Abstract
We present a solvable model that predicts the folding kinetics of two-state proteins from their native structures. The model is based on conditional chain entropies. It assumes that folding processes are dominated by small-loop closure events that can be inferred from native structures. For CI2, the src SH3 domain, TNfn3, and protein L, the model reproduces two-state kinetics, and it predicts well the average Φ-values for secondary structures. The barrier to folding is the formation of predominantly local structures such as helices and hairpins, which are needed to bring nonlocal pairs of amino acids into contact.
Keywords: protein folding kinetics, two-state folding, folding cooperativity, Φ-value analysis, effective contact order, loop-closure entropy, master equation
Protein-folding kinetics is usually modeled in either of three ways. First, there are mass-action models that capture the amplitudes and decay rates of the exponentials in the folding or unfolding relaxation process (Ikai and Tanford 1971; Tsong et al. 1971; Dill and Chan 1997; Englander 2000). Mass-action models are useful for cataloging the different types of kinetic behavior but give no insight into molecular structures or mechanisms. Such models do not predict other experimental properties, such as Φ-values. Second, there are all-atom or lattice-model simulations that can explore sequence-structure relationships (e.g., see Duan and Kollman 1998; Shea and Brooks III 2001; Daggett 2002). They are usually limited by computational power to short time scales and to studying restricted conformational ensembles. Third, between these macroscopic and microscopic extremes, another type of model has recently emerged. This class of models uses knowledge of the native structure to infer the sequences of folding events (Alm and Baker 1999; Debe and Goddard III 1999; Galzitskaya and Finkelstein 1999; Munoz and Eaton 1999; Shoemaker et al. 1999; Clementi et al. 2000; Hoang and Cieplak 2000; Ivankov and Finkelstein 2001; Li and Shakhnovich 2001; Portman et al. 2001; Alm et al. 2002; Bruscolini and Cecconi 2002; Bruscolini and Pelizzola 2002; Flammini et al. 2002; Klimov and Thirumalai 2002; Micheelsen et al. 2003). Some of these models define partially folded states with one or two contiguous sequences of native-like ordered residues (Alm and Baker 1999; Galzitskaya and Finkelstein 1999; Munoz and Eaton 1999; Alm et al. 2002). Others are based on a Go-model energy function that enforces the global stability of the native state (Clementi et al. 2000; Hoang and Cieplak 2000; Li and Shakhnovich 2001).
We describe here a folding model of the third type. Our model uses knowledge of the native structure to predict the kinetics. However, it differs from previous models in several respects. First, our model focuses on chain entropies and estimates loop lengths from the graph-theoretical concept of effective contact order ECO (see below). We follow time sequences of loop-closure events, because we expect that these events reveal how the kinetics is encoded in the native structure. We assume that folding proceeds mostly through closures of small loops, and that large-loop closures are much slower and less important processes. Second, our model focuses on contacts within the chain, not on whether residues are native-like or not (Alm and Baker 1999; Galzitskaya and Finkelstein 1999; Munoz and Eaton 1999), because we think the formation of contacts is a more physical description of the folding process. Therefore, in our model, partially folded states are characterized by formed contacts, not by contiguous stretches of native-like ordered residues, as in other simple models. Third, the folding kinetics is described by a master equation that can be solved directly for the macrostates considered here, without stochastic simulations such as molecular dynamics or Monte Carlo. Hence, the present treatment can handle the full spectrum of temporal events.
The present work is related to a recent model of protein zipping (Weikl and Dill 2003a,b). Our fundamental units of protein structure are contact clusters. A contact cluster is a collection of contacts that is localized on a contact map, corresponding roughly to the main structural elements of the native structure. Examples of contact clusters are turns, α-helices, β-strand pairings, and tertiary pairings of helices. A central quantity in our models is the effective contact order ECO (Dill et al. 1993; Fiebig and Dill 1993). The ECO is the length of the loop that has to be closed in order to form a contact, given a set of previously formed contacts or contact clusters. The premise is that the formation of the nonlocal contact clusters requires the prior formation of other, more local, clusters.
