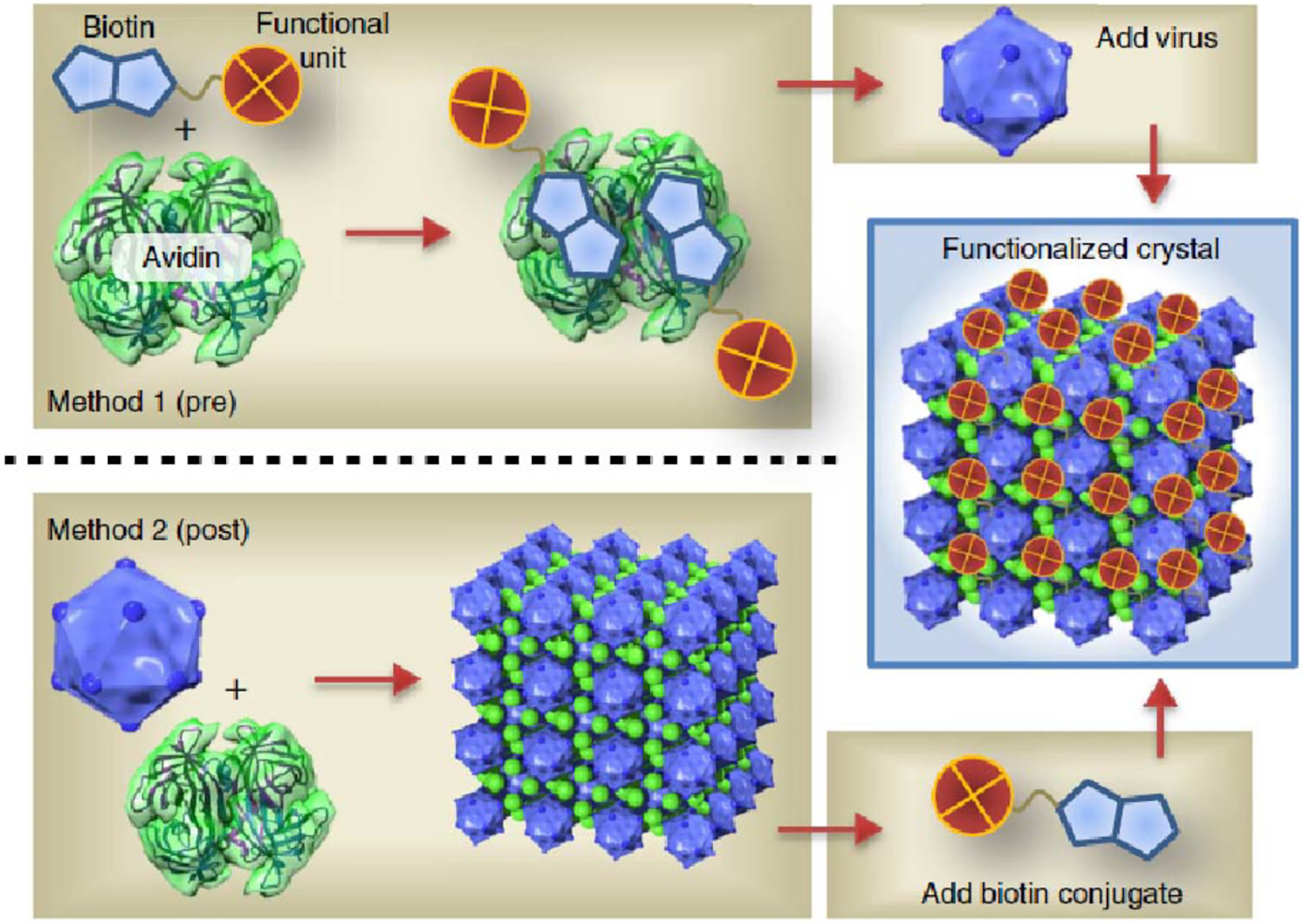
Pre- and post-functionalization of CCMV-avidin co-crystals through biotin-avidin interactions. Method 1 and 2 describe the pre- and post-functionalization approaches, respectively. Both methods yield a functionalized 3D crystalline array. Adapted with permission from Ref.279. Copyright 2014 NPG.
Charged dendritic polymers provide a modular synthetic system for mediating protein assembly through electrostatic interactions. Upon the incubation of CCMV with a cationic PAMAM dendrimer, Kostiainen et al. formed a hybrid 3D protein-polymer array.271 By screening differently charged cationic polymers and ionic environments, they determined that effectors carrying a charge greater than +4 (corresponding to four cationic amines) were necessary to achieve complexation. In a follow-up study, Liljestrom et al. incubated ferritin cages with PAMAM to yield ordered 3D lattices.523 Screening different salt conditions allowed them to control the lattice packing between cubic and hexagonal arrangements.
Following up on this work, Douglas and coworkers used cationic dendrimers to pre-organize the VLP P22.293 VLP P22 exhibits a negative charge on its surface and is able to bind to the capsid decoration protein (Dec). Upon creating C2 symmetric Dec proteins and incubating them with P22, the researchers were able to lock the P22 cages into place after initially templating 3D lattice formation via interaction with the dendritic polymer (Figure 72). The strong binding of Dec to P22 produced a highly crosslinked protein material which contributed to capsid stabilization. The dendrimer-mediated templating step was important in the preparation of the material, as simple mixing of Dec with P22 cages led to the formation of amorphous protein aggregates.
Figure 72.

Construction of a VLP-based macromolecular framework. Negatively charged P22 VLPs are mixed with either a) Dec cementing proteins or b) positively charged PAMAM generation 6 dendrimers (G6) to form an amorphous array or an ordered array, respectively. c) High ionic strength conditions disrupt the P22-G6 interaction. d) Dec cementing proteins added to the P22-G6 lattice lock the P22 particles in place, preserving the ordered structure. e) High ionic strength conditions are used to wash away the G6 dendrimers, leaving behind a protein-only lattice. Adapted with permission from Ref.293. Copyright 2018 ACS.
Interactions between proteins and small molecules, proteins, or polymers bearing complementary charge states exploit electrostatic interactions to facilitate ordered assemblies. These assemblies highlight the generalizability of the approach for future development.
3.6.4. 3D protein-DNA hybrid lattices
The base pairing of complementary nucleic acid sequences is another type of interaction that has been widely used to organize biomolecules into ordered arrays.524,525 Researchers have used nucleic acids to create an expansive library of nanoscale architectures, primarily through the highly specific Watson-Crick base-pairing interactions between DNA strands with designed sequences.303–306 Important advantages of incorporating nucleic acids into designed assemblies include predictable interparticle distances, controllable annealing/melting temperatures, and precise spatial addressability controlled by sequence design.306,526,527
The predictability of nucleic acid sequence-dependent pairing interactions allows researchers to rationally design assemblies and has been used synergistically with proteins to create hybrid materials. Exploiting the specificity of DNA, Strable et al. conjugated single-stranded DNA onto the surface of cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) cages and incubated them with another batch of CPMV labeled with complementary DNA strands.307 At 4 °C, the CPMV-DNA conjugates assembled into small hexagonal arrays and grew into 3D aggregates after heating to 35 – 40 °C. In later reports, researchers have been able to create more ordered lattices using DNA. For example, Cigler et al. successfully utilized DNA and AuNPs to organize VLP Qβ cages into ordered 3D lattices.528 By decorating the surface of the Qβ cages and AuNPs with DNA, the researchers were able to form particles with a corona of DNA strands having similar effective radii to the cages, and enabled the formation of 3D lattices detectable by SAXS.
Building on earlier studies in which complementary DNA strands conjugated to nanoparticle surfaces were used to build lattices,529,530 the Mirkin Group has explored the extended assembly of proteins into ordered assemblies mediated by DNA base-pairing.297 The chemically rich protein surfaces were selectively conjugated to DNA to facilitate interparticle connectivity and control spacing. Brodin et al. developed protein-DNA hybrid superlattices using two different variants of the enzyme catalase as building blocks. The surface amine residues were functionalized with azide moieties and further labeled with DNA strands via azide-alkene cycloaddition (Figure 73). The resulting protein-DNA conjugates and DNA-bearing AuNPs were mixed and thermally annealed in different combinations to yield single- and multi-component enzyme crystals that retain enzymatic activity upon assembly. Follow-up studies demonstrated that lattice arrangements of protein and nanoparticle components, as well as pathways of crystallization, could be tuned by controlling the DNA labeling location on the protein and modulating repulsive interactions between the DNA-bearing nanoparticles.290,531
Figure 73.

Multicomponent protein-DNA lattices. a) Synthesis and assembly of a protein-DNA lattice. (i) The surfaces of both catalases are first functionalized with N3 moieties. (ii) They are then conjugated with two distinct DNA strands (Oligo A and B) via strain-promoted cycloaddition “click chemistry.” (iii) Hybridization of linker strands to the DNA-protein conjugates and subsequent mixing of the two (iv) results in the assembly of the proteins into a BCC unit cell. b) Illustrations of single protein, binary protein, and binary protein-AuNP lattices mediated by DNA hybridization. Adapted with permission from Ref.297. Copyright 2015 National Academy of Sciences.
Hayes et al. increased the complexity of the protein-DNA conjugated building block by creating self-assembled Janus nanoparticles (i.e., protein-DNA constructs modified with two sets of DNA strands of distinct sequences capable of orthogonal assembly with additional DNA-bearing AuNPs).532 First, they created a GFP variant with evenly distributed Lys residues and a single Cys on the surface. Disulfide chemistry was used to label the Cys residue with a single DNA strand while N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) ester chemistry was used to conjugate the Lys residues to DNA strands with an orthogonal sequence (Figure 74a). This procedure created a building block with a set of orthogonally addressable DNA-binding domains. Another batch of GFP was labeled with a complementary strand at the Cys and a different DNA sequence at the Lys residues. Annealing the two types of GFP-DNA building blocks yielded dimers linked by a DNA duplex and exposing two sets of DNA strands of different sequence on either side. The protein-DNA Janus dimers were integrated into multi-component superlattices upon mixing with DNA-conjugated AuNPs and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), or AuNPs of different sizes, bearing sequences complementary to both sides of the Janus particle (Figure 74b–c). The low symmetry of the Janus particle design enabled the formation of complex multicomponent lattices whose lattice dimensions could be selectively and anisotropically controlled by changing the length of one set of interparticle DNA connectors.
Figure 74.
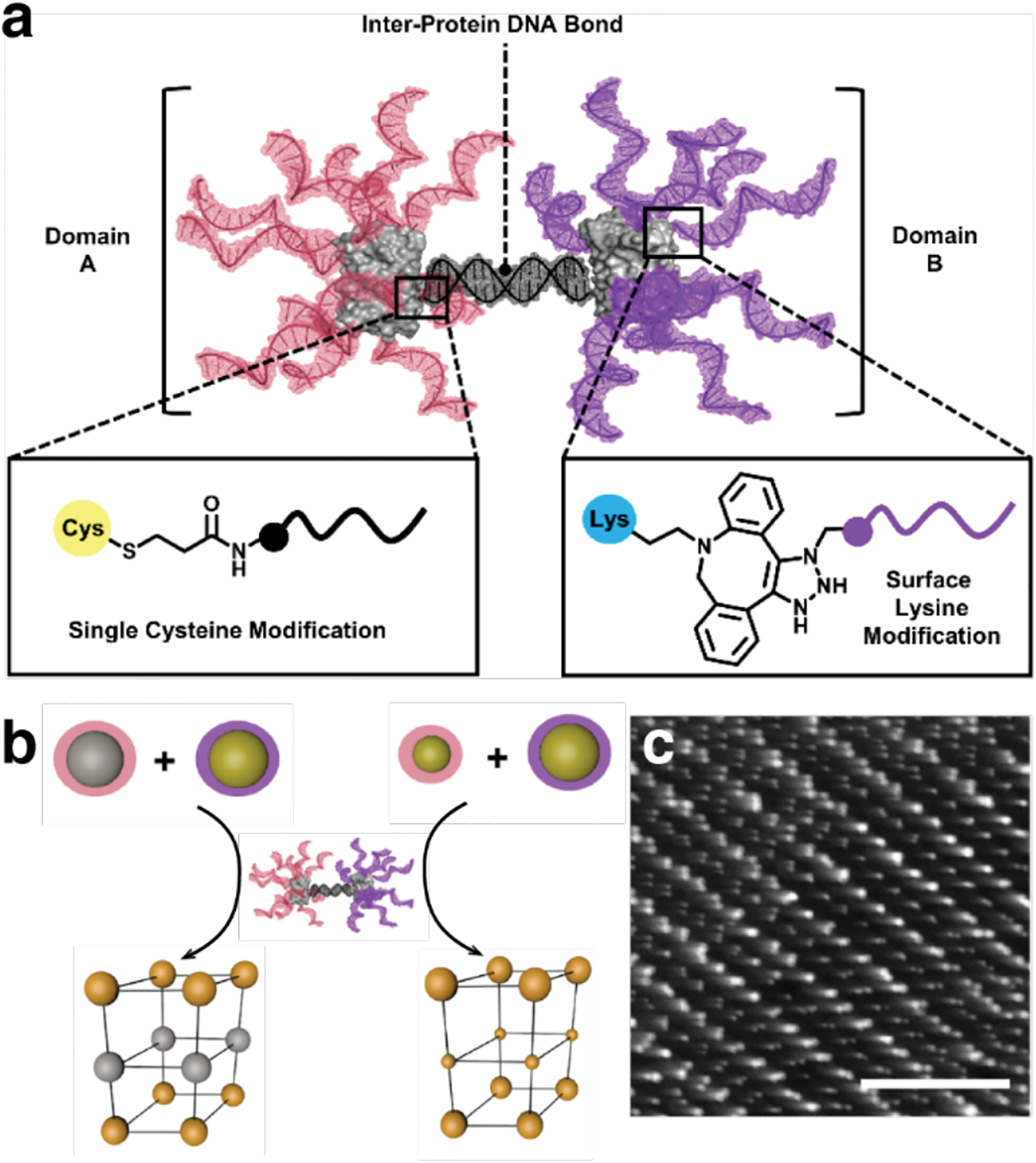
Protein-DNA Janus nanoparticles as building blocks for complex, multicomponent superlattices. a) Design of protein-DNA Janus nanoparticle. b) Multicomponent superlattices composed of Janus nanoparticles and (left) 10 nm AgNPs and AuNPs or (right) 5 and 10 nm AuNPs. c) TEM micrograph of the superlattice from (b) (right) embedded in silica reveals layers of 5 and 10 nm AuNPs. Adapted with permission from Ref.532. Copyright 2018 ACS.
Winegar et al. addressed DNA-directed protein crystallization in the context of single crystal formation. They systematically studied how DNA sequence, length, and protein-attachment position affect the formation and packing of GFP crystals.533 Upon crystallization of GFP and GFP-DNA conjugates, the researchers observed different packing arrangements, indicating that DNA affected the protein-protein interactions. Interestingly, the crystal contacts were observed between two proteins while electron density corresponding to DNA was not detected. Furthermore, the length and labeling position of DNA was found to affect the crystallization of GFP. Longer DNA strands inhibited crystallization, while different positions did not hinder the protein-protein interactions. Through this study, the effects of protein labeling on self-assembly were elucidated to better design 3D assemblies. Most recently, Partridge et al. showed that replacing a highly conserved protein-protein interaction with DNA-DNA interactions provided a means to modulate the crystallographic packing of proteins through programmable DNA sequences, which in some cases could be crystallographically resolved.534
As described in section 3.5.3, Subramanian et al. have contributed a different approach to the design of nucleoprotein architectures by designing and studying the assembly properties of metal-binding RIDC3-DNA chimeras.298 The formation of the resulting 3D crystals depended on the intricate balance of Watson-Crick base-pairing, metal-protein binding, and nucleic acid-protein interactions.
Given the large body of work in the areas of protein and DNA assembly in isolation, the synergistic effects of combining the two types of biological building blocks represents an exciting avenue of research for the development of functional biomaterials.535
4. Properties, Functions and Applications of Designed Protein Assemblies
As summarized in Section 2.1, natural protein assemblies present an immense structural diversity across many length scales. Their structures and dimensionality are intimately connected to their properties and biological functions. However, while the structures of protein assemblies generally dictate their function, shape and structure alone are not sufficient to carry out biological roles. Indeed, the activities of protein assemblies often require stimuli-responsive behavior and dynamic interactions with the environment, which cannot be simply derived from a static structure.
Given the inherent challenge of designing protein-protein interactions and self-assembly, early efforts in designed protein assembly or protein nanotechnology have justifiably focused on developing tools and strategies to construct protein assemblies with desired shapes and structures (Section 3). Within the last decade, the field has begun to transition from purely structure-building to the generation of new properties and functions. This rapid progress has not only been enabled by advances in the field of biomolecular design, but also by the outstanding chemical and structural versatility of proteins as building blocks (compared to other biomolecular building blocks like DNA/RNA or peptides), their facile manipulation and production in large quantities by cells, and their capacity to be readily interfaced with biological and abiological components.
In this Section, we aim to provide an overview of designed protein assemblies with emergent properties, functions, and applications that reach beyond mere “structure”, ranging from highly stable and switchable/reconfigurable systems (Sections 4.1 and 4.2) to protein assemblies that serve as active scaffolds (Section 4.3), dynamic assemblies with novel material properties (Section 4.4), and architectures with sophisticated biochemical functions (Section 4.5). It is important to note that there are many protein- or peptide-based systems/materials that fit under these classifications.105,536–539 As in the previous Sections, for the sake of focus, we will only cover designed and structurally well-defined protein architectures whose properties, functions, and applications derive from their self-assembly. For natural protein assemblies which have been engineered or tailored for added functions, the reader is referred to other excellent reviews.81,82,85,86
4.1. Stability of protein assemblies
Although protein stabilization by self-assembly is not an added function per se, it is an emergent property that can have important implications for potential functions and applications of a protein. Most natural proteins are only stable in a narrow window of temperature, pH and other solution conditions, in addition to being prone to chemical and physical denaturation. Thus, their use in industrial processes often requires extensive engineering, chemical modification or immobilization.540–548 For example, covalent crosslinking of enzyme assemblies, aggregates or crystals is commonly applied to increase their stability and durability under processing conditions.129,549–552 Similarly, from a biological perspective, stabilization of a protein can impart resistance to degradation by proteases553,554 and raise its tolerance to mutations, thereby increasing the extent of its evolvability.
It is safe to predict that the assembly of any protein building block into well-ordered oligomers or extended structures is likely to improve its stability by increasing the number of favorable intermolecular interactions, decreasing the total solvent-exposed surface area, and restricting the conformational space of each building block.110 Yet, the stability of designed protein assemblies, or the stabilization of protein components due to self-assembly, has only been explicitly reported in a few instances. As mentioned in section 3.3.4, Huard et al. redesigned the intermonomer interfaces in the 24-meric ferritin cage to make its self-assembly dependent on Cu2+ coordination (Figure 37).401 The engineered ferritin monomer MIC1 enabled the isolation of individual ferritin monomers and study of their properties. The authors found that MIC1 became significantly more resistant to unfolding upon Cu-directed self-assembly, as evidenced by an increase of its thermal denaturation midpoint from 39 °C (monomer) to ≥ 87 °C (cage) and the guanidine hydrochloride unfolding midpoint from 1 M (monomer) to 5.2 M (cage) (Figure 75a), based on CD spectroscopy results. Cage formation alone was estimated to stabilize each MIC1 monomer by 30 kJ/mol, a value comparable to the folding free energy of a stable, globular protein like cyt c.555 Cu2+ coordination made an additional stabilization contribution of 3–6 kJ/mol per monomer.
Figure 75.

Thermal and chemical stability of designed protein assemblies and their components. a) Denaturation of MIC1 in various assembly states (monomer, Cu2+-mediated cage, cage + EDTA, cage + EDTA + Cu2+ (rescued assembly)) induced by GuHCl titration (left) or thermal denaturation (right) monitored by CD spectroscopy at 222 nm. b) Stability of monomeric and self-assembled RIDC3 in THF and iPrOH. c) Thermal and pH-dependent stability of TRAP cages tracked by native PAGE and ns-TEM. d) Thermally induced unfolding of the Ico8 protein cage and the TriEst subunit monitored by changes in molar ellipticity at 222 nm (left) and by light scattering (right). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.401. Copyright 2013 NPG. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.204. Copyright 2014 National Academy of Sciences. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.200. Copyright 2019 NPG. (d) Adapted with permission from Ref.142. Copyright 2019 ACS.
Using UV-vis spectroscopy and ns-TEM, Brodin et al. determined that their Zn-mediated 1D and 2D RIDC3 assemblies (Sections 3.4.3 and 3.5.3, Figure 46) were not only thermostable up to ~70 °C and ~90 °C respectively, but also maintained their structural integrity and dispersity in polar organic solvents like tetrahydrofuran (THF) and isopropyl alcohol (iPrOH) at ≥90% (v/v) concentrations. In contrast, individual RIDC3 monomers unfolded at 30% (v/v) THF and 50% (v/v) iPrOH, demonstrating the drastic stabilization effect of self-assembly (Figure 75b).204 Because the metal-directed assembly process is minimally invasive and the protein monomers can be recovered in their native form upon metal chelation, this strategy is promising for generating heterogeneous enzyme catalyst systems that can operate under industrial processing conditions.
More recently, Malay et al. reported that their Au+-directed, TRAP cages with an unusual snub-cube geometry (Section 3.3.3, Figure 35) were also highly stable.200 Through gel-electrophoresis and TEM experiments, these ~ 2 MDa cages were found to resist disassembly at high temperatures (≥95 °C), in a wide range of solution pH conditions (pH 3 to13), and in the presence of high concentrations of chaotropes (≥7 M urea, ≥5% SDS) (Figure 75c). Despite their high stability, the TRAP cages could be readily disassembled by adding chemical reducing agents that induce dissociation of the Au-Cys coordination bonds.
The stabilization effects are not limited to metal-directed protein assemblies. Hsia et al. observed that their computationally designed icosahedral cage (I3–01, Section 3.3.2, Figure 32) could maintain its structure at up to 80 °C and 6.7 M guanidine hydrochloride, owing both to the stability of the individual trimeric building blocks and the hydrophobic inter-trimer interfaces.392 The high stability of I3–01 also made it robust to genetic fusion, enabling its modification with multiple copies of GFP or designed protein pentamers without perturbation of the underlying icosahedral architecture.
Similarly, Cristie-David et al. reported an extremely stable icosahedral assembly (Ico8) designed through the fusion of a trimeric esterase (TriEst) with pentameric coiled coils (Section 3.3.1, Figure 29). The researchers determined by CD and DLS measurements that Ico8 cages remained intact at 120 °C or in 8 M guanidine hydrochloride, while the TriEst building blocks were denatured at 75 °C or in 1.5 M guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl).142 (Figure 75d) Interestingly, Ico8 displays considerable conformational flexibility due to the flexible peptide linker between the TriEst and coiled-coil components, indicating that structural rigidity is not necessary for high stability as has been suggested for viral capsids.556–558 Importantly, like MIC1 and RIDC3 assemblies, the TriEst system provides another compelling example of how cooperative effects arising from the formation of multiple inter-subunit interactions during self-assembly can lead to a dramatic stabilization of the individual protein building blocks.
4.2. Stimuli-responsive and reconfigurable protein assemblies
A critical feature of natural proteins and protein assemblies is their ability to respond to environmental stimuli by changing their structure or assembly state.45,85,559 Such structural responsiveness and reconfigurability are imperative for the cellular control of protein functions in time and space. In chemical terms, responsiveness and reconfigurability are associated with reversible interactions that can be readily formed and broken without excessive energy input and can be controlled by mild chemical and physical stimuli. Such bonding fluidity within protein-protein interfaces enables, for example, microtubule extension (polymerization) and shrinkage (depolymerization) in a nucleotide-dependent fashion,560 viral capsid assembly/disassembly and morphology changes,561 and highly cooperative hemoglobin-O2 binding that is at the same time modulated allosterically by pH, temperature, CO2 and biphosphoglycerate.562
Traditionally, protein assembly design has focused on the optimization of energetically favorable interactions between the protein components (or within a protein sequence) to obtain the thermodynamically preferred products.145,563–565 This focus on energy minimization has favored singular architectures that assemble predominantly via the formation of quasi-irreversible, hydrophobic interactions and thus reside in deep energy minima. This mode of self-assembly is prone to produce kinetically trapped, disordered aggregates and yields structures that are rigid and static. In contrast, the free-energy landscape of a responsive/reconfigurable protein assembly should contain multiple minima that the system can occupy in a condition-dependent manner. Such a traversable energy landscape can, in essence, be realized with any mode of protein-protein association that is mediated by metal coordination (so long as the metal ions are substitution labile),195,200,202,204,397 electrostatic interactions,272 ligands270,466,485 or host-guest interactions,264,413 reversible covalent bonds,225 nucleic acid base pairing,440 depletion forces,566,567 and surface interactions.227,496These types of interactions are reversible and readily modulated by mild stimuli, enabling error-correction and greatly facilitating the formation of well-ordered protein architectures with proper tuning of assembly conditions.357
Another important advantage of externally controllable assembly strategies is their modularity. They open the door to multiple different assembly states from a single protein building block, which is difficult to achieve solely through the design of direct protein-protein interactions. Many such protein assemblies were described in Section 3 as well as in other reviews; some notable examples include the construction of alternatively structured lattices and arrays of ferritin,471,512 CCMV,272 M13 phage,566,568 LecA,483 TMV,475,567 lectin268 and RhuA227. As we will discuss further in Section 4.3, such lattices and arrays have been used as versatile scaffolds for constructing functional materials.
In this section, we will highlight some studies that explicitly touch on the responsiveness and reconfigurability of protein assemblies and the functions/properties that stem from tunable protein-protein interactions or assembly strategies. We also note that there have been exciting advances in the rational design of protein-based switches and responsive signaling systems based on protein dimerization events;190,320,322,323,336,355,356,359 we refer the reader to the extensive literature on these topics.310,569
4.2.1. Stimuli-responsive protein assemblies
It is important to note that responsiveness (a landscape with many energetic minima) does not preclude structural order and stability (a landscape with deep energetic minima). Indeed, the aforementioned Zn-directed 1D, 2D and 3D RIDC3 crystalline arrays202,204 and the Au-mediated TRAP cages200 are exceptionally stable with respect to chemical and thermal denaturation, yet they can be readily disassembled upon chelation of the metal ions or chemical reduction. In fact, RIDC3 arrays provide an apt example for reconfigurability, since the kinetics of the Zn-mediated self-assembly process can be controlled by adjusting solution pH or the metal concentration to direct the assembly toward kinetically (1D nanotubes) or thermodynamically (2D and 3D crystalline arrays) preferred products.202,204 Furthermore, the 1D nanotubular RIDC3 assemblies can be directly converted into 2D assemblies by raising the temperature to or above 80 °C, lowering the solution pH or lowering Zn concentration.202
In artificial cage-like protein assemblies, stimulus-responsive assembly/disassembly behavior is critically relevant to their proposed controllable molecular encapsulation and release functions. For example, such behavior is displayed by the Au-TRAP architecture as outlined above.200 Cristie-David et al. designed a trimeric TriEst-peptide chimera, based on their protein-fusion-mediated assembly strategy described earlier (Section 3.3.3), wherein the peptide domain was engineered with an i/i+4 bis-His motif to form a trimeric coiled-coil domain upon metal coordination.397 The researchers observed a moderately efficient formation of the desired tetrahedral cage complex in the presence of Ni2+ (65–75% yield). As designed, treatment with metal chelators or lowering of solution pH induced complex dissociation.
Similarly, the disassembly of Fe3+- and Zn2+-dependent BMC3 cages (Section 3.3.3, Figure 36) designed by Golub et al. could be triggered not only by elevated temperatures (≥70 °C) or metal chelation, but also by treatment with the strong chemical reductant dithionite (Ered < −500 mV).195 By contrast, ascorbate, a weaker reductant (Ered > −100 mV), was considerably less effective, as it has a higher reduction potential than the Fe3+-tris-hydroxamate centers responsible for the formation of the C3 symmetric vertices. The redox-dependent switchability of BMC3 cages mimics a key feature of bacterial siderophores: in the cytosol, reduction of the tightly bound Fe3+ centers to Fe2+ labilizes the ions, thus promoting their release.400 Importantly, owing to their tightly packed shells, BMC3 cages could encapsulate small fluorophores and release them upon chelation-driven disassembly.
Aida and coworkers have taken advantage both of their reversible assembly strategy and the inherent properties of their GroEL building block to design switchable 1D assemblies.203,417,439,440 As described in Section 3.4.3 (Figure 45), the barrel-shaped GroEL complex, modified with SP moieties that undergo isomerization to MC on its top and bottom faces, polymerized into micrometer-long nanotubes in the presence of divalent ions, which bind to MC in a 2:1 ratio.417 As reversible SP-MC isomerization can be effectively triggered by UV (SP→MC) and visible (MC→SP) light, the researchers were able to control nanotube assembly and dissociation by irradiating the solution, thus providing the first example of light-controllable, artificial protein assemblies.439
Further expanding the versatility of the GroEL system, Kashiwagi et al. engineered an alternative strategy for nanotube assembly. The Cys-modified GroEL barrels were conjugated to complementary DNA strands (GroEL10a and GroEL10b) and assembled through multivalent strand complementarity into stable 1D nanotubes.440 In this case, nanotube disassembly could be triggered by a strand displacement reaction, wherein an invading DNA strand was added and formed a more thermodynamically stable duplex with the GroEL-DNA conjugate than the duplex connecting the building blocks, thus disrupting the binding between hybridized GroEL-DNA units and disassembling the nanotube.
In addition, Biswas et al. leveraged the natural ability of GroEL to undergo ATP-dependent conformational changes, which is essential for its biological function as a protein-folding chaperone, to establish an alternative trigger for nanotube disassembly.203 The researchers demonstrated that Mg-mediated GroELMC nanotubes, containing on average 20 GroELMC units, could be dissociated into smaller units upon incubation with ATP (Figure 76a). This observation was attributed to a chemomechanical effect, in which the ATP-mediated conformational changes in GroELMC led to a decrease in the multivalency of MC-Mg-MC interactions between the building blocks. They further demonstrated that this effect was specific to ATP, CTP, and UTP, which trigger conformational changes in GroEL, but was not observed with ITP or GTP, thus providing strong support for the proposed basis of the chemomechanical effect.
In a similar vein, Campos et al. designed a toroidal protein assembly whose formation could be induced by a fold-switching mechanism involving a small monomeric protein, chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2).363 The design was based on the observation that in the P622 symmetric crystal lattices of CI2 obtained under certain solution conditions, the C-terminal β-strand of each monomer was displaced from the hydrophobic protein core to associate with a crystallographically related neighbor. Based on the assumption that this domain-swapping event could stabilize the dodecameric, D6-symmetric substructures seen in the lattices, the researchers engineered CI2 to destabilize the interactions between the hydrophobic protein core and the C-terminal β-strand. The resulting variant CI2eng was indeed observed to form hexameric and dodecameric assemblies in solution. Thermodynamic and structural analyses of CI2eng and its assemblies indicated that the assembly was promoted by the C-terminal displacement from the monomers to expose their hydrophobic cores, which in turn stabilized the key inter-monomer interactions. The researchers could assert control over CI2eng assembly both by temperature, which modulates CIeng conformational equilibrium, and the addition of a peptide sequence corresponding to the C-terminal strand, thus providing an exciting demonstration of metamorphic protein engineering570 for stimuli-responsive architectures (Figure 76b).
In another set of examples for conformationally gated protein assembly, Yan and coworkers took advantage of the switchability of the signaling protein calmodulin (CaM), which undergoes a large Ca2+-dependent structural transformation to bind target proteins and peptides. In one study, the researchers developed a bifunctional linker composed of a phenothiazine headgroup that specifically associates with Ca2+-bound CaM and a rhodamine group that dimerizes through π-π stacking interactions.571 This linker was designed to induce Ca2+-mediated CaM dimerization. In a second study, the rhodamine group was replaced by various collagen-like proline-hydroxyproline-glycine repeat domains ((POG)n; n = 6, 10 or 14) intended to promote CAM homotrimerization.572 In both cases, the researchers observed reversible, Ca2+-dependent formation of CaM assemblies. With the rhodamine-based linkers, Ca2+ addition generated helical filaments, whereas with the POG-based linkers, spherical, cage-like assemblies were observed. The helical pitch of the filaments and the sizes of the cages could be tuned by adjusting Ca2+ concentration and the length of the POG domains, respectively. The researchers were also able to confirm the intended linker-mediated CaM dimerization and trimerization processes. They further suggested that CaM molecules must form an interlocked dimer to enable the formation of the observed supramolecular assemblies, although the structural basis for how these dimers form and interconnect remains to be experimentally established.
In another variation of their approach, the same research group employed adenylate kinase (AKe) as a conformationally-gated protein building block, which undergoes considerable compaction upon binding to the bifunctional ligand diadenosine-5-pentaphosphate (Ap5A).485 As described in Section 4.5.4, AKe modified with a polyvaline tail (AKe-MV) formed filamentous assemblies with a 20 nm diameter, which were reversibly converted into well-ordered 2D sheets upon Ap5A addition (Figure 76c). In analogy to other synthetic amphiphilic systems, this structural transformation was attributed to a change in the shape of the AKe-MV amphiphile from a conical to a cylindrical configuration, which favor tubular and planar packing, respectively.
