Abstract
We investigated the effects of human selection for yellow endosperm color, representing increased carotenoid content, on two maize genes, the Y1 phytoene synthase and PSY2, a putative second phytoene synthase. Multiple polymorphic sites were identified at Y1 and PSY2 in 75 white and yellow maize inbred lines. Many polymorphic sites showed strong association with the endosperm color phenotype at Y1, but no detectable association was found at PSY2. Nucleotide diversity was equivalent for whites and yellows at PSY2 but was 19-fold less in yellows than in whites at Y1, consistent with the white ancestral state of the gene. The strong sequence haplotype conservation within yellows at Y1 and a significant, negative Tajima's D both verified positive selection for yellow endosperm. We propose that two independent gain-of-function events associated with insertions into the promoter of the Y1 gene and upregulation of expression in endosperm have been incorporated into yellow maize.
INTRODUCTION
Selection is a major force affecting local levels of genetic variation in a species, and domestication is a form of selection. Maize is believed to have been domesticated from teosinte ∼10,000 years ago (Eyre-Walker et al., 1998; Wang et al., 1999; White and Doebley, 1999; Buckler et al., 2001). The observed morphological differences between maize and teosinte are the result of selection at five major genetic regions (Doebley et al., 1990), one of which is teosinte branched1 (tb1), and many minor regions. Diversity analyses at the tb1 gene (Wang et al., 1999) revealed a partial selective sweep in the promoter region of maize tb1, characterized by reduced diversity and strong allelic associations, suggesting a regulatory mutation as the target of selection.
Other genes not involved in the domestication process are likely to have undergone selective sweeps as a result of selection in the recent history of maize. The su1 locus showed significant linkage disequilibrium (LD) extending over a distance of 7000 bp, in contrast to a distance of 2000 bp or less observed in other maize genes (Remington et al., 2001). This larger extent of LD was attributed to recent selection for sugar and starch levels in the kernel. Other examples of positive selection affecting local levels of variation have been reported in maize (Tenaillon et al., 2001; Thornsberry et al., 2001; Vigouroux et al., 2002b; Whitt et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2002), Arabidopsis (Kawabe et al., 2000; Le Corre et al., 2002), Drosophila (Benassi et al., 1999; Depaulis et al., 1999; Rozas et al., 2001; Harr et al., 2002), rice (Olsen and Purugganan, 2002), and human (Gilad et al., 2002).
The yellow/orange endosperm phenotype (referred to hereafter as yellow) has been a target of breeding selection since the early 20th century, when the nutritional advantage of increased carotenoids in yellow maize was recognized (Mangelsdorf and Fraps, 1931). The gene product is phytoene synthase (Buckner et al., 1996), the enzyme that converts geranylgeranylpyrophosphate to phytoene, an essential enzyme in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway. In the presence of the Y1 gene product, carotenoids are produced in the endosperm tissue, yielding the yellow endosperm phenotype; in its absence, carotenoids cannot be synthesized, resulting in a lack of color, or white endosperm. Both yellow and white phenotypes of maize have been targets of selection, the former as a result of nutritional content and the latter as a result of the preference for white maize products in some human cultures (reviewed by Poneleit, 2001). The proposed ancestor of maize, teosinte, has white endosperm (J. Doebley, personal communication); thus, white is hypothesized to be the ancestral state of the gene. The yellow endosperm phenotype is thought to have originated as a naturally occurring variant. There is no known fitness advantage to carotenoids in the endosperm, and the current prevalence of yellow phenotypes is entirely the result of artificial selection that occurred in the past century.
The Y1 gene was cloned by transposon tagging (Buckner et al., 1996) and mapped to chromosome 6. One allelic form is expressed in leaves, embryo, and endosperm, whereas the other is expressed in leaves and embryo only (Buckner et al., 1996). Other phytoene synthase genes are predicted to exist in the maize genome (Buckner et al., 1996). We have identified a second gene, PSY2 (PHYTOENE SYNTHASE2), with significant protein similarity to the Y1 phytoene synthase. PSY2 shows high mRNA levels in leaves but appears to have little if any influence on the level of carotenoids in the endosperm tissue (our unpublished observations). Therefore, PSY2 should not have been subjected to the same human selection as the Y1 gene and is an appropriate control in studies of the effects of selection on the Y1 gene.
The goals of this study were to compare genetic diversity and LD at the Y1 yellow endosperm gene and the PSY2 gene, to search for evidence of positive directional selection, to identify the causal sequence variant that determines the yellow phenotype, and to assess the usefulness of candidate gene–based association studies in identifying genes associated with traits subject to selection. To this end, the Y1 gene was sequenced from 41 yellow or orange endosperm lines and 34 white endosperm lines. Portions of the PSY2 gene also were sequenced using the same test set of lines.
RESULTS
Nucleotide Variation and Selection at Y1
The maize Y1 gene was sequenced from a set of 75 maize inbred lines that were selected to maximize genetic diversity; this set included 3 orange endosperm public lines, 23 yellow endosperm public lines, 15 yellow endosperm private lines, 22 white endosperm public lines, and 12 white endosperm private lines (Table 1). The seven analyzed regions covered 4512 bp of the 5995 bp, or 75% of the Y1 GenBank reference sequence, including all coding regions. The sequenced regions of the Y1 gene contain 32 insertions/deletions (indels) of varying sizes, 85 noncoding single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), and 21 coding SNPs (for a complete alignment of polymorphic positions, see supplemental data online). Fourteen of the indels and 52 of the noncoding SNPs are defined here as informative for LD analysis, or having a rare allele frequency of >0.1. Of the 21 coding SNPs, 17 are informative and 10 produce amino acid changes (see supplemental data online). In addition, two microsatellite regions exist within the Y1 gene. A CCA repeat is located just before the most common transcriptional start site (Buckner et al., 1996; Phelps et al., 1996) at positions 1877 to 1909 of the Y1 GenBank reference sequence, and the number of repeats observed in the maize inbred lines varies from 5 to 16. Some of the white endosperm lines have a (CCA)4TCACCA compound repeat. Several short simple sequence repeats also can be identified in the immediate vicinity of the CCA repeat: a TGC repeat at positions 1838 to 1843 and a TCTCA repeat at positions 1865 to 1874. A mononucleotide T repeat is present in Y1 at positions 2717 to 2728 of the published sequence within the second intron. This repeat varies from 8 to 13, with three of the lines, PI583846, W17, and W21, having 11 T mononucleotide repeats with A in the second position. Both the CCA and the T mononucleotide repeats have partially overlapping length distributions for the two phenotypic classes.
Table 1.
