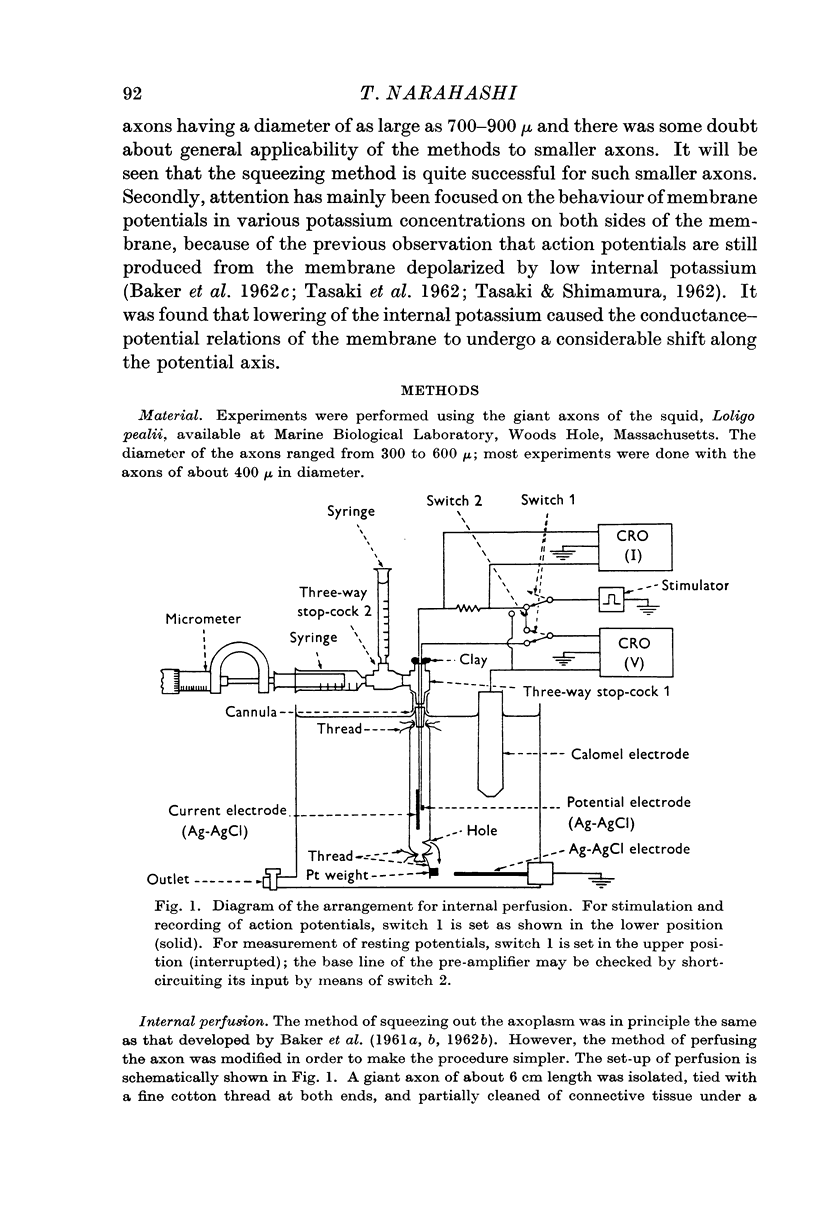
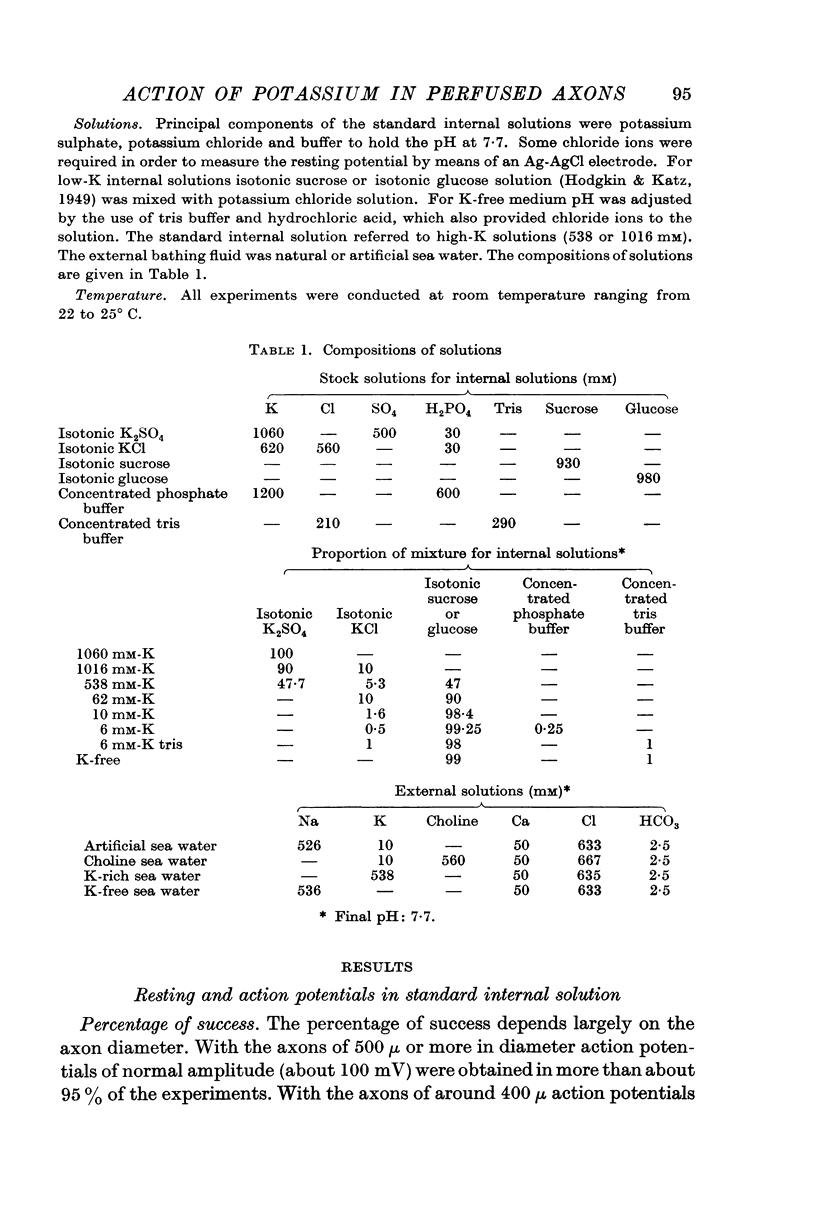
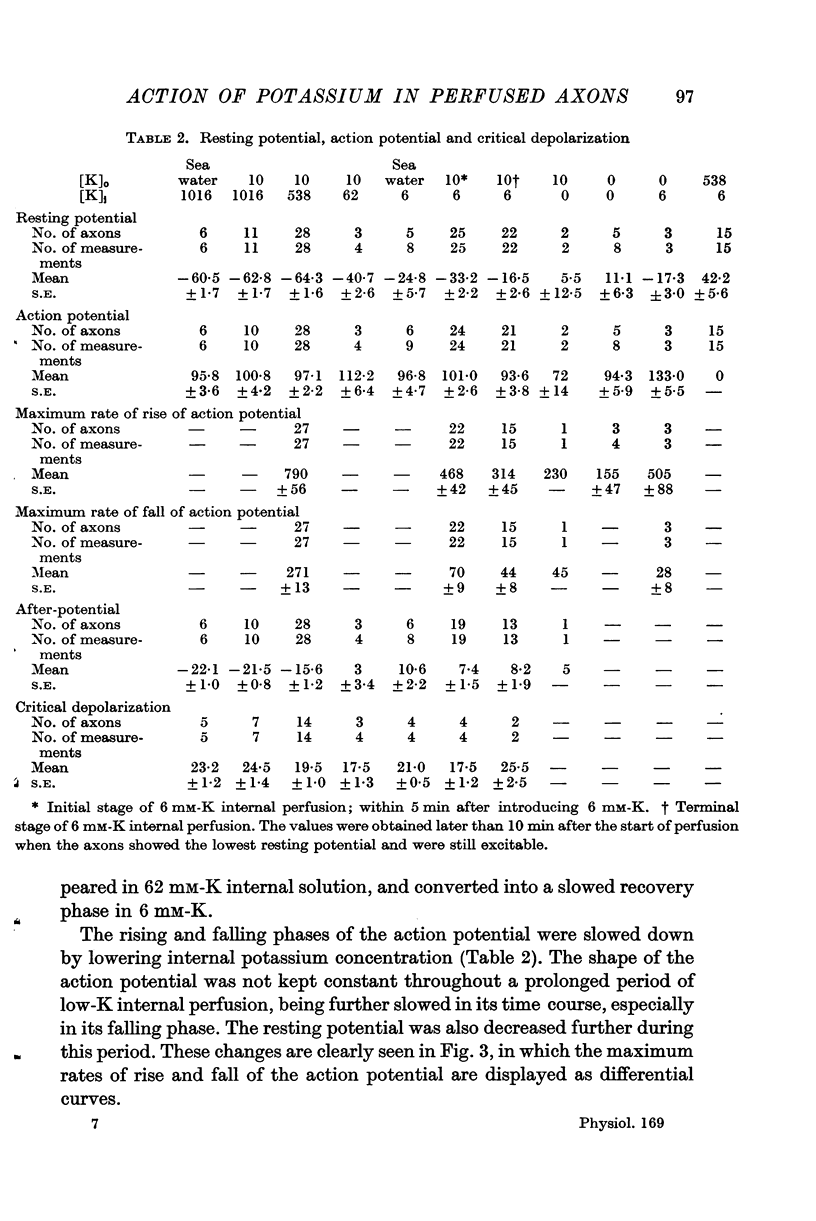
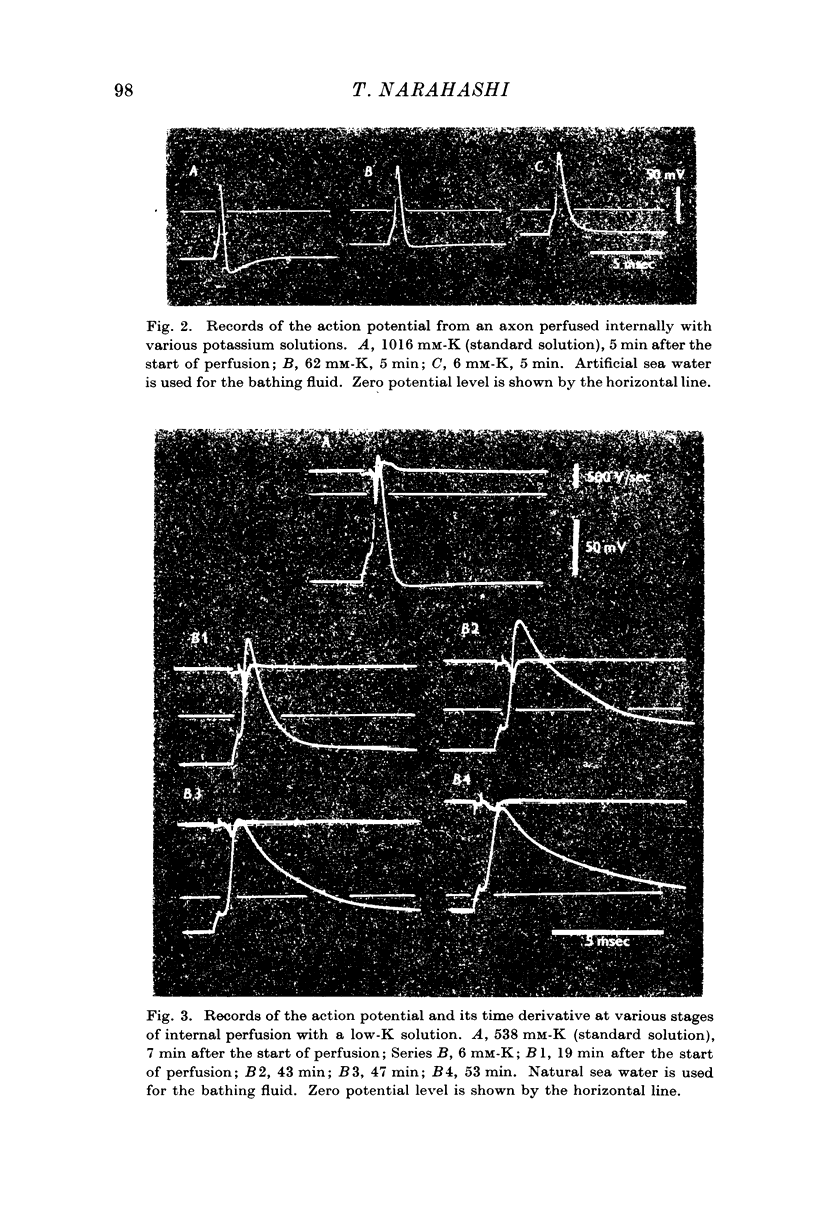
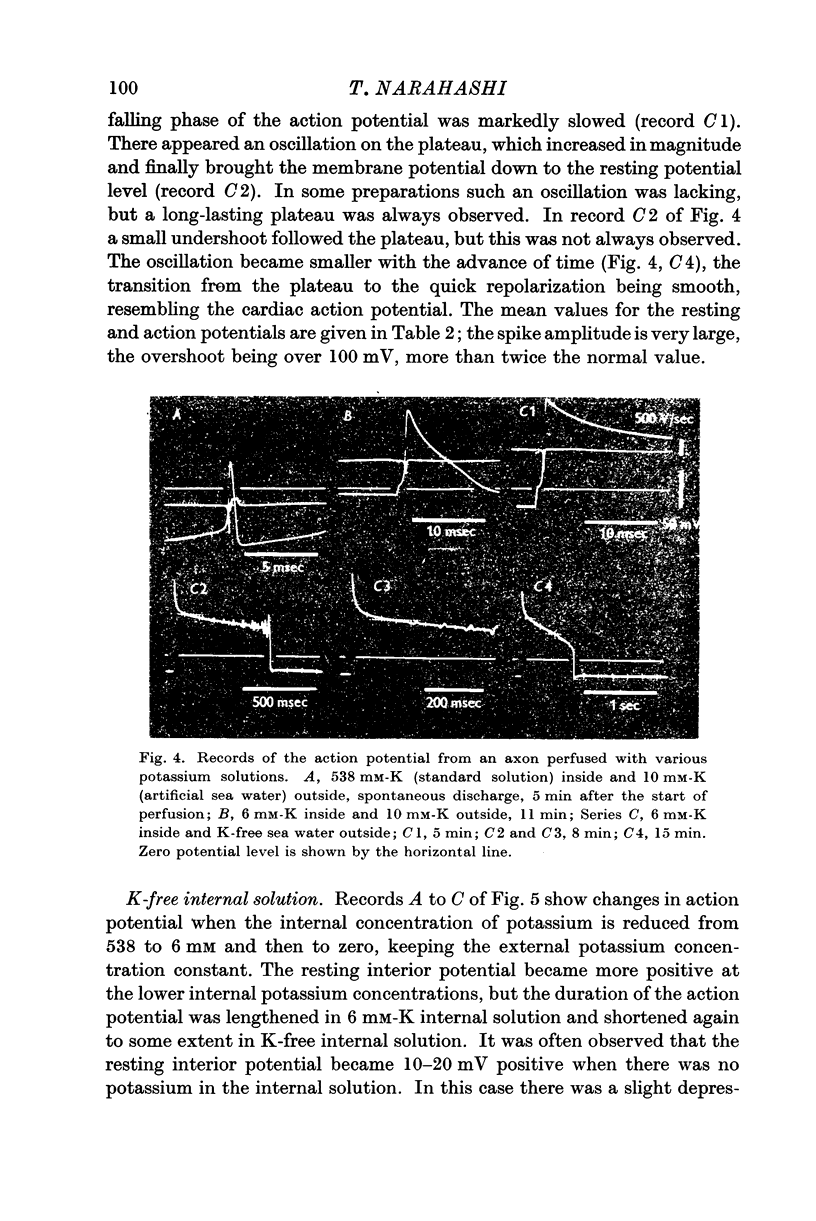
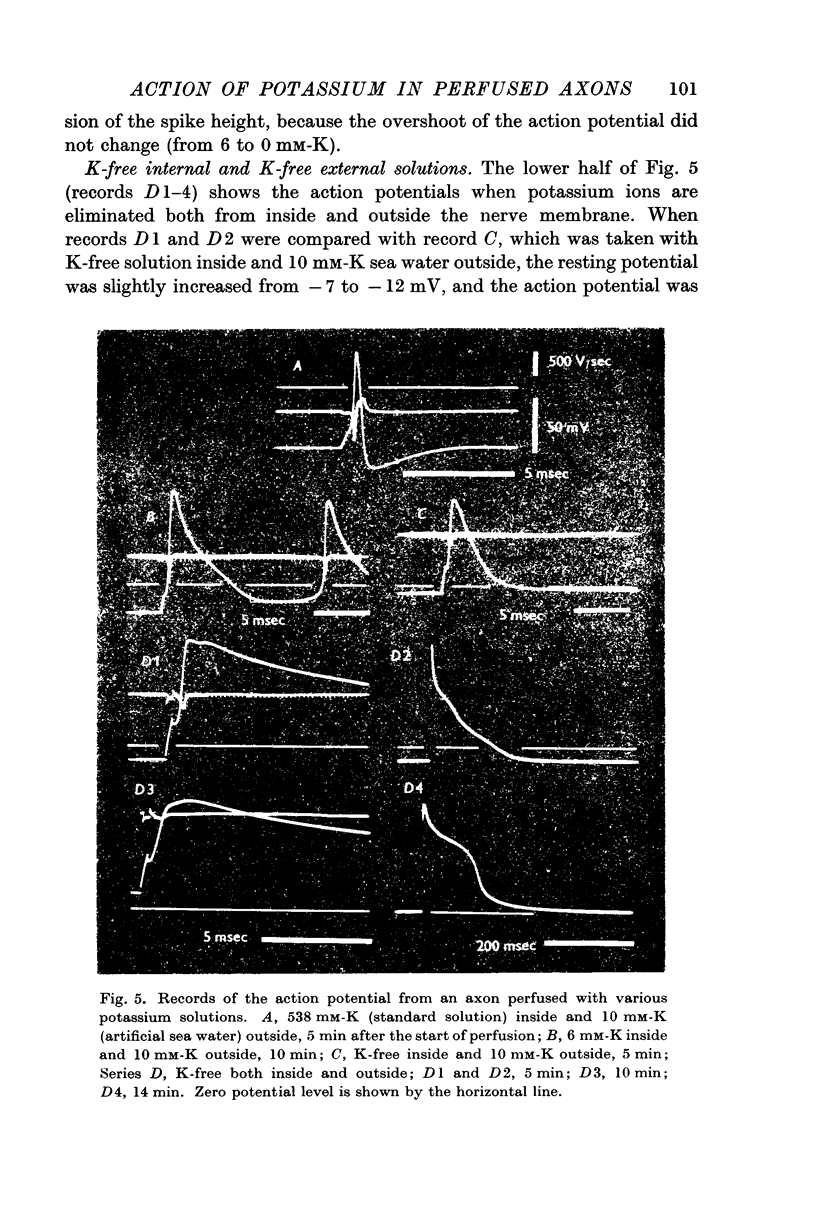
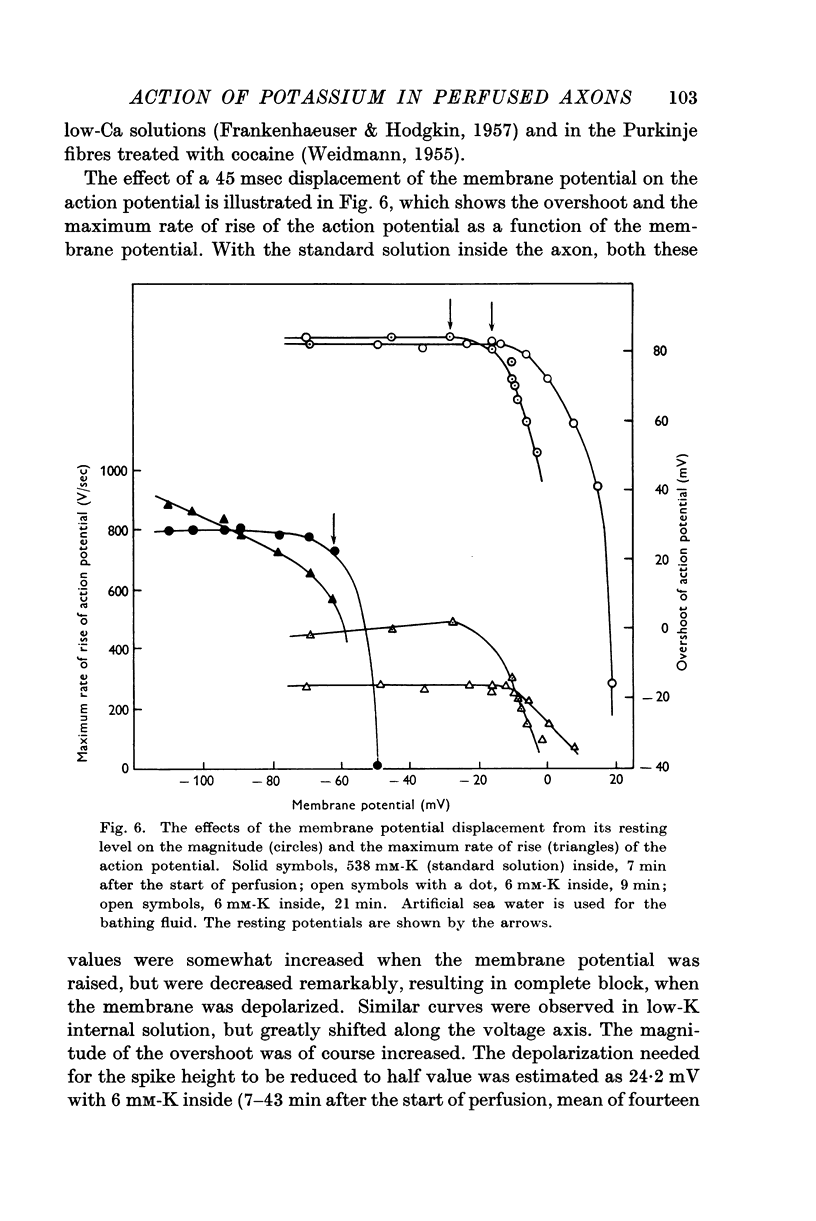
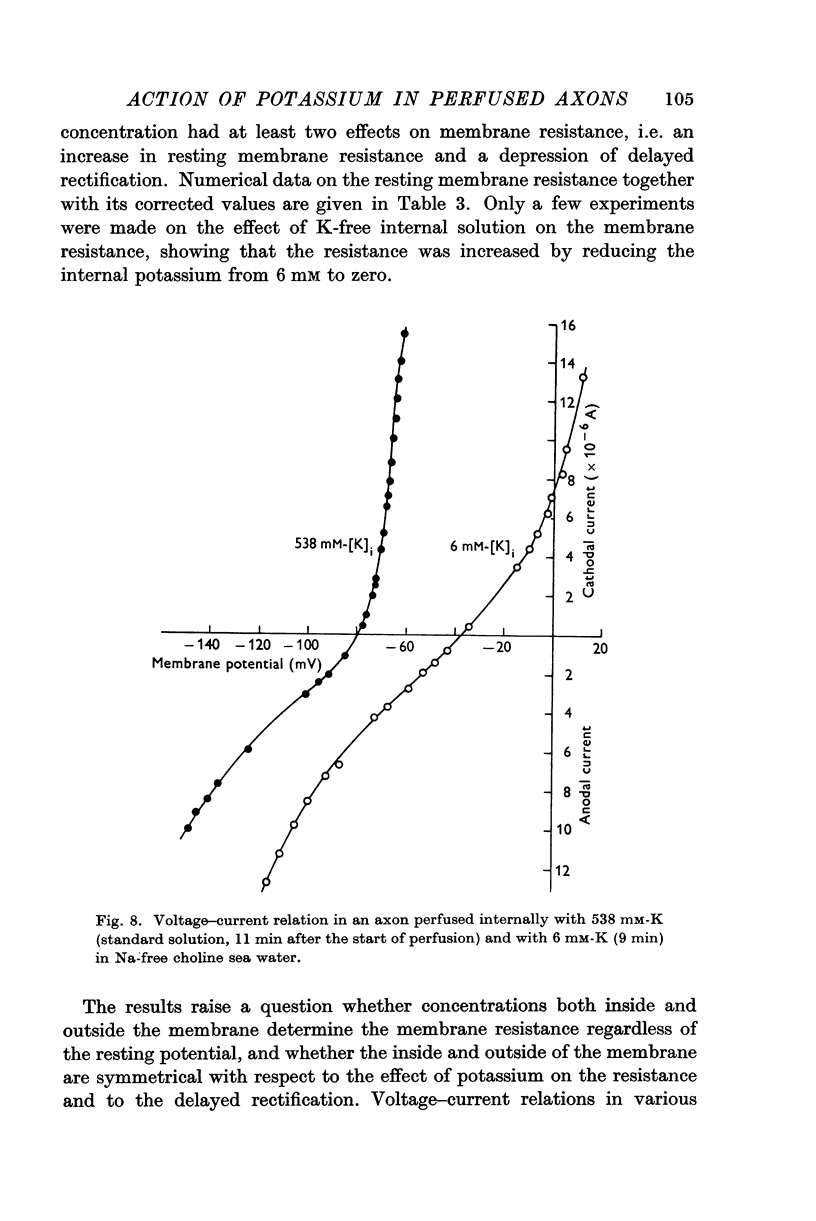
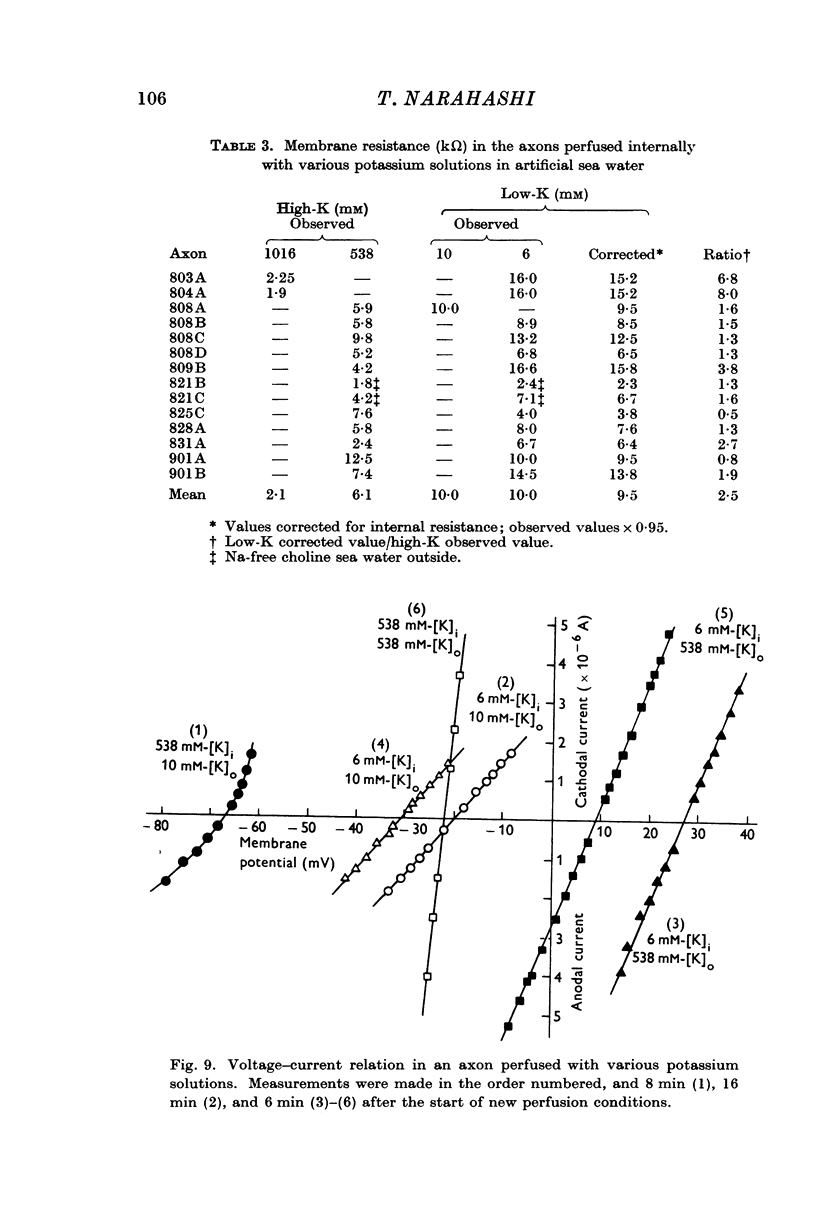
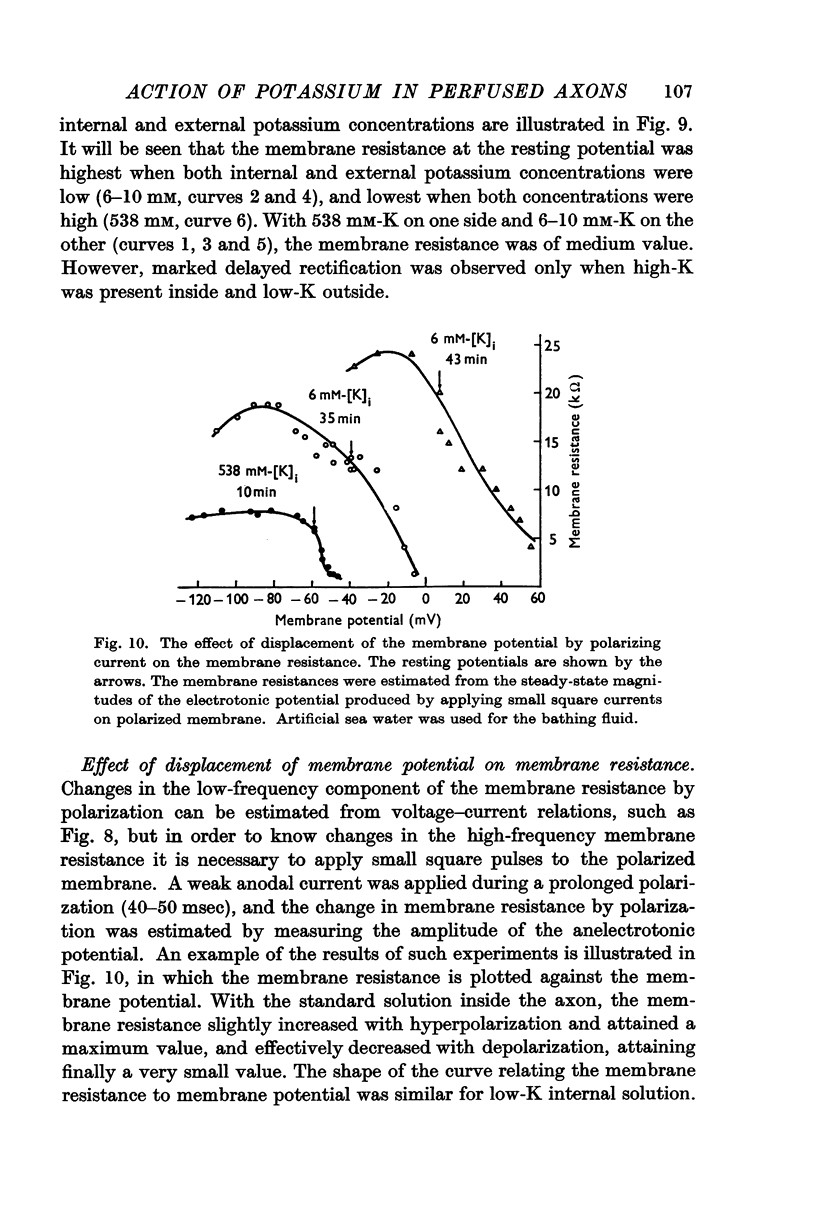
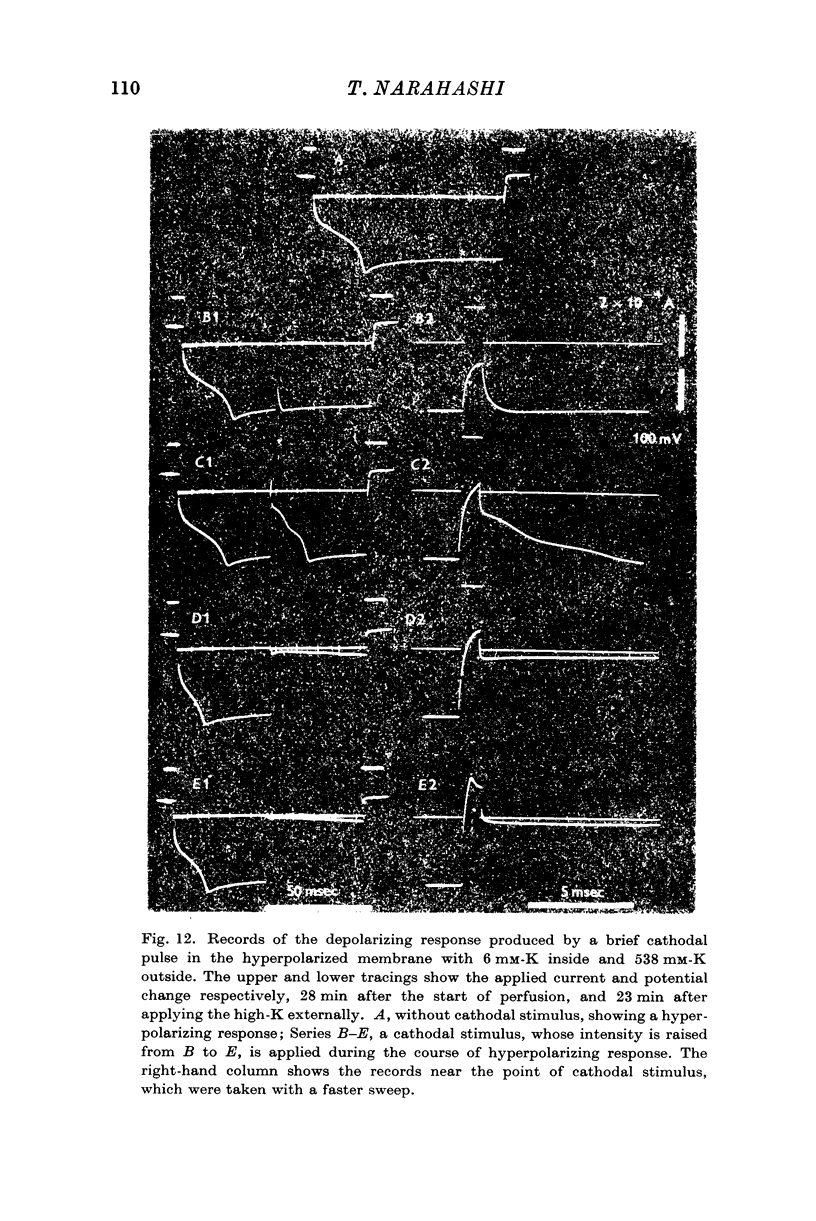
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. Potassium chloride movement and the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Apr;151:154–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the axoplasm of giant nerve fibres with artificial solutions. