Abstract
Hoxb8 mutant mice exhibit compulsive grooming and hair removal dysfunction similar to humans with the OCD-spectrum disorder, trichotillomania. Since, in the mouse brain, the only detectable cells that label with Hoxb8 cell lineage appear to be microglia, we suggested that defective microglia cause the neuropsychiatric disorder. Does the Hoxb8 mutation in microglia lead to neural circuit dysfunctions? We demonstrate that Hoxb8 mutants contain corticostriatal circuit defects. Golgi staining, ultra-structural, and electrophysiological studies of mutants reveal excess dendritic spines, pre- and post-synaptic structural defects, long-term potentiation and miniature postsynaptic current defects. Hoxb8 mutants also exhibit hyperanxiety and social behavioral deficits similar to mice with neuronal mutations in Sapap3, Slitrk5 and Shank3, reported models of OCD and autism spectrum disorders (ASD’s). Long-term treatment of Hoxb8 mutants with fluoxetine, a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), reduces excessive grooming, hyperanxiety and social behavioral impairments. These studies provide linkage between the neuronal defects induced by defective Hoxb8-microglia, and neuronal dysfunctions directly generated by mutations in synaptic components that result in mice that display similar pathological grooming, hyperanxiety and social impairment deficits. Our results shed light on Hoxb8 microglia driven circuit-specific defects and therapeutic approaches that will become essential to developing novel therapies for neuropsychiatric diseases such as OCD and ASD’s with Hoxb8-microglia being the central target.
Introduction
Grooming is an evolutionarily well-conserved innate behavior of rodents and other mammalian species that is essential for survival. The grooming circuit induces hierarchically ordered set of actions, which in Hoxb8 mutants are characterized by compulsive excessive grooming, hair removal and lesions at the sites of overgrooming1–2, 6–7,37. Hoxb8 mutant analysis suggested that defective microglia underlie the behavioral deficits7. How Hoxb8 gene disruption alters neural circuit, induces behavioral dysfunctions and cause neuronal pathology has neither been addressed nor has such ensuing neural damage been previously defined. Functional imaging in humans8–9,53 and genetic mutational studies in SAPAP3, Slitrk5 and Shank33–5 mutant mice has pointed to corticostriato-thalamo-cortical circuit defects as a basis for OCD-pathogenesis10–13,15,22.
To address the role of Hoxb8 gene function in neuronal pathology we examined neuronal integrity of Hoxb8 mutants and evaluated corticostriatal structural and functional synaptic impairments. We further demonstrate that Hoxb8 mutants exhibit anxiety and social interaction behavioral dysfunction in addition to pathological grooming. These behaviors in mutants are rescued by long-term fluoxetine treatment similar to humans16. This work ties together Hoxb8 gene induced neural pathology with the neural SAPAP3, SlitrK5 and Shank3 mutant3–5 mice models of OCD and ASD. We infer that the Hoxb8 gene in the Hoxb8 cell lineage normally modulate the corticostriatal circuit and controls grooming behavior. The absence of Hoxb8 function in microglia leads to aberrant modulation and physical impairment of these neural circuits leading to OCD-like compulsive behavior in mice.
Material and Methods
All experiments were approved by the The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), University of Utah.
Electron microscopy (EM)
Tissues were fixed (24h) in 1% formaldehyde, 2.5% glutaraldehyde, 3% sucrose, and 1 mM MgSO4 in 0.1 M cacodylate buffer, osmicated (60 min) in 0.5% OsO4 in 0.1 M cacodylate buffer, processed in maleate buffer for en bloc staining with uranyl acetate, and processed for resin embedding52. 60–90 nm sections were mounted onto Formvar® films and imaged (GATAN Ultrascan 4000) at 80 KeV (JEOL-JEM-1400-EM, 5,000x magnification and nanometer resolution) from 1X1X1 mm3 tissue volume. IR-tools mosaicked TEM data and corrected aberrations and electron-optical distortions after mosaic construction on individual tiles. All statistics used for EM analysis per sample per genotype and grouped analysis is summarized in Supplementary table 2. Sample size for data analysis was determined by power analysis and literature3, 5. Spine and synapse quantification was performed by an experimenter blinded to genotype and the brain region.
Slice electrophysiology
Slices from isolated brains were placed in ice-cold (4°C) oxygenated Sucrose-based Artificial Cerebral Spinal Fluid (ACSF) (95% O2/5% CO2) containing (in mM): Sucrose (180.0), KCl (3.0), Na2PO4 (1.4), MgSO4 (3.0), NaHCO3 (26.0), glucose (10.0), and CaCl2 (0.5). ACSF contained (in mM): NaCl (126.0), KCl (3.0), Na2PO4 (1.4), MgSO4 (1.0), NaHCO3 (26.0), glucose (10.0), and CaCl2 (2.5) (pH 7.3–7.4, 290–300 mOsm).
Corticostriatal LTP
Field excitatory post-synaptic potentials (fEPSPs) were recorded (30–31°C) from slices perfused with oxygenated ACSF (2.5 mL/min). Concentric bipolar stimulating electrodes were placed in dorsomedial striatum (DMS) at its interface with corpus callosum17–19. Recording microelectrodes were placed near (250 µm) stimulating electrodes in DMS. fEPSPs were evoked with 100 µs stimuli (1–40 V, stimulation strength 50% of minimal and maximal fEPSP amplitudes).
Whole-cell recordings
Acute brain slices (300 µm thickness) were cut and recovered (45–60 min) in a submerged chamber (31° C) with ACSF (in mM) 125 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 2.0 CaCl2, 1 MgCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 25 NaHCO3 and 15 D-glucose (pH 7.4, 300–310 mOsm) and perfused with oxygenated (95% O2/5% CO2) ACSF at 2 ml/min at 31° C. Internal solution was (in mM) 107 CsMeSO3, 10 CsCl, 3.7 NaCl, 5 TEA-Cl, 20 HEPES, 0.2 EGTA, 5 lidocaine, 4 ATP-magnesium and 0.3 GTP-sodium salt (pH 7.3, 298–301 mOsm). Data were sampled at 10 kHz with low- and high-pass filter set to 1 kHz and 3 Hz. Sample size for data analysis was determined by power analysis and literature. Sample size for all electrophysiological experiments was determined based on the literature3–5, 17–20.
Grooming behavior
Grooming assay used vibration sensitive platforms and laboras software for data analysis. Parameters extracted from grooming assay is shown in Supplementary table 3.
Elevated plus maze, open field and light-dark test
Anxiety was tested in plus maze (5X35X 15X40 cm), open field (40X40X35 cm) and light-dark arena (40X40X35 cm). Mouse movement was tracked using ANY-Maze software. Parameters extracted from anxiety assay are shown in Supplementary table 4.
Three-Chambered social assay
30 minute Social assay was performed in three-chambered compartment. Test mouse was placed in center while intruder mouse in right with left chamber being empty. After placing test mouse at the center for 10-minute habituation, left and right doors were opened for test mouse to interact with empty or intruder chamber. Test mice movements were tracked using Laboras.
