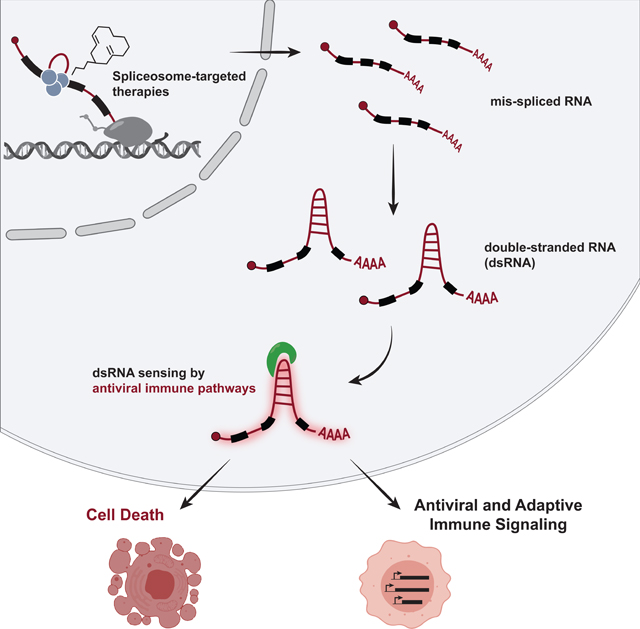
SUMMARY
Many oncogenic insults deregulate RNA splicing, often leading to hypersensitivity of tumors to spliceosome-targeted therapies (STTs). However, the mechanisms by which STTs selectively kill cancers remain largely unknown. Herein, we discover that mis-spliced RNA itself is a molecular trigger for tumor killing through viral mimicry. In MYC-driven triple-negative breast cancer, STTs cause widespread cytoplasmic accumulation of mis-spliced mRNAs, many of which form double-stranded structures. Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding proteins recognize these endogenous dsRNAs, triggering antiviral signaling and extrinsic apoptosis. In immune-competent models of breast cancer, STTs cause tumor cell-intrinsic antiviral signaling, downstream adaptive immune signaling, and tumor cell death. Furthermore, RNA mis-splicing in human breast cancers correlates with innate and adaptive immune signatures, especially in MYC-amplified tumors that are typically immune-cold. These findings indicate that dsRNA-sensing pathways respond to global aberrations of RNA splicing in cancer and provoke the hypothesis that STTs may provide unexplored strategies to activate anti-tumor immune pathways.
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Tumor transcriptomes are replete with indications of deregulated RNA splicing, such as aberrant retention of introns and alterations in both canonical and alternative splicing (Venables, 2004; Zhang and Manley, 2013; Dvinge and Bradley, 2015; Kahles et al., 2018). Many tumor features contribute to this deregulation, including recurrent mutations to RNA splicing factors in both solid and hematologic malignancies (Darman et al., 2015; DeBoever et al., 2015; Graubert et al., 2012; E. Kim et al., 2015; Seiler et al., 2018a; Wang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2015). Non-spliceosome-associated oncogenic alterations, such as hyperactivation of the transcription factor MYC, have also been shown to broadly deregulate splicing and lead to increased reliance on components of pre-mRNA splicing (David et al., 2010; Das et al., 2012; Hubert et al., 2013; Hsu et al., 2015; Koh et al., 2015), in part through elevated synthesis of pre-mRNA and consequent burden on the spliceosome. As a result, cancers driven by MYC, spliceosome mutations, and other oncogenic events are highly sensitive to further genetic and pharmacologic perturbations of the spliceosome (Chan et al., 2017; Hsu et al., 2015; Hubert et al., 2013; Koh et al., 2015; Lee et al., 2016; Obeng et al., 2016; Seiler et al., 2018b; Shirai et al., 2017). This has led to clinical evaluation of small molecule spliceosome modulators in patients (NCT02841540), the development of additional classes of therapeutics targeting the spliceosome (Berg et al., 2012; Pawellek et al., 2014; Han et al., 2017; Sidarovich et al., 2017; Uehara et al., 2017), and the study of spliceosome-targeted therapies in aggressive and poor prognosis tumors that lack targeted therapy options, like triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Small molecule splicing modulators have been explored as anti-cancer therapeutics for over 20 years (Nakajima et al., 1996; Kaida et al., 2007), but their downstream mechanisms of selective anti-tumor activity are not well understood. While spliceosome modulators are known to induce transcriptome-wide mis-splicing, previous work has focused on mis-splicing of specific genes to explain tumor cell death and other phenotypes associated with splicing perturbation. For instance, cell cycle arrest phenotypes have been attributed to mis-splicing of genes encoding cell cycle regulators such as p27 (Kaida et al., 2007; Yoshimoto et al., 2017), Mdm4 (Bezzi et al., 2013), or cell division cycle (CDC) proteins (Hubert et al., 2013). Likewise, alternative splicing of BCL2 family genes is thought to induce activation of apoptosis in some contexts (Aird et al., 2019; Larrayoz et al., 2016; Moore et al., 2010). These important studies highlight the impact of individual mis-spliced mRNAs and their encoded proteins, but also emphasize that culprit mis-spliced genes may vary widely across individual tumors and their diverse transcriptomes. This leaves open the question of whether there are more generalized pathways that govern tumor cell response to spliceosome-targeted therapies (STTs), especially in tumor types that exhibit heightened dependency on RNA splicing.
The current study reveals that mis-spliced mRNAs themselves are a class of macromolecules that are sensed upon spliceosome inhibition, triggering an antiviral immune response and TNBC cell death. We show that STTs cause widespread accumulation of intron-containing transcripts and double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) in the cytoplasm of TNBC cells. These endogenous intron-containing dsRNAs trigger an antiviral immune response via multiple dsRNA binding proteins, including those that activate the signaling integrator MAVS. Notably, STTs trigger both tumor cell-intrinsic antiviral signaling and adaptive immune signaling in animal models of breast cancer. Moreover, intrinsic defects in RNA splicing in primary human breast malignancies correlate with evidence of immune engagement and associate with improved disease-free survival in breast cancer patients. These findings point to dysregulated splicing as an unanticipated approach by which to trigger tumor-intrinsic dsRNA antiviral signaling, and provide mechanistic insight to explain, in part, the selective anti-cancer activity of STTs.
RESULTS
Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Stimulate Antiviral Signaling in MYC-Driven Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
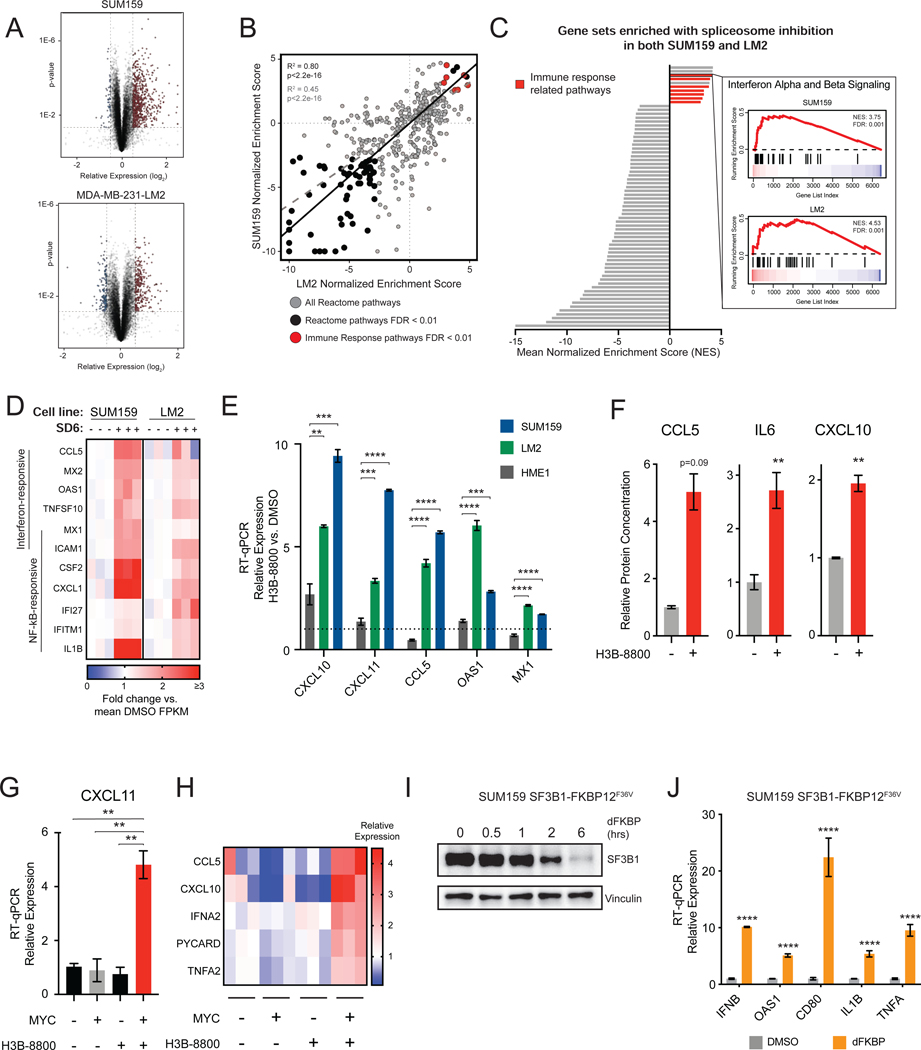
Previous studies have demonstrated that MYC-driven cancers such as triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) are sensitive to partial pharmacologic and genetic perturbation of the spliceosome (Hsu et al., 2015; Koh et al., 2015). However, the pathways that are activated by and coordinate cell fate decision-making in response to spliceosome inhibition are largely unknown. We integrated two unbiased approaches –gene expression analysis and forward genetic screening –to investigate these pathways. First, we characterized the transcriptional changes of two MYC-driven TNBC cell lines, SUM159 and MDA-MB-231-LM2 (LM2) (Kessler et al., 2012; Hsu et al., 2015), following treatment with the small molecule spliceosome modulator sudemycin D6 (SD6) (Lagisetti et al., 2013) (Figure 1A). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) (Subramanian et al., 2005) revealed that transcriptional changes in response to spliceosome inhibition were highly correlated between the two cell lines (Figure 1B), suggesting that a common set of cellular pathways may respond to acute splicing perturbation. Consistent with previous reports, cell cycle and RNA processing pathways were downregulated in response to spliceosome inhibition (Hsu et al., 2015; Hubert et al., 2013; Seiler et al., 2018b). Surprisingly, immune signaling pathways, including interferon alpha and beta signaling, were among the most significant positively enriched pathways (Figure 1C). Upregulation of both interferon-stimulated genes (e.g. OAS1, MX1) and NF-kB responsive genes (e.g. TNF, IL1B) indicate activation of an antiviral transcriptional program in response to spliceosome inhibition (Figure 1D). Induction of IFNB expression preceded the expression of well-characterized interferon-responsive genes, suggesting activation of IFN-responsive antiviral signaling (Figure S1A). These results are not unique to SD6, as treatment of SUM159 and LM2 cells with H3B-8800 (Seiler et al., 2018b), a structurally distinct spliceosome modulator currently in clinical trials (NCT02841540), resulted in similar upregulation of an antiviral transcriptional program of mRNAs (Figure 1E, Figures S1B and S1C) and secretion of their encoded proteins (Figure 1F). Together, these data support the model that inhibition of splicing induces an antiviral immune transcriptional response.
Figure 1. Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Stimulate Antiviral Signaling in MYC-Driven Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
(A) Volcano plot of RNA-seq gene expression changes due to spliceosome inhibition for two MYC-driven TNBC cell lines, SUM159 and LM2, treated with SD6 or DMSO (n=3 biological replicates).
(B, C) Spliceosome inhibition leads to activation of immune signatures in MYC+ TNBC cells. (B) Scatterplot of gene sets enriched in SUM159 and LM2 after SD6 treatment. Gene sets with FDR <0.01 in both cell lines are black. Immune-related gene sets are red. Pearson correlation between all pathways shown as dashed gray line (R2 =0.45, p<2.2e-16); between pathways with FDR<0.01 as black line (R2=0.80, p<2.2e-16). (C) Immune-related transcriptional pathways are among the most positively enriched. Gene sets with FDR <0.01 in both cell lines are shown, with immune-related gene sets in red (7 of 10 positively enriched pathways). The GSEA trace of Interferon Alpha and Beta Signaling is shown as an example.
(D) Spliceosome inhibition with SD6 leads to activation of interferon stimulated and NF-kB responsive genes. Heatmap of RNA-seq data shows relative expression (mean FPKM fold change vs. DMSO) of leading edge genes from enriched immune-related transcriptional pathways in panel (C).
(E) Spliceosome inhibition activates antiviral signaling in TNBC cells but not in non-transformed MECs. SUM159 and LM2 and non-transformed MECs (HME1) were treated with the same dose of H3B-8800. Gene expression assayed by RT-qPCR.
(F) Spliceosome inhibition leads to production of cytokines and chemokines. Conditioned media from SUM159 cells ± H3B-8800 was measured for CCL5, IL6, and CXCL10 (mean ± SEM, n=2 technical replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(G, H) MYC hyperactivation primes antiviral transcriptional changes in response to spliceosome inhibition. HMECs with inducible MYC were treated ± 4-OHT (to induce MYC) ± H3B-8800. Transcription of (G) CXCL11 and (H) other antiviral signaling targets was assayed by RT-qPCR.
(I, J) Chemical genetic degradation of SF3B1 upregulates interferon-stimulated and NF-kB responsive genes. SUM159s engineered with endogenous SF3B1 knockout and exogenous SF3B1-FKBP12F36V cDNA expression were (I) treated with dFKBP ligand to deplete SF3B1. (J) Gene expression assayed by RT-qPCR.
Bar plots of RT-qPCR data in (E), (G), and (J) are expressed relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
**p<0.01, ***p<0.001, **** p<0.0001. See also Figure S1.
Notably, H3B-8800 induced antiviral transcriptional programs in MYC-driven TNBC cells to a much greater extent than non-transformed mammary epithelial cells (Figure 1E). Given that MYC hyperactivation has been shown to increase sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition, we asked whether MYC hyperactivation alone is sufficient to prime activation of such antiviral programs upon spliceosome inhibition using human mammary epithelial cells engineered with inducible MYC-ER transgene (MYC-ER HME1) (Hsu et al., 2015; Kessler et al., 2012). Strikingly, the combination of MYC hyperactivation and H3B-8800 treatment induced robust activation of antiviral signaling programs (Figures 1G and 1H), but the individual perturbations did not, strongly suggesting that oncogenic MYC can prime antiviral immune response to spliceosome inhibition.
To confirm that activation of antiviral transcriptional signaling was due to on-target inhibition of spliceosome activity, we evaluated the effects of chemical-genetic depletion of SF3B1, the protein target of SD6 and H3B-8800. Expression of SF3B1-FKBP12F36V in SUM159 cells with knockout of endogenous SF3B1 enabled selective and dose-dependent perturbation of SF3B1 function (Figure S1D; (Nabet et al., 2018)). Similar to treatment with STTs, degradation of SF3B1-FKBP12F36V induced expression of IFN and NF-kB responsive genes (Figures 1I and 1J). From these data, we conclude that spliceosome perturbation induces an antiviral transcriptional response in MYC-driven TNBCs.
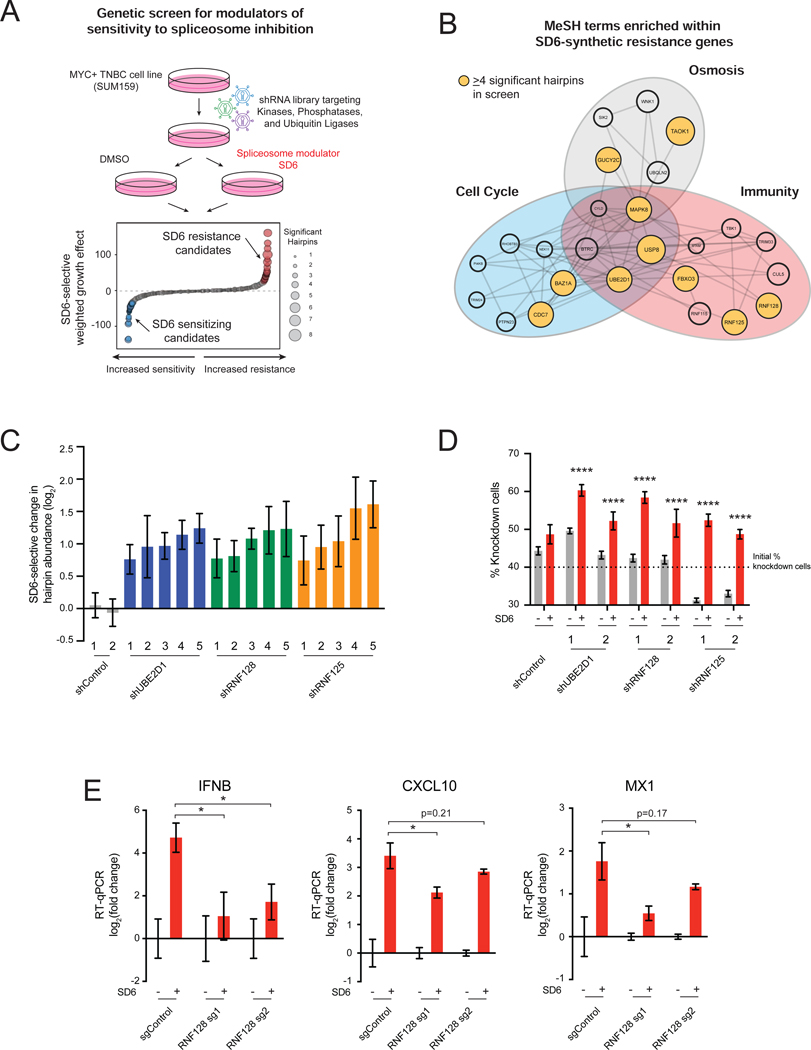
Components of Antiviral Response Pathways Modulate Sensitivity to Spliceosome Inhibition Second, we sought to identify genes required for sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition in TNBC cells. We performed a forward genetic screen with a shRNA library (18,370 shRNAs targeting 1,837 genes) targeting signal transducing protein classes (kinases, phosphatases, and ubiquitin ligases). SUM159 cells transduced with the retroviral shRNA library were grown in the presence or absence of SD6 (Figure 2A). The shRNA abundance in tumor cell genomic DNA was quantified in initial and treated samples by sequencing. We focused our downstream analysis on shRNAs that increased in abundance specifically in the SD6-treated state, referred to as “resistance candidates” because candidate knockdown conferred resistance to spliceosome inhibition (Table S1). MeSH term enrichment analysis (Yu, 2018) of the top 50 resistance candidates revealed a cluster of genes involved in immune response (Figure 2B, Table S2), suggesting that immune pathways may regulate tumor cell response to spliceosome-targeted therapies (STTs). StringDB analysis of resistance candidates revealed enrichment of pathways related to immunity and regulation of signaling downstream of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) sensing (Figure S2A). Notably, 5 of the top 30 resistance candidates were documented modulators of dsRNA-sensing pathways (Figure S2B) (Arimoto et al., 2007; Zeng et al., 2009; Mallampalli et al., 2013; Li et al., 2015; Song et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2017). shRNAs targeting these modulators were consistently enriched upon partial spliceosome inhibition (Figure 2C, Figures S2C and S2D). These data suggest that activation of dsRNA sensing and signaling pathways contributes to sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. Indeed, independent competition-based assays validated that depletion of RNF128, RNF125, and UBE2D1 increased resistance to spliceosome inhibition (Figure 2D, Figures S2E–S2G). As these genes have been shown to mediate activation of antiviral transcriptional programs, we tested whether their depletion would suppress antiviral immune transcriptional activation induced by spliceosome inhibition. Knockout of RNF128 suppressed induction of immune signaling transcriptional changes upon treatment with SD6 (Figure 2E). Collectively, these unbiased transcriptomic and genetic approaches suggest that partial inhibition of the spliceosome induces antiviral signaling in tumor cells, and that these pathways regulate tumor cell survival in response to STTs.
Figure 2. Components of Antiviral Response Pathways Modulate Sensitivity to Spliceosome Inhibition.
(A, B) Immunity-related genes confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. (A) shRNA screen for genes that modulate sensitivity to spliceosome-targeted therapies. SUM159 cells were transduced with an shRNA library and cultured ± SD6. Waterfall plot shows combined SD6-selective growth effect of each gene, calculated as a weighted effect of knockdown by multiple shRNAs. SD6 resistance candidates are red. SD6 sensitizing candidates are blue. (B) MeSH term enrichment analysis of top 50 resistance candidates. Enriched MeSH terms (FDR<0.1) grouped by related function. Node size represents number of shRNAs that significantly conferred resistance (≥4 significant shRNAs highlighted in yellow).
(C, D) Knockdown of UBE2D1, RNF128, and RNF125 confers resistance to spliceosome inhibition. (C) For each gene, the top five independent shRNAs from the screen are plotted along with two negative control shRNAs. log2 (fold change) calculated based on change in shRNA abundance in SD6 vs. DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=4 biological replicates). shRNAs with log2 (fold change) > 0.5 and p-value ≤ 0.05 shown. (D) SUM159 cells transduced with RNF128, RNF125, or UBE2D1-targeting or control shRNAs were mixed (40%) with SUM159-E2 Crimson cells (60%) and cultured ± SD6. Shown is the percentage of cells expressing a given shRNA for DMSO and SD6 treated samples (mean ± SEM, n=6 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(E) RNF128 is required for SD6-induced antiviral signaling. SUM159 cells expressing two RNA128-targeting or negative control sgRNAs were tested for expression of IFNB, CXCL10, and MX1 ± SD6 treatment. Data shown as expression relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
*p<0.05, ****p<0.0001. See also Figure S2 and Tables S1 and S2.
Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Cause Cytoplasmic Accumulation of Double-Stranded RNA in TNBC Cells
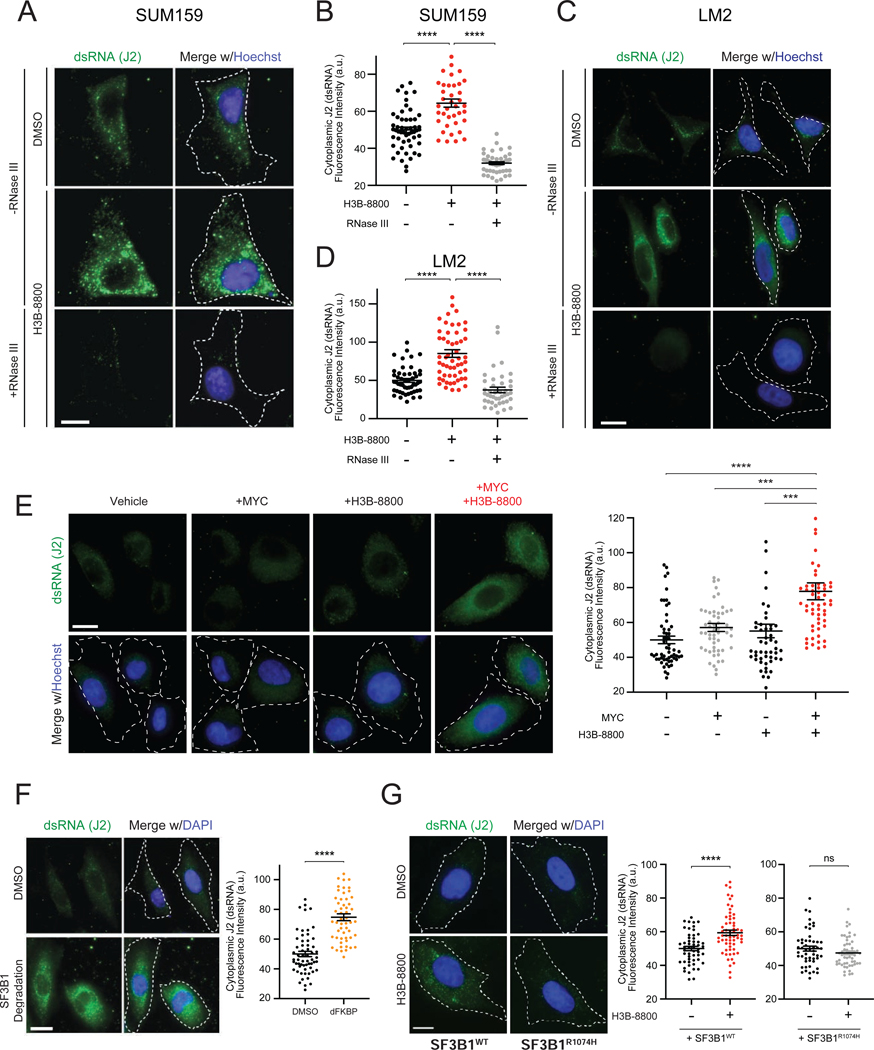
We next investigated the trigger of antiviral signaling in response to spliceosome inhibition. Our genetic screen indicated that dsRNA antiviral signaling pathways modulate cancer cell response to STTs, suggesting that spliceosome perturbation may lead to accumulation of dsRNA. Immunofluorescence staining using a dsRNA-specific antibody (J2 antibody) (Schönborn et al., 1991) across multiple TNBC lines revealed that H3B-8800 induced significant increases in cytoplasmic dsRNA (Figures 3A–3D, Figures S3A and S3B). The J2 signal was abolished by dsRNA-specific RNase III treatment, indicating that the J2 antibody specifically recognized accumulation of dsRNA structures (Figures 3A–3D). In contrast to these MYC-driven TNBC models, non-transformed HME1 cells did not exhibit increased J2 signal at the same dose of H3B-8800 (Figure S3C). Notably, in the MYC-ER HME1 system, the combination of MYC hyperactivation and H3B-8800 led to a significant increase in dsRNA accumulation compared to MYC or H3B-8800 alone (Figure 3E), indicating that MYC is sufficient to prime accumulation of dsRNAs in response to spliceosome inhibition. Importantly, in both the TNBC and MYC-ER HME1 experimental systems, dsRNA accumulated prominently in the cytoplasm (representative images in Figures 3A, 3C and 3E, Figures S3A and S3B), where dsRNA sensing proteins have been shown to engage dsRNA viruses and other dsRNA species.
Figure 3. Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Cause Cytoplasmic Accumulation of Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) in TNBC Cells.
(A-D) Spliceosome inhibition induces cytoplasmic dsRNA accumulation. (A, C) Cellular dsRNA was evaluated with anti-dsRNA (J2) immunofluorescence (IF) in (A) SUM159 and (C) LM2 cells ± H3B-8800. RNase III treatment used as negative control for dsRNA signal. Scale bars, 10μm. Images representative of 3 experiments. (B, D) Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity for (B) SUM159 and (D) LM2.
(E) Spliceosome inhibition in combination with MYC hyperactivation induces cytoplasmic dsRNA accumulation. HMECs with inducible MYC were treated ± 4-OHT (to induce MYC) ± H3B-8800 and assessed for dsRNA with J2 antibody. Scale bars, 10μm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal.
(F) SF3B1 degradation induces cytoplasmic dsRNA accumulation. Left, IF labeling of dsRNA (J2) in SUM159 SF3B1-FKBP12F36V cells ± dFKBP. Images representative of 2 experiments. Scale bars, 20μm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal.
(G) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses accumulation of dsRNA after H3B-8800 treatment. Left, IF labeling of dsRNA (J2) in SUM159 cells expressing SF3B1WT and SF3B1R1074H ± H3B-8800. Scale bars, 10μm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal.
All quantification plots of dsRNA signal intensity are mean ± SEM from >35 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
*p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. See also Figure S3.
Next, we established that direct perturbation of the spliceosome induced dsRNA accumulation. Degradation of exogenous SF3B1-FKBP12F36V in an endogenous SF3B1 knockout background resulted in accumulation of cytoplasmic dsRNA (Figure 3F), phenocopying the effect of H3B-8800. To further confirm SF3B1-on-target effect of H3B-8800 as the source of dsRNA accumulation, we utilized exogenously expressed SF3B1R1074H (Figures S3D and S3G), which confers resistance to small molecules targeting SF3B1 (Seiler et al., 2018b; Yokoi et al., 2011) (Figure S3E and S3H). SF3B1R1074H expression suppressed H3B-8800-induced intron retention (Figure S3F) and increase in J2 signal (Figure 3G, Figure S3I). These results indicate that spliceosome inhibition leads to widespread accumulation of cytoplasmic dsRNA in MYC-driven TNBC cells. Together with activation of antiviral signaling by spliceosome inhibition (Figures 1 and 2), these observations support the model that STTs exert a therapeutic effect, at least in part, via dsRNA-sensing and downstream antiviral signaling.
Intron-Retained RNAs Accumulate in the Cytoplasm and Form dsRNA in Response to Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies
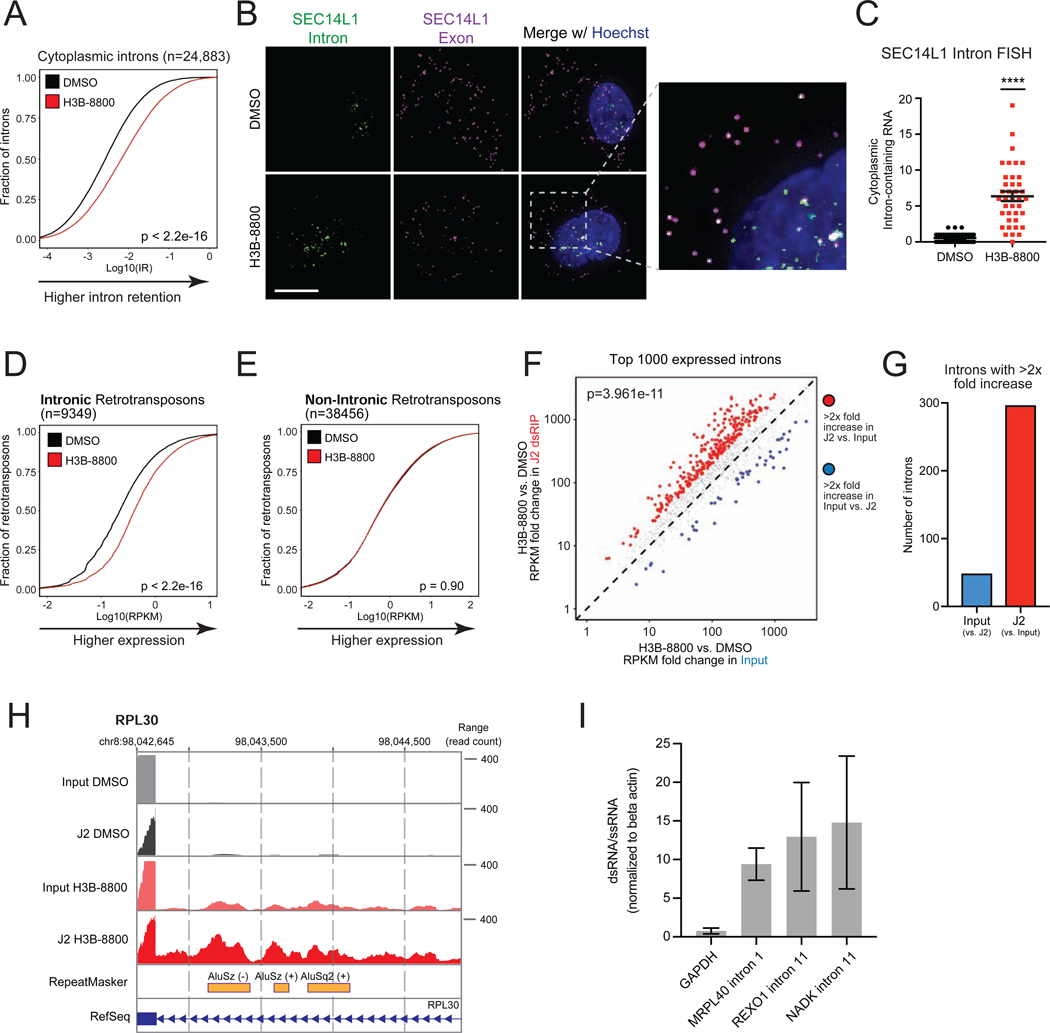
We then sought to investigate the source of cytoplasmic dsRNA in response to acute spliceosome inhibition. Spliceosome perturbations induce transcriptome-wide defects in splicing, including intron retention, but the extent to which these intron-retained transcripts are exported and accumulate in the cytoplasm is unclear. Some intron-containing gene isoforms have well-characterized biological functions in the cytoplasm (Buckley et al., 2014), and certain cancer-associated neoepitopes are derived from intron-retained RNA (Smart et al., 2018). However, the majority of intron-retained RNAs are predicted to be degraded by quality control mechanisms (Braunschweig et al., 2014; Doma and Parker, 2007; Popp and Maquat, 2013; Wong et al., 2013; Zhang and Manley, 2013). Surprisingly, we found that acute spliceosome perturbation led to widespread accumulation of intron-retained transcripts in the cytoplasm of TNBC cells. Poly (A) RNA-seq of cytoplasmic fraction RNA of SUM159 cells treated with H3B-8800 (Figure S4A) revealed a significant increase in intron retention (IR) across 24,883 introns (Figure 4A, Figure S4B). Investigation of individual RNA localization using RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) revealed a significant increase in intron-containing RNA in the cytoplasm after H3B-8800 treatment (Figures 4B and 4C, Figures S4C–S4F). Importantly, overlapping intronic and exonic foci indicates these cytoplasmic introns are present in the context of unspliced transcripts, as opposed to intron lariats or off-target probe recognition. Based on these results, we conclude that acute spliceosome inhibition induces global accumulation of mis-spliced, intron-containing RNA in the cytoplasm.
Figure 4. Intron-Retained RNAs Accumulate in the Cytoplasm and Form dsRNA in Response to Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies.
(A-C) Spliceosome inhibition leads to cytoplasmic intron retention in TNBC cells. (A) RNA-seq was performed on cytoplasmic RNA from SUM159 ± H3B-8800 and intron retention (IR) was assessed. Empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean IR scores (n=2 biological replicates) shown. A rightward shift in the red curve indicates increased IR (p<2.2e-16, Mann-Whitney U). (B) RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images of retained introns and surrounding exon sequences for SEC14L1 ± H3B-8800. Arrows indicate overlapped intron and exon foci. Scale bars, 10μm. (C) Quantification of cytoplasmic intron-retained mRNAs per cell (mean ± SEM from >35 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(D, E) Intron-residing retrotransposons increase in abundance in the cytoplasm of TNBC cells after H3B-8800. Empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean RPKMs are plotted for (D) 9,349 intron-residing retrotransposons or (E) 38,456 non-intronic retrotransposons detected in RNA-seq. A rightward shift in the red curve indicates increased expression in intronic retrotransposons (p<2.2e-16, Mann-Whitney U) but not non-intronic retrotransposons (p = 0.90, Mann-Whitney U).
(F, G, H) Retained introns induced by spliceosome inhibition form dsRNA. SUM159 cells ± H3B-8800 (n=2 biological replicates). dsRNA was enriched by J2 immunoprecipitation followed by poly(A) RNA-seq (J2 dsRIP-seq). (F) Scatterplot of intron expression fold changes ± H3B-8800 of the top 1000 introns ranked by expression (RPKM). (G) Number of retained introns with >2× increase in input or J2-dsRIP (compared to the other state). (H) Representative intron-embedded retrotransposons (RPL30 gene).
(I) Introns retained after H3B-8800 form dsRNA structures. Lysates from SUM159 cells ± H3B-8800 were treated ± RNaseONE, a ssRNA specific ribonuclease. Relative RNA levels were quantified via RT-qPCR (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates). Data shown are relative to ACTB mRNA, a well-characterized ssRNA.
****p<0.0001. See also Figure S4.
Given that spliceosome inhibition induced substantial accumulation of cytoplasmic intron-retained RNAs and dsRNA, we hypothesized that intron-retained mRNAs were a source of cytoplasmic dsRNA. Previous studies have shown that introns form double-stranded structures in the nucleus (Saldi et al., 2014; Sun et al., 2019) and that a large proportion of retrotransposable elements (e.g. LINE, SINE/Alus) in the genome are located in introns (Sela et al., 2007). Notably, there was a significant increase in expression of over 9,000 intron-residing retrotransposons, including LINE and SINE/Alu elements, after H3B-8800 treatment (Figure 4D, Figure S4G). In contrast, expression of retrotransposons residing outside of intronic regions did not substantively change (Figure 4E, Figure S4H). Therefore, in contrast to primarily intergenic endogenous retroviral elements induced by DNA demethylating agents (Chiappinelli et al., 2015; Mehdipour et al., 2020; Roulois et al., 2015), we conclude that acute perturbation of splicing reveals a previously unexplored class of endogenous double-stranded RNAs that may serve as triggers of an antiviral response.
To directly assess the composition of dsRNAs that accumulate after spliceosome inhibition, we performed dsRNA immunoprecipitation using the J2 antibody followed by poly (A) RNA-seq (J2 dsRIP-seq). Introns retained after spliceosome inhibition were significantly enriched by J2 dsRIP-seq (Figures 4F and 4G), suggesting pervasive formation of double-stranded secondary structure. Among those genes with highly J2-enriched retained introns was RPL30 (Figure 4H), which contains inverted Alu elements that contribute to a long stretch of predicted dsRNA structure (Figure S4I). Interestingly, introns without retrotransposons were also enriched by J2 and predicted to form lengthy, continuous double-stranded structures (Figures S4J and S4K), suggesting that introns broadly contribute to accumulation of dsRNA. Probing of RNA structure using ssRNA digestion followed by RT-qPCR revealed J2-enriched introns were enriched 10–15 fold for dsRNA structure (Figure 4I), supporting their contribution to the pool of dsRNA following spliceosome inhibition. Collectively, these data support the hypothesis that spliceosome inhibition causes accumulation of intron-retained RNAs, which form double-stranded structures that accumulate in the cytoplasm.
Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Activate Extrinsic Apoptosis via Antiviral dsRNA Sensing Pathways
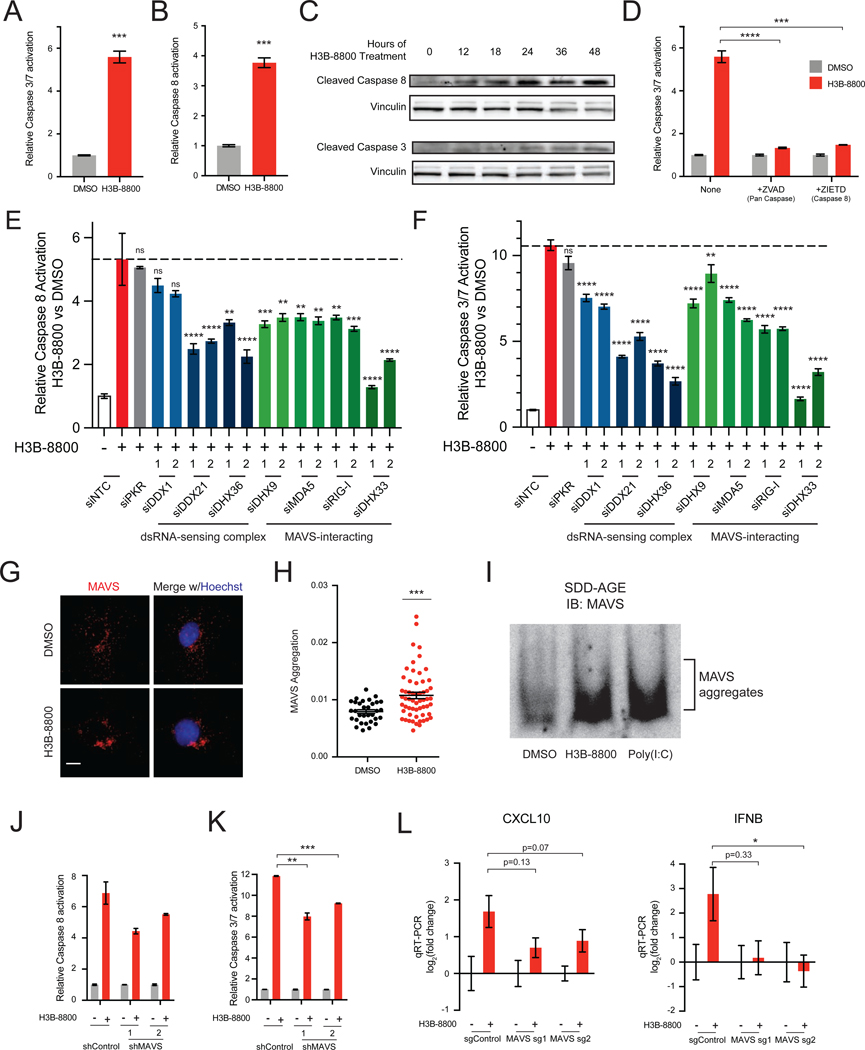
Our data thus far indicate that STTs cause cytoplasmic accumulation of dsRNA in MYC-driven TNBC. Recognition of cytoplasmic dsRNA has been shown to activate an antiviral transcriptional response, and in some contexts, induce extrinsic apoptosis (Kibler et al., 1997; Gil and Esteban, 2000; Iordanov et al., 2005; Takahashi et al., 2006; Sears et al., 2011; El Maadidi et al., 2014). However, previous work has suggested that STTs induce apoptosis through alternative splicing of BCL2 family genes (Larrayoz et al., 2016; Moore et al., 2010), which mediate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway (Elmore, 2007). Thus, we sought to determine whether extrinsic or intrinsic pathways drive apoptosis in response to STTs. Consistent with prior studies, both H3B-8800 and SD6 activated downstream effector caspases-3 and −7 (Figure 5A, Figure S5A). Notably, both STTs activated caspase-8 (Figure 5B, Figure S5B), an initiator caspase of extrinsic apoptosis. Likewise, in MYC-ER HME1 cells, the combination of MYC hyperactivation and H3B-8800 led to robust induction of both caspases-3 and −7 and caspase-8 activity (Figures S5C and S5D). Additionally, expression of SF3B1R1074H suppressed activation of both caspase-8 and caspases-3 and −7, suggesting that apoptotic cell death is indeed due to on-target spliceosome inhibition (Figure S5E and S5F). Caspase-8 cleavage occurred within 12 hours, preceding caspase-3 cleavage (Figure 5C). Strikingly, inhibition of both caspase-8 and 10, initiators of extrinsic apoptosis, suppressed activation of downstream effector caspases by H3B-8800 and SD6 (Figure 5D, Figure S5G). In contrast, inhibition of caspase-9, an initiator of intrinsic apoptosis, did not significantly suppress caspase-3 and −7 activation (Figure S5G), suggesting intrinsic mechanisms do not play a primary role in activation of apoptosis, at least in the context of TNBC. Additionally, necroptosis is not a primary pathway of cell death as inhibition of RIPK3 did not impede H3B-8800-induced cell death (Figure S5H–S5J). Together, these results indicate that the induction of apoptosis by spliceosome inhibition occurs through extrinsic mechanisms in breast cancer.
Figure 5. Spliceosome-Targeted Therapies Activate Extrinsic Apoptosis via Antiviral dsRNA Sensing Pathways.