Germplasm List
| Lines | Features |
|---|---|
| Public orange inbred lines | |
| 1033-A Catsul | Inbred from Uruguay |
| PI186217 | Argentinian inbred line |
| PI270297 | 41:2504B Amargo inbred line; Argentina |
| Public yellow inbred lines | |
| 66A4-2 | Howe's Early Alberta, very early open-pollinated variety |
| Ames 12734 | Indian chief; Huffmann variety × Illinois low ear |
| Ames 23427 | Reid Yellow dent |
| Ames 23476 | [(V3 × Wf9)S1 Wf9] |
| Ames 24575 | Yellow pearl popcorn inbred |
| B73 | Reid; Iowa Stiff Stalk Synthetic |
| H60 | Pride of Saline; Wooster Clarage; Lancaster; NSS |
| Inbred Lo32 | Italian inbred |
| Mo17 | Lancaster surecrop; Krug |
| PI221785 | South African inbred |
| PI221788 | South African inbred |
| PI340837 | Selection from Japanese hull-less white |
| PI542777 | South American popcorn inbred |
| PI583350 | Guatemalan inbred |
| PI583351 | Brazilian inbred |
| PI583352 | Ecuadorian inbred |
| PI587132 | Unknown |
| PI593015 | Hi34 inbred with Antigua 2D parentage |
| PI595553 | Yellow flint materials from Mexico, Cuba, Dominican Republic, South America, St. Vincent, Guatemala, Surinam, and India |
| PI595554 | Materials from Mexico, Central America, Caribbean, Ecuador, Colombia, and Argentina |
| PI595559 | Tuxpeno, ETO Amarillo, Caribbean, and Brazilian germplasm; downy mildew resistance incorporation from Thailand and The Philippines |
| PI595562 | Materials from Mexico, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Antigua, South America, India, Puerto Rico, and Central America |
| PI595566 | CIMMYT Syn Amarillo TSR |
| SC60 | Gourd seed; U.S. southern dent |
| Private yellow inbred lines | |
| Y-1 | Southern United States 3 |
| Y-2 | SSS B14 derived |
| Y-3 | Central cornbelt SSS/NSS mix |
| Y-4 | Tropical 4 |
| Y-5 | Early cornbelt public C0109 |
| Y-6 | Cornbelt NSS mix |
| Y-7 | Southern United States 2 |
| Y-8 | European flint (F2) |
| Y-9 | NSS cornbelt IODENT/OH43 |
| Y-10 | Tropical 3 |
| Y-11 | NSS cornbelt |
| Y-12 | Tropical 1 |
| Y-13 | Tropical 2 |
| Y-14 | Southern United States 1 |
| Public white inbred lines | |
| Ames 22026 | Narrow Grain Evergreen white sweetcorn inbred |
| Ames 22443 | Silver King; Northwest dent |
| Ames 22754 | Reid Yellow dent |
| Ames 22758 | Neal paymaster; Snelling stiff stalk |
| Ames 23418 | Black Mexican; Spanish gold; Purdue yellow dent |
| CIze 127 | Boone county white; White Mastodon; Tuxpan |
| NC296 | Jamaican hybrid; Cuban flint; Tuxpeno (acquired from M.M. Goodman) |
| PI221733 | Potchefstroom Pearl |
| PI221738 | Hickory King |
| PI340836 | Japanese hull-less popcorn inbred |
| Public white inbred lines | |
| PI340838 | White rice popcorn inbred |
| PI406108 | Lancaster surecrop |
| PI550442 | Open-pollinated variety Laguna (U.S. Department of Agriculture corn from Mexico) |
| PI550545 | Inbred from Nepal |
| PI561605 | Syn A1/87014 from Cameroon |
| PI583846 | Mo17 white composite |
| PI595531 | Tuxpeno germplasm from Mexico; also Central American and Colombian materials |
| PI595532 | Crosses among Mexican, Colombian, Caribbean, Central American, Indian, Thai, and Filipino lines |
| PI595539 | Tuxpeno germplasm from Mexico; some Central American materials |
| PI595546 | ∼30% downy mildew resistance from The Philippines; also from Argentina, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Honduras, India, Mexico, and the United States |
| PI595547 | Tuxpeno, Cuban flints, and ETO (from Central and South America, Mexico, and the United States) |
| Stock 6 | Minnesota #13 |
| Private white inbred lines | |
| W16 | Public MOSQA |
| W17 | Public W94 |
| W2 | Public V63 |
| W20 | Public W94,V80 |
| W21 | Public Krug K174-312-B1; white Mo17 (seven doses) |
| W28 | Unknown |
| W37 | HI 22 W |
| W45 | PI451693; derived from seven Cuzco populations and one early U.S. dent population |
| W50 | Illinois High Oil |
| W6 | Public V63 |
| W7 | Southern dent |
| W8 | Public KY216 |
| Other Zea species | |
| 9475 | Z. perennis; Mexico |
| 9476 | Z. diploperennis; Mexico |
| 11083 | Z. luxurians; Nicaragua |
| 11407 | Z. mays subsp parviglumis; Mexico |
| 11396 | Z. mays subsp mexicana; Mexico |
| 12823 | Z. mays subsp mexicana; Mexico |
The calculated measure of diversity, π, for the entire test set is 8.4 × 10−3. However, the yellow endosperm lines have a π value of 0.54 × 10−3 and white endosperm lines have a π value of 10.2 × 10−3 (Table 2). Based on this measure of diversity, white endosperm lines are 19-fold more diverse than yellow endosperm lines. The value of Watterson's estimator, θw, for white endosperm lines is 7.0 × 10−3, which is four times greater than the value for yellow endosperm lines, 1.7 × 10−3 (Table 2). The low diversity observed in the yellow endosperm lines is consistent with a strongly significant (P < 0.001) negative Tajima's D value (−2.4), indicating a preponderance of rare polymorphisms and a strong departure from neutrality. By contrast, the diversity of simple sequence repeat (SSR) length variants does not show dramatic differences between yellows and whites. Heterozygosity values are 0.70 (yellows) and 0.67 (whites) for the CCA repeat at nucleotides 1877 to 1909 and 0.54 (yellows) and 0.77 (whites) for the T repeat at nucleotides 2717 to 2728. However, the length variant distributions of both the CCA repeat and the T repeat are significantly different (Kolmogorov-Smirnov goodness-of-fit test, P < 0.0001).
Table 2.
Summary of Y1 and PSY2 DNA Sequence Variation
| Loci | Sites | π (×10−3) | θw (×10−3) | Tajima's D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1a | ||||
| All | Total | 8.41 | 6.44 | 1.04 (NS) |
| Silent | 10.86 | 8.39 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | 2.68 | 1.88 | ||
| Yellow | Total | 0.54 | 1.79 | −2.39b |
| Silent | 0.57 | 2.09 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | 0.44 | 0.79 | ||
| White | Total | 10.19 | 7.14 | 1.60 (NS) |
| Silent | 13.20 | 9.25 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | 3.20 | 2.23 | ||
| PSY2c | ||||
| All | Total | 8.49 | 7.75 | 0.30 (NS) |
| Silent | 11.62 | 10.49 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | – | – | ||
| Yellow | Total | 7.59 | 6.70 | 0.45 (NS) |
| Silent | 10.52 | 9.23 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | 0.88 | 0.91 | ||
| White | Total | 8.59 | 8.80 | −0.08 (NS) |
| Silent | 11.90 | 11.87 | ||
| Nonsynonymous | – | – |
π, nucleotide diversity/site; θw, Watterson's estimator (calculated using the no-recombination assumption); NS, not significant (P > 0.10). Estimates are based on all nucleotide sites. Dashes indicate that the measure of diversity for that particular set of lines cannot be calculated.