Fluoxetine treatment
Mice that underwent fluoxetine or saline treatment were acclimated in home cages for > 7 days. WT and mutants were intraperitoneally injected (5 mg/kg) with fluoxetine once a day for one day, one, five and thirteen weeks. Sample size for all behavioral and drug treatment conditions were determined by literature 3–5 and power analysis.
All behavioral experiments were conducted blindly with the experimenter blind to genotype and drug treatment conditions.
Results
Hoxb8 mutants show altered pre and postsynaptic structures
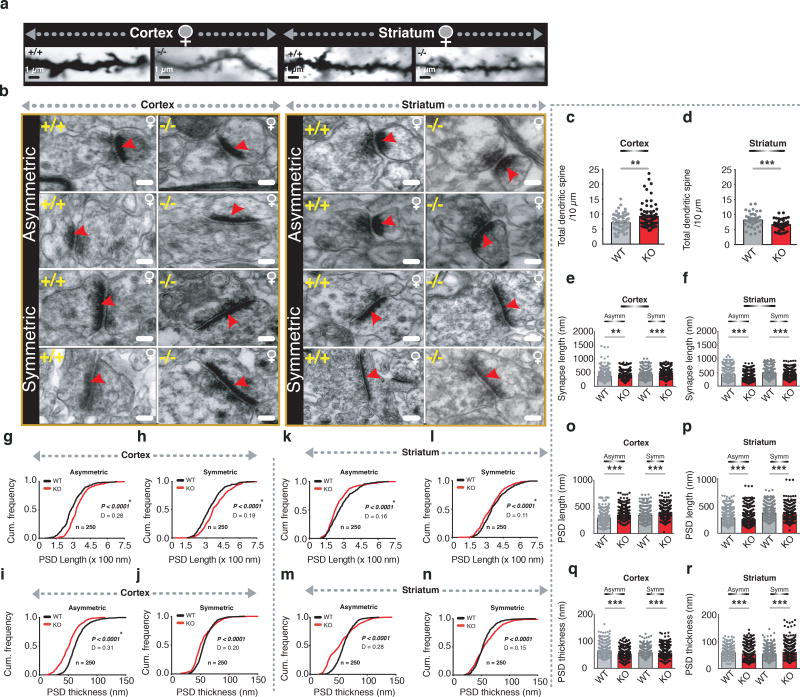
We first determined if Hoxb8 mutants show altered corticostriatal synapse morphology similar to those shown to be defective in SAPAP3 and Slitrk5 mutant mice, well studied mouse models of OCD. We measured dendritic spine density in frontal cortical and striatal neurons using golgi-cox staining. Mutants exhibit significantly higher spine density in frontal cortex but lower density in striatum (Fig. 1a, 1c–1d) implying distinct effects of Hoxb8 mutation on spine maintenance within cortex and striatum. Spines averaged per mouse reproduced the average value (Supplementary table 1d–1e). To identify the dendritic spine density changes in OCD specific striatal brain regions, as opposed to global spine density changes in the entire striatum, we quantified spine density from dorso and ventro-medial striatum of WT and Hoxb8 mutants. Spine density in Hoxb8 mutants increased significantly in both dorso- and ventro-medial striatal regions (Supplementary Fig. 1c, 1e, 1d, 1f) without affecting spine density from visual cortex (Supplementary Fig. 1b, 1g), a control brain region that is independent of OCD circuit. These data suggests that distinct striatal sub-regions show diverse dendritic spine phenotype.
Figure 1. Altered cortical and striatal synapses in Hoxb8 mutants.
a) Representative dendritic spines from 6 months old WT and Hoxb8 female mutant mice from frontal cortical and dorsal striatal regions. Scale bar: 1 µm. b) Representative electron microscopic images of cortical-asymmetric, cortical-symmetric, striatal-asymmetric and striatal-symmetric synapses from 6 months old WT and Hoxb8 mutant brains and visualized using Viking software 52, 54. Scale bar: 100 nm c, d) Significantly increased cortical (P=0.0034, F=9.118, 28 WT and 29 mutant neurons, 2–3 healthy dendrites per neuron) (c) but decreased (d) striatal spine density (P=0.001, F=10.488, 13 WT and 18 mutant neurons, 2–3 healthy dendrites per neuron) in female Hoxb8 mutants (3 litters per group, 8 months old mice) using golgi staining (Fd Neurotechnologies inc). ‘n’ represents the total dendrites analyzed per genotype per brain region. e, f) Bar plot displaying significantly increased synapse length at cortical asymmetric (P=0.00012, F=14.8310) and symmetric (P<0.0001, F=19.8205) (e) but a significantly decreased striatal asymmetric (P<0.0001, F=138.0321) and symmetric synapses (P<0.0001, F=37.9242) (f). (g–j) Cumulative probability plot demonstrating a significant rightward shift in the PSD length in Hoxb8 mutants compared to WT mice (g, P<0.0001, D=0.2815; h, P<0.0001, D=0.1992) but a significant leftward shift in PSD thickness for cortical asymmetric and cortical symmetric synapses (i, P<0.0001, D=0.3187; j, P<0.0001, D=0.2045). (k–n) A contrasting significant decrease (leftward shift) within striatal-asymmetric (k, P<0.0001, D=0.1595) and symmetric (l, P<0.0001, D=0.1156) synapses for PSD length and PSD thickness (m, P<0.0001, D=0.28; n, P<0.0001, D=0.15). (o–p) Bar graph representation of significantly increased PSD length at cortical-asymmetric (P<0.0001, F=93.2869) and cortical-symmetric (P<0.0001, F=53.6979) (o) synapses of Hoxb8 mutants but a contrasting decrease within striatal-asymmetric (p) (P<0.0001, F= 22.1849) and striatal-symmetric synapses (p) (P<0.0001, F= 18.1742). (q–r) Bar graph representation of significantly decreased PSD thickness at cortical-asymmetric (P<0.0001, F=192.3888) and cortical-symmetric (P=0.014, F=5.9328) (q) synapses of Hoxb8 mutants but a contrasting increase within striatal-asymmetric (P<0.0001, F=30.8782) and striatal-symmetric (P<0.0001, F=17.4861) (r) synapses. Red arrow represents post-synaptic density in individual synapse. All analysis was conducted on WT and Hoxb8 mutant female mice brains. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s posthoc test (c–f, o–r). Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, (g-n).
