PMC User Guide
PubMed Central® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM). This guide is meant to help you use PMC to find and read articles of interest to you. Answers to many common questions about PMC are available in the PMC FAQ.
September 2025 - PMC Search Functionality and User Experience Updated
In order to provide users with the benefits of a new search on a reasonable timeline, the new PMC search represents a minimum-viable-product (MVP) approach. NLM is committed to continued PubMed Central development, including iteratively adding functions and improving the system based on user needs and feedback to ensure that PMC remains a trusted and accessible source of biomedical literature today and in the future. For more information about this update, please see NCBI Insights: New PMC Search.
Tip: If you are a researcher seeking to submit an author manuscript to PMC, visit the NIHMS. (For more information on submissions to PMC, see For Authors.)
PMC Journal List
The PMC Journal List (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/journals/) contains journals that 1) have an agreement with NLM to make the final published version of all their articles, or all their NIH-funded articles, available in PMC or 2) are historically-significant journals from the Biomedical Journal Digitization project.
PMC also includes individual articles from other journals, either deposited as manuscripts by the authors in support of a funder mandate, or by the publisher through a Selective Deposit arrangement; These journals are not searchable in the PMC Journal List. Try a separate search of the NLM Catalog: Journals referenced in the NCBI Databases or try the user guide section on how to search PMC for articles from a specific journal.

- Click on the info button for guidance on how to search PMC for articles from a specific volume/issue of a journal, and to learn more about the scope of the PMC Journal List.
- To search for a journal or set of journals enter your search terms into the "Search for Journals" search box. The search only looks for words in a journal's title. You may also search for a specific journal using the NLM Unique ID, the unique identifier for a journal in the NLM Catalog, assigned by NLM.
- Auto-complete options are presented to help you find specific journals.
- Clear your search results with the "Reset to Full Journal List" link.
- a) Narrow your search results using the filters on the right-hand side of the page. See the Journal List Field descriptions for details about the specific fields. b) On a mobile device, filters are available by clicking on the icon in the upper right corner of your display.
- Download the full journal list in comma separated value format (csv) using the "Download full journal list" link.
- Download the results of your search and/or filtering in csv format with the "Download results" link.
- For each journal that matches your search terms and filter options, a record with basic bibliographic data and information about PMC coverage is displayed.
- Use the "See all articles in PMC from this journal" link in each record to run a search to retrieve all articles for the journal in PMC.
- A Journal Note section will display when there is information available about gaps in PMC's content coverage for a journal or other important changes in a journal's agreement type with NLM.
- A Title History section will display when there is a history of title changes for a journal over time. Click on the linked journal title(s) in this section to view the additional journal record(s).
Journal List Field Descriptions
For each journal record, the following data fields are displayed:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Journal title | The title of the journal |
| NLM Title Abbreviation | The unique abbreviation of a journal title, assigned by NLM, used in citations. |
| Publisher | The publisher of the journal. |
| ISSN (print) | ISSN, the 8-digit standardized international code used to identify the print version of the journal. |
| ISSN (online) | ISSN, the 8-digit standardized international code used to identify the electronic (online) version of the journal. |
| NLM Unique ID | The unique identifier for the journal in the NLM Catalog, assigned by NLM. |
| Most Recent | The volume and year of the most recent content archived in PMC. |
| Earliest | The volume and year of the earliest content archived in PMC. |
| Release Delay (Embargo) | How soon after publication the journal makes its content available in PMC by default. Some publishers make individual articles available sooner than the default embargo shown in the journal list. |
| Agreement Status | Shows if a journal’s participation agreement is active or not. Possible values are:
|
| Agreement to Deposit | Shows the type of agreement the journal was deposited under. Possible values are:
|
| Journal Note | A Journal Note section is displayed when there are gaps in coverage, changes in agreement type, or other information about the journal. |
| Title History | A Title History section is displayed if a journal has undergone a title change over time. Each current and predecessor title is listed, along with PMC coverage. |
PMC Article Search
To search for full-text articles in PMC, type a term or concept into the search box at the top of any PMC page and run the search. Suggestions will display as you type your search terms.
For many searches, it is not necessary to use special tags or syntax, though PMC does support more structured searching and filters to refine your results and help you find the information you are seeking. The PMC Citation Search tool is also available to find PMC articles by specific citation information.
Tip: Searches are not case sensitive.
Learn to search by:
Author | Journal | Volume and Issue | Collection | Funder | License | Publication Date | Article Property
Other search topics:
- UPDATED Searching for a Specific Article
- Phrase Searching
- NEW Proximity Searching
- UPDATED Truncating Search Terms
- Combining Search Terms with Boolean Operators
- UPDATED Using Search Field Tags
By Author
In the search box, enter the author's full name or their last name followed by initials, without punctuation. If you only know the author's last name, use the author search field tag [au] as shown in an example below.
Author names are automatically truncated to account for varying initials and designations such as Jr. To turn off the truncation, use double quotes around the author's name with the author search field tag [au] as shown in an example below.
| Author Searches | Search Query Examples |
|---|---|
| Full Name | David Lipman david lipman |
| Last Name and Given Name Initials | Lipman DJ lipman dj |
| Last Name (with author search field tag [au]) | lipman[au] |
| Last Name and Given Name Initials (with truncation turned off by using quotes) | "smith j"[au] |
By Journal
In the search box, enter the journal title, the NLM journal title abbreviation, or the ISSN, the 8-digit standardized international code used to identify journals.
| Journal Search | Search Query Examples |
|---|---|
| Full journal title | Journal of the Medical Library Association journal of the medical library association |
| Full journal title with journal search field tag | "Journal of the Medical Library Association"[ta] "Journal of the Medical Library Association"[journal] |
| Journal title abbreviation | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A |
| Journal title abbreviation with journal title abbreviation search field tag | "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A"[ta] "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A"[journal] |
| ISSN | 1948-7193 1948-7193[ta] 1948-7193[journal] |
![]() Journal Search Tips
Journal Search Tips
- If a journal title or abbreviation includes a special character (e.g., parentheses, brackets, ampersands), enter the title or abbreviation without the special characters.
- For complete retrieval of indexed items, we recommend a search using the full journal title or the journal title abbreviation as older articles may not have an ISSN.
- If you are searching using the full journal title or title abbreviation in the search box along with additional search terms, it is helpful to use quotation marks around a journal's title, e.g., obesity "preventing chronic disease"[journal].
By Volume and Issue
To retrieve all the articles in PMC from a specific volume or issue of a journal, include the volume number or the volume and issue number in a journal search query.
| Volume and Issue Search | Search Query Examples |
|---|---|
| Find all articles in volume 111 issue 3 of the Journal of the Medical Library Association | J Med Libr Assoc[ta] AND 111[volume] AND 3[issue] |
| Find all articles in volume 6 of the journal, BMC Biomedical Engineering. | "BMC Biomed Eng"[ta] AND 6[volume] |
| Find all articles in volume 2022 of the journal, Advances in Orthopedics. | "Adv Orthop"[ta] AND 2022[volume] |
| Find all articles in a journal with the ISSN of 1091-6490 in volume 7 issue 6. | 1091-6490[ta] AND 7[volume] AND 6[issue] |
Tip: Use the PMC Citation Search tool to easily build a search for a specific volume or issue of a journal.
