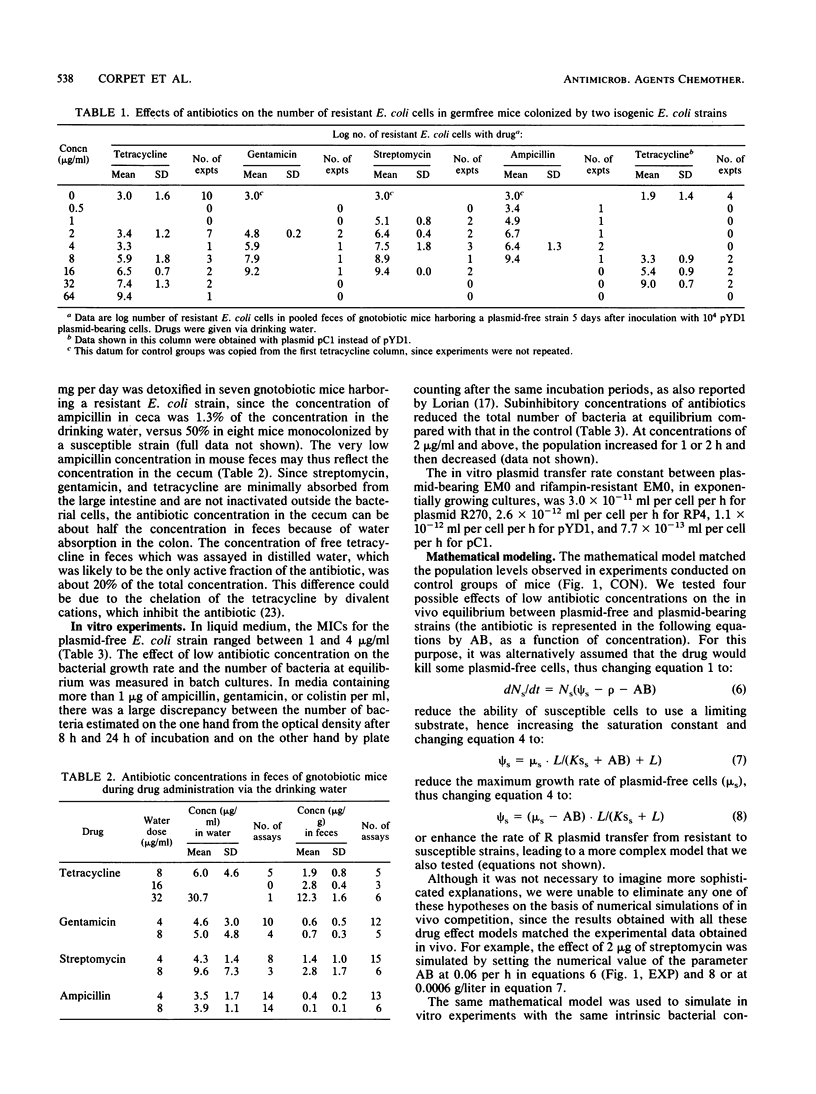
Abstract
The minimum antibiotic concentrations for selecting an R plasmid in vivo were determined in germfree mice colonized by two isogenic strains of Escherichia coli, one of which carried an R plasmid. Seventy groups of three gnotobiotic mice were given low doses of ampicillin, colistin, flumequin, gentamicin, tetracycline, or streptomycin via drinking water for 2 weeks. The equilibrium between susceptible and resistant populations of bacteria was monitored daily in feces and compared with that of control mice given pure water. This model yielded reproducible data, and dose and response were strongly correlated. The minimum selecting doses ranged from 0.9 to 12.8 micrograms/ml of water, depending on the antibiotic and the R plasmid. The use of mathematical models and complementary in vitro experiments accounted for the effect of the low antibiotic levels.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouma J. E., Lenski R. E. Evolution of a bacteria/plasmid association. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):351–352. doi: 10.1038/335351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet D. E. Antibiotic residues and drug resistance in human intestinal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):587–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet D. E. Antibiotic resistance from food. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 5;318(18):1206–1207. doi: 10.1056/nejm198805053181818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet D. E. Ecological factors influencing the transfer of plasmids in vitro and in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18 (Suppl 100):127–132. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_c.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corpet D. E., Lumeau S. Antibiotic residues and R-plasmid selection: are in vitro methods good models? Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Apr;264(1-2):178–184. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(87)80138-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coste M., Gouet P., Escoula L. Ampicillin inactivation in the caecum of axenic, gnotoxenic and conventional lambs: interaction with resistant or sensitive Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1325–1330. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A. Differences between bacteria grown in vitro and in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):175–195. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Iflah Y., Raibaud P., Rousseau M. Antagonisms among isogenic strains of Escherichia coli in the digestive tracts of gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):957–969. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.957-969.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Iflah Y., Raibaud P., Tancrede C., Rousseau M. R-plasmic transfer from Serratia liquefaciens to Escherichia coli in vitro and in vivo in the digestive tract of gnotobiotic mice associated with human fecal flora. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.981-990.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Freter R. R., Brickner H. Experimental and mathematical models of Escherichia coli plasmid transfer in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):60–84. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.60-84.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. M. Antibiotic exposure and resistance in mixed bacterial populations. Theor Popul Biol. 1987 Dec;32(3):326–346. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(87)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT D., ELSWORTH R., TELLING R. C. The continuous culture of bacteria; a theoretical and experimental study. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):601–622. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebek G., Egger R. R-selection of subbacteriostatic tetracyclin-concentrations. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1983 Sep;255(2-3):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. R., Stewart F. M., Rice V. A. The kinetics of conjugative plasmid transmission: fit of a simple mass action model. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V. Antibiotiques à concentrations subinhibitrices. Effet sur la morphologie et la croissance. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1977 May;25(5):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., De Freitas C. C. Minimal antibiotic concentrations of aminoglycosides and beta-lactam antibiotics for some gram-negative bacilli and gram-positive cocci. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):599–603. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A., O'Brien J. J., Campbell N. Antibiotic residues and their recovery from animal tissues. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;41(1):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A., Marshall B., Cisneros R., Levy S. B. Competition between congenic Escherichia coli K-12 strains in vivo. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.74-79.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecquet S., Andremont A., Tancrède C. Selective antimicrobial modulation of the intestinal tract by norfloxacin in human volunteers and in gnotobiotic mice associated with a human fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1047–1052. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins L. D., Gaines S. A., Pocurull D. W., Mercer H. D. Animal model for determining the no-effect level of an antimicrobial drug on drug resistance in the lactose-fermenting enteric flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):661–665. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A. Incompatibility group P plasmids: genetics, evolution, and use in genetic manipulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:77–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