To identify whether the Hoxb8 mutation affects synaptic structures, we examined asymmetric (excitatory) and symmetric (inhibitory) cortical and striatal synapses using electron microscopy (EM). Representative synapses are displayed and modeled (Fig. 1b,Supplementary Fig. 3a). At asymmetric and symmetric cortical synapses, synaptic length increased significantly compared to WT (Fig. 1e, Supplementary Fig. 2m–2n). Contrastingly, synaptic length decreased significantly at striatal asymmetric and symmetric synapses (Fig. 1f, Supplementary Fig. 2o–2p) suggesting defective but contrasting cortical and striatal structural synapse in mutants. To determine post-synaptic alteration, we quantified postsynaptic density (PSD) length and thickness. PSD length in mutants shifted rightward (Fig. 1g–1h) in cumulative distribution and was significantly longer at asymmetric and symmetric cortical synapses (Fig. 1o). Contrastingly, PSD thickness of asymmetric and symmetric cortical synapses of mutants shifted leftward in cumulative distribution (Fig. 1i–1j) and were significantly smaller than WT (Fig. 1q). Synaptic expansion in mutants concurrently increased pre-synaptic diameter at asymmetric and symmetric synapses, but expanded postsynaptic diameter only at asymmetric synapses (Supplementary Fig. 3b–3e, 3j, 3l, Supplementary table 1). To identify if synaptic structural changes affect active zone, we quantified active zone length and thickness at cortical synapses. Mutants exhibit longer active zones at asymmetric and symmetric synapses (Supplementary-Fig. 2a–2b, 2i, Supplementary Table 1). Changes in the active zone thickness were insignificant at either of the synapses (Supplementary Fig. 2k) although cumulative distribution showed statistical significance for symmetric synapses (Supplementary-Fig. 2d, 2c, Supplementary Table 1). Together the data imply that the Hoxb8 mutation affects the cortical pre- and post-synapses and results in synaptic expansion at asymmetric and symmetric synapses. Because we detected synaptic expansion within frontal cortical synapses, we asked if such structural alteration result in more or stronger synapses? We analyzed total excitatory and inhibitory synapses within frontal cortex and observed that mutants exhibit significantly increased mono- and total asymmetric but not symmetric synapses (Supplementary Fig. 2q–t) implying increased synaptic density in mutants in consistence with synaptic structural modification.
In contrast to cortex, Hoxb8 mutants showed a significant reduction of PSD length (Fig. 1p) and shifted cumulative distribution leftward at asymmetric (Fig. 1k) and symmetric (Fig. 1l) striatal synapses. PSD thickness of asymmetric and symmetric striatal synapses in mutants was significantly greater than WT (Fig. 1r) and shifted cumulative distribution rightward (Fig. 1m–1n). Synaptic contraction concurrently reduced pre and postsynaptic diameter with leftward shifting of cumulative distribution (Supplementary-Fig. 3f–3i, 3k, 3m, Supplementary Table 1). Similar to pre- and postsynaptic contraction, mutants exhibit smaller active zones at asymmetric and symmetric synapses (Supplementary-Fig. 2e–2f, 2j, Supplementary Table 1). Contrast to cortex, active zone thickness shrunk at asymmetric but expanded significantly at symmetric striatal synapses (Supplementary Fig. 2g–2h, 2l, Supplementary Table 1) indicating that Hoxb8 mutation affects striatal and cortical synapses differentially (Supplementary-Table 1c, Supplementary Table 2). Synaptic analysis revealed a significant increase in mono and total synapses at asymmetric excitatory but reduced mono and total synapses at symmetric synapses (Supplementary Fig. 2u–2x) in mutants consistent with the synaptic structural modification at cortical and striatal synapses in Hoxb8 mutants leading to an increased excitation at the corticostriatal circuit as has been reported for SAPAP3, Slitrk5 and Shank3 mutant mice3–5.
Altered CNQX-insensitive long-term potentiation and miniature excitatory currents in Hoxb8 mutants
We investigated whether altered pre- and postsynaptic structure observed in frontal cortex and striatum affected corticostriatal neurotransmission in Hoxb8 mutants. The input-output (IO) curves, slope normalized to peak response, field potential amplitudes and paired-pulse ratio at striatal synapses revealed insignificant difference between mutant and WT slices (Supplementary Fig. 4a–4c, Fig. 2a) in response to layer 5/6 cortical fiber stimulation implying that the electrophysiological properties and short-term plasticity is intact in mutants.
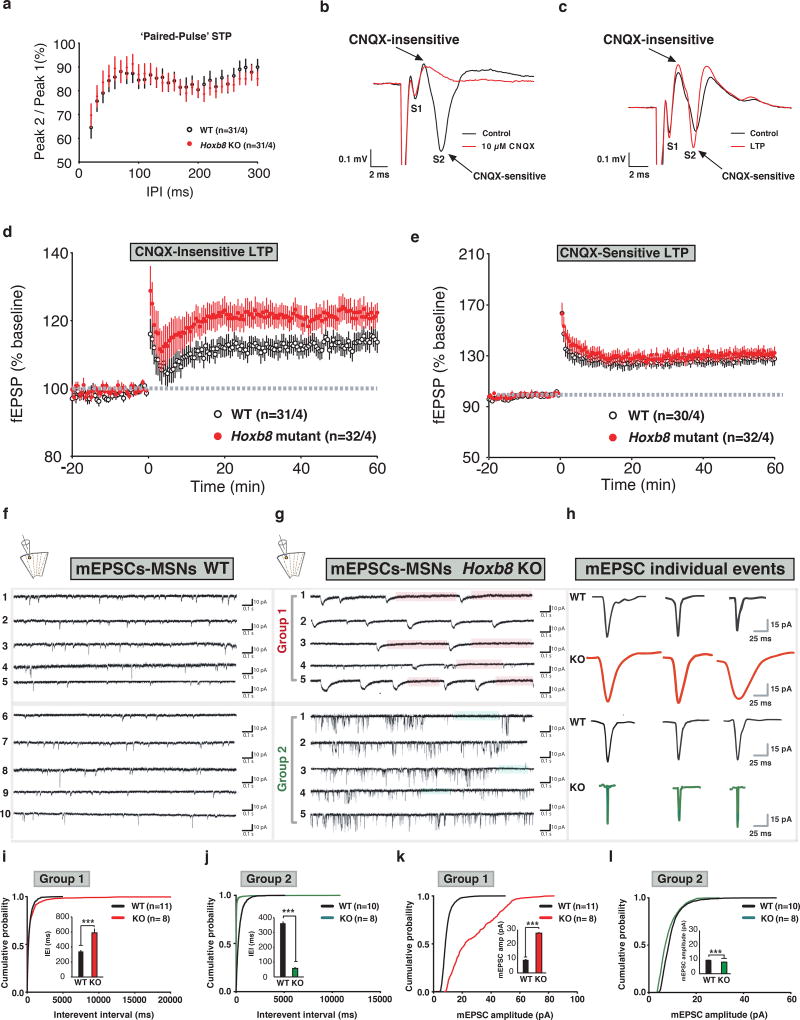
Figure 2. Altered CNQX independent form of LTP and miniature EPSCs in Hoxb8 mutants at corticostriatal synapses.