One orange/yellow endosperm line, Ames 24575, and one white endosperm line, PI595547, were excluded because of missing data.
0.001 < P < 0.01.
Two orange/yellow endosperm lines, Y-4 and PI595559, were excluded from analysis because of excessive missing data.
Y1 SNP Haplotype Graphs
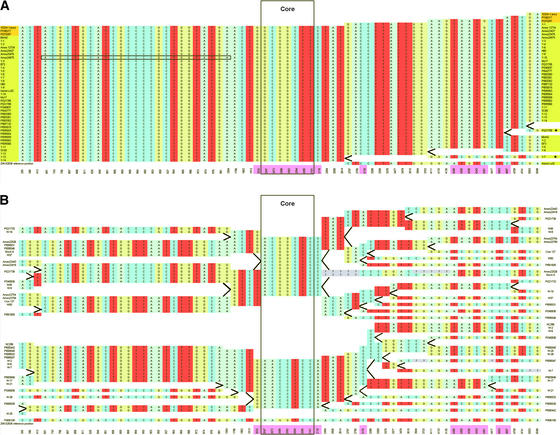
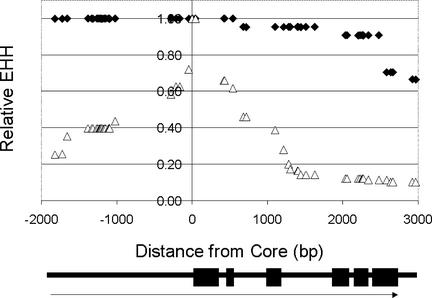
SNP haplotype graphs and the extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH) measure were used to visualize the effects of selection in the region of the Y1 gene. The EHH and haplotype bifurcation method, recently described in human (Sabeti et al., 2002), begins with the identification of core SNP haplotypes. For Y1, we chose to define the core region by the only two SNP polymorphisms completely associated with the endosperm color phenotype, nucleotides 2047 and 2101, both of which are located in the first exon and produce silent mutations. The decay of LD (and increase in diversity) is followed by evaluating informative SNPs encountered at increasing distances from the core; this is quantitated as extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH; see Methods). Each newly encountered SNP results in bifurcation of the respective haplotype. Thus, the yellow endosperm lines have a single haplotype in the defined core that remains conserved toward the 5′ end of the gene (Figure 1A). However, toward the 3′ end, the single haplotype splits, culminating in two putative recombinant lines, PI221788 and Y-7 (Figure 1, asterisks), a rare haplotype with Inbred Lo32, and two more common haplotypes shared by the remaining lines. The yellow endosperm lines have a single haplotype at the core and thus a starting EHH value of 1.0 that only declines toward the 3′ end, to 66% of the core EHH value (Figure 2). By contrast, the white endosperm lines have three haplotypes at the core (Figure 1B), one of which is a singleton, thereby yielding a starting EHH value of 0.476. The EHH value for whites declines to 25% of its starting value on the 5′ side and 10% on the 3′ side. (Figure 2). For both phenotypic classes, the bifurcation of haplotypes occurs more rapidly at the 3′ end than at the 5′ end of the gene; however, the disintegration of the core haplotypes is much greater for white endosperm lines than for yellow endosperm lines.
Figure 1.
Y1 SNP Haplotype Graphs.
The Y1 SNP haplotype graphs depict all polymorphic SNPs with a rare allelic variant frequency of >10%. The horizontal rows correspond to the individuals used in this study, and the vertical columns represent the relevant SNP positions. The core is defined by the two completely associated SNPs located at positions 2047 and 2101 of the published Y1 sequence; all other SNP positions are indicated relative to the published sequence (with coding SNP position numbers highlighted in pink). The graphs depict the breakdown of the core haplotypes traversing from the core toward the 5′ and 3′ ends (as described by Sabeti et al., 2002). The orientation for each graph is in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
(A) Yellow haplotype graph. At the core region, only one haplotype is identified. Regions outlined with boldface lines represent data that can be inferred as a result of the high conservation seen within the yellow endosperm lines.
(B) White haplotype graph. Gray areas indicate missing data. Data cannot be inferred for the missing white endosperm genotypes because of the high variability observed among the white endosperm lines. Three haplotypes are found at the core region.
Figure 2.
Y1 Relative EHH Graph.
The SNP positions delineating the core at the Y1 gene are Y1 GenBank positions 2047 and 2101. Therefore, the 0-value point on the graph is set between the two positions, at 2074. All distances are calculated from this position. EHH is calculated for each of the SNPs used in the Y1 SNP haplotype graphs. The y values shown are the ratios of the EHH of the SNP at that particular distance from the core to the initial EHH value that is specific for each respective phenotype (Sabeti et al., 2002); this is referred to as the relative EHH. Diamonds indicate data obtained from the yellow endosperm test set, and triangles refer to the white endosperm set. The starting EHH value at the core for the yellow endosperm lines is 1.00, whereas the starting EHH value for the white endosperm lines is 0.476. The scheme below the graph shows the x axis position relative to the Y1 gene; blocks indicate exons.
Variability within Y1 Yellow Endosperm Lines
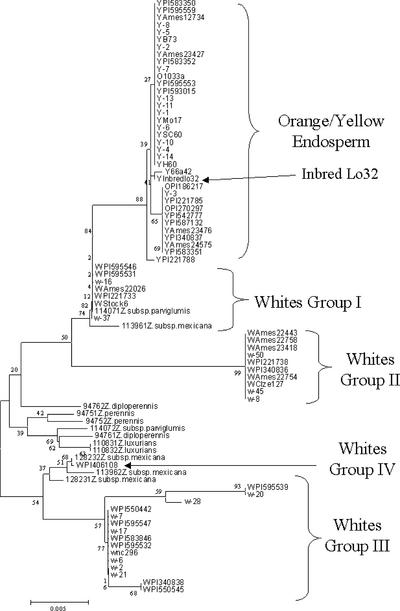
Buckner et al. (1996) compared two yellow inbred lines, B73 and Q60, and found only one allelic difference, at position 4657. B73 has a C, whereas Q60 has an A, resulting in an amino acid change from Thr (ACT) to Asn (AAT). In addition, Buckner et al. (1996) identified a 345-bp Tourist element at position 5085/5087 within the 3′ untranslated region of B73 only. This element, presumably brought in by recombination, has a polyadenylation site that accounts for the different transcript sizes for B73 and Q60. In our study, comparisons of 41 yellow endosperm lines showed 7 lines with a C at position 4657 and 34 lines with an A. Five of the lines with a C at this position also have the Tourist element, whereas none of the lines with an A have this insertion. Of the two lines with a C at position 4657 and no insertion at 5085/5087, Inbred Lo32 demonstrates unique sequence patterns in relation to the other yellow endosperm inbred lines, whereas lines Y-7 and PI221788 show evidence of recombination at positions 4064 and 5003, respectively.
