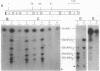
Abstract
Nod factors are signal molecules produced by Azorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, and Rhizobium species that trigger nodule formation in leguminous host plants. The backbone of Nod factors consists of a beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine oligosaccharide from which the N-acetyl group at the nonreducing end is replaced by a fatty acid. The nodABC gene products are necessary for backbone biosynthesis. By incubation of cell extracts from Azorhizobium caulinodans with radioactive uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine, Nod factor precursors were identified and characterized as beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosamine oligosaccharides. By analysis of different nod gene mutants and by expression of nodC in Escherichia coli, the N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity was ascribed to the NodC protein. The results suggest that the first step in biosynthesis of Nod factors is the assembly of the oligosaccharide chain.
Full text
PDF

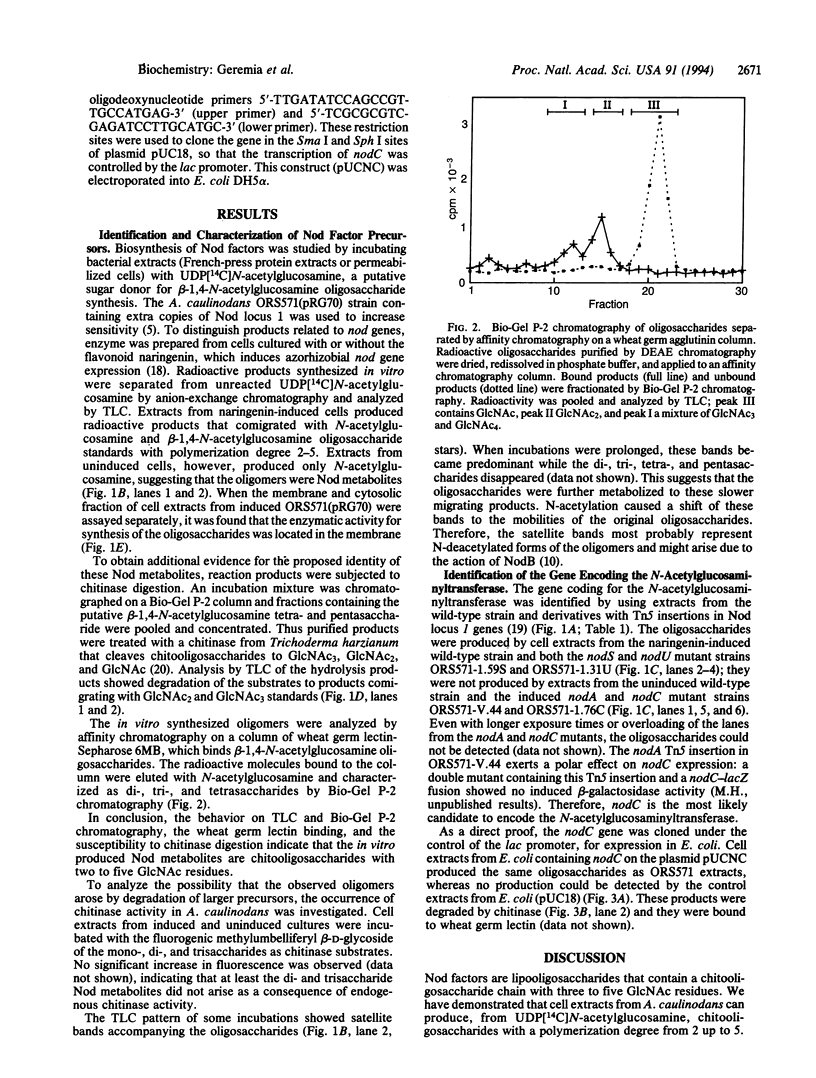


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson E. M., Long S. R. Homology of Rhizobium meliloti NodC to polysaccharide polymerizing enzymes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):439–442. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E. CSD2, CSD3, and CSD4, genes required for chitin synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the CSD2 gene product is related to chitin synthases and to developmentally regulated proteins in Rhizobium species and Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1764–1776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. J., Heidstra R., Spaink H. P., Hartog M. V., Meijer E. A., Hendriks T., Schiavo F. L., Terzi M., Bisseling T., Van Kammen A. Rhizobium Lipooligosaccharides Rescue a Carrot Somatic Embryo Mutant. Plant Cell. 1993 Jun;5(6):615–620. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellé F., Rosenberg C., Dénarié J. The Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, and Azorhizobium NodC proteins are homologous to yeast chitin synthases. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):443–446. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Rhizobium--plant signal exchange. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):655–660. doi: 10.1038/357655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen D., Mergaert P., Geremia R. A., Goormachtig S., Van Montagu M., Holsters M. Identification of nodSUIJ genes in Nod locus 1 of Azorhizobium caulinodans: evidence that nodS encodes a methyltransferase involved in Nod factor modification. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goethals K., Gao M., Tomekpe K., Van Montagu M., Holsters M. Common nodABC genes in Nod locus 1 of Azorhizobium caulinodans: nucleotide sequence and plant-inducible expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):289–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00261190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Röhrig H., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Schell J. Rhizobium NodB protein involved in nodulation signal synthesis is a chitooligosaccharide deacetylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):625–629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Kondorosi E., Kondorosi A., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nod C of Rhizobium meliloti in Escherichia coli: role of the nod C gene product in nodulation. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2425–2430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Transmembrane orientation and receptor-like structure of the Rhizobium meliloti common nodulation protein NodC. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):583–588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Roth L. E., Stacey G. Immunogold localization of the NodC and NodA proteins of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4583–4588. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4583-4588.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerouge P., Roche P., Faucher C., Maillet F., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):781–784. doi: 10.1038/344781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergaert P., Van Montagu M., Promé J. C., Holsters M. Three unusual modifications, a D-arabinosyl, an N-methyl, and a carbamoyl group, are present on the Nod factors of Azorhizobium caulinodans strain ORS571. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1551–1555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. P., Relić B., Talmont F., Lewin A., Promé D., Pueppke S. G., Maillet F., Dénarié J., Promé J. C., Broughton W. J. Broad-host-range Rhizobium species strain NGR234 secretes a family of carbamoylated, and fucosylated, nodulation signals that are O-acetylated or sulphated. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Dec;6(23):3575–3584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P., Debellé F., Maillet F., Lerouge P., Faucher C., Truchet G., Dénarié J., Promé J. C. Molecular basis of symbiotic host specificity in Rhizobium meliloti: nodH and nodPQ genes encode the sulfation of lipo-oligosaccharide signals. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1131–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90290-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan J., Carlson R. W., Spaink H. P., Bhat U. R., Barbour W. M., Glushka J., Stacey G. A 2-O-methylfucose moiety is present in the lipo-oligosaccharide nodulation signal of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8789–8793. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultze M., Quiclet-Sire B., Kondorosi E., Virelizer H., Glushka J. N., Endre G., Géro S. D., Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti produces a family of sulfated lipooligosaccharides exhibiting different degrees of plant host specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):192–196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Sheeley D. M., van Brussel A. A., Glushka J., York W. S., Tak T., Geiger O., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N., Lugtenberg B. J. A novel highly unsaturated fatty acid moiety of lipo-oligosaccharide signals determines host specificity of Rhizobium. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):125–130. doi: 10.1038/354125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Cruz J., Hidalgo-Gallego A., Lora J. M., Benitez T., Pintor-Toro J. A., Llobell A. Isolation and characterization of three chitinases from Trichoderma harzianum. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):859–867. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Brussel A. A., Bakhuizen R., van Spronsen P. C., Spaink H. P., Tak T., Lugtenberg B. J., Kijne J. W. Induction of pre-infection thread structures in the leguminous host plant by mitogenic lipo-oligosaccharides of Rhizobium. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):70–72. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5066.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]