a) Paired-pulse ratio is unchanged in mutants (P=0.3453, F (28, 1680)=1.086 for interaction; P<0.0001, F (28,1680)=10.09 for interpulse interval, P=0.9560, F(1, 60)=0.003074 for genotype; P<0.0001, F(60,1680)=76.89 for subjects matching). Paired-pulse ratio of the fEPSP amplitudes was assessed using inter-pulse intervals between 20–300 ms in 10 ms intervals. Single stimuli were given to slices every 30 s for a 30 min to collect baseline. Representative traces and measurements are the average from five consecutive traces. b) Representative trace of field potentials in ±CNQX condition (black and red trace). S1, non-synaptic and S2, synaptically mediated component. Overlaid traces show the sensitivity of S1 and S2 component to CNQX. c) Overlaid trace of field potential recording under control (black) and LTP (red) condition showing S1 and S2 components. Scale bar, 0.1mV (Y-axis) and 2 ms (X-axis). d) Increased CNQX-insensitive LTP for WT (black) and mutants (red) (P=0.1665, F (60, 3300)=1.177 for interaction; P=0.0014, F(60, 3300)=1.642 for interpulse interval, P=0.0378, F(1, 55)=4.531 for genotype; P<0.0001, F (55, 3300) = 524.5 for matched subjects). LTP was induced by high frequency stimulation (1 second/100 Hz). Low frequency stimulation was resumed for 60 min to quantify LTP relative to baseline. e) Normal CNQX-sensitive LTP for WT (black) and mutants (red) (P=0.9477, F(60, 3060)=0.7213 for interaction; P=0.0316, F(60, 3060)=1.371 for time; P=0.558, F(1, 51)=0.3471 for genotype and P<0.0001, F(51, 3060)=476.7 for matched subjects, Two-way ANOVA repeated measures). Significance was determined at P<0.05. Data were excluded if the slope of fEPSPs during the 30 min baseline changed by >20%. f, g) AMPA receptor mediated mEPSC recording traces at −70 mV from dorsomedial striatal MSNs from parasiggital corticostriatal acute brain slices for WT (left) and Hoxb8 mutants (n=3 mice per genotype, 3 week old) isolated in the presence of TTX (1 µM), DL-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (50 µM), D-Serine (10 µM), Picrotoxin (100 µM) and Gabazine (5 µM) to block action potential, NMDA, GABA and GABAA receptors, respectively in whole cell voltage clamp recording configuration. Based on kinetics, the electrophysiological property of mEPSC events such as decay time and frequency, the responses from Hoxb8 mutants were classified into group 1 and 2. Orange and green bars on the traces represent time periods where no mEPSC activity was detected. Cartoon on the top shows the location of pipette positioning and recording within striatum h) mEPSC individual representative events for WT and Hoxb8 mutants from group 1 and group 2 type of MSN neuronal responses. The amplitude varied among individual events. Small, medium and large amplitude events were recorded and analyzed. (i–l) Cumulative probability plot of WT and Hoxb8 mutants showing rightward shift in the curve for Hoxb8 mutants for inter-event interval and mEPSC amplitudes for group 1 (i, P=0.002, D= 0.08375; P=0.00029, F=13.18906 for inset; k, P<0.0001, D=0.6917; P<0.0001, F=2654.712 for inset) and group 2 neurons (j, P<0.0001, D=0.7023; P<0.0001, F=949.241; l, P<0.0001, D=0.2040; P<0.0001, F=111.279 for inset). Inset represents bar graph from the same data set. ‘n’ represents the number of neurons patched per experimental group obtained from 3 WT and 3 Hoxb8 mutants. Atleast 100 events were sampled per neuron. Series and input resistance were monitored continuously and neuronal recordings were discarded if these parameter changed by > 20%. All experiments were conducted blindly in which the experimenter was unaware of the electrophysiological outcome of different cell types within dorsal striatum. mEPSC’s were analyzed using Minianalysis Synaptosoft software. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s posthoc test for bar graphs, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, (i–l). 6 months old WT and Hoxb8 mutant brain slices were used for the slice electrophysiological experiments.
To probe presynaptic plasticity, population spike responses were measured in dorsal striatum. Single pulse layer 5/6 cortical stimulation evoked a population spike that was dependent on synaptic glutamate release and postsynaptic α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPA)/kainate receptors17. Population spike consisted of non-synaptic (S1, source current) presynaptic component and synaptically mediated postsynaptic component (S2, sink current)17–19, 23 (Fig. 2b–2c). Because of non-laminar striatal organization, sink and source currents a) overlap in space b) arise from action potentials with shorter latency c) are- CNQX-insensitive and interchangeable measures of presynaptic depolarization.
In control experiments, CNQX, (AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist) blocked the S2 but not S1 component (Fig. 2b) indicating that the action potential dependent component is CNQX-sensitive (S2), while the independent component is CNQX-insensitive (S1). To investigate whether mutants show changes in S2 versus S1, tetanic stimulation was applied to DMS and LTP was measured. Strikingly, the S1 increased significantly in mutants compared to WT (Fig. 2d) without affecting the S2 (Fig. 2e) suggesting that the loss of the Hoxb8 gene affects CNQX-independent (cortical driven) but not CNQX-dependent (intra-striatal) LTP. S1 versus S2 field potential amplitudes did not differ significantly (Supplementary Fig. 4d) implying that the postsynaptic striatal output is smaller despite presynaptic changes consistent with the reduced spine density, synapse and PSD length of mutants (Fig. 1d, 1f, 1p) at striatal synapses analyzed.
Because cortical and striatal spine density and PSD morphology was altered, we questioned if electrophysiological signature of such synaptic change exist in DMS. We recorded AMPA-receptor mediated excitatory miniature evoked postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) from dorsal MSNs. Two distinct mEPSC types were detected in MSN’s of mutants that were distinguishable by response kinetics and decay time and categorized into slow (Group 1) and fast (Group 2) miniature events (Fig. 2g–2h, Supplementary Fig. 4f). Representative events are displayed in Fig. 2h. Group 1 MSNs of mutants exhibit significantly longer inter-event interval (IEI) with higher amplitudes (Fig. 2g, 2i, 2k) while group 2 MSNs showed significantly reduced IEI and mEPSC amplitudes relative to WT mice (Fig. 2g, 2j, 2l) implying that the probability of the presynaptic neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic AMPA receptors might be affected in opposite way. These effects were prominent when rise and decay times (Supplementary Fig. 4g–j), mEPSC charge, event half-width (Supplementary Fig. 4k–n) and frequency (Supplementary Fig. 5a–5b) were analyzed. The relationship between a) mEPSC amplitude and 10–90% rise time (Supplementary Fig. 5c–5d), b) amplitude and average rise rate (Supplementary Fig. 5e–5f), and c) event half width and 10–90% rise time (Supplementary Fig. 5g–5h), were distinguishable between WT and mutants. These data imply that mEPSC events of MSNs are affected in mutants at single neuronal level.
Hoxb8 mutants show impaired grooming, anxiety and social behaviors
To determine the role of Hoxb8 mutation in grooming, we used 24-hour automatic laboras platform containing sensitive vibration detectors to detect grooming and non-grooming behaviors20. Reproducibly6,7, laboras detected significantly higher self-grooming behavior in mutants compared to WT mice (Fig. 3a, Supplementary Table 3–4).
