Abstract
Advanced NSCLC patients harboring EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET rearrangements derive benefit from treatment with ALK and RET TKIs but not immune checkpoint inhibitors. New immunotherapeutic approaches, such as immunization against growth factors, can be of particular interest for combination treatment in these patients. Here, we investigated the effects of anti-EGF antibodies generated by vaccination (anti-EGF VacAbs), TKIs and combinations in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET NSCLC cell lines. We found that EGF and tumor growth factor alpha (TGFα) significantly decreased the antiproliferative activity of the RET inhibitor BLU-667 in CCDC6-RET cells and brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in EML4-ALK translocated cells. The addition of anti-EGF VacAbs reversed the effects of EGF and TGFα, potentiated the antitumor effects of the kinase inhibitors and delayed the appearance in vitro of resistant clones. Western blotting demonstrated that the combination of anti-EGF VacAbs with ALK or RET TKIs effectively suppressed EGFR downstream pathways in EML4-ALK translocated and CCDC6-RET cells, respectively. In conclusion, anti-EGF VacAbs significantly increased the antitumor activity of TKIs in ALK and RET-positive cell lines. Clinical trials of an EGF vaccine in combination with ALK and RET TKIs are warranted.
Introduction
In Western countries, mutations in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) gene are the most common targetable alterations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), followed by rearrangements involving anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and rearranged during transfection (RET) genes [1]. Targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are currently the standard first line therapy for advanced NSCLC patients with ALK alterations, having demonstrated significantly better clinical activity than chemotherapy regimens [[2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7]]. Regarding RET rearranged tumors, several multi-target TKIs have been tested in clinical trials with 18–47% objective response rates (ORR) and 4.5–7.3 months of progression-free survival (PFS) [8,9], clearly inferior to the outcomes to EGFR or ALK targeted therapies. However novel, highly selective RET inhibitors such as BLU-667 [10], LOXO-292 [11] and RXDX-105 [12] have been developed in recent years and are currently being tested in this patient population. ORR of 68% and median PFS of 18.4 months have been recently reported for LOXO-292, leading to approval by the United States Food and drug Administration (FDA) [13].
The introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors against programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and PD-1 ligand (PD-L1) has represented a milestone in the treatment of advanced NSCLC. Although preclinical studies suggested immune escape through activation of the PD-1 pathway in EGFR and ALK driven tumors [[14], [15], [16]], single agent checkpoint inhibitors have shown little activity in EGFR-mut or EML4-ALK positive patients as first or second line treatment [[17], [18], [19]]. In addition, phase I and II studies in pretreated or treatment naive EGFR and ALK positive NSCLC patients have failed to demonstrate any clinical benefit of the addition of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors to TKI therapy. In some cases, a significant increase in the frequency of grade 3 or 4 adverse events such as interstitial lung disease or hepatic toxicity were observed, leading to the discontinuation of the trials [[20], [21], [22]]. In consequence, anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents, alone or in combination, are not recommended for first line treatment in EGFR or ALK-positive NSCLC, and TKIs remain the treatment of choice for patients with these drivers, who should receive chemotherapy before even considering immunotherapy [[17], [18], [19],23]. Regarding RET-rearranged tumors, they are characterized by low PD-L1 expression, low tumor mutation burden (TMB) and, similarly to ALK-positive patients, poor responses to anti-PD1/PD-L1 agents, with ORR 0–6% and median PFS of 2–3 months [19,24,25].
In summary, checkpoint inhibitors do not show clinical benefit in EGFR, ALK and RET-positive patients and new immunotherapeutic approaches that can be safely combined with kinase inhibitors can be of particular interest in this setting. We recently reported that anti-EGF antibodies generated by vaccination (anti-EGF VacAbs) significantly enhanced the antitumor effects of EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mut cells [26], and vaccination against EGF is currently been tested in combination with afatinib in the phase Ib EPICAL clinical trial (NCT03623750) [27]. In the present study, we have found that ALK and RET positive NSCLC secreted tumor growth factor alpha (TGFα) in an autocrine manner, and that both human epidermal growth factor (EGF) and TGFα significantly decreased the antitumor activity of brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in EML4-ALK translocated cells and the RET inhibitor BLU-667 in CCDC6-RET positive cells. The addition of anti-EGF VacAbs reversed the effects of EGF and TGFα, potentiated the antitumor activity of the TKIs and delayed the appearance of resistant clones. Our results provide a rationale for clinical trials of ALK and RET inhibitors in combination with anti-EGF vaccination in EML4-ALK and RET-positive NSCLC patients.
Materials and methods
Rabbit antibodies and ELISAs
Anti-EGF VacAbs were obtained by immunizing rabbits with 4 injections of an EGF-like protein (Scotia Biologics Ltd., Aberdeen, UK) combined with Montanide adjuvant (Seppic, Paris, France). Pre-immunization sera from immunized rabbits were collected and purified to be used as control antibodies (C-Abs). All sera were purified by Melon gel and treated by caprylic acid to remove contaminants. The final preparation was analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Briefly, recombinant human EGF (2 μg/mL) or TGFα (2 μg/mL) were attached on wells of a flat bottom 96 plate, wells were blocked, incubated with serial dilutions of anti-EGF VacAbs and afterwards with goat anti-rabbit antibodies conjugated with peroxidase (GAR—Po). Finally, a substrate solution was added for 20 min, the reaction stopped with 1 N NaOH and plates read at 405 nm an Infinite M Plex microplate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland).
ELISA was also used to determine the concentrations of EGF and TGF-α in the conditioned medium of cell lines. Cell supernatants from cultures grown in serum-free medium for 48 h were collected and cleared by centrifugation. EGF and TGF-α were assayed using Quantiquine ELISA human EGF and TGF-α immunoassay (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Materials and cell lines
TKIs were purchased from Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX) or MedChem Express (Monmouth Junction, NJ), EGF from Cell Signaling Technologies (Beverly, MA) and antibodies for Western blotting to Cell Signaling Technology or Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). All tissue culture materials were obtained from Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific (Paisley, Scotland, UK). Three cell lines were used in the study; H3122, H2228, LC-2/ad, which harbor EML4-ALKv1, EML4-ALKv3 andCCDC6-RET fusions, respectively. The H3122 and H2228 cells were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, Virginia) while the LC-2/ad cells were purchased from the European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures General Collection (ECACC, Salisbury, United Kingdom). All of them were maintained in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 50 mg/mL penicillin-streptomycin, 2 mM l-glutamine in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Cells were weekly tested for mycoplasms and authenticated by monthly genotyping for their driver alterations, TP53 mutations and a panel of 20 polymorphisms. After no more than 15 passages, cells were discarded and new, low-passage vials were thawed.
Cell growth, viability, colony formation and emergence of resistant assays
To assess the effects of drugs, cells were seeded at 2000 (H3122 and LC-2/ad) or 6000 (H2228) per well in 96-well plates, allowed to attach for 24 h in RPMI+10% FBS, washed twice with PBS and treated with EGF or TGFα (10 ng/mL), antibodies, kinase inhibitors or combinations for 72 h in RPMI+0.5% human serum (HS). For calculation of growth curves, cells were seeded at 1000 (LC-2/ad) or 2000 (H2228) per well and treated for 0, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h or each 48 h during 16 days. After treatment, cells were incubated with medium containing 0.75 mg/mL Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT, Sigma Aldrich, St Louis, MO) for 1–2 h at 37 °C. Culture medium was removed; formazan crystals reabsorbed in DMSO (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and cell numbers were estimated using an Infinite M Plex microplate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). Data were derived from at least three independent experiments.
