Abstract
Many gram-negative plant and animal pathogenic bacteria employ a type III secretion (T3S) system to inject effector proteins into the cytosol of eukaryotic host cells. The membrane-spanning T3S apparatus is associated with an ATPase that presumably provides the energy for the secretion process. Here, we describe the role of the predicted ATPase HrcN from the plant pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pathovar vesicatoria. We show that HrcN hydrolyzes ATP in vitro and is essential for T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. Stability of HrcN in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria depends on the conserved HrcL protein, which interacts with HrcN in vitro and in vivo. Both HrcN and HrcL bind to the inner membrane protein HrcU and specifically localize to the bacterial membranes under T3S-permissive conditions. Protein-protein interaction studies revealed that HrcN also interacts with the T3S substrate specificity switch protein HpaC and the global T3S chaperone HpaB, which promotes secretion of multiple effector proteins. Using an in vitro chaperone release assay, we demonstrate that HrcN dissociates a complex between HpaB and the effector protein XopF1 in an ATP-dependent manner, suggesting that HrcN is involved in the release of HpaB-bound effectors. Effector release depends on a conserved glycine residue in the HrcN phosphate-binding loop, which is crucial for enzymatic activity and protein function during T3S. There is no experimental evidence that T3S can occur in the absence of the ATPase, in contrast to recent findings reported for animal pathogenic bacteria.
The majority of gram-negative bacteria employ a type III secretion (T3S) system to transport proteins across both bacterial membranes. The term “T3S system” refers to translocation-associated and flagellar T3S systems that probably evolved from a common ancestor (24). Both T3S systems consist of a structurally conserved membrane-spanning basal body, which presumably contains two pairs of cylindrical rings in the inner and outer membrane (21, 74). The flagellar basal body is connected to an extracellular hook and the flagellar filament, which is the key bacterial motility organelle. In contrast, the basal body of translocation-associated T3S systems is associated with an extracellular pilus (plant pathogens) or needle (animal pathogens), which serves as a conduit for secreted proteins to the host-pathogen interface (32). Translocation-associated T3S systems translocate bacterial effector proteins directly into the eukaryotic host cell cytosol and are major pathogenicity determinants of most plant and animal pathogenic bacteria. Translocation of effector proteins is mediated by the T3S translocon, a predicted transport channel that inserts into the host plasma membrane (12, 20, 32). Since T3S translocon mutants are completely nonpathogenic, effector protein delivery is presumably crucial for the host-pathogen interaction.
The signal for T3S and translocation is often located in the N-terminal regions of secreted proteins and is not conserved on the amino acid level (32, 33, 41). In addition to the T3S signal, efficient secretion of some T3S substrates also depends on cytoplasmic T3S chaperones, which are small, acidic, and leucine-rich proteins. T3S chaperones bind to effector or translocon proteins and promote stability and/or secretion of their cognate interaction partners (26, 32, 54). While most known T3S chaperones are specific for one or several homologous T3S substrates, a few chaperones with a broad substrate specificity for effector proteins have been described (54).
Several chaperones from flagellar and translocation-associated T3S systems of animal pathogenic bacteria were shown to interact with the cytoplasmic ATPase of the T3S system (1, 31, 62, 71). The ATPase forms a ring structure associated with the secretion apparatus at the inner bacterial membrane and was predicted to provide the energy for the secretion process (50, 74, 75). Experimental evidence reported for the T3S-associated ATPase of the animal pathogenic bacterium Salmonella enterica suggests that ATP hydrolysis is required to release effectors from their cognate chaperones. Furthermore, the ATPase presumably unfolds effector proteins prior to their secretion. T3S substrates have to be at least partially unfolded before passage through the secretion channel, which has an inner diameter of 2 to 3 nm and is thus too narrow for fully folded proteins (1, 9, 43). Interestingly, however, it has recently been reported that T3S in flagellar and translocation-associated T3S systems from animal pathogenic bacteria can also occur in the absence of a functional ATPase (48, 55). According to a current model, the ATPase promotes the initial docking of T3S substrates to the secretion apparatus, whereas subsequent progression of proteins through the T3S system presumably depends on the proton motive force (PMF) (1, 48, 55, 72).
In our laboratory, we study T3S in the plant pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pathovar vesicatoria, which is the causal agent of bacterial spot disease in pepper and tomato. The T3S system from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria is encoded by the chromosomal hrp (hypersensitive response and pathogenicity) gene cluster, which consists of 25 genes in eight operons and is activated in planta or in special minimal media by the products of two regulatory genes, HrpG and HrpX (10, 16, 65, 67, 70). HrpG is a member of the OmpR family of two-component system response regulators and controls the expression of a genome-wide regulon including hrpX (52, 70). HrpX is an AraC-type transcriptional activator that binds to a conserved DNA motif (plant-inducible promoter box; consensus, TTCGC-N15-TTCGC) which is present in the promoter regions of most HrpG-regulated genes (38, 67). The isolation of a constitutively active version of hrpG, hrpG*, was key for the analysis of hrp genes under noninducing conditions and thus for the establishment of an in vitro secretion assay (58, 69). The analysis of bacterial culture supernatants revealed that the X. campestris pv. vesicatoria T3S system secretes at least two different sets of proteins, i.e., (i) extracellular components of the secretion apparatus such as the pilus protein HrpE, the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA, and the pilus assembly protein HrpB2, and (ii) 20 to 30 effector proteins that are translocated into the plant cell cytosol (53, 57, 58, 61, 66). Secretion of different sets of T3S substrates is presumably controlled by Hpa (Hrp-associated) proteins that are encoded in the hrp gene cluster and contribute to bacterial pathogenicity (13, 14, 35). One example is the T3S chaperone HpaB, which promotes secretion and translocation of multiple effector proteins, including AvrBs1, AvrBs3, AvrBsT, XopC, XopJ, and XopF1 (13). HpaB interacts with several effector proteins (AvrBs1, AvrBs3, and XopF1) that do not share sequence homology on the amino acid level, indicating that HpaB is a general T3S chaperone with a broad substrate specificity (13, 14).
In addition to HpaB, T3S in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria is controlled by the cytoplasmic HpaC protein, which interacts with HpaB. HpaC promotes secretion of translocon and effector proteins and inhibits secretion of the pilus assembly protein HrpB2. It was therefore postulated that HpaC acts a substrate specificity switch protein of the T3S system (14, 42). Since both HpaB and HpaC bind to the inner membrane protein HrcV, they presumably act as linker proteins between T3S substrates and the secretion apparatus (13, 14).
HrcV is one out of 11 proteins encoded by the hrp gene cluster that are conserved among plant and animal pathogenic bacteria and presumably constitute the core structural elements of the secretion apparatus. They were therefore termed Hrc (Hrp conserved) followed by a letter, which refers to the nomenclature of Yersinia Ysc (Yersinia secretion) proteins (34). HrcC, which belongs to the secretin protein family, forms a multimeric protein channel and is the only known outer membrane component of the T3S system from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria (68). Six Hrc proteins (HrcU, HrcV, HrcR, HrcS, HrcT, and HrcD) insert into the inner membrane, whereas HrcQ, HrcL, and HrcN are cytoplasmic proteins that presumably associate with the cytoplasmic site of the secretion apparatus (7, 57, 68). HrcQ belongs to the YscQ protein family, members of which are involved in the formation of the cytoplasmic ring of the T3S apparatus (73). HrcN and HrcL are homologous to T3S-associated ATPases and their cognate negative regulators, respectively (6, 8, 46).
In X. campestris pv. vesicatoria, the contribution of the predicted ATPase HrcN to T3S has not yet been studied. Like other T3S-associated ATPases, HrcN is homologous to the β subunit of F0F1 ATPases and contains the Walker boxes A and B that are predicted to mediate ATP binding and hydrolysis (32, 64, 75). In this study, we show that HrcN from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria hydrolyzes ATP in vitro and is essential for T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. In vitro assays revealed that HrcN dissociates a complex between the effector protein XopF1 and the general T3S chaperone HpaB in an ATP-dependent manner, suggesting that HrcN is involved in the release of HpaB-bound effectors. Notably, however, HrcN is also required for T3S of translocon and pilus proteins that do not depend on HpaB for efficient secretion. Protein studies revealed that stability of HrcN depends on HrcL, which binds to HrcN in vitro and in vivo. Both proteins interact with the conserved inner membrane protein HrcU and specifically colocalize to the bacterial membranes under secretion-permissive conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. Escherichia coli cells were grown at 37°C in lysogeny broth (LB) or Super medium (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains were cultivated at 30°C in nutrient-yeast-glycerol medium (23) or in minimal medium A (5) supplemented with sucrose (10 mM) and Casamino Acids (0.3%). Plasmids were introduced into E. coli by electroporation and into X. campestris pv. vesicatoria by conjugation, using pRK2013 as a helper plasmid in triparental matings (30). Antibiotics were added to the media at the following final concentrations if not stated otherwise: ampicillin, 100 μg/ml; kanamycin, 25 μg/ml; rifampin (rifampicin), 100 μg/ml; spectinomycin, 100 μg/ml; tetracycline, 10 μg/ml.
TABLE 1.
Published bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Relevant characteristicsa | Reference(s) or source |
|---|---|---|
| X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains | ||
| 85-10 | Pepper race 2; wild type; Rifr | 17, 39 |
| 85* | 85-10 derivative containing the hrpG* mutation | 69 |
| 85E*ΔhrcU | hrcU deletion mutant derivative of strain 85E* | 66 |
| 85*ΔhpaC | hpaC deletion mutant derivative of strain 85* | 14 |
| 82-8 | Pepper race 1; wild type; Rifr | 17, 39 |
| 82* | 82-8 derivative containing the hrpG* mutation | 69 |
| E. coli strains | ||
| BL21(DE3) | F−ompT hsdSB (rB− mB−) gal dcm (DE3) | Stratagene, Heidelberg, Germany |
| DH5α | F−recA hsdR17(rK− mK+) φ80dlacZΔM15 | Bethesda Research Laboratories, Bethesda, Md. |
| DH5α λpir | F−recA hsdR17(rK− mK+) φ80dlacZΔM15 [λpir] | 44 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pBluescript(II) KS | Phagemid, pUC derivative; Apr | Stratagene |
| pUC119 | ColE1 replicon; Apr | 63 |
| pC3003 | pUC19 containing a triple c-myc tag; Apr | Kindly provided by J. Kämper; unpublished |
| pRK2013 | ColE1 replicon, TraRK+ Mob+; Kmr | 30 |
| pOK1 | Suicide vector; sacB sacQ mobRK2 oriR6K; Smr | 35 |
| pGEX-2TKM | GST expression vector; ptac GST lacIq pBR322 ori; Apr, derivative of pGEX-2TK with polylinker of pDSK604 | GE Healthcare, Munich, Germany (25) |
| pGhpaB | pGEX-2TKM expressing GST-HpaB | 14 |
| pGhpaC | pGEX-2TKM expressing GST-HpaC | 14 |
| pDSK602 | Broad-host-range vector; contains triple lacUV5 promoter; Smr | 25 |
| pDSK604 | Derivative of pDSK602 with modified polylinker | 25 |
| pDMhpaB | pDSK604 derivative encoding HpaB-c-Myc | 13 |
| pDMhpaC | pDSK604 derivative encoding HpaC-c-Myc | 14 |
| pLAFR6 | RK2 replicon, Mob+ Tra−; multicloning site flanked by transcription terminators; Tcr | 11 |
| pL6xopC356 | pLAFR6 derivative encoding XopC1-200-AvrBs3Δ2 under control of the native promoter | 51 |
| pL6xopJ356 | pLAFR6 derivative encoding XopJ1-155-AvrBs3Δ2 under control of the native promoter | 51 |
Ap, ampicillin; Km, kanamycin; Rif, rifampin; Sm, spectinomycin; Tc, tetracycline.