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:330–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. Replacement of the protoplasm of a giant nerve fibre with artificial solutions. Nature. 1961 Jun 3;190:885–887. doi: 10.1038/190885a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER P. F., HODGKIN A. L., SHAW T. I. The effects of changes in internal ionic concentrations on the electrical properties of perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1962 Nov;164:355–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp007026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG J. J., SCHMIDT R. F. Prolonged action potentials and regenerative hyperpolarizing responses in Purkinje fibers of mammalian heart. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;272:127–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00420020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITZHUGH R. Thresholds and plateaus in the Hodgkin-Huxley nerve equations. J Gen Physiol. 1960 May;43:867–896. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE E. P., JOHNSON E. A. Solutions of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations for squid axon treated with tetraethylammonium and in potassium-rich media. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1961 Jun;39:275–293. doi: 10.1038/icb.1961.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS C. L., JOHNSON E. A. Intracellular ionic injection in rabbit ventricular fibres. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1962 Apr;40:85–92. doi: 10.1038/icb.1962.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H., KAO C. Y., ALTAMIRANO M. Bioelectric effects of ions microinjected into the giant axon of Loligo. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):245–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K., KIMURA Y. The resting potential and intracellular potassium of skeletal muscle in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Jun;55:239–244. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE J. W. Excitation of the squid axon membrane in isosmotic potassium chloride. Nature. 1959 Jan 24;183(4656):265–266. doi: 10.1038/183265b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OIKAWA T., SPYROPOULOS C. S., TASAKI I., TEORELL T. Methods for perfusing the giant axon of Loligo pealii. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Jun;52:195–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OOYAMA H., WRIGHT E. B. Activity of potassium mechanism in single Ranvier node during excitation. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:67–93. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUBEN J. P., WERMAN R., GRUNDFEST H. The ionic mechanisms of hyperpolarizing responses in lobster muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:243–265. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL J. R. An anodal threshold phenomenon in the squid giant axon. Nature. 1958 Nov 15;182(4646):1370–1370. doi: 10.1038/1821370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEMPFLI R. Is the resting potential of Ranvier nodes a potassium potential? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Aug 28;81:265–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON W. K. Membrane potential changes and ion movements in the frog sartorius muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Aug;50(1):105–128. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030500108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. Demonstration of two stable states of the nerve membrane in potassium-rich media. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:306–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKII, SHIMAMURA M. Further observations on resting and action potential of intracellularly perfused squid axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Sep 15;48:1571–1577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.9.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKII, WATANABE A., TAKENAKA T. Resting and action potential of intracellularly perfused squid giant axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1177–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAS J. M. Experimentally altered structure related to function in the lobster axon with an extrapolation to molecular mechanisms in excitation. J Cell Physiol. 1958 Aug;52(1):89–125. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030520107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBIAS J. M. Injury and membrane potentials in frog muscle after depleting potassium and producing other changes by soaking in potassium free salt solution or distilled water. J Cell Physiol. 1950 Aug;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030360102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Effects of calcium ions and local anesthetics on electrical properties of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):568–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT E. B., OOYAMA H. Role of cations, potassium, calcium, and sodium during excitation of frog single nerve fiber. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:94–109. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