Other polymorphisms are found within the Y1 region of yellow endosperm lines. All of the lines except Inbred Lo32 have the Ins2 insertion at positions 1397 to 1776. A few polymorphic sites exist within the insertion, thereby dividing the yellow endosperm inbred lines, with the exception of Inbred Lo32, into two groups (Figure 3). One group contains a form of the Ins2 insertion with a 2-bp deletion in the direct repeat defining the insertion and an A at position 1768. This group contains only the 10-repeat allele of the CCA microsatellite. The other group does not have the deletion and has a G at position 1768. Inbred Lo32 is the only yellow line without the Ins2 insertion, but it has a similarly sized insertion of 378 bp at the Y1 GenBank position 448/449, ∼1 kb upstream from the Ins2 insertion. This insertion has no sequence similarity to the Ins2 insertion or to any other known sequences and shows no evidence of insertion site duplication. Several other nucleotide variants in Inbred Lo32 are not present in any other lines, thus establishing its uniqueness. A few of the other lines also possess rare variations either within the Ins2 insertion or at some position in the Y1 region, including 66a4-2, PI595554, PI595562, Y-12, and PI587132. In addition, two lines, Y-7 and PI221788, show evidence of recombination toward the 3′ end.
Figure 3.
Neighbor-Joining Tree of Y1 Sequences.
Sequences in the region defined by GenBank positions 1331 to 2185 obtained from all Z. mays inbred lines and exotic lines were constructed using the Kimura two-parameter model. Bootstrap values are shown as percentages over 1000 replicates. Maize inbred lines are denoted with W, Y, or O before the name, indicating the phenotype white, yellow, or orange, respectively.
Variability within Zea Species
A limited survey of species in the genus Zea was performed in a small region of Y1, defined by nucleotides 1331 to 2185 of the Y1 GenBank sequence, using the Y1-4 primer set to generate PCR products (see supplemental data online). The analyzed region contained the insertion site of Ins2, the CCA microsatellite, and a portion of the first coding region that included the two completely associated SNPs. Each of the lines, including Z. luxurians 11083, Z. mays subsp mexicana 11396, Z. mays subsp mexicana 12823, Z. mays subsp parviglumis 11407, Z. perennis 9475, and Z. diploperennis 9476, was heterozygous at the Y1 locus and thus yielded two haplotypes. None of the 12 haplotypes had the Ins2 insertion. In addition, all of the haplotypes had the white allele at each of the two completely associated SNP positions. The CCA microsatellite showed some overlap of allele sizes with Z. mays subsp mays, but new alleles, including two short ones (three and four repeats), were encountered only in the other species. Inclusion of lines from the other Zea species also identified a few new polymorphisms; however, the haplotypes were similar to those observed in white endosperm lines (see supplemental data online). None of the haplotypes resembled the yellow haplotypes in this region.
Phylogenetic Analysis of the Y1 Region Containing the Promoter and the First Exon
A neighbor-joining tree was constructed for the region defined by nucleotides 1331 to 2185 of the Y1 sequence. This particular region was selected because it contained the Ins2 insertion site, the CCA microsatellite, and the two completely associated SNPs and also because of the additional data accumulated in this region in other Zea species. The results revealed a single grouping for the yellow endosperm lines, dispersal of the white endosperm lines into three groups, and an assemblage that included a majority of the haplotypes from the other Zea species (Figure 3). One white endosperm line, PI406108, had the same haplotype as Z. mays subsp mexicana 12823 and grouped with the noncultivated Zea species. Also, a Z. mays subsp parviglumis haplotype and a Z. mays subsp mexicana haplotype both assembled with other white endosperm lines in group I (Figure 3).
Genetic Mapping of PSY2
The position of PSY2 on chromosome 8 was confirmed through mapping on the maize-oat addition lines (Ananiev et al., 1997) (supplied by E. Ananiev, Pioneer, Johnston, IA) and by hybridization of the PSY2 EST overgo probe to a BAC contig that has been assigned to chromosome 8. PSY2 maps in bin 7 of chromosome 8, near the public marker 8.07_csu572 (data not shown).
Nucleotide Polymorphism at PSY2
The analyzed PSY2 sequence spans a region of ∼1300 bp and has been amplified from the 75 maize lines. Two lines, Y-4 and PI595559, were heterozygous in the region and were not analyzed further. The reading frame of the PSY2 gene was determined by comparison with the Y1 gene. The protein sequence similarity between PSY2 and Y1 in the analyzed region of PSY2 is 77%. The intron-exon junctions are conserved between Y1 and PSY2, and regions spanning nucleotides 1 to 87, 222 to 457, 777 to 969, and 1101 to 1262 correspond to exons 3, 4, 5, and 6 of Y1, respectively. There are 40 polymorphic sites or regions in the PSY2 sequence analyzed here. Two are highly variable microsatellite regions, one containing TCCG repeats followed by imperfect TCCA repeats and the other having a mononucleotide T repetitive region followed by a CTT repeat. Both are found within introns, and the number of repeats for each region is not associated with the endosperm color phenotype (as determined by Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests). There are 15 indels, only 9 of which have a rare allele frequency of >0.1. The remaining 24 polymorphic sites are SNPs, 7 of which are in coding sequence. Of those seven coding SNPs, three are noninformative and four are silent mutations (see supplemental data online). Of the 17 noncoding SNPs, 9 are informative.
There is no observable distinction in the levels of DNA variation at PSY2 between the two phenotypic classes. The diversity measures, π and θw, are equivalent for yellow and white endosperm lines (Table 2), and there is no evidence of departure from neutrality, because the Tajima's D values are not significant.
Associations with the Endosperm Color Phenotype
Seventy-eight of the 81 informative SNP and indel polymorphisms in Y1 are associated with endosperm color at a significance level of 0.001. Two polymorphic sites are completely associated with the phenotype: a G-to-A transition at position 2047 and a T-to-C transition at position 2101, both yielding silent mutations. In addition, two indels show strong but incomplete associations with the phenotype. One is a 14-bp insertion located in the 5′ regulatory region; it is found in all but one of the white endosperm lines and in none of the yellow endosperm lines. The other, a 382-bp Ins2 insertion (Buckner et al., 1996), also located in the 5′ regulatory region, is found in all of the yellows except Inbred Lo32 and in none of the whites. By contrast, none of the polymorphic sites in PSY2 shows significant association with endosperm color.
Comparison of Intragenic LD at Y1 and PSY2
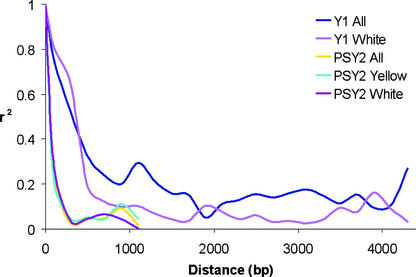
Plots of the pair-wise LD measure r2 indicate that LD declines to 0.1 at a distance of 1000 bp in white endosperm lines at Y1 (Figure 4), whereas an estimation of LD for yellow lines is not possible because of the paucity of informative SNP sites. When white and yellow germplasm are analyzed together, LD declines to r2 = 0.1 at ∼2000 bp (Figure 4). This extended level of LD can be attributed to selection in the yellow germplasm.