Plant material and plant inoculations.
The near-isogenic pepper cultivars Early Cal Wonder (ECW), ECW-10R, and ECW-30R (39) were grown and inoculated with X. campestris pv. vesicatoria as described previously (10). Briefly, bacteria were inoculated into the intercellular spaces of leaves using a needleless syringe at a concentration of 2 × 108 CFU ml−1 in 1 mM MgCl2 if not stated otherwise. The appearance of disease symptoms and the hypersensitive response (HR) were scored over a period of 1 to 7 days after inoculation. For better visualization of the HR, leaves were bleached in 70% ethanol.
Generation of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria mutants. (i) hrcN deletion mutant.
To create a 1,260-bp in-frame deletion of hrcN (deletion of codons 13 to 432), we amplified the flanking regions of hrcN including the first 36 and the last 33 bp of the gene by PCR and cloned the PCR products into the ApaI/BamHI sites of the suicide plasmid pOK1. The resulting construct, pOKΔhrcN, was conjugated into X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85-10, 85*, 85*ΔhpaC, and 82*. Double crossovers resulted in hrcN deletion mutants, which were selected as described previously (35). The sequences of primers used in this study are available upon request.
(ii) hrcLN double deletion mutant.
For the generation of an hrcLN double deletion mutant, the 1-kb upstream region of hrcL including the first 45 bp of hrcL and the 1-kb downstream region of hrcN including the last 336 bp of hrcN were amplified by PCR and cloned into the ApaI/BamHI sites of pOK1. The resulting construct, pOKΔhrcLN, was conjugated into strain 85*. Double crossovers resulted in strain 85*ΔhrcLN.
(iii) hrcUP24T mutant.
For the introduction of a point mutation in hrcU, we amplified fragments corresponding to 1 kb upstream and 1 kb downstream of codon 24 from hrcU. Both PCR products overlap by 9 bp spanning codons 22 to 24. Mutations of codons 22 (GAA replaced by GAG, a silent mutation that creates an Eco91I restriction site) and 24 (CCG replaced by ACC, leading to a replacement of proline by threonine in HrcU) were introduced by primer sequences. PCR products were digested with XbaI/Eco91I and Eco91I/SalI and cloned into the XbaI/SalI sites of plasmid pOK1. The resulting construct, pOKhrcUP24T, was conjugated into strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcLN. Double crossovers resulted in strains 85*hrcUP24T and 85*hrcUP24TΔhrcLN, respectively.
Generation of expression constructs. (i) hrcL and hrcN expression constructs.
For the generation of hrcN and hrcL expression constructs, hrcN and hrcL were amplified by PCR from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of pDSK604, giving pDhrcN and pDhrcL. To generate a dicistronic construct expressing hrcL and hrcN, a genomic fragment carrying both genes was amplified by PCR and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of pDSK604, giving pDhrcLN.
For the construction of a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged HrcL derivative, hrcL was amplified by PCR and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of pC3003 in frame with a triple-c-Myc epitope-encoding sequence. The resulting insert was ligated into the EcoRI/HindIII sites of plasmid pDSK602, giving pDMhrcL. To generate an N-terminally Strep epitope-tagged HrcL derivative, hrcL was amplified by PCR and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of pDSK604, giving pDStrephrcL. The Strep epitope-encoding sequence was included in the primer sequence. For the generation of a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-HrcL fusion protein, hrcL was amplified by PCR and cloned into the EcoRI/XhoI sites of pGEX-2TKM, respectively, downstream and in frame with the GST-encoding sequence.
To generate a Strep-tagged HrcN derivative, hrcN was amplified by PCR and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of plasmid pDSK604, giving pDStrephrcN. The Strep epitope-encoding sequence was included in the primer sequence. For the generation of a Strep-hrcNG175C expression construct, a point mutation leading to amino acid exchange G175C was introduced by site-directed mutagenesis. For this, an hrcN fragment comprising codons 170 to 443 was amplified and used to replace a PstI/SacI fragment of pDStrephrcN, giving pDStrephrcNG175C. This construct encodes an HrcN derivative in which the P-loop motif 170AAAGVGKS177 is replaced by amino acids 170AAAGVCKS177. To express hrcNG175C with a C-terminal c-Myc epitope-encoding sequence, the insert of construct pDStrephrcNG175C was amplified by PCR and introduced into the EcoRI/SacI sites of plasmid pC3003. The resulting insert was cloned into the EcoRI/HindIII sites of pDSK602, giving pDMhrcNG175C.
(ii) xopF1 expression construct.
To generate an xopF1-c-myc expression construct, xopF1 was amplified by PCR from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 and cloned into the EcoRI/SacI sites of pC3003 in frame with a triple-c-Myc epitope-encoding sequence. The resulting insert was ligated into the EcoRI/HindIII sites of pDSK602, giving pDMxopF1.
Protein secretion studies and immunoblot analysis.
In vitro secretion assays were performed as described previously (15). Briefly, bacteria were incubated in secretion medium (58) in the presence or absence of the protonophore carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) as indicated. CCCP was added to the secretion medium at final concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 5 μM. Equal amounts of bacterial total cell extracts and culture supernatants were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting. We used polyclonal antibodies specific for HrpF (15), XopA (53), HrpE (66), AvrBs3 (37), HrpB2 (57), and HrcN (57) and monoclonal anti-c-Myc (Roche Applied Science, Mannheim, Germany), anti-GST (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Freiburg, Germany), and anti-Strep (IBA GmbH, Göttingen, Germany) antibodies. Horseradish peroxidase-labeled anti-rabbit, anti-mouse, and anti-goat antibodies (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) were used as secondary antibodies. Antibody reactions were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech).
Protein-protein interaction studies.
For Strep pull-down assays, proteins were synthesized in E. coli BL21(DE3) and bacterial cells from 50-ml cultures were resuspended in 3 ml buffer W (100 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) and broken with a French press. One hundred microliters of lysate containing Strep epitope-tagged proteins was incubated with 40 μl Strep-Tactin Sepharose (IBA GmbH) for 30 min at room temperature. Unbound E. coli proteins were removed by washing twice with buffer W. Immobilized proteins were incubated for 1 h with 600 μl E. coli lysate containing the putative interaction partner. Unbound proteins were removed by washing four times with buffer W. Bound proteins were eluted with 40 μl elution buffer (buffer W with 2.5 mM desthiobiotin) for 2 h at room temperature. Five microliters of total protein lysate and 20 μl of eluted proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The same blot was always incubated with an anti-c-Myc antibody and with an anti-Strep antibody.
GST pull-down assays were performed as described previously (14). Briefly, GST and GST fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3), and bacterial cells from 50 ml cultures were broken with a French press. GST and GST fusions were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with a c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of the putative interaction partner. Bound proteins were eluted with 10 mM reduced glutathione. Five microliters of total protein lysates and 20 μl of eluted proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting.
For coimmunoprecipitation experiments, X. campestris pv. vesicatoria was grown in minimal medium A supplemented with sucrose and Casamino Acids. Cells of 50-ml exponentially growing cultures were harvested by centrifugation, resuspended in 3 ml immunoprecipitation buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 1 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 10% [vol/vol] glycerol, 5 mM dithiothreitol, 0.15% [vol/vol] Nonidet P-40), and lysed with a French press. Insoluble cell debris was removed by centrifugation, and 1 ml of lysate was incubated for 1 h with 2 μl of anti-c-Myc antibody (Roche Applied Science) at 4°C to capture c-Myc epitope-tagged proteins. The immunocomplexes were incubated with 25 μl protein G-agarose beads (Roche Applied Science) overnight at 4°C. The protein G-agarose matrix was washed four times with 1 ml immunoprecipitation buffer and resuspended in 40 μl Laemmli buffer. Five microliters of total cell lysate and 20 μl of immunoprecipitate were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The same blot was incubated with an anti-c-Myc antibody and an HrcN-specific antiserum. To avoid detection of the light and heavy chains of the immunoprecipitating antibody, we used TrueBlot immunoglobulin G (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) as a secondary antibody.
ATPase assay.
For the analysis of ATPase activity, Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were synthesized in E. coli BL21(DE3) and purified using Strep-Tactin Sepharose as described above. Immobilized proteins were eluted by incubation with 40 μl buffer E for 2 h, and ATPase activity was determined using a malachite green phosphatase assay kit (BioAssay Systems, Hayward, CA). Nine micrograms of purified Strep-HrcN or StrepHrc-NG175C and 25 μl of 100 mM ATP dissolved in buffer W were incubated in a total volume of 900 μl at 37°C for 30 min according to the manufacturer's instructions. To determine the Km value of HrcN, we used ATP at final concentrations ranging from 0 to 30 mM ATP. For the measurement of the ATPase activity, 100 μl of reaction mixture was added to 700 μl buffer W and 200 μl malachite green reagent after 1, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 min and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. Color development was stopped with 34% citric acid, and the absorbance of triplicate samples was measured at 650 nm. For the calculation of the amounts of released phosphate, the absorbance was compared to the absorbance of a phosphate standard curve according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Chaperone release assay.
For the chaperone release assay, we modified the protocol described by Akeda and Galan (1). GST-HpaB was expressed in E. coli, immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose as described previously (14), and incubated for 1 h with an E. coli lysate containing XopF1-c-Myc. The Sepharose matrix was washed four times with phosphate-buffered saline to remove unbound proteins and incubated with 1 μg purified Strep-HrcN or StrepHrc-NG175C dissolved in buffer W (see above) in the presence of 150 μM ATP or ATPγS for 1 h. Unbound proteins were removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant was precipitated with trichloroacetic acid and resuspended in 20 μl Laemmli buffer. Twenty microliters of bound proteins and 20 μl of precipitated supernatants were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. The same blot was always incubated first with an anti-c-Myc antibody and then with an anti-GST antibody.
RNA analyses.
For reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) analysis, bacteria were grown in nutrient-yeast-glycerol medium. RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were performed as described previously (52). hrcN and hrpB2 transcripts were amplified by PCR using gene-specific primers.
Subcellular localization studies.
For subcellular localization of proteins, bacteria were grown overnight in minimal medium A supplemented with sucrose and Casamino Acids. Bacterial cells from 50-ml cultures were resuspended in 3 ml of 100 mM HEPES and lysed with a French press. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation, and 1 ml of each lysate was centrifuged at 200,000 × g for 90 min at 4°C. Protein levels were adjusted to be similar according to optical density at 600 nm. The pellet, which corresponds to the membrane fraction, was resuspended in 1 ml of 100 mM HEPES. Membrane and soluble fractions were mixed with Laemmli buffer, and 20 μl total bacterial lysate and membrane and soluble fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, Coomassie blue staining (data not shown), or immunoblotting.
RESULTS
The predicted ATPase HrcN is an essential pathogenicity factor.
To investigate the contribution of HrcN to the T3S and pathogenicity of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria, we generated a nonpolar mutation in hrcN, which is the fourth gene in the hrpB operon (27). For this, we deleted codons 13 to 432 of hrcN in the X. campestris pv. vesicatoria wild-type strain 85-10 (see Materials and Methods). The hrcN deletion mutant strain, 85-10ΔhrcN, encodes a truncated protein containing only the first 12 and the last 11 amino acids of HrcN. For phenotypic studies, strains 85-10 and 85-10ΔhrcN were inoculated into leaves of susceptible ECW and resistant ECW-10R pepper plants. ECW-10R plants carry the resistance gene Bs1 and recognize the effector AvrBs1, which is delivered by strain 85-10. Translocation of AvrBs1 into Bs1-expressing pepper plants results in the activation of plant defense responses that are associated with an HR, a rapid local cell death at the infection site (25, 36).
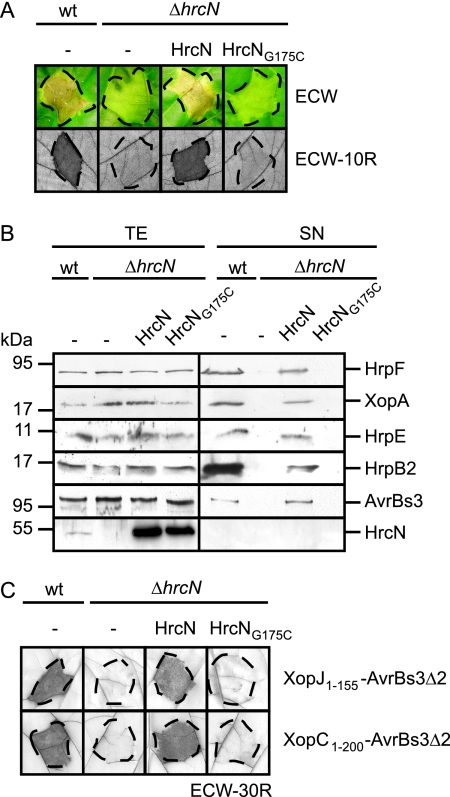
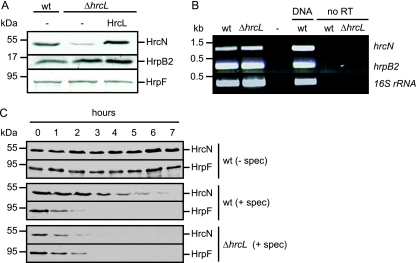
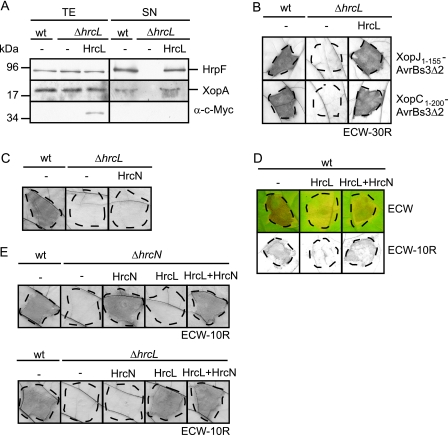
As expected, strain 85-10 caused water-soaked lesions in ECW plants and induced the HR in ECW-10R plants; however, no macroscopic plant reactions were observed with strain 85-10ΔhrcN (Fig. 1A). The hrcN mutant phenotype was complemented by an N-terminally Strep epitope-tagged HrcN derivative (construct pDStrephrcN), suggesting that loss of pathogenicity was specifically due to the deletion of hrcN (Fig. 1A). To investigate whether HrcN protein function depends on the conserved phosphate-binding (P) loop (also termed Walker box A; consensus, G/AXXXXGKT/S) (64, 75), the conserved glycine residue at position 175 of HrcN was replaced by cysteine (see Materials and Methods). Figure 1A shows that the corresponding Strep epitope-tagged mutant derivative HrcNG175C failed to complement the phenotype of the hrcN deletion mutant. This was not due to protein instability, since both Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were detectable in comparable amounts in protein extracts (Fig. 1B, last panel).
FIG. 1.
The predicted ATPase HrcN is essential for T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. (A) HrcN is essential for the interaction of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria with the plant. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85-10 (wild type [wt]) and 85-10ΔhrcN (ΔhrcN) carrying the empty vector (−) or expressing Strep-hrcN (HrcN) and Strep-hrcNG175C (HrcNG175C) as indicated were inoculated into susceptible ECW and resistant ECW-10R pepper plants. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 days after inoculation. For better visualization of the HR in ECW-10R plants, leaves were bleached in ethanol 3 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas. (B) HrcN is crucial for efficient in vitro T3S. Strain 85* (wt) and 85*ΔhrcN (ΔhrcN) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing Strep-HrcN or Strep-HrcNG175C as indicated were incubated in secretion medium. Total protein extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting, using HrpF-, XopA-, HrpE-, HrpB2-, AvrBs3-, and HrcN-specific antibodies. HrpF, XopA, HrpE, and HrcN were analyzed in strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcN. For the analysis of AvrBs3 secretion, we used strains 82* and 82*ΔhrcN, which naturally deliver AvrBs3. Note that HrpB2 secretion was analyzed in the hpaC deletion mutant strains 85*ΔhpaC and 85*ΔhrcNΔhpaC, since HrpB2 secretion in hpaC wild-type strains is at the detection limit of the HrpB2-specific antibody (42). (C) HrcN is essential for translocation of XopJ and XopC. XopJ1-155-AvrBs3Δ2 and XopC1-200-AvrBs3Δ2 were synthesized in strains 85-10 and 85-10ΔhrcN carrying the empty vector (−) or the Strep-hrcN or Strep-hrcNG175C expression construct as indicated. Bacteria were inoculated into AvrBs3-responsive ECW-30R pepper plants. Three days after inoculation, leaves were bleached in ethanol to better visualize the HR. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas.
HrcN is crucial for T3S and effector protein translocation.
Next, we investigated the contribution of HrcN to T3S in vitro. For this, we used X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* and a corresponding hrcN deletion mutant. Strain 85* is a derivative of strain 85-10 which expresses hrpG*, a constitutively active version of the master regulatory gene hrpG. The chromosomal hrpG* gene allows expression of hrp genes under conditions that are normally repressive for hrp gene induction and is key for in vitro T3S (69). However, bacterial growth of hrpG* strains in planta is like wild-type growth (69). Similarly to strain 85-10ΔhrcN (see above), strain 85*ΔhrcN failed to induce plant reactions in susceptible and resistant pepper plants, suggesting that hrpG* cannot compensate for the loss of hrcN (data not shown). For the analysis of in vitro T3S, strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcN were incubated in secretion medium. Total cell extracts and culture supernatants were analyzed by immunoblotting, using specific antibodies for the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA, the pilus protein HrpE, the pilus assembly protein HrpB2, and the effector AvrBs3. For the analysis of AvrBs3 secretion, we used strains 82* and 82*ΔhrcN; these are hrpG* derivatives of strain 82-8, which naturally expresses avrBs3. All proteins tested were secreted by the wild-type strain but were not detectable in the culture supernatants of hrcN deletion mutants, suggesting that secretion of these proteins depends on HrcN (Fig. 1B). The secretion deficiency was complemented by Strep-HrcN but not by the mutant derivative Strep-HrcNG175C (Fig. 1B) (see above).
In addition to in vitro T3S, we analyzed the contribution of HrcN to translocation of selected effector proteins by use of a reporter-based in vivo assay, which allows monitoring of the translocation of proteins that are not easily detectable in culture supernatants (14). For this, we used the established reporter protein AvrBs3Δ2, which is a derivative of the effector AvrBs3 and lacks amino acids 2 to 152, which harbor the secretion and translocation signal. However, AvrBs3Δ2 still induces the HR in AvrBs3-responsive ECW-30R pepper plants when expressed in planta or fused to a functional translocation signal (51, 60). We analyzed translocation of the effector fusions XopC1-200-AvrBs3Δ2 and XopJ1-155-AvrBs3Δ2 by strains 85-10 and 85-10ΔhrcN. As expected, both fusion proteins induced the HR in ECW-30R pepper plants when delivered by strain 85-10 (16, 51) (Fig. 1C). In contrast, no HR induction was observed with derivatives of strain 85-10ΔhrcN, suggesting that translocation of both proteins depends on HrcN (Fig. 1C). The deficiency in HR induction was complemented by Strep-HrcN but not by Strep-HrcNG175C (Fig. 1C). In summary, these data indicate that HrcN is essential for T3S and translocation.
HrcN hydrolyzes ATP in vitro.
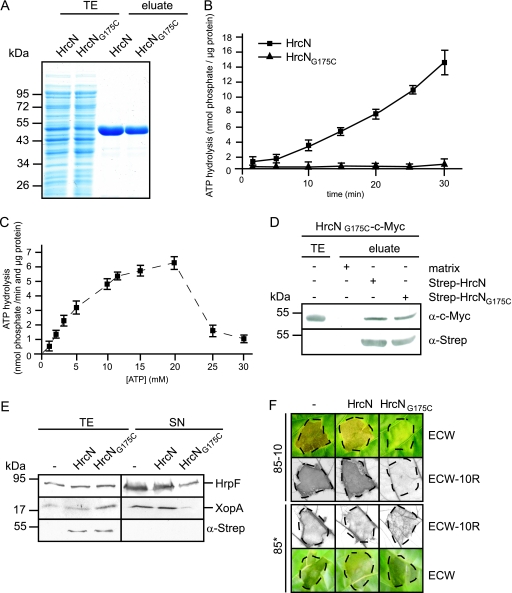
The homology of HrcN to ATPases prompted us to investigate whether HrcN hydrolyzes ATP in vitro. For this, Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were purified from E. coli to near homogeneity using Strep-Tactin Sepharose (Fig. 2A) and subjected to a malachite green phosphatase assay (see Materials and Methods). This colorimetric assay allows the quantification of free phosphate, which forms a green complex with malachite green and molybdate. Figure 2B shows that Strep-HrcN hydrolyzed ATP in a linear time-dependent manner, releasing approximately 400 pmol phosphate per minute per μg protein. This activity is slightly higher than the activity measured with the flagellar T3S-associated ATPase FliI (350 pmol phosphate per minute per μg protein) (46). No ATP hydrolysis was detected for purified Strep-HrcNG175C (Fig. 2B). Measurements of the enzymatic activity of HrcN at different substrate concentrations revealed an increase in the ATPase activity in a range of 3 to 20 mM ATP, with an apparent Km value of 9.4 mM, as determined using an Eadie-Hofstee plot (Fig. 2C). However, the ATPase activity of HrcN was inhibited in the presence of more than 20 mM ATP (Fig. 2C). Similar observations were previously reported for the ATPase YscN from Yersinia enterocolitica (8).
