Abstract
Exceptional advances have been made recently in our understanding of the signaling pathways that control cellular growth, differentiation, and survival. These processes are regulated by extracellular stimuli such as cytokines, cell-cell interactions, and cell-matrix interactions, which trigger a series of intracellular events culminating in the modulation of specific genes. STATs are a highly homologous group of transcription factors that are activated by various pathways and regulate many of the genes controlling cellular function. STATs are activated by tyrosine phosphorylation and modulated by serine phosphorylation, placing them at a convergence point for numerous intracellular signaling pathways. Given the importance of STATs in the control of normal physiologic processes, it is not surprising that inappropriate activation of these proteins has been found in human malignancies. A number of distinct mechanisms have been elucidated by which STATs are activated inappropriately, including autocrine or paracrine stimulation of normal receptors and increased activity of tyrosine kinases through enhanced expression, mutations, or the presence of activating proteins. Furthermore, inappropriate STAT serine phosphorylation has been found in several tumors as well. The increased understanding of signaling pathways in tumors can be translated into therapeutic strategies that have the potential to be more selective and less toxic than current anti-cancer treatments. Approaches which may be effective include the development of antagonists of receptors that can trigger STAT activation, inhibitors of the tyrosine and serine kinases that phosphorylate and activate STATs, agents that decrease STAT levels or inhibit their recruitment to kinases, and molecules that can prevent the binding of STATs to target DNA sequences. Thus, elucidation of cellular and biochemical processes in tumors has enhanced our understanding of the pathogenesis of malignancies and may provide the basis for significant advances in therapy.
Full text
PDF

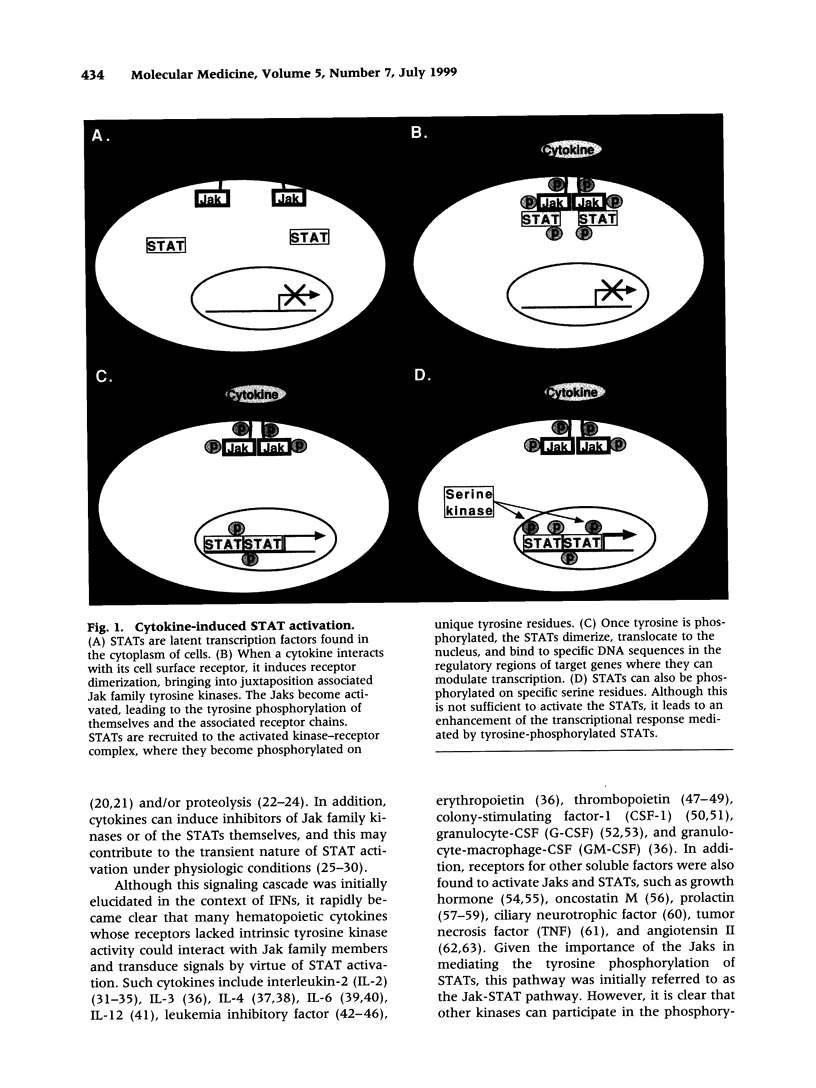


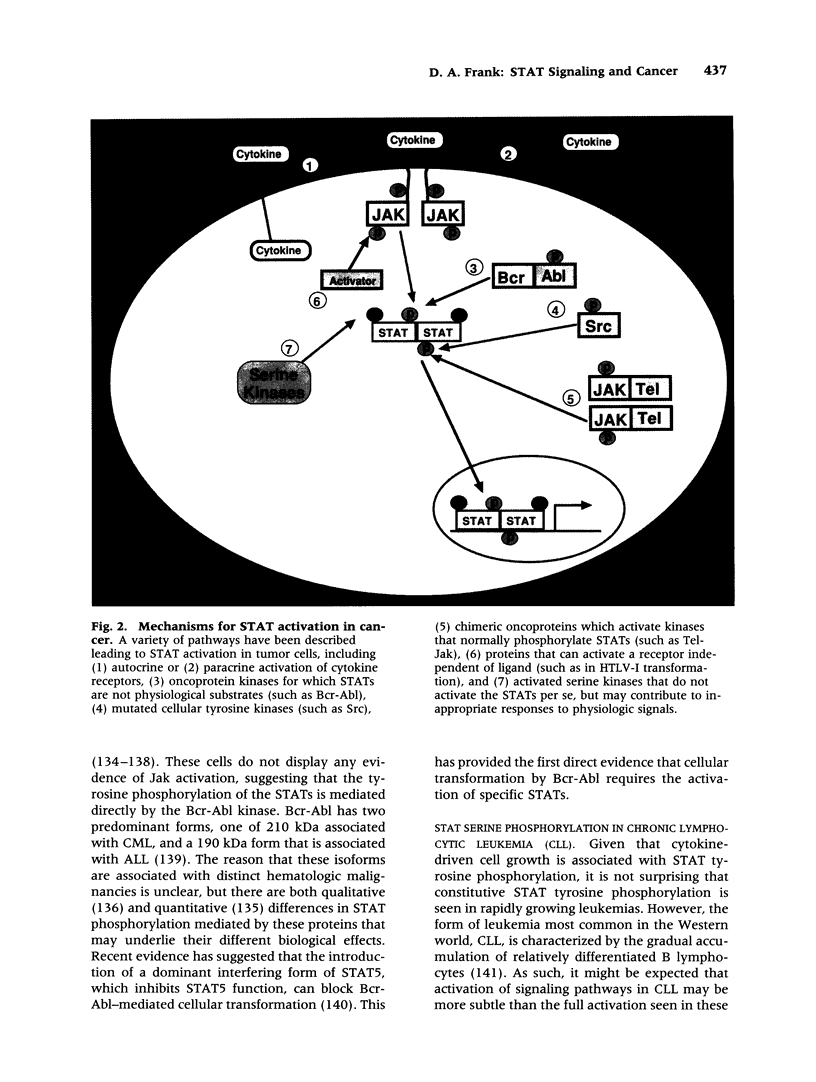






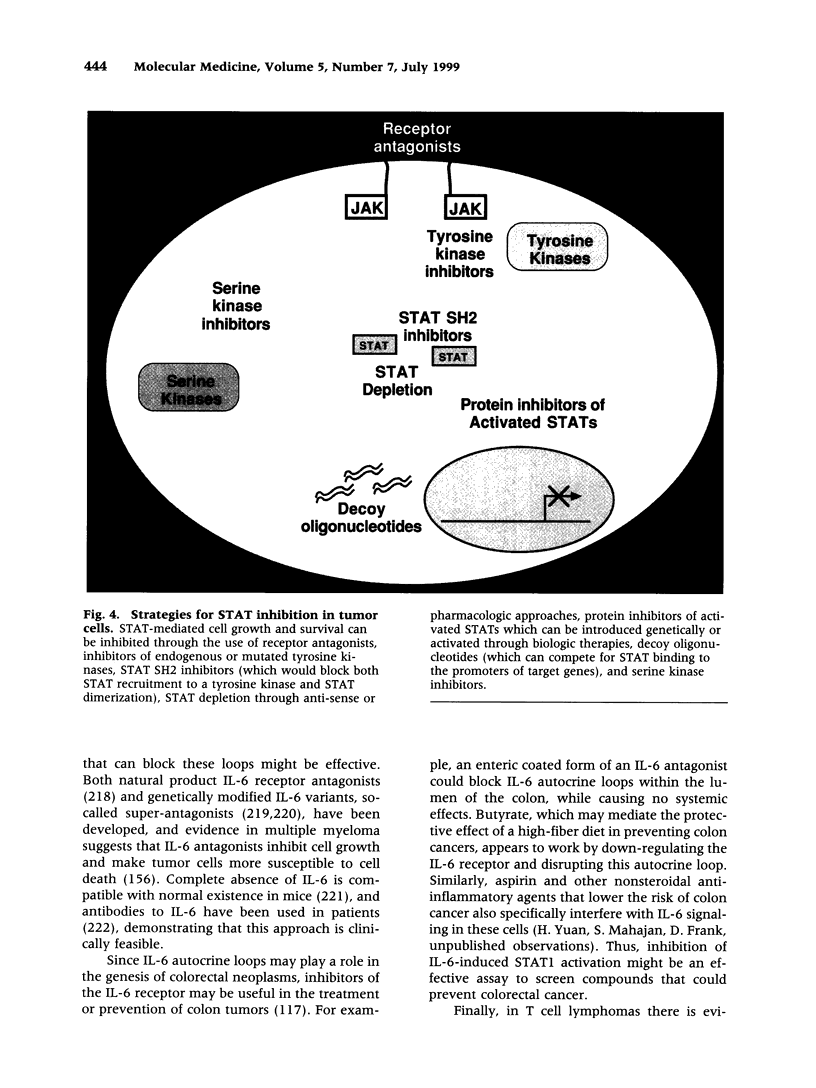












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe A., Emi N., Tanimoto M., Terasaki H., Marunouchi T., Saito H. Fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to a novel gene CEV14 in acute myelogenous leukemia after clonal evolution. Blood. 1997 Dec 1;90(11):4271–4277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. C., Jones R. M., Morimoto C., Leavitt P., Barut B. A. Response patterns of purified myeloma cells to hematopoietic growth factors. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1915–1924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aragane Y., Kulms D., Luger T. A., Schwarz T. Down-regulation of interferon gamma-activated STAT1 by UV light. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Oct 14;94(21):11490–11495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argetsinger L. S., Campbell G. S., Yang X., Witthuhn B. A., Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Carter-Su C. Identification of JAK2 as a growth hormone receptor-associated tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90415-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon C. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Ortaldo J. R., Rees R. C., Larner A. C., Johnston J. A., O'Shea J. J. Interleukin 12 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of STAT4 in human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7307–7311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barut B., Chauhan D., Uchiyama H., Anderson K. C. Interleukin-6 functions as an intracellular growth factor in hairy cell leukemia in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2346–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI116839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beadling C., Guschin D., Witthuhn B. A., Ziemiecki A., Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M., Cantrell D. A. Activation of JAK kinases and STAT proteins by interleukin-2 and interferon alpha, but not the T cell antigen receptor, in human T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5605–5615. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besser D., Bromberg J. F., Darnell J. E., Jr, Hanafusa H. A single amino acid substitution in the v-Eyk intracellular domain results in activation of Stat3 and enhances cellular transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1401–1409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.2.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. J., Thekkumkara T. J., Thomas W. G., Conrad K. M., Baker K. M. Angiotensin II stimulates sis-inducing factor-like DNA binding activity. Evidence that the AT1A receptor activates transcription factor-Stat91 and/or a related protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31443–31449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S., Eckner R., Grossman S., Oldread E., Arany Z., D'Andrea A., Livingston D. M. Cooperation of Stat2 and p300/CBP in signalling induced by interferon-alpha. Nature. 1996 Sep 26;383(6598):344–347. doi: 10.1038/383344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binari R., Perrimon N. Stripe-specific regulation of pair-rule genes by hopscotch, a putative Jak family tyrosine kinase in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1994 Feb 1;8(3):300–312. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boccaccio C., Andò M., Tamagnone L., Bardelli A., Michieli P., Battistini C., Comoglio P. M. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature. 1998 Jan 15;391(6664):285–288. doi: 10.1038/34657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Frank D. A., Schindler C., Greenberg M. E. Characterization of a pathway for ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling to the nucleus. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1575–1579. doi: 10.1126/science.7504325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonni A., Sun Y., Nadal-Vicens M., Bhatt A., Frank D. A., Rozovsky I., Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D., Greenberg M. E. Regulation of gliogenesis in the central nervous system by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Science. 1997 Oct 17;278(5337):477–483. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5337.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsellino N., Belldegrun A., Bonavida B. Endogenous interleukin 6 is a resistance factor for cis-diamminedichloroplatinum and etoposide-mediated cytotoxicity of human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 15;55(20):4633–4639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Stahl N., Yancopoulos G. D. STAT3 activation by cytokines utilizing gp130 and related transducers involves a secondary modification requiring an H7-sensitive kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6915–6919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg J. F., Fan Z., Brown C., Mendelsohn J., Darnell J. E., Jr Epidermal growth factor-induced growth inhibition requires Stat1 activation. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Jul;9(7):505–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg J. F., Horvath C. M., Besser D., Lathem W. W., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3 activation is required for cellular transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2553–2558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.5.2553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg J. F., Horvath C. M., Wen Z., Schreiber R. D., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptionally active Stat1 is required for the antiproliferative effects of both interferon alpha and interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7673–7678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchdunger E., Mett H., Trinks U., Regenass U., Müller M., Meyer T., Beilstein P., Wirz B., Schneider P., Traxler P. 4,5-bis(4-fluoroanilino)phthalimide: A selective inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor signal transduction pathway with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Aug;1(8):813–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchdunger E., Zimmermann J., Mett H., Meyer T., Müller M., Druker B. J., Lydon N. B. Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative. Cancer Res. 1996 Jan 1;56(1):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P. Epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1971 Jul;28(1):3–13. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197107)28:1<3::aid-cncr2820280104>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldenhoven E., van Dijk T. B., Solari R., Armstrong J., Raaijmakers J. A., Lammers J. W., Koenderman L., de Groot R. P. STAT3beta, a splice variant of transcription factor STAT3, is a dominant negative regulator of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):13221–13227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. S., Yu C. L., Jove R., Carter-Su C. Constitutive activation of JAK1 in Src-transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1997 Jan 31;272(5):2591–2594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.5.2591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X., Tay A., Guy G. R., Tan Y. H. Activation and association of Stat3 with Src in v-Src-transformed cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;16(4):1595–1603. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.4.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlesso N., Frank D. A., Griffin J. D. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins in hematopoietic cell lines transformed by Bcr/Abl. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):811–820. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Ohno-Jones S., Tamura S., Buchdunger E., Zimmermann J., Lydon N. B., Gilliland D. G., Druker B. J. CGP 57148, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, inhibits the growth of cells expressing BCR-ABL, TEL-ABL, and TEL-PDGFR fusion proteins. Blood. 1997 Dec 15;90(12):4947–4952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Tomasson M. H., Barker G. F., Golub T. R., Gilliland D. G. The TEL/platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGF beta R) fusion in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia is a transforming protein that self-associates and activates PDGF beta R kinase-dependent signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Dec 10;93(25):14845–14850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson W. E. Interferon-alpha-induced activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins in malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Sep;4(9):2219–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlett-Falcone R., Landowski T. H., Oshiro M. M., Turkson J., Levitzki A., Savino R., Ciliberto G., Moscinski L., Fernández-Luna J. L., Nuñez G. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity. 1999 Jan;10(1):105–115. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai S. K., Nichols G. L., Rothman P. Constitutive activation of JAKs and STATs in BCR-Abl-expressing cell lines and peripheral blood cells derived from leukemic patients. J Immunol. 1997 Nov 15;159(10):4720–4728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty A., White S. M., Schaefer T. S., Ball E. D., Dyer K. F., Tweardy D. J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor activation of Stat3 alpha and Stat3 beta in immature normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Blood. 1996 Oct 1;88(7):2442–2449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi P., Reddy M. V., Reddy E. P. Src kinases and not JAKs activate STATs during IL-3 induced myeloid cell proliferation. Oncogene. 1998 Apr 2;16(13):1749–1758. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaturvedi P., Sharma S., Reddy E. P. Abrogation of interleukin-3 dependence of myeloid cells by the v-src oncogene requires SH2 and SH3 domains which specify activation of STATs. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jun;17(6):3295–3304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.6.3295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Sadowski H. B., Kohanski R. A., Wang L. H. Stat5 is a physiological substrate of the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Mar 18;94(6):2295–2300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Vinkemeier U., Zhao Y., Jeruzalmi D., Darnell J. E., Jr, Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of a tyrosine phosphorylated STAT-1 dimer bound to DNA. Cell. 1998 May 29;93(5):827–839. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81443-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilcote R. R., Brown E., Rowley J. D. Lymphoblastic leukemia with lymphomatous features associated with abnormalities of the short arm of chromosome 9. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 1;313(5):286–291. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508013130503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin Y. E., Kitagawa M., Su W. C., You Z. H., Iwamoto Y., Fu X. Y. Cell growth arrest and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 mediated by STAT1. Science. 1996 May 3;272(5262):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5262.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. D., Liao J., Liu B., Rao X., Jay P., Berta P., Shuai K. Specific inhibition of Stat3 signal transduction by PIAS3. Science. 1997 Dec 5;278(5344):1803–1805. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5344.1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Lebman D. A., Rothman P. Mechanism and regulation of immunoglobulin isotype switching. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:229–270. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Uyttendaele H., Domanski P., Yan H., Krolewski J. J. p135tyk2, an interferon-alpha-activated tyrosine kinase, is physically associated with an interferon-alpha receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3518–3522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Baltimore D. Transformation of an interleukin 3-dependent hematopoietic cell line by the chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210bcr/abl protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9312–9316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daley G. Q., Van Etten R. A., Baltimore D. Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the P210bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):824–830. doi: 10.1126/science.2406902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danial N. N., Losman J. A., Lu T., Yip N., Krishnan K., Krolewski J., Goff S. P., Wang J. Y., Rothman P. B. Direct interaction of Jak1 and v-Abl is required for v-Abl-induced activation of STATs and proliferation. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Nov;18(11):6795–6804. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.11.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danial N. N., Pernis A., Rothman P. B. Jak-STAT signaling induced by the v-abl oncogene. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1875–1877. doi: 10.1126/science.7569929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997 Sep 12;277(5332):1630–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5332.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delphin S., Stavnezer J. Characterization of an interleukin 4 (IL-4) responsive region in the immunoglobulin heavy chain germline epsilon promoter: regulation by NF-IL-4, a C/EBP family member and NF-kappa B/p50. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):181–192. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druker B. J., Tamura S., Buchdunger E., Ohno S., Segal G. M., Fanning S., Zimmermann J., Lydon N. B. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 1996 May;2(5):561–566. doi: 10.1038/nm0596-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T. A., Masuhara M., Yokouchi M., Suzuki R., Sakamoto H., Mitsui K., Matsumoto A., Tanimura S., Ohtsubo M., Misawa H. A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK kinases. Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):921–924. doi: 10.1038/43213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Mahajan S., Ritz J. B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J Clin Invest. 1997 Dec 15;100(12):3140–3148. doi: 10.1172/JCI119869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Mahajan S., Ritz J. Fludarabine-induced immunosuppression is associated with inhibition of STAT1 signaling. Nat Med. 1999 Apr;5(4):444–447. doi: 10.1038/7445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Robertson M. J., Bonni A., Ritz J., Greenberg M. E. Interleukin 2 signaling involves the phosphorylation of Stat proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7779–7783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Robertson M. J., Bonni A., Ritz J., Greenberg M. E. Interleukin 2 signaling involves the phosphorylation of Stat proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7779–7783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. A., Varticovski L. BCR/abl leads to the constitutive activation of Stat proteins, and shares an epitope with tyrosine phosphorylated Stats. Leukemia. 1996 Nov;10(11):1724–1730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Schindler C., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr The proteins of ISGF-3, the interferon alpha-induced transcriptional activator, define a gene family involved in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7840–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Zhang J. J. Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):1135–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujio Y., Kunisada K., Hirota H., Yamauchi-Takihara K., Kishimoto T. Signals through gp130 upregulate bcl-x gene expression via STAT1-binding cis-element in cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1997 Jun 15;99(12):2898–2905. doi: 10.1172/JCI119484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Jove R. Activation of STAT transcription factors in oncogenic tyrosine kinase signaling. J Biomed Sci. 1998;5(2):79–85. doi: 10.1007/BF02258360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Yu C. L., Hudnall A., Catlett R., Nelson K. L., Smithgall T., Fujita D. J., Ethier S. P., Jove R. Constitutive activation of Stat3 in fibroblasts transformed by diverse oncoproteins and in breast carcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Dec;8(12):1267–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianni M., Terao M., Fortino I., LiCalzi M., Viggiano V., Barbui T., Rambaldi A., Garattini E. Stat1 is induced and activated by all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Blood. 1997 Feb 1;89(3):1001–1012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gishizky M. L., Witte O. N. Initiation of deregulated growth of multipotent progenitor cells by bcr-abl in vitro. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):836–839. doi: 10.1126/science.1375394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollob J. A., Schnipper C. P., Murphy E. A., Ritz J., Frank D. A. The functional synergy between IL-12 and IL-2 involves p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and is associated with the augmentation of STAT serine phosphorylation. J Immunol. 1999 Apr 15;162(8):4472–4481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub T. R., Barker G. F., Lovett M., Gilliland D. G. Fusion of PDGF receptor beta to a novel ets-like gene, tel, in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with t(5;12) chromosomal translocation. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub T. R., Goga A., Barker G. F., Afar D. E., McLaughlin J., Bohlander S. K., Rowley J. D., Witte O. N., Gilliland D. G. Oligomerization of the ABL tyrosine kinase by the Ets protein TEL in human leukemia. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Aug;16(8):4107–4116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.8.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux-Gruart V., Gouilleux F., Desaint C., Claisse J. F., Capiod J. C., Delobel J., Weber-Nordt R., Dusanter-Fourt I., Dreyfus F., Groner B. STAT-related transcription factors are constitutively activated in peripheral blood cells from acute leukemia patients. Blood. 1996 Mar 1;87(5):1692–1697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Pallard C., Dusanter-Fourt I., Wakao H., Haldosen L. A., Norstedt G., Levy D., Groner B. Prolactin, growth hormone, erythropoietin and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor induce MGF-Stat5 DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2005–2013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07192.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouilleux F., Wakao H., Mundt M., Groner B. Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of Stat5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4361–4369. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandis J. R., Drenning S. D., Chakraborty A., Zhou M. Y., Zeng Q., Pitt A. S., Tweardy D. J. Requirement of Stat3 but not Stat1 activation for epidermal growth factor receptor- mediated cell growth In vitro. J Clin Invest. 1998 Oct 1;102(7):1385–1392. doi: 10.1172/JCI3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo D., Dunbar J. D., Yang C. H., Pfeffer L. M., Donner D. B. Induction of Jak/STAT signaling by activation of the type 1 TNF receptor. J Immunol. 1998 Mar 15;160(6):2742–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque S. J., Flati V., Deb A., Williams B. R. Roles of protein-tyrosine phosphatases in Stat1 alpha-mediated cell signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25709–25714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D. A., Binari R., Nahreini T. S., Gilman M., Perrimon N. Activation of a Drosophila Janus kinase (JAK) causes hematopoietic neoplasia and developmental defects. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2857–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel R. L., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr The rapid inactivation of nuclear tyrosine phosphorylated Stat1 depends upon a protein tyrosine phosphatase. EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6262–6268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser P. J., Agrawal D., Hackney J., Pledger W. J. STAT3 activation accompanies keratinocyte differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Oct;9(10):847–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heim M. H., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Contribution of STAT SH2 groups to specific interferon signaling by the Jak-STAT pathway. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1347–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.7871432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert D. M., Kopf M., Mock B. A., Köhler G., Rudikoff S. Interleukin 6 is essential for in vivo development of B lineage neoplasms. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):243–248. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert D. M., Migone T. S., Kopf M., Leonard W. J., Rudikoff S. Distinct tumorigenic potential of abl and raf in B cell neoplasia: abl activates the IL-6 signaling pathway. Immunity. 1996 Jul;5(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho J. M., Beattie B. K., Squire J. A., Frank D. A., Barber D. L. Fusion of the ets transcription factor TEL to Jak2 results in constitutive Jak-Stat signaling. Blood. 1999 Jun 15;93(12):4354–4364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvai A. E., Xu L., Korzus E., Brard G., Kalafus D., Mullen T. M., Rose D. W., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Nuclear integration of JAK/STAT and Ras/AP-1 signaling by CBP and p300. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Feb 18;94(4):1074–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Wong S. C., McKnight S. L. Identification and purification of human Stat proteins activated in response to interleukin-2. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):321–329. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou X. S., Melnick M. B., Perrimon N. Marelle acts downstream of the Drosophila HOP/JAK kinase and encodes a protein similar to the mammalian STATs. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):411–419. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe G. R., Benito E., Castelleto R., Cornée J., Estève J., Gallagher R. P., Iscovich J. M., Deng-ao J., Kaaks R., Kune G. A. Dietary intake of fiber and decreased risk of cancers of the colon and rectum: evidence from the combined analysis of 13 case-control studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Dec 16;84(24):1887–1896. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.24.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Kerr I. M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 1995 Feb;11(2):69–74. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89000-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Yamamoto K., Silvennoinen O. Signaling through the hematopoietic cytokine receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:369–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilaria R. L., Jr, Van Etten R. A. P210 and P190(BCR/ABL) induce the tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of multiple specific STAT family members. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 6;271(49):31704–31710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.49.31704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Ridge S. A., Papadopoulos P., Cotter F., Ludwig W. D., Fonatsch C., Rieder H., Ostertag W., Bartram C. R., Wiedemann L. M. The fusion of TEL and ABL in human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is a rare event. Br J Haematol. 1995 May;90(1):222–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jousset C., Carron C., Boureux A., Quang C. T., Oury C., Dusanter-Fourt I., Charon M., Levin J., Bernard O., Ghysdael J. A domain of TEL conserved in a subset of ETS proteins defines a specific oligomerization interface essential to the mitogenic properties of the TEL-PDGFR beta oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1997 Jan 2;16(1):69–82. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalvakolanu D. V., Sen G. C. Differentiation-dependent activation of interferon-stimulated gene factors and transcription factor NF-kappa B in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3167–3171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. H., Shankaran V., Dighe A. S., Stockert E., Aguet M., Old L. J., Schreiber R. D. Demonstration of an interferon gamma-dependent tumor surveillance system in immunocompetent mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 23;95(13):7556–7561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Schindler U., Smiley S. T., Grusby M. J. Stat6 is required for mediating responses to IL-4 and for development of Th2 cells. Immunity. 1996 Mar;4(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Sun Y. L., Hoey T., Grusby M. J. Impaired IL-12 responses and enhanced development of Th2 cells in Stat4-deficient mice. Nature. 1996 Jul 11;382(6587):174–177. doi: 10.1038/382174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karras J. G., Wang Z., Coniglio S. J., Frank D. A., Rothstein T. L. Antigen-receptor engagement in B cells induces nuclear expression of STAT5 and STAT6 proteins that bind and transactivate an IFN-gamma activation site. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):39–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano M., Hirano T., Matsuda T., Taga T., Horii Y., Iwato K., Asaoku H., Tang B., Tanabe O., Tanaka H. Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):83–85. doi: 10.1038/332083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan K. D., Shuai K., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Bothwell A. L. Induction of the Ly-6A/E gene by interferon alpha/beta and gamma requires a DNA element to which a tyrosine-phosphorylated 91-kDa protein binds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6806–6810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. M., Farkas D. L., Chakraborty A., Dyer K. F., Tweardy D. J., Abernethy J. L., Edington H. D., Donnelly S. S., Becker D. Systemic interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) treatment leads to Stat3 inactivation in melanoma precursor lesions. Mol Med. 1999 Jan;5(1):11–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood J. M., Strawderman M. H., Ernstoff M. S., Smith T. J., Borden E. C., Blum R. H. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Jan;14(1):7–17. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Wijdenes J., Zhang X. G., Jourdan M., Boiron J. M., Brochier J., Liautard J., Merlin M., Clement C., Morel-Fournier B. Murine anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for a patient with plasma cell leukemia. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1198–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B., Zhang X. G., Lu Z. Y., Bataille R. Interleukin-6 in human multiple myeloma. Blood. 1995 Feb 15;85(4):863–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolla V., Lindner D. J., Xiao W., Borden E. C., Kalvakolanu D. V. Modulation of interferon (IFN)-inducible gene expression by retinoic acid. Up-regulation of STAT1 protein in IFN-unresponsive cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 3;271(18):10508–10514. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.18.10508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolla V., Weihua X., Kalvakolanu D. V. Modulation of interferon action by retinoids. Induction of murine STAT1 gene expression by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 11;272(15):9742–9748. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.15.9742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopf M., Baumann H., Freer G., Freudenberg M., Lamers M., Kishimoto T., Zinkernagel R., Bluethmann H., Köhler G. Impaired immune and acute-phase responses in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 24;368(6469):339–342. doi: 10.1038/368339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korzus E., Torchia J., Rose D. W., Xu L., Kurokawa R., McInerney E. M., Mullen T. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. Transcription factor-specific requirements for coactivators and their acetyltransferase functions. Science. 1998 Jan 30;279(5351):703–707. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5351.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotanides H., Reich N. C. Requirement of tyrosine phosphorylation for rapid activation of a DNA binding factor by IL-4. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1265–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.7694370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk J., Sandberg A. A. A possible subgroup of ALL with 9p-. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1983 Aug;9(4):383–385. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(83)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Commane M., Flickinger T. W., Horvath C. M., Stark G. R. Defective TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in STAT1-null cells due to low constitutive levels of caspases. Science. 1997 Nov 28;278(5343):1630–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5343.1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Kalafus D., Ogliastro M. H., Kioussi C., Xu L., Torchia J., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Differential use of CREB binding protein-coactivator complexes. Science. 1998 Jan 30;279(5351):700–703. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5351.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Gutterman J. U., Talpaz M. The molecular genetics of Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 13;319(15):990–998. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810133191506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., David M., Feldman G. M., Igarashi K., Hackett R. H., Webb D. S., Sweitzer S. M., Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Finbloom D. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1730–1733. doi: 10.1126/science.8378773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaman D. W., Pisharody S., Flickinger T. W., Commane M. A., Schlessinger J., Kerr I. M., Levy D. E., Stark G. R. Roles of JAKs in activation of STATs and stimulation of c-fos gene expression by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;16(1):369–375. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Migone T. S., Tsang M., Friedmann M., Weatherbee J. A., Zhou L., Yamauchi A., Bloom E. T., Mietz J., John S. The role of shared receptor motifs and common Stat proteins in the generation of cytokine pleiotropy and redundancy by IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-13, and IL-15. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Liao J., Rao X., Kushner S. A., Chung C. D., Chang D. D., Shuai K. Inhibition of Stat1-mediated gene activation by PIAS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Sep 1;95(18):10626–10631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look D. C., Pelletier M. R., Tidwell R. M., Roswit W. T., Holtzman M. J. Stat1 depends on transcriptional synergy with Sp1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30264–30267. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look D. C., Roswit W. T., Frick A. G., Gris-Alevy Y., Dickhaus D. M., Walter M. J., Holtzman M. J. Direct suppression of Stat1 function during adenoviral infection. Immunity. 1998 Dec;9(6):871–880. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80652-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C., Gillespie G. A., Pike J. W. Leukemia inhibitory factor as a mediator of JAK/STAT activation in murine osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Nov;10(11):1644–1650. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650101106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T. C., Garcia R., Medveczky M. M., Jove R., Medveczky P. G. Activation of STAT transcription factors by herpesvirus Saimiri Tip-484 requires p56lck. J Virol. 1997 Sep;71(9):6677–6682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.9.6677-6682.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T. C., Prator P. C., Medveczky M. M., Medveczky P. G. The Lck binding domain of herpesvirus saimiri tip-484 constitutively activates Lck and STAT3 in T cells. J Virol. 1999 Feb;73(2):1689–1694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.2.1689-1694.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo H., Hanratty W. P., Dearolf C. R. An amino acid substitution in the Drosophila hopTum-l Jak kinase causes leukemia-like hematopoietic defects. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1412–1420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra F., Choudhury G. G., Abboud H. E. Interferon-gamma-mediated activation of STAT1alpha regulates growth factor-induced mitogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1996 Sep 1;98(5):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI118905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrero M. B., Schieffer B., Paxton W. G., Heerdt L., Berk B. C., Delafontaine P., Bernstein K. E. Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):247–250. doi: 10.1038/375247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matikainen S., Ronni T., Lehtonen A., Sareneva T., Melén K., Nordling S., Levy D. E., Julkunen I. Retinoic acid induces signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1, STAT2, and p48 expression in myeloid leukemia cells and enhances their responsiveness to interferons. Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Jun;8(6):687–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto A., Masuhara M., Mitsui K., Yokouchi M., Ohtsubo M., Misawa H., Miyajima A., Yoshimura A. CIS, a cytokine inducible SH2 protein, is a target of the JAK-STAT5 pathway and modulates STAT5 activation. Blood. 1997 May 1;89(9):3148–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meydan N., Grunberger T., Dadi H., Shahar M., Arpaia E., Lapidot Z., Leeder J. S., Freedman M., Cohen A., Gazit A. Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature. 1996 Feb 15;379(6566):645–648. doi: 10.1038/379645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. J., Campbell G. S., Cochran B. H., Argetsinger L. S., Larner A. C., Finbloom D. S., Carter-Su C., Schwartz J. Growth hormone induces a DNA binding factor related to the interferon-stimulated 91-kDa transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):4701–4704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone T. S., Lin J. X., Cereseto A., Mulloy J. C., O'Shea J. J., Franchini G., Leonard W. J. Constitutively activated Jak-STAT pathway in T cells transformed with HTLV-I. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):79–81. doi: 10.1126/science.7604283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikita T., Campbell D., Wu P., Williamson K., Schindler U. Requirements for interleukin-4-induced gene expression and functional characterization of Stat6. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):5811–5820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.10.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., Rahill B. M., Boss J. M., Lairmore M. D., Durbin J. E., Waldman J. W., Sedmak D. D. Human cytomegalovirus inhibits major histocompatibility complex class II expression by disruption of the Jak/Stat pathway. J Exp Med. 1998 Mar 2;187(5):675–683. doi: 10.1084/jem.187.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani Y., Bonavida B., Koishihara Y., Akamatsu K., Ohsugi Y., Yoshida O. Sensitization of human renal cell carcinoma cells to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) by anti-interleukin 6 monoclonal antibody or anti-interleukin 6 receptor monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):590–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morella K. K., Bruno E., Kumaki S., Lai C. F., Fu J., Wang H. M., Murray L., Hoffman R., Timour M., Bénit L. Signal transduction by the receptors for thrombopoietin (c-mpL) and interleukin-3 in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells. Blood. 1995 Jul 15;86(2):557–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. W., Kirstein M. N., Valentine M. B., Dittmer K. G., Shapiro D. N., Saltman D. L., Look A. T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994 Mar 4;263(5151):1281–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.8122112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mui A. L., Wakao H., Kinoshita T., Kitamura T., Miyajima A. Suppression of interleukin-3-induced gene expression by a C-terminal truncated Stat5: role of Stat5 in proliferation. EMBO J. 1996 May 15;15(10):2425–2433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Briscoe J., Laxton C., Guschin D., Ziemiecki A., Silvennoinen O., Harpur A. G., Barbieri G., Witthuhn B. A., Schindler C. The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in interferon-alpha/beta and -gamma signal transduction. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):129–135. doi: 10.1038/366129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naka T., Narazaki M., Hirata M., Matsumoto T., Minamoto S., Aono A., Nishimoto N., Kajita T., Taga T., Yoshizaki K. Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor. Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):924–929. doi: 10.1038/43219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Kaltoft K., Nordahl M., Röpke C., Geisler C., Mustelin T., Dobson P., Svejgaard A., Odum N. Constitutive activation of a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3 in mycosis fungoides: tyrphostin AG490 inhibits Stat3 activation and growth of mycosis fungoides tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jun 24;94(13):6764–6769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.13.6764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Svejgaard A., Skov S., Odum N. Interleukin-2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of stat3 in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3082–3086. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak U., Mui A., Miyajima A., Paradiso L. Formation of STAT5-containing DNA binding complexes in response to colony-stimulating factor-1 and platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 2;271(31):18350–18354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallard C., Gouilleux F., Bénit L., Cocault L., Souyri M., Levy D., Groner B., Gisselbrecht S., Dusanter-Fourt I. Thrombopoietin activates a STAT5-like factor in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2847–2856. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallard C., Gouilleux F., Charon M., Groner B., Gisselbrecht S., Dusanter-Fourt I. Interleukin-3, erythropoietin, and prolactin activate a STAT5-like factor in lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):15942–15945. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.15942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park O. K., Schaefer T. S., Nathans D. In vitro activation of Stat3 by epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 26;93(24):13704–13708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.13704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters P., Raynaud S. D., Cools J., Wlodarska I., Grosgeorge J., Philip P., Monpoux F., Van Rompaey L., Baens M., Van den Berghe H. Fusion of TEL, the ETS-variant gene 6 (ETV6), to the receptor-associated kinase JAK2 as a result of t(9;12) in a lymphoid and t(9;15;12) in a myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1997 Oct 1;90(7):2535–2540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard J. V., Loo P., Sills M. A., Munster D., Pomponi S. A., Wright A. E. Characterization of an interleukin 6 cytokine family antagonist protein from a marine sponge, Callyspongia sp. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 29;271(13):7281–7284. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.13.7281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollak C., Hagemeijer A. Abnormalities of the short arm of chromosome 9 with partial loss of material in hematological disorders. Leukemia. 1987 Jul;1(7):541–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajotte D., Sadowski H. B., Haman A., Gopalbhai K., Meloche S., Liu L., Krystal G., Hoang T. Contribution of both STAT and SRF/TCF to c-fos promoter activation by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1996 Oct 15;88(8):2906–2916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Hedges A. R., Laakso K., Wynder E. L. Metabolic epidemiology of large bowel cancer: fecal bulk and constituents of high-risk North American and low-risk Finnish population. Cancer. 1978 Dec;42(6):2832–2838. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197812)42:6<2832::aid-cncr2820420644>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Cochran K. J., Cameron C., Le J. M., Tantravahi R., Ritz J. Characterization of a cell line, NKL, derived from an aggressive human natural killer cell leukemia. Exp Hematol. 1996 Feb;24(3):406–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. S., Bernard O. A., Berger R., Gilliland D. G. Fusion of Huntingtin interacting protein 1 to platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGFbetaR) in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with t(5;7)(q33;q11.2). Blood. 1998 Jun 15;91(12):4419–4426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman P., Li S. C., Gorham B., Glimcher L., Alt F., Boothby M. Identification of a conserved lipopolysaccharide-plus-interleukin-4-responsive element located at the promoter of germ line epsilon transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5551–5561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):290–293. doi: 10.1038/243290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozman C., Montserrat E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Oct 19;333(16):1052–1057. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199510193331606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin Grandis J., Chakraborty A., Melhem M. F., Zeng Q., Tweardy D. J. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression and function decreases proliferation of head and neck squamous carcinoma but not normal mucosal epithelial cells. Oncogene. 1997 Jul 24;15(4):409–416. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff-Jamison S., Chen K., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor induces the tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Stat 5 in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4215–4218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff-Jamison S., Chen K., Cohen S. Induction by EGF and interferon-gamma of tyrosine phosphorylated DNA binding proteins in mouse liver nuclei. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1733–1736. doi: 10.1126/science.8378774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff-Jamison S., Zhong Z., Wen Z., Chen K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and lipopolysaccharide activate Stat3 transcription factor in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 2;269(35):21933–21935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rui H., Kirken R. A., Farrar W. L. Activation of receptor-associated tyrosine kinase JAK2 by prolactin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5364–5368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski H. B., Shuai K., Darnell J. E., Jr, Gilman M. Z. A common nuclear signal transduction pathway activated by growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.8397445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saharinen P., Ekman N., Sarvas K., Parker P., Alitalo K., Silvennoinen O. The Bmx tyrosine kinase induces activation of the Stat signaling pathway, which is specifically inhibited by protein kinase Cdelta. Blood. 1997 Dec 1;90(11):4341–4353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor C. I., Dziubinski M. L., Yu C. L., Jove R., Ethier S. P. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor and STAT-3 activation in autonomous proliferation of SUM-102PT human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1997 Mar 1;57(5):978–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler M., Durstin M. A., Frank D. A., Okuda K., Kaushansky K., Salgia R., Griffin J. D. The thrombopoietin receptor c-MPL activates JAK2 and TYK2 tyrosine kinases. Exp Hematol. 1995 Aug;23(9):1040–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler M., Winkler T., Verma S., Byrne C. H., Shrikhande G., Salgia R., Griffin J. D. Hematopoietic growth factors signal through the formation of reactive oxygen species. Blood. 1999 May 1;93(9):2928–2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Ciapponi L., Lahm A., Demartis A., Cabibbo A., Toniatti C., Delmastro P., Altamura S., Ciliberto G. Rational design of a receptor super-antagonist of human interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):5863–5870. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06931.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino R., Lahm A., Salvati A. L., Ciapponi L., Sporeno E., Altamura S., Paonessa G., Toniatti C., Ciliberto G. Generation of interleukin-6 receptor antagonists by molecular-modeling guided mutagenesis of residues important for gp130 activation. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1357–1367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer T. S., Sanders L. K., Nathans D. Cooperative transcriptional activity of Jun and Stat3 beta, a short form of Stat3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9097–9101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Kashleva H., Pernis A., Pine R., Rothman P. STF-IL-4: a novel IL-4-induced signal transducing factor. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1350–1356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaller J., Frantsve J., Aster J., Williams I. R., Tomasson M. H., Ross T. S., Peeters P., Van Rompaey L., Van Etten R. A., Ilaria R., Jr Transformation of hematopoietic cell lines to growth-factor independence and induction of a fatal myelo- and lymphoproliferative disease in mice by retrovirally transduced TEL/JAK2 fusion genes. EMBO J. 1998 Sep 15;17(18):5321–5333. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.18.