Figure 4.
Measurement of LD for Both Phytoene Synthase Loci.
Measurement was performed by averaging r2 values over a distance of 200 bp and plotting the values against distance (bp). The Y1 yellow test set was not included in the graph because of the nearly complete lack of data points in the Y1 region.
Although the sequence length analyzed at the PSY2 gene is threefold to fourfold less than that analyzed at the Y1 gene, the length is sufficient to observe r2 levels decreasing rapidly within 250 bp (Figure 4). Separation of the data set into white and yellow phenotypic classes yields similar LD graphs for the PSY2 gene.
Comparison of LD between Private and Public Lines at Y1
An ancillary LD analysis was performed in the Y1 region to assess differences in LD between public and private lines. Average levels of LD, as measured by r2, were calculated over 1-kb intervals for both the public and private sets, irrespective of phenotypic classification. The first 1-kb interval showed an almost twofold difference between private and public lines, with private lines showing higher averages of r2. The differences in LD between public and private lines declined steadily with increasing distance until the 3- to 4-kb region, in which r2 values for the public lines were 1.4-fold greater than those in the private lines. This trend continued into the next interval.
DISCUSSION
Two closely related genes, the Y1 phytoene synthase and PSY2, a putative second phytoene synthase gene, were chosen to study the effects of breeding selection on genetic diversity and LD in maize. Both of these genes could be considered candidate genes for the endosperm color trait, by virtue of their homology with phytoene synthase, if the gene(s) controlling the trait was not identified previously. Therefore, the Y1/PSY2 comparison represents a good case for assessing the usefulness of candidate gene–based association studies or selective sweep approaches to identify genes associated with traits subject to selection.
Sequence analyses clearly differentiate the Y1 and PSY2 genes. A large number of SNP and indel polymorphisms at Y1 were associated significantly with phenotype, whereas no polymorphic sites at the PSY2 gene showed an association. Admittedly, if population structure effects were taken into consideration, some of the associations at Y1 may not have been significant; however, the utility of PSY2 in this study is meant to control for these effects. The nucleotide diversity (π) values shown by PSY2 and Y1 for the entire test set are nearly equivalent and intermediate in relation to diversity values observed in other maize genes (White and Doebley, 1999). However, the patterns of polymorphism with respect to phenotype differ greatly between the two genes (a χ2 contingency test using numbers of parsimony informative polymorphic sites normalized for length proved that the patterns were significantly different at P = 0.004). The equivalence in genetic diversity between the two endosperm phenotype classes at PSY2 suggests that selection does not act on this gene, whereas the 19-fold difference in nucleotide diversity (π) between the yellow and white maize genotypes at Y1 suggests its involvement in the trait. Reduced diversity within the yellow lines at Y1 is accompanied by an excess of rare alleles (Tajima D = −2.4), as expected for recovery from a selective sweep (for a review of measures of selection, see Kreitman, 2000). Phylogenetic analysis of the Y1 promoter and exon 1 (Figure 3) provides even more evidence of selection for the yellow endosperm phenotype and the ancestral nature of the white endosperm allele.
Sequence results from tb1, a putative domestication gene, show a 61-fold reduction of diversity (π) in maize relative to Z. mays subsp parviglumis in the 5′ regulatory region and a 35-fold reduction of θw (Wang et al., 1999). However, within the transcriptional unit of tb1, the difference in diversity between maize and Z. mays subsp parviglumis is much less, with π and θw values both approximately threefold greater in Z. mays subsp parviglumis. Within the promoter region of Y1, yellow maize shows close to zero diversity, in contrast to white lines, which have average levels of diversity (π = 16.4 × 10−3). Within the transcriptional unit of Y1, the ratio of diversity between whites and yellows is 11× (π = 7.3 × 10−3 versus π = 0.67 × 10−3) and 2.5× (θw= 5.5 × 10−3 versus π = 2.2 × 10−3), approximately equivalent to the difference between maize and Z. mays subsp parviglumis at tb1. Thus, Y1 shows a similar selective sweep pattern in the 5′ regulatory region, as observed with tb1, but somewhat less rapid recovery from the selective sweep in the transcribed region.
Increased LD is another expected effect of selection. As a result of the high haplotype conservation within yellow lines, the measurement of LD in yellow lines only is not possible, whereas the decline in LD within white endosperm lines is quite rapid (Figure 4). For the entire set of maize inbred lines, observations of the r2 measure of LD at Y1 are similar to previous observations at other maize genes (Remington et al., 2001), with r2 declining to 0.1 at a distance of ∼2000 bp. Although averages of r2 over the 1000- to 4000-bp range indicate that LD is approximately threefold greater in the entire test set than in the white endosperm lines (Y1 all r2 average = 0.172 versus Y1 white r2 average = 0.058), we expected the influence of the yellow lines in the entire test set to be much greater in terms of the level and extent of LD. Both the EHH measure and unpublished long-range observations of haplotype patterns surrounding Y1 indicate that the selective sweep exhibited by the yellow endosperm germplasm persists for a much longer distance than the r2 measure indicates. These observations demonstrate the limitations of this LD measure for the identification of long-distance LD and raise the question of what constitutes useful levels of LD for qualitative traits. LD at PSY2 declines rapidly, as expected, within ∼100 to 200 bp, a result comparable to previously reported data for chromosome 1 (Tenaillon et al., 2001). The difference in LD between the Y1 and PSY2 genes may be attributable to the difference in the genomic locations of these two genes, rather than to a specific effect of selection. However, the patterns of diversity and association, in addition to the LD information, clearly select the Y1 gene over PSY2 in a candidate gene–based approach designed to identify the gene(s) associated with carotenoids in the endosperm.
Because private maize inbred lines may have experienced an additional bottleneck not related to domestication in their population history, the possibility that these lines may have introduced an increased LD effect as a result of this bottleneck cannot be excluded completely. However, the analysis of LD for public versus private maize inbred lines at Y1 did not indicate a significant difference between public and private average r2 values in the Y1 region.
Identification of the phenotype-determining sequence variant is the ultimate goal of association studies. The reduced diversity within the yellow endosperm lines at Y1 suggests that yellow endosperm is a gain-of-function mutation resulting from the upregulation of Y1 gene expression in the endosperm (Buckner et al., 1996). However, the causative sequence variant is unclear because of the presence of multiple associations with phenotype that are either complete or highly significant. Two polymorphisms within the analyzed regions of Y1 were associated completely with phenotype. Both are coding SNPs located in exon 1 at positions 2047 and 2101, and both are silent mutations. White maize has the same allele as the other tested Zea species at these two positions. Whether or not the two silent coding SNPs are causative, their locations are indicative of the region containing the causal variant. Because the two SNPs are in close proximity to the regulatory region and the core haplotype for the yellow endosperm lines does not bifurcate toward the 5′ end, the regulatory region is the probable site of a causative variant (Figure 1A). The variant also may be unidentified, lying either farther upstream or in an unanalyzed region of the Y1 gene.