As previously mentioned, because computational protein design approaches largely target structures that lie in deep free-energy minima, the de novo design of conformationally switchable proteins and protein assemblies represents a substantial challenge. Toward this goal, Boyken et al. recently reported the construction of pH-switchable protein assemblies by computational design.357 The researchers took advantage of parametric helical bundles as building blocks and of His side chains as pH-sensitive elements. The repeating geometric cross-sections of the helical bundles allowed extensive H-bonding networks to be built in a modular fashion by tuning the number of His residues, whose protonation at low pH would disrupt the H-bond networks and result in repulsion across the inter-monomer interfaces. Using the HBNet platform in Rosetta (Section 3.2.1), the researchers generated several stable dimeric and trimeric helical bundle architectures (termed pRO’s) whose structures closely matched the computed models. Native mass spectrometry experiments indicated that these structures displayed pH-dependent disassembly as designed. The position and cooperativity of the pH transition could be finely tuned over a pH range from 4 to 6 by modulating the number and positioning of H-bonding and hydrophobic interaction layers. The researchers further demonstrated that pRO’s disassembled under low pH conditions could interact with lipid membranes through their exposed hydrophobic cores, efficiently disrupt liposomes in vitro and incorporate into lysosomal membranes in cells. In a related approach, Chen et al. used a set of orthogonal heterodimers they had previously designed with HBNet189 to develop protein logic gates.190 Fusion of two different monomeric domains with each other enabled the design of dimerization domains that could bring together two halves of a split reporter fused to the cognate monomeric domains. This enabled the development of two- and three-input logic gates, including AND, OR, and NOR gates, in which the activation of the split reporter was controlled by the presence or absence of the relevant dimerization domains according to the relevant logic gate.
A computational interface design strategy was also used to tune assembly and disassembly properties of metal-switchable protein oligomers. As described in Section 3.2.2 (Figure 26), Kakkis et al. engineered a cyt cb562 variant termed TriCyt1, which assembled into homotrimers in low to near-quantitative yields (12% to 95%) upon coordinating various mid-to-late first-row transition metals (Mn2+ to Cu2+) within a hexa-His motif.196 Using the crystal structures of the resulting trimers (M:TriCyt13) as a template, computationally prescribed mutations were incorporated to stabilize the inter-monomer interfaces with additional hydrophobic and H-bonding interactions. The resulting variants, termed TriCyt2 and TriCyt3, were shown by AUC to quantitatively switch between monomeric and trimeric states upon addition/removal of metal ions (TriCyt2) or tuning of solution pH (TriCyt3), thus furnishing a multi-responsive assembly by rational design.
4.2.2. Reconfigurable protein assemblies
The examples described in this section thus far have highlighted the diverse strategies for designing switchable protein architectures whose assembly and disassembly could be externally turned on and off. Arguably more challenging is the design of protein architectures which can interconvert between two or more well-defined structural states in a reversible and stimuli-responsive manner, while remaining in the assembled state. Such behavior is not only crucial for constructing protein assemblies with adaptive and regulable functions (such as allostery), but also for fabricating protein-based materials with emergent mechanical properties. In contrast to the rapidly growing number of switchable protein assemblies, relatively few such structurally adaptive systems obtained by design have been reported so far.
The nanoporous, 2D lattices of the engineered protein C98RhuA (Section 3.5.2, Figure 51) offer a notable example of an adaptive system.225 Owing to the short, but highly flexible disulfide bonds that link the C98RhuA monomers, these lattices are coherently dynamic, i.e., they can coherently transition between “open” and “closed” states upon application of minimal mechanical force (Figure 77a).
Figure 77.
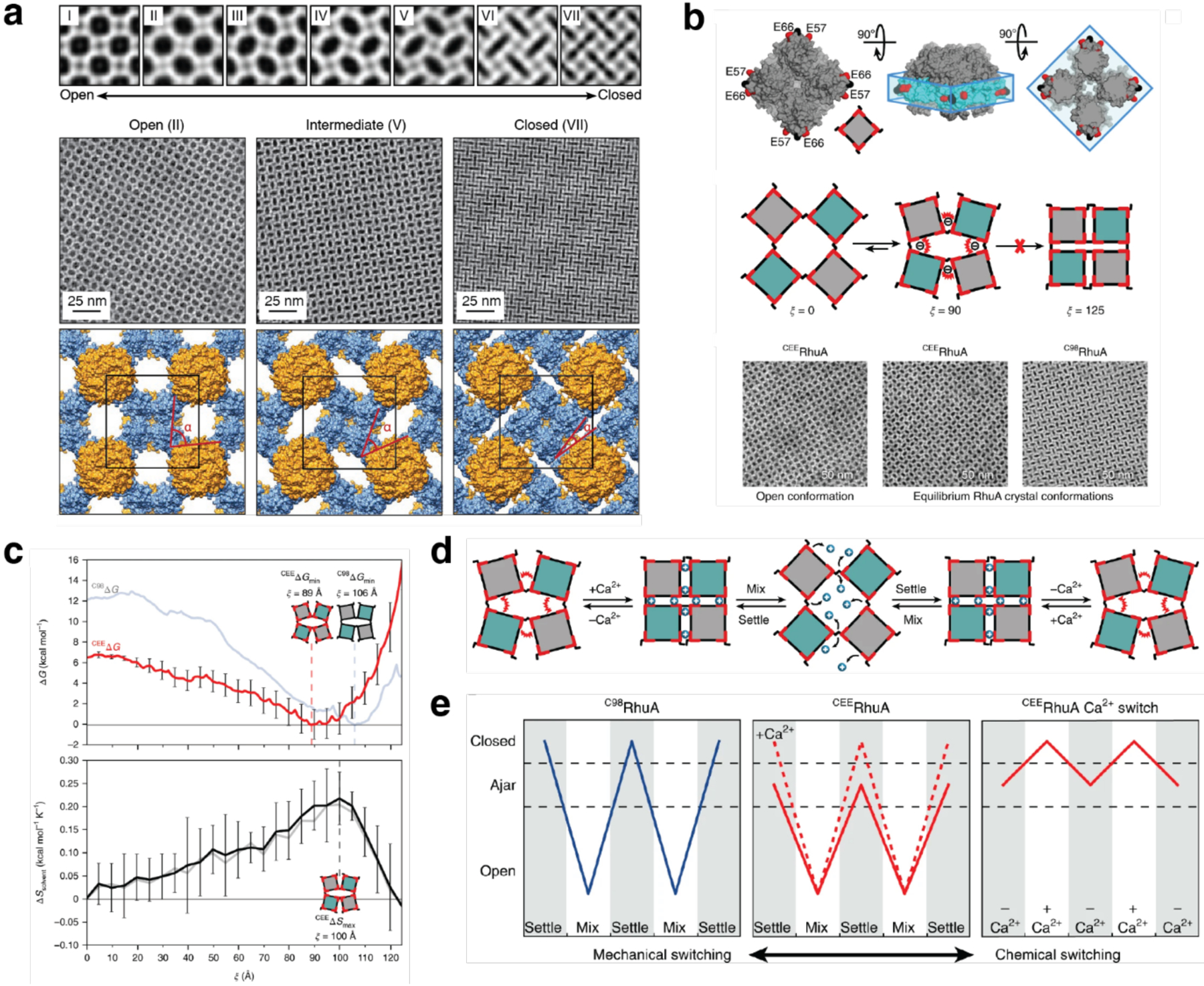
Lattice reconfiguration behavior of disulfide-linked RhuA crystals. a) Dynamic, auxetic nature of C98RhuA crystals. From top: reconstructed 2D images of seven distinct conformational states of the 2D crystals (I-VII); Magnified views of states II, V and VII; structural models of conformations II, V and VII with unit cells and hinge angles (α) between RhuA molecules highlighted in black and red. b) Surface representation (top) of a CEERhuA tetramer with residues 98 and 57/66 colored in black and red, respectively. Illustration of CEERhuA lattice dynamics (middle) and ns-TEM images of lattices (bottom) with open and equilibrium states for CEERhuA and closed state for C98RhuA. c) Free-energy and solvent entropy profiles for CEERhuA (red and black lines) and C98RhuA (faint blue and grey lines). d) Chemical and mechanical reconfiguration behavior of CEERhuA lattices. e) While C98RhuA crystals exhibit only one mechanical reconfiguration mode, CEERhuA crystals have two modes of mechanical switching and an additional purely Ca2+-induced, chemical switching mode. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.225. Copyright 2016 NPG. (b-e) Adapted with permission from Ref.226. Copyright 2018 NPG.
The C98RhuA lattices are also noteworthy in that their conformational free-energy landscape has been quantitatively established. Alberstein et al. defined the free-energy landscape by a unidimensional reaction coordinate (ξ) that corresponded to the ellipticity of the lattice pores by taking advantage of the symmetry and coherent structural dynamics of C98RhuA lattices.226 All-atom MD simulations revealed a relatively shallow landscape with a distinct energy minimum corresponding to an almost fully-closed state. The free energy landscape of C98RhuA lattices was determined through grid inhomogeneous solvation theory (GIST) calculations to be dictated almost entirely by solvent entropy. Upon confirming that the predicted equilibrium populations of lattice conformational states were quantitatively matched by experimental characterization, the researchers rationally engineered the C98RhuA surfaces with negatively charged Glu residues (CEERhuA) to favor a more open lattice conformation at equilibrium (Figure 77b–c). The Glu sidechains also created another handle for lattice dynamics actuation, as divalent metal coordination to CEERhuA crystals triggered lattice closing. The CEERhuA assembled into a lattice whose structure could be both mechanically and chemically actuated (Figure 77d–e). The simultaneous presence of structural order/integrity and flexibility, which are often mutually exclusive in designed systems, is an important design principle for adaptive protein assemblies. This requirement is also met in 3D lattices of cage-like proteins that are mediated by flexible linkages512,513 and adaptive polymer matrices.295,573
Allostery is a key biological concept in the dynamic control of protein functions,110,574,575 which refers to the control of a binding or catalytic process by a chemical event at a distinct site in the protein. To the best of our knowledge, there are only a few examples of designed, allosteric protein assemblies that fit this definition, excluding the many examples of natural proteins that have been reengineered to be switchable.363,576,577 In such an example, Churchfield et al. sought to construct a flexible oligomeric protein assembly in which structural changes induced by metal binding could be mechanically transmitted onto a distant site to elicit a chemical event.232,233 For this goal, they employed a previously designed, Zn-templated, tetrameric cyt cb562 assembly (Zn4:C81/C96 RIDC14; Section 3.2.3),210 whose interfaces were redesigned with fluid hydrophobic interactions and two pairs of disulfide bonds. Based on the observation that Zn4:C81/C96 RIDC14 underwent a considerable separation of one of the intermonomer interfaces, the researchers incorporated an additional disulfide bond into this interface to create a mechanically strained quaternary architecture bearing three pairs of disulfide bonds (C38/C81/C96RIDC14). Structural and biophysical analyses indicated that C38/C81/C96RIDC14 was indeed an allosteric system in which Zn2+ binding and dissociation were remotely coupled to the reversible formation and breakage of a disulfide bond over a distance >14 Å (Figure 78).
Figure 78.
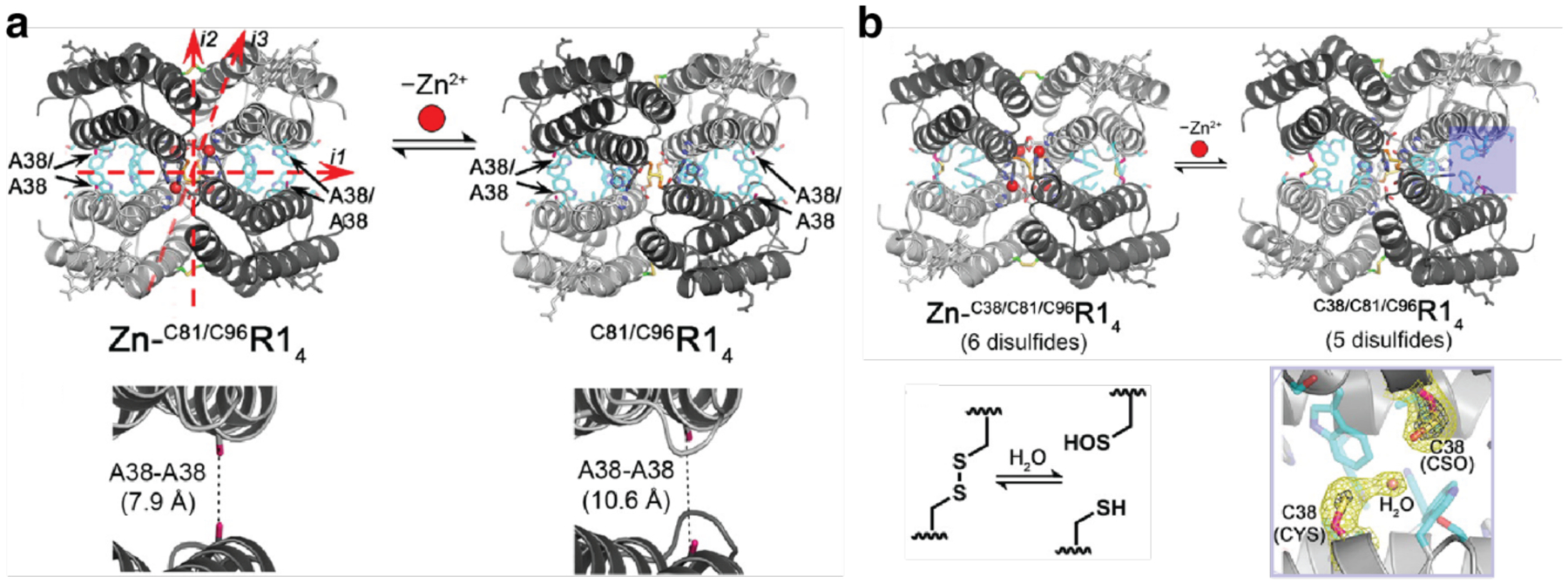
Allosteric metalloprotein assemblies with strained disulfide bonds. a) Scheme showing structural rearrangements in the Zn-C81/C96RIDC14 (labeled as R1) tetramer upon Zn2+ removal (top) and close-up view of A38-A38 residue pairs (bottom). b) Crystal structures of Zn-C28/C81/C96R14 and the metal-free C28/C81/C96R14 (top); hydrolytic dissociation of a disulfide bond and close-up view of the broken C38-C38 disulfide bond, forming a Cys and Cys sulfenic acid (bottom). Adapted with permission from Ref.232. Copyright 2016 ACS.
More recently, Ghanbarpour et al. exploited domain swapping as a means to design allosteric control of protein function in human cellular retinol binding protein II (hCRBPII).320 It was previously observed that certain mutations in hCRBPII yield domain-swapped dimers which undergo large conformational changes upon retinal binding.319 After identifying key residues responsible for the ligand-induced structural transformation (i.e., mechanical coupling), the researchers installed a His2Cys metal binding site at the interface of the mobile domain of the dimer distant from the retinal binding site. The resulting system displayed a five-fold difference in the Zn2+ binding affinity between the retinal-bound and -unbound forms, thus establishing an allosteric system with remote coupling between ligand- and metal-binding events.
4.3. Encapsulation, scaffolding and structural organization by designed protein assemblies
Natural proteins and protein assemblies with well-defined shapes and higher-order geometries usually serve as active scaffolds for different functions, such as storage, protection from degradation, transport, and structural templating. The ordered structural features enable accurate control of the position, orientation, and geometry of all the components. Moreover, the specific shapes of protein assemblies often correlate with their functions. For example, hollow cages such as ferritin and viral capsids serve to store large amounts of iron minerals and genomic material and isolate them from the environment.
Inspired by such natural examples, many designed protein assemblies have been utilized as versatile scaffolds for constructing functional materials. Particularly in comparison to synthetic systems (e.g., polymers, MOFs, or covalent-organic frameworks (COFs)), protein architectures are attractive scaffolds because of their biocompatibility, immense structural diversity, ease of functionalization and versatility in function. For example, artificial protein cages can serve as biological containers for encapsulation, release or transport of different cargo such as nucleic acids, proteins, and drugs; they can also act as fluorescent candles for detection or nanoparticle vaccines when fused to specific functional domains.392 2D protein arrays can serve as structural templates for long-range nanoparticle organization; they can also act as mimics of natural light-harvesting membranes when photoactive proteins are used as building blocks.469
In this section, we highlight the use of designed protein assemblies as containers, scaffolds for structure determination and structural templates for the immobilization and organization of biological and synthetic components. We also note that there is a substantial body of research focusing on natural protein assemblies/arrays (e.g., viral or porous protein lattices) as scaffolds that have been modified to serve as templates and containers.578–580 We refer the reader to the extensive literature on these topics.85,94,578–581
4.3.1. Encapsulation
As summarized in Section 3.3.2, icosahedral protein cages with large diameters are desirable carriers for macromolecule packaging and delivery. In one study, Bale et al. reported two-component icosahedral protein cages with large diameters (24 to 40 nm) that assembled rapidly when the individual components were mixed in vitro.391 Such structural and assembly features allowed the cage to encapsulate macromolecular cargo in a controllable manner. In further pursuit of this application, the authors engineered the trimeric and pentameric building blocks of an I53–50 cage with positively charged residues on its interior surface. By mixing negatively charged GFP (−30) with the two components of the I53–50 cage, seven to eleven GFP molecules were trapped per icosahedral cage due to electrostatic interactions, occupying roughly 11 to 17% of the interior volume in low salt solution based on fluorescence intensity and UV-vis absorbance measurements (Figure 79a). To precisely control the number of GFP molecules encapsulated per cage, the same group built GFP-tagged assemblies using genetic fusion instead of electrostatic interactions (Figure 79a).392 They first fused sfGFP to one or both termini of the monomeric subunit from a trimer and the resulting construct formed icosahedral cages (I3–01 ctGFP) with 60 or 120 copies of sfGFP. Then, they applied the same design strategy to generate assemblies with 12 or 24 copies of sfGFP using a previously reported two-component tetrahedral cage (T33–21).389 All the designed sfGFP-nanocage assemblies with GFP copy numbers from 12 to 120 could be used as “standard candles” to correlate fluorescence intensity and GFP copy number.
Figure 79.
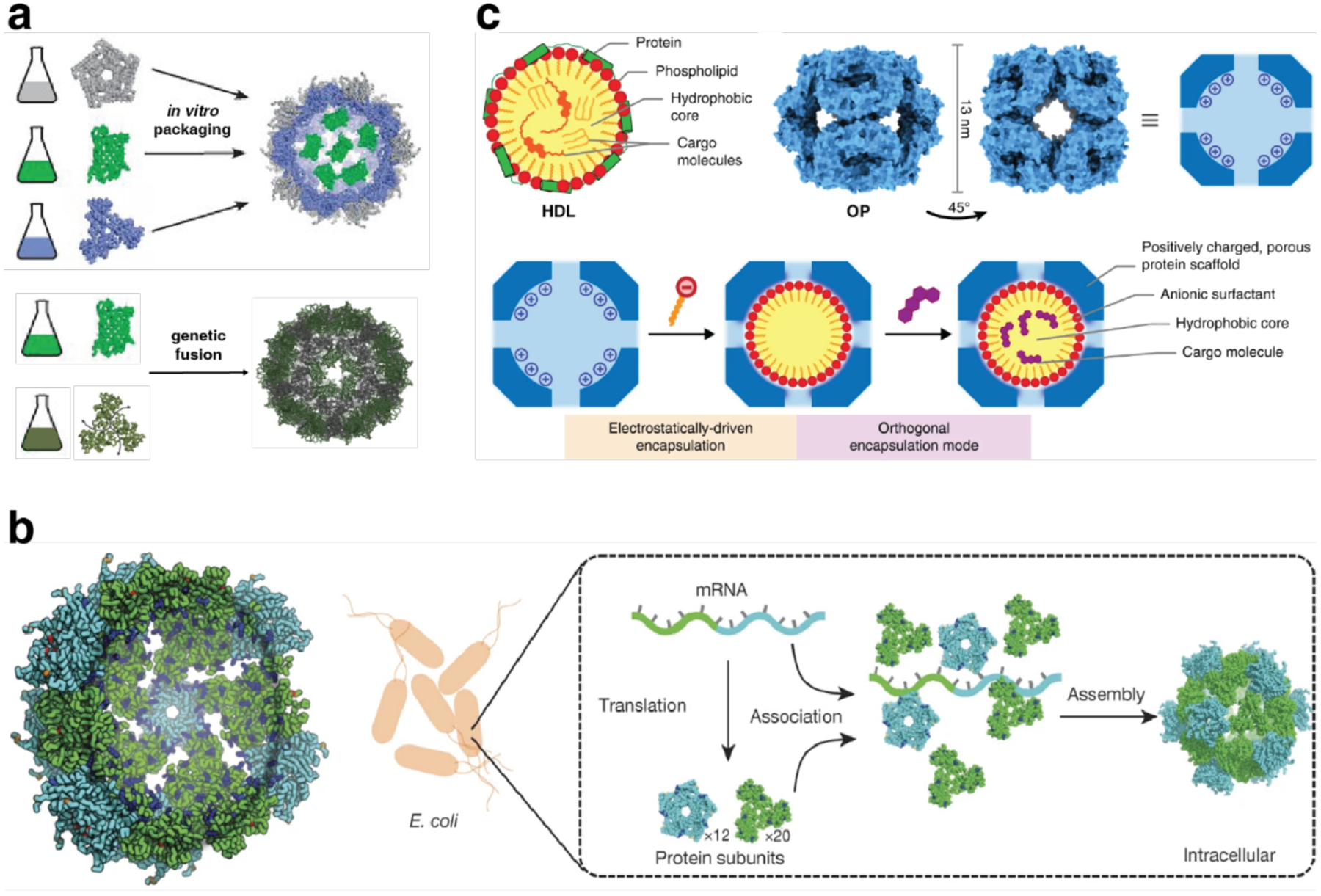
Encapsulation within artificial protein cages. a) Encapsulation of supercharged GFP in a positively charged I53–50 cage variant and formation of I3–01 ctGFP cage by genetic fusion. b) Design model of I-53–50-v1 (left). Synthetic nucleocapsids encapsulate their own mRNA genomes while assembling into icosahedral capsids inside E. coli cells (right). c) Self-assembly of lipoprotein-mimetic capsids. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.391. Copyright 2016 AAAS; Adapted with permission from Ref.392. Copyright 2016 NPG. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.582. Copyright 2017 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.583. Copyright 2020 NPG.
Besides encapsulation of functional proteins such as sfGFP, icosahedral protein cages can provide a blank slate to evolve desired properties such as encapsulation of nucleic acids. Butterfield et al. started with a two-component icosahedral protein cage (I53–50-v1), containing a large internal volume and positively charged residues on its interior surface, to package its own full-length genome, but with low efficiency (Figure 79b).582 After several rounds of selection, the evolved nucleocapsids (I53–50-v4) showed higher genome packaging efficiency, improved stability in blood, and an extended in vivo circulation time in mice. The resulting synthetic nucleocapsids packaged one full-length RNA genome for every 11 icosahedral cages. By combining computational design and optimization in the evolution process, this study demonstrated that artificial protein cages could acquire virus-like genome packaging and protection properties based on a bottom-up approach.
Edwardson et al. also took advantage of electrostatic interactions to convert a designed porous octahedral protein cage186 (O3–33, as discussed in section 3.3.2) into a nucleic acid delivery vehicle. Six solvent-exposed residues on the luminal surface of O3–33 were mutated to Arg to create a positively supercharged capsule. The new variant of O3–33, the OP cage, demonstrated a high binding affinity to oligonucleotides. The OP cage was first tested as an siRNA delivery vehicle and shown to modulate gene expression in mammalian cells.275 The researchers then repurposed the OP cage to encapsulate poorly water-soluble small molecules through a two-tier host-guest approach.583 (Figure 79c) Anionic surfactants were introduced to the positively charged interior of the designed protein cage, forming protein-scaffolded micelles within the cavity. The hydrophobic core of the resulting construct was suitable for encapsulating small nonpolar molecules such as the fluorescent dye Nile Red or the chemotherapeutic agent lapatinib. Moreover, altering the lipid composition enabled fine-tuning of the binding affinity and release kinetics for different cargo molecules. The resulting hybrid particles composed of protein cages and amphiphilic molecules are promising scaffolds for delivering nonpolar therapeutic cargo molecules to cells as they can establish a practical balance of serum stability, efficient cellular uptake, and intracellular release.
Alongside cage-like protein assemblies, GroEL nanotubes have also been utilized for encapsulation towards drug delivery applications. The nanotubes retain GroEL’s inherent binding affinity for denatured proteins if the guest is added before Mg2+-mediated assembly.417 This property was exploited for drug encapsulation. Irreversibly denatured α-lactalbumin, which binds to the barrel interior, was conjugated to a drug molecule through a cleavable linker and loaded into the nanotube. The drug release profile was studied in vitro under various ATP concentrations, as the nanotube underwent chemomechanical scission in response to ATP. The exterior surface of the nanotube was also functionalized with a boronic acid derivative known to activate the cytosolic uptake of proteins. The modified nanotubes were shown to enter HeLa cells and responded to intracellular ATP to disassemble and release loaded cargo. Preliminary biodistribution studies in a tumor-carrying mouse model showed preferential accumulation of the nanotubes in tumor tissues.203 Furthermore, cell uptake studies carried out with length-controlled GroEL nanotubes showed tubes shorter than 100 nm to have efficient uptake into HEP3B cells, with a general trend indicating length-dependent uptake efficiency that favors shorter tubes.201
4.3.2. Scaffolding for applications in structural biology
As demonstrated by an increasing number of examples, the structural order and uniformity of designed protein assemblies can be invaluable in scaffolding of molecular/biomolecular guests for structure determination by XRD and cryoEM.581,584,585 Compared to small molecule crystals, 3D protein lattices exhibit larger channel and pore diameters that permit the sequestration of large exogenous molecules and even proteins.586 Another advantage of protein building blocks lies in their chemically rich surfaces, which can be augmented through protein engineering and specifically functionalized by bioconjugation. Exploiting both characteristics, protein crystals have been used as crystallographic hosts to immobilize normally “uncrystallizable” molecules for structure determination. In an early example, Ni et al. immobilized a flexible heme peptide fragment, microperoxidase (MP9cb562), within a designed, metal-mediated protein cage.395 The tetrahedral cage, which featured a 35 Å-wide cavity, was used to capture MP9cb562 in its interior via the coordination of the heme cofactor to a His residue located in the lumen. This anchoring strategy enabled the determination of the cage-peptide cocrystal at atomic resolution and the crystallographic characterization of a microperoxidase for the first time (Figure 80a).
Figure 80.
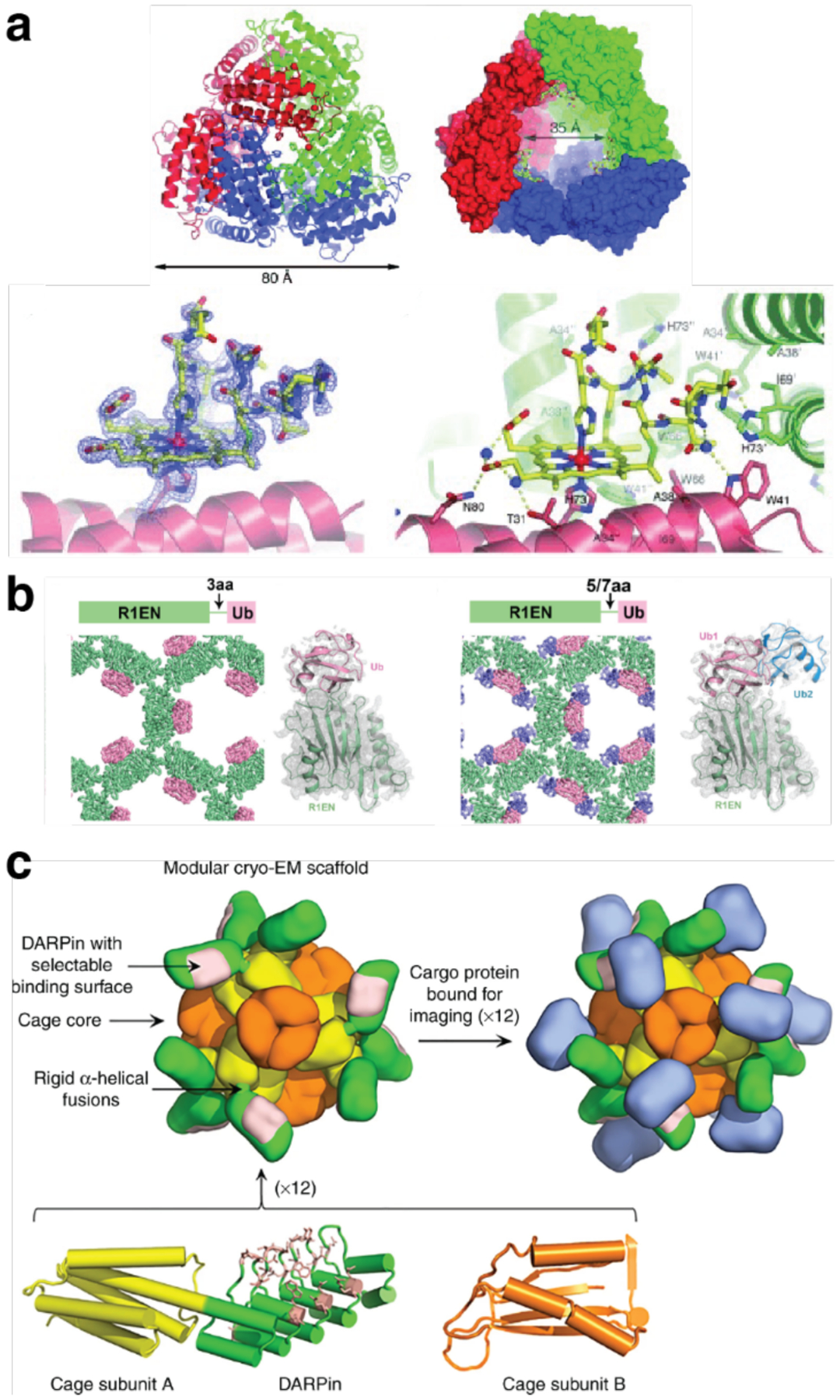
Protein assemblies as scaffolds for structure determination. a) Crystal structure of the tetrahedral protein cage architecture of Zn30:CFMC-112 (top) and of the microperoxidase (MP9cb562) immobilized within the cage cavity (bottom). b) Diagrams and crystal structures of the fusion proteins R1EN-Ub. c) Design of a modular protein scaffold for cryo-EM imaging. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.395. Copyright 2010 Wiley. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.584. Copyright 2018 ACS. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.588. Copyright 2019 NPG.
To further develop scaffold-assisted crystallography techniques in an engineered protein crystal with large pores, Huber et al. used the CJ crystal system.587 CJ crystals are composed of a single protein, a variant of CJ0, a putative periplasmic polyisoprenoid-binding protein from Campylobacter jejuni, and feature 13 nm-wide solvent channels. After designing Cys residues pointing into the large pores, the researchers were able to immobilize an array of small molecules via disulfide bond formation at the designed Cys residues and visualize the electron densities of the anchored molecules by XRD analysis.
In addition to peptides and small molecules, 3D protein lattices can also be used to host other proteins for crystallographic structure determination. Maita demonstrated the immobilization of ubiquitin through C-terminal genetic fusion to honeycomb lattice-forming protein R1EN.584 The large 11 nm pores within the R1EN lattice were able to accommodate several copies of the target in a symmetric fashion. Three R1EN-ubiquitin constructs were crystallized with various linker lengths under the same conditions as the original R1EN (Figure 80b). The ubiquitin structure was solved at 1.7–2.4 Å resolution and was almost identical to the previously published structure.
Following recent technical advances, cryo-EM has become a very powerful and now-common tool for macromolecular structure determination. In contrast to XRD, cryo-EM does not require crystalline samples and provides the distinct advantage of capturing snapshots of protein assemblies in a solution-like state, thus enabling the study of dynamic systems. However, cryoEM methods have their own intrinsic technical limitations and challenges.589 For example, image processing and 3D structure reconstruction can be particularly challenging for small proteins (<50 – 100 kDa),585 due to the low signal-to-noise ratio in single-particle imaging.590 To break through this size barrier in cryo-EM, one strategy is to attach the imaging target to a larger host or scaffold structure. Along these lines, the Yeates Group explored the potential of artificial tetrahedral protein cages (T33–21389 and T33–31,591 Section 3.3.2) as modular, symmetrical scaffolding systems for cryo-EM.585 Using a rigid, continuous, α-helical linker, the researchers genetically fused 12 copies of a 17-kDa protein (Ankyrin repeat protein, DARPin) to the exterior of tetrahedral cages. The resulting construct was amenable to structural analysis by single-particle cryo-EM, revealing structural details of the DARPin adaptor component at resolutions ranging from 3.5 to 5.5 Å. Taking advantage of the ability of DARPin adaptors to recognize and tightly bind protein targets, the same scaffold was used to bind and symmetrically display 12 copies of GFP, a 26-kDa protein (Figure 80c).588 The GFP molecules were associated rigidly enough with the host cage to be resolved at 3.8 Å by cryo-EM/single-particle reconstruction. These results demonstrate that proteins considerably smaller than the proposed limit of 50 kDa for cryo-EM reconstruction can be visualized clearly when arrayed in an ordered fashion on a designed symmetric protein scaffold, thereby expanding the accessible target size range that can be studied by cryo-EM.