For colony formation, LC-2/ad cells were seeded at 1000 cells per well in 6-well plates, incubated overnight and treated with BLU667 (100 nM), anti-EGF VacAbs (1/50 dilution factor) and combination. Culture media (RPMI-1640 + 10% FBS) and compounds were changed every three days. On day 15, media was removed and wells washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). The colonies were fixed with methanol for 25 min at room temperature, stained with 0.5% of crystal violet for 15 min, washed with distilled water and allowed to dry overnight. Images were captured with a Bio-Rad ChemiDoc MP Imaging System.
To study the acquisition of resistance to TKIs, we seeded 350 H2228 and LC-2/ad cells per well in 96-well plates, using two plates per treatment (120 wells). Cells were allowed to attach and the treatments were started after 24 h in RPMI+10% FBS. Media were changed every week, plates were inspected thrice a week under the microscope, and wells >50% confluent were scored as positive [28].
Western blot and flow cytometry analysis
Cells were treated with EGF (10 ng/mL), C-Abs, anti-EGF VacAbs, ALK and RET TKIs or combinations for 2 or 24 h in RPMI +0.5% HS. After washing twice with cold PBS, cultures were scraped into RIPA buffer and proteins were analyzed by Western blotting, as described [26]. Membranes were read with a Bio-Rad ChemiDocMP Imaging System.
For flow cytometry experiments, cells were treated for 24 h under the same conditions described for Western blotting, trypsinized and centrifuged. Cell cycle and cell death analyses were performed as described [26].
Results
Anti-EGF VacAbs blocked the stimulatory effects of EGF and TGFα on cell proliferation and downstream pathways in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET NSCLC cell lines
First, we used ELISA to titrate the purified anti-EGF VacAbs and found that the preparation had a titer of 1:16,000 against human EGF. We also found that the anti-EGF VacAbs cross-reacted with human TGFα, showing a titer of 1:1000 against this growth factor.
Next, we tested the effects of EGF and TGFα at 10 ng/mL on three NSCLC cell lines, NCI-H3122, NCI-H2228 and LC-2/ad. The NCI-H3122 and NCI-H2228 cells carry variant 1 (E13:A20) and variant 3a (E6:A20) EML4-ALK fusions; while the LC-2/ad harbors a CCDC6-RET fusion. The addition of EGF to cells growing in 0.5% human serum stimulated growth in the 3 lines tested, particularly in NCI-H2228, where the effect reached 60–70% at 72 h. Regarding TGFα, it also increased the proliferation of the NCI-H2228 and LC-2/ad cells, although to a lesser extent than EGF. The addition of anti-EGF VacAbs suppressed the growth promoting effects of EGF and TGFα in all the cell lines tested, while control antibodies (C-Abs) had no activity (Supplementary Fig. 1A-E).
Western blotting experiments were subsequently performed to study EGFR downstream pathways (Supplementary Fig. 1F-G). As expected, EGF at 2 h strongly induced the phosphorylation of the EGFR receptor but had little effect on pSTAT3 or pAkt in the three cell lines tested, while pErk1/2 activation was observed in H2228 and also in LC-2/ad cells at concentrations as low as 0.01 pg/mL (Supplementary Fig. 1H). Anti-EGF VacAbs completely abolished the EGF-induced activation of EGFR, while C-Abs showed no activity. When the incubation time was expanded to 24 h, we observed that EGF activated not only EGFR but also Erk1/2 in H2228 and H3122 cells and Akt in H2228 and LC-2/ad. These effects were partly or completely reversed when anti-EGF VacAbs were present (Supplementary Fig. 2). Remarkably, EGF down-regulated total EGFR expression in H3122 and LC-2/ad cells, although pEGFR levels remained elevated.
Finally, we investigated if the H2228, H3122 and LC-2/ad cell lines secreted EGF and TGFα. To this end, cells were incubated for 48 h in serum-free medium and the concentrations of the two ligands quantified by ELISA. We found levels of 1.4 pg EGF/mL and 7.4 pg TGFα/mL for H2228 and 2.1 pg EGF/mL and 57.3 pg TGFα/m L in the case of H3122, while EGF was undetectable in LC-2/ad conditioned medium and TGFα was found at 2.4 pg/mL.
EGF and TGFα significantly reduced the antitumor effects of ALK and RET TKIs on EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET NSCLC cells
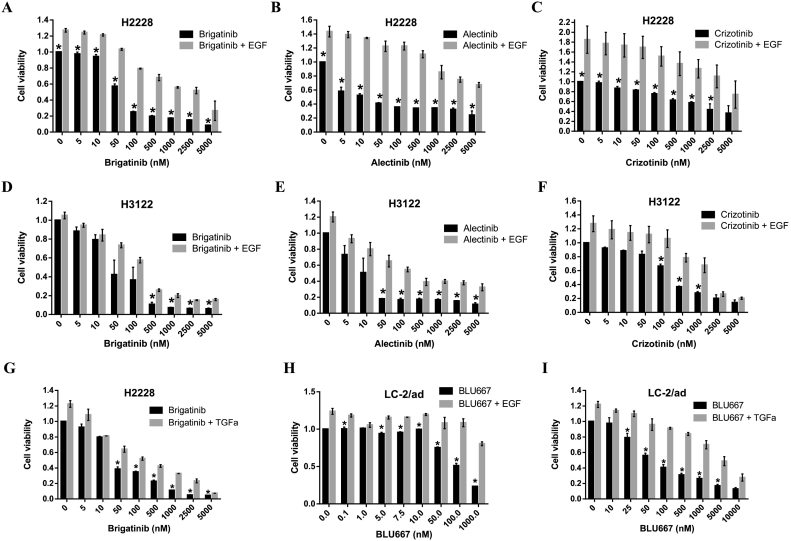
We subsequently characterized the effects of EGF and TGFα on the antiproliferative activity of kinase inhibitors in our panel of NSCLC cells. In cell viability experiments, we found that the presence of EGF or TGFα (Fig. 1A-G) significantly reduced the antitumor effects of brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in the H2228 and H3122 cell lines, at all concentrations tested. Similarly, the antiproliferative activity of the RET inhibitor BLU-667 was significantly impaired in the LC-2/ad cell line when EGF or TGFα were present (Fig. 1H-I). The effect was particularly strong in the case of H2228 cells treated with ALK TKIs.
Fig. 1.
Effects of EGF on the sensitivity of ALK and RET translocated cells to ALK and RET TKIs. The TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated and EGF or TGFα at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-I) Results of 72 h proliferation assays. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 compared to EGF treated cells.
Experiments performed in H3122 cells grown in presence of EGF revealed that ALK TKIs were capable of reducing the levels of pSTAT3 at low concentrations, around 5 nM for brigatinib, 50 nM for alectinib and 100 nM for crizotinib (Supplementary Fig. 3). In contrast, complete inhibition of pAkt required higher dosages of TKI (50 nM, 500 nM and 5 μM, respectively). Brigatinib and alectinib but not crizotinib also blocked the phosphorylation of Erk1/2 in presence of EGF although, in contrast with Akt or STAT3, the inhibition was not complete even at the highest concentrations of drug. In fact, in the case of brigatinib, the inhibitory effect on pErk1/2 was lost at concentrations ≥1 μM. Finally, alectinib and crizotinib did not altered EGFR activation in H3122, while brigatinib showed a weak stimulating effect.