The four variants within the Y1 gene that show the strongest associations with the phenotype are the two coding SNPs, a small 14-bp insertion found in all but one of the whites and none of the yellows (between nucleotides 697 and 698), and the Ins2 insertion (nucleotides 1397 to 1776). The possibility that the two silent coding SNPs affect mRNA stability is not excluded; however, it should be a tissue-specific effect, because no effect on the carotenoid levels in other tissues has been reported. The 14-bp deletion in the promoter of yellow lines also may affect its function in the endosperm. However, in our opinion, the most likely scenario involves the Ins2 insertion. The 382-bp mobile element, discovered previously in the c1 gene (Paz-Ares et al., 1987), the bronze upstream region (Ralston et al., 1988), and the region between a1 and sh2 on chromosome 3 (Yao et al., 2002), is present in all but one of the yellow lines and is absent from all of the white lines. Buckner et al. (1996) reported that not all yellows analyzed in their unpublished study had the Ins2 insertion; however, the only yellow endosperm line in our study without the Ins2 insertion had an insertion of almost identical size (378 bp) 1 kb upstream from the Ins2 insertion site. This finding suggests that insertions in the 5′ regulatory region may cause increased expression of the gene product in the endosperm. This is a common phenomenon in maize. Clegg and Durbin (2000) reported that most of the mutations that caused phenotypic differences were the result of transposon insertions. Another group's work on tb1 also suggested that the extreme phenotypic variation between maize and teosinte was the result of selection for an unidentified variant in the regulatory region (Wang et al., 1999). Indeed, Buckner et al. (1996) found that the Ins2 insertion provides an alternative transcription start site.
The observed patterns of diversity and LD among yellows at the Y1 gene appear to be uncommon in maize (Tenaillon et al., 2001), except in the cases of postdomestication selection (Remington et al., 2001; Thornsberry et al., 2001). The variations that exist within Ins2-containing yellows at the Y1 gene lie within the two microsatellite regions and the Ins2 insertion itself. With regard to the two microsatellites, there is little difference in the heterozygosity values between yellows and whites at both SSR loci, indicating that sufficient time has passed since the origin of the haplotype for SSR diversity to recover; this observation is consistent with the rapid mutation rates of SSRs (Vigouroux et al., 2002a). However, the spectrum of allelic variants at both SSR loci is significantly different between the whites and the yellows (P < 0.0001). Recently, Vigouroux et al. (2002b) found evidence of selection among the SSRs with reduced diversity in U.S. inbred lines of maize. Our observations indicate that high microsatellite heterozygosity may be observed in the presence of strong selection. Long-range reduction of diversity in yellows and fully recovered microsatellite diversity may be reconciled by assuming strong separation between yellow and white germplasm pools. This separation would have to be maintained over sufficient time to generate the observed level of diversity within yellows. Otherwise, recombinational events would reduce the LD and equalize diversity between whites and yellows except in the immediate vicinity of the causative mutation.
The age and history of the mutational events leading to the yellow endosperm phenotype are unknown. We hypothesize that at least two independent mutational events occurred: one represented by the inbred line Lo32, having a highly divergent haplotype, and one represented by the lines carrying the Ins2 insertion. The presence of several SNPs within Ins2 most likely indicates that the original insertion event is relatively old. There are essentially two forms: the Ins2 with a 2-bp deletion and an A at position 1768, completely linked to the (CCA)10 microsatellite variant; and the Ins2 with a 2-bp insertion, a G at position 1768, and several CCA size variants. An alternative yet unlikely explanation is that the two slightly different forms of Ins2 inserted independently into the same site of the same haplotype. Given that the two most distant Ins2 haplotypes differ by 2 bp (not counting indels) and a previous estimate of the average synonymous rate of substitution of 6.5 × 10−9 per year (Gaut et al., 1996), we have estimated that the two forms of the Ins2 element diverged ∼400,000 years ago. This estimate predates maize domestication, which is proposed to have occurred ∼10,000 years ago (Wang et al., 1999). The possibility of gene conversion driven by one of the other Ins sequences present in the genome also cannot be excluded. We conclude that at least three different yellow endosperm gain-of-function alleles were incorporated into the modern germplasm. Two events incorporated slightly divergent versions of the same ancestral Ins2 insertion, and the third was the insertion represented by the Inbred Lo32 line. The 20th century expansion in the cultivation of yellow maize in the United States may have involved a larger number of introgression events selected from the yellow alleles that were maintained in relative genetic isolation from the white germplasm in the ancestral domesticated population; however, the introgression events are postulated to have originated from predomestication mutational events.
We have demonstrated here the maintenance of large differences in diversity between white and yellow maize at the Y1 locus across at least a 6-kb sequence. Investigation of the extent of this signature of selection in the 1-MB genomic region surrounding Y1 is ongoing. The extended patterns of differences in sequence diversity can be attributed to selection for the yellow endosperm phenotype followed by reproductive isolation by early farmers. This was facilitated by the ease of visual phenotype determination and the fact that the presence of carotenoids in the endosperm is a single-gene trait.
METHODS
Plant Material
Maize (Zea mays) inbred lines were obtained from both the National Germplasm Research Laboratory (North Central Regional Plant Introduction Station, Ames, IA) and Pioneer Hi-Bred International (Johnston, IA). All lines were selected based on their degree of unrelatedness to obtain a diverse test set of germplasm. To this end, microsatellite-based dendrograms and pedigree relationships were used in the selection of Pioneer lines, whereas public lines were selected from the National Germplasm Research Laboratory Germplasm Resources Information Network on the basis of available pedigree information. Leaves of 2-week-old plants, grown in a greenhouse, were harvested and freeze-dried.
DNA Extraction
Leaf material was either ground in liquid nitrogen using a mortar and pestle or pulverized using steel balls and a paint shaker. DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Maxi-Prep extraction kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Primer Sets and PCR
Primers were designed from the published Y1 sequence (Buckner et al., 1996) and the PSY2 cDNA sequence using the Primer3.0 program (Rozen and Skaletsky, 1998) with the following conditions: product size between 400 and 600 bases, primer size of ∼18 bases, annealing temperature of 55°C, ideal GC content of 50%, no more than three consecutive identical nucleotides, and a 2-base GC clamp (Table 3; see also supplemental data online). T3 (5′-AATTAACCCTCACTAAAGGG-3′) and T7 (5′-GTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC-3′) tags were added to the 5′ ends of the forward and reverse primers, respectively, to facilitate direct sequencing of the PCR products. PCR was performed using a Perkin-Elmer 9700 thermocycler under the following conditions: 95°C for 10 min; 10 cycles of 94°C for 1 min, 55°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 1 min; 35 cycles of 95°C for 30 s and 68°C for 1 min; 92°C for 7 min; and then a constant temperature of 4°C. The 25-μL PCR mix consisted of 50 ng of DNA, 10 μM of each primer, 1× PE buffer II (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA), 2 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM of each deoxynucleotide triphosphate, 5% DMSO, 1.25 units of AmpliTaq Gold (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems), and sterile water. PCR products (4 μL) were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Products obtained from PCR using Z. luxurians 11083, Z. mays subsp mexicana 11396, Z. mays subsp mexicana 12823, Z. mays subsp parviglumis 11407, Z. perennis 9475, and Z. diploperennis 9476 were cloned using the Promega pGEM-T Easy Vector System I (Promega, Madison, WI) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Sixteen individual clones were chosen for each cloned PCR product and sequenced individually. All Y1 and PSY2 primers were tested on the maize-oat addition lines (Ananiev et al., 1997) to ensure that the products were amplified from the expected chromosome.