FIG. 2.
HrcN hydrolyzes ATP in vitro. (A) Purification of Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C. Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were purified from E. coli using Strep-Tactin Sepharose. E. coli total cell extracts (TE) and proteins eluted from the matrix (eluate) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (B) ATPase activity of Strep-tagged HrcN. ATP hydrolysis by purified Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C was measured using a malachite green phosphatase assay over a period of 30 min after application of malachite green reagent (see Materials and Methods). Error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) ATPase activity of HrcN is inhibited by high substrate concentrations. ATP hydrolysis by purified Strep-HrcN was measured after 10 min as described for panel B at ATP concentrations ranging from 1 to 30 mM. (D) HrcNG175C self-interacts and interacts with wild-type HrcN. Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were immobilized on a Sepharose matrix and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HrcNG175C-c-Myc. As a negative control, HrcNG175C-c-Myc was incubated with the matrix alone. The total extract of hrcNG175C-c-myc-expressing E. coli (TE) and eluted proteins (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using c-Myc- and Strep-specific antibodies. (E) Overexpression of Strep-hrcNG175C affects in vitro T3S of HrpF and XopA. Strain 85* carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C as indicated was incubated in secretion medium. Total protein extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against HrpF, XopA, and the Strep epitope. (F) Overexpression of Strep-hrcNG175C affects bacterial pathogenicity. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85-10 and 85* carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing Strep-HrcN or Strep-HrcNG175C as indicated were inoculated into susceptible ECW and resistant ECW-10R pepper plants. For better visualization of the HR, leaves were bleached in ethanol 3 days after inoculation. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas.
Since the enzymatic activity of T3S-associated ATPases presumably depends on the oligomerization state of the protein (4, 19, 56), we investigated whether the G175C mutation affects the interaction of HrcN with itself. Homo-oligomerization was shown for HrcN from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria and Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri by E. coli and yeast two-hybrid-based interaction studies (2, 7). Here, Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were synthesized in E. coli, immobilized on Strep-Tactin Sepharose, and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged HrcNG175C derivative. HrcNG175C-c-Myc was detected in the eluates of Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C, suggesting that it interacts with wild-type HrcN and with itself (Fig. 2D). Taken together, these data indicate that the conserved glycine residue at position 175 is required for catalytic activity but not for self-interaction of HrcN. Loss of enzymatic activity of HrcNG175C presumably explains the failure of this HrcN derivative to complement the hrcN mutant phenotype (see above, Fig. 1).
Next, we investigated whether the mutant derivative HrcNG175C exerts a dominant-negative effect on the host-pathogen interaction. Figure 2E shows that ectopic expression of Strep-HrcNG175C in strain 85* affects in vitro T3S as shown for the secretion of the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA. Furthermore, in the wild-type strain 85-10, ectopic expression of Strep-HrcNG175C leads to a significant decrease in symptom formation in susceptible and resistant pepper plants, respectively (Fig. 2F). However, the negative effect of Strep-HrcNG175C on the host-pathogen interaction was less pronounced in strain 85*, suggesting that constitutive expression of the hrpG regulon partially counteracts the inhibitory effect of Strep-HrcNG175C in vivo (Fig. 2F). We speculate that a mixture of wild-type HrcN and HrcNG175C leads to the assembly of nonfunctional ATPase complexes.
HrcN interacts with HpaB and HpaC and dissociates a complex between HpaB and the effector protein XopF1.
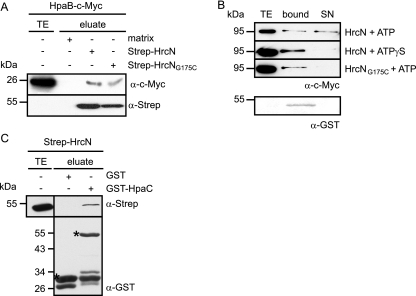
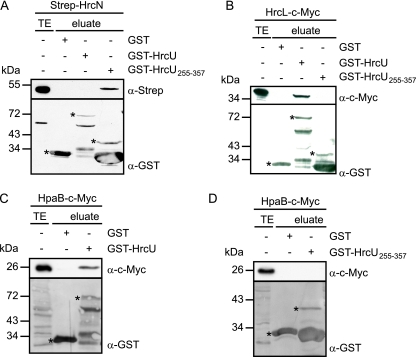
The essential role of HrcN during T3S prompted us to investigate whether HrcN interacts with the T3S chaperone HpaB (13, 14, 42). For this, Strep-HrcN was immobilized on Strep-Tactin Sepharose and incubated with a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged HpaB derivative. HpaB-c-Myc specifically bound to Strep-HrcN but not to the matrix alone, suggesting that both proteins interact. A similar result was obtained for the catalytically inactive Strep-HrcNG175C derivative (Fig. 3A).
FIG. 3.
HrcN dissociates the HpaB-XopF1 effector complex. (A) Interaction studies with HrcN and HpaB. Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were immobilized on Strep-Tactin Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HpaB-c-Myc. Total cell extracts (TE) and eluted proteins (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against the c-Myc and the Strep epitopes. (B) HrcN releases the HpaB-bound effector protein XopF1. Purified Strep-HrcN or Strep-HrcNG175C was incubated with the GST-HpaB/XopF1-c-Myc complex in the presence of ATP or the nonhydrolyzable ATP derivative ATPγS as indicated. The total cell lysate of E. coli expressing XopF1-c-Myc (TE), bound proteins (bound), and proteins in the supernatant (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using c-Myc- and GST-specific antibodies. (C) HrcN interacts with the T3S substrate specificity switch protein HpaC. GST and GST-HpaC were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing Strep-HrcN. The total cell lysate containing Strep-HrcN (TE) and eluted proteins (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against the Strep epitope and GST, respectively. GST and GST fusion proteins are indicated by asterisks.
It was previously reported that the T3S-associated ATPase InvC from S. enterica dissociates a chaperone-effector complex in an ATP-dependent manner (1). To analyze whether HrcN from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria behaves similarly, we immobilized a complex consisting of a GST-HpaB fusion protein and the effector protein XopF1-c-Myc on glutathione-Sepharose. XopF1 was previously shown to interact with HpaB (14). The GST-HpaB/XopF1-c-Myc complex was incubated with purified Strep-HrcN in the presence of ATP (see Materials and Methods) (1), and proteins bound and released from the matrix were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against GST and the c-Myc epitope, respectively. As expected, GST-HpaB was present only in the matrix-bound fraction, whereas XopF1-c-Myc was also detected in the supernatant, suggesting that it was released from the chaperone (Fig. 3B). We did not detect release of XopF1-c-Myc in the presence of the nonhydrolyzable ATP derivative ATPγS or the catalytically inactive Strep-HrcNG175C protein (Fig. 3B). The latter observation was not due to a lack of protein-protein interaction, since Strep-HrcNG175C binds to HpaB (Fig. 3A). Taken together, our results indicate that HrcN releases the effector protein XopF1 from the global T3S chaperone HpaB in an ATP-dependent manner.
In addition to HpaB, we investigated a possible interaction between HrcN and the substrate specificity switch protein HpaC. For this, GST and a GST-HpaC fusion protein were synthesized in E. coli, immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose, and incubated with a bacterial lysate containing Strep-HrcN. Figure 3C shows that Strep-HrcN coelutes with GST-HpaC, but not with GST alone. Taking our results together, we conclude that HrcN binds to both HpaB and HpaC.
HrcN interacts with the conserved HrcL protein.
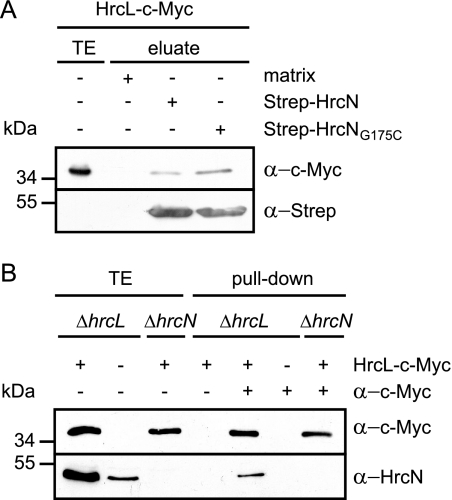
In animal pathogenic bacteria it was shown that T3S-associated ATPases interact with members of the YscL/FliH family of cytoplasmic proteins that presumably negatively regulate the ATPase activity (8, 46, 47). Heterodimerization of HrcN and HrcL from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria was previously observed by bacterial two-hybrid-based interaction studies (7). To confirm the interaction between HrcL and HrcN, we performed in vitro pull-down assays. For this, we immobilized Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C on Strep-Tactin Sepharose and incubated them with an E. coli lysate containing a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of HrcL. Figure 4A shows that HrcL-c-Myc was present in the eluate of Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C but did not elute with the matrix alone, suggesting that HrcL specifically binds to HrcN. To confirm the interaction between HrcL and HrcN in vivo, we performed coimmunoprecipitation studies. Due to the lack of an HrcL-specific antibody, HrcL was synthesized with a C-terminal c-Myc epitope in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85*ΔhrcL grown in secretion-permissive medium. Immunoblot analyses revealed that HrcN coimmunoprecipitated with HrcL-c-Myc but was not detectable in the precipitate in the absence of c-Myc-specific antibody or HrcL-c-Myc (Fig. 4B). These results indicate that HrcN and HrcL are present in a protein complex in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. Unfortunately, we could not investigate a possible influence of HrcL on the ATPase activity of HrcN, since Strep-HrcL is only weakly expressed in E. coli and could not be purified in sufficient amounts for enzyme activity assays. We encountered similar problems with GST-tagged HrcL, suggesting that HrcL derivatives are not well expressed or are unstable in E. coli.
FIG. 4.