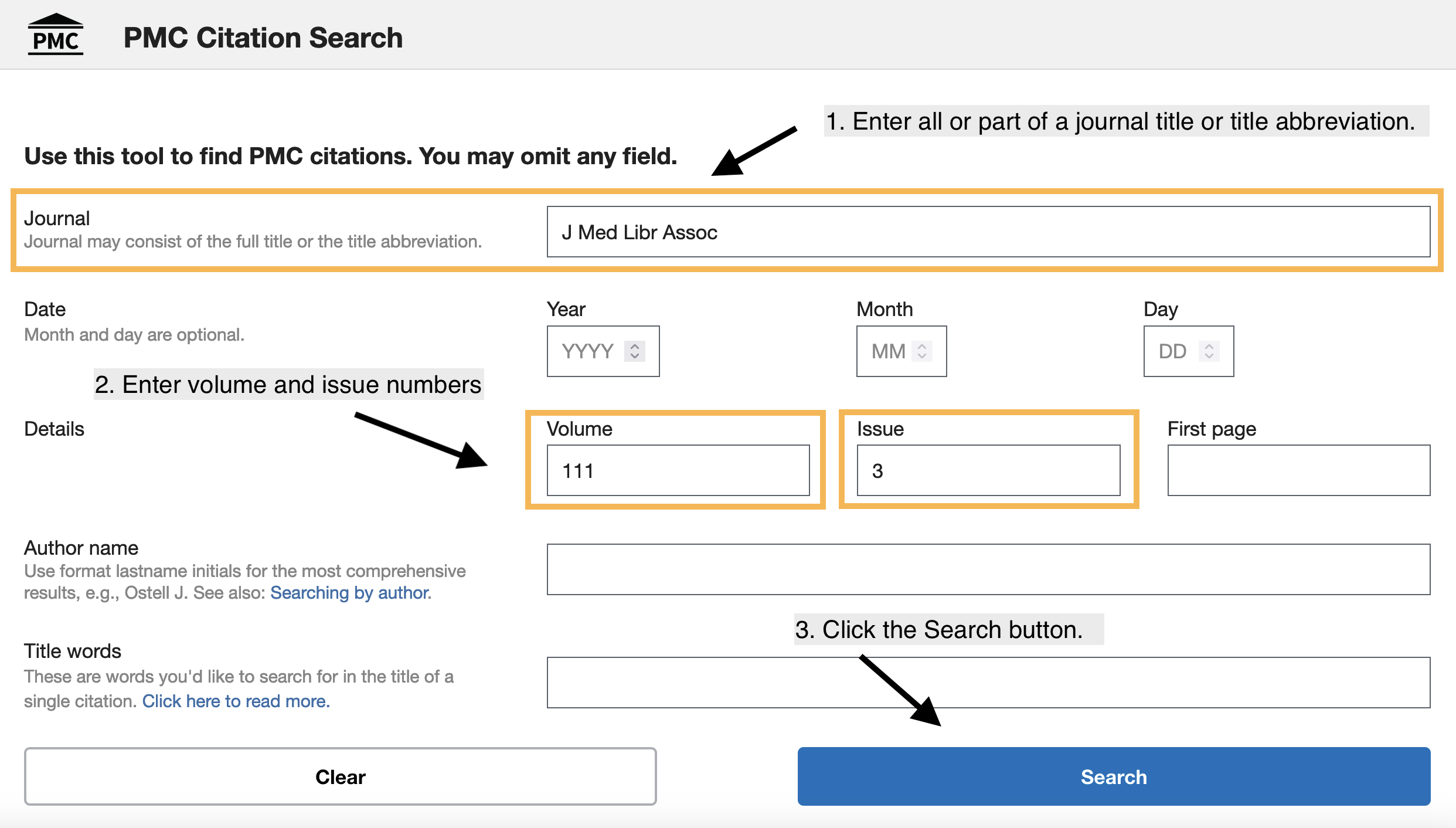
The example shown in Figure 2 is a search of PMC for all the articles in the journal with the title abbreviation "J Med Libr Assoc" that are in volume 111, issue 3. The steps are described below.
- Enter the full journal title or journal title abbreviation in the Journal field.
- Enter a volume number and/or desired an issue number in the Volume and Issue fields.
- Click the Search button at the bottom of page to conduct your search.
Select the “Include embargoed articles” option in the Text Availability section of the filters on the lefthand side of the search results to include embargoed articles in the results (see item #4 in the section titled Understand the Search Results Page.)
By Collection
Explore the contents of collections in PMC by entering the appropriate preset PMC search filter(s):
| Collection | Search Query |
|---|---|
| Author Manuscripts | "author manuscript"[filter] |
| NIH Preprints | preprint[filter] |
| Open Access Subset | "open access"[filter] |
| Digitized Historical Biomedical Journals | "is scanned"[filter] |
Learn more about all of PMC's unique historical collections, open access and text mining collections, funder collections, and more on the PMC Collections page.
By Funder
Use or append the preset search filters shown in the Search Query column below to find articles supported by funding organizations that have formally partnered with NLM to use PMC as a repository for their funded research.
| Research Funder | Search Query |
|---|---|
| National Institutes of Health (NIH) | "nih funded"[filter] |
| Administration for Community Living (ACL) | "acl funded"[filter] |
| Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) | "ahrq funded"[filter] |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | "cdc funded"[filter] |
| Food and Drug Administration (FDA) | "fda funded"[filter] |
| Office of Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) |
"aspr funded"[filter] |
| Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) | "epa funded"[filter] |
| National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) | "nasa funded"[filter] |
| National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) | "nist funded"[filter] |
| US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) | "dhs funded"[filter] |
| US Department of Veterans Affairs | "va funded"[filter] |
See PMC and Research Funder Policies for additional information.
By License
Limit your search results to articles in the PMC Open Access Subset with specific Creative Commons (CC) licenses by appending the preset search filters shown in the Search Query column below. For descriptions of these licenses, please see the Creative Commons site, About the Licenses. Please note that not all articles in the Open Access Subset have a CC license.
These filters are based on license information provided in the articles by publishers and other content providers.
| License type | Search Query |
|---|---|
| Any CC license | "cc license"[filter] |
| CC BY (Attribution) | "cc by license"[filter] |
| CC BY-ND (Attribution, no derivatives) | "cc by-nd license"[filter] |
| CC BY-NC (Attribution, noncommercial) | "cc by-nc license"[filter] |
| CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution, noncommercial, no derivatives) | "cc by-nc-nd license"[filter] |
| CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution, noncommercial, share-alike) | "cc by-nc-sa license"[filter] |
| CC BY-SA (Attribution, share-alike) | "cc by-sa license"[filter] |
| CC0 (Public domain) | "cc0 license"[filter] |
By Date
Enter dates into the search box using the format YYYY/MM/DD[pubdate], or enter a date range using a colon (:) between each date followed by a date search field tag.