Our model predicts average Φ-values for secondary structural elements that are in good agreement with the experimentally observed values for several two-state proteins. It shows that Φ-value distributions can be understood from loop-closure events that are defined by the native topology of a protein. The importance of topology for routes and Φ-values has also been noted previously by other groups (Alm and Baker 1999; Munoz and Eaton 1999; Clementi et al. 2000; Vendruscolo et al. 2001; Alm et al. 2002).
To compute the dynamics, we use a master equation. Several previous studies of the folding kinetics of lattice heteropolymer models have also been based on master equation methods (Leopold et al. 1992; Chan and Dill 1993; Cieplak et al. 1998; Ozkan et al. 2001, 2002, 2003; Schonbrun and Dill 2003). These methods have the advantage that they require no ad hoc assumptions about what the transition state is. The transition state emerges in a direct physical way from the solution to the master equation. However, the lattice models are too simplified to treat specific amino acid sequences or specific protein structures. Lattice models focus on transitions between microstates, the individual chain conformations, as these are the fundamental units of structure in such models. Our present master equation describes transitions between macrostates, defined by the contact clusters of a given protein structure. In this way, the present model aims to make closer contact with experiments.
The model
Contact clusters
To compute the folding kinetics, we start with the native contact map, the matrix in which element (i,j) equals 1 if the residues i and j are in contact, and equals 0 otherwise. Two residues are defined as being in contact if the distance between their Cα or Cβ atoms is <6 Angstroms.
Next, we divide the native contact map into contact clusters. Each contact cluster corresponds to a structural element of the protein. Two contacts (i,j) and (k,l) are defined as being in the same cluster if they are close together on the contact map, according to the distance criterion that |i − k| + |j − l| ≤ 4. We define two types of clusters, local and nonlocal. Clusters are local if they contain at least one local contact (i,j) having contact order CO = |i − j| ≤ 6. Local clusters include helices, turns, or β-hairpins, for example. A cluster is nonlocal if it has no local contacts; examples include β-strand pairings other than hairpins, and the tertiary interactions of helices. To qualify as nonlocal, a cluster must also have more than two contacts; isolated nonlocal contacts are not considered to be clusters. Similarly, we do not consider as contributing to clusters any peripheral contacts (i,j) with a minimum distance |i − k| + |j − l| = 4 to the other contacts in the cluster. In general, typical contact maps have only a few isolated nonlocal or peripheral contacts. Figure 1 ▶ shows examples of clusters, specifically for chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 (CI2) and the src SH3 domain. By our criteria, CI2 has five local clusters and two nonlocal clusters (β2β3 and β1β4), and the src SH3 domain has six local clusters and two nonlocal clusters (RT-β4 and β1β5).
Figure 1.

Native contact maps and contact clusters for CI2 (PDB file 1COA) and the src SH3 domain (1SRL).
States and free energies
We assume that each cluster is either formed or not; we neglect partial degrees of formation. Thus, for a protein with M clusters, there are 2M possible states that describe the progression to the native state. Each of these macrostates is characterized by a vector n = {n1,n2, . . .,nM}, where ni = 1 indicates that cluster i is formed and ni = 0 indicates that cluster i is not formed.
In our model, the free energy of the protein as a function of the state n of cluster formation is given by:
 |
(1) |
Each cluster i that is formed (ni = 1) contributes to the free energy Fn of the state n with two terms, a state-dependent free energy of loop closure c • ℓi(n) (initiation-free energy), and a free energy fi for forming the cluster contacts (propagation-free energy). Here, c is a loop-closure parameter. The quantity ℓi = ℓi(n) is the initiation ECO (Weikl and Dill 2003a) for cluster i. The initiation ECO of a cluster is the length of the smallest loop that must be closed in order to form that cluster from the other existing clusters. For a local cluster, the initiation ECO is the smallest CO among the contacts. For a nonlocal cluster, the initiation ECO depends on the presence of other clusters in the state n.