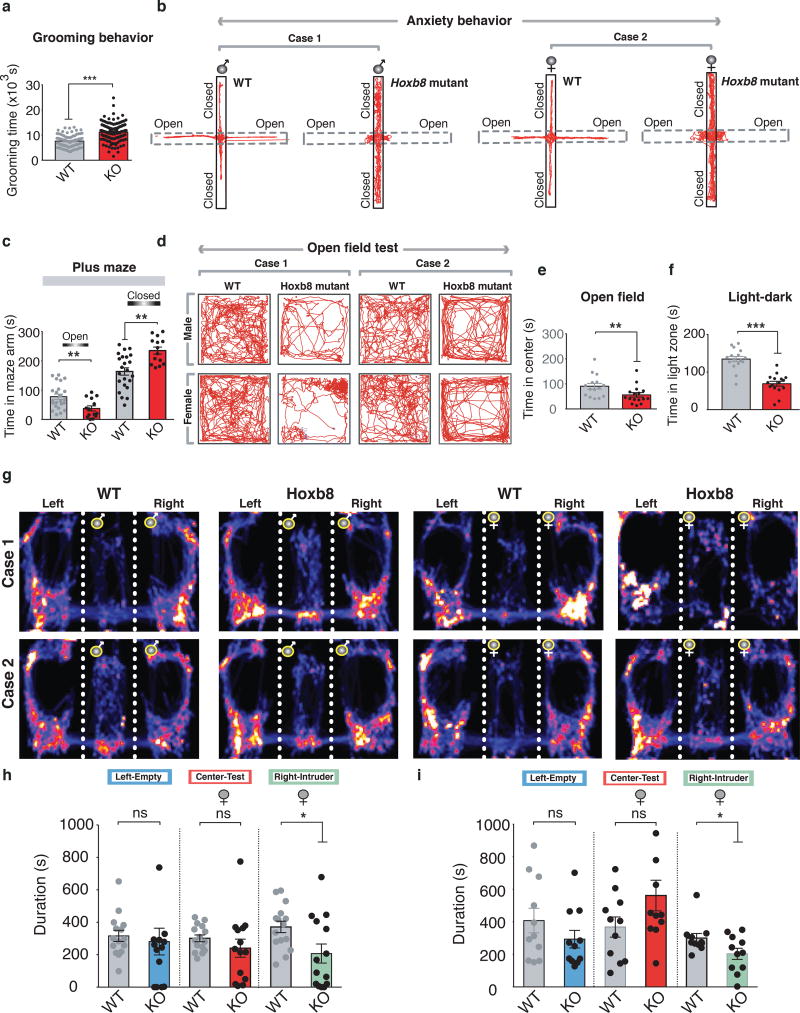
Figure 3. Altered Grooming, anxiety and social behaviors in Hoxb8 mutants.
a) Mutants show increased grooming (P<0.0001, F=59.115628) in 24 hour grooming assay as compared to WT mice (4–12 months old). b) Representative track plots of male WT, male mutants, female WT and female mutants in 5 minute elevated plus maze test under ambient light conditions. Note the movement of mutants pertained to closed as compared to open chamber. c) Hoxb8 mutants (6–8 months old) spend reduced time in open (P=0.00474, F=9.10139) and increased time in closed arm (P=0.0005, F=14.7216) (left panel). d) Representative track plots of male WT and male mutant (upper panel), female WT and female mutant (lower panel) in the open field test. e, f) Mutants (6–8 months old) spend significantly reduced (P=0.02369, F=5.70155) time- at the center of the open field in a 30 minute open field test and within the light zone (P=0.00027, F=15.4018) (right panel) in 5 minute light-dark test (illumination 600 Lx). g) Representative heat maps of individual male and female WT and Hoxb8 mutants (Case 1–2) during three-chambered social interaction assay with an empty left chamber and an intruder in the right chamber (same sex as the test mouse). h) Female mutants (6–8 months old) spent significantly reduced time with the intruder mouse in the right chamber (P=0.1148, F=15.40186 for left chamber non-contact duration; P=0.3004, F=2.6407275 for the total duration in the center; P=0.0222, F=5.8829406 for total contact duration with the intruder) in social interaction assay. Data represents Mean±SEM, uses one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD posthoc test for comparison. ns, not significant P>0.05, *P<0.05). i) Bar graph representation of the comparison of social interaction pattern of female Hoxb8 mutants and WT mice (6–8 months old) with an empty chamber (left) and a cage-mate (right) (P=0.0861, F=3.27635 for the non contact duration with the left chamber; P=0.427, F=0.65771 for total duration in the center; P=0.0095, F=8.325 for total contact duration with intruder). The cage-mate was of same age and sex as of experimental mice. All bar graph data represents mean±SEM. Data comparison, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD posthoc test was used for group comparison. ns, P>0.05 not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.001. 4–12 months old mice were used for grooming behavior, 6–8 months old mice for elevated plus maze, open field and social behavioral tests. All test mice were conditioned for 5–15 minutes in specific experimental rooms prior to the experiments. All behavioral experiments were conducted during day light period of the light/dark cycle. All experiments were conducted blindly without the knowledge of experimenter to genotypes.
Two features common to OCD and ASD, are hyperanxiety and social behavioral deficits3–5,13. We investigated whether such behaviors in mutants are altered. In plus maze test, mutants spent significantly more time in closed arm compared to WT mice (Fig 3b–3c) without altering distance in closed arm (Supplementary Fig. 6a) implying that mutants are more anxious in plus maze. Mutants spent significantly decreased time in open arm under different light intensities (1.7 fold at 75 lx, 2.7 fold at 100 lx; Supplementary Fig. 6b), traveled for shorter distances (1.5 fold, 75 lx; 3.2 fold, 100 lx; Supplementary Fig. 6c) and had longer latencies (3.7 fold, 75 lx; 4.9 fold, 100 lx; Supplementary Fig. 6d) than controls.
In open field test, an additional indicator of anxiety level, mutants exhibit significantly reduced- time at the center (Fig. 3d–3e), line crossings, entries and circling numbers (Supplementary Fig. 6f–6e) implying higher anxiety levels relative to controls. Both male and female mutants showed higher anxiety levels (Supplementary Table 5). In light-dark test, mutants spent reduced time in light (Fig. 3f) and more time in dark chamber (Supplementary Fig. 6h) compared to WT mice without affecting the total light zone entries (Supplementary Fig. 6i). All these anxiety tests suggested that Hoxb8 mutants exhibit hyperanxiety levels relative to controls.
We tested social behaviors in Hoxb8 mutants using a three-chambered social assay in which the test subject (WT or mutant, male or female) is placed at the center, with an empty left chamber and an intruder mouse in the right chamber. Mutants spent significantly reduced time socially interacting with the intruder (Fig. 3h). Heat maps derived from male and female mutants (Fig. 3g) during social assay show evidence that female mutants exhibit significantly higher social impairment compared to males. To determine whether mutants interact normally with cage-mates, test mice were challenged to interact with a cage-mate in social assay. Mutants showed a significant social deficit even with a cage-mate, a defect that was confined to the female mutants (Fig. 3i, Supplementary Fig. 6j) indicating that female mutants show higher detectable social impairment than males.