(A-D) Spliceosome inhibition activates apoptosis via extrinsic mechanisms. (A) Caspases-3 and −7 activity from SUM159s ± H3B-8800. (B) Caspase-8 activity from SUM159s ± H3B-8800. (C) Immunoblotting time course shows cleavage of caspase-8 precedes cleavage of caspase-3 in response to spliceosome inhibition in SUM159 cells. (D) H3B-8800-induced apoptosis requires the extrinsic initiator caspase-8. SUM159s ± H3B-8800 and no caspase inhibitor, pan-caspase inhibitor (ZVAD), or caspase-8 inhibitor (ZIETD) were measured for caspases-3 and −7.
(E, F) Multiple dsRNA sensors contribute to activation of extrinsic apoptosis and downstream effector caspases upon spliceosome inhibition. SUM159 cells were transfected with control (NTC) siRNA or siRNA targeting the indicated genes, treated ± H3B-8800, and assessed for (E) caspase-8 and (F) caspases-3 and −7 (mean ± SEM, n≥3 biological replicates, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test).
(G-I) Spliceosome inhibition causes aggregation of the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS. (G) MAVS immunofluorescence (IF) of SUM159 cells ± H3B-8800. Scale bars, 10μm. (H) MAVS aggregation quantified by inverse dispersal of IF signal (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (I) P5 mitochondrial fraction was prepared from SUM159 cells ± H3B-8800 or transfected with poly (I:C). MAVS aggregation analyzed by SDD-AGE.
(J, K) Knockdown of MAVS suppresses activation of extrinsic apoptosis and downstream effector caspases upon spliceosome inhibition. SUM159 cells expressing control or MAVS-targeted shRNA were treated ± H3B-8800 and assessed for (J) caspase-8 and (K) caspases-3 and −7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(L) MAVS knockout suppresses upregulation of antiviral signaling in TNBC cells treated with H3B-8800. SUM159 cells expressing two independent MAVS sgRNAs assessed for CXCL10 and IFNB expression ± H3B-8800. Data shown relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
Bar plots in panels (A), (B), and (D) of caspase activity shown as mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. See also Figure S5.
Extrinsic apoptosis can be activated through mechanisms that are dependent on cell surface death receptors. We observed that after H3B-8800, death receptor related ligands and receptors were not substantially upregulated (Figures S5K–S5N). Additionally, cFLIP splicing and isoform expression was not changed (Figures S5O and S5P). Knockdown of TNFR1 did not significantly suppress induction of apoptosis (Figures S5Q–S5S). These data suggest that extrinsic apoptosis is activated in a death receptor-independent manner.
Prior studies have shown that recognition of cytoplasmic dsRNA can trigger death receptor-independent extrinsic apoptosis (Gil and Esteban, 2000; El Maadidi et al., 2014). Our genetic screen (Figure 2) implicated the RIG-I-like Receptor (RLR) dsRNA sensing pathway in sensitivity to STTs, suggesting that spliceosome inhibition activates extrinsic apoptosis via dsRNA binding proteins, including RLRs. While there are several dsRNA sensors in the human proteome (Andrejeva et al., 2004; Kang et al., 2002; Liu et al., 2014; Sumpter et al., 2005; Yoneyama et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2011a, 2011b), their potential redundancy in sensing endogenous dsRNAs and/or stimulating cell death is poorly understood. To systematically test their role in H3B-8800-induced extrinsic apoptosis, we depleted individual dsRNA binding proteins, including RLRs, using multiple independent siRNAs (Figure S5T) and tested STT-induced extrinsic apoptosis. Depletion of several dsRNA binding proteins partially suppressed activity of caspase-8 and downstream activation of apoptosis upon H3B-8800 treatment (Figures 5E and 5F), while knockdown of others had no effect, suggesting there may be selectivity of dsRNA sensors that recognize endogenous dsRNA accumulation and stimulate apoptosis. The observation that RIG-I and MDA5, which recognize distinct pools of dsRNA (Hornung et al., 2006; Kato et al., 2008; Schmidt et al., 2009; Goubau et al., 2014; Linehan et al., 2018), both contribute to apoptosis suggests diversity in the types of dsRNA that accumulate upon spliceosome perturbation. Collectively, these results indicate that recognition of dsRNAs induced by STTs contributes to downstream activation of apoptosis. However, the observed partial suppression of extrinsic apoptosis suggests there may be redundancy in dsRNA-recognition pathways or that other pathways contribute to apoptosis.
Several of these dsRNA sensors (MDA5, RIG-I, DHX9, and DHX33) converge on activation of the mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) to induce two independent arms of downstream antiviral signal transduction: transcriptional changes and induction of apoptosis (Kawai et al., 2005; Lei et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2014; Meylan et al., 2005; Seth et al., 2005; Xu et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2011b). We hypothesized that spliceosome inhibition activates the signaling integrator MAVS, resulting in initiation of an antiviral response. Activation of MAVS results in its aggregation on the mitochondrial membrane (Hou et al., 2011). Indeed, H3B-8800 induced aggregation of MAVS in both SUM159 and LM2 cells, as assessed by immunofluorescence imaging (Figures 5G and 5H, Figures S5U and S5V) and SDD-AGE followed by immunoblotting (Figures 5I and S5W). Knockdown of MAVS partially suppressed extrinsic apoptosis (Figures 5J and 5K, Figure S5X). The observed partial suppression of extrinsic apoptosis suggests there may be additional pathways that initiate extrinsic apoptosis. Consistent with this, the dsRNA-sensors DHX36, DDX21, and DDX1 are partially required for H3B-8800-induced extrinsic apoptosis, but have not, to our knowledge, been characterized to signal through MAVS. Finally, knock-out of MAVS impaired antiviral transcriptional changes upon H3B-8800 treatment (Figure 5L, Figures S5Y and S5Z). Taken together, these data support the model that STTs induce accumulation of dsRNA and consequently activate dsRNA-sensing pathways (likely MAVS-dependent and –independent), leading to upregulation of an antiviral transcriptional program and activation of extrinsic apoptosis.
RNA Splicing Inhibition Induces Antiviral and Adaptive Immune Signaling in Immune-Competent Models of Breast Cancer
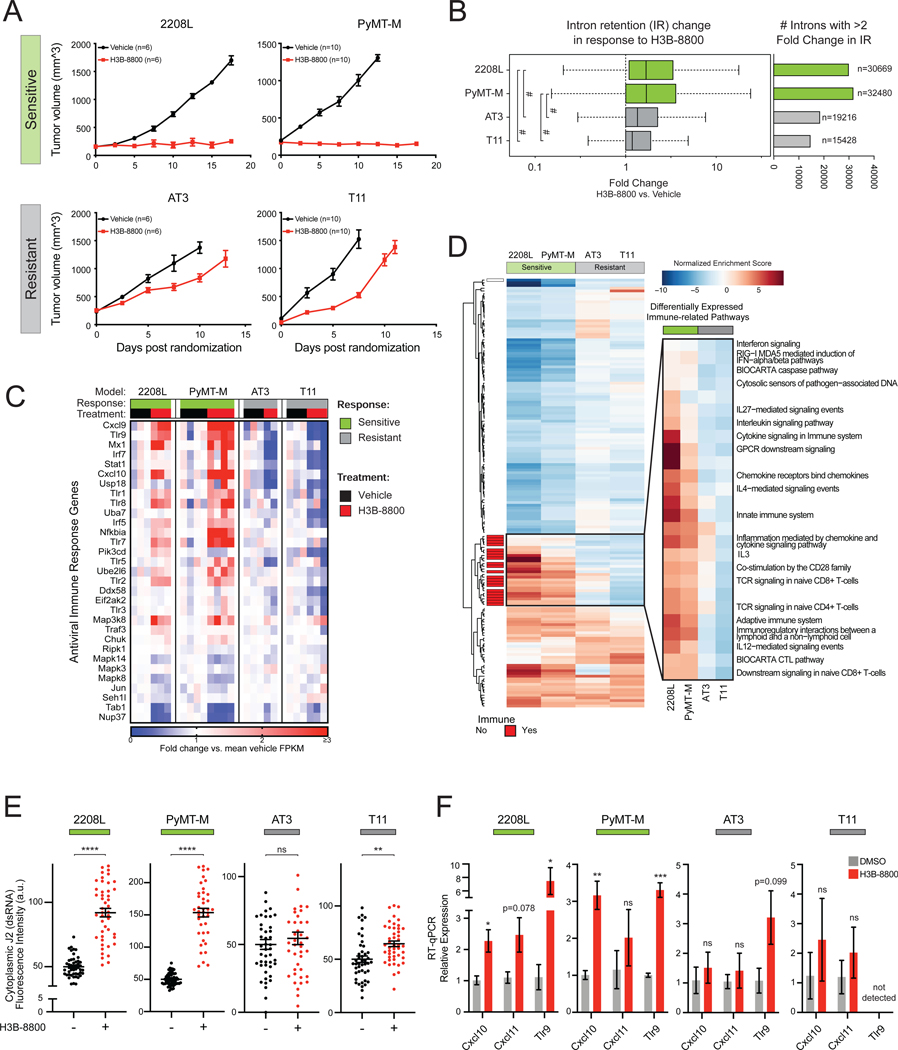
Antiviral signaling through dsRNA pathways induces tumor cell death through a variety of mechanisms, including cell autonomous apoptosis (Der et al., 1997; Kibler et al., 1997) as well as production of cytokines and type 1 IFNs that recruit an adaptive immune response (Chiappinelli et al., 2015; Roulois et al., 2015; Topper et al., 2017; Elion et al., 2018; Ishizuka et al., 2019). While STTs trigger tumor cell death in a cell autonomous manner (Figure 5), robust induction of antiviral transcriptional programs by STTs prompts the hypothesis that such antiviral signaling may also serve as a beacon for downstream host immune surveillance. Therefore, we assessed the impact of spliceosome inhibition on TNBC in an immune-competent host using multiple transplantable syngeneic murine tumor models (2208L, PyMT-M, AT3, and T11). Consistent with prior work (Seiler et al., 2018b), H3B-8800 treatment was well tolerated. Notably, the effect of spliceosome perturbation on tumor progression varied significantly across these models. H3B-8800 significantly impaired tumor progression in 2208L and PyMT-M tumor models (“sensitive” models), while only modestly delaying tumor growth in AT3 and T11 models (“resistant” models) (Figure 6A), indicating H3B-8800 is differentially efficacious as a single agent across TNBC models.
Figure 6. RNA Splicing Inhibition Induces Antiviral and Adaptive Signaling in Immune Competent Models of Breast Cancer.
(A) H3B-8800 impairs tumor progression heterogeneously across syngeneic murine TNBC tumor models. 2208L and PyMT-M tumor progression was significantly impaired (termed sensitive), while AT3 and T11 tumors progressed (termed resistant) (mean ± SEM number of animals plotted).
(B) H3B-8800 results in higher global intron retention in sensitive tumor models (p<2.2e-16, Mann-Whitney U). Boxplot (left) of transcriptome-wide IR scores. Bar plot (right) indicates number of introns with >2-fold change in IR in H3B-8800 vs. Vehicle-treated tumors.
(C) H3B-8800 stimulates expression of antiviral signaling genes in sensitive tumor models. Genes shown are part of KEGG and Reactome antiviral signaling-related pathways. Relative expression calculated as mean FPKM fold change vs. vehicle.
(D) Immune pathways are strongly induced by H3B-8800 in sensitive tumor models but not in resistant tumor models. Pathways shown from MSigDB C2 Canonical Pathways have GSEA FDR<0.05 in either both of the sensitive or both of the resistant models. Immune pathways (red) are annotated based on leading edge genes.
(E) Spliceosome inhibition leads to accumulation of cytoplasmic dsRNA in sensitive syngeneic models of TNBC in vitro. Cell lines derived from syngeneic mouse TNBC models were assessed for cytoplasmic dsRNA using J2-immunofluorescence. Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity shown (mean ± SEM from ≥40 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(F) H3B-8800 induces transcriptional activation of antiviral immune signaling in sensitive syngeneic models of TNBC in vitro. Cell lines were treated with H3B-8800 and immune transcriptional activation was measured via RT-qPCR. Data are relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, #p<2.2e-16. See also Figure S6 and Table S3.
To investigate the mechanisms contributing to this differential sensitivity, we performed bulk tumor RNA sequencing. Splicing analysis showed that H3B-8800 induced widespread IR across all models. Notably, H3B-8800 induced a significantly greater increase in global IR in sensitive tumor models (Figure 6B) compared to resistant tumor models. The underlying causes of the increased global intron retention in sensitive models are currently unknown, but could be a consequence of multiple mechanisms including partial defects in spliceosome function (e.g. somatic spliceosome mutations (Lee et al., 2016; Obeng et al., 2016; Seiler et al., 2018b; Shirai et al., 2017), increased global transcription rates and corresponding burden on pre-mRNA splicing machinery (e.g. MYC hyperactivation (Hsu et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2012)), impaired quality control of mis-spliced mRNA (e.g. defects in NMD), or other forms of deregulation in RNA processing. Nonetheless, this observation indicates that elevated levels of intron-retained mRNA correlates with efficacy of spliceosome-targeted therapy in these immune-competent models of TNBC.
To further study the underlying causes for differential sensitivity, we queried the differential effects of H3B-8800 on transcriptional programs in sensitive versus resistant models using a DESeq2 multifactor model (Love et al., 2014) followed by enrichment analysis. Pathways upregulated in sensitive models were almost exclusively immune-related pathways, in particular those related to antiviral signaling, cytokine and chemokine signaling, and adaptive immunity (Figures S6A and S6B). H3B-8800 significantly upregulated expression of antiviral signaling genes in sensitive models, which had greater induction of IR, but not in resistant models (Figure 6C). As an orthogonal approach, we performed GSEA on genes differentially expressed in H3B-8800-treated compared to vehicle-treated tumors. Hierarchical clustering of pathways commonly enriched amongst models revealed a pronounced cluster comprised almost exclusively of antiviral and adaptive immune pathways enriched solely in sensitive tumor models (Figure 6D and Table S3). These findings provide evidence that STTs activate not only tumor antiviral signaling but also adaptive immune signaling in models sensitive to this single agent regimen. Furthermore, these pathways are negatively enriched in resistant tumor models, supporting the hypothesis that activation of antiviral immune signaling is crucial for the antitumor activity of STTs.
The observation that H3B-8800 induced strong antiviral transcriptional patterns specifically in sensitive tumor models supports the hypothesis that the STT-induced dsRNA-antiviral response observed in human TNBC models (Figures 1–5) also occurs in these sensitive murine TNBC cells. To confirm that gene expression changes in non-tumor cells did not confound our analysis, we derived in vitro cell lines from these syngeneic models to investigate the tumor cell-intrinsic response to STT. While H3B-8800 induced IR across all models in vitro, H3B-8800 induced more IR in the 2208L and PyMT-M cell lines (from sensitive tumor models) than in AT3 and T11 cell lines (from resistant tumor models) (Figure S6C), consistent with results from bulk tumors in vivo. Additionally, H3B-8800 treatment induced significantly greater accumulation of dsRNA in 2208L and PyMT-M cell lines than in AT3 and T11 cell lines (Figure 6E). Importantly, H3B-8800 induced antiviral transcriptional targets Cxcl10, Cxcl11, Tlr9 (Figure 6F) and secretion of CXCL10 protein (Figure S6D) in sensitive cell lines but had little or no effect in resistant cell lines (Figure 6F), suggesting that intron retention and dsRNA accumulation correlate with downstream induction of antiviral pathways in murine TNBC cells. Notably, cell lines from resistant tumor models (AT3 and T11) were largely recalcitrant to H3B-8800-induced cell death (Figure S6E). In contrast, H3B-8800 strongly induced apoptosis in tumor cells from the 2208L tumor model, consistent with its strong activation of dsRNA-antiviral programs and sensitivity to H3B-8800 in vivo (Figure S6E). Interestingly, H3B-8800 did not induce caspase-8 in tumor cells from the PyMT-M tumor model despite a strong activation of dsRNA antiviral response, possibly due to suppression of caspase-8 activity by the PyMT viral oncoprotein (Courtneidge and Smith, 1983; Tsang et al., 2016). Consistent with this observation, prior reports indicate that induction of antiviral transcriptional programs and apoptotic (caspase-8) mechanisms downstream of dsRNA sensing can be independent (Lei et al., 2009), and that these two outputs may be disengaged in some contexts. These results raise the possibility that H3B-8800-mediated tumor control in the PyMT-M model (and perhaps other tumor contexts) may occur through tumor cell non-autonomous mechanisms, a hypothesis that requires further investigation. Together, these data further support the model that accumulation of mis-spliced and double-stranded RNA induces antiviral signaling pathways within tumor cells.
Our RNA-seq analysis indicated that in addition to antiviral signaling, signatures associated with adaptive immune engagement were upregulated in sensitive syngeneic models. H3B-8800 treatment led to increased expression of several T cell chemoattractants (such as Cxcl9 and Cxcl10) and corresponding adaptive immune gene sets (Figures 6C and 6D). On closer examination, expression of Cd4 and multiple common markers of T cell activation were increased in sensitive (but not resistant) models with H3B-8800 treatment (Figures S6F–S6I), which supports potential engagement of host T cells. We also assessed the “cytolytic index”, the co-expression of both granzyme A (Gzma) and perforin (Prf1), as a proxy for CD8+ T cell activity (Rooney et al., 2015). Notably, the cytolytic index was increased following H3B-8800 selectively in sensitive models (Figure S6J), suggesting CD8+ T cell activation in response to treatment with H3B-8800. Indeed, tumor infiltration of CD8+ T cells was significantly increased upon H3B-8800 treatment in PyMT-M tumors (Figures S6K and S6L), consistent with upregulation of gene sets related to T cell co-stimulation and T cell receptor signaling (Figure 6D). Overall, these findings support the model that spliceosome inhibition induces upregulation of both antiviral and adaptive immune signaling in tumor cells, and provoke the hypothesis that STTs may, in some contexts, stimulate anti-tumor immunity, an area of study that requires further investigation.
Defects in RNA Splicing and MYC Amplification Correlate with Immune Response in Human Breast Cancer
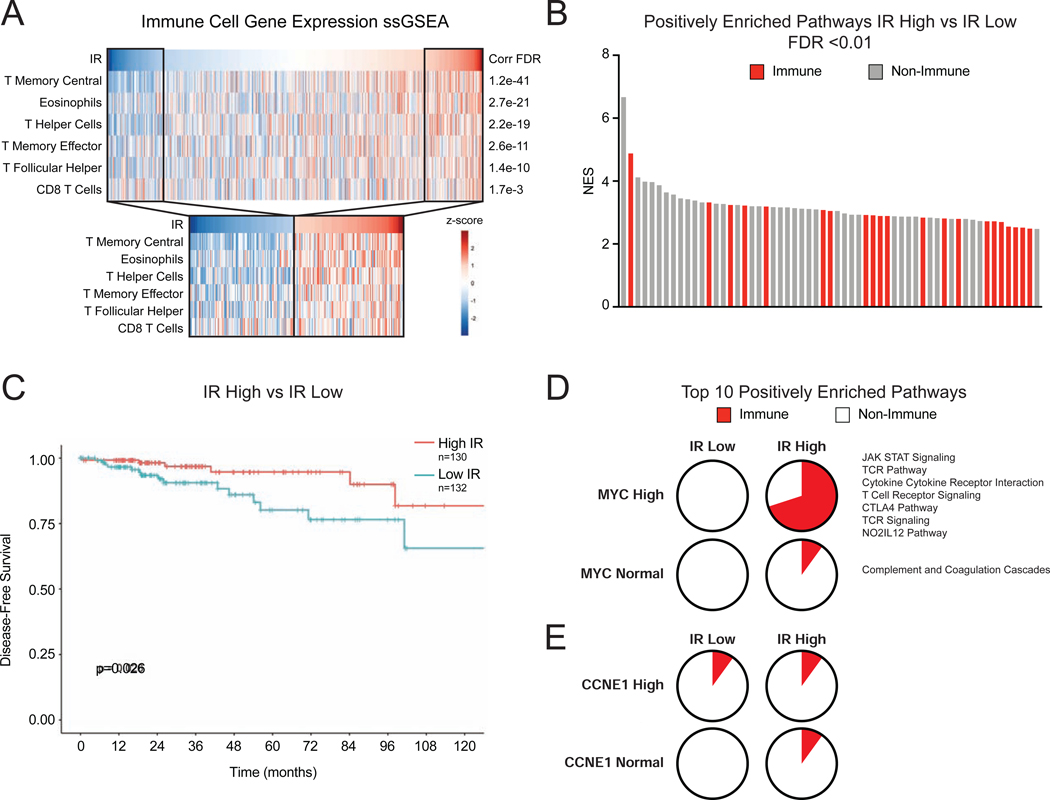
The observations that global defects in tumor RNA splicing may activate adaptive immune signaling in murine models of breast cancer raise the question of whether similar effects occur in human breast cancer. While the effects of STTs have not yet been evaluated in breast cancer patients, we hypothesized that tumors with intrinsic global defects in splicing (as indicated by widespread IR) may instigate an immune response. To evaluate this hypothesis, we computed global IR levels across 983 TCGA primary breast tumors (Koboldt et al., 2012) and tested whether elevated IR correlates with expression signatures of tumor infiltrating immune cells using immune cell single sample GSEA analysis (Barbie et al., 2009). Remarkably, tumor IR levels significantly correlated with previously characterized T cell immune infiltration signatures (Bindea et al., 2013), including helper, memory, and effector T cells (Figure 7A and Table S4). When IR was considered as a categorical variable (high being >1 SD above and low being >1 SD below the cohort mean), IR continued to associate significantly with the same signatures (Figure 7A). We then used GSEA to more broadly query gene expression differences between tumors with high and low intrinsic IR. Notably, immune signaling-related pathways made up 36% of significantly positively enriched pathways (FDR ≤ 0.01) (Figure 7B). Tumor mutational burden (TMB), a feature of cancers previously shown to be associated with immune recruitment and anti-tumor immunity (Rizvi et al., 2015; Snyder et al., 2014), was negatively correlated with IR levels in this cohort (Figure S7A), suggesting tumor-intrinsic IR is a distinct feature correlating with immune engagement. Importantly, high IR is associated with improved patient disease-free survival (Figure 7C), suggesting that improved tumor control may be, in part, due to increased immune engagement seen in tumors with high levels of RNA mis-splicing.