In general, the initiation ECO also depends on the sequence through which those clusters are formed. However, to apply the master equation formalism, we need a free energy, and thus, we require a definition of initiation ECO that is only a function of state. For this purpose, we use the following scheme. If only one nonlocal cluster is formed in a certain state, the initiation ECO of that cluster is the smallest ECO among the cluster contacts, given all the local clusters formed in that state. If multiple nonlocal clusters are present in a state, we consider all of the possible sequences along which these clusters can form, and determine the one having the smallest sum of ECOs. For instance, for a state with two nonlocal clusters, Ci and Cj, there are two sequences as follows: (1) Ci → Cj, and (2) Cj → Ci. The minimum ECOs for the clusters are determined sequentially: ℓi(1) and ℓj(1) along sequence (1), and ℓi(2) and ℓj(2) along sequence (2). If ℓi(1) + ℓj(1) is smaller than ℓi(2) + ℓj(2), the initiation ECOs ℓi and ℓj of the clusters i and j in the given state are taken to be ℓi(1) and ℓj(1). The initiation ECOs ℓi and ℓj are an estimate for the smallest loop lengths required to form the two clusters in the state.
In equation 1, the free-energy cost of the loops is estimated by a simple linear approximation in the loop length. This is not unreasonable, as the range of relevant ECOs only spans roughly one order of magnitude, from about ℓ ≃ 3 to ℓ ≃ 30 or 40. In general, determining the free energy of a chain molecule with multiple constraints or contacts is a complicated and unsolved problem. For the simpler problem of hairpin-like loop closures, several estimates have been given in the literature (e.g., see Chan and Dill 1990; Galzitskaya and Finkelstein 1999; Ivankov and Finkelstein 2001).
In principle, this model could treat the detailed energetics of each folding route, if each of the M clusters were characterized by its own free energy fi. But here, we consider a simpler version of the model. We assume that there are only two parameters for the free energy of formation, fi = fl for propagating any local cluster, and fi = fnl for propagating any nonlocal cluster. To obtain two-state folding and agreement with experimental Φ-values, we find that fl must be non-negative and fnl must be negative. This is consistent with the experimental observation that local structures, such as helices or β-hairpins, are generally unstable in isolation. Similar in spirit, the diffusion-collision model of Karplus and Weaver assumes that microdomains, for example, helices, are individually unstable (Karplus and Weaver 1976, 1994). Thus, the rate-limiting barrier to folding in our model turns out to be the formation of mostly local structures needed to reduce the ECOs of nonlocal clusters. The driving force for overcoming this barrier is the favorable free energy fnl of assembling the nonlocal clusters.
The predicted free-energy landscape of the src SH3 domain is shown in Figure 2 ▶, using the parameters fl = 0 and c = 0.5 kBT, where kBT is Boltzmann’s constant × temperature. The value of fnl is chosen so that the equilibrium probability that the two nonlocal clusters RT-β4 and β1β5 are both folded (native state) is 0.9, which gives fnl = −6.6 kBT for src SH3. With these parameter settings, we obtain a good agreement with average experimental Φ-values for the src SH3 domain and other two-state folders (see below). For clarity, we show in the figure only a reduced set of states on the basis of the five major clusters RT, β2β3, β3β4, RT-β4, and β1β5. The three small clusters T, DT, and H have negligible effects on the folding kinetics and on the Φ-values. Only states differing by the formation of a single cluster are kinetically connected. The uphill steps in this model either are steps in which a local cluster is formed, or steps involving high ECOs. The downhill steps are steps in which a nonlocal cluster is formed with a low ECO, or steps in which a local cluster significantly reduces the ECOs of previously formed nonlocal clusters. The model predicts two main folding routes. Along the upper route (E) β1β5 folds after (D) RT-β4; along the lower route, they form in the opposite order. Along these routes, the barriers (highest free-energies states) are the states in which two clusters are formed, BD and BC for the upper route, and AC for the lower route.
Figure 2.
Energy landscape for the src SH3 domain as a function of the five major clusters: A, RT; B, β2β3; C, β3β4; D, RT-β4; and E, β1β5 (see Fig. 1 ▶). Here, BD, for example, means that only clusters B and D are formed. The free energies given by equation 1 are shown in blue (the units are kBT). (Red arrows) Uphill steps in folding direction; (green arrows) downhill steps. For clarity, states with free energies larger than four kBT are neglected.