Fluoxetine treatment of Hoxb8 mutants alleviates grooming, anxiety and social impairment behaviors
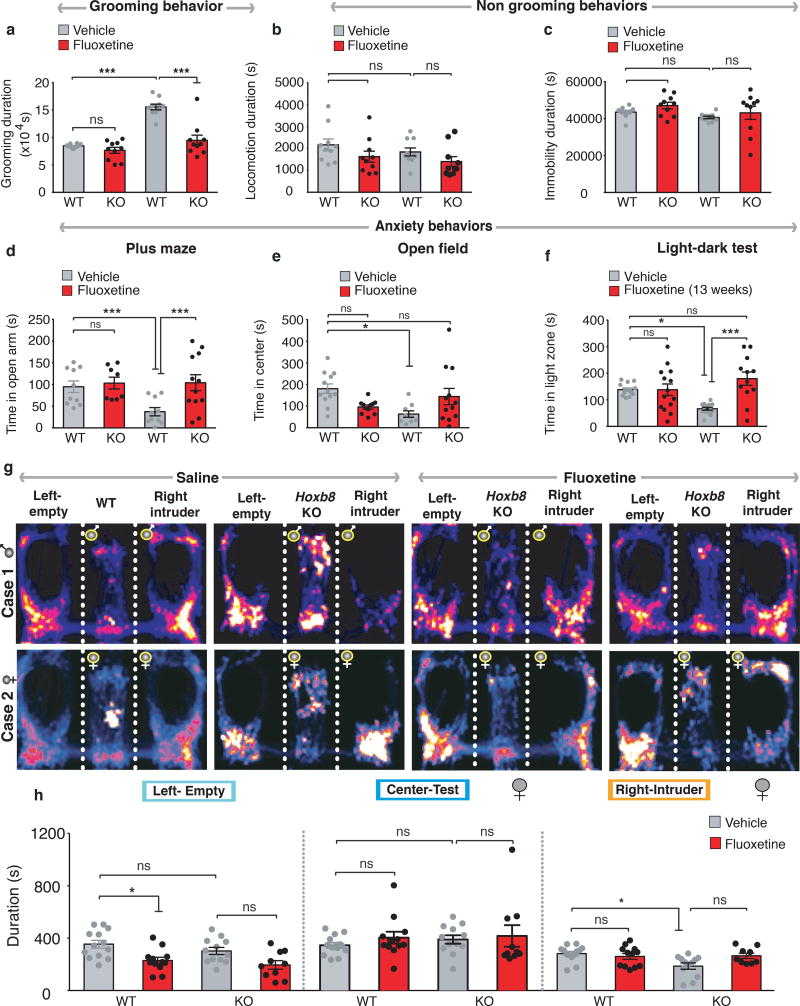
We evaluated whether fluoxetine ameliorates behavioral abnormalities in Hoxb8 mutants. One week, but not one-day treatment reduced grooming time of mutants without significantly affecting the WT mice (Supplementary Fig. 7a). No sedative effect was detected as measured by locomotion and immobility between saline or fluoxetine-treated groups, implying the appropriateness of drug dosage (Fig. 4b–4c). To determine long-term effects of fluoxetine on anxiety, mutants and WT mice were chronically treated for five weeks. In plus maze test, treated mutants spent a 3.4 fold increased time in open-arm compared to saline-treated mutants (Fig. 4d). Treated mutants that spent more time at the center of the open field compared to saline treated mutants did not reach WT-levels (Fig. 4e) implying a partial rescue. When exposed to a novel intruder, treated mutants compared to WT mice spent a reduced time in empty chamber and similar time at the center or with the intruder mouse (Fig. 4g–4h) implying that the treatment resulted in improved social behaviors. To investigate if the alleviated behaviors are sustained during chronic fluoxetine treatment, mutants and WT mice were treated with fluoxetine upto thirteen weeks. Anxiety and exploratory locomotion were tested using light-dark and open field tests. The distance at the center or periphery of open field (Supplementary Fig. 7b–7c) and the time in light zone (Supplementary Fig. 7d) reached WT-like levels implying extensive rescue. Amount of time spent by mutants in light zone during light-dark exploration increased to WT-levels (Fig. 4f). These data demonstrate that fluoxetine treatment alleviates pathological grooming, anxiety and aberrant social behaviors in Hoxb8 mutants.
Figure 4. Rescue of grooming, anxiety and social behaviors by chronic fluoxetine treatment.
a) Rescue of grooming behavior in age- and sex-matched Hoxb8 mutants (6–12 months) treated with 5 mg/kg fluoxetine in post 5 week treated Hoxb8 mutants (P=0.0001, F(1, 36)=18.95 for interaction; P<0.0001, F(1, 36)= 32.43 for drug; P<0.0001, F(1,36)=54.23 for genotype). b, c) 5-week treatment did not affect locomotion (b, P=0.8259, F(1, 36)= 0.04911 for interaction; P=0.0434, F(1, 36)=4.385 for drug; P=0.2486, F(1,36)=1.375 for genotype) and immobility duration (c, P=0.8108, F(1, 36)=0.05817 for interaction; P=0.1552, F(1,36)=2.108 for drug; P=0.1074, F(1,36)=2.726 for genotype) significantly in mutants. d, e) 5-week treated mutants show increased time in the open arm and the center of the open field. Complete rescue was observed in the plus maze test (d, P=0.0595, F(1,36)=3.788 for interaction; P=0.0170, F(1,36)=6.261 for drug; P= 0.0675, F(1,36)= 3.554 for genotype) but a partial rescue was noted in the open field test (e, P=0.0022, F(1,36)=10.71 for interaction; P= 0.9404, F(1,36)=0.005653 for drug; P=0.1790, F(1,36)=1.871 for genotype) f) 13 week treated Hoxb8 mutants spend more time like WT mice in the light zone as compared to untreated mutants in 5 minute light-dark test (P=0.0013, F(1, 49)=11.56 for interaction; P= 0.0014, F(1,49)=11.50 for drug; P=0.3651, F(1,49)=0.8359 for genotype). g) Representative heat maps of saline- and fluoxetine-treated male and female WT and Hoxb8 mutants (Case 1–2) during three-chambered social interaction assay with an empty left chamber and an intruder in the right chamber (same sex as test mouse). Rescue of social interaction is more prominent in female Hoxb8 mutants. h)Hoxb8 mutants show WT-like interaction time with the intruder mouse post two-week fluoxetine treatment in three-chambered social interaction test. The experimental female mouse was placed in the center chamber. The left chamber was left empty and the right chamber consisted of an intruder mouse of same sex as the experimental mouse (P=0.7438, F(1, 43)=0.1082 for interaction; P=0.0002, F(1,43)=16.45 for drug; P=0.1429, F(1,49)=2.227 for genotype for the time in left chamber; P=0.7295, F(1, 43)=0.1211 for interaction; P=0.3615, F(1,43)=0.8509 for drug; P=0.5411, F(1,49)=0.3796 for genotype for the time in the center chamber; P=0.1147, F(1, 43)=2.593 for interaction; P=0.5048, F(1,43)=0.4523 for drug; P= 0.0126, F(1,49)=6.776 for genotype for the time in the right chamber). 6–12 months old age-matched WT and Hoxb8 mutants were used for the experiments.