Figure 7. Defects in RNA Splicing and MYC Amplification Associate with Immune Response in Human Breast Cancer.
(A) Intron retention (IR) correlates with signatures of immune infiltration in human breast cancer. Scores from ssGSEA analysis of immune cell gene signatures were computed and correlated to IR levels in BRCA tumors (n=983) in TCGA. Heatmaps show IR level across tumors and ssGSEA scores for signatures that have Pearson correlation q-value of <0.01, ranked by q-value. Subset heatmaps show tumors with IR level >1 z-score from the mean.
(B) Immune-related gene sets are enriched in tumors with high IR. GSEA with MSigDB C2 Canonical Pathways was used to compare gene expression of tumors with high vs. low IR (>1 z-score from mean). Bar plot of NES of positively enriched gene sets (FDR <0.01). Red indicates immune-related gene set.
(C) Tumors with high IR have improved disease-free survival (DFS). Kaplan-Meier plot shows DFS for patients with breast tumors (TCGA). High IR tumors have improved DFS (p=0.026, log-rank test).
(D, E) MYC-amplified breast tumors exhibit increased IR-associated immune signaling pathway activity. GSEA was used to compare gene expression patterns of human tumors divided into cohorts based on IR levels and MYC amplification. (D) Pie charts represent the percent of immune-related pathways among the top 10 enriched pathways ranked by NES. In the High IR, High MYC cohort, 7 of 10 pathways are related to immune signaling. (E) In comparison, CCNE1 amplified tumors do not exhibit increased IR-associated immune signaling.
MYC has been demonstrated to suppress immune engagement (Bernards et al., 1986; Casey et al., 2018, 2017, 2016; Kortlever et al., 2017; Topper et al., 2017) and drive poor prognosis breast cancers (Al-Kuraya et al., 2004; Aulmann et al., 2006; Deming et al., 2000; Robanus-Maandag et al., 2003; Schlotter et al., 2003). However, this study has uncovered that oncogenic MYC primes cancer cells to activate antiviral immune signaling in the context of spliceosome perturbation. Therefore, we hypothesized that MYC amplification in tumor cells might augment the immune signaling associated with high baseline RNA mis-splicing. To test this, we divided tumors into four cohorts based on MYC copy number (amplified or normal as measured by GISTIC) and intron retention (IR high or low using aforementioned cutoffs). Utilizing GSEA, we compared gene expression patterns of tumors in each of these cohorts to determine enrichment profiles unique to each group. Importantly, 7 of the top 10 enriched pathways in the high IR high MYC cohort were related to immune signaling (Figure 7D), while high IR normal MYC cohort exhibited enrichment of only 1 immune pathway. This same pattern was not observed with CCNE1, another commonly amplified gene in breast cancer (Figure 7E), suggesting a unique interaction between MYC and IR to induce immune signaling. These data are concordant with previous work (Hsu et al., 2015) demonstrating that MYC drives sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. More broadly, this lends evidence to the idea that IR burden may be a quantifiable intrinsic feature of tumors, and that IR burden above a threshold could promote immune signaling in certain oncogenic contexts (like MYC amplification). The strong correlation of defective RNA processing and T cell recruitment could arise through multiple non-mutually exclusive mechanisms like activation of antiviral signaling and consequent recruitment of T cells, expression of neo-antigens, or others yet to be elucidated. Nonetheless, these data provoke the hypothesis that global RNA splicing defects, whether tumor intrinsic or induced by acute spliceosome inhibition, may stimulate adaptive immune responses.
DISCUSSION
Small molecule modulators of the spliceosome exhibit potent anti-tumor activity across many cancers, though the mechanisms by which they kill tumors have been unclear. Important studies have characterized the mis-splicing of single genes or gene families in response to spliceosome inhibition, leading the field to focus on these aberrant protein products to explain sensitivity to spliceosome therapeutics. In contrast, we find that mis-spliced RNA itself may have an unrealized, broader function as a macromolecule in dictating tumor cell sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. Our results show that tumor cell death is associated with accumulation and recognition of intron-resident dsRNA and subsequent activation of antiviral immune pathways. These results highlight endogenous mis-spliced RNA as an unexpected substrate for dsRNA sensors that can be leveraged therapeutically to engage a tumor cell-intrinsic immune response. Activation of tumor-intrinsic immune signaling via dsRNA-recognition pathways has been studied recently in the context of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (Chiappinelli et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2018; Roulois et al., 2015; Stone et al., 2017) and ADAR perturbations (Gannon et al., 2018; Ishizuka et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2018). However, in these scenarios it is unclear whether there is selectivity in dsRNA induction across tumor types or between tumor and non-malignant tissues. This study identifies introns as a distinctive source of endogenous dsRNA substrates that can be differentially induced in cancer cells, particularly those with hyperactivation of the MYC oncogene.
As recent clinical trials have demonstrated profound albeit heterogeneous success in modulating the immune system to treat cancer (Sharma et al., 2017), the community has searched for tumor-intrinsic features that dictate whether the immune system can be stimulated to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. For instance, tumor mutational burden (TMB) and high burden of clonal tumor neoantigens have been shown to drive T cell infiltration into the tumor (McGranahan et al., 2016) and these features strongly associate with success of immune-checkpoint blockade (Cristescu et al., 2018; Goodman et al., 2017; Hugo et al., 2016; Rizvi et al., 2015; Yarchoan et al., 2017). However, DNA aberrations (e.g. somatic mutations) are likely only one among many characteristics of tumors that drive tumor recognition by the immune system. We provide evidence that a high burden of RNA mis-splicing (in the form of intron retention) may be an unexplored feature of some cancers that engages tumor antiviral signaling and downstream adaptive immunity. Indeed, analysis of primary breast cancers supports this hypothesis, with tumors that harbor high levels of intron retention also exhibiting overexpression of gene expression programs enriched for immune pathways, especially in tumors with MYC amplification. This observation suggests that inherent RNA processing defects, which are a pervasive but heterogeneous feature of cancers, may induce tumor-intrinsic immune signaling in some contexts. It also raises the therapeutic hypothesis that RNA splicing defects may prime sensitivity to immune-checkpoint blockade or other therapies that engage adaptive immunity.
Finally, our results engender the idea that activation of cell-intrinsic antiviral immunity may be a common mechanism that responds to widespread splicing defects across cancer and other disease states. Aberrations in macromolecules such as DNA and protein are recognized by well-established pathways, such as the DNA damage response (DDR) and unfolded protein response (UPR). These pathways regulate coordinated responses to these aberrations to either restore cellular homeostasis or cause cell death, and in some contexts, serve as potent oncogenic checkpoints to prevent tumorigenesis. In contrast, while we are aware of important quality control mechanisms for RNA such as nonsense-mediated decay, it has been unclear whether there are signaling pathways that sense widespread mis-splicing of RNA and dictate cell fate (e.g. apoptosis). We provide evidence that dsRNA sensing and antiviral signaling may serve as such a coordinated response for widespread mis-splicing of RNA, with intron-resident dsRNAs serving as a trigger for this response. Our data support the involvement of multiple dsRNA sensors, including but not limited to those that interface with MAVS, in dictating cell fate in response to widespread RNA mis-splicing. Our data suggest the presence of diverse pools of intron-containing dsRNA and concordant dsRNA sensors that trigger this antiviral immune response. In the future, it will be important to elucidate which pools of endogenous dsRNAs stimulate dsRNA-sensors, and how the varied genetic/epigenetic context of cancer drivers like MYC may influence these dsRNA pools and sensors and prime tumors to dsRNA antiviral immune responses. More broadly, aberrantly spliced transcripts may be similarly sensed as dsRNA triggers in other pathologies with well characterized RNA processing defects such as Alzheimer’s disease, which is characterized by broad accumulation of mis-spliced RNA (Bai et al., 2013; Raj et al., 2018; Vaquero-Garcia et al., 2016; Wyss-Coray, 2006). This raises the exciting possibility that antiviral immune signaling, a critical component of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, may be activated by surveillance and sensing of aberrantly spliced RNAs. Overall, our findings reveal dsRNA-mediated antiviral immunity as a sensing and response mechanism for broad cellular splicing defects, suggesting that deregulated RNA processing may contribute to cellular antiviral pathway activation in cancer and other diseases.
LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
This study has focused on exploring the tumor cell-intrinsic responses to STTs, revealing that spliceosome inhibition triggers accumulation of dsRNA and activation of antiviral signaling pathways. Moreover, acute therapeutic spliceosome inhibition is sufficient in some contexts to stimulate both antiviral and adaptive immune signaling, as well as tumor T cell infiltration. However, further studies are needed to investigate the contribution of the adaptive immune response to the anti-tumoral activity of STTs. There are several outstanding questions requiring investigation. How does tumor-cell intrinsic activation of antiviral pathways in the context of STT treatment or other scenarios of RNA misprocessing communicate to the host adaptive immune compartment? What compartments of the adaptive immune system, if any, are required for STT anti-cancer efficacy? What are the effects of STTs on immune cell types and do they elicit counter-balancing effects on anti-tumor immunity? These areas of exploration will be critical to exploring whether STTs can be leveraged to galvanize the immune system against aggressive, immune-cold tumors like TNBC.
STAR Methods
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead Contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Thomas Westbrook (thomasw@bcm.edu).
Materials Availability
All unique/stable reagents generated in this study are available from the Lead Contact with a completed Materials Transfer Agreement.
Data and Code Availability
The datasets generated during this study are available in GEO [GSE163411, GSE163414, GSE163181, GSE163188, GSE163232].
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
For cell line studies, SUM159 (female) cells were cultured in F12 media supplemented with 5% FBS, 10mM HEPES, 5ug/mL insulin, and 1ug/mL hydrocortisone. MDA-MB-231 (female), MDA-MB-231-LM2 (female) (Minn et al., 2005), and 293T cells were cultured in DMEM media supplemented with 10% FBS. BT549 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 media supplemented with 10% FBS. HME1 (female) cells were cultured in MEGM (Lonza, CC-3150). MYC-ER HME1 cells were cultured in MEGM and treated with 10uM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) where indicated to induce MYC hyperactivation. PyMT-M (female), 2208L (female), and AT3 (female) cells were cultured in DMEM media supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% Penicillin Streptomycin. T11 (female) cells were cultured in DMEM/F12 media supplemented with 10% FBS, 5ug/mL insulin, 1ug/mL hydrocortisone, 10ng/mL EGF, and 1% Penicillin Streptomycin. These cell lines were routinely tested for Mycoplasma contamination in the laboratory. All cell lines were incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2.
For in vivo animal studies, all animal protocols related to mouse experiments were approved by the Baylor College of Medicine Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol AN-6672). 4–5-week-old female C57BL/6J and BALB/c AnNHsd mice were obtained from The Jackson Laboratory (000664) and Envigo (4701F), respectively. Mice were housed in ventilated cages in a pathogen-free animal facility under a 14hr light/10hr dark cycle. 2208L, PyMT-M, and AT3 tumors were randomized onto vehicle or H3B-8800 at 150–250mm3 for long term response studies or 300–500mm3 for short term studies. Animals were allocated into treatment groups so that the average tumor size in both groups was similar. T11 tumors were randomized onto vehicle or H3B-8800 one day post tumor transplant. Sample size was determined for each syngeneic model separately based on previous tumor kinetic data.
METHOD DETAILS
Cell culture
Stable cell lines expressing shRNAs, sgRNAs, or cDNA were generated by retroviral or lentiviral transduction using 8ug/mL polybrene. Cells were selected using puromycin (1ug/mL). Transient depletion of genes using siRNA was achieved by reverse transfection of cell with 10pmol siRNA in RNAiMax for 12 hours. Depletion of target genes using shRNA or siRNA was confirmed using RT-qPCR. Knockout of genes using sgRNAs or expression of exogenous cDNA was confirmed using Western blotting. See Table S5 for sequences of shRNAs used. See Table S5 for sequences of siRNAs used. See Key Resources Table for sgRNAs used.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE.
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-SF3B1 | Bethyl | Cat#A300–996A |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-Vinculin | Sigma | Cat#V9131 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG M2 | Sigma | Cat#F1804 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-βActin | Sigma | Cat#A1978 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-αTubulin DM1A | Cell Signaling | Cat#3873 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-H3 | Millipore | Cat#07–690 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-Cleaved Caspase 8 18C8 | Cell Signaling | Cat#9496 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Cleaved Caspase 3 | Cell Signaling | Cat#9661 |
| Mouse monoclonal anti-RAN Clone 20 | BD Biosciences | Cat#610340 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-DR5 D4E9 | Cell Signaling | Cat#8074 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-TNFR2 | Cell Signaling | Cat#3727 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-DR4 D9S1R | Cell Signaling | Cat#42533 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-TNFR1 C25C1 | Cell Signaling | Cat#3736 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-DR6 E8D21 | Cell Signaling | Cat#93026 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-cFLIP D5J1E | Cell Signaling | Cat#56343 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-MAVS | Cell Signaling | Cat#3993 |
| Mouse monoclonal J2 (anti-dsRNA) | Scicons | Cat#10010500 |
| Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG | Invitrogen | Cat#A11029 |
| Alexa Fluor 594 goat anti-rabbit IgG | Invitrogen | Cat#A11012 |
| Rabbit monoclonal anti-CD8a D4W2Z | Cell Signaling | Cat#98941 |
| Bacterial and Virus Strains | ||
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Biological Samples | ||
| Syngeneic mouse tumors | Laboratory of Xiang H.-F. Zhang | N/A |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| H3B-8800 | Seiler et al., 2018 | N/A |
| SD6 | Lagisetti et al., 2013 | N/A |
| dTAG-51 | Nabet et al., 2018 | N/A |
| Z-VAD-FMK | R&D Systems | Cat#FMK001 |
| Z-IETD-FMK | R&D Systems | Cat#FMK007 |
| Z-AEVD-FMK | R&D Systems | Cat#FMK009 |
| Z-LEHD-FMK | R&D Systems | Cat#FMK008 |
| RNase III | Applied Biosystems | Cat#A2290 |
| RNaseOne | Promega | Cat#M4261 |
| SuperScript III | ThermoFisher Scientific | Cat#18080093 |
| SYBR Select Master Mix | Applied Biosciences | Cat#4472908 |
| Hoechst 33342, trihydrochloride, trihydrate | Life Technologies | Cat#H3570 |
| Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Roche | Cat#11836170001 |
| Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail 2 | Sigma | Cat#P5726 |
| Clarity ECL Substrate | Bio-Rad | Cat#170–5060 |
| Q5 High-Fidelity 2X MasterMix | New England Biosciences | Cat#M04292 |
| RNasin Plus | Promega | Cat#N2111 |
| Protein A Dynabeads | Invitrogen | Cat#10001D |
| Propidium Iodide | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#P4864 |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| RT2 Profiler PCR Array Human Antiviral Response | Qiagen | Cat#330321 |
| Milliplex Human Cytokine/Chemokine Panel 1 | MilliporeSigma | Cat#HCYTOMAG-60K |
| CellTiterGlo | Promega | Cat#G7570 |
| Caspase-Glo 3/7 | Promega | Cat#G8090 |
| Caspase-Glo 8 | Promega | Cat#G8200 |
| Pierce BCA Protein Assay | Thermo Scientific | Cat#23225 |
| Deposited Data | ||
| SUM159 SD6 RNA-Seq | This manuscript | GEO#GSE163414 |
| LM2 SD6 RNA-Seq | This manuscript | GEO#GSE163411 |
| SUM159 Cytoplasmic RNA-Seq | This manuscript | GEO#GSE163232 |
| SUM159 J2 dsRIPseq | This manuscript | GEO#GSE163188 |
| Syngeneic model RNA-Seq | This manuscript | GEO#GSE163181 |
| TCGA RNA-Seq Data | Koboldt et al., 2012 | dbGaP: phs000178.v10.p8; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/gap/cgi-bin/study.cgi?study_id=phs000178.v10.p8 |
| TCGA RNA-Seq Clinical Data | The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network | https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/ |
| Experimental Models: Cell Lines | ||
| Human: 293T | ATCC | Cat#ATCC CRL-3216 |
| Human: SUM159 (female) | BioIVT | Cat#SUM-159PT |
| Human: MDA-MB-231-LM2 (female) | Minn et al., 2005 | N/A |
| Human: HME1 (female) | Infinity | Cat#hTERT-HME1 |
| Human: HME1 MYC-ER | Kessler et al., 2012 | N/A |
| Human: SUM159 SF3B1−/− SF3B1-FKBP12F36V | This manuscript | N/A |
| Human: MDA-MB-231 (female) | ATCC | Cat#ATCC HTB-122 |
| Human: BT549 (female) | ATCC | Cat#ATCC HTB-26 |
| Human: SUM159 SF3B1WT | This manuscript | N/A |
| Human: SUM159 SF3B1R1074H | This manuscript | N/A |
| Human: MDA-MB-231-LM2 SF3B1WT | This manuscript | N/A |
| Human: MDA-MB-231-LM2 SF3B1R1074H | This manuscript | N/A |
| Mouse: p53−/− 2208L (female) | Laboratory of Xiang H.-F. Zhang | N/A |
| Mouse: p53−/− T11 (female) | Laboratory of Xiang H.-F. Zhang | N/A |
| Mouse: MMTV PyMT-M (female) | Laboratory of Xiang H.-F. Zhang | N/A |
| Mouse: AT3 (female) | Laboratory of Xiang H.-F. Zhang | N/A |
| Experimental Models: Organisms/Strains | ||
| Mouse: BALB/c AnNHsd (female) | Envigo | Cat#4701F |
| Mouse: C57BL/6J (female) | Jackson Laboratory | Cat#000664 |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| See Table S5 for shRNA sequences | Rousseaux et al., 2018 | N/A |
| See Table S5 for siRNA sequences | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/rnai/synthetic-rnai-analysis/ambion-silencer-select-sirnas.html |
| See Table S6 for Primer Sequences used for RT-qPCR | Integrated Data Technologies | N/A |
| See Table S7 for smFISH probe sequences | Biosearch Technologies, Inc. | N/A |
| shRNA Genomic Amplification Forward Primer: TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTA | Integrated Data Technologies | N/A |
| shRNA Genomic Amplification Reverse Primer: GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTATAAACGGTTGGTCTTCCAA | Integrated Data Technologies | N/A |
| sgRNA Control Sequence: GTCCTGGCAGGGCTGTGGTG | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/genome-editing/geneart-crispr/crispr-libraries/lentiarray-crispr-libraries.html |
| RNF128 sgRNA-1 Sequence: CACGAATTTCACGGTGCCCA | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/genome-editing/geneart-crispr/crispr-libraries/lentiarray-crispr-libraries.html |
| RNF128 sgRNA-2 Sequence: GAAATTCGTGTGCGGGTTAC | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/genome-editing/geneart-crispr/crispr-libraries/lentiarray-crispr-libraries.html |
| MAVS sgRNA-1 Sequence: GTACTTCATTGCGGCACTGA | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/genome-editing/geneart-crispr/crispr-libraries/lentiarray-crispr-libraries.html |
| MAVS sgRNA-2 Sequence: GGGTATTGAAGAGATGCCAG | ThermoFisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/us/en/home/life-science/genome-editing/geneart-crispr/crispr-libraries/lentiarray-crispr-libraries.html |
| SF3B1 crRNA-1 Sequence: AAGAUCGCCAAGACUCACGA | Dharmacon | Cat#CR-020061–01 |
| Edit-tracrRNA | Dharmacon | Cat#U-002000 |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| pINDUCER20-Cas9 | This manuscript | N/A |
| pHAGE-PGK-E2 Crimson | This manuscript | N/A |
| pHAGE-PGK-SF3B1-FKBP12F36V | This manuscript | N/A |
| pINDUCER20-SF3B1WT | This manuscript | N/A |
| pINDUCER20-SF3B1R1074H | This manuscript | N/A |
| pCW-Cas9 | Wang et al., 2014 | Addgene (Plasmid #50661) |
| pInducer20 | Meerbrey et al., 2011 | Addgene (Plasmid #44012) |
| Software and Algorithms | ||
| SAMtools (v1.4) | Li et al., 2009 | https://github.com/samtools/ |
| Hisat2 (v2.0.4) | Kim et al., 2015 | https://daehwankimlab.github.io/hisat2/ |
| Cufflinks (v2.2.1) | Trapnell et al., 2010 | https://github.com/cole-trapnell-lab/cufflinks |
| FeatureCounts (v1.6.2) | Liao et al., 2014 | http://subread.sourceforge.net/ |
| MSigDB | Subramanian et al., 2005; Liberzon et al., 2011 | http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsea/msigdb |
| Mouse gene expression pathways | Baderlab | http://baderlab.org/GeneSets |
| RefSeq Annotation | NCBI | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/ |
| DESeq2 | Love et al., 2014 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html |
| Pysam | Li et al., 2009 | https://github.com/pysam-developers/pysam |
| RepeatMasker (open-4.0.5) | Institute for Systems Biology | http://www.repeatmasker.org/ |
| Metascape | Zhou et al., 2019 | https://metascape.org/gp/index.html#/main/step1 |
| Cutadapt | Martin, 2011 | https://cutadapt.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html |
| Bowtie2 | Langmead and Salzberg, 2012 | https://github.com/BenLangmead/bowtie2 |
| Meshes (v1.8.0) | Yu, 2018 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/meshes.html |
| StringDB (v11.0) | Szklarczyk et al., 2018 | https://string-db.org/ |
| NIS-Element AR | Nikon | AR 4.30.01 |
| ImageJ | NIH | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html |
| RNAfold | Institute for Theoretical Cehmistry | http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi |
| Adobe Photoshop | Adobe | N/A |
| ssGSEA | Barbie et al., 2009 | https://github.com/broadinstitute/ssGSEA2.0 |
| STAR aligner (v2.3.1) | Dobin et al., 2013 | https://github.com/alexdobin/STAR |
| TCGAbiolinks | Colaprico et al., 2015 | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/TCGAbiolinks.html |
| Other | ||
| N/A | N/A | N/A |
Vectors and virus production
Lentiviruses and retroviruses were generated by transfection of 293Ts with appropriate shRNA, sgRNA, or cDNA construct with packaging plasmids using Mirus Bio’s TransitIT transfection reagent. Viral supernatants were harvested 48 hours after transfection.