HrcN interacts with the conserved HrcL protein. (A) In vitro interaction studies with HrcL and HrcN. Strep-HrcN and Strep-HrcNG175C were immobilized on Sepharose matrix and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HrcL-c-Myc. Bacterial total cell extracts (TE) and proteins eluted from the matrix (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using c-Myc- and Strep epitope-specific antibodies. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments with HrcN and HrcL in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. Strains 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL) and 85*ΔhrcN (ΔhrcN) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing HrcL-c-Myc as indicated were incubated in the presence or absence of a c-Myc-specific antibody coupled to protein G-Sepharose as indicated. Bacterial total cell extracts (TE) and proteins bound to the Sepharose matrix (pull-down) were analyzed by immunoblotting using c-Myc- and HrcN-specific antibodies.
Stability of HrcN depends on HrcL.
In the course of our protein studies we noticed reduced HrcN levels in strain 85*ΔhrcL (Fig. 5A). This was specifically due to the deletion of hrcL, since wild-type levels of HrcN were restored by ectopic expression of a c-Myc epitope-tagged HrcL derivative in strain 85*ΔhrcL (Fig. 5A). In contrast to the case for HrcN, the amounts of the pilus assembly protein HrpB2 and the putative translocon protein HrpF were not affected in strain 85*ΔhrcL (Fig. 5A). Since HrpB2 is encoded in the same operon as HrcN, it was unlikely that deletion of hrcL affected transcript stability. Nevertheless, we performed semiquantitative RT-PCR experiments. Figure 5B shows that hrcN and hrpB2 transcript levels were comparable in strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcL.
FIG. 5.
HrcL contributes to HrcN stability. (A) HrcN protein amounts are reduced in the absence of HrcL. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85* (wild type [wt]) and 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing HrcL-c-Myc as indicated were grown in minimal medium A supplemented with sucrose and Casamino Acids. Total protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using HrcN-, HrpB2-, and HrpF-specific antibodies. (B) Transcription of hrcN is not affected in an hrcL deletion mutant. RNA was isolated from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85* (wt) and 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL). RT-PCR was performed using cDNA and primers specific for hrcN, hrpB2, and the 16S rRNA, which was amplified as a constitutive control. As a positive control for the PCR, we used genomic DNA of strain 85* (DNA). As negative controls, the template was replaced by water (−) or the reaction was performed in the absence of RT (no RT). Amplicons were separated on a 2% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. (C) Protein stability of HrcN is decreased in an hrcL deletion mutant. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strains 85* (wt) and 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL) were grown in minimal medium A supplemented with sucrose and Casamino Acids. Bacterial cultures were adjusted to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.2 and incubated at 30°C in the absence or presence of spectinomycin (spec) at a final concentration of 400 μg/ml. Samples were taken over a period of 7 h after addition of spectinomycin. Equal amounts of total protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using HrcN- and HrpF-specific antibodies, respectively.
To investigate whether HrcL contributes to HrcN protein stability, we blocked protein synthesis in strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcL with spectinomycin, which inhibits the elongation factor G cycle and the peptidyl tRNA translocase reaction (18). The HrcN levels in strain 85* decreased 3 hours after addition of spectinomycin, whereas in the hrcL deletion mutant, the HrcN protein level was reduced earlier (Fig. 5C). This result cannot be explained by a general effect of HrcL on protein stability, since the amounts of the translocon protein HrpF were comparable in strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcL (Fig. 5C). Taken together, our data suggest that HrcL contributes to HrcN protein stability in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria.
Overexpression of HrcL affects bacterial pathogenicity.
We previously reported that HrcL is an essential pathogenicity factor that is required for the efficient secretion of the effector protein AvrBs3 and the pilus assembly protein HrpB2 (57). Here, we show that HrcL is also required for secretion of the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA and for translocation of the effector proteins XopJ1-155-AvrBs3Δ2 and XopC1-200-AvrBs3Δ2, suggesting that HrcL has a general impact on type III-dependent protein export (Fig. 6A and B). The secretion and translocation deficiency of hrcL deletion mutants was complemented with a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged HrcL derivative, suggesting that the observed phenotypes were specifically due to the deletion of hrcL (Fig. 6A and B). In contrast, overproduction of Strep epitope-tagged HrcN in strain 85-10ΔhrcL did not compensate for the loss of bacterial pathogenicity and HR induction caused by the hrcL deletion, indicating that the effect of the hrcL deletion cannot be bypassed by overproduction of the ATPase (Fig. 6C and data not shown).
FIG. 6.
The conserved HrcL protein is essential for T3S and effector protein translocation. (A) HrcL is essential for in vitro T3S of HrpF and XopA. Strains 85* (wild type [wt]) and 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing HrcL-c-Myc as indicated were incubated in secretion medium. Total cell extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against HrpF, XopA, and the c-Myc epitope. (B) HrcL is essential for translocation of XopJ and XopC. XopJ1-155-AvrBs3Δ2 or XopC1-200-AvrBs3Δ2 was synthesized in strains 85-10 (wt) and 85-10ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL) carrying the empty vector or synthesizing HrcL-c-Myc as indicated, and bacteria were inoculated into AvrBs3-responsive ECW-30R pepper plants. Three days after inoculation, leaves were bleached in ethanol. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas. (C) Overproduction of HrcN does not bypass the effect of the hrcL mutation. Strains 85-10 and 85-10ΔhrcL carrying the empty vector or expressing Strep-hrcN as indicated were inoculated into resistant ECW-10R pepper plants. Three days after inoculation, leaves were bleached in ethanol. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas. (D) Overexpression of hrcL affects the host-pathogen interaction. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85-10 (wt) carrying the empty vector (−) or expressing hrcL-c-myc or both hrcL and hrcN from construct pDhrcLN as indicated was inoculated into resistant ECW-10R and susceptible ECW pepper plants. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 days after inoculations. For better visualization of the HR, leaves were bleached in ethanol 3 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas. (E) Construct pDhrcLN complements the hrcL and hrcN mutant phenotypes. Strains 85-10 (wt), 85-10ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL), and 85-10ΔhrcN (ΔhrcN) carrying the empty vector (−) or expressing hrcL-c-myc, hrcN, or both hrcL and hrcN from plasmid pDhrcLN as indicated were inoculated into resistant ECW-10R pepper plants. Leaves were bleached in ethanol 3 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas.
Interestingly, ectopic expression of hrcL-c-myc in strain 85-10 led to a significant reduction in disease symptoms and the HR in susceptible and resistant pepper plants, respectively (Fig. 6D). Similar results were obtained with untagged HrcL (data not shown). In contrast, plant reactions were not reduced when hrcL was ectopically expressed together with hrcN in strain 85-10 (Fig. 6D). The corresponding expression construct pDhrcLN complemented the phenotype of hrcL and hrcN deletion mutants, suggesting that both hrcL and hrcN were expressed (Fig. 6E). We therefore conclude that the dominant-negative effect of HrcL overexpression on the host-pathogen interaction can be counteracted by increased levels of HrcN. As described above for the ectopic expression of hrcNG175C (Fig. 2F), the negative effect of ectopic hrcL expression was less pronounced in strain 85*, suggesting that constitutive expression of the hrpG regulon compensates at least in part for the negative effect of elevated HrcL levels (data not shown).
HrcN, HrcL, and HpaB colocalize to the bacterial membrane under secretion-inducing conditions.
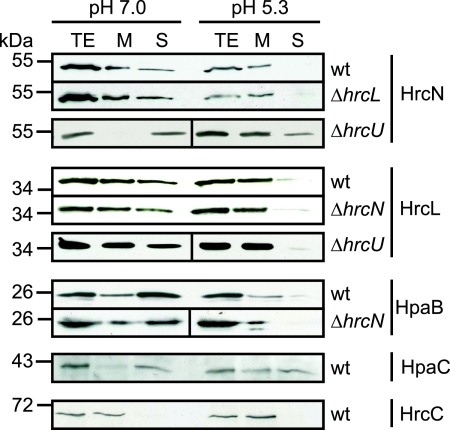
Next, we investigated the subcellular localization of HrcN and HrcL under secretion-permissive and nonpermissive conditions. For this, strain 85* was incubated in minimal medium A at pH 5.3 (secretion permissive) and pH 7.0 (secretion nonpermissive). Membrane fractions and soluble proteins were separated by ultracentrifugation and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. When bacteria were incubated at pH 7.0, HrcN was detected in the membrane and the soluble fraction, which confirms previous localization data (Fig. 7) (57). However, at pH 5.3 the amounts of soluble HrcN were significantly reduced, suggesting a shift to the membranes that is dependent on the activation of the secretion apparatus (Fig. 7). A similar shift in HrcN localization was observed in strain 85*ΔhrcL, suggesting that HrcL is not required for membrane association of HrcN (Fig. 7).
FIG. 7.
Subcellular localization studies with HrcN and HrcL. HrcN, HrcL, and HpaB colocalize to the bacterial membranes upon activation of the T3S system. Strains 85* (wild type [wt]) 85*ΔhrcL (ΔhrcL), 85*ΔhrcN (ΔhrcN), and 85E*ΔhrcU (ΔhrcU) were grown in minimal medium A supplemented with sucrose and Casamino Acids under secretion-permissive (pH 5.3) and nonpermissive (pH 7.0) conditions. Membrane (M) and soluble (S) fractions were separated by ultracentrifugation. For the analysis of HrcL, HpaB, and HpaC, proteins were synthesized as C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged derivatives. Total protein extracts (TE), M, and S were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against HrcN, HrcC, and the c-Myc epitope.
To analyze the localization of HrcL, the c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of HrcL was synthesized in strains 85* and 85*ΔhrcN. HrcL-c-Myc was detected in the membrane and the soluble fraction under nonpermissive secretion conditions (pH 7.0). Under secretion-permissive conditions, however, we observed a shift of HrcL-c-Myc to the membranes in both strains, similar to the case for HrcN. As a control, the blot was reacted with an antibody against the outer membrane secretin HrcC (68). As expected, HrcC was present only in total cell extracts and the membrane fraction (Fig. 7). Taken together, our data suggest that HrcN and HrcL colocalize to the bacterial membranes upon activation of the T3S system. Notably, we obtained a similar result for a c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of the global T3S chaperone HpaB (Fig. 7). Membrane association of HpaB-c-Myc under secretion-permissive conditions was comparable in wild-type and hrcN deletion mutant strains, suggesting that the ATPase HrcN is not essential for the docking of HpaB to the bacterial membranes upon activation of the T3S system (Fig. 7). We also investigated the localization of the T3S substrate specificity switch protein HpaC, which interacts with HpaB and HrcN (14) (Fig. 3C). Under nonpermissive secretion conditions the c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of HpaC was detected predominantly in the soluble fraction. Under secretion-permissive conditions, however, comparable amounts of HpaC-c-Myc were present in both the soluble and the membrane fractions, suggesting that membrane association of HpaC is enhanced upon activation of the T3S system (Fig. 7).
HrcN, HrcL, and HpaB interact with the conserved inner membrane protein HrcU.