When the same experiments were performed in the H2228 cells, a strong inhibition of STAT3 and Akt phosphorylation was also observed at low concentrations of ALK TKIs (Supplementary Fig. 3). In the case of brigatinib, however, the effect on pAkt was lost at concentrations ≥1 μM. Regarding Erk1/2 and EGFR, a complex picture emerged. In presence of EGF, alectinib weakly increased pEGFR levels at high concentrations, while crizotinib and brigatinib activated the receptor at concentrations ≥100 nM. Regarding pErk1/2, crizotinib had a weak inhibitory effect while alectinib and brigatinib at ≥0.5 μM stimulated Erk1/2 phosphorylation.
Finally, regarding the CCDC6-RET cell line, BLU-667 in presence of EGF partly suppressed Erk1/2 phosphorylation only at concentrations ≥500 nM (Supplementary Fig. 3G). No significant effects were observed on pAkt, while pSTAT3 was only inhibited at 5 μM. Unexpectedly, a stimulatory effect on pEGFR was observed at intermediate concentrations of BLU-667.
Anti-EGF VacAbs potentiated the antiproliferative effects of kinase inhibitors in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET translocated cell lines
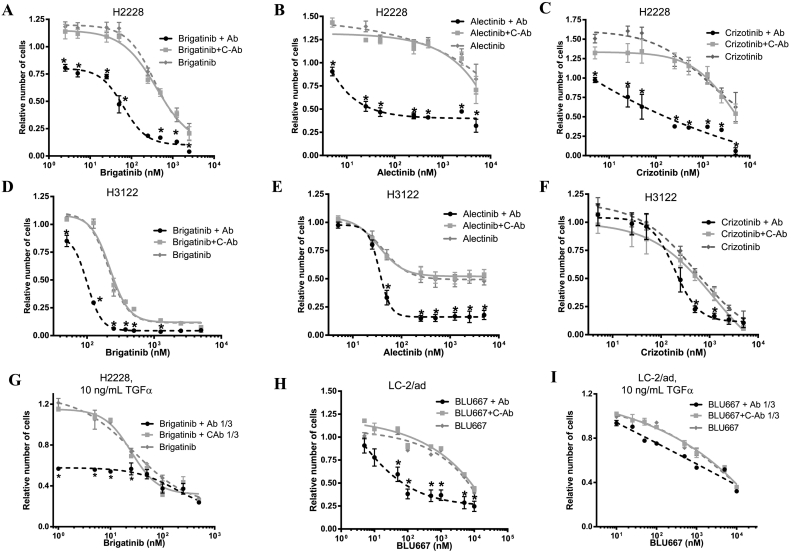
Since EGF and TGFα strongly reduced the activity of ALK and RET inhibitors in NSCLC cell lines, we hypothesized that anti-EGF VacAbs would reverse these effects. MTT proliferation assays, flow cytometry, colony formation and long-term proliferation experiments were used to test this hypothesis. The results of the MTT proliferation assays, performed in presence of 10 mg/mL EGF, are presented in Fig. 2 and Supplementary Table 1. Anti-EGF VacAbs significantly increased the activity of brigatinib, alectinib and, to a lesser extent, crizotinib, in the H3122 cell line. Consequently, the IC50s of the ALK TKIs were 2- to 20-fold lower in presence of the antibodies. The effects of anti-EGF VacAbs were stronger in the H2228 cells, where a 10- to >100 fold reduction of the IC50s for brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib was observed. In the LC-2/ad cells, the antiproliferative effects of BLU-667 were also robustly enhanced by the anti-EGF VacAbs, with a 1000-fold reduction in the IC50. In all cases, control antibodies failed to show any effect. Finally, dose-response experiments in LC2/Ad cells demonstrated a significant blockade of the antitumor effects of BLU-667 also at 1 ng/mL of EGF, which was fully reversed by anti-EGF VacAbs (Supplementary Fig. 4A-B).
Fig. 2.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with ALK and RET inhibitors in ALK and RET translocated cell lines, respectively. TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated, EGF or TGFα at 10 ng/mL, antibodies at 1/50 or 1/5 dilution in experiments with EGF and TGFα, respectively. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-I) Results of 72 h proliferation assays. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM.*, P < 0.05 compared to C-Ab treated cells. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
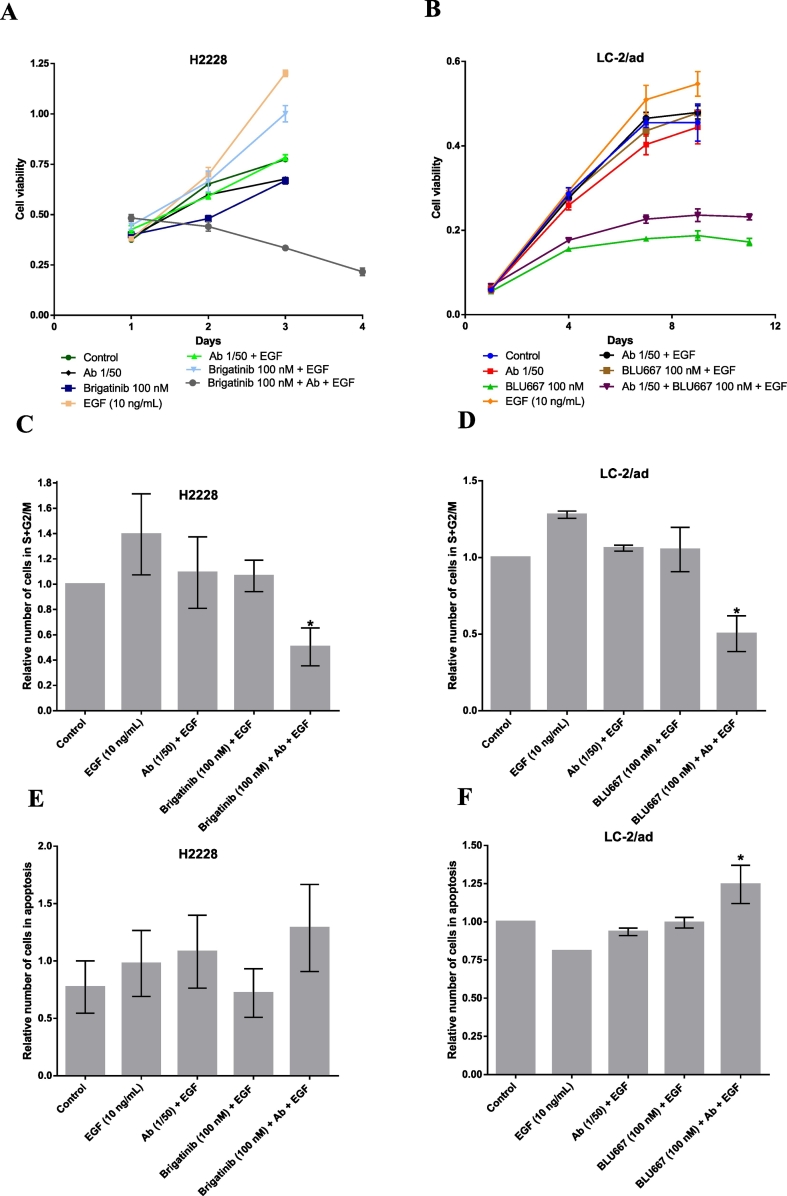
Growth curves of the H2228 and LC-2/ad cell lines at 4–15 days confirmed a very limited antiproliferative activity of brigatinib and BLU-667 at 100 nM in presence of EGF, which was greatly potentiated if anti-EGF VacAbs were added (Fig. 3A-B). Colony formation experiments in LC-2/ad showed similar results (Supplementary Fig. 4C). Cell cycle and Annexin V experiments were performed in H2228 and LC-2/ad to further investigate these effects. The addition of EGF significantly increased the number of cells in S + G2/M, as expected, while anti-EGF VacAbs, brigatinib or BLU-667 single agent had modest effects. However, when the TKIs were combined with the antibodies, a significant reduction in the percentage of proliferating cells was observed (Fig. 3C-D). Regarding Annexin V, a preliminary experiment demonstrated that the presence of EGF blocked TKI-induced apoptosis in LC-2/ad cells at concentrations of BLU-667 up to 100 nM (Supplementary Fig. 4D). The addition of anti-EGF VacAbs prevented this blockade, triggering cell death at 100 nM drug (Fig. 3F). In contrast, the differences in the percentage of apoptotic cells did not reach statistical significance in the case of H2228 and brigatinib 100 nM (Fig. 3E).