To search by a single date, use the format YYYY/MM/DD[date field]. The month and day are optional.
| Date Searche Scenarios | Search Query Examples |
|---|---|
| Search by a single date: Find all articles about "blood pressure" that were published on 2020/06/01. |
blood pressure AND 2020/06/01[dp]
|
| Search for a date range: Find all articles about "heart disease" with an electronic publication date between 2020/01/01 and 2020/10/15. Note the colon ( :) between the two dates to specify the range. |
heart disease AND 2020/01/01:2020/10/15[epdat] |
| Search for a relative date range: Find all articles by the author "lipman dj" that have gone live in PMC within the last 5 years. You can use: "last X days"[date field]"last X months"[date field]"last X years"[date field]where Xis the number of days, months, or years immediately preceding today's date. |
lipman dj AND "last 5 years"[pmcrdat] |
The available date fields are:
- Date of Publication [dp] - The date an article was first made available in print or electronic format, based on data provided to PMC
- Electronic Publication Date [epdat] (if applicable)
- Print Publication Date [ppdat] (if applicable)
- PMC Live Date [pmcrdat] - The date the PMCID is accessible in PMC. For embargoed articles, this date is updated when the embargo lifts
- Entry Date [edat] - Date used for PMC processing, such as "Most Recent" sort order. This date is not populated for embargoed articles
Deposit date data are not available.
By Article Property
Search or append a search with any of the following queries to find articles with these specific properties in PMC:
| Article property | Search Query |
|---|---|
| Has supplementary material | hassuppdata |
| Has a "Data Availability" and/or a "Data Accessibility" section | hasdataavail |
| Has references tagged with a proper type to be rendered as data citations | hasdatacitations |
| Has supplementary material and/or data availability/accessibility section (best option for finding papers that may have openly accessible datasets associated) | hasassociateddata |
| Has abstract | hasabstract |
| Has plain language summary | hasplainlanguagesummary |
| Has a conflict of interest statement | hascois |
| Has PDF | "has pdf"[filter] |
| Has a preprint version also available in PMC | "has preprint"[filter] |
| Has video | "has video"[filter] |
| Is a scanned article | "is scanned"[filter] |
| Is an expression of concern about an article | articletypeexpressionofconcern |
| Is an articles that has a published expression of concern | hasexpressionofconcernin |
| Is a correction to an article | articletypecorrection |
| Is an article that has a published correction | haserratumin |
| Is a retraction of an article | articletyperetraction |
| Is an article that has been retracted | hasretractionin |
| Is ahead of print | "ahead of print"[filter] |
| Is in PMC and under embargo | "pmc embargo"[filter] |
| Is an NIH Manuscript | hasnihmsid |
Searching for a Specific Article
UPDATED FEATURE: Searching by article title has been improved.
To search for a specific article in PMC, paste the article title into the search box without quotes or punctuation. Alternatively, you can include citation details such as the author, journal name, and the year the article was published in the search box and the citation sensor will automatically analyze your query for citation information to return the correct record. You do not need to use field tags or Boolean operators.
You can also search for a specific article using a location ID, such as a DOI. For more information, see the details about the Location ID [lid] field tag.
Phrase Searching
Many phrases are recognized by the subject translation table used in PMC's automatic term mapping (ATM) feature. For example, if you enter influenza in birds, PMC recognizes this phrase as a MeSH concept.
You can bypass ATM and search for a specific phrase using the following formats:
Enclose the phrase in double quotes: "kidney allograft"
- If you use quotes and the phrase is not found in the phrase index, the quotes are ignored, and the terms are processed using automatic term mapping. The message
"Quoted phrase not found in phrase index"will display at the top of your search results.
Use a search tag: kidney allograft[tiab]
- If you use a search tag and the phrase is not found in the phrase index, the phrase will be broken into separate terms. For example,
"psittacine flight"is not in the phrase index, so a search forpsittacine flight[tiab]is broken up and translated as:
("psittaciformes"[MeSH Terms] OR "psittaciformes"[All Fields] OR "psittacine"[All Fields] OR "psittacines"[All Fields]) AND "flight"[Title/Abstract]
Use a hyphen: kidney-allograft
- If you use a hyphen and the phrase is not found in the phrase index, the search will not return any results for that phrase.
- Hyphenated phrases matching a MeSH term or entry term will include those terms in the search translation. If you want to prevent such mapping, put the hyphenated phrase inside double quotes:
"heart-attack"
When you enter search terms as a phrase, PMC will not perform the automatic term mapping that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy. For example, "health planning" will include citations that are indexed to the MeSH term, Health Planning, but will not include the more specific terms, e.g., Health Care Rationing, Health Care Reform, Health Plan Implementation, that are included in the automatic MeSH mapping.
Proximity Searching
NEW FEATURE: Proximity search is now available in PMC.
You can use proximity searching to search for multiple terms appearing in any order within a specified distance of one another in the following fields:
Acknowledgements [ack]
Affiliation [ad]
All Fields [all]
Body – All Words [body]
Conflict of Interest Statement [coi]
Corporate Author [cn]
Data Availability [das]
Figure/Table Caption [capt]
Grant Number [gr]
Methods [meth]
Reference [refr]
Section Title [sect]
Title [ti]
Title/Abstract [tiab]
To create a proximity search in PMC, enter your terms using the following format:
"search terms"[field:~N]
Search terms = Two or more words enclosed in double quotes
- There is no limit to the number of words you can search together in proximity; however, the more terms you enter, the more restrictive your search becomes. Using the Boolean operator AND to combine terms may be more appropriate than combining many terms into one proximity search.
Field = The search field tag for one of the allowable fields.
- You can use the full search field tags such as [Title], [Title/Abstract], and [Affiliation], or the abbreviated versions such as [ti], [tiab], and [ad]. See Search Field Descriptions and Tags for more information.
N = The maximum number of words appearing between your search terms
-
What
Nvalue to use will depend on your search. Try changing theNvalue and comparing the results to find what works best for your search. - A higher
Ncreates a broader, more comprehensive search; this will typically retrieve more results overall, but some of these results may be less relevant. Using the Boolean operator AND to combine terms may be more appropriate than proximity searching with a largeNvalue. - A lower
Ncreates a narrower, more precise search; this will typically retrieve fewer results that are highly relevant, but may exclude other relevant results. - If
N=0, the quoted terms will appear next to each other--with no other words in between. - For the affiliation field only, an
Nvalue of 1,000 or less will search for the double quoted terms together within the same affiliation, rather than spread across all affiliations on the record.
More information about proximity searching:
- Results will include your quoted terms in any order. If you would like to search for an exact phrase with terms appearing in a specific order, use a phrase search instead.
- Automatic Term Mapping is not applied to the quoted terms.
- Proximity searching is not compatible with wildcards (*). If the double quoted terms in a proximity search include a wildcard (*), the proximity operator will be ignored.
- You can combine proximity searches with other terms using Boolean operators; for example,
"hip pain"[Title:~4] AND stretching - Booleans and stopwords included in quoted terms for proximity search are searched like regular keywords.