4.3.3. Scaffolding of biological molecules
The examples described above highlight the use of protein assemblies as structural scaffolds for encapsulation and structural determination. In many cases, the scaffolding effect of protein assemblies can also lead to new, synergistic functions that are unattainable with the individual components. For example, co-encapsulation of two enzymes in a protein crystal lattice can enable a cascade of catalytic reactions. Towards this end, Nguyen et al. redesigned a protein crystal to entrap lipase B and alcohol dehydrogenase to carry out a two-step reaction within a protein crystal in vivo.592 The cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV) programs infected cells to produce the polyhedrin monomer (PhM) protein, which forms the polyhedral crystal (PhC) during cellular replication. The PhC protects CPV particles from damage. The researchers redesigned PhM, by deleting a 38-residue portion of the monomer, to form hollow PhC cages with 5-nm wide cavities that are suitable for enzyme encapsulation. Overexpression of this PhM mutant along with the two enzymes targeted for encapsulation produced crystals with both enzymes entrapped in the crystal cavities inside the cell. Interestingly, the composite crystal demonstrated 1.9-fold and 3.8-fold higher reactivity of the cascade reaction compared to the wild-type crystal and the mixture of the free enzymes, respectively. The enhanced reactivity was attributed to the efficient diffusion of the substrate and intermediate through the expanded channels within the nanoporous crystal. This study demonstrates that in vivo protein crystallization is a promising approach toward generating artificial biocatalyst platforms by immobilizing different enzymes in nanoporous protein scaffolds.
McConnell et al. covalently attached two enzymes known to act synergistically in cellulose degradation to the surface of previously reported tetrahedral cages (Section 3.3.2, Figure 30) using a sortase enzyme to catalyze their tethering to the designed scaffold via a polyglycine tag.593 The enzyme-modified cages demonstrated enhanced activity in a cellulose degradation assay compared to free enzymes in solution or unmodified cages.
Crystalline 2D protein arrays are promising biotechnological scaffolds due to their ability to display polypeptides with high density and nanoscale tunability/reconfigurability. Engineering the surfaces of 2D protein lattices enables selective organization of the target biomolecules in a site-dependent manner. To generate functionalized 2D protein materials from the bottom up, Subramanian et al. developed an enzyme-directed surface modification approach to site-selectively tailor the surface of 2D protein crystals by using Sfp phosphopantetheinyl transferase (PPTase). Two different designed, self-assembled protein arrays (2D Zn-mediated RIDC3 crystals and disulfide-linked C98RhuA lattices), whose surfaces can be tagged with functional sites (short peptide ybbR or molecular tag CoA), were prepared for enzymatic modification by Sfp PPTase (Figure 81a).594 Notably, the site-specific modification of both 2D arrays could be carried out genetically or chemically without disrupting the underlying crystal lattice packing, characterized by TEM images of the protein crystals and confocal microscopy images of the labeled tags. This study highlights the potential for chemoenzymatic modification of 2D protein arrays towards the hierarchical construction of multicomponent protein systems.
Figure 81.

Scaffolding of biological molecules. a) Design of peptide-tagged RIDC3 arrays for enzymatic labeling. b) Structural model and ns-TEM image of cTRP246SS-scMHC (left); Structural diagram of the cTRP246SS-scTrimer4–1BB, with the single-chain trimer rendered in space filling representation (right). c) Covalently linked nanosheets composed of EBFP2 (donor) and EGFP (acceptor) proteins. Within the nanosheets, energy absorbed by donors can be transferred to acceptors by direct FRET or successive donor-to-donor transfers, conferring light harvesting properties to the nanosheets. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.594. Copyright 2020 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.595. Copyright 2020 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.469. Copyright 2019 ACS.
Bradley and coworkers have designed a circular tandem repeat architecture with α-helical repeats to generate circular protein nanoparticles that could display multiple copies of functional protein domains.595 Their approach centered on deconstructing a large toroid of 24 left-handed, α-helical repeats (cTRP24) into monomers with 3, 4, 6, 8, or 12 repeats. Assembly of the monomers back into the 24-repeat structure allowed for multiple copies of a functional protein to be displayed on the larger oligomer via attachment to each monomer. Initially, only the 12-repeat monomer (cTRP2412) assembled into the 24-repeat oligomer. Subsequent design of disulfide bonds to the putative interfaces in the oligomer yielded stable, disulfide-stapled dimers from the 12-repeat monomer (cTRP2412SS) and tetramers from the 6-repeat monomer(cTRP246SS). Finally, various cargo proteins, including single-chain class I major histocompatibility complex molecule (scMHC) and single-chain tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily ligand trimers, were displayed on the disulfide-stapled oligomers either by genetic fusion or by specific labeling with the SpyCatcher protein ligation domain or the SH2 peptide-binding domain (Figure 81b). The attached proteins remained active, and the formation of oligomers with multiple copies of each protein possessed properties such as avidity that were unattainable with monomeric proteins.
Covalent assembly of proteins into a 2D array can lead to emerging functions due to the highly ordered patterning and spacing between the components. Li et al. designed a 2D protein nanosheet as a light-harvesting system by covalent assembly of EBFP2 (donor) and EGFP (acceptor) proteins, in which the fluorescent chromophores were evenly distributed and adopted a fixed orientation (Figure 81c).469 By varying the length of the inducing linker, the distance between adjacent chromophores and the overall size of the assembly could be optimized to enhance energy transfer efficiency.
Zhang et al. reported the design of single-layer porous protein nanosheets for the precise separation of nanoparticles.477 The researchers cross-linked a TMVCP variant with Cys residues on the outer surface of the ring via Cu2+-catalyzed disulfide-bond formation to yield ordered 2D nanosheets (Section 3.5.2). The resulting single-layer 2D nanosheets with regular 4 nm-wide pores extended over tens of micrometers in width. Based on the single-layer nanosheets, the authors prepared ultrafiltration membranes with a thickness of 40 nm that could precisely separate particles around 4 nm in diameter with high selectivity and exhibited water permeance up to ~7000 L m−2h−1bar−1.
4.3.4. Scaffolding of inorganic and synthetic components
The ability to control the spatial arrangement, orientation and geometry of assembled nano-objects such as metal nanoparticles with high precision is crucial to attain collective optical, magnetic and electronic properties.101,596 Given their ability to encapsulate various cargos and monodisperse structures as discussed above, protein cages such as ferritin and virus capsids have proven to be attractive scaffolds for the integration of synthetic components. Kostiainen et al. leveraged electrostatic interactions between iron oxide-loaded ferritin cages (recombinant magnetoferritin particles) with photodegradable Newkome-type dendrons that lead to self-assembly of micrometer-sized crystals with fcc lattices.597 The ordered superstructures could be disassembled by an optical stimulus that degraded the dendrons. Magnetometry studies revealed that the crystallographic order imparted by self-assembly induced dipole-dipole magnetostatic interactions between the magnetic nanoparticles, which manifest in the hysteresis loops of field-dependent magnetization and field-cooled temperature-dependent magnetization studies. The dipolar-coupled assemblies displayed magnetic properties that deviate from traditional superparamagnetism seen in isolated magnetoferritin particles. Upon UV-triggered disassembly, the released magnetoferritin particles regained their superparamagnetic properties. Okuda et al. synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticles with a narrow size distribution using apoferritin.598 Moreover, the authors used Ce3+ ions to bridge ferritin cages and form 2D (domain size over 500 nm) and 3D arrays (octahedral or prism-like) of CeO2 nanoparticles encapsulated within the cages.
Maity et al. employed ferritin crystals as scaffolds to study Au sub-nanocluster nucleation under reducing conditions.599 They first replaced two residues at the metal accumulation center of ferritin with Cys to pre-organize Au ions within the cage lumen, then obtained Au-treated ferritin single crystals and cross-linked them with glutaraldehyde to facilitate structural investigation by XRD. Upon treatment of these crystals with a strong reduction agent (NaBH4), the researchers were able to track the movement of Au ions toward the three-fold symmetric ferritin cage channels where the ions formed sub-nanoclusters. The ion migration and cluster formation were accompanied by changes in the side chain conformations of Au-bound amino acids, providing insights on dynamic metal-protein interactions involved in metal cluster formation.
Protein cage superlattice scaffolds are not limited to single-component systems. As described in Section 3.6.3.2 (Figure 71), Lijestrom et al. electrostatically assembled avidin and CCMV cages into binary crystals with bcc lattices responsive to external stimuli, such as pH and ionic strength.279 Furthermore, avidin-biotin interactions enabled selective lattice functionalization pre- and post-assembly with various synthetic molecules, including fluorescent dyes, enzymes, and plasmonic nanoparticles. Mikkila et al. combined ferritin, phthalocyanines (Pc) and 1,3,6,8-pyrenetetrasulfonic acid (PTSA) to form ternary fcc crystals with photoactive properties.309 The design strategy was based on the formation of a Pc/PTSA complex through electrostatic and π-π interactions, which in turn could bind to the ferritin cages via charge interactions to induce crystallization. The resulting crystals retained photoactive properties such as fluorescence at 695 nm and efficient light-induced singlet O2 production, which hold great promise in various applications such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), water treatment and diagnostic array development. Using Thermotoga maritima ferritin (TmFtn) as a host protein for enzyme encapsulation, Chakraborti et al. generated binary crystals consisting of cargo-encapsulated TmFtn and Au nanoparticles (AuNPs).600 The TmFtn cage was capable of salt-mediated reversible assembly/disassembly and its negatively charged lumen enabled encapsulation the positively charged guest proteins such as +36GFP and lysozyme. TmFtin-encapsulated lysozyme retained its enzymatic activity both in solution and within the superlattice of TmFtn-AuNP co-crystals.
As discussed in section 3.6.1 (Figure 64), the Beck Group has relied on electrostatic interactions to assemble binary protein lattices based on oppositely charged ferritin cages.277 This protein assembly strategy enabled the formation of mixed nanoparticle architectures, which was demonstrated by loading cerium oxide and cobalt oxide nanoparticles into positively and negatively charged ferritin cages, respectively (Figure 82a). The controlled assembly of these protein-nanoparticle composites via electrostatic interactions led to the formation of highly ordered binary nanoparticle superlattices as free-standing crystals hundreds of micrometers in size. The binary protein-nanoparticle crystals could function as versatile, highly modular materials for various applications due to the functional diversity of nanoparticles that could be loaded into the ferritin pores.601
Figure 82.
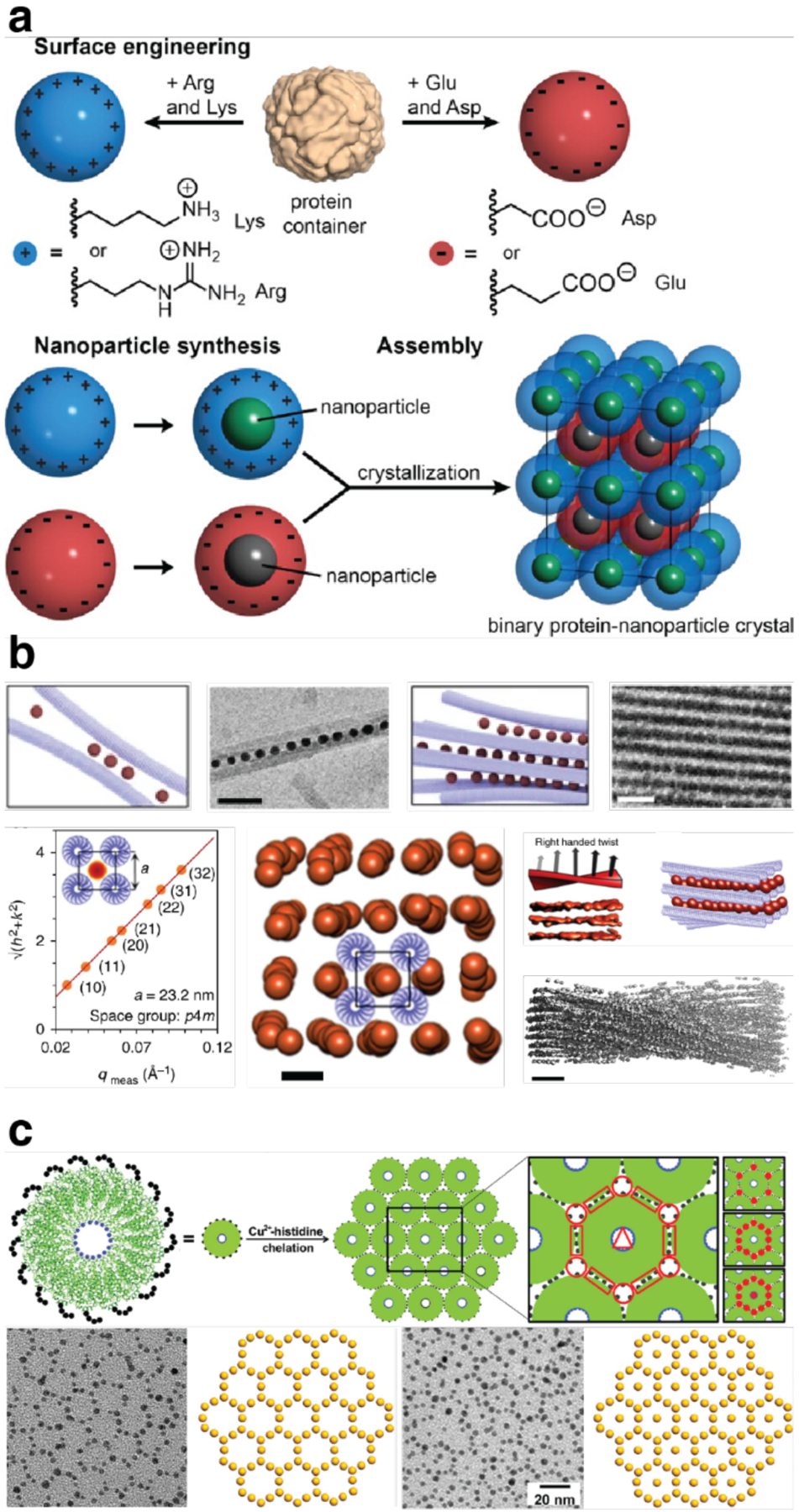
Protein assemblies as scaffolding of inorganic components. a) Scheme for the assembly of binary nanoparticle superlattices based on charged protein containers. b) Hierarchical structure of the superlattice wires composed of TMVs and AuNPs. c) Self-assembly of highly ordered 2D AuNP lattices directed by TMV monolayer sheets. (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.277. Copyright 2016 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.296. Copyright 2017 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.479. Copyright 2019 Wiley.
In a follow-up study, the same group demonstrated that the free-standing nanoparticle superlattices are catalytically active and can be reused for multiple reaction cycles.602 Specifically, the CeO2 nanoparticles were shown to display oxidase and peroxidase-like activity. Compared to free nanoparticles in solution, which are prone to aggregation and are hard to reuse, well-ordered CeO2 nanoparticles in superlattices were stabilized by the protein scaffold without losing access to reactants due to channels within the crystal and protein cage pores, and therefore retained high activity after several reaction cycles. The researchers also found that the binary protein lattice can be transformed to a unary cubic lattice composed only of the negatively charged ferritin variant under high Mg2+ concentration conditions, which were also used to organize metal oxide nanoparticles.507 As illustrated in these studies, protein cage superlattices are versatile and tunable platforms to construct functional hybrid materials with modular biological/inorganic components.
Ring-shaped proteins tend to stack and form 1D nanotubes with a central hollow channel, which could serve as a template for 1D nanoparticle assembly (Section 3.3). Ardini et al. prepared 1D nanotubes by metal-induced self-assembly of ring-shaped peroxiredoxin with an engineered N-terminal His-tag and divalent metal ions such as Ni2+, Zn2+ and Co2+.603 The well-stacked protein rings have been applied to successfully capture and arrange colloidal Ni2+-modified AuNPs into 1D arrays. The formation of such nano-peapod complexes strictly depended on nanoparticle dimensions as the peroxiredoxin template could only capture ultrasmall AuNPs (~1.6 nm) in a size-selective manner. Similarly, Manuguri et al. installed a His-tag as a metal-binding site in the 7-nm diameter pore of the peroxiredoxin and used the engineered protein to organize iron oxyhydroxide nanoparticles.604 Changing the pH caused the peroxiredoxin bound to nanoparticles to stack, thus confining the nanoparticles to extended 1D assemblies. Both studies demonstrate that the peroxiredoxin-based 1D nanotube is a versatile template to induce one-dimensional nanoparticle assembly.
The SP1 dodecamer, which naturally forms nanotubes, has been an appealing scaffold to organize QDs.291 Miao et al. have taken advantage of electrostatic interactions between SP1 protein nanorings and CdTe QDs to make sandwich nanowires, bundles and irregular networks. Detailed characterization by AFM, TEM and DLS indicated that the size of QDs, as well as the structural topology of the SP1 nanoring, played critical roles in the formation of the superstructures. Moreover, combining different sizes of QDs in the protein nanowires enabled efficient FRET, suggesting that the ordered QD arrays could be promising scaffolds for designing artificial light-harvesting systems. The design strategy was further applied to functionalize covalently linked 2D SP1 nanosheets with QDs.230 The nanosheets were decorated with CdTe QDs that bound electrostatically to the negatively charged surface of SP1-based assemblies. The ordered arrangements of QDs of different sizes on protein nanosheets, which served as donor and acceptor chromophores, yielded a pronounced FRET phenomenon. The light-harvesting behavior of these protein-QD nanosheets emulates the thylakoid membranes of natural chloroplasts.
Highly rigid GroEL nanotubes (Sections 3.4.3 and 4.2.1) have also served as scaffolds for nanoparticle organization.292 Prior to metal-mediated assembly, MC-modified GroEL barrels were loaded with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SNPs) bearing a dopamine sulfonate zwitterionic ligand coating and hydrophobic, catechol-modified fluorescent dyes. The hydrophobic modification of the surface was required for the association of SNPs with the barrel cavity, which naturally binds to denatured proteins. Under a magnetic field, SNP-loaded nanotubes assembled into thick bundles, while removing the field returned them to the dispersed nanotube state. This process could be repeated over multiple cycles without causing denaturation of the nanotubes. Importantly, SNPs that were not housed in a protein nanotube sheath remained in an aggregated state when the magnetic field was removed. This work marked the first experimental observation of lateral aggregation of 1D SNP arrays, which had been predicted by theory. The rigid GroEL nanotubes proved to be an ideal SNP array scaffold for experimental observation of this phenomenon.
Superlattice wires represent another class of 1D protein assemblies. Such wires have been prepared through multivalent electrostatic association between anionic TMV rods and functional, cationic, glue-like components. The Kostiainen Group first reported superlattice wire formation in a system composed of TMV and spherical AuNPs.296 The ordered association of the components was carried out by progressively lowering the ionic strength of the solution using sequential dialysis steps and was reversible with increased ionic strength. The superlattices assembled following a cooperative self-assembly pathway that proceeded in a zipper-like fashion, where nanoparticles crosslinked TMV rods into bundles. In cross-sections, the wires showed square lattice (p4m) packing of the TMV rods, rather than the hexagonal geometry commonly observed for the packing of rod viruses (Figure 82b). This observation was explained by the relatively large size of the AuNPs (d ~ 12 nm) in this system, which could bridge four TMV rods to form the close-packed square lattice. In contrast, smaller nanoparticles bound at most to three rods due to steric constraints, which induced hexagonal packing. The consistent interparticle distance within the lattice was controlled by competing repulsive (between AuNPs) and attractive (between AuNPs and virus rods) interactions. The right-handed helicity of the virus rods was imparted on the helical twist of the superstructure, leading to structure-dependent chiral plasmonic optical properties within the material. Proof-of-concept experiments were carried out to demonstrate the potential application of the superlattice wires as plasmonic polarizers by decorating the structures with cationic magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
In a related study, the same group generated photoactive TMV bundles with hexagonal packing using a peripherally crowded ZnPc as a cationic glue.605 Within the scaffolds, the ZnPc acted as a photosensitizer to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) under illumination with visible light. The immobilization of ZnPc within the fibers thus gave rise to a heterogeneous catalyst that could be easily purified by physical methods and had a high solvent-accessible area owing to the high aspect ratio of the structures. The bundles could be immobilized and irradiated over multiple cycles within a microfluidic device, showing consistent production of ROS. This self-assembled material was proposed as a promising, biodegradable catalyst system for applications in green organic synthesis and wastewater treatment.
Most of the examples described in this section thus far have highlighted the template-based design strategy to prepare nanoparticle assemblies. The Schiller Group developed a bottom-up approach, termed protein adaptor-based nano-object assembly (PABNOA), to prepare template-free assemblies of different plasmonically-active AuNP nanoarchitectures.448 Specifically, they designed protein adaptors with genetically encoded interaction sites to guide the assembly of AuNPs. The interactions between geometrically defined protein adaptors (modified Hcp1 toroidal protein building block) and AuNPs induced the self-assembly of different hybrid architectures including 1D chains, networks and stars. Interestingly, the interparticle distance between AuNPs could be controlled by different assembly conditions. The functionality of the different NP architectures could be extended by co-transcriptional encoding of unnatural amino acids as additional site-specific modification sites on the protein adaptors for covalent attachment of dye molecules.
The Trent Group introduced the strategy of using crystalline 2D protein assemblies as templates to generate ordered nanoparticle arrays.606 They used Cys-modified heat shock protein 60 (HSP60), a chaperonin subunit that assembles into hollow octadecameric double-ring structures, with nine subunits per ring and 3- or 9-nm apical pores depending on the presence of an apical loop in the monomer. The Cys residue was located in a solvent-exposed position on the apical side of the monomer. The engineered HSP60 monomers were crystallized into disk-shaped, hexagonally packed 2D templates with periodically arranged thiol groups serving as binding sites to organize AuNPs or CdSe-ZnS QDs into arrays in a size-selective manner. The size selectivity was attributed to the accessibility and positioning of Cys residues, along with the pore size of the templates. The same group further explored the templating and patterning of nanoparticle arrays using chaperonin assembled by heat shock protein TF55β.607 The designed variant formed cage structures with a 20-nm diameter and a core containing 180 imidazole groups from the 18 N-terminal His10 peptides. The chaperonin cages adopted hexagonal 2D packing and the His-rich cores within the lattices served as templates for the synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticle arrays (Ni-Pd or Co-Pd). The average size of the NPs corresponded to the interior diameter of the chaperonin cage and their patterning in arrays reflected the structure of the underlying 2D protein lattice.
Protein assemblies can also be used as chemically active scaffolds to induce nanoparticle assembly. Brodin et al. demonstrated that 2D Zn-RIDC3 arrays could function as redox-active scaffolds for templated growth of Pt0 nanocrystals.204 Specifically, the Zn-porphyrin (ZnP) cofactor in each Zn-RIDC3 building block is redox-inactive in its ground state but becomes a strong reductant/oxidant upon irradiation with visible light. Upon incubation with Pt2+ and light excitation, Zn-RIDC3 arrays displayed uniform coverage with Pt NPs with a narrower size distribution than a) Pt NPs produced in solution in the absence of the protein arrays or b) Pt NPs on protein arrays formed in the absence of light, as characterized by SEM and ns-TEM images. This study illustrated that the supramolecular protein assemblies not only played an important role as structural templates but could also actively control the growth of redox-active NPs due to the specific functional activity of the component protein build blocks.
Thomas et al. used a 2D protein array as a versatile platform for the assembly of multicomponent nanostructures by functionalizing the building blocks with specific tags to recruit various components.487 Starting with a computationally redesigned protein called TTM that forms hexagonal 2D arrays upon Ca2+ triggered assembly, the researchers further modified the protein building block with different functional tags (e.g., hexa-His tag, gold-binding peptide, biotinylation tag). The resulting 2D arrays were used as 2D scaffolds for the fabrication of hybrid materials by binding AuNPs and proteins to the functionalized array surface. These proof-of-concept studies demonstrated that protein-based 2D arrays hold great potential for constructing versatile hybrid materials with promising applications in sensing, medicine, and energy harvesting.
Zhang et al. modified TMVCP disks to direct self-assembly of AuNPs and QDs into ordered nanostructures.479 TMVCP was modified with two distinct mutations: a Cys residue in the center of the TMVCP disk and a His residue on the outer surface of the disk. The combination of these mutations enabled both self-assembly of 2D TMVCP monolayer sheets via Cu2+-His interactions and formation of highly ordered 2D AuNP lattices in three different geometries based on three different binding modes between AuNPs and TMVCP disks (Figure 82c). Similarly, assemblies incorporating two types of QDs arranged in honeycomb and hexagonal lattices were obtained by using the 2D protein nanosheets as templates. Moreover, because the TMVCP nanosheets contained two different functional groups, they could direct the co-assembly of AuNPs and QDs simultaneously, thus giving rise to binary functional NP lattices. Recently, Du et al. have also reported ordered binding of AuNPs to p4212 C98RhuA lattices modified with an additional Cys residue.608
4.4. Mechanical properties of designed protein assemblies
From the mechanosensitive Piezo proteins609 and cytoskeletal fibers at the nm-to-μm scale,114 to extracellular protein composites (e.g., silk, skin, hair) with macroscopic dimensions,610–612 protein-based materials possess outstanding mechanical properties (e.g., toughness, strength, elasticity, self-healing, etc.) that are central to their biological functions.114,613,614 These mechanical properties derive chiefly from how structural components within these materials are interconnected, hierarchically organized, and interfaced with other materials.114,613,614 Therefore, there is much interest in understanding and manipulating how intermolecular interactions are translated into mechanical properties upon assembly and organization at extended length scales. Much of the work in protein-materials engineering has centered on structural proteins including collagens, elastins, resilins and silks, which combine many attractive features such as biocompatibility, biodegradability and processability.615,616 These materials are characterized by peptide-repeat sequences that give rise to interconnected secondary structure motifs with local order, often dispersed within a non-ordered matrix.
In contrast, the protein assemblies discussed in this review are composed of building blocks with well-defined tertiary structures and have been intentionally designed to possess structural order at all length scales. While these assemblies often result in crystalline materials, the highly tunable interprotein interactions that dictate assembly formation can manifest a wide range of mechanical properties. For example, artificial protein cages held by an extensive network of hydrophobic interfaces possess Young’s moduli in the range of 0.1 – 1 GPa, typical of virus capsids with high mechanical strengths. In contrast, metal-directed, 1D protein nanotubes display moduli that are orders of magnitude smaller (0.1 – 30 MPa),419 more similar to flexible natural materials such as fibrin and elastin. Notably, as alluded to in Section 4.2.2, there are several emerging examples of reconfigurable protein assemblies/arrays that display outstanding mechanical properties owing to their unique compositions and connectivities.
2D C98RhuA lattices were previously introduced as crystalline arrays with coherent in-plane dynamics, enabled by the short yet flexible disulfide linkages between the C4 symmetric protein units. Due to the rotary motion of the proteins with respect to their neighbors, coupled with the overall P4212 plane group symmetry, C98RhuA lattices expand in the x dimension to the same extent as in the y dimension and vice versa. Thus, C98RhuA lattices are auxetic and possess the thermodynamically smallest possible Poisson’s ratio (ν) for an isotropic crystalline material of ν = −1, the first such material designed and constructed at the molecular scale. This behavior stands in contrast to common materials, which expand longitudinally when compressed transversely, corresponding to positive ν values.617 Due to their unusual mechanical behavior, auxetic materials have been proposed for use in smart textiles, actuated filtration, sensing, and biomedical devices, as well as piezoelectric materials.618,619
Indeed, Zhang et al. recently demonstrated a potential route to generate a piezoelectric system through surface-templated C98RhuA self-assembly.227 A structural analysis of the C98RhuA building blocks revealed a very large dipole moment (1200 D) aligned with the protein’s principal C 4 symmetry axis (Section 3.5.6; Figure 62). As the C98RhuA lattices assembled in solution have p4212 symmetry, which is associated with an alternating up-down arrangement of the monomers, their overall dipole moment is zero. In contrast, lattices assembled at the mica interface are p4 symmetric, resulting in co-aligned C98RhuA dipole moments within the lattice. Formally, lattices of coaligned dipoles are “electrets”, or polarized dielectric materials with a permanent dipole. Importantly, because C98RhuA lattices isotropically expand and contract in plane, they are calculated to carry a lattice conformation-dependent polarization density (0.008–0.016 C·m−2) and predicted to be piezoelectric.
The combination of crystalline protein lattices with flexible linkages can also be used to construct 3D protein materials with bulk-scale mechanical properties. To obtain thermoresponsive 3D lattices of P. furiosus ferritin (pI ~ 4.5–5.5), Välimäki et al. synthesized linear-branched diblock copolymers consisting of a cationic multivalent dendron with a linear thermoresponsive polymer (pDEGMA) tail.620 Electrostatic interactions between the negatively charged ferritin and the dendron resulted in the formation of an fcc lattice (a = 18.55 nm). Notably, heating the lattice to 50 °C, above the cloud point temperature of pDEGMA (Tcp ~ 31 °C), induced a ~ 2% contraction to a = 18.18 nm owing to the compaction of the pDEGMA chains, thus yielding a thermoresponsive material displaying negative thermal expansion.
In a similar vein, Bailey et al. exploited the synthetic modularity of protein-metal-organic frameworks (protein-MOFs) to synthesize six different ferritin-MOF lattices from a combination of two metal ions and three ditopic linkers.513 The thermostabilities of all six ferritin-MOFs were tunable with the addition of molecular crowding agents. Furthermore, one of the bcc frameworks (fdh-Ni-ferritin) underwent a reversible and isotropic first-order phase transition near-room temperature, with the unit cell dimensions decreasing by 1.3% at 33–34 °C within a transition window of ≤1 °C, corresponding to a volumetric change of 4%. The lattice compaction was fully reversed at 25 °C, yielding a hysteresis window of nearly 10 °C (Figure 83a), which is a property that may be exploited in sensing and memory devices. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and XRD measurements showed that these transitions were first-order and could be attributed to a diffusionless rearrangement of the organic linker connecting the metal nodes on the ferritin building blocks. Such extremely sharp phase transitions are rare in biological systems and typically associated with order-to-disorder transitions.621–623 In solid-state materials, these phase transitions typically involve electronic/spin-state changes.624,625 The thermomechanical behavior of the fdh-Ni-ferritin framework demonstrates the benefits of modular protein design strategies in discovering novel material properties that cannot be predicted from first principles.621–623
Figure 83.
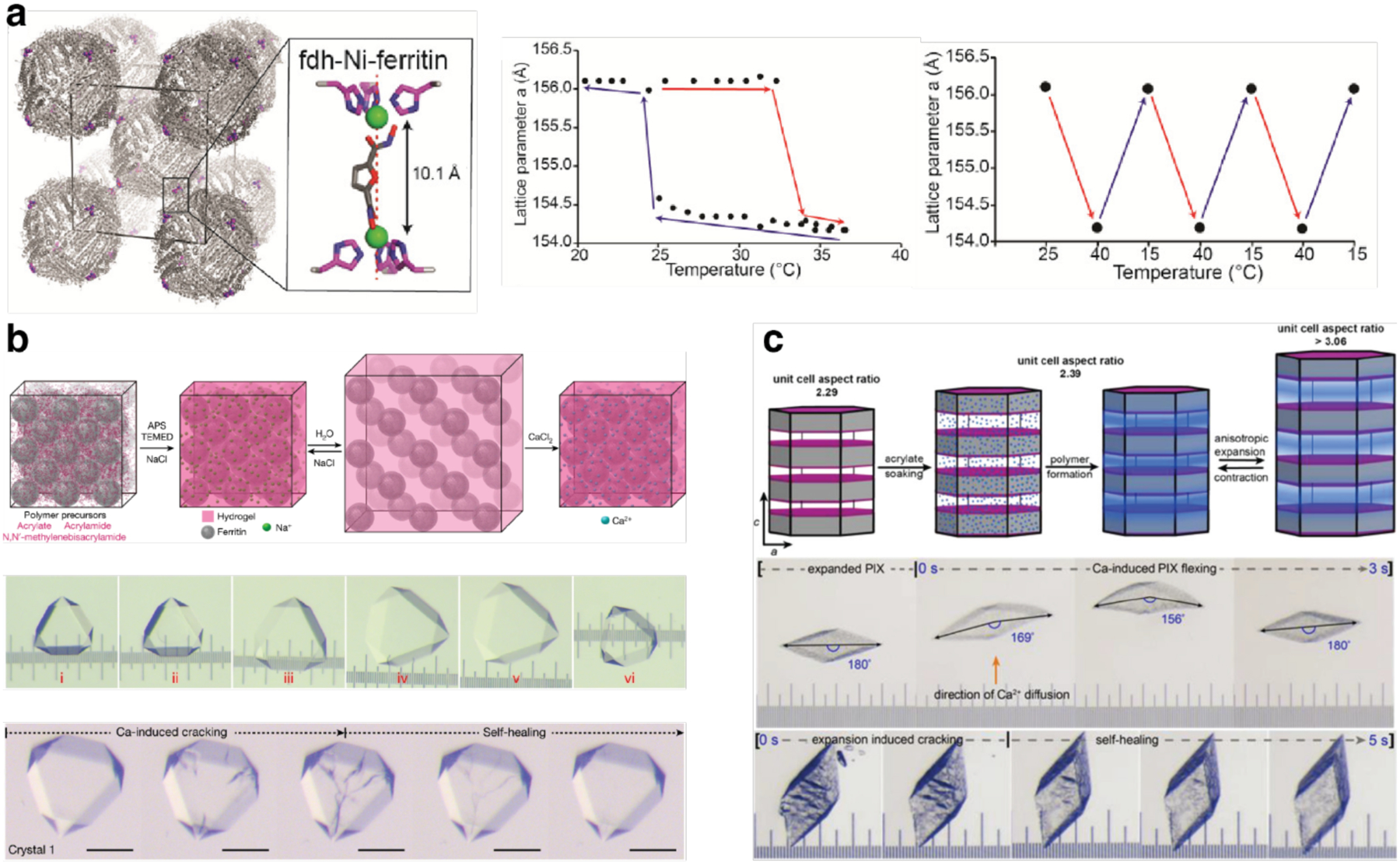
Mechanical properties of protein-MOFs and ferritin-PIX. a) fdh-Ni-ferritin lattice unit cell with a close-up view of the interfacial connectivity (left). Thermal hysteresis loop (middle) and reversible cycling (right) of the fdh-Ni-ferritin lattice expansion/contraction. b) Schematic representation (top) and light micrographs (middle) showing the formation, expansion and contraction of ferritin-PIX. Light micrographs of ferritin-PIX (bottom) showing the self-healing behavior of cracks that appear during Ca-induced contraction. c) Schematic representation of the reversible anisotropic expansion/contraction of rhombohedral raft−ferritin-PIX (top). Light micrographs of the rhombohedral raft−ferritin-PIX crystal showing cation-induced bending motion (middle) and self-healing behavior (bottom). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.513. Copyright 2020 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.295. Copyright 2018 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.573. Copyright 2021 ACS.