Table 3.
Analyzed Segments of the Y1 and PSY2 Genes
| Region | Sequence Range |
Primersa | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | |||
| 1 | 140 to 564 | Y1-1 | 5′ regulatory region |
| 2 | 625 to 1179 | Y1-2 | 5′ regulatory region |
| 3 | 1367 to 2343 | Y1-3, Y1-4, Y1-5, Y1-6 |
Ins2, CAA microsatellite, first exon |
| 4 | 2438 to 2812 | Y1-7 | Exon 2, intron 2 |
| 5 | 3105 to 3836 | Y1-8 | Exon 3, intron 3 |
| 6 | 3903 to 4788 | Y1-9, Y1-10, Y1-11 |
Introns 3, 4, and 5; exons 4, 5, and part of 6 |
| 7 | 4789 to 5340 | Y1-12, Y1-13, Y1-14 |
Last exon, 3′ untranslated region |
| PSY2 | |||
| 1 | 317 to 422 | PSY2-1 | Nucleotide 1 corresponds to nucleotide 3191 of Y1, exon 3 |
| 2 | 570 to 705 | PSY2-2 | Exons 4 and 5 |
| 3 | 708 to 994 | PSY2-3 | Exons 5 and 6 |
See primer sets in the supplemental data online.
DNA Sequencing and Polymorphism Identification
PCR products were treated with exonuclease I and shrimp alkaline phosphatase (United States Biochemical, Cleveland, OH) and then sequenced directly from both the T3 and T7 primers using an ABI 3700 sequencer (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems). The sequencing reactions were performed using the ABI PRISM BigDye Terminator version 3.0 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Perkin-Elmer/Applied Biosystems) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The sequences were imported into Sequencher (Gene Codes Corp., Ann Arbor, MI), aligned, and scrutinized for sequence polymorphisms. Identified polymorphisms were recorded in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet (Redmond, WA). Polymorphisms observed in only one of the test lines were disregarded unless they were seen in both the forward and reverse sequencing reads of that particular line. Polymorphisms that could not be typed were designated “N.” In addition, multiple (8 to 16) sequences were obtained from cloned PCR products of the related Zea species. These sequences were aligned; singleton polymorphisms were disregarded (in the manner described above), and the two alleles from each of the six heterozygous maize relatives were identified.
DNA Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including π (Nei, 1987), Watterson's estimator of θ (Watterson, 1975; Nei, 1987), and Tajima's D (Tajima, 1989), were obtained using DNAsp version 3 (Rozas and Rozas, 1999). The r2 (Hill and Robertson, 1968) linkage disequilibrium (LD) graphs were constructed using data collected from DNAsp and Microsoft Excel; only single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with a rare allele frequency of >10% were used to calculate r2. Values of r2 were averaged over 200-bp increments and plotted against physical distance. The Y1 neighbor-joining tree (Saitou and Nei, 1987) was constructed using MEGA software (Kumar et al., 2001) with the following parameters: Kimura 2 parameter model (Kimura, 1980), both transitions and transversions included, the pair-wise deletion option, and 1000 bootstrap replicates. In addition, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test (Smirnov, 1939) was used to compare the microsatellite allele distributions for the two phenotypic classes.
Y1 SNP Haplotype and Extended Haplotype Homozygosity Graphs
Y1 SNP haplotype graphs (Figure 1) were constructed by first defining a region of core SNPs. The haplotype combinations within the region are referred to as the “core haplotypes,” and the decay of LD with distance from the core is evaluated by examining informative SNPs (defined here as those SNPs with a rare allele frequency of >0.1) both proximal and distal to the defined core region. Whenever a new SNP is encountered, the haplotype branches. In this way, the breakdown of the haplotypes, signifying the decay of LD in the area, can be visualized. This method is presented by Sabeti et al. (2002).
Sabeti et al. (2002) also describe extended haplotype homozygosity (EHH) as a way to measure the breakdown of LD from the core. EHH is defined as “the probability that two randomly chosen chromosomes carrying a tested core haplotype are homozygous at all SNPs for the entire interval from the core region to the distance x” (Sabeti et al., 2002), where x is the distance between the core and each respective SNP. Homozygosity is a derivation of heterozygosity (Nei, 1973) and is described in the equation
k
Homozygosity = Σ pi2,
i = 1
where pi is the frequency of the ith allele and k is the number of alleles. The alleles in this case are the haplotypes. EHH is reported on a scale from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating that all haplotypes are different and 1 meaning that all haplotypes are the same. Relative EHH (Sabeti et al., 2002) is the ratio of the EHH at x to the EHH at the core.
Mapping of PSY2
The position of PSY2 in the maize genome was obtained through hybridization of a 40-bp overgo probe, designed from the PSY2 EST, to all BACs that were being used in the construction of a maize physical map at DuPont. In addition, all primer sets were tested by PCR on a set of maize-oat addition lines (Ananiev et al., 1997) to confirm their chromosomal locations.
Upon request, materials integral to the findings presented in this publication will be made available in a timely manner to all investigators on similar terms for noncommercial research purposes. To obtain materials, please contact A. Rafalski, J-Antoni.Rafalski@usa.dupont.com.
Accession Numbers
All sequences from the analyzed regions listed in Table 3 were submitted to GenBank and are identified by the following accession number ranges: Y1 region 1, AY296260 to AY296334; Y1 region 2, AY296335 to AY296408; Y1 region 3, AY296409 to AY296483; Y1 region 4, AY300233 to AY300305; Y1 region 5, AY300306 to AY300380; Y1 region 6, AY300381 to AY300455; Y1 region 7, AY300456 to AY300529; PSY2 region 1, AY300530 to AY300602; PSY2 region 2, AY300603 to AY300676; and PSY2 region 3, AY300677 to AY300751. All 11 sequences (five lines with two alleles per line and one line with only one allele) obtained from Z. mays relatives, in the region defined by nucleotides 1331 to 2185 of the ZMU32636 reference sequence, also were submitted (AY301027 to AY301037). The accession number for PSY2 is AY108547.1 and for PARTIAL PHYTOENE SYNTHASE2 it is AY266046.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Smith and D. Bhattramakki for their assistance with germplasm selection, P. Biddle and M. Dolan for sequencing support, our colleagues at DuPont (especially S. Tingey) for helpful advice and support, E. Ananiev for overgo probe hybridization and for supplying the maize-oat addition lines, and J. Sherrier, J. Doebley, E. Buckler, and J. Hawk for helpful comments and suggestions.
Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at www.plantcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1105/tpc.012526.
Footnotes
Online version contains Web-only data.
References
- Ananiev, E.V., Riera-Lizarazu, O., Rines, H.W., and Phillips, R.L. (1997). Oat-maize chromosome addition lines: A new system for mapping the maize genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 3524–3529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benassi, V., Depaulis, F., Meghlaoui, G.K., and Veuille, M. (1999). Partial sweeping of variation at the Fbp2 locus in a west African population of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16, 347–353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler, E.S., 4th, Thornsberry, J.M., and Kresovich, S. (2001). Molecular diversity, structure and domestication of grasses. Genet. Res. 77, 213–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckner, B., Miguel, P.S., Janick-Buckner, D., and Bennetzen, J.L. (1996). The y1 gene of maize codes for phytoene synthase. Genetics 143, 479–488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg, M.T., and Durbin, M.L. (2000). Flower color variation: A model for the experimental study of evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 7016–7023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depaulis, F., Brazier, L., and Veuille, M. (1999). Selective sweep at the Drosophila melanogaster Suppressor of Hairless locus and its association with the In(2L)t inversion polymorphism. Genetics 152, 1017–1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebley, J., Stec, A., Wendel, J., and Edwards, M. (1990). Genetic and morphological analysis of a maize-teosinte F2 population: Implications for the origin of maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 9888–9892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre-Walker, A., Gaut, R.L., Hilton, H., Feldman, D.L., and Gaut, B.S. (1998). Investigation of the bottleneck leading to the domestication of maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4441–4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaut, B.S., Morton, B.R., McCaig, B.C., and Clegg, M.T. (1996). Substitution rate comparisons between grasses and palms: Synonymous rate differences at the nuclear gene Adh parallel rate differences at the plastid gene rbcL. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 10274–10279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilad, Y., Rosenberg, S., Przeworski, M., Lancet, D., and Skorecki, K. (2002). Evidence for positive selection and population structure at the human MAO-A gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 862–867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harr, B., Kauer, M., and Schlotterer, C. (2002). Hitchhiking mapping: A population-based fine-mapping strategy for adaptive mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12949–12954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill, W.G., and Robertson, A. (1968). Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 38, 226–231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe, A., Yamane, K., and Miyashita, N.T. (2000). DNA polymorphism at the cytosolic phosphoglucose isomerase (PgiC) locus of the wild plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 156, 1339–1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. (1980). A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16, 111–120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman, M. (2000). Methods to detect selection in populations with applications to the human. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 1, 539–559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S., Tamura, K., Jakobsen, I.B., and Nei, M. (2001). MEGA2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software. Bioinformatics 17, 1244–1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Corre, V., Roux, F., and Reboud, X. (2002). DNA polymorphism at the FRIGIDA gene in Arabidopsis thaliana: Extensive nonsynonymous variation is consistent with local selection for flowering time. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19, 1261–1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf, P.C., and Fraps, G.S. (1931). A direct quantitative relationship between vitamin A in corn and the number of genes for yellow pigmentation. Science 73, 241–242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. (1973). Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70, 3321–3323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M. (1987). Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. (New York: Columbia University Press).
- Olsen, K.M., and Purugganan, M.D. (2002). Molecular evidence on the origin and evolution of glutinous rice. Genetics 162, 941–950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares, J., Ghosal, D., Wienand, U., Peterson, P.A., and Saedler, H. (1987). The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 6, 3553–3558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps, T.L., Hall, A.E., and Buckner, B. (1996). Microsatellite repeat variation within the y1 gene of maize and teosinte. J. Hered. 87, 396–399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poneleit, C.G. (2001). Breeding white endosperm corn. In Specialty Corns, 2nd ed, A.R. Hallauer, ed (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), pp. 235–273.
- Ralston, E.J., English, J.J., and Dooner, H.K. (1988). Sequence of three bronze alleles of maize and correlation with the genetic fine structure. Genetics 119, 185–197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington, D.L., Thornsberry, J.M., Matsuoka, Y., Wilson, L.M., Whitt, S.R., Doebley, J., Kresovich, S., Goodman, M.M., and Buckler, E.S., 4th (2001). Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11479–11484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J., Gullaud, M., Blandin, G., and Aguade, M. (2001). DNA variation at the rp49 gene region of Drosophila simulans: Evolutionary inferences from an unusual haplotype structure. Genetics 158, 1147–1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozas, J., and Rozas, R. (1999). DnaSP version 3: An integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15, 174–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen, S., and Skaletsky, H.J. (1998). Primer3. http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/genome_software/other/primer3.html.
- Sabeti, P.C., et al. (2002). Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 419, 832–837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N., and Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, N.V. (1939). Estimation of deviation between empirical distribution functions in two independent samples. Bull. Moscow Univ. 2, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, F. (1989). Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123, 585–595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenaillon, M.I., Sawkins, M.C., Long, A.D., Gaut, R.L., Doebley, J.F., and Gaut, B.S. (2001). Patterns of DNA sequence polymorphism along chromosome 1 of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9161–9166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry, J.M., Goodman, M.M., Doebley, J., Kresovich, S., Nielsen, D., and Buckler, E.S., 4th (2001). Dwarf8 polymorphisms associate with variation in flowering time. Nat. Genet. 28, 286–289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigouroux, Y., Jaqueth, J.S., Matsuoka, Y., Smith, O.S., Beavis, W.D., Smith, J.S.C., and Doebley, J. (2002. a). Rate and pattern of mutation at microsatellite loci in maize. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19, 1251–1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigouroux, Y., McMullen, M., Hittinger, C.T., Houchins, K., Schulz, L., Kresovich, S., Matsuoka, Y., and Doebley, J. (2002. b). Identifying genes of agronomic importance in maize by screening microsatellites for evidence of selection during domestication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9650–9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.L., Stec, A., Hey, J., Lukens, L., and Doebley, J. (1999). The limits of selection during maize domestication. Nature 398, 236–239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson, G.A. (1975). On the number of segregating sites in genetic models without recombination. Theor. Popul. Biol. 7, 256–276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White, S.E., and Doebley, J.F. (1999). The molecular evolution of terminal ear1, a regulatory gene in the genus Zea. Genetics 153, 1455–1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt, S.R., Wilson, L.M., Tenaillon, M.I., Gaut, B.S., and Buckler, E.S., 4th (2002). Genetic diversity and selection in the maize starch pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 12959–12962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H., Zhou, Q., Li, J., Smith, H., Yandeau, M., Nikolau, B.J., and Schnable, P.S. (2002). Molecular characterization of meiotic recombination across the 140-kb multigenic a1-sh2 interval of maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 6157–6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L., Peek, A.S., Dunams, D., and Gaut, B.S. (2002). Population genetics of duplicated disease-defense genes, hm1 and hm2, in maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.) and its wild ancestor (Zea mays ssp. parviglumis). Genetics 162, 851–860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.