Example
Search PMC for records with the terms "rationing" and "healthcare" appearing within 2 words of each other - in any order - in the Title field:
"rationing healthcare"[Title:~2]
Search results may include: rationing healthcare, healthcare rationing, rationing in healthcare, rationing scarce healthcare, rationing strategies in healthcare, rationing limited healthcare and more.
Example
Search PMC for records with the terms "patient," "physician", and "relationship" appearing next to each other - in any order - in the Title/Abstract fields:
"patient physician relationship"[Title/Abstract:~0]
Since N=0, the quoted terms must appear next to each other with no other words in between them, although they can still appear in any order. Search results may include patient physician relationship, physician patient relationship, etc.
Example
You can build queries that combine proximity searches with other terms using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT):
"accidental overdose"[Title/Abstract:~3] AND acetaminophen
Truncating Search Terms
UPDATE: PMC now searches for unlimited variations of truncated terms. Additionally, multiple wildcards can now be used in the same term.
To create a wildcard search in PMC, use an asterisk (*) to substitute for 0 or more characters in a term or phrase. For example, flavor* finds terms that begin with the root term flavor, such as flavored, flavorful, flavoring, and more variations of this term.
- A wildcard (*) substitutes for 0 or more characters
- Terms must begin with at least 4 characters before the first wildcard:
colo* - Multiple wildcards can be used in the same term:
organi*ation*
To use wildcards in a phrase search, use any of the following formats:
- Enclose the phrase in double quotes:
"clinical laboratory test*" - Use a search tag:
clinical laboratory test*[tiab] - Use a hyphen:
clinical-laboratory-test*
Phrases can include more than one wildcard: "uter* muscle*"
Wildcards turn off Automatic Term Mapping (ATM) and the process that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy. For example, "brain neoplasm*" will not map to the MeSH term Brain Neoplasms or include any of the more specific terms, e.g., Cerebral Ventricle Neoplasms, Infratentorial Neoplasms, etc.
Wildcards can be particularly useful to capture variations of a phrase, since phrase searches already turn off automatic term mapping and do not otherwise include alternate spellings or singular/plural forms. For example, searching for "tumo*r associated macrophage*" retrieves variations of the phrase such as: "tumor associated macrophage", "tumour associated macrophage", "tumor associated macrophages", and "tumour associated macrophages".
Combining Search Terms with Boolean Operators (AND, OR, NOT)
Enter Boolean operators in uppercase characters to combine or exclude search terms:
- AND retrieves results that include all of the search terms.
- OR retrieves results that include at least one of the search terms.
- NOT excludes the retrieval of terms from your search.
Use parentheses to group terms as desired.
Search Tips for Boolean Operators
Combine Tagged Search Terms Using Boolean Operators
Boolean operators must be used when combining tagged search terms.
"smith j"[au] AND 2001:2021[pubdate]
Stop Automatic Term Mapping from interpreting terms as a phrase
air bladder fistula
Automatic term mapping (ATM) recognizes “air bladder” as a phrase. ATM maps the phrase “air bladder” and the word “fistula” to relevant terms.
air AND bladder AND fistula
ATM maps each individual term “air”, “bladder”, and “fistula” to relevant terms.
View the Search Details to see how your search was translated.
Using Search Field Tags
You can search for a term in a specific field by including a search field tag after the term; for example, UCLA[ad] will search for the term UCLA in the affiliation field only.
More information about using search field tags:
- The search field tag must be enclosed in square brackets.
- Case and spacing do not matter:
cancer[mh]=Cancer[mh]. - Search field tags turn off Automatic Term Mapping (ATM), limiting your search to the specified term only.
- Using a search field tag after multiple terms will attempt to search those terms as a phrase:
kidney allograft[tiab]. If the phrase is not found in the phrase index, the individual terms will be combined with the Boolean AND, and the search tag will only be applied to the final term. - To search multiple terms in the same field, each term must be tagged individually:
child[ti] nutrition[ti] development[ti].
Search Field Descriptions and Tags
UPDATE: Some search fields have been added or updated in PMC search. New items are highlighted with NEW.
Search field descriptions and their corresponding tags are listed in the table below.
| Search Field Name | Tag |
|---|---|
| Acknowledgements | [ack] |
| Affiliation | [ad] |
| All Fields | [all] |
| Author | [au] |
| Author – Identifier NEW | [auid] |
| Body - All Words NEW | [body] |
| Conflict of Interest Statement NEW | [cois] |
| Corporate Author NEW | [cn] |
| Data Availability NEW | [das] |
| EC/RN Number | [rn] |
| Editor NEW | [ed] |
| Electronic Publication Date | [epdat] |
| Entry Date | [edat] |
| Figure/Table Caption | [capt] |
| Filter | [filter] |
| First Author Name NEW | [fauth] |
| Full Author Name | [fau] |
| Grant Number | [gr] |
| Investigator NEW | [ir] |
| Issue | [iss] |
| Journal Title | [ta] |
| Language NEW | [la] |
| Last Author Name NEW | [lauth] |
| Location ID NEW | [lid] |
| MeSH Major Topic | [majr] |
| MeSH Subheading | [sh] |
| MeSH Terms | [mh] |
| Methods | [meth] |
| NLM Unique ID NEW | [jid] |
| Pagination | [pg] |
| PMCID | [uid] |
| PMC Live Date | [pmcrdat] |
| PubMed ID | [pmid] |
| Print Publication Date NEW | [ppdat] |
| Publication Date | [dp] |
| Reference | [refr] |
| Reference Author | [refa] |
| Section Title | [sect] |
| Supplementary Concept | [nm] |
| Title | [ti] |
| Title/Abstract | [tiab] |
| Volume | [vol] |
Acknowledgements [ack]
Includes all words in the acknowledgement section of an article (e.g., "National Institutes of Health[ack]").
Affiliation [ad]
Includes the institutional affiliation and address (including email address, when available) of the authors of the article as it appears in the journal.
Searching for terms in the affiliation field searches in all author affiliations on a record. For example, a search for Hopkins[ad] AND Bloomberg[ad] can find these terms spread across multiple authors' affiliations on the same record.
To search for multiple terms appearing within the same affiliation, use a proximity search. You can also search affiliations using a phrase search; however, we suggest using a proximity search for more comprehensive results because affiliation data may be provided in a variety of ways for the same institution. For example, a search for "Hopkins Bloomberg"[ad:~25] will find any record where the words "Hopkins" and "Bloomberg" appear in the same affiliation, with no more than twenty-five words between each term.
All Fields [all]
Untagged terms and terms tagged with [all] are processed using Automatic Term Mapping (ATM). Terms that do not map are searched in all search fields except for Entry Date. Terms enclosed in double quotes or including wildcards (*) will be searched in all fields and are not processed using Automatic Term Mapping. PMC ignores stopwords.
Author [au]
To search for an author, enter the last name followed by a space and up to the first two initials followed by a space and, if applicable, a suffix abbreviation. Initials and suffixes may be omitted when searching.
PMC automatically truncates author names to account for varying initials, e.g., o'brien j[au] will retrieve o'brien ja, o'brien jb, o'brien jc jr, as well as o'brien j. To turn off this automatic truncation, enclose the author's name in double quotes and qualify with [au] in brackets, e.g., "o'brien j"[au] to retrieve just o'brien j.