Master equation
In this section, we describe the folding dynamics. We use the master equation,
 |
(2) |
which gives the time evolution of the probability Pn(t) that the protein is in state n at time t. Here, wnm is the transition rate from state m to n. The master equation can be written in matrix form
 |
(3) |
where P(t) is the vector with elements Pn(t), and the matrix elements of W are given by
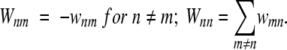 |
(4) |
The transition rates are given in terms of the free energies by
 |
(5) |
where to is a reference time scale. The only transitions that are assigned to have nonzero rates wnm are those incremental steps that change the state n by a single cluster unit. This is enforced by the term δ|n–m|,1 in equation 5, where the Kronecker δi,j is one for i = j and zero otherwise. The condition |n–m| = 1 is only satisfied by pairs of states n = {n1, . . .,nM} and m = {m1, . . .,mM} with nk ≠ mk for a single cluster k, and with nk = mk for all other clusters. The transition rates (eq. 5) satisfy detailed balance, wnmPme = wmnPne, where Pne ~ exp[–Fn/(kBT)] is the equilibrium weight for the state n. We have chosen here the Glauber dynamics with wnm ~ (1 + exp[(Fn − Fm)/(kBT)])−1. Another standard choice satisfying detailed balance is the Metropolis dynamics, which should lead to equivalent results.
The detailed balance property of the transition rates implies that the eigenvalues of the matrix W are real. One of the eigenvalues is zero, corresponding to the equilibrium distribution, whereas all other eigenvalues are positive (van Kampen 1992). The solution to the master equation is given by
 |
(6) |
where Yλ is the eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue λ, and the coefficients cλ are determined by the initial condition P(t = 0). For t → ∞, the probability distribution P(t) tends toward the equilibrium distribution Pe ~ Y0 where Y0 is the eigenvector with eigenvalue λ = 0.
Solving the master equation gives a set of 2M eigenvalues, each with its associated eigenvector. Each eigenvalue represents a relaxation rate. As initial conditions at t = 0, we start from the state in which no clusters are formed. This corresponds to folding from high temperatures or high-denaturant concentrations.
Results
The cooperativity in two-state kinetics
The signature of two-state kinetics is the existence of one slow relaxation process (described by a single exponential), separated in time from 2M − 1 fast relaxations (a burst phase). Figure 3 ▶ shows the eigenvalue spectra for CI2 and the src SH3 domain, based on using the parameters c = 0.5 kBT, local cluster-free energy fl = 0, and a nonlocal cluster-free energy chosen so that the equilibrium native population with all nonlocal clusters formed has probability 0.9. The latter condition leads to fnl = −7.9 kBT for CI2, and fnl = −6.6 kBT for src SH3. Figure 4 ▶ shows the predicted folding dynamics for the src SH3 domain.
Figure 3.
Eigenvalue spectra for CI2 and the src SH3 domain in units of 1/to where to is the reference time scale for the transition rates (equation 5).
Figure 4.

(Top) Time evolution of the formation probability P for the major clusters of the src SH3 domain during folding (see Fig. 1 ▶). (Bottom) Time evolution of state probabilities for the exemplary path 0 → B → BC → BCD → BCDE → ABCDE of the src SH3 domain (see also Fig. 2 ▶). The initial state at time t = 0 is the denatured state in which none of the clusters is formed.
The spectra in Figure 3 ▶ show that for these proteins, the eigenvalues do separate into a slow single-exponential step and a burst phase, consistent with the experimental observation of two-state behavior. The slowest relaxation rate λ1 is about one order of magnitude smaller than the other nonzero eigenvalues (see Fig. 3 ▶). At times, t ≳ 1/λ1, the probability distribution (eq. 6) is well approximated by P(t) ≃ c0Y0 + c1Y1 exp[− λ1t], where Y0 is the eigenvector with eigenvalue 0, which characterizes the equilibrium state, and Y1 is the eigenvector with eigenvalue λ1.