RNA isolation and library preparation
Total RNA (1ug/sample) was used as input for the TruSeq Stranded mRNA HT Prep Kit (Illumina). Libraries were made following Illumina’s recommended protocol, except for dsRNA libraries. For library preparation of J2 enriched dsRNA, first stranded cDNA synthesis was performed using SuperScript III (ThermoFisher Scientific) with the following modifications: RNA was heated to 70°C for 3 minutes to reduce secondary structure, followed by reverse transcription for 10 minutes at 25°C, 50 minutes at 50°C, and 15 minutes at 70°C. Amplified libraries were purified and quantified using the KAPA quantification kit (Roche). Libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500 instrument as 75-bp paired-end reads. In Figures 1A–1D SD6 gene expression analyses, cells were treated with DMSO or SD6 GI40 dose (200nM for SUM159 and 50nM for LM2).
Alignment of sequencing data
After demultiplexing, reads for both human and mouse samples were processed using SAMtools (v1.4) (Li et al., 2009) and aligned using the splice aware aligner Hisat2 (v2.0.4) (Kim, Langmead and Salzberg, 2015) with default parameters. The coordinates and gene annotations used in all subsequent analyses were based on the human (hg38/GRCh38) and mouse (mm10/GRCm38) reference genome builds and the corresponding UCSC RefSeq genes unless otherwise noted.
Gene expression and retrotransposon expression analysis
Gene expression FPKM values used for downstream GSEA analyses were obtained using the cufflinks suite (v2.2.1) (Trapnell et al., 2010). For analysis of differential gene expression changes in “sensitive” vs. “resistant” syngeneic tumors after H3B-8800 treatment, the following pipeline was employed: featureCounts (v1.6.2) (Liao, Smyth and Shi, 2014) was used to quantify counts, followed by interaction analysis using DESeq2 (Love, Huber and Anders, 2014) with the following design: ~ response + treatment + response:treatment. Annotations for repeat elements were obtained from RepeatMasker (open-4.0.5). Counting of reads mapped to annotated repeat elements was performed using the Python module Pysam (Li et al., 2009). Expression was then RPKM normalized.
Pathway enrichment analysis
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed on genes differentially expressed after spliceosome inhibition in human cell lines and syngeneic murine tumors (p≥0.05). Reactome pathways from the MSigDB database (Liberzon et al., 2011; Subramanian et al., 2005) were used for human data analysis; the “Mouse_AllPathways_June_24_2016_symbol.gmt” pathway collection from the Bader lab (http://baderlab.org/GeneSets), consisting of C2 Canonical Pathways (C2 CP) was used for mouse GSEA data analysis. Pathway over-representation of genes with differential gene expression changes in “sensitive” vs. “resistant” syngeneic tumors after H3B-8800 treatment was performed using Metascape (Zhou et al., 2019) using C2 CP annotations.
Intron retention (IR) analysis
Hisat2-aligned reads were filtered for proper-paired reads (-f 2 flag in SAMtools). Intron annotations were parsed from UCSC RefSeq gene annotation files and were filtered to exclude features that overlap genomic loci on the same strand. Reads mapping to introns were counted using Pysam. For each intron feature, we defined the following two read classes: (1) “intronic” reads mapping at least 6 bases contiguously within the intron and (2) “spanning” reads with ends mapping to the flanking exons. The intron retention (IR) score was then computed as the ratio of the RPKM-normalized “intronic” read density over the RPKM-normalized “spanning” read density. In order to compare commonly expressed IR events across samples, introns with <10 spanning RPKM in any sample were excluded from all analyses. Statistical analyses were performed using R. Empirical cumulative distributions of IR scores were compared, and p-values estimated using a Mann-Whitney U test.
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). Synthesis of cDNA was done using the High-Capacity RNA-to-cDNA Kit (Applied Biosystems). RT-qPCR was performed using the SYBR Select Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) on 20ng of input cDNA. Relative transcript abundance was normalized (GAPDH for human samples, 18s for mouse samples) and assessed using the Applied Biosystems StepOne Software v2.1. Data were calculated as log2(fold change) relative to control data using the ΔΔCt method. All experiments were performed in biological triplicate. For intron retention analysis, primer sets were designed to measure intron-containing transcripts and fully spliced transcripts. Intron retention was calculated as the ratio of intron-containing transcripts over fully spliced transcripts. Data were calculated as fold change relative to control data using the ΔΔCt method. For enzymatic dsRNA structure probing, relative transcript abundance was normalized (ACTB) and data were calculated as fold change relative to control data using the ΔΔCt method. In Figure 1G–H, MYC-ER HME1 cells were treated with 10nM 4-OHT and 10nM H3B-8800. In Figure 2E, SUM159 cells were treated with 200nM SD6. In Figures 5J and S5W, SUM159 cells were treated 15nM H3B-8800. In Figure 4, SUM159 cells were treated with 100nM H3B-8800. In Figure S5F, SUM159 cells were treated with 100nM H3B-8800. In Figure 6I, syngeneic tumor-derived cell lines were treated with 50nM H3B-8800. In Figure 6K, syngeneic tumor-derived cell lines were treated with 25nM H3B-8800. See Table S6 for primer sequences.
RT2 Profiler PCR Array
Innate immune transcriptional changes in response to treatment with H3B-8800 were measured using RT2 Profiler PCR Array Human Antiviral Response (Qiagen, 330231) following treatment of SUM159s (DMSO or 25nM H3B-8800) and LM2s (DMSO or 25nM H3B-8800). Relative transcript abundance was normalized to B2M and assessed using the Applied Biosystems StepOne Software v2.1. Data were calculated as fold change relative to control data using the ΔΔCt method. All experiments were performed in biological triplicate.
Luminex Cytokine Analysis
SUM159 cells were treated with DMSO or 25nM H3B-8800 and conditioned media was collected for analysis using the Luminex Assay. Conditioned media was incubated overnight with analyte targeted beads and analyte concentration was calculated based on analyte standard curve. Concentration was normalized to cell number determined by Hoechst 33342 (Life Technologies) staining of a duplicate plate, followed by nuclei counting using the Celigo Imaging Cell Cytometer (Brooks).
SUM159 SF3B1- FKBP12F36V cell line generation and assays
The FKBP12F36V fragment (Nabet et al., 2018) was fused to the C-terminus of SF3B1 cDNA and cloned into a pHAGE-PGK backbone. Cas9 was amplified from pCW-Cas9 (Wang et al., 2014) and cloned into pINDUCER20 to allow for dox-inducible Cas9 expression (Meerbrey et al., 2011). This vector was transduced into SUM159 cells and was selected with neomycin. A clone was selected to generate SUM159-Cas9 cells with homogenous Cas9 expression and inducibility. SUM159 cells stably expressing dox-inducible Cas9 were transduced with the SF3B1-FKBP12F36V lentivirus and then selected with puromycin. To knock out the endogenous SF3B1 locus, Cas9 expression was turned on with 500 ng/mL of doxycycline for 24 hours, followed by 48 hour co-transfection of Edit-R tracrRNA (Dharmacon) and crRNA targeting the first intron-exon junction of SF3B1. A single clone was then selected, and Western blotting was used to confirm knockout of the endogenous protein and expression of SF3B1- FKBP12F36V. SF3B1 degradation was assayed using 10nM dTAG-51 (Nabet et al., 2018) for the stated durations. Gene expression analysis in Figure 1J was performed following treatment with DMSO or 10nM dTAG-51. Immunofluorescence assay in Figure 3F were performed following 10nM dTAG-51 treatment.
Western blot
Cell lysates were collected in RIPA Buffer + Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche, 11836170001) + Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail 2 (Sigma, P5726), then mixed with 6× Laemmli SDS reducing buffer (Alfa Aesar, J61337) before incubation at 95°C for 10 minutes. Protein lysates were quantified using Pierce BCA Protein Assay (Thermo Scientific, 23225). Samples were loaded for SDS-PAGE using homemade tris-glycine gels and run in SDS running buffer.
Proteins were transferred using wet transfer to 0.45μM Nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare Life Science, 10600007). The membrane was blocked for 1 hours using 5% BSA in TBS-T (0.1% Tween-20 in 1× TBS) and incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4°C. The membrane was then washed 3 times in TBS-T for 5 minutes before incubation with the secondary antibody at RT for 2 hours. The membrane was then washed 3 times with TBST before incubation with Clarity Western ECL Substrate (Bio-Rad, 170–5060) and imaging with the ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad).
shRNA screen
SUM159s were transduced with a MSCV-based retroviral library (Rousseaux et al., 2018) containing a total of 18,370 shRNAs divided into two separate pools at a MOI of 0.5 and a target representation of 1000 cellular integrations for each shRNA. After transduction, cells were selected for 3 days in puromycin, then split into parallel +/− SD6 arms (in quadruplicate) and cultured for 12 population doublings. During this time, cells were passaged every 3 days (6 passages for DMSO treated, 7 passages for SD6 treated). After selection (T0) and at each subsequent passage, 20 million cells were collected from each replicate and stored at −80°C. Cell pellets from T0 and the final passage were used for downstream analysis.
Library preparation and sequencing
The QIAamp DNA Blood Midi kit (QIAGEN) was used to extract genomic DNA from cell pellets followed by ethanol precipitation to clean and concentrate. Half-hairpin sequences were amplified from the genomic DNA (primers 5’- TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTAGTGAAGCCACAGATGTA-3’ and 5’- GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGTATAAACGGTTGGTCTTCCAA-3’) using Q5 High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix (NEB). PCR reactions were cleaned up using Agencourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter) followed by measurement of the concentration of the target amplicon using the Agilent 4200 TapeStation. DNA samples were indexed using the Nextera XT kit (Illumina) and size selected to remove spurious amplification products using the PippinHT (Sage Science). Indexed and size-selected samples were quantified using the KAPA Illumina Library Quantification kit (KAPA Biosystems) and pooled at equal concentration prior to sequencing using the HiSeq 2500 System (Illumina) in single-end, 100bp, high-output mode using v4 SBS reagents.
Data processing and analysis
Cutadapt (Martin, 2011) was used to remove adapter sequences from reads, followed by alignment to the reference library using Bowtie 2 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012) in end-to-end mode, allowing up to a maximum of 3 mismatches/indels compared to the reference sequence. The number of reads mapping to each shRNA in each sample was then extracted from the SAM files and DESeq2 (Love, Huber and Anders, 2014) was used to determine the fold-change in abundance of each shRNA between the vehicle and SD6-treated arms after 12 population doublings. shRNA-level fold-change estimates were combined to gene-level estimates by summing the individual fold-changes of all “significant” shRNAs (p-value <0.05 and absolute fold-change > 0.5) mapped to a given gene. Gene-level p-values were calculated by combining the individual p-values of all “significant” shRNAs mapping to a given gene using Fisher’s method. Gene-level weighted growth effects were calculated by multiplying the gene-level fold change by the -log10 (gene-level p-value).
Screen candidate MeSH and StringDB analysis
Analysis of over-represented Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) was performed using the R package “meshes” (v1.8.0) (Yu, 2018) with the following parameters: MeSHDb = ‘MeSH.Hsa.eg.db’, database = ‘gene2pubmed’ and category = ‘C’. For Cytoscape visualization, individual genes in MeSH term categories were set as nodes and common MeSH terms as edges. Pathway over-representation for screen candidates was performed using StringDB (v11.0) (Szklarczyk et al., 2019).
Competition assays
SUM159 cells were transduced with MSCV retroviral shRNAs targeting Firefly luciferase (shControl), RNF128, RNF125, UBE2D1, or USP1 and selected for three days with puromycin. After selection, these cells were mixed at a 40:60 ratio with SUM159 cells transduced with pHAGE-PGK-E2 Crimson and grown in 96-well plates in the presence of DMSO or 200nM SD6. At seeding and when the cells reached confluence, cells were passaged and the percentage of E2-Crimson-positive cells was measured by flow cytometry. The percentage of shRNA knockdown cells was calculated as the percentage of non-E2 Crimson positive cells.
Fluorescent immunohistochemistry
Cells were washed with PBS, fixed with 4% (v/v) formaldehyde for 15 minutes at room temperature, washed 3 × with PBS, and permeabilized with 0.5% (v/v) Triton-X for 10 minutes at RT. Cells were blocked with 3% BSA in PBS for 15 minutes at RT before incubating with primary antibody (monoclonal anti-dsRNA J2 (Scicons, 10010500) (Schönborn et al., 1991), monoclonal anti-MAVS (Cell Signaling, 24930)) diluted in blocking buffer at 4°C overnight. Cells were washed 3 × with PBS before incubation with secondary antibody (Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen, A11029) for J2 antibody and Alexa Fluor 594 goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen, A11012) for MAVS antibody), Hoechst 33342 (Invitrogen, H3570), and Phalloidin (Invitrogen, A12381) for 1 hour at RT in the dark. Cells were washed 3 × with PBS before mounting on coverslips with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories, H-1000).
J2 immunofluorescence imaging and analysis
SUM159, MDA-MB-231, and BT549 cells were treated with DMSO or 100nM H3B-8800 before processing. LM2 cells were treated with DMSO or 50nM H3B- before processing. In Figure 3E, MYC-ER HME1 cells were treated with 10nM 4-OHT and 20nM H3B-8800. In Figure S3C, SUM159 and HME1 cells were treated with DMSO or 50nM H3B-8800 before processing. In Figure 6J, syngeneic tumor-derived cell lines were treated with DMSO or 20nM H3B-8800 before processing. When indicated, cells were incubated with 4U RNaseIII (Applied Biosystems, A2290) in reaction buffer at 37C for 4 hours as instructed after permeabilization. For J2 dsRNA imaging, cells were imaged and analyzed on a Nikon Eclipse Ti-E inverted microscope with the NIS-Element AR 4.30 software. Briefly, images were captured with Z-stacked (0.3um) setting under 60X oil objective lens and Andor Zyla 4.2 sCMOS camera. For quantification the cytoplasmic J2 intensity, a ROI defining cytoplasm was determined by the Hoechst and Phalloidin staining for each cell. The average fluorescent intensity for defined ROIs and background from the same image were directly measured by the NIS-Element AR software. J2 intensity for each cell was defined by difference between the ROI and background intensity. J2 intensity was normalized to mean intensity in the DMSO treated state for each experiment. Plots shown in figures are from one representative experiment of more than three independent experiments.
SF3B1R1074H cell line generation and assays
The SF3B1R1074H mutant was generated in pDONR221 using the QuikChange II Site Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent). SF3B1WT and SF3B1R1074H were FLAG-tagged then cloned into pINDUCER20 to allow for dox-inducible expression. This vector was transduced into SUM159 and LM2 cells. H3B-8800 dose curve assay was performed by treating SUM159 and LM2 cells with 1ug/mL doxycycline followed by the indicated concentration of H3B-8800. Cell numbers were determined by Hoechst 33342 staining, followed by nuclei counting using the Celigo Imaging Cell Cytometer (Brooks). Western blot analysis of inducible protein expression was performed with the same treatment conditions. Intron retention following treatment of SUM159 cells ± 1 ug/mL doxycycline for 24 hours followed by 12 hours of treatment with 100nM H3B-8800 using RT-qPCR. Immunofluorescence assays were performed ± 1 ug/mL doxycycline for 24 hours followed by DMSO or 50nM H3B-8800 treatment.
Cellular fractionation
SUM159 cells were treated with 100nM H3B-8800 or DMSO, collected in biological duplicate in ice-cold PBS, then spun down at 180g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Supernatant was removed, and cells were lysed in cytoplasmic lysis buffer (CLB: 10mM HEPES, pH 7.9, 10mM KCl, 1mM MgCl2, 0.5mM EDTA, 1mM DDT, 0.1% Igepal CA-630, 1 U/ul RNasin Plus) for 5 minutes on ice. Lysates were spun down at 1000g for 5 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant, or cytoplasmic fraction, was transferred to separate tubes for collecting RNA and protein. The cell pellet was washed once with CLB and lysed on ice in high salt nuclear lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4, 300 mM NaCl, 1mM MgCl2, 0.5% Igepal CA-630, 0.1% SDS) for 5 minutes on ice. The lysate was then divided for collecting RNA and protein. Equal cell-normalized quantities of protein were analyzed by Western blot to confirm fractional purity (total H3 for nuclear fraction, α-Tubulin for cytoplasmic fraction).
RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization
Custom Stellaris® FISH probes were designed against SEC14L1 and SETD1A by utilizing the Stellaris® RNA FISH Probe Designer (Biosearch Technologies, Inc., Petaluma, CA) available online at www.biosearchtech.com/stellarisdesigner (see Table S8 for probe sequences). The probe sets were hybridized with TAMRA (intronic probe sets) and Quasar 670® (exonic probe sets). RNA FISH was performed following the manufacturer’s instructions available online at www.biosearchtech.com/stellarisprotocols. with minor modifications. In brief, SUM159 cells were treated with DMSO or 100nM H3B-8800. Fixation and permeabilization were performed as described for immunofluorescence. After permeabilization, cells were washed 2 × with PBS and 1× with Wash Buffer A (Bioresearch Technologies, SMF-WA1–60) with 10% (v/v) formamide (Ambion, AM9342) at RT for 5 minutes. Coverslips were than incubated in the Hybridization Buffer (Bioresearch Technologies, #SMF-HB1–10) with 10% (v/v) formamide containing indicated probes at 37°C overnight in a humidified chamber. Coverslips were washed with Wash Buffer A at 37°C for 30 minutes, then incubated with Wash Buffer A containing Hoechst for 37°C for 30 minutes. Samples were then washed with Wash Buffer B (Bioresearch Technologies, #SMF-WB1–20) at RT for 5 minutes. Coverslips were mounted onto microscope slides with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories, H-1000). All steps following hybridization were done protected from light. Imaging was performed and processed as previously described using a GE Healthcare DVLive epifluorescence microscope. After imaging, Z-stacks were transformed into a 2D image by maximal projection. Cytoplasmic intron and exon foci for each cell were manually counted by the ImageJ software. Plots shown in figures are representative of two independent experiments.
dsRNA immunoprecipitation (J2 dsRIP)
Protein A Dynabeads were washed and resuspended in NT-2 buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Igepal CA-630). Per sample, 100ul of beads were pre-bound to 5 ug of anti-dsRNA mAb (J2) overnight at 4°C. SUM159 cells were treated with 100nM H3B-8800 or DMSO, collected in biological duplicate in ice-cold PBS, then spun down at 180g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Supernatant was removed, and cells were lysed in 1mL RIP buffer (25 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Igepal CA-630, 1 U/ul RNasin Plus) for 5 minutes on ice. The supernatant was transferred to a new Eppendorf. Total RNA was harvested from 10% input lysate using Trizol. For immunoprecipitation, 100 ul of J2-bound Protein A Dynabeads was added to the remaining lysate and incubated for 3 hours at 4°C with constant mixing. Beads were washed three times with NT-2 buffer, transferred to a new tube, and then washed three times with high salt wash buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4, 300 mM NaCl, 1mM MgCl2, 0.5% Igepal CA-630, 0.1% SDS). J2-bound dsRNA was harvested directly from beads with Trizol. Chloroform was added at a ratio of 1:5, and RNA was isolated from the aqueous phase using the RNA Clean and Concentrator columns (Zymo).
RNA structure prediction
RNA structure prediction was done using the RNAfold web server (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAfold.cgi) with default options.
Enzymatic dsRNA structure probing
SUM159 cells were treated with 100nM H3B-8800 or DMSO, collected in biological triplicate in ice-cold PBS, then spun down at 180g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Supernatant was removed and cells were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. Cells were lysed in 1mL RIP buffer (25 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.1% Igepal CA-630, 1 U/ul RNasin Plus) for 5 minutes on ice. The supernatant was transferred to a new Eppendorf. Lysates were treated with or without 5U RNaseOne (Promega, M4261) for 30 minutes at room temperature. RNA was harvested using Trizol. Chloroform was added at a ratio of 1:5, and RNA was isolated from the aqueous phase using the RNA Clean and Concentrator columns (Zymo). First stranded cDNA synthesis was performed using SuperScript III (ThermoFisher Scientific) with the following modifications: RNA was heated to 70°C for 3 minutes to reduce secondary structure, followed by reverse transcription for 10 minutes at 25°C, 50 minutes at 50°C, and 15 minutes at 70°C. Transcript abundance was measured using RT-qPCR using the SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) on 20ng of input cDNA. Relative transcript abundance in samples treated with and without RNaseOne was normalized (ACTB) and assessed using the Applied Biosystems StepOne Software v2.1. The dsRNA/ssRNA fold enrichment was calculated using the ΔΔCt method comparing relative transcript abundance in the sample treated with RNaseOne to the sample treated without RNaseOne.