Author – Identifier [auid] NEW
The author identifier includes a unique identifier associated with an author, corporate or investigator name, if supplied by a publisher. The field includes the organization authority that established the unique identifier, such as, ORCID, ISNI, VIAF, e.g., "orcid 0000-0001-5027-4446"[auid].
Body – All Words [body] NEW
Includes all words and numbers in the body of an article except for the Abstract and References. Replaces Article Body [article] and Text Word [tw]
Conflict of Interest Statement [coi] NEW
The conflict of interest statement from the published article. Conflict of interest statements are available when supplied by the publisher.
To retrieve all articles that contain conflict of interest statements, use the query hascois.
Corporate Author [cn] NEW
Corporate author identifies the corporate or collective authorship of an article. Corporate names display exactly as they appear in the journal.
Data Availability [das] NEW
Includes all words and numbers from the data availability statement, when available.
EC/RN Number [rn]
EC/RN numbers are assigned by:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Substance Registration System for Unique Ingredient Identifiers (UNIIs), e.g.,
Y92OUS2H9B[rn] - The Enzyme Commission (EC) to designate a particular enzyme, e.g.,
"EC 1.1.1.57"[rn] - The Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) for Registry Numbers, e.g.,
2751-14-6[rn]
The EC/RN number search field includes both the Registry Number and the Related Registry Number (available in the NLM MeSH Browser).
Use of the [rn] tag will restrict the retrieval of search results to the MEDLINE-indexed subset of PMC.
Editor [ed] NEW
Includes the editors of the article.
Electronic Publication Date [epdate]
The date of the electronic publication, when available. Dates or date ranges must be entered using the format YYYY/MM/DD [epdat] (e.g., 2021/04/06[epdat]). The month and day are optional (e.g., 2021[epdat] or 2021/03[epdat]). To enter a date range, insert a colon (:) between the dates (e.g., 2020:2021[epdat] or 2021/01:2021/04[epdat]).
Entry Date [edat]
This date represents the date the full text of the article is publicly available. For most articles, this is the same as PMC Live Date. However, this date is not populated for embargoed articles. This date is used primarily for PMC processing.
Figure/Table Caption [capt]
Includes all words and numbers in the figure and table captions of an article.
Filter [filter]
Technical tags used by PMC to qualify results. See the Search PMC sections for examples of tagged search filters.
First Author Name [fauth] NEW
The first personal author name on an article.
Full Author Name [fau]
The full author names from all articles for which full names are provided to PMC from the publisher. Full author searching can be entered in natural or inverted order, e.g., "julia s wong" or "wong julia s". See Author [au] for more information on author searching.
Grant Number [gr]
The grant number search field includes research grant numbers, contract numbers, or both that designate financial support by agencies of the US PHS (Public Health Service), and other national or international funding sources. The four parts of the grant data are:
- number, e.g., LM05545
- PHS 2-character grant abbreviation, e.g., LM
- institute acronym, e.g., NLM NIH HHS
- country, e.g., United States
Each individual grant part can be searched using [gr], e.g., NIH[gr]
More information about NIH grant numbers and tips for searching: NIH grant numbers, e.g., 5R01CA101211-03, typically have three main parts:
- A prefix that indicates the type of grant, e.g., 5R01.
- An 8-character serial number consisting of a 2-letter NIH institute/center code and a 6-digit number, e.g., CA101211.
- A suffix that includes additional data such as grant year.
To search for an individual NIH grant number, use the 8-character serial number and the [gr] tag (e.g., ca101211[gr]).
Investigator [ir] NEW
Names of principal investigator(s) or collaborators who contributed to the research. Search names following the author field format, for example: soller b[ir].
Issue [iss]
The number of the journal issue in which the article is published.
Journal Title [ta]
The journal title abbreviation, full journal title, or ISSN number (e.g., J Biol Chem, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 0021-9258). If a journal title contains parentheses or brackets, enter the name without the parentheses or brackets, e.g., Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) as "Proc Bayl Univ Med Cent.
The PMC Journal List is available to browse journal titles, holdings and embargo information. Or use the Journals Database look up the full name, abbreviation, and ISSN number of a journal.
Language [la] NEW
The language search field includes the language in which the article was published. You may search using either the language or the first three characters of most languages, e.g., chi[la] retrieves the same results as chinese[la]. The most notable exception is jpn[la] for Japanese.
Last Author Name [lauth] NEW
The last personal author name on an article.
Location ID [lid] NEW
Includes the DOI or publisher ID that serves the role of pagination to locate an online article. For the best results when searching on DOIs, enclose the entire DOI in double quotes, e.g., "10.1093/nar/gkr1184"[lid]. Replaces DOI [doi].
MeSH Major Topic [majr]
A MeSH term that is one of the main topics discussed in the article. See MeSH Terms below.
Use of [majr] will restrict the retrieval of search results to the MEDLINE-indexed subset of PMC.
MeSH Subheadings [sh] or [subHeading]
MeSH Subheadings are used with MeSH terms to help describe more completely a particular aspect of a subject. For example, the drug therapy of asthma is displayed as asthma/drug therapy.
The MeSH Subheading field allows users to "free float" Subheadings, e.g., "hypertension[mh] AND toxicity[sh]"
MeSH Subheadings automatically include the more specific Subheading terms under the term in a search. To turn off this automatic feature, use the search syntax [sh:noexp], e.g., "therapy[sh:noexp]".
Use of [sh] will restrict the retrieval of search results to the MEDLINE-indexed subset of PMC.
MeSH Terms [mh]
NLM's Medical Subject Headings controlled vocabulary of biomedical terms that is used to describe the subject of each journal article in MEDLINE. MeSH contains more than 23,000 terms and is updated annually to reflect changes in medicine and medical terminology. MeSH terms are arranged hierarchically by subject categories with more specific terms arranged beneath broader terms.
MEDLINE articles are automatically indexed with MeSH terms using a well-refined algorithm. Applying the MeSH vocabulary ensures that articles are uniformly indexed by subject, whatever the author's words. For more information, see Frequently Asked Questions about Indexing for MEDLINE.
Use of [mh] will restrict the retrieval of search results to the MEDLINE-indexed subset of PMC.
For more information about MeSH searching, please see PubMed User Guide: MeSH Terms.
Methods [meth]
UPDATE: All terms from the methods field are now indexed and searchable in PMC search. Previously, only key terms from the methods field were indexed.
Includes words from the methods section of the article.
NLM Unique ID [jid] NEW
The NLM ID is the alpha-numeric identifier for the cited journal that was assigned by the NLM Integrated Library System LocatorPlus, e.g., 0375267[jid].
Pagination [pg]
Enter only the first page number on which the article appears. The result will display the full pagination of the article, but this field is searchable using only the first page number.
PMCID [uid]
Unique identifier for a PMC article. Search without the PMC prefix when using the [UID] field tag, e.g., 10040002[UID].
Users can also search for PMC or NIH manuscript identifiers without a field tag using the appropriate prefix followed by the ID number, e.g., PMC2600426
To retrieve all NIH manuscripts, use the query hasnihmsid.