Finally, it is important to note that most biological materials such as skin, muscle or bone are not phase-pure or uniform. They are composites of different types of structural components hierarchically organized at different length scales, which enables the combination of properties such as strength, toughness, flexibility, damage tolerance, and self-healing.626,627 In contrast, the highly crystalline, compositionally uniform protein materials described above are highly brittle, have limited flexibility that depends on the bonding interactions which maintain the protein lattice, and are incapable of self-healing.
To address these limitations, Zhang et al. sought to create a composite material where 3D protein crystals are fully integrated with synthetic hydrogel polymers.295 The researchers took advantage of the mesoporosity of Ca2+-directed, HuHF fcc crystals, to thoroughly infuse the lattice channels with acrylate/acrylamide monomers and form a polymer matrix that non-covalently bonded to the underlying protein lattice. The resulting polymer-integrated crystals (PIX) had a ~1 GPa modulus, typical of protein and small-molecule crystals. Despite this high stiffness, the ferritin-PIX displayed notable mechanical properties stemming from their flexibility: 1) They isotropically expanded to nearly 600% of their original volume while retaining crystalline periodicity and faceted polyhedral morphologies. 2) After substantial expansion (separation of the ferritin molecules in the lattice by more than 50 Å), the ferritin-PIX contracted back to their original state when solution ionic strength was increased and fully regained atomic-level periodicity (Figure 83b). Polymer integration and the expansion/contraction process were frequently observed to improve XRD quality, yielding a very high resolution (~1.1 Å) crystal structure of ferritin. 3) Due to the dynamic bonding interactions between the hydrogel network and ferritin molecules, the ferritin-PIX displayed efficient self-healing behavior (Figure 83b).
Due to the cubic symmetry of the Ca2+-mediated HuHF crystals and the isotropic expansion/contraction of the polymer network within the protein lattice, the structural dynamics of ferritin-PIX were also isotropic. In a subsequent study, Han et al. sought to achieve directional/anisotropic dynamic behavior by controlling the spatial distribution of hydrogel networks within ferritin-PIX.573 They employed a ferritin variant that self-assembled upon Ca2+ coordination into rhombohedral lattices composed of stacked hexagonal protein layers, which enabled an anisotropic patterning of the hydrogel matrix that formed in crystallo. The resulting ferritin-PIX indeed displayed directional expansion/contraction in response to changes in solution ionic strength, whereby the aspect ratio of the crystals increased/decreased by more than 30% (Figure 83c). These PIX also displayed rapid bending motions in response to directional influx of cation gradients (bending rates of >10° per second) and were capable of rapid self-healing like the isotropic ferritin-PIX. These studies collectively indicate that it is possible to attain some of the salient mechanical properties of sophisticated biological devices like skeletal muscles through the proper design of self-assembled protein architectures and their simple integration with synthetic materials.
4.5. Biochemical functions of designed protein assemblies
Alongside the construction of biomaterials with emergent physical and mechanical properties, a major goal in designing protein assemblies is to engineer new biochemical functions that can ultimately be integrated into living systems. As we discuss in this section, designed protein assemblies not only enable the generation of new-to-nature biochemical activities that would be difficult to achieve with small (non-assembled) proteins, but also provide a unique platform for understanding and manipulating protein structure-function relationships without evolutionary constraints. The studies described below also highlight how rapidly the field of protein assembly design has transitioned from structure-building to function-building, thereby producing systems that demonstrate in vivo activities and successful interfacing with cellular systems.
4.5.1. Binding and recognition
Perhaps the most mechanistically straightforward biochemical function for a protein or protein assembly is the recognition and binding to targets for downstream effects. As summarized in Section 4.3.3, an important advantage of designed protein assemblies in this regard is the ability to display biological recognition elements with potentially controllable valency and periodicity. Particularly exciting is the design of protein arrays for scaffolding antibodies that may mimic and even go beyond the valences of IgG (bivalent), IgA (tetravalent), and IgM (decavalent) in the context of stable and readily modifiable platforms. In an early study, Wagner and colleagues reported a series of ring-shaped assemblies of genetically fused dihydrofolate reductase dimers (DHFR2), which were self-assembled via chemical dimerizers (bis-MTX) and varied in size and composition from two to eight monomers.628 Based on these nanoring architectures, Li et al. constructed self-assembled antibody nanorings (CSANs) from fusions of DHFR2 with single-chain anti-CD3 antibodies, affording valences of eight to ten (Figure 84a).629 Through flow cytometry measurements, it was determined that the octavalent anti-CD3 CSANs in particular demonstrated improved affinity to CD3 expressing cells compared to the parental monoclonal antibody (mAb) UCHT-1. Moreover, the researchers found that anti-CD3 CSANs and the parental mAb UCHT-1 demonstrated a similar cellular internalization mechanism. In contrast to mAb, no significant T-cell proliferation was observed after the treatment of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with the bivalent and octavalent anti-CD3 CSANs. mAb and anti-CD3 CSANs also exhibited distinct effects on T-cell receptor internalization and IL-2 receptor expression.
Figure 84.
Design of protein assemblies with specific target recognition and binding properties. a) Scheme of the assembly and disassembly of octavalent anti-CD3 scFv antibody targeting T cell receptors. b) Design and characterization of HA nanoparticle immunogens (qsMosaic-I53_dn5 and qsCocktail-I53_dn5). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.629. Copyright 2010 ACS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.630. Copyright 2021 NPG.
To further evaluate the efficacy of CSANs as prosthetic antigen receptors (PARs) in vivo, the same group developed bispecific PARs that selectively target the human CD3 receptor and human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), which is overexpressed on multiple carcinomas and cancer stem cells.631 The designed bispecific CSANs stably bound to T cell surfaces for > 4 days in vitro, while being easily disassembled on the cell membrane by treatment with the nontoxic FDA-approved drug, trimethoprim. Furthermore, the study also demonstrated that CSANs could nongenetically generate reversibly modified T cells that were capable of eradicating target solid tumors.
Based on the design principles developed to build symmetric two-component nanocages,186,389,391 Divine et al. recently described a general approach for building precisely oriented antibody assemblies without the need for covalent modification.394 As described in Section 3.3.2 (Figure 33), such “antibody nanocages” (AbCs) were produced by leveraging the inherent two-fold symmetry of IgG antibodies, which drove nanocage self-assembly in combination with properly designed Fc-binding homo-oligomers. The authors prepared a series of AbCs with dihedral, tetrahedral, octahedral, and icosahedral architectures bearing 2, 6, 12, and 30 antibodies per nanocage, respectively. Compared to free antibodies or Fc-fusions, the binding of designed antibody nanocages to cell-surface receptors showed enhanced signaling in DR5-mediated apoptosis, Tie2-mediated angiogenesis, CD40 activation, and T cell proliferation. Moreover, antibody nanocages composed of α-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and FcACE2 fusion proteins also increased SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization.
In a slightly different structural context, Boyoglu-Barnum et al. transformed previously reported, artificial two-component icosahedral protein cages into nanoparticle immunogens that induce potently neutralizing and broadly protective antibody responses against influenza viruses.630 The researchers genetically fused hemagglutinin (HA) ectodomains from the four strains in licensed 2017–2018 seasonal influenza vaccines to the N terminus of a trimer (I53_dn5B). The resulting trimeric construct (HA-I53_dn5B) was mixed with I53_dn5A pentamer to generate a mosaic nanoparticle immunogen that co-displayed the four HAs (qsMosaic-I53_dn5). Similarly, nanoparticle immunogens with individual HAs were purified and mixed in equimolar amounts to prepare a “cocktail” immunogen that contained four individual HA-displaying nanoparticles (qsCocktail-153_dn5) (Figure 84b). In several animal models, both qsMosaic-I53_dn5 and qsCocktail-153_dn5 elicited antibody responses against vaccine-matched strains that were equivalent to or better than commercial quadrivalent influenza vaccines. Simultaneously, these immunogens induced broadly protective antibody responses to heterologous viruses by targeting the subdominant yet conserved HA stem. Following a similar design approach, protein nanoparticles displaying virus antigens such as glycoprotein632,633, HIV envelope trimers634 and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domains635 have also shown promise in inducing potent immune responses as potential vaccine development candidates.
In addition to the multivalent display of proteins that bind to biological targets, protein assemblies can also be designed to directly bind small molecules. Park et al. redesigned a C3-symmetric homotrimer, which they had previously designed with HBNet, to bind amantadine, an FDA-approved drug that is also C3-symmetric.636 The resulting protein bound amantadine with an affinity of 24 μM and a crystal structure revealed decent similarity with the design model (RMSD = 0.63 Å), though there were differences in the hydrogen bonding interactions between the protein and the ligand. Rittle et al. reported that a penta-His Fe(II) binding site designed through their MASCoT approach was capable of binding nitric oxide (NO).347 Addition of the NO donor diethylammonium NONOate to the iron-loaded protein in anaerobic conditions resulted in spectroscopic features consistent with an {FeNO}7 species. A crystal structure of the complex featured electron density above the iron center that was modeled as a bound NO ligand.
4.5.2. Membrane-related functions
Aside from displaying antibodies for protein binding, protein assemblies have also been designed for interactions with cellular membranes and membrane components. Sundquist, King and colleagues reported artificial protein assemblies (enveloped protein nanocages or EPNs) that directed their own release from human cells and could deliver cargo to other cells.637 For this purpose, the building blocks of a previously designed icosahedral cage (I3–01, Section 3.3.2, Figure 32) were genetically fused to a signal peptide sequence for N-myristoylation in its N-terminus to enable membrane binding. In addition, a sequence (p6Gag from HIV-1) for the recruitment of endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) machinery was also attached to its C-terminus to generate the construct EPN-1 (Figure 85a). When expressed in human embryonic kidney 293T cells, a small but significant amount (13.3%) of EPN-1 was found to be released into the culture medium in the form of multiple, 25-nm cages contained inside 107 ± 44 nm membrane envelopes (EPNs) (Figure 85a). Mutational analyses indicated that all three protein components were necessary for EPN release from the kidney cells. Vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein (VSV-G) could be recruited into EPNs, allowing their fusion with HeLa cells and delivery of cargo proteins into these cells. The researchers demonstrated the generality and modularity of EPN design with several more successful constructs that carried a variety of membrane-binding, self-assembly and ESCRT-recruiting elements, including designed, self-assembling protein cages with octahedral symmetry (O3–33).
Figure 85.
Protein assemblies designed for interactions with cellular membranes and membrane components. a) Central slice from a cryo-EM tomographic reconstruction of a released EPN (left), structural models of the 3D cryo-EM reconstruction from EPN-1 (middle) and I3–01 nanocage (right). b) 2D array functionalization by genetic or post-translational fusions (top) and 3D reconstruction of clustered TIE2 with or without the presence of 2D arrays (bottom). c) Structure of water-soluble hexameric WSHC6 determined by XRD and the ion conductivity of the 12-helix TMHC6 transmembrane channel (left) and ion conductance of TMHC6 with different cations (right). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.637. Copyright 2016 NPG. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.489. Copyright 2021 NPG. (c) Adapted with permission from Ref.359. Copyright 2020 NPG.
More recently, Ben-Sasson et al. reported that computationally designed, binary 2D protein arrays could interact with cell membranes and control membrane receptor clustering.489 They took advantage of the two-component, hexagonal protein arrays composed of D2 and D3 symmetric building blocks, which were shown to self-assemble in vitro and in vivo with high fidelity (Section 3.5.5, Figure 60). An advantage of the two-component system is that the co-assembly process can be controlled by mixing. Due to their robustness, the 2D arrays could be genetically and post-translationally modified with other proteins and ligands for cell-surface receptors, such as GFP and TIE2, respectively. This allowed the researchers to demonstrate that these arrays can induce the clustering of membrane proteins and activate downstream signaling processes (Figure 85b). Specifically, super-resolution microscopy experiments revealed extensive remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton underneath the 2D-array-induced TIE2 clusters, whereas high-resolution AFM imaging confirmed that the in vivo-assembled arrays maintained the same hexagonal architecture observed under in vitro conditions. It was also observed that the extensive 2D arrays tailored with ligands for epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) suppressed endocytosis in a tunable fashion, whereas smaller particles such as designed protein cages were readily taken up by cells and degraded in lysosomes. The researchers proposed that the ability of designed 2D arrays to inhibit endocytosis without inducing signaling could help improve the efficacy of signaling-pathway antagonists by extending receptor engagement and immune evasion.
In another recent development, Xu et al. engineered oligomeric transmembrane pores that assemble in membranes in vitro and in vivo.359 Using a two-step strategy, the researchers first designed a water-soluble hexamer of coiled-coil motifs to generate a 12-helix barrel (WSHC6) whose crystal structure closely matched the computational design. The outward-facing residues of WSHC6 were then redesigned to promote membrane insertion, yielding the construct TMHC6 (Figure 85c). This construct was expressed as a hexamer in the membranes of E. coli cells and was highly thermostable. Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments with Trichoplusia ni insect cells expressing the TMHC6 pore indicated ion conductance, with higher selectivity observed for K+ compared to other monovalent cations such as Na+. (Figure 85c) This selectivity was likely due to the size of the transmembrane pore, which was large enough to allow partially dehydrated K+ ions, but not fully hydrated Na+ ions, to pass through.
4.5.3. Catalysis
As illustrated by the aforementioned cage-like and 2D scaffolding systems, the enhancement of binding between protein assemblies and their targets can have many potential biological applications. However, binding and recognition alone cannot trigger more complex biochemical functions such as catalysis. Such functions require proteins to not only bind and organize substrate and solvent molecules, but also act upon them in a choreographed fashion to enable chemical transformations. In a way, the difference in complexity between “a binder” and “a catalyst” is similar to the difference between a stable protein structure sitting in a deep energy well and a dynamic one that can traverse a complex free-energy landscape with many minima (see Section 4.2). Given the inherent reactivities of metal ions, the majority of successes in enzyme design has involved the construction of protein structures with active sites containing metal ions or metallocofactors.638–645 Most of these engineered metalloenzymes are constructed by repurposing the active sites or cavities of pre-existing protein scaffolds in order to circumvent the need for designing a protein structure from scratch.638,640 An important advantage of designed protein assemblies for enzymatic functions is that they provide extensive protein-protein interfaces where catalytic sites can be built without evolutionary constraints. This advantage has been successfully used in recent years.
The first example of a designed protein assembly with enzymatic activity was reported by Der et al.343 In their efforts to generate a stable C2 symmetric dimer of a model helix-turn-helix domain (Rab4-binding domain of rabenosyn), the researchers incorporated two His4-Zn2+ coordination sites and computationally modeled the dimeric interfaces (Section 2.2.2, Figure 12, Figure 86a).342 One of the resulting constructs, termed MID1, formed a stable dimer with high Zn2+ affinity at the interface (Kd < 30 nM). However, the crystal structure of MID1 revealed that the two Zn centers were coordinated by a His3 rather than the intended His4 coordination motif. Noticing the similarity of the resulting His3:Zn2+ centers positioned in hydrophobic niches to the catalytic sites of natural Zn-dependent enzymes, the researchers examined the catalytic activity of the MID1-Zn2+ dimer. This construct was found to be quite active toward the hydrolysis of model substrates p-nitrophenyl acetate (pNPA) and p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP), with rate accelerations of 7 × 105 and 1 × 104 and kcat/Km values of 630 M−1 s−1 and 14 M−1 s−1 for pNPA and pNPP, respectively.343 The finding that relatively high catalytic efficiencies could be obtained in a minimally designed interface suggested that metal-mediated protein interfaces could provide a powerful strategy for the rational engineering and evolution of new catalytic activities.
Figure 86.

Designed protein assemblies as metalloenzymes. a) Studies of kinetic properties of cyt cb562 variants for pNPA and ampicillin hydrolysis (top). Representative LB/agar plates in the absence and presence of 0.8 mg/L ampicillin streaked with cells expressing C96RIDC1 and A104AB3 (bottom). b) Emulating metalloenzyme biogenesis from Zn-mediated assembly and the hydrolysis of fluorogenic ester catalyzed by MID1sc (top). Michaelis-Menten plots and stereoselectivity of the hydrolysis reaction using MID1sc (yellow) and MID1sc10 (green). (a) Adapted with permission from Ref.205. Copyright 2014 AAAS. (b) Adapted with permission from Ref.207. Copyright 2018 AAAS.
Following up on this concept, Song et al. developed an artificial metallo-β-lactamase that functioned in vivo.205 The researchers used the Zn-directed, D2-symmetric tetramer of the cyt cb562 variant C96RIDC1 (Zn4: C96RIDC14) (Section 3.2.4, Figure 25) as a scaffold. While preserving the four, coordinatively saturated Zn sites to stabilize the tetrameric assembly, they designed four additional three-coordinate Zn2+ centers into one of the C2 symmetric interfaces to generate a series of catalytically active protein complexes. One of the variants, Zn8:K104AAB34, displayed enzymatic activity not only for ester hydrolysis (kcat = 0.2 s−1 and kcat/Km = 120 M−1 s−1 for pNPA at pH 10), but also for the more challenging β-lactam hydrolysis reaction (kcat/Km = 115 M−1 min−1 for ampicillin, a β-lactam antibiotic). Leveraging the previous observation that C96RIDC1 derivatives were capable of assembling into the designed tetramers by selectively binding Zn2+ in the periplasm of E. coli cells,210,367 the researchers then demonstrated that Zn8:K104AAB34 was also catalytically active in bacterial cells, allowing them to survive in the presence of moderate concentrations of ampicillin. This construct thus represented the first designed protein assembly to confer a functional benefit to a living organism.
The in vivo effect of Zn8:K104AAB34 on cell viability enabled the researchers to improve the artificial enzyme’s β-lactamase activity by directed evolution. The optimized variant K104A/E57GAB3 had a three-fold higher catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) 115 M−1 min−1, a catalytic proficiency (kcat/Km/kuncat) of 2.3 × 106 M−1, and a four-fold enhanced selectivity over pNPA hydrolysis (Figure 86a). Unexpectedly, the crystal structure of Zn8:K104A/E57GAB34 revealed a substantially altered architecture compared to that of Zn8:AB34. Notably, the E57G mutation, which emerged in the course of in vivo screening, was found to increase the mobility of an otherwise-ordered loop near the active site and enhance substrate binding through hydrophobic interactions, which is a key feature of natural β-lactamases.646,647 Follow-up studies using related tetrameric β-lactamases further established that the local structural flexibility/rigidity near the metal active sites can have substantial effects on the evolvability of β-lactamase activities206 and that symmetry-related residues in protein-protein interfaces may have outsized effects on catalysis.646–648
Studer et al. recently adopted a similar strategy to convert the aforementioned MID1-Zn dimer into a highly efficient, single-chain esterase.207 Using the MID1-Zn dimer crystal structure as a guide, the MID1 monomers were appropriately linked through C-N terminus gene fusion. The resulting construct was subjected to an extensive series of redesign, rational and random mutagenesis and gene shuffling steps, which were coupled to an activity screen for the hydrolysis of a fluorogenic substrate. These directed-evolution steps led to a variant (MID1sc10) with a remarkably high catalytic performance (kcat = 1.6 s−1, kcat/Km = 980,000 M−1 min−1, kcat/Km/kuncat = 9.3 × 1010 M−1) and stereoselectivity (~1000-fold kinetic preference for S over R enantiomer), on par with highly evolved natural enzymes.649 (Figure 86b) In addition to hydrolysis reactions, Lewis acidic metal ions can catalyze a number of abiological reactions, including the Diels-Alder reaction.650 Basler et al. used the MID1-Zn dimer as a starting point to design and evolve an artificial Diels-Alderase.344 After multiple rounds of directed evolution, the researchers obtained an enzyme with >99% enantioselectivity and the highest reported catalytic proficiency of any Diels-Alderase, thereby demonstrating that interfacial metal active sites can be used to develop enzymes for reactions that are typically considered abiological.
Although the scope of designed metalloprotein assemblies with catalytic activities have thus far been limited to Zn-based hydrolases and Diels-Alderases, the examples summarized above demonstrate the immense potential to generate new and evolvable activities in nascent protein interfaces. Given the genetic economy with which metal ions can nucleate protein-protein interactions and simultaneously provide inherent reactivities, these examples also implicate a potential role of metal-templated protein assembly in the evolution of modern metalloenzymes.368,369,651
5. Future directions and challenges
Proteins are nature’s premier building blocks for sophisticated molecular machines and materials, which has inspired scientists from diverse disciplines to try their own hand at designing protein assemblies with the structural and functional complexity of natural assemblies. In this review, we have summarized the remarkable progress that has been made in the rational design and construction of protein assemblies in the last two decades. To tackle the chemical and structural complexity of molecular interactions that guide protein self-assembly, scientists have devised many computational,392 chemical91 and protein engineering86 strategies to create an ever-expanding design toolkit. These advances have enabled the construction of complex protein architectures, ranging from small oligomers196,360 and cage-like assemblies127,195 to extended 1D structures202,224, as well as 2D128,225 and 3D crystals.470,513 Many of these assemblies are not only stable, but also demonstrate dynamic, adaptive and stimuli-responsive behavior.
Importantly, the field of protein nanotechnology has made a swift transition from structure-building to property- and function-building. Protein materials with novel mechanical properties,616 catalytically652 and optically597 active systems, and assemblies that interface with cellular components489,637 and possess bona fide biological functions,205 all reported within the last five years, aptly illustrate the field’s transition toward function-building. The protein assembly design field has greatly benefited from contemporaneous technological advances in the characterization of static and dynamic structural protein assembly features,157 the development of computational methodologies,157 as well as new protein biochemistry and molecular biology tools.86 Perhaps more importantly, these advances have been enabled by our growing understanding of molecular interactions and self-assembly, and the combination of knowledge from diverse disciplines such as protein design, supramolecular chemistry, inorganic chemistry, nanotechnology, polymer chemistry and physics.
What are some of the challenges and prospects of protein nanotechnology in the coming years? As usual, one needs to look no further than the structural and functional sophistication of natural protein assemblies or protein-based materials (e.g., multicomponent machines like photosystem II653 or dynamic materials like cytoskeletal filaments654) for inspiration. Despite our expanding design toolkit for controlling protein self-assembly (Section 2), essentially all the protein structures described in this review are symmetrical or periodic and consist of one, and at most two, protein components (Section 3). Often, these artificial assemblies are built for stability rather than dynamic or responsive behavior. Thus, an important technical challenge will be to improve the accuracy and efficiency of computational protein design methods, while also incorporating responsive elements/fluid bonds (e.g., metal coordination,200 electrostatic,272 polar489 and water-mediated interactions193) to enable the self-assembly of dynamic, multicomponent architectures via the simultaneous formation of multiple protein-protein interfaces. The presence of responsive elements will be instrumental in asserting control over self-assembly kinetics and for constructing reconfigurable and far-from-equilibrium systems.
Along these lines, it will be important to look beyond simple self-assembly. The formation of most natural protein-based machines and materials does not happen spontaneously from a one-pot mixture of building blocks. Instead, their assembly is often directed by templates (e.g., membranes,489,655 chaperones,656 polynucleotide sequences657) and takes place in a stepwise, spatially and temporally controlled fashion. Thus, it will be necessary to design/tailor protein building blocks for association not only with other proteins but also with external templates, and once again, to incorporate responsive/externally tunable interactions to access spatiotemporal control over protein assembly. Likewise, the construction of protein-based materials at the micrometer- or longer length scales will require us to think beyond the design of short-range, non-covalent interactions, which is the traditional realm of protein design. Considering other design elements, such as protein shape, charge, charge distribution, hydrophilic/hydrophobic patterning, etc. will enable the exploitation of other forces (electrostatic/dipole, magnetic, depletion, phase separation, etc.) and external fields to build hierarchical protein architectures at extended length scales.91
While the structure of a protein assembly is the obvious immediate target for design, it is hardly sufficient for obtaining a desired property or function. Indeed, the greater challenge in the design of functional protein assemblies does not stem from designing a particular structure with high accuracy, but rather from the fact that we possess an insufficient understanding of structure-property or structure-function relationships in proteins (except perhaps for simple functions like binding and recognition). For example, if we did not know the function of hemoglobin, we might still deduce from its globin fold and heme coordination environment that it is likely involved in small-molecule binding and not electron transfer. Yet, we would not be able to predict that it functions as a reversible O2 transporter that displays positive cooperativity and allosteric modulation by CO2 and BPG.658 Similarly, it would not be possible to describe the mechanical properties and nucleotide-dependent assembly/disassembly behavior of microtubules simply from 3D structures of α- and β-tubulin and the intermolecular interfaces between them.659,660
Given this current knowledge gap between structure and property/function, we believe that it is impractical to solely rely on the conventional, deterministic protein design approach of “one design → one structure → one function”, which is challenging in its own right and inherently limited to one or few functional outcomes in the best-case scenario. More favorable, in our opinion, would be an alternative design pathway of “one design → multiple structural outcomes → multiple functional outcomes”. In this pathway, condition-dependent protein-protein interactions would enable one or few building blocks to yield a multitude of protein assemblies (for example, via switchable interactions), which in turn would provide a higher likelihood of obtaining the desired functions as well as the discovery of serendipitous ones. The key to the execution of this strategy would be modular protein assembly strategies (e.g., reconfigurable systems described in Section 4) coupled with efficient functional selection or screening methods, similar to those successfully used in the directed evolution of artificial enzymes and other functional proteins.
In closing, the structural and functional sophistication of natural protein assemblies and materials – which have evolved through functional selection over millions of years – may appear far out of reach for rational design. Yet, rational design is unbounded by the synthetic restrictions of living systems and has access to an unlimited source of building blocks, chemical tools and assembly strategies. Indeed, as we have attempted to describe in this review, the field of protein nanotechnology has, in very short order, produced artificial protein assemblies and materials whose structural and functional attributes also lie beyond those of natural systems. Given the large momentum of this field and its expanding interdisciplinary scope, it would not be a big stretch to predict that there will soon be artificial protein assemblies used in real-life applications (e.g., as pharmaceutical agents,661 catalysts in industrial processes,662,663 or device components664) and incorporated into the life cycles of organisms for synthetic biological purposes.
Acknowledgments
We thank L. Zhang, R. Subramanian, R. Alberstein and J. Esselborn for extensive discussions and assistance. Research by the Tezcan Lab described in this Review was supported by the following agencies: US Department of Energy (DOE) Basic Energy Sciences (BES) (Division of Materials Sciences, Biomolecular Materials, DE-SC0003844 for the design and construction of dynamic protein assemblies and protein MOFs), National Science Foundation (DMR-2004558 for the design of 2- and 3D protein assemblies; CHE-1607145 for metalloprotein/enzyme design), National Institutes of Health (R01-GM138884 for metalloprotein/enzyme design) and US Army Research Office (W911NF-19-1-0228 for polymer-integrated protein crystals). Additional support was provided by DOE-BES, as part of the Energy Frontier Research Centers program: CSSAS-The Center for the Science of Synthesis Across Scales-under Award Number DE-SC0019288 (for interfacial protein assembly) and NASA (80NSSC18M0093; ENIGMA: Evolution of Nanomachines in Geospheres and Microbial Ancestors (NASA Astrobiology Institute Cycle 8). The Tezcan Lab is additionally supported by the UC San Diego Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (UCSD MRSEC, DMR-2011924). We gratefully acknowledge support by a NSERC postdoctoral fellowship to N.A. and NIH training grants to A.K. (Chemistry Biology Interfaces; T32GM112584) and A.M.H. (Molecular Biophysics, T32 GM008326).
List of abbreviations
- AFM
Atomic force microscopy
- Ala
Alanine
- Arg
Arginine
- Asp
Aspartic acid
- AUC
Analytical ultracentrifugation
- AuNP
Gold nanoparticle
- Bipy
Bipyridine
- BPG
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
- CCMV
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus
- CD
Circular dichroism
- COF
Covalent-organic framework
- Cys
Cysteine
- Cyt
Cytochrome
- DLS
Dynamic light scattering
- dsDNA
Double-stranded DNA
- cryo-EM
Cryogenic electron microscopy
- EDC
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
- FRET
Förster resonance energy transfer
- GFP
Green fluorescent protein
- Glu
Glutamic acid
- GST
Glutathione-S-transferase
- HA
Hydroxamic acid
- Hcp1
Hemolysin-coregulated protein 1
- His
Histidine
- HRP
Horseradish peroxidase
- HuHF
Human heavy chain ferritin
- Lys
Lysine
- MDPSA
Metal-directed protein self-assembly
- MeTIR
Metal-templated interface redesign
- MOF
Metal-organic framework
- ns-TEM
Negative stain transmission electron microscopy
- NHS
N-hydroxysuccinimide
- NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- PAMAM
Polyamidoamine
- Pc
Phthalocyanine
- PDB
Protein Data Bank
- pDEGMA
Poly(di(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate)
- PEG
Polyethylene glycol
- pI
Isoelectric point
- pNPA
p-nitrophenyl acetate
- pNPP
p-nitrophenyl phosphate
- QD
Quantum dot
- RhB
Rhodamine B
- RhuA
l-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase
- rMeTIR
Reverse metal-templated interface redesign
- SAXS
Small angle X-ray scattering
- sfGFP
Superfolder green fluorescent protein
- SP1
Stable protein 1
- TMV
Tobacco mosaic virus
- TMVCP
Tobacco mosaic virus coat protein
- TRAP
Tryptophan RNA-binding attenuation protein
- VLP
Virus-like particle
- XRD
X-ray diffraction
Biographies
Jie Zhu received his B.S. degree (2011) in Chemistry from Sun Yat-sen University and his Ph.D. degree (2018) from Virginia Tech, where he worked with the late Prof. Karen Brewer and Prof. Amanda Morris on developing supramolecular complexes for photodynamic therapy and metal-organic frameworks for CO2 chemical transformations. Currently, he is a postdoctoral scholar in the Tezcan Group at University of California, San Diego. His research interests focus on developing novel artificial protein-based materials and metal-organic frameworks.
Nicole Avakyan completed her B.Sc. (2011) and Ph.D. (2018) degrees in Chemistry at McGill University, under the supervision of Prof. Hanadi Sleiman. As an undergraduate, she worked on the synthesis and characterization of platinum(II)-based guanine quadruplex binders for chemotherapeutic applications. In her graduate work, she focused on DNA-based nanomaterials, developing methods to reprogram and manipulate DNA assembly using simple self-assembly principles. She joined the Tezcan Group at the University of California, San Diego as an NSERC postdoctoral fellow in 2019, working on rational design of nucleoprotein architectures through hierarchical co-assembly of proteins and nucleic acids, as well as 2D protein assembly.
Albert A. Kakkis received his B.A. in Chemistry (2016) from Pomona College. As an undergraduate, he worked in the lab of Prof. Cynthia Selassie, performing computational studies to predict the impact of active site mutations on the thermal stability of lipases. He is currently a Ph.D. candidate in the Tezcan Group at the University of California, San Diego, where his research focuses on the de novo design of metalloproteins harboring redox-dependent functions.
Alexander M. Hoffnagle received his B.A. in Biochemistry, B.A. in Biophysics, and M.S. in Chemistry from the University of Pennsylvania in 2018, where he was a graduate of the Roy and Diana Vagelos Scholars Program in the Molecular Life Sciences. As an undergraduate, he worked in the laboratory of Prof. Jessica Anna on multi-dimensional spectroscopy of molecules in photosystem I. He is currently a Ph.D. candidate in the Tezcan Group at the University of California, San Diego, where his research focuses on the de novo design of functional metalloproteins and protein assemblies.
Kenneth Han received his B.S. degree in Chemical Biology from University of California, Berkeley in 2017. During his undergraduate career, he joined the laboratory of Prof. Matthew Francis and studied protein-drug conjugates for therapeutic purposes. He then joined the laboratory of Prof. Akif Tezcan to pursue a Ph.D. in Chemistry at the University of California, San Diego. His research focuses on the design, synthesis, and application of polymer-integrated protein crystals.