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour J. F., Talpaz M., Cabanillas F., Wetzler M., Kurzrock R. Serum interleukin-6 levels correlate with prognosis in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1995 Mar;13(3):575–582. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1995.13.3.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda K., van Deursen J., Sangster M. Y., Sarawar S. R., Carson R. T., Tripp R. A., Chu C., Quelle F. W., Nosaka T., Vignali D. A. Lack of IL-4-induced Th2 response and IgE class switching in mice with disrupted Stat6 gene. Nature. 1996 Apr 18;380(6575):630–633. doi: 10.1038/380630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimozaki K., Nakajima K., Hirano T., Nagata S. Involvement of STAT3 in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-induced differentiation of myeloid cells. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 3;272(40):25184–25189. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirota K., LeDuy L., Yuan S. Y., Jothy S. Interleukin-6 and its receptor are expressed in human intestinal epithelial cells. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1990;58(4):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02890085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):550–554. doi: 10.1038/315550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Halpern J., ten Hoeve J., Rao X., Sawyers C. L. Constitutive activation of STAT5 by the BCR-ABL oncogene in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene. 1996 Jul 18;13(2):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Ihle J. N., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Interferon-induced nuclear signalling by Jak protein tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):583–585. doi: 10.1038/366583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvennoinen O., Schindler C., Schlessinger J., Levy D. E. Ras-independent growth factor signaling by transcription factor tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1736–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.8378775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. R., Rai U., Fanburg B. L., Cochran B. H. Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway by reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol. 1998 Dec;275(6 Pt 1):C1640–C1652. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1998.275.6.C1640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov S., Nielsen M., Bregenholt S., Odum N., Claesson M. H. Activation of Stat-3 is involved in the induction of apoptosis after ligation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on human Jurkat T cells. Blood. 1998 May 15;91(10):3566–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Buckle G. J., Hafler D. A., Frank D. A., Höllsberg P. HTLV-I-infected T cells evade the antiproliferative action of IFN-beta. Virology. 1999 May 10;257(2):314–321. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Farruggella T. J., Boulton T. G., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr, Yancopoulos G. D. Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science. 1995 Mar 3;267(5202):1349–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7871433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Willson T. A., Viney E. M., Murray L. J., Rayner J. R., Jenkins B. J., Gonda T. J., Alexander W. S., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A. A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature. 1997 Jun 26;387(6636):917–921. doi: 10.1038/43206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcklin E., Wissler M., Gouilleux F., Groner B. Functional interactions between Stat5 and the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature. 1996 Oct 24;383(6602):726–728. doi: 10.1038/383726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun W. H., Pabon C., Alsayed Y., Huang P. P., Jandeska S., Uddin S., Platanias L. C., Rosen S. T. Interferon-alpha resistance in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line is associated with lack of STAT1 expression. Blood. 1998 Jan 15;91(2):570–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symes A. J., Corpus L., Fink J. S. Differences in nuclear signaling by leukemia inhibitory factor and interferon-gamma: the role of STAT proteins in regulating vasoactive intestinal peptide gene expression. J Neurochem. 1995 Nov;65(5):1926–1933. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65051926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symes A., Lewis S., Corpus L., Rajan P., Hyman S. E., Fink J. S. STAT proteins participate in the regulation of the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene by the ciliary neurotrophic factor family of cytokines. Mol Endocrinol. 1994 Dec;8(12):1750–1763. doi: 10.1210/mend.8.12.7708062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Noguchi K., Shi W., Tanaka T., Matsumoto M., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat3 gene leads to early embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):3801–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.3801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Tanaka T., Shi W., Matsumoto M., Minami M., Kashiwamura S., Nakanishi K., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T., Akira S. Essential role of Stat6 in IL-4 signalling. Nature. 1996 Apr 18;380(6575):627–630. doi: 10.1038/380627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto S., Mulloy J. C., Cereseto A., Migone T. S., Patel B. K., Matsuoka M., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K., Kamihira S., White J. D. Proliferation of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma cells is associated with the constitutive activation of JAK/STAT proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 9;94(25):13897–13902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.13897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. E., Tosato G. Regulation of B-cell growth and immunoglobulin gene transcription by interleukin-6. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):452–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teglund S., McKay C., Schuetz E., van Deursen J. M., Stravopodis D., Wang D., Brown M., Bodner S., Grosveld G., Ihle J. N. Stat5a and Stat5b proteins have essential and nonessential, or redundant, roles in cytokine responses. Cell. 1998 May 29;93(5):841–850. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81444-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierfelder W. E., van Deursen J. M., Yamamoto K., Tripp R. A., Sarawar S. R., Carson R. T., Sangster M. Y., Vignali D. A., Doherty P. C., Grosveld G. C. Requirement for Stat4 in interleukin-12-mediated responses of natural killer and T cells. Nature. 1996 Jul 11;382(6587):171–174. doi: 10.1038/382171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasson M. H., Williams I. R., Hasserjian R., Udomsakdi C., McGrath S. M., Schwaller J., Druker B., Gilliland D. G. TEL/PDGFbetaR induces hematologic malignancies in mice that respond to a specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Blood. 1999 Mar 1;93(5):1707–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traxler P. M., Furet P., Mett H., Buchdunger E., Meyer T., Lydon N. 4-(Phenylamino)pyrrolopyrimidines: potent and selective, ATP site directed inhibitors of the EGF-receptor protein tyrosine kinase. J Med Chem. 1996 Jun 7;39(12):2285–2292. doi: 10.1021/jm960118j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trock B., Lanza E., Greenwald P. Dietary fiber, vegetables, and colon cancer: critical review and meta-analyses of the epidemiologic evidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Apr 18;82(8):650–661. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.8.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkson J., Bowman T., Garcia R., Caldenhoven E., De Groot R. P., Jove R. Stat3 activation by Src induces specific gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2545–2552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.5.2545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweardy D. J., Wright T. M., Ziegler S. F., Baumann H., Chakraborty A., White S. M., Dyer K. F., Rubin K. A. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor rapidly activates a distinct STAT-like protein in normal myeloid cells. Blood. 1995 Dec 15;86(12):4409–4416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valgeirsdóttir S., Paukku K., Silvennoinen O., Heldin C. H., Claesson-Welsh L. Activation of Stat5 by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is dependent on phosphorylation sites in PDGF beta-receptor juxtamembrane and kinase insert domains. Oncogene. 1998 Jan 29;16(4):505–515. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Sadowski H. B., Watling D., Rogers N. C., Gilman M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces phosphorylation of multiple JAK family kinases and STAT proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;16(4):1759–1769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.4.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakao H., Gouilleux F., Groner B. Mammary gland factor (MGF) is a novel member of the cytokine regulated transcription factor gene family and confers the prolactin response. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2182–2191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06495.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. S., Ritz J., Frank D. A. IL-2 induces STAT4 activation in primary NK cells and NK cell lines, but not in T cells. J Immunol. 1999 Jan 1;162(1):299–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Miller W. H., Jr, Scheinberg D. A., Itri L. M., Hittelman W. N., Vyas R., Andreeff M., Tafuri A., Jakubowski A. Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1385–1393. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watling D., Guschin D., Müller M., Silvennoinen O., Witthuhn B. A., Quelle F. W., Rogers N. C., Schindler C., Stark G. R., Ihle J. N. Complementation by the protein tyrosine kinase JAK2 of a mutant cell line defective in the interferon-gamma signal transduction pathway. Nature. 1993 Nov 11;366(6451):166–170. doi: 10.1038/366166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson C. J., Miller W. R. Elevated levels of members of the STAT family of transcription factors in breast carcinoma nuclear extracts. Br J Cancer. 1995 Apr;71(4):840–844. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegenka U. M., Buschmann J., Lütticken C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. Acute-phase response factor, a nuclear factor binding to acute-phase response elements, is rapidly activated by interleukin-6 at the posttranslational level. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):276–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Mapping of Stat3 serine phosphorylation to a single residue (727) and evidence that serine phosphorylation has no influence on DNA binding of Stat1 and Stat3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Jun 1;25(11):2062–2067. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.11.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Z., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Z., Baer M. R., Block A. W., Baumann H., Wetzler M. Expression of signal transducers and activators of transcription proteins in acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Cancer Res. 1998 Jul 15;58(14):3173–3180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S., Nalabolu S. R., Aster J. C., Ma J., Abruzzo L., Jaffe E. S., Stone R., Weissman S. M., Hudson T. J., Fletcher J. A. FGFR1 is fused with a novel zinc-finger gene, ZNF198, in the t(8;13) leukaemia/lymphoma syndrome. Nat Genet. 1998 Jan;18(1):84–87. doi: 10.1038/ng0198-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Fu X. Y., Plate J., Chong A. S. IFN-gamma induces cell growth inhibition by Fas-mediated apoptosis: requirement of STAT1 protein for up-regulation of Fas and FasL expression. Cancer Res. 1998 Jul 1;58(13):2832–2837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Kang S. H., Heidenreich O., Okerholm M., O'Shea J. J., Nerenberg M. I. Constitutive activation of different Jak tyrosine kinases in human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) tax protein or virus-transformed cells. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1548–1555. doi: 10.1172/JCI118193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Watanabe S., Miyazato A., Ohya K. i., Ikeda U., Shimada K., Komatsu N., Hatake K., Miura Y., Ozawa K. Tec and Jak2 kinases cooperate to mediate cytokine-driven activation of c-fos transcription. Blood. 1998 Mar 1;91(5):1496–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan R., Small S., Desplan C., Dearolf C. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Identification of a Stat gene that functions in Drosophila development. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Burakoff S. J. Involvement of proteasomes in regulating Jak-STAT pathways upon interleukin-2 stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1997 May 30;272(22):14017–14020. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.22.14017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Jove R., Burakoff S. J. Constitutive activation of the Janus kinase-STAT pathway in T lymphoma overexpressing the Lck protein tyrosine kinase. J Immunol. 1997 Dec 1;159(11):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. L., Meyer D. J., Campbell G. S., Larner A. C., Carter-Su C., Schwartz J., Jove R. Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science. 1995 Jul 7;269(5220):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.7541555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Wegenka U. M., Lütticken C., Buschmann J., Decker T., Schindler C., Heinrich P. C., Horn F. The signalling pathways of interleukin-6 and gamma interferon converge by the activation of different transcription factors which bind to common responsive DNA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1657–1668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. J., Vinkemeier U., Gu W., Chakravarti D., Horvath C. M., Darnell J. E., Jr Two contact regions between Stat1 and CBP/p300 in interferon gamma signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Dec 24;93(26):15092–15096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.26.15092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q., Nowak I., Vonderheid E. C., Rook A. H., Kadin M. E., Nowell P. C., Shaw L. M., Wasik M. A. Activation of Jak/STAT proteins involved in signal transduction pathway mediated by receptor for interleukin 2 in malignant T lymphocytes derived from cutaneous anaplastic large T-cell lymphoma and Sezary syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 20;93(17):9148–9153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.17.9148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Blenis J., Li H. C., Schindler C., Chen-Kiang S. Requirement of serine phosphorylation for formation of STAT-promoter complexes. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):1990–1994. doi: 10.1126/science.7701321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Nichols J. E., Bulun S. E., Mendelson C. R., Simpson E. R. Aromatase P450 gene expression in human adipose tissue. Role of a Jak/STAT pathway in regulation of the adipose-specific promoter. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 7;270(27):16449–16457. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.27.16449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):95–98. doi: 10.1126/science.8140422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong C., Yan R., August A., Darnell J. E., Jr, Hanafusa H. Unique signal transduction of Eyk: constitutive stimulation of the JAK-STAT pathway by an oncogenic receptor-type tyrosine kinase. EMBO J. 1996 Sep 2;15(17):4515–4525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Coutre P., Mologni L., Cleris L., Marchesi E., Buchdunger E., Giardini R., Formelli F., Gambacorti-Passerini C. In vivo eradication of human BCR/ABL-positive leukemia cells with an ABL kinase inhibitor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999 Jan 20;91(2):163–168. doi: 10.1093/jnci/91.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]