PMC Live Date [pmcrdat]
The date the article was first available in PMC. For embargoed articles, this is the date that the PMCID and the citation was made available. When the embargo lifts, this date is updated to the date the full text became available.
Dates or date ranges must be entered using the format YYYY/MM/DD, e.g. "2021/04/06[pmcrdat]". The month and day are optional (e.g., "2021[pmcrdat]" or "2021/03[pmcrdat]". To enter a date range, insert a colon (:) between each date (e.g., "2020:2021[pmcrdat]" or "2021/01:2021/04[pmcrdat]").
PubMed ID [pmid]
Unique identifier for the PubMed record for a PMC article.
Print Publication Date [ppdat] NEW
The date of the print publication, when available. Dates or date ranges must be entered using the format YYYY/MM/DD[ppdat] (e.g., 2021/04/06[ppdat]). The month and day are optional (e.g., 2021[ppdat] or 2021/03[ppdat). To enter a date range, insert a colon (:) between the dates (e.g., 2020:2021 [ppdat] or 2021/01:2021/04[ppdat]).
Publication Date [dp] or [pubdate]
The date that the article was published. The date on which the article was first made available in final, edited form, whether in print or electronic ( i.e., online) format.
Dates or date ranges must be searched using the format YYYY/MM/DD, e.g. "1998/03/06[dp]". The month and day are optional (e.g., "2021[dp]" or "2021/03[dp]").
To enter a date range, insert a colon (:) between each date (e.g., "2019:2021[dp]" or "2021/01:2021/04[dp]").
Use the following format to search X days, months, or years immediately preceding today's date where X = numeric value:
"last X days"[dp]"last X months"[dp]"last X year"[dp]
Reference [refr]
Includes words and numbers in the titles in an article references section.
Reference Author [refa]
Includes authors cited in an article references section.
PMC references do not list the full author name. The format to search for a reference author is the same as article Author searching.
Section Title [sect]
Includes words and numbers in an article section title.
Supplementary Concept [nm]
Includes chemical, protocol or disease terms. Synonyms to the supplementary concepts will automatically map when tagged with [nm]. This field was implemented in mid-1980; however, many chemical names are searchable as MeSH terms before that date.
Use of the [nm] tag will restrict the retrieval of search results to the MEDLINE-indexed subset of PMC.
Title [ti]
Words and numbers included in the title of an article.
Title/Abstract [tiab] NEW
UPDATE: This field replaces the previous Abstract [ab] field and now includes the title data in addition to abstract data.
Includes all words and numbers in the title and abstract of an article. English language abstracts are taken directly from the published article. If an article does not have a published abstract, PMC does not create one.
Volume [vol]
The number of the journal volume in which an article is published.
View Your Search Results
UPDATE: The new PMC Search includes an updated search results page that is more mobile-friendly and consistent with the rest of the PMC website. These updates include:
- The default sort order is "Relevance".
- The "Sort By" options have been updated (see below for more details).
- 10 results are displayed per page.
- The filters interface has been streamlined to include the most-used filters. Other filtering options are available via search field tags.
- The search results include snippets from the article. Snippets and highlighted terms are selected based on relatedness to your query.
Understand the Search Results Page | Sort Your Search Results Display | Filter Your Search Results | Download Your Search Results | View the Search Details
Understand the Search Results Page

As shown in Figure 3, on the search results page, you can:
- Click on the record title to access an article.
- See snippets and highlighted terms that are displayed below the article citation. Snippets are selected based on relatedness to your query.
- Sort your results by Relevance, Most Recent, or Publication date. Click the up/down arrow next to the selected sort option to toggle between ascending or descending order. The reverse sort option will not display when relevance sort order is selected.
- Expand the search details bar to view how PMC translated your query by clicking on the green "Search Details" box.
- Select "Include" to include embargoed articles in your search results; select "Exclude" to exclude embargoed articles from your search results.
- Save your search results as a text summary, PubMed format, CSV, or PMCID list file.
- See the total number of articles returned by your search below the save button.
- Filter your search results by Results by Year Timeline, Publication Date, Publication Stage, or Collection.
- Provide feedback or get help on using PMC.
Sort Your Search Results
PMC search results are default displayed by relevance ranking, with 10 results per page.
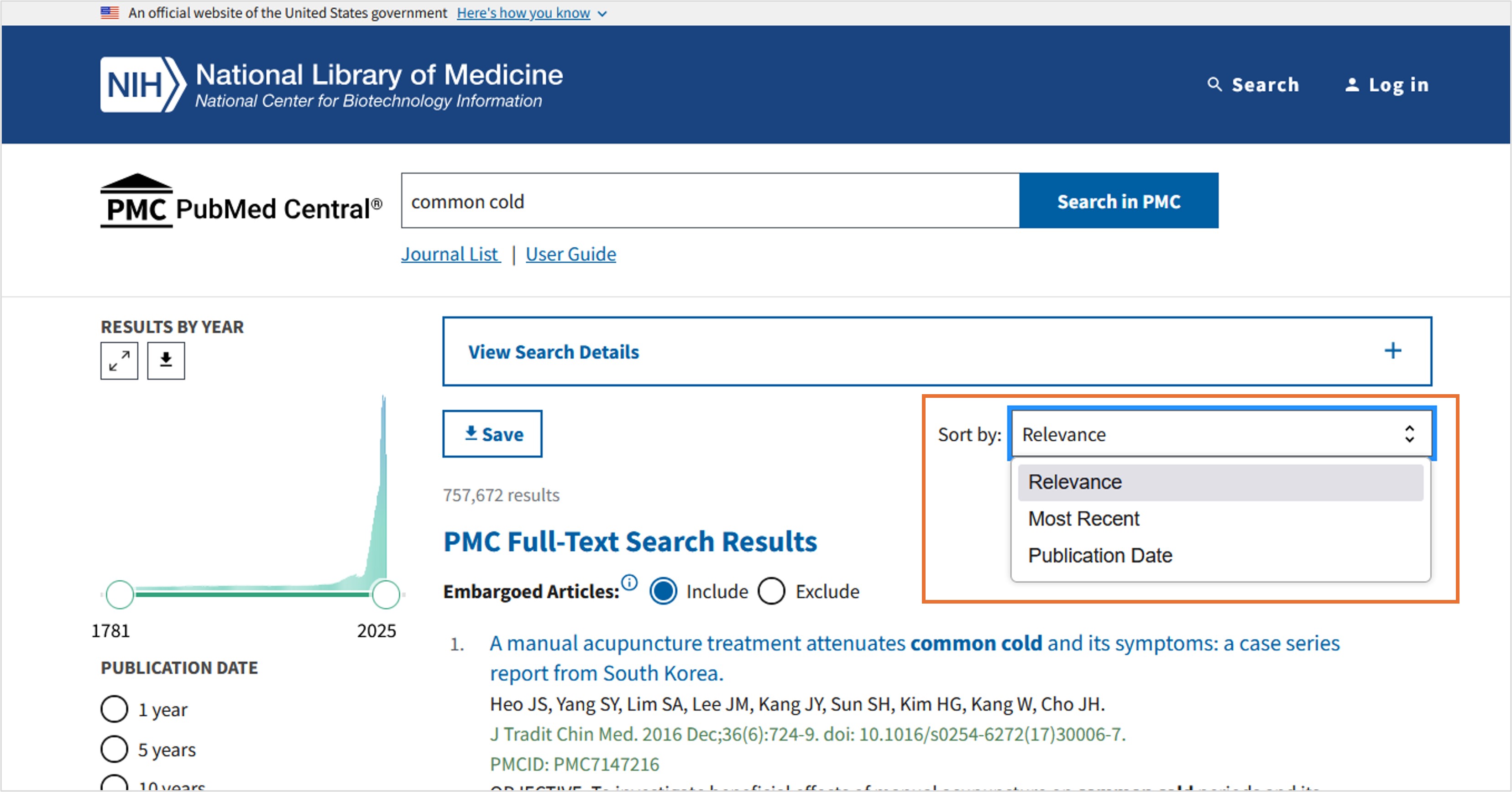
As shown in Figure 4, you can use the "Sort by" drop-down menu at the top of the search results page to change the sort order.