Yiying Li received her B.S. degree from the College of Chemistry and Molecular Sciences at Wuhan University in 2018. As an undergraduate, she worked on organic synthesis methodology and CO2 electroreduction with gold-metal oxide nanoparticles. She then joined the Tezcan Group to pursue a Ph.D. at the University of California, San Diego. Her research interests center on the design of metal-mediated protein assemblies.
Zhiyin Zhang received her B.S. degree in Chemistry from Zhejiang University in 2018. As an undergraduate, she worked on transition metal catalyzed C-H activation. She then joined the Tezcan Group to pursue a Ph.D. in Chemistry at the University of California, San Diego. Currently, her research focuses on extended protein assembly mediated by supramolecular interactions or carried out at interfaces.
Tae Su Choi received his B.S. degree (2012) and Ph.D. (2017) in Chemistry at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) under the supervision of Prof. Hugh Kim on the mechanism and modulation of amyloid self-assembly. Currently, he is a postdoctoral scholar in Prof. Akif Tezcan’s research group at the University of California, San Diego. His research interest is de novo design of selective metal-binding proteins and development of artificial phosphatase activity.
Youjeong (Yui) Na received her B.S. degree (2019) in Pharmacological Chemistry at the University of California, San Diego. She worked as an undergraduate researcher in the Prof. Stanley J. Opella’s laboratory, studying the structure of G-protein coupled receptors using NMR spectroscopy. She joined the Tezcan Group to pursue her Ph.D. in the following year. Her research focuses on the biomedical applications of polymer-integrated protein crystals (PIX). As a student member of MRSEC, her goal is to design polymer-protein hybrid materials that harness the unique structural and functional features of both types of building blocks.
Chung-Jui Yu was born in Taipei, Taiwan. He received his B.S. in Chemistry from the University of California, Berkeley in 2015 and his Ph.D. in Chemistry from Northwestern University in 2020, where he worked under the supervision of Prof. Danna E. Freedman on understanding electron-electron and electron-nuclear spin dynamics in molecular quantum bits. He is currently a postdoctoral scholar in Prof. Akif Tezcan’s research group at the University of California, San Diego. His research focuses on the development of new dynamic nuclear polarization methodologies with model metalloprotein assemblies and investigating novel magnetism in 3D protein architectures.
F. Akif Tezcan was born and raised in Istanbul, Turkey. He received his B.A. degree in Chemistry from Macalester College and his Ph.D. degree from the California Institute of Technology (Caltech), where he worked with Prof. Harry Gray and Prof. Jay Winkler on the folding and redox properties of metalloproteins. He continued his research career at Caltech as a postdoctoral fellow in Prof. Doug Rees’ group, where he focused on structural investigations of nitrogenase complexes. He joined the University of California, San Diego in 2005, where he is currently Professor of Chemistry, Biochemistry and Materials Science and Leslie Orgel Faculty Scholar. His research interests revolve around the use of chemical tools and principles to address biological questions and to create new biological materials.
References
- (1).Urey HC On the Early Chemical History of the Earth and the Origin of Life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1952, 38, 351–363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).Miller SL The Formation of Organic Compounds on the Primitive Earth. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1957, 69, 260–275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).Miller SL; Urey HC Organic Compound Synthesis on the Primitive Earth. Science 1959, 130, 245–251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).Miller SL; Urey HC; Oro J Origin of Organic Compounds on the Primitive Earth and in Meteorites. J. Mol. Evol 1976, 9, 59–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (5).Joyce GF Rna Evolution and the Origins of Life. Nature 1989, 338, 217–224 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (6).Gilbert W Origin of Life: The Rna World. Nature 1986, 319, 618–618 [Google Scholar]
- (7).Weis WI; Drickamer K Structural Basis of Lectin-Carbohydrate Recognition. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1996, 65, 441–473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (8).Dwek RA Glycobiology: Toward Understanding the Function of Sugars. Chem. Rev 1996, 96, 683–720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).Lis H; Sharon N Lectins: Carbohydrate-Specific Proteins That Mediate Cellular Recognition. Chem. Rev 1998, 98, 637–674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).Bertozzi CR; Kiessling LL Chemical Glycobiology. Science 2001, 291, 2357–2364 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).Gabius H-J; Siebert H-C; André S; Jiménez-Barbero J; Rüdiger H Chemical Biology of the Sugar Code. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 740–764 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12).Ochman H; Lawrence JG; Groisman EA Lateral Gene Transfer and the Nature of Bacterial Innovation. Nature 2000, 405, 299–304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (13).Joyce GF The Antiquity of Rna-Based Evolution. Nature 2002, 418, 214–221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).Caprara MG; Nilsen TW Rna: Versatility in Form and Function. Nat. Struct. Biol 2000, 7, 831–833 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15).Chen I; Christie PJ; Dubnau D The Ins and Outs of DNA Transfer in Bacteria. Science 2005, 310, 1456–1460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (16).Stubbe J; van Der Donk WA Protein Radicals in Enzyme Catalysis. Chem. Rev 1998, 98, 705–762 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (17).Benkovic SJ; Hammes-Schiffer S A Perspective on Enzyme Catalysis. Science 2003, 301, 1196–1202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).Garcia-Viloca M; Gao J; Karplus M; Truhlar DG How Enzymes Work: Analysis by Modern Rate Theory and Computer Simulations. Science 2004, 303, 186–195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (19).Ciccia A; Elledge SJ The DNA Damage Response: Making It Safe to Play with Knives. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 179–204 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (20).Lindahl T; Wood RD Quality Control by DNA Repair. Science 1999, 286, 1897–1905 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).Kunkel TA; Bebenek K DNA Replication Fidelity. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2000, 69, 497–529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Catterall WA Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1995, 64, 493–531 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (23).Long SB; Campbell EB; Mackinnon R Voltage Sensor of Kv1.2: Structural Basis of Electromechanical Coupling. Science 2005, 309, 903–908 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (24).Jiang Y; Ruta V; Chen J; Lee A; MacKinnon R The Principle of Gating Charge Movement in a Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel. Nature 2003, 423, 42–48 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).Chang G; Spencer RH; Lee AT; Barclay MT; Rees DC Structure of the Mscl Homolog from Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: A Gated Mechanosensitive Ion Channel. Science 1998, 282, 2220–2226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (26).Perozo E; Kloda A; Cortes DM; Martinac B Physical Principles Underlying the Transduction of Bilayer Deformation Forces During Mechanosensitive Channel Gating. Nat. Struct. Biol 2002, 9, 696–703 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).Perozo E; Cortes DM; Sompornpisut P; Kloda A; Martinac B Open Channel Structure of Mscl and the Gating Mechanism of Mechanosensitive Channels. Nature 2002, 418, 942–948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (28).Dill KA Dominant Forces in Protein Folding. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7133–7155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).Newberry RW; Raines RT Secondary Forces in Protein Folding. ACS Chem. Biol 2019, 14, 1677–1686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (30).Onuchic JN; Luthey-Schulten Z; Wolynes PG Theory of Protein Folding: The Energy Landscape Perspective. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem 1997, 48, 545–600 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (31).Dobson CM Protein Folding and Misfolding. Nature 2003, 426, 884–890 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (32).Dobson CM; Sali A; Karplus M Protein Folding: A Perspective from Theory and Experiment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 1998, 37, 868–893 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (33).Jones S; Thornton JM Principles of Protein-Protein Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1996, 93, 13–20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (34).Lo Conte L; Chothia C; Janin J The Atomic Structure of Protein-Protein Recognition Sites. J. Mol. Biol 1999, 285, 2177–2198 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (35).Sheinerman FB; Norel R; Honig B Electrostatic Aspects of Protein-Protein Interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2000, 10, 153–159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (36).Hung AY; Sheng M Pdz Domains: Structural Modules for Protein Complex Assembly. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 5699–5702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (37).Janin J; Bahadur RP; Chakrabarti P Protein-Protein Interaction and Quaternary Structure. Q. Rev. Biophys 2008, 41, 133–180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (38).Hamm HE The Many Faces of G Protein Signaling. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 669–672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (39).Virkamaki A; Ueki K; Kahn CR Protein-Protein Interaction in Insulin Signaling and the Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Invest 1999, 103, 931–943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (40).Saltiel AR; Kahn CR Insulin Signalling and the Regulation of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Nature 2001, 414, 799–806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (41).Nelson N; Ben-Shem A The Complex Architecture of Oxygenic Photosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2004, 5, 971–982 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (42).Nelson N; Yocum CF Structure and Function of Photosystems I and Ii. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 2006, 57, 521–565 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (43).Howard JB; Rees DC Structural Basis of Biological Nitrogen Fixation. Chem. Rev 1996, 96, 2965–2982 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (44).Rutledge HL; Tezcan FA Electron Transfer in Nitrogenase. Chem. Rev 2020, 120, 5158–5193 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (45).Marsh JA; Teichmann SA Structure, Dynamics, Assembly, and Evolution of Protein Complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2015, 84, 551–575 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (46).dos Remedios CG; Chhabra D; Kekic M; Dedova IV; Tsubakihara M; Berry DA; Nosworthy NJ Actin Binding Proteins: Regulation of Cytoskeletal Microfilaments. Physiol. Rev 2003, 83, 433–473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (47).Tojkander S; Gateva G; Lappalainen P Actin Stress Fibers--Assembly, Dynamics and Biological Roles. J. Cell Sci 2012, 125, 1855–1864 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (48).Boeynaems S; Alberti S; Fawzi NL; Mittag T; Polymenidou M; Rousseau F; Schymkowitz J; Shorter J; Wolozin B; Van Den Bosch L et al. Protein Phase Separation: A New Phase in Cell Biology. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 420–435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (49).Chiesa G; Kiriakov S; Khalil AS Protein Assembly Systems in Natural and Synthetic Biology. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (50).Bajaj M; Blundell T Evolution and the Tertiary Structure of Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng 1984, 13, 453–492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (51).Quiocho FA Carbohydrate-Binding Proteins: Tertiary Structures and Protein-Sugar Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1986, 55, 287–315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (52).Gether U Uncovering Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Endocr. Rev 2000, 21, 90–113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (53).Beratan DN; Betts JN; Onuchic JN Protein Electron Transfer Rates Set by the Bridging Secondary and Tertiary Structure. Science 1991, 252, 1285–1288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (54).Levy ED; Teichmann S Structural, Evolutionary, and Assembly Principles of Protein Oligomerization. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci 2013, 117, 25–51 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (55).Levy ED; Erba EB; Robinson CV; Teichmann SA Assembly Reflects Evolution of Protein Complexes. Nature 2008, 453, 1262–1265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (56).Dill KA; Ozkan SB; Shell MS; Weikl TR The Protein Folding Problem. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2008, 37, 289–316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (57).Anfinsen CB Principles That Govern the Folding of Protein Chains. Science 1973, 181, 223–230 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (58).Haber E; Anfinsen CB Side-Chain Interactions Governing the Pairing of Half-Cystine Residues in Ribonuclease. J. Biol. Chem 1962, 237, 1839–1844 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (59).Sali A; Blundell TL Comparative Protein Modelling by Satisfaction of Spatial Restraints. J. Mol. Biol 1993, 234, 779–815 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (60).Eisenhaber F; Persson B; Argos P Protein Structure Prediction: Recognition of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Structural Features from Amino Acid Sequence. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 1995, 30, 1–94 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (61).Jones DT Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Based on Position-Specific Scoring Matrices. J. Mol. Biol 1999, 292, 195–202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (62).Zhang Y I-Tasser Server for Protein 3d Structure Prediction. BMC Bioinf. 2008, 9, 40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (63).Kelley LA; Sternberg MJ Protein Structure Prediction on the Web: A Case Study Using the Phyre Server. Nat. Protoc 2009, 4, 363–371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (64).Hardin C; Pogorelov TV; Luthey-Schulten Z Ab Initio Protein Structure Prediction. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2002, 12, 176–181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (65).Harbury PB; Plecs JJ; Tidor B; Alber T; Kim PS High-Resolution Protein Design with Backbone Freedom. Science 1998, 282, 1462–1467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (66).Dahiyat BI; Mayo SL De Novo Protein Design: Fully Automated Sequence Selection. Science 1997, 278, 82–87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (67).Grigoryan G; Degrado WF Probing Designability Via a Generalized Model of Helical Bundle Geometry. J. Mol. Biol 2011, 405, 1079–1100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (68).Regan L; DeGrado WF Characterization of a Helical Protein Designed from First Principles. Science 1988, 241, 976–978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (69).Koga N; Tatsumi-Koga R; Liu G; Xiao R; Acton TB; Montelione GT; Baker D Principles for Designing Ideal Protein Structures. Nature 2012, 491, 222–227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (70).Koepnick B; Flatten J; Husain T; Ford A; Silva D-A; Bick MJ; Bauer A; Liu G; Ishida Y; Boykov A et al. De Novo Protein Design by Citizen Scientists. Nature 2019, 570, 390–394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (71).Jaenicke R; Lilie H Folding and Association of Oligomeric and Multimeric Proteins In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Matthews, C. R, Ed.; Academic Press, 2000; Vol. 53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (72).Keskin O; Tuncbag N; Gursoy A Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions from the Molecular to the Proteome Level. Chem. Rev 2016, 116, 4884–4909 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (73).Kumari N; Yadav S Modulation of Protein Oligomerization: An Overview. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol 2019, 149, 99–113 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (74).Minton AP Implications of Macromolecular Crowding for Protein Assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2000, 10, 34–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (75).Bishop KJM; Wilmer CE; Soh S; Grzybowski BA Nanoscale Forces and Their Uses in Self-Assembly. Small 2009, 5, 1600–1630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (76).Gabrys PA; Zornberg LZ; Macfarlane RJ Programmable Atom Equivalents: Atomic Crystallization as a Framework for Synthesizing Nanoparticle Superlattices. Small 2019, 15, 1805424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (77).Grzelczak M; Vermant J; Furst EM; Liz-Marzán LM Directed Self-Assembly of Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3591–3605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (78).Kao J; Thorkelsson K; Bai P; Rancatore BJ; Xu T Toward Functional Nanocomposites: Taking the Best of Nanoparticles, Polymers, and Small Molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev 2013, 42, 2654–2678 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (79).Li W; Palis H; Merindol R; Majimel J; Ravaine S; Duguet E Colloidal Molecules and Patchy Particles: Complementary Concepts, Synthesis and Self-Assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev 2020, 49, 1955–1976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (80).Zhang W-B; Yu X; Wang C-L; Sun H-J; Hsieh IF; Li Y; Dong X-H; Yue K; Van Horn R; Cheng SZD Molecular Nanoparticles Are Unique Elements for Macromolecular Science: From “Nanoatoms” to Giant Molecules. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 1221–1239 [Google Scholar]
- (81).Reedy CJ; Gibney BR Heme Protein Assemblies. Chem. Rev 2004, 104, 617–649 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (82).Howorka S Rationally Engineering Natural Protein Assemblies in Nanobiotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2011, 22, 485–491 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (83).Lai YT; King NP; Yeates TO Principles for Designing Ordered Protein Assemblies. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 653–661 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (84).Bailey JB; Subramanian RH; Churchfield LA; Tezcan FA Chapter Eleven - Metal-Directed Design of Supramolecular Protein Assemblies In Method Enzymol.; Pecoraro VL, Ed.; Academic Press, 2016; Vol. 580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (85).Pieters BJ; van Eldijk MB; Nolte RJ; Mecinovic J Natural Supramolecular Protein Assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev 2016, 45, 24–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (86).Nguyen TK; Ueno T Engineering of Protein Assemblies within Cells. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2018, 51, 1–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (87).Cannon KA; Ochoa JM; Yeates TO High-Symmetry Protein Assemblies: Patterns and Emerging Applications. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2019, 55, 77–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (88).Churchfield LA; Tezcan FA Design and Construction of Functional Supramolecular Metalloprotein Assemblies. Acc. Chem. Res 2019, 52, 345–355 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (89).Fegan A; White B; Carlson JC; Wagner CR Chemically Controlled Protein Assembly: Techniques and Applications. Chem. Rev 2010, 110, 3315–3336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (90).Bai Y; Luo Q; Liu J Protein Self-Assembly Via Supramolecular Strategies. Chem. Soc. Rev 2016, 45, 2756–2767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (91).Luo Q; Hou C; Bai Y; Wang R; Liu J Protein Assembly: Versatile Approaches to Construct Highly Ordered Nanostructures. Chem. Rev 2016, 116, 13571–13632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (92).Wang X; Liu X; Huang X Bioinspired Protein-Based Assembling: Toward Advanced Life-Like Behaviors. Adv. Mater 2020, 32, e2001436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (93).Norn CH; Andre I Computational Design of Protein Self-Assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2016, 39, 39–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (94).Aumiller WM; Uchida M; Douglas T Protein Cage Assembly across Multiple Length Scales. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 3433–3469 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (95).Kuan SL; Bergamini FRG; Weil T Functional Protein Nanostructures: A Chemical Toolbox. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 9069–9105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (96).Hamley IW Protein Assemblies: Nature-Inspired and Designed Nanostructures. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 1829–1848 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (97).Solomonov A; Shimanovich U Self-Assembly in Protein-Based Bionanomaterials. Isr. J. Chem 2020, 60, 1152–1170 [Google Scholar]
- (98).Beloqui A; Cortajarena AL Protein-Based Functional Hybrid Bionanomaterials by Bottom-up Approaches. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2020, 63, 74–81 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (99).Hansen WA; Khare SD Recent Progress in Designing Protein-Based Supramolecular Assemblies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2020, 63, 106–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (100).Majsterkiewicz K; Azuma Y; Heddle JG Connectability of Protein Cages. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2255–2264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (101).Korpi A; Anaya-Plaza E; Valimaki S; Kostiainen M Highly Ordered Protein Cage Assemblies: A Toolkit for New Materials. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 2020, 12, e1578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (102).Dehsorkhi A; Castelletto V; Hamley IW Self-Assembling Amphiphilic Peptides. J. Pept. Sci 2014, 20, 453–467 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (103).Lapenta F; Aupič J; Strmšek Ž; Jerala R Coiled Coil Protein Origami: From Modular Design Principles Towards Biotechnological Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 3530–3542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (104).Katyal P; Meleties M; Montclare JK Self-Assembled Protein- and Peptide-Based Nanomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng 2019, 5, 4132–4147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (105).Beesley JL; Woolfson DN The De Novo Design of Alpha-Helical Peptides for Supramolecular Self-Assembly. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2019, 58, 175–182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (106).Levin A; Hakala TA; Schnaider L; Bernardes GJL; Gazit E; Knowles TP J. Biomimetic Peptide Self-Assembly for Functional Materials. Nat. Rev. Chem 2020, 4, 615–634 [Google Scholar]
- (107).Pizzi A; Pigliacelli C; Bergamaschi G; Gori A; Metrangolo P Biomimetic Engineering of the Molecular Recognition and Self-Assembly of Peptides and Proteins Via Halogenation. Coordin. Chem. Rev 2020, 411, 213242 [Google Scholar]
- (108).Song Q; Cheng Z; Kariuki M; Hall SCL; Hill SK; Rho JY; Perrier S Molecular Self-Assembly and Supramolecular Chemistry of Cyclic Peptides. Chem. Rev 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (109).Willbold D; Strodel B; Schröder GF; Hoyer W; Heise H Amyloid-Type Protein Aggregation and Prion-Like Properties of Amyloids. Chem. Rev 2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (110).Goodsell DS; Olson AJ Structural Symmetry and Protein Function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 2000, 29, 105–153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (111).Yuan Y; Tam MF; Simplaceanu V; Ho C New Look at Hemoglobin Allostery. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 1702–1724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (112).Springer BA; Sligar SG; Olson JS; Phillips GN Mechanisms of Ligand Recognition in Myoglobin. Chem. Rev 1994, 94, 699–714 [Google Scholar]
- (113).Nogales E Structural Insights into Microtubule Function. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2000, 69, 277–302 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (114).Janmey PA Mechanical Properties of Cytoskeletal Polymers. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 1991, 3, 4–11 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (115).Howard J Mechanical Signaling in Networks of Motor and Cytoskeletal Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2009, 38, 217–234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (116).Fagan RP; Fairweather NF Biogenesis and Functions of Bacterial S-Layers. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2014, 12, 211–222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (117).Sleytr UB; Schuster B; Egelseer EM; Pum D S-Layers: Principles and Applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev 2014, 38, 823–864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (118).Lopez MG; Diez M; Alfonso V; Taboga O Biotechnological Applications of Occlusion Bodies of Baculoviruses. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2018, 102, 6765–6774 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (119).Li YV Zinc and Insulin in Pancreatic Beta-Cells. Endocrine 2014, 45, 178–189 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (120).Coulibaly F; Chiu E; Ikeda K; Gutmann S; Haebel PW; Schulze-Briese C; Mori H; Metcalf P The Molecular Organization of Cypovirus Polyhedra. Nature 2007, 446, 97–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (121).Ozimek P; Veenhuis M; van der Klei IJ Alcohol Oxidase: A Complex Peroxisomal, Oligomeric Flavoprotein. FEMS Yeast. Res 2005, 5, 975–983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (122).Mateu MG Assembly, Stability and Dynamics of Virus Capsids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2013, 531, 65–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (123).He D; Marles-Wright J Ferritin Family Proteins and Their Use in Bionanotechnology. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 651–657 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (124).Ahnert SE; Marsh JA; Hernandez H; Robinson CV; Teichmann SA Principles of Assembly Reveal a Periodic Table of Protein Complexes. Science 2015, 350, aaa2245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (125).Shen J-R Photosystem Ii: Protein Components, Structure and Electron Transfer In Reference Module in Life Sciences; Elsevier, 2020 [Google Scholar]
- (126).Bahadur RP; Chakrabarti P; Rodier F; Janin J A Dissection of Specific and Non-Specific Protein-Protein Interfaces. J. Mol. Biol 2004, 336, 943–955 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (127).Padilla JE; Colovos C; Yeates TO Nanohedra: Using Symmetry to Design Self Assembling Protein Cages, Layers, Crystals, and Filaments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2001, 98, 2217–2221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (128).Sinclair JC; Davies KM; Venien-Bryan C; Noble ME Generation of Protein Lattices by Fusing Proteins with Matching Rotational Symmetry. Nat Nanotechnol 2011, 6, 558–562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (129).Sontz PA; Bailey JB; Ahn S; Tezcan FA A Metal Organic Framework with Spherical Protein Nodes: Rational Chemical Design of 3D Protein Crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 11598–11601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (130).Lanci CJ; MacDermaid CM; Kang SG; Acharya R; North B; Yang X; Qiu XJ; DeGrado WF; Saven JG Computational Design of a Protein Crystal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2012, 109, 7304–7309 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (131).Laniado J; Yeates TO A Complete Rule Set for Designing Symmetry Combination Materials from Protein Molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2020, 117, 31817–31823 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (132).Yeates TO; Liu Y; Laniado J The Design of Symmetric Protein Nanomaterials Comes of Age in Theory and Practice. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2016, 39, 134–143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (133).Yeates TO Geometric Principles for Designing Highly Symmetric Self-Assembling Protein Nanomaterials. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2017, 46, 23–42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (134).Tsai CJ; Zheng J; Zanuy D; Haspel N; Wolfson H; Aleman C; Nussinov R Principles of Nanostructure Design with Protein Building Blocks. Proteins 2007, 68, 1–12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (135).Caulder DL; Raymond KN Supermolecules by Design. Acc. Chem. Res 1999, 32, 975–982 [Google Scholar]
- (136).Holliday BJ; Mirkin CA Strategies for the Construction of Supramolecular Compounds through Coordination Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2001, 40, 2022–2043 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (137).Northrop BH; Zheng Y-R; Chi K-W; Stang PJ Self-Organization in Coordination-Driven Self-Assembly. Acc. Chem. Res 2009, 42, 1554–1563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (138).Yoshizawa M; Klosterman JK; Fujita M Functional Molecular Flasks: New Properties and Reactions within Discrete, Self-Assembled Hosts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2009, 48, 3418–3438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (139).Yaghi OM; O'Keeffe M; Ockwig NW; Chae HK; Eddaoudi M; Kim J Reticular Synthesis and the Design of New Materials. Nature 2003, 423, 705–714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (140).Sciore A; Su M; Koldewey P; Eschweiler JD; Diffley KA; Linhares BM; Ruotolo BT; Bardwell JC; Skiniotis G; Marsh EN Flexible, Symmetry-Directed Approach to Assembling Protein Cages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2016, 113, 8681–8686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (141).Badieyan S; Sciore A; Eschweiler JD; Koldewey P; Cristie-David AS; Ruotolo BT; Bardwell JCA; Su M; Marsh ENG Symmetry-Directed Self-Assembly of a Tetrahedral Protein Cage Mediated by De Novo-Designed Coiled Coils. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 1888–1892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (142).Cristie-David AS; Chen J; Nowak DB; Bondy AL; Sun K; Park SI; Banaszak Holl MM; Su M; Marsh ENG Coiled-Coil-Mediated Assembly of an Icosahedral Protein Cage with Extremely High Thermal and Chemical Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2019, 141, 9207–9216 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (143).Cannon KA; Nguyen VN; Morgan C; Yeates TO Design and Characterization of an Icosahedral Protein Cage Formed by a Double-Fusion Protein Containing Three Distinct Symmetry Elements. ACS Synth. Biol 2020, 9, 517–524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (144).Boas FE; Harbury PB Potential Energy Functions for Protein Design. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2007, 17, 199–204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (145).Samish I; MacDermaid CM; Perez-Aguilar JM; Saven JG Theoretical and Computational Protein Design. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem 2011, 62, 129–149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (146).Mackerell AD Jr. Empirical Force Fields for Biological Macromolecules: Overview and Issues. J. Comput. Chem 2004, 25, 1584–1604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (147).Weiner SJ; Kollman PA; Case DA; Singh UC; Ghio C; Alagona G; Profeta S; Weiner P A New Force-Field for Molecular Mechanical Simulation of Nucleic-Acids and Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1984, 106, 765–784 [Google Scholar]
- (148).Brooks BR; Bruccoleri RE; Olafson BD; States DJ; Swaminathan S; Karplus M Charmm - a Program for Macromolecular Energy, Minimization, and Dynamics Calculations. J. Comput. Chem 1983, 4, 187–217 [Google Scholar]
- (149).Hermans J; Berendsen HJC; Vangunsteren WF; Postma JPM A Consistent Empirical Potential for Water-Protein Interactions. Biopolymers 1984, 23, 1513–1518 [Google Scholar]
- (150).Mayo SL; Olafson BD; Goddard WA Dreiding - a Generic Force-Field for Molecular Simulations. J. Phys. Chem 1990, 94, 8897–8909 [Google Scholar]
- (151).Jorgensen WL; Tirado-Rives J Potential Energy Functions for Atomic-Level Simulations of Water and Organic and Biomolecular Systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2005, 102, 6665–6670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (152).Lazaridis T; Karplus M Effective Energy Functions for Protein Structure Prediction. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2000, 10, 139–145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (153).Mohanty D; Dominy BN; Kolinski A; Brooks CL; Skolnick J Correlation between Knowledge-Based and Detailed Atomic Potentials: Application to the Unfolding of the Gcn4 Leucine Zipper. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinf 1999, 35, 447–452 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (154).Dehouck Y; Gilis D; Rooman M A New Generation of Statistical Potentials for Proteins. Biophys J 2006, 90, 4010–4017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (155).Alford RF; Leaver-Fay A; Jeliazkov JR; O'Meara MJ; DiMaio FP; Park H; Shapovalov MV; Renfrew PD; Mulligan VK; Kappel K et al. The Rosetta All-Atom Energy Function for Macromolecular Modeling and Design. J. Chem. Theory Comput 2017, 13, 3031–3048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (156).Looger LL; Dwyer MA; Smith JJ; Hellinga HW Computational Design of Receptor and Sensor Proteins with Novel Functions. Nature 2003, 423, 185–190 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (157).Kuhlman B; Bradley P Advances in Protein Structure Prediction and Design. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2019, 20, 681–697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (158).Dunbrack RL Jr. Rotamer Libraries in the 21st Century. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2002, 12, 431–440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (159).Dunbrack RL Jr.; Karplus M Backbone-Dependent Rotamer Library for Proteins. Application to Side-Chain Prediction. J. Mol. Biol 1993, 230, 543–574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (160).Ponder JW; Richards FM Tertiary Templates for Proteins - Use of Packing Criteria in the Enumeration of Allowed Sequences for Different Structural Classes. J. Mol. Biol 1987, 193, 775–791 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (161).Tuffery P; Etchebest C; Hazout S; Lavery R A New Approach to the Rapid Determination of Protein Side Chain Conformations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn 1991, 8, 1267–1289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (162).Kono H; Doi J A New Method for Side-Chain Conformation Prediction Using a Hopfield Network and Reproduced Rotamers. J. Comput. Chem 1996, 17, 1667–1683 [Google Scholar]
