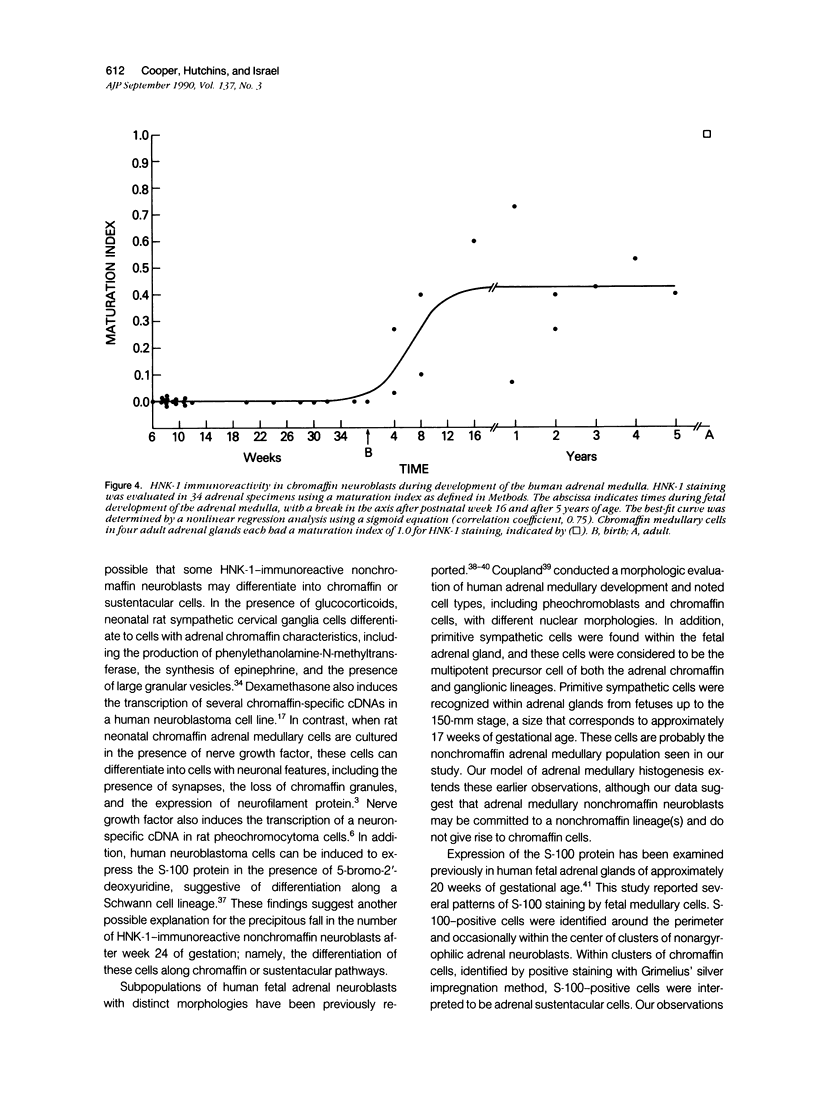
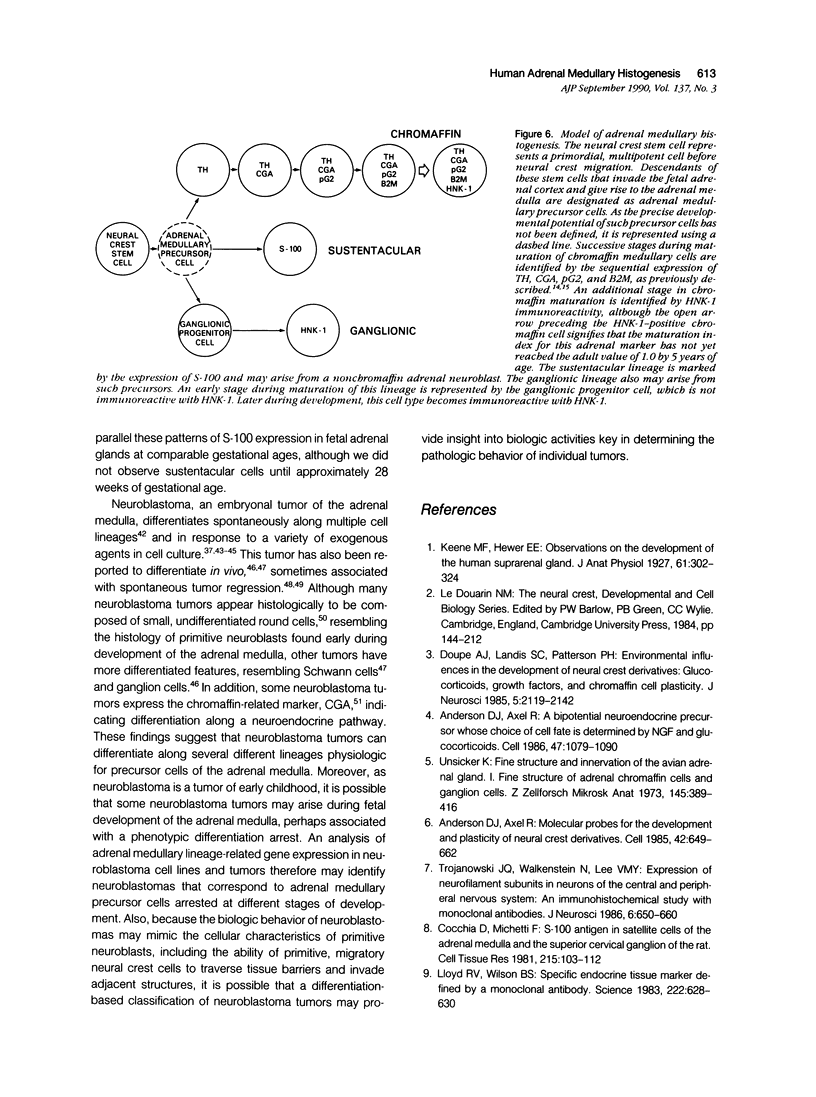
Abstract
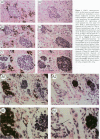
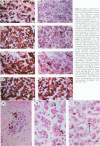
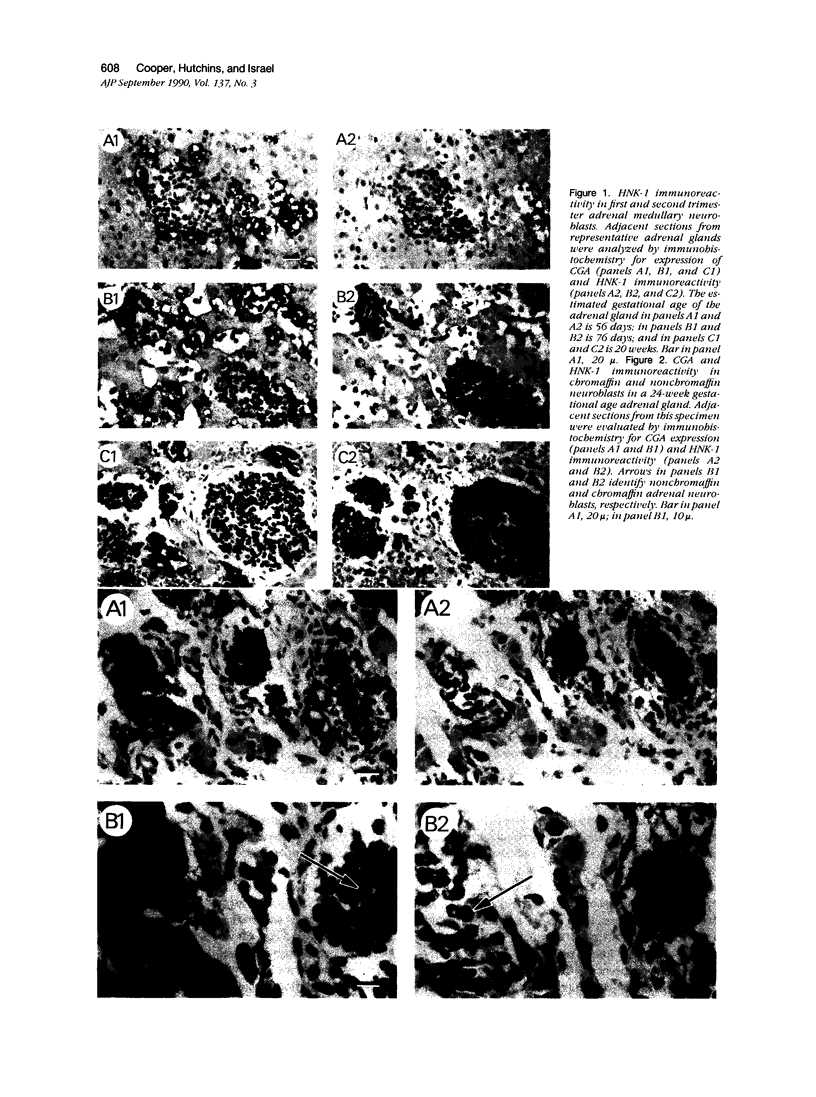
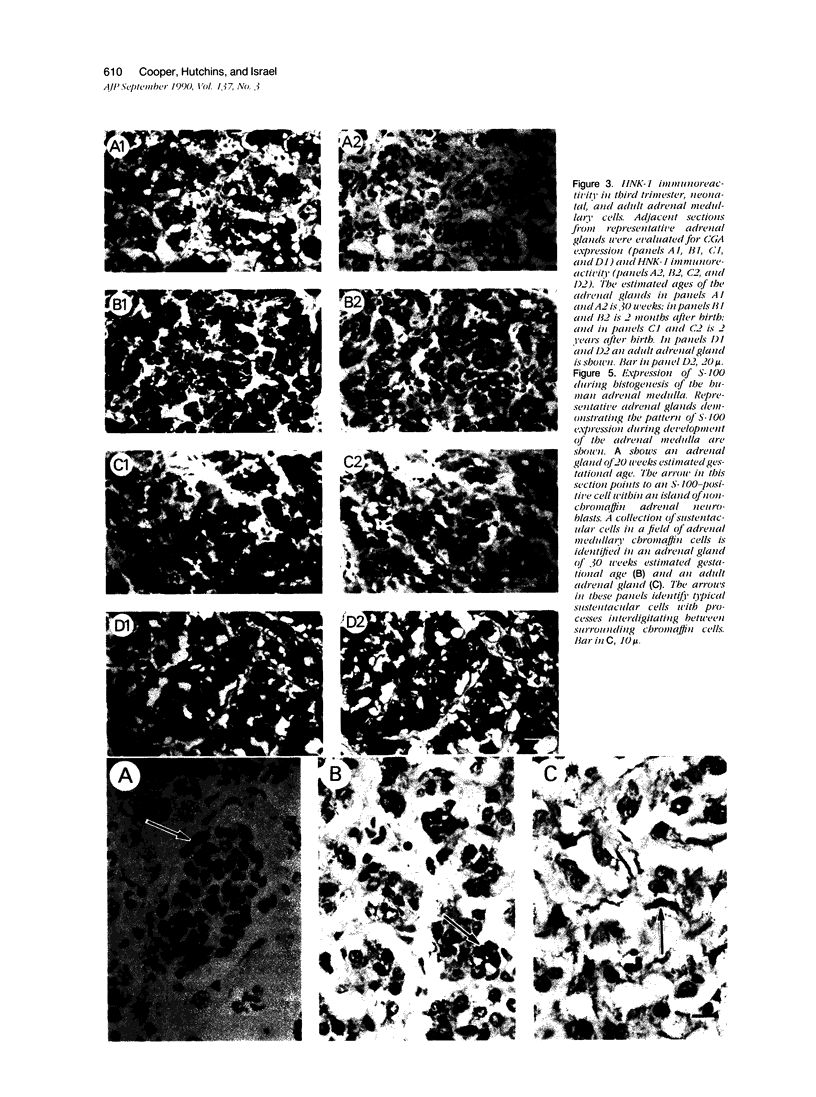
The authors previously evaluated the expression of a panel of chromaffin-related genes during histogenesis of the human adrenal medulla. In these studies, chromaffin and nonchromaffin adrenal neuroblasts were identified. To better characterize these nonchromaffin neuroblasts, the authors evaluated two additional markers: HNK-1, an antibody recognizing the migratory neural crest cell; and S-100, a protein expressed by sustentacular cells of the adrenal medulla. HNK-1 immunoreactivity was found in both chromaffin and nonchromaffin cell types at different times during development, marking the nonchromaffin lineage during the second trimester of gestation as well as the chromaffin lineage in the neonatal period. In addition, S-100 expression was noted in some nonchromaffin neuroblasts, and sustentacular cells were first identified at approximately 28 weeks of gestational age. These data suggest a model of human adrenal medullary histogenesis that incorporates the chromaffin, ganglionic, and sustentacular lineages known to constitute the adult adrenal medulla.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Yeats J. C., Causon R., Brown M. J., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y and its flanking peptide in human endocrine tumors and plasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1199–1204. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. A bipotential neuroendocrine precursor whose choice of cell fate is determined by NGF and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. Molecular probes for the development and plasticity of neural crest derivatives. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroffio A., Dupin E., Le Douarin N. M. Clone-forming ability and differentiation potential of migratory neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M. Analysis of the early stages of trunk neural crest migration in avian embryos using monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Dev Biol. 1986 May;115(1):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M., Fraser S. E. Cell lineage analysis reveals multipotency of