The typical time evolution of the folding process predicted by the model is as follows. We have two time scales, t ≃ to and tF ≃ 1/λ1. Time to is a characteristic of the burst phase in the model and tF is the single-exponential folding time. At the earliest times, t < to, single local clusters start to form; examples are the clusters A, B, and C of the src SH3 domain (see Fig. 2 ▶). As shown in Figure 4 ▶, on this time scale, each cluster is only weakly populated, with a probability <10%. Any structures having larger-scale organization—cluster pairs, triplets, etc.—have negligible populations. At intermediate times, tF ≳ t ≳ to, there is a crossover from the burst phase to the single-exponential folding process. During these intermediate times, cluster pairs (AC, BC, BD) begin to form. Figure 2 ▶ shows that these pairwise clusters are the barrier events; that is, they represent the conformational states of maximum free energy obtained during folding. Finally, on the longest time scale, t ≃ tF, the pairwise and triplet clusters reach sufficiently high populations to assemble into multicluster complexes, proceeding downhill in free energy to the native structure.
What is the basis for the cooperativity of folding in our model, that is, for the separation of time scales? First, the formation of local structures in our model reduces the loop-closure entropies for the formation of the nonlocal structures. Second, only the nonlocal structures have favorable propagation-free energies fi = fnl < 0. Hence, the formation of the nonlocal structures stabilizes the overall fold, and thus, also the local structures. The barrier arises from the positive-free energies in equation 1, due to the formation of local structures and loops (see Fig. 2 ▶). Interestingly, if we set the free energies for local structure formation to be negative by several kBT, we obtain fast multiexponential downhill folding, without a barrier. On the basis of the experiments and theory, such downhill folding has been postulated recently for the protein BBL (Garcia-Mira et al. 2002).
To understand the cooperative folding in the model, it is instructive to turn off the loop-closure term in equation 1 by setting c = 0. Then, all M clusters are independent of each other. In that case, there is no cooperativity. It can be shown that the matrix W then has the eigenvalues λ = j/to, where j is an integer between 0 and M, the number of clusters. Each of these eigenvalues has a population that is given by the binomial coefficient j!/[j!(M − j)!]. This gives a broad non-two-state spectrum. Hence, the separation of time scales—and the two-state cooperativity—arise in this model from the coupling of the clusters via the loop-closure term in equation 1.
To see the magnitude of the barrier, note that the fold-ing rate λ1 is related to the height of the energy barrier on the folding landscape. For comparison, consider a mass-action model with three states D ↔ T ↔ N (denatured state, transition state, native state) and transition rates as in equation 5. The folding rate is given, to a very good approximation, by: (1/2) for barrier energies
for barrier energies  . The factor of 1/2 comes from the fact that a molecule in state T can jump to both D and N, with almost equal probability, as both sides of high-barrier transition states are steep downhills. Now, for the energy landscape of the src SH3 domain shown in Figure 2 ▶, the minimum barrier has free-energy 2.4 kBT for state BD. The corresponding barrier crossing rate of (1/2)t−1o exp[−2.4] is in good agreement with the folding rate λ1 ≃ 0.05/to (see Fig. 3 ▶).
. The factor of 1/2 comes from the fact that a molecule in state T can jump to both D and N, with almost equal probability, as both sides of high-barrier transition states are steep downhills. Now, for the energy landscape of the src SH3 domain shown in Figure 2 ▶, the minimum barrier has free-energy 2.4 kBT for state BD. The corresponding barrier crossing rate of (1/2)t−1o exp[−2.4] is in good agreement with the folding rate λ1 ≃ 0.05/to (see Fig. 3 ▶).
Experiments have been interpreted either as indicating that burst phases involve structure formation or that burst phases are processes of nonstructured polymer collapse, depending on the protein and the experimental method (Callender et al. 1998; Eaton et al. 1998; Gruebele et al. 1998; Englander 2000; Parker and Marqusee 2000; Ferguson and Fersht 2003). In our model, the burst phase is a process of structure formation. Nonstructured collapse is beyond the scope or resolution of our model, because the model has only a single fully unstructured state—the state in which none of the clusters is formed. The burst phase in our model captures fast pre-equilibration events within the denatured state in response to initiating the folding conditions at t = 0. In the model, this denatured state is an ensemble of macrostates on one side of the barrier in the energy landscape (see Fig. 2 ▶). It is reasonable to assume that such pre-equilibration events within the denatured state exist also for real proteins. However, whether these events can be detected as burst phases in experiments should depend on the initial conditions, experimental probes, etc.