- (163).DeMaeyer M; Desmet J; Lasters I All in One: A Highly Detailed Rotamer Library Improves Both Accuracy and Speed in the Modelling of Sidechains by Dead-End Elimination. Fold. Des 1997, 2, 53–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (164).Lovell SC; Word JM; Richardson JS; Richardson DC The Penultimate Rotamer Library. Proteins 2000, 40, 389–408 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (165).Holm L; Sander C Fast and Simple Monte-Carlo Algorithm for Side-Chain Optimization in Proteins - Application to Model-Building by Homology. Proteins: Struct, Funct, Genet 1992, 14, 213–223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (166).Hellinga HW; Richards FM Optimal Sequence Selection in Proteins of Known Structure by Simulated Evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1994, 91, 5803–5807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (167).Godzik A In Search of the Ideal Protein-Sequence. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 409–416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (168).Dahiyat BI; Mayo SL Protein Design Automation. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 895–903 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (169).Voigt CA; Gordon DB; Mayo SL Trading Accuracy for Speed: A Quantitative Comparison of Search Algorithms in Protein Sequence Design. J. Mol. Biol 2000, 299, 789–803 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (170).Kuhlman B; Baker D Native Protein Sequences Are Close to Optimal for Their Structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2000, 97, 10383–10388 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (171).Desmet J; Demaeyer M; Hazes B; Lasters I The Dead-End Elimination Theorem and Its Use in Protein Side-Chain Positioning. Nature 1992, 356, 539–542 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (172).Goldstein RF Efficient Rotamer Elimination Applied to Protein Side-Chains and Related Spin Glasses. Biophys J 1994, 66, 1335–1340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (173).Koehl P; Delarue M Application of a Self-Consistent Mean Field Theory to Predict Protein Side-Chains Conformation and Estimate Their Conformational Entropy. J. Mol. Biol 1994, 239, 249–275 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (174).Lee C Predicting Protein Mutant Energetics by Self-Consistent Ensemble Optimization. J. Mol. Biol 1994, 236, 918–939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (175).Looger LL; Hellinga HW Generalized Dead-End Elimination Algorithms Make Large-Scale Protein Side-Chain Structure Prediction Tractable: Implications for Protein Design and Structural Genomics. J. Mol. Biol 2001, 307, 429–445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (176).Mou Y; Huang PS; Hsu FC; Huang SJ; Mayo SL Computational Design and Experimental Verification of a Symmetric Protein Homodimer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2015, 112, 10714–10719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (177).Vakser IA Protein-Protein Docking: From Interaction to Interactome. Biophys J 2014, 107, 1785–1793 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (178).Katchalski-Katzir E; Shariv I; Eisenstein M; Friesem AA; Aflalo C; Vakser IA Molecular Surface Recognition: Determination of Geometric Fit between Proteins and Their Ligands by Correlation Techniques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1992, 89, 2195–2199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (179).Gray JJ; Moughon S; Wang C; Schueler-Furman O; Kuhlman B; Rohl CA; Baker D Protein-Protein Docking with Simultaneous Optimization of Rigid-Body Displacement and Side-Chain Conformations. J. Mol. Biol 2003, 331, 281–299 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (180).Dominguez C; Boelens R; Bonvin AM Haddock: A Protein-Protein Docking Approach Based on Biochemical or Biophysical Information. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 1731–1737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (181).Kozakov D; Hall DR; Xia B; Porter KA; Padhorny D; Yueh C; Beglov D; Vajda S The Cluspro Web Server for Protein-Protein Docking. Nat. Protoc 2017, 12, 255–278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (182).Yan Y; Tao H; He J; Huang SY The Hdock Server for Integrated Protein-Protein Docking. Nat. Protoc 2020, 15, 1829–1852 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (183).Leaver-Fay A; Tyka M; Lewis SM; Lange OF; Thompson J; Jacak R; Kaufman K; Renfrew PD; Smith CA; Sheffler W et al. Rosetta3: An Object-Oriented Software Suite for the Simulation and Design of Macromolecules. Method Enzymol. 2011, 487, 545–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (184).Karanicolas J; Corn JE; Chen I; Joachimiak LA; Dym O; Peck SH; Albeck S; Unger T; Hu W; Liu G et al. A De Novo Protein Binding Pair by Computational Design and Directed Evolution. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 250–260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (185).Doyle L; Hallinan J; Bolduc J; Parmeggiani F; Baker D; Stoddard BL; Bradley P Rational Design of Alpha-Helical Tandem Repeat Proteins with Closed Architectures. Nature 2015, 528, 585–588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (186).King NP; Sheffler W; Sawaya MR; Vollmar BS; Sumida JP; Andre I; Gonen T; Yeates TO; Baker D Computational Design of Self-Assembling Protein Nanomaterials with Atomic Level Accuracy. Science 2012, 336, 1171–1174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (187).Shen H; Fallas JA; Lynch E; Sheffler W; Parry B; Jannetty N; Decarreau J; Wagenbach M; Vicente JJ; Chen J et al. De Novo Design of Self-Assembling Helical Protein Filaments. Science 2018, 362, 705–709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (188).Gonen S; DiMaio F; Gonen T; Baker D Design of Ordered Two-Dimensional Arrays Mediated by Noncovalent Protein-Protein Interfaces. Science 2015, 348, 1365–1368 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (189).Chen Z; Boyken SE; Jia M; Busch F; Flores-Solis D; Bick MJ; Lu P; VanAernum ZL; Sahasrabuddhe A; Langan RA et al. Programmable Design of Orthogonal Protein Heterodimers. Nature 2019, 565, 106–111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (190).Chen Z; Kibler RD; Hunt A; Busch F; Pearl J; Jia M; VanAernum ZL; Wicky BIM; Dods G; Liao H et al. De Novo Design of Protein Logic Gates. Science 2020, 368, 78–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (191).Song WJ; Sontz PA; Ambroggio XI; Tezcan FA Metals in Protein-Protein Interfaces. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2014, 43, 409–431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (192).Sontz PA; Song WJ; Tezcan FA Interfacial Metal Coordination in Engineered Protein and Peptide Assemblies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2014, 19, 42–49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (193).Salgado EN; Ambroggio XI; Brodin JD; Lewis RA; Kuhlman B; Tezcan FA Metal Templated Design of Protein Interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2010, 107, 1827–1832 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (194).Salgado EN; Lewis RA; Mossin S; Rheingold AL; Tezcan FA Control of Protein Oligomerization Symmetry by Metal Coordination: C2 and C3 Symmetrical Assemblies through Cuii and Niii Coordination. Inorg. Chem 2009, 48, 2726–2728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (195).Golub E; Subramanian RH; Esselborn J; Alberstein RG; Bailey JB; Chiong JA; Yan X; Booth T; Baker TS; Tezcan FA Constructing Protein Polyhedra Via Orthogonal Chemical Interactions. Nature 2020, 578, 172–176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (196).Kakkis A; Gagnon D; Esselborn J; Britt RD; Tezcan FA Metal-Templated Design of Chemically Switchable Protein Assemblies with High-Affinity Coordination Sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2020, 59, 21940–21944 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (197).Radford RJ; Nguyen PC; Ditri TB; Figueroa JS; Tezcan FA Controlled Protein Dimerization through Hybrid Coordination Motifs. Inorg. Chem 2010, 49, 4362–4369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (198).Salgado EN; Radford RJ; Tezcan FA Metal-Directed Protein Self-Assembly. Acc. Chem. Res 2010, 43, 661–672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (199).Salgado EN; Faraone-Mennella J; Tezcan FA Controlling Protein-Protein Interactions through Metal Coordination: Assembly of a 16-Helix Bundle Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 13374–13375 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (200).Malay AD; Miyazaki N; Biela A; Chakraborti S; Majsterkiewicz K; Stupka I; Kaplan CS; Kowalczyk A; Piette B; Hochberg GKA et al. An Ultra-Stable Gold-Coordinated Protein Cage Displaying Reversible Assembly. Nature 2019, 569, 438–442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (201).Sim S; Niwa T; Taguchi H; Aida T Supramolecular Nanotube of Chaperonin Groel: Length Control for Cellular Uptake Using Single-Ring Groel Mutant as End-Capper. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 11152–11155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (202).Brodin JD; Ambroggio XI; Tang C; Parent KN; Baker TS; Tezcan FA Metal-Directed, Chemically Tunable Assembly of One-, Two- and Three-Dimensional Crystalline Protein Arrays. Nat. Chem 2012, 4, 375–382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (203).Biswas S; Kinbara K; Niwa T; Taguchi H; Ishii N; Watanabe S; Miyata K; Kataoka K; Aida T Biomolecular Robotics for Chemomechanically Driven Guest Delivery Fuelled by Intracellular Atp. Nat. Chem 2013, 5, 613–620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (204).Brodin JD; Carr JR; Sontz PA; Tezcan FA Exceptionally Stable, Redox-Active Supramolecular Protein Assemblies with Emergent Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2014, 111, 2897–2902 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (205).Song WJ; Tezcan FA A Designed Supramolecular Protein Assembly with in Vivo Enzymatic Activity. Science 2014, 346, 1525–1528 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (206).Song WJ; Yu J; Tezcan FA Importance of Scaffold Flexibility/Rigidity in the Design and Directed Evolution of Artificial Metallo-Beta-Lactamases. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 16772–16779 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (207).Studer S; Hansen DA; Pianowski ZL; Mittl PRE; Debon A; Guffy SL; Der BS; Kuhlman B; Hilvert D Evolution of a Highly Active and Enantiospecific Metalloenzyme from Short Peptides. Science 2018, 362, 1285–1288 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (208).Radford RJ; Tezcan FA A Superprotein Triangle Driven by Nickel(Ii) Coordination: Exploiting Non-Natural Metal Ligands in Protein Self-Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 9136–9137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (209).Burazerovic S; Gradinaru J; Pierron J; Ward TR Hierarchical Self-Assembly of One-Dimensional Streptavidin Bundles as a Collagen Mimetic for the Biomineralization of Calcite. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2007, 46, 5510–5514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (210).Medina-Morales A; Perez A; Brodin JD; Tezcan FA In Vitro and Cellular Self-Assembly of a Zn-Binding Protein Cryptand Via Templated Disulfide Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 12013–12022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (211).Boyken SE; Chen Z; Groves B; Langan RA; Oberdorfer G; Ford A; Gilmore JM; Xu C; DiMaio F; Pereira JH et al. De Novo Design of Protein Homo-Oligomers with Modular Hydrogen-Bond Network-Mediated Specificity. Science 2016, 352, 680–687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (212).Li W; Wang J; Zhang J; Wang W Molecular Simulations of Metal-Coupled Protein Folding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2015, 30, 25–31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (213).Der BS; Jha RK; Lewis SM; Thompson PM; Guntas G; Kuhlman B Combined Computational Design of a Zinc-Binding Site and a Protein-Protein Interaction: One Open Zinc Coordination Site Was Not a Robust Hotspot for De Novo Ubiquitin Binding. Proteins 2013, 81, 1245–1255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (214).Singh R; Whitesides GM Thiol-Disulfide Interchange In The Chemistry of Sulfur-Containing Functional Groups; Patai S, Ed.; J. Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: London, 1993; Vol. Supplement S [Google Scholar]
- (215).Fass D Disulfide Bonding in Protein Biophysics. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2012, 41, 63–79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (216).Liu H; May K Disulfide Bond Structures of Igg Molecules: Structural Variations, Chemical Modifications and Possible Impacts to Stability and Biological Function. mAbs 2012, 4, 17–23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (217).Pajvani UB; Hawkins M; Combs TP; Rajala MW; Doebber T; Berger JP; Wagner JA; Wu M; Knopps A; Xiang AH et al. Complex Distribution, Not Absolute Amount of Adiponectin, Correlates with Thiazolidinedione-Mediated Improvement in Insulin Sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 12152–12162 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (218).DiChiara AS; Li RC; Suen PH; Hosseini AS; Taylor RJ; Weickhardt AF; Malhotra D; McCaslin DR; Shoulders MD A Cysteine-Based Molecular Code Informs Collagen C-Propeptide Assembly. Nat. Commun 2018, 9, 4206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (219).Patel SD; Rajala MW; Rossetti L; Scherer PE; Shapiro L Disulfide-Dependent Multimeric Assembly of Resistin Family Hormones. Science 2004, 304, 1154–1158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (220).Ponnuswamy N; Cougnon FBL; Clough JM; Pantoş GD; Sanders JKM Discovery of an Organic Trefoil Knot. Science 2012, 338, 783–785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (221).Corbett PT; Leclaire J; Vial L; West KR; Wietor JL; Sanders JK; Otto S Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry. Chem. Rev 2006, 106, 3652–3711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (222).Cougnon FBL; Sanders JKM Evolution of Dynamic Combinatorial Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res 2012, 45, 2211–2221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (223).Banatao DR; Cascio D; Crowley CS; Fleissner MR; Tienson HL; Yeates TO An Approach to Crystallizing Proteins by Synthetic Symmetrization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2006, 103, 16230–16235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (224).Ballister ER; Lai AH; Zuckermann RN; Cheng Y; Mougous JD In Vitro Self-Assembly of Tailorable Nanotubes from a Simple Protein Building Block. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2008, 105, 3733–3738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (225).Suzuki Y; Cardone G; Restrepo D; Zavattieri PD; Baker TS; Tezcan FA Self-Assembly of Coherently Dynamic, Auxetic, Two-Dimensional Protein Crystals. Nature 2016, 533, 369–373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (226).Alberstein R; Suzuki Y; Paesani F; Tezcan FA Engineering the Entropy-Driven Free-Energy Landscape of a Dynamic Nanoporous Protein Assembly. Nat. Chem 2018, 10, 732–739 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (227).Zhang S; Alberstein RG; De Yoreo JJ; Tezcan FA Assembly of a Patchy Protein into Variable 2d Lattices Via Tunable Multiscale Interactions. Nat. Commun 2020, 11, 3770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (228).Zhou K; Chen H; Zhang S; Wang Y; Zhao G Disulfide-Mediated Reversible Two-Dimensional Self-Assembly of Protein Nanocages. Chem. Commun 2019, 55, 7510–7513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (229).Phillips JJ; Millership C; Main ER Fibrous Nanostructures from the Self-Assembly of Designed Repeat Protein Modules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2012, 51, 13132–13135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (230).Zhao L; Zou H; Zhang H; Sun H; Wang T; Pan T; Li X; Bai Y; Qiao S; Luo Q et al. Enzyme-Triggered Defined Protein Nanoarrays: Efficient Light-Harvesting Systems to Mimic Chloroplasts. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 938–945 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (231).Miao L; Fan Q; Zhao L; Qiao Q; Zhang X; Hou C; Xu J; Luo Q; Liu J The Construction of Functional Protein Nanotubes by Small Molecule-Induced Self-Assembly of Cricoid Proteins. Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 4092–4095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (232).Churchfield LA; Medina-Morales A; Brodin JD; Perez A; Tezcan FA De Novo Design of an Allosteric Metalloprotein Assembly with Strained Disulfide Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 13163–13166 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (233).Churchfield LA; Alberstein RG; Williamson LM; Tezcan FA Determining the Structural and Energetic Basis of Allostery in a De Novo Designed Metalloprotein Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 10043–10053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (234).Chiou NR; Epstein AJ Polyaniline Nanofibers Prepared by Dilute Polymerization. Adv. Mater 2005, 17, 1679–1683 [Google Scholar]
- (235).Grill L; Dyer M; Lafferentz L; Persson M; Peters MV; Hecht S Nano-Architectures by Covalent Assembly of Molecular Building Blocks. Nat Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 687–691 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (236).El-Kaderi HM; Hunt JR; Mendoza-Cortes JL; Cote AP; Taylor RE; O'Keeffe M; Yaghi OM Designed Synthesis of 3d Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2007, 316, 268–272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (237).Waller PJ; Gandara F; Yaghi OM Chemistry of Covalent Organic Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res 2015, 48, 3053–3063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (238).Rebek J Jr Host–Guest Chemistry of Calixarene Capsules. Chem. Commun 2000, 637–643 [Google Scholar]
- (239).Chen G; Jiang M Cyclodextrin-Based Inclusion Complexation Bridging Supramolecular Chemistry and Macromolecular Self-Assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40, 2254–2266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (240).Masson E; Ling XX; Joseph R; Kyeremeh-Mensah L; Lu XY Cucurbituril Chemistry: A Tale of Supramolecular Success. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1213–1247 [Google Scholar]
- (241).Liu Z; Nalluri SKM; Stoddart JF Surveying Macrocyclic Chemistry: From Flexible Crown Ethers to Rigid Cyclophanes. Chem. Soc. Rev 2017, 46, 2459–2478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (242).Cram DJ; Cram JM Host-Guest Chemistry: Complexes between Organic Compounds Simulate the Substrate Selectivity of Enzymes. Science 1974, 183, 803–809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (243).Cram D The Design of Molecular Hosts, Guests, and Their Complexes. Science 1988, 240, 760–767 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (244).Lehn JM Supramolecular Chemistry: Receptors, Catalysts, and Carriers. Science 1985, 227, 849–856 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (245).Qu DH; Wang QC; Zhang QW; Ma X; Tian H Photoresponsive Host-Guest Functional Systems. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 7543–7588 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (246).Yang YW; Sun YL; Song N Switchable Host-Guest Systems on Surfaces. Acc. Chem. Res 2014, 47, 1950–1960 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (247).Sasmal R; Das Saha N; Schueder F; Joshi D; Sheeba V; Jungmann R; Agasti SS Dynamic Host-Guest Interaction Enables Autonomous Single Molecule Blinking and Super-Resolution Imaging. Chem. Commun 2019, 55, 14430–14433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (248).Ooi HW; Kocken JMM; Morgan FLC; Malheiro A; Zoetebier B; Karperien M; Wieringa PA; Dijkstra PJ; Moroni L; Baker MB Multivalency Enables Dynamic Supramolecular Host-Guest Hydrogel Formation. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2208–2217 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (249).Appel EA; Biedermann F; Hoogland D; Del Barrio J; Driscoll MD; Hay S; Wales DJ; Scherman OA Decoupled Associative and Dissociative Processes in Strong yet Highly Dynamic Host-Guest Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 12985–12993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (250).Kitagishi H; Kakikura Y; Yamaguchi H; Oohora K; Harada A; Hayashi T Self-Assembly of One- and Two-Dimensional Hemoprotein Systems by Polymerization through Heme-Heme Pocket Interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2009, 48, 1271–1274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (251).Oohora K; Onoda A; Hayashi T Supramolecular Assembling Systems Formed by Heme-Heme Pocket Interactions in Hemoproteins. Chem. Commun 2012, 48, 11714–11726 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (252).Mori Y; Minamihata K; Abe H; Goto M; Kamiya N Protein Assemblies by Site-Specific Avidin-Biotin Interactions. Org. Biomol. Chem 2011, 9, 5641–5644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (253).Minamihata K; Goto M; Kamiya N Control of a Tyrosyl Radical Mediated Protein Cross-Linking Reaction by Electrostatic Interaction. Bioconjug. Chem 2012, 23, 1600–1609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (254).Fairhead M; Veggiani G; Lever M; Yan J; Mesner D; Robinson CV; Dushek O; van der Merwe PA; Howarth M Spyavidin Hubs Enable Precise and Ultrastable Orthogonal Nanoassembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 12355–12363 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (255).Kurppa K; Hytonen VP; Nakari-Setala T; Kulomaa MS; Linder MB Molecular Engineering of Avidin and Hydrophobin for Functional Self-Assembling Interfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 120, 102–109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (256).Singh S; Kluger R Self-Assembly of a Functional Triple Protein: Hemoglobin-Avidin-Hemoglobin Via Biotin-Avidin Interactions. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 2875–2882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (257).Guo D-S; Uzunova VD; Assaf KI; Lazar AI; Liu Y; Nau WM Inclusion of Neutral Guests by Water-Soluble Macrocyclic Hosts – a Comparative Thermodynamic Investigation with Cyclodextrins, Calixarenes and Cucurbiturils. Supramol. Chem 2015, 28, 384–395 [Google Scholar]
- (258).Barrow SJ; Kasera S; Rowland MJ; del Barrio J; Scherman OA Cucurbituril-Based Molecular Recognition. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 12320–12406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (259).Zhang L; Wu Y; Brunsveld L A Synthetic Supramolecular Construct Modulating Protein Assembly in Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2007, 46, 1798–1802 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (260).Zhang W; Luo Q; Miao L; Hou C; Bai Y; Dong Z; Xu J; Liu J Self-Assembly of Glutathione S-Transferase into Nanowires. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5847–5851 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (261).Uhlenheuer DA; Young JF; Nguyen HD; Scheepstra M; Brunsveld L Cucurbit[8]Uril Induced Heterodimerization of Methylviologen and Naphthalene Functionalized Proteins. Chem. Commun 2011, 47, 6798–6800 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (262).Hou C; Huang Z; Fang Y; Liu J Construction of Protein Assemblies by Host-Guest Interactions with Cucurbiturils. Org. Biomol. Chem 2017, 15, 4272–4281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (263).Wang R; Qiao S; Zhao L; Hou C; Li X; Liu Y; Luo Q; Xu J; Li H; Liu J Dynamic Protein Self-Assembly Driven by Host-Guest Chemistry and the Folding-Unfolding Feature of a Mutually Exclusive Protein. Chem. Commun 2017, 53, 10532–10535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (264).Si C; Li J; Luo Q; Hou C; Pan T; Li H; Liu J An Ion Signal Responsive Dynamic Protein Nano-Spring Constructed by High Ordered Host-Guest Recognition. Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 2924–2927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (265).Dang DT; Nguyen HD; Merkx M; Brunsveld L Supramolecular Control of Enzyme Activity through Cucurbit[8]Uril-Mediated Dimerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2013, 52, 2915–2919 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (266).McGovern RE; Fernandes H; Khan AR; Power NP; Crowley PB Protein Camouflage in Cytochrome C-Calixarene Complexes. Nat. Chem 2012, 4, 527–533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (267).Rennie ML; Doolan AM; Raston CL; Crowley PB Protein Dimerization on a Phosphonated Calix[6]Arene Disc. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2017, 56, 5517–5521 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (268).Ramberg KO; Engilberge S; Skorek T; Crowley PB Facile Fabrication of Protein-Macrocycle Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2021, 143, 1896–1907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (269).Beshara CS; Jones CE; Daze KD; Lilgert BJ; Hof F A Simple Calixarene Recognizes Post-Translationally Methylated Lysine. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 63–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (270).Yang G; Zhang X; Kochovski Z; Zhang Y; Dai B; Sakai F; Jiang L; Lu Y; Ballauff M; Li X et al. Precise and Reversible Protein-Microtubule-Like Structure with Helicity Driven by Dual Supramolecular Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 1932–1937 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (271).Kostiainen MA; Hiekkataipale P; de la Torre JA; Nolte RJM; Cornelissen JJLM Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Virus-Polymer Complexes. J. Mater. Chem 2011, 21, 2112–2117 [Google Scholar]
- (272).Kostiainen MA; Hiekkataipale P; Laiho A; Lemieux V; Seitsonen J; Ruokolainen J; Ceci P Electrostatic Assembly of Binary Nanoparticle Superlattices Using Protein Cages. Nat Nanotechnol 2013, 8, 52–56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (273).Yang R; Chen L; Yang S; Lv C; Leng X; Zhao G 2d Square Arrays of Protein Nanocages through Channel-Directed Electrostatic Interactions with Poly(Alpha, L-Lysine). Chem. Commun 2014, 50, 2879–2882 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (274).Korpi A; Ma C; Liu K; Nonappa; Herrmann A; Ikkala O; Kostiainen MA Self-Assembly of Electrostatic Cocrystals from Supercharged Fusion Peptides and Protein Cages. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 318–323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (275).Edwardson TGW; Mori T; Hilvert D Rational Engineering of a Designed Protein Cage for Sirna Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 10439–10442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (276).Simon AJ; Zhou Y; Ramasubramani V; Glaser J; Pothukuchy A; Gollihar J; Gerberich JC; Leggere JC; Morrow BR; Jung C et al. Supercharging Enables Organized Assembly of Synthetic Biomolecules. Nat. Chem 2019, 11, 204–212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (277).Kunzle M; Eckert T; Beck T Binary Protein Crystals for the Assembly of Inorganic Nanoparticle Superlattices. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 12731–12734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (278).Kostiainen MA; Kasyutich O; Cornelissen JJ; Nolte RJ Self-Assembly and Optically Triggered Disassembly of Hierarchical Dendron-Virus Complexes. Nat. Chem 2010, 2, 394–399 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (279).Liljestrom V; Mikkila J; Kostiainen MA Self-Assembly and Modular Functionalization of Three-Dimensional Crystals from Oppositely Charged Proteins. Nat. Commun 2014, 5, 4445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (280).Beck T; Tetter S; Kunzle M; Hilvert D Construction of Matryoshka-Type Structures from Supercharged Protein Nanocages. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2015, 54, 937–940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (281).Sun H; Miao L; Li J; Fu S; Guo A; Si C; Dong Z; Luo Q; Yu S; Xu J et al. Self-Assembly of Cricoid Proteins Induced by “Soft Nanoparticles”: An Approach to Design Multienzyme Cooperative Antioxidative Systems. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5461–5469 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (282).Wimley WC; Gawrisch K; Creamer TP; White SH Direct Measurement of Salt-Bridge Solvation Energies Using a Peptide Model System: Implications for Protein Stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1996, 93, 2985–2990 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (283).Wilson DN; Doudna Cate JH The Structure and Function of the Eukaryotic Ribosome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol 2012, 4, a011536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (284).McGinty RK; Tan S Nucleosome Structure and Function. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 2255–2573 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (285).Saveleva MS; Eftekhari K; Abalymov A; Douglas TEL; Volodkin D; Parakhonskiy BV; Skirtach AG Hierarchy of Hybrid Materials-the Place of Inorganics-in-Organics in It, Their Composition and Applications. Front. Chem 2019, 7, 179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (286).Descalzo AB; Martinez-Manez R; Sancenon F; Hoffmann K; Rurack K The Supramolecular Chemistry of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2006, 45, 5924–5948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (287).Li C; Iscen A; Sai H; Sato K; Sather NA; Chin SM; Alvarez Z; Palmer LC; Schatz GC; Stupp SI Supramolecular-Covalent Hybrid Polymers for Light-Activated Mechanical Actuation. Nat. Mater 2020, 19, 900–909 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (288).Chen Y; Phipps ML; Werner JH; Chakraborty S; Martinez JS DNA Templated Metal Nanoclusters: From Emergent Properties to Unique Applications. Acc. Chem. Res 2018, 51, 2756–2763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (289).Taylor-Pashow KM; Della Rocca J; Huxford RC; Lin W Hybrid Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Chem. Commun 2010, 46, 5832–5849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (290).McMillan JR; Brodin JD; Millan JA; Lee B; Olvera de la Cruz M; Mirkin CA Modulating Nanoparticle Superlattice Structure Using Proteins with Tunable Bond Distributions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 1754–1757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (291).Miao L; Han J; Zhang H; Zhao L; Si C; Zhang X; Hou C; Luo Q; Xu J; Liu J Quantum-Dot-Induced Self-Assembly of Cricoid Protein for Light Harvesting. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3743–3751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (292).Sim S; Miyajima D; Niwa T; Taguchi H; Aida T Tailoring Micrometer-Long High-Integrity 1d Array of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in a Nanotubular Protein Jacket and Its Lateral Magnetic Assembling Behavior. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 4658–4661 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (293).McCoy K; Uchida M; Lee B; Douglas T Templated Assembly of a Functional Ordered Protein Macromolecular Framework from P22 Virus-Like Particles. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3541–3550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (294).Praetorius F; Dietz H Self-Assembly of Genetically Encoded DNA-Protein Hybrid Nanoscale Shapes. Science 2017, 355, eaam5488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (295).Zhang L; Bailey JB; Subramanian RH; Groisman A; Tezcan FA Hyperexpandable, Self-Healing Macromolecular Crystals with Integrated Polymer Networks. Nature 2018, 557, 86–91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (296).Liljestrom V; Ora A; Hassinen J; Rekola HT; Nonappa; Heilala M; Hynninen V; Joensuu JJ; Ras RHA; Torma P et al. Cooperative Colloidal Self-Assembly of Metal-Protein Superlattice Wires. Nat. Commun 2017, 8, 671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (297).Brodin JD; Auyeung E; Mirkin CA DNA-Mediated Engineering of Multicomponent Enzyme Crystals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2015, 112, 4564–4569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (298).Subramanian RH; Smith SJ; Alberstein RG; Bailey JB; Zhang L; Cardone G; Suominen L; Chami M; Stahlberg H; Baker TS et al. Self-Assembly of a Designed Nucleoprotein Architecture through Multimodal Interactions. ACS Cent. Sci 2018, 4, 1578–1586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (299).Mou Y; Yu JY; Wannier TM; Guo CL; Mayo SL Computational Design of Co-Assembling Protein-DNA Nanowires. Nature 2015, 525, 230–233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (300).Park JI; Nguyen TD; de Queiros Silveira G; Bahng JH; Srivastava S; Zhao G; Sun K; Zhang P; Glotzer SC; Kotov NA Terminal Supraparticle Assemblies from Similarly Charged Protein Molecules and Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun 2014, 5, 3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (301).Grigoryan G; Kim YH; Acharya R; Axelrod K; Jain RM; Willis L; Drndic M; Kikkawa JM; DeGrado WF Computational Design of Virus-Like Protein Assemblies on Carbon Nanotube Surfaces. Science 2011, 332, 1071–1076 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (302).Chen X; Wang Y; Wang P Peptide-Induced Affinity Binding of Carbonic Anhydrase to Carbon Nanotubes. Langmuir 2015, 31, 397–403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (303).Pinheiro AV; Han D; Shih WM; Yan H Challenges and Opportunities for Structural DNA Nanotechnology. Nat Nanotechnol 2011, 6, 763–772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (304).Linko V; Dietz H The Enabled State of DNA Nanotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2013, 24, 555–561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (305).Hong F; Zhang F; Liu Y; Yan H DNA Origami: Scaffolds for Creating Higher Order Structures. Chem. Rev 2017, 117, 12584–12640 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (306).Seeman NC; Sleiman HF DNA Nanotechnology. Nat. Rev. Mater 2017, 3, 17068 [Google Scholar]
- (307).Strable E; Johnson JE; Finn MG Natural Nanochemical Building Blocks: Icosahedral Virus Particles Organized by Attached Oligonucleotides. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1385–1389 [Google Scholar]
- (308).McMillan JR; Hayes OG; Winegar PH; Mirkin CA Protein Materials Engineering with DNA. Acc. Chem. Res 2019, 52, 1939–1948 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (309).Mikkila J; Anaya-Plaza E; Liljestrom V; Caston JR; Torres T; Escosura Ade L; Kostiainen MA Hierarchical Organization of Organic Dyes and Protein Cages into Photoactive Crystals. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1565–1571 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (310).Marianayagam NJ; Sunde M; Matthews JM The Power of Two: Protein Dimerization in Biology. Trends Biochem. Sci 2004, 29, 618–625 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (311).Voss S; Klewer L; Wu YW Chemically Induced Dimerization: Reversible and Spatiotemporal Control of Protein Function in Cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2015, 28, 194–201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (312).Milroy LG; Grossmann TN; Hennig S; Brunsveld L; Ottmann C Modulators of Protein-Protein Interactions. Chem. Rev 2014, 114, 4695–4748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (313).Bennett MJ; Choe S; Eisenberg D Domain Swapping: Entangling Alliances between Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1994, 91, 3127–3131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (314).Liu Y; Eisenberg D 3d Domain Swapping: As Domains Continue to Swap. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 1285–1299 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (315).Mascarenhas NM; Gosavi S Understanding Protein Domain-Swapping Using Structure-Based Models of Protein Folding. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol 2017, 128, 113–120 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (316).Green SM; Gittis AG; Meeker AK; Lattman EE One-Step Evolution of a Dimer from a Monomeric Protein. Nat. Struct. Biol 1995, 2, 746–751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (317).Murray AJ; Head JG; Barker JJ; Brady RL Engineering an Intertwined Form of Cd2 for Stability and Assembly. Nat. Struct. Biol 1998, 5, 778–782 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (318).Kuhlman B; O'Neill JW; Kim DE; Zhang KY; Baker D Conversion of Monomeric Protein L to an Obligate Dimer by Computational Protein Design. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2001, 98, 10687–10691 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (319).Assar Z; Nossoni Z; Wang W; Santos EM; Kramer K; McCornack C; Vasileiou C; Borhan B; Geiger JH Domain-Swapped Dimers of Intracellular Lipid-Binding Proteins: Evidence for Ordered Folding Intermediates. Structure 2016, 24, 1590–1598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (320).Ghanbarpour A; Pinger C; Esmatpour Salmani R; Assar Z; Santos EM; Nosrati M; Pawlowski K; Spence D; Vasileiou C; Jin X et al. Engineering the Hcrbpii Domain-Swapped Dimer into a New Class of Protein Switches. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2019, 141, 17125–17132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (321).Ha JH; Karchin JM; Walker-Kopp N; Huang LS; Berry EA; Loh SN Engineering Domain-Swapped Binding Interfaces by Mutually Exclusive Folding. J. Mol. Biol 2012, 416, 495–502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (322).Ha JH; Karchin JM; Walker-Kopp N; Castaneda CA; Loh SN Engineered Domain Swapping as an on/Off Switch for Protein Function. Chem. Biol 2015, 22, 1384–1393 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (323).Karchin JM; Ha JH; Namitz KE; Cosgrove MS; Loh SN Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly. Sci. Rep 2017, 7, 44388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (324).Nandwani N; Surana P; Negi H; Mascarenhas NM; Udgaonkar JB; Das R; Gosavi S A Five-Residue Motif for the Design of Domain Swapping in Proteins. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (325).Correia BE; Bates JT; Loomis RJ; Baneyx G; Carrico C; Jardine JG; Rupert P; Correnti C; Kalyuzhniy O; Vittal V et al. Proof of Principle for Epitope-Focused Vaccine Design. Nature 2014, 507, 201–206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (326).Correia BE; Ban YE; Holmes MA; Xu H; Ellingson K; Kraft Z; Carrico C; Boni E; Sather DN; Zenobia C et al. Computational Design of Epitope-Scaffolds Allows Induction of Antibodies Specific for a Poorly Immunogenic Hiv Vaccine Epitope. Structure 2010, 18, 1116–1126 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (327).Ofek G; Guenaga FJ; Schief WR; Skinner J; Baker D; Wyatt R; Kwong PD Elicitation of Structure-Specific Antibodies by Epitope Scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2010, 107, 17880–17887 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (328).Azoitei ML; Correia BE; Ban YE; Carrico C; Kalyuzhniy O; Chen L; Schroeter A; Huang PS; McLellan JS; Kwong PD et al. Computation-Guided Backbone Grafting of a Discontinuous Motif onto a Protein Scaffold. Science 2011, 334, 373–376 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (329).Azoitei ML; Ban YE; Julien JP; Bryson S; Schroeter A; Kalyuzhniy O; Porter JR; Adachi Y; Baker D; Pai EF et al. Computational Design of High-Affinity Epitope Scaffolds by Backbone Grafting of a Linear Epitope. J. Mol. Biol 2012, 415, 175–192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (330).Procko E; Berguig GY; Shen BW; Song Y; Frayo S; Convertine AJ; Margineantu D; Booth G; Correia BE; Cheng Y et al. A Computationally Designed Inhibitor of an Epstein-Barr Viral Bcl-2 Protein Induces Apoptosis in Infected Cells. Cell 2014, 157, 1644–1656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (331).Berger S; Procko E; Margineantu D; Lee EF; Shen BW; Zelter A; Silva DA; Chawla K; Herold MJ; Garnier JM et al. Computationally Designed High Specificity Inhibitors Delineate the Roles of Bcl2 Family Proteins in Cancer. eLife 2016, 5, e20352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (332).Stranges PB; Machius M; Miley MJ; Tripathy A; Kuhlman B Computational Design of a Symmetric Homodimer Using Beta-Strand Assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2011, 108, 20562–20567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (333).Huang PS; Love JJ; Mayo SL A De Novo Designed Protein Protein Interface. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 2770–2774 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (334).Jha RK; Leaver-Fay A; Yin S; Wu Y; Butterfoss GL; Szyperski T; Dokholyan NV; Kuhlman B Computational Design of a Pak1 Binding Protein. J. Mol. Biol 2010, 400, 257–270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (335).Dang LT; Miao Y; Ha A; Yuki K; Park K; Janda CY; Jude KM; Mohan K; Ha N; Vallon M et al. Receptor Subtype Discrimination Using Extensive Shape Complementary Designed Interfaces. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2019, 26, 407–414 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (336).Foight GW; Wang Z; Wei CT; Jr Greisen P; Warner KM; Cunningham-Bryant D; Park K; Brunette TJ; Sheffler W; Baker D et al. Multi-Input Chemical Control of Protein Dimerization for Programming Graded Cellular Responses. Nat Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1209–1216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (337).Moreira IS; Fernandes PA; Ramos MJ Hot Spots—a Review of the Protein–Protein Interface Determinant Amino-Acid Residues. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinf 2007, 68, 803–812 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (338).Fleishman SJ; Whitehead TA; Ekiert DC; Dreyfus C; Corn JE; Strauch EM; Wilson IA; Baker D Computational Design of Proteins Targeting the Conserved Stem Region of Influenza Hemagglutinin. Science 2011, 332, 816–821 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (339).Procko E; Hedman R; Hamilton K; Seetharaman J; Fleishman SJ; Su M; Aramini J; Kornhaber G; Hunt JF; Tong L et al. Computational Design of a Protein-Based Enzyme Inhibitor. J. Mol. Biol 2013, 425, 3563–3575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (340).Radford RJ; Brodin JD; Salgado EN; Tezcan FA Expanding the Utility of Proteins as Platforms for Coordination Chemistry. Coordin. Chem. Rev 2011, 255, 790–803 [Google Scholar]