Cell viability assays
PI positive cells were assessed by incubating cells with 1:100 dilution of Propidium Iodide (Sigma Aldrich, P4864) for 15 minutes before counting using the Celigo Imaging Cell Cytometer (Brooks). Number of PI positive foci was normalized to cell number determined by Hoechst 33342 staining of a duplicate plate, followed by nuclei counting using Celigo Imaging Cell Cytometer (Brooks). Cell viability was assessed by incubating CellTiterGlo (Promega, G7570) with cells for 10 minutes in a 96-well plate and measuring luminescence with a plate reader (Molecular Devices). SUM159 cells were treated with 50nM H3B-8800. Luminescence was normalized to cell number as described above.
Luminescent apoptosis assays
Caspase-3/7 and Caspase-8 activity was assessed in breast cancer lines by incubating Caspase-Glo 3/7 (Promega, G8090) and −8 (Promega, G8200) reagent with cells for one hour in a 96-well plate and measuring luminescence with a plate reader (Molecular Devices). SUM159 and LM2 cells were treated with 50nM H3B-8800 for 36 hours or with 200nM SD6 and 1ug/mL ZVAD, ZIETD, Z-AEVD, or Z-LEHD (R&D Systems) as annotated. MYC-ER HME1 cells were treated with 10nM 4-OHT and 20nM H3B-8800. 2208L, PyMT-M, AT3, and 2208L cells were treated with 50nM H3B-8800. Luminescence was normalized to cell number determined by Hoechst 33342 staining of a duplicate plate, followed by nuclei counting using the Celigo Imaging Cell Cytometer (Brooks).
MAVS immunofluorescence aggregation imaging and analysis
LM2 and SUM159 cells were treated with DMSO, 20nM H3B-8800, or .5ug/mL p (I:C) (Sigma Aldrich, P1530). High resolution imaging was performed on a GE Healthcare DVLive epifluorescence image restoration microscope using an Olympus PlanApo 60×/1.42 NA objective and a 1.9k × 1.9x sCMOS camera. Z stacks (0.25μm) were acquired before applying a conservative restorative algorithm for quantitative image deconvolution. Max intensity projections were generated and used for image analysis. To quantify the spatial distribution of the MAVS signal, we measured a dispersion index using a custom-made MATLAB script. Briefly, z-stacks were transformed into a 2D image by maximal projection. Single cells were then manually segmented using an interactive polygonal ROI. The dispersion index of the MAVS signal for each cell was then determined as follows: first, the MAVS signal was segmented using an Otsu thresholding method, and the weighted centroid location of the resulting mask was determined using the underlying pixel intensities. Then, the distance between each pixel of the MAVS mask to the weighted centroid was calculated and the dispersion index was defined as the mean of these distances. Aggregation was calculated as the inverse of the dispersion index.
Semi-Denaturing Detergent Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (SDD-AGE)
SUM159 and LM2 cells treated with DMSO or 20nM H3B-8800 were washed with ice-cold PBS and detached using a cell scraper. Cells were pelleted, resuspended in Buffer A (10mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 10mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 M D-mannitol, and Roche EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail), and lysed by repeated douncing. Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 1000 × g for 5 minutes, and the supernatant was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 minutes at 4°C to isolate the P5 mitochondrial fraction. SDD-AGE was performed according to a previously published protocol (Halfmann and Lindquist, 2008) with slight modifications. Crude P5 mitochondria was resuspended in 1 × sample buffer (0.5 × TBE, 10% glycerol, 2% SDS, and 0.0025% bromophenol blue) and run on a vertical agarose gel (1.5% agarose with 0.1% SDS in 1 × TBE) in running buffer (1 × TBE with 0.1% SDS) for 45 minutes at a constant 100 V in 4°C. Protein was transferred using capillary transfer overnight to a nitrocellulose membrane for immunoblotting.
In vivo tumor studies
Tumor chunks were transplanted into clear mammary fat pad of 4–5 week old female C57BL/6J or BALB/c AnNHsd female mice. 2208L, PyMT-M, and AT3 tumors were randomized onto vehicle or H3B-8800 (8 mg/kg in 0.5% methylcellulose daily) at 150–250mm3 for long term response studies or 300–500mm3 for short term studies. T11 tumors were randomized onto vehicle or H3B-8800 one day post tumor transplant. Tumor volume was measured using calipers three days per week. Tumors were harvested between 1500 and 2000 mm3. Tissue chunks were stored in RNAlater for gene expression profiling. Tissue for IHC analysis was fixed in PFA, 70% EtOH, then paraffin embedded.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and quantification
Tumor chunks were fixed in 10% formalin overnight at 4°C overnight, and subsequently transferred into 70% ethanol, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned at regular intervals. Slides were deparaffinized and hydrated using xylene, graded ethyl alcohol, and dH2O. After antigen retrieval, 15 minutes of steaming at 90°C with pressure in 0.1M Tris-HCl, pH 9.0, sections were treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution for 5 minutes. Sections were incubated with primary antibody (CD8a, Cell Signaling 98941 diluted 1:100) for 1hr at RT. Sections were then incubated with Envision Labelled Polymer-HRP (Dako) for 30 minutes at RT. DAB+ solution (DakoCytomation) was then added to section, incubated for 15 minutes, followed by application of DAB Sparkle Enhancer (Biocare). Sections were counterstained with Harris Hematoxylin. Counting of CD8a+ stained cells was done using the Count Tool in Adobe Photoshop.
Immune signature single sample GSEA (ssGSEA)
Analysis of immune cell gene signatures was performed using single sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (Barbie et al., 2009). Marker genes for immune cell types were obtained from (Bindea et al., 2013). Heatmaps display z-score normalized IR levels and ssGSEA scores across samples, with “high” and “low” IR being defined as having an IR level outside one standard deviation of the mean.
TCGA intron retention and immune pathway analysis
Intron retention analysis was performed on BRCA TCGA RNA sequencing datasets (Koboldt et al., 2012). TCGA fastq reads were mapped using the STAR aligner (v2.3.1) (Dobin et al., 2013) onto the hg19/GRCh37 reference genome as previously described (Hsu et al., 2015). Level of intron retention (IR level) within each sample was calculated as the number of introns with IR scores > 0.01, as defined previously. “High” and “Low” IR were defined as having an IR level outside one standard deviation of the mean. RSEM normalized gene expression data from TCGA was obtained from the Broad GDAC Firehose. Copy number was obtained from cBioPortal as GISTIC2.0 data. Copy number analysis was done by segregating tumors based on a score of ≥ 1 (“High”) versus ≤ 0 (“Low” or normal). GSEA was performed using C2 Canonical Pathway annotations. TMB was obtained from GDC mutation data using the TCGAbiolinks R package (Colaprico et al., 2015). Survival data was obtained from the GDC portal and KM curves were plotted using the survminer R package. P-values were calculated using log-rank test.
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Data are typically mean ± SEM. Data were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test between two groups, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, or Mann-Whitney U test as appropriate. GraphPad Prism or R were used to generate all charts and statistical analyses. Statistical details of experiments, including statistical tests and sample sizes used, can be found in the figure legends. All experiments were performed on biological replicates unless otherwise specified.
Supplementary Material
(A) Spliceosome inhibition induces IFNB transcription followed by induction of interferon-stimulated genes. SUM159 cells were treated with SD6 for the indicated times and gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. Data are shown as expression relative to DMSO treated samples (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(B, C) Treatment with small molecule spliceosome inhibitor H3B-8800 induces activation of antiviral signaling genes. Gene expression of (B) SUM159s and (C) LM2s was measured upon 48 hours of H3B-8800 treatment using RT-qPCR. Gene expression changes (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are represented as relative to DMSO treated samples.
(D) Chemical genetic dTAG system can be used to specifically target SF3B1 for proteasomal degradation. Bifunctional dFKBP ligand targets exogenous SF3B1-FKBP12F36V for proteasomal degradation upon recruitment of the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRBN.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
(A) Immune signaling pathway components are enriched among genes that confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. StringDB functional enrichment analysis was performed on the top 50 SD6 resistance candidates identified by the shRNA screen. Functionally enriched Reactome Pathways with FDR < 0.001 are shown.
(B) Modulators of antiviral immune signaling response confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. Combined SD6-selective growth effect (log2) of each gene is plotted on the x-axis. Graphed is the weighted gene level sum of the effect of knockdown by multiple shRNAs (represented by the size of the bubble). Candidates with ≥4 hairpins that confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition and are implicated in innate immune response are colored red.
(C, D) Knockdown of USP1 and FBXO3 confers resistance to SD6. shRNAs targeting (C) USP1 and (D) FBXO3 confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. Five independent shRNAs targeting these genes were enriched with SD6 treatment, as compared to negative control shRNAs (ZBTB1 and TBC1D1). log2(fold change) is calculated based on the hairpin abundance in the SD6 treated samples as compared to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=4 biological replicates). Hairpins with log2(fold change) > 0.5 and p-value ≤ 0.05 are shown.
(E) Two independent UBE2D1-targeting shRNAs decreased expression of UBE2D1in SUM159 cells. UBE2D1 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(F) Two independent RNF128-targeting shRNAs cause decreased expression of RNF128 in SUM159 cells. RNF128 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(G) Two independent RNF125-targeting shRNAs cause decreased expression of RNF125 in SUM159 cells. RNF125 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
***p<0.001, **** p<0.0001
(A, B) Cytoplasmic accumulation of dsRNA in TNBC cell lines after H3B-8800. (A) Left, immunofluorescent staining of dsRNA (J2), cytoskeleton (phalloidin), and nuclei (Hoechst) in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Scale bars, 20µm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (B) Left, immunofluorescent staining of dsRNA (J2), cytoskeleton (phalloidin), and nuclei (Hoechst) in BT549 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Scale bars, 20µm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(C) Spliceosome inhibition causes cytoplasmic accumulation of dsRNA in TNBC cells but not in non-transformed mammary epithelial cells. Immunofluorescence labeling of dsRNA using anti-dsRNA (J2) antibody in SUM159 and (non-transformed) HME1 cells treated with the same dose of H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity is shown (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(D-H) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant mitigates sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. (D-F) SUM159 and (G, H) LM2 cells were engineered with doxycycline-inducible FLAG-tag SF3B1WT or SF3B1R1074H. (D, G) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1 (FLAG) and endogenous SF3B1 was measured by Western blot. (E, H) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses sensitivity to high doses of H3B-8800. (F) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses intron retention of U2AF2 in response to 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800.
(I) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses accumulation of dsRNA after spliceosome inhibitor treatment. Overexpression of SF3B1R1074H suppresses accumulation of dsRNA after treatment with H3B-8800 for 24 hours in LM2 cells. Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity in LM2 cells expressing SF3B1WT or SF3B1R1074H is shown (mean ± SEM from >50 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001
(A) Confirmation of purity of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions by histone H3 and α-Tubulin immunoblots. Shown are two biological replicates per condition.
(B) Spliceosome perturbation leads to aberrant splicing, such as retention of introns. Schematic of intron retention (IR) analysis of RNA-seq data. IR score is calculated as the ratio of intron read RPKM (unprocessed read coverage) to intron-spanning read RPKM (processed read coverage).
(C) Spliceosome inhibition leads to cytoplasmic intron retention of SEC14L1. Pileup of cytoplasmic reads mapping to the SEC14L1 intron and surrounding exons. Data are representative of biological duplicates for each condition.
(D, E) Spliceosome inhibition leads to accumulation of intron-retained RNAs in the cytoplasm. (D) RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images of retained introns and surrounding exon sequences for an intron in SETD1A after treatment with H3B-8800 for 12 hours. Arrows indicate overlapped intron and exon foci. Scale bars, 10µm. (E) Quantification of number of intron-retained mRNAs per cell is shown (mean ± SEM from >35 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(F) Spliceosome inhibition leads to cytoplasmic intron retention of SETD1A. Pileup of cytoplasmic reads mapping to the SETD1A intron and surrounding exons. Data are representative of biological duplicates for each condition.
(G) Intron-residing retrotransposons increase in expression after H3B-8800. Empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean retrotransposon RPKMs are plotted for 9,349 expressed elements. A rightward shift in the red curve indicates increased expression. Subclasses of retrotransposons such as short (left) and long (right) interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs and LINEs, respectively) also show increased expression after 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800 (p<2.2e16 for all comparisons by Mann-Whitney U test).
(H) Non-intronic retrotransposons show no change in expression after H3B-8800. Left, empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean retrotransposon RPKMs are plotted for 22,410 expressed elements. Non-intronic SINEs (left) and LINEs (right) show no increase in expression after 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800.
(I) J2-enriched retrotransposon-containing introns are predicted to form double stranded secondary structure. Structure analysis using RNAfold predicts a long stretch of double-stranded secondary structure comprised primarily of the inverted Alu-repeat regions of the J2-dsRIP enriched intron in RPL30.
(J, K) Introns not containing retrotransposons form double stranded secondary structure. (J) Pileup of J2 dsRIP-seq reads across an intron and exon in REXO1 and (K) predicted double-stranded secondary structure.
****p<0.0001
(A) Spliceosome inhibition activates caspases-3 and -7. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(B) Spliceosome inhibition activates caspase-8. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspase-8 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(C, D) Spliceosome inhibition in combination with MYC hyperactivation activates extrinsic apoptosis. Human mammary epithelial cells engineered with inducible MYC hyperactivation were treated for 4 hours ± 4-OHT (to induce MYC hyperactivation) followed by 32 hours ± H3B-8800 for a total treatment time of 36 hours. Cells were then assayed for (C) caspase-8 and (D) caspases-3 and -7 activation (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(E, F) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses activation of extrinsic apoptosis after H3B-8800 treatment. SUM159 cells expressing SF3B1WT and SF3B1R1074H were treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for activation of (E) caspase-8 and (F) caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(G) Spliceosome inhibitor-induced caspases-3 and -7 activity is dependent on activation of extrinsic apoptosis. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 and no caspase inhibitor, pan-caspase inhibitor (ZVAD), caspase-8 inhibitor (ZIETD), caspase-10 inhibitor (Z-AEHD), and caspase-9 inhibitor (Z-LEHD) for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay.
(H) Three independent RIPK3-targeting siRNAs decrease expression of RIPK3 in SUM159s. RIPK3 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control siRNA cell line.
(I, J) RIPK3 does not contribute to sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. SUM159 cells were transfected with either control (NTC) or RIPK3-targeting siRNA and treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for (I) cell viability using CellTiterGlo and (J) cell death using PI permeability (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(K) Extrinsic apoptosis ligands or receptors are not induced within 24 hours of spliceosome inhibition. Transcriptional changes upon treatment of SUM159s with H3B-8800 were measured using RNA-seq. Gene expression is represented as fold change relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(L) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of DR5 or TNFR2. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of DR5 and TNFR2 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to RAN shown.
(M) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of DR4. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of DR4 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to Vinculin shown.
(N) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of TNFR1 or DR6. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of TNFR1 and DR6 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to RAN shown.
(O) Spliceosome inhibition leads to increased c-FLIP protein level. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of c-FLIP isoforms was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to Vinculin shown.
(P) Spliceosome inhibition does not lead to mis-splicing of c-FLIP. RMATS analysis of RNA-seq from SUM159 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours reveals no significant difference in c-FLIP exon 7 usage.
(Q) Three independent TNFR1-targeting siRNAs decrease expression of TNFR1 in SUM159s. TNFR1 levels were assessed using Western blotting, with RAN probed as a load control.
(R, S) Knockdown of TNFR1 does not suppress activation of extrinsic apoptosis. SUM159 cells were transfected with either control (NTC) or TNFR1 targeting siRNA and treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for activation of (R) caspase-8 and (S) caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(T) Independent siRNAs decrease expression of the indicated genes in SUM159s. PKR, DDX1, DDX21, DHX36, DHX9, MDA5, RIG-I, and DHX33 expression levels (mean ± SEM) are calculated relative to expression in the control siRNA cell line.
(U, V) Spliceosome inhibition causes aggregation of the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS. (U) Immunofluorescence imaging of MAVS reveals that 12 hours of H3B-8800 treatment of LM2s results in aggregation of MAVS. Scale bars, 10µm. (V) MAVS aggregation was measured by change in dispersal of MAVS IF signal. MAVS aggregation (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) is defined as the inverse dispersion factor, which is calculated based on the dispersion of signal from the weighted centroid of MAVS signal.
(W) Spliceosome inhibition leads to aggregation of MAVS in LM2s, indicating activation. P5 mitochondrial fraction was prepared from LM2 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours or transfected with poly(I:C) and MAVS aggregation was analyzed by SDD-AGE.
(X) Two independent MAVS-targeting shRNAs decrease expression of MAVS in SUM159s. MAVS expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(Y) Two independent MAVS-targeting sgRNAs decrease protein level of MAVS in SUM159s. MAVS protein levels were measuring using Western blotting.
(Z) MAVS knockout suppresses upregulation of antiviral transcriptional changes. SUM159 dox-inducible Cas9 cells transduced with two independent sgRNAs targeting MAVS and cultured with dox to induce genomic editing of MAVS. MAVS knockout suppresses upregulation of CD80, MX1, and CCL5 upon 48 hours of H3B-8800 treatment relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001
(A, B) Immune-related pathways are significantly enriched in sensitive versus resistant tumor models. (A) Multivariate analysis comparing changed transcriptional programs upon H3B-8800 in “sensitive” models compared to “resistant” models yielded 1,564 differentially changed genes. Enrichment analysis of these genes using Metascape KEGG (mmu) and Reactome (R-MMU) pathways identified almost exclusively immune-related pathways as significantly enriched. (B) Metascape network visualizing pathways enriched in A. Among these pathways are three major clusters of pathways relating to antiviral immune signaling, cytokine and chemokine signaling, and adaptive immune signaling.
(C) Spliceosome inhibition differentially induces intron retention in sensitive versus resistant syngeneic models of TNBC in vitro. Cell lines derived from syngeneic tumor models were treated for 12 hours with H3B-8800 and intron retention was measured using RT-qPCR. Data are shown as expression relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(D) Spliceosome inhibition leads to production of cytokines and chemokines. Conditioned media collected from PyMT-M cells treated ± H3B-8800 for 60 hours was collected and the concentration of CXCL10 was measuring using the Luminex bead array (mean ± SEM, n=2 technical replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). Analyte concentration was normalized to cell number.
(E) Spliceosome inhibition leads to activation of caspase-8 in cells derived from the 2208L syngeneic tumor model. Cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours and assayed for caspase-8 activation (mean + SEM, n=3 biological replicates) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(F-I) H3B-8800 treatment leads to increased Cd4, Cd25, and Pd1 expression in responsive syngeneic models. Graphed is the relative FPKM from RNA-seq of (F) 2208L, (G) PyMT-M, (H) AT3, and (I) T11 treated with Vehicle or H3B-8800 (mean ± SEM, n≥2 tumors per treatment group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(J) Immune cytolytic index (CYT) increases in H3B-8800-sensitive tumor models and decreases in resistant tumor models after H3B-8800 treatment. CYT is calculated as the geometric mean of granzyme A (Gzma) and perforin (Prf1) FPKM.
(K, L) Spliceosome inhibition leads to increased CD8+ T cell infiltration. PyMT-M FFPE tumor sections treated with Vehicle (n=8) or H3B-8800 (n=7) were used for immunohistochemical staining using the CD8a antibody. (K) Quantification of number of CD8a+ cells per 10X field of view. Boxplot shows mean ± IQR. (L) Images shown are representative of the mean CD8a+ cells per 10X field for each of the treatment groups.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01
(A) Tumors with high levels of IR are not those with high TMB. Plotted are the TMB levels for tumors with high and low levels of IR, with TMB levels higher in those tumors with low IR levels (two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test).
Table S3. Syngeneic TNBC Model GSEA Pathway Enrichment, Related to Figure 6
Table S7. smFISH probe sequences, Related to STAR Methods
Highlights.
Spliceosome-targeted therapies (STTs) induce widespread mis-spliced mRNA in cancer
Mis-spliced, intron-retained mRNAs are an unexplored source of endogenous dsRNA
STTs trigger antiviral signaling and extrinsic apoptosis in TNBCs via dsRNA sensors
RNA mis-splicing in human breast cancers correlates with immune signatures
Acknowledgements
E.A.B. and J.H.W. are supported by Baylor Research Advocates for Student Scientists and the NIH (T32GM120011, E.A.B.). F.G. is supported by CPRIT (RP160283). J.K.M. is supported by Susan G. Komen (PDF17487931). This project was supported by the Advanced Technology Cores at BCM: Genomic and RNA Profiling Core (NCI: CA125123), Cytometry and Cell Sorting Core (CPRIT-RP180672), and Integrated Microscopy Core (NIH: DK56338 and CA125123; CPRIT: RP150578 and RP170719). This work was supported by the Dan L. Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center (NCI P30: CA125123) and Pathology Core of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center. The results shown here are based upon data generated by the TCGA Research Network: https://www.cancer.gov/tcga. I.G. is supported by the NIH (R01GM082837) and NSF (PHY-1147498, PHY-1430124, and PHY-1427654). J.H.W., W.W., X.H.-F.Z., and T.F.W. are supported by The McNair Medical Institute. X.H.-F.Z. and T.F.W. are supported by the DOD (1W81XWH-18-1-0573). T.F.W. is supported by the NIH and NCI (U01 CA214125, 1R01CA215226, 1R01CA215452), The Welch Foundation (Q-0007), prior research funding from H3Biomedicine, and the CRUK Grand Challenge and the Mark Foundation for Cancer Research (C5470/A27144 to T.F.W. as a member of the SPECIFICANCER Team).