- Relevance (default) - PMC Relevancy sort uses the BM25 algorithm to return articles related to your search term(s).
- Most Recent – Articles sorted by Most Recent are displayed in reverse date added order: last in, first out. The date used for sorting is the date an article became fully available in PMC, not the publication date. Embargoed articles display at the end of the search results. The secondary sort is PMCID.
- Publication Date – Articles sorted by Publication Date are displayed in reverse chronological order: newest to oldest.
When sorting by Most Recent or by Publication Date, you can reverse the sort order by clicking the up/down arrow next to the selected sort option to toggle between ascending or descending order. The reverse sort option will not display when Relevance sort order is selected.
Filter Your Search Results
UPDATE: The filters interface has been streamlined to include the most-used filters.
Use the filters on the left-hand side of the page (see area #8 in Figure 3) to narrow your search results.
Filter your results by:
Results by Year Timeline
Click and drag the sliders on the Publication Date timeline to change the date range for your search. Click the download button to download a CSV file including the number of records retrieved per year.
To reset the timeline, click “Clear filters” in the green banner at the top of your search results.
Publication Date
To filter your results by Publication Date, click 1 year, 5 years, 10 years, or enter a custom range. Only a year is required.
Publication Stage
- Published journal article - content published in a scholarly journal
- Author manuscript - peer-reviewed author manuscripts accepted for publication in a journal
- Preprint - preprint versions of articles collected through the NIH Preprint Pilot, made public prior to peer review
Collections
- PMC Open Access Subset - The PMC Open Access Subset includes journal articles and preprints that are made available under license terms that allow reuse
- Historical back issues - Historical back issues refers to digitized content from print journals made available in PMC through the Biomedical Journal Digitization Projects
Download Your Search Results
Use the Save button to download citations to a file.
- Click the Save button.
- Choose a Results Selection from the menu:
- All results on this page (to download more than the default 10 results, click "Show More Results" at the bottom of your search results until the number of results you would like to download is displayed)
- All results (up to a maximum of 10,000 results)
- Choose the file Format from the menu: Summary (text), PubMed, CSV, or PMCID list
Saving a large set of results may take several minutes.
View the Search Details
PMC may modify or add additional search terms to your search to optimize retrieval, such as: MeSH terms, British/American spellings, singular/plural word forms, and other synonyms.
You can view the details of how PMC translated your search in the expandable Search Details bar below the search bar (see area #4 in Figure 3). Only the translation of your most recent search will be available in the Search Details box.
View an Article
This section highlights some of the key functionality available in PMC's article display.

If you want to
-
Search for full-text articles in PMC: The search bar supports search across the articles in the PMC archive. On mobile devices click the magnifying glass icon to access the search bar.
-
View publication dates related to an article: a) The citation display indicates the date an article was first made available in print or electronic format, based on data provided to PMC. b) Other dates — such as submission, acceptance, and issue dates — may be viewed under the Article Notes section.
-
View the corresponding PubMed record: Click on the PMID link.
-
View references within the article: Hover over or click on any linked reference in the article to view the complete reference list entry.
-
See the "Actions" section found in the right-hand column on desktop or across the top of an article on mobile devices to take the following actions:
- View an article on its publisher's website: Click on The "View on publisher site" button on desktop, or the external link icon on mobile devices.
- Download a PDF of the article: Click on the PDF button on a desktop, or the download arrow on a mobile device. Note: PDFs may not be available for all articles.
- Get a formatted citation of the article: Click on the blue “Cite” button on desktop, or the quotation mark icon on mobile devices, to get formatted citation information. Copy the citation formatted in AMA, MLA, APA, or NLM style. In addition, the Cite box includes a link to download the citation in NBIB format.
- Save an article to a My NCBI collection: Click the blue “Collections” button on desktop, or the bookmark icon on mobile devices, to add an article to any of your collections in My NCBI. When an article has been added to a collection, the icon in the desktop button turns white. You can also use this button to create a new collection before adding an article to it.
- Share an article: Click on the “Permalink” button on desktop or the share icon on mobile devices, and then select "Copy" from the pop-up.
-
See the "Resources" section found in the right-hand column on desktop or click on the "three dots" icon at the top of an article on mobile devices to access the following resources:
- View articles similar to the article you are viewing: Click "Similar articles" to open a list of articles from PubMed that are similar to the one you are reading. Click an article title to view the record in PubMed, or click the "See all in PubMed" link to see the full list of similar articles available from PubMed.
- View articles that cite the article you are viewing: Click "Cited by other articles" to see a list of articles from PubMed that cite the one you are reading. Click an article title to view the record in PubMed, or click the "See all in PubMed" link to see a full list of articles available from PubMed.
- Access links to related content in other NCBI databases: Click "Links to NCBI Databases" to open the section and see available links to related records in other NCBI databases. Click on the name of the NCBI database to navigate to that resource.
-
Navigate sections within an article: Navigate to specific article section headings by clicking on an item in the "On this page" navigation menu. On mobile devices, this navigation menu can be accessed by clicking on the menu icon. Items in the "On this page" menu depend primarily on the structure of the article as submitted by the publisher, and may vary between articles.
-
Find data related to the article: PMC collects any data citations, data availability statements and supplementary materials included in the article in an Associated Data section at the end of the article. This section will only display on articles that have one or more of these features in the article. You can navigate to this section from the "Associated Data" item in the navigation menu. You can also find links to applicable NCBI databases in the "Links to NCBI Databases" section of the "Resources" section or in the "Related information" section of an article's corresponding PubMed record.
Appendices
Automatic Term Mapping | Stopwords | Cookies | Character Conversions | PMC URL Format
Automatic Term Mapping (ATM)
Untagged terms that are entered in the search box are matched (in this order) against a Subject translation table (including MeSH - Medical Subject Headings), a Journals translation table, the Author index, and an Investigator (Collaborator) index.
When a match is found for a term or phrase in a translation table the mapping process is complete and does not continue on to the next translation table.
To see how your terms were translated, check the Search Details. If you want to report a translation that does not seem accurate for your search topic, please send the information to the NLM Help Desk.