The membrane association of HrcN and HrcL under T3S-permissive conditions (see above) prompted us to investigate whether both proteins interact with conserved inner membrane components of the secretion apparatus. We therefore tested a possible interaction of HrcN and HrcL with HrcU, which belongs to the YscU/FlhB family of inner membrane proteins. HrcU and homologs contain four predicted transmembrane domains and a C-terminal cytoplasmic region that is proteolytically cleaved and presumably involved in substrate recognition (3, 28, 40, 42, 45, 59). For interaction studies, we used GST fusion proteins containing full-length HrcU or amino acids 255 to 357 of HrcU, which correspond to the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. GST-HrcU and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose and incubated with E. coli lysates containing Strep-HrcN or HrcL-c-Myc. Figure 8A shows that Strep-HrcN preferentially coelutes with the GST derivative containing the C-terminal domain of HrcU but not the full-length HrcU protein. Since GST-HrcU was recently shown to be proteolytically cleaved, we assume that the protein is correctly folded (42). In contrast to Strep-HrcN, HrcL-c-Myc was detected only in the eluate of GST-HrcU and not in that of GST-HrcU255-357. We therefore speculate that HrcN and HrcL bind to different sites in HrcU (Fig. 8B). Notably, however, membrane association of HrcN and HrcL in an hrcU deletion mutant strain under T3S-permissive conditions was like that in the wild type, suggesting that HrcU is not crucial for the docking of the ATPase complex to the bacterial membranes (Fig. 7).
FIG. 8.
Interaction studies with HrcN and HrcL. (A) HrcN binds to the C-terminal domain of HrcU. GST, GST-HrcU and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing Strep-HrcN. Total cell extracts (TE) and eluted proteins (eluate) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the Strep epitope and GST. GST and GST fusion proteins are indicated by asterisks. (B) HrcL interacts with the conserved HrcU protein. GST, GST-HrcU, and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HrcL-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the c-Myc epitope and GST. (C) HpaB interacts with HrcU. GST and GST-HrcU were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HpaB-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed as described for panel B. (D) Interaction studies with HpaB and HrcU255-357. GST and GST-HrcU255-357 were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with an E. coli lysate containing HpaB-c-Myc. TE and eluate were analyzed as described for panel B.
In addition to HrcN and HrcL, we analyzed a possible interaction between the global T3S chaperone HpaB and HrcU. Similarly to HrcL-c-Myc, a C-terminally c-Myc epitope-tagged derivative of HpaB coeluted with GST-HrcU but not with the GST derivative containing the C-terminal domain of HrcU (Fig. 8C and D). We conclude from our results that a protein complex containing HrcN, HrcL, and HpaB binds to the conserved inner membrane protein HrcU.
An hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant is defective in T3S and pathogenicity.
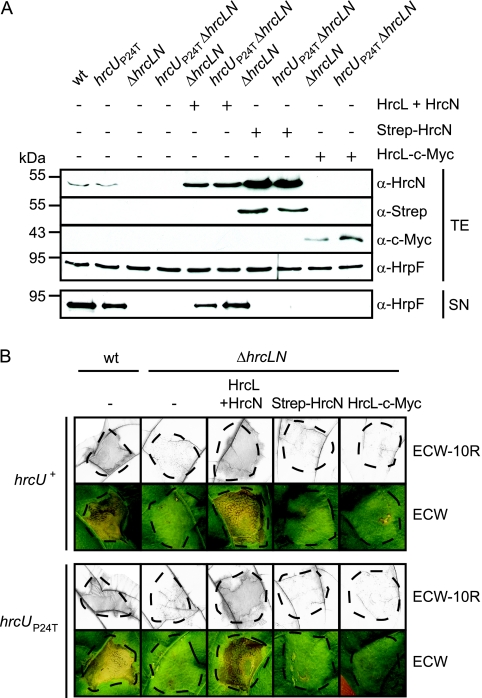
In S. enterica it was recently shown that flagellar assembly and T3S can occur in the absence of the hrcL and hrcN homologs fliH and fliI, albeit in reduced amounts, suggesting that the presence of a functional ATPase is not crucial for secretion (48, 55). To test this hypothesis for X. campestris pv. vesicatoria, we deleted both hrcL and hrcN from the genome of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* and analyzed the corresponding double deletion mutant strain 85*ΔhrcLN for in vitro T3S and pathogenicity. When bacteria were incubated in secretion medium, the translocon protein HrpF was not detectable in the culture supernatant of strain 85*ΔhrcLN (Fig. 9A). Furthermore, strain 85*ΔhrcLN did not induce phenotypic reactions when inoculated into resistant ECW-10R and susceptible ECW pepper plants, suggesting that effector protein translocation is abolished (Fig. 9B). The mutant phenotype of strain 85*ΔhrcLN was complemented by plasmid pDhrcLN, which expresses both hrcL and hrcN (see above). In contrast, no complementation was observed upon expression of hrcL or hrcN alone (Fig. 9A and B).
FIG. 9.
An hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant is impaired in in vitro T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. (A) In vitro T3S of the translocon protein HrpF is abolished in an hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant. Strains 85* (wild type [wt]), 85*hrcUP24T (hrcUP24T), 85*ΔhrcLN (ΔhrcLN), and 85*hrcUP24TΔhrcLN (hrcUP24TΔhrcLN) carrying the empty vector (−) or synthesizing Strep-HrcN, HrcL-c-Myc, or both HrcL and HrcN from construct pDhrcLN as indicated were incubated in secretion medium. Total protein extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against HrcN, HrpF, the c-Myc, and the Strep epitope. (B) An hrcL hrcN double deletion mutant does not elicit phenotypic reactions in susceptible and resistant pepper plants. Strains 85* (wt) and 85*ΔhrcLN (ΔhrcLN) containing the hrcU wild-type (hrcU+) or the hrcUP24T (hrcUP24T) gene and carrying the empty vector (−) or Strep-hrcN, hrcL-c-myc, and hrcL hrcN expression constructs, as indicated, were inoculated into resistant ECW-10R and susceptible ECW pepper plants. For better visualization of the HR, leaves were bleached in ethanol 2 days after inoculation. Disease symptoms were photographed 7 days after inoculation. Dashed lines indicate the inoculated areas.
We also introduced a mutation into codon 24 of hrcU from strain 85*ΔhrcLN that leads to an amino acid change from proline to threonine in HrcU (P24T). The proline residue at position 24 is conserved in HrcU and the HrcU homolog FlhB and is located outside of the transmembrane helices of these proteins. The equivalent mutation in FlhB (P28T) was shown to substantially improve bacterial motility and secretion in the S. enterica fliH fliI double deletion mutant (48). In X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85*hrcUP24TΔhrcLN, however, the P24T mutation in HrcU did not change the hrcLN mutant phenotype; i.e., it did not restore T3S and effector protein translocation in the absence of a functional ATPase (Fig. 9A and B). In the hrcL hrcN wild-type strain 85*hrcUP24T, the P24T mutation in HrcU did not affect HrpF secretion in vitro or the plant-pathogen interaction (Fig. 9A and B). This suggests that the proline residue at position 24 of HrcU is not essential for T3S and pathogenicity. Taken together, our experimental data did not provide evidence that the ATPase HrcN is dispensable for T3S in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria.
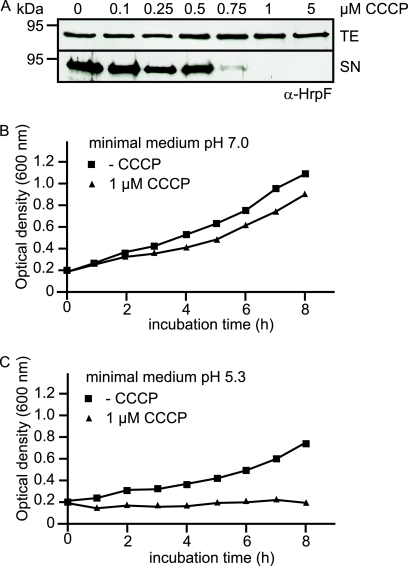
The protonophore CCCP inhibits in vitro T3S and bacterial growth.
Next, we investigated a possible contribution of the PMF to T3S in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. It was previously shown for the animal pathogenic bacteria Y. enterocolitica and S. enterica that T3S is inhibited by the protonophore CCCP, suggesting a role of PMF during T3S (48, 55, 72). Here, we incubated X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* in secretion medium in the absence or presence of CCCP at final concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 5 μM. Total cell extracts and culture supernatants were analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody directed against the putative translocon protein HrpF. Notably, intracellular levels of HrpF in strain 85* were unaffected by addition of CCCP; however, HrpF was not detected in the culture supernatant at a final CCCP concentration of 1 μM, suggesting an inhibitory effect of CCCP on in vitro T3S (Fig. 10A). We also analyzed a possible influence of CCCP on bacterial growth in vitro. For this, strain 85* was incubated in minimal medium at pH 7.0 (T3S-restrictive conditions) and pH 5.3 (T3S-permissive conditions) in the presence or absence of 1 μM CCCP, and the optical density of the cultures was monitored over 8 hours. Figure 10B shows that bacterial growth in minimal medium at pH 7.0 was reduced in the presence of CCCP. Furthermore, at pH 5.3 CCCP led to an arrest of bacterial growth, suggesting that under T3S-permissive conditions, 1 μM CCCP inhibits both in vitro T3S and bacterial multiplication (Fig. 10C).
FIG. 10.
The protonophore CCCP negatively affects in vitro T3S and bacterial growth of X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. (A) In vitro T3S of HrpF is inhibited by a final CCCP concentration of 1 μM. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* was incubated in secretion medium in the absence or presence of CCCP at final concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 5 μM as indicated. Total cell extracts (TE) and culture supernatants (SN) were analyzed by immunoblotting using an HrpF-specific antibody. (B) CCCP affects bacterial growth in minimal medium. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* was incubated in minimal medium at pH 7.0 in the presence or absence of 1 μM CCCP as indicated, and the optical density of the cultures was measured over 8 hours. (C) CCCP inhibits bacterial multiplication under secretion-permissive conditions. X. campestris pv. vesicatoria strain 85* was incubated in minimal medium at pH 5.3 as described for panel B, and the optical density was measured over 8 hours.
DISCUSSION
T3S-associated ATPases have long been predicted to be the key energizers of the T3S system. So far, the role of the ATPase during T3S has been intensively studied in animal pathogenic bacteria. In contrast, little is known about T3S-associated ATPases from plant pathogenic bacteria. In this study, we demonstrate that HrcN from the plant pathogenic bacterium X. campestris pv. vesicatoria is an active ATPase that is crucial for T3S and bacterial pathogenicity. In vitro and in vivo protein-protein interaction studies revealed that HrcN interacts with HrcL, which belongs to the conserved YscL/FliH protein family. HrcL homologs from animal pathogenic bacteria were shown to bind to the T3S-associated ATPase and to negatively regulate the enzymatic activity (6, 8, 46). Although for technical reasons we could not address the latter point, we noticed that HrcL positively regulates HrcN protein stability. Interestingly, however, elevated amounts of HrcL interfere with bacterial pathogenicity and T3S. This negative effect was counteracted by increased levels of HrcN, suggesting that the ratio of ATPase and the putative regulator is important. Similar observations were previously reported for the flagellar HrcL and HrcN homologs FliH and FliI from S. enterica (47).