Discussion
Targeted disruption of Hoxb8 gene causes brain specific6,7 compulsive hair removal behavior closely resembling the OCD spectrum disorder Trichotillomania in humans21. We now show that Hoxb8 loss of function results in synaptic and physiological defects within cortico-striatal circuit. This CS defect in mutants resulted in frontal cortical synaptic expansion and striatal synaptic contraction. The increased cortical synapse and spine density within frontal cortex in conjunction with increased dendritic spines in dorso- and ventro-medial sub-regions of striatum implicate a potential increase in excitatory corticostriatal synapse.
These synaptic modifications were also detectable electrophysiologically. At circuit level we detected impaired CNQX independent striatal synaptic LTP. This plasticity may emerge from changes in presynaptic mPFC neurons synapsing onto striatal mSNs during action potential firing at frequencies that induce synaptic plasticity. mEPSC recordings from individual mSNs showed two distinct mEPSCs, higher amplitude, low-frequency and longer IEI (group 1) and the lower amplitude, high-frequency and reduced IEI (group 2) implying the sensitivity of whole-cell recordings to measure synaptic properties of MSNs.
Mutants exhibit grooming, anxiety and social behavioral impairment. Fluoxetine alleviates grooming, anxiety and social deficits in mutants similar to Sapap3, Slitrk5 and Shank3 based OCD/ASD mouse models and human OCD patients9,34,14,24–25,35–36,50–51.
A direct correlation of immune dysfunction and neuropsychiatric disorders is observed in major depression, OCD, Autism, Schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease38–49. Consequences of Hoxb8 gene deficiency that results in corticostriatal synaptic aberration provides an independent way that brain appear to utilize to mediate and modulate repetitive behaviors. Interestingly, the loss of Hoxb8 gene function that results in excessive grooming behavior was not restricted to repetitive behaviors since we detected fluoxetine-sensitive hyperanxiety and social behavioral deficit in Hoxb8 mutants similar to trichotillomania-type OCD patients26–27, 49–51.
Although the causative agents of the neuropsychiatric disorder in Hoxb8-mutant mice versus Sapap3, Slitrk5, and Shank3 mutant mice are very different, defective microglia versus defective synaptic components, the end results, both in terms of behavioral deficits, including high levels of anxiety and the affected neural circuits, the corticostriatal interface, are very similar. These results strongly support the hypothesis that in the absence of proper maintenance of circuit modulation by Hoxb8-microglia, very similar neural circuit damage ensues in Hoxb8, Sapap3, Slitrk5 and Shank3 mutant mice, resulting in very similar behavioral pathology.
Hoxb8 gene thus appears to play an important role in maintaining brain homeostasis in regulating corticostriatal circuit function and behavioral output. Hoxb8 gene dysfunction would alter synaptic morphology and physiological properties and thereby affect behaviors, the output of which would depend on the constellation of genetic and environmental insults pertinent to individual patient. Such models tie together immune dysfunctions, particularly pertaining to Hoxb8 gene function through microglia28–34, the brain’s immune system, with repetitive and anxiety behaviors and a spectrum of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank A. Boulet and K. Higgins for insightful discussions on the manuscript and editing. S.K. Chen for experimental discussion; H. Eldering, Metris for technical support, Shotaro Matsuoka for genotyping, A. Gosdis, and V. Krishnegowda for their participation in early experiments. This work was supported by Seed grant and research instrumentation funding from University of Utah to N.N and M.R.C, HHMI, NIH/NEI, EY02576-36, EY015128-8 and EY014800-08 (P30) to B.W.J and R.M.
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Sachs BD. The development of grooming and its expression in adult animals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988;525:1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb38591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Graybiel AM, Saka E. A genetic basis for obsessive grooming. Neuron. 2002;33(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00575-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Welch JM, Lu J, Rodriguiz RM, Trotta NC, Peca J, Ding JD, et al. Cortico-striatal synaptic defects and OCD-like behaviours in Sapap3-mutants. Nature. 2007;448:894–900. doi: 10.1038/nature06104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shmelkov SV, Hormigo A, Jing D, Proenca CC, Bath KG, Milde T, et al. Slitrk5 deficiency impairs corticostriatal circuitry and leads to obsessive-compulsive-like behaviours in mice. Nature medicine. 2010;16:598–602. doi: 10.1038/nm.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peca J, Feliciano C, Ting JT, Wang W, Wells MF, Venkatraman TN, et al. Shank3 mutants display autistic-like behaviours and striatal dysfunction. Nature. 2011;472:437–442. doi: 10.1038/nature09965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Greer JM, Capecchi MR. Hoxb8 is required for normal grooming behaviour in mice. Neuron. 2002;33:23–34. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen SK, Tvrdik P, Peden E, Cho S, Wu S, Spangrude G, et al. Hematopoietic origin of pathological grooming in Hoxb8 mutants. Cell. 2010;141:775–785. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Graybiel AM. Habits, rituals, and the evaluative brain. Annual review of neuroscience. 2008;31:359–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.29.051605.112851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fineberg NA, Chamberlain SR, Hollander E, Boulougouris V, Robbins TW. Translational approaches to obsessive-compulsive disorder: from animal models to clinical treatment. British journal of pharmacology. 2011;164:1044–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Menzies L, Chamberlain SR, Laird AR, Thelen SM, Sahakian BJ, Bullmore ET. Integrating evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychological studies of obsessive-compulsive disorder: the orbitofronto-striatal model revisited. Neuroscience and biobehavioural reviews. 2008;32:525–549. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Beucke JC, Sepulcre J, Talukdar T, Linnman C, Zschenderlein K, Endrass T, Kaufmann C, Kathmann N. (2013). Abnormally high degree connectivity of the orbitofrontal cortex in obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(6):619–29. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ahmari SE, Spellman T, Douglass NL, Kheirbek MA, Simpson HB, Deisseroth K, et al. Repeated cortico-striatal stimulation generates persistent OCD-like behaviour. Science. 2013;340:1234–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.1234733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schmeisser MJ, Ey E, Wegener S, Bockmann J, Stempel AV, Kuebler A, et al. Autistic-like behaviours and hyperactivity in mice lacking ProSAP1/Shank2. Nature. 2012;486:256–260. doi: 10.1038/nature11015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Krebs G, Heyman I. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents. Archives of disease in childhood. 2014 doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-306934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shepherd GM. Corticostriatal connectivity and its role in disease. Nature reviews. Neuroscience. 2013;14:278–291. doi: 10.1038/nrn3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Geller DA, Hoog SL, Heiligenstein JH, Ricardi RK, Tamura R, Kluszynski S, et al. Fluoxetine treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents: a placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. 2001;40:773–779. doi: 10.1097/00004583-200107000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen YH, Harvey BK, Hoffman AF, Wang Y, Chiang YH, Lupica CR. MPTP-induced deficits in striatal synaptic plasticity are prevented by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor expressed via an adeno-associated viral vector. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2008;22:261–275. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8797com. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cordingley GE, Weight FF. Non-cholinergic synaptic excitation in neostriatum: pharmacological evidence for mediation by a glutamate-like transmitter. British journal of pharmacology. 1986;88:847–856. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb16258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Malenka RC, Kocsis JD. Presynaptic actions of carbachol and adenosine on corticostriatal synaptic transmission studied in vitro. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 1988;8:3750–3756. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03750.