Fig. 3.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with ALK and RET TKIs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines, respectively. TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-B) Growth curves of proliferation assays at 4 and 16 days, respectively. (C-D) Percentage of cells in S + G2/M phase by flow cytometry. (E-F) Percentage of apoptotic cells by annexin V analysis. Final concentrations of the selected TKIs were 100 nM brigatinib in H2228 (A, C, E) and 100 nM BLU-667 in LC-2/ad (B, D, F). Results shown are representative of three different experiments. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS. Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
In addition to EGF, we had observed that anti-EGF VacAbs recognized TGFα, although with a significantly lower titer. In consequence, we analyzed if anti-EGF VacAbs could also reverse the deleterious effect of TGFα in the activity of ALK and RET inhibitors. We found that the antibodies significantly increased the antiproliferative activity of brigatinib in H2228 cells when TGFα was present. In contrast, limited effects were observed in the case of LC-2/ad cells treated with BLU-667 and TGFα (Fig. 3C, Supplementary Table 1).
Anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with TKIs efficiently block the EGFR signal transduction pathways in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET translocated cell lines
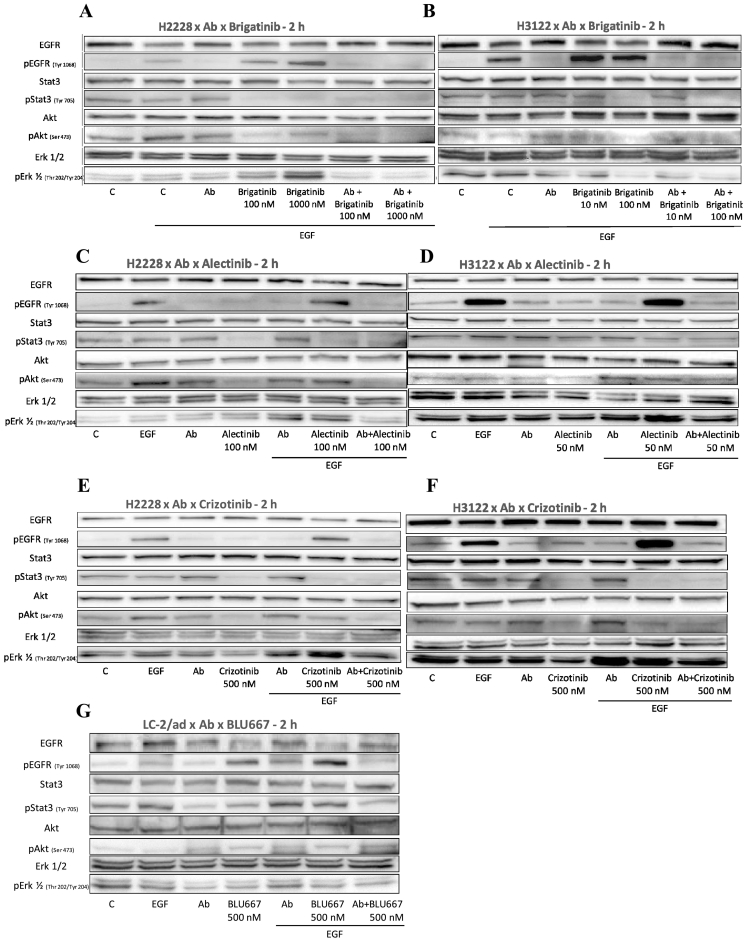
Western blotting after a 2 h incubation period was used to analyze the effects of kinase inhibitors and anti-EGF VacAbs on the activation of EGFR, Erk1/2, Akt and STAT3. A first set of experiments revealed that, in presence of EGF, brigatinib at 100 or 1000 nM inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3 and, to a lesser extent, Akt, but significantly increased the levels of pEGFR and pErk1/2 in H2228 cells, as previously observed. The addition of anti-EGF VacAbs reversed this stimulatory effect and, consequently, the combination of anti-EGF VacAbs and brigatinib achieved complete inhibition of pEGFR, pAkt and pSTAT3, and almost complete of pErk1/2 (Fig. 4A). In the case of the H3122 cells, brigatinib in presence of EGF stimulated EGFR but not Erk1/2 phosphorylation and, again, complete or almost complete inhibition of pEGFR, pAkt, pErk1/2 and pSTAT3 was observed when the ALK TKI was combined with anti-EGF VacAbs (Fig. 4B).
Fig. 4.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with ALK and RET TKIs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines, respectively. Western blot analysis of selected markers in different cell lines. TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. Final concentrations of the selected TKIs were 100 nM and 1000 nM brigatinib in H2228 (A), 10 nM and 100 nM brigatinib in H3122 (B), 100 nM alectinib in H2228 (C), 50 nM alectinib in H3122 (D), 500 nM crizotinib in H2228 (E), 500 nM crizotinib in H3122 (F) and 500 nM BLU-667 in LC-2/ad (G). Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS, incubation time 2 h; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Subsequent experiments with alectinib and crizotinib in H2228 and H3122 cells showed that, at the concentrations tested, the inhibitory activity of both TKIs on pErk1/2 and pAkt was significantly impaired if EGF was added. Interestingly, crizotinib but not alectinib also increased the levels of pEGFR in this setting, while activation of Erk1/2 by alectinib was observed in H2228 cells (Fig. 4C-F, compare lanes “Alectinib” vs “Alectinib/EGF” or “Crizotinib” vs “Crizotinib/EGF”). Consequently, only the combination ALK TKI + anti-EGF VacAbs achieved an effective blockade of EGFR, Erk1/2, Akt and STAT3 activation when EGF was present.
In the case of the RET+ LC-2/ad cell line, Western blotting revealed BLU-667 stimulated EGFR phosphorylation at the concentration tested (500 nM), an effect that was blocked with the addition of anti-EGF VacAbs (Fig. 4G, compare lanes “BLU-667” vs. “Ab+BLU-667”). The combination of the two agents was also clearly superior in the inhibition of STAT3 and Erk1/2 phosphorylation, while the effects on Akt did not seem significant.