Pull-down assays with HrcN and HrcL from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria showed that both proteins bind to the inner membrane protein HrcU, suggesting that they exist in a hetero-oligomeric protein complex that is associated with the T3S system at the inner membrane. HrcU belongs to the FlhB/YscU family of inner membrane proteins that are presumably involved in substrate recognition and interact with T3S substrate specificity switch proteins (3, 7, 22, 29, 42, 45). Experimental evidence reported for animal pathogenic bacteria suggested that binding of T3S substrate specificity switch proteins induces a conformational change in the C-terminal domain of FlhB/YscU family members and thus alters the substrate specificity of the secretion apparatus (22, 49). In agreement with this model, we have previously shown that the T3S substrate specificity switch protein HpaC interacts with the C-terminal domain of HrcU from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria (42). Notably, we did not observe an interaction between HpaC and full-length HrcU, suggesting that binding of HpaC to the C-terminal domain of HrcU depends on a certain protein conformation that is altered in the context of the full-length HrcU protein (42). Here, we obtained similar results for the ATPase HrcN, which preferentially binds to the C-terminal domain of HrcU but not to full-length HrcU. In contrast to HrcN, HrcL interacts with the full-length HrcU protein but no interaction was detected between HrcL and the C-terminal domain of HrcU, suggesting that HrcN and HrcL do not compete for the same binding site in HrcU. We conclude from our data that a protein complex containing HrcN and HrcL interacts with HrcU and that binding of HrcN to HrcU might be favored by a certain conformation of the HrcU C-terminal domain. Notably, the results of fractionation studies suggest that HrcN and HrcL specifically localize to the bacterial membranes under secretion-permissive conditions. So far, membrane association of the ATPase has been reported only for HrcN from the plant pathogens Pseudomonas syringae and X. campestris pv. vesicatoria (56, 57). However, it was not yet known that localization of the ATPase can be altered under secretion-permissive conditions. Based on our observations, it is tempting to speculate that activation of the T3S system leads to conformational changes in components of the secretion apparatus at the inner membrane that promote docking of the ATPase complex. However, since HrcU is not crucial for membrane localization of HrcN and HrcL, it is conceivable that multiple components of the secretion apparatus contribute to the association of HrcN and HrcL with the bacterial membranes.
The results of our protein-protein interaction studies show that HrcN binds to the global T3S chaperone HpaB, which colocalizes with HrcN and HrcL to the bacterial membranes under secretion-permissive conditions. Similarly to HrcN and HrcL, HpaB interacts with the inner membrane protein HrcU, suggesting that it is part of a hetero-oligomeric protein complex that contains HrcN and HrcL and associates with the secretion apparatus. Using an in vitro chaperone release assay previously described by Akeda and Galan (1), we could show that HrcN dissociates a complex between the effector protein XopF1 and HpaB in an ATP-dependent manner. HrcN-mediated release of XopF1 depends on a conserved glycine residue in HrcN that is located in the P-loop motif and is crucial for ATP hydrolysis and T3S. This indicates that the ATPase activity and hence presumably the dissociation of HpaB-effector complexes play a key role in T3S in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. Similar findings were previously reported for the T3S-associated ATPase InvC from the animal pathogen S. enterica, suggesting that the T3S ATPase is required for release of chaperone-bound effector proteins (1). However, the results of our in vitro secretion assays also indicate that HrcN function must go beyond the dissociation of HpaB-effector complexes. We found that HrcN is also crucial for secretion of T3S substrates that do not depend on HpaB for efficient secretion, such as the pilus protein HrpE, the pilus assembly protein HrpB2, and the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA. T3S chaperones that promote secretion of these proteins have not yet been identified in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mutant studies suggest that secretion of HrpE is independent of all known T3S control proteins and presumably does not require the assistance of a helper protein (14; D. Büttner, unpublished data). In contrast, efficient secretion of the putative translocon proteins HrpF and XopA depends on the substrate specificity switch protein HpaC (42). It was previously shown that HpaC binds to translocon and effector proteins and to the conserved HrcV and HrcU proteins at the inner membrane, suggesting that it is involved in targeting proteins to the secretion apparatus (14). Here, we found that HpaC also interacts with HrcN. The ATPase might therefore provide a docking site for HpaC and thus promote secretion of HpaC-bound translocon proteins. However, the precise mechanisms underlying HrcN-dependent secretion of extracellular components of the secretion apparatus such as pilus and translocon proteins are not yet understood.
The model of the ATPase as the key energizer of the T3S system was recently challenged by the finding that T3S in S. enterica can occur, albeit at reduced efficiency, in the absence of both the ATPase FliI and its regulator FliH. FliI-FliH-independent protein secretion was substantially improved in the presence of point mutations in the conserved inner membrane proteins FlhA and FlhB, suggesting that the ATPase is dispensable for T3S (48, 55). It has therefore been proposed that progression of T3S substrates through the secretion apparatus depends on the PMF (48, 55, 72). In agreement with this hypothesis, in vitro T3S in the animal pathogenic bacteria S. enterica and Y. enterocolitica is inhibited by final CCCP concentrations of more than 10 μM (48, 55, 72). Notably, in X. campestris pv. vesicatoria a CCCP concentration of 1 μM is sufficient to prevent detectable in vitro secretion of the putative translocon protein HrpF. However, 1 μM CCCP also inhibits bacterial multiplication under secretion-permissive conditions. It therefore cannot be excluded that loss of in vitro T3S in the presence of CCCP is due to a general inhibitory effect of the protonophore on the bacterial metabolism.
In vitro T3S assays with a X. campestris pv. vesicatoria hrcN hrcL double deletion mutant strain revealed that secretion of HrpF is abolished in the absence of both HrcN and HrcL. This is in contrast to the case for the fliH fliI mutant of S. enterica and suggests that the ATPase is crucial for the activity of the T3S system from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria. The hrcLN mutant phenotype could not be reverted by introduction of a P24T point mutation in HrcU, although the equivalent mutation in the HrcU homolog FlhB from S. enterica substantially increased bacterial motility and T3S in the fliH fliI double deletion mutant (48). In future studies, it will therefore be interesting to investigate whether the contribution of different energy sources such as ATP and the PMF to T3S varies among plant and animal pathogenic bacteria.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to U. Bonas for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank M. Jordan for excellent technical assistance and C. Schubert for RNA isolation.
This work was supported by a grant from the Sonderforschungsbereich SFB 648 Molekulare Mechanismen der Informationsverarbeitung in Pflanzen to D.B.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 29 December 2008.
REFERENCES
- 1.Akeda, Y., and J. E. Galan. 2005. Chaperone release and unfolding of substrates in type III secretion. Nature 437911-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alegria, M. C., C. Docena, L. Khater, C. H. Ramos, A. C. da Silva, and C. S. Farah. 2004. New protein-protein interactions identified for the regulatory and structural components and substrates of the type III secretion system of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas axonopodis pathovar citri. J. Bacteriol. 1866186-6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allaoui, A., S. Woestyn, C. Sluiters, and G. R. Cornelis. 1994. YscU, a Yersinia enterocolitica inner membrane protein involved in Yop secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1764534-4542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Andrade, A., J. P. Pardo, N. Espinosa, G. Perez-Hernandez, and B. Gonzalez-Pedrajo. 2007. Enzymatic characterization of the enteropathogenic Escherichia coli type III secretion ATPase EscN. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 468121-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 1996. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
- 6.Auvray, F., A. J. Ozin, L. Claret, and C. Hughes. 2002. Intrinsic membrane targeting of the flagellar export ATPase FliI: interaction with acidic phospholipids and FliH. J. Mol. Biol. 318941-950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Berger, C. 2005. Ph.D. thesis. Martin-Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Germany.
- 8.Blaylock, B., K. E. Riordan, D. M. Missiakas, and O. Schneewind. 2006. Characterization of the Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion ATPase YscN and its regulator, YscL. J. Bacteriol. 1883525-3534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blocker, A., N. Jouihri, E. Larquet, P. Gounon, F. Ebel, C. Parsot, P. Sansonetti, and A. Allaoui. 2001. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri“needle complex”, a part of its type III secreton. Mol. Microbiol. 39652-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bonas, U., R. Schulte, S. Fenselau, G. V. Minsavage, B. J. Staskawicz, and R. E. Stall. 1991. Isolation of a gene-cluster from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria that determines pathogenicity and the hypersensitive response on pepper and tomato. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 481-88. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bonas, U., R. E. Stall, and B. Staskawicz. 1989. Genetic and structural characterization of the avirulence gene avrBs3 from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol. Gen. Genet. 218127-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Büttner, D., and U. Bonas. 2002. Port of entry—the type III secretion translocon. Trends Microbiol. 10186-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Büttner, D., D. Gürlebeck, L. D. Noël, and U. Bonas. 2004. HpaB from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria acts as an exit control protein in type III-dependent protein secretion. Mol. Microbiol. 54755-768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Büttner, D., C. Lorenz, E. Weber, and U. Bonas. 2006. Targeting of two effector protein classes to the type III secretion system by a HpaC- and HpaB-dependent protein complex from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol. Microbiol. 59513-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Büttner, D., D. Nennstiel, B. Klüsener, and U. Bonas. 2002. Functional analysis of HrpF, a putative type III translocon protein from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. J. Bacteriol. 1842389-2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Büttner, D., L. Noël, J. Stuttmann, and U. Bonas. 2007. Characterization of the non-conserved hpaB-hrpF region in the hrp pathogenicity island from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 201063-1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Canteros, B. I. 1990. Ph.D. thesis. University of Florida, Gainesville, FL.