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Quinn LP, Stean TO, Chapman H, Brown M, Vidgeon-Hart M, Upton N, et al. Further validation of LABORAS using various dopaminergic manipulations in mice including MPTP-induced nigro-striatal degeneration. Journal of neuroscience methods. 2006;156:218–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Diefenbach GJ, Tolin DF, Hannan S, Crocetto J, Worhunsky P. Trichotillomania: impact on psychosocial functioning and quality of life. Behaviour research and therapy. 2005;43:869–884. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2004.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burguiere E, Monteiro P, Feng G, Graybiel AM. Optogenetic stimulation of lateral orbitofronto-striatal pathway suppresses compulsive behaviours. Science. 2013;340:1243–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.1232380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen YH, Harvey BK, Hoffman AF, Wang Y, Chiang YH, Lupica CR. MPTP-induced deficits in striatal synaptic plasticity are prevented by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor expressed via an adeno-associated viral vector. FASEB J. 2008;22(1):261–75. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8797com. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gkogkas CG, Khoutorsky A, Ran I, Rampakakis E, Nevarko T, Weatherill DB, et al. Autism-related deficits via dysregulated eIF4E–dependent translational control. Nature. 2013;493:371–377. doi: 10.1038/nature11628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Han S, Tai C, Westenbroek RE, Yu FH, Cheah CS, Potter GB, et al. Autistic-like behaviour in Scn1a+/− mice and rescue by enhanced GABA-mediated neurotransmission. Nature. 2012;489:385–390. doi: 10.1038/nature11356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sakai Y, Narumoto J, Nishida S, Nakamae T, Yamada K, Nishimura T, et al. Corticostriatal functional connectivity in non-medicated patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. European psychiatry: the journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists. 2011;26:463–469. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2010.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harrison BJ, Soriano-Mas C, Pujol J, Ortiz H, López-Solà M, Hernández-Ribas R, et al. Altered corticostriatal functional connectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Archives of general psychiatry. 2009;66:1189–1200. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ransohoff RM, Liu L, Cardona AE. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: multipurpose players in neuroinflammation. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007;82:187–204. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(07)82010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Stevens B, Allen NJ, Vazquez LE, Howell GR, Christopherson KS, Nouri N, et al. The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell. 2007;131(6):1164–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ransohoff RM, Cardona AE. The myeloid cells of the central nervous system parenchyma. Nature. 2010;468(7321):253–62. doi: 10.1038/nature09615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Paolicelli RC, Bolasco G, Pagani F, Maggi L, Scianni M, Panzanelli P, et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science. 2011;333(6048):1456–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.1202529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Prinz M, Priller J, Sisodia SS, Ransohoff RM. Heterogeneity of CNS myeloid cells and their roles in neurodegeneration. Nature Neuroscience. 2011;14(10):1227–35. doi: 10.1038/nn.2923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schafer DP, Lehrman EK, Kautzman AG, Koyama R, Mardinly AR, Yamasaki R, et al. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron. 2012;74(4):691–705. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Frick LR, Williams K, Pittenger C. Microglial dysregulation in psychiatric disease. Clinical and developmental immunology. 2013:608654. doi: 10.1155/2013/608654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Moore ML, Eichner SF, Jones JR. Treating functional impairment of autism with selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors. The Annals of pharmacotherapy. 2004;38:1515–1519. doi: 10.1345/aph.1D543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, Zagursky K, Novotny S, Wasserman S, et al. A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviours in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:582–589. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Graybiel AM, Rauch SL. Toward a neurobiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuron. 2000;28:343–347. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ashwood P, Wills S, Van de Water J. The immune response in autism: a new frontier for autism research. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;80:1–15. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1205707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Da Rocha FF, Correa H, Teixeira AL. Obsessive-compulsive disorder and immunology: a review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32:1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.12.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kronfol Z, Remick DG. Cytokines and the brain: implications for clinical psychiatry. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:683–694. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.157.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lang UE, Puls I, Muller DJ, Strutz-Seebohm N, Gallinat J. Molecular mechanisms of schizophrenia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20:687–702. doi: 10.1159/000110430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Leonard BE, Myint A. The psychoneuroimmunology of depression. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2009;24:165–175. doi: 10.1002/hup.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Strous RD, Shoenfeld Y. Schizophrenia, autoimmunity and immune system dysregulation: a comprehensive model updated and revisited. J Autoimmun. 2006;27(2):71–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2006.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hounie AG, Cappi C, Cordeiro Q, Sampaio AS, Moraes I, Rosario MC, et al. TNF-alpha polymorphisms are associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosci Lett. 2008;442:86–90. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF, et al. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature. 2009;460:748–752. doi: 10.1038/nature08185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shi J, Levinson DF, Duan J, Sanders AR, Zheng Y, Pe'er I, Dudbridge F, Holmans PA, Whittemore AS, Mowry BJ, et al. Common variants on chromosome 6p22.1 are associated with schizophrenia. Nature. 2009;460:753–757. doi: 10.1038/nature08192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D, Werge T, Pietilainen OP, Mors O, Mortensen PB, et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature. 2009;460:744–747. doi: 10.1038/nature08186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Luthi A, Lüscher C. Pathological circuit function underlying addiction and anxiety disorders. Nature Neuroscience. 2014;12:1635–43. doi: 10.1038/nn.3849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Markarian Y, Larson MJ, Aldea MA, Good D, Berkeljon A, Murphy TK, et al. Multiple pathways to functional impairment in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clin Psychol Rev. 2010;30(1):78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2009.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Koran LM, Ringold A, Hewlett W. Fluoxetine for trichotillomania: an open clinical trial. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1992;28(2):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rossi A, Barraco A, Donda P. Fluoxetine: a review on evidence based medicine. Ann. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry. 2004;3(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1475-2832-3-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Marc RE, Liu W. Fundamental GABAergic amacrine cell circuitries in the retina: nested feedback, concatenated inhibition, and axosomatic synapses. J Comp Neurol. 2000;425:560–582. doi: 10.1002/1096-9861(20001002)425:4<560::aid-cne7>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Di Martino A, Kelly C, Grzadzinski R, Zuo XN, Mennes M, Mairena MA, et al. Aberrant striatal functional connectivity in children with autism. Biological psychiatry. 2011;69:847–856. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.10.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Anderson JR, Jones BW, Yang JH, Shaw MV, Watt CB, Koshevoy P, et al. A computational framework for ultrastructural mapping of neural circuitry. PLoS biology. 2009;7:e1000074. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.