some avian neural crest cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):161–164. doi: 10.1038/335161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou K. H., Ilyas A. A., Evans J. E., Quarles R. H., Jungalwala F. B. Structure of a glycolipid reacting with monoclonal IgM in neuropathy and with HNK-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarone V., Spengler B. A., Meyers M. B., Biedler J. L., Ross R. A. Phenotypic diversification in human neuroblastoma cells: expression of distinct neural crest lineages. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchia D., Michetti F. S-100 antigen in satellite cells of the adrenal medulla and the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. An immunochemical and immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;215(1):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00236252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Helman L. J., Evans A. E., Swamy S., O'Connor D. T., Helson L., Israel M. A. Chromogranin A expression in childhood peripheral neuroectodermal tumors. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;271:175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Cohen P. S., Helman L. J., Mennie R. J., Israel M. A. Human neuroblastoma tumor cell lines correspond to the arrested differentiation of chromaffin adrenal medullary neuroblasts. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. J., Hutchins G. M., Mennie R. J., Israel M. A. Beta 2-microglobulin expression in human embryonal neuroblastoma reflects its developmental regulation. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3694–3700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A. Structure and significance of beta2-microglobulin. Fed Proc. 1976 Apr;35(5):1171–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai C., Garriga G., McIntire S. L., Horvitz H. R. A genetic pathway for the development of the Caenorhabditis elegans HSN motor neurons. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):638–646. doi: 10.1038/336638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Giraud P., Hotchkiss A., Brownstein M. J. Enkephalins and VIP in human pheochromocytomas and bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1982;33:387–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., Chatten J., D'Angio G. J., Gerson J. M., Robinson J., Schnaufer L. A review of 17 IV-S neuroblastoma patients at the children's hospital of philadelphia. Cancer. 