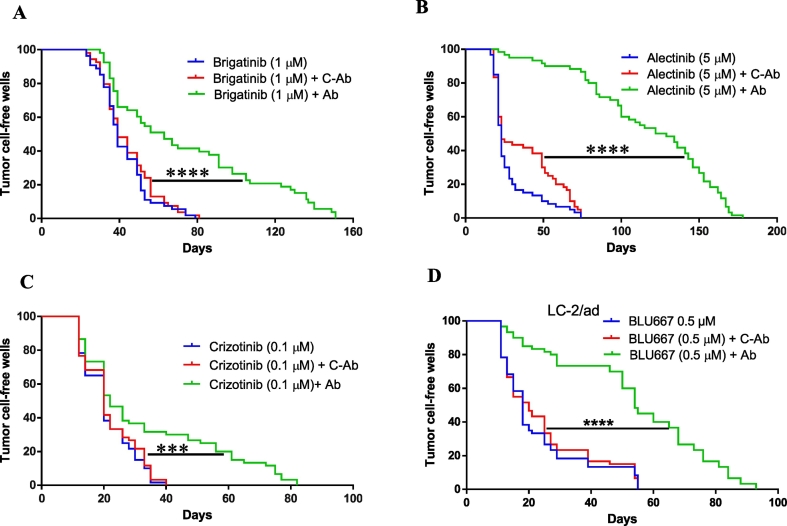
Anti-EGF VacAbs delay in vitro the emergence of resistance to ALK-TKIs
Activation of the EGFR pathway is one of the mechanisms associated with intrinsic and acquired resistance to ALK TKIs [[29], [30], [31]]. In consequence, we decided to investigate the effects of anti-EGF VacAbs on the emergence of resistance to ALK and RET TKIs in vitro. Low confluence H2228 and LC-2/ad cultures growing in 96-well plates were treated with brigatinib (1 μM), alectinib (5 μM), crizotinib (0.1 μM), BLU-667 (0.5 μM), anti-EGF VacAbs (1/10 dilution) or a combination, wells were inspected three times per week and those reaching 50% confluence were scored as positive. We found that the presence of the anti-EGF VacAbs significantly delayed the emergence of resistant colonies to the four ALK and RET TKIs tested, while C-Abs had no effect (Fig. 5, Supplementary Fig. 5). In the case of brigatinib and crizotinib, resistant colonies appeared in all wells after 40 and 80 days, respectively, compared to 82 and 150 when anti-EGF VacAbs were present. But the strongest effect of the antibodies was observed for BLU-667 and alectinib, with resistant colonies in 50% of the wells after 25 days in absence of anti-EGF VacAbs compared to 65 days for BLU-667 and 105 days for alectinib when the antibodies were present.
Fig. 5.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in emergence of resistance to ALK and RET TKIs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. (A-D) Emergence of resistant colonies to brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in H2228 and to BLU667 in LC-2/ad under different conditions. Medium was RPMI+10% FBS, no EGF was added.
Discussion
Mutations in the EGFR gene, EML4-ALK and RET fusions are the most frequent druggable drivers in advanced NSCLC, being present in around 20% of patients in Western countries. First line treatment with TKIs is the standard of care in these cases, while immune checkpoint inhibitors have not shown any clinical benefit, alone or in combination with TKIs [[17], [18], [19], [20], [21], [22]]. This fact is probably a consequence of the un-inflamed microenvironment present in EGFR, ALK and RET tumors, with frequently low PD-L1 levels, lack of T-cell infiltration and low tumor mutation burden [25,32]. In consequence, new immunotherapeutic approaches that can be safely and effectively combined with TKIs could be of great interest in EGFR/ALK/RET positive patients. Vaccination against EGF, also referred to EGF-PTI [33], does not induce significant toxic side-effects and represents a novel immunotherapeutic strategy that, instead of activating the T-cells, targets the B-cells in order to generate antibodies that neutralize circulating EGF, thus preventing its binding to EGFR. We have recently reported that anti-EGF VacAbs significantly enhance the antitumor effects of EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mut NSCLC cell line models [26] and a Phase I trial of an EGF vaccine in combination with afatinib is currently underway [27]. In the study presented here, we also demonstrate that anti-EGF VacAbs potentiate the antitumor effects of ALK and RET TKIs in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET NSCLC cell line models, significantly enhancing the blockade of downstream oncogenic activation pathways and delaying the emergence of resistance.
Despite the initial clinical benefit, EML4-ALK patients treated with ALK TKIs acquire resistance and progress after 12–18 months of treatment [30,34,35]. In addition, a small but significant percentage of ALK-positive tumors present intrinsic resistance and do not respond to first line TKI therapy [36]. Several lines of evidence indicate that the EGF/EGFR/MAPK pathway is involved in both types of resistance. The addition of exogenous EGF and TGFα has been shown to reduce the sensitivity of EML4-ALK cells growing in vitro to the ALK inhibitor TAE684 by blocking its inhibitory effects on Erk1/2 and STAT3 phosphorylation [37,38]. In addition, the RAS-MAPK pathway, but not other downstream effectors such as PI-3 K or JAK/STAT, has been described to be essential for survival in EML4-ALK tumor cells; and combined treatment with MEK and ALK inhibitors has been proposed for EML4-ALK patients [39]. In H3122 cells with acquired resistance to crizotinib, expression of TGFα [40] or EGF, EGFR, ErbB-2 and ErbB-3 was found to be upregulated and treatment with EGFR-TKIs induced apoptosis in resistant but not in parental cells [41]. More importantly, it has been reported that EGF-mediated activation of EGFR impaired binding of TKIs to ALK, ROS1, RET and NTRK1 fusion oncoproteins, shifted adaptor protein binding from these oncoproteins to EGFR and facilitated bypass through MAPK and other downstream pathways [42]. Taken together, these results lead to the suggestion that the addition of agents targeting EGFR activation in fusion-positive NSCLC patients would reduce the risk of developing drug resistance [42]. However, the only two trials published combining ALK with EGFR TKIs have reported substantial toxicity leading to reduction of dosages and discontinuation of the studies [43] [44]. Consequently, in the clinical setting, EGFR TKIs do not seem to be a viable alternative to block EGF/EGFR pathway in fusion positive patients. In contrast, immunization against EGF, which targets the growth factor instead of the membrane receptor, does not induce significant toxic side effects and could be safely combined with TKIs [27,33]. At this respect, our results suggest that vaccination against EGF can not only prevent the emergence of acquired resistance to ALK TKIs but also be effective in patients with intrinsic resistance to these agents, since anti-EGF VacAbs potentiated the activity of TKIs in H2228 and H3122 cells, reversing the deleterious effect of EGF and effectively blocking EGFR and Erk1/2 phosphorylation.
Our study has some limitations. First, the effects of the anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with ALK TKIs could not be further tested in xenograft studies. Xenografts models involve athymic mice, which cannot be easily vaccinated against EGF or other proteins due to their defective immune system. A second limitation of our study is related to the nature of the polyclonal antibodies used, which were raised against human EGF but also recognized TGFα, probably as a consequence of the 42% homology between the two proteins [45]. However, the titer of the anti-EGF VacAbs against TGFα was low and did not allow us to fully characterize their anti-TGFα effects at the molecular level. The autocrine production of TGFα in the EML4-ALK cells tested and the significant deleterious effect of this growth factor against ALK and RET TKIs indicate that the effects of an anti-EGF vaccine that be further enhanced with a combined vaccination against TGFα. Finally, a third limitation of our study was that we only studied EGFR and not other receptors of the ErbB family. Both EGF and TGFα are known to bind to EGFR but to induce two kinds of receptor dimers, the EGFR/EGFR homodimer and the EGFR/ErbB-2 heterodimer, which could play a differential role in the effects of the anti-EGF VacAbs and the combination with TKIs.
Several EML4-ALK variants with different breaking points have been identified, being variant 1 (v1) and variant 3 a/b (v3a/b) the most common [46]. The EML4-ALKv1 has been associated with a better response to ALK TKIs, while v3 seems to correlate with a higher frequency of metastatic disease, shorter PFS and worse overall survival (OS) to first and second line TKIs [47,48]. In our study, we found that the H2228 cell line, which carries v3, was more strongly stimulated by EGF than the H3122 cell line, harboring v1 (Fig. 1). Also, the deleterious effects of EGF on the activity of brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib were particularly intense in H2228 cells (Fig. 2) and, unexpectedly, the three ALK TKIs were found to induce Erk1/2 and/or EGFR activation in presence of EGF. In consequence, the benefits of the addition of anti-EGF VacAbs were more pronounced in the H2228 cell line (Fig. 2, Fig. 4). These results suggest that the combination of ALK TKIs with anti-EGF vaccine might be particularly beneficial in patients carrying EML4-ALKv3.