- (341).Churchfield LA; George A; Tezcan FA Repurposing Proteins for New Bioinorganic Functions. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 245–258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (342).Der BS; Machius M; Miley MJ; Mills JL; Szyperski T; Kuhlman B Metal-Mediated Affinity and Orientation Specificity in a Computationally Designed Protein Homodimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2012, 134, 375–385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (343).Der BS; Edwards DR; Kuhlman B Catalysis by a De Novo Zinc-Mediated Protein Interface: Implications for Natural Enzyme Evolution and Rational Enzyme Engineering. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 3933–3940 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (344).Basler S; Studer S; Zou Y; Mori T; Ota Y; Camus A; Bunzel HA; Helgeson RC; Houk KN; Jimenez-Oses G et al. Efficient Lewis Acid Catalysis of an Abiological Reaction in a De Novo Protein Scaffold. Nat. Chem 2021, 13, 231–235 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (345).Lu Y; Yeung N; Sieracki N; Marshall NM Design of Functional Metalloproteins. Nature 2009, 460, 855–862 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (346).Cook SA; Hill EA; Borovik AS Lessons from Nature: A Bio-Inspired Approach to Molecular Design. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 4167–8410 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (347).Rittle J; Field MJ; Green MT; Tezcan FA An Efficient, Step-Economical Strategy for the Design of Functional Metalloproteins. Nat. Chem 2019, 11, 434–441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (348).Vrancken JPM; Tame JRH; Voet ARD Development and Applications of Artificial Symmetrical Proteins. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J 2020, 18, 3959–3968 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (349).Grueninger D; Treiber N; Ziegler MO; Koetter JW; Schulze MS; Schulz GE Designed Protein-Protein Association. Science 2008, 319, 206–209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (350).Wolynes PG Symmetry and the Energy Landscapes of Biomolecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 1996, 93, 14249–14255 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (351).Lang D; Thoma R; Henn-Sax M; Sterner R; Wilmanns M Structural Evidence for Evolution of the Beta/Alpha Barrel Scaffold by Gene Duplication and Fusion. Science 2000, 289, 1546–1550 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (352).Fortenberry C; Bowman EA; Proffitt W; Dorr B; Combs S; Harp J; Mizoue L; Meiler J Exploring Symmetry as an Avenue to the Computational Design of Large Protein Domains J. Am. Chem. Soc 2011, 133, 18026–18029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (353).Voet AR; Noguchi H; Addy C; Simoncini D; Terada D; Unzai S; Park SY; Zhang KY; Tame JR Computational Design of a Self-Assembling Symmetrical Beta-Propeller Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2014, 111, 15102–15107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (354).Lin YR; Koga N; Vorobiev SM; Baker D Cyclic Oligomer Design with De Novo Alphabeta-Proteins. Protein Sci. 2017, 26, 2187–2194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (355).Fallas JA; Ueda G; Sheffler W; Nguyen V; McNamara DE; Sankaran B; Pereira JH; Parmeggiani F; Brunette TJ; Cascio D et al. Computational Design of Self-Assembling Cyclic Protein Homo-Oligomers. Nat. Chem 2017, 9, 353–360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (356).Mohan K; Ueda G; Kim AR; Jude KM; Fallas JA; Guo Y; Hafer M; Miao Y; Saxton RA; Piehler J et al. Topological Control of Cytokine Receptor Signaling Induces Differential Effects in Hematopoiesis. Science 2019, 364, eaav7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (357).Boyken SE; Benhaim MA; Busch F; Jia M; Bick MJ; Choi H; Klima JC; Chen Z; Walkey C; Mileant A et al. De Novo Design of Tunable, Ph-Driven Conformational Changes. Science 2019, 364, 658–664 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (358).Lu P; Min D; DiMaio F; Wei KY; Vahey MD; Boyken SE; Chen Z; Fallas JA; Ueda G; Sheffler W et al. Accurate Computational Design of Multipass Transmembrane Proteins. Science 2018, 359, 1042–1046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (359).Xu C; Lu P; Gamal El-Din TM; Pei XY; Johnson MC; Uyeda A; Bick MJ; Xu Q; Jiang D; Bai H et al. Computational Design of Transmembrane Pores. Nature 2020, 585, 129–134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (360).Kobayashi N; Yanase K; Sato T; Unzai S; Hecht MH; Arai R Self-Assembling Nano-Architectures Created from a Protein Nano-Building Block Using an Intermolecularly Folded Dimeric De Novo Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 11285–11293 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (361).Kobayashi N; Inano K; Sasahara K; Sato T; Miyazawa K; Fukuma T; Hecht MH; Song C; Murata K; Arai R Self-Assembling Supramolecular Nanostructures Constructed from De Novo Extender Protein Nanobuilding Blocks. ACS Synth. Biol 2018, 7, 1381–1394 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (362).Kim YE; Kim YN; Kim JA; Kim HM; Jung Y Green Fluorescent Protein Nanopolygons as Monodisperse Supramolecular Assemblies of Functional Proteins with Defined Valency. Nat. Commun 2015, 6, 7134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (363).Campos LA; Sharma R; Alvira S; Ruiz FM; Ibarra-Molero B; Sadqi M; Alfonso C; Rivas G; Sanchez-Ruiz JM; Romero Garrido A et al. Engineering Protein Assemblies with Allosteric Control Via Monomer Fold-Switching. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (364).Tolbert AE; Ervin CS; Ruckthong L; Paul TJ; Jayasinghe-Arachchige VM; Neupane KP; Stuckey JA; Prabhakar R; Pecoraro VL Heteromeric Three-Stranded Coiled Coils Designed Using a Pb(Ii)(Cys)3 Template Mediated Strategy. Nat. Chem 2020, 12, 405–411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (365).Mills JH; Sheffler W; Ener ME; Almhjell PJ; Oberdorfer G; Pereira JH; Parmeggiani F; Sankaran B; Zwart PH; Baker D Computational Design of a Homotrimeric Metalloprotein with a Trisbipyridyl Core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2016, 113, 15012–15017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (366).Salgado EN; Lewis RA; Faraone-Mennella J; Tezcan FA Metal-Mediated Self-Assembly of Protein Superstructures: Influence of Secondary Interactions on Protein Oligomerization and Aggregation. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 6082–6084 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (367).Brodin JD; Medina-Morales A; Ni T; Salgado EN; Ambroggio XI; Tezcan FA Evolution of Metal Selectivity in Templated Protein Interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 8610–8617 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (368).Armstrong RN Mechanistic Diversity in a Metalloenzyme Superfamily. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 13625–13632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (369).Bergdoll M; Eltis LD; Cameron AD; Dumas P; Bolin JT All in the Family: Structural and Evolutionary Relationships among Three Modular Proteins with Diverse Functions and Variable Assembly. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 1661–1670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (370).Volbeda A; Hol WG Pseudo 2-Fold Symmetry in the Copper-Binding Domain of Arthropodan Haemocyanins. Possible Implications for the Evolution of Oxygen Transport Proteins. J. Mol. Biol 1989, 206, 531–546 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (371).Salgado EN; Brodin JD; To MM; Tezcan FA Templated Construction of a Zn-Selective Protein Dimerization Motif. Inorg. Chem 2011, 50, 6323–6329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (372).Chaikuad A; Pilka ES; De Riso A; von Delft F; Kavanagh KL; Venien-Bryan C; Oppermann U; Yue WW Structure of Human Aspartyl Aminopeptidase Complexed with Substrate Analogue: Insight into Catalytic Mechanism, Substrate Specificity and M18 Peptidase Family. BMC Struct Biol 2012, 12, 14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (373).Douglas T; Young M Viruses: Making Friends with Old Foes. Science 2006, 312, 873–875 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (374).Young M; Willits D; Uchida M; Douglas T Plant Viruses as Biotemplates for Materials and Their Use in Nanotechnology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 2008, 46, 361–384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (375).Wang Z; Gao H; Zhang Y; Liu G; Niu G; Chen X Functional Ferritin Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng 2017, 11, 633–646 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (376).Lai YT; Cascio D; Yeates TO Structure of a 16-Nm Cage Designed by Using Protein Oligomers. Science 2012, 336, 1129–1129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (377).Lai YT; Tsai KL; Sawaya MR; Asturias FJ; Yeates TO Structure and Flexibility of Nanoscale Protein Cages Designed by Symmetric Self-Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 7738–7743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (378).Lai YT; Reading E; Hura GL; Tsai KL; Laganowsky A; Asturias FJ; Tainer JA; Robinson CV; Yeates TO Structure of a Designed Protein Cage That Self-Assembles into a Highly Porous Cube. Nat. Chem 2014, 6, 1065–1071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (379).Lai YT; Hura GL; Dyer KN; Tang HY; Tainer JA; Yeates TO Designing and Defining Dynamic Protein Cage Nanoassemblies in Solution. Sci. Adv 2016, 2, e1501855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (380).Patterson DP; Desai AM; Holl MM; Marsh EN Evaluation of a Symmetry-Based Strategy for Assembling Protein Complexes. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 1004–1012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (381).Fletcher JM; Harniman RL; Barnes FRH; Boyle AL; Collins A; Mantell J; Sharp TH; Antognozzi M; Booth PJ; Linden N et al. Self-Assembling Cages from Coiled-Coil Peptide Modules. Science 2013, 340, 595–599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (382).Woolfson DN The Design of Coiled-Coil Structures and Assemblies In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Parry DADand Squire JM, Eds.; Academic Press, 2005; Vol. 70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (383).Huang P-S; Oberdorfer G; Xu C; Pei XY; Nannenga BL; Rogers JM; DiMaio F; Gonen T; Luisi B; Baker D High Thermodynamic Stability of Parametrically Designed Helical Bundles. Science 2014, 346, 481–485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (384).Thomson AR; Wood CW; Burton AJ; Bartlett GJ; Sessions RB; Brady RL; Woolfson DN Computational Design of Water-Soluble A-Helical Barrels. Science 2014, 346, 485–488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (385).Dawson WM; Martin FJO; Rhys GG; Shelley KL; Brady RL; Woolfson DN Coiled Coils 9-to-5: Rational De Novo Design of A-Helical Barrels with Tunable Oligomeric States. Chem. Sci 2021, 12, 6923–6928 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (386).Gradišar H; Božič S; Doles T; Vengust D; Hafner-Bratkovič I; Mertelj A; Webb B; Šali A; Klavžar S; Jerala R Design of a Single-Chain Polypeptide Tetrahedron Assembled from Coiled-Coil Segments. Nat. Chem. Biol 2013, 9, 362–366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (387).Patterson DP; Su M; Franzmann TM; Sciore A; Skiniotis G; Marsh EN Characterization of a Highly Flexible Self-Assembling Protein System Designed to Form Nanocages. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 190–199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (388).Cristie-David AS; Koldewey P; Meinen BA; Bardwell JCA; Marsh ENG Elaborating a Coiled-Coil-Assembled Octahedral Protein Cage with Additional Protein Domains. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1893–1900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (389).King NP; Bale JB; Sheffler W; McNamara DE; Gonen S; Gonen T; Yeates TO; Baker D Accurate Design of Co-Assembling Multi-Component Protein Nanomaterials. Nature 2014, 510, 103–108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (390).Cannon KA; Park RU; Boyken SE; Nattermann U; Yi S; Baker D; King NP; Yeates TO Design and Structure of Two New Protein Cages Illustrate Successes and Ongoing Challenges in Protein Engineering. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 919–929 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (391).Bale JB; Gonen S; Liu Y; Sheffler W; Ellis D; Thomas C; Cascio D; Yeates TO; Gonen T; King NP et al. Accurate Design of Megadalton-Scale Two-Component Icosahedral Protein Complexes. Science 2016, 353, 389–394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (392).Hsia Y; Bale JB; Gonen S; Shi D; Sheffler W; Fong KK; Nattermann U; Xu C; Huang PS; Ravichandran R et al. Design of a Hyperstable 60-Subunit Protein Dodecahedron. Nature 2016, 535, 136–139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (393).Wargacki AJ; Worner TP; van de Waterbeemd M; Ellis D; Heck AJR; King NP Complete and Cooperative in Vitro Assembly of Computationally Designed Self-Assembling Protein Nanomaterials. Nat. Commun 2021, 12, 883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (394).Divine R; Dang HV; Ueda G; Fallas JA; Vulovic I; Sheffler W; Saini S; Zhao YT; Raj IX; Morawski PA et al. Designed Proteins Assemble Antibodies into Modular Nanocages. Science 2021, 372, eabd9994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (395).Ni TW; Tezcan FA Structural Characterization of a Microperoxidase inside a Metal-Directed Protein Cage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2010, 49, 7014–7018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (396).Miyamoto T; Kuribayashi M; Nagao S; Shomura Y; Higuchi Y; Hirota S Domain-Swapped Cytochrome Cb(562) Dimer and Its Nanocage Encapsulating a Zn-So4 Cluster in the Internal Cavity. Chem. Sci 2015, 6, 7336–7342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (397).Cristie-David AS; Marsh ENG Metal-Dependent Assembly of a Protein Nano-Cage. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 1620–1629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (398).Pearson RG Hard and Soft Acids and Bases. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1963, 85, 3533–3539 [Google Scholar]
- (399).Wong GB; Kappel MJ; Raymond KN; Matzanke B; Winkelmann G Coordination Chemistry of Microbial Iron Transport Compounds. 24. Characterization of Coprogen and Ferricrocin, Two Ferric Hydroxamate Siderophores. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1983, 105, 810–815 [Google Scholar]
- (400).Crumbliss AL Iron Bioavailability and the Coordination Chemistry of Hydroxamic Acids. Coordin. Chem. Rev 1990, 105, 155–179 [Google Scholar]
- (401).Huard DJ; Kane KM; Tezcan FA Re-Engineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly. Nat. Chem. Biol 2013, 9, 169–176 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (402).Zhang SL; Zang JC; Zhang XR; Chen H; Mikami B; Zhao GH “Silent” Amino Acid Residues at Key Subunit Interfaces Regulate the Geometry of Protein Nanocages. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10382–10388 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (403).Zhang S; Zang J; Wang W; Chen H; Zhang X; Wang F; Wang H; Zhao G Conversion of the Native 24-Mer Ferritin Nanocage into Its Non-Native 16-Mer Analogue by Insertion of Extra Amino Acid Residues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2016, 55, 16064–16070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (404).Wang WM; Wang LL; Chen H; Zang JC; Zhao X; Zhao GH; Wang HF Selective Elimination of the Key Subunit Interfaces Facilitates Conversion of Native 24-Mer Protein Nanocage into 8-Mer Nanorings. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 14078–14081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (405).Zang JC; Chen H; Zhang XR; Zhang CX; Guo J; Du M; Zhao GH Disulfide-Mediated Conversion of 8-Mer Bowl-Like Protein Architecture into Three Different Nanocages. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (406).Yu Y; Lutz S Circular Permutation: A Different Way to Engineer Enzyme Structure and Function. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 18–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (407).Jorda J; Leibly DJ; Thompson MC; Yeates TO Structure of a Novel 13 Nm Dodecahedral Nanocage Assembled from a Redesigned Bacterial Microcompartment Shell Protein. Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 5041–5044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (408).Azuma Y; Herger M; Hilvert D Diversification of Protein Cage Structure Using Circularly Permuted Subunits. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 558–561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (409).Azuma Y; Edwardson TGW; Hilvert D Tailoring Lumazine Synthase Assemblies for Bionanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 3543–3557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (410).Wagstaff J; Lowe J Prokaryotic Cytoskeletons: Protein Filaments Organizing Small Cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2018, 16, 187–201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (411).Fletcher DA; Mullins RD Cell Mechanics and the Cytoskeleton. Nature 2010, 463, 485–492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (412).Knowles TP; Vendruscolo M; Dobson CM The Amyloid State and Its Association with Protein Misfolding Diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2014, 15, 384–396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (413).Hou C; Li J; Zhao L; Zhang W; Luo Q; Dong Z; Xu J; Liu J Construction of Protein Nanowires through Cucurbit[8]Uril-Based Highly Specific Host-Guest Interactions: An Approach to the Assembly of Functional Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2013, 52, 5590–5593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (414).Kitagishi H; Oohora K; Yamaguchi H; Sato H; Matsuo T; Harada A; Hayashi T Supramolecular Hemoprotein Linear Assembly by Successive Interprotein Heme-Heme Pocket Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 10326–10327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (415).Onoda A; Takahashi A; Oohora K; Onuma Y; Hayashi T Fibrous Supramolecular Hemoprotein Assemblies Connected with Synthetic Heme Dimer and Apohemoprotein Dimer. Chem. Biodivers 2012, 9, 1684–1692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (416).Abe S; Pham TT; Negishi H; Yamashita K; Hirata K; Ueno T Design of an in-Cell Protein Crystal for the Environmentally Responsive Construction of a Supramolecular Filament. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2021, 60, 12341–12345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (417).Biswas S; Kinbara K; Oya N; Ishii N; Taguchi H; Aida T A Tubular Biocontainer: Metal Ion-Induced 1d Assembly of a Molecularly Engineered Chaperonin. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 7556–7557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (418).Miranda FF; Iwasaki K; Akashi S; Sumitomo K; Kobayashi M; Yamashita I; Tame JR; Heddle JG A Self-Assembled Protein Nanotube with High Aspect Ratio. Small 2009, 5, 2077–2084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (419).Brodin JD; Smith SJ; Carr JR; Tezcan FA Designed, Helical Protein Nanotubes with Variable Diameters from a Single Building Block. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 10468–10471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (420).Hyman P; Denyes J Bacteriophages in Nanotechnology: History and Future In Bacteriophages; Harper DR, Abedon ST, Burrowes BHand McConville ML, Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2018 [Google Scholar]
- (421).Czapar AE; Steinmetz NF Plant Viruses and Bacteriophages for Drug Delivery in Medicine and Biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2017, 38, 108–116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (422).De Santis E; Ryadnov MG Peptide Self-Assembly for Nanomaterials: The Old New Kid on the Block. Chem. Soc. Rev 2015, 44, 8288–8300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (423).Wei G; Su Z; Reynolds NP; Arosio P; Hamley IW; Gazit E; Mezzenga R Self-Assembling Peptide and Protein Amyloids: From Structure to Tailored Function in Nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev 2017, 46, 4661–4708 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (424).Smith AM; Acquah SF; Bone N; Kroto HW; Ryadnov MG; Stevens MS; Walton DR; Woolfson DN Polar Assembly in a Designed Protein Fiber. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2004, 44, 325–328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (425).OĽeary LE; Fallas JA; Bakota EL; Kang MK; Hartgerink JD Multi-Hierarchical Self-Assembly of a Collagen Mimetic Peptide from Triple Helix to Nanofibre and Hydrogel. Nat. Chem 2011, 3, 821–828 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (426).Bowerman CJ; Nilsson BL Self-Assembly of Amphipathic Beta-Sheet Peptides: Insights and Applications. Biopolymers 2012, 98, 169–184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (427).Egelman EH; Xu C; DiMaio F; Magnotti E; Modlin C; Yu X; Wright E; Baker D; Conticello VP Structural Plasticity of Helical Nanotubes Based on Coiled-Coil Assemblies. Structure 2015, 23, 280–289 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (428).Burgess NC; Sharp TH; Thomas F; Wood CW; Thomson AR; Zaccai NR; Brady RL; Serpell LC; Woolfson DN Modular Design of Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 10554–10562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (429).Xu C; Liu R; Mehta AK; Guerrero-Ferreira RC; Wright ER; Dunin-Horkawicz S; Morris K; Serpell LC; Zuo X; Wall JS et al. Rational Design of Helical Nanotubes from Self-Assembly of Coiled-Coil Lock Washers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 15565–15578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (430).Lee MJ; Mantell J; Hodgson L; Alibhai D; Fletcher JM; Brown IR; Frank S; Xue W-F; Verkade P; Woolfson DN et al. Engineered Synthetic Scaffolds for Organizing Proteins within the Bacterial Cytoplasm. Nat. Chem. Biol 2018, 14, 142–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (431).McPartland L; Heller DM; Eisenberg DS; Hochschild A; Sawaya MR Atomic Insights into the Genesis of Cellular Filaments by Globular Proteins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2018, 25, 705–714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (432).Nagarkar RP; Hule RA; Pochan DJ; Schneider JP Domain Swapping in Materials Design. Biopolymers 2010, 94, 141–155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (433).Kitagishi H; Oohora K; Hayashi T Thermodynamically Controlled Supramolecular Polymerization of Cytochrome B 562. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 194–200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (434).Oohora K; Onoda A; Kitagishi H; Yamaguchi H; Harada A; Hayashi T A Chemically-Controlled Supramolecular Protein Polymer Formed by a Myoglobin-Based Self-Assembly System. Chem. Sci 2011, 2, 1033–1038 [Google Scholar]
- (435).Oohora K; Burazerovic S; Onoda A; Wilson YM; Ward TR; Hayashi T Chemically Programmed Supramolecular Assembly of Hemoprotein and Streptavidin with Alternating Alignment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2012, 51, 3818–3821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (436).Nagano S; Banwell EF; Iwasaki K; Michalak M; Palka R; Zhang KYJ; Voet ARD; Heddle JG Understanding the Assembly of an Artificial Protein Nanotube. Adv Mater Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600846 [Google Scholar]
- (437).Nguyen TK; Negishi H; Abe S; Ueno T Construction of Supramolecular Nanotubes from Protein Crystals. Chem. Sci 2019, 10, 1046–1051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (438).Bai Y; Luo Q; Zhang W; Miao L; Xu J; Li H; Liu J Highly Ordered Protein Nanorings Designed by Accurate Control of Glutathione S-Transferase Self-Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 10966–10969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (439).Sendai T; Biswas S; Aida T Photoreconfigurable Supramolecular Nanotube. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 11509–11512 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (440).Kashiwagi D; Sim S; Niwa T; Taguchi H; Aida T Protein Nanotube Selectively Cleavable with DNA: Supramolecular Polymerization of “DNA-Appended Molecular Chaperones”. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 26–29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (441).Weissman JS; Hohl CM; Kovalenko O; Kashi Y; Chen S; Braig K; Saibil HR; Fenton WA; Horwich AL Mechanism of Groel Action: Productive Release of Polypeptide from a Sequestered Position under Groes. Cell 1995, 83, 577–587 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (442).Kashiwagi D; Shen HK; Sim S; Sano K; Ishida Y; Kimura A; Niwa T; Taguchi H; Aida T Molecularly Engineered “Janus Groel”: Application to Supramolecular Copolymerization with a Higher Level of Sequence Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2020, 142, 13310–13315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (443).Wang WX; Dgany O; Wolf SG; Levy I; Algom R; Pouny Y; Wolf A; Marton I; Altman A; Shoseyov O Aspen Sp1, an Exceptional Thermal, Protease and Detergent-Resistant Self-Assembled Nano-Particle. Biotechnol. Bioeng 2006, 95, 161–168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (444).Heyman A; Levy I; Altman A; Shoseyov O Sp1 as a Novel Scaffold Building Block for Self-Assembly Nanofabrication of Submicron Enzymatic Structures. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1575–1579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (445).Medalsy I; Dgany O; Sowwan M; Cohen H; Yukashevska A; Wolf SG; Wolf A; Koster A; Almog O; Marton I et al. Sp1 Protein-Based Nanostructures and Arrays. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 473–477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (446).Sun H; Zhao L; Wang T; An G; Fu S; Li X; Deng X; Liu J Photocontrolled Reversible Morphology Conversion of Protein Nanowires Mediated by an Azobenzene-Cored Dendrimer. Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 6001–6004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (447).Sun H; Zhang X; Miao L; Zhao L; Luo Q; Xu J; Liu J Micelle-Induced Self-Assembling Protein Nanowires: Versatile Supramolecular Scaffolds for Designing the Light-Harvesting System. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 421–428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (448).Schreiber A; Huber MC; Colfen H; Schiller SM Molecular Protein Adaptor with Genetically Encoded Interaction Sites Guiding the Hierarchical Assembly of Plasmonically Active Nanoparticle Architectures. Nat. Commun 2015, 6, 6705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (449).Cate JH; Yusupov MM; Yusupova GZ; Earnest TN; Noller HF X-Ray Crystal Structures of 70s Ribosome Functional Complexes. Science 1999, 285, 2095–2104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (450).Lin J; Ly H; Hussain A; Abraham M; Pearl S; Tzfati Y; Parslow TG; Blackburn EH A Universal Telomerase Rna Core Structure Includes Structured Motifs Required for Binding the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2004, 101, 14713–14718 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (451).Eitoku M; Sato L; Senda T; Horikoshi M Histone Chaperones: 30 Years from Isolation to Elucidation of the Mechanisms of Nucleosome Assembly and Disassembly. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2008, 65, 414–444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (452).Jinek M; Chylinski K; Fonfara I; Hauer M; Doudna JA; Charpentier E A Programmable Dual-Rna-Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (453).Pum D; Toca-Herrera JL; Sleytr UB S-Layer Protein Self-Assembly. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2013, 14, 2484–2501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (454).Hampp N Bacteriorhodopsin as a Photochromic Retinal Protein for Optical Memories. Chem. Rev 2000, 100, 1755–1776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (455).Caspar DL; Goodenough DA; Makowski L; Phillips WC Gap Junction Structures. I. Correlated Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Diffraction. J. Cell Biol 1977, 74, 605–628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (456).Scheuring S; Ringler P; Borgnia M; Stahlberg H; Muller DJ; Agre P; Engel A High Resolution Afm Topographs of the Escherichia Coli Water Channel Aquaporin Z. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4981–4987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (457).Nannenga BL; Iadanza MG; Vollmar BS; Gonen T Overview of Electron Crystallography of Membrane Proteins: Crystallization and Screening Strategies Using Negative Stain Electron Microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci 2013, Chapter 17, 17.15.11–17.15.11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (458).Wukovitz SW; Yeates TO Why Protein Crystals Favour Some Space-Groups over Others. Nat. Struct. Biol 1995, 2, 1062–1067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (459).Kim T; Park JY; Hwang J; Seo G; Kim Y Supramolecular Two-Dimensional Systems and Their Biological Applications. Adv. Mater 2020, 32, e2002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (460).Huang G; Mei Y Assembly and Self-Assembly of Nanomembrane Materials - from 2d to 3d. Small 2018, 14, e1703665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (461).Gopalakrishnan S; Xu J; Zhong F; Rotello VM Strategies for Fabricating Protein Films for Biomaterials Applications. Adv. Sustain. Syst 2021, 5, 2000167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (462).Jiang T; Xu C; Liu Y; Liu Z; Wall JS; Zuo X; Lian T; Salaita K; Ni C; Pochan D et al. Structurally Defined Nanoscale Sheets from Self-Assembly of Collagen-Mimetic Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 4300–4308 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (463).Magnotti EL; Hughes SA; Dillard RS; Wang S; Hough L; Karumbamkandathil A; Lian T; Wall JS; Zuo X; Wright ER et al. Self-Assembly of an Alpha-Helical Peptide into a Crystalline Two-Dimensional Nanoporous Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 16274–16282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (464).Poulos S; Agah S; Jallah N; Faham S Symmetry Based Assembly of a 2 Dimensional Protein Lattice. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (465).Nauli S; Farr S; Lee YJ; Kim HY; Faham S; Bowie JU Polymer-Driven Crystallization. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 2542–2551 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (466).Ringler P; Schulz GE Self-Assembly of Proteins into Designed Networks. Science 2003, 302, 106–109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (467).Heyman A; Medalsy I; Dgany O; Porath D; Markovich G; Shoseyov O Float and Compress: Honeycomb-Like Array of a Highly Stable Protein Scaffold. Langmuir 2009, 25, 5226–5229 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (468).Zhao L; Li Y; Wang T; Qiao S; Li X; Wang R; Luo Q; Hou C; Xu J; Liu J Photocontrolled Protein Assembly for Constructing Programmed Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 75–83 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (469).Li X; Qiao S; Zhao L; Liu S; Li F; Yang F; Luo Q; Hou C; Xu J; Liu J Template-Free Construction of Highly Ordered Monolayered Fluorescent Protein Nanosheets: A Bioinspired Artificial Light-Harvesting System. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1861–1869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (470).Zhou K; Zang J; Chen H; Wang W; Wang H; Zhao G On-Axis Alignment of Protein Nanocage Assemblies from 2d to 3d through the Aromatic Stacking Interactions of Amino Acid Residues. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11323–11332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (471).Zheng B; Zhou K; Zhang T; Lv C; Zhao G Designed Two- and Three-Dimensional Protein Nanocage Networks Driven by Hydrophobic Interactions Contributed by Amyloidogenic Motifs. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4023–4028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (472).Butler PJ Assembly of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle. Nature 1971, 233, 25–27 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (473).Durham AC; Klug A Polymerization of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Protein and Its Control. Nat. New Biol 1971, 229, 42–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (474).Durham AC; Finch JT; Klug A States of Aggregation of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Protein. Nat. New Biol 1971, 229, 37–42 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (475).Bruckman MA; Soto CM; McDowell H; Liu JL; Ratna BR; Korpany KV; Zahr OK; Blum AS Role of Hexahistidine in Directed Nanoassemblies of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Coat Protein. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1606–1616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (476).Zhang J; Zhou K; Wang Q Tailoring the Self-Assembly Behaviors of Recombinant Tobacco Mosaic Virus by Rationally Introducing Covalent Bonding at the Protein-Protein Interface. Small 2016, 12, 4955–4959 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (477).Zhang S; Zhang J; Fang W; Zhang Y; Wang Q; Jin J Ultralarge Single-Layer Porous Protein Nanosheet for Precise Nanosize Separation. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6563–6569 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (478).Zhang J; Wang X; Zhou K; Chen G; Wang Q Self-Assembly of Protein Crystals with Different Crystal Structures Using Tobacco Mosaic Virus Coat Protein as a Building Block. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1673–1679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (479).Zhang J; Zhou K; Zhang Y; Du M; Wang Q Precise Self-Assembly of Nanoparticles into Ordered Nanoarchitectures Directed by Tobacco Mosaic Virus Coat Protein. Adv. Mater 2019, 31, e1901485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (480).Qiao SP; Lang C; Wang RD; Li XM; Yan TF; Pan TZ; Zhao LL; Fan XT; Zhang X; Hou CX et al. Metal Induced Self-Assembly of Designed V-Shape Protein into 2d Wavy Supramolecular Nanostructure. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 333–341 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (481).Yang M; Song WJ Diverse Protein Assembly Driven by Metal and Chelating Amino Acids with Selectivity and Tunability. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (482).Sakai F; Yang G; Weiss MS; Liu Y; Chen G; Jiang M Protein Crystalline Frameworks with Controllable Interpenetration Directed by Dual Supramolecular Interactions. Nat. Commun 2014, 5, 4634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (483).Yang G; Ding HM; Kochovski Z; Hu R; Lu Y; Ma YQ; Chen G; Jiang M Highly Ordered Self-Assembly of Native Proteins into 1d, 2d, and 3d Structures Modulated by the Tether Length of Assembly-Inducing Ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2017, 56, 10691–10695 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (484).Liu R; Kochovski Z; Li L; Yin YW; Yang J; Yang G; Tao G; Xu A; Zhang E; Ding HM et al. Fabrication of Pascal-Triangle Lattice of Proteins by Inducing Ligand Strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2020, 59, 9617–9623 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (485).Xu M; Zeng R; Xiang J; Yan Q Shaping Protein Amphiphilic Assemblies Via Allosteric Effect: From 1d Nanofilament to 2d Rectangular Nanosheet. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2019, 141, 13724–13728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (486).Matthaei JF; DiMaio F; Richards JJ; Pozzo LD; Baker D; Baneyx F Designing Two-Dimensional Protein Arrays through Fusion of Multimers and Interface Mutations. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5235–5239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (487).Thomas A; Matthaei JF; Baneyx F A Self-Assembling Two-Dimensional Protein Array Is a Versatile Platform for the Assembly of Multicomponent Nanostructures. Biotechnol. J 2018, 13, e1800141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (488).Chen Z; Johnson MC; Chen J; Bick MJ; Boyken SE; Lin B; De Yoreo JJ; Kollman JM; Baker D; DiMaio F Self-Assembling 2d Arrays with De Novo Protein Building Blocks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2019, 141, 8891–8895 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (489).Ben-Sasson AJ; Watson JL; Sheffler W; Johnson MC; Bittleston A; Somasundaram L; Decarreau J; Jiao F; Chen J; Mela I et al. Design of Biologically Active Binary Protein 2d Materials. Nature 2021, 589, 468–473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (490).Fromherz P Electron Microscopic Studies of Lipid Protein Films. Nature 1971, 231, 267–268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (491).Uzgiris EE; Kornberg RD Two-Dimensional Crystallization Technique for Imaging Macromolecules, with Application to Antigen--Antibody--Complement Complexes. Nature 1983, 301, 125–129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (492).Engel A; Hoenger A; Hefti A; Henn C; Ford RC; Kistler J; Zulauf M Assembly of 2-D Membrane Protein Crystals: Dynamics, Crystal Order, and Fidelity of Structure Analysis by Electron Microscopy. J. Struct. Biol 1992, 109, 219–234 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (493).Stahlberg H; Fotiadis D; Scheuring S; Rémigy H; Braun T; Mitsuoka K; Fujiyoshi Y; Engel A Two-Dimensional Crystals: A Powerful Approach to Assess Structure, Function and Dynamics of Membrane Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2001, 504, 166–172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (494).Brisson A; Olofsson A; Ringler P; Schmutz M; Stoylova S Two-Dimensional Crystallization of Proteins on Planar Lipid Films and Structure Determination by Electron Crystallography. Biol. Cell 1994, 80, 221–228 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (495).Bourg IC; Lee SS; Fenter P; Tournassat C Stern Layer Structure and Energetics at Mica-Water Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9402–9412 [Google Scholar]