1980 Mar 1;45(5):833–839. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800301)45:5<833::aid-cncr2820450502>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. E., Gerson J., Schnaufer L. Spontaneous regression of neuroblastoma. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1976 Nov;44:49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX F., DAVIDSON J., THOMAS L. B. Maturation of sympathicoblastoma into ganglioneuroma; report of 2 patients with 20-and 46-year survivals respectively. Cancer. 1959 Jan-Feb;12(1):108–116. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195901/02)12:1<108::aid-cncr2820120116>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman L. J., Thiele C. J., Linehan W. M., Nelkin B. D., Baylin S. B., Israel M. A. Molecular markers of neuroendocrine development and evidence of environmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2336–2339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga T., Fujita T. Sustentacular cells in the fetal human adrenal medulla are immunoreactive with antibodies to brain S-100 protein. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;236(3):733–735. doi: 10.1007/BF00217246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene M. F. Observations on the Development of the Human Suprarenal Gland. J Anat. 1927 Apr;61(Pt 3):302–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Mailhammer R., Wernecke H., Faissner A., Sommer I., Goridis C., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):153–155. doi: 10.1038/311153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Künemund V., Jungalwala F. B., Fischer G., Chou D. K., Keilhauer G., Schachner M. The L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate of neural cell adhesion molecules is involved in cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):213–223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT M., SPECTOR S., SJOERDSMA A., UDENFRIEND S. ELUCIDATION OF THE RATE-LIMITING STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN THE PERFUSED GUINEA-PIG HEART. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M., Braham K., Caillaud J. M., Carlu C., Tursz T. HNK-1 antibody detects an antigen expressed on neuroectodermal cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1775–1780. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Sisson J. C., Shapiro B., Verhofstad A. A. Immunohistochemical localization of epinephrine, norepinephrine, catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes, and chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells and tumors. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hamberger B., Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Granberg P. O., Efendić S., Terenius L., Goldstein M., Luft R. Enkephalin- and somatostatin-like immunoreactivities in human adrenal medulla and pheochromocytoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4079–4083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell G. D., Forbes M. E., Christie D. S. Analysis of the development of cellular subsets present in the neural crest using cell sorting and cell culture. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):557–568. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry R. C., Helfand S. L., Quarles R. H., Roder J. C. Recognition of myelin-associated glycoprotein by the monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):376–378. doi: 10.1038/306376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickmann M., Fawcett J. W., Keynes R. J. The migration of neural crest cells and the growth of motor axons through the rostral half of the chick somite. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Dec;90:437–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Aoyama C., Chiba T., Newton W. A., Jr Prognostic subgroups for undifferentiated neuroblastoma: immunohistochemical study with anti-S-100 protein antibody. Hum Pathol. 1985 May;16(5):471–476. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidell N. Retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition and morphologic differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Apr;68(4):589–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Mobtaker H., Mann K., Nunnemacher G., Jason W. J., Dayal Y., Delellis R. A., Adelman L., Wolfe H. J. Anti-lymphocyte antibody Leu-7 (HNK-1) recognizes a constituent of neuroendocrine granule matrix. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Sep;34(9):1213–1216. doi: 10.1177/34.9.2426347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triche T. J., Askin F. B. Neuroblastoma and the differential diagnosis of small-, round-, blue-cell tumors. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jul;14(7):569–595. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojanowski J. Q., Walkenstein N., Lee V. M. Expression of neurofilament subunits in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system: an immunohistochemical study with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1986 Mar;6(3):650–660. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-03-00650.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos M., Scarpa S., Ross R. A., Triche T. J. Differentiation of human neuroblastoma recapitulates neural crest development. Study of morphology, neurotransmitter enzymes, and extracellular matrix proteins. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):484–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunamoto K., Todo S., Imashuku S., Kato K. Induction of S 100 protein by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 1;48(1):170–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. C., Aoyama H., Lipinski M., Tursz T., Thiery J. P. Identical reactivity of monoclonal antibodies HNK-1 and NC-1: conservation in vertebrates on cells derived from the neural primordium and on some leukocytes. Cell Differ. 1984 Aug;14(3):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(84)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker G. C., Dellagi K., Schmitt C., Brouet J. C., Thiery J. P. Heterogeneity of human anti-MAG IgM as revealed by their reactivity on avian embryonic tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Feb;67(2):352–361. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkel S. B., Itabashi H. H. The natural history of neuroblastic cells in the fetal adrenal gland. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):225–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K. Fine structure and innervation of the avian adrenal gland. I. Fine structure of adrenal chromaffin cells and ganglion cells. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Dec 6;145(3):389–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00307164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., Duband J. L., Thiery J. P. A cell surface determinant expressed early on migrating avian neural crest cells. Brain Res. 1983 Aug;285(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]