In summary, our results demonstrate that anti-EGF VacAbs significantly potentiate the antiproliferative effects of ALK and RET TKIs in EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET cell lines, suppressing the deleterious effects of EGF and TGFα, delaying the emergence of resistant clones, and effectively blocking, in combination, the activation of downstream pathways. Based on these findings; phase I trials of anti-EGF vaccines in combination with ALK and RET TKIs are warranted in ALK and RET-positive NSCLC patients.
The following are the supplementary data related to this article.
Effects of anti-EGF antibodies (1/25 dilution in presence of EGF, 1/3 in presence of TGFα) on the sensitivity of ALK and RET translocated cell lines to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cells were grown in medium plus 0.5% HS and 10 ng/mL EGF or TGFα. The IC50 values are referred to control wells where TKIs and Abs were absent. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAb; TKI, tyrosine-kinase inhibitor.
Effects of EGF, TGFα and anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Antibodies were added at the final dilutions indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-E) Results of 72 h proliferation assays of anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Concentration of growth factors was 10 ng/mL. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 compared to C-Ab treated cells. (F) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 2 h. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs. EGF was used at 10 ng/mL (G) Quantification of pErk bands in replicate Western blotting. Results are expressed in arbitrary units, the 100 value corresponding to pErk in control, serum-starved cells not stimulated with growth factors. (H) Western blot analysis of pErk and pEGFR in LC-2/Ad cells at different concentrations of EGF, incubation time 2 h. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of EGF and anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Antibodies were added at the final dilutions indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-C) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 24 h. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of EGF on the sensitivity of ALK and RET translocated cells to ALK and RET TKIs. TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-G) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 2 h.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with BLU-667 in a RET translocated cell line. (A, B) Proliferation assays. TKI was added at the final concentrations indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 1 or 0.1 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS, incubation time 72 h. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05 compared to C-Ab treated cells. (C) Colony formation assay. BLU-667 was added at the final concentration indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+10% FBS. (D) Percentage of apoptotic cells by annexin V analysis. BLU-667 was added at the final concentrations indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in emergence of resistance to ALK and RET TKIs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. (A-D) Emergence of resistant colonies to brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in H2228 and to BLU667 in LC-2/ad under different conditions. Medium was RPMI+10% FBS.
Supplementary materials
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Jordi Codony-Servat: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - original draft. Silvia García-Roman: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - original draft. Miguel Ángel Molina-Vila: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing, Supervision. Jordi Bertran-Alamillo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis. Santiago Viteri: Resources, Writing - review & editing. Erik d'Hondt: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing, Supervision. Rafael Rosell: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing - review & editing, Supervision.
Declaration of competing interest
Erik d'Hondt is an employee of In3Bio. The rest of the authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgements
We thank Isabel Crespo and the Cytomics core facility of the Institut d'Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS) for technical assistance. The study was funded by grants F and G from In3Bio.
References
- 1.Hirsch F.R., Scagliotti G.V., Mulshine J.L., Kwon R., Curran W.J., Jr., Wu Y.L., Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rosell R., Carcereny E., Gervais R., Vergnenegre A., Massuti B., Felip E., Palmero R., Garcia-Gomez R., Pallares C., Sanchez J.M., Porta R., Cobo M., Garrido P., Longo F., Moran T., Insa A., De Marinis F., Corre R., Bover I., Illiano A., Dansin E., de Castro J., Milella M., Reguart N., Altavilla G., Jimenez U., Provencio M., Moreno M.A., Terrasa J., Munoz-Langa J., Valdivia J., Isla D., Domine M., Molinier O., Mazieres J., Baize N., Garcia-Campelo R., Robinet G., Rodriguez-Abreu D., Lopez-Vivanco G., Gebbia V., Ferrera-Delgado L., Bombaron P., Bernabe R., Bearz A., Artal A., Cortesi E., Rolfo C., Sanchez-Ronco M., Drozdowskyj A., Queralt C., de Aguirre I., Ramirez J.L., Sanchez J.J., Molina M.A., Taron M., Paz-Ares L. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rosell R., Moran T., Queralt C., Porta R., Cardenal F., Camps C., Majem M., Lopez-Vivanco G., Isla D., Provencio M., Insa A., Massuti B., Gonzalez-Larriba J.L., Paz-Ares L., Bover I., Garcia-Campelo R., Moreno M.A., Catot S., Rolfo C., Reguart N., Palmero R., Sanchez J.M., Bastus R., Mayo C., Bertran-Alamillo J., Molina M.A., Sanchez J.J., Taron M., G. Spanish Lung Cancer Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:958–967. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mok T.S., Wu Y.L., Thongprasert S., Yang C.H., Chu D.T., Saijo N., Sunpaweravong P., Han B., Margono B., Ichinose Y., Nishiwaki Y., Ohe Y., Yang J.J., Chewaskulyong B., Jiang H., Duffield E.L., Watkins C.L., Armour A.A., Fukuoka M. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:947–957. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Maemondo M., Inoue A., Kobayashi K., Sugawara S., Oizumi S., Isobe H., Gemma A., Harada M., Yoshizawa H., Kinoshita I., Fujita Y., Okinaga S., Hirano H., Yoshimori K., Harada T., Ogura T., Ando M., Miyazawa H., Tanaka T., Saijo Y., Hagiwara K., Morita S., Nukiwa T. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;362:2380–2388. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Solomon B.J., Mok T., Kim D.W., Wu Y.L., Nakagawa K., Mekhail T., Felip E., Cappuzzo F., Paolini J., Usari T., Iyer S., Reisman A., Wilner K.D., Tursi J., Blackhall F., Investigators P. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1408440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Soria J.C., Tan D.S.W., Chiari R., Wu Y.L., Paz-Ares L., Wolf J., Geater S.L., Orlov S., Cortinovis D., Yu C.J., Hochmair M., Cortot A.B., Tsai C.M., Moro-Sibilot D., Campelo R.G., McCulloch T., Sen P., Dugan M., Pantano S., Branle F., Massacesi C., de Castro G., Jr. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2017;389:917–929. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30123-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Drilon A., Hu Z.I., Lai G.G.Y., Tan D.S.W. Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018;15:150. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ackermann C.J., Stock G., Tay R., Dawod M., Gomes F., Califano R. Targeted therapy for RET-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: clinical development and future directions. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019;12:7857–7864. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S171665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Subbiah V., Gainor J.F., Rahal R., Brubaker J.D., Kim J.L., Maynard M., Hu W., Cao Q., Sheets M.P., Wilson D., Wilson K.J., DiPietro L., Fleming P., Palmer M., Hu M.I., Wirth L., Brose M.S., Ou S.I., Taylor M., Garralda E., Miller S., Wolf B., Lengauer C., Guzi T., Evans E.K. Precision targeted therapy with BLU-667 for RET-driven cancers. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:836–849. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guo R., Schreyer M., Chang J.C., Rothenberg S.M., Henry D., Cotzia P., Kris M.G., Rekhtman N., Young R.J., Hyman D.M., Drilon A. Response to selective RET inhibition with LOXO-292 in a patient with RET fusion-positive lung cancer with leptomeningeal metastases. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019;3 doi: 10.1200/PO.19.00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Drilon A., Fu S., Patel M.R., Fakih M., Wang D., Olszanski A.J., Morgensztern D., Liu S.V., Cho B.C., Bazhenova L., Rodriguez C.P., Doebele R.C., Wozniak A., Reckamp K.L., Seery T., Nikolinakos P., Hu Z., Oliver J.W., Trone D., McArthur K., Patel R., Multani P.S., Ahn M.J. A phase I/Ib trial of the VEGFR-sparing multikinase RET inhibitor RXDX-105. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:384–395. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.FDA approves first RET inhibitorNat. Biotechnol. 2020;38:662. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0568-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Akbay E.A., Koyama S., Carretero J., Altabef A., Tchaicha J.H., Christensen C.L., Mikse O.R., Cherniack A.D., Beauchamp E.M., Pugh T.J., Wilkerson M.D., Fecci P.E., Butaney M., Reibel J.B., Soucheray M., Cohoon T.J., Janne P.A., Meyerson M., Hayes D.N., Shapiro G.I., Shimamura T., Sholl L.M., Rodig S.J., Freeman G.J., Hammerman P.S., Dranoff G., Wong K.K. Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:1355–1363. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Azuma K., Ota K., Kawahara A., Hattori S., Iwama E., Harada T., Matsumoto K., Takayama K., Takamori S., Kage M., Hoshino T., Nakanishi Y., Okamoto I. Association of PD-L1 overexpression with activating EGFR mutations in surgically resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014;25:1935–1940. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ota K., Azuma K., Kawahara A., Hattori S., Iwama E., Tanizaki J., Harada T., Matsumoto K., Takayama K., Takamori S., Kage M., Hoshino T., Nakanishi Y., Okamoto I. Induction of PD-L1 expression by the EML4-ALK oncoprotein and downstream signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015;21:4014–4021. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee C.K., Man J., Lord S., Links M., Gebski V., Mok T., Yang J.C. Checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer-a meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017;12:403–407. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mok T.S.K., Wu Y.L., Kudaba I., Kowalski D.M., Cho B.C., Turna H.Z., Castro G., Jr., Srimuninnimit V., Laktionov K.K., Bondarenko I., Kubota K., Lubiniecki G.M., Zhang J., Kush D., Lopes G., K.-. Investigators Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 1819-1830;393(2019) doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32409-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mazieres J., Drilon A., Lusque A., Mhanna L., Cortot A.B., Mezquita L., Thai A.A., Mascaux C., Couraud S., Veillon R., Van Den Heuvel M., Neal J., Peled N., Fruh M., Ng T.L., Gounant V., Popat S., Diebold J., Sabari J., Zhu V.W., Rothschild S.I., Bironzo P., Martinez A., Curioni-Fontecedro A., Rosell R., Lattuca-Truc M., Wiesweg M., Besse B., Solomon B., Barlesi F., Schouten R.D., Wakelee H., Camidge D.R., Zalcman G., Novello S., Ou S.I., Milia J., Gautschi O. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with advanced lung cancer and oncogenic driver alterations: results from the IMMUNOTARGET registry. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:1321–1328. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gettinger S., Hellmann M.D., Chow L.Q.M., Borghaei H., Antonia S., Brahmer J.R., Goldman J.W., Gerber D.E., Juergens R.A., Shepherd F.A., Laurie S.A., Young T.C., Li X., Geese W.J., Rizvi N. Nivolumab plus erlotinib in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:1363–1372. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ahn M.J. Combination of osimertinib with durvalumab in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: is there room for reinvestigation? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019;14:766–767. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Spigel D.R., Reynolds C., Waterhouse D., Garon E.B., Chandler J., Babu S., Thurmes P., Spira A., Jotte R., Zhu J., Lin W.H., Blumenschein G., Jr. Phase 1/2 study of the safety and tolerability of nivolumab plus crizotinib for the first-line treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase translocation - positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (CheckMate 370) J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:682–688. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Martinez P., Peters S., Stammers T., Soria J.C. Immunotherapy for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:2691–2698. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Offin M., Guo R., Wu S.L., Sabari J., Land J.D., Ni A., Montecalvo J., Halpenny D.F., Buie L.W., Pak T., Liu D., Riely G.J., Hellmann M.D., Benayed R., Arcila M., Kris M.G., Rudin C.M., Li B.T., Ladanyi M., Rekhtman N., Drilon A. Immunophenotype and response to immunotherapy of RET-rearranged lung cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019;3 doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Singal G., Miller P.G., Agarwala V., Li G., Kaushik G., Backenroth D., Gossai A., Frampton G.M., Torres A.Z., Lehnert E.M., Bourque D., O'Connell C., Bowser B., Caron T., Baydur E., Seidl-Rathkopf K., Ivanov I., Alpha-Cobb G., Guria A., He J., Frank S., Nunnally A.C., Bailey M., Jaskiw A., Feuchtbaum D., Nussbaum N., Abernethy A.P., Miller V.A. Association of patient characteristics and tumor genomics with clinical outcomes among patients with non-small cell lung cancer using a clinicogenomic database. JAMA. 2019;321:1391–1399. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Codony-Servat J., Garcia-Roman S., Molina-Vila M.A., Bertran-Alamillo J., Gimenez-Capitan A., Viteri S., Cardona A.F., D'Hondt E., Karachaliou N., Rosell R. Anti-epidermal growth factor vaccine antibodies enhance the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and delay the emergence of resistance in EGFR mutant lung cancer cells. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:1324–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karachaliou N., Cardona-Zorrilla A.F., Rodriguez-Abreu D., Cobo-Dols M., Reguart N., Viteri Ramirez S., Codony Servat J., Molina-Vila M.A., D'Hondt E., Rosell R. Afatinib plus EGF pathway targeting immunization (EGF-PTI) as first line therapy for EGFR mutant NSCLC: the EPICAL study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:S118–S119. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tricker E.M., Xu C., Uddin S., Capelletti M., Ercan D., Ogino A., Pratilas C.A., Rosen N., Gray N.S., Wong K.K., Janne P.A. Combined EGFR/MEK inhibition prevents the emergence of resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:960–971. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Katayama R., Shaw A.T., Khan T.M., Mino-Kenudson M., Solomon B.J., Halmos B., Jessop N.A., Wain J.C., Yeo A.T., Benes C., Drew L., Saeh J.C., Crosby K., Sequist L.V., Iafrate A.J., Engelman J.A. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung cancers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003316. 120ra117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Doebele R.C., Pilling A.B., Aisner D.L., Kutateladze T.G., Le A.T., Weickhardt A.J., Kondo K.L., Linderman D.J., Heasley L.E., Franklin W.A., Varella-Garcia M., Camidge D.R. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:1472–1482. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sasaki T., Koivunen J., Ogino A., Yanagita M., Nikiforow S., Zheng W., Lathan C., Marcoux J.P., Du J., Okuda K., Capelletti M., Shimamura T., Ercan D., Stumpfova M., Xiao Y., Weremowicz S., Butaney M., Heon S., Wilner K., Christensen J.G., Eck M.J., Wong K.K., Lindeman N., Gray N.S., Rodig S.J., Janne P.A. A novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011;71:6051–6060. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dong Z.Y., Zhang J.T., Liu S.Y., Su J., Zhang C., Xie Z., Zhou Q., Tu H.Y., Xu C.R., Yan L.X., Li Y.F., Zhong W.Z., Wu Y.L. EGFR mutation correlates with uninflamed phenotype and weak immunogenicity, causing impaired response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2017;6 doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1356145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rosell R., Neninger E., Nicolson M., Huber R.M., Thongprasert S., Parikh P.M., D'Hondt E. Pathway targeted immunotherapy: rationale and evidence of durable clinical responses with a novel, EGF-directed agent for advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016;11:1954–1961. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.08.