1. Subject Translation Table
UPDATED: The Subject Translation Table has been augmented to include additional British and American spellings, singular and plural word forms, and other synonyms to provide more consistent and comprehensive search retrieval.
The Subject Translation Table contains:
- British and American spellings
- Pairs: singular and plural word forms, synonyms, and other closely related terms
- Drug brand name to generic name translations
- MeSH terms
- The See-Reference mappings (also known as entry terms) for MeSH terms
- MeSH Subheadings
- Terms derived from the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) that have equivalent synonyms or lexical variants in English
- Supplementary concept (substance) names and their synonyms
If a match is found in this translation table, the term will be searched as MeSH (that includes the MeSH term and any specific terms indented under that term in the MeSH hierarchy), and in all fields.
For example, if you enter bacterial infections in the search box, PMC will translate this search to: "bacterial infections"[MeSH Terms] OR ("bacterial"[All Fields] AND "infections"[All Fields]) OR "bacterial infections"[All Fields]
If you enter an entry term for a MeSH term, the translation will also include an all fields search for the MeSH term associated with the entry term. For example, a search for sore throat will translate to: "pharyngitis"[MeSH Terms] OR "pharyngitis"[All Fields] OR ("sore"[All Fields] AND "throat"[All Fields]) OR "sore throat"[All Fields]
Substance name mappings do not include a mapping for individual terms in a phrase, e.g., IL-22 will not include IL[All Fields] AND 22[All Fields].
MeSH term mappings that include a standalone number or single character do not include a mapping for individual terms in a phrase, e.g., Protein C will not include Protein[All Fields] or C[All Fields].
2. Journals Translation Table
The Journals translation table contains the:
- full journal title
- title abbreviation
- ISSN and eISSN number
These will automatically map to the journal abbreviation that is used to search journals in PMC and in all fields. For example, a search for tissue barriers will translate to: "tissue barriers"[Journal] OR ("tissue"[All Fields] AND "barriers"[All Fields]) OR "tissue barriers"[All Fields]
3. Author Index
If the term is not found in the above tables, and is not a single term, PMC checks the author index for a match.
More information about author searching:
- PMC automatically truncates a search for an author's name to account for varying initials, e.g., colins c retrieves colins cc, colins cl, colins cm, colins cp, as well as colins c.
- When combining multiple authors, to avoid a match with full author names, include initials or use the [au] search tag, e.g.,
ryan[au] james[au]. Author names comprised of only stopwords, e.g.,as a, are not searched as authors if they are part of phrase,chemical burn as a danger, unless the search only includes the author name, e.g.,as a. - You can search for a name in natural or inverted order, e.g.,
julia s wongorwong julia s. - A comma following the last name for searching is optional. For some names, however, it is necessary to distinguish which name is the last name by using the comma following the last name, e.g.,
james, ryan. - Omit periods after initials and put all suffixes at the end, e.g.,
vollmer charles jr - Initials and suffixes are not required, if you include a middle initial or suffix, you will only retrieve citations for articles that were published using the middle initial or suffix.
- To distinguish author initials that may match a full author name use the [fau] search tag, e.g.,
peterson do[fau].
4. Investigator (Collaborator) Index UDPATED
If the term is not found in the above tables, except for Author, and is not a single term, the investigator index is consulted for a match. The investigator (collaborator) index includes full names, if available. Enter a full investigator name in natural or inverted order, e.g., harry janes or janes harry.
5. If No Match is Found?
PMC breaks apart the phrase and repeats the above automatic term mapping process until a match is found. PMC ignores stopwords in searches.
If there is no match, the individual terms will be combined (ANDed) together and searched in all fields.
When a search includes terms that were tagged with a search field during the automatic term mapping process and retrieves zero results, the system triggers a subsequent search using "Schema: all". "Schema: all" modifies the search by removing the automatically added search field tags and then searches each term in all fields.
Report Problems with Automatic Term Mapping:
If you want to report a translation that does not seem accurate for your search topic, please write to the PMC Help Desk with the information.
Stopwords
PMC searches use the same stopwords that are used in PubMed. Stopwords are common, but uninformative words such as "a" or "about" that are eliminated from searches. See PubMed Stopwords for the list.
Please note, stopwords in phrase searches and proximity searches are not ignored.
Cookies
A "cookie" is information stored by a web server on your computer. See the NLM Privacy Policy for additional information.
In the case of PMC, cookies are used to store information about your interactions that may be needed later to perform a particular function.
To use interactive features, you need to enable cookies on your computer. Please consult your browser's Help for information on enabling cookies.
If you have problems using cookie-dependent features of PMC even after enabling cookies, possible reasons may include:
- Cookies are blocked by your provider or institution. Check with your Internet provider and/or the system administrator at your institution to see if cookies can be accepted.
- Your computer's date and time settings are incorrect. Check your computer's time settings to ensure that they are correct.
Character Conversions
Special characters (e.g., pound sign, dollar sign) included in a PMC search may hold specific search syntax meaning, whereas others are converted to spaces. (See PubMed Character Conversions for more information.) However, in the abstracts and full-text of PMC articles, all characters are represented as accurately as possible
PMC URL Format
In many cases, the first URL path segment will identify the resource type. Subsequent path segments identify the specific resource, and sometimes sub-resources. Query string parameters are used to filter or refine results, and to specify the response format.
In many cases, there are multiple URLs that will access the same resource. In these cases, we identify one as the canonical URL (shown bold in the table below), and use of the ancillary URLs will cause a redirect to the canonical one.
| Resource type | URL(s) |
|---|---|
| List of journals (PMC Journal List) | /journals/ |
| List of journals in PMC Journal List matching search | /journals/?term=respiratory |
| Specific journal entry in the PMC Journal List |
/journals/?term=7505876 /journals/?term="Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America" /journals/?term="Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A" |
| Search result listing all articles available in PMC for a specific journal |
/journals/issn/1091-6490/ /ivip/1091-6490/ |
| Search result listing all articles available in PMC for a specific issue | /ivip/0021-9738/117/8/ |
| Article full-text HTML |
/articles/PMC2814059/ /articles/PMC2814059 /articles/2814059/ /articles/2814059.3/ /articles/pmid/20126278/ /articles/doi/10.1371/currents.RRN1147 /ivip/0021-9738/117/9/2380/ Note: Unlike the other formats, the DOI format above does not allow an optional slash at the end because DOIs can contain slashes. A trailing slash would be interpreted as being part of the DOI. |
| Article full-text PDF | /articles/PMC2150930/pdf/ |
| Figure | /articles/PMC2278217/figure/F5/ |
| Table | /articles/PMC2278217/table/T1/ |
| Author manuscript full-text HTML | /articles/mid/NIHMS20955/ |
| URLs are relative to pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. The URL formats shown in bold identify the canonical URLs; use of the ancillary URLs will cause a redirect to the canonical URL. Note that the trailing slash is optional (except for the DOI format as noted above, where a trailing slash would be interpreted as being part of the DOI). The canonical URL format will almost always end in a trailing slash. |
|
Provide Feedback and Request Search Help
Please reach out to the NLM Help Desk to provide feedback or request help with any questions.