During folding or unfolding, certain conformations will be populated transiently. If the populations of those conformations are always small, we call them hidden intermediates (Ozkan et al. 2002). The population of a hidden intermediate conformation rises to a maximum, Pmax, then falls as the protein ultimately becomes fully folded. The term hidden means that Pmax is always small enough that it does not contribute an additional kinetic phase; that is, the folding kinetics is two-state. Here, we consider two quantities: (1) We compute Pmax for the transient states. For simplicity, we consider only the five major clusters: RT, β2β3, β3β4, RT-β4, and β1β5. (2) We look at the elements of the eigenvector Y1, the eigenvector corresponding to the smallest eigenvalue λ1. These elements show how the various conformations grow and decay with rate λ1 as folding proceeds. Table 1 shows that the maximum population Pmax correlates well with the elements of Y1. For a typical route of src SH3, Figure 4 ▶ (bottom) illustrates the decay of the denatured state and hidden intermediates and the growth of the native state, all with rate λ1.
Table 1.
Maximum probability Pmaxand Y1 elements for transient states of the src SH3 domain
| state | Pmax | Y1 element |
| C | 0.13 | 0.21 |
| B | 0.062 | 0.10 |
| A | 0.047 | 0.08 |
| BD | 0.016 | 0.019 |
| BC | 0.010 | 0.017 |
| AC | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| BCD | 0.015 | 0.010 |
| ABD | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| ACE | 0.004 | 0.001 |
Average Φ-values for secondary structural elements
The effects of a mutation on the folding kinetics are often explored through experimental measurements of a Φ-value, which is defined as:
 |
(7) |
where kf is the folding rate of the native protein and ΔG is its stability, and k′f and ΔG′ are the corresponding quantities for the mutant protein.
Because the minimal structural units in our model are clusters of contacts, we do not calculate Φ-values for single-residue mutations. Rather, we consider whole helices and strands as units. To compare with experiments, we average the experimental Φ-values over all of the residues composing a given secondary structural element.
To calculate average Φ-values for secondary structures, we consider mutations that change the free-energy fi of a contact cluster according to
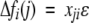 |
(8) |
where xji is the fraction of residues of the secondary structural element j that are involved in contacts of the cluster i, and ɛ is a small energy. For example, if the secondary structural element j contains m1 residues, and m2 ≤ m1 of these residues appear in contacts of the cluster i, we have xji = m2/m1. Note that 0 ≤ xji ≤ 1, where the value xji = 1 is obtained if the whole secondary structural element j has contacts in cluster i. Thus, the Φ-value for the secondary structural element j is given by equation 7 with
 |
(9) |
where λ′1 is the smallest non-zero eigenvalue of the mutant with cluster-free energies fi → fi + Δfi(j), and
 |
(10) |
For ɛ ≪ kBT, we find that the calculated Φ-values are nearly independent of ɛ. We choose here ɛ = 0.01 kBT.
Predicted Φ-values are compared with experiments in Figure 5 ▶. The theoretical Φ-values were calculated with the same parameters for all four proteins (see figure caption). The predicted values agree well with the experimental values. This comparison indicates that the folding kinetics of these proteins is dominated by generic features of the fold topology, rather than by the specific energetic details—that is, which residues form contacts, how much hydrogen bonds or hydrophobic interactions are worth, the details of side-chain packing, etc. In the case of protein G (see Fig. 6 ▶), the experimental Φ-value distribution is largely reproduced by making the additional assumption that the α-helix cluster has a free-energy fi = −2.0 kBT, rather than the value fi = 0 kBT that we have otherwise used for local clusters (see Fig. 5 ▶). However, even without changing this parameter, the Φ-value distribution reflects the features of the experimental distribution that the Φ-values for the strands β3 and β4 are larger than those for β1 and β2.
Figure 5.
(Gray bars) Theoretical and (black bars) average experimental Φ-value distributions for the secondary structural elements of CI2, the src SH3 domain, TNfn3, and protein L. The parameter of the loop closure term is c = 0.5, and the free energy of the local clusters is fl = 0. The free energy fnl of the nonlocal clusters is chosen so that the probability that all nonlocal clusters are formed is 0.9 in equilibrium.