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peters S., Camidge D.R., Shaw A.T., Gadgeel S., Ahn J.S., Kim D.W., Ou S.I., Perol M., Dziadziuszko R., Rosell R., Zeaiter A., Mitry E., Golding S., Balas B., Noe J., Morcos P.N., Mok T., Investigators A.T. Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:829–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Camidge D.R., Kim H.R., Ahn M.J., Yang J.C., Han J.Y., Lee J.S., Hochmair M.J., Li J.Y., Chang G.C., Lee K.H., Gridelli C., Delmonte A., Garcia Campelo R., Kim D.W., Bearz A., Griesinger F., Morabito A., Felip E., Califano R., Ghosh S., Spira A., Gettinger S.N., Tiseo M., Gupta N., Haney J., Kerstein D., Popat S. Brigatinib versus crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;379:2027–2039. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1810171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ma D., Zhang Y., Xing P., Hao X., Wang M., Wang Y., Shan L., Xin T., Liang H., Du Y., Zhang Z., Liang L., Li J. Clinical features and outcomes of ALK rearranged non-small cell lung cancer with primary resistance to crizotinib. Thorac. Cancer. 2019;10:1213–1219. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tanizaki J., Okamoto I., Okabe T., Sakai K., Tanaka K., Hayashi H., Kaneda H., Takezawa K., Kuwata K., Yamaguchi H., Hatashita E., Nishio K., Nakagawa K. Activation of HER family signaling as a mechanism of acquired resistance to ALK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:6219–6226. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yamada T., Takeuchi S., Nakade J., Kita K., Nakagawa T., Nanjo S., Nakamura T., Matsumoto K., Soda M., Mano H., Uenaka T., Yano S. Paracrine receptor activation by microenvironment triggers bypass survival signals and ALK inhibitor resistance in EML4-ALK lung cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:3592–3602. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hrustanovic G., Olivas V., Pazarentzos E., Tulpule A., Asthana S., Blakely C.M., Okimoto R.A., Lin L., Neel D.S., Sabnis A., Flanagan J., Chan E., Varella-Garcia M., Aisner D.L., Vaishnavi A., Ou S.H., Collisson E.A., Ichihara E., Mack P.C., Lovly C.M., Karachaliou N., Rosell R., Riess J.W., Doebele R.C., Bivona T.G. RAS-MAPK dependence underlies a rational polytherapy strategy in EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2015;21:1038–1047. doi: 10.1038/nm.3930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tani T., Yasuda H., Hamamoto J., Kuroda A., Arai D., Ishioka K., Ohgino K., Miyawaki M., Kawada I., Naoki K., Hayashi Y., Betsuyaku T., Soejima K. Activation of EGFR bypass signaling by TGFalpha overexpression induces acquired resistance to alectinib in ALK-translocated lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016;15:162–171. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang G., Scarborough H., Kim J., Rozhok A.I., Chen Y.A., Zhang X., Song L., Bai Y., Fang B., Liu R.Z., Koomen J., Tan A.C., Degregori J., Haura E.B. Coupling an EML4-ALK-centric interactome with RNA interference identifies sensitizers to ALK inhibitors. Sci. Signal. 2016;9 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaf5011. rs12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vaishnavi A., Schubert L., Rix U., Marek L.A., Le A.T., Keysar S.B., Glogowska M.J., Smith M.A., Kako S., Sumi N.J., Davies K.D., Ware K.E., Varella-Garcia M., Haura E.B., Jimeno A., Heasley L.E., Aisner D.L., Doebele R.C. EGFR mediates responses to small-molecule drugs targeting oncogenic fusion kinases. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3551–3563. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Janne P.A., Shaw A.T., Camidge D.R., Giaccone G., Shreeve S.M., Tang Y., Goldberg Z., Martini J.F., Xu H., James L.P., Solomon B.J. Combined pan-HER and ALK/ROS1/MET inhibition with dacomitinib and crizotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: results of a phase I study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016;11:737–747. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sequist L.V., Han J.Y., Ahn M.J., Cho B.C., Yu H., Kim S.W., Yang J.C., Lee J.S., Su W.C., Kowalski D., Orlov S., Cantarini M., Verheijen R.B., Mellemgaard A., Ottesen L., Frewer P., Ou X., Oxnard G. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:373–386. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30785-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: structure and biological activities. J. Cell. Biochem. 1986;32:293–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sasaki T., Rodig S.J., Chirieac L.R., Janne P.A. The biology and treatment of EML4-ALK non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2010;46:1773–1780. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Christopoulos P., Endris V., Bozorgmehr F., Elsayed M., Kirchner M., Ristau J., Buchhalter I., Penzel R., Herth F.J., Heussel C.P., Eichhorn M., Muley T., Meister M., Fischer J.R., Rieken S., Warth A., Bischoff H., Schirmacher P., Stenzinger A., Thomas M. EML4-ALK fusion variant V3 is a high-risk feature conferring accelerated metastatic spread, early treatment failure and worse overall survival in ALK(+) non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2018;142:2589–2598. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Christopoulos P., Kirchner M., Endris V., Stenzinger A., Thomas M. EML4-ALK V3, treatment resistance, and survival: refining the diagnosis of ALK(+) NSCLC. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018;10:S1989–S1991. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.05.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Effects of anti-EGF antibodies (1/25 dilution in presence of EGF, 1/3 in presence of TGFα) on the sensitivity of ALK and RET translocated cell lines to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cells were grown in medium plus 0.5% HS and 10 ng/mL EGF or TGFα. The IC50 values are referred to control wells where TKIs and Abs were absent. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAb; TKI, tyrosine-kinase inhibitor.
Effects of EGF, TGFα and anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Antibodies were added at the final dilutions indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-E) Results of 72 h proliferation assays of anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Concentration of growth factors was 10 ng/mL. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05 compared to C-Ab treated cells. (F) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 2 h. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs. EGF was used at 10 ng/mL (G) Quantification of pErk bands in replicate Western blotting. Results are expressed in arbitrary units, the 100 value corresponding to pErk in control, serum-starved cells not stimulated with growth factors. (H) Western blot analysis of pErk and pEGFR in LC-2/Ad cells at different concentrations of EGF, incubation time 2 h. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of EGF and anti-EGF VacAbs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. Antibodies were added at the final dilutions indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-C) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 24 h. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of EGF on the sensitivity of ALK and RET translocated cells to ALK and RET TKIs. TKI's were added at the final concentrations indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS in all cases. (A-G) Western blot analysis of selected markers, incubation time 2 h.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in combination with BLU-667 in a RET translocated cell line. (A, B) Proliferation assays. TKI was added at the final concentrations indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 1 or 0.1 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS, incubation time 72 h. Data were pooled from at least three different experiments and presented as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05 compared to C-Ab treated cells. (C) Colony formation assay. BLU-667 was added at the final concentration indicated, antibodies at a 1/50 dilution and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+10% FBS. (D) Percentage of apoptotic cells by annexin V analysis. BLU-667 was added at the final concentrations indicated and EGF at 10 ng/mL. Medium was RPMI+0.5% HS. C-Ab, control antibodies; Ab, anti-EGF VacAbs.
Effects of anti-EGF VacAbs in emergence of resistance to ALK and RET TKIs in ALK and RET translocated cell lines. (A-D) Emergence of resistant colonies to brigatinib, alectinib and crizotinib in H2228 and to BLU667 in LC-2/ad under different conditions. Medium was RPMI+10% FBS.
Supplementary materials