- 18.Carter, A. P., W. M. Clemons, D. E. Brodersen, R. J. Morgan-Warren, B. T. Wimberly, and V. Ramakrishnan. 2000. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407340-348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Claret, L., S. R. Calder, M. Higgins, and C. Hughes. 2003. Oligomerization and activation of the FliI ATPase central to bacterial flagellum assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 481349-1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Coombes, B. K., and B. B. Finlay. 2005. Insertion of the bacterial type III translocon: not your average needle stick. Trends Microbiol. 1392-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cornelis, G. R. 2006. The type III secretion injectisome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4811-825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cornelis, G. R., C. Agrain, and I. Sorg. 2006. Length control of extended protein structures in bacteria and bacteriophages. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9201-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Daniels, M. J., C. E. Barber, P. C. Turner, M. K. Sawczyc, R. J. W. Byrde, and A. H. Fielding. 1984. Cloning of genes involved in pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris using the broad host range cosmid pLAFR1. EMBO J. 33323-3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Desvaux, M., M. Hebraud, I. R. Henderson, and M. J. Pallen. 2006. Type III secretion: what's in a name? Trends Microbiol. 14157-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Escolar, L., G. Van den Ackerveken, S. Pieplow, O. Rossier, and U. Bonas. 2001. Type III secretion and in planta recognition of the Xanthomonas avirulence proteins AvrBs1 and AvrBsT. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2287-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Feldman, M. F., and G. R. Cornelis. 2003. The multitalented type III chaperones: all you can do with 15 kDa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 219151-158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fenselau, S., and U. Bonas. 1995. Sequence and expression analysis of the hrpB pathogenicity operon of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria which encodes eight proteins with similarity to components of the Hrp, Ysc. Spa, and Fli secretion systems. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 8845-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ferris, H. U., Y. Furukawa, T. Minamino, M. B. Kroetz, M. Kihara, K. Namba, and R. M. Macnab. 2005. FlhB regulates ordered export of flagellar components via autocleavage mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 28041236-41242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ferris, H. U., and T. Minamino. 2006. Flipping the switch: bringing order to flagellar assembly. Trends Microbiol. 14519-526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Figurski, D., and D. R. Helinski. 1979. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 761648-1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gauthier, A., and B. B. Finlay. 2003. Translocated intimin receptor and its chaperone interact with ATPase of the type III secretion apparatus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1856747-6755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ghosh, P. 2004. Process of protein transport by the type III secretion system. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68771-795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Guttman, D. S., B. A. Vinatzer, S. F. Sarkar, M. V. Ranall, G. Kettler, and J. T. Greenberg. 2002. A functional screen for the type III (Hrp) secretome of the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Science 2951722-1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.He, S. Y., K. Nomura, and T. S. Whittam. 2004. Type III protein secretion mechanism in mammalian and plant pathogens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1694181-206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Huguet, E., K. Hahn, K. Wengelnik, and U. Bonas. 1998. hpaA mutants of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria are affected in pathogenicity but retain the ability to induce host-specific hypersensitive reaction. Mol. Microbiol. 291379-1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jones, J. D., and J. L. Dangl. 2006. The plant immune system. Nature 444323-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Knoop, V., B. Staskawicz, and U. Bonas. 1991. Expression of the avirulence gene avrBs3 from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is not under the control of hrp genes and is independent of plant factors. J. Bacteriol. 1737142-7150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Koebnik, R., A. Krüger, F. Thieme, A. Urban, and U. Bonas. 2006. Specific binding of the Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria AraC-type transcriptional activator HrpX to plant-inducible promoter boxes. J. Bacteriol. 1887652-7660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kousik, C. S., and D. F. Ritchie. 1998. Response of bell pepper cultivars to bacterial spot pathogen races that individually overcome major resistance genes. Plant Dis. 82181-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lavander, M., L. Sundberg, P. J. Edqvist, S. A. Lloyd, H. Wolf-Watz, and A. Forsberg. 2002. Proteolytic cleavage of the FlhB homologue YscU of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is essential for bacterial survival but not for type III secretion. J. Bacteriol. 1844500-4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lloyd, S. A., M. Norman, R. Rosqvist, and H. Wolf-Watz. 2001. Yersinia YopE is targeted for type III secretion by N-terminal, not mRNA, signals. Mol. Microbiol. 39520-532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lorenz, C., S. Schulz, T. Wolsch, O. Rossier, U. Bonas, and D. Büttner. 2008. HpaC controls substrate specificity of the Xanthomonas type III secretion system. PLoS Pathog. 4e1000094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Marlovits, T. C., T. Kubori, A. Sukhan, D. R. Thomas, J. E. Galan, and V. M. Unger. 2004. Structural insights into the assembly of the type III secretion needle complex. Science 3061040-1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ménard, R., P. J. Sansonetti, and C. Parsot. 1993. Nonpolar mutagenesis of the ipa genes defines IpaB, IpaC, and IpaD as effectors of Shigella flexneri entry into epithelial cells. J. Bacteriol. 1755899-5906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Minamino, T., T. Iino, and K. Kutsukake. 1994. Molecular characterization of the Salmonella typhimurium flhB operon and its protein products. J. Bacteriol. 1767630-7637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Minamino, T., and R. M. MacNab. 2000. FliH, a soluble component of the type III flagellar export apparatus of Salmonella, forms a complex with FliI and inhibits its ATPase activity. Mol. Microbiol. 371494-1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Minamino, T., and R. M. MacNab. 2000. Interactions among components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and its substrates. Mol. Microbiol. 351052-1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Minamino, T., and K. Namba. 2008. Distinct roles of the ATPase FliI and proton motive force in bacterial flagellar export. Nature 451485-488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Minamino, T., and A. P. Pugsley. 2005. Measure for measure in the control of type III secretion hook and needle length. Mol. Microbiol. 56303-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Müller, S. A., C. Pozidis, R. Stone, C. Meesters, M. Chami, A. Engel, A. Economou, and H. Stahlberg. 2006. Double hexameric ring assembly of the type III protein translocase ATPase HrcN. Mol. Microbiol. 61119-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Noël, L., F. Thieme, J. Gäbler, D. Büttner, and U. Bonas. 2003. XopC and XopJ, two novel type III effector proteins from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. J. Bacteriol. 1857092-7102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Noël, L., F. Thieme, D. Nennstiel, and U. Bonas. 2001. cDNA-AFLP analysis unravels a genome-wide hrpG-regulon in the plant pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol. Microbiol. 411271-1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Noël, L., F. Thieme, D. Nennstiel, and U. Bonas. 2002. Two novel type III system-secreted proteins of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria are encoded within the hrp pathogenicity island. J. Bacteriol. 1841340-1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Parsot, C., C. Hamiaux, and A. L. Page. 2003. The various and varying roles of specific chaperones in type III secretion systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 67-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Paul, K., M. Erhardt, T. Hirano, D. Blair, and K. T. Hughes. 2008. Energy source of flagellar type III secretion. Nature 451489-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pozidis, C., A. Chalkiadaki, A. Gomez-Serrano, H. Stahlberg, I. Brown, A. P. Tampakaki, A. Lustig, G. Sianidis, A. S. Politou, A. Engel, N. J. Panopoulos, J. Mansfield, A. P. Pugsley, S. Karamanou, and A. Economou. 2003. Type III protein translocase: HrcN is a peripheral ATPase that is activated by oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 27825816-25824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rossier, O., G. Van den Ackerveken, and U. Bonas. 2000. HrpB2 and HrpF from Xanthomonas are type III-secreted proteins and essential for pathogenicity and recognition by the host plant. Mol. Microbiol. 38828-838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rossier, O., K. Wengelnik, K. Hahn, and U. Bonas. 1999. The Xanthomonas Hrp type III system secretes proteins from plant and mammalian pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 969368-9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sorg, I., S. Wagner, M. Amstutz, S. A. Muller, P. Broz, Y. Lussi, A. Engel, and G. R. Cornelis. 2007. YscU recognizes translocators as export substrates of the Yersinia injectisome. EMBO J. 263015-3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Szurek, B., O. Rossier, G. Hause, and U. Bonas. 2002. Type III-dependent translocation of the Xanthomonas AvrBs3 protein into the plant cell. Mol. Microbiol. 4613-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Thieme, F., R. Koebnik, T. Bekel, C. Berger, J. Boch, D. Buttner, C. Caldana, L. Gaigalat, A. Goesmann, S. Kay, O. Kirchner, C. Lanz, B. Linke, A. C. McHardy, F. Meyer, G. Mittenhuber, D. H. Nies, U. Niesbach-Klosgen, T. Patschkowski, C. Ruckert, O. Rupp, S. Schneiker, S. C. Schuster, F. J. Vorholter, E. Weber, A. Puhler, U. Bonas, D. Bartels, and O. Kaiser. 2005. Insights into genome plasticity and pathogenicity of the plant pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria revealed by the complete genome sequence. J. Bacteriol. 1877254-7266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Thomas, J., G. P. Stafford, and C. Hughes. 2004. Docking of cytosolic chaperone-substrate complexes at the membrane ATPase during flagellar type III protein export. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1013945-3950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Vieira, J., and J. Messing. 1987. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1533-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Walker, J. E., M. Saraste, M. J. Runswick, and N. J. Gay. 1982. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1945-951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Weber, E., C. Berger, U. Bonas, and R. Koebnik. 2007. Refinement of the Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria hrpD and hrpE operon structure. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 20559-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Weber, E., T. Ojanen-Reuhs, E. Huguet, G. Hause, M. Romantschuk, T. K. Korhonen, U. Bonas, and R. Koebnik. 2005. The type III-dependent Hrp pilus is required for productive interaction of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria with pepper host plants. J. Bacteriol. 1872458-2468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Wengelnik, K., and U. Bonas. 1996. HrpXv, an AraC-type regulator, activates expression of five of the six loci in the hrp cluster of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. J. Bacteriol. 1783462-3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wengelnik, K., C. Marie, M. Russel, and U. Bonas. 1996. Expression and localization of HrpA1, a protein of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria essential for pathogenicity and induction of the hypersensitive reaction. J. Bacteriol. 1781061-1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wengelnik, K., O. Rossier, and U. Bonas. 1999. Mutations in the regulatory gene hrpG of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria result in constitutive expression of all hrp genes. J. Bacteriol. 1816828-6831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wengelnik, K., G. Van den Ackerveken, and U. Bonas. 1996. HrpG, a key hrp regulatory protein of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is homologous to two-component response regulators. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 9704-712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wilharm, G., S. Dittmann, A. Schmid, and J. Heesemann. 2007. On the role of specific chaperones, the specific ATPase, and the proton motive force in type III secretion. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 29727-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wilharm, G., V. Lehmann, K. Krauss, B. Lehnert, S. Richter, K. Ruckdeschel, J. Heesemann, and K. Trulzsch. 2004. Yersinia enterocolitica type III secretion depends on the proton motive force but not on the flagellar motor components MotA and MotB. Infect. Immun. 724004-4009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Yip, C. K., T. G. Kimbrough, H. B. Felise, M. Vuckovic, N. A. Thomas, R. A. Pfuetzner, E. A. Frey, B. B. Finlay, S. I. Miller, and N. C. Strynadka. 2005. Structural characterization of the molecular platform for type III secretion system assembly. Nature 435702-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Yip, C. K., and N. C. Strynadka. 2006. New structural insights into the bacterial type III secretion system. Trends Biochem. Sci. 31223-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zarivach, R., M. Vuckovic, W. Deng, B. B. Finlay, and N. C. Strynadka. 2007. Structural analysis of a prototypical ATPase from the type III secretion system. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14131-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]