Figure 6.
Comparison of theoretical and experimental Φ-value distributions. (White bars) Theoretical Φ-values for the same parameters as in Fig. 5 ▶; (black bars) average experimental Φ-values; (gray bars) theoretical Φ-values when assuming that the free energy of the α-helix cluster is fi = −0.5 kBT, deviating from the standard value fl = 1.5 kBT for the local clusters.
Conclusions
We have developed a simple model of the folding kinetics of two-state proteins. The model aims to predict the folding rates of the fast and slow processes, the folding routes, and Φ-values for a protein, if the native structure is given. The dominant folding routes are found to be those having small ECOs, that is, steps that involve only small loop closures. The model parameters include c, an intrinsic free energy for loop closure; fl, the free energy for propagating contacts in local structures; and fnl, the free energy for propagating nonlocal contacts. The model predicts that the barrier to two-state folding is the formation of local structural elements like helices and hairpins, and that the steps involving their assembly into larger and more native-like structure are downhill in free energy.
Acknowledgments
We thank KeFan for a critical reading of the manuscript.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Article and publication are at http://www.proteinscience.org/cgi/doi/10.1110/ps.03403604.
References
- Alm, E. and Baker, D. 1999. Prediction of protein-folding mechanisms from free-energy landscapes derived from native structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96 11305–11310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm, E., Morozov, A.V., Kortemme, T., and Baker, D. 2002. Simple physical models connect theory and experiment in protein folding kinetics. J. Mol. Biol. 322 463–476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruscolini, P. and Cecconi, F. 2003. Mean-field approach for a statistical mechanical model of proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 119 1248–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Bruscolini, P. and Pelizzola, A. 2002. Exact solution of the Munoz-Eaton model for protein folding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 258101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender, R.H., Dyer, R.B., Gilmanshin, R., and Woodruff, W.H. 1998. Fast events in protein folding: The time evolution of primary processes. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 49 173–202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.S. and Dill, K.A. 1990. The effects of internal constraints on the configurations of chain molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 92 3118–3135. [Google Scholar]
- ———. 1993. Energy landscapes and the collapse dynamics of homopolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 99 2116–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak, M., Henkel, M., Karbowski, J., and Banavar, J.R. 1998. Master equation approach to protein folding and kinetic traps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 3654– 3657. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, C., Nymeyer, H., and Onuchic, J.N. 2000. Topological and energetic factors: What determines the structural details of the transition state ensemble and “en-route” intermediates for protein folding? An investigation for small globular proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 298 937–953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggett, V. 2002. Molecular dynamics simulations of the protein unfolding/folding reaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 35 422–429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debe, D.A. and Goddard III, W.A. 1999. First principles prediction of protein folding rates. J. Mol. Biol. 294 619–625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill, K.A. and Chan, H.S. 1997. From Levinthal to pathways to funnels. Nat. Struct. Biol. 4 10–19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill, K.A., Fiebig, K.M., and Chan, H.S. 1993. Cooperativity in protein-folding kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 90 1942–1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y. and Kollman, P.A. 1998. Pathways to a protein folding intermediate observed in a 1-microsecond simulation in aqueous solution. Science 282 740–744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, W.A., Munoz, V., Thompson, P.A., Henry, E.R., and Hofrichter, J. 1998. Kinetics and dynamics of loops, α-helices, β-hairpins, and fast-folding proteins. Acc. Chem. Res. 31 741–753. [Google Scholar]
- Englander, S.W. 2000. Protein folding intermediates and pathways studied by hydrogen exchange. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 29 213–238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, N. and Fersht, A.R. 2003. Early events in protein folding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13 75–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiebig, K.M. and Dill, K.A. 1993. Protein core assembly processes. J. Chem. Phys. 98 3475–3487. [Google Scholar]
- Flammini, A., Banavar, J.R., and Maritan, A. 2002. Energy landscape and native-state structure of proteins—a simplified model. Europhys. Lett. 58 623–629. [Google Scholar]