- (496).Pyles H; Zhang S; De Yoreo JJ; Baker D Controlling Protein Assembly on Inorganic Crystals through Designed Protein Interfaces. Nature 2019, 571, 251–256 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (497).McPherson A Introduction to Protein Crystallization. Methods 2004, 34, 254–265 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (498).Derewenda Z Application of Protein Engineering to Enhance Crystallizability and Improve Crystal Properties. Acta Crystallogr, Sect. D 2010, 66, 604–615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (499).Lawson DM; Artymiuk PJ; Yewdall SJ; Smith JM; Livingstone JC; Treffry A; Luzzago A; Levi S; Arosio P; Cesareni G et al. Solving the Structure of Human H Ferritin by Genetically Engineering Intermolecular Crystal Contacts. Nature 1991, 349, 541–544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (500).Banyard SH; Stammers DK; Harrison PM Electron Density Map of Apoferritin at 2.8-a Resolution. Nature 1978, 271, 282–284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (501).Rypniewski WR; Holden HM; Rayment I Structural Consequences of Reductive Methylation of Lysine Residues in Hen Egg White Lysozyme: An X-Ray Analysis at 1.8-a Resolution. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 9851–9858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (502).Rayment I; Rypniewski WR; Schmidt-Base K; Smith R; Tomchick DR; Benning MM; Winkelmann DA; Wesenberg G; Holden HM Three-Dimensional Structure of Myosin Subfragment-1: A Molecular Motor. Science 1993, 261, 50–58 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (503).Cooper DR; Boczek T; Grelewska K; Pinkowska M; Sikorska M; Zawadzki M; Derewenda Z Protein Crystallization by Surface Entropy Reduction: Optimization of the Ser Strategy. Acta Crystallogr, Sect. D: Biol. Crystallogr 2007, 63, 636–645 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (504).Derewenda ZS; Vekilov PG Entropy and Surface Engineering in Protein Crystallization. Acta Crystallogr, Sect. D: Biol. Crystallogr 2006, 62, 116–124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (505).Yamada H; Tamada T; Kosaka M; Miyata K; Fujiki S; Tano M; Moriya M; Yamanishi M; Honjo E; Tada H et al. 'Crystal Lattice Engineering', an Approach to Engineer Protein Crystal Contacts by Creating Intermolecular Symmetry: Crystallization and Structure Determination of a Mutant Human Rnase 1 with a Hydrophobic Interface of Leucines. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 1389–1397 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (506).Du M; Zhou K; Yu R; Zhai Y; Chen G; Wang Q Noncovalent Self-Assembly of Protein Crystals with Tunable Structures. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1749–1757 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (507).Kunzle M; Eckert T; Beck T Metal-Assisted Assembly of Protein Containers Loaded with Inorganic Nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem 2018, 57, 13431–13436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (508).Forse GJ; Ram N; Banatao DR; Cascio D; Sawaya MR; Klock HE; Lesley SA; Yeates TO Synthetic Symmetrization in the Crystallization and Structure Determination of Cela from Thermotoga Maritima. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 168–178 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (509).Laganowsky A; Zhao M; Soriaga AB; Sawaya MR; Cascio D; Yeates TO An Approach to Crystallizing Proteins by Metal-Mediated Synthetic Symmetrization. Protein Sci. 2011, 20, 1876–1890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (510).Radford RJ; Lawrenz M; Nguyen PC; McCammon JA; Tezcan FA Porous Protein Frameworks with Unsaturated Metal Centers in Sterically Encumbered Coordination Sites. Chem. Commun 2011, 47, 313–315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (511).Broomell CC; Birkedal H; Oliveira CLP; Pedersen JS; Gertenbach JA; Young M; Douglas T Protein Cage Nanoparticles as Secondary Building Units for the Synthesis of 3-Dimensional Coordination Polymers. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3167–3171 [Google Scholar]
- (512).Bailey JB; Zhang L; Chiong JA; Ahn S; Tezcan FA Synthetic Modularity of Protein-Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 8160–8166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (513).Bailey JB; Tezcan FA Tunable and Cooperative Thermomechanical Properties of Protein-Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2020, 142, 17265–17270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (514).Olsen LR; Dessen A; Gupta D; Sabesan S; Sacchettini JC; Brewer CF X-Ray Crystallographic Studies of Unique Cross-Linked Lattices between Four Isomeric Biantennary Oligosaccharides and Soybean Agglutinin. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 15073–15080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (515).Dessen A; Gupta D; Sabesan S; Brewer CF; Sacchettini JC X-Ray Crystal Structure of the Soybean Agglutinin Cross-Linked with a Biantennary Analog of the Blood Group I Carbohydrate Antigen. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 4933–4942 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (516).Dotan N; Arad D; Frolow F; Freeman A Self-Assembly of a Tetrahedral Lectin into Predesigned Diamondlike Protein Crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 1999, 38, 2363–2366 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (517).Beyeh NK; Nonappa; Liljestrom V; Mikkila J; Korpi A; Bochicchio D; Pavan GM; Ikkala O; Ras RHA; Kostiainen MA Crystalline Cyclophane-Protein Cage Frameworks. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8029–8036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (518).Rennie ML; Fox GC; Perez J; Crowley PB Auto-Regulated Protein Assembly on a Supramolecular Scaffold. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2018, 57, 13764–13769 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (519).Engilberge S; Rennie ML; Dumont E; Crowley PB Tuning Protein Frameworks Via Auxiliary Supramolecular Interactions. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10343–10350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (520).Guagnini F; Huber A; Alex JM; Marx F; Crowley PB Porous Assembly of an Antifungal Protein Mediated by Zinc and Sulfonato-Calix[8]Arene. J. Struct. Biol 2021, 213, 107711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (521).Vandebroek L; Noguchi H; Kamata K; Tame JRH; Van Meervelt L; Parac-Vogt TN; Voet ARD Shape and Size Complementarity-Induced Formation of Supramolecular Protein Assemblies with Metal-Oxo Clusters. Cryst. Growth Des 2021, 21, 1307–1313 [Google Scholar]
- (522).Vandebroek L; Noguchi H; Kamata K; Tame JRH; Van Meervelt L; Parac-Vogt TN; Voet ARD Hybrid Assemblies of a Symmetric Designer Protein and Polyoxometalates with Matching Symmetry. Chem. Commun 2020, 56, 11601–11604 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (523).Liljestrom V; Seitsonen J; Kostiainen MA Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Soft Matter Nanoparticle Cocrystals with Tunable Lattice Parameters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11278–11285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (524).Winfree E; Liu F; Wenzler LA; Seeman NC Design and Self-Assembly of Two-Dimensional DNA Crystals. Nature 1998, 394, 539–544 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (525).Seeman NC Nucleic Acid Junctions and Lattices. J. Theor. Biol 1982, 99, 237–247 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (526).Yang YR; Liu Y; Yan H DNA Nanostructures as Programmable Biomolecular Scaffolds. Bioconjug. Chem 2015, 26, 1381–1395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (527).Liu N; Liedl T DNA-Assembled Advanced Plasmonic Architectures. Chem. Rev 2018, 118, 3032–3053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (528).Cigler P; Lytton-Jean AK; Anderson DG; Finn MG; Park SY DNA-Controlled Assembly of a Natl Lattice Structure from Gold Nanoparticles and Protein Nanoparticles. Nat. Mater 2010, 9, 918–922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (529).Mirkin CA; Letsinger RL; Mucic RC; Storhoff JJ A DNA-Based Method for Rationally Assembling Nanoparticles into Macroscopic Materials. Nature 1996, 382, 607–609 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (530).Park SY; Lytton-Jean AK; Lee B; Weigand S; Schatz GC; Mirkin CA DNA-Programmable Nanoparticle Crystallization. Nature 2008, 451, 553–556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (531).Wang MX; Brodin JD; Millan JA; Seo SE; Girard M; Olvera de la Cruz M; Lee B; Mirkin CA Altering DNA-Programmable Colloidal Crystallization Paths by Modulating Particle Repulsion. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5126–5132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (532).Hayes OG; McMillan JR; Lee B; Mirkin CA DNA-Encoded Protein Janus Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 9269–9274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (533).Winegar PH; Hayes OG; McMillan JR; Figg CA; Focia PJ; Mirkin CA DNA-Directed Protein Packing within Single Crystals. Chem 2020, 6, 1007–1017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (534).Partridge BE; Winegar PH; Han Z; Mirkin CA Redefining Protein Interfaces within Protein Single Crystals with DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2021, 143, 8925–8934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (535).Stephanopoulos N Hybrid Nanostructures from the Self-Assembly of Proteins and DNA. Chem 2020, 6, 364–405 [Google Scholar]
- (536).Bellomo EG; Wyrsta MD; Pakstis L; Pochan DJ; Deming TJ Stimuli-Responsive Polypeptide Vesicles by Conformation-Specific Assembly. Nat. Mater 2004, 3, 244–248 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (537).Anzini P; Xu C; Hughes S; Magnotti E; Jiang T; Hemmingsen L; Demeler B; Conticello VP Controlling Self-Assembly of a Peptide-Based Material Via Metal-Ion Induced Registry Shift. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 10278–10281 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (538).Yan C; Pochan DJ Rheological Properties of Peptide-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical and Other Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev 2010, 39, 3528–3540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (539).Chockalingam K; Blenner M; Banta S Design and Application of Stimulus-Responsive Peptide Systems. Protein Eng. Des. Sel 2007, 20, 155–161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (540).Iyer PV; Ananthanarayan L Enzyme Stability and Stabilization - Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Environment. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1019–1032 [Google Scholar]
- (541).Jiang X; Bishop EJ; Farid RS A De Novo Designed Protein with Properties That Characterize Natural Hyperthermophilic Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1997, 119, 838–839 [Google Scholar]
- (542).Korkegian A; Black ME; Baker D; Stoddard BL Computational Thermostabilization of an Enzyme. Science 2005, 308, 857–860 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (543).Malakauskas SM; Mayo SL Design, Structure and Stability of a Hyperthermophilic Protein Variant. Nat. Struct. Biol 1998, 5, 470–475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (544).Eijsink VG; Bjork A; Gaseidnes S; Sirevag R; Synstad B; van den Burg B; Vriend G Rational Engineering of Enzyme Stability. J. Biotechnol 2004, 113, 105–120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (545).Hao J; Berry A A Thermostable Variant of Fructose Bisphosphate Aldolase Constructed by Directed Evolution Also Shows Increased Stability in Organic Solvents. Protein Eng. Des. Sel 2004, 17, 689–697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (546).Lele BS; Murata H; Matyjaszewski K; Russell AJ Synthesis of Uniform Protein-Polymer Conjugates. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3380–3387 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (547).Heredia KL; Maynard HD Synthesis of Protein-Polymer Conjugates. Org. Biomol. Chem 2007, 5, 45–53 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (548).Ge J; Lu DN; Liu ZX; Liu Z Recent Advances in Nanostructured Biocatalysts. Biochem. Eng. J 2009, 44, 53–59 [Google Scholar]
- (549).Margolin AL; Navia MA Protein Crystals as Novel Catalytic Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2001, 40, 2204–2222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (550).St. Clair NL; Navia MA Cross-Linked Enzyme Crystals as Robust Biocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 114, 7314–7316 [Google Scholar]
- (551).Gupta MN; Perwez M; Sardar M Protein Crosslinking: Uses in Chemistry, Biology and Biotechnology. Biocatal. Biotransform 2020, 38, 178–201 [Google Scholar]
- (552).Govardhan CP Crosslinking of Enzymes for Improved Stability and Performance. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 1999, 10, 331–335 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (553).Liu Q; Xun G; Feng Y The State-of-the-Art Strategies of Protein Engineering for Enzyme Stabilization. Biotechnol. Adv 2019, 37, 530–537 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (554).Ó’Fágáin C Enzyme Stabilization—Recent Experimental Progress. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2003, 33, 137–149 [Google Scholar]
- (555).Mines GA; Pascher T; Lee SC; Winkler JR; Gray HB Cytochrome C Folding Triggered by Electron Transfer. Chem. Biol 1996, 3, 491–497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (556).Perlmutter JD; Hagan MF Mechanisms of Virus Assembly. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem 2015, 66, 217–239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (557).Roos WH; Bruinsma R; Wuite GJL Physical Virology. Nat. Phys 2010, 6, 733–743 [Google Scholar]
- (558).Roos WH; Gertsman I; May ER; Brooks CL 3rd; Johnson JE; Wuite GJ Mechanics of Bacteriophage Maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2012, 109, 2342–2347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (559).Perkins JR; Diboun I; Dessailly BH; Lees JG; Orengo C Transient Protein-Protein Interactions: Structural, Functional, and Network Properties. Structure 2010, 18, 1233–1243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (560).Kirschner M; Mitchison T Beyond Self-Assembly: From Microtubules to Morphogenesis. Cell 1986, 45, 329–342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (561).Zlotnick A Theoretical Aspects of Virus Capsid Assembly. J. Mol. Recognit 2005, 18, 479–490 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (562).Antonini E; Brunori M Hemoglobin. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1970, 39, 977–1042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (563).Lippow SM; Tidor B Progress in Computational Protein Design. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2007, 18, 305–311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (564).Fleishman SJ; Baker D Role of the Biomolecular Energy Gap in Protein Design, Structure, and Evolution. Cell 2012, 149, 262–273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (565).Dawson WM; Rhys GG; Woolfson DN Towards Functional De Novo Designed Proteins. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2019, 52, 102–111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (566).Gibaud T; Barry E; Zakhary MJ; Henglin M; Ward A; Yang Y; Berciu C; Oldenbourg R; Hagan MF; Nicastro D et al. Reconfigurable Self-Assembly through Chiral Control of Interfacial Tension. Nature 2012, 481, 348–351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (567).Li T; Zan X; Winans RE; Wang Q; Lee B Biomolecular Assembly of Thermoresponsive Superlattices of the Tobacco Mosaic Virus with Large Tunable Interparticle Distances. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2013, 52, 6638–6642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (568).Heo K; Jin HE; Kim H; Lee JH; Wang E; Lee SW Transient Self-Templating Assembly of M13 Bacteriophage for Enhanced Biopiezoelectric Devices. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 716–723 [Google Scholar]
- (569).Ross B; Mehta S; Zhang J Molecular Tools for Acute Spatiotemporal Manipulation of Signal Transduction. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2016, 34, 135–142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (570).Lella M; Mahalakshmi R Metamorphic Proteins: Emergence of Dual Protein Folds from One Primary Sequence. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 2971–2984 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (571).Xu M; Zeng R; Xiang J; Yan Q Self-Assembly of Switchable Protein Nanocages Via Allosteric Effect. CCS Chem 2020, 2, 2223–2232 [Google Scholar]
- (572).Xu M; Liu L; Yan Q Allosterically Activated Protein Self-Assembly for the Construction of Helical Microfilaments with Tunable Helicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 2018, 57, 5029–5032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (573).Han K; Bailey JB; Zhang L; Tezcan FA Anisotropic Dynamics and Mechanics of Macromolecular Crystals Containing Lattice-Patterned Polymer Networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2020, 142, 19402–19410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (574).Cui Q; Karplus M Allostery and Cooperativity Revisited. Protein Sci. 2008, 17, 1295–1307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (575).Changeux JP Allostery and the Monod-Wyman-Changeux Model after 50 Years. Annu. Rev. Biophys 2012, 41, 103–133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (576).Strickland D; Moffat K; Sosnick TR Light-Activated DNA Binding in a Designed Allosteric Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2008, 105, 10709–10714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (577).Chen RP; Blackstock D; Sun Q; Chen W Dynamic Protein Assembly by Programmable DNA Strand Displacement. Nat. Chem 2018, 10, 474–481 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (578).Kowalski AE; Johnson LB; Dierl HK; Park S; Huber TR; Snow CD Porous Protein Crystals as Scaffolds for Enzyme Immobilization. Biomater. Sci 2019, 7, 1898–1904 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (579).Huber TR; Hartje LF; McPherson EC; Kowalski AE; Snow CD Programmed Assembly of Host-Guest Protein Crystals. Small 2017, 13, 1602703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (580).Uchida M; McCoy K; Fukuto M; Yang L; Yoshimura H; Miettinen HM; LaFrance B; Patterson DP; Schwarz B; Karty JA et al. Modular Self-Assembly of Protein Cage Lattices for Multistep Catalysis. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 942–953 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (581).Ward AR; Snow CD Porous Crystals as Scaffolds for Structural Biology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2020, 60, 85–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (582).Butterfield GL; Lajoie MJ; Gustafson HH; Sellers DL; Nattermann U; Ellis D; Bale JB; Ke S; Lenz GH; Yehdego A et al. Evolution of a Designed Protein Assembly Encapsulating Its Own Rna Genome. Nature 2017, 552, 415–420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (583).Edwardson TGW; Tetter S; Hilvert D Two-Tier Supramolecular Encapsulation of Small Molecules in a Protein Cage. Nat. Commun 2020, 11, 5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (584).Maita N Crystal Structure Determination of Ubiquitin by Fusion to a Protein That Forms a Highly Porous Crystal Lattice. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 13546–13549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (585).Yeates TO; Agdanowski MP; Liu Y Development of Imaging Scaffolds for Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2020, 60, 142–149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (586).Koshiyama T; Kawaba N; Hikage T; Shirai M; Miura Y; Huang CY; Tanaka K; Watanabe Y; Ueno T Modification of Porous Protein Crystals in Development of Biohybrid Materials. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 264–269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (587).Huber TR; McPherson EC; Keating CE; Snow CD Installing Guest Molecules at Specific Sites within Scaffold Protein Crystals. Bioconjug. Chem 2018, 29, 17–22 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (588).Liu YX; Huynh DT; Yeates TOA 3.8 Angstrom Resolution Cryo-Em Structure of a Small Protein Bound to an Imaging Scaffold. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 1864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (589).Challenges for Cryo-Em. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (590).Renaud J-P; Chari A; Ciferri C; Liu W.-t.; Rémigy H-W; Stark H; Wiesmann C Cryo-Em in Drug Discovery: Achievements, Limitations and Prospects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2018, 17, 471–492 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (591).Bale JB; Park RU; Liu Y; Gonen S; Gonen T; Cascio D; King NP; Yeates TO; Baker D Structure of a Designed Tetrahedral Protein Assembly Variant Engineered to Have Improved Soluble Expression. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 1695–1701 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (592).Nguyen TK; Abe S; Kasamatsu M; Maity B; Yamashita K; Hirata K; Kojima M; Ueno T In-Cell Engineering of Protein Crystals with Nanoporous Structures for Promoting Cascade Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater 2021, 4, 1672–1681 [Google Scholar]
- (593).McConnell SA; Cannon KA; Morgan C; McAllister R; Amer BR; Clubb RT; Yeates TO Designed Protein Cages as Scaffolds for Building Multienzyme Materials. ACS Synth. Biol 2020, 9, 381–391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (594).Subramanian RH; Suzuki Y; Tallorin L; Sahu S; Thompson M; Gianneschi NC; Burkart MD; Tezcan FA Enzyme-Directed Functionalization of Designed, Two-Dimensional Protein Lattices. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1050–1062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (595).Correnti CE; Hallinan JP; Doyle LA; Ruff RO; Jaeger-Ruckstuhl CA; Xu Y; Shen BW; Qu A; Polkinghorn C; Friend DJ et al. Engineering and Functionalization of Large Circular Tandem Repeat Protein Nanoparticles. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 2020, 27, 342–350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (596).Saif B; Yang P Metal-Protein Hybrid Materials with Desired Functions and Potential Applications. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater 2021, 4, 1156–1177 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (597).Kostiainen MA; Ceci P; Fornara M; Hiekkataipale P; Kasyutich O; Nolte RJ; Cornelissen JJ; Desautels RD; van Lierop J Hierarchical Self-Assembly and Optical Disassembly for Controlled Switching of Magnetoferritin Nanoparticle Magnetism. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6394–6402 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (598).Okuda M; Suzumoto Y; Yamashita I Bioinspired Synthesis of Homogenous Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Two- or Three-Dimensional Nanoparticle Arrays Using Protein Supramolecules. Cryst. Growth Des 2011, 11, 2540–2545 [Google Scholar]
- (599).Maity B; Abe S; Ueno T Observation of Gold Sub-Nanocluster Nucleation within a Crystalline Protein Cage. Nat. Commun 2017, 8, 14820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (600).Chakraborti S; Korpi A; Kumar M; Stepien P; Kostiainen MA; Heddle JG Three-Dimensional Protein Cage Array Capable of Active Enzyme Capture and Artificial Chaperone Activity. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3918–3924 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (601).Jutz G; van Rijn P; Santos Miranda B; Böker A Ferritin: A Versatile Building Block for Bionanotechnology. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 1653–1701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (602).Lach M; Kunzle M; Beck T Free-Standing Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Superlattices Constructed with Engineered Protein Containers Show in Crystallo Catalytic Activity. Chemistry 2017, 23, 17482–17486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (603).Ardini M; Giansanti F; Di Leandro L; Pitari G; Cimini A; Ottaviano L; Donarelli M; Santucci S; Angelucci F; Ippoliti R Metal-Induced Self-Assembly of Peroxiredoxin as a Tool for Sorting Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles into One-Dimensional Clusters. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8052–8061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (604).Manuguri S; Webster K; Yewdall NA; An Y; Venugopal H; Bhugra V; Turner A; Domigan LJ; Gerrard JA; Williams DE et al. Assembly of Protein Stacks with in Situ Synthesized Nanoparticle Cargo. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5138–5145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (605).Anaya-Plaza E; Aljarilla A; Beaune G; Nonappa; Timonen JVI; de la Escosura A; Torres T; Kostiainen MA Phthalocyanine-Virus Nanofibers as Heterogeneous Catalysts for Continuous-Flow Photo-Oxidation Processes. Adv. Mater 2019, 31, e1902582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (606).McMillan RA; Paavola CD; Howard J; Chan SL; Zaluzec NJ; Trent JD Ordered Nanoparticle Arrays Formed on Engineered Chaperonin Protein Templates. Nat. Mater 2002, 1, 247–252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (607).McMillan RA; Howard J; Zaluzec NJ; Kagawa HK; Mogul R; Li YF; Paavola CD; Trent JD A Self-Assembling Protein Template for Constrained Synthesis and Patterning of Nanoparticle Arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2005, 127, 2800–2801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (608).Du M; Zhou K; Wang X; Zhang J; Zhang Y; Dong J; Wu L; Qiao Z; Chen G; Wang Q Precise Fabrication of De Novo Nanoparticle Lattices on Dynamic 2d Protein Crystalline Lattices. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1154–1160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (609).Coste B; Xiao B; Santos JS; Syeda R; Grandl J; Spencer KS; Kim SE; Schmidt M; Mathur J; Dubin AE et al. Piezo Proteins Are Pore-Forming Subunits of Mechanically Activated Channels. Nature 2012, 483, 176–181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (610).Altman GH; Diaz F; Jakuba C; Calabro T; Horan RL; Chen J; Lu H; Richmond J; Kaplan DL Silk-Based Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 401–416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (611).Almine JF; Bax DV; Mithieux SM; Nivison-Smith L; Rnjak J; Waterhouse A; Wise SG; Weiss AS Elastin-Based Materials. Chem. Soc. Rev 2010, 39, 3371–3379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (612).Chattopadhyay S; Raines RT Review Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Wound Healing. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (613).van Hest JC; Tirrell DA Protein-Based Materials, toward a New Level of Structural Control. Chem. Commun 2001, 1897–1904 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (614).Buehler MJ; Yung YC Deformation and Failure of Protein Materials in Physiologically Extreme Conditions and Disease. Nat. Mater 2009, 8, 175–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (615).Hu X; Cebe P; Weiss AS; Omenetto F; Kaplan DL Protein-Based Composite Materials. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 208–215 [Google Scholar]
- (616).Sun J; Su J; Ma C; Gostl R; Herrmann A; Liu K; Zhang H Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Engineered Protein-Based Adhesives and Fibers. Adv. Mater 2020, 32, e1906360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (617).Greaves GN; Greer AL; Lakes RS; Rouxel T Poisson's Ratio and Modern Materials. Nat. Mater 2011, 10, 823–837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (618).Evans KE; Alderson A Auxetic Materials: Functional Materials and Structures from Lateral Thinking! Adv. Mater 2000, 12, 617–628 [Google Scholar]
- (619).Baughman RH Auxetic Materials: Avoiding the Shrink. Nature 2003, 425, 667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (620).Valimaki S; Mikkila J; Liljestrom V; Rosilo H; Ora A; Kostiainen MA Hierarchically Ordered Supramolecular Protein-Polymer Composites with Thermoresponsive Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2015, 16, 10201–10213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (621).Okada Y; Tanaka F Cooperative Hydration, Chain Collapse, and Flat Lcst Behavior in Aqueous Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Solutions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 4465–4471 [Google Scholar]
- (622).Li P; Banjade S; Cheng HC; Kim S; Chen B; Guo L; Llaguno M; Hollingsworth JV; King DS; Banani SF et al. Phase Transitions in the Assembly of Multivalent Signalling Proteins. Nature 2012, 483, 336–340 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (623).Cule D; Hwa T Denaturation of Heterogeneous DNA. Phys. Rev. Lett 1997, 79, 2375–2378 [Google Scholar]
- (624).Sato O Dynamic Molecular Crystals with Switchable Physical Properties. Nat. Chem 2016, 8, 644–656 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (625).Shao ZW; Cao X; Luo HJ; Jin P Recent Progress in the Phase-Transition Mechanism and Modulation of Vanadium Dioxide Materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 581–605 [Google Scholar]
- (626).Fratzl P; Weinkamer R Nature's Hierarchical Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci 2007, 52, 1263–1334 [Google Scholar]
- (627).Meyers MA; Chen P-Y; Lin AY-M; Seki Y Biological Materials: Structure and Mechanical Properties. Prog. Mater. Sci 2008, 53, 1–206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (628).Carlson JC; Jena SS; Flenniken M; Chou TF; Siegel RA; Wagner CR Chemically Controlled Self-Assembly of Protein Nanorings. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 7630–7638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (629).Li Q; So CR; Fegan A; Cody V; Sarikaya M; Vallera DA; Wagner CR Chemically Self-Assembled Antibody Nanorings (Csans): Design and Characterization of an Anti-Cd3 Igm Biomimetic. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2010, 132, 17247–17257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (630).Boyoglu-Barnum S; Ellis D; Gillespie RA; Hutchinson GB; Park YJ; Moin SM; Acton OJ; Ravichandran R; Murphy M; Pettie D et al. Quadrivalent Influenza Nanoparticle Vaccines Induce Broad Protection. Nature 2021, 592, 623–628 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (631).Petersburg JR; Shen J; Csizmar CM; Murphy KA; Spanier J; Gabrielse K; Griffith TS; Fife B; Wagner CR Eradication of Established Tumors by Chemically Self-Assembled Nanoring Labeled T Cells. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6563–6576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (632).Marcandalli J; Fiala B; Ols S; Perotti M; de van der Schueren W; Snijder J; Hodge E; Benhaim M; Ravichandran R; Carter L et al. Induction of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by a Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccine for Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Cell 2019, 176, 1420–1431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (633).Ueda G; Antanasijevic A; Fallas JA; Sheffler W; Copps J; Ellis D; Hutchinson GB; Moyer A; Yasmeen A; Tsybovsky Y et al. Tailored Design of Protein Nanoparticle Scaffolds for Multivalent Presentation of Viral Glycoprotein Antigens. eLife 2020, 9, e57659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (634).Brouwer PJM; Antanasijevic A; Berndsen Z; Yasmeen A; Fiala B; Bijl TPL; Bontjer I; Bale JB; Sheffler W; Allen JD et al. Enhancing and Shaping the Immunogenicity of Native-Like Hiv-1 Envelope Trimers with a Two-Component Protein Nanoparticle. Nat. Commun 2019, 10, 4272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (635).Walls AC; Fiala B; Schafer A; Wrenn S; Pham MN; Murphy M; Tse LV; Shehata L; O'Connor MA; Chen C et al. Elicitation of Potent Neutralizing Antibody Responses by Designed Protein Nanoparticle Vaccines for Sars-Cov-2. Cell 2020, 183, 1367–1382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (636).Park J; Selvaraj B; McShan AC; Boyken SE; Wei KY; Oberdorfer G; DeGrado W; Sgourakis NG; Cuneo MJ; Myles DAA et al. De Novo Design of a Homo-Trimeric Amantadine-Binding Protein. eLife 2019, 8, e47839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (637).Votteler J; Ogohara C; Yi S; Hsia Y; Nattermann U; Belnap DM; King NP; Sundquist WI Designed Proteins Induce the Formation of Nanocage-Containing Extracellular Vesicles. Nature 2016, 540, 292–295 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (638).Schwizer F; Okamoto Y; Heinisch T; Gu Y; Pellizzoni MM; Lebrun V; Reuter R; Kohler V; Lewis JC; Ward TR Artificial Metalloenzymes: Reaction Scope and Optimization Strategies. Chem. Rev 2018, 118, 142–231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (639).Thomas CM; Ward TR Artificial Metalloenzymes: Proteins as Hosts for Enantioselective Catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev 2005, 34, 337–346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (640).Chen K; Arnold FH Engineering New Catalytic Activities in Enzymes. Nat. Catal 2020, 3, 203–213 [Google Scholar]
- (641).Lewis JC; Coelho PS; Arnold FH Enzymatic Functionalization of Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40, 2003–2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (642).Nastri F; Chino M; Maglio O; Bhagi-Damodaran A; Lu Y; Lombardi A Design and Engineering of Artificial Oxygen-Activating Metalloenzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev 2016, 45, 5020–5054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (643).Reed CJ; Lam QN; Mirts EN; Lu Y Molecular Understanding of Heteronuclear Active Sites in Heme-Copper Oxidases, Nitric Oxide Reductases, and Sulfite Reductases through Biomimetic Modelling. Chem. Soc. Rev 2021, 50, 2486–2539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (644).Yu F; Cangelosi VM; Zastrow ML; Tegoni M; Plegaria JS; Tebo AG; Mocny CS; Ruckthong L; Qayyum H; Pecoraro VL Protein Design: Toward Functional Metalloenzymes. Chem. Rev 2014, 114, 3495–3578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (645).Zastrow ML; Pecoraro VL Designing Functional Metalloproteins: From Structural to Catalytic Metal Sites. Coordin. Chem. Rev 2013, 257, 2565–2588 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (646).Scrofani SD; Chung J; Huntley JJ; Benkovic SJ; Wright PE; Dyson HJ Nmr Characterization of the Metallo-Beta-Lactamase from Bacteroides Fragilis and Its Interaction with a Tight-Binding Inhibitor: Role of an Active-Site Loop. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 14507–14514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (647).Tomatis PE; Fabiane SM; Simona F; Carloni P; Sutton BJ; Vila AJ Adaptive Protein Evolution Grants Organismal Fitness by Improving Catalysis and Flexibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 2008, 105, 20605–20610 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (648).Yu J; Yang J; Seok C; Song WJ Symmetry-Related Residues as Promising Hotspots for the Evolution of De Novo Oligomeric Enzymes. Chem. Sci 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (649).Bar-Even A; Noor E; Savir Y; Liebermeister W; Davidi D; Tawfik DS; Milo R The Moderately Efficient Enzyme: Evolutionary and Physicochemical Trends Shaping Enzyme Parameters. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 4402–4410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (650).Pindur U; Lutz G; Otto C Acceleration and Selectivity Enhancement of Diels-Alder Reactions by Special and Catalytic Methods. Chem. Rev 1993, 93, 741–761 [Google Scholar]
- (651).Eck RV; Dayhoff MO Evolution of the Structure of Ferredoxin Based on Living Relics of Primitive Amino Acid Sequences. Science 1966, 152, 363–366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (652).DiMarco RL; Heilshorn SC Multifunctional Materials through Modular Protein Engineering. Adv. Mater 2012, 24, 3923–3940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (653).Zabret J; Bohn S; Schuller SK; Arnolds O; Moller M; Meier-Credo J; Liauw P; Chan A; Tajkhorshid E; Langer JD et al. Structural Insights into Photosystem Ii Assembly. Nat. Plants 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (654).Mattila PK; Lappalainen P Filopodia: Molecular Architecture and Cellular Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2008, 9, 446–454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (655).White SH; von Heijne G The Machinery of Membrane Protein Assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol 2004, 14, 397–404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (656).Ellis RJ Molecular Chaperones: Assisting Assembly in Addition to Folding. Trends Biochem. Sci 2006, 31, 395–401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (657).Klug A The Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle: Structure and Assembly. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci 1999, 354, 531–535 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (658).Ackers GK; Doyle ML; Myers D; Daugherty MA Molecular Code for Cooperativity in Hemoglobin. Science 1992, 255, 54–63 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (659).Janke C; Magiera MM The Tubulin Code and Its Role in Controlling Microtubule Properties and Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2020, 21, 307–326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (660).Weisenberg RC; Deery WJ; Dickinson PJ Tubulin-Nucleotide Interactions During the Polymerization and Depolymerization of Microtubules. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 4248–4254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (661).Dimitrov DS Therapeutic Proteins In Therapeutic Proteins: Methods and Protocols; Voynov Vand Caravella JA, Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2012 [Google Scholar]
- (662).Arbige MV; Shetty JK; Chotani GK Industrial Enzymology: The Next Chapter. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1355–1366 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (663).Kirk O; Borchert TV; Fuglsang CC Industrial Enzyme Applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2002, 13, 345–351 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (664).Torculas M; Medina J; Xue W; Hu X Protein-Based Bioelectronics. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng 2016, 2, 1211–1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