Footnotes
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Spliceosome inhibitors generate intron-retaining mis-spliced RNAs then activate downstream antiviral signaling and apoptosis in tumors in mouse models of breast cancer.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Aird D, Teng T, Huang C-L, Pazolli E, Banka D, Cheung-Ong K, Eifert C, Furman C, Wu ZJ, Seiler M, et al. , 2019. Sensitivity to splicing modulation of BCL2 family genes defines cancer therapeutic strategies for splicing modulators. Nat. Commun 10, 137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kuraya K, Schraml P, Torhorst J, Tapia C, Zaharieva B, Novotny H, Spichtin H, Maurer R, Mirlacher M, Köchli O, et al. , 2004. Prognostic relevance of gene amplifications and coamplifications in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64, 8534–8540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrejeva J, Childs KS, Young DF, Carlos TS, Stock N, Goodbourn S, Randall RE, 2004. The V proteins of paramyxoviruses bind the IFN-inducible RNA helicase, mda-5, and inhibit its activation of the IFN- promoter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 101, 17264–17269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto K, Takahashi H, Hishiki T, Konishi H, Fujita T, Shimotohno K, 2007. Negative regulation of the RIG-I signaling by the ubiquitin ligase RNF125. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 104, 7500–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulmann S, Adler N, Rom J, Helmchen B, Schirmacher P, Sinn HP, 2006. c-myc amplifications in primary breast carcinomas and their local recurrences. J. Clin. Pathol 59, 424–428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai B, Hales CM, Chen P-C, Gozal Y, Dammer EB, Fritz JJ, Wang X, Xia Q, Duong DM, Street C, et al. , 2013. U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex and RNA splicing alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 110, 16562–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbie DA, Tamayo P, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Moody SE, Dunn IF, Schinzel AC, Sandy P, Meylan E, Scholl C, et al. , 2009. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 462, 108–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg MG, Wan L, Younis I, Diem MD, Soo M, Wang C, Dreyfuss G, 2012. A Quantitative High-Throughput In Vitro Splicing Assay Identifies Inhibitors of Spliceosome Catalysis. Mol. Cell. Biol 32, 1271–1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R, Dessain SK, Weinberg RA, 1986. N-myc amplification causes down-modulation of MHC class I antigen expression in neuroblastoma. Cell 47, 667–674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezzi M, Teo SX, Muller J, Mok WC, Sahu SK, Vardy LA, Bonday ZQ, Guccione E, 2013. Regulation of constitutive and alternative splicing by PRMT5 reveals a role for Mdm4 pre-mRNA in sensing defects in the spliceosomal machinery. Genes Dev. 27, 1903–1916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Waldner M, Obenauf AC, Angell H, Fredriksen T, Lafontaine L, Berger A, et al. , 2013. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity 39, 782–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunschweig U, Barbosa-Morais NL, Pan Q, Nachman EN, Alipanahi B, Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis T, Frey B, Irimia M, Blencowe BJ, 2014. Widespread intron retention in mammals functionally tunes transcriptomes. Genome Res. 24, 1774–1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley PT, Khaladkar M, Kim J, Eberwine J, 2014. Cytoplasmic intron retention, function, splicing, and the sentinel RNA hypothesis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 5, 223–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey SC, Baylot V, Felsher DW, 2017. MYC: Master Regulator of Immune Privilege. Trends Immunol. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey SC, Baylot V, Felsher DW, 2018. The MYC oncogene is a global regulator of the immune response. Blood. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y, Do R, Walz S, Fitzgerald KN, Gouw AM, Baylot V, Gutgemann I, Eilers M, et al. , 2016. MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science (80-. ). 352, 227–231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S, Sridhar P, Kirchner R, Lock YJ, Herbert Z, Buonamici S, Smith P, Lieberman J, Petrocca F, 2017. Basal-A Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Selectively Rely on RNA Splicing for Survival. Mol. Cancer Ther 16, 2849–2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiappinelli KB, Strissel PL, Desrichard A, Li H, Henke C, Akman B, Hein A, Rote NS, Cope LM, Snyder A, et al. , 2015. Inhibiting DNA Methylation Causes an Interferon Response in Cancer via dsRNA Including Endogenous Retroviruses. Cell 162, 974–986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaprico A, Silva TC, Olsen C, Garofano L, Cava C, Garolini D, Sabedot TS, Malta TM, Pagnotta SM, Castiglioni I, et al. , 2015. TCGAbiolinks: an R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, e71–e71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge SA, Smith AE, 1983. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature 303, 435–439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristescu R, Mogg R, Ayers M, Albright A, Murphy E, Yearley J, Sher X, Liu XQ, Lu H, Nebozhyn M, et al. , 2018. Pan-tumor genomic biomarkers for PD-1 checkpoint blockade–based immunotherapy. Science (80-. ). 362, eaar3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darman RB, Seiler M, Agrawal AA, Lim KH, Peng S, Aird D, Bailey SL, Bhavsar EB, Chan B, Colla S, et al. , 2015. Cancer-Associated SF3B1 Hotspot Mutations Induce Cryptic 3’ Splice Site Selection through Use of a Different Branch Point. Cell Rep. 13, 1033–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S, Anczuków O, Akerman M, Krainer AR, 2012. Oncogenic splicing factor SRSF1 is a critical transcriptional target of MYC. Cell Rep. 1, 110–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David CJ, Chen M, Assanah M, Canoll P, Manley JL, 2010. HnRNP proteins controlled by c-Myc deregulate pyruvate kinase mRNA splicing in cancer. Nature 463, 364–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBoever C, Ghia EM, Shepard PJ, Rassenti L, Barrett CL, Jepsen K, Jamieson CHM, Carson D, Kipps TJ, Frazer KA, 2015. Transcriptome sequencing reveals potential mechanism of cryptic 3’ splice site selection in SF3B1-mutated cancers. PLoS Comput. Biol 11, e1004105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming SL, Nass SJ, Dickson RB, Trock BJ, 2000. C-myc amplification in breast cancer: A meta-analysis of its occurrence and prognostic relevance. Br. J. Cancer 83, 1688–1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der SD, Yang Y-L, Weissmann C, Williams BRG, 1997. A double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway mediating stress-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 94, 3279–3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR, 2013. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doma MK, Parker R, 2007. RNA Quality Control in Eukaryotes. Cell 131, 660–668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvinge H, Bradley RK, 2015. Widespread intron retention diversifies most cancer transcriptomes. Genome Med. 7, 45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Maadidi S, Faletti L, Berg B, Wenzl C, Wieland K, Chen ZJ, Maurer U, Borner C, 2014. A Novel Mitochondrial MAVS/Caspase-8 Platform Links RNA Virus-Induced Innate Antiviral Signaling to Bax/Bak-Independent Apoptosis. J. Immunol 192, 1171–1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion DL, Jacobson ME, Hicks DJ, Rahman B, Sanchez V, Gonzales-Ericsson PI, Fedorova O, Pyle AM, Wilson JT, Cook RS, 2018. Therapeutically Active RIG-I Agonist Induces Immunogenic Tumor Cell Killing in Breast Cancers. Cancer Res. 78, 6183–6195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmore S, 2007. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol 35, 495–516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon HS, Zou T, Kiessling MK, Gao GF, Cai D, Choi PS, Ivan AP, Buchumenski I, Berger AC, Goldstein JT, et al. , 2018. Identification of ADAR1 adenosine deaminase dependency in a subset of cancer cells. Nat. Commun 9, 5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J, Esteban M, 2000. Induction of apoptosis by the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR): mechanism of action. Apoptosis 5, 107–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman AM, Kato S, Bazhenova L, Patel SP, Frampton GM, Miller V, Stephens PJ, Daniels GA, Kurzrock R, 2017. Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther 16, 2598–2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goubau D, Schlee M, Deddouche S, Pruijssers AJ, Zillinger T, Goldeck M, Schuberth C, Van der Veen AG, Fujimura T, Rehwinkel J, et al. , 2014. Antiviral immunity via RIG-I-mediated recognition of RNA bearing 5′-diphosphates. Nature 514, 372–375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graubert TA, Shen D, Ding L, Okeyo-Owuor T, Lunn CL, Shao J, Krysiak K, Harris CC, Koboldt DC, Larson DE, et al. , 2012. Recurrent mutations in the U2AF1 splicing factor in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Genet 44, 53–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfmann R, Lindquist S, 2008. Screening for amyloid aggregation by Semi-Denaturing Detergent-Agarose Gel Electrophoresis. J. Vis. Exp [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T, Goralski M, Gaskill N, Capota E, Kim J, Ting TC, Xie Y, Williams NS, Nijhawan D, 2017. Anticancer sulfonamides target splicing by inducing RBM39 degradation via recruitment to DCAF15. Science 356, eaal3755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornung V, Ellegast J, Kim S, Brzozka K, Jung A, Kato H, Poeck H, Akira S, Conzelmann K-K, Schlee M, et al. , 2006. 5’-Triphosphate RNA Is the Ligand for RIG-I. Science (80-. ). 314, 994–997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou F, Sun L, Zheng H, Skaug B, Jiang Q-X, Chen ZJ, 2011. MAVS Forms Functional Prion-like Aggregates to Activate and Propagate Antiviral Innate Immune Response. Cell 146, 448–461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu TY-T, Simon LM, Neill NJ, Marcotte R, Sayad A, Bland CS, Echeverria GV, Sun T, Kurley SJ, Tyagi S, et al. , 2015. The spliceosome is a therapeutic vulnerability in MYC-driven cancer. Nature 525, 384–388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert CG, Bradley RK, Ding Y, Toledo CM, Herman J, Skutt-Kakaria K, Girard EJ, Davison J, Berndt J, Corrin P, et al. , 2013. Genome-wide RNAi screens in human brain tumor isolates reveal a novel viability requirement for PHF5A. Genes Dev. 27, 1032–1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo W, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Song C, Moreno BH, Hu-Lieskovan S, Berent-Maoz B, Pang J, Chmielowski B, Cherry G, et al. , 2016. Genomic and Transcriptomic Features of Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma. Cell 165, 35–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordanov MS, Ryabinina OP, Schneider P, Magun BE, 2005. Two mechanisms of caspase 9 processing in double-stranded RNA- and virus-triggered apoptosis. Apoptosis 10, 153–66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka JJ, Manguso RT, Cheruiyot CK, Bi K, Panda A, Iracheta-Vellve A, Miller BC, Du PP, Yates KB, Dubrot J, et al. , 2019. Loss of ADAR1 in tumours overcomes resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nature 565, 43–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahles A, Lehmann K-V, Toussaint NC, Hüser M, Stark SG, Sachsenberg T, Stegle O, Kohlbacher O, Sander C, Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, et al. , 2018. Comprehensive Analysis of Alternative Splicing Across Tumors from 8,705 Patients. Cancer Cell 34, 211–224.e6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaida D, Motoyoshi H, Tashiro E, Nojima T, Hagiwara M, Ishigami K, Watanabe H, Kitahara T, Yoshida T, Nakajima H, et al. , 2007. Spliceostatin A targets SF3b and inhibits both splicing and nuclear retention of pre-mRNA. Nat. Chem. Biol 3, 576–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang D, Gopalkrishnan RV, Wu Q, Jankowsky E, Pyle AM, Fisher PB, 2002. mda-5: An interferon-inducible putative RNA helicase with double-stranded RNA-dependent ATPase activity and melanoma growth-suppressive properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 99, 637–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H, Takeuchi O, Mikamo-Satoh E, Hirai R, Kawai T, Matsushita K, Hiiragi A, Dermody TS, Fujita T, Akira S, 2008. Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. J. Exp. Med 205, 1601–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, Coban C, Kumar H, Kato H, Ishii KJ, Takeuchi O, Akira S, 2005. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol 6, 981–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler JD, Kahle KT, Sun T, Meerbrey KL, Schlabach MR, Schmitt EM, Skinner SO, Xu Q, Li MZ, Hartman ZC, et al. , 2012. A SUMOylation-Dependent Transcriptional Subprogram Is Required for Myc-Driven Tumorigenesis. Science (80-. ). 335, 348–353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibler KV, Shors T, Perkins KB, Zeman CC, Banaszak MP, Biesterfeldt J, Langland JO, Jacobs BL, 1997. Double-stranded RNA is a trigger for apoptosis in vaccinia virus-infected cells. J. Virol 71, 1992–2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL, 2015. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E, Ilagan JO, Liang Y, Daubner GM, Lee SC-W, Ramakrishnan A, Li Y, Chung YR, Micol J-B, Murphy ME, et al. , 2015. SRSF2 Mutations Contribute to Myelodysplasia by Mutant-Specific Effects on Exon Recognition. Cancer Cell 27, 617–630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koboldt DC, Fulton RS, McLellan MD, Schmidt H, Kalicki-Veizer J, McMichael JF, Fulton LL, Dooling DJ, Ding L, Mardis ER, et al. , 2012. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490, 61–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh CM, Bezzi M, Low DHP, Ang WX, Teo SX, Gay FPH, Al-Haddawi M, Tan SY, Osato M, Sabò A, et al. , 2015. MYC regulates the core pre-mRNA splicing machinery as an essential step in lymphomagenesis. Nature 523, 96–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortlever RM, Sodir NM, Wilson CH, Burkhart DL, Pellegrinet L, Brown Swigart L, Littlewood TD, Evan GI, 2017. Myc Cooperates with Ras by Programming Inflammation and Immune Suppression. Cell 171, 1301–1315.e14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagisetti C, Palacios G, Goronga T, Freeman B, Caufield W, Webb TR, 2013. Optimization of antitumor modulators of pre-mRNA splicing. J. Med. Chem 56, 10033–10044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B, Salzberg SL, 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrayoz M, Blakemore SJ, Dobson RC, Blunt MD, Rose-Zerilli MJJ, Walewska R, Duncombe A, Oscier D, Koide K, Forconi F, et al. , 2016. The SF3B1 inhibitor spliceostatin A (SSA) elicits apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells through downregulation of Mcl-1. Leukemia 30, 351–360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee SC-W, Dvinge H, Kim E, Cho H, Micol J-B, Chung YR, Durham BH, Yoshimi A, Kim YJ, Thomas M, et al. , 2016. Modulation of splicing catalysis for therapeutic targeting of leukemia with mutations in genes encoding spliceosomal proteins. Nat. Med 22, 672–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei Y, Moore CB, Liesman RM, O’Connor BP, Bergstralh DT, Chen ZJ, Pickles RJ, Ting JPY, 2009. MAVS-Mediated Apoptosis and Its Inhibition by Viral Proteins. PLoS One 4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li D, Xie P, Zhao F, Shu J, Li L, Zhan Y, Zhang L, 2015. F-box protein Fbxo3 targets Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase for ubiquitination and degradation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 458, 941–945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 2009. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y, Smyth GK, Shi W, 2014. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30, 923–930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP, 2011. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 27, 1739–1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin CY, Lovén J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM, Burge CB, Bradner JE, Lee TI, Young RA, 2012. Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell 151, 56–67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linehan MM, Dickey TH, Molinari ES, Fitzgerald ME, Potapova O, Iwasaki A, Pyle AM, 2018. A minimal RNA ligand for potent RIG-I activation in living mice. Sci. Adv 4, e1701854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H, Golji J, Brodeur LK, Chung FS, Chen JT, DeBeaumont RS, Bullock CP, Jones MD, Kerr G, Li L, et al. , 2018. Tumor-derived IFN triggers chronic pathway agonism and sensitivity to ADAR loss. Nat. Med 25, 95–102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Lu N, Yuan B, Weng L, Wang F, Liu Y-J, Zhang Z, 2014. The interaction between the helicase DHX33 and IPS-1 as a novel pathway to sense double-stranded RNA and RNA viruses in myeloid dendritic cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol 11, 49–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love MI, Huber W, Anders S, 2014. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo N, Nixon MJ, Gonzalez-Ericsson PI, Sanchez V, Opalenik SR, Li H, Zahnow CA, Nickels ML, Liu F, Tantawy MN, et al. , 2018. DNA methyltransferase inhibition upregulates MHC-I to potentiate cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in breast cancer. 9, 248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallampalli RK, Coon TA, Glasser JR, Wang C, Dunn SR, Weathington NM, Zhao J, Zou C, Zhao Y, Chen BB, 2013. Targeting F box protein Fbxo3 to control cytokine-driven inflammation. J. Immunol 191, 5247–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M, 2011. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal 17, 10. [Google Scholar]
- McGranahan N, Furness AJS, Rosenthal R, Ramskov S, Lyngaa R, Saini SK, Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, Birkbak NJ, Hiley CT, et al. , 2016. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science (80-. ). 351, 1463–1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerbrey KL, Hu G, Kessler JD, Roarty K, Li MZ, Fang JE, Herschkowitz JI, Burrows AE, Ciccia A, Sun T, et al. , 2011. The pINDUCER lentiviral toolkit for inducible RNA interference in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 108, 3665–3670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdipour P, Marhon SA, Ettayebi I, Chakravarthy A, Hosseini A, Wang Y, de Castro FA, Loo Yau H, Ishak C, Abelson S, et al. , 2020. Epigenetic therapy induces transcription of inverted SINEs and ADAR1 dependency. Nature. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, Bartenschlager R, Tschopp J, 2005. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 437, 1167–1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minn AJ, Gupta GP, Siegel PM, Bos PD, Shu W, Giri DD, Viale A, Olshen AB, Gerald WL, Massagué J, 2005. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436, 518–524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore MJ, Wang Q, Kennedy CJ, Silver PA, 2010. An Alternative Splicing Network Links Cell-Cycle Control to Apoptosis. Cell 142, 625–636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabet B, Roberts JM, Buckley DL, Paulk J, Dastjerdi S, Yang A, Leggett AL, Erb MA, Lawlor MA, Souza A, et al. , 2018. The dTAG system for immediate and target-specific protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol 14, 431–441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H, Hori Y, Terano H, Okuhara M, Manda T, Matsumoto S, Shimomura K, 1996. New antitumor substances, FR901463, FR901464 and FR901465. II. Activities against experimental tumors in mice and mechanism of action. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 49, 1204–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obeng EA, Chappell RJ, Seiler M, Chen MC, Campagna DR, Schmidt PJ, Schneider RK, Lord AM, Wang L, Gambe RG, et al. , 2016. Physiologic Expression of Sf3b1(K700E) Causes Impaired Erythropoiesis, Aberrant Splicing, and Sensitivity to Therapeutic Spliceosome Modulation. Cancer Cell 30, 404–417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawellek A, McElroy S, Samatov T, Mitchell L, Woodland A, Ryder U, Gray D, Lührmann R, Lamond AI, 2014. Identification of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Pre-mRNA Splicing. J. Biol. Chem 289, 34683–34698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp MW-L, Maquat LE, 2013. Organizing principles of mammalian nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Annu. Rev. Genet 47, 139–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj T, Li YI, Wong G, Humphrey J, Wang M, Ramdhani S, Wang Y-C, Ng B, Gupta I, Haroutunian V, et al. , 2018. Integrative transcriptome analyses of the aging brain implicate altered splicing in Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet 50, 1584–1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, Lee W, Yuan J, Wong P, Ho TS, et al. , 2015. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science (80-. ). 348, 124–128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robanus-Maandag EC, Bosch CAJ, Kristel PM, Hart AAM, Faneyte IF, Nederlof PM, Peterse JL, van de Vijver MJ, 2003. Association of C-MYC amplification with progression from the in situ to the invasive stage in C-MYC-amplified breast carcinomas. J. Pathol 201, 75–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney MS, Shukla SA, Wu CJ, Getz G, Hacohen N, 2015. Molecular and genetic properties of tumors associated with local immune cytolytic activity. Cell 160, 48–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roulois D, Loo Yau H, Singhania R, Wang Y, Danesh A, Shen SY, Han H, Liang G, Jones PA, Pugh TJ, et al. , 2015. DNA-Demethylating Agents Target Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inducing Viral Mimicry by Endogenous Transcripts. Cell 162, 961–73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseaux MWC, Vázquez-Vélez GE, Al-Ramahi I, Jeong HH, Bajić A, Revelli JP, Ye H, Phan ET, Deger JM, Perez AM, et al. , 2018. A druggable genome screen identifies modifiers of α-synuclein levels via a tiered cross-species validation approach. J. Neurosci 38, 9286–9301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saldi TK, Ash PE, Wilson G, Gonzales P, Garrido‐Lecca A, Roberts CM, Dostal V, Gendron TF, Stein LD, Blumenthal T, et al. , 2014. TDP‐1, the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of TDP‐43, limits the accumulation of double‐stranded RNA. EMBO J. 33, 2947–2966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlotter CM, Vogt U, Bosse U, Mersch B, Waßmann K, 2003. C-myc, not HER-2/neu, can predict recurrence and mortality of patients with node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A, Schwerd T, Hamm W, Hellmuth JC, Cui S, Wenzel M, Hoffmann FS, Michallet M-C, Besch R, Hopfner K-P, et al. , 2009. 5’-triphosphate RNA requires base-paired structures to activate antiviral signaling via RIG-I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 106, 12067–12072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönborn J, Oberstrass J, Breyel E, Tittgen J, Schumacher J, Lukacs N, 1991. Monoclonal antibodies to double-stranded RNA as probes of RNA structure in crude nucleic acid extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 2993–3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears N, Sen GC, Stark GR, Chattopadhyay S, 2011. Caspase-8-mediated Cleavage Inhibits IRF-3 Protein by Facilitating Its Proteasome-mediated Degradation. J. Biol. Chem 286, 33037–33044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M, Peng S, Agrawal AA, Palacino J, Teng T, Zhu P, Smith PG, Buonamici S, Yu L, Caesar-Johnson SJ, et al. , 2018a. Somatic Mutational Landscape of Splicing Factor Genes and Their Functional Consequences across 33 Cancer Types. Cell Rep. 23, 282–296.e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler M, Yoshimi A, Darman R, Chan B, Keaney G, Thomas M, Agrawal AA, Caleb B, Csibi A, Sean E, et al. , 2018b. H3B-8800, an orally available small-molecule splicing modulator, induces lethality in spliceosome-mutant cancers. Nat. Med 24, 497–504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela N, Mersch B, Gal-Mark N, Lev-Maor G, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Ast G, 2007. Comparative analysis of transposed element insertion within human and mouse genomes reveals Alu’s unique role in shaping the human transcriptome. Genome Biol. 8, R127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth RB, Sun L, Ea C-K, Chen ZJ, 2005. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 122, 669–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA, Ribas A, 2017. Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 168, 707–723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai CL, White BS, Tripathi M, Tapia R, Ley JN, Ndonwi M, Kim S, Shao J, Carver A, Saez B, et al. , 2017. Mutant U2AF1-expressing cells are sensitive to pharmacological modulation of the spliceosome. Nat. Commun 8, 14060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidarovich A, Will CL, Anokhina MM, Ceballos J, Sievers S, Agafonov DE, Samatov T, Bao P, Kastner B, Urlaub H, et al. , 2017. Identification of a small molecule inhibitor that stalls splicing at an early step of spliceosome activation. Elife 6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart AC, Margolis CA, Pimentel H, He MX, Miao D, Adeegbe D, Fugmann T, Wong KK, Van Allen EM, 2018. Intron retention is a source of neoepitopes in cancer. Nat. Biotechnol 36, 1056–1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, Yuan J, Zaretsky JM, Desrichard A, Walsh LA, Postow MA, Wong P, Ho TS, et al. , 2014. Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med 371, 2189–2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song G, Liu B, Li Z, Wu H, Wang P, Zhao K, Jiang G, Zhang L, Gao C, 2016. E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF128 promotes innate antiviral immunity through K63-linked ubiquitination of TBK1. Nat. Immunol 17, 1342–1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone ML, Chiappinelli KB, Li H, Murphy LM, Travers ME, Topper MJ, Mathios D, Lim M, Shih I-M, Wang T-L, et al. , 2017. Epigenetic therapy activates type I interferon signaling in murine ovarian cancer to reduce immunosuppression and tumor burden. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 114, E10981–E10990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, et al. , 2005. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 102, 15545–15550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumpter R, Loo Y-M, Foy E, Li K, Yoneyama M, Fujita T, Lemon SM, Gale M, 2005. Regulating Intracellular Antiviral Defense and Permissiveness to Hepatitis C Virus RNA Replication through a Cellular RNA Helicase, RIG-I. J. Virol 79, 2689–2699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L, Fazal FM, Li P, Broughton JP, Lee B, Tang L, Huang W, Kool ET, Chang HY, Zhang QC, 2019. RNA structure maps across mammalian cellular compartments. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 26, 322–330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P, et al. , 2019. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D607–D613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K, Kawai T, Kumar H, Sato S, Yonehara S, Akira S, 2006. Roles of caspase-8 and caspase-10 in innate immune responses to double-stranded RNA. J. Immunol 176, 4520–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper MJ, Vaz M, Chiappinelli KB, DeStefano Shields CE, Niknafs N, Yen R-WC, Wenzel A, Hicks J, Ballew M, Stone M, et al. , 2017. Epigenetic Therapy Ties MYC Depletion to Reversing Immune Evasion and Treating Lung Cancer. Cell 171, 1284–1300.e21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L, 2010. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol 28, 511–5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang JL, Jia SH, Parodo J, Plant P, Lodyga M, Charbonney E, Szaszi K, Kapus A, Marshall JC, 2016. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Caspase-8 Abrogates Its Apoptotic Activity and Promotes Activation of c-Src. PLoS One 11, e0153946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara T, Minoshima Y, Sagane K, Sugi NH, Mitsuhashi KO, Yamamoto N, Kamiyama H, Takahashi K, Kotake Y, Uesugi M, et al. , 2017. Selective degradation of splicing factor CAPERα by anticancer sulfonamides. Nat. Chem. Biol 13, 675–680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero-Garcia J, Barrera A, Gazzara MR, González-Vallinas J, Lahens NF, Hogenesch JB, Lynch KW, Barash Y, 2016. A new view of transcriptome complexity and regulation through the lens of local splicing variations. Elife 5, e11752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables JP, 2004. Aberrant and alternative splicing in cancer. Cancer Res. 64, 7647–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Brooks AN, Fan J, Wan Y, Gambe R, Li S, Hergert S, Yin S, Freeman SS, Levin JZ, et al. , 2016. Transcriptomic Characterization of SF3B1 Mutation Reveals Its Pleiotropic Effects in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 30, 750–763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T, Wei JJ, Sabatini DM, Lander ES, 2014. Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Science (80-. ). 343, 80–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong JJ-L, Ritchie W, Ebner OA, Selbach M, Wong JWH, Huang Y, Gao D, Pinello N, Gonzalez M, Baidya K, et al. , 2013. Orchestrated intron retention regulates normal granulocyte differentiation. Cell 154, 583–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyss-Coray T, 2006. Inflammation in Alzheimer disease: driving force, bystander or beneficial response? Nat. Med 12, 1005–1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L-G, Wang Y-Y, Han K-J, Li L-Y, Zhai Z, Shu H-B, 2005. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol. Cell 19, 727–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan M, Hopkins A, Jaffee EM, 2017. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med 377, 2500–2501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi A, Kotake Y, Takahashi K, Kadowaki T, Matsumoto Y, Minoshima Y, Sugi NH, Sagane K, Hamaguchi M, Iwata M, et al. , 2011. Biological validation that SF3b is a target of the antitumor macrolide pladienolide. FEBS J. 278, 4870–4880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama M, Kikuchi M, Natsukawa T, Shinobu N, Imaizumi T, Miyagishi M, Taira K, Akira S, Fujita T, 2004. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol 5, 730–737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto R, Kaida D, Furuno M, Burroughs AM, Noma S, Suzuki H, Kawamura Y, Hayashizaki Y, Mayeda A, Yoshida M, 2017. Global analysis of pre-mRNA subcellular localization following splicing inhibition by spliceostatin A. RNA 23, 47–57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G, 2018. Using meshes for MeSH term enrichment and semantic analyses. Bioinformatics 34, 3766–3767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Z, Song H, Jia M, Zhang J, Wang W, Li Q, Zhang L, Zhao W, 2017. USP1–UAF1 deubiquitinase complex stabilizes TBK1 and enhances antiviral responses. J. Exp. Med 214, 3553–3563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W, Xu M, Liu S, Sun L, Chen ZJ, 2009. Key Role of Ubc5 and Lysine-63 Polyubiquitination in Viral Activation of IRF3. Mol. Cell 36, 315–325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Lieu YK, Ali AM, Penson A, Reggio KS, Rabadan R, Raza A, Mukherjee S, Manley JL, 2015. Disease-associated mutation in SRSF2 misregulates splicing by altering RNA-binding affinities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 112, E4726–E4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J, Manley JL, 2013. Misregulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing in cancer. Cancer Discov. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Kim T, Bao M, Facchinetti V, Jung SYY, Ghaffari AAA, Qin J, Cheng G, Liu Y-J, 2011a. DDX1, DDX21, and DHX36 helicases form a complex with the adaptor molecule TRIF to sense dsRNA in dendritic cells. Immunity 34, 866–78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Yuan B, Lu N, Facchinetti V, Liu Y-J, 2011b. DHX9 Pairs with IPS-1 To Sense Double-Stranded RNA in Myeloid Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol 187, 4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK, 2019. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun 10, 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(A) Spliceosome inhibition induces IFNB transcription followed by induction of interferon-stimulated genes. SUM159 cells were treated with SD6 for the indicated times and gene expression was measured using RT-qPCR. Data are shown as expression relative to DMSO treated samples (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(B, C) Treatment with small molecule spliceosome inhibitor H3B-8800 induces activation of antiviral signaling genes. Gene expression of (B) SUM159s and (C) LM2s was measured upon 48 hours of H3B-8800 treatment using RT-qPCR. Gene expression changes (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are represented as relative to DMSO treated samples.
(D) Chemical genetic dTAG system can be used to specifically target SF3B1 for proteasomal degradation. Bifunctional dFKBP ligand targets exogenous SF3B1-FKBP12F36V for proteasomal degradation upon recruitment of the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRBN.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001
(A) Immune signaling pathway components are enriched among genes that confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. StringDB functional enrichment analysis was performed on the top 50 SD6 resistance candidates identified by the shRNA screen. Functionally enriched Reactome Pathways with FDR < 0.001 are shown.
(B) Modulators of antiviral immune signaling response confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. Combined SD6-selective growth effect (log2) of each gene is plotted on the x-axis. Graphed is the weighted gene level sum of the effect of knockdown by multiple shRNAs (represented by the size of the bubble). Candidates with ≥4 hairpins that confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition and are implicated in innate immune response are colored red.
(C, D) Knockdown of USP1 and FBXO3 confers resistance to SD6. shRNAs targeting (C) USP1 and (D) FBXO3 confer resistance to spliceosome inhibition. Five independent shRNAs targeting these genes were enriched with SD6 treatment, as compared to negative control shRNAs (ZBTB1 and TBC1D1). log2(fold change) is calculated based on the hairpin abundance in the SD6 treated samples as compared to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=4 biological replicates). Hairpins with log2(fold change) > 0.5 and p-value ≤ 0.05 are shown.
(E) Two independent UBE2D1-targeting shRNAs decreased expression of UBE2D1in SUM159 cells. UBE2D1 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(F) Two independent RNF128-targeting shRNAs cause decreased expression of RNF128 in SUM159 cells. RNF128 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(G) Two independent RNF125-targeting shRNAs cause decreased expression of RNF125 in SUM159 cells. RNF125 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
***p<0.001, **** p<0.0001
(A, B) Cytoplasmic accumulation of dsRNA in TNBC cell lines after H3B-8800. (A) Left, immunofluorescent staining of dsRNA (J2), cytoskeleton (phalloidin), and nuclei (Hoechst) in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Scale bars, 20µm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). (B) Left, immunofluorescent staining of dsRNA (J2), cytoskeleton (phalloidin), and nuclei (Hoechst) in BT549 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Scale bars, 20µm. Right, quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(C) Spliceosome inhibition causes cytoplasmic accumulation of dsRNA in TNBC cells but not in non-transformed mammary epithelial cells. Immunofluorescence labeling of dsRNA using anti-dsRNA (J2) antibody in SUM159 and (non-transformed) HME1 cells treated with the same dose of H3B-8800 for 24 hours. Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity is shown (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(D-H) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant mitigates sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. (D-F) SUM159 and (G, H) LM2 cells were engineered with doxycycline-inducible FLAG-tag SF3B1WT or SF3B1R1074H. (D, G) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1 (FLAG) and endogenous SF3B1 was measured by Western blot. (E, H) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses sensitivity to high doses of H3B-8800. (F) Doxycycline-induced expression of exogenous SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses intron retention of U2AF2 in response to 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800.
(I) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses accumulation of dsRNA after spliceosome inhibitor treatment. Overexpression of SF3B1R1074H suppresses accumulation of dsRNA after treatment with H3B-8800 for 24 hours in LM2 cells. Quantification of cytoplasmic dsRNA signal intensity in LM2 cells expressing SF3B1WT or SF3B1R1074H is shown (mean ± SEM from >50 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001
(A) Confirmation of purity of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions by histone H3 and α-Tubulin immunoblots. Shown are two biological replicates per condition.
(B) Spliceosome perturbation leads to aberrant splicing, such as retention of introns. Schematic of intron retention (IR) analysis of RNA-seq data. IR score is calculated as the ratio of intron read RPKM (unprocessed read coverage) to intron-spanning read RPKM (processed read coverage).
(C) Spliceosome inhibition leads to cytoplasmic intron retention of SEC14L1. Pileup of cytoplasmic reads mapping to the SEC14L1 intron and surrounding exons. Data are representative of biological duplicates for each condition.
(D, E) Spliceosome inhibition leads to accumulation of intron-retained RNAs in the cytoplasm. (D) RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) images of retained introns and surrounding exon sequences for an intron in SETD1A after treatment with H3B-8800 for 12 hours. Arrows indicate overlapped intron and exon foci. Scale bars, 10µm. (E) Quantification of number of intron-retained mRNAs per cell is shown (mean ± SEM from >35 cells per group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(F) Spliceosome inhibition leads to cytoplasmic intron retention of SETD1A. Pileup of cytoplasmic reads mapping to the SETD1A intron and surrounding exons. Data are representative of biological duplicates for each condition.
(G) Intron-residing retrotransposons increase in expression after H3B-8800. Empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean retrotransposon RPKMs are plotted for 9,349 expressed elements. A rightward shift in the red curve indicates increased expression. Subclasses of retrotransposons such as short (left) and long (right) interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs and LINEs, respectively) also show increased expression after 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800 (p<2.2e16 for all comparisons by Mann-Whitney U test).
(H) Non-intronic retrotransposons show no change in expression after H3B-8800. Left, empirical cumulative distribution curves of mean retrotransposon RPKMs are plotted for 22,410 expressed elements. Non-intronic SINEs (left) and LINEs (right) show no increase in expression after 12 hours of treatment with H3B-8800.
(I) J2-enriched retrotransposon-containing introns are predicted to form double stranded secondary structure. Structure analysis using RNAfold predicts a long stretch of double-stranded secondary structure comprised primarily of the inverted Alu-repeat regions of the J2-dsRIP enriched intron in RPL30.
(J, K) Introns not containing retrotransposons form double stranded secondary structure. (J) Pileup of J2 dsRIP-seq reads across an intron and exon in REXO1 and (K) predicted double-stranded secondary structure.
****p<0.0001
(A) Spliceosome inhibition activates caspases-3 and -7. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(B) Spliceosome inhibition activates caspase-8. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspase-8 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(C, D) Spliceosome inhibition in combination with MYC hyperactivation activates extrinsic apoptosis. Human mammary epithelial cells engineered with inducible MYC hyperactivation were treated for 4 hours ± 4-OHT (to induce MYC hyperactivation) followed by 32 hours ± H3B-8800 for a total treatment time of 36 hours. Cells were then assayed for (C) caspase-8 and (D) caspases-3 and -7 activation (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(E, F) Expression of spliceosome modulator-resistant SF3B1R1074H mutant suppresses activation of extrinsic apoptosis after H3B-8800 treatment. SUM159 cells expressing SF3B1WT and SF3B1R1074H were treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for activation of (E) caspase-8 and (F) caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(G) Spliceosome inhibitor-induced caspases-3 and -7 activity is dependent on activation of extrinsic apoptosis. SUM159s treated with or without SD6 and no caspase inhibitor, pan-caspase inhibitor (ZVAD), caspase-8 inhibitor (ZIETD), caspase-10 inhibitor (Z-AEHD), and caspase-9 inhibitor (Z-LEHD) for 48 hours were measured for activation of caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test) using luminescent Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay.
(H) Three independent RIPK3-targeting siRNAs decrease expression of RIPK3 in SUM159s. RIPK3 expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control siRNA cell line.
(I, J) RIPK3 does not contribute to sensitivity to spliceosome inhibition. SUM159 cells were transfected with either control (NTC) or RIPK3-targeting siRNA and treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for (I) cell viability using CellTiterGlo and (J) cell death using PI permeability (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(K) Extrinsic apoptosis ligands or receptors are not induced within 24 hours of spliceosome inhibition. Transcriptional changes upon treatment of SUM159s with H3B-8800 were measured using RNA-seq. Gene expression is represented as fold change relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(L) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of DR5 or TNFR2. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of DR5 and TNFR2 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to RAN shown.
(M) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of DR4. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of DR4 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to Vinculin shown.
(N) Spliceosome inhibition does not change protein levels of TNFR1 or DR6. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of TNFR1 and DR6 was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to RAN shown.
(O) Spliceosome inhibition leads to increased c-FLIP protein level. SUM159 cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours and expression of c-FLIP isoforms was assessed using Western blotting. Protein level relative to Vinculin shown.
(P) Spliceosome inhibition does not lead to mis-splicing of c-FLIP. RMATS analysis of RNA-seq from SUM159 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours reveals no significant difference in c-FLIP exon 7 usage.
(Q) Three independent TNFR1-targeting siRNAs decrease expression of TNFR1 in SUM159s. TNFR1 levels were assessed using Western blotting, with RAN probed as a load control.
(R, S) Knockdown of TNFR1 does not suppress activation of extrinsic apoptosis. SUM159 cells were transfected with either control (NTC) or TNFR1 targeting siRNA and treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours. Cells were then assayed for activation of (R) caspase-8 and (S) caspases-3 and -7 (mean ± SEM, n=2 biological replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(T) Independent siRNAs decrease expression of the indicated genes in SUM159s. PKR, DDX1, DDX21, DHX36, DHX9, MDA5, RIG-I, and DHX33 expression levels (mean ± SEM) are calculated relative to expression in the control siRNA cell line.
(U, V) Spliceosome inhibition causes aggregation of the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS. (U) Immunofluorescence imaging of MAVS reveals that 12 hours of H3B-8800 treatment of LM2s results in aggregation of MAVS. Scale bars, 10µm. (V) MAVS aggregation was measured by change in dispersal of MAVS IF signal. MAVS aggregation (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) is defined as the inverse dispersion factor, which is calculated based on the dispersion of signal from the weighted centroid of MAVS signal.
(W) Spliceosome inhibition leads to aggregation of MAVS in LM2s, indicating activation. P5 mitochondrial fraction was prepared from LM2 cells treated with H3B-8800 for 12 hours or transfected with poly(I:C) and MAVS aggregation was analyzed by SDD-AGE.
(X) Two independent MAVS-targeting shRNAs decrease expression of MAVS in SUM159s. MAVS expression levels (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test) are calculated relative to expression in the control shRNA cell line.
(Y) Two independent MAVS-targeting sgRNAs decrease protein level of MAVS in SUM159s. MAVS protein levels were measuring using Western blotting.
(Z) MAVS knockout suppresses upregulation of antiviral transcriptional changes. SUM159 dox-inducible Cas9 cells transduced with two independent sgRNAs targeting MAVS and cultured with dox to induce genomic editing of MAVS. MAVS knockout suppresses upregulation of CD80, MX1, and CCL5 upon 48 hours of H3B-8800 treatment relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001
(A, B) Immune-related pathways are significantly enriched in sensitive versus resistant tumor models. (A) Multivariate analysis comparing changed transcriptional programs upon H3B-8800 in “sensitive” models compared to “resistant” models yielded 1,564 differentially changed genes. Enrichment analysis of these genes using Metascape KEGG (mmu) and Reactome (R-MMU) pathways identified almost exclusively immune-related pathways as significantly enriched. (B) Metascape network visualizing pathways enriched in A. Among these pathways are three major clusters of pathways relating to antiviral immune signaling, cytokine and chemokine signaling, and adaptive immune signaling.
(C) Spliceosome inhibition differentially induces intron retention in sensitive versus resistant syngeneic models of TNBC in vitro. Cell lines derived from syngeneic tumor models were treated for 12 hours with H3B-8800 and intron retention was measured using RT-qPCR. Data are shown as expression relative to DMSO (mean ± SEM, n=3 biological replicates).
(D) Spliceosome inhibition leads to production of cytokines and chemokines. Conditioned media collected from PyMT-M cells treated ± H3B-8800 for 60 hours was collected and the concentration of CXCL10 was measuring using the Luminex bead array (mean ± SEM, n=2 technical replicates, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). Analyte concentration was normalized to cell number.
(E) Spliceosome inhibition leads to activation of caspase-8 in cells derived from the 2208L syngeneic tumor model. Cells were treated with H3B-8800 for 48 hours and assayed for caspase-8 activation (mean + SEM, n=3 biological replicates) using luminescent Caspase-Glo assay.
(F-I) H3B-8800 treatment leads to increased Cd4, Cd25, and Pd1 expression in responsive syngeneic models. Graphed is the relative FPKM from RNA-seq of (F) 2208L, (G) PyMT-M, (H) AT3, and (I) T11 treated with Vehicle or H3B-8800 (mean ± SEM, n≥2 tumors per treatment group, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test).
(J) Immune cytolytic index (CYT) increases in H3B-8800-sensitive tumor models and decreases in resistant tumor models after H3B-8800 treatment. CYT is calculated as the geometric mean of granzyme A (Gzma) and perforin (Prf1) FPKM.
(K, L) Spliceosome inhibition leads to increased CD8+ T cell infiltration. PyMT-M FFPE tumor sections treated with Vehicle (n=8) or H3B-8800 (n=7) were used for immunohistochemical staining using the CD8a antibody. (K) Quantification of number of CD8a+ cells per 10X field of view. Boxplot shows mean ± IQR. (L) Images shown are representative of the mean CD8a+ cells per 10X field for each of the treatment groups.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01
(A) Tumors with high levels of IR are not those with high TMB. Plotted are the TMB levels for tumors with high and low levels of IR, with TMB levels higher in those tumors with low IR levels (two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t-test).
Table S3. Syngeneic TNBC Model GSEA Pathway Enrichment, Related to Figure 6
Table S7. smFISH probe sequences, Related to STAR Methods
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during this study are available in GEO [GSE163411, GSE163414, GSE163181, GSE163188, GSE163232].