- Galzitskaya, O.V. and Finkelstein, A.V. 1999. A theoretical search for folding/unfolding nuclei in three-dimensional protein structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96 11299–11304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Mira, M.M., Sadqi, M., Fischer, N., Sanchez-Ruiz, J.M., and Munoz, V. 2002. Experimental identification of downhill protein folding. Science 298 2191–2195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruebele, M., Sabelko, J., Ballew, R., and Ervin, J. 1998. Laser temperature jump induced protein refolding. Acc. Chem. Res. 31 699–707. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, T.X. and Cieplak, M. 2000. Sequencing of folding events in Go-type proteins. J. Chem. Phys. 113 8319–8328. [Google Scholar]
- Ikai, A. and Tanford, C. 1971. Kinetic evidence for incorrectly folded intermediate states in the refolding of denatured proteins. Nature 230 100–102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivankov, D.N. and Finkelstein, A.V. 2001. Theoretical study of a landscape of protein folding-unfolding pathways. Folding rates at midtransition. Biochemistry 40 9957–9961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus, M. and Weaver, D.L. 1976. Protein-folding dynamics. Nature 260 404–406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ———. 1994. Protein-folding dynamics: The diffusion-collision model and experimental data. Protein Sci. 3 650–668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimov, D.K. and Thirumalai, D. 2002. Stiffness of the distal loop restricts the structural heterogeneity of the transition state ensemble in SH3 domains. J. Mol. Biol. 317 721–737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leopold, P.E., Montal, M., and Onuchic, J.N. 1992. Protein folding funnels: A kinetic approach to the sequence-structure relationship. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 89 8721–8725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. and Shakhnovich, E.I. 2001. Constructing, verifying, and dissecting the folding transition state of chymotrypsin inhibitor 2 with all-atom simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98 13014–13018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micheelsen, M.A., Rischel, C., Ferkinghoff-Borg, J., Guerois, R., and Serrano, L. 2003. Mean first-passage time analysis reveals rate-limiting steps, parallel pathways and dead ends in a simple model of protein folding. Europhys. Lett. 61 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, V. and Eaton, W.A. 1999. A simple model for calculating the kinetics of protein folding from three-dimensional structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96 11311–11316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, S.B., Bahar, I., and Dill, K.A. 2001. Transition states and the meaning of Φ-values in protein folding kinetics. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8 765–769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, S.B., Dill, K.A., and Bahar, I. 2002. Fast-folding protein kinetics, hidden intermediates, and the sequential stabilization model. Protein Sci. 11 1958–1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ———. 2003. Computing the transition state populations in simple protein models. Biopolymers 68 35–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker, M.J. and Marqusee, S. 2000. A statistical appraisal of native state hydrogen exchange data: Evidence for a burst phase continuum? J. Mol. Biol. 300 1361–1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portman, J.J., Takada, S., and Wolynes, P.G. 2001. Microscopic theory of protein folding rates. I. Fine structure of the free energy profile and folding routes from a variational approach. J. Chem. Phys. 114 5069–5081. [Google Scholar]
- Schonbrun, J. and Dill, K.A. 2003. Fast protein folding kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100 12678–12682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea, J.-E. and Brooks III, C.L. 2001. From folding theories to folding proteins: A review and assessment of simulation studies of protein folding and unfolding. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 52 499–535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker, B.A., Wang, J., and Wolynes, P.G. 1999. Exploring structures in protein folding funnels with free energy functionals: The transition state ensemble. J. Mol. Biol. 287 675–694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong, T.Y., Baldwin, R.L., and Elson, E.L. 1971. The sequential unfolding of ribonuclease A: Detection of a fast initial phase in the kinetics of unfolding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 68 2712–2715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kampen, N.G. 1992. Stochastic processes in physics and chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
- Vendruscolo, M., Paci, E., Dobson, C.M., and Karplus, M. 2001. Three key residues form a critical contact network in a protein folding transition state. Nature 409 641–645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weikl, T.R. and Dill, K.A. 2003a. Folding rates and low-entropy-loss routes of 2-state proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 329 585–598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ———. 2003b. Folding kinetics 2-state proteins: Effect of circularization, permutation, and crosslinks. J. Mol